
PART NO. Z1-004-772, IB020522
Dec. 2010
General
Description
User’s Manual
Regulated DC Power Supply
PAT-T Series
8 kW type
PAT20-400T
PAT30-266T
PAT40-200T
PAT60-133T
Installation and
Preparation
Connecting the Load
Basic Operation
External Control
Parallel/Series Operation
Remote Control
1
2
3
4
5
6
PAT80-100T
PAT160-50T
PAT250-32T
PAT350-22.8T
PAT500-16T
PAT650-12.3T
PAT850-9.4T
Maintenance
Specifications
7
8
Appx

Thank you for purchasing the PAT-T Series Regulated DC
About Operation Manual
Power Supply.
The operation manual for the PAT-T Series is consisting of the
“User’s Manual” (this manual) and the “Communication Interface Manual”.
This manual is intended for users of the product or persons
teaching other users on how to operate the product.
The manual assumes that the reader has knowledge about
Power Supply.
• User’s manual (this manual)
The User’s manual is intended for first-time users of this
product. It provides an overview of the product and notes on
usage. It also explains how to configure the product, operate the product, perform maintenance on the product, and
so on. Read this manual thoroughly to use the functions of
the product effectively.
This manual is designed to be read from beginning to end.
We recommend that you
product for the first time.
You can also review this manual when you are confused
about an operation or when a problem occurs.
read it thoroughly before using this
This product information can also be obtained using the *IDN?
remote control command.
Trademarks
Microsoft and Windows are registered trademarks of Microsoft
Corporation in the United States and/or other countries.
Other company names and product names used in this manual are generally trademarks or registered trademarks of the
respective companies.
Copyright
Reproduction and reprinting of this operation manual, whole or
partially, without our permission is prohibited.
Both unit specifications and manual contents are su bject to
change without notice.
© 2010 Kikusui Electronics Corporation
• The communication interface manual
The communication interface manual describes the content
of the commands.
The interface manual is written for readers with sufficient
basic knowledge of how to control instruments using a
personal computer.
The interface manual is provided in HTML format on the
accompanied CD-ROM (a portion of the manual is in PDF
format). You can view the Operating environment Window s
98 or later. You can view it using Microsoft Internet Explorer
5.5 or later. You can view the PDF file using Adobe Reader
6.0 or later.
If you find any incorrectly arranged or missing pages in the
manual, they will be replaced. If the manu
a new copy can be provided for a fee. In either case, please
contact Kikusui distributor/agent, and provide the “Kikusui Part
No.” given on the cover.
The Operation Manual has been prepared with the utmost
care; however, if you have any questions, or note any errors or
omissions, please contact Kikusui distributor/agent.
After reading, always keep the manual nearby so that you may
refer to it as needed.
al gets lost or soiled,
Applicable firmware version of the PAT-T
Series
This manual applies to PAT-T Series with firmware version
5.0x.
When making an inquiry about the product, please provide us
with the following information.
• Model (indicated at the top section on the front panel)
•Firmware version (See page 1-6 .)
•Serial number (indicated at the bottom section on the rear
panel)
For the safe use and safe maintenance of this product, the
Safety Symbols
Notations Used in This Manual
WARNING
DESCRIPTION
following symbols are used throughout this manual and on the
product. Note the meaning of each of the symbols to ensure
safe use of the product. (Not all symbols may be used.)
or
Indicates that a high voltage (over 1000 V) is used here.
Touching the part causes a possibly fatal electric
shock. If physical contact is required by your work,
start work only after you make sure that no voltage is
output here.
DANGER
Indicates an imminently hazardous situation which, if
ignored, will result in death or serious injury.
WARNING
Indicates a potentially hazardous situation which, if
ignored, could result in death or serious injury.
CAUTION
Indicates a potentially hazardous situation which, if
ignored, may result in damage to the product and other
property.
Shows that the act indicated is prohibited.
• In this manual, the PAT-T Series regulated DC power supply
is often simply referred to as “the PAT.”
• The word “PC” used in this manual is a generic term for
personal computers and workstations.
• The following marks are used with the explanations in this
manual.
Indicates a potentially hazardous situation which, if
ignored, could result in death or serious injury.
CAUTION
Indicates a potentially hazardous situation which, if
ignored, may result in damage to the product and
other property.
Indicates information that you should know.
Explanation of terminology or operation principle.
See
Indicates reference to detailed information.
Indicates a general danger, warning, or caution.
When this symbol is marked on the product, see
the relevant sections in this manual.
Indicates a caution for hot surface of the product.
When this symbol is marked on the product, see
the relevant sections in this manual.
Protective conductor terminal.
Chassis (frame) terminal.
On (supply)
Off (supply)
In position of a bi-stable push control
Out position of a bi-stable push control
SHIFT+key name (marked in blue)
Indicates an operation in which a switch marked in blue is
pressed while holding down the SHIFT switch.
CFxx : x
The first two characters “CF” indicates a configuration
setting, and the next two-digit number indicates the
CONFIG parameter number. The character after the colon
indicates the selected setting.
PAT-T 8kW i

The following safety precautions must be observed to avoid
Safety Precautions
fire hazards, electric shock, accidents, and other failures. Keep
them in mind and make sure to observe them.
Using the product in a manner that is not specified in this
manual may impair the protection functions provided by the
product.
n
o
i
t
a
r
e
p
O
Manual
Users
• This product must be used only by qualified personnel who
understand the contents of this operation manual.
• If an unqualified personnel is to use the product, be sure the
product is handled under the supervision of qualified
personnel (those who have electrical knowledge). This is to
prevent the possibility of personal injury.
Purpose of use
•Never use the product for purposes other than the product's
intended use.
• This product is not designed or manufactured for general
home or consumer use.
Line
Voltage
Relocation
•Lower the POWER switch lever to turn it off.
• Remove all wiring.
• When transporting the product, be sure to use the original
packing materials.
• The product weighs over 20 kg. When moving the product,
have more than one person carry it. The weight of the
product is indicated on the rear panel of the product and in
the specification table in this manual.
•Be sure to include the manual.
Check?
Operation
• Before using the product, be sure to check the input power
voltage and that there is no abnormality in the appearance
of the power cable. Be sure to turn off the switchboard
breaker before checking.
•If a malfunction or abnormality is detected on the product,
stop using it immediately, and remove the power cable from
the switchboard. Make sure the product is not used until it is
completely repaired.
• Use cables or wires with sufficiently large current capacity
for output wires and load cables.
• Do not disassemble or modify the product. If you need to
modify the product, contact your Kikusui distributor/agent.
Input power
• Use the product within the rated input power voltage range.
• For applying power, use the power cable provided. For
details, see the respective page in the operation manual.
• This product is an equipment of IEC Overvoltage Category
II (energy-consuming equipment supplied from the fixed
installation).
Cover
• Some parts inside the product may cause physical hazards.
Do not remove the external cover.
N
L
G
Grounding
• This product is an IEC Safety Class I equipment (equipment
with a protective conductor terminal). To prevent electric
shock, be sure to connect the protective conductor terminal
of the product to electrical ground (safety ground).
Maintenance and inspection
• To prevent electric shock, be sure to unplug the product
before carrying out maintenance or inspection. Do not
remove the external cover.
• Check periodically that there are no tears or breaks in the
power cord and the test lead covering.
• If the panel needs cleaning, gently wipe using a soft cloth
with water-diluted neutral detergent. Do not use volatile
chemicals such as benzene or thinner.
• To maintain the performance and safe operation of the
product, it is recommended that periodic maintenance,
inspection, cleaning, and calibration be performed.
Service
•Kikusui service engineers will perform internal service on
the product. If the product needs adjustment or repairs,
contact your Kikusui distributor/agent.
ii PAT- T 8kW

Warning label
Precautions Concerning Installation
• There is a warning label affixed to the product. If this label
tears or falls off, replace with a new label. If you need a new
label, contact your Kikusui agent or distributor.
PAT- T
Top panel
Label
Be sure to observe the following precautions when
installing the product.
• Do not use the product in a flammable atmosphere.
To prevent the possibility of explosion or fire, do not use the
product near alcohol, thinner or other combustible materials,
or in an atmosphere containing such vapors.
• Avoid locations where the product is exposed to high
temperature or direct sunlight.
Do not install the product near a heater or in areas subject
to drastic temperature changes.
Operating temperature range: 0 °C to +50 °C (32
Storage temperature range: -25
•Avoid humid environments.
Do not install the product in high-humidity locations–near a
boiler, humidifier, or water supply.
Operating humidity range: 20 %rh to 85 %rh (no condensation)
Storage humidity range: 90 %rh or less (no condensation)
Condensation may occur even within the operating relative
humidity range. If this happens, do not use the product until
the condensation dries up completely.
•Be sure to use the product indoors.
This product is designed for safe indoor use.
• Do not install the product in a corrosive atmosphere.
Do not install the product in a corrosive atmosphere or in
environments containing sulfuric acid mist, etc. This may
cause corrosion of various conductors and bad contacts of
connectors leading to malfunction and failure, or in the worst
case, a fire.
However, operation in such environments may be possible
through alteration. If you want to use the PAT in such
environments, consult your Kikusui agent or distributor.
• Do not install the product in a dusty location.
Accumulation of dust can lead to electric shock or fire.
• Do not use the product where ventilation is poor.
The product employs a forced air cooling system. Air is
taken in from the air inlet on the front panel and exhausted
from the air outlet on the rear panel. Secure adequate
space around the product to prevent the possibility of fire
caused by accumulation of heat.
Allow at least 20 cm of space between the air inlet/outlet
and the wall (or obstacles). Hot air (approximately 20
higher than the ambient temperature) is exhausted from the
air outlet. Do not place objects that are affected by heat
near the air outlet.
• Do not place objects on the product.
Placing heavy objects on top of the product may cause
failures.
• Do not install the product on an inclined surface or location
subject to vibrations.
The product may fall or tip over causing damages and
injuries.
• Do not use the product in a location where strong magnetic
or electric fields are nearby or a location where large
amount of distortion and noise is present on the input power
supply waveform.
The product may malfunction.
• Do not use the product near highly sensitive measuring
instruments or transceivers.
The noise generated by the product may affect them.
°
C to +70 °C (-13 °F to 158 °F)
°
F
to 122
°
F
°
)
C
PAT-T 8kW iii

The PAT is a low-noise, highly efficient Constant Voltage (CV)/
Product Overview
Features
Constant Current (CC) automatic crossover power supply that
employs a software switching system.
Capable to expand the system up to a maximum output of 40
kW by the master-slave parallel operation.
Communication functions for remote control also come
standard with the product.
The all models can also receive three-phase 200 Vac and
inputthree-phase 400 Vac input. In this manual, the threephase 400 Vac input models are often simply referred to as
“400 V input model.”
• Reduction of harmonic current and power transmission
loss
The power-factor improvement circuit reduces the effects of
harmonic currents on the input power line. It also
suppresses the peak current and reduces the power
transmission loss.
• Master-Slave parallel operation
Up to five power supplies can be connected in parallel to
expand the output power to 40 kW.
(You can expand the output pow
two PAT850-9.4T power supplies in parallel.)
• Output limit function
Yo u can set the upper limit of current and voltage that is
applied when setting the output.
This function is used to prevent setting inappropriate value
by mistake.
• Remote interface
Equipped with RS232C as standard. You can select the
GPIB, USB or LAN interface as a factory option.
The remote interface complies with IEEE 488.2 std 1992
and SCPI Specification 1999.0. Because the LAN interface
complies with the LXI standard, the construction of a highly
cost-effective system is possible.
•High efficiency and low noise
The PAT is a highly efficient, low-noise power supply that
employs a software switching system.
High power conversion efficiency has reduced the rise in the
internal temperature and has contributed to the product’s
compact and light design.
• Downsized input distribution device
The input distribution device (breaker) can be downsized,
because the built-in power-factor improvement circ
reduces the required input current.
• Preset memory function of settings
Up to three output setting presets (combination of current
and voltage) can be saved.
Yo u can simply select a preset to set the output without
having to set the voltage and current every time you use the
PAT.
• Output on/off delay function
Yo u can set a delay until the output is actually turned on or
off after turning the OUTPUT switch on or off.
For example, this feature is useful if you want to turn the
output on/off by setting a time offset according to the load
characteristics.
er to 16 kW by connecting
uit
iv PAT- T 8kW

Contents
1
2
Safety Symbols .........................................................................................................i
Notations Used in This Manual .................................................................................i
Safety Precautions ................................................................................................... ii
Precautions Concerning Installation ........................................................................ iii
Product Overview .................................................................................................... iv
Features ..................................................................................................................iv
Contents by Function ............................................................................................. vii
Front panel ............................................................................................................ viii
Rear panel ................................................................................................................x
Installation and Preparation
1.1 Checking the Package Contents..............................................................................1-2
1.2 Rack Mounting the Product......................................................................................1-3
1.3 Connecting the Power Cable ...................................................................................1-4
1.4 Turning On ..............................................................................................................1-6
Connecting the Load
2.1 Load Considerations................................................................................................2-2
2.2 Load Cable...............................................................................................................2-4
2.3 Connecting to the Output terminal ...........................................................................2-6
3
4
Basic Operation
3.1 Measured Value Display and Setting Display (Setting the Output Voltage and Output
Current)....................................................................................................................3-2
3.2 Output Operation .....................................................................................................3-3
3.3 Constant Voltage (CV) and Constant Current (CC) Power Supplies.......................3-5
3.4 Using the PAT as a CV or CC Power Supply (Setting the Output Voltage and Output
Current)....................................................................................................................3-7
3.5 Protection Functions and Alarms .............................................................................3-8
3.5.1 Overvoltage protection (OVP) and overcurrent protection (OCP) ................3-9
3.5.2 Other Protection Functions .........................................................................3-12
3.6 CONFIG Settings ...................................................................................................3-14
3.7 Preset Memory Function........................................................................................3-23
3.8 Lock Function.........................................................................................................3-24
3.9 Switching from Remote to Local Mode ..................................................................3-25
3.10 Remote Sensing Function......................................................................................3-25
3.11 Factory Default Settings.........................................................................................3-28
External Control
4.1 Overview of External Control ...................................................................................4-2
4.2 J1 Connector............................................................................................................4-2
4.3 Output terminal Insulation........................................................................................4-5
4.3.1 When the Output terminal Is Not Grounded (Floating) .................................4-6
4.3.2 When the Output terminal Is Grounded........................................................4-7
4.4 Controlling the Output Voltage.................................................................................4-9
4.4.1 External Voltage (Vext) Control ....................................................................4-9
4.4.2 External resistance (Rext) control...............................................................4-11
PAT-T 8kW v

5
6
4.5 Controlling the Output Current...............................................................................4-13
4.5.1 External Voltage (Vext) Control.................................................................. 4-13
4.5.2 External Resistance (Rext) Control ............................................................ 4-15
4.6 Controlling the Output On/Off ................................................................................ 4-17
4.7 Shutdown Control Using External Contact ............................................................ 4-19
4.8 External Monitoring................................................................................................4-21
Parallel/Series Operation
5.1 Master-Slave Parallel Operation..............................................................................5-2
5.1.1 Functions during Master-Slave Parallel Operation.......................................5-2
5.1.2 Connection (Parallel Operation) ...................................................................5-4
5.1.3 Master-Slave Parallel Operation Setup........................................................ 5-7
5.1.4 Starting the Master-Slave Parallel Operation ...............................................5-8
5.2 Series Operation......................................................................................................5-9
5.2.1 Functions during series operation ................................................................5-9
5.2.2 Load Connection (Series Operation).......................................................... 5-11
5.2.3 Series Operation Setup ..............................................................................5-12
5.2.4 Starting the Series Operation.....................................................................5-12
Remote Control
6.1 Remote Control Overview........................................................................................6-2
6.2 Interface Setup ........................................................................................................6-3
6.2.1 RS232C Control (Standard Equipped)......................................................... 6-3
6.2.2 GPIB Interface (Option)................................................................................ 6-5
6.2.3 USB Interface (Option).................................................................................6-6
6.2.4 LAN interface (Option)..................................................................................6-7
6.3 Contents of the Included CD-ROM..........................................................................6-9
6.4 Installing the VISA library....................................................................................... 6-10
6.5 Command Details .................................................................................................. 6-11
7
8
Appendix
Index
Maintenance
7.1 Inspection ................................................................................................................ 7-2
7.2 Cleaning...................................................................................................................7-2
7.3 Calibration................................................................................................................7-5
7.3.1 Calibration Overview .................................................................................... 7-5
7.3.2 Calibration Procedure...................................................................................7-6
Specifications
A.1 Options ....................................................................................................................A-2
A.2 Troubleshooting.......................................................................................................A-4
vi PAT-T 8kW

