Page 1

75000 Series C
Configuration and User Guide
Keysight E8491B IEEE 1394 PC Link to VXI
Page 2

Page 3

Notices
© Keysight Technologies, Inc. 1999-2019
No part of this manual may be reproduced in any form or by any means
(including electronic storage and retrieval
or translation into a foreign language)
without prior agreement and written consent from Keysight Technologies, Inc. as
governed by United States and international copyright laws.
Manual Part Number
E8491-90001
Edition
Third Edition, August 2019
Published by
Keysight Technologies, Inc.
900 S. Taft Ave.
Loveland, CO 80537 USA
Sales and Technical Support
To contact Keysight for sales and technical support, refer to the support links on
the following Keysight websites:
www.keysight.com/find/E8491B
(product-specific information and support, software and documentation
updates)
www.keysight.com/find/assist (world-
wide contact information for repair and
service)
Declaration of Conformity
Declarations of Conformity for this product and for other Keysight products may
be downloaded from the Web. Go to
http://keysight.com/go/conformity and
click on “Declarations of Conformity.” You
can then search by product number to
find the latest Declaration of Conformity.
Technology Licenses
The hardware and/or software described
in this document are furnished under a
license and may be used or copied only in
accordance with the terms of such
license.
Warranty
THE MATERIAL CONTAINED IN THIS
DOCUMENT IS PROVIDED “AS IS,” AND
IS SUBJECT TO BEING CHANGED,
WITHOUT NOTICE, IN FUTURE EDITIONS. FURTHER, TO THE MAXIMUM
EXTENT PERMITTED BY APPLICABLE
LAW, KEYSIGHT DISCLAIMS ALL WARRANTIES, EITHER EXPRESS OR IMPLIED,
WITH REGARD TO THIS MANUAL AND
ANY INFORMATION CONTAINED
HEREIN, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED
TO THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR A
PARTICULAR PURPOSE. KEYSIGHT
SHALL NOT BE LIABLE FOR ERRORS OR
FOR INCIDENTAL OR CONSEQUENTIAL
DAMAGES IN CONNECTION WITH THE
FURNISHING, USE, OR PERFORMANCE
OF THIS DOCUMENT OR OF ANY INFORMATION CONTAINED HEREIN. SHOULD
KEYSIGHT AND THE USER HAVE A SEPARATE WRITTEN AGREEMENT WITH
WARRANTY TERMS COVERING THE
MATERIAL IN THIS DOCUMENT THAT
CONFLICT WITH THESE TERMS, THE
WARRANTY TERMS IN THE SEPARATE
AGREEMENT SHALL CONTROL.
Keysight Technologies does not warrant
third-party system-level (combination of
chassis, controllers, modules, etc.) performance, safety, or regulatory compliance unless specifically stated.
DFARS/Restricted Rights
Notices
If software is for use in the performance
of a U.S. Government prime contract or
subcontract, Software is delivered and
licensed as “Commercial computer software” as defined in DFAR 252.227-7014
(June 1995), or as a “commercial item” as
defined in FAR 2.101(a) or as “Restricted
computer software” as defined in FAR
52.227-19 (June 1987) or any equivalent
agency regulation or contract clause.
Use, duplication or disclosure of Software
is subject to Keysight Technologies’ standard commercial license terms, and nonDOD Departments and Agencies of the
U.S. Government will receive no greater
than Restricted Rights as defined in FAR
52.227-19(c)(1-2) (June 1987). U.S. Government users will receive no greater
than Limited Rights as defined in FAR
52.227-14 (June 1987) or DFAR 252.2277015 (b)(2) (November 1995), as applicable in any technical data.
Page 4

Safety Information
The following general safety precautions must be observed during all
phases of operation of this instrument.
Failure to comply with these precautions or with specific warnings or operating instructions in the product
manuals violates safety standards of
design, manufacture, and intended use
of the instrument. Keysight Technologies assumes no liability for the customer's failure to comply with these
requirements.
General
Do not use this product in any manner not
specified by the manufacturer. The protective features of this product must not be
impaired if it is used in a manner specified in
the operation instructions.
Before Applying Power
Verify that all safety precautions are taken.
Make all connections to the unit before
applying power. Note the external markings
described under “Safety Symbols”.
Ground the Instrument
Keysight chassis’ are provided with a
grounding-type power plug. The
instrument chassis and cover must be
connected to an electrical ground to
minimize shock hazard. The ground pin
must be firmly connected to an electrical ground (safety ground) terminal at
the power outlet. Any interruption of
the protective (grounding) conductor
or disconnection of the protective
earth terminal will cause a potential
shock hazard that could result in personal injury.
Do Not Operate in an Explosive
Atmosphere
Do not operate the module/chassis in
the presence of flammable gases or
fumes.
Do Not Operate Near Flammable
Liquids
Do not operate the module/chassis in
the presence of flammable liquids or
near containers of such liquids.
Cleaning
Clean the outside of the Keysight module/chassis with a soft, lint-free,
slightly dampened cloth. Do not use
detergent or chemical solvents.
Do Not Remove Instrument Cover
Only qualified, service-trained personnel who are aware of the hazards
involved should remove instrument
covers. Always disconnect the power
cable and any external circuits before
removing the instrument cover.
Keep away from live circuits
Operating personnel must not remove
equipment covers or shields. Procedures involving the removal of covers
and shields are for use by servicetrained personnel only. Under certain
conditions, dangerous voltages may
exist even with the equipment
switched off. To avoid dangerous electrical shock, DO NOT perform procedures involving cover or shield removal
unless you are qualified to do so.
DO NOT operate damaged
equipment
Whenever it is possible that the safety
protection features built into this product have been impaired, either through
physical damage, excessive moisture,
or any other reason, REMOVE POWER
and do not use the product until safe
operation can be verified by servicetrained personnel. If necessary, return
the product to a Keysight Technologies
Sales and Service Office for service and
repair to ensure the safety features are
maintained.
DO NOT block the primary
disconnect
The primary disconnect device is the
appliance connector/power cord when
a chassis used by itself, but when
installed into a rack or system the disconnect may be impaired and must be
considered part of the installation.
Do Not Modify the Instrument
Do not install substitute parts or perform any unauthorized modification to
the product. Return the product to a
Keysight Sales and Service Office to
ensure that safety features are maintained.
In Case of Damage
Instruments that appear damaged or
defective should be made inoperative
and secured against unintended operation until they can be repaired by
qualified service personnel
Do NOT block vents and fan exhaust:
To ensure adequate cooling and ventilation, leave a gap of at least 50mm
(2") around vent holes on both sides of
the chassis.
Do NOT operate with empty slots: To
ensure proper cooling and avoid damaging equipment, fill each empty slot
with an AXIe filler panel module.
Do NOT stack free-standing chassis:
Stacked chassis should be rackmounted.
All modules are grounded through the
chassis: During installation, tighten
each module's retaining screws to
secure the module to the chassis and
to make the ground connection.
Operator is responsible to maintain
safe operating conditions. To ensure
safe operating conditions, modules
should not be operated beyond the full
temperature range specified in the
Environmental and physical specification. Exceeding safe operating conditions can result in shorter lifespan,
improper module performance and
user safety issues. When the modules
are in use and operation within the
specified full temperature range is not
maintained, module surface temperatures may exceed safe handling conditions which can cause discomfort or
burns if touched. In the event of a
module exceeding the full temperature
range, always allow the module to cool
before touching or removing modules
from the chassis.
vi
Page 5

