Page 1

USB Wireless LAN CARD
User Manual
Page 2

Content
1. Product Introduction………………………………………………………………………………..2
2. USB Wireless LAN CARD Installation ……………………………………………………………4
3. Software Installation………………………………………………………………………………...6
4. Appendix………..…………………………………………………………………………………..18
USB Wireless LAN Card 1
Page 3
1. Product Introduction
Thank you for using USB WLAN product. This installation guide will help you install USB
Wireless LAN CARD and connect to the Internet quick & easy.
■ Package Contents
1. USB Wireless LAN CARD
2. Quick Installation Guide
3. Manual & Driver CD Disc
4. USB cable (Optional)
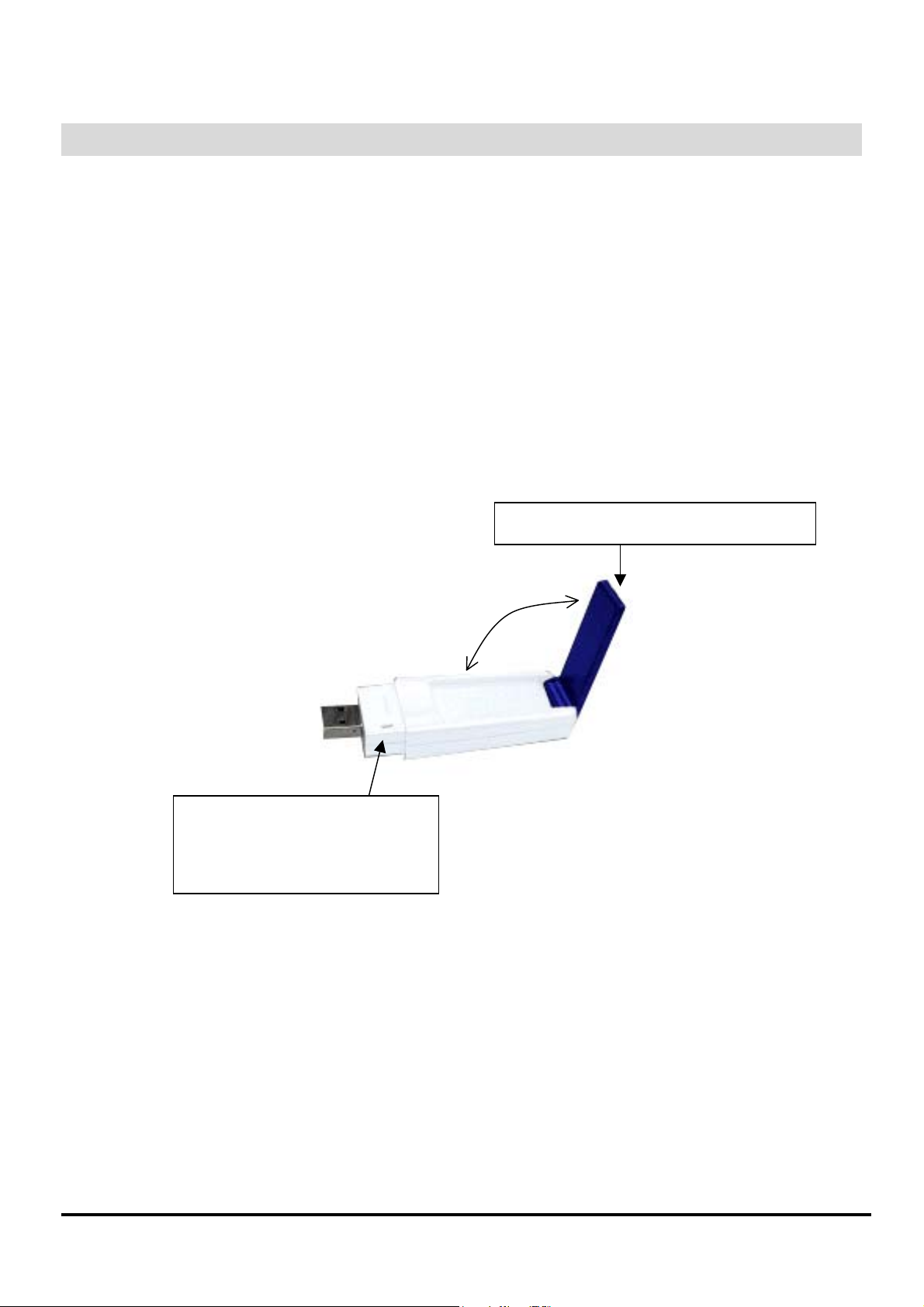
■ Form Factor
LED Indicator:
Green: Connected
Blinking: Not connected
High performance antenna
90°
■ System Requirements
1. Desktop/ Laptop with USB port and CD-ROM driver
2. Operating System: Linux/ Mac OS X/ Windows 98 SE/ME/2000/XP
USB Wireless LAN Card 2
Page 4
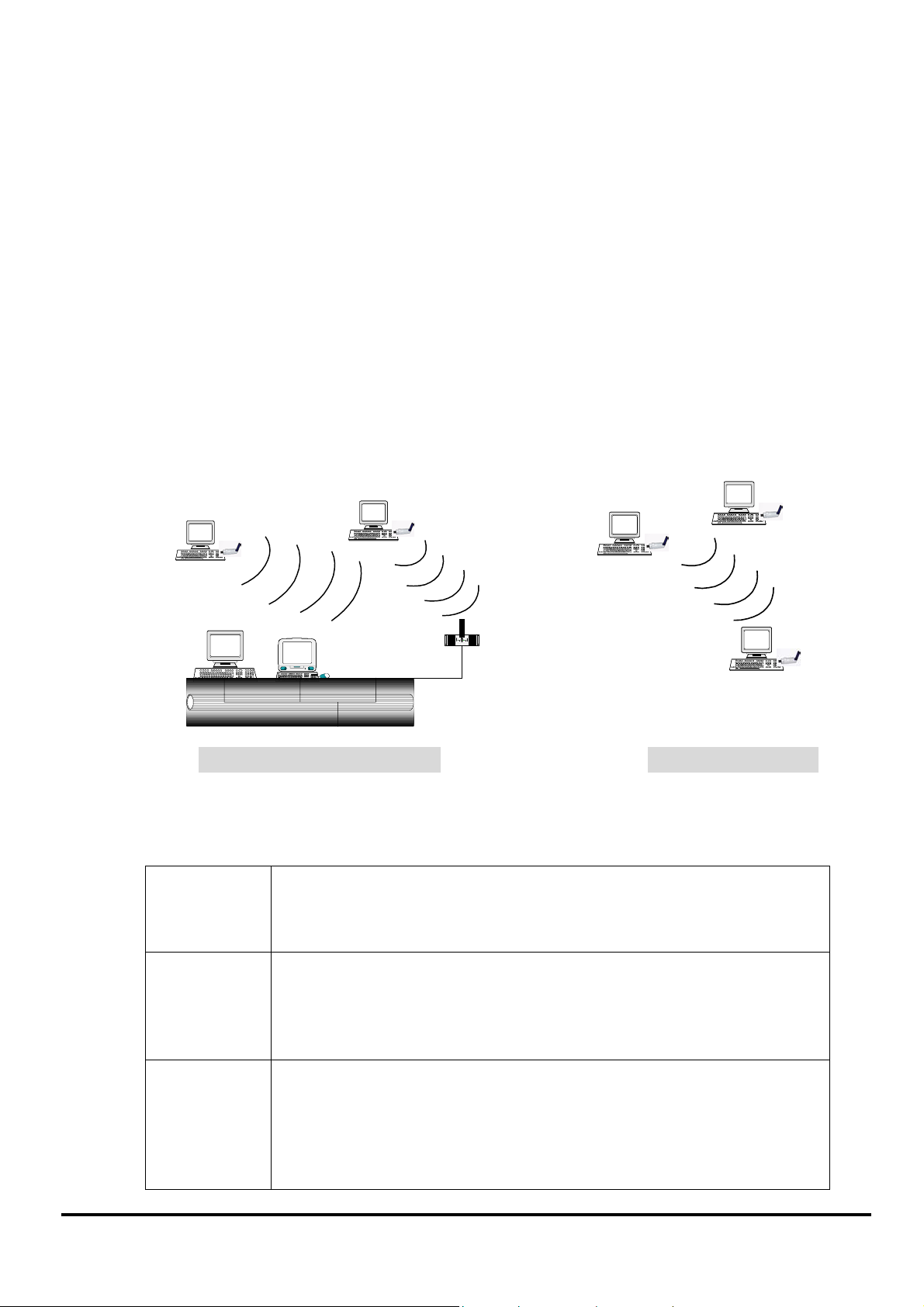
■ Applied Environments
There are two application modes for this WLAN card, the “Ad-Hoc mode” and the “Infrastructure
mode”. (For further explain, please refer to the “WLAN Application Modes” below) Different modes
require different settings. Please check the environment first.