Contents by Function
Trobleshooting... See “A.2 Troubleshooting” on page A-4
•I want to check the accessories.
➔
1.1, “Checking the Package Contents”
p. 1-2
• The installation space is limited. How much space is
needed around the air inlet and outlet?
➔
“Precautions Concerning Installation”
p. iii
•How do I connect the AC power supply?
➔
1.3, “Connecting the Power Cable”
p. 1-4
• What kind of wires should be used to connect to the AC
power supply?
➔
1.3, “Connecting the Power Cable”
p. 1-4
• What kind of wires should be used to connect the load?
➔
2.2, “Load Cable”
p. 2-4
• The wire connecting the load is long (distance to the load
is long), but stable voltage is required.
➔
3.10, “Remote Sensing Function”
p. 3-25
•How do I rack mount the PAT? What kind of parts is
needed?
➔
“ Options”
p. A-2
•How do I set the communication conditions for remote
control?
➔
6.2, “Interface Setup”
p. 6-3
•How do I control the output voltage using an external DC
voltage?
➔
4.4.1, “External Voltage (Vext) Control”
p. 4-9
•How do I increase the current capacity in parallel
operation?
➔
5.1, “Master-Slave Parallel Operation”
p. 5-2
•How do I reset the PAT to factory default settings?
➔
3.11, “Factory Default Settings”
p. 3-28
•How can I use the PAT as a constant voltage power supply
(CV)?
➔
3.4, “Using the PAT as a CV or CC Power
Supply (Setting the Output Voltage and
Output Current)”
p. 3-7
•How can I use the PAT as a constant voltage current
supply (CC)?
•I would like to operate the PAT at a given voltage. How do
I register the voltage in the preset memory?
➔
3.7, “Preset Memory Function”
p. 3-23
•How do I set the upper limit to prevent the voltage from
being increased too much?
➔
“ Setting limit function”
p. 3-10
•How do I set the voltage in fine resolution?
➔
“ Fine adjustment function”
p. 3-7
•How do I set the protection function to prevent damage to
the load?
➔
3.5, “Protection Functions and Alarms”
p. 3-8
➔
3.5.1, “Overvoltage protection (OVP) and
overcurrent protection (OCP)”
p. 3-9
•How do I cut off the output at a different time from other
power supplies?
➔
“ Output on/off delay functions”
p. 3-4
•How can I monitor the output voltage and output current?
➔
4.8, “External Monitoring”
p. 4-21
•How do I temporarily lock the keys?
➔
3.8, “Lock Function”
p. 3-24
•How do I use the sample program for remote control?
➔
For information about remote control, see
the accompanying CD-ROM.
---
•How do I display a slave unit's current during parallel
operation?
5.1.1, “Functions during Master-Slave
Parallel Operation”
p. 5-2
•How do I clean the dust filter?
➔
“Cleaning the Dust Filter”
p. 7-2
•How do I check for breaks and tears in the insulation?
➔
7.1, “Inspection”
p. 7-2
•How do I calibrate the PAT-T series?
➔
7.3, “Calibration”
p. 7-5
Preparation
Setting
Operation
Maintenance
PAT-T 8kW vii
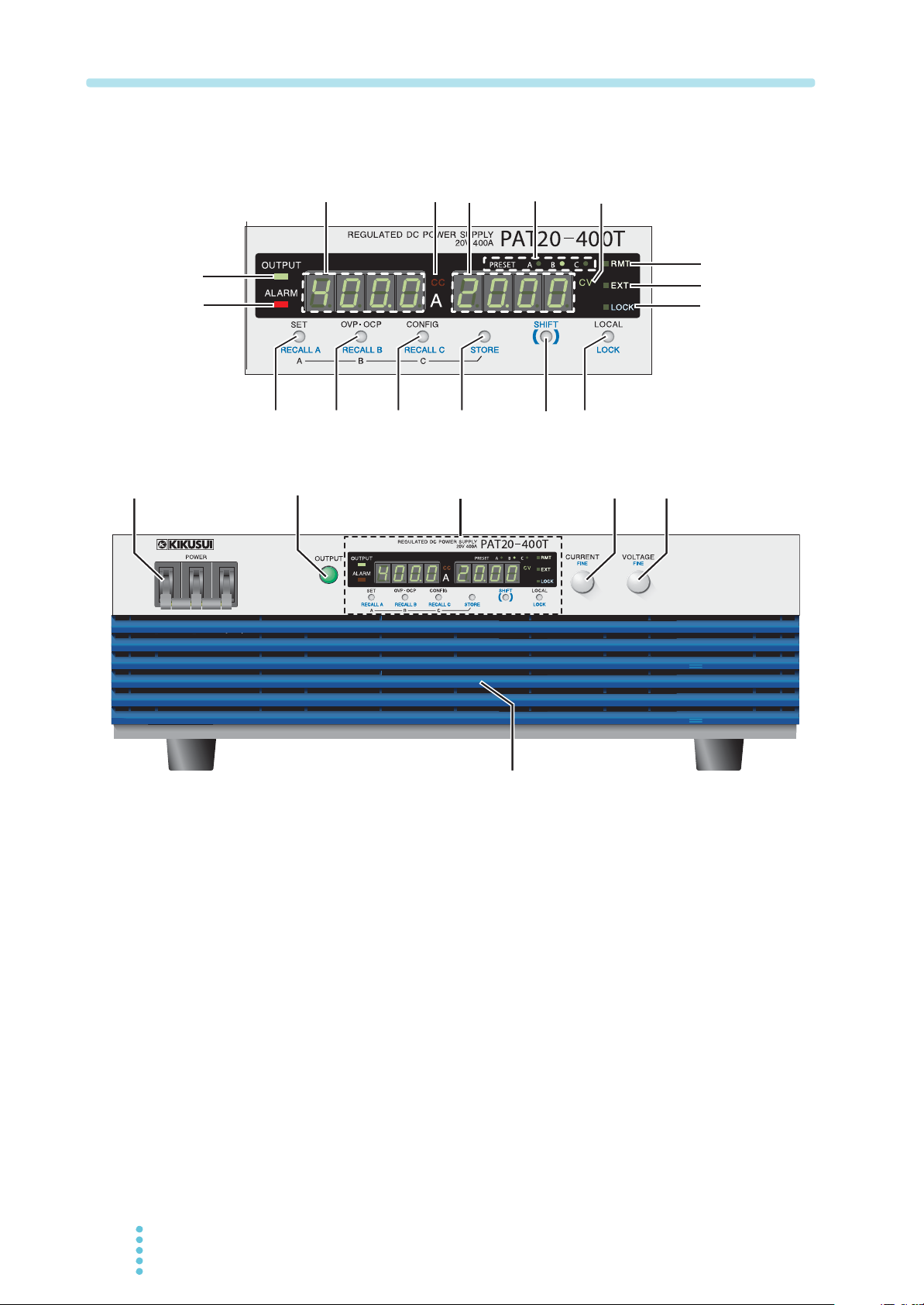
Front panel
0-
1
2
3
4
5
Display and swiches
11
12
OUTPUT
ALARM
16
6
17
8
7
0-
CCCC
C
C
AV
18
19
PRESET
9
A
20
10
C
CV
V
RMTRMT
EXTEXT
LOCK
B
21
13
14
15
Examples of PAT20-400T
viii PAT-T 8kW
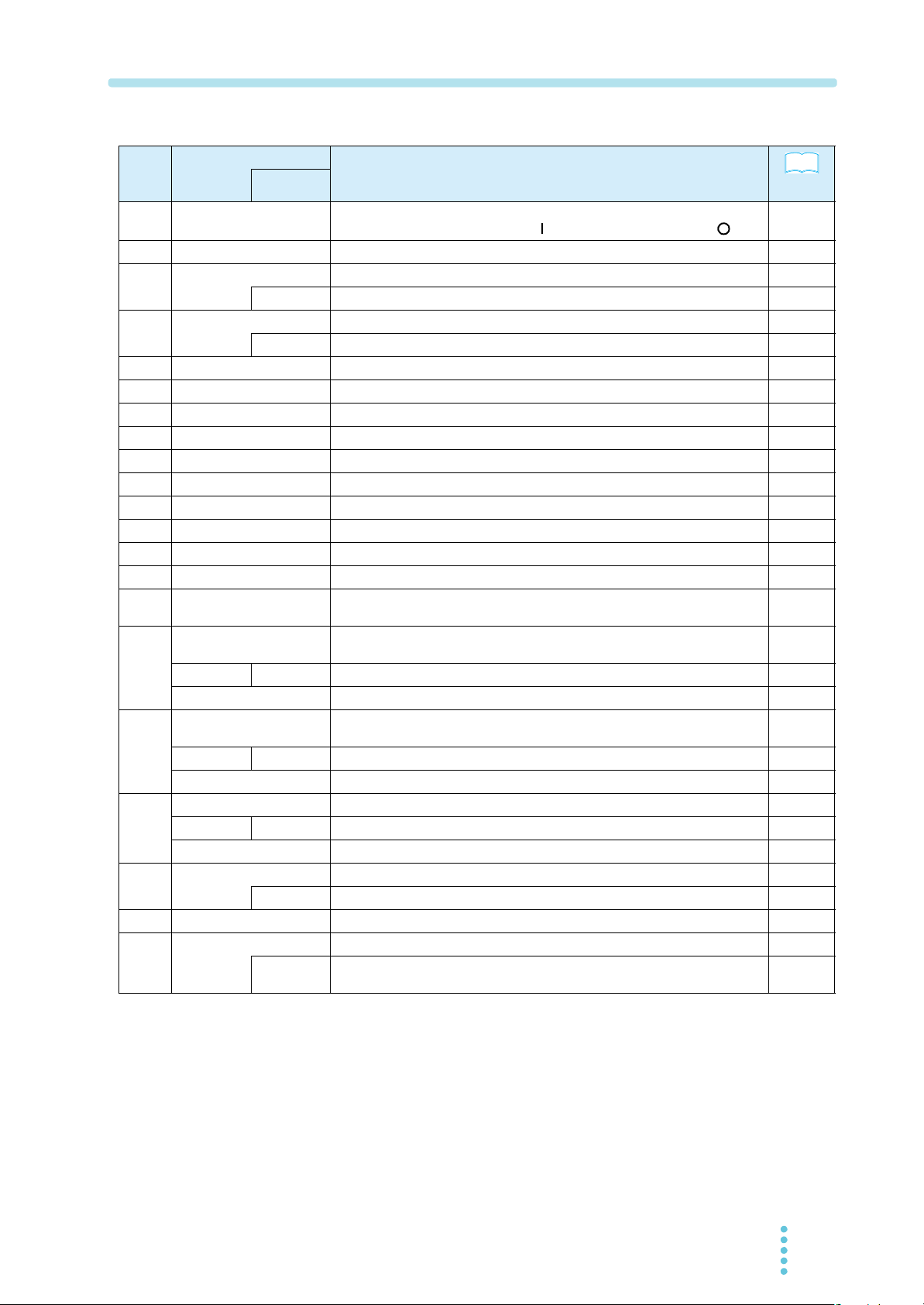
No.
POWER
1
OUTPUT
2
CURRENT knob
3
VOLTAGE knob
4
Air inlet (louver)
5
Ammeter
6
CC
7
Voltmeter
8
PRESET
9
CV
10
OUTPUT LED
11
ALARM LED
12
RMT LED
13
EXT LED
14
LOCK LED
15
SET
16
– RECALL A
A
17
OVP•OCP
– RECALL B
B
CONFIG
18
– RECALL C
C
–
19
SHIFT
20
LOCAL
21
Name
FINE
FINE
STORE
LOCK
+SHIFT
Function
Power on/off lever
Raise the lever to turn the power on ( ). Lower to turn the power off ( ).
Output on/off switch.
Used to set the current value or select the CONFIG parameter number.
Current adjustment knob when the fine adjustment function is enabled.
Used set the voltage value or change the CONFIG parameter setting.
Voltage adjustment knob when the fine adjustment function is enabled.
Inlet for taking in air from the outside. A dust filter is built in.
Displays the current value or the CONFIG parameter number.
Illuminates in constant current mode.
Displays the voltage value or the CONFIG parameter setting.
The LED of the preset memory in use illuminates.
Illuminates during constant voltage mode.
Illuminates when output is on and turns off when output is off.
Illuminates when a protection circuit is activated.
Illuminates when operating in remote control.
Illuminates when operating in external control.
Illuminates when panel operations except turning the output on/off and viewing
settings.
Switch with an LED for setting and checking the output voltage or output
current.
Switch for recalling the value of preset memory A
Switch for saving the value to preset memory A. Press STORE and then A.
Switch with an LED for setting and checking the trip points of the overvoltage
protection (OVP) and overcurrent protection (OCP).
Switch for recalling the value of preset memory B
Switch for saving the value to preset memory B. Press STORE and then B.
Switch with an LED for setting various conditions concerning the operation.
Switch for recalling the value of preset memory C
Switch for saving the value to preset memory C. Press STORE and then C.
–
Switch for storing the preset memory
Switch for calling up the functions marked in blue characters.
Switch for changing between remote and local modes.
Switch for disabling only the operations that change the settings (keeping the
display and recall operations enabled).
See
Page
1-6
3-3
–
3-7
–
3-7
7-2
–
3-7
–
3-23
3-7
3-2
3-8
3-25
4-2
3-24
3-7
3-23
3-23
3-9
3-23
3-23
3-14
3-23
3-23
–
3-23
i
3-25
3-24
PAT-T 8kW ix
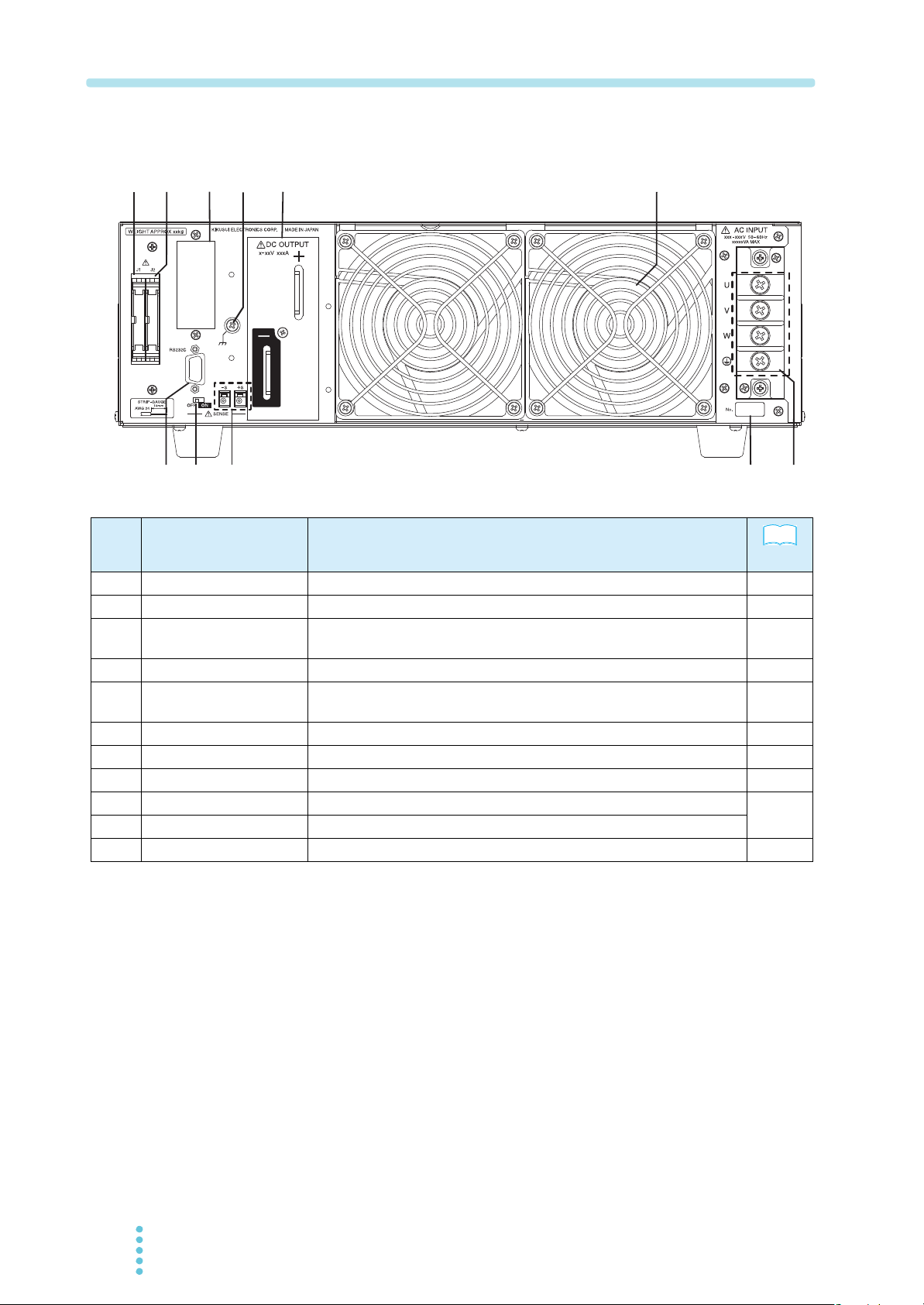
Rear panel
24
23
22
25
26
27
32
31
30
No. Name Function
J1
22
J2
23
Option slot
24
Chassis terminal
25
DC OUTPUT
26
Air outlet
27
AC INPUT
28
Serial number
29
Sensing terminal
30
Sensing switch
31
RS232C
32
Connector for external analog control.
Connector for parallel operation.
Slot for installing the optional interface board (GPIB, USB or LAN). A factory
option.
Terminal used to ground the output.
Output terminal.
Exhaust port for cooling.
Input terminal.
The serial number of the PAT.
A terminal used to connect the sensing wires.
Switch for enabling/disabling remote sensing.
Connector for the RS-232C cable.
29
28
See
Page
4-2
5-4
6-5
6-6
2-6
2-4
2-6
iii
1-4
–
3-25
6-3
x PAT-T 8kW

1
Installation and Preparation
This chapter describes the procedures
of unpacking and preparation of the
PAT before use.

1.1 Checking the Package Contents
When you receive the product, check that all accessories are included and that the
accessories have not been damaged during transportation.
If any of the accessories are damaged or missing, contact your Kikusui agent or
distributor.
We recommend that all packing materials be saved, in case the product needs to be
transported at a later date.
OUTPUT terminal cover
[Q1-500-106]
OUTPUT terminal cover set (2 sets)
[M5-101-009]
[M4-100-009]
Output terminal bolt (M12) (2 sets)
(PAT20-400T/30-266T)
[M3-111-010]
[M5-100-012]
[M1-100-027]
Pins 30 pcs.
[84-49-0100]
[M1-100-019]
[M5-101-008]
[M4-100-008]
Output terminal bolt (M10) (2 sets)
(PAT40-200T/60-133T/80-100T/160-50T)
[M1-100-013]
[M5-101-007]
[M4-100-007]
Output terminal bolt (M8) (2 sets)
(PAT250-32T/350-22.8T/500-16T
/650-12.3T/850-9.4T)
[M3-112-027]
Socket
2 pcs.
Protection cover
2 sets
[84-49-0161]
J1/J2 connector kit
User’s manual (This manual,
[Z1-004-772]
[84-49-0160]
1 pc.
)
[91-80-6940]
Chassis connection wire set (1 set)
CD-ROM (
[SA-6038]
1 pc.
)
Fig.1-1 Accessories
1-2 PAT-T 8kW
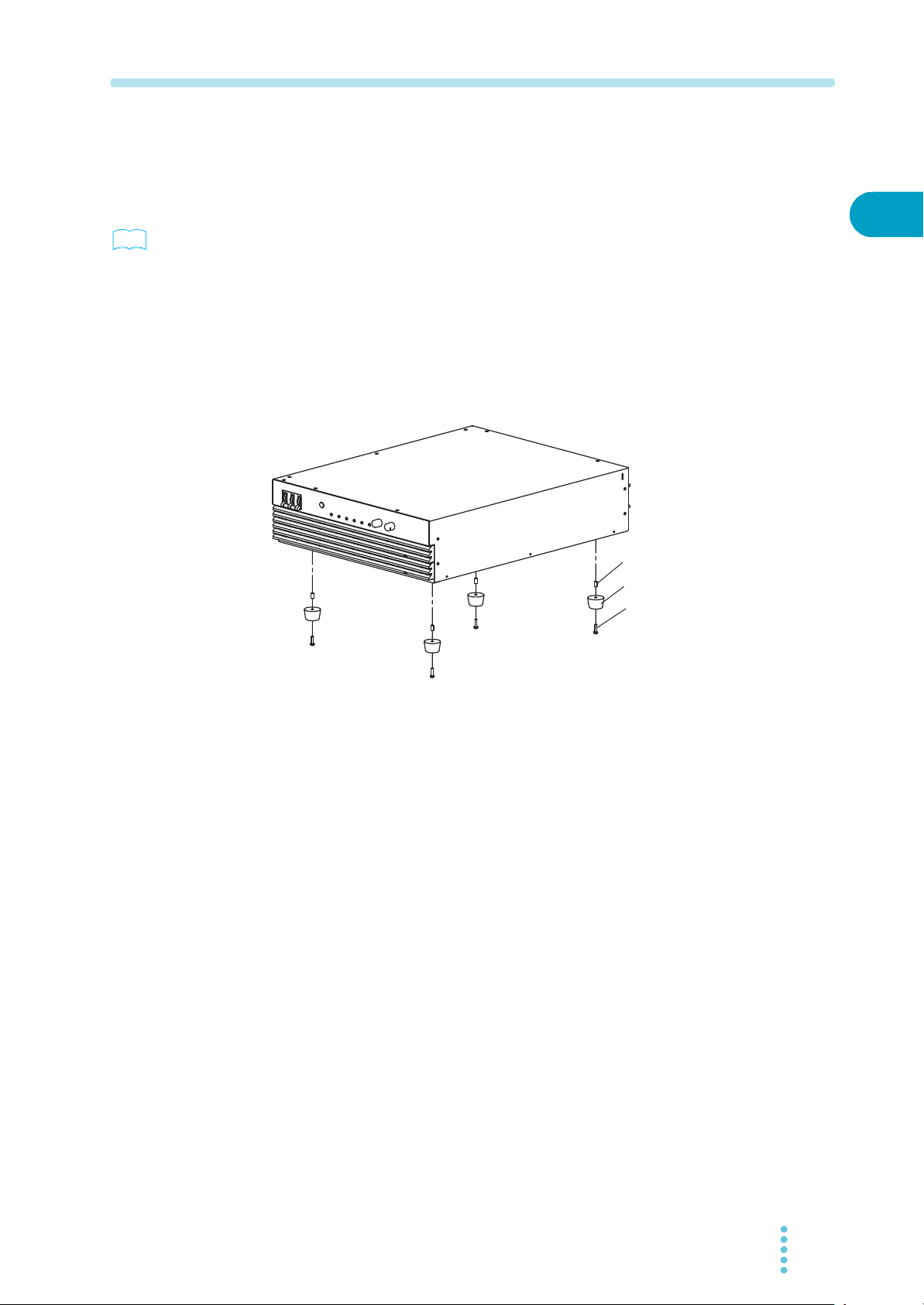
1.2 Rack Mounting the Product
Remove the rubber feet before rack mounting the product to a frame. Fig.1-2 shows
how to remove the rubber feet.
See
p. 1-3
For details on rack mounting, see the KRB3-TOS or KRB150-TOS Operation
Manual.
Install the suitable support angles applying to the used rack system to support the
instrument.
We recommend that you keep all the parts so that you can use them again when you
detach the product from the frame.
To reattach the rubber feet, use the screws that you removed.
1
Collars (4 locations)
Rubber feet (4 locations)
Attachment screws
(4 locations)
M4 screw
( )
Maximum depth: 16 mm
Installation and Preparation
Fig.1-2 Removing the rubber feet
Removing the rubber feet
Unfasten the screws and remove the four rubber feet.
PAT-T 8kW 1-3
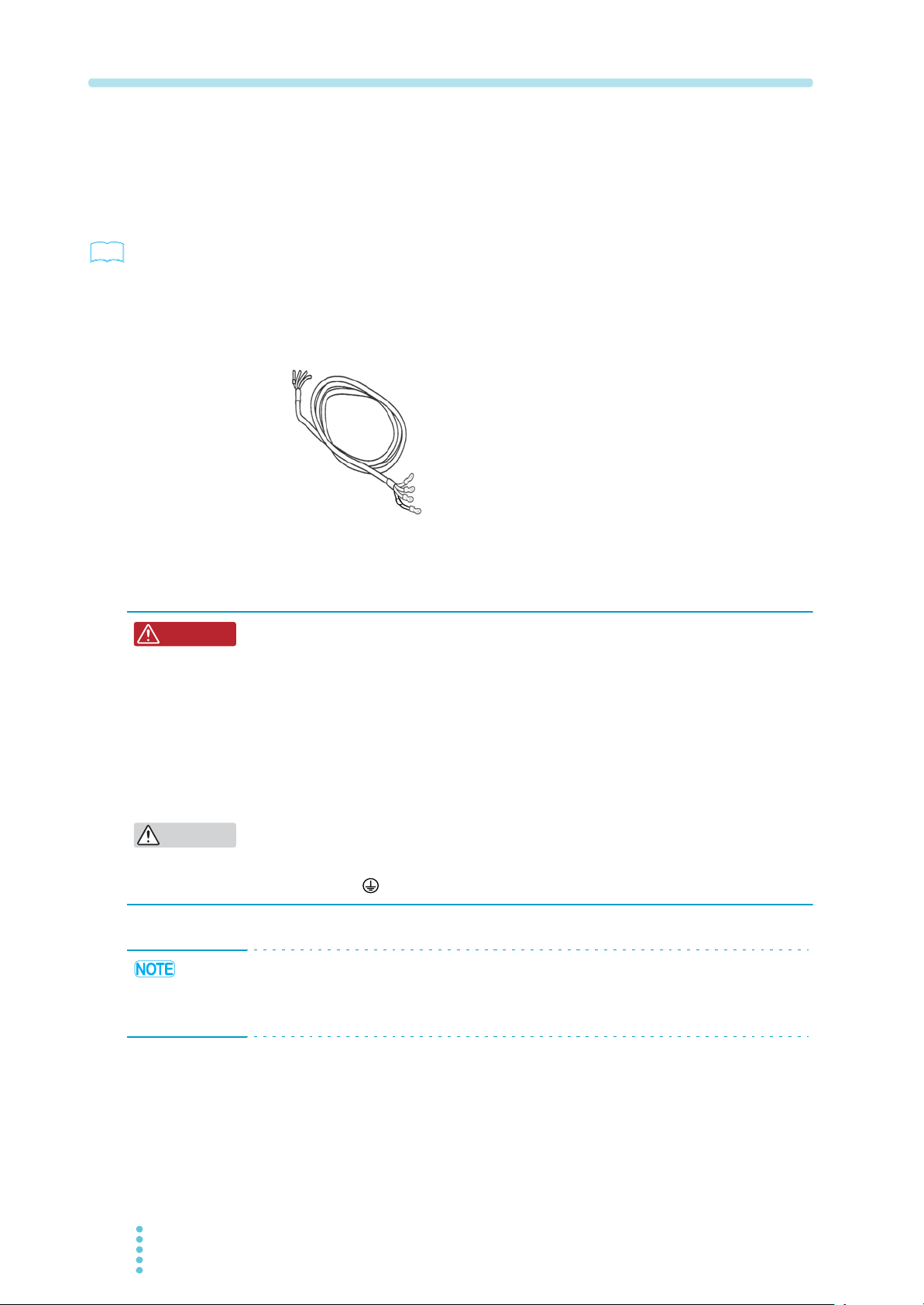
1.3 Connecting the Power Cable
Three-phase power cable
(AC8-4P4M-M6C)
This product is designed as an equipment of IEC Overvoltage Category II (energy-
consuming equipment supplied from the fixed installation).
See
p. 1-4
W ARNING
This product does not come with a power cable. The optional power cable (AC8-
4P4M-M6C) has crimping terminals (round M6 terminals, 12 mm wide) attached on
its PAT end. However, the switchboard end of the power cable has not been prepared
for connection. When you use the cable, attach crimping terminals to it that match
the screws of the switchboard that you will connect it to.
Fig.1-3 Optional power cable
Exercise the following precautions when preparing the power cable.
Possible electric shock.
• Turn off the switchboard breaker (switch that cuts off the power
supply from the switchboard) before making the connection.
• This product is an IEC Safety Class I equipment (equipment with a
protective conductor terminal). Be sure to ground the product to
prevent electric shock.
• Connect the ground terminal to earth ground.
• Be sure to have a qualified engineer connect the power cable to the
switchboard.
CAUTION
1-4 PAT-T 8kW
• Inside the power supply, an appropriate protective circuit is connected to
the input terminal. Be sure to connect the wires correctly by matching the
U, V, W, and (GND) between the switchboard and the product.
• The POWER switch of the product can be used to disconnect the product from
the AC line in an emergency. Provide adequate space around the POWER switch
so that the POWER switch can be turned off at any time.
Use a four-core PVC insulated cable for 600 Vac with a nominal cross-sectional
area of at least 8 mm
2
(At least 5 mm2 for 400 V input model.)
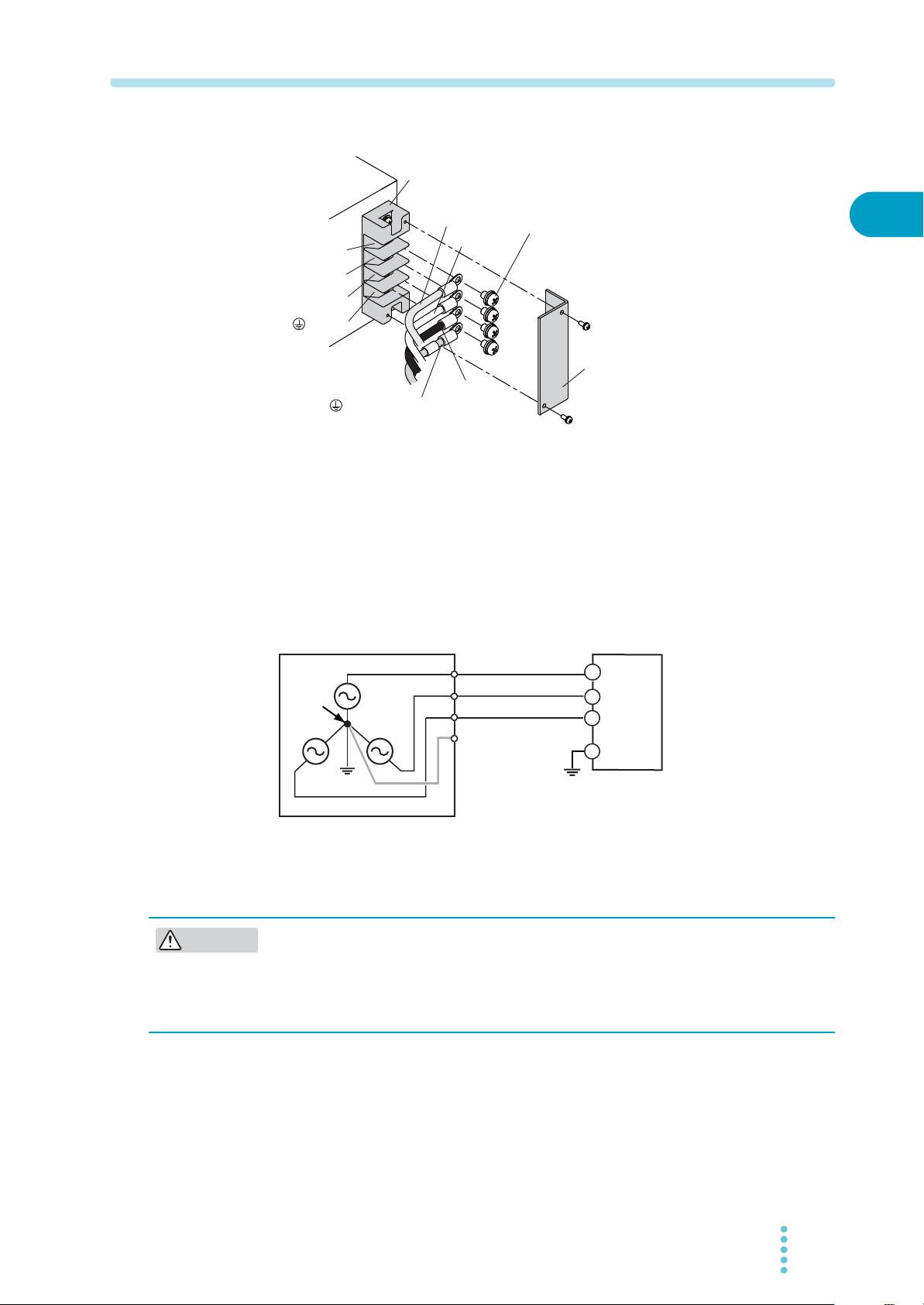
Connection procedure
GND
AC INPUT terminal block
(GND)
(GND): Green
W: Black
V: White
U: Red
W
V
U
Terminal cover
M6 screws
CAUTION
Fig.1-4 Connecting the power cable
(example in which the optional power cable is used)
1
1
Check that the AC power line meets the nominal input rating of the
product.
A model with a nominal input rating of 200 Vac to 240 Vac can receive voltages within
the range of 180 Vac to 250 Vac. 400 V input models (whose nominal input rating is
400 Vac) can receive voltages within the range of 360 Vac to 440 Vac. The frequency is
50 Hz or 60 Hz.
Power supply equipment
Neutral
point
Be sure to ground the neutral point.
N
Not used
Three-phase three wire
Three-phase four wire
Input voltage between U-G, V-G and W-G : ±254 Vac max
PAT
U
V
W
G
Only 400 V input models
*
Fig.1-5 Required power supply equipment
Installation and Preparation
*
The PAT may be damaged.
• Do not connect a 400 V input model to a power line if the voltage between
any of the line’s phase terminals and the ground shown in
Fig.1-5
exceeds 254 Vac.
2
3
Check that the POWER switch is turned off.
Attach crimping terminals to the cable that are appropriate for the PAT,
and then connect the cable to the AC INPUT terminal block as shown in
Fig.1-4.
PAT-T 8kW 1-5
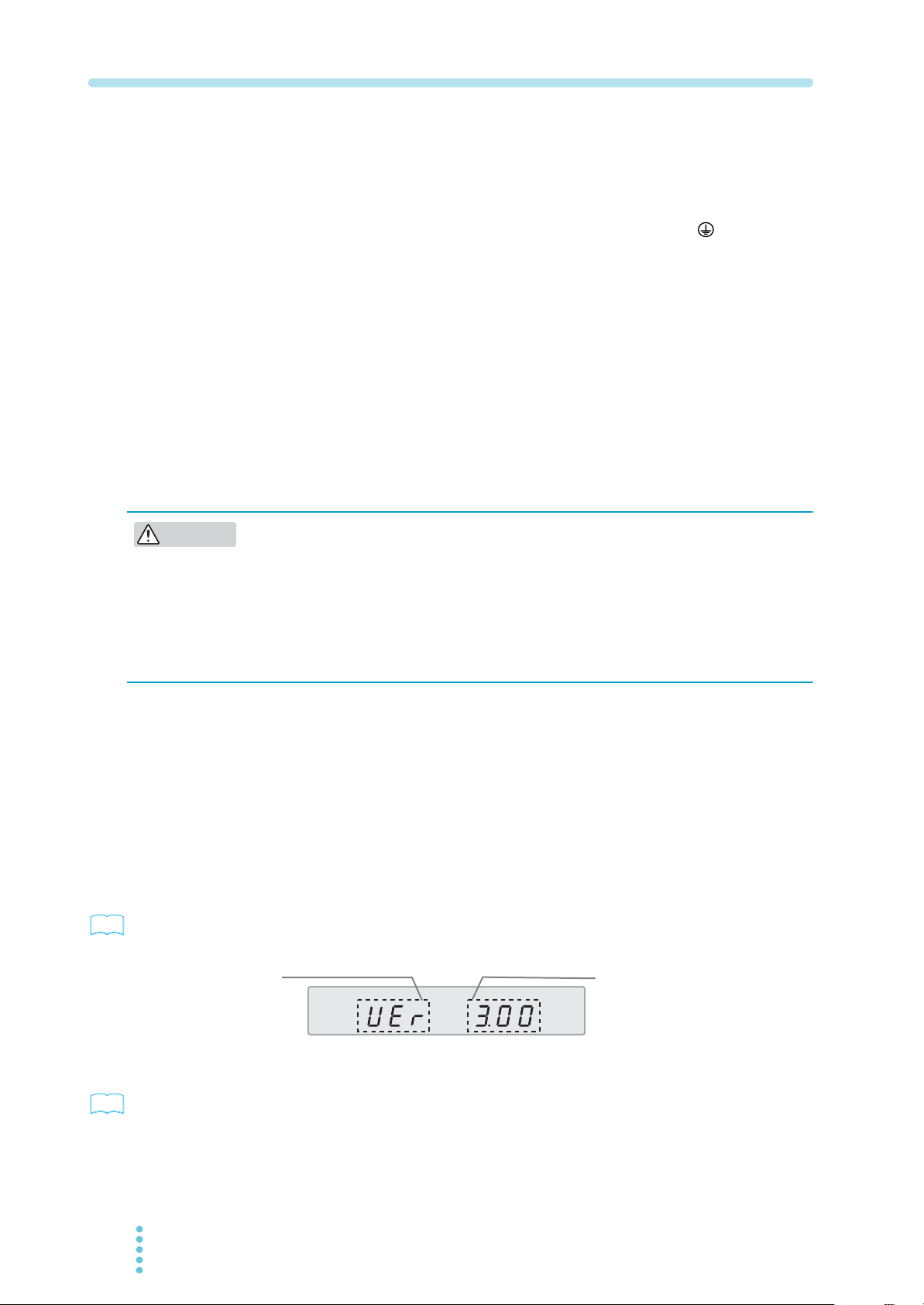
4
Attach appropriate crimp terminals to the switchboard end of the power
cable.
5
Turn off the switchboard breaker.
6
Connect the power cable by matching the U, V, W, and (GND) of the
switchboard.
Precautions Concerning Grounding (Earth)
Be sure to ground the product for your safety.
Make sure to connect the GND terminal of the AC INPUT terminal block to the
GND terminal of the switchboard.
1.4 Turning On
See
CAUTION
p. 3-2
• The CONFIG parameters can be configured so that the output is
automatically turned on when the POWER switch is turned on. When this
function is enabled, the PAT powers up with the output turned on even if
the output was off when the PAT was turned off the last time. However,
there is a possibility that a load may break, if you connect a different load
and turn the POWER and output on simultaneously without changing the
OVP and OCP settings to appropriate values.
Tur ning the POWER switch on
1
Check that the power cable is correctly connected.
2
Raise the lever and turn the POWER switch on.
If an odd sound, odd odor, fire, or smoke occurs around or in the PAT, lower the
POWER lever to turn it off.
3
Check the firmware version on the front panel display.
The voltmeter and ammeter show the PAT firmware version for approximately 1
second. The measuring value will be shown after the firmware version is displayed.
Indicates the version
OUTPUT
ALARM
A V
Firmware version
C
PRESET
A
RMT
B
EXTEXT
LOCK
Fig.1-6 Firmware version display at power-on (example for Ver.3.00)
See
p. 3-28
If the POWER switch is turned on for the first time after purchasing the PAT, the
PAT starts up in a factory default condition.
An inrush current flows up to 100 Amax. (40 Amax. for 400 V input model) when
the POWER switch is turned on. In particular, check that sufficient current capacity
1-6 PAT-T 8kW
is available in the AC power line and the switchboard if you are using multiple PATs
See
AV
CAUTION
and turning on the POWER switches simultaneously.
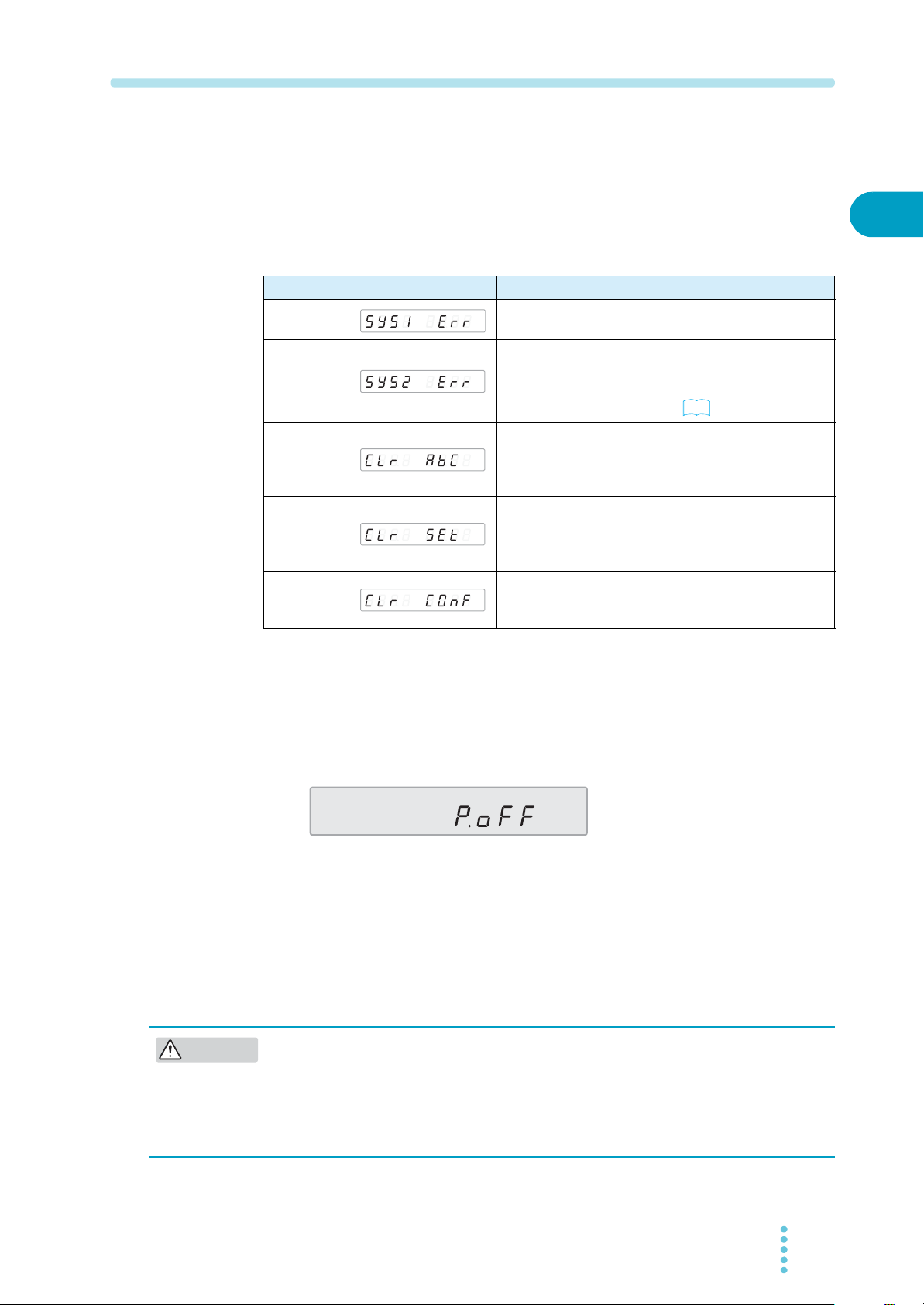
If front panel display shows indicated in Table 1-1 after power-on, follow the
corresponding remedy. If the remedy does not correct the problem, contact your
Kikusui agent or distributor.
1
Table 1-1 Panel display during and after power-on
Panel Display Cause and Remedy
SYS1 ERR
SYS2 ERR
CLR ABC
CLR SET
CLR CONF
AV
AV
AV
AV
The PAT may have malfunctioned. Contact your
Kikusui agent.
The calibration has not been completed normally.
Recalibrate. If “SYS2 ERR” appears even after
recalibration, the PAT may have malfunctioned.
Contact your Kikusui agent. ( p. 7-5)
Preset memories A, B, and C have been reset to
factory default settings because the values were
abnormal. To continue the operation, press any panel
switch.
The voltage and current calibration values have been
reset to factory default settings, because the values
were abnormal. To continue the operation, press any
panel switch.
The CONFIG settings have been reset to factory
default values, because the values were abnormal.To
continue the operation, press any panel switch.
Installation and Preparation
Tur ning the POWER switch off
Lower the POWER switch lever to turn it off.
When the POWER switch is turned off, the front panel display shows the characters
indicated in the following figure for about 10 to 15 seconds.
C
A
OUTPUT
ALARM
A V
PRESET
Fig.1-7 Display at power-off
The PAT stores the panel settings (excluding output on/off condition) immediately
before the POWER switch is turned off. For these items, the PAT starts up using the
settings that existed when the POWER switch was turned off the last time.
If the POWER switch is turned off immediately after changing the settings, the last
settings may not be stored.
• When turning the POWER switch off and then back on, allow at least 10
seconds (40 seconds for 400 V input model) after the fan stops.
Repeated ON/OFF of the POWER switch at short intervals can cause
damage to the inrush current limiter or shorten the service life of the
POWER switch and the internal input fuse.
RMT
B
CV
EXTEXT
LOCK
PAT-T 8kW 1-7