Safety Symbols
A CAUTION denotes a hazard. It
calls attention to an operating procedure or practice, that, if not correctly performed or adhered to
could result in damage to the
product or loss of important data.
Do not proceed beyond a CAUTION
notice until the indicated conditions are fully understood and met.
A WARNING denotes a hazard. It
calls attention to an operating procedure or practice, that, if not correctly performed or adhered to,
could result in personal injury or
death. Do not proceed beyond a
WARNING notice until the indicated conditions are fully understood and met.
Products display the following symbols:
Warning, risk of electric
shock
Refer to manual for additional safety information.
Earth Ground.
Chassis Ground.
Alternating Current (AC).
Direct Current (DC)
vii
Page 6

viii
Page 7

Contents
1 Introduction
Using the IEEE 1394 Serial Bus in VXI Systems . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
2 Interface Installation and Configuration
Using this Chapter. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
Component Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
The Keysight E8491B PC Link to VXI Interconnect. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
The OHCI-Compatible PCI-to-IEEE 1394 Host Adapter . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
The Keysight I/O Libraries . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Using this Manual. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Chapter 2: Interface Installation and Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Chapter 3: VXI Programming Using the IEEE 1394 Serial Bus. . . . . . . . 14
Chapter 4: IEEE 1394 Fundamentals and Interface Overview . . . . . . . . 14
Appendix A: Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Appendix B: Editing the E8491B Resource Manager Configuration . . . 14
Additional Information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Step 1: Installing the IEEE 1394 Host Adapter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
Connecting the Power Cable . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
Where to go Next . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
Step 2: Installing the E8491B Interconnect . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
Connecting the E8491B to the Host Adapter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
Alternate Configurations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
Where to go Next . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
Step 3: Installing VXI Instruments . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
Installing C-size Instruments. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
Installing A- and B-size Instruments . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
Step 4: Installing the Keysight I/O Libraries . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
Configuring the E8491B Interconnect . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
Editing the E8491B Configuration. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
Editing the E8491B Configuration on Windows 95 Platforms . . . . . . . . 32
Step 5: Installing Keysight VXIplug&play Instrument Drivers . . . . . . . . . . . 33
Step 6. Verifying the Installation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
Using Instrument Soft Front Panels . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
Viewing the Resource Manager Output . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
Troubleshooting Installation Problems. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
Running the Resource Manager. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
3 VXI Programming Using the IEEE 1394 Serial Bus
Using this Chapter. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
Programming Register-Based and Message-Based VXI Instruments. . . . . 41
Opening Instrument Sessions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
Keysight VXIplug&play . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
Keysight VISA . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
SICL . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
Optimizing Programs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
Block Data Transfers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
Block Transfers using Keysight VXIplug&play Drivers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
Block Transfers using Keysight VISA. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46
Keysight E8491B IEEE 1394 to VXI User Guide ix
Page 8

Keysight E8491B Triggering . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
Using Triggers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
Configuring the E8491B Trig In and Trig Out Ports . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 51
Triggering Example . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 51
Trigger Pull Up . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 54
Using Keysight E8491B Shared Memory . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 54
Locating E8491B Shared Memory. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 55
Locating Shared Memory Using Keysight VISA . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 55
Locating Shared Memory Using SICL . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 55
Locating Shared Memory by Viewing the Resource Manager Output . . 55
Example Programs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 56
Storing Readings in Shared Memory - Keysight VISA Example . . . . . . . 57
Storing Readings in Shared Memory - SICL Example . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 61
4 IEEE 1394 Fundamentals and Interface Overview
Using this Chapter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 65
IEEE 1394 Topology and Terminology . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 66
Features of the IEEE 1394 Bus . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 67
Optimizing the Configuration. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 68
IEEE 1394 Data Transfer Protocol. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 69
Asynchronous Data Transfers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 70
Fair Arbitration Protocol. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 70
VXI Data Transfers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 70
OHCI-Compatible Host Adapter and Interface Cable . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 71
The Keysight E8491B PC to VXI Interconnect . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 72
Using the Keysight E8491B with the Keysight E1406 Command Module74
The Keysight I/O Libraries. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 74
A Specifications
Interface Characteristics. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 77
VXI Characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 78
General . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 78
CLK 10 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 78
External Trigger Input . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 78
External Trigger Output . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 79
Trigger Delays . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 79
Cooling . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 79
B Editing the Keysight E8491B Resource Manager Configuration
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 81
Configuration File Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 81
The names.cf Configuration File . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 84
The oride.cf Configuration File. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 84
The vmedev.cf Configuration File . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 84
The cmdrsrvt.cf Configuration File . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 84
The dynamic.cf Configuration File . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 85
The irq.cf Configuration File. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 85
The ttltrig.cf Configuration File . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 85
x Keysight E8491B IEEE 1394 to VXI User Guide
Page 9

The vximanuf.cf Configuration File . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 85
The vximodel.cf Configuration File . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 86
Utility Function Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 86
Using ivxisc . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 86
Using iclear . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 88
Keysight E8491B IEEE 1394 to VXI User Guide xi
Page 10

xii Keysight E8491B IEEE 1394 to VXI User Guide
Page 11

Keysight E8491B IEEE 1394 PC Link to VXI
Configuration and User Guide
1 Introduction
Using the IEEE 1394 Serial Bus in VXI Systems
The IEEE 1394 Serial Bus (FireWire) is a high-speed bus that has been
implemented as an I/O interface between external PCs and Keysight VXI
systems. The bus links the PC backplane to the VXI mainframe backplane. This
manual describes the implementation, configuration, and use of this interface.
Component Overview
Implementation of the IEEE 1394 serial bus as an I/O interface for Keysight VXI
systems is provided through three components and two operating systems:
– Keysight E8491B PC Link to VXI Interconnect
– OHCI-compatible PCI-to-IEEE 1394 Host Adapter
– Keysight I/O Libraries
– WIN 95 and WIN NT operating systems
The Keysight E8491B PC Link to VXI Interconnect
The E8491B is the VXI hardware that links the VXI mainframe backplane to the
IEEE 1394 serial bus. The E8491B is a 1-slot, C-size, message-based device that
is installed in mainframe slot 0.
The OHCI-Compatible PCI-to-IEEE 1394 Host Adapter
The OHCI PCI-to-1394 Host Adapter card is installed in the PC and links the
computer’s (PCI) backplane to the IEEE 1394 bus. The OHCI adapter has three
external IEEE 1394 ports and can support up to 16 E8491Bs.
The Keysight I/O Libraries
The Keysight I/O Libraries provide the Keysight VISA and Keysight SICL drivers
required to use the E8491B. Included with the libraries are the drivers for the
OHCI-compatible host adapter.
13
Page 12

