
User Guide
®
KINOVA
Gen3
Ultra lightweight
robot

Contents
Introduction............................................................................................................................................................... 6
Welcome.......................................................................................................................................................................6
About this document............................................................................................................................................... 6
Normal use definition..............................................................................................................................................6
Risk assessment........................................................................................................................................................7
EU Declaration of Incorporation.......................................................................................................................... 7
FCC Declaration of Comformity........................................................................................................................... 8
Safety directives and warnings......................................................................................................................... 10
Warranty.....................................................................................................................................................................12
Disclaimer.................................................................................................................................................................. 12
Acronyms and abbreviations.............................................................................................................................. 13
Robot components................................................................................................................................................. 16
Overview.....................................................................................................................................................................16
Base..............................................................................................................................................................................16
Controller quick connect system............................................................................................................. 17
Controller connector panel.......................................................................................................................20
Actuators...................................................................................................................................................................20
Interface module..................................................................................................................................................... 21
Vision module.......................................................................................................................................................... 23
Robot communications and network interfaces.........................................................................................24
Getting started........................................................................................................................................................27
Overview.................................................................................................................................................................... 27
What's in the case?................................................................................................................................................27
Manipulating the robot joints when the robot is powered off...............................................................28
Robot mounting options......................................................................................................................................28
Mounting the robot on a tabletop......................................................................................................... 28
Mounting the robot on a horizontal surface without the table clamp...................................... 30
Mounting the robot on a wall or ceiling...............................................................................................32
Robot power adapter and E-stop.....................................................................................................................34
Powering on the robot..........................................................................................................................................35
Power-up, booting, and initialization sequence.......................................................................................... 35
Resetting the robot to factory settings......................................................................................................... 36
Operating the robot...............................................................................................................................................36
Supported gamepad controllers............................................................................................................. 36
Home and retract positions...................................................................................................................... 41
Putting the robot into admittance using the interface buttons....................................................41
Connecting a computer to the robot...............................................................................................................42
Connecting a computer to the robot via Ethernet (for the first time)........................................42
KINOVA® KORTEX™ Web App...................................................................................................................44
Changing the robot wired connection IP address and connecting the robot to a LAN..........46
Connecting a computer to the robot via Wi-Fi.................................................................................. 46
Dimensions, specifications, and capabilities................................................................................................ 48
Schematic and dimensions - 7 DoF spherical wrist...................................................................................48
Technical Specifications.......................................................................................................................................49

Sensors.......................................................................................................................................................................52
Base readings available............................................................................................................................. 53
Tool readings available...............................................................................................................................53
Actuators readings available................................................................................................................... 54
Interface readings available..................................................................................................................... 54
Gripper readings available........................................................................................................................ 54
Effective workspace.............................................................................................................................................. 55
Maximum payload vs. workspace.................................................................................................................... 56
Interface, expansion, and vision........................................................................................................................57
Interface module expansion - tips for installing tools............................................................................. 57
End effector reference design................................................................................................................. 58
Removing end cap from Interface module...........................................................................................61
Robotiq Adaptive Grippers installation (optional).............................................................................61
Robotiq 2F-85 Gripper tool configuration........................................................................................... 63
Interface module bolting pattern...........................................................................................................64
Interface module user expansion connector pinout........................................................................64
Using interface module expansion to control devices via API......................................................66
Spring-loaded connector pinout............................................................................................................. 66
Accessing Vision module color and depth streams................................................................................... 67
Concepts and terminology..................................................................................................................................69
Robot key concepts............................................................................................................................................... 69
Terminology reference...........................................................................................................................................71
General mathematics and robotics.........................................................................................................71
Features, components and functionalities.......................................................................................... 73
Control and Operation Modes..................................................................................................................74
Robot control...........................................................................................................................................................75
High-level and low-level robot control.......................................................................................................... 75
High-level and low-level robot control methods overview.................................................................... 75
Control features...................................................................................................................................................... 77
Singularity avoidance.................................................................................................................................. 77
Protection zones........................................................................................................................................... 77
Angular limits.................................................................................................................................................78
Cartesian limits.............................................................................................................................................80
Control modes overview..................................................................................................................................... 80
Trajectory control modes........................................................................................................................... 81
Joystick control modes...............................................................................................................................82
Admittance modes.......................................................................................................................................82
Configurations and safeties...............................................................................................................................84
Configurable parameters.................................................................................................................................... 84
Control library configuration................................................................................................................... 84
Base configuration.......................................................................................................................................85
Actuators configuration.............................................................................................................................86
Interface configuration...............................................................................................................................86
Device configuration....................................................................................................................................87
Vision configuration.....................................................................................................................................87
Safety items.............................................................................................................................................................88
Base (controller) safeties..........................................................................................................................88
Actuators safeties........................................................................................................................................89
Interface module safeties..........................................................................................................................91

KINOVA® KORTEX™ Web App User Guide........................................................................................................93
Introduction.............................................................................................................................................................. 93
Purpose...................................................................................................................................................................... 93
Device availability of Web App..........................................................................................................................93
Platform and browser support..........................................................................................................................95
User login.................................................................................................................................................................. 95
Web App layout and navigation........................................................................................................................96
Robot control panel..............................................................................................................................................101
Pose virtual joystick control....................................................................................................................101
Angular virtual joystick control.............................................................................................................102
Virtual joystick keyboard shortcuts.....................................................................................................103
Admittance modes panel.........................................................................................................................105
Actions panel................................................................................................................................................105
Camera panel............................................................................................................................................... 106
Snapshot tool...............................................................................................................................................106
Main pages..............................................................................................................................................................106
Configurations page group......................................................................................................................106
Safeties........................................................................................................................................................... 110
Operations page group..............................................................................................................................110
Systems page group...................................................................................................................................121
Users................................................................................................................................................................125
KINOVA® KORTEX™ Developer Guide............................................................................................................. 128
Introduction............................................................................................................................................................ 128
Devices and services...........................................................................................................................................128
Available services.................................................................................................................................................129
Users, connections and sessions....................................................................................................................129
Services, methods, and messages................................................................................................................. 130
KINOVA® KORTEX™ API and Google Protocol Buffer................................................................................130
Service client-server model..............................................................................................................................130
Notifications............................................................................................................................................................ 131
Blocking and non-blocking calls...................................................................................................................... 131
Robot servoing modes.........................................................................................................................................131
High-level servoing....................................................................................................................................132
Low-level servoing.....................................................................................................................................132
Device routing........................................................................................................................................................ 133
Error management............................................................................................................................................... 133
KINOVA® KORTEX™ GitHub repository...........................................................................................................133
KINOVA® KORTEX™ ROS packages and GitHub repository overview..................................................134
KINOVA® KORTEX™ MATLAB® API and GitHub repository overview................................................... 134
Working with camera streams using GStreamer...................................................................................... 134
Windows command examples............................................................................................................... 135
Linux command examples.......................................................................................................................135
KINOVA® KORTEX™ ROS vision module package and Github overview..............................................136
Guidance for advanced users........................................................................................................................... 137
Overview...................................................................................................................................................................137
Reference frames and transformations....................................................................................................... 137
Standard Cartesian reference frames................................................................................................. 137
Homogeneous transforms.......................................................................................................................137
Homogeneous transform matrices - 7 DoF spherical wrist........................................................ 138

Vision module sensors reference frames..........................................................................................140
Denavit-Hartenberg (DH) parameters - 7 DoF spherical wrist................................................... 141
7 DoF singular configurations..........................................................................................................................143
Inertial parameters definition..........................................................................................................................145
Inertial parameters of the 7 DoF robot........................................................................................................ 145
Maintenance and troubleshooting................................................................................................................. 149
Maintenance...........................................................................................................................................................149
Troubleshooting..................................................................................................................................................... 151
Base controller LEDs................................................................................................................................. 152
How to respond to safety warnings and errors.............................................................................. 152
Contacting Kinova support...................................................................................................................... 154
KINOVA® Gen3 Ultra lightweight robot User Guide 6
Introduction
Welcome
Welcome to the KINOVA® Gen3 Ultra lightweight robot.
Thank you for choosing our robot as a tool for your pathbreaking research needs.
This document is meant to provide you with all the information you need to get up and running with your
new robot and get the most out of it.
We are here to help you in your journey. If you need any help or have any questions about how to get to
where you're going with the robot, please feel free to contact our support team:
www.kinovarobotics.com/support
About this document
User Guide contents and warnings.
Read all instructions before using this product and any third-party options.
Read all warnings on the product and in this guide.
This document contains information regarding product setup and operation. It is intended for Kinova
product end users.
All third-party product names, logos, and brands appearing herein are the property of their respective
owners and are for identification purposes only. Their use in this document is not meant to imply
endorsement by Kinova.
Kinova has made every effort to ensure that this document is accurate, accessible and complete. As
part of our commitment to continuous improvement, we welcome any comments or suggestions at
www.kinovarobotics.com/support.
From time to time, Kinova will make udpates to this document. To download the most up to date version
of this document, visit the product technical resources page at www.kinovarobotics.com/knowledge-hub/
gen3-ultra-lightweight-robot.
For general inquiries please contact us at +1 (514) 277-3777
Normal use definition
This section describes the normal use of the robot.
The definition of normal use includes lifting, pushing, pulling, or manipulating (without a gripper or other
end effector attached) a maximum load of:
• mid-range, continuous: 4 kg
• full-reach, temporary: 4.5 kg
• full-reach, continuous 1.1 kg
The robot is designed to hold, move, and manipulate objects in the user environment. However, for some
loads in certain positions (near maximum load and reach), holding an object for an extended period of time
may result in heating. To protect the robot hardware from excessive heat, safety thresholds shut down the
robot if the temperature rises above a certain threshold. Before this is reached, an API notification will be
rendered as a user alert on the KINOVA® KORTEX™ Web App.
The robot includes a number of temperature-related safeties:
• base - CPU core and ambient temperatures
• actuators - CPU core and motor temperatures
• interface module - CPU core and gripper motor temperatures
If you receive any temperature warnings, put down any object as soon as is practical and place the robot
into a stable rest position to allow it to cool down.

KINOVA® Gen3 Ultra lightweight robot User Guide 7
During normal operation, the robot joints are subject to heating. The joints are normally covered in plastic
rings to protect the user from the metal surfaces which may become hot.
Risk assessment
Before proceeding it is imperative that a risk assessment be performed (note that this is required by law
in many countries). As it is a machine, the safety of the robot depends on how well it is integrated with its
environment and with other machines.
The recommended international standards for conducting a risk assessment are as follows:
• ISO 12100
• ISO 10218-2
The risk assessment should take into consideration all activities carried out in the context of the robot
application, including (but not limited to):
• teaching the robot (during set-up)
• development of the robot installation
• robot troubleshooting
• robot maintenance
• everyday robot operation
The risk assessment must be completed before integration of the robot in an application and should address
configuration settings as well as the need for any additional emergency stop buttons.
EU Declaration of Incorporation
The Declaration of Conformity is a self-declared assessment produced and signed by a manufacturer of a
product to assert that the product meets all of the requirements of the applicable directives.
In the case of KINOVA® Gen3 Ultra lightweight robot KR L53 0007, the applicable directives that are eligible
for CE declaration are the following:
• Machinery Directive 2006/42/EC
• Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) Directive 2014/30/EU
The Machinery Directive 2006/42/EC Article 2 (g) states that:
‘Partly completed machinery’ means an assembly which is almost machinery but which cannot in
itself perform a specific application. A drive system is partly completed machinery. Partly completed
machinery is only intended to be incorporated into or assembled with other machinery or other
partly completed machinery or equipment, thereby forming machinery to which this Directive
applies; is not eligible to CE marking by its own because it is an “incomplete machine.”
Based on this definition, our product Gen3 Ultra lightweight robot KR L53 0007 is considered partly
completed machinery because it has no specific application. The robot application is determined when it is
incorporated in a system, given an end-effector and expected workpieces. Once the product is incorporated
into a complete system and the system complies to all applicable directives, then the integrator is permitted
to issue a Declaration of Conformity and affix a CE marking to the completed machine. For incomplete
machinery, a Declaration of Incorporation (DoI) is required from the manufacturer. The Declaration of
Incorporation for the robot is inserted below.

KINOVA® Gen3 Ultra lightweight robot User Guide 8
EU DECLARATION OF INCORPORATION (In accordance with ISO/IEC 17050-1:2004)
Manufacturer:
Kinova Robotics
4333 Boulevard de la Grande-Allée,
Boisbriand, QC J7H 1M7, Canada
Telephone: +1 514-277-3777
Manufacturer’s authorized EU representative :
Kinova Europe GmbH
Grosskitzighofer. Str. 7a,
86853 Langerringen
Telephone: +49 8248 8887-928
Description and identification of the partially completed machine(s):
Product and function : Robot (Multi-axis manipulator)
Models :
KINOVA® Gen3 Ultra lightweight robot L53 0007
KINOVA® Gen3 Ultra lightweight robot L53 0006
KINOVA® Gen3 Ultra lightweight robot shall only be put into service upon being integrated into a
final complete machine (robot system, cell or application), which conforms with the provisions of the
Machinery Directive and other applicable Directives.
When this incomplete machine is integrated and becomes a complete machine, the integrator is
responsible for determining that the completed machine fulfils all applicable directives and updating the
relevant harmonized standards, other standards and documents.
It is declared that the above products, for what is supplied, fulfil the following directives as detailed
below:
• Machinery Directive 2006/42/EC The following essential health and safety requirements are
applied and fulfilled :
1.1.2, 1.1.3, 1.1.5, 1.2.1, 1.2.4.3, 1.2.6, 1.3.4, 1.3.8.1, 1.5.1,
1.5.2, 1.5.6, 1.5.10, 1.6.3, 1.7.2, 1.7.4
• Electromagnetic Compatibility
(EMC) Directive 2014/30/EU
The partly completed machinery is also compliant with the following relevant standards:
• IEC 62368-1:2014/AC:2015 Audio/video, information and communication technology
equipment - Part 1: Safety requirements
• ISO 12100:2010 Safety of machinery - General principles for design - Risk
assessment and risk reduction
• IEC 61000-6-1:2016 Electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) - Part 6-1: Generic
standards - Immunity for residential, commercial and lightindustrial environments
• IEC 61000-6-3:2016 Electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) - Part 6-3: Generic
standards - Emission standard for residential, commercial and
light-industrial environments
The manufacturer or its authorised representative will undertake to transmit, in response to a reasoned
request by the national authorities, relevant information on the partly completed machinery.
The Technical Construction File is kept and maintained at the corporate headquarters of Kinova
Robotics located at 4333 Boulevard de la Grande-Allée, Boisbriand, QC J7H 1M7, Canada.
Louis-Joseph Caron L'Écuyer
Chief Operaon Officer & Co-Founder
Boisbriand Canada, 08 August 2019

KINOVA® Gen3 Ultra lightweight robot User Guide 9
FCC Declaration of Comformity
FCC Regulatory Disclosures: This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a
Class B digital device, pursuant to part 15 of the FCC Rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable
protection against harmful interference in a residential installation. This equipment generates, uses and can
radiate radio frequency energy and, if not installed and used in accordance with the instructions, may cause
harmful interference to radio communications. However, there is no guarantee that interference will not
occur in a particular installation. If this equipment does cause harmful interference to radio or television
reception, which can be determined by turning the equipment off and on, the user is encouraged to try to
correct the interference by one or more of the following measures:
• Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna
• Increase the separation between the equipment and receiver
• Connect the equipment into an outlet on a circuit different from that to which the receiver is
connected
• Consult the dealer or an experienced radio/TV technician for help
The Declaration of Conformity for the robot is inserted below.
FCC SUPPLIER'S DECLARATION OF CONFORMITY
Manufacturer:
Kinova Robotics
4333 Boulevard de la Grande-Allée,
Boisbriand, QC J7H 1M7, Canada
Telephone: +1 514-277-3777
Description and identification of the devices:
Product and function : Robot (Multi-axis manipulator)
Models :
KINOVA® Gen3 Ultra lightweight robot L53 0007
KINOVA® Gen3 Ultra lightweight robot L53 0006
These devices contains the following certified modular transmitter : FCC ID A3LSIP007AFS00
These devices comply with Part 15 of the FCC Rules and Regulations for Information Technology
Equipment :
• FCC 47 CFR Part 15, Subpart B – Verification
Operation is subject to the following two conditions:
(1) these devices may not cause harmful interference, and
(2) these devices must accept any interference received, including interference that may cause undesired
operation.
We, the responsible party Kinova Robotics, declare that the products Gen3 Ultra lightweight robot KR
L53 0007 and Gen3 Ultra lightweight robot KR L53 0006 are to conform to the applicable FCC rules and
regulations. The method of testing was in accordance with the appropriate measurement standards, and
all necessary steps have been taken to ensure that all production units of these devices will continue to
comply with the Federal Communications Commission's requirements.
Boisbriand Canada, 11 October 2019
Louis-Joseph Caron L'Écuyer
Chief Operaon Officer & Co-Founder
KINOVA® Gen3 Ultra lightweight robot User Guide 10
Safety directives and warnings
Directives, warnings and safety considerations for the KINOVA®Gen3 Ultra lightweight
robot.
IMPORTANT
Before operating the robot for the first time, ensure that you have read, completely understood and
complied with all of the following directives, warnings and cautionary notes. Failure to do so may result in
serious injury or death to the user, damage to the robot, or a reduction in its useful life.
Table 1: Safety
There is no mechanical brake on the robot. If the power supply is cut or an unrecoverable error
occurs, be aware that the robot will fall. However, mechanisms are in place within the actuators will
slow the descent in the absence of external power.
For your personal
safety, and that of others, it is
strongly recommended that
the following be carried out:
For your personal
safety, and that of others,
never:
- risk assessment, before integration of the robot into a given application.
- hazard analysis, before integration into an environment which includes
atomized flammable dust / particles or explosive / flammable gases, etc.
- use the robot near a flame or source of heat.
- use the robot to submerge objects in water.
- exceed the maximum specified payload.
- attempt to stop the robot or prevent its movement by holding it (except
in admittance mode).
- install the robot base within 20 cm of your body (base contains a Wi-Fi
transmitter).
- power up and boot, reboot, or update the firmware of the robot unless
the robot is in a stable position.
- the robot does not encounter any obstacles (persons or objects).
Although inherently safe in its default configuration, disabling the robot
safeties requires that the user be responsible for ensuring a secure
working space.
- the end effector never collides with a hard surface.
For your personal
safety, and that of others,
always ensure that:
- the grasping of objects by gripper fingers is stable, to prevent the risk of
dropped or thrown objects (if using a gripper).
- the wrist is supported before turning the power off (otherwise it may fall
and cause damage).
- eye protection is worn when manipulating fragile objects with the robot.
- the working area is safe when containers of hot (or extremely cold)
liquids are to be manipulated with the robot.
- the robot working area is safe if sharp objects are to be handled by the
robot
- the robot has its base securely fixed to the work surface when in
operation.
- before using the robot, it is confirmed that there are no warnings.
- the robot is protected adequately before being used near any messy
process (e.g. welding or painting).

KINOVA® Gen3 Ultra lightweight robot User Guide 11
When using a tool and payload with the robot, ensure that the robot is configured with the
parameters of the tool and payload using the Web App or robot Kinova.Api.ControlConfig API.
For more details, see the API documentation on GitHub and the "Interface, expansion, and vision"
section of the robot User Guide. The robot may behave in an unexpected manner if the tool and payload
parameters are not properly configured.
When mounting the robot in a wall or ceiling mount, ensure that special considerations and
configurations set out in the user guide are followed, including analysis of the mounting surface, use of
the base locking screw, orientation of the base connector panel, and configuration of the gravity vector.
High-level force control is supported as an experimental feature. Users should exercise caution.
Low-level torque control is for advanced users only and should only be used by users who
know what they are doing. It is very important to carefully monitor the torque commands sent to the
actuators to ensure that excessive values are not sent. Incorrect use can lead to rapid movements that
can be dangerous for people and equipment. Make sure that the area around the robot is clear before
experimenting with torque control.
Do not power on the product if any external damage to the vision module is apparent.
Do not attempt to open the vision module.
To avoid eyesight injury from wide angle infrared laser light, do not view the front-facing surface of
the vision module through magnifying optical elements.
The robot should not be used without the provided emergency stop connected.
Do not operate the robot when the relative humidity exceeds the maximum specified limit. In
such a case, put down any object in the gripper, bring the robot to a resting position and wait until the
humidity decreases to an allowable value.
The robot is not certified for use in applications in sterile environments (e.g. food production,
pharmaceuticals, medical, surgical).
Table 2: General
Do not connect the USB ports on the base to one another.
It is recommended that surge protection be used to protect the robot against external surges on
the main AC line which might be caused by lightning or other abnormal conditions.
The base must be mounted as specified in the installation section, with particular attention to the
bolt pattern, strength requirements and any table or tripod-specific mounting.
Any end effector must be mounted as specified in the installation section (including bolt pattern,
power requirements, etc.).
Table 3: Maintenance
Do not use the robot in heavy rain. If this happens, contact Kinova support to schedule
maintenance by an authorized Kinova technician.