1-8 PAT-T 8kW
2
Connecting the Load
This chapter describes the
consideration to be given to the load,
explains how to connect the load wires,
and explains how to connect to the
output terminals.
2.1 Load Considerations
Note that the output will become unstable if the following types of loads are
connected.
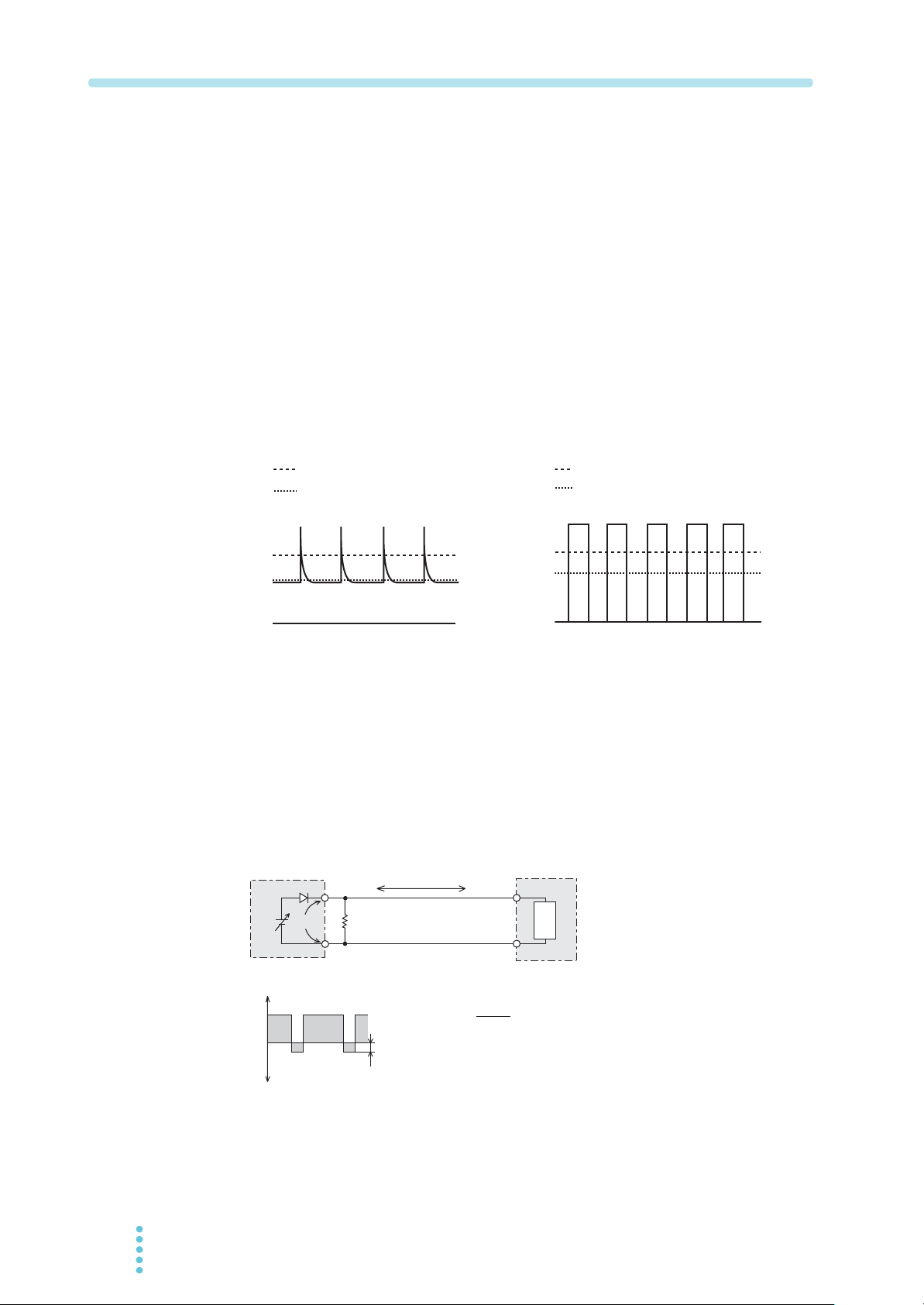
Load with peaks and pulse-shaped current
The PAT indicates only mean values. Even when the indicated value is less than the
preset current value, the peak values may actually exceed the preset current value. If
this happens, the PAT is instantaneously put into constant-current operation mode,
and the output voltage drops accordingly.
For these types of loads, you must increase the preset current value or increase the
current capacity.
Preset constant current value
Ammeter reading
(average value)
Preset constant c
Ammeter reading
(average value)
urrent value
Fig.2-1 Load current with peaks Fig.2-2 Pulse-shaped load current
Load that generates reverse current to the power supply
The PAT cannot absorb reverse current from the load. Therefore, if a regenerative
load (such as an inverter, converter, or transformer) is connected, the output voltage
increases and becomes unstable.
For these types of loads, connect a resistor RD as shown in Fig.2-3 to bypass the
reverse current. However, the amount of current to the load decreases by max.
reverse current I
rp.
−
IO
+
EO
Equivalent circuit of the PAT
+IO
0
-IO
Output current waveform
RD
Irp
Reverse current
Load
Regenerative load
[V]
E
RD[Ω] ≤
I
O
[A]
rp
RD: Reverse current bypass dummy load
E
O: Output voltage
I
rp
: Max. reverse current
Fig.2-3 Remedy for regenerative load
2-2 PAT-T 8kW
CAUTION
• Use a resistor with sufficient rated power for resistor RD.
• If a resistor with insufficient rated power for the circuit is used, resistor RD
may burn out.
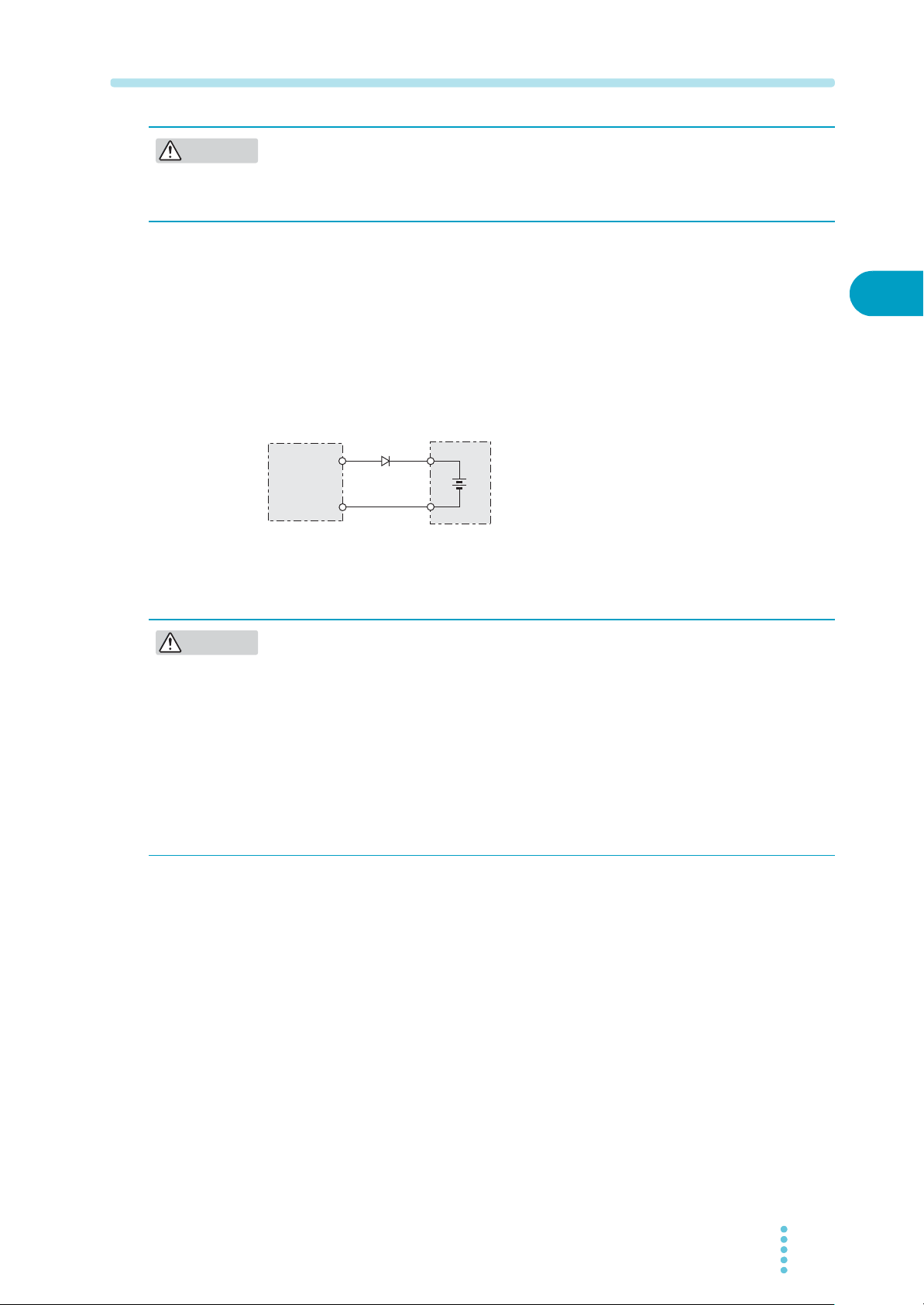
Load with accumulated energy
Connecting a load with accumulated energy, such as a battery, to the PAT may cause
current to flow from the load to the internal circuit of the PAT. This current may
damage the PAT or reduce the life of the battery.
For this type of loads, connect a reverse-current-prevention diode (DRP) between the
PAT and the load in series as shown in
Fig.2-4.
This cannot be used in conjunction with remote sensing.
RP
D
DRP: Reverse-current-prevention diode
PAT
Load with accumulated
energy
Fig.2-4 Remedy against load with accumulated energy
2
Connecting the Load
CAUTION
• Use a reverse-current-prevention diode (DRP) complied to the following
references.
Reverse voltage withstand capacity :
At least twice the rated output voltage of the PAT.
Forward current capacity :
Three to ten times the rated output current of the PAT.
A diode with small loss.
•Be sure to take into account the heat generated by reverse-current-
prevention diode D
RP. Reverse-current-prevention diode DRP may burn out
with inadequate heat dissipation.
PAT-T 8kW 2-3