Introduction Using the IEEE 1394 Serial Bus in VXI Systems
Using this Manual
This manual is organized to help you install, configure, and begin using the IEEE
1394 serial bus as quickly and efficiently as possible. The following information
outlines the contents of the other chapters, and identifies the areas of
programming a VXI system that are NOT covered in this manual.
Chapter 2: Interface Installation and Configuration
This chapter contains information on installing the E8491B hardware and its
drivers (the Keysight I/O Libraries). Also included is information on installing VXI
instruments, installing Keysight VXIplug&play drivers, and on verifying the
system.
Chapter 3: VXI Programming Using the IEEE 1394 Serial Bus
This chapter contains the information necessary to begin communicating with
VXI instruments through the E8491B and IEEE 1394 serial bus. The chapter
contains information on optimizing system performance using block data
transfers, and also covers triggering and using E8491B shared memory.
Chapter 4: IEEE 1394 Fundamentals and Interface Overview
This chapter describes the IEEE 1394 serial bus and how it is implemented in
Keysight VXI systems. It defines the bus terminology and data transfer protocol.
Appendix A: Specifications
Appendix A contains the operating and performance specifications of the
E8491B.
Appendix B: Editing the E8491B Resource Manager Configuration
Appendix B contains information on editing your VXI system configuration as set
by the resource manager. It describes selected configuration files and utility
functions used to view and modify your configuration.
Additional Information
Programming the E8491B is through Keysight VISA and Keysight SICL functions.
Although this manual identifies the specific functions used, you will need to refer
to the Keysight VISA and Keysight SICL manuals for detailed information.
Also, included with the Keysight I/O Libraries is the utility ‘I_O Config’. This utility
is used to configure the E8491B and has a help file associated with it.
14 Keysight E8491B IEEE 1394 PC Link to VXI User Guide
Page 13

Using the IEEE 1394 Serial Bus in VXI Systems Introduction
Pop-up or pull-down menus displayed by the Keysight I/O
Libraries software will show I/O Libraries as “I_O Libraries” and I/O
Config as “I_O Config” because the “/” cannot be displayed. The
“/” character is therefore replaced by the underscore character.
Keysight E8491B IEEE 1394 PC Link to VXI User Guide 15
Page 14

Introduction Using the IEEE 1394 Serial Bus in VXI Systems
16 Keysight E8491B IEEE 1394 PC Link to VXI User Guide
Page 15

Keysight E8491B IEEE 1394 PC Link to VXI
Configuration and User Guide
2 Interface Installation and
Configuration
Using this Chapter
This chapter contains information necessary to install and configure the IEEE
1394 host adapter (if required) and the Keysight E8491B interconnect. The
installation sequence and other topics covered in this chapter are as follows:
Step 1: Installing the IEEE 1394 Host Adapter page 17
Step 2: Installing the E8491B Interconnect page 22
Step 3: Installing VXI Instruments page 25
Step 4: Installing the Keysight I/O Libraries page 29
Step 5: Installing Keysight VXIplug&play Instrument
Drivers page 33
Step 6. Verifying the Installation page 34
Troubleshooting Installation Problems page 39
Running the Resource Manager page 39
Step 1: Installing the IEEE 1394 Host Adapter
The IEEE 1394 adapter shipped as Option 001 to the Keysight E8491B is an
OHCI-compatible PCI-to-IEEE 1394 Host Adapter. Included with the adapter is a
cable for powering IEEE 1394 devices and a 4.5m interface cable.
Refer to your computer’s documentation for specific
instructions about the installation of PCI adapters.
If your personal computer (PC) currently has a Solectron OHCI403
PCI-to- IEEE 1394 host adapter, a later version OHCI-compatible
PCI-to-IEEE 1394 host adapter or a built-in IEEE 1394 port,
proceed to Step 2: Installing the Keysight E8491 Interconnect.
17
Page 16

Interface Installation and Configuration Using this Chapter
External
IEEE 1394
Connectors
12 VDC
Power Connector
The layout of a typical host adapter is shown in Figure 2-1.
Figure 2-1 Layout of a Typical OHCI-Compatible PCI-to-IEEE 1394 Host Adapter.
Turn off and disconnect the power to your computer and to
any peripheral devices before installing the host adapter.
Refer to your computer’s documentation for specific
instructions about the installation of PCI adapters.
1 Remove the computer chassis cover to expose the expansion slots and
external access covers.
2 Locate an unused, unobstructed PCI bus expansion slot (Figure 2-2) that
supports bus mastering. (PCI bus slots are usually white or ivory.) See your
computer documentation to determine if the PCI slot supports bus mastering.
18 Keysight E8491B IEEE 1394 PC Link to VXI User Guide
Page 17