KINOVA® Gen3 Ultra lightweight robot User Guide 12
Immediately following exposure to saline air conditions, contact Kinova support to schedule
maintenance by authorized Kinova technician.
The controller mating interface must be kept free of dust and moisture to protect the electrical
contacts. Wipe down the surface with a soft dry cloth to keep the surface of the interface clean.
Warranty
This section describes the Kinova warranty terms.
Subject to the terms of this clause, Kinova warrants to End User that the Products are free of defects in
materials and workmanship that materially affect their performance for a period of two (2) years from the
date Kinova ships the Products to the End User ("Delivery Date").
Kinova agrees to repair or replace (at Kinova's option) all Products which fail to conform to the relevant
warranty provided that:
1. notification of the defect is received by Kinova within the warranty period specified above;
2. allegedly defective Products are returned to Kinova, (at the End User’s expense, with Kinova's prior
authorization) within thirty (30) days of the defect becoming apparent;
3. the Products have not been altered, modified or subject to misuse, incorrect installation, maintenance,
neglect, accident or damage caused by excessive current or used with incompatible parts;
4. the End User is not in default under any of its obligations under this Agreement;
5. replacement Products must have the benefit of the applicable warranty for the remainder of the
applicable warranty period.
If Kinova diligently repairs or replaces the Products in accordance with this section, it will be deemed to
have no further liability for a breach of the relevant warranty.
Allegedly defective Products returned to Kinova in accordance with this contract will, if found by Kinova
on examination not to be defective, be returned to the End User. Kinova may charge a fee for examination
and testing.
The warranty cannot be assigned or transferred and is to the sole benefit of the End User.
Where the Products have been manufactured and supplied to Kinova by a third party, any warranty granted
to Kinova in respect of the Products may be passed on to the End User.
Kinova is entitled in its absolute discretion to refund the price of the defective Products in the event that
such price has already been paid.
Disclaimer
KINOVA® and the Kinova logo are registered trademarks of Kinova inc., herein referred to as Kinova.
KORTEX™ is a trademark of Kinova inc.
All other brand and product names are trademarks or registered trademarks of their respective owners.
The mention of a product name does not necessarily imply an endorsement by Kinova. This manual is
furnished under a lease agreement and may only be copied or used in accordance with the terms of
such lease agreement. Except as permitted by the lease agreement, no part of this publication may be
reproduced, stored in any retrieval system, or transmitted, modified in any form or by any means, electronic,
mechanical, recording, or otherwise, without prior written consent of Kinova.
The content of this manual is furnished for informational use only and is subject to change without notice.
It should not be construed as a commitment by Kinova. Kinova assumes no responsibility or liability for any
errors or inaccuracies that may appear in this document.
Changes are periodically made to the information herein and will be incorporated into new editions of this
publication. Kinova may make improvements and/or changes to the products and/or software programs
described in this publication at any time.
Any questions or comments concerning this document, the information it contains or the product it
describes may be addressed through the support page on the Kinova website:

KINOVA® Gen3 Ultra lightweight robot User Guide 13
www.kinovarobotics.com/support
Kinova would like to thank you for your contribution, while retaining the right to use or distribute whatever
information you supply in any way it believes appropriate (without incurring any obligations to you).
Acronyms and abbreviations
API
Application Programming Interface
CIDR
Classless Inter-Domain Routing
CISPR
Comité International Spécial des Perturbations Radioélectriques
EE
End Effector
EMI
Electromagnetic Interference
FOV
Field of View
fps
frames per second
GPIO
General-Purpose Input/Output
HDMI
High-Definition Multimedia Interface
IC
Integrated Circuit
IEEE
Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers
I2C
Inter-Integrated Circuit (bus)
I/O
Input / Output
IP
Ingress Protection or Internet Protocol
IT
Information Technology
ISO
International Organization for Standardization

KINOVA® Gen3 Ultra lightweight robot User Guide 14
LED
Light-Emitting Diode
n/c
no connection
NVRAM
Non-Volatile Random-Access Memory
PC
Personal Computer
ROS
Robot Operating System
RPC
Remote Procedure Call
RPM
Revolutions Per Minute
RS
Recommended Standard
Rx
Receiver
SSID
Service Set IDentifier
TCP
Transmission Control Protocol
Tx
Transmitter
UART
Universal Asynchronous Receiver-Transmitter
UDP
User Datagram Protocol
USB
Universal Serial Bus
UL
Underwriters Laboratory
UV
Ultraviolet light
VLAN
Virtual Local Area Network

KINOVA® Gen3 Ultra lightweight robot User Guide 15
WEEE
Waste of Electrical and Electronic Equipment
KINOVA® Gen3 Ultra lightweight robot User Guide 16
Robot components
Overview
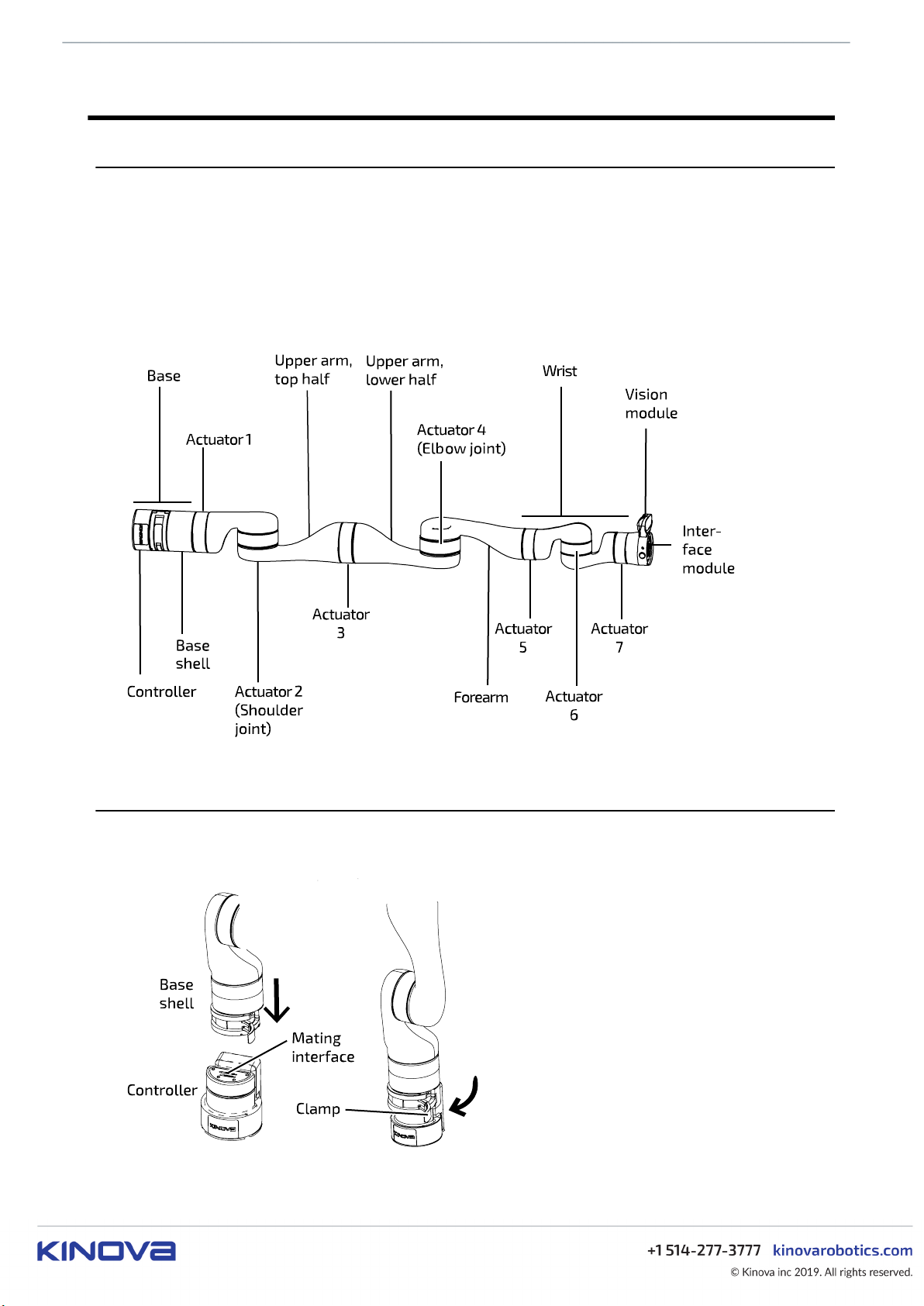
This section describes the main components of the KINOVA® Gen3 Ultra lightweight robot.
The robot consists of:
• base (base shell and controller)
• actuators
• interface module
• vision module
The following image shows the main components of the robot.
Figure 1: Robot main components (7 DoF model shown)
Base
This section describes the purpose, components, and functionalities of the robot base.
The Gen3 Ultra lightweight robot base features a quick connect base.
Figure 2: Quick connect base