2.2 Load Cable
W ARNING
To prevent the possibility of fire.
• Use a load cable with sufficient current capacity with respect to the
rated output current of the PAT.
• The output terminal and its area nearby gets very high temperature,
use the cable with sufficient heat resistance higher than
85 °C of the covering materials.
Possible electric shock.
• Use a load cable with a higher voltage rating than the isolation
voltage of the PAT. For the isolation voltage of each model, see
Chapter 8, “Specifications.”
■ Current capacity of the load cable
If their current rating exceeds the maximum rated output current, the cable will
remain intact even if the load is short-circuited. Load cables must be rated to carry
the maximum rated output current of the PAT.
■ Allowable current of the cable dependent on the maximum allowable
temperature of the cable insulation
The cable temperature is determined by a current-caused resistance loss, ambient
temperature, and thermal resistance to the outside.
capacity of current that can flow through a heat-resistant PVC wire (single wire)
having a maximum allowable temperature of 60 °C when the wire is stretched
horizontally in the air at an ambient temperature of 30 °C. If the condition is such
that PVC wires with lower heat-resistant temperature are used, the ambient
temperature exceeds 30 °C, or the wires are bundled resulting in low heat radiation,
the current capacity needs to be reduced.
Table 2-1 shows the allowable
2-4 PAT-T 8kW
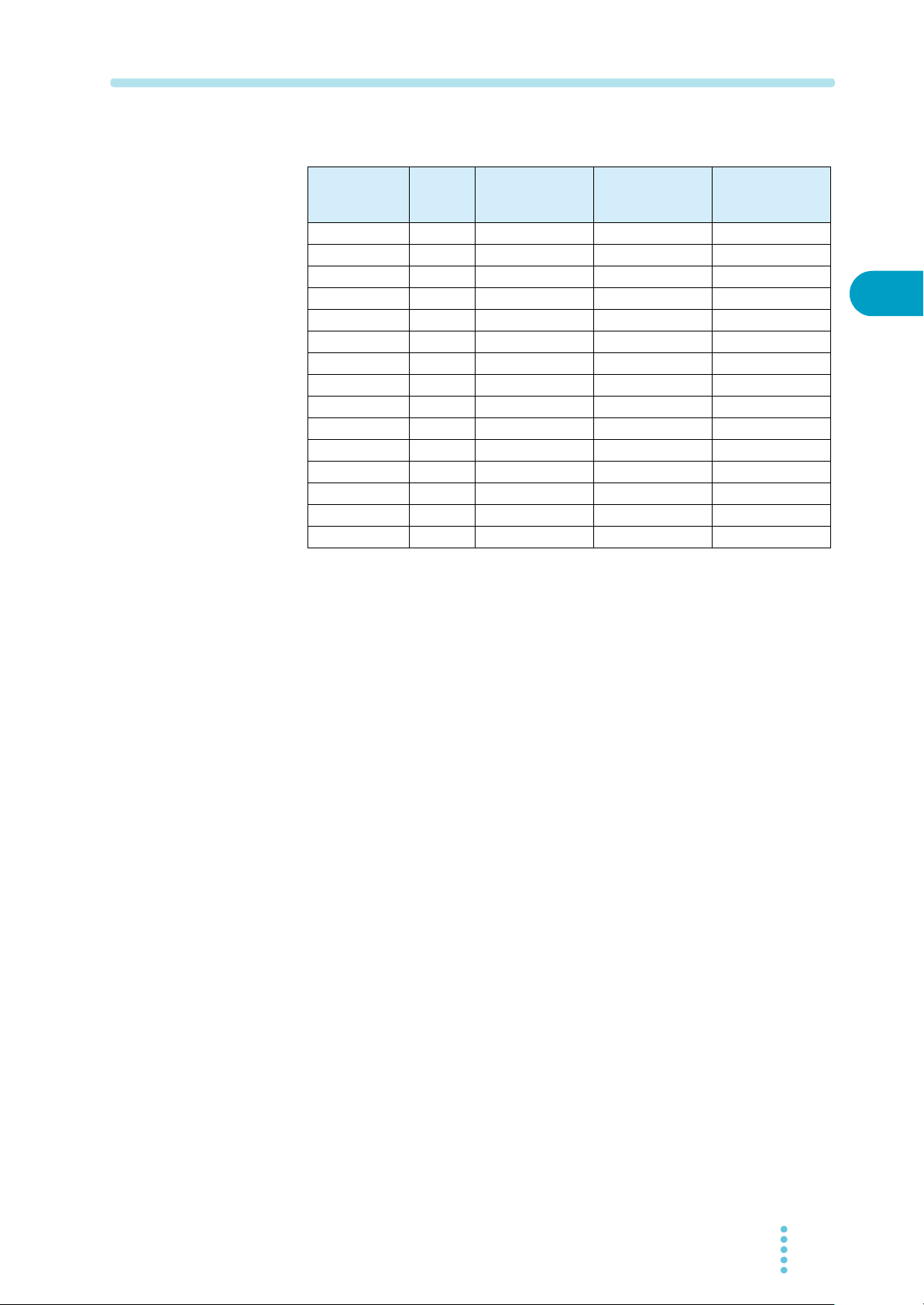
Table 2-1 Nominal cross-sectional area of cables and allowable
currents
Nominal cross-
sectional area
2
]
[mm
2 14 (2.08) 27 10
3.5 12 (3.31) 37 -
5.5 10 (5.26) 49 20
8 8 (8.37) 61 30
14 6 (13.3) 88 50
22 4 (21.15) 115 80
30 2 (33.62) 139 -
38 1 (42.41) 162 100
50 1/0 (53.49) 190 -
60 2/0 (67.43) 217 -
80 3/0 (85.01) 257 200
100 4/0 (107.2) 298 -
125 - - 344 -
150 - - 395 300
200 - - 469 400
*1. Excerpts from Japanese laws related to electrical equipment.
AWG
(Reference cross-
sectional area)
[mm
■ Taking measures against noise
Allowable current
2
]
[A] (Ta = 30 °C)
*1
Current
recommended by
Kikusui [A]
2
Connecting the Load
When connecting wires that have the same heat-resistant temperature, more current
can flow by separating the wires to make heat radiation as great as possible.
However, installing the + (pos.) and - (neg.) output wires of the load cable side by
side or bundling them together is more effective against unwanted noise. The
Kikusui-recommended currents shown in
Table 2- 1 are allowable current values that
have been reduced in consideration of the potential bundling of load cables. Use
these values as a guideline when connecting load cables.
■ Limitations of the sensing function
All wires have resistance. The voltage drop in wires becomes greater as the wire
becomes longer or the current becomes larger. This results in the voltage applied at
the load end to be smaller. The PAT has a sensing function that compensates for this
voltage drop up to approximately 0.6 V for a single line. If the voltage drop exceeds
this level, wires having a greater sectional area should be used.
PAT-T 8kW 2-5
2.3 Connecting to the Output terminal
See
W ARNING
p. 3-25
Possible electric shock.
• Be sure to turn the POWER switch off before touching the output
terminal.
• Be sure to attach the OUTPUT terminal cover after wiring the load.
Connection procedure
After the installation of the OUTPUT terminal cover for the output terminal, the
portion of the terminal cover is on top of the sensing terminal. In case the remote
sensing is used, install the OUTPUT terminal cover after wiring of the sensing
cable.
OUTPUT terminal cover
The portion of sensing terminal is
covered by its plastic terminal cover.
Fig.2-5 Attachment completion of the OUTPUT terminal cover
■ How to use the OUTPUT terminal cover for the output terminal
Cut the sleeve of the O UTPUT terminal cover for the appropriate size of the load
cable which goes through its OUTPUT terminal cover.
Ø10
Ø20
Ø30
Ø36
Ø10
Ø20 Line
Ø30 Line
Ø36 Line
Cut the OUTPUT terminal
co
ver of the load cable.
Fig.2-6 OUTPUT terminal cover
2-6 PAT-T 8kW
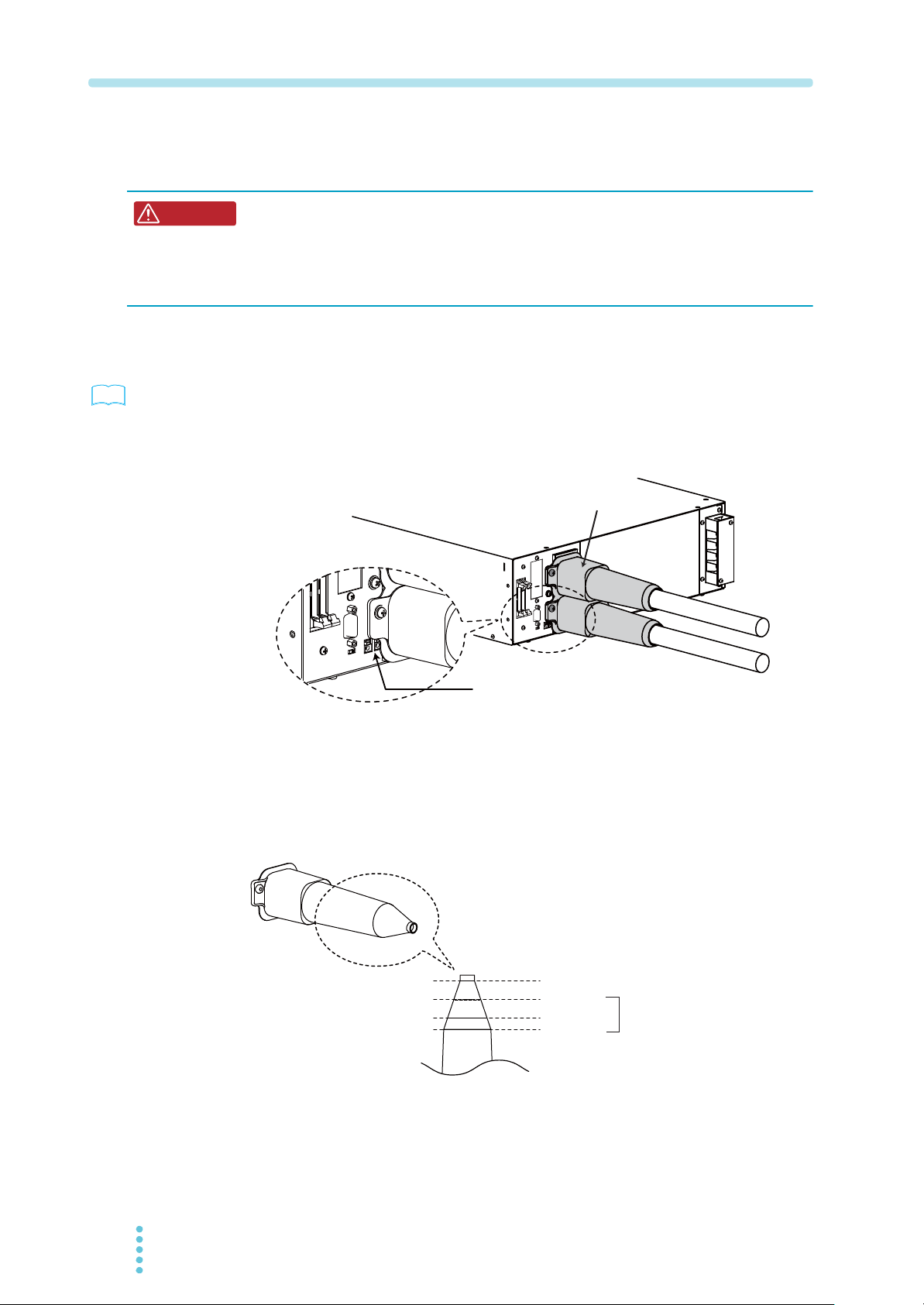
Connection preparation
Chassis connection wire
Screw
1
Turn the POWER switch off.
2
Using the chassis connection wire set that comes with the package,
connect the chassis terminal to either the negative or positive DC
output terminal.
The output terminal has a hole used to connect the chassis connection cable that comes
with the package.
2
Connecting the Load
See
p. 8-4, p. 8-7
Fig.2-7 Connecting the chassis connection wire
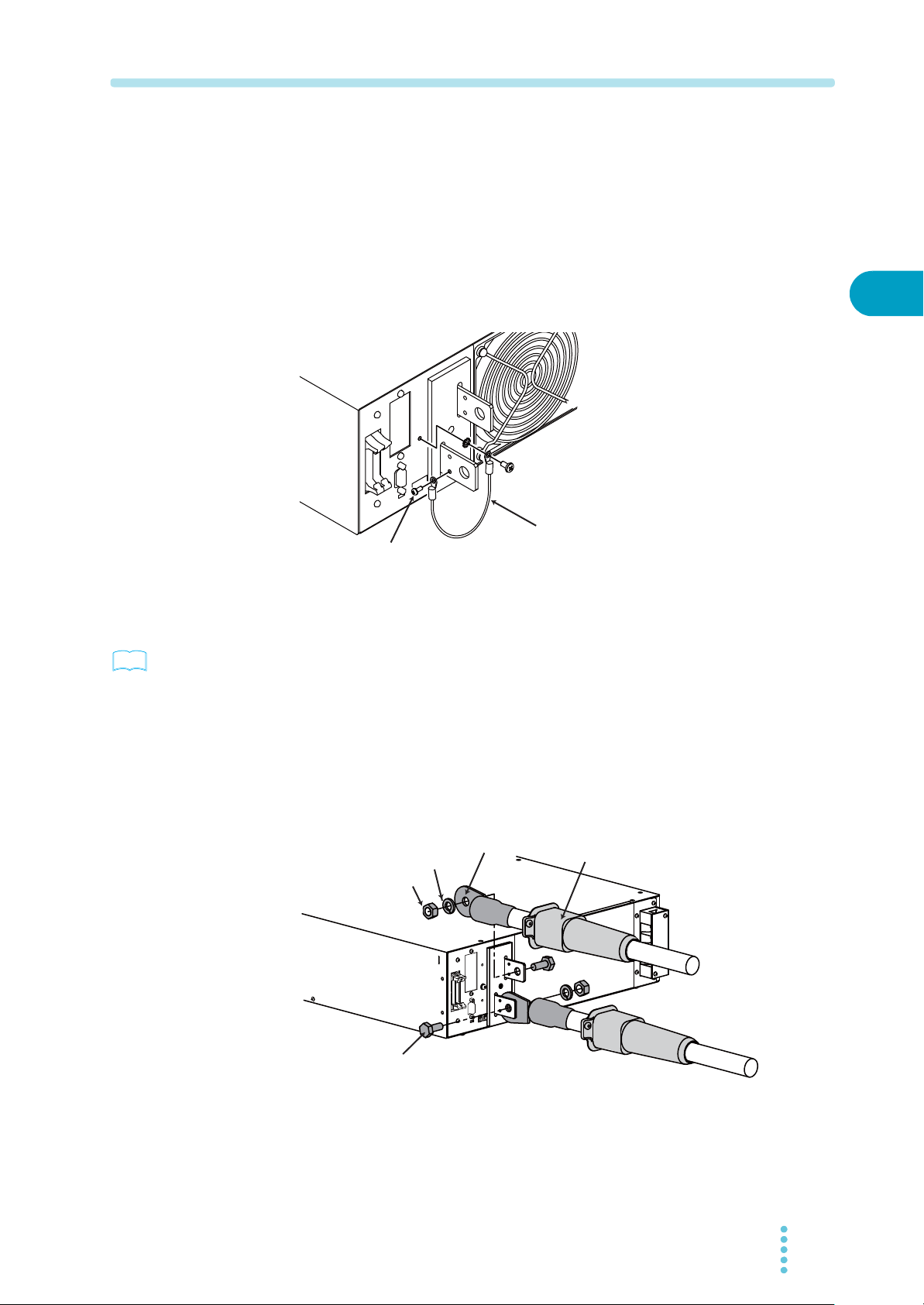
3
Attach crimping terminals to the load cable.
The output terminal has a hole for connecting the load cable. Attach the crimping
terminal that matches the bolt used.
4
Insert the load cable through the OUTPUT terminal cover.
5
Connect the load cable on the rear panel.
Insert the bolt for the positive (+) terminal from right side, and the negative (-) terminal
from left side as you face, then fix it using the nut and spring washers. Connect the
load cable straight forward (vertical angle against the surface of the output terminal).
Crimp terminal
Spring washer
Nut
OUTPUT terminal cover
Bolt
Fig.2-8 Connection of the load cable
PAT-T 8kW 2-7
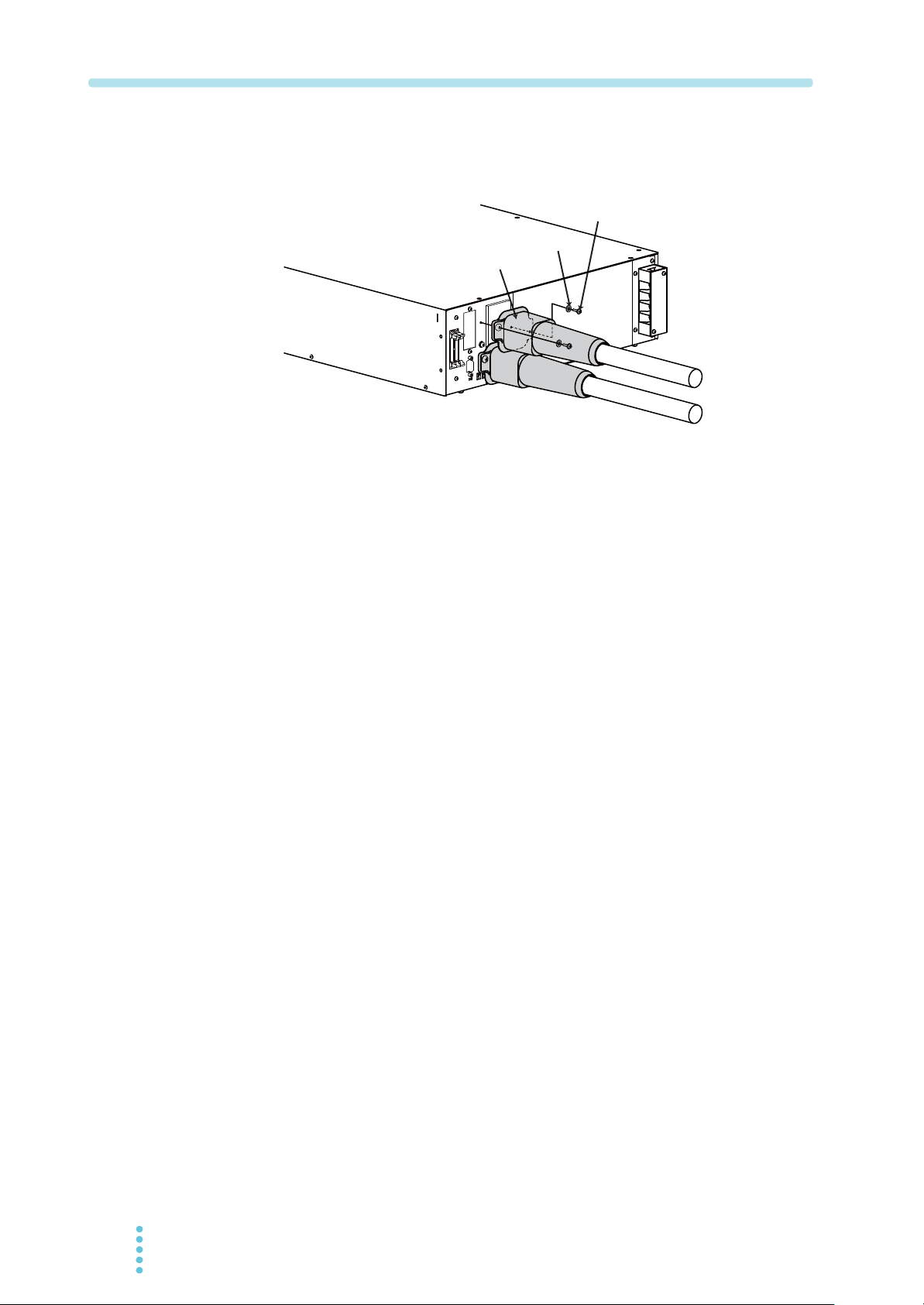
6
Install the OUTPUT terminal cover on the rear panel.
Uses the attached screws to install the OUTPUT terminal cover firmly and make sure
they are not loosen.
Screw
Washer
OUTPUT terminal cover
Fig.2-9 Attachment of the OUTPUT terminal cover
2-8 PAT-T 8kW
3
Basic Operation
This chapter describes how to turn on/
off the output and the basic operations
that you can carry out from the front
panel.

3.1 Measured Value Display and Setting Display
EXTEXT
RMT
LOCK
PRESET
A
B
C
A V
OUTPUT
ALARM
On
(Setting the Output Voltage and Output Current)
The panel display has two modes. One mode displays the measured values of the
output voltage and output current, and the other mode displays the settings. These
See
p. 3-7
two modes can be distinguished by the on/off state of the SET, OVP
CONFIG switches.
■ Measured value display
The measured value display shows the present output terminal voltage and load
current. In this mode, the LEDs of the SET, OVP•OCP, and CONFIG switches are
all off.
You can change the output voltage and current settings in the measured value
display mode.
OUTPUT
ALARM
A
PRESET
A V
RMT
B
CV
EXTEXT
LOCK
C
Switch turned off
Fig.3-1 Measured value display example
•OCP, and
See
p. 3-23
■ Setting display
The following three states are available.
• Setting display of the output voltage and output current
Press the SET switch. The switch LED illuminates. The present output voltage
and current are displayed.
OUTPUT
ALARM
A
PRESET
A V
RMT
B
EXTEXT
LOCK
C
On
Fig.3-2 Setting display example of the output voltage and output
current
If you save or recall a preset memory, the panel display shows the preset memory
values.
• Setting display of the overvoltage and overcurrent protection
Press the OVP•OCP switch. The switch LED illuminates. The present
overvoltage and overcurrent settings are displayed.
Fig.3-3 Setting display example of the overvoltage and
overcu rrent protection
3-2 PAT-T 8kW

• Setting display of the system configuration
See
Press the CONFIG switch. The switch LED illuminates.The system
configuration settings are displayed.
C
OUTPUT
ALARM
A
PRESET
A V
RMT
B
EXTEXT
LOCK
Fig.3-4 Setting display example of the system configuration
3.2 Output Operation
The OUTPUT switch is a toggle switch.
When you press the OUTPUT switch and the output turns on, the OUTPUT LED
illuminates. When you press the OUTPUT switch and the output turns off, the
OUTPUT LED turns off.
If the output is turned on, the present setting is output. If you change the setting
while the output is on, the change is applied to the output.
See
p. 4-17
It is possible to control on/off of the output by external control.
On
OUTPUT
ALARM
A V
Fig.3-5 Output on display example
On
PRESET
3
Basic Operation
C
A
RMT
B
CV
EXTEXT
LOCK
p. 3-28
p. 4-17
CAUTION
Output on/off when power is turned on
By factory default, the output is off when the power is turned on. You can set the
output state at power-on to on (CF25: ON) in the CONFIG settings.
If you set the output state at power-on to on, check the OVP trip point setting before
you turn off the POWER switch.
If the breaker trip setting that is applied when an OVP or OCP activates is set to
“trip” (CF28: ON) and the OVP trip point is set lower than the output voltage
setting, the OVP will activate every time you turn the POWER switch on and the
POWER switch will turn off.
If the condition above occurs and you are unable to change any of the settings, turn
the POWER switch on while holding down the SHIFT switch to reset the PAT to
factory default settings.
• If the OVP/OCP settings are not appropriate when you change the load,
the load may break.
PAT-T 8kW 3-3

Output on/off delay functions
See
p. 3-16
You can set a delay (0.1 s to 10.0 s) until the output is actually turned on or off after
you turn the OUTPUT switch on or off. This function is useful if you want to turn
the output on/off by setting a time offset according to the load characteristics.
To enable this function, set the output on delay (CF10: 0.1 to 10.0) and output off
delay (CF11: 0.1 to 10.0) of the CONFIG parameter. You can set separate delays for
on and off.
The OUTPUT LED blinks while the output on/off delay function is in operation.
Press the OUTPUT switch while the OUTPUT LED is blinking to cancel the output
on/off delay.
Press the OUTPUT switch while holding down the SHIFT switch while the
OUTPUT LED is blinking to cancel the output on/off delay and forcibly switch the
output.
Output on Output off
OUTPUT
LED
OUTPUT
LED
Off OffBlinking On Blinking
Output on
Output off Output off
DelayDelay
Output on
Output on
Off
Cancel delay
Blinking Blinking
Output on
Blinking
Output off
Output on
Output off
Cancel delay
OnOn
See
p. 3-19
Output off
Delay
Cancel output off delay
Output off by force
Output off
On
OUTPUT
LED
Delay Delay
Cancel output on delay
Output on
Off Off
Output off Output off
Output on by force
Blinking Blinking
Output on
Delay Delay
Fig.3-6 Output on/off delay action
Setting the output-on startup state
When the output state at power-on is set to on, you can choose to make the PAT start
as a constant voltage (CV) power supply or as a constant current (CC) power supply.
To use this function, set the output-on startup state (CF32: CV/CC) in the CONFIG
settings. To start the PAT as a constant voltage (CV) power supply, select CV
prioritization (CF32: CV). To start the PAT as a constant current (CC) power supply,
select CC prioritization (CF32: CC).
3-4 PAT-T 8kW

3.3 Constant Voltage (CV) and Constant Current
RL>R
A
B
A
B
(CC) Power Supplies
The PAT has a constant voltage power supply function that maintains the output
voltage at a constant level and a constant current power supply function that
maintains the output current at a constant level even when the load changes. The
condition in which the PAT is operating as a constant voltage power supply is called
the constant voltage (CV) mode. The condition in which the PAT is operating as a
constant current power supply is called the constant current (CC) mode. The
operation mode is determined by the following three values.
• Preset output voltage (Vs)
3
• Preset output current (Is)
• Load resistance (RL)
The operation modes are described below.
Vmax
Vs
Output voltage Vout
A
0
Output current Iout
c
p
B
L=Rc
R
Crossover point
RL <Rc
q
ImaxIs
A = CV mode area
B = CC mode area
Vs = Preset voltage
Is = Preset current
Rc = Vs/Is (Ohm’s Law)
R
L = Load resistance
Vmax = Maximum preset voltage
Imax = Maximum preset current
Fig.3-7 Constant voltage operation and constant current
operation
Fig.3-7 shows the operation modes of the PAT. We denote the load resistance as RL
and the resistance calculated from the preset current and voltage as Rc (Rc = Vs/Is).
The power supply is designed so that it operates in CV mode in area
and CC
mode in area . The boundary is the line defined by RL = Rc. This line represents
the load at which the output voltage and the preset voltage are equal and the output
current and preset current are equal. If load resistance R
Rc, the operating point is in area
, and the PAT operates in CV mode (point p). In
L is greater than resistance
this case, preset current Is is the current limit.
Basic Operation
When operating in CV mode, the output voltage is maintained at the preset voltage.
Output current I is determined by the relationship defined by the equation I = Vs/R
L.
It is a current less than current limit Is. In this mode, the actual current that flows is
not necessarily equal to the specified value.
For loads in which transient peak current flows, preset current Is must be set so that
the peak value does not reach the current limit.
Conversely, if load resistance RL is less than resistance Rc, the operating point is in
area
, and the PAT operates in CC mode (point q). In this case, preset voltage Vs
is the voltage limit.
PAT-T 8kW 3-5