Using this Chapter Interface Installation and Configuration
PCI expansion slots
(usually white or ivory)
shared slot
Figure 2-2 Locating a PCI bus Expansion Slot.
Many computer PCI systems have one pair of ISA and PCI slots
close to each other. This saves space and allows you to install
either an ISA card or a PCI card in the slot pair.
Keysight E8491B IEEE 1394 PC Link to VXI User Guide 19
Page 18
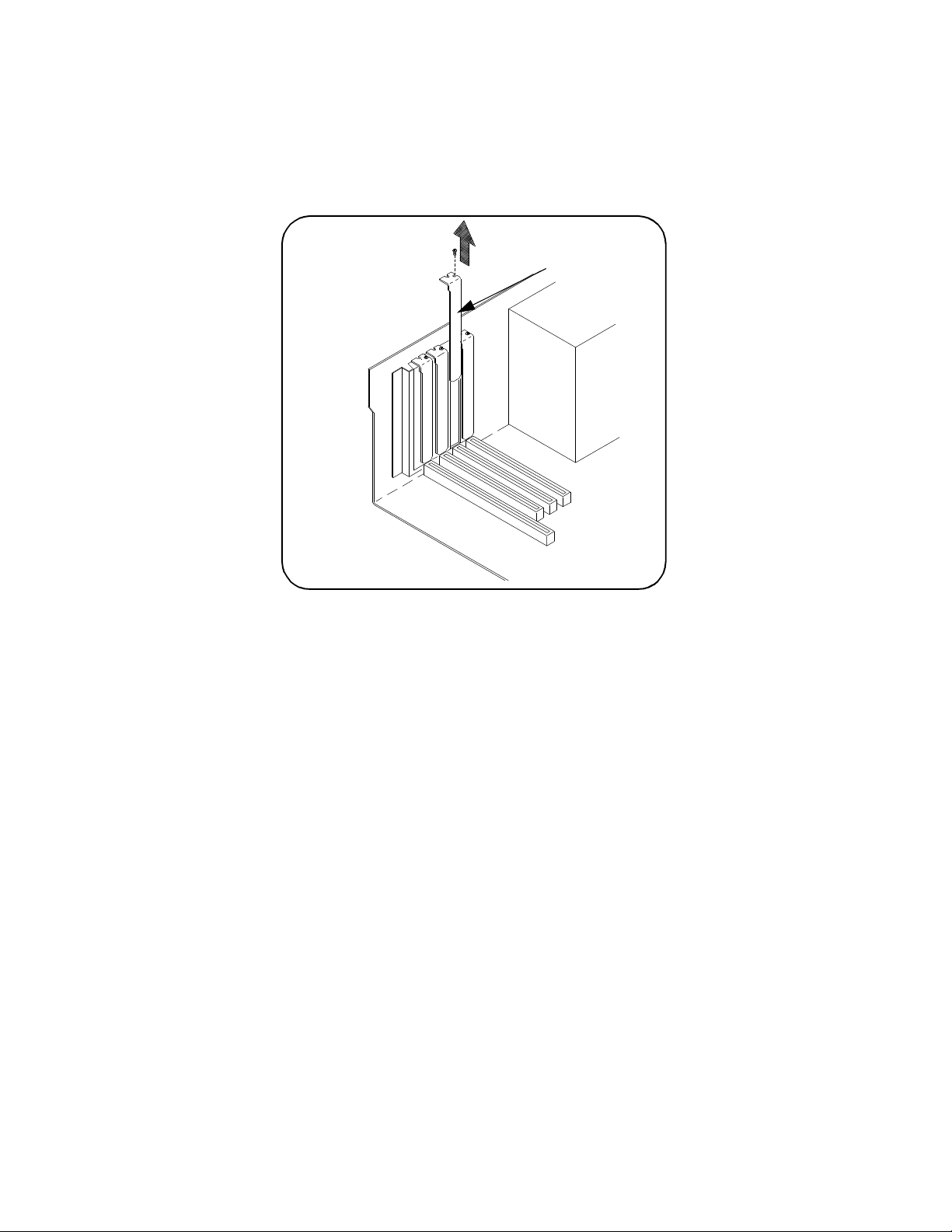
Interface Installation and Configuration Using this Chapter
3 Remove the corresponding expansion slot cover from the computer chassis
(Figure 2-3).
expansion slot cover
Figure 2-3 Removing the PC Expansion Slot Cover.
20 Keysight E8491B IEEE 1394 PC Link to VXI User Guide
Page 19

Using this Chapter Interface Installation and Configuration
Host
Adapter
4 Align the bus contacts on the bottom of the host adapter with the PCI bus
slot. Carefully, but firmly, press the adapter into the slot.
Figure 2-4 Installing the Host Adapter.
5 Secure the host adapter bracket to the computer chassis with the screw from
the expansion slot cover removed in step C.
Connecting the Power Cable
6 Connect the power cable between the adapter and the PC as shown in Figure
2-5. This provides power from the adapter to devices along the interface via
the interface cable. This allows you to cycle power on any VXI mainframe in
multi-frame systems without affecting other frames. The power is also
available to other IEEE 1394 devices that may be part of the interface
network. The host adapter is capable of supplying 12V with a maximum
current draw of 0.5 amps total to all three IEEE 1394 connectors.
Keysight E8491B IEEE 1394 PC Link to VXI User Guide 21
Page 20

Interface Installation and Configuration Using this Chapter
Host
Adapter
Power In
(From System
Power Out
(To Disk Drives)
12V DC
Connector
Power
Power Supply)
Figure 2-5 Connecting the Power Cable Between the PC and the Host Adapter.
7 Replace the computer cover. Connect one end of the interface cable to either
adapter external connector.
Where to go Next
– If you are installing the IEEE 1394 interface for the first time:
Continue with “Step 2: Installing the E8491B Interconnect.”
– If the E8491B and your VXI instruments are already installed:
Proceed to “Step 4: Installing the Keysight I/O Libraries.” Note that the
Keysight I/O Libraries contain the OHCI-compatible host adapter drivers.
Refer to Chapter 4: IEEE 1394 Fundamentals and Interface
Overview for more information on the OHCI-compatible
PCI-to-IEEE 1394 host adapter.
Step 2: Installing the E8491B Interconnect
The E8491B interconnect links the IEEE 1394 bus to the backplane of the VXI
mainframe. The E8491B is a C-size device with VXI Resource Manager and Slot 0
capability.
There are no configuration switches on the E8491B. The device’s logical address
is 0 and it provides the system’s resource manager functionality via software that
is part of the Keysight I/O Libraries. Its VXI servant area is 255, therefore; it is the
interface to all VXI devices with logical addresses between 1 and 255. The
E8491B is normally, but not required to be, installed in mainframe slot 0.
22 Keysight E8491B IEEE 1394 PC Link to VXI User Guide
Page 21

Using this Chapter Interface Installation and Configuration
Retaining
Screws
Extraction
Levers
Slide the module
into the mainframe
until it plugs into the
backplane connectors
Seat the module by
pushing in the
extraction levers
Refer to “Alternate Configurations” for information on using the
E8491B with the Keysight E1406 Command Module and using it in
VXI-MXI systems.
1 If power is applied to the VXI mainframe, remove power to the VXI
mainframe and disconnect all power sources that may be applied
to any instruments.
2 Insert the E8491B into mainframe slot 0 by aligning the module
with the guides inside the mainframe (Figure 2-6). Slowly push the
module into the slot until it seats in the backplane connectors. It
may be necessary to pull out (not remove) the retaining screws in
order to seat the device securely in the connectors.
Figure 2-6 Installing the E8491B in the VXI Mainframe.
3 Tighten the retaining screws on the top and bottom of the module.
Keysight E8491B IEEE 1394 PC Link to VXI User Guide 23
Page 22