KINOVA® Gen3 Ultra lightweight robot User Guide 17
The base is a two-part structure securing the robot onto its physical mounting point and connecting the
robot to power and control signals. This consists of:
• controller
• base shell
The controller is the "brains" of the robot. The internal components of the controller include:
• CPU
• Wi-Fi / Bluetooth adapter (Only Wi-Fi is used at present)
• Ethernet switch
• USB hub
• temperature sensor
• accelerometer/gyroscope
A Linux web server runs on the controller and manages connectivity between the controller and the arm
devices, and between the controller and an external computer.
The controller includes a connector panel at the rear for connecting to power and external devices.
The controller has four mounting holes (M6) on its underside. The controller is shipped connected with
screws to a circular mounting plate with through holes for mounting to surfaces and a slot to put a clamp
between the robot and the plate for quick setup and takedown tabletop mounting.
Figure 3: Mounting plate
The mounting plate can also be removed from the controller by removing the screws, giving access to the
four mounting holes and allowing the controller to be mounted directly on the surface.
The base shell, meanwhile, is the bottom part of the robotic arm shell connected to the first actuator. It
mounts onto the controller and is secured in place with an integrated clamp.
A mating interface on the top of the controller provides an electrical connection between the base shell
and the controller.
Note: The controller mating interface needs to be kept free of dust and moisture to protect the electrical
contacts. Wipe down with a soft dry cloth to keep the interface clean.
The clamping mechanism and mating interface allow the robot to be quickly and easily removed from the
controller while leaving the controller mounted in place with cables still connected.
Controller quick connect system
This section describes the controller quick connect system.
The base of the robot is equipped with a quick connect system that allows for simple connect / disconnect
of the base shell and controller. This allows the arm to be quickly detached from the mounting point of the
arm without disconnecting any cables. This can be useful for transport, for removal of the arm for servicing
or for convenient re-siting of the arm between multiple installation sites.
Note: Be careful to avoid damage to the electrical contacts on the mating interface of the controller when
the base shell is disconnected. Make sure to keep the surface dry and free from dust.
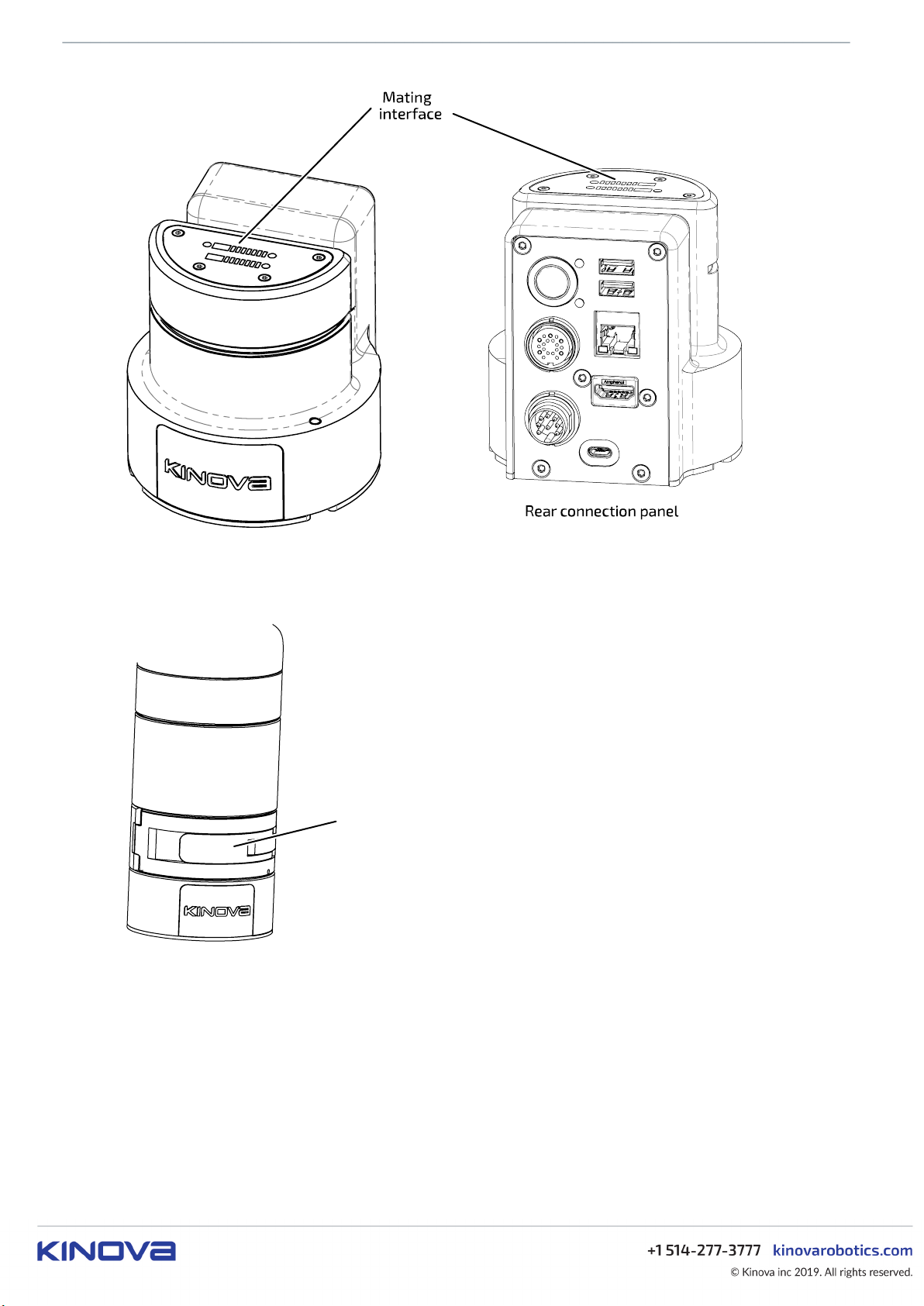
KINOVA® Gen3 Ultra lightweight robot User Guide 18
Clamp
Figure 4: Controller quick connect
The base shell slides over and onto the controller, establishing an electrical connection with the arm. The
base shell is secured in place on the controller by closing the front clamp.
Figure 5: Base shell installation
To remove the arm from the controller, flip open the clamp and slide off the base shell.
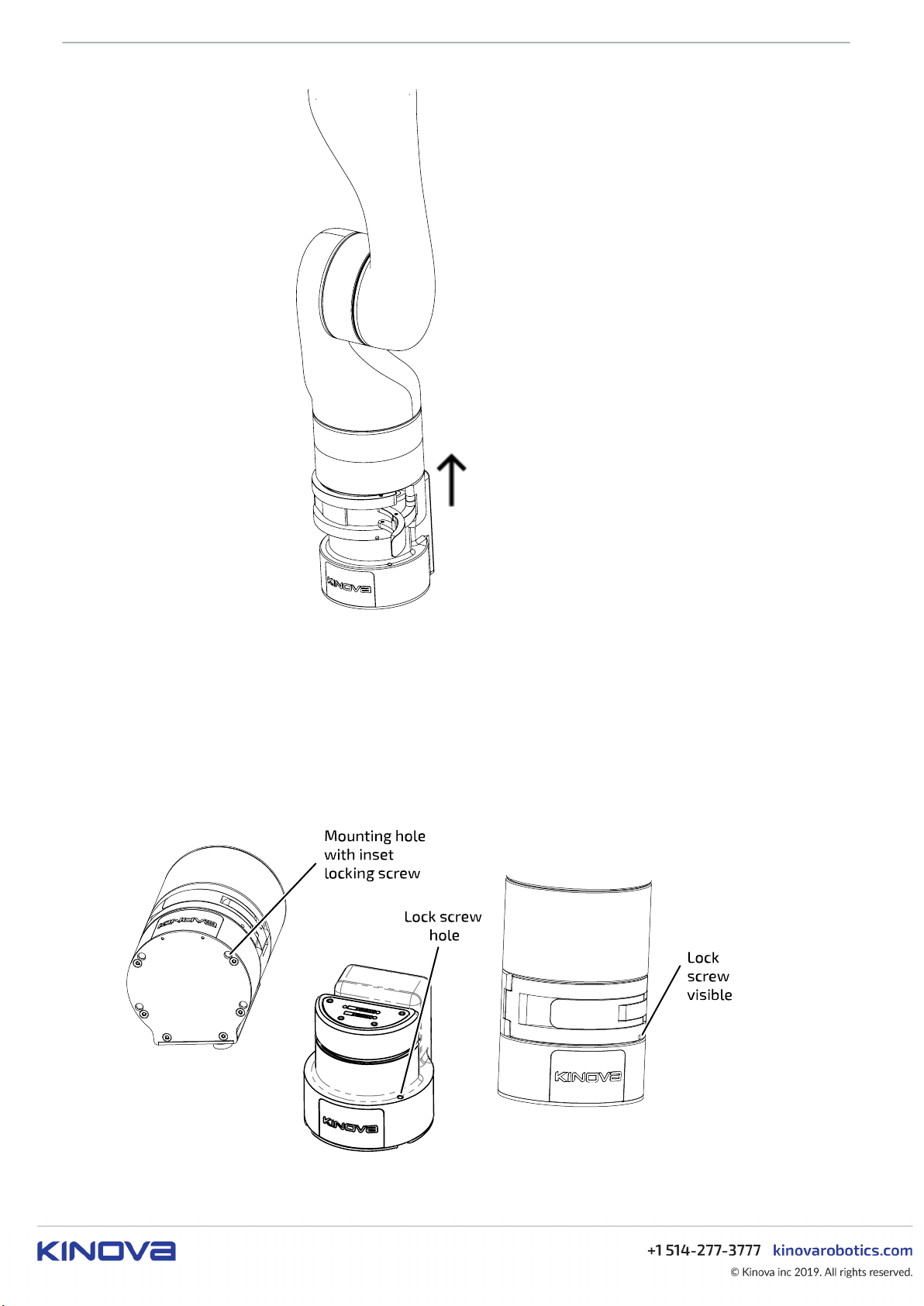
KINOVA® Gen3 Ultra lightweight robot User Guide 19
Figure 6: Base shell and arm removal
The controller features a locking screw within the mounting hole on the front bottom left (from the
perspective of an observer behind the connector panel). Turning the locking screw with a 3 mm hex key
clockwise will cause the screw to go forward and protrude through a hole above the top surface of the
controller a few mm until it reaches the end of its travel. If the base shell is already clamped onto the
controller when this is done, the set screw will interface with a mechanism on the clamp and prevent the
clamp from opening until the set screw is withdrawn. This serves as a safety mechanism. There is a hole on
the clamp where the end of the lock screw can be seen when it is fully engaged. Confirm visually that the
lock screw is not engaged before trying to open the clamp.
Figure 7: Lock screw mechanism
KINOVA® Gen3 Ultra lightweight robot User Guide 20
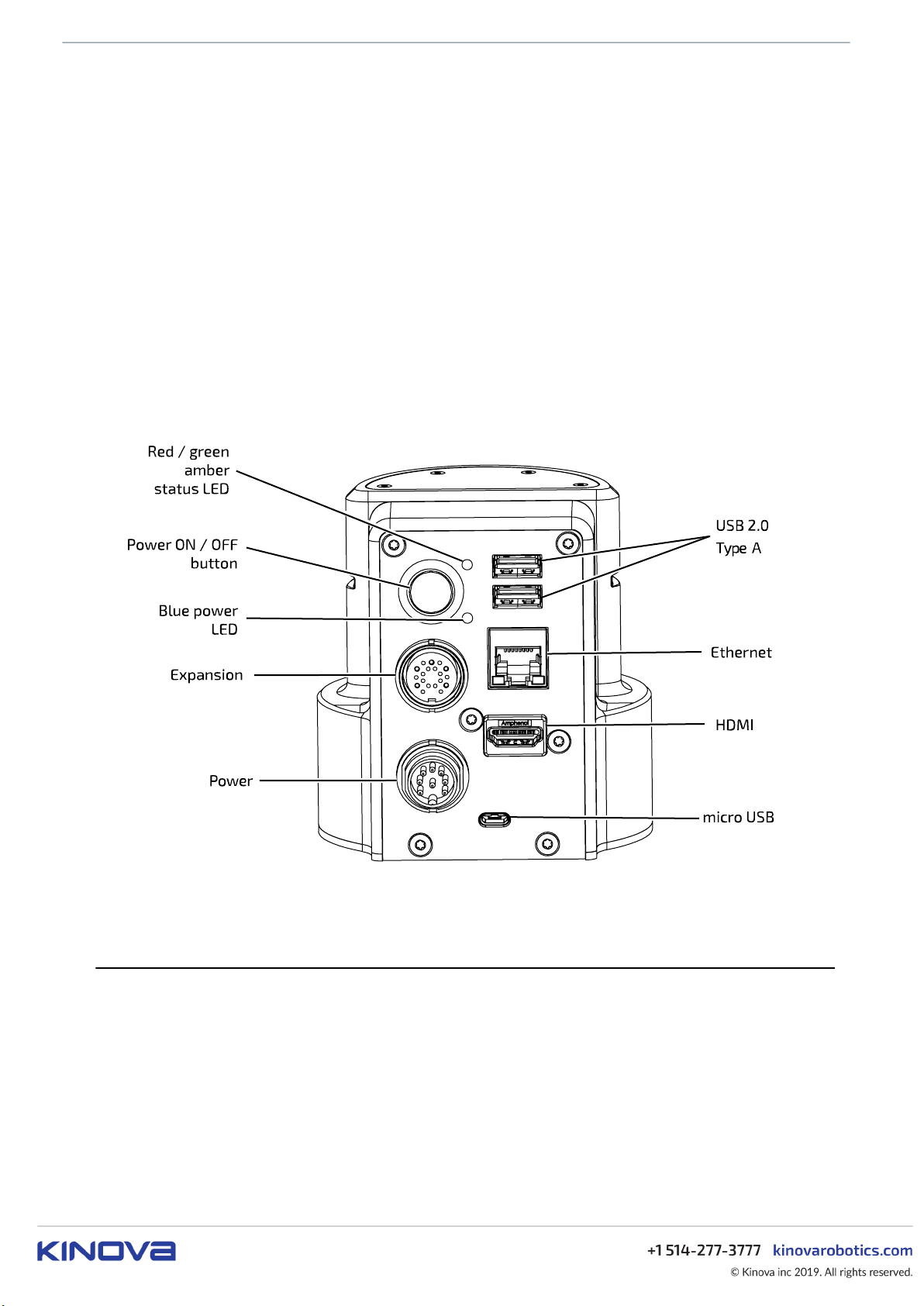
Controller connector panel
This section describes the controller connector panel of the robotic arm.
The controller connector panel is located at the rear of the controller. It features the following elements:
• On / Off power switch
• blue power LED indicator
• red / amber / green status LED indicator
• HDMI Out (camera video*)
• Micro USB (internal use)
• USB 2.0, type A - qty 2 - for wired controller. Top port 1 A for charging. Bottom port 500 mA max, for
peripherals.
• RJ-45 Gigabit Ethernet (LAN)
• Binder-USA 09 0463 90 19 (joystick, discrete I/O, E-Stop, expansion)
• Lumberg 0317 08 (power)
Note: Cables connected to the base controller must be less than 3 m in length. If not, you must perform a
risk analysis. Cables longer than 3 m can potentially have an effect on radio frequency emissions and the
immunity of the product.
Figure 8: Controller connector panel
* to be implemented in future software release
Actuators
This section provides an overview of the robot actuators.
The rotational motion at each of the joints of the robot is powered by rotary actuators. There is one actuator
for each joint. Each actuator allows for potentially unlimited rotation in either direction (There are software
limits however on some joints however to avoid collisions between robot shell segments).
There are two sizes of actuator:
• small
• large
KINOVA® Gen3 Ultra lightweight robot User Guide 21
Each actuator has:
• torque sensing
• current and temperature sensing on each motor phase
Wrist joints use small actuators, while large actuators are used for other joints. All actuators are equipped
with a 100:1 strain wave gear for smooth motion.
The actuators are connected to each other and to the interconnect board using a series of 41-pin flex cables.
These cables convey:
• power
• 2 x full-duplex 100 Mbps Ethernet
º one for 1 kHz control
º one for vision / expansion data traffic
Actuator Specifications:
• actuator speed (maximum, unloaded):
º 25 RPM (small)
º 13 RPM (large)
• actuator torque (small):
º 13 N·m (nominal)
º 34 N·m (peak)
• actuator torque (large):
º 32 N·m (nominal)
º 54 N·m (peak)
Interface module
This section describes the interface module.
The interface module provides an interface for connecting a gripper or other tools at the end of the arm.
The interface module also provides a mounting point and connection for the vision module.
The interface module has a connection interface at the end of the arm, and is surrounded on the sides by a
bracelet shell. The vision module is mounted on the top of the bracelet.
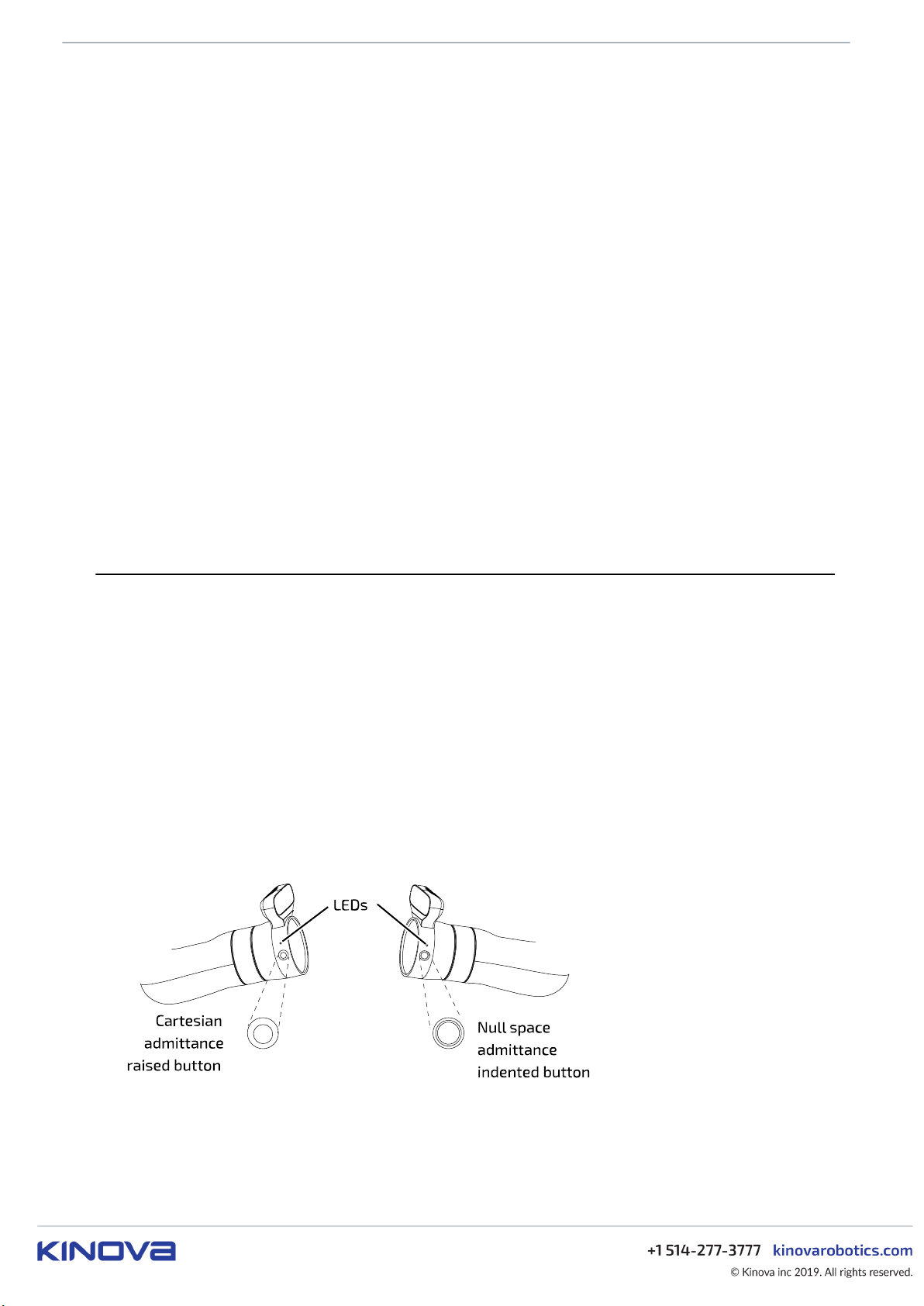
The bracelet includes two buttons used to activate admittance modes to interact with the robot. By default
the button on the right hand side (viewed from behind) puts the arm into Cartesian admittance while the
button on the left puts the arm into null space admittance. The two buttons can be distinguished easily by
touch without looking; the Cartesian admittance mode button sticks out from the surface in the center,
while the null admittance mode button is slightly indented in in the center and ring-shaped.
Note: Only one of the buttons can be active at any given time. If you press the two buttons together or in
close succession, the button pressed later will take effect.
The bracelet also includes two amber LEDs.
The interface module takes a 41-pin input from the last actuator of the robot.
KINOVA® Gen3 Ultra lightweight robot User Guide 22
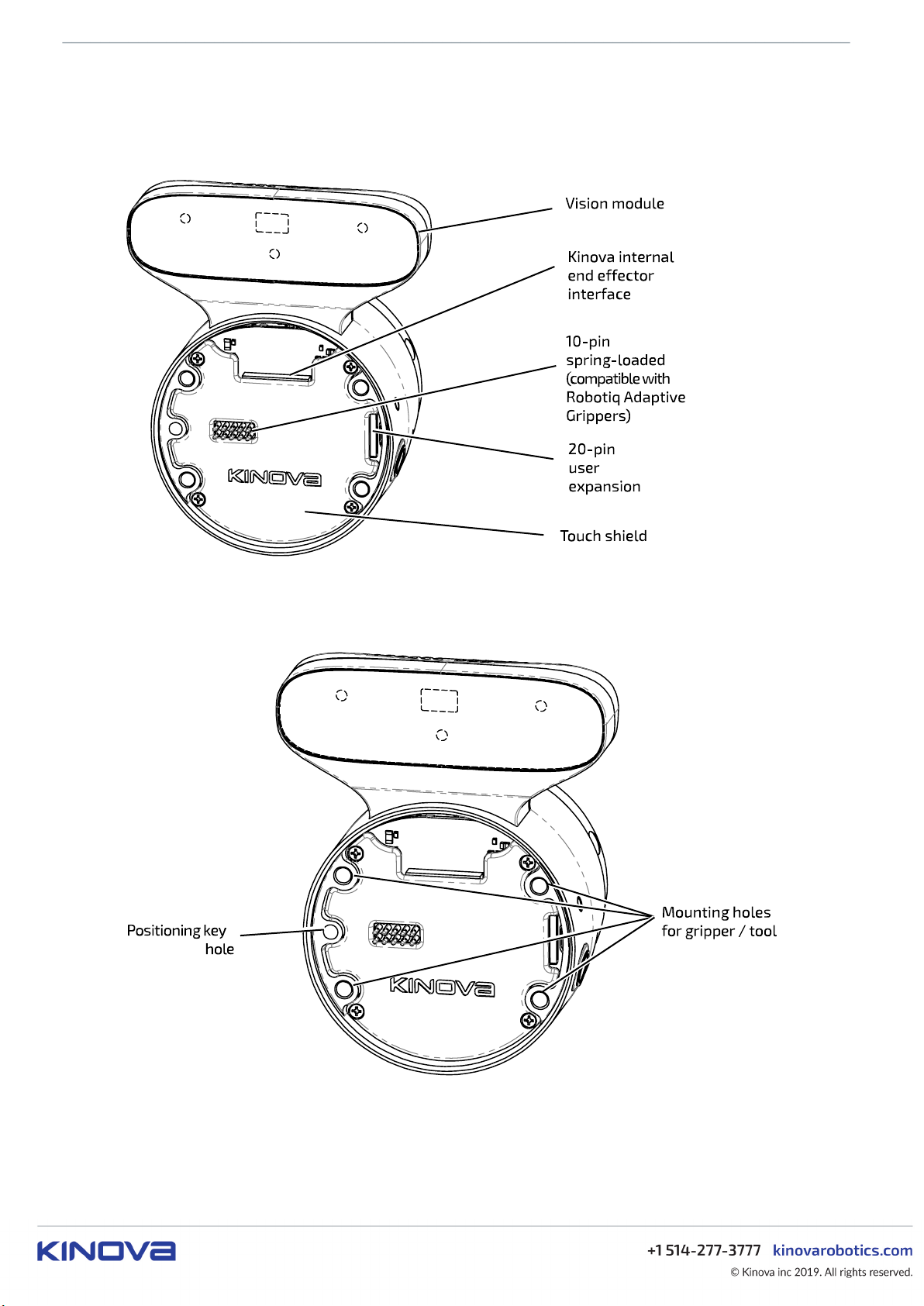
The interface exposes connectors that allow different tools to be integrated with the robot. It features:
• Kinova internal end-effector interface
• 10-pin spring-loaded connector with RS-485 (compatible with Robotiq Adaptive Grippers)
• 20-pin user expansion interface
Figure 9: Interface module
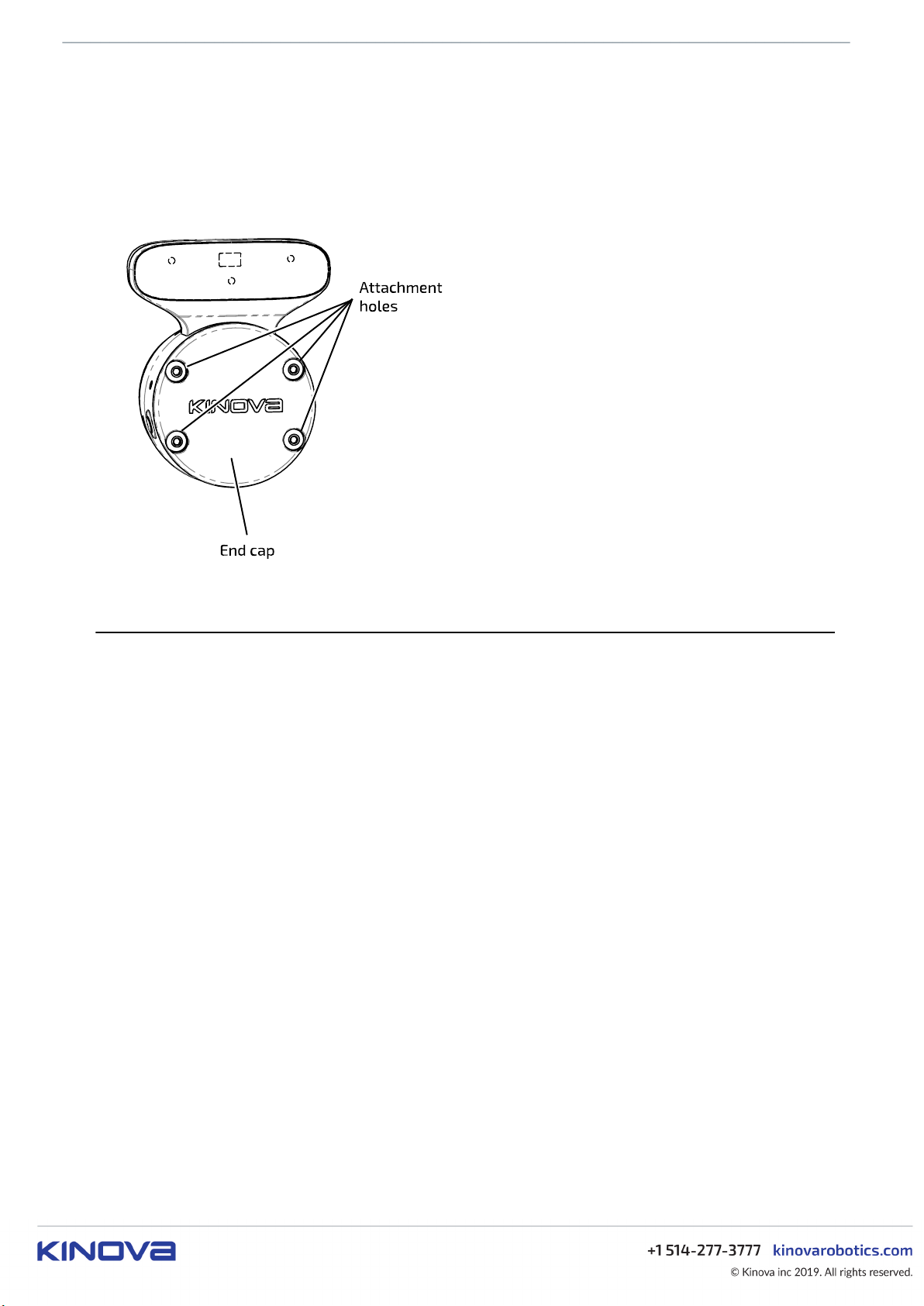
The interface also includes four mounting holes for physical mounting of a tool and a position key hole used
for alignment of the tool in the right orientation.
Figure 10: Mounting holes and positioning key hole
The interface module includes a 6-axis accelerometer / gyroscope. The module also includes an Ethernet
switch to route connectivity and control data between the interface module and the vision module and any
connected tool (e.g. gripper).
KINOVA® Gen3 Ultra lightweight robot User Guide 23
Note: The printed circuit board (PCB) of the interface module is partially covered with a touch shield
with holes to expose only the output connectors - 10-pin spring loaded connector, 20-pin user expansion
connector, and Kinova internal end effector interface.
Note: When there is no tool present, an end cap needs to be installed over the face of the interface module
to ensure compliance with EMI/EMC. Kinova provides an end cap with the robot. This end cap is attached
to the interface with screws using the mounting holes on the interface. The end cap needs to be removed
to attach a tool to the robot.
Figure 11: End cap
Vision module
This section describes the Vision module.
The vision module is a module provided by Kinova to enable robotic computer vision applications.
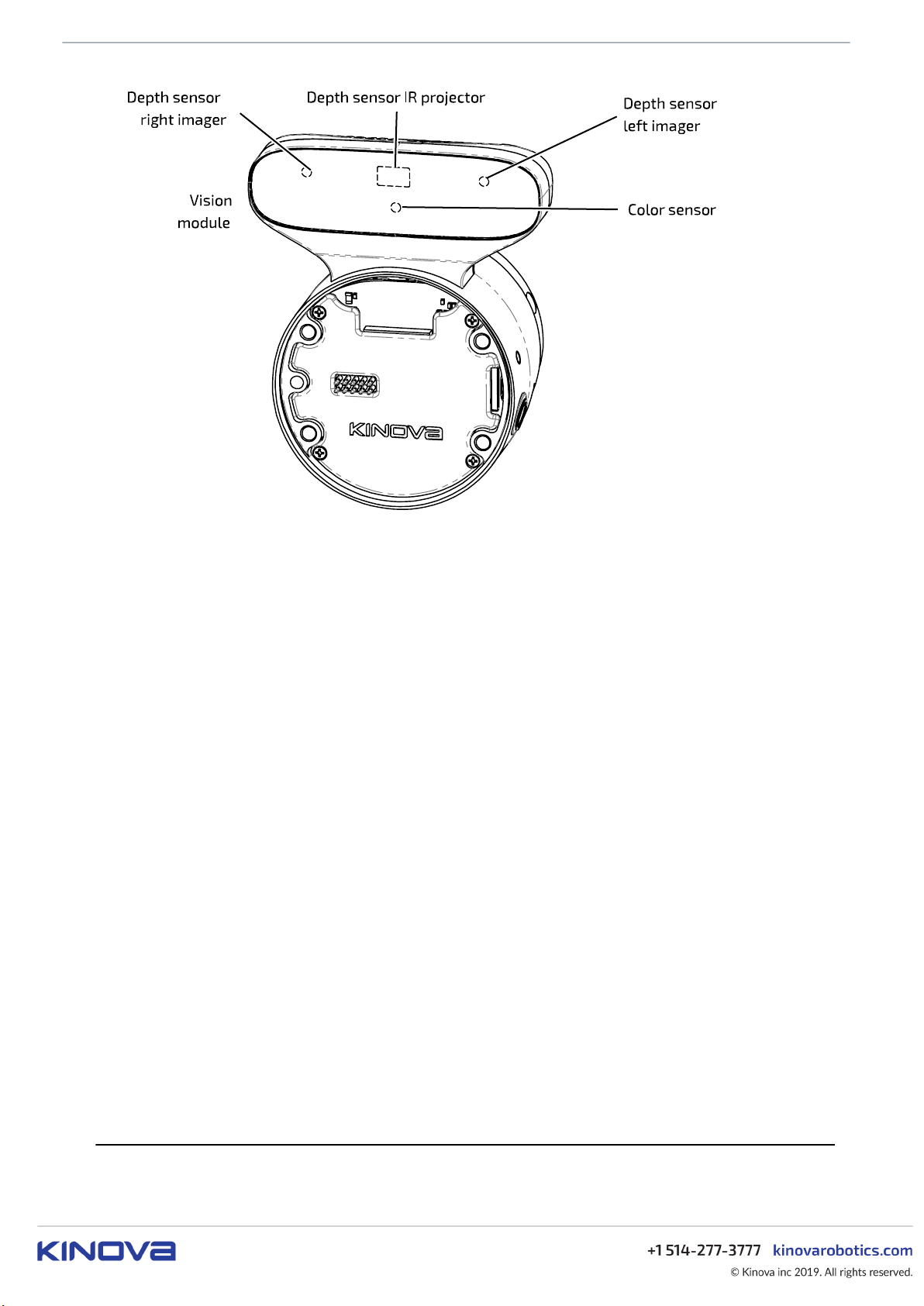
The vision module is included as part of the interface module. A housing containing sensors protrudes from
the top of the Interface module. The sensors are contained on the front face of the housing, facing out
parallel to the axis of the last actuator.
The Vision module is used to capture and stream image data captured looking in the direction the end of
the arm / end effector is pointed. The Vision module includes both a color camera (Omnivision OV5640)
and a stereo depth sensor (Intel® RealSense™ Depth Module D410).
KINOVA® Gen3 Ultra lightweight robot User Guide 24
Figure 12: Vision module sensors
The color sensor captures a 2D array of RGB pixel data representating the field of view from the perspective
of the sensor.
The depth sensor includes an IR projector and two stereo imagers - left and right. Here left and right are
from the perspective of an observer looking out from the sensor toward the imaged region. The depth
sensor captures a 2D array of pixels and the depth for each pixel within the field of view of the sensor.
Together, the two sensors allow the capture of RGBD (color and depth) data. Both camera sensors can be
configured using the KINOVA® KORTEX™ VisionConfig interface.
Note that performance for the Vision module depth sensor may be degraded at temperatures below 0° C.
For more details, please consult the depth sensor data sheet.
The color and depth sensors data streams are made accessible to developers through a computer with a
connection to the robot. For more information on accessing these data streams programatically, see here.
Vision module specifications
Color sensor:
• resolution, frame rates (fps), and fields of view (FOV):
º 1920 x 1080 (16:9) @ 30, 15 fps; FOV 47 ± 3° (diagonal)
º 1280 x 720 (16:9) @ 30, 15 fps; FOV 60 ± 3° (diagonal)
º 640 x 480 (4:3) @ 30, 15 fps; FOV 65 ± 3° (diagonal)
º 320 x 240 (4:3)@ 30, 15 fps; FOV 65 ± 3° (diagonal)
• focusing range - 30 cm to ∞
Depth sensor:
• resolution, frame rates (fps), and fields of view (FOV):
º 480 x 270 (16:9) @ 30, 15, 6 fps; FOV 72 ± 3° (diagonal)
º 424 x 240 (16:9) @ 30, 15, 6 fps; FOV 72 ± 3° (diagonal)
• minimum depth distance (min-Z) - 18 cm
Robot communications and network interfaces
This section describes communications and network interfaces within the robot.
KINOVA® Gen3 Ultra lightweight robot User Guide 25
The devices in the robot, from the base of the arm through the chain of actuators, to the interface
module at the end of the arm, are daisy chained together using 41-pin flex cables which carry power and
communications.
The base, actuators, and interface module each contain an Ethernet switch. The Ethernet port on the
connector panel of the base controller allows an external computer to connect to the Ethernet switch of
the base.
The Kinova vision module and any 3rd party tool that makes use of Ethernet communications user
expansion pins in the interface connect directly to the interface module Ethernet switch. Other tools (for
example any gripper interfacing using the 10-pin spring loaded connector on the interface) will interface
instead with the interface module CPU (which is connected to the Ethernet switch).
Together, this enables dual Ethernet networks between all the devices (base, actuators, interface, Vision
module, and end effector tools) with data carried between the base and interface over the 41-pin flex cables.
This is accessible from a client computer via the 1 Gbps Ethernet port on the base controller connector
panel.
The flex cables carry two distinct 100 Mbps Ethernet communications channels.
• one is for control and monitoring of actuators, interface module, and gripper (if present)
• the other is for data transmission for the vision module and expansion.
Each device connected to one of the Ethernet switches has an IP address to allow routing of
communications, transmitted using UDP.
The actuators and interface module have the following default IP addresses:
Table 4: Actuator and gripper IP addresses
Device IP address
Actuator 1 10.10.0.10
Actuator 2 10.10.0.11
Actuator 3 10.10.0.12
Actuator 4 10.10.0.13
Actuator 5 10.10.0.14
Actuator 6 10.10.0.15
Actuator 7 10.10.0.16
Interface module 10.10.0.17
The expansion devices (Vision module and expansion tool peripherals) have the following IP addresses:
Table 5: Expansion IP addresses
Expansion Devices IP address
Vision module 10.20.0.100
Expansion device 10.20.0.200/24*
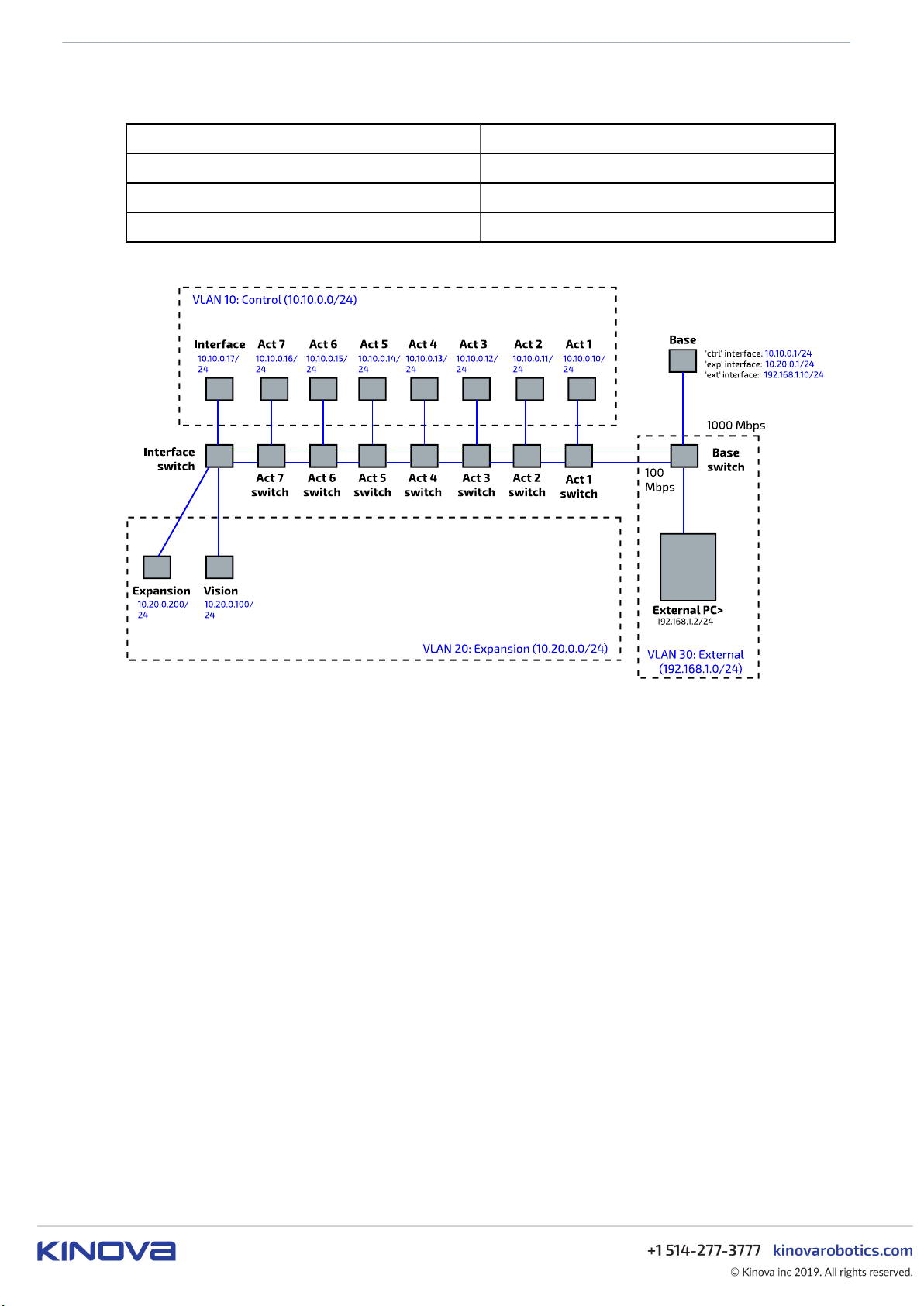
The robot Ethernet network features three VLANs:
• VLAN 10 : control
• VLAN 20 : expansion
• VLAN 30 : external
The base has network interfaces to all three of these VLANs:
KINOVA® Gen3 Ultra lightweight robot User Guide 26
Table 6: Base network interface IP addresses
VLAN IP address
CTRL interface IP address 10.10.0.1/24*
EXP interface IP address 10.20.0.1/24*
EXT interface IP address 192.168.1.10/24*
The graphic below illustrates the topology of the networks.
* CIDR notation
KINOVA® Gen3 Ultra lightweight robot User Guide 27
Getting started
Overview
This section describes how to get started with the arm.
The pages that follow lead you through getting started with the robot. This includes:
• unboxing
• physically mounting the robot securely
• provisioning electrical power
• controlling the robot using an Xbox gamepad
• moving the robot in admittance using physical buttons
• connecting a computer to the robot
•
connecting to the KINOVA® KORTEX™ Web App
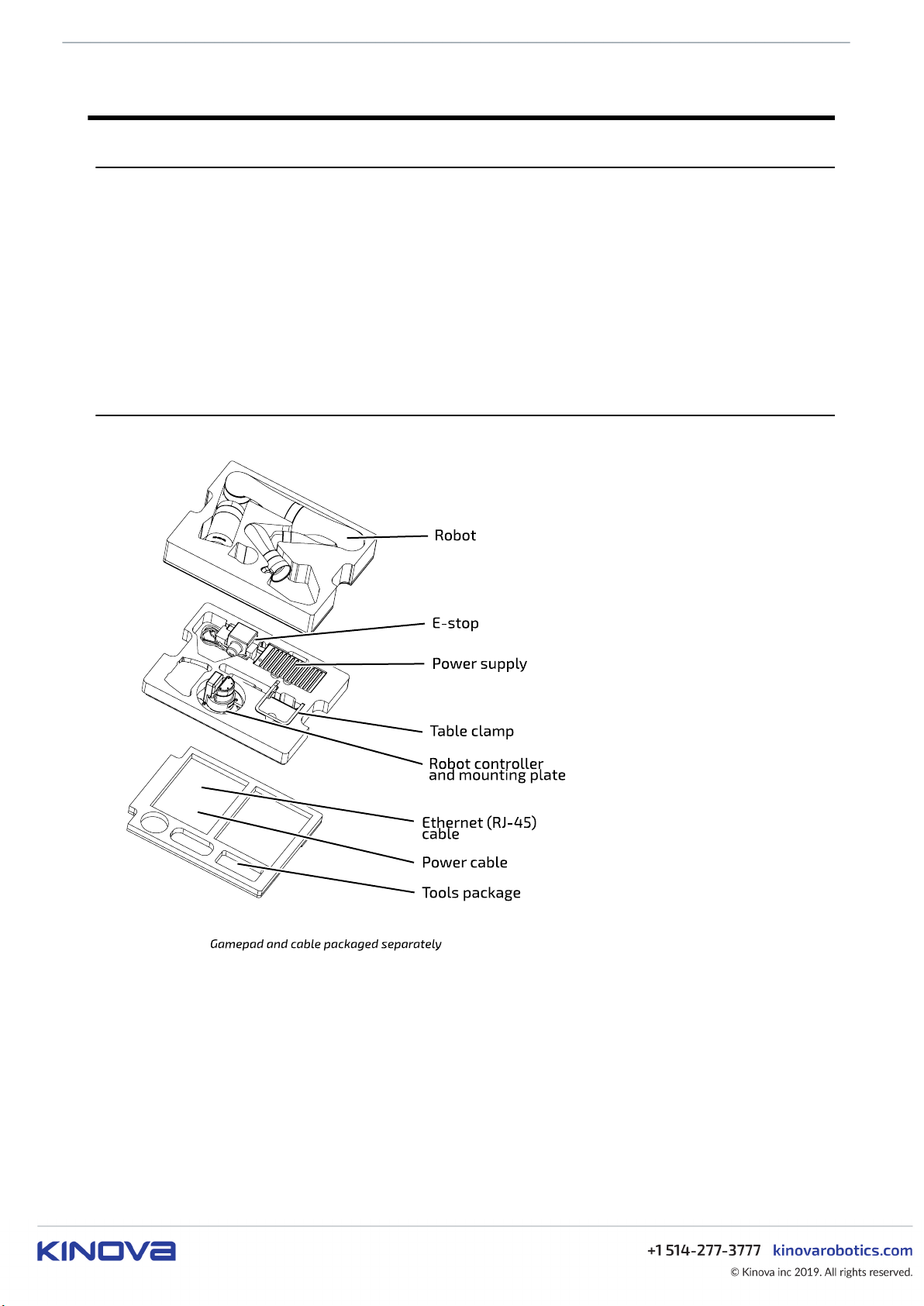
What's in the case?
This section describes the KINOVA® Gen3 Ultra lightweight robot shipping case contents.
Figure 13: Gen3 Ultra lightweight robot shipping case contents
The shipping case contains the following contents.
At the top of the interior of the box, you will find the Quick Start Guide. The Quick Start Guide is a large
printed visual guide.
The Quick Start guide provides a handy reference for first steps, and should have you up and running within
30 minutes. Make sure to keep the Quick Start Guide as a reference for people in your team or organization
getting newly acquainted with your robot. The Quick Start Guide is also available on the Kinova website:
www.kinovarobotics.com/knowledge-hub/gen3-ultra-lightweight-robot
The contents of the box are arranged in three layers from top to bottom. These packing layers can be
removed from the box to unpack the contents.
KINOVA® Gen3 Ultra lightweight robot User Guide 28
In the top layer:
• Robot
In the second layer:
• Power adapter and cable with integrated emergency stop (E-stop) button
• Table clamp
• Mounting plate and robot controller
The bottom area contains:
• Ethernet (RJ-45) cable
• Power cable
• Bag with useful tools and fasteners
º hex keys: 3, 4 and 5 mm
º M5 screws (qty. 4)
An Xbox gamepad and cable are shipped with the robot, but packaged separately.
There is also space for storage of papers and other items.
Note: The shipping case is also useful for transportation and storage of the robot. Make sure to save it and
the packing layers within for future use.
Manipulating the robot joints when the robot is powered off
This describes how to manipulate the robot joints when the robot is powered off.
When the robot is powered on, the actuators will hold their position and prevent the joints from moving
in response to external forces and torques. When the power is on, the arm will not move except when
commanded. The arm joints are stiff and you will not be able to rotate the joints with your hands.
When the robot is powered off, as it is when you first receive the robot, the joints can be moved by hand
slowly.
Note: If you move the joints too quickly, mechanisms within the joints will limit the speed.
This moveability of the joints when the robot is unpowered is useful when taking the robot out of the box
and setting it up to get started. This lets you arrange the joints of the robot into a stable, balanced position
prior to mounting and powering on the robot.
Robot mounting options
This section describes the physical mounting options for the robot.
The first step to getting started with the arm after unboxing is to physically mount the arm in a stable
manner so that the robot can be connected and used.
The most basic mounting option uses the mounting plate and a table clamp to quickly mount the robot on
a tabletop in a "right side up," vertical orientation.
However, if is also possible to mount the robot in different ways, as well as different orientations, depending
on the needs of your particular application. The sections that follow will describe this in more detail.
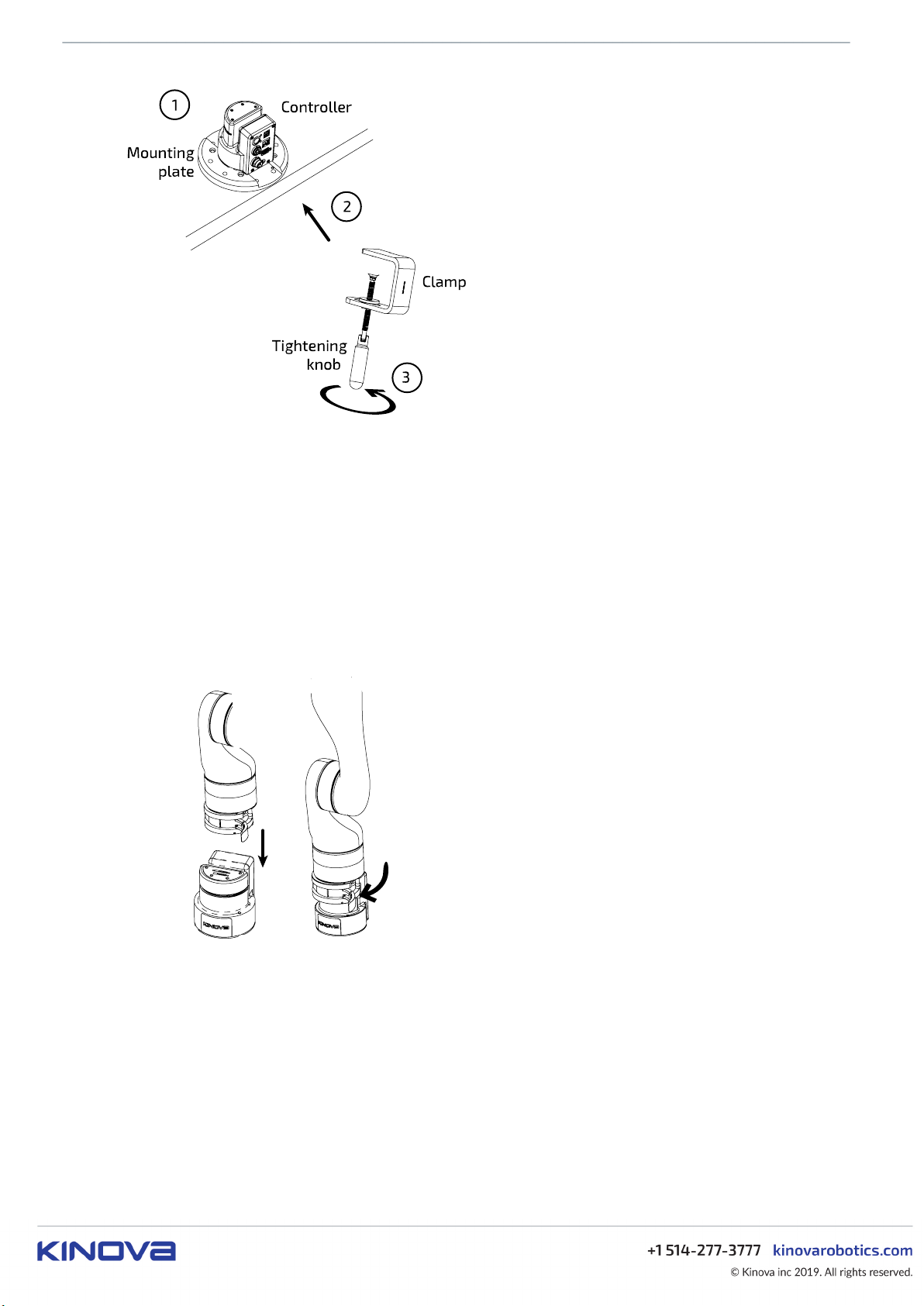
Mounting the robot on a tabletop
This section describes the procedure for mounting the robot oriented vertically on the edge
of a tabletop using the clamp.
Before you begin
The robot should have the joints of the robot unfolded so that it is in a stable, balanced
position ready for mounting.
About this task
The robot is mounted to a tabletop using the base mounting plate and a table clamp.
Note: The table must be large and sturdy to support a tabletop edge mounting. If the table is too small or
too flimsy, the weight of the robot at the table edge combined with the movement vibrations may render
it unstable.
KINOVA® Gen3 Ultra lightweight robot User Guide 29
Procedure
1. Place the base controller and mounting plate on the tabletop, next to the edge.
Note: You can place the controller in one of two orientations. Either with the connector panel facing out
toward the edge of the table, or with the front side of the base controller facing out.
2. Turn the tightening knob on the table clamp to open up the clamp and then slide the clamp into the slot
between the mounting plate and the bottom of the base controller.
3. Turn the tightening knob by hand until the mounting plant is firmly clamped to the table top.
Note: Do not overtorque.
4. Make sure that the clamp at the bottom of the robot base shell is opened. While holding the robot, you can
now lower the base shell of the robot onto and over the base controller.
5. Once the robot is fully lowered onto the base controller, close the clamp to secure the robot in place on
the base controller.
Note: The clamp must be properly closed to ensure stability of the robot. Damage can potentially be done
to the robot if it is operated while unstable.
Results
The robot is now mounted on the tabletop.