When operating in CC mode, the output current is maintained at the preset current.
Output voltage V is determined by the relationship defined by the equation V = Is
×
RL. It is a voltage less than voltage limit Vs. In this mode, the actual voltage that is
applied is not necessarily equal to the specified value.
For loads that generate transient surge voltage, preset voltage Vs must be set so that
the surge voltage does not reach the voltage limit.
■ Crossover point
CV mode and CC mode switch automatically according to the changes in the load.
The point at which the mode switches is called the crossover point.
For example, if the load changes and the output current reaches the current limit
when operating in CV mode, the operation mode automatically switches to CC to
protect the load. Likewise, if the output voltage reaches the voltage limit when
operating in CC mode, the operation mode automatically switches to CV.
CV and CC mode operation example
This section uses a power supply with a rated output voltage of 100 V and a rated
output current of 10 A as an example.
A load resistance (RL) of 8 Ω is connected to the output terminals of the power
supply. The output voltage and output current are set to 30 V and 5 A, respectively.
In this case, Rc = 30 V/5 A = 6
operation mode is CV. If you want to increase the voltage in CV mode, the voltage
can be increased up to the voltage defined by the following equation: Vs = Is
Substituting the values, we obtain Vs = 5A
voltage above this point, the crossover point is reached, and the operation mode
automatically switches to CC mode. To maintain CV mode, increase the current
limit.
Ω. Since, 8 Ω is greater than 6 Ω (RL > Rc), the
× RL.
× 8 Ω = 40 V. If you try to increase the
Next a load resistance (RL) of 5 Ω is connected to the output terminals of the power
supply. The output voltage and output current are set to 30 V and 5 A, respectively.
In this case, Rc = 30 V/5 A = 6
Ω. Since, 5 Ω is less than 6 Ω (RL < Rc), the
operation mode is CC. If you want to increase the current in CC mode, the current
can be increased up to the current defined by the following equation: Is = Vs/R
Substituting the values, we obtain Is = 30 V/5
Ω = 6 A. If you try to increase the
L.
current above this point, the crossover point is reached, and the operation mode
automatically switches to CV mode. To maintain CC mode, increase the voltage
limit.
3-6 PAT-T 8kW

3.4 Using the PAT as a CV or CC Power Supply
See
(Setting the Output Voltage and Output
Current)
When using the PAT as a constant voltage power supply, the preset current is the
limit that can flow through the load.
When using the PAT as a constant current power supply, the preset voltage is the
limit that can be applied to the load.
If the specified limit is reached, the operation mode automatically switches. If the
operation mode switches, the CV LED or CC LED changes to indicate the switch.
1
Turn the POWER switch off.
2
Connect the load to the output terminal.
3
Turn the POWER switch on.
If the OUTPUT LED on the display is illuminated, press the OUTPUT switch to turn
the output off.
4
Check that the SET switch is illuminated.
If it is not, press the SET switch so that you can set the voltage and current.
3
Basic Operation
p. 3-19
5
Turn the VOLTAGE knob to set the voltage.
6
Turn the CURRENT knob to set the current.
7
Press the OUTPUT switch.
The OUTPUT LED on the display illuminates, and the voltage and current are delivered
to the output terminal.
The CV LED illuminates when the PAT is operating as a constant voltage power supply.
The CC LED illuminates when the PAT is operating as a constant current power supply.
You can set the voltage and current by carrying out step 5 and step 6 while
checking the actual output voltage or current with the output turned on.
You can only use the CONFIG settings to set the output-on startup state (CF32:
prioritize CV or CC) .
Fine adjustment function
This function increases the resolution of the VOLTAGE and CURRENT knobs. By
turning the VOLTAGE or CURRENT knob while holding down the SHIFT key, you
can set the value using finer resolution.
The display resolution of the preset voltage and preset current does not change even
if you use the fine adjustment function. Therefore, the displayed value may not
change even if you turn the knob. The display changes when the amount of change
reaches the minimum displayed digit of the preset voltage or current.
PAT-T 8kW 3-7

3.5 Protection Functions and Alarms
The PAT is equipped with the following protection function.
• Overvoltage protection (OVP)
• Overcurrent protection (OCP)
• Overheat protection (OHP)
• Overheat protection of the bleeder circuit (BOHP)
• Fan failure protection (FAN)
• Incorrect sensing connection protection (SENSE)
• Input open-phase protection (PHASE)
• Shut down (SD)
Alarm occurrence and release
Alarm occurrence
When a protection function activates, the PAT behaves as follows:
See
p. 3-19
See
p. 3-10
to p. 3-13
• The output turns off.
For the overvoltage protection (OVP), overcurrent protection (OCP), and
shutdown (SD), you can select breaker trip in the CONFIG settings.
• The ALARM LED on the front panel display illuminates, then the cause of alarm
occurrence and the current measuring value displays alternately.
When the breaker trip is selected in overvoltage protection (OVP) or overcurrent
protection (OCP) or shutdown (SD), the front panel display shows the characters
indicated as power off respectively for about 10 to 15 seconds.
• The ALARM signal is output from pin 5 of the J1 connector.
The ALARM signal is delivered 10 to 15 seconds even if the breaker is tripped.
• The breaker trips (only on 400 V input models).
If the overheat protection (OHP) activates, the breaker trips. The ALARM LED
illuminates, and the PAT shows the OHP power-off display tor 10 to 15 seconds.
■ Verifying the cause of alarm occurrence
When the “cause of alarm occurrence” and the “present measuring value” displays
alternately, you can change the status of display by pressing the switch specified as
follows. It is helpful to verify the cause of alarm occurrence. Note that the displayed
setting value can not be changed.
See
p. 3-16
CONFIG switch
SET switch Displays “the cause of alarm occurrence” and “the present setting value.”
OVP•OCP switch
3-8 PAT-T 8kW
Displays “the cause of alarm occurrence” and “the parameter number of
alarm cause display (CF01).”
Displays “the cause of alarm occurrence” and “the setting value of OVP/
OCP trip point.”

Releasing the alarm
■ When the breaker trips (when the POWER switch turns off)
After eliminating the cause of the alarm occurrence, turn on the POWER switch.
■ When the output turns off
Turn off the POWER switch, eliminate the cause the alarm occurrence, and then
turn the POWER switch back on.
If you cannot clear the alarm even when all of the causes of the alarm occurrence are
eliminated, the PAT may have malfunctioned. If this happens, stop using the PAT
and contact your Kikusui agent or distributor.
The cause of the alarm occurrences are described in the protection functions.
3
3.5.1 Overvoltage protection (OVP) and overcurrent protection (OCP)
See
p. 3-19
The overvoltage protection (OVP) and overcurrent protection (OCP) functions
activate under the following conditions.
■ Conditions in which the OVP is activated
• When the output terminal voltage exceeds the specified voltage (OVP trip
point).
• When the sensing wire comes loose.
• When there is a problem with the PAT.
■ Conditions in which the OCP is activated
• When the output current exceeds the specified current (OCP trip point).
• When there is a problem with the PAT.
The user must set appropriate values for the OVP and OCP trip points. Be sure to
first set the OVP and OCP trip points to comply with the load immediately after
installing the PAT or changing the load.
Breaker trip function when the OVP or OCP is activated
You can select whether to trip the breaker (CF28: ON/OFF) when the OVP or OCP
function activates.
Basic Operation
OVP and OCP trip point settings
The OVP operates on the output terminal voltage. If you want to activate the
function on the voltage across the load, set the OVP trip point by considering the
voltage drop in the load cable.
PAT-T 8kW 3-9

p. 8-8
See
1
Press the OVP•OCP switch.
The OVP•OCP switch LED illuminates, and the specified OVP/OCP trip point is
shown on the display.
2
While viewing the panel display, turn the VOLTAGE knob to set the OVP
trip point or the CURRENT knob to set the OCP trip point.
If the voltage setting is limited in the CONFIG settings (CF29: ON), the OVP trip
point cannot be set lower than the present preset output voltage.
If the current setting is limited in the CONFIG settings (CF30: ON), the OCP trip point
cannot be set lower than the present preset output current.
Setting limit function
The PAT allows limits to be placed on the voltage and current settings through
CONFIG settings so that the overvoltage protection (OVP trip point) and the
overcurrent protection (OCP trip point) settings are not exceeded.
This function prevents the output from being turned off when you accidentally set
the voltage or current to a value exceeding the OVP or OCP when the output is on.
If you select to limit the voltage setting (CF29: ON), the output voltage can no
longer be set to a value to approximately 95% of the OVP trip point. In addition, the
OVP trip point can no longer be set to a value less than the preset output voltage.
If you select to limit the current setting (CF30: ON), the output current can no
longer be set to a value to approximately 95% of the OCP trip point. In addition, the
OCP trip point can no longer be set to a value less than the preset output current.
Checking the OVP or OCP operation
The OVP or OCP is a function for protecting the load. Once you set the OVP or
OCP trip point, check that the OVP or OCP works before you connect the load by
carrying out the procedure below.
If the voltage limit setting is enabled in the CONFIG settings (CF29: ON), the
output voltage cannot be set higher than the OVP trip point. Thus, you will not be
able to check the OVP operation.
If the current setting limit is enabled in the CONFIG settings (CF30: ON), the
output current cannot be set higher than the OCP trip point. Thus, you will not be
able to check the OCP operation.
1
Check that the OUTPUT LED on the display is not illuminated.
2
Set the output voltage to a value less than the OVP trip point.
3
Press the OUTPUT switch to turn the output on.
The OUTPUT LED illuminates.
4
Turn the VOLTAGE knob slowly clockwise.
When the setting value of output voltage exceeds OVP trip point, the ALARM LED on
the front panel display illuminates and either of the POWER switch or the output will
be turned off (Depending on the CONFIG settings).
3-10 PAT-T 8kW

When the POWER switch is turned off, the ALARM LED illuminates even the power
turns off, and the overvoltage protection (OVP) power-off display will be displayed for
about 10 to 15 seconds. When the output is turned off, OVP function display and the
measuring value are displayed alternately and the ALARM LED continues to be
illuminated.
C
On
OUTPUT
ALARM
A
PRESET
A V
RMT
B
CV
EXTEXT
LOCK
Fig.3-8 Overvoltage protection (OVP) alarm display
C
On
OUTPUT
ALARM
A
PRESET
A V
RMT
B
CV
EXTEXT
LOCK
Fig.3-9 Overvoltage protection (OVP) power-off display
5
Check that the POWER switch is turned off.
Make sure that the POWER switch is in "off" position.
6
Short the output terminal.
7
Turn the POWER switch on again.
3
Basic Operation
8
Check that the OUTPUT LED on the display is not illuminated.
9
Set the output current to a value less than the OCP trip point.
10
Press the OUTPUT switch to turn the output on.
The OUTPUT LED illuminates.
11
Turn the CURRENT knob slowly clockwise.
When the setting value of output current exceeds OCP trip point, the ALARM LED on
the front panel display illuminates and either of the POWER switch or the output will
be turned off (Depending on the CONFIG settings).
When the POWER switch is turned off, the ALARM LED illuminates even the power
turns off, and the overcurrent protection (OCP) power-off display will be displayed for
about 10 to 15 seconds. When the output is turned off, OCP function display and the
measuring value are displayed alternately and the ALARM LED continues to be
illuminated.
C
On
OUTPUT
ALARM
A
PRESET
A V
RMT
B
CV
EXTEXT
LOCK
Fig.3-10 Overcurrent protection (OCP) alarm display
C
On
OUTPUT
ALARM
A
PRESET
A V
RMT
B
CV
EXTEXT
LOCK
Fig.3-11 Overcurrent protection (OCP) power-off display
If you do not change the preset output, the OVP or OCP will activate again.
PAT-T 8kW 3-11

3.5.2 Other Protection Functions
EXTEXT
RMT
LOCK
PRESET
A
B
C
A V
OUTPUT
ALARM
CV
On
Overheat protection (OHP)
Overheat protection of the bleeder circuit (BOHP)
This function is activated when the internal temperature of the PAT rises
abnormally, and the output turns off (the breaker trips for 400 V input models when
overheat protection (OHP) activates).
It protects the PAT from the following conditions.
• When the PAT is used in an environment exceeding the operation temperature
range temperaaa
• When the PAT is used with the intake or exhaust port blocked
If you turn the POWER switch back on without correcting the condition that caused
the OHP or BOHP, the OHP or BOHP will be activated again.
After the OHP activates on a 400 V input model, it takes between 30 minutes and 1
hour for the internal temperature to decrease. Allow sufficient time for the PAT to
cool down before turning the POWER switch on.
A
PRESET
On
OUTPUT
ALARM
A V
C
RMT
B
CV
EXTEXT
LOCK
Fig.3-12 Overheat protection (OHP) alarm display
C
On
OUTPUT
ALARM
A
PRESET
A V
RMT
B
CV
EXTEXT
LOCK
Fig.3-13 Overheat protection (OHP) power-off display
(only on 400 V input model)
Fig.3-14 Overheat protection alarm display for the bleeder circuit
(BOHP)
Fan failure protection (FAN)
This function is activated when the fan rotation drops to an abnormal level, and the
output turns off.
C
A
PRESET
On
OUTPUT
ALARM
A V
Fig.3-15 Alarm display of fan failure protection (FAN)
RMT
B
CV
EXTEXT
LOCK
3-12 PAT-T 8kW

Incorrect sensing connection protection (SENSE)
Not set to trip the breaker (OFF)
Set to trip the breaker (ON)
This function is activated when the remote sensing wires are connected with the
polarity reversed of + (pos.) and - (neg.), and the output turns off.
C
On
OUTPUT
ALARM
A
PRESET
A V
RMT
B
CV
EXTEXT
LOCK
Fig.3-16 Alarm display of incorrect sensing connection protection
(SENSE)
Input open-phase protection (PHASE)
Three-phase input power supply may operate normally even when one of the phase
is open. However, operating the PAT in an open-phase condition puts stress on the
PAT and may cause a malfunction.
To prevent a malfunction from abnormal input, this function is activated when one
or more phase is open among the three-phase input, and the turns off.
C
On
OUTPUT
ALARM
A
PRESET
A V
RMT
B
CV
EXTEXT
LOCK
3
Basic Operation
See
See
p. 4-19
p. 3-19
Fig.3-17 Alarm display of input open-phase protection (PHASE)
Shutdown (SD)
Shutdown is not activated as a result of the PAT detecting an error. It is a function
used to turn off the output by applying an external signal to the J1 connector on the
rear panel when an abnormal condition occurs.
You can select whether to trip the breaker (CF27: ON/OFF) when the shutdown
signal is applied.
C
A
PRESET
On
OUTPUT
ALARM
A V
Fig.3-18 Alarm display of the shutdown (SD)
A
PRESET
On
OUTPUT
ALARM
A V
Fig.3-19 Shutdown power-off display (SD)
RMT
B
CV
EXTEXT
LOCK
C
RMT
B
CV
EXTEXT
LOCK
PAT-T 8kW 3-13

3.6 CONFIG Settings
CONFIG settings are used to set the system configuration of the PAT. You can set or
display the parameters in
PAT is a label that indicates a list of CONFIG parameters and settings.
Table 3-1 CONFIG parameters
Table 3-1 in the CONFIG settings. On the top panel of the
Parameter
number
Indication on the top
panel label
Description of the setting or display
CF01 ALARM Alarm cause display
CF02 REMOTE SENSING Remote sensing status display
CF10 ON DELAY Output on delay setting
CF11 OFF DELAY Output off delay setting
CF12 PRESET KEYLOCK Preset recall setting while locked
CF13
CF20
CF21
CF22
CF23
CF24
ERR TRACE
CV CONTROL
CC CONTROL
EXT OUT CTRL
PWR ON/OFF STATUS
PARALLEL
Communication error display setting
CV control source setting
CC control source setting
External control logic setting of the output on/off
Status signal setting of the power on/off
Setting the number of units in Master-Slave Parallel Operation
CF25 POWER ON OUTPUT Output status setting at power-on
CF26
CF27
CF28
CF29
CF30
CF32
CF40
CF41
CF42
CF43
CF50
CF51
CF52
CF53
CF54
CF55
CF56
CF57
MASTER/SLAVE
BREAKER TRIP (SD)
BREAKER TRIP
V SETTING LIMIT
I SETTING LIMIT
START UP
BAUDRATE
DATABITS
STOPBITS
FLOW
VERSION
GPIB ADDRESS
VENDOR ID
PRODUCT ID
ADDON I/F
DHCP CLIENT
AUTO IP ADDRESS
IP ADDRESS (1)
Master-slave parallel operation setting
Breaker trip setting when the shutdown signal is applied
Breaker trip setting when the OVP or OCP is activated
Voltage limit setting
Current limit setting
*2
*2
Output-on startup state setting
RS232C data rate setting
RS232C data length setting
RS232C stop bit setting
*1
RS232C flow control setting
Interface version display
GPIB address setting
Vendor ID display
Product ID display
Remote interface setting
DHCP setting
*6
AUTO IP address setting
IP address display (1)
*3
*1, *4
*5
*5
*1, *3
*6
*6
*1
*2
*2
*2
*1
*2
*1, *2
*1
*1
*2
*1
*1
*1
CF58
CF59
CF60
CF61
IP ADDRESS (2)
IP ADDRESS (3)
IP ADDRESS (4)
LAN STATUS
IP address display (2)
IP address display (3)
IP address display (4)
LAN status display
*6
*6
*6
*6
*1. The setting is possible even when the product is used as a slave unit.
*2. Cannot be set when the output is on.
*3. Only when the factory option GPIB, USB or LAN interface is installed.
*4. Only when the factory option GPIB interface is installed.
*5. Only when the factory option USB interface is installed.
*6. Only when the factory option LAN interface is installed.
3-14 PAT-T 8kW

Setup and view procedure of CONFIG parameters
CF01, CF02, CF50, CF52, CF53 and CF57 to CF61 are parameters only for viewing
the status. You cannot set them.
CF50 to CF61 appear only when the option board is installed. The display of the
setting varies depending on the interface option.
Parameter number
CF (CONFIG) + a 2-digit number
OUTPUT
ALARM
A V
PRESET
A
Setting Display
C
RMT
B
EXTEXT
LOCK
Fig.3-20 CONFIG parameter display example
1
Press the CONFIG switch.
The switch LED illuminates. The ammeter displays the parameter number, and the
voltmeter displays the present setting.
2
Turn the CURRENT knob to select the parameter number.
3
Turn the VOLTAGE knob to change the setting.
If you select a new setting, it blinks.
When the setting is blinking, the new setting is not entered until you press a switch. If
you do not want to change the setting, turn the VOLTAGE knob and select the setting
that illuminates (not blinking) to return to the original setting.
You cannot set CF20, CF21, CF22, CF24, CF26, CF29, and CF30 when the output is
on. The present setting is displayed, but it cannot be changed even if you turn the
VOLTAGE knob.
4
To set or display other parameters, repeat step 2 and step 3 .
To exit from the CONFIG settings, proceed to step 5 .
5
Press any of the switch from SET, OVP•OCP, CONFIG or OUTPUT
switch. If it is set to the slave unit, press CONFIG switch.
It will exit from the CONFIG setting to reflect the setting conditions.
Even when the POWER switch is turned off, the setting description will be reflected.
3
Basic Operation
PAT-T 8kW 3-15

CONFIG parameter details
See
CF01 Alarm cause display
Displays the cause of the alarm occurrence (while the ALARM LED is illuminated).
If there are multiple causes, the sum of each cause is displayed.
Display Description
0 Not an alarm condition (ALARM LED is off)
1 Overvoltage protection (OVP)
2 Overcurrent protection (OCP)
4 overheat protection (OHP)
8 Input open-phase protection (PHASE)
16 Incorrect sensing connection protection (SENSE)
32 Fan failure protection (FAN)
64 Shut down (SD)
128 Overheat protection of the bleeder circuit (BOHP)
CF02 Remote sensing status display
See
See
p. 3-25
Displays the state of the sensing switch on the rear panel.
Display Description
oFF Remote sensing is off
on Remote sensing is on
CF10 Output on delay setting
Set the delay from the time the OUTPUT switch is pressed until the output turns on.
p. 3-4
When exiting from the CONFIG settings by the OUTPUT switch, the output on
delay function is activated at the some time for which setting conditions were set by
the output on delay settings.
Settings Description
oFF No delay (factory default)
0.1 to 10.0 Output on delay. Unit: s, resolution: 0.1
CF11 Output off delay setting
Set the delay from the time the OUTPUT switch is pressed until the output turns off.
p. 3-4
When exiting from the CONFIG settings by the OUTPUT switch, the output off
delay function is activated at the some time for which setting conditions were set by
the output off delay settings.
Settings Description
oFF No delay (factory default)
0.1 to 10.0 Output off delay. Unit: s, resolution: 0.1
3-16 PAT-T 8kW

CF12 Preset recall setting while locked
See
p. 3-24
Sets whether preset memory values can be recalled even when the lock function is
enabled.
Settings Description
0 Able to recall preset memory values in the locked condition
1
Unable to recall preset memory values in the locked condition (factory
default)
CF13 Communication error display setting
Sets whether to display communication errors by performing a device trace.
Displays the error number when the PAT is in remote mode, and there is at least one
error in the SCPI error queue. The setting is possible even when the product is used
as a slave unit.
OUTPUT
ALARM
A
PRESET
A V
RMT
B
EXTEXT
LOCK
C
Fig.3-21 Error display example (Err-100 example)
Settings Description
oFF Not display communication errors (factory default)
on Display communication errors
3
Basic Operation
See
p. 4-9, p. 4-11
See
p. 4-13,
p. 4-15
CF20 CV control source setting
Selects the constant voltage control mode. Cannot be set when the output is on.
Settings Description
0 Panel control (factory default)
1 External voltage control EXT-V
2 External resistance control EXT-R 10 kΩ → MAX OUT
3 External resistance control EXT-R 10 kΩ → 0 OUT (FAIL SAFE)
4 External voltage control EXT-V (FAST)
CF21 CC control source setting
Select the constant current control mode. Cannot be set when the output is on.
Settings Description
0 Panel control (factory default)
1 External voltage control EXT-V
2 External resistance control EXT-R 10 kΩ → MAX OUT
3 External resistance control EXT-R 10 kΩ → 0 OUT (FAIL SAFE)
4 External voltage control EXT-V (FAST)
PAT-T 8kW 3-17

CF22 External control logic setting of the output on/off
See
See
See
p. 4-17
p. 4-22
p. 5-2
Sets the logic used to control the output on/off using an external contact (J1
connector). Cannot be set when the output is on.
Select “H” when not controlling the output on/off with an external contact.
Settings Description
H Turn the output on with a high signal (factory default)
L Turn the output on with a low signal
CF23 Status signal setting of the power on/off
Sets whether to output a low level signal while the power is on or off when
monitoring the power on/off status externally (through the J1 connector). The
setting is possible even when the product is used as a slave unit.
Settings Description
0 Output a low level signal while the power is on (factory default)
1 Output a low level signal for 10 to 15 s when the power is off
CF24 Setting the number of units in Master-Slave Parallel Operation
Sets the total number of units which consists of the master unit and the slave units
under the Master-Slave Parallel Operation. However, it can not be set when the
output is turned on.
See
See
p. 3-3
p. 5-7
On models other than the PAT850-9.4T
Settings Description
1 to 5 Setting the total number of units 1 (factory default) to 5
On the PAT850-9.4T
Settings Description
1 1 unit (factory default)
2 2 units
CF25 Output status setting at power-on
Sets the output state when the POWER switch is turned on. This setting is invalid
when the output is turned off using an external contact.
Settings Description
oFF Output is off at power-on (factory default)
on Output is on at power-on
CF26 Master-Slave parallel operation setting
Sets the PAT condition during master-slave parallel operation. Cannot be set when
the output is on. The setting is possible even when the product is used as a slave unit.
Settings Description
0 Master unit or independent operation (factory default)
1 Slave unit
3-18 PAT-T 8kW