Interface Installation and Configuration Using this Chapter
VXI
PC
VXI
VXI
VXI
PC
VXI
VXI VXI
TREE CONFIGURATION
DAISY-CHAIN CONFIGURATION
*
*
A second connection creates a closed loop and is not allowed
Connecting the E8491B to the Host Adapter
4 Connect the interface cable from the host adapter to E8491B port A, B, or C.
The ports are identical and unused ports are available to connect additional
E8491Bs and other IEEE 1394 devices in a daisy-chain or tree configuration
(Figure 2-7). Notice that there can be no closed loops.
Figure 2-7 IEEE 1394 Interface Configurations.
I/O performance is impacted slightly by the hardware configuration.The VXI
mainframe with the fewest number of hops (cable links) to the PC has the highest
priority. However, each mainframe has equal access to the bus during each data
transfer interval.
Alternate Configurations
Refer to Chapter 4: IEEE 1394 Fundamentals and Interface Overview
for information on the topology and terms associated with the IEEE
1394 bus.
Certain applications may include the E1406A Command Module as an GPIB
interface to selected instruments. In this configuration, the E8491B must be the
resource manager since its logical address is always 0. It is generally installed in
mainframe slot 0 so that it also provides the system’s slot 0 functionality.
24 Keysight E8491B IEEE 1394 PC Link to VXI User Guide
Page 23

Using this Chapter Interface Installation and Configuration
If you want the E1406 to provide slot 0 functionality in addition to providing an
GPIB interface, set its configuration as follows:
1 Set the E1406 logical address to a value other than 0.
2 Set the Slot 0 and System Controller switches to “Enable” (default).
3 Set the CLK 10 source to “Internal” (default).
4 Set the VME BTO Disable switch to 0 - Enable (default). Set VME Bus Timeout
(BTO) on the E8491B to ‘Off’ (see “Editing the
E8491B Configuration” later in this chapter).
5 Set the E1406 servant area to include the logical addresses of those
instruments it is to control. Note:
E1406 servant area = (E1406 logical address + 1) through
(E1406 logical address + servant area switch setting)
6 Install the E1406 in slot 0.
If the E1406 is not the slot 0 device, its slot 0 functionality must be disabled.
From step 2 above, set the E1406A Slot 0 and System Controller switches to
“Disable”. From step 4, set its VME BTO Disable switch 1 and ensure that VME
Bus Timeout (BTO) on the E8491B is set to ‘On’.
If you are using the E8491B in a configuration with multiple mainframes linked
with VXI-MXI extender cards, the E8491B must be the resource manager;
however, VME Bus Timeout (BTO) must be disabled (off - Step 4 above). Again,
the E8491B is generally installed in mainframe slot 0 so that it also provides the
system’s slot 0 functionality. Refer to the MXI documentation for configuration
guidelines based on where the E8491B is installed.
Where to go Next
– If you are installing the IEEE 1394 interface for the first time:
Continue with “Step 3: Installing VXI Instruments.”
– If your VXI instruments are already installed:
Proceed to “Step 4: Installing the Keysight I/O Libraries.”
Step 3: Installing VXI Instruments
Generally, any VXI instrument can be installed in any slot other than slot 0.
When installing instruments, notice that the E8491B and the IEEE 1394 bus do
not extend the (VXI) backplane between frames in multi-frame VXI systems (MXI
cards are required). This means that the multimeter and multiplexers in a VXI
scanning multimeter for example, must be installed in the same mainframe (in
adjacent slots). Devices sharing the VXI Local bus must also be installed in the
same mainframe.
Keysight E8491B IEEE 1394 PC Link to VXI User Guide 25
Page 24

Interface Installation and Configuration Using this Chapter
Installing C-size Instruments
Figure 2-8 shows the installation of C-size instruments.
retaining
screws
extraction
seat the module
pushing in the
extraction levers
slide the module
into the mainframe
until it plugs into the
backplane connectors
Figure 2-8 Installing C-size Instruments.
To prevent damage to the VXI instruments being installed,
remove power from the mainframe or set the power switch to
Off or Standby before installing the instruments.
1 Insert the instrument into the mainframe by aligning the instrument with the
card guides inside the mainframe. Slowly push the instru ment into the slot
until it seats in the backplane connectors. The front panel of the instrument
should be even with the front edges of the mainframe.
2 Tighten the retaining screws on the top and bottom of the module.
All instruments within the VXI mainframe are grounded
through the mainframe chassis. During installation, tighten
the instruments’ retaining screws to secure the instrument
to the mainframe and to make the ground connection.
26 Keysight E8491B IEEE 1394 PC Link to VXI User Guide
Page 25

Using this Chapter Interface Installation and Configuration
Installing A- and B-size Instruments
A- and B-size instruments can also be installed in the mainframe. These
instruments are installed using a module carrier:
– Keysight E1403C A/B-size Module Carrier extends the P1 connector on the
VXIbus backplane and mounts the (A/B-size) modules flush with C-size
modules. This carrier is recommended for Hewlett-Packard B-size,
slave-only devices which have the P1 connector.
– Keysight E1407A A/B Module Carrier extends the P1and P2 connectors on
the VXIbus backplane. This carrier is recommended for B-size, slave-only
devices which have the P1/P2 connectors.
To prevent damage to the VXI instruments, install the
instruments when the mainframe is turned off.
Figure 2-9 shows the installation of a B-size instrument using a module carrier.
The procedure is described in the following three steps.
1 Install the E1403 or E1407 A/B-size Module Carrier into the mainframe. This
is done by aligning the top and bottom of the carrier with the card guides and
slowly pushing the carrier into the mainframe. The front of the carrier should
be even with the front edges of the mainframe.
2 Slide the A- or B-size instrument into the carrier until it connects.
3 Tighten the retaining screws on the top and bottom of the instrument.
All instruments within the VXI mainframe are grounded
through the mainframe chassis. During installation, tighten
the instruments’ retaining screws to secure the instrument
to the mainframe and to make the ground connection.
Keysight E8491B IEEE 1394 PC Link to VXI User Guide 27
Page 26

Interface Installation and Configuration Using this Chapter
Figure 2-9 Installing A- and B-size VXI Instruments.
28 Keysight E8491B IEEE 1394 PC Link to VXI User Guide
Page 27