Infrastructure mode: Via “Access Point” (AP) to connect to the Internet. This mode further gives
wireless access to Internet or data sharing under a previously wired
environment.
Ad-Hoc mode: Connecting to other computer with WLAN card. This mode does not need AP to
connect to each other.
WIRELESS
Ad-Hoc
iMac
Test
On On
Smart
Replace
Load BatteryLine
Battery
Boost
Battery
INFRASTRUCTURE
Infrastructure mode Ad-Hoc mode
■ WLAN Application Modes
Ad-Hoc Mode
Infrastructure
Mode
Advantages Comparing to Ad-Hoc mode, Infrastructure mode has the following
Ad-Hoc mode is a Peer-to-Peer mode. Without an AP, computers can also
connect to each other by USB Wireless LAN CARD. With this mode,
computers are able to share data or connect to the Internet if one of them
is already connected to.
Infrastructure mode including an AP, unlike Ad-Hoc mode, enabling users
to best utilizes the frequency bandwidth of the AP.
This mode enables users to integrate wired and wireless infrastructures.
Through APs, wireless users are able to access wired resources, for
example: Internet, database, and printers.
advantages:
Longer distance: Through AP, the wireless access distance is longer.
Roaming: The wireless devices can move within the AP support
area.
Integration of wired and wireless environment.
USB Wireless LAN Card 3
Page 5