CF27 Breaker trip setting when the shutdown signal is applied
See
See
See
p. 3-13
p. 3-9
p. 3-10
Sets whether to trip the breaker (turn the POWER switch off) when an external
shutdown (SD) signal is applied. The setting is possible even when the product is
used as a slave unit.
Settings Description
oFF Not trip (tu rn the output off) (factory default)
on Tri p ( t urn the POWER switch off)
CF28 Breaker trip setting when the OVP or OCP is activated
Sets whether to trip the breaker (turn the POWER switch off) when the overvoltage
protection (OVP) or overcurrent protection (OCP) is activated. The setting is
3
possible even when the product is used as a slave unit.
Settings Description
oFF Not trip (tu rn the output off) (factory default)
on Tri p ( t urn the POWER switch off)
CF29 Voltage limit setting
Sets whether to limit the output voltage setting so that it does not exceed the
overvoltage protection setting (to approximately 95% of the OVP trip point) Cannot
be set when the output is on.
Basic Operation
See
p. 3-10
Settings Description
oFF Not limit (factory default)
on Limit
CF30 Current limit setting
Sets whether to limit the output current setting so that it does not exceed the
overcurrent protection setting (to approximately 95% of the OCP trip point) Cannot
be set when the output is on.
Settings Description
oFF Not limit (factory default)
on Limit
CF32 Output-on startup state setting
You can set the state that the PAT starts up in when the output state at power-on is
set to on. This cannot be set when the output is on.
When you select to prioritize CC, set CV to 10 % or more of the rated value. A
current that is greater than the CC setting may flow through the load when the
output is turned on. Depending on the state of the connected load, the PAT may not
start with the settings that you have selected.
Settings Description
CV CV (constant voltage) is prioritized (factory default)
CC CC (constant current) is prioritized
PAT-T 8kW 3-19

CF40 RS232C data rate setting
See
See
p. 6-3
p. 6-3
Sets the baud rate of RS232C. The setting is possible even when the product is used
as a slave unit.
Settings Description
1.2 1 200 bps
2.4 2 400 bps
4.8 4 800 bps
9.6 9 600 bps
19.2 19 200 bps (factory default)
38.4 38 400 bps
CF41 RS232C data length setting
Sets the RS232C data length. The setting is possible even when the product is used
as a slave unit.
Settings Description
7bIt 7 bits
8bIt 8 bits (factory default)
CF42 RS232C stop bit setting
See
See
p. 6-3
p. 6-3
Sets the RS232C stop bit. The setting is possible even when the product is used as a
slave unit.
Settings Description
1bIt 1 bit (factory default)
2bIt 2 bits
CF43 RS232C flow control setting
Sets whether to perform flow control of RS232C. The setting is possible even when
the product is used as a slave unit.
Settings Description
oFF Disable flow control
on Enable flow control (factory default)
CF50 Interface version display
Displays the version of the factory option interface. Displayed only when the
interface is installed.
Display Description
1.00 Interface version
3-20 PAT-T 8kW

CF51 GPIB address setting
See
p. 6-5
Sets the GPIB address. The settings are displayed only when the factory option
GPIB interface is installed. The setting is possible even when the product is used as
a slave unit.
Settings Description
1 to 30 Specify the address between 1 (factory default) and 30
CF52 Vendor ID display
Displays the vendor ID. Displayed only when the factory option USB interface is
installed.
Display Description
0b3E 0x0B3E
3
CF53 Product ID display
Displays the product ID. Displayed only when the factory option USB interface is
installed.
Display Description
100E 0x100E
Basic Operation
CF54 Remote interface setting
Sets the remote interface that is to be used. Displayed only when the factory option
interface is installed. The displayed settings vary depending on the installed
interface option. The setting is possible even when the product is used as a slave
unit.
The installed interface becomes the default.
When the GPIB interface is installed
Settings Description
232C Use RS232C for the remote interface
GPib Use GPIB for the remote interface (factory default)
When the USB interface is installed
Settings Description
232C Use RS232C for the remote interface
uSb Use USB for the remote interface (factory default)
When the LAN interface is installed
Settings Description
232C Use RS232C for the remote interface
uSb Use LAN for the remote interface (factory default)
PAT-T 8kW 3-21

See
See
p. 6-5
CF55 DHCP setting
Select whether or not to obtain an IP address from a DHCP server. Displayed
only when the factory option LAN interface is installed.
When the fixed IP address is used, set to turning off.
Settings Description
oFF Not to use the DHCP server
on Use the DHCP server (factory default)
p. 6-7
CF56 AUTO IP address setting
When the DHCP is not used or not enable to be used, set whether to fix the IP
address automatically. The IP address assigned by the AUTO IP is 169.254.x.x
(x is 0 to 254). Displayed only when the factory option LAN interface is
installed.
When the fixed IP address is used, set to turning off.
Settings Description
oFF Not to use the AUTO IP function
on Use the AUTO IP function (factory default)
CF57 to CF60 IP address display
Confirm the setting IP address. Displayed only when the factory option LAN
interface is installed.
The IP address is just displayed-it cannot be set from the panel. To set a fixed IP
address, access the PAT through a Web browser.
When you access the PAT through a Web browser, do so under conditions in
which a DHCP server or AUTO IP can be used.
For information about the PAT-T series from a Web browser, see the
accompanying CD-ROM.
Parameter
number
CF57 0 to 255 Display the 1st number of the IP address
CF58 0 to 255 Display the 2nd number of the IP address
CF59 0 to 255 Display the 3rd number of the IP address
CF60 0 to 255 Display the 4th number of the IP address
Display Description
CF61 LAN status display
Display the status of the LAN interface. Displayed only when the factory option
LAN interface is installed.
Display Description
Stby Stand by state (the LAN can not be used)
nFLt No fault state (the LAN is functioned properly)
FLt Fault state (the LAN is not functioned properly)
LAn Display identifying the LAN
3-22 PAT-T 8kW

3.7 Preset Memory Function
The PAT has a function that stores up to three combinations of voltage setting and
current setting. You can store a combination by selecting memory switch A
(PRESET A), B (PRESET B), or C (PRESET C).
RECALL switches allow you to recall any of the three preset memory values.
Storing the preset memory values
1
Press the SET switch.
The SET switch LED illuminates, and the specified voltage and current are shown on
the panel.
2
While viewing the panel display, turn the VOLTAGE knob to set the
voltage preset memory value, the CURRENT knob to set the current
preset memory value.
3
Press the STORE switch while holding down the SHIFT switch.
PRESET A, B, and C LEDs blink in the display.
4
Press any memory switch (A, B or C) to be stored, and save the value
of preset memory.
The selected preset memory (A, B or C) illuminates on the display.
3
Basic Operation
You can save preset memory values by carrying out step 3 and step 4 with the
output turned on while displaying the measured values (SET switch turned off).
After saving the preset memory values, press the SET switch to check them.
Recalling the preset memory values
1
Press the SET switch.
The SET switch LED illuminates, and the specified voltage and current are shown on
the panel.
2
While holding down the SHIFT switch, press the RECALL switch in
which the preset memory values you want to recall is stored.
The LED of the recalled preset memory values (PRESET A, B, or C) illuminates.
If no load is connected, it takes a long time for the output voltage to rise.
You can recall preset memory values by carrying out step 2 above with the output
turned on while displaying the measured values (SET switch turned off). If the
recalled memory value exceeds the OVP or OCP trip point, the OVP or OCP
function trips.
If the voltage or current setting is limited in the CONFIG settings (CF29 or CF30:
ON) and the recalled preset memory values exceed the OVP or OCP trip point, the
output setting is limited to approximately 95 % of the OVP or OCP trip point. Then,
PRESET A, B, or C LED corresponding to the preset memory that was recalled
illuminates for approximately 1 second and turns off.
PAT-T 8kW 3-23

See
p. 3-17
You can set CF12 to 0 CONFIG parameter to enable preset memory values to be
recalled even in the locked condition.
3.8 Lock Function
The PAT has a lock function that prevents the settings from being changed
inadvertently.
The following operations are disabled in the locked condition (the LOCK LED on
the display is illuminated).
• Setting of the current and voltage.
• Setting of the OVP and OCP.
• Setting of the CONFIG parameters.
• Saving and recalling of preset memories.
See
p. 3-17
You can set CONFIG parameter CF12 to 0 to enable preset memory values to be
recalled even in the locked condition.
OUTPUT
ALARM
A
B
CCCC
A V
PRESET
C
RMT
EXTEXT
On
LOCK
Fig.3-22 Panel display example in the locked condition
■ Setting
1
Set all the required parameters such as the output voltage and output
current.
2
Press the LOCK (SHIFT+LOCAL) switch.
The LOCK LED on the display illuminates, and the lock is enabled.
■ Release
To release the lock function, hold down LOCK (SHIFT+LOCAL) switch until the
LOCK LED on the display turns off.
3-24 PAT-T 8kW

3.9 Switching from Remote to Local Mode
EXTEXT
LOCK
PRESET
A
B
C
A V
OUTPUT
ALARM
CCCC
On
RMT
When the PAT is operating under remote control, the RMT LED on the display
illuminates.
Fig.3-23 Panel display example in remote mode
To switch from the remote mode to the local mode (panel operation) from the panel,
press the LOCAL switch.
If the local lockout (llo) is specified in remote mode, the PAT does not switch to
local mode (panel operation) even when the LOCAL switch is pressed.
IEEE488.1 ren or SYST:LOC to clear the local lockout (llo).
3.10 Remote Sensing Function
The remote sensing function is used to reduce the influence of voltage drops due to
the load cable resistance and stabilize the output voltage across the load.
See
p. 2-5
The remote sensing function of the PAT can compensate up to approximately 0.6 V
for a single line. Select a load cable with sufficient current capacity so that the
voltage drop in the load cable does not exceed the compensation voltage. When the
remote sensing is performed, apply the voltage of sensing point (at the load
terminal) which does not exceed the rated output voltage. When the remote sensing
is performed at near to the maximum output voltage, the output is limited at the
maximum voltage (105 % of the rated output voltage).
3
Transmist
Basic Operation
To perform remote sensing, an electrolytic capacitor may be required at the sensing
point (load terminal).
Connection of the sensing cable
W ARNING
Possible electric shock or damage to the internal circuitry.
• Never wire the cable to the sensing terminals while the POWER
switch is turned on.
• For sensing cables, use cables with a higher voltage rating than the
isolation voltage of the PAT. Protect the uncovered section of the
shielded wire by using insulation tubes with a withstand voltage
greater than the isolation voltage of the PAT. For the isolation
voltage of each model, see
• The sensing terminals are at approximately the same potential as
the - (neg.) output terminal of the PAT. Insert the wire so that the
wire scraps protruding from the sensing terminals do not come in
contact with the chassis. Also, insert wires to the terminals so that
the stripped sections do not protrude from the terminals.
Chapter 8, “Specifications.”
PAT-T 8kW 3-25

See
+
+
–
–
C
+S
-S
OFF ON
2-core shielded wire
Connect an
electrolytic
capacitor as
necessary.
Load
Output terminal
Chassis terminal
Sensing terminal
Sensing switch
PAT
Switch is ON
p. 3-16
If the sensing wires come loose, the output voltage across the load cannot be
stabilized and may cause excessive voltage to be applied to the load. If an
appropriate OVP trip point is set, the OVP trips and prevents excessive voltage
output.
After you are done using the remote sensing function, remove the sensing wires, and
be sure to turn off remote sensing using the sensing switch.
You can check the sensing switch status using the CONFIG settings (CF02).
■ Notes when connecting the sensing cable
Use AWG24 wires to connect to the sensing terminals. Remove 10 mm of the wire
covering.
Insert the wire while holding down
this section with a screwdriver.
STRIP-GAUGE
10mm
AWG 24
-
S +S
Fig.3-24 Connection to the sensing terminal
Ye s
No
The wire is directly in
contact with the chassis.
No
The wire scrap is in
contact with the chassis.
Fig.3-25 Appropriate and inappropriate connections
Fig.3-26 Remote sensing connection
3-26 PAT-T 8kW

See
Fig.3-24
1
Turn the POWER switch off.
2
Turn on the sensing switch on the rear panel.
3
As shown in Fig.3-26, connect the sensing cable between the sensing
terminal and the load terminal.
To decrease output ripple voltages resulting from inductive effects, use a two-core
shielded wire for the sensing wires. Connect the shield to the - (neg.) terminal.
If you cannot use shielded wires, twist the + (pos.) and - (neg.) wires thoroughly.
Remove the covering from the sensing wires appropriately before connecting them.
■ Electrolytic capacitor connected at the load end
If the inductance in the wire is large, the following symptoms may appear. Twisting
the load wires reduces the inductance, thereby stabilizing the output. However, if
this does not solve the problem, connect an electrolytic capacitor at the load end.
• Oscillation
If the wiring to a load is long, the phase shift caused by the inductance and
capacitance of the wiring becomes non-negligible, thereby causing oscillation.
• Fluctuating output
If the load current changes suddenly to pulse form, the output voltage may
increase due to the effects from the inductance component of the wiring.
3
Basic Operation
Electrolytic capacitor required
Capacitance: 0.1 μF to several-hundred μF
Withstand voltage: Greater than or equal to 120 % of the rated output voltage of
the PAT
■ When inserting a mechanical switch between the PAT and the load
If you are using a mechanical switch that is inserted between the PAT and the load to
turn on/off the connection between them, insert a switch also in the sensing wire as
shown in
Fig.3-27 and turn on/off the load wire and the sensing wire
simultaneously. Be sure to turn off the OUTPUT switch or POWER switch before
turning on/off the mechanical switch.
S
+
Load
+
+
C
–
–
+S
–S
–
Fig.3-27 On/Off using the mechanical switch
PAT-T 8kW 3-27

3.11 Factory Default Settings
Turning ON the POWER switch while holding down the SHIFT switch initializes
the settings to factory default. Carry out this operation when you want to reset all
settings to factory default values. The factory default settings are given in the tables
below.
Table 3-2 Factory dfault settings of basic parameters
Basic Item Setting
Output voltage 0 V
Output current 105 % of the rated output current
Overvoltage protection (OVP) 111.5 % of the rated output voltage
Overcurrent protection (OCP) 111.5 % of the rated output current
Preset memory values A/B/C Voltage: 0 V, Current: 105 % of the rated output current
Table 3-3 Factory default settings of the CONFIG parameters
Parameter
number
CF10 Output on delay setting OFF
CF11 Output off delay setting OFF
CF12 Preset recall setting while locked 1 (unable to recall)
CF13 Communication error display setting OFF (not displayed)
CF20 CV control source setting 0 (panel control)
CF21 CC control source setting 0 (panel control)
CF22 External control logic setting of the output on/off H
CF23 Status signal setting of the power on/off 0 (POWER ON STATUS)
CF24 Setting the number of units in Master-Slave Parallel
CF25 Output status setting at power-on OFF (output off at power-on)
CF26 Master-slave parallel setting 0 (master unit)
CF27 Breaker trip setting when the shutdown signal is
CF28 Breaker trip setting when the OVP or OCP is activated OFF (not trip)
CF29 Voltage limit setting OFF (not limit)
CF30 Current limit setting OFF (not limit)
CF32 Output-on startup state setting CV (CV is prioritized)
CF40 RS232C data rate setting 19.2 (kbit/s)
CF41 RS232C data length setting 8 bit
CF42 RS232C stop bit setting 1 bit
CF43 RS232C flow control setting ON (Xon/off flow control)
CF51
CF52
CF55
CF56
*1. Only when the factory option GPIB is installed.
*2. Only when the factory option GPIB, USB or LAN interface is installed.
*3. Interface installed by factory option.
*4. Only when the factory option LAN interface is installed.
Operation
applied
*1
GPIB address setting 1
*2
Remote interface setting
*4
DHCP setting ON (Use the DHCP server)
*4
AUTO IP address setting ON (Use the AUTO IP function)
Operating condition
(CONFIG parameter)
Setting
1 (1 unit)
OFF (not trip)
GPIB, USB or LAN
*3
3-28 PAT-T 8kW

4
External Control
This chapter describes external analog
control and remote monitoring using
the J1 connector.

4.1 Overview of External Control
[84-49-0110]
W ARNING
The J1 connector on the rear panel of the PAT can be used to perform external
control listed below.
• Output voltage control
Control using external voltage or external resistance
• Output current control
Control using external voltage or external resistance
• Output on/off using external contact
• Shutdown using external contact (turn off the output or POWER switch)
When the PAT is operating under external control, the EXT LED on the front panel
display illuminates.
OUTPUT
ALARM
A
CCCC
A V
PRESET
RMT
B
EXTEXT
LOCK
On
C
Fig.4-1 Display example during external control operation
4.2 J1 Connector
At the factory shipment, the protection socket is attached to the J1 connector. Keep
this protection socket and be sure to attach when the J1 connector is not used. If the
protection socket is damaged or lost, contact Kikusui distributor/agent.
Fig.4-2 Protection socket
Possible electric shock.
• The J1 connector contains pins that are at the same electric
potential as the output terminal. If you are not using the J1
connector, be sure to insert the protective socket provided.
• Be sure to use the protective cover on the sockets.
A connector kit is provided for connecting the J1 connector. The connector kit
consists of connector parts conforming to the MIL standard made by Omron.
The single contact connection tool and contact removal tool are not provided. Please
obtain your own tools.
4-2 PAT-T 8kW
For information on how to obtain the tools and consumable parts, contact your
Kikusui agent or distributor.

Table 4-1 Connector parts by Omron needed to connect the J1
connectorJ1
Product Model Kikusui parts no. Notes
Single contact connection tool XY2B-7006 Y2-070-001 Not included.
Contact removal tool XY2E-0001 Y2-070-002 Not included.
Pin (contact) XG5W-0031 84-49-0100 Recommended wire size AWG24
(UL-1061).
Socket XG5M-2632-N 84-49-0160 MIL standard type socket.
Protection cover (semi cover) XG5S-1301 84-49-0161 –
For details about how to use the products, refer Omron’s catalog.
4
External Control
PAT-T 8kW 4-3

Table 4-2 connector pin arrangement
J
A position of
the pin number
that looked at
from the panel
side.
13
17
21
25
Pin
No.
1
1
2
5
6
10
9
14
18
22
26
Signal Name Description
STATUS COM
1
STATUS COM
2
PWR ON/OFF
3
STATUS
Common for status signals from pin 3 through 7.
Common for status signals from pin 3 through 7.
PWR ON STATUS (CF23: 0): Output a low level signal while the power is on.
*2
PWR OFF STATUS (CF23: 1): Output a low level signal when the power is off.
*1
*1
(open collector output by a photocoupler*3)
OUT ON STATUS
4
ALM STATUS Turns on when the OVP, OCP, OHP, PHASE, SENSE, FAN, or BOHP is activated or
5
CC STATUS
6
CV STATUS
7
On when the output is on (open collector output by a photocoupler*3).
when a shutdown signal is applied (open collector output by a photocoupler).
On during CC operation (open collector output by a photocoupler*3).
On during CV operation (open collector output by a photocoupler*3).
*3
8 AUX Reserved.
9 AUX Reserved.
10 I SUM IN Current signal input terminal in Master-Slave Parallel Operation
*1
ect the cable to
11
D COM
Digital signal common for pins 12 and 14
When the remote sensing is used, connect the cable to the negative electrode (-S)
of the sensing input, and when the remote sensing is not used, conn
the negative (-) output (same as pin 13).
SHUT DOWN Shutdown (trips the POWER switch or turns the output off when a low TTL level signal
12
is applied. The internal circuit is pulled up to +5 V through 10 kΩ).
13 D COM Same as pin 11.
OUT ON/OFF
CONT
14
Output on/off terminal
Turn off when a low (or high) TTL level signal is applied. The internal circuit is
pulled up to +5 V through 10 kΩ.
*1
15
A COM
Analog signal common for pins 16, 18, 20, and 22.
Connected to the negative electrode (-S) of the sensing input when remote sensing is
used; connected to - (neg.) output when remote sensing is not used.
(Same as pins 17, 19, 21, and 23.)
16 I MON Output current monitor (Outputs 0 % to 100 % of the rated current using 0 V to 10 V).
17 A COM Same as pin 15.
18 V MON Output voltage monitor (Outputs 0 % to 100 % of the rated voltage using 0 V to 10 V).
19 A COM Same as pin 15.
EXT CC CONT External voltage control of output current (0 % to 100 % of the rated outpu t voltage
20
using 0 V to 10 V) or external resistance control of output current.
• 0 % to 100 % of the rated output current in the range of 0 kΩ to 10 kΩ (CF21: 2)
• 100 % to 0 % of the rated output current in the range of 0 kΩ to 10 kΩ (CF21: 3)
21 A COM Same as pin 15.
EXT CV CONT External voltage control of output voltage (0 % to 100 % of the rated output voltage
22
using 0 V to 10 V) or external resistance control of output voltage.
• 0 % to 100 % of the rated output voltage in the range of 0 kΩ to 10 kΩ (CF20: 2)
• 100 % to 0 % of the rated output voltage in the range of 0 kΩ to 10 kΩ (CF20: 3)
23 A COM Same as pin 15.
24 PRL IN COMP Correction signal input terminal du ring master-slave parallel operation.
25 PRL IN- Negative electrode input terminal during master-slave parallel operation.
26 PRL IN+ Positive electrode input terminal during master-slave parallel operation.
*1. Use the shortest possible wires for the common wires.
*2. Status signal setting of the power on/off (CF23): Either one specified in the CONFIG settings is activated.
*3. Open collector output: Maximum voltage of 30 V and maximum current of 8 mA. It is insulated from
the control circuit.
4-4 PAT-T 8kW

4.3 Output terminal Insulation
Note the following points and insulate the output terminals.
W ARNING
CAUTION
• Possible electric shock. For safety reasons, even if the output
terminal is grounded, make sure the insulation capacity of the
output terminal (including the sensing terminal) is greater than the
isolation voltage of the PAT. For the isolation voltage of each model,
see Chapter 8, “Specifications.”
If you cannot obtain a cable with sufficient rated voltage, secure
adequate withstand voltage by passing the cable through an
insulation tube with a withstand voltage greater than the isolation
voltage of the PAT.
• The signal wire may burn out. If the PAT is to be controlled through an
external voltage (Vext), do not ground it (leave it floating).
The cable and load that are connected to the output terminal (including the sensor
terminal) must have an insulation capacity that is greater than the isolation voltage
of the PAT with respect to the chassis.
Isolation voltage indicates the maximum allowed voltage that appears across the
output terminal of the power supply unit and the protective conductor terminal
(chassis terminal).
4
External Control
PAT-T 8kW 4-5

4.3.1 When the Output terminal Is Not Grounded (Floating)
The output terminal of the PAT is isolated from the protective conductor terminal.
By connecting the GND wire of the power cable to the ground terminal of the
switchboard, the chassis of the PAT is set to ground potential as shown in
Pins 10 through 26 of the J1 connector on the rear panel (for external control and
output monitoring) are at approximately the same potential as the - (neg.) output
terminal of the PAT. Cables and devices that are connected to these pins must also
have an insulation capacity that is greater than or equal the isolation voltage of the
PAT.
PAT
J1 J2
Since the output terminal is
floating, the section indicated
in gray must have an
insulation capacity that is
greater than the isolation
voltage of the PAT with
respect to the chassis.
–
+
+
–
Vext
Rext
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
1
7
8
9
Insulated
Insulated
J1 connector
11 13 15 17 19 21 23
When remote sensing is not used:
Connect to the negative output terminal
When remote sensing is used:
Connect to -S terminal of sensing
Approx. the same potential as
the negative output terminal
Approx. the same potential as
the negative output terminal
Fig.4-3.
1
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
SENS
+S
–S
DC
Load
OUTPUT
+
–
+
–
Fig.4-3 When the output terminal is not grounded
AC
INPUT
U
V
W
4-6 PAT-T 8kW

4.3.2 When the Output terminal Is Grounded
If the positive output terminal is connected to the chassis terminal, the terminal is at
ground potential as shown in
output terminal (including the sensing terminal) will only require an insulation
capacity that is greater than the maximum output voltage of the PAT with respect to
the chassis. There is no need to provide insulation greater than the isolation voltage
of the PAT.
The same holds true when the negative terminal is connected to the chassis terminal.
The cable and load require an insulation capacity that is greater than the maximum
output voltage of the PAT.
Fig.4-4. The cable and load that are connected to the
PAT
Since the + (pos.) output
terminal is at ground
potential, the section
indicated in gray must have
an insulation capacity that is
greater than the maximum
output voltage of the PAT
with respect to the chassis.
–
+
+
–
Vext
Rext
SENS
DC
OUTPUT
+
Load
–
J1 J2
1
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
+S
–S
Insulated
J1 connector
11 13 15 17 19 21 23
When remote sensing is not used:
Connect to the negative output terminal
When remote sensing is used:
Connect to -S terminal of sensing
Approx. the same potential as
the negative output terminal
Approx. the same potential as
the negative output terminal
Insulated
+
–
1
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
U
V
W
4
External Control
AC
INPUT
Chassis terminal wire
Fig.4-4 When the output terminal is grounded
If the external voltage (Vext) output is grounded for the case shown in Fig.4-4, the
output is short-circuited (which can cause accidents).
For safety reasons, connect either output terminal to the chassis terminal unless your
application requires the output terminal to be floating.
PAT-T 8kW 4-7