Using this Chapter Interface Installation and Configuration
Step 4: Installing the Keysight I/O Libraries
The Keysight I/O Libraries CD contains the software required to use the IEEE
1394 interface in a VXI system. It also includes the OHCI-compatible host
adapter drivers.
Refer to Chapter 4: IEEE 1394 Fundamentals and Interface Overview
for more information on the Keysight I/O Libraries and related software.
If your PC indicates that new hardware has been found after applying
power, do the following:
a. Select “Driver from disk provided by hardware manufacturer”-Press
OK.
b. Insert the I/O Libraries CD in your CD ROM drive.
c. Point or browse to the drive letter for the CD ROM. Press OK.
d. You will be instructed to install the driver that matches the hardware.
Begin by performing the following steps.
1 Apply power to your PC. Close all open applications and insert the I/O
Libraries CD into your PC CD-ROM drive. Inserting the CD automatically
activates the installer. If the installer does not activate, select Start / Run and
type <drive>:SETUP.EXE where <drive> designates the CD drive. Do not apply
power to the VXI mainframe.
2 Review the information and license agreements presented at the beginning of
the installation process.
3 Continue through the installation process as directed by the installer. Be sure
to indicate that you want Keysight I/O Libraries support for the E8491B
interface installed by clicking on the box next to “Install
E8491 VXI Components.”
4 Read the Readme.txt file if you choose then select “Do not configure the
interfaces at this time” in the next window.
5 After the installation is complete, re-start the computer.
Configuring the E8491B Interconnect
1 Connect the IEEE 1394 interface cable between the host adapter (PC) and
one of the IEEE 1394 ports on the E8491B front panel.
2 Turn on the VXI mainframe.
From the Keysight I/O Libraries program group created when the libraries were
installed (Start >> Programs >> Keysight I_O Libraries), click on ‘I_O Config’
(Figure 2-10).
Keysight E8491B IEEE 1394 PC Link to VXI User Guide 29
Page 28

Interface Installation and Configuration Using this Chapter
Figure 2-10The Keysight I/O Libraries Program Group.
An alternative is to click on the Keysight icon in the lower right-hand corner of
your monitor which is placed there following the installation of the I/O Libraries
and configuring the E8491B. Clicking on the Keysight icon brings up a pop-up
menu like that shown in Figure 2-13. Click on “Run I/O Config”. Either method
described in this step brings up a configuration window similar to Figure 2-11.
Select E8491 in the “Available Interface Types” box and click the ‘Configure’
button.
interface name
interface number
Figure 2-11The Keysight I/O Libraries I/O Config Utility.
The E8491B uses the SICL interface name ‘vxi’ and the VISA interface name ‘VXI’
(Figure 2-12). The VISA interface number is assigned by the ‘I/O Config’ utility
and is unique to each E8491B. The interface name and number identify each
mainframe in multi-frame VXI systems, and are also used in addressing each
instrument in the mainframe. The unique interface number allows instruments
with the same logical addresses to be installed in different mainframes, but in the
same system.
30 Keysight E8491B IEEE 1394 PC Link to VXI User Guide
Page 29

Using this Chapter Interface Installation and Configuration
The “Locate” button on the “E8491 VXI Board Configuration” screen can be used
to help you identify and keep track of all the mainframes in a multi-mainframe
system.
Figure 2-12Editing the E8491B Configuration.
3 Figure 2-11 returns with the SICL Name and VISA Name inserted. Click OK to
close the utility and complete the configuration.
Editing the E8491B Configuration
When it is necessary to edit your configuration, click ‘I_O Config’ in the
Keysight I/O Libraries program group (Figure 2-10). To edit the E8491B, click
(highlight) the configured interface (“vxi VXI0”) in the utility (Figure 2-11). This
activates the ‘Edit’ and ‘Remove’ buttons at the bottom of the window.
Keysight E8491B IEEE 1394 PC Link to VXI User Guide 31
Page 30

Interface Installation and Configuration Using this Chapter
If you want to change the SICL interface name and number to something more
descriptive, use the ‘SICL Interface Name’ field. You can change the VISA
interface number using the up/down arrows next to the ‘VISA Interface Name’
field. The SICL and VISA interface names (and numbers) do not have to be the
same.
Make a note of the interface name and number, as they are used in addressing
instruments in the mainframe (see “Chapter 3: VXI Programming Using the IEEE
1394 Serial Bus” for more information).
The ‘Help’ button provides information on each item in the window.
Editing the E8491B Configuration on Windows 95 Platforms
After installing the Keysight I/O Libraries and configuring the E8491B on the Windows
95 platform, an Keysight icon is placed in the bottom right corner of your PC monitor
(Figure 2-13).
Figure 2-13Editing Your Configuration on Windows 95 Platforms.
Clicking on the icon brings up the following menu items:
Hide Resource Manager Messages
Enable/disable displaying resource manager messages during mainframe
power-on or during a E8491B reset.
Edit VXI Resource Manager
Allows you to edit the Resource Manager configuration files and/or to run the
Resource Manager.
Refresh VXI Resource Manager
Resets and runs the Resource Manger on all VXI mainframes in your system. You
must “refresh” (re-run) the resource manager each time changes are made to its
configuration. NOTE: The resource manager will run automatically whenever the
mainframe is powered on.
Run VISA Assistant
Activates the Keysight VISA Assistant utility. This utility displays all devices
connected to the interface and their VISA interface address. It provides other
32 Keysight E8491B IEEE 1394 PC Link to VXI User Guide
Page 31

Using this Chapter Interface Installation and Configuration
information on drivers, formatted I/O, memory and other attributes. Formatted
I/O allows you to send a SCPI command to a device to confirm communication
with the device or simply to set a command parameter or to query a device state.
Run I/O Config
Runs the I/O Config utility and brings up the “I/O Config - Interface Configuration
Application” window shown in figure 2-11.
View Documentation
Selects the Readme.txt, the VISA Help file or the SICL Help file for viewing.
Run Event Viewer
Brings up the event viewer for viewing the Applications Log for your PC.
VISA Logging
Enables/disables the VISA logging, runs the event viewer or the debug window.
Hide Keysight I/O Control
Removes the Keysight icon in the lower right-hand corner of your Windows
95/NT window task bar. To re-install the icon, go to the START button >>
Programs >> Keysight I_O Libraries and click on Keysight I_O Libs Control.
Exit
Terminates the Keysight I/O Libraries Control.
For E8491 Controllers to work, the Keysight I/O Libraries Control must
be running. Executing “Exit” will disable E8491B operation.
About Keysight I/O Libraries Control
Provides the Keysight I/O Libraries Control version number.
Step 5: Installing Keysight VXIplug&play Instrument Drivers
There are no SCPI instrument drivers installed in, or downloaded to, the
E8491B. While this does not impact message-based instruments, register-based
instruments in IEEE 1394 based systems are usually programmed using their
VXIplug&play drivers.
The Keysight VXIplug&play drivers are located on the Keysight Universal
Instrument Drivers CD which ships with the E8491B and with each VXI
instrument.The installer program on the driver CD is similar to that on the I/O
libraries CD.
Once the drivers have been installed, reboot the PC.
Keysight E8491B IEEE 1394 PC Link to VXI User Guide 33
Page 32