2. USB Wireless LAN Card Installation
Note: The screens showed below are from Windows 2000. For other Windows system, the steps are the same, but
the screens shown will be a little different.
1. After plugging USB Wireless LAN Card, the USB stick, into your PC, it will automatically find
and alert a New USB Device. Click “Next” to continue.
2. You’ll see the following screen. Please choose the default item (with “Recommended”) and click
“Next”.
3. Please choose “CD ROM”, and insert the “Manual & Driver CD-ROM”, then click “Next”.
USB Wireless LAN Card 4
Page 6

3. Your PC will recognize the device of “USB Wireless LAN Card”, and click “Next” to install driver.
4. Finally, click the “Finish” to leave this dialogue window.
5. After installation, please check whether the installation is success.
Start→Setting→Control Panel
Double click “System”→click “Hardware”→Device manager→Network Adapters. If the
install is success, it should include “USB Wireless Lan CARD” item.
USB Wireless LAN Card 5
Page 7

3. Software Installation
1. Insert the “Manual & Driver CD-ROM” into the CD-ROM driver of your PC, and you’ll see the
software installation window as shown below.
2. Click “Setup Driver & Utility”, and choose the “default” item through the installation process.
3. After successful installation, you’ll see the new icon appear in the Icon Tray.
4. The software will automatically search for available APs for connecting to the Internet.
5. If the installation fell, the Icon appeared is in red color.
USB Wireless LAN Card 6
Page 8