KINOVA® Gen3 Ultra lightweight robot User Guide 30
What to do next
You can now proceed to connect the robot to the power supply and E-stop.
Mounting the robot on a horizontal surface without the table clamp
This section describes how to mount the robot on a horizontal surface without the table
clamp..
About this task
Here, we describe mounting the robot in a vertical orientation on a flat, horizontal surface,
affixing the mounting plate or controller base to the surface using screws and sunk holes in
the surface.
Procedure
1. Choose whether to mount the robot base controller directly onto the surface, or whether to use the
mounting plate.
2. Using either the mounting plate bolting pattern or the controller bolting pattern or as a guide, drill holes
into the surface. If the controller is to be mounted directly to the surface, the holes will have to be drilled
all the way through the mounting surface.
3. Use appropriate screws to mount either the base controller or the mounting plate to the surface. If the
base controller is mounted directly, the screws will need to go through the mounting surface from the
other side.
Controller mounting plate bolting pattern
This section describes the bolting pattern of the mounting plate. This is useful when
mounting the robot to a surface using the mounting plate.
Overview
The mounting plate is attached to the bottom of the base controller. The mounting plate has two sets of M8
screw holes (4) and one set of counter-sunk M6 screw holes (4) available for mounting the plate to a surface.

KINOVA® Gen3 Ultra lightweight robot User Guide 31
Mounting details
Figure 14: Mounting plate bolting pattern
Base controller underside bolting pattern
This section describes the bolting pattern on the underside of the base controller. This is
useful when you want to affix the robot base directly to a surface.
Overview
The underside of the controller has four M6 screw holes for mounting purposes. These holes are used for
attaching the mounting plate to the controller. When the mounting plate is removed, these holes can be
used for mounting the controller directly to a surface. In that case, holes must be drilled through the surface
so that screws can go through from the other side and into the controller mounting holes from underneath.
One of the screw holes in the controller base features an inset locking screw. Turning the locking screw
clockwise to the end of its travel (using a 3 mm hex key) while the base shell is clamped to the controller will
lock the two together and prevent the clamp from being opened.

KINOVA® Gen3 Ultra lightweight robot User Guide 32
Mounting details
Figure 15: Base and mounting holes
Figure 16: Base mounting holes pattern
Mounting the robot on a wall or ceiling
This section describes how to mount the robot on a wall or ceiling.

KINOVA® Gen3 Ultra lightweight robot User Guide 33
The procedure for mounting is generally similar to that of mounting onto a horizontal surface:
1. Choose whether to mount the controller directly to the surface, or using the mounting plate.
2. Drill holes in an appropriate pattern in the surface based on the appropriate bolting pattern diagram.
3. Attach the controller or mounting plate to the surface with appropriate screws.
There are however important differences.
It is essential to follow all special considerations for wall and ceiling mounting. This includes the need to:
• perform a careful analysis of the proposed mounting surface
• mount and clamp the robot onto the controller with the locking screw engaged before mounting the
robot on the surface
• configure the gravity vector and compute any needed transformations between the user / lab
reference frame and the robot base frame to account for the new orientation of the robot base
Special considerations and configurations for wall and ceiling mounts
This section describes special considerations that are important for wall and ceiling
mounts.
For safety reasons, there are special preparations and steps that need to be undertaken before mounting
the robot on a wall or ceiling.
Before trying to mount the arm on a wall or ceiling, perform a comprehensive analysis of weight,
torque, and vibrations and ensure the material is stable enough.
The locking screw on the bottom left front of the controller must be screwed in fully with a hex key
while the base shell is clamped on. This will block the clamp from being opened while the arm is mounted
on a wall or ceiling, and provides an added measure of security. The robot therefore needs to be clamped to
the controller and the lock screw adjusted before trying to mount the robot.
For wall mounting, the robot needs to be mounted with the controller connector panel facing
downwards. This is to prevent water ingress at the connector panel.
Note: A robot mounted in a ceiling mount is not certified for ingress protection.
Note: In a wall or ceiling mount, the gravity vector will have a different orientation than usual with respect
to the base reference frame. It will be necessary to set the gravity vector using the Kinova Web App
or Kinova.Api.ControlConfig API. If the gravity vector is not configured appropriately, the robot
control library will not be able to properly compensate for torques due to gravity on the robot and the robot
will behave in unexpected ways.
Note: The Cartesian control of the robot is by default in relation to the base reference frame. This base
reference frame will be rotated relative to the natural reference frame of the perspective of the user /
operator. You will need to apply the appropriate coordinate transformations to control the robot in these
orientations.
Adjusting the controller locking screw to secure base clamp
This section describes how to adjust the controller locking screw to secure the clamp on
the base.
Before you begin
You will need a 3 mm hex key.
About this task
Adjusting the controller locking screw while the base shell is attached and clamped locks
the clamp shut and prevents it from being opened. This improves the safety of the robot
when mounted on a wall or ceiling

KINOVA® Gen3 Ultra lightweight robot User Guide 34
Procedure
1. If the mounting plate is attached to the controller, one of the screws connecting the mounting plate to the
controller from below has to be removed to get at the locking screw. Identify the mounting hole with the
lock screw and remove it using the 3 mm hex key.
2. If the base shell and the robot are not already installed onto the controller, slide the base shell onto the
controller and close the clamp.
3. Using the same hex key, insert the end of the key into the mounting hole until the hex key engages with
the head of the lock screw. Turn the lock screw until it stops at the end of its travel. There is a hole on the
front of the clamp where the end of the lock screw can be seen when the lock screw is engaged with the
clamp mechanism. Confirm that you can see the screw.
4. Test the clamp to ensure that you can not open it.
Robot power adapter and E-stop
This section describes the power adapter and E-stop.
The power adapter allows power to be supplied to the robot using a wall outlet as a source. The cable
from the power adapter connects to the power connector on the base controller using a Lumberg 0322 08
connector.