Interface Installation and Configuration Using this Chapter
If you are updating an existing VXI system to use the E8491B and
IEEE 1394 serial bus, we highly recommend that you obtain the
latest version of the Keysight VXIplug&play drivers. Information
on the latest drivers available can be found on the World Wide
Web at http://www.Keysight.com/go/inst_drivers .
Step 6. Verifying the Installation
Once you have installed the hardware, the I/O Libraries, the VXIplug&play
drivers, and have re-booted the PC, you should now verify the installation. This
ensures that you can communicate with instruments in the system over the IEEE
1394 interface. Two ways to check your system are to run an instrument’s soft
front panel, or to view the output of the system’s resource manager.
Using Instrument Soft Front Panels
Soft front panels are part of the instruments’ VXIplug&play drivers. A soft front
panel is activated from the ‘Vxipnp’ program group as shown in Figure 2-14.
Click to activate a
soft front panel
Figure 2-14Selecting a VXIplug&play Soft Front Panel.
34 Keysight E8491B IEEE 1394 PC Link to VXI User Guide
Page 33

Using this Chapter Interface Installation and Configuration
When the system hardware and software are properly installed and the PC is
communicating with the mainframe, the soft front panel will be opened and a
connection made to the instrument as shown in Figure 2-15.
Correct interface
name and logical
Green ‘Active’
indicator shows
Figure 2-15Soft Front Panel Indicating PC - Mainframe Communication.
Viewing the Resource Manager Output
Another way to determine if your system is properly configured is to view the
output of the resource manager. The easiest way to view the output is using the
I/O Libraries’ ‘I/O Config’ utility.
1 Press the Keysight I/O Libraries Control icon in the lower right-hand side of
your monitor and select “Edit VXI Resource Manager”. In the Resource
Manager pop-up window, select “RM Output”. The resource manager output
Keysight E8491B IEEE 1394 PC Link to VXI User Guide 35
Page 34

Interface Installation and Configuration Using this Chapter
will show the “VXI Current Configuration” with all devices it can communicate
with listed in the “VXI Device Table”.
2 Click on Start >> Programs >> I_O Config to bring up the I/O Config window
(Figure 2-11).
3 Select the “Configured Interfaces” name corresponding to the E8491B to bing
up the E8491 VXI Board Configuration window (Figure 2-12).
36 Keysight E8491B IEEE 1394 PC Link to VXI User Guide
Page 35

Using this Chapter Interface Installation and Configuration
4 Perform steps 1, 2 and 3 in Figure 2-16.
1. Select Enable Advanced to activate the Advanced Settings controls.
2. Click Resource Manager to bring up the window below.
3. Click RM Output to view the resource manager
output.
Figure 2-16Viewing the Resource Manager Output using ‘I/O Config’.
Keysight E8491B IEEE 1394 PC Link to VXI User Guide 37
Page 36

Interface Installation and Configuration Using this Chapter
Figure 2-17 is a partial listing of a typical resource manager output.
Figure 2-17Typical Resource Manager Output (partial listing).
38 Keysight E8491B IEEE 1394 PC Link to VXI User Guide
Page 37

Using this Chapter Interface Installation and Configuration
Troubleshooting Installation Problems
The following list of troubleshooting items may help you get your E8491B
interface working properly if you have encountered problems verifying
installation.
1 It is very important that you upgrade the PC BIOS to the latest version your PC
manufacturer provides whether your PC is new or old. Many early versions of
the PCI BIOS contained bugs. Upgrading to the latest version of BIOS will
eliminate those bugs upgraded by the new BIOS. A BIOS upgrade and a video
driver upgrade may be required to fix PCI-related problems even on a new PC.
2 Make sure the PCI BIOS is correctly configured. New PC’s have a BIOS flag
that usually reads “Plug&Play OS” or “Running Windows 95”. This must be set
appropriately for the OS you are using; Win 95 is a plug&play OS whereas,
Win NT is not.
3 The E8491B requires installation of the PCI-to-IEEE 1394 host adapter card in
a bus-mastering PCI slot. Consult your PC’s user manual to determine which
slots are bus-mastering (it is possible that all slots are bus-mastering).
4 In addition to the above, you may need to move the E8491B to a separate IRQ
line in the PC. PCI allows up to four devices sharing an IRQ line. However, due
to bugs in some cards, this doesn’t always work and you may need to have
one IRQ per card. Moving the IRQ is not easy and whether it can be done will
depend on which operating system you are using and on the details of the
BIOS implementation of your PC.
Running the Resource Manager
The I/O Libraries Control utility must be running to enable the resource manager
to run. The resource manager initializes and prepares the VXI system for use. The
I/O Libraries Control utility is installed when the E8491B interface is configured
using ‘I/O Config’. It can be accessed by clicking on the Keysight logo in the
lower right hand corner of your Windows panel. The resource manager will run
when:
– mainframe power is applied or cycled
– the E8491B faceplate “Reset” button is pressed
– activated from the ‘I/O Config’ utility
– activated from the ‘I/O Control’ icon (see Figure 2-13)
In VXI systems with multiple E8491Bs (mainframes), individual mainframes can
be turned off without affecting other mainframes in the system. When a
mainframe is turned on, the resource manager reconfigures the mainframe.
The resource manager will only run if the I/O Libraries Control
utility is started.
Keysight E8491B IEEE 1394 PC Link to VXI User Guide 39
Page 38

Interface Installation and Configuration Using this Chapter
40 Keysight E8491B IEEE 1394 PC Link to VXI User Guide
Page 39

Keysight E8491B IEEE 1394 PC Link to VXI
Configuration and User Guide
3 VXI Programming Using the IEEE
1394 Serial Bus
Using this Chapter
This chapter contains examples and general information for programming VXI
systems over the IEEE 1394 serial bus. The contents of the chapter include:
Programming Register-Based and Message-Based VXI
Instruments page 41
Opening Instrument Sessions page 41
Optimizing Programs page 42
Keysight E8491B Triggering page 49
Using Keysight E8491B Shared Memory page 54
Example Programs page 56
Programming Register-Based and Message-Based VXI Instruments
There are no SCPI instrument drivers for register-based instruments installed in,
or downloaded to, the E8491B. Therefore, register-based instruments are
programmed over the IEEE 1394 bus using either their
VXIplug&play drivers, or through register-level peeks and pokes using
Keysight VISA or SICL.
Message-based instruments are programmed using Keysight VXIplug&play
drivers, or using SCPI commands embedded in Keysight VISA or SICL function
calls.
VXIplug&play drivers for Keysight register-based and message-based
instruments are contained on the Keysight Universal Instrument Drivers CD
which ships with each Keysight VXI instrument.
Opening Instrument Sessions
Programs which run over the IEEE 1394 interface begin by opening a session
between the VXI instrument and the driver or I/O library (VISA or SICL). An
address that includes the interface name and number (described in Chapter 2)
and the instrument’s logical address is used in opening these sessions.
Following are three segments that open sessions to an E1563A Digitizer in
Keysight VXIplug&play, Keysight VISA, and SICL programs.
41
Page 40