When using the external voltage (Vext)
+
+
–
+
–
–
2-core shielded wire
Vex t PAT
Output is short-circuited
by the grounding of Vext,
causing current to flow.
+Ground the positive
output terminal.
Prohibited
×
J1
Approx. the same
potential as the negative
output terminal
Connect the wires so that the output is not shorted as shown in Fig.4-5 and Fig.4-6.
CAUTION
The signal wire may burn out.
•
The signal wire may burn out. Leave the Vext output floating.
•
If you are connecting the shield to the Vext side, do not connect the shield
to the output terminal of the PAT.
Fig.4-5 A connection in which the output is short-circuited by the
grounding of Vext (example of a prohibited connection)
Vext PAT
+
–
2-core shielded wire
+
–
Prohibited
×
J1
Approx. the same
potential as the negati
output terminal
+Ground the positive
+
output terminal.
–
ve
Output is short-circuited
by the shield, causing
current to flow.
Fig.4-6 A connection in which the output is short-circuited by the
shield (example of a prohibited connection)
4-8 PAT-T 8kW

4.4 Controlling the Output Voltage
W ARNING
This section explains the method used to control the output voltage using an external
voltage (Vext) in the range 0 V to approx. 10 V or an external resistor (Rext) in the
range 0 kΩ to approx. 10 kΩ.
The output voltage will change approximately 5 ms after the value of the applied
external voltage or resistance changes.
If no load is connected, it takes a long time for the output voltage to fall.
Possible electric shock.
• The insulation of the Vext or Rext and the connected cable should
be greater than the isolation voltage of the PAT. For the isolation
voltage of each model, see
• When using shielded wires for the connection, protect the uncovered
section of the shielded wire by using insulation tubes with a
withstand voltage greater than the isolation voltage of the PAT.
4.4.1 External Voltage (Vext) Control
Chapter 8, “Specifications.”
4
See
p. 3-17
To control the output voltage using Vext, set the CV control source in the CONFIG
settings to one of the following two modes.
Voltage
(V)
EXT-V (CF20: 1)
Controlled output voltage
EXT-V(FAST) (CF20: 4)
Controlled output voltage
10
Received external
0
Delay time
voltage signal
Time (ms)
Fig.4-7 Voltage change example with CV control
(external voltage signal: 0 V to 10 V)
• EXT-V CV CONT (CF20: 1)
The output voltage (Eo) varies in the range of 0 to the rated output voltage
(Ertg) by setting the external voltage (Vext) in the range of 0 V to 10 V.
Eo = Ertg × Vext /10 [V] Vext = 10 × Eo /Ertg [V]
Because the PAT processes the signal internally, there is a delay between when
the input signal is received and when the output voltage starts changing.
External Control
• EXT-V (FAST) CV CONT (CF20: 4)
The output voltage (Eo) varies in the range of 0 to the rated output voltage
(Ertg) by setting the external voltage (Vext) in the range of 0 V to 10 V.
Eo = Ertg × Vext /10 [V] Vext = 10 × Eo /Ertg [V]
PAT-T 8kW 4-9

The output voltage starts changing at almost the same time that the input signal
is received. There is almost no delay.
In this mode, you cannot perform calibration of the output voltage control using
external voltage. You can approach the desired output by making subtle
adjustments to the input signal.
CAUTION
• The signal wire may burn out. Leave the Vext output floating.
• Make sure the polarity of Vext is correct. If the polarity is reversed, the
PAT may break.
• Do not apply voltage or reverse voltage exceeding 10.5 V across the
external voltage control pins. Doing so may break the PAT.
External voltage (Vext) connection
Use a low-noise and stable voltage source for Vext. The noise in Vext is multiplied
by the amplification factor of the PAT and appears at the output. Thus, the output
ripple noise may not meet the PAT’s specifications.
To minimize the influence of noise on the output, use a two-core shielded wire or a
twisted-pair wire to connect the control terminals and Vext. Make the wires as short
as possible. Susceptibility to the effects of noise increases as the wires get longer.
When wires are long, proper operation may be hindered even if a cable with anti-
noise measures is used.
When using a shielded cable, connect the shield to the - (neg.) output terminal. If the
shield needs to be connected to the Vext side,
(Vext)” on page 4-8.
See “When using the external voltage
Pins 21 and 22 of the J1 connector are used.
PAT
Output terminal
J1
Chassis terminal
Vext
Two-core shielded or
twisted-pair wire
+
–
21
22
Sensing terminal
+S
-S
21
25
Fig.4-8 Connection of the output voltage control using external
voltage
J1
12
22
26
4-10 PAT-T 8kW

4.4.2 External resistance (Rext) control
See
p. 3-17
To control the output voltage using Rext, select the CV control source in the
CONFIG settings from the following two modes.
• EXT-R CV CONT 10 kΩ → MAX OUT (CF20: 2)
The output voltage (Eo) varies in the range of 0 to the rated output voltage
(Ertg) by setting the external resistance (Rext) in the range of 0 k
Eo = Ertg × Rext / 10 [V] Rext = 10 × Eo / Ertg [V]
• EXT-R (FAIL SAFE) CV CONT 10 kΩ → 0 OUT (CF20: 3)
The output voltage (Eo) varies in the range of the rated output voltage (Ertg) to
0 by setting the external resistance (Rext) in the range of 0 kΩ to 10 k
Eo = Ertg × (10-Rext) / 10 [V] Rext = 10 × (Ertg-Eo) / Ertg [V]
Ω to 10 kΩ.
Ω.
4
• If Rext comes loose when using the 10 kΩ → MAX OUT CV mode, excessive
voltage may be applied to the load. For safety reasons, it is recommended that
fail-safe 10 k
• If you are using fixed resistors for Rext and controlling the output voltage by
switching through them, use a short-circuit or continuous type switch.
Ω → 0 OUT CV mode be used.
External Control
PAT-T 8kW 4-11

External resistance (Rext) connection
For Rext, use a 1/2 W or larger metal film or wire-wound type resistor with good
temperature coefficient and small aging effect.
To minimize the influence of noise on the output, use a two-core shielded wire or a
twisted-pair wire to connect the control terminals and Rext. Make the wires as short
as possible. Susceptibility to the effects of noise increases as the wires get longer.
When wires are long, proper operation may be hindered even if a cable with anti-
noise measures is used.
When using a shielded cable, connect the shield to the - (neg.) output terminal.
Pins 21 and 22 of the J1 connector are used.
Rext
Two-core shielded or
twisted-pair wire
PAT
Output terminal
J1
Chassis terminal
21
22
Sensing terminal
+S
-S
J1
12
21
22
26
25
Fig.4-9 Connection of the output voltage control using Rext
4-12 PAT-T 8kW

4.5 Controlling the Output Current
This section explains the method used to control the output current using an external
voltage (Vext) in the range 0 V to approx. 10 V or an external resistor (Rext) in the
range 0 k
Ω to approx. 10 kΩ.
W ARNING
Possible electric shock.
• The insulation of the Vext or Rext and the connected cable should
be greater than the isolation voltage of the PAT. For the isolation
voltage of each model, see
• When using shielded wires for the connection, protect the
uncovered section of the shielded wire by using insulation tubes
with a withstand voltage greater than the isolation voltage of the
PAT.
Chapter 8, “Specifications.”
4.5.1 External Voltage (Vext) Control
See
p. 3-17, p. 4-9
To control the output voltage using Vext, set the CV control source in the CONFIG
settings to one of the following two modes.
• EXT-V CC CONT (CF21: 1)
The output current (Io) varies in the range of 0 to the rated output current (Irtg)
by setting the external voltage (Vext) in the range of 0 V to 10 V.
Io = Irtg × Vext / 10 [A] Vext = 10 × Io / Irtg [A]
4
External Control
CAUTION
Because the PAT processes the signal internally, there is a delay between when
the input signal is received and when the output current starts changing.
• EXT-V (FAST) CC CONT (CF21: 4)
The output current (Io) varies in the range of 0 to the rated output current (Irtg)
by setting the external voltage (Vext) in the range of 0 V to 10 V.
Io = Irtg × Vext / 10 [A] Vext = 10 × Io / Irtg [A]
The output current starts changing at almost the same time that the input signal
is received. There is almost no delay.
In this mode, you cannot perform calibration of the output current control using
external voltage. You can approach the desired output by making subtle
adjustments to the input signal.
• The signal wire may burn out. Leave the Vext output floating.
•Make sure the polarity of Vext is correct. If the polarity is reversed, the
PAT may break.
• Do not apply voltage or reverse voltage exceeding 10.5 V across the
external voltage control pins. Doing so may break the PAT.
PAT-T 8kW 4-13

External voltage (Vext) connection
Use a low-noise and stable voltage source for Vext. The noise in Vext is multiplied
by the amplification factor of the PAT and appears at the PAT output. Thus, the
output ripple noise may not meet the PAT’s specifications.
To minimize the influence of noise on the output, use a two-core shielded wire or a
twisted-pair wire to connect the control terminals and Vext. Make the wires as short
as possible. Susceptibility to the effects of noise increases as the wires get longer.
When wires are long, proper operation may be hindered even if a cable with anti-
noise measures is used.
When using a shielded cable, connect the shield to the - (neg.) output terminal. If the
shield needs to be connected to the Vext side,
(Vext)” on page 4-8.
Pins 19 and 20 of the J1 connector are used.
See “When using the external voltage
Vext
Two-core shielded or
twisted-pair wire
+
–
PAT
Output terminal
J1
Chassis terminal
19
20
Sensing terminal
+S
-S
J1
12
19
20
26
25
Fig.4-10 Connection of the output current control using Vext
4-14 PAT-T 8kW

4.5.2 External Resistance (Rext) Control
See
p. 3-17
To control the output current using Rext, select the CC control source in the
CONFIG settings from the following two modes.
• EXT-R CC CONT 10 kΩ → MAX OUT (CF21: 2)
The output current (Io) varies in the range of 0 to the rated output current (Irtg)
by setting the external resistance (Rext) in the range of 0 kΩ to 10 kΩ.
Io = Irtg × Rext / 10 [A] Rext = 10 × Io / Irtg [A]
• EXT-R (FAIL SAFE) CC CONT 10 kΩ → 0 OUT (CF21: 3)
The output current (Io) varies in the range of the rated output current (Irtg) to 0
by setting the external resistance (Rext) in the range of 0 kΩ to 10 kΩ.
Io = Irtg × (10-Rext) / 10 [A] Rext = 10 × (Irtg-Io) / Irtg [A]
4
• If Rext comes loose when using the 10 kΩ → MAX OUT CC mode, excessive
current may flow through the load. For your safety, it is recommended that fail-
safe 10 k
• If you are using fixed resistors for Rext and controlling the output voltage by
switching through them, use a short-circuit or continuous type switch.
Ω → 0 OUT CC mode be used.
External Control
PAT-T 8kW 4-15

External resistance (Rext) connection
For Rext, use a 1/2 W or larger metal film or wire-wound type resistor with good
temperature coefficient and small aging effect.
To minimize the influence of noise on the output, use a two-core shielded wire or a
twisted-pair wire to connect the control terminals and Rext. Make the wires as short
as possible. Susceptibility to the effects of noise increases as the wires get longer.
When wires are long, proper operation may be hindered even if a cable with anti-
noise measures is used.
When using a shielded cable, connect the shield to the - (neg.) output terminal.
Pins 19 and 20 of the J1 connector are used.
PAT
Output terminal
J1
Chassis terminal
Two-core shielded or
J1
12
19
20
twisted-pair wire
26
25
Rext
19
20
Sensing terminal
+S
-S
Fig.4-11 Connection of the output current control using Rext
4-16 PAT-T 8kW

4.6 Controlling the Output On/Off
W ARNING
This section explains the method used to control the on/off of the output by
connecting an external contact.
Possible electric shock.
• The insulation of the external contact (S) and the connected cable
should be greater than the isolation voltage of the PAT. For the
isolation voltage of each model, see
• When using shielded wires for the connection, protect the uncovered
section of the shielded wire by using insulation tubes with a
withstand voltage greater than the isolation voltage of the PAT.
To minimize the influence of noise on the output, use a two-core shielded wire or a
twisted-pair wire to connect the control terminals and the external contact. Make the
wires as short as possible. Susceptibility to the effects of noise increases as the wires
get longer. When wires are long, proper operation may be hindered even if a cable
with anti-noise measures is used.
When using a shielded cable, connect the shield to the - (neg.) output terminal.
Chapter 8, “Specifications.”
4
See
p. 3-18
To control the output on/off using external contact, select the external control logic
setting of output on/off in the CONFIG settings from the following two modes.
• Turn the output on with a high signal (default) (CF22: H)
The output turns on when pin 14 of the J1 connector is set high (TTL level) or
opened.
• Turn the output on with a low signal (CF22: L)
The output turns on when pin 14 of the J1 connector is set low (TTL level).
If the output is set to off using an external contact, the OUTPUT switch on the front
panel is invalid. If you are not controlling the output using an external contact, turn
the output on by setting the external control logic setting of output on/off in the
CONFIG settings to high (CF22: H).
indicates the point when the
OUTPUT switch is pressed.
External
contact
Output
H = On
L = Off
On
Off
External Control
The OUTPUT switch is
disabled. The output is
not delivered even if
the switch is pressed.
The output is on using an
external contact. Thus, the
OUTPUT switch is enabled.
To output again using
an external contact,
turn it off once.
Table 4-3 Output on/off control (example in which the output is on
at high)
PAT-T 8kW 4-17

External contact connection.
Two-core shielded or
twisted-pair wire
S
Rela
Extend this
line
Pins 13 and 14 of the J1 connector are used.
The release voltage across pins 13 and 14 is approx. 5 V maximum, and the short
circuit current is approx. 500 μA maximum. (The internal circuit is pulled up to 5 V
through 10 kΩ.)
Use parts with a contact rating of 5 Vdc and 0.5 mA for the external contact.
If multiple units are used under floating conditions and a single external contact is
used to turn on/off the output, isolate the signal to each unit such as by using a relay
on the external contact signal.
Two-core shielded or
PAT
Output terminal
J1
Output terminal
J1
12
13
14
twisted-pair wire
S
13
14
Sensing terminal
+S
26
25
-S
Fig.4-12 On/Off control connection using an external contact
■ For long-distance wiring
When wiring over a great distance, use a small relay and extend the coil side of the
relay.
Fig.4-13 On/Off control using an external contact (for long-
distance wiring)
4-18 PAT-T 8kW

4.7 Shutdown Control Using External Contact
W ARNING
This section explains the method used to trip the breaker (turn the POWER switch
off) or turn the output off using external contact.
Possible electric shock.
• The insulation of the external contact (S) and the connected cable
should be greater than the isolation voltage of the PAT. For the
isolation voltage of each model, see
• When using shielded wires for the connection, protect the
uncovered section of the shielded wire by using insulation tubes
with a withstand voltage greater than the isolation voltage of the
PAT.
Chapter 8, “Specifications.”
See
p. 3-19
To minimize the influence of noise on the output, use a two-core shielded wire or a
twisted-pair wire to connect the control terminals and the external contact. Make the
wires as short as possible. Susceptibility to the effects of noise increases as the wires
get longer. When wires are long, proper operation may be hindered even if a cable
with anti-noise measures is used.
When using a shielded cable, connect the shield to the - (neg.) output terminal.
To control the shutdown using an external contact, select the breaker trip setting
when the shutdown signal is applied in the CONFIG settings from the following two
modes.
• Not trip (default) (CF27: OFF)
The output turns off when pin 12 of the J1 connector is set low (TTL level). The
breaker is not tripped.
To recover, set pin 12 high (TTL) or open the pin and turn the POWER switch
off and then back on.
• Trip (CF27: ON)
The breaker trips when pin 12 of the J1 connector is set low (TTL level). To
recover, set pin 12 high (TTL) or open the pin and turn on the POWER switch.
4
External Control
PAT-T 8kW 4-19

Shutdown control connection
Output terminal
Chassis terminal
Sensing terminal
+S
-S
PAT
J1
S
Two-core shielded or
twisted-pair wire
25
11
26
12
12
J1
11
12
Pins 11 and 12 of the J1 connector are used.
The release voltage across pins 11 and 12 is approx. 5 V maximum, and the short
circuit current is approx. 500 μA maximum. (The internal circuit is pulled up to 5 V
through 10 kΩ.)
Use parts with a contact rating of 5 Vdc and 0.5 mA for the external contact.
Fig.4-14 Shutdown control connection using an external contact
■ For long-distance wiring
When wiring over a great distance, use a small relay and extend the coil side of the
relay.
Two-core shielded or
twisted-pair wire
Extend this
line
S
Rela
Fig.4-15 Shutdown control connection using an external contact
(for long-distance wiring)
4-20 PAT-T 8kW

4.8 External Monitoring
External monitoring of the output voltage and output current
The J1 connector consists of monitor outputs for output voltage and output current.
Table 4-4 Monitor output of output voltage and output current
Pin No. Signal name Description
15 and 17 A COM
18 V MON
16 I MON
Common for remote control input
Common terminal of the output monitor
Monitor output of output voltage
0 V to approx. 10 V for 0 to the rated output voltage
Monitor output of output current
0 V to approx. 10 V for 0 to the rated output current
4
CAUTION
• Shorting V MON and I MON to A COM can cause damage to the PAT.
• Monitor output rating
Output impedance: 1 kΩ or less
Maximum output current: Approx. 10 mA
The monitor outputs are used to monitor the DC voltage (mean value).
They cannot be used to accurately monitor the AC components (ripple, transient
response, etc.) of the actual output voltage or current.
External Control
PAT-T 8kW 4-21

External monitoring of the operation mode
The J1 connector consists of status outputs that can be used to externally monitor
the operating condition of the PAT. The status outputs consist of the following five
items.
The outputs are open collector outputs of photocouplers; they are insulated from the
internal circuits of the PAT.
The maximum rating of each signal terminal is as follows:
• Maximum voltage: 30 V
• Maximum current (Sink): 8 mA
Ta b l e 4 - 5 S ta t us output
Pin No. Signal name Description Circuit
7 CV STATUS
6 CC STATUS
5 ALM STATUS
4 OUT ON STATUS
PWR ON/OFF
3
STATUS*
1 and 2 STATUS COM
1
Set to low level when in constant voltage mode.
Photocoupler collector output
Set to low level when in constant current mode.
Photocoupler collector output
Set to low level when a protection function is activated.
Photocoupler collector output
Set to low level when output is turned off.
Photocoupler collector output
Set to low level when the POWER switch is on (PWR
ON STATUS) or when the POWER switch is turned off
(POWER OFF STATUS: approx. 10 to 15 seconds).
Photocoupler collector output
Common for status output
Photocoupler emitter output
7
6
5
4
3
1,2
See
p. 3-18
*1 Status signal setting of the power on/off in the CONFIG settings is used to select
whether to output a low level signal when the power is ON (CF23: 0) or when the
power is off (CF23: 1).
4-22 PAT-T 8kW

5
Parallel/Series Operation
This chapter describes the functions of
the master-slave series and parallel
operations as well as the connection,
setup, and operation procedures.

5.1 Master-Slave Parallel Operation
See
Master unit
Slave unit
In master-slave parallel operation, PATs of the same model are connected to form a
system, and one PAT is designated as the master, while the other PATs are
designated as slaves. You can control the whole system by operating the master.
The output current can be expanded using master-slave parallel operation
(maximum output current: the rated output current of a unit
connected in parallel).
• Maximum number of units that can be connected is five including the master.
(Two for the PAT850-9.4T.)
The difference in the output voltage and output current between the master unit and
the slave unit is within approximately 5 % of the rating.
× number of units
CAUTION
• Only PATs of the same model can be connected in master-slave parallel
operation.
• When using the PAT by itself, disconnect the parallel operation
connections. Otherwise, the PAT may not operate properly.
5.1.1 Functions during Master-Slave Parallel Operation
The functions of the PAT during master-slave parallel operation are as follows:
Voltage display and current display
The voltage is displayed only on the master unit. It is not appeared on the display of
the slave unit.
The total value of current in which the number of unit connected in the parallel
operation is displayed in the current display part of the master unit. As for the
voltage display part, the voltage value which was set at as the last setting on the
master unit will be displayed. When the maximum output current value exceeds
999.9, the maximum current displays 9
999.
p. 3-18
different from the setting condition which were set by CONFIG setting in the
“setting the number of units in Master-Slave Parallel Operation” (CF24), the current
value on the display will not be shown properly.
If the actual number of connected units in Master-Slave Parallel Operation was
C
On
OUTPUT
ALARM
OUTPUT
ALARM
A
PRESET
A V
A
CCCC
PRESET
A V
RMT
B
CV
EXTEXT
LOCK
C
RMT
B
EXTEXT
On
LOCK
Fig.5-1 Panel display example during parallel operation
(examples of output current 840 A)
5-2 PAT-T 8kW

You can only display the current on a slave unit. The current appears on the ammeter
EXTEXT
RMT
LOCK
PRESET
A
B
C
A V
OUTPUT
ALARM
CCCC
On
On
Slave unit
See
CAUTION
when the STORE switch is pressed.
When a device whose firmware version is earlier than 5.00 is being used as a slave
unit, the currents of the slave units cannot be displayed.
Fig.5-2 Slave unit display example during parallel operation
(examples of output current is 5 A)
See
See
CAUTION
p. 3-25
Chapter 4
p. 4-21
• If the firmware version of the PAT40-200T is prior to 3.00, the total current
is not displayed on the master unit when connected in the parallel
operation. The current value is displayed on each unit. It is necessary to
update the firmware version to 3.00 to display the total value on the
master u nit. When connecting the unit in the parallel operation, do not
combine the unit with the firmware version prior to 3.00 of the PAT40-
200T, it may causes the mis-operation.
5
Contact your Kikusui distributor/agent when the firmware version prior to
3.00 of the PAT40-200T is combined in the system of master slave
parallel operation. Refer to the page
1-6 , “1.4 Turning On" for
confirmation of the firmware version.
Remote sensing
Available only on the master unit.
External control
Available only on the master unit.
External monitoring
• External monitoring of output voltage (V MON)
Can be monitored on the master unit.
Parallel/Series Operation
• External monitoring of output current (I MON)
Can be monitored on the master unit.
• Status monitors
The status of the constant voltage operation (CV STATUS), constant current
operation (CC STATUS), output on, and POWER switch on can be monitored on
each master and slave unit. However, slave units always output the status of the
constant current operation.
For details on ALM STATUS, see the “Alarms” below.
• Do not connect the common wires of the master and slave monitors
outside the PAT. If the wire connecting the load comes loose, the common
wire will break.
PAT-T 8kW 5-3

Alarm
[84-49-0110]
If an alarm is detected, the units behave as follows:
• Master unit
If an alarm is detected on the master unit, alarms on the slave units are also
activated, and the output of the entire system is turned off or the breaker trips.
• Slave unit
If an alarm signal is applied from the master unit, the output is turned off or the
breaker trips on the slave unit independently.
See
p. 3-19
In determining whether to function the breaker trip when the alarm is detected, it
can be set by the config setting (CF27). To do the breaker trip as to when the OVP/
OCP trips, it is set by the config setting (CF28) on the master unit and (CF27) on the
slave unit.
See
p. 3-9, p. 5-8
■ Releasing the alarm
If the breaker trips, turn the power switch on after eliminating the cause of the
alarm. If the output is turned off, turn the power switch off from the slave unit and
the master unit in this order, after eliminating the cause of the alarm, turn the power
switch on from the slave unit and the master unit in this order.
5.1.2 Connection (Parallel Operation)
Up to five units including the master unit (Two for the PAT850-9.4T) can be
connected.
Connecting the signal wires (parallel operation)
Fig.5-5 and Fig.5-6 shows an example when connecting two slave units.
If you are using the optional parallel operation power cable (PC01-PAT), you can
use it immediately as it is already assembled.
Fig.5-3 Optional parallel operation power
cable (PC01-PAT)
See
p. 4-3
If you are using the J1/J2 connector kit that comes with the package, refer to Fig.5-5
to make the connection. For tools needed for the connection, see Table 4- 1 .
At the factory shipment, the protection socket is attached to the J1/J2 connector.
Keep this protection socket and be sure to attach when the J1/J2 connector is not
used. If the protection socket is damaged or lost, contact Kikusui distributor/agent.
Fig.5-4Protection socket
5-4 PAT-T 8kW