KINOVA® Gen3 Ultra lightweight robot User Guide 35
The cable from the power adapter to the robot includes an integrated push-button E-stop connected in
series. The E-stop allows users to shut down the robot quickly in case of an emergency.
To engage the E-stop, press down on the red button on top of the E-stop. This will cut the power to the robot,
causing it to shut it down.
When the power is cut, the robot will descend. There are mechanisms within the large actuators to
slow the fall of the arm for safety purposes. However, it is recommended that if possible, users cradle the
robot as it falls.
To disengage the E-stop, rotate the button clockwise until it pops up.
Powering on the robot
This section describes how to connect the robot to an electrical power source.
The robot is powered by a 24V power supply (P/N DTM300PW240D2).
To power up the robot:
1. Connect the captive cable from the power supply to the circular Lumberg connector on the rear connector
panel in the controller of the robot, rotating the outer cylindrical locking shell of the connector until it is
just tight enough to secure the connector.
2. Plug the power supply into a wall outlet.
3. Push the power button and hold in for 3 seconds to power up the robot. This will initiate the power up
sequence.
Note: When the robot is properly powered on, the blue power LED will be illuminated green.
Note: Do NOT hold the power button down for too long. Holding the button for 10 seconds will result
in a factory reset.
Power-up, booting, and initialization sequence
This section describes the LED indications during the power-up sequence.
When the power button is held in to initiate a power-up, the robot will go through a regular boot up and
initialization sequence.
As part of the sequence, the base controller will check the firmware version of the robot devices. If one or
more of the devices are at an earlier version than the base controller, these devices will be updated.
The base LEDs will provide visual feedback as to the progress through the sequence, as follows:

KINOVA® Gen3 Ultra lightweight robot User Guide 36
Table 7: Power-up sequence LEDs indications
Sequence step LEDs indications
System booting
Firmware update of devices (if needed)
System initializing
System operating normally
From start to finish, the process should take no more than 30 seconds, except during a firmware update.
• Blue power LED, blinking
• Status LED, off
• Blue power LED, blinking
• status LED, solid
• Blue power LED, solid
• Status LED, amber, solid
• Blue power LED, off
• Status LED, green, solid
Resetting the robot to factory settings
This section describes how to reset the robot to factory settings.
About this task
At some point you may find it useful or necessary to roll back configurations on the robot
to factory defaults. This will return the robot to the state it was in when you received the
robot.
Note: This procedure assumes you are starting with the robot powered on. If the robot is already powered
off, you can start at step 3.
Note: Be sure that that this is what you want to do. This will erase all user-defined configurations including
protection zones, network settings, actions, user profiles, etc.
Procedure
1. Place the robot in a stable position.
2. Press and hold the base power button to power off the robot.
3. Press and hold the power button for 10 seconds.
4. The green status LED will go on to confirm the factory reset.
5. Release the power button. The robot will then boot with factory default configuration settings.
Operating the robot
This section gives an overview of the methods of controlling the robot.
There are three ways to operate the robot:
• physical gamepad (Xbox controller)
•
virtual joysticks over a network connection (KINOVA® KORTEX™ Web App virtual joysticks)
•
programmatically (KINOVA® KORTEX™ API)
Supported gamepad controllers
This section describes the supported gamepad controllers of the robot.
The robot currently supports the Xbox gamepad (USB wired connection only; Bluetooth for future
development).
Connecting an Xbox gamepad to the robot
This section describes how to connect an Xbox gamepad to the robot.
Before you begin
You will need:

KINOVA® Gen3 Ultra lightweight robot User Guide 37
Xbox gamepad
•
micro USB to USB-A cable
•
About this task
An Xbox gamepad can be used to operate the robot.
Note: The robot currently only supports a wired connection for the gamepad.
Procedure
1. Connect the micro USB connector plug of the cable into the micro USB port on the Xbox gamepad.
2. Connect the USB-A end of the cable into one of the two USB-A connectors on the base controller of the
robot.
Default gamepad control maps - Xbox gamepad
This section describes the default controller maps between the Xbox gamepad and the
actions on the robot.
Gamepad mappings overview
The robot has three default control maps for the Xbox gamepad.
1. Twist linear (controls the robot by velocity)
2. Twist angular (controls the robot by velocity)
3. Joint (controls the robot joint by joint by velocity)
General controls
Some controls apply the same across all maps. These are controls for:
• Entering an admittance mode
• Changing the active control map to the next or previous map in the list
• Opening and closing the gripper
• Clearing faults - a fault state will make itself known through a red LED on the base controller of the
robot. Pressing the left bumper clears the fault and returns the LED to green.
• Applying emergency stop - this will stop the robot.
• Reaching home or retract position
The available control maps are in a sequential list, starting with Twist linear and ending with Joint, as listed
above. Pressing the View or Menu buttons will cause the active control map to switch to the previous or
next control map on the list. The list can be thought of as circular - selecting previous when on the first map
will cycle around to the last map, and conversely, selecting the next map when on the last map will cycle
around to the first.
Table 8: General control mappings (common controls applying to ALL maps)
Action Control
Reach defined pose
Navigate
controller maps
Gripper command
Clear fault Left
Stop robot Right
Retract pose A (hold down)
Home pose B (hold down)
button
previous View button
next Menu button
close Left
trigger
open Right
bumper

KINOVA® Gen3 Ultra lightweight robot User Guide 38
Figure 17: General control maps with Xbox gamepad
Twist linear mapping
Twist linear is the default gamepad mapping when the robot is turned on and the controller
is connected. In this mode the end effector is translated in space with respect to the
Cartesian base frame. The end effector orientation does not change in this mapping. The
user controls the linear velocity of the end effector, including the linear speed.
Table 9: Twist linear - general controls plus:
Action Control
Toggle admittance
Cartesian X
translation command
Cartesian Y
translation command
Cartesian Z
translation command
Speed decrease down D-pad
Cartesian X
button
Nullspace Y
- down
+ up
Left stick
+ left
- right
- down
Right stick
+ up

KINOVA® Gen3 Ultra lightweight robot User Guide 39
Apply E-stop
Clear fault
Gripper close
Gripper open
Toggle Nullspace
Admittance
Toggle
Cartesian Admittance
Cartesian
translation Z
Cartesian
translation Y
Cartesian
translation X
Previous control mapping
Next control mapping
Hold to reach
home pose
Hold to reach
retract pose
Speed
+ / -
z
y
x
Z rotation
Y rotation
X rotation
Action Control
increase up
Figure 18: Twist linear controls with Xbox gamepad
Twist angular mapping
Twist angular can be thought of as a companion to the Twist linear control mapping. In Twist linear, the end
effector is translated with respect to the base reference frame while leaving the orientation unchanged. In
Twist angular, the control is pure rotation of the tool within the tool reference frame, around the three axes
of that frame. The user controls the angular velocity of the end effector in relation to those three axes.
Twist linear and Twist angular together specify a twist (consisting of three linear velocity terms and three
angular velocity terms) to be applied to the end effector (Cartesian control).

KINOVA® Gen3 Ultra lightweight robot User Guide 40
Apply E-stop
Clear fault
Gripper close
Gripper open
Toggle Nullspace
Admittance
Toggle
Cartesian Admittance
Z
rotation
Y
rotation
X
rotation
Previous control mapping
Next control mapping
Speed + / -
Hold to reach
home pose
Hold to reach
retract pose
Table 10: Twist angular - general controls plus:
Action Control
Toggle admittance
Cartesian Y
rotation command
Cartesian X
rotation command
Cartesian Z
rotation command
Cartesian X
Nullspace Y
- left
+ right
- down
+ up
- left
+ right
decrease downSpeed
increase up
button
L stick
R stick
D-pad
Figure 19: Twist angular controls with Xbox gamepad
Joint mapping

KINOVA® Gen3 Ultra lightweight robot User Guide 41
Joint control offers direct control of the rotational movement of the joint actuators. In this mode you can
toggle through the joints (actuators) one by one, starting with the first and going through in increasing
order. On reaching the last actuator, it will then cycle back to the first. The joint angular speed (ω) can be
controlled.
Table 11: Joint - general controls plus:
Action Control
Toggle admittance Joint X button
Joint speed
Speed
Navigate joints
ω-
ω+
increase up
decrease down
Previous left
Next right
left
right
L stick
D-pad
Figure 20: Joint controls with Xbox gamepad
Home and retract positions
This section describes the home and retract positions of the robot.
The robot includes two pre-configured poses that can be reached using the Xbox gamepad.
The home position sets the robot into a convenient "ready" position. The home position is reached by
holding down the B button on the Xbox gamepad.
The retract position folds the robot up into a compact pose. This can be a useful position to out the robot
into for periods when it will not be in use. The retract position is reached by holding down the A button on
the Xbox gamepad.
Putting the robot into admittance using the interface buttons
This section describes how to put the robot into admittance modes using the buttons on
the sides of the interface module.
The interface module has two buttons on its side that can be used to temporarily put the robot into
admittance. This can be a convenient way to take ahold of the robot and move it into a desired position, or
to explore the flexibility of the arm at a particular position.

KINOVA® Gen3 Ultra lightweight robot User Guide 42
The two interface module buttons each offer access to one admittance mode.
Figure 21: Interface module admittance buttons
The button with the raised solid circle shape is for Cartesian admittance, in which the end effector of the
robot moves in response to force exerted on it.
The button with the indented or ring shape is for null space admittance. In this mode the end effector stays
in a fixed position and orientation, while the other joints move within the null space available at the given
end effector (seven degrees of freedom to specify six coordinates of position and orientation gives a free
degree of liberty to move within different solutions of the inverse kinematics of a given pose).
To engage one of the admittance modes, hold down the button and exert a moderate amount of force on the
robot. The arm will be in admittance mode as long as the button is held down. When the button is released,
the robot will no longer be in admittance mode and will return to the previously engaged control mode.
Connecting a computer to the robot
This section gives an overview of the methods available to connect a computer to the robot.
There are two ways of connecting a computer to the robot arm:
• Ethernet (direct or over a small local network)
• Wi-Fi
Connecting a computer to the robot via Ethernet (for the first time)
This section describes the procedure to connect a computer to the robot via a wired
connection for the first time. This procedure requires some configuration of the computer's
network adapter.
About this task
This procedure is required to connect a computer to the computer for the first time via a
wired Ethernet connection. This requires some configuration of the computer. The following
procedure describes details for Windows 10. The details will be somewhat different for
other OS platforms, but the high level steps will be the same.
Procedure
1. Connect an RJ-45 Ethernet cable from your computer's wired network adapter to the base Ethernet port.
2. On your computer, open Control Panel > Network and Internet > Network and Sharing Center

KINOVA® Gen3 Ultra lightweight robot User Guide 43
3. Select Change adapter settings
4. Select wired Ethernet adapter (i.e. Local Area Connection) and choose Properties.
5. Select Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4) and choose Properties.

KINOVA® Gen3 Ultra lightweight robot User Guide 44
6. Select Use the following IP address and enter IPv4 address:192.168.1.11 and Subnet mask:
255.255.255.0
7. Press OK.
Results
Your computer is now connected physically to the robot and ready to communicate.
What to do next
You can now access the Web App.
KINOVA® KORTEX™ Web App
This section gives an overview of the Web App.
The Web App provides a HTML Web browser based GUI to interact with the arm and perform basic tasks
without using programming commands.

KINOVA® Gen3 Ultra lightweight robot User Guide 45
The Web App allows users to control and configure the robot via the GUI.
This includes:
• Real-time control of the robot in different modes using different virtual joysticks
• Setting the arm into admittance modes to manipulate the arm using external forces / torques
• Viewing the feed from the Vision module color sensor
• Configuring
º robot performance parameters and safety thresholds
º protection zones
º network settings
º backup management
º user profiles
• Reading
º system information
º notifications
• Defining robot poses and trajectories
• Managing control mappings for physical controllers
• Monitoring robot parameters
• Upgrading the robotic arm firmware
The Web App can be run from either a desktop / laptop PC connected by wired Ethernet to the arm, or from
any computer on the same local network. This includes local Wi-Fi neworks. The Web App is a responsive
web application, and can be run from both mobile devices (smartphone or tablet) or desktop computers.
The Web App is described in detail in the KINOVA® KORTEX™ Web App User Guide section.
Accessing the KINOVA® KORTEX™ Web App
This section describes how to launch the Web App.
Before you begin
You should be using a computer that is connected to the robot either over a wired (direct or
over local area network) or wireless connection and you should have the IP address of the
robot on the network over which you are connected.
About this task
Procedure
1. From the computer web browser, enter the appropriate IP address for the arm base to access the Web App.
Note: By default, the IP address to use here is 192.168.1.10. If you have configured the arm so that
the computer and arm are both connected to the same local area network, whether wired or over Wi-Fi,
use the new configured IP address.

KINOVA® Gen3 Ultra lightweight robot User Guide 46
2. If the connection between the arm and computer is configured correctly, the Web application should
launch and present a login window. In the login window, enter the following credentials:
• username: admin
• password: admin
3. Click CONNECT. The application will initialize. If all is successful, the application will open to a Monitoring
screen that displays live parameters for the robot.
Changing the robot wired connection IP address and connecting the robot to a LAN
This section describes how to change the robot's wired connection IP address and connect
the robot to a local area network (LAN).
Before you begin
You need to have already established a wired connection to your computer via Ethernet cable
and the computer's local network adapter port. You will need information about the
available IP addresses on the local area network (LAN) to which you want to connect the
robot.
About this task
This procedure is used to configure the robot so that you can connect a computer to the
robot remotely over your local area network.
Note: For security reasons, we do not recommend connecting the robot to a WAN. The network should be
a simple local area network with low traffic.
Procedure
1. Open the Web application and go to the Networks page. Open the Ethernet tab.
2. Modify the IPv4 address, IPv4 subnet mask, and IPv4 gateway to match an available IP address with the
IP address range of your network.
Note: Once you modify the robot network parameters, your client computer will lose connection with
the robotic arm.
3. Physically disconnect the robot from your computer and connect it via Ethernet cable to your LAN at a
network switch.
4. Restore IP settings compatible with the LAN on your computer's local network adapter and connect your
computer physically to the LAN.
5. From your computer, ping the robot at its newly configured robot IP address to confirm that
communication is established.
What to do next
From your computer web browser, enter the new robot IP address to access the Web App.
Connecting a computer to the robot via Wi-Fi
This section describes the procedure to connect a computer to the robot via Wi-Fi .

KINOVA® Gen3 Ultra lightweight robot User Guide 47
Before you begin
You will need to have a wired connection between the computer and robot to carry out this
procedure.
About this task
The robot features a Wi-Fi adapter. This allows the arm to connect to a local Wi-Fi
connection. Once this connection is established, other devices on the same Wi-Fi network
can then connect to the robot wirelessly.
Procedure
1. On a computer connected to the arm via Ethernet, open the Web App and connect to the arm.
2. Select Networks in the main navigation panel of the Web App to go to the Networks page.
3. Select the Wi-Fi tab.
4. The Wi-Fi tab will list all of the detected Wi-Fi networks. Choose one of the networks, and click the
corresponding Connect text button.
Note: It is not recommended to connect to Wi-Fi networks which are potentially insecure. Security
settings of at least WPA2 are recommended.
5. A pop-up window will appear to sign in to the network, with information about the signal strength and
security settings. Enter the password for the network and click the CONNECT button. Take note of the
IPv4 address that the robotic arm obtains after clicking the CONNECT button
6. On any wireless device connected to the same Wi-Fi network, open a Web browser and type the IP address
that the robot obtained at Step 5 (This address corresponds to the robot's address on the Wi-Fi network).
7. At the Login screen, enter the appropriate user name and password, and click the CONNECT button.
Results
You are now connected to the Web App through the Wi-Fi network adapter of the robot. You
can now configure, monitor, and control the robot wirelessly.
Warning: A Wi-Fi connection is not recommended for 1 kHz (low-level) control of the robot due to potential
latency issues - a wired connection must be used for this purpose.

KINOVA® Gen3 Ultra lightweight robot User Guide 48
Dimensions, specifications, and capabilities
Schematic and dimensions - 7 DoF spherical wrist
This section provides a schematic diagram of the system and its physical dimensions.
Figure 22: 7 DoF spherical wrist frames definition and dimensions
The image above defines reference frames for the base, joints (when all joint angles = 0) and end effector.
Each frame is defined in terms of the previous frame via a transformation matrix. The diagram also indicates
the link lengths and lateral offset values (measurements in mm).
The maximum reach of the robot, as defined by the distance from the shoulder (actuator 2 frame) to the
interface module frame, is 90.2 cm.
Table 12: 7 DoF spherical wrist robot geometric parameters
Description Length (mm)
Base to actuator 1 156.4
Base to shoulder (actuator 2) 284.8
First half upper arm length
(actuator 2 to actuator 3)
Second half upper arm length
(actuator 3 to actuator 4)
Forearm length - elbow to
wrist (actuator 4 to actuator 5)
First wrist length (actuator 5 to actuator 6) 105.9
210.4
210.4
208.4

KINOVA® Gen3 Ultra lightweight robot User Guide 49
Description Length (mm)
Second wrist length (actuator 6 to actuator 7) 105.9
Last actuator to interface module 61.5
Joint 1-2 offset 5.4
Joint 2-3 offset 6.4
Joint 3-4 offset 6.4
Joint 4-5 offset 6.4
Technical Specifications
This section provides the technical specifications for the KINOVA® Gen3 Ultra lightweight
robot, categorized for ease of reference. Some of these also appear within the main body of
the text.
Table 13: Safety / Security
Feature Detail
Safety alarm (power monitor) ≥ 10A (maximum current)
Position monitoring default and user-defined protection zones.
Thermal monitor
warning / shutdown above
maximum operating temperature
Table 14: Environmental
Parameter Value(s)
Temperature
Relative humidity (non-condensing) 15% to 90% (operating)
Pressure 70 kPa to 106 kPa **
Sound pressure level (nominal) < 55.5 dBA
Universal Power Supply (external) 300 W
Input Voltage 100 - 240 VAC
Input Frequency 50 - 60 Hz
-30 °C to 35°C (operating)
-30 °C to 50 °C (storage)
Power supply ingress protection IP42
Table 15: Controller (base)
Feature Detail
power indicator blue LED
status indicator red/amber/green LED
USB 2.0 (two ports) Xbox gamepad connect; 1 A charging
(top), 500 mA USB peripherals (lower)
Gigabit Ethernet (RJ-45) for development PC connection
Wi-Fi (IEEE 802.11a/b/g/n)
KINOVA® KORTEX™ Web App and API

KINOVA® Gen3 Ultra lightweight robot User Guide 50
Feature Detail
HDMI 1.4a (for future use)
circular connector [Binder-USA 09 0463 90 19]
circular connector [Lumberg 0317 08] power
sensors voltage, current, temperature,
joystick, discrete I/O, emergency
line assert, expansion
accelerometer and gyroscope
Table 16: Robot
Parameter Value(s)
Weight 8.2 kg (with vision module, no gripper)
Payload
Maximum reach (fully extended) 902 mm (7 DoF)
Degrees of freedom 7 DoF
Actuators
Wrist interaction buttons qty 2 (user-configurable*; default for null
4 kg (mid-range continuous; no gripper)
4.5 kg (full-reach peak / temporary; no gripper)
1.1 kg (full-reach continuous; no gripper)
qty 3 (small)
qty 4 (large)
space and Cartesian admittance control)
Power supply voltage 24 VDC (nominal, 18 to 30 V)
Materials
100 Mbps Ethernet for real-time 1 kHz control
Communciations and control
100 Mbps Ethernet for vision module / expansion
Carbon fiber shell
Aluminum
Table 17: Actuators
Feature Value(s)
Sensors current sensors (motor), temperatures
(motor), voltage, torque, position
Table 18: Interface module
Feature Function
Vision module color and depth sensing
Wrist status LEDs admittance mode indication
Kinova internal end-effector interface connector Kinova internal use*
10-pin spring-loaded connector RS-485 (compatible with
Robotiq Adaptive Grippers)

KINOVA® Gen3 Ultra lightweight robot User Guide 51
Feature Function
100 Mbps Ethernet
UART (3.3V)
20-pin user expansion connector
[AVX/Kyocera 046288020000846+]
3.3V @ 0.1A for signaling
Sensors accelerometer and gyroscope,
I2C (3.3V)
GPIO (3.3V, qty 4)
24V @ 0.5A
voltage, temperature
Table 19: Vision
Feature Detail
480 x 270 (16:9) @ 30, 15, 6 fps
Depth sensor
Color sensor
424 x 240 (16:9) @ 30, 15, 6 fps
FOV: 72 ± 3° (diagonal)
minimum depth distance - 18 cm
1920 x 1080 (16:9) @ 30, 15 fps; FOV 47 ± 3°
(diagonal)
1280 x 720 (16:9) @ 30, 15 fps ; FOV 60 ± 3°
(diagonal)
640 x 480 (4:3) @ 30, 15 fps; FOV 65 ± 3° (diagonal)
320 x 240 (4:3) @ 30, 15 fps; FOV 65 ± 3° (diagonal)
focusing range - 30 cm to ∞
Table 20: Software / control
Feature Detail
Low-level control torque, position, velocity, current
High-level control Cartesian twist (linear and angular
velocity) and wrench (force and
torque - EXPERIMENTAL) , joint speed
High-level control features (mode dependent)
Servoing modes high-level, low-level
Data recorder*
Velocity
Angular position of individual joints
Angular speed of individual joints
protection zones - rectangular, spheric, cylindrical
singularity handling
logging of position, speed, temperature,
torque, battery, etc. (user-configurable)
user-configurable
Supported ROS distribution Kinetic Kame
Boot time 45 s

KINOVA® Gen3 Ultra lightweight robot User Guide 52
Feature Detail
Internal communication frequency 1 kHz
* to be implemented in future software release
** subject to future change
Sensors
This section describes the robot sensors.
The robot contains a number of sensors to provide feedback on the status of the robot. This data is used by
the robot for internal monitoring and control.
The robot components contain the following sensors:
Base sensors
• voltage
• current
• temperature
• 6-axis accelerometer / gyroscope
Actuator sensors
• motor phases current sensors (one per phase)
• motor phases temperature sensors (one per phase)
• CPU temperature sensor
• input voltage sensor
• Hall effect sensors for BLDC motor drive
• absolute rotary position encoder
• incremental rotary position encoder
• torque sensors
Interface module sensors
• voltage monitoring (future enhancement)
• temperature sensors (CPU, accelerometer and board)
• 6-axis accelerometer / gyroscope
Vision module
• temperature sensors (CPU, board)
Gripper sensors (for connected gripper)
• motor temperature
• motor voltage
• motor current
• position
Access to sensors data
Data from some sensors can be read by users using the APIs or through the Monitoring page of the Web
Application.
The API method RefreshFeedback() in the BaseCyclic API returns a data structure with readings
from sensors in:
• base and end effector tool
• actuators
• interface module
• gripper (if gripper connected)
For detailed information on how to unpack this data in an application, see the BaseCyclic API
documentation on the KINOVA® KORTEX™ GitHub repo.
The following tables give more information about the sensor data.