Software Utility
1. Click the icon and the software utility window shows up.
2. Status window allows you to change Operation Mode, Channel, SSID, Tx Rate, Int Roaming,
and Radio. It also shows the connecting signal and quality for you to adjust related
infrastructures and configurations.
3. Statistics window: It shows the real time transmitting and receiving status.
USB Wireless LAN Card 7
Page 9

4. Site Survey window: Click “Scan” to search all available WLAN devices and their status in
current environment. Double click the device you want to connect.
5. Encryption window: USB Wireless LAN Card is able to provide 64/128Bit encryption.
USB Wireless LAN Card 8
Page 10

6. Advanced window: It provides you to adjust PREAMBLE, Fragmentation Threshold,
RTS/CTS Threshold, and Power Save function.
7. Profiles window: It provides customers to change settings and save them in the configuration
file.
USB Wireless LAN Card 9
Page 11

8. Info window: It shows the latest software version and MAC address.
USB Wireless LAN Card 10
Page 12

Appendix
1. Operation Mode:
USB Wireless Lan Card has two modes, ‘Infrastructure’ and ‘Ad-Hoc’. The default setting is
“Infrastructure”.
(Please refer to the Product Introduction)
2. Channel:
The channel setting should follow the regulation of the local government. For ‘Infrastructure’
mode, the channel does not need to be set. It will automatically change to the same channel as AP’s.
In ‘Ad-Hoc’ mode, users can change the channel to match the connected computer.
3. SSID:
When STA (WLAN card) is in Ad-Hoc mode, all connecting STA should have the same SSID.
When STA is in Infrastructure mode, the SSID will change to the same as AP’s SSID.
Important: Capital and non-capital are different words in SSID setting.
4. Tx Rate:
It determine STA’s transmitting rate. There are 5 rated to choose, 1, 2, 5.5, 11Mbps, and Auto. The
default setting is “Auto”.
5. Int. Roaming: Its default setting is ‘Disable’, and does not need to be adjusted.
6. Radio:
The default setting is ‘ON’. It means to stop the STA’s RF function. If your WLAN card is
embedded, you can stop its function by turning the Radio “ON”.
7. Encryption:
USB Wireless Lan Card provides 64/128bits encryption. Choose “disable”, if you do not need this
function.
When using Encryption, there are two configurations to setting:
Choose from encryption key 1~4 to encrypt.
For 64bits encryption:
Using letters & numbers: 5 digits (“a-z”,”A-Z”,”0-9”)
Hexadecimal: 10 digits (“a-f”,”A-F”,”0-9”)
For 128bits encryption:
Using letters & numbers: 13 digits (“a-z”,”A-Z”,”0-9”)
Hexadecimal: 26 digits (“a-f”,”A-F”,”0-9”)
Choose the Authentication type from open system, share key, and auto type. The default setting
USB Wireless LAN Card 11
Page 13

is ‘auto’.
8. PREAMBLE:
This function determines the PREAMBLE TYPE that physical layer’s PLCP will use. There are
three modes to choose: LONG, SHORT, and AUTO. The default setting is AUTO, and the system
will automatically choose the optimized mode.
9. Tx Power Level (mW): Does not open to change.
10. Fragmentation Threshold:
This configuration determines whether needs to fragment the Frame during transmit. When
fragment, if the transmit fell, computer only resent the fell frame instead of the whole file again.
When the frequency band used is not clear, i.e. The S/N ratio is low, transmit is easier to fell. Under
this situation, fragmentation is a good way to increase efficiency.
11. RTS/CTS:
When frame smaller than the RTS Threshold value, the STA will automatically transmit the frame
if the channel is available. If the channel is used, STA will follow the 802.11b regulation that would
ask the receiving device whether to send the frame. This will take more time for devices to check
with each other, but it also prevents the loss of frames.
12. Power Save:
Determine whether to use power saving mode. The default setting is ‘Disable’.
USB Wireless LAN Card 12
 Loading...
Loading...