W ARNING
W ARNING
CAUTION
Possible electric shock.
• The J1/J2 connector contains pins that are at the same electric
potential as the output terminal. If you are not using the J1/J2
connector, be sure to insert the protective socket provided.
• Be sure to use the protective cover on the sockets.
CAUTION
• To prevent errors, if the firmware versions of the devices are different
when you perform master-slave parallel operation, use a device whose
firmware version is 5.0X or later as the master unit.
Slave unit 1 Slave unit 2Master unit
J1
10 10 10 10 10
I SUM IN
11
D COM
12
SHUT DOWN
13
D COM
14
OUT ON/OFF CONT
24
PRL IN COMP
25
PRL IN –
26
PRL IN+
J2 J1 J2 J1
11
12
13
14
24
25
26
11
12
13
14
24
25
26
11
12
13
14
24
25
26
11
12
13
14
24
25
26
5
Fig.5-5 Connection for parallel operation (two slave units)
1
Choose the power supply that is to be the master unit.
2
Connect the J2 connector on the rear panel of the master unit to the J1
connector on the rear panel of slave unit 1 using the parallel operation
power cable (PC01-PAT).
If you are not using the PC01-PAT, connect pins 10 to 14 and 24 to 26.
3
Connect the J2 connector on the rear panel of slave unit 1 to the J1
connector on the rear panel of slave unit 2 using the parallel operation
power cable (PC01-PAT).
If you are not using the PC01-PAT, connect pins 10 to 14 and 24 to 26.
If slave units 3 and 4 are available, connect them in a similar manner.
Connecting the load (parallel operation)
• Possible electric shock. Be sure to turn the POWER switch off
before touching the output terminal. Be sure to attach the OUTPUT
terminal cover after wiring the load.
• When connecting the output terminal to the chassis terminal, be sure that
the output terminal of the same polarity (positive or negative) for both the
master and slave units is connected to the chassis terminal. If you
connect the output terminal of different polarities for the master and slave
units, the output is short-circuited through the GND cable of the power
cable. This not only impedes the retrieval of correct voltage but also may
burn out the chassis terminal cable.
Parallel/Series Operation
PAT-T 8kW 5-5

• If necessary, connect the electrolytic capacitor with the range in value
See
from several hundreds to several ten thousands of μF to the end of load
terminal. The inductance of wiring and the phase transition by capacity
cannot be disregarded, and the oscillation might be occurred. The
electrolytic capacitor prevents the oscillation. The withstanding voltage of
the electrolytic capacitor must be used for the range of 120 % or more of
the ratings output voltage.
•Twist the positive and negative wires together and make the connection
to the load using the shortest wire length possible. Oscillation may occur
as a result of wiring inductance.
Output terminal
See
p. 2-6
p. 2-4
Chassis terminal
Master unit
Output terminal
Chassis terminal
Slave unit 1
Output terminal
Chassis terminal
Slave unit 2
When connecting
the negative side
to the chassis
terminal
Load or relay terminal block
Fig.5-6 Load connection for parallel operation (two slave units)
1
Turn off the POWER switches on all power supply units to be connected
in parallel.
2
Remove the OUTPUT terminal cover.
3
Connect the load wires to the output terminals of the master and slave
units.
4
As shown in Fig.5-6, connect the load wires of the master and slave
units to the load. If you use a relay terminal block, make sure that the
wires used to connect the master and slave units are as short as
poss
ible.
Use load cables with sufficient current capacity. In addition, use the shortest load
cables of the same length and cross-sectional area from each power supply to the load.
Wire the signal cable of the J1 and J2 connectors and load cables as far apart as possible.
5
Connect the output terminals (+ or) of the master and slave units to the
chassis terminal.
Use the same polarities for the output terminals of the master and slave units.
If you are using the master and slave units under floating conditions, do not connect
the output terminals to the chassis terminal.
6
Attach the OUTPUT terminal cover.
If slave units 3 and 4 are available, connect them in a similar manner.
5-6 PAT-T 8kW

5.1.3 Master-Slave Parallel Operation Setup
Designating the master and slave units
See
See
See
CAUTION
p. 3-18
p. 3-18
p. 5-2
• If the firmware versions of the devices are different when you perform
master-slave parallel operation, use a device whose firmware version is
5.0X or later as the master unit.
Turn the output off and designate the master and slave units of the master-slave
parallel operation. Set CF26 to 0 for the master unit and 1 for the slave units.
The settings take effect when you exit from the CONFIG settings.
Setting the number of units in Master-Slave Parallel Operation
(Including the Master unit)
Turn the output off and set the number of units (CF24) in Master-Slave Parallel
Operation.
The setting conditions become effective when you exit from CONFIG settings.
5
Setting the voltage and current
The voltage and current are set on the master unit. The total value of the master and
slave units are delivered for the current.
When the setting number of units is set by the config setting (CF24) under the
master-slave parallel operation, the maximum output current value (105 % of the
rated output current of the product times number of units connected in parallel
operation) is set, and it's value will be displayed when it is set to the setting value
display (lights up the SET switch). The voltage value is set with the last setting of
the master unit. When the OUTPUT switch is pressed with keeping this condition,
its setting value will be output. Set the value as desired.
Parallel/Series Operation
Setting the overvoltage protection (OVP) and overcurrent
protection (OCP) of the master unit
See
p. 3-9
See
p. 3-14
PAT-T 8kW 5-7
Use the master-slave parallel operation, set the overvoltage protection (OVP) and
overcurrent protection (OCP) of the master unit.
When the setting number of units is set by the config setting (CF24) under the
master-slave parallel operation, the maximum over current protection value (111.5
% of the rated output current of the product times number of units connected in
parallel operation) is set, and it's value will be displayed when it is set to the OVP/
OCP setting value display (lights up the OVP/OCP switch). The value of over
voltage protection is set with the last setting of the master unit.
CONFIG parameters that can be set on the slave unit
• CF13 Error message display setting
• CF23 Status signal setting of the power on/off
• CF26 Master-slave parallel setting

• CF27 Breaker trip setting when the shutdown signal is applied
• CF28 Breaker trip setting when the OVP or OCP is activated
• CF40 to CF43 RS232C settings
• CF51 GPIB address setting
• CF54 Remote interface setting
• Make sure to match the number of units in Master-Slave Parallel Operation for
the setting number (CF24) and the actual number of connected units. If the
setting number of units are different from the actual number of units, it is unable
to set properly for such a current value setting (including EXT CC CONT),
overcurrent protection (OCP) setting, and also the measured current value will
not be appeared properly on the display.
5.1.4 Starting the Master-Slave Parallel Operation
Tur ning the power on
CAUTION
1
Turn on the POWER switch of the slave units.
2
Turn on the POWER switch of the master unit.
Tur ning the power off
1
Turn off the POWER switch of the slave units.
2
Turn off the POWER switch of the master unit.
• When turning the POWER switch off and then back on, allow at least 10
seconds (40 seconds for 400 V input model) after the fan stops.
Repeated on/off of the POWER switch at short intervals can cause
damage to the inrush current limiter and shorten the service life of the
POWER switch and internal input fuse.
Tur ning the output on/off
Turn the output on/off using the OUTPUT switch on the master unit.
5-8 PAT-T 8kW

5.2 Series Operation
W ARNING
Unit 1
Unit 2
See
• Models with output voltages of 250 V or more cannot be connected
in series. Connecting the models in series would be dangerous
because the output voltage would exceed the isolation voltage of
the PAT.
See
p. 4-5
Two of any one of the following models can be connected in series: PAT20-400T,
PAT30-266T, PAT40-200T, PAT60-133T, PAT80-100T, and PAT160-50T. Master-
slave operation is not possible. The total of the output voltages of the two units is
supplied to the load. The voltage setting accuracy is the same as that of each unit.
5.2.1 Functions during series operation
The functions of the PAT during series operation are as follows:
Voltage display and current display
Add the voltages of unit 1 and unit 2 to obtain the total output voltage.
A
B
PRESET
PRESET
A
B
See
Chapter 4
OUTPUT
ALARM
OUTPUT
ALARM
A V
A V
Fig.5-7 Panel display example during series operation
External control
Can be used.
5
C
RMT
CV
EXTEXT
LOCK
C
RMT
CV
EXTEXT
LOCK
Parallel/Series Operation
p. 4-21
External monitoring
W ARNING
PAT-T 8kW 5-9
• When monitoring the output voltage or current during series
operation, the common electric potential of the monitor signal of
unit 1 and unit 2 is different.
• External monitoring of output voltage (V MON)
The output voltage of each unit can be monitored.
• External monitoring of output current (I MON)
The output current of each unit can be monitored.
• Status monitors
Constant voltage operation (CV STATUS), constant current operation (CC
STATUS), output on status, POWER switch on status, and so on can be
monitored on each unit.

Remote sensing
See
p.3-25
CAUTION
When you perform remote sensing, connect the PATs in series, and then connect the
sensing line to them as shown in
Fig.5-8.
• If the sensing wires are not connected properly, the load may be exposed
to excessive voltage and the PATs may be damaged.
• Connect an electrolytic capacitor (C) with a capacitance of a few
hundreds of
μF to a few tens of thousands of μF to the load terminals as
necessary. The wiring inductance and capacitance can cause phase
shifting at a level that must be dealt with and can also cause oscillation.
Connecting an electrolytic capacitor will prevent such oscillation.
Use an electrolytic capacitor with a withstand voltage that is 120% or
more of the total of the rated output voltages of the PATs that are
connected in series.
Unit 1
Output terminal
Chassis terminal
Sensing terminal
OFF ON
Swich is ON
Unit 2
Output terminal
Chassis terminal
+S
-S
+
+
Load
–
C
–
Connect an
electrolytic
capacitor as
necessary.
See
p. 3-9, p. 5-12
Sensing terminal
Sensing swich
OFF ON
Swich is ON
+S
-S
Fig.5-8 Connecting the sensing wires during series operation
Alarm
All of the alarms that are detected on a single unit are also detected during series
operation.
■ Releasing the alarm
If the breaker trips, turn the power switch on after eliminating the cause of the
alarm. If the output is turned off, turn the power switch off of the unit 1 and the unit
2 in this order, after eliminating the cause of the alarm, turn the power switch on of
the unit 1 and the unit 2 in this order.
5-10 PAT-T 8kW

5.2.2 Load Connection (Series Operation)
See
W ARNING
CAUTION
• Possible electric shock. Be sure to turn the POWER switch off
before touching the output terminal. Be sure to attach the OUTPUT
terminal cover after wiring the load.
• Connect an electrolytic capacitor (C) with a capacitance of a few
hundreds of μF to a few tens of thousands of μF to the load terminals as
necessary. The wiring inductance and capacitance can cause phase
shifting at a level that must be dealt with and can also cause oscillation.
Connecting an electrolytic capacitor will prevent such oscillation.
Use an electrolytic capacitor with a withstand voltage that is 120% or
more of the total of the rated output voltages of the PATs that are
connected in series.
Load or relay terminal block
Output terminal
Chassis terminal
Unit 1
Output terminal
5
See
p. 2-6
p. 2-4
Chassis terminal
Unit 2
Fig.5-9 Load connection for series operation
(Example in which the negative terminal of unit 2 is
connected to the chassis terminal)
1
Turn off the POWER switches on all power supply units to be connected
in series.
2
Remove the OUTPUT terminal cover.
3
As shown in Fig.5-9, connect the load and the PAT using the load wires.
Use load cables with sufficient current capacity. Connect the load wires at the shortest
length possible. If the voltage drop in the output cable is large, the difference in the
potential between power supply units and the load effect become large.
4
Connect the output terminals of unit 1 and unit 2.
5
Connect one of the negative terminal or the positive terminal of unit 1 or
unit 2 to the chassis terminal.
6
Attach the OUTPUT terminal cover.
When connecting the negative
side of unit 2 to the chassis terminal
Parallel/Series Operation
PAT-T 8kW 5-11

5.2.3 Series Operation Setup
See
CAUTION
Setting the voltage and current
See
Fig.5-7
The voltage and current are set on each unit. The voltage that is delivered is the sum
of the voltages of the two units. Set the same value for the current on each unit.
Setting the overvoltage protection (OVP) and overcurrent
protection (OCP)
p. 3-9
Overvoltage protection (OVP) and overcurrent protection (OCP) must be configured
on each unit when carrying out series operation. Set the same values on each unit.
5.2.4 Starting the Series Operation
Tur ning the power on/off
Turn on/off the POWER switches on unit 1 and unit 2.
• When turning the POWER switch off and then back on, allow at least 10
seconds (at least 40 seconds for 400 V input model) after the fan stops.
Repeated on/off of the POWER switch at short intervals can cause
damage to the inrush current limiter and shorten the service life of the
POWER switch and internal input fuse.
Tur ning the output on/off
Turn on/off the OUTPUT switches on unit 1 and unit 2.
5-12 PAT-T 8kW

6
Remote Control
This chapter provides a general
explanation of the remote control
function. For details on commands, see
the Communication Interface Manual
on the
accompanied CD-ROM.

6.1 Remote Control Overview
In addition to using the front panel, the PAT can be controlled remotely using the
following interfaces.
• RS232C interface
• GPIB interface (factory option)
• USB interface (factory option)
• LAN interface (factory option)
The PAT is equipped with RS232C as standard.
If the factory option interface board is installed, you can use GPIB, USB or LAN.
The GPIB, RS232C, USB and LAN interfaces cannot be used simultaneously.
The remote interface complies with IEEE Std 488.2-1992 and SCPI Specification
1999.0.
Use the SCPI commands only after you have understood the SCPI command syntax
for the PAT.
When the PAT is operating under remote control, the RMT LED on the display on
the front panel illuminates. To switch from the remote mode to the local mode
(panel operation) from the panel, press the LOCAL switch.
Instrument Interface Standards
The PAT conforms to the following standards.
• IEEE Std 488.2-1992 IEEE Standard Codes, Formats, Protocols, and Common
Commands For Use With IEEE Std 488.1-1987
• IEEE Std 488.1-1987 IEEE Standard Digital Interface for Programmable
Instrumentation
• Standard Commands for Programmable Instruments (SCPI) version 1999.0
• Universal Serial Bus Specification Rev 2.0
• Universal Serial Bus Test and Measurement Class Specification (USBTMC) Rev
1.0
• Universal Serial Bus Test and Measurement Class, Subclass USB488
Specification (USBTMC-USB488) Rev 1.0
• TCP/IP instrument Protocol Specification VXI-11 Rev 1.0
6-2 PAT-T 8kW

6.2 Interface Setup
[P1-000-093]
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
D-sub 9-pin female
D-sub 9-pin female
Wiring configuration of the cross cable
: Communication lline used of this producct
#4-40UNC
Inch screw
#4-40UNC
Inch screw
1: CD (carrier detect)
2: RXD (receive data)
3: TXD (transmit data)
4: DTR (data terminal ready)
5: GND (signal ground)
6: DSR (data set ready)
7: RTS (request to send)
8: CTS (clear to send)
9: RI (ring indicator)
Facing the PAT rear panel
*
*
*
*
*
6.2.1 RS232C Control (Standard Equipped)
When the PAT is shipped from the factory, the RS232C connector has a cover. Keep
the cover so that you can attach it to the RS232C connector when the connector is
not in use. For safety, always attach the cover to the RS232C connector when the
connector is not being used. If the cover is damaged or lost, contact your Kikusui
agent or distributor.
Fig.6-1 RS232C connector cover
The RS232C port on the PAT is a standard D-sub 9-pin male connector.
Check that the POWER switches of the PAT and computer are off, and connect the
PAT to the computer using a standard cross cable (null modem cable).
Use a D-sub 9-pin female-to-female AT type for the cross cable. Fig.6-2 shows the
connector pin arrangement.
See
p. 3-15,
p. 3-21
The PAT does not use hardware handshaking (as shown in the cross cable example
2).
6
Fig.6-2 9-pin AT type connector
RS232C configuration
1
If an option board is installed, select RS232C in the CONFIG settings
(CF54: 232C).
Remote Control
2
In the CONFIG settings, set the RS232C data rate (CF40), RS232C
data length (CF41), RS232C stop bit (CF42), and RS232C flow con t r ol
PAT-T 8kW 6-3
(CF43).
For the settings, see Table 6-1.

Protocol
Resume transmission
DC3
TXD
RXD
The RS232C terminal must pause transmission
within 10 characters after receiving DC3.
Within 10
characters
DC1
Pause
PAT
Code Function ASCII code
DC1 (Xon) Request to send 11H
DC3 (Xoff) Transmission stop request 13H
Table 6-1 shows the RS232C protocol. Underline indicates factory default
condition. The value inside the parentheses is the CONFIG setting value.
Table 6-1 RS232C protocol
Item Setting
Connector 9-pin D-sub terminal on the rear panel
Baudrate 1 200 bps/ 2 400 bps/ 4 800 bps/ 9 600 bps/ 19 200 bps/ 38400 bps
(1.2/2.4/4.8/9.6/19.2/38.4)
Data length (8 bits or 7 bits)
Stop bit (1 bit or 2 bits)
Parity Fixed to none
Flow (X-flow control) XFLOW / None (on/off)
Break signal
The break signal functions as a substitute for the IEEE488.1 dcl/sdc (Device Clear,
Selected Device Clear) message.
RS232C communication
Use flow control for RS232C communication. DC (device control) codes are used
as control codes.
Transmission/reception may not work correctly through unilateral transmission.
Table 6-2 DC codes
Fig.6-3 RS232C terminal and transmission control of the PAT
6-4 PAT-T 8kW

6.2.2 GPIB Interface (Option)
See
This interface valid only when the factory option GPIB interface board is installed.
GPIB connection
Use a standard IEEE488 cable to connect the PAT to the computer.
GPIB configuration
1
p. 3-15,
p. 3-21
Select GPIB (CF54: GPIb) in the CONFIG settings.
2
Set the address (CF51: 1 to 30) in the CONFIG settings.
The address is set to 1 as factory default setting.
GPIB function
Table 6-3 GPIB function
Function Subset Description
Source handshaking SH1 Full capability
Acceptor handshaking AH1 Full capability
Ta lk e r T6 Function available
Listener L4 Function available
Service request SR1 Full capability
Remote local RL1 Full capability
Parallel polling PP0 No capability
Device clear DC1 Full capability
Device trigger DT1 Full capability
Controller C0 No capability
Electrical interface E1 Open collector driver
6
Remote Control
Service request
Service request and serial polling functions are implemented.
PAT-T 8kW 6-5

6.2.3 USB Interface (Option)
This interface valid only when the factory option USB interface board is installed.
See
p. 6-10
A device driver supporting USB T&M Class (USBTMC) is required to control the
PAT through the USB interface. The USBTMC driver is automatically installed by
the VISA library.
USB configuration
See
p. 3-15,
p. 3-21
Select USB (CF54: uSb) in the CONFIG settings.
Service request
The PAT is equipped with service request and serial polling functions.
USB function
Complies with USB Specification 2.0.
Complies with USBTMC Specification 1.0 and USBTMC-USB488 Specification
1.0.
Data rate: 12 Mbps maximum (full speed)
VID (vendor ID): 0x0B3E
PID (product ID): 0x100E
You can check the VID (CF52) and PID (CF53) in the CONFIG settings.
6-6 PAT-T 8kW

6.2.4 LAN interface (Option)
This interface valid only when the factory option LAN interface board is installed.
See
p. 6-10
To use the LAN interface to control the PAT, middleware that supports the VXI-11
protocol must be installed on the controller. The middleware is installed
automatically by the VISA library.
There is a Web browser interface to the PAT embedded in the LAN interface board.
You can configure the LAN interface settings from your PC’s Web browser.
For information about be set in detail of the LAN interface, see the accompanying
CD-ROM.
For information on topics such as connecting to your corporate LAN, your IP
address, your host name, and security, contact your network administrator.
LAN connection
Use a standard LAN cable (category 5 and straight) to connect the PAT to a network
hub or router. Use a crossover cable when making a direct connection.
LAN setting
See
See
p. 3-22
p. 3-22
Normally, you should use a DHCP server to set the IP address automatically.
1
Select LAN (CF54 : LAn) by the CONFIG setting.
2
Select DHCP (CF55 : On) by the CONFIG setting.
3
Select AUTO IP (CF56 : On) by the CONFIG setting.
If you are connecting the PAT and the PC directly, set DHCP (CF55) to OFF, and set
AUTO IP (CF56) to ON to set the IP address automatically. You cannot set the IP
address from the panel. To set a fixed IP address, first set the IP address
automatically, and then set a fixed address by accessing the PAT through a Web
browser.
You can use the CONFIG settings (CF57 to CF60) to check the IP address.
When you are going to use a fixed IP address over a long period of time or at
intervals, we recommend that you specify a host name. To set a host name, access
the PAT through a Web browser.
6
Service request
The PAT is equipped with service request and serial polling functions.
Remote Control
LAN function
Depending on the operation that you perform through your Web browser, the PAT
may need to connect to the Internet.
Comply with LXI Class C, Specification 1.2
Comply with VXI-11 protocol
Communication speed: Maximum 100 Mbps (Auto negotiation)
PAT-T 8kW 6-7

DHCP client function
LAN RESET
REBOOT
LAN
NON AUTO-MDIX
NB01334-1
REBOOT switch
LAN RESET switch
*
Push here by using a fine point tool
AUTO IP function
From your Web browser, you can (Internet Explorer version 7.0 or later; Mozilla
Firefox version
3.0 or later; Opera version 9.0 or later or Safari version 3.0 or later):
• LAN setting, Security setting
• Use of temporary control application
• Firmware update
Fig.6-4 REBOOT switch and LAN RESET switch
■ REBOOT switch
When you keep pressing the "REBOOT" switch for more than 2 seconds, the LAN
will reboot. However, the setting condition of LAN interface will not be changed.
W ARNING
■ LAN RESET switch
When you keep pressing the "LAN RESET" switch for more than 2 seconds, all of
the setting of LAN interface returns to the factory default setting. It can be used
when neither the security password nor IP address are forgotten.
Either switch doesn't reflect to the panel setting of the product. In case the product is
in the state of remote mode, it can be switched (from the panel operation) to the
local mode.
• There are possible damage on the equipment or an electric shock.
The LAN interface can be accessed from any place on the network.
Set the security when it is necessary.
Security can be set by the password protection and the host
limitation by IP address. Refer to the accompanying CD-ROM for
setting procedure.
• Do not touch neither REBOOT switch nor LAN RESET switch inadvertently
while the automatic measurement system is in operation. It may cause to mis-
operation.
• The LAN interface should be shifted remotely by the command unlike other
interfaces. Set it by the SCPI command "SYSTem:REMote" to the remote state.
When you do a remote programming, transmit this command to the front of the
program.
6-8 PAT-T 8kW

6.3 Contents of the Included CD-ROM
Put the included CD-ROM into the CD-ROM drive. A start window will appear
momentarily. If the start window does not appear, open the CD-ROM in Windows
Explorer, and then double-click index.html to display the start window.
•Driver
IVI-COM
KI-VISA
• Operation manual
User’s Manual (PDF)
Communication Interface Manual (HTML)
6
Remote Control
PAT-T 8kW 6-9

6.4 Installing the VISA library
VISA (Virtual Instrument Software Architecture) was developed by the
VXIplug&play Systems Alliance. It is the standard specification for measurement
instrument connection software.
You have to install one of the following VISA libraries (driver software that is
implemented according to the VISA specifications).
Do not install multiple VISA libraries on the same PC. Doing so may cause errors.
VISA libraries that are older than the specified version do not support USB.
• NI-VISA by National Instruments (Ver. 3.0 or later, Ver. 3.2 or later for Windows
2000 and Windows XP)
• Agilent VISA by Agilent Technologies (Agilent IO Libraries M01.00 or later)
• KI-VISA Ver. 3.0.0 or later
Installing KI-VISA
KI-VISA is Kikusui’s original VISA library that supports VXIplug&play VISA
Specifications. You can download the most recent version of this library from the
Kikusui Electronics Corporation website (http://www.kikusui.co.jp/en/download/).
KI-VISA is not required if NI-VISA or Agilent VISA is already installed.
1
Load the accompanying CD-ROM into the CD-ROM drive.
2
Move to the VISA folder using the menu program of the CD-ROM or
Explorer.
3
Double-click Kivisa_x_x_x.exe.
The value for x varies depending on the revision of the VISA library stored on the CD-
ROM.
4
Proceed with the installation according to the instructions on the
screen.
After you install KI-VISA, the KI-VISA Instrument Explorer opens.
5
Click KI-VISA Config.
6
Click the USB(USBTMC) tab and then Run Driver
Wizard(WINUSB.SYS).
6-10 PAT-T 8kW
 Loading...
Loading...