KINOVA® Gen3 Ultra lightweight robot User Guide 53
Base readings available
Table 21: Base readings available through API
Field name Description
arm_voltage arm voltage in V
arm_current arm current in A
temperature_cpu CPU temperature in °C
temperature_ambient ambient temperature in °C
imu_acceleration_x IMU measured acceleration (X-Axis)
of base in m / s
2
imu_acceleration_y IMU measured acceleration (Y-Axis)
of base in m / s
2
imu_acceleration_z IMU measured acceleration (Z-Axis)
of base in m / s
2
imu_angular_velocity_x IMU measured angular velocity (X-
Axis) ωxof base in ° / s
imu_angular_velocity_y IMU measured angular velocity (Y-
Axis) ωy of base in ° / s
imu_angular_velocity_z IMU measured angular velocity (Z-
Axis) ωz of base in ° / s
Tool readings available
Table 22: Tool readings available via API
Field name Description
tool_pose_x Measured Cartesian position
(X-axis) of the tool in m
tool_pose_y Measured Cartesian position
(Y-axis) of the tool in m
tool_pose_z Measured Cartesian position
(Z-axis) of the tool in m
tool_pose_theta_x Measured Cartesian orientation
(X-axis) of the tool in °
tool_pose_theta_y Measured Cartesian orientation
(Y-axis) of the tool in °
tool_pose_theta_z Measured Cartesian orientation
(Z-axis) of the tool in °
tool_twist_linear_x Measured Cartesian linear
velocity (X-Axis) of the tool in m / s
tool_twist_linear_y Measured Cartesian linear
velocity (Y-Axis) of the tool in m / s
tool_twist_linear_z Measured Cartesian linear
velocity (Z-Axis) of the tool in m / s

KINOVA® Gen3 Ultra lightweight robot User Guide 54
Field name Description
tool_twist_angular_x Measured Cartesian angular
velocity (X-Axis) of the tool in ° / s
tool_twist_angular_y Measured Cartesian angular
velocity (Y-Axis) of the tool in ° / s
tool_twist_angular_z Measured Cartesian angular
velocity (Z-Axis) of the tool in ° / s
Actuators readings available
Table 23: Actuators readings available via API
Field name Description
position angular position of the actuator in °
velocity angular velocity of the actuator in ° / sec
torque torque in N·m
current_motor motor current in A
voltage main board voltage in V
temperature_motor actuator motor temperature in °C (highest of three 3
phases)
temperature_core microcontroller temperature in °C
Interface readings available
Table 24: Interface readings available via API
Field name Description
imu_acceleration_X IMU measured acceleration (X-Axis) of interface
module in m / s
imu_acceleration_Y IMU measured acceleration (Y-Axis) of interface
module in m / s
imu_acceleration_Z IMU measured acceleration (Z-Axis) of interface
module in m / s
imu_angular_velocity_X IMU measured angular velocity (X-Axis) ωx of
interface module in ° / s
2
2
2
imu_angular_velocity_Y IMU measured angular velocity (Y-Axis) ωy of
interface module in ° / s
imu_angular_velocity_Z IMU measured angular velocity (Z-Axis) ωz of
interface module in ° / s
voltage main board voltage in V
temperature_core microcontroller temperature in °C
Gripper readings available

KINOVA® Gen3 Ultra lightweight robot User Guide 55
126.1°
126.1°
37.2
R900.6
301.2
284.8
340.2
Ø 124.3
479.8
y
z
x
Table 25: Gripper readings available through API
Field name Description
position position of gripper fingers in percentage (0-100%)
velocity velocity of gripper fingers in percentage (0-100%)
current_motor current consumed by gripper motor (mA)
voltage motor voltage (V)
temperature_motor motor temperature (°C)
Effective workspace
This section provides information on the effective workspace of the robot.
Effective workspace overview
The effective workspace refers to the region in three-dimensional space which is reachable by the robot end
effector. This is impacted by several factors, including the number and length of the links, the joint ranges,
and the shape of the links
There are two definitions of effective workspace, the first being larger than the second.
1. Nominal (or reachable) workspace - the set of all locations in the three-dimensional space reachable by
the end effector through at least one combination of end effector position and orientation
2. Dextrous workspace - the subset of the nominal workspace in which the end effector still has the
full freedom to move, both in translation (three degrees of freedom) and in rotation (three degrees of
freedom)
Detailed information
The following graphic illustrates a two-dimensional cross-section of the nominal workspace for the robot.
Figure 23: 7 DoF robot nominal workspace (measurements in mm)

KINOVA® Gen3 Ultra lightweight robot User Guide 56
Maximum payload vs. workspace
This section describes the variation of maximum payload over the workspace and
depending on the type of use.
Overview
The maximum payload of the robot is the maximum mass that the robot can hold up and carry around.
This is generally not one constant figure, but will depend on a few factors.
• radial distance from the base - the maximum payload the robot can handle will be highest closest to
the base, and will go down as the end effector gets farther out from the base axis.
• temporary vs. continuous - the robot will have a maximum payload that can be handled temporarily
for a short period of time. However, continued use of the arm with that payload for an indefinite period
will cause the arm to heat up, as the heat generated by the strain on the actuator exceeds the rate at
which heat can be dissipated. However, a smaller mass can be handled for an indefninite period. This
is referred to as the continuous payload limit.
The maximum payload will also depend on whether a gripper is attached or not, with some of the payload
capability reduced to lift the weight of the gripper.

KINOVA® Gen3 Ultra lightweight robot User Guide 57
Interface, expansion, and vision
Interface module expansion - tips for installing tools
This section describes what is needed to install and integrate a new tool onto the interface
module.
At some point, you may want to install a new tool such as a gripper or sensor onto the robot.

KINOVA® Gen3 Ultra lightweight robot User Guide 58
Generally, this involves two steps.
1. Physically mounting the tool using the screw holes available on the Interface module face.
Note: The holes on the Interface module face are laid out to allow easy installation of Robotiq Adaptive
Grippers using the four supplied M5 Socket Head Cap Screws (SHCS include O-rings for compliance with
the IP rating for sealing). For other third-party tools, it may be necessary to create a mounting structure
matching the provided interface module bolting pattern, as discussed in the End effector reference design
section.
2. Integration of Robotiq Adaptive Grippers to the robot power and control signals uses the 10-pin springloaded connector. Other third-party tools can use the signals on this and / or the 20-pin user expansion
connector. Currently power and Ethernet expansion are available via the user expansion connector. The
pinout details are described in later sections.
Note: If designing or installing your own tool or end effector, remember to take into consideration the field
of view of the depth sensor when designing the length of the tool to avoid hindering the effectiveness of
the vision module depth sensor.
End effector reference design
This section provides guidance to developers on developing and integrating a new end
effector tool with the robot.
Introduction
The KINOVA® Gen3 Ultra lightweight robot is designed for maximum extensibility. As such, the robot has a
user expansion interface designed to simplify the development required to incorporate different sensors,
end effectors or other tools/boards. The supported user interfaces are listed in the section Interface module
user expansion connector pinout.
Kinova provides a reference design package which includes mechanical and electrical modular interfaces.
Mechanical interface
The mechanical interface is a flanged circular structure which converts the interface module bolting pattern
to the ISO 9409-1-A50 mounting plate pattern common to many industrial robots.
Kinova recommends that the mechanical interface part of your end effector be machined from solid
aluminium, though for applications where no payload will be attached (only sensors or PCBs), a 3D-printed
interface part may suffice.

KINOVA® Gen3 Ultra lightweight robot User Guide 59
Note: If a 3D printed interface is used, perform an evaluation of the forces involved to ensure that adequate
safety factors are observed.
Note: The structure includes openings at the top and bottom of the structure for the passage of cabling
for the electrical interface. As a result, the mounting structure does NOT in itself provide ingress or EMI
protection.
Figure 24: Reference design mechanical interface (details in reference design package)
The flange includes four mounting holes corresponding to the four mounting holes on the interface module.
The rear face of the structure also includes a positioning key corresponding to the positioning key hole on
the interface module to ensure that the structure is aligned with the right orientation.
Electrical interface
The electrical reference design acts as a breakout, giving access to:
• 24 V / 0.5 A
• 5 V / 2 A / 10 W, from 24 V (through a DC-DC buck converter)
• Expansion Ethernet (100 Mbit, through a RJ-45 port)
•
GPIO, I2C and UART
Figure 25: Reference design electrical interface (details in reference design package)

KINOVA® Gen3 Ultra lightweight robot User Guide 60
Mounting structure installation overview
The following general steps are required to install the reference design mounting structure on the robot:
• If you have not already done so, remove the end cap from the interface module, preserving the four
screws and the O-ring. The screws and O-ring are used for the installation of the mounting structure.
• Align the rear face of the mounting structure with the interface module.
Note: Ensure that the positioning key aligns with the positioning key hole on the interface module.
• Use a 20 pin flat flex cable to connect the user expansion port on the interface module to the input
connector on the mounting structure electrical interface.
• Place the O-ring around the mounting structure.
• Bring the mounting structure together with the interface and attach using the four screws.
With the mounting structure in place, an end effector tool can be mounted and integrated electrically.
Reference design package
The reference design package is available for download on the Kinova website: kinovarobotics.com/
knowledge-hub/gen3-ultra-lightweight-robot
The package includes several useful files to help you with building an end effector. You may use these files
as is or as a starting point to design your own end effector. The package contents include:
• STL file of the mechanical interface, for 3D-printing
• STEP file and PDF drawing of the mechanical interface, for machining
• STEP file of the Kinova breakout PCB for integration into CAD programs
• KR13933.ASY file which directs the assembly of the PCB (including the BOM)
• KR13933.PCB which directs the PCB fabrication (including Gerber files)
• KR13933.SCH which includes the circuit board schematic diagrams
Tool configuration
To fully integrate an end effector tool with the robot control and cyclic feedback, you will need to configure
the tool information using either the Web App Robot Configurations page or the API via the
SetToolConfiguration() function in Kinova.Api.ControlConfig.
You will need to configure:
• transform for the reference frame of the tool in relation to robot interface module frame
• mass of mechanical interface + end effector tool
• coordinates of center of mass of mechanical interface + end effector tool in terms of interface module
reference frame
Configuring the transform ensures that the robot is aware of the geometry of the tool in relation to the rest
of the robot to calculate and accurately report the tool position.
Configuring the mass and center of mass coordinates of the tool ensures that the control libraries of the
robot can properly take into account the presence of the tool mass in the control of the robot.
Payload configuration
If you want to carry a known payload mass with the tool, you will need to configure the payload
information using either the Web App Robot Configurations page or the API via the
SetPayloadConfiguration() function in Kinova.Api.ControlConfig.
For this you will need to configure:
• mass of the the payload
• coordinates of the center of mass of the payload in terms of the tool frame.
Similar to the configuration of tool mass and center of mass coordinates, configuring the payload ensures
that the control libraries of the robot can properly take into account the presence of the tool mass in the
control of the robot.

KINOVA® Gen3 Ultra lightweight robot User Guide 61
Controlling the end effector via interface expansion
With your end effector tool physically mounted on the mechanical interface, integrated electrically via the
electrical interface, and properly configured, you can communicate with and control the end effector tool
via the expansion interface. For more details, see Using interface module expansion to control devices via
API.
Removing end cap from Interface module
This section describes how to remove the end cap from the interface module to expose the
expansion interfaces.
Before you begin
You will need a 3 mm hex key.
About this task
The robot ships originally with an end cap over the interface. Attaching an end effector to
the robot requires removing the end cap first. Removing the end cap exposes expansion
and end-effector connection points.
When removing the end cap, there is an O-ring exposed which must be conserved. The O-ring is used to
provide protection against water ingress and EMI at the junction between the robot interface and the end
effector.
Procedure
1. The end cap is held onto the robot interface using four M5 button head cap screws. Using a 3 mm hex key,
remove the screws and preserve them.
2. Remove the end cap, and set aside with the screws.
3. You will see an O-ring on removing the end cap.
Note: Set aside the O-ring with the screws and end cap for safe keeping. The screws and O-ring will be used
when attaching an end effector tool (as described in the end effector reference design). The cap needs to
be replaced whenever an end effector is not installed.
Robotiq Adaptive Grippers installation (optional)
This section describes the procedure for installing a Robotiq Adaptive Grippers on the robot.
Before you begin
You will need four M5 Socket Head Cap Screws and 4 mm hex key (supplied).
You will also need to have removed the interface end cap (robot comes with end cap connected). You will
need the O-ring that was exposed when the end cap was removed.

KINOVA® Gen3 Ultra lightweight robot User Guide 62
About this task
This procedure describes the installation for Robotiq Adaptive Grippers (Robotiq 2F-85,
2F-140, or Hand-E Gripper) on the interface module of the robot. The interface module
allows easy mounting of Robotiq Adaptive Grippers. This procedure mechanically mounts
the gripper on the robot and integrates the gripper with the robot in terms of electrical
power and control. The interface module has four mounting holes corresponding to the bolt
pattern on the gripper. The 10 spring-loaded pins on the interface mate with a contact plate
on the inside of the Robotiq Gripper to establish electrical supply and controls.
Figure 26: Robotiq Adaptive Gripper (Robotiq 2F-85 Gripper shown)
Procedure
1. Prepare the four supplied M5 Socket Head Cap Screws and a 4 mm hex key.

KINOVA® Gen3 Ultra lightweight robot User Guide 63
2. Place the O-ring around the diameter of the gripper. The O-ring protects the junction between the
interface module and gripper from water ingress and EMI.
3. Locate the positioning key on the Robotiq Gripper and the corresponding hole on the interface module
face.
4. Position the gripper interface against the Interface module interface so that the positioning key of the
gripper is in the positioning key hole of the interface module and the 10-pin spring-loaded connector of
the interface module is aligned with the corresponding mating interface on the gripper.
5. Insert the four screws through the front face of the gripper. Tighten each screw in sequence until they are
all snug (do not overtighten).
Results
The Robotic Gripper will now be mechanically installed on the robot. The gripper is also
fully integrated with the robot for power and controls. The robot provides power to the
gripper, and the gripper can be controlled using either the provided gamepad or the
KINOVA® KORTEX™ Web App virtual joysticks.
What to do next
For your personal safety, it is strongly recommended that you read the user
documentation for the Robotiq Gripper before use.
Robotiq 2F-85 Gripper tool configuration
This section describes tool configuration settings to use for the Robotiq 2F-85 Gripper.
The following are settings to enter for ToolConfiguration in the Web App Robot Configuration
page or using the Kinova.Api.ControlConfig API.
Table 26: ToolConfiguration settings
Transform (from interface
module frame to tool frame)
Setting Value
X 0
Y 0
Z 0.120 m
θ
X
θ
Y
0
0

KINOVA® Gen3 Ultra lightweight robot User Guide 64
Setting Value
Center of mass coordinates
θ
Z
Tool mass 0.925 kg
X 0
Y 0
Z 0.058 m
0
Interface module bolting pattern
This section describes the bolting pattern for a tool interfacing with the Interface module.
Drill pattern for mounting screws and position key
The drill pattern below is for the four mounting screws. Openings to accommodate the required cables
connections with the connectors also need to be added. The use of a 4 mm dowel pin to accurately localize
the positioning key hole is optional but strongly recommended.
Figure 27: Mounting holes for gripper/tool (all dimensions in mm)
Interface module user expansion connector pinout
This section describes the functionality available at the interface module user expansion
connector.

KINOVA® Gen3 Ultra lightweight robot User Guide 65
The interface module user expansion connector pin assignment is described in the table below.
Figure 28: Interface module user expansion connector
Table 27: Interface module user expansion pinout
Pin Name Comment
1 +24V USER
2 +24V USER
3 GND
4 GND
5 ETH_RX_P
6 ETH_RX_N
7 GND signal return path
8 ETH_TX_P
9 ETH_TX_N
10 GND signal return path
11 +3V3 3.3V / 100 mA; can be used for small IC or sensor
12 UART_TXD signal 3.3V
24V / 0.5A power; a protection device limits current shared between gripper and
user expansion port to 1A total.
power return path
Ethernet Rx 100Mbps (connected with EXP bus)
Ethernet Tx 100Mbps (connected with EXP bus)
13 UART_RXD signal 3.3V
14 GND signal return path
15 I2C_SCL
I2C clock - 3.3V

KINOVA® Gen3 Ultra lightweight robot User Guide 66
Pin Name Comment
16 I2C_SDA
17 GPIO1
18 GPIO2
19 GPIO3
20 GPIO4
I2C data - 3.3V
General Purpose Input / Output 3.3V
Using interface module expansion to control devices via API
This section describes how to find additional information to make use of interface module
expansion pins for bridging to connected devices via UART, I2C, or GPIO.
Overview
The interface module expansion connector offers three interfaces for bridging to connected
devices:
UART
•
I2C
•
GPIO
•
The reference design section gives guidance on connecting an end effector device mechanically and
electrically.
Controlling the end effector device via UART, I2C, or GPIO
Controlling the interfaced device via UART, I2C, or GPIO is done via the KINOVA® KORTEX™ API using the
Kinova.Api.InterconnectConfig service.
Examples of using UART, I2C, and GPIO as a bridge to communciate with and control a device can be seen
on the KINOVA® KORTEX™ GitHub repository.
• C++ examples
• Python examples
Spring-loaded connector pinout
This section describes the pinout of the spring-loaded connector.

KINOVA® Gen3 Ultra lightweight robot User Guide 67
The spring-loaded connector pin assignment is described in the table below.
Figure 29: Spring-loaded connector
Table 28: Spring-loaded connector pinout
Pin Name Comment
1 GND
2 GND
3 +24V
4 +24V
5 PRESENT end device presence detection (connect to GND on end device)
6 N/C no connection
7 RS485_N
8 RS485_P
9 GND signal return path
10 N/C no connection
power return path
24V / 1A power for end device (current limit shared with interface module user
expansion port)
RS-485 signal pair (bidirectional)
Accessing Vision module color and depth streams
This section describes access to the video module color and depth streams.
The video module sensors capture two video streams:
• color
• depth
The data from these streams is sent from the vision module back to the base controller via the vision /
expansion channel carried over the internal flex cable links.

KINOVA® Gen3 Ultra lightweight robot User Guide 68
These two streams are accessible via the Real Time Streaming Protocol (RTSP) on a computer connected
to the robot (with transport over real-time transport protocol (RTP)).
Using the default IP address settings for the base controller, the two streams are accessible via:
• color sensor stream: rtsp://<base IPv4 address>/color
• depth sensor stream: rtsp://<base IPv4 address>/depth
For the default configuration of the base controller network interface, this would give:
• rtsp://192.168.1.10/color
• rtsp://192.168.1.10/depth
Note: Examples in the documentation will use the default base controller IP setting for simplicity.
Streams specifications
• pixel format: Z16 pixel format - 16 bits LSB transferred as grayscale
• H.264 baseline profile (constant bitrate)
• RTSP server listening on port 554 (default)
• maximum of two simultaneous connections per stream
• inactivity timeout of 30 seconds
The KINOVA® KORTEX™ Developer Guide section of the user guide describes in more detail how to work
with the vision module camera streams.
For more guidance on configuring the vision module using the KINOVA® KORTEX™ API, see the vision
examples on the KINOVA® KORTEX™ GitHub repository:
• C++ vision examples
• Python vision examples

KINOVA® Gen3 Ultra lightweight robot User Guide 69
Concepts and terminology
Robot key concepts
This section describes some important concepts related to the robot.
Actions
An action is something that the user wants the robot to do. An action can be invoked explicitly, in the context
of a Sequence or associated to a controller device (button/joystick/gamepad) event. This can include (but
is not limited to):
• sending a command to the robot
• playing a simple trajectory
• toggling admittance mode
• changing a position or motion parameter
• applying emergency stop or clear faults
• adding a delay
• sending a gripper command
• executing or stopping an action
• playing a pre-computed trajectory
The full set of action types is defined in the Base API.
Control modes
A control mode is one of several modalities of controlling the motion of the robot while it is in run mode.
Different modes provide different means to describe or guide the desired motion. The control modes for
the arm are:
• angular joystick
• Cartesian joystick
• Cartesian trajectory
• angular trajectory
• Cartesian admittance
• joint admittance
• null space admittance
Event
An event is something of interest that happens related to the robot. Users can get informed with
notifications about related events by subscribing to the appropriate topic.
Factory settings
Factory settings are the configuration settings of the robot as they were when the robot arrived from the
manufacturer. A robot can be returned to factory settings, which includes the base configuration and the
network settings.
Map
A map is a set of associations between controller device inputs and actions to be triggered by those inputs
when the map is active.
Mappings
A mapping is a full definition of the possible correspondances between controller device inputs and actions
that are triggered by those inputs when the mapping is active. A mapping can consist of multiple maps, for
example to enable multiple different modes on the same controller device.
Notifications
A notification is a log of an event related to a particular topic that happens while a user is using the robot.
A notification will include the user profile, type of event, details of the event (if applicable), and a timestamp.
Operating mode

KINOVA® Gen3 Ultra lightweight robot User Guide 70
Operating modes are the different operational states of the robot. The operating modes for the arm are:
• update - in process of update
• update completed - update is completed successfully
• update failed - update process started but failed to complete successfully
• shutting down - arm is in process of shutting down
• run - normal operating mode. Arm is ready to accept control inputs.
• fault - robot is in an error state
Protection zone
A protection zone defines a three-dimensional region with respect to the robot base where the end effector
or arm is either prevented from entering or where its speed is limited. Protection zones are used for
enabling obstacle avoidance. For the robot, protection zones can be one of three shapes:
• cylinder
• rectangular prism
• sphere
Sequence
A sequence is an ordered list of actions.
Servoing mode
A servoing mode is a modality through which commands are transmitted to robot devices during operation.
The servoing modes are as follows:
• high-level servoing - user(s) control the robot by sending a single command to the base. The base
manages the low-level details of executing the command, breaking it down, applying any relevant
high-level protections, and routing commands to the desired devices via a 1 kHz communication loop
with the devices.
º single-level - a single user sends commands to a base
• low-level servoing - the user controls the robot by sending a series of actuator commands to the base
via a user-controlled loop. The base routes these commands to the desired device via its own 1 kHz
communication loop with the actuators.
Topic
A set of related robot events to which the user can subscribe and receive notifications as part of a Publisher-
Subscriber (pub-sub) arrangement. There are a number of different topics, including:
• user
• controller device input
• safety
• action or sequence
• connection / disconnection of arm, controller, or tool
• configuration change or backup
• factory restore
• protection zone
• control, operation, or servoing mode
Upgrade package
An upgrade package is an image containing firmware updates for all modules on the robot (base, actuator,
interface, vision).
User profiles
A user profile is a collection of basic information about the person using the robot, along with credentials
(username and password) for access. A user profile allows access to the robot to be controlled based on
login credentials, and allows permissions for reading, updating, and deleting different configuration items
to be controlled. The user profile also allows notifications for events happening during a user's session to
be associated with the user. Notifications that were sent by the robot can be viewed in the Web App >
Notifications page if the Web App is open and connected to the robot before the notifications were
sent.

KINOVA® Gen3 Ultra lightweight robot User Guide 71
Terminology reference
The following sections serve as a reference for terminology used with the robot.
For ease of reference, the terminology reference section has been divided into the following categories:
• General mathematics and robotics
• Features, components and functionalities
• Control and Operation Modes
General mathematics and robotics
Axis
A fixed line with direction and units. It is used for the measurement of coordinates or
angles, in relation to which is specified the robot motion (in linear or rotational fashion).
Base Frame
The reference frame located at the center of the bottom surface of the arm's base. This
serves as the origin frame in Cartesian space.
Cartesian Space
The Euclidean space described by x, y and z axes of the Cartesian coordinate system.
Center of Mass
Unique point of a rigid body where an applied force will generate only linear acceleration
(and no angular acceleration)
Closed loop control
Control of a device where the device is controlled in relation to the different between
sensed current state and goal state. Used on the robot for control of actuators.
Coordinate System
A system used to represent a position in three-dimensional space, consisting of three
coordinate axes and an origin. The term "frame" is also used to designate a coordinate
system.
Degrees of Freedom (DoF)
The number of independent directions or joints of the robot, which would allow the robot to
move its end effector through the required sequence of motions. For arbitrary positioning,
six degrees of freedom are needed: three for position and three for orientation.
Endpoint
The nominal commanded position that the robot will try to reach with the tool center point
at the end of a motion path.
Euler Angle
Describes the rotation in three dimensions of a rigid body in terms of a sequence of three
rotations with respect to a coordinate system.
Gravity Vector
Vector representing direction and magnitude of the local force of gravity, expressed in
terms of the robot base frame.
Joint Angle
Describes the position of every joint of a robot as as series of angles.
Joint Space
The set of all possible joint positions.

KINOVA® Gen3 Ultra lightweight robot User Guide 72
Null Space
The mathematical space of joint speeds where the robot can change its configuration
(generate joint speed and motion) without changing the end-effector pose (Null Twist at
the end effector).
Orientation
The orientation of a rigid body describes the pure rotations that should be applied to the
body to move it from a reference placement to its current placement.
Path
The continuous locus of points (or positions in three dimensional space) traversed by the
tool center point and described in a specified coordinate system.
Path (Angular)
The set of at least two angular poses, through which the actuator values angles should
pass during motion.
Path (Cartesian)
The set of at least two Cartesian poses, through which the tool of the robot should pass
during motion.
Payload
The object that is carried or manipulated by the robot tool.
Pose
Describes the position and orientation of a rigid body in Cartesian space.
Position
The definition of an object's location in 3D space, usually defined by a 3D coordinate system
using X, Y, and Z coordinates.
Tool Configuration
Configurations made to enable use of a tool at the end effector position of the robot. This
consists of the mass and center of mass of the tool, and the tool transform.
Tool Frame
A coordinate system attached to the end effector tool.
Tool Transform
Transformation (translation and orientation) between the interface module reference
frame and the reference frame of the tool attached to the end of the robot.
Trajectory
A time-parametrized path in the robot workspace that can be defined by the user.
Twist
Generalized velocity vector, which is a combination of translational velocity and rotational
velocity. Term comes from Screw Theory.
Wrench
Generalized force (vector which is a combination of linear force and torques). Term comes
from Screw Theory.
Vector
Mathematical representation of physical quantities that have both magnitude and
direction, expressed in terms of a coordinate system.

KINOVA® Gen3 Ultra lightweight robot User Guide 73
Features, components and functionalities
Admittance
In this document, admittance is used to refer to human-robot interaction modes. In these
modes, the robot will respond to external efforts applied on the body and tool and generate
a motion to follow these efforts.
Base
Refers to the stationary base structure of a robot arm that supports the first arm joint.
Base support
The stable platform to which the base is attached
End Effector
The device at the end of a robot, designed to directly interact with the environment. Also
referred to as tool.
Joint
Section of the manipulator system which allows one rotational degree of freedom.
Path Planning
Computation of a path to reach a goal pose subject to applicable constraints and criteria.
Payload - Maximum
The maximum mass that the robot can manipulate at a specified speed, acceleration/
deceleration, center of gravity location (offset), and repeatability in continuous operation
over a specified working space, specified in kilograms.
Pinch Point
Any location on the robot (or its accessories) which poses a risk of injury to fingers or other
appendages close by.
Protection Zone
A volume in space where the motion of the robot can be limited for safety purposes.
Redundancy
Occurs when the manipulator (robot) has more degrees of freedom than it needs to execute
a given task. Applicable to 7 DoF robot.
Redundancy Optimization
Method used to avoid a singularity by using redundant degrees-of-freedom motion (if
available).
Safeties
Hardware limitations which are monitored to increase robot safety.
Singularity Avoidance
Strategy to avoid configurations where the robot loses its ability to move the end effector
in a given direction no matter how it moves its joints.
Tool
See End Effector.

KINOVA® Gen3 Ultra lightweight robot User Guide 74
Control and Operation Modes
Angular Mode
Independent joint control, whereby each axis of the manipulator is controlled separately.
Cartesian Mode
Mode used to control the velocities (translation and orientation) of the tool in Cartesian
space.
Cartesian Admittance Mode
Allows the application of external force to the tool, so as to guide the arm to a new position.
Joint Admittance Mode
Allows the application of external force at the links to rotate joints.
Null Space Admittance Mode
Robot configuration can be changed by applying external forces at the links without
affecting the tool pose.
Trajectory Mode
Mode allowing user to specify an endpoint (in joint space or Cartesian space) that the robot
should reach.

KINOVA® Gen3 Ultra lightweight robot User Guide 75
Robot control
High-level and low-level robot control
This section describes the concepts of high-level and low-level robot control
There are two levels of controlling the movement of the robot:
• high-level
• low-level
High-level is the default on boot-up and offers the safest and most straight-forward control.
In both high-level and low-level, commands are sent through the robot base.
In high-level control, commands are sent to the base via a single command using the Kinova.Api.Base
API. These commands are processed by Kinova robot control libraries. The robot control libraries apply
high-level control features like singularity avoidance, protection zones, and joint limits, and break down
the command into smaller commands that the base will send to the individual robot actuators via its 1 kHz
communication loop with the actuators.
In low-level control, the user sends a series of small, incremental commands to the actuator and gripper as
part of a user-defined loop (at a rate up to 1 kHz) using the Kinova.Api.BaseCyclic API. The base
receives these commands and forwards them to the appropriate actuators and the gripper via the 1 KHz
communication loop between the base and robot devices.
High-level is simpler to use, and offers added protections, but is slower due to the overhead of processing
by the Kinova control library.
Low-level offers lighter and faster commands and finer-grained control, but the user is responsible for more
of the low-level details.
For more information, see the KINOVA® KORTEX™ Developer Guide section of the User Guide.
High-level and low-level robot control methods overview
This section lists robot control methods available through the API.
High-level (Kinova.Api.Base)
Table 29: Send or play a trajectory (Cartesian or joint)
Method Description
PlayCartesianTrajectory
(ConstrainedPose)
PlayCartesianTrajectoryPosition
(ConstrainedPosition)
PlayCartesianTrajectoryOrientation
(ConstrainedOrientation)
PlayJointTrajectory
(ConstrainedJointAngles)
Moves to the specifed pose (with specified
Cartesian constraint on trajectory)
Moves to the specifed position (with specified
Cartesian constraint on trajectory)
Moves to the specifed orientation (with specified
Cartesian constraint on trajectory)
Moves to the specified joint angles (with specified
joint constraint on trajectory)
PlaySelectedJointTrajectory
(ConstrainedJointAngle)
PlayPreComputedJointTrajectory
(PreComputedJointTrajectory)
Moves specifed joint to the specifed joint angle
(with specified joint constraint on trajectory)
Play pre-computed angular trajectory

KINOVA® Gen3 Ultra lightweight robot User Guide 76
Table 30: Send Cartesian command to tool
Method Description
SendTwistCommand (TwistCommand) Sends a twist command to tool (velocity and
angular velocity)
SendTwistJoystickCommand
(TwistCommand)
(EXPERIMENTAL) SendWrenchCommand
(WrenchCommand)
(EXPERIMENTAL)
SendWrenchJoystickCommand
(WrenchCommand)
Note: High-level force control is supported, but as an experimental feature only. Users should exercise
caution.
Sends a twist joystick command to tool. The twist
values sent to this call are expected to be a ratio of
maximum value (between -1.0/+1.0)
Force control. Sends a wrench command to tool
(force and torque)
Force control. Sends a wrench joystick command
to tool. The wrench values sent to this call are
expected to be a ratio of maximum value (between
-1.0/+1.0)
Table 31: Sent command to joints
Method Description
SendJointSpeedsCommand (JointSpeeds) Sends a joint speeds command, that is the desired
speed of one or many joints
SendSelectedJointSpeedCommand
(JointSpeed)
SendJointSpeedsJoystickCommand
(JointSpeeds)
Sends a speed command for a specific joint
Sends the desired joystick speeds for one or
multiple joints. Values sent to this call are expected
to be a ratio of maximum value (between -1.0/+1.0)
SendSelectedJointSpeedJoystickCommand
(JointSpeed)
Sends a joystick speed for a specific joint. Value
sent to this call is expected to be a ratio of
maximum value (between -1.0/+1.0)
Table 32: Initiate admittance control
Method Description
SetAdmittance (Admittance) Sets the robot in the chosen admittance mode
(Cartesian, joint, null space)
Table 33: Send gripper commands
Method Description
SendGripperCommand (GripperCommand) Sends a command to move the gripper. Commands
the fingers of the gripper in either position or
velocity.

KINOVA® Gen3 Ultra lightweight robot User Guide 77
Low-level (Kinova.Api.BaseCyclic)
Table 34: Low-level cyclic commands
Method Description
Refresh (Command) Commands refresh (with feedback). Command
actuators position, angular velocity, torque
(ADVANCED USERS ONLY), actuator motor
current, and gripper finger motors.
RefreshCommand (Command) Commands refresh (no feedback). Command
actuators position, angular velocity, torque
(ADVANCED USERS ONLY), actuator motor
current, and gripper finger motors.
Note: Low-level actuator torque control is for advanced users only and should only be used by users who
know what they are doing. It is very important to carefully monitor the torque commands sent to the
actuators to ensure that excessive torque values are not sent. Incorrect use can lead to rapid movements
that can be dangerous for people and equipment. Make sure that the area around the robot is clear before
experimenting with torque control.
Control features
This section gives an overview of control features of the robot.
The robot has the following control features that improve the safety and usability of the robot, and protect
it from damage:
• singularity avoidance
• protection zones
• angular limits
• Cartesian limits
Singularity avoidance
This section describes the Singularity avoidance feature of the robotic arm.
A singularity refers to any robot configuration (set of joint angles) which causes the Jacobian
transformation matrix relating actuator rotation speed to end effector velocities to be ill-conditioned, thus
rendering the solution mathematically unstable (determinant of the Jacobian matrix loses rank).
At a singularity, the mobility of the robot is reduced, meaning the arbitrary motion of the manipulator in a
Cartesian direction is lost (losing a degree of freedom). This occurs when two or more robot axes become
colinear, leading to unpredictable / extreme joint velocities when trying to attain a certain Cartesian pose.
For example, when two axes become colinear in space, rotation of one can be canceled by counter-rotation
of the other, leaving the actual joint location indeterminate. Near a singularity a small linear end effector
motion requires disproportionately large angular velocities of the actuators.
Note: The robot controller firmware features capabilities to handle / avoid singularities in any 'Cartesian'
mode. As a singularity cannot occur unless inverse kinematics are calculated, singularities do not occur in
any of the 'joint' modes.
Note: The robot behavior may change somewhat at or near a singularity. For example, the tool speed may
be reduced or the motion may deviate from the commanded motion.
For more information on robot singularity configurations, see here.
Protection zones
This section describes the protection zones feature of the robot.
Overview
With this feature, the user defines protection zones programmatically or by using the Web App, based on
a few basic geometric shapes. Moreover, the user can specify a speed limitation in the envelope of defined
thickness surrounding each protection zone.

KINOVA® Gen3 Ultra lightweight robot User Guide 78
One or more protection zones can be configured to define geometric volumes about the robot base, where
the motion of the robot end effector is either limited or precluded.
By defining suitable protection zones, the robot can be set to avoid collisions with known fixed obstacles in
the immediate environment of the robot while in operation.
Note: Protection zones are active only in Cartesian control modes. These protections are not available in
angular control modes.
Note: If multiple protection zones are used, we recommend that the same envelope speed limitations be
used for each.
Note: Envelope-only protection zones, where all the dimensions of the protection zone are set to zero but
the envelope thickness is set to a non-zero value are NOT supported.
Robot tool behavior
The tool of the robot will never enter protection zones. If the robot is commanded to enter or pass through
a protection zone, any motion of the tool will toward the inside of the protection zone will stop at the outer
boundary of the protection zone. The tool will be able to "slide" on the outer surface of the zone but not
enter inwards.
The tool can move within the surrounding envelope, but at a reduced speed.
Checkpoints and behavior of checkpoints
Additional checkpoints are used for protection zones and are defined for the robot at the center of the
reference frames of joints 3, 4, 5, and 6.
Note: The vision module is NOT currently included in the defined checkpoints. It is possible that the vision
module can enter into a protection zone. Use caution when moving the end of the robot near a protection
zone.
For these checkpoints, the motion will stop at the outer surface of the protection zone. Checkpoints will
move within the envelope surrounding a protection zone, but at a reduced speed.
Protection zone shapes
Protection zones can be defined using one of three basic shape types:
• rectangular prism - position of center, length, width, and height dimensions, and angular orientation
of the rectangular prism are configurable
• cylindrical - position of center, radius, height, and angular orientation of the cylinder are configurable.
• spherical - position of center and radius of sphere are configurable
A planar or disc-shaped protection zone can be defined by setting the thickness of the zone to zero in either
a rectangular prism or cylindrical protection zone.
Editing protection zones
Protection zones can be defined, edited, and deleted using either the Web App or the developer API.
Angular limits
This section describes angular limits used in robot high-level control.
Overview
When controlling the robot in high-level, the robot control library applies a number of different angular
limits for safety purposes. This includes limits on:
• joint position
• joint speed
• joint acceleration
• joint torques
• joint command speed
• joint command acceleration
The limits applied in a particular situation depend on the current high-level control mode.

KINOVA® Gen3 Ultra lightweight robot User Guide 79
7 DoF spherical wrist robot angular limits
Table 35: Joint position limits
Actuator
1 - ∞ + ∞
2 - 128.9° + 128.9°
3 - ∞ + ∞
4 - 147.8° + 147.8°
5 - ∞ + ∞
6 - 120.3° + 120.3°
7 - ∞ + ∞
Table 36: Joint speed limits
Actuator Limit (magnitude)
all joints 50 ° / s (0.8727 rad / s)
Table 37: Joint acceleration limits
Actuator Limit (magnitude)
Angular range
Lower limit Upper limit
all joints
Table 38: Joint torques soft limits
Actuators Limit (magnitude)
large (joints 1 - 4) 39.0 N * m
small (joints 5 - 7) 9.0 N * m
Table 39: Joint command speed limits
Actuators Limit (magnitude)
all joints 50 ° / s (0.8727 rad / s)
Table 40: Joint command acceleration limits
Actuators Limit (magnitude)
large (joints 1 - 4)
small (joints 5 - 7)
Control modes and relevant joint limits
572.95 ° / s2 (10.0 rad / s2)
57.3 ° / s2 (1.0 rad / s2)
572.95 ° / s2 (10.0 rad / s2)
Control mode Joint limits applied
Cartesian trajectory joint position, joint speed
angular trajectory joint position, joint speed, joint acceleration,
joint torque (for pre-computed trajectories)

KINOVA® Gen3 Ultra lightweight robot User Guide 80
Control mode Joint limits applied
Cartesian joystick joint position, joint speed
angular joystick joint position, joint speed, joint acceleration, joint
command speed, joint command acceleration
Cartesian admittance joint angle, joint speed
joint admittance joint angle, joint speed
null space admittance joint angle, joint speed
Behavior at joint limits
When joint limits are reached, the behavior of the robot will be altered depending on the type of limitation.
Limit Behavior when limit is reached
joint acceleration and joint command acceleration joint acceleration will max out at acceleration limit
joint speed and joint command speed acceleration goes to zero and joint
speed will max out at speed limit
joint position joint speed goes to zero and motion of
the joint will stop at the limit position
Cartesian limits
This section describes limits used in robot high-level control.
Overview
Safety limits on the motion of the robot in Cartesian modes are applied as follows:
• In Cartesian joystick, the magnitude (vector norm) of the linear and rotational speeds of the tool are
capped. Twist commands whose linear and / or rotation speed exceed these limits will be re-scaled
proportionally so that the magnitudes of tool linear and angular speeds will not exceed the limits, but
the commanded directions of tool movement will be respected.
• For all Cartesian modes, the individual joint speeds will be capped at their limits. The speed of all joints
will be proportionally scaled so that:
º no individual joint exceeds the speed limit
º the desired direction of motion is respected
• For all Cartesian modes, joint positions will be capped at their limits.
7 DoF spherical wrist robot Cartesian limitations
Limit Value
linear 0.2 m / stwist soft limit
angular 20 ° / s (0.3491 rad / s)
linear 0.3 m / stwist hard limit
angular 50 ° / s (0.8727 rad / s)
Control modes overview
This section gives an overview of the control modes of the robot.

KINOVA® Gen3 Ultra lightweight robot User Guide 81
The robot is controllable via a number of control modes:
• trajectory modes
º angular trajectory
º Cartesian trajectory
• joystick control modes
º Cartesian joystick
º angular joystick
• admittance modes
º Cartesian admittance
º joint admittance
º null space admittance
Users do not select the control mode directly. The robot software will set the robot into the control mode
depending on the control action currently being used with the robot. The following sections describe the
internal control modes.
Trajectory control modes
This section describes the Trajectory Control modes of the robot.
Using Trajectory Control modes, the user can command the robot to a desired endpoint.
There are two ways a trajectory can be defined.
Users can provide an endpoint, and the let the control software of the robot compute how to follow a path
to reach the endpoint. The robot controller computes an interpolated trajectory (between current pose and
target pose) to reach the final position while satisfying configured limits, and commands the robot to follow
this trajectory. These trajectories, once defined, can be played back. This is a good setting when you want
the robot to go to a desired end state but you are not concerned about how it goes about getting there.
Users can supply a pre-computed trajectory to the robot. A pre-computed trajectory is generally autogenerated by some sort of path planning software or algorithm rather than built manually. A pre-computed
trajectory is defined as a time series of settings for joints angular positions, velocities, and accelerations
at each timestamp. The robot control software will verify that the trajectory is valid and reasonable,
satisfying configured limits. Users can indicate a desired continuity mode for the trajectory against which
the trajectory can be checked (position, or position and velocity, or position, velocity and acceleration).
The robot control library will perform the following validations on the pre-computed trajectory:
• trajectory is non-empty
• for each trajectory point, position, velocity, and acceleration values must be provided for each joint
in the robot
• trajectory contains no NaN values
• timestamp of the first trajectory point must be 0.000 seconds and the difference in time stamps
between successive points must be 0.001 seconds
• joint positions, speeds, accelerations, and torques must be within robot joint limits
• continuity - the trajectory is continuous in terms of (user can specify which of these continuity checks
to apply):
º position - joint position variation between successive timesteps is less than the maximum
variation (based on joint speed limit)
º speed - speed values are consistent (within tolerances) with derivative of position
º acceleration - acceleration values are consistent (within tolerances) with derivative of speed
• trajectory execution (when starting the trajectory) - the joint positions and speeds for the first point
in the trajectory must match the initial robot joint positions and speeds
Note: For safety reasons, trajectories failing any of the validation checks will be rejected, and you will
receive an error notification. To get more detailed information about why a particular trajectory failed, use
the method GetTrajectoryErrorReport() in Kinova.Api.Base.
In Cartesian Trajectory mode the endpoint is defined in terms of the desired Cartesian space pose of the
tool center. This mode enables singularity avoidance. Cartesian Trajectory mode is not compatible with precomputed trajectories.

KINOVA® Gen3 Ultra lightweight robot User Guide 82
In Angular Trajectory mode the endpoint is defined in terms of the desired joint angles for the actuators.
Angular Trajectory mode can be activated by sending either the endpoint joint state alone or via a precomputed trajectory.
Users have the option to apply constraints to trajectories. There are three options available for constraints:
• duration - the time period (in seconds) in which the trajectory is to be carried out
• speed - the maximum speed (meters / second for Cartesian, degrees / second for angular) of the
motion while carrying out the trajectory
• no constraint - the robot will go to the endpoint without the time or speed being specified
Note: If a requested trajectory constraint will cause angular limits to be exceeded in the course of the
trajectory, (e.g. the duration is too short and requires a speed or acceleration that is not feasible) the
trajectory will be rejected.
In angular trajectories, all three options are available (duration, speed, no constraint).
In Cartesian trajectories, the speed constraint or no constraint options are available.
Trajectory control modes are set by sending a trajectory using the appropriate API methods, or via the Web
App Actions page.
Joystick control modes
This section describes the Joystick Control modes of the robot.
Joystick Control modes provide the user the ability to create a desired motion of the robot by sending
commands to the robot. This is done using joystick control inputs (physical gamepad or virtual joystick) or
directly using API commands.
In Cartesian Joystick mode the motion of the robot end effector, both linear and angular, is controlled.
Cartesian joystick is entered by:
• sending API twist commands (specify linear and angular velocity of the end effector)
• activating Xbox gamepad Twist linear and Twist angular modes
• sending Web App Pose virtual joystick control inputs in velocity control
This mode provides for singularity avoidance and obstacle avoidance (protection zones).
For Cartesian control, the reference frames for translation and orientation control are configurable:
Table 41: Cartesian reference frames options
Cartesian frame mode Reference frame for translation Reference frame for orientation
mixed mode base tool
tool mode tool tool
base mode base base
Note: Orientations are defined using an z-y-x Tait-Bryan extrinsic convention. That is, rotation about the
fixed x-axis, followed by rotation about the fixed y-axis, followed by rotation about the fixed z-axis.
In Angular Joystick mode the joints of the robot are moved in angular space using joint angular velocity
commands or joystick control inputs provided to the actuators. The joints can be moved individually or
together.
Angular joystick mode can be entered by:
• sending API joint speed commands
• activating Xbox gamepad Joint mapping
• sending commands via Web App Angular virtual joystick
Admittance modes
This section describes the Admittance modes of the arm.
By setting the control mode of the arm to admittance mode, the user can manually apply external effort on
the robot and it will move accordingly.

KINOVA® Gen3 Ultra lightweight robot User Guide 83
In Cartesian Admittance mode, the user manipulates the tool. A spherical workspace centered on actuator
two is defined. If the user tries to extend the robot beyond this workspace, the robot will resist and come
back inside the workspace.
In Joint Admittance mode the joints of the robot rotate according to the external torques applied.
In Null Space Admittance mode, the end effector stays in the same pose while the user manipulates the
joints of the arm (within the null space). The arm moves within the null space according to the torques
applied.
Note: For all three admittance modes, the robot control library will automatically adapt to the
user-configured gravity vector, tool, and payload information. The user is responsible for correctly
defining the gravity vector, as well as tool and payload information using either the Web App or API
(Kinova.Api.ControlConfig). Incorrect configuration of these parameters can cause unexpected
behavior in admittance modes.
There are four ways to put the robot into admittance:
• use the method SetAdmittance in the API.
• Web App control panel admittance mode selection
• admittance selection buttons on Xbox gamepad modes (Twist linear and angular modes for Cartesian
and Null space admittance, Joint mode for Joint admittance)
• admittance mode physical buttons on the interface module (for Cartesian and Null space admittance
modes).
Note: Motion in admittance modes is constrained by internal safety limits for the robot on velocity
and torques. This includes Cartesian linear velocity limits and joint limits for angular velocity and
torque. Admittance mode performance is also tuned using configurable parameters. The values for these
parameters are not currently user-configurable, but will be available for configuration in a future software
release.

KINOVA® Gen3 Ultra lightweight robot User Guide 84
Configurations and safeties
Configurable parameters
This section lists the configurable parameters of the robot and gives guidance on how to
configure them.
The robotic arm includes a number of parameters that can be configured to customize the operation of the
robot.
These parameters can be configured using the appropriate KINOVA™ KORTEX® APIs. For more details on
how to perform configuration using the APIs, see the API documentation..
Some of these parameters can also be configured using the Web App GUI, which can be accessed as follows:
1. Open the Web App
2. Navigate to the Robot Configurations page
The following tables give a summary of the configurable parameters.
Control library configuration
Table 42: Control modes configuration (Kinova.Api.ControlConfig)
Configurable item Description
Defines global value for gravitational acceleration vector (x,y,z) in relation to
the base frame in units of m/s2.
Global gravity vector
Tool configuration
Payload configuration
Note: Configuration of the gravity vector is necessary to mount the robot in
arbitrary orientations (e.g. wall mount, ceiling mount). Accurate configuration
of the direction and strength of gravity is important for the robot to properly
compensate for torques due to gravity on the robot actuators.
• Set Cartesian transform of x, y, z (m) and θx, θy, and θz of tool frame in
relation to interface module frame.
Note: The Cartesian pose feedback available in base cyclic
communications uses the pose of the tool frame in relation to the base
frame. The specific choice of the tool frame will therefore impact the
readings for the current Cartesian pose.
• Set tool mass (kg), and tool mass center position x, y, z (m)
Note: The mass and center of mass of the tool need to be configured for
the robot control libraries to properly adapt the control of the robot to the
additional mass of the tool.
Set payload mass (kg) and mass center of payload x,y,z (m) in relation to the tool
frame.
Note: The mass and center of mass of the payload need to be configured for the
robot control libraries to properly adapt the control of the robot to the additional
mass of the payload.

KINOVA® Gen3 Ultra lightweight robot User Guide 85
Configurable item Description
Set the reference frame convention for translation and orientation to use with
Cartesian Twist and Wrench commands. There are three options:
• Mixed - translation reference frame = base frame and orientation
reference frame = tool frame
Cartesian
reference frame
• Tool - tool reference frame used for both translation and orientation
reference frames
• Base - base reference frame used for both translation and orientation
reference frames
Note: Changing the reference frame convention will affect the readings that are
provided for the current Cartesian pose of the end effector tool.
Base configuration
Table 43: Base configuration (Kinova.Api.Base)
Configurable item Description
User Profiles Create, read, update and delete user profiles
Create, read, update and delete protection zones (for obstacle avoidance).
Configurable parameters are:
• enabled / disabled
• zone shape type (rectangular prism, cylinder, sphere)
Protection Zone
Control Mapping Create, read control mapping
Action Create, read, update, delete action
Sequence Create, read, update, delete a sequence of actions
IPv4
Communication
Interface
• zone origin and orientation
• zone dimensions
• envelope thickness
• zone limitation types (velocity) and values
• envelope limitation types (velocity) and values
Set IPv4 configured (for specified network adapter):
• IP address
• subnet mask
• default gateway
Enable communication interface:
• network type (Wi-Fi or Ethernet)
• enabled/disabled
Wi-Fi
TCP bridge
to hardware
Restore factory
settings
Restore factory
product configuration
Set:
• SSID
• security key
• automatic connection allowed
• country code
Enable or disable
Delete all configurations and reverts settings to factory defaults (except
network settings)
Restore product configuration to factory product configuration

KINOVA® Gen3 Ultra lightweight robot User Guide 86
Actuators configuration
Table 44: Actuator configuration (Kinova.Api.ActuatorConfig)
Configurable item Description
Axis offsets Set actuator axis offset position
Torque offset Set actuator torque offset value
Set actuator control mode. Options:
• position
Control mode
Control loop
parameters
• velocity
• current
• torque
Configure an individual control loop parameter:
• joint or motor position
• joint or motor velocity
• joint torque
• motor current
Configure:
• error saturation value
• output saturation value
• kAz
• kBz
• error dead band value
Set vector drive parameters:
Vector drive
parameters
Encoder derivative
parameters
Command mode
Servoing Enable servoing
• kpq
• kiq
• kpd
• kid
Set encoder derivative parameters:
• maximum window width
• minimum encoder tick count
Set command mode. Options:
• cyclic - cyclic data only
• asynchronous - configuration messages only
• cyclic jitter compensation using position or posi tion and velocity inputs
Note: These options are available in the API but should NOT be used
Interface configuration
Table 45: Interface configuration (Kinova.Api.InterconnectConfig)
Configurable item Description
UART communciations Configure interface UART - enable /
disable, speed, word length, stop bits, parity
Ethernet communications Configure interface Ethernet
port - speed, duplex mode
GPIO Configure interface GPIOs - mode,
pull mode, value, default value

KINOVA® Gen3 Ultra lightweight robot User Guide 87
Configurable item Description
I2C Configure interface I2C - enable /
disable, mode, addressing mode
Device configuration
Table 46: Device configuration (Kinova.Api.DeviceConfig)
Configurable item Description
Run mode Set device run mode (Run, Calibration, Configuration, Debug, Tuning)
IPv4 settings
Safeties Enable / disable, set warning and/or error threshholds for specific safeties
(For devices other than base) Set device IPv4 address, subnet mask, default
gateway
Vision configuration
Table 47: Vision configuration (Kinova.Api.VisionConfig)
Configurable item Description
Set several discrete vision sensor settings:
Color sensor
• resolution - 320 x 240, 640 x 480, 1280 x 720, 1920 x 1080
• frame rate - 15 or 30 fps
Sensor settings
• bit rate - 10, 15, 20, or 25 Mbps
Depth sensor:
• resolution - 424 x 240, 480 x 270
• frame rate - 6, 15, or 30 fps
Note: Higher frame rate or resolution requires a higher data rate for best
results
Focus actions
Sensor options
Perform a focus action on a sensor.
Note: Only supported for color sensor
• Start / pause continuous focus
• Focus now
• Disable focus
• Set to focus on x,y point within sensor view pixel coordinates
• Set a manual focus distance between infinity and a close plane
Set the value of any one of a number of camera settings options.
Color image settings:
• brightness
• contrast
• saturation

KINOVA® Gen3 Ultra lightweight robot User Guide 88
Configurable item Description
Depth camera settings
• exposure
• gain
• enable auto-exposure
• visual presets
• frames queue size
• enable error polling
• enable output trigger
• depth unit setting in m
• stereo depth camera baseline distance in mm
Intrinsic parameters Set the intrinsic parameters for a chosen sensor:
• resolution
• principal point - horizontal and vertical coordinates of principal point of
image, as pixel offsets from left and top edge respectively
• focal length - horizontally and vertically as multiple of pixel width and
height
• distortion coefficients
º k1 - first radial distortion coefficient
º k2 - second radial distortion coefficient
º k3 - third radial distortion coefficient
º p1 - first tangential distortion coefficient
º p2 - second tangential distortion coefficient
Extrinsic parameters Set sensor extrinsic parameters:
• rotation matrix from depth to color sensor
• translation vector from depth to color sensor
Safety items
This section is a reference for Safety items viewable and configurable in the Web App
Configuration page.
Overview
Safety items, and their associated warning and error thresholds are viewable within the Configuration page
of the Web App. There are three categories of safeties:
• Base (controller) safeties
• Actuators safeties
• Interface module safeties
The tables that follow give more information about the safeties, including:
• Description - significance of the safety item
• Hard limit (lower) - the minimum allowable value for the item
• Hard limit (upper) - the maximum allowable value for the item
• Default warning / error threshold - default configurations for the safety thresholds.
Base (controller) safeties
The following Base-related Safety items are viewable in the Web App.

KINOVA® Gen3 Ultra lightweight robot User Guide 89
Table 48: Base Safety items
Safety Item Description
Firmware
Update Failure
Ambient
Temperature
Core
Temperature
Joint Fault
Joint
Detection
Error
Network
Initialization
Error
Maximum
Current
Indicates a failure in the
firmware update process.
The ambient temperature is
above upper limit
The core temperature is
above upper limit
At least one joint is in a fault
state
The number of detected
joints does not match the
configured arm joint count.
Arm is detected but control
bus link is down n/a n/a
The base current reading is
above upper limit
Hard
limit
lower warning
upper
n/a n/a
0.0 °C 70.0 °CMaximum
90.0 °C 80.0 °C
0.0 °C 75.0 °CMaximum
100.0 °C 85.0 °C
n/a n/a
n/a n/a
0.0 A 9.0 A
12.0 A 10.0 A
Default
threshold
error
Minimum
Voltage
Maximum
Voltage
Emergency
Stop Activated
Inrush Current
Limiter Fault
Actuators safeties
The base voltage reading is
below lower limit
Note: The minimum voltage
must be lower than the
maximum voltage
The base voltage reading is
above upper limit.
Note: The maximum voltage
must be higher than the
minimum voltage
Emergency stop activated.
Note: electronic protection
cannot be deactivated
Inrush current limiter fault
triggered.
Note: electronic protection
cannot be deactivated
16.0 V 18.0 V
24.0 V 16.0 V
24.0 V 30.0 V
31.0 V 31.0 V
n/a n/a
n/a n/a
The following actuator-related Safety items are viewable and configurable in the Web App.

KINOVA® Gen3 Ultra lightweight robot User Guide 90
Table 49: Actuator Safety items
Safety Item Description Hard limit
The error between
the command and the
Following Error
Small
Max Velocity
Large
Small
Maximum
Torque
Large
Magnetic Position
reported position is above
upper limit.
Note: Only active when in
servoing state
The computed velocity
of the actuator is greater
than threshold °/sec.
Torque reading higher
than x N·m.
Position step of more
than threshold °/ms
has been read on the
magnetic sensor.
250 °/s 200 °/s
150 °/s 120 °/s
52 N·m 51.3 N·m
105 N·m 104.5 N·m
lower warning
upper
0° 3.0°
10° 5.0°
0 °/s 180 °/s
0 °/s 100 °/s
0 N·m 29.4 N·m
0 N·m 56.7 N·m
0° 3.0°
20° 5.0°
Default
threshold
error
Hall Position
Hall Sequence
Input Encoder
Hall Mismatch
Input Encoder
Index Mismatch
Input Encoder
Magnetic Mismatch
Maximum
Motor Current
Small
Large
Small
Large
Position step of more
than threshold °/ms
Invalid Hall sequence
detected.
The Hall sensor position
value doesn’t match the
input optical encoder
position within +/threshold degrees.
Input encoder index
position mismatch
The input optical encoder
position value doesn’t
match with the magnetic
encoder position within
+/- threshold degrees.
The measured current of
the motor is above upper
limit
0° n/a
10° 0.4285°
0° n/a
10° 0.2145°
n/a n/a
0° 1.5°
10° 2.0°
0 500
2000 1000
0° 10°
45° 15°
0 A 6.0 A
8.0 A 7.0 A
0 A 10.0 A
12.0 A 11.0 A

KINOVA® Gen3 Ultra lightweight robot User Guide 91
Safety Item Description Hard limit
The voltage reading is
below lower limit.
Note: The minimum
Minimum Voltage
Maximum Voltage
Maximum Motor
Temperature
Maximum Core
Temperature
voltage thresholds must
be lower than the
maximum voltage
thresholds.
The voltage reading is
above upper limit.
Note: The maximum
voltage thresholds must
be higher than the
minimum voltage
thresholds.
Motor temp is above
upper limit
Core temp above upper
limit
80.0 °C 75.0 °C
100.0 °C 90.0 °C
lower warning
upper
16.0 V 18.0 V
24.0 V 16.0 V
24.0 V 30.0 V
31.0 V 31.0 V
0.0 °C 60.0 °C
0.0 °C 80.0 °C
Default
threshold
error
Non-Volatile
Memory Corrupted
Motor Driver Fault
Emergency
Line Asserted
Watchdog Triggered Watchdog was triggered n/a n/a
Non-volatile memory
corrupt
Driver chip reported a
major fault
Note: electronic
protection cannot be
deactivated
Emergency line asserted.
Motor drive disabled
n/a n/a
n/a n/a
n/a n/a
Interface module safeties
The following Interface module-related Safety items are viewable and configurable in the Web App.
Table 50: Interface Safety items
Maximum
Motor Current
The measured motor
current in the connected
3rd party gripper (if
compatible gripper is
attached) is above the
higher limit. If gripper is
not present the safety is
disabled.
lower warningSafety Item Description Hard limit
upper
n/a n/a
Default
threshold
error

KINOVA® Gen3 Ultra lightweight robot User Guide 92
Maximum Motor
Temperature
The motor temperature
of the connected
3rd party gripper (if
compatible gripper is
attached) is above the
higher limit. If gripper is
not present the safety is
disabled.
lower limit
Note: minimum voltage
thresholds must be
below maximum voltage
thresholds
upper limit
Note: maximum voltage
thresholds must be
above minimum voltage
thresholds
lower warningSafety Item Description Hard limit
upper
Default
threshold
n/a n/a
16.0 V 18.0 VMinimum Voltage Voltage reading below
24.0 V 16.0 V
24.0 V 30.0Maximum Voltage Voltage reading above
31.0 V 31.0
error
Temperature
Non-Volatile
Memory
Corrupted
Emergency
Line Asserted
Watchdog
Triggered
Core temperature above
upper limit
0.0 °C 80.0 °CMaximum Core
100.0 °C 90.0 °C
Non-volatile memory
corrupt n/a n/a
Emergency line
asserted. Motor drive
n/a n/a
disabled
Watchdog triggered
n/a n/a

KINOVA® Gen3 Ultra lightweight robot User Guide 93
KINOVA® KORTEX™ Web App User Guide
Introduction
The following sections describe the KINOVA® KORTEX™ Web App. The Web App is used for controlling,
configuring and monitoring the robot.
This pages that follow describe the purpose, layout, and use of the Web App.
Purpose
This section describes the purpose of the Web App.
The Web App is an HTML GUI (Graphical User Interface) that runs on the robot. This web interface allows
users to configure, control and monitor the robot through a web browser interface from a computer
connected to the robot over a wired Ethernet or Wi-Fi connection.
Device availability of Web App
This section describes the device availability of the Web App.
The Web App is a responsive web application. It is designed to adapt itself to various aspect ratios and
resolutions enabling it to run on multiple platforms that support the Google Chrome browser. This includes:
• desktop / laptop computer
• tablet computer
• smartphone
Figure 30: Desktop

KINOVA® Gen3 Ultra lightweight robot User Guide 94
Figure 31: Tablet

KINOVA® Gen3 Ultra lightweight robot User Guide 95
Figure 32: Smartphone
Platform and browser support
This section describes platform and browser support for the Web App.
The Web App has the following platform and browser support.
Operating system support
• Microsoft Windows 7/8/10
• Ubuntu LTS 16.04
• Android 8.1 and higher
• Mac OS and iOS
Browser support
• Chrome
• Firefox
• Safari
Other platforms and browsers are not currently supported - some features may work differently in those
cases.
User login
This section describes how to log in to the Web App.
After establishing a network connection between your device and the robot, open a web browser and enter
the IP address for the robot base external interface.

KINOVA® Gen3 Ultra lightweight robot User Guide 96
The Web App will launch, ending in a login popup.
Enter your user name and password and press the CONNECT button.
The default username and password when the robot first arrives are:
• username: admin
• password: admin
Figure 33: User login
On pressing CONNECT, the Web App will launch and initialize. While it is doing this, the Web App will give
visual feedback to the user on the status of initialization of the application.
Figure 34: Initializing...
Web App layout and navigation
This section describes the layout and navigation of the Web App.

KINOVA® Gen3 Ultra lightweight robot User Guide 97
The Web App screen is divided into several main sections:
• Main navigation panel
• Main information panel
• Notification bar
• Shortcuts panel
• Robot control panel
• Mode indicator, user icon, and E-stop
Figure 35: Web App Layout
Pages menu
In the middle of the screen is the main information panel containing the contents of each page of the
application. The page can be changed from a pages menu on the left of the screen. This menu is hidden by
default, but can be lauched by clicking / tapping the menu icon in the upper left.

KINOVA® Gen3 Ultra lightweight robot User Guide 98

KINOVA® Gen3 Ultra lightweight robot User Guide 99
The page options are organized into groups:
•
Configurations
º
Robot
º
Controllers
º
Wireless & Networks
•
Safeties
•
Operations
º
Actions
º
Protection Zones
º
Camera
•
Systems
º
System Information
º
Monitoring
º
Upgrade
•
Users

KINOVA® Gen3 Ultra lightweight robot User Guide 100
In the upper right hand corner of the screen are four indicators / controls:
•
Notifications indicator - number of most important notifications. Clicking allows notifications
to be read.
•
User profile icon - Shows the user session icon
• Control mode - status of the control mode situation of the robot. There are four icons to indicate the
mode / state:
º
Warning - robot in warning state
º
Error - robot is in a fault state
º
Idle - robot is not currently being controlled by any user session; waiting
º
Playing - a sequence is being played on the robot
º
Running - the robot is being actively controlled by a user
º
Admittance - robot is being controlled in an admittance mode
•
Emergency Stop (E-stop) - button control which when pressed / tapped will initiate the
emergency stop of the robot.
Clicking on any of these items displays a pop-up showing further information.
Robot control panel
The control panel is on the bottom of the screen, and consists of a group of six buttons. Three are to launch
pop-up windows for virtual joystick controls and admittance mode toggles:
•
Pose Virtual Joystick
•
Angular mode control
•
Admittance controls
The virtual joysticks allow you to control the movement of the robot without the use of a physical controller.
Admittance mode lets you to move the robot with your hands in one of three (Cartesian, joint, and null
space) admittance modes.
In the same area there are three other controls:
•
Play action - brings up a window to play a selected action
•
Camera feed - brings up a window to view camera feed
•
Snapshot - allows user to capture a Cartesian, angular, or gripper pose
 Loading...
Loading...