VXI Programming Using the IEEE 1394 Serial Bus Using this Chapter
Keysight VXIplug&play
ViSession vi;
// open device (VXIplug&play) session to the E1563
errStatus = hpe1563_init(“VXI0::24::INSTR”,VI_FALSE,
VI_FALSE, &vi);
Keysight VISA
ViSession defaultRM, id;
//open device (VISA) session to the Keysight E1563
viOpenDefaultRM (&defaultRM);
viOpen (defaultRM, “VXI0::24::INSTR”,VI_NULL,VI_NULL,
&id);
SICL
INST id;
// open device (SICL) session to the Keysight E1563
id = iopen(“vxi,24”)
Or, to open an interface session to the E8491B:
INST id;
// open (SICL) session to the VXI interface
id = iopen(“vxi”)
The E8491B IEEE 1394 interconnect uses the VISA interface name VXI<n> or
SICL interface name vxi. The interface number is assigned using the ‘I/O Config’
utility (see Chapter 2). In the examples above, the logical address of the E1563
digitizer is 24 and INSTR indicates a VISA instrument control resource.
Optimizing Programs
Programs that run over the IEEE 1394 serial bus are optimized by transferring
data between the PC and the instrument in blocks. The following section
identifies Keysight VISA and SICL functions that perform block transfers.
Refer to “Chapter 4: IEEE 1394 Fundamentals and Interface
Overview” for detailed information on data transfers using the
IEEE 1394 data transfer protocol.
42 Keysight E8491B IEEE 1394 PC Link to VXI User Guide
Page 41

Using this Chapter VXI Programming Using the IEEE 1394 Serial Bus
Block Data Transfers
VXIplug&play drivers for selected instruments contain functions that perform
block transfers. You will need to consult the driver help file to determine if the
driver for a particular instrument supports block transfers.
The following Keysight VISA functions perform block transfers over the
IEEE 1394 serial bus:
viMoveIn8 viMoveOut8 viMove
viMoveIn16 viMoveOut16 viMoveAsync
viMoveIn32 viMoveOut32
The following extended SICL function is unique to the E8491B (must be used on the
E8491B) and is used for block transfers over the bus:
iblockmovex
Additionally, the extended SICL functions shown below must be used when
porting SICL programs to the IEEE 1394 bus from other I/O interfaces:
imapx
iunmapx
ipeekx8, ipeekx16, ipeekx32
ipokex8, ipokex16, ipokex32
These functions are covered in detail in the SICL documentation.
The following examples demonstrate how to set up and perform block transfers
using Keysight VXIplug&play and Keysight VISA functions.
Block Transfers using Keysight VXIplug&play Drivers
This program performs a block transfer of 2,000 readings using the
E1563A digitizer and its VXIplug&play driver.
// 1563VPNP.CPP - This program transfers a block of 2,000 readings
from the // Keysight E1563 digitizer to the computer using the
VXIplug&play driver's
// hpe1563_fetchAll_Q function. 2,000 readings is the maximum number
of
// readings that can be transferred using the function.
#include "hpe1563.h"// include the driver header file
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <windows.h>
// project files: 1563vpnp.cpp, hpe1563.lib
// Specify the addressing path.
#define E1563 "VXI0::64::INSTR" // VXI addressing
// prototypes
void check(ViSession vi, ViStatus error);
Keysight E8491B IEEE 1394 PC Link to VXI User Guide 43
Page 42

VXI Programming Using the IEEE 1394 Serial Bus Using this Chapter
void main(void)
{
ViSession vi;
ViStatus errStatus;
ViInt16 rdgs[2000];
ViInt16 *dataPtr;// pointer to cast readings to 16-bit integers
ViReal64 range;// range variable for reading conversions
int i;
long dataArrayLen=2000;// return 2,000 readings using
// hpe1563_fetchAll_Q
ViInt32 numRdgs;
ViChar err_message[256];
dataPtr = rdgs;// set pointer to rdgs array
// open a VXIplug&play device session and reset the digitizer
errStatus = hpe1563_init(E1563,0,1,&vi);
if( VI_SUCCESS > errStatus)
{
hpe1563_error_message( vi, errStatus, err_message);
printf("Unable to open %s\n", E1563);
printf("hpe1563_init() returned error message %s\n",
err_message);
return;
}
// enable digitizer error detection
hpe1563_errorQueryDetect(vi, 1);
// set a 5s timeout period to allow functions to complete
errStatus = hpe1563_timeOut(vi, 5000);
check(vi, errStatus);
// configure the digitizer to take 2,000 post-trigger readings
// not to exceed 4V on channel 1
errStatus=hpe1563_configure(vi, 1, 4.0, 2000,1);
check(vi, errStatus);
// set an immediate trigger
errStatus = hpe1563_trigEvent(vi, 1, hpe1563_TRIG_IMM, 0.0);
check(vi, errStatus);
// set the minimum sample period
errStatus = hpe1563_sampTim(vi, hpe1563_SAMP_TIM_MIN);
check(vi, errStatus);
// disable digitizer error detection
hpe1563_errorQueryDetect(vi, 0);
// initiate the digitizer
errStatus = hpe1563_initImm(vi);
// pause 3 ms (1.3e-6 * 2000) to allow readings to complete
Sleep (3);
44 Keysight E8491B IEEE 1394 PC Link to VXI User Guide
Page 43

Using this Chapter VXI Programming Using the IEEE 1394 Serial Bus
// fetch readings from the digitizer's A24 space
errStatus = hpe1563_fetchAll_Q(vi, dataArrayLen, (ViInt32 *)rdgs,
&numRdgs );
// confirm readings transferred are valid by printing first 5
readings
dataPtr = (ViInt16 *)rdgs;
// query digitizer reading range
errStatus = hpe1563_range_Q(vi, 1, &range);
printf("Reading samples are:\n\n");
for (i=0; i<10; i+=2)
{
printf("%lf\n\n",dataPtr[i]*range/32768);
}
// reset digitizer following the transfer
errStatus = hpe1563_reset(vi);
// close the device session
hpe1563_close(vi);// Keysight VXIplug&play session
}
//*******************************************************************
****
// error checking routine
void check (ViSession vi, ViStatus errStatus)
{
ViInt32 inst_err;
ViChar err_message[256];
if(VI_SUCCESS > errStatus)
{
if(hpe1563_INSTR_ERROR_DETECTED == errStatus)
{
/* query instrument error */
hpe1563_dcl(vi);/* send a device clear */
hpe1563_error_query(vi, &inst_err, err_message);
/* display the error */
printf("Instrument Error : %ld, %s\n", inst_err, err_message);
}
else
{
/* get driver error message */
hpe1563_error_message(vi, errStatus, err_message);
/* display the error */
printf("E1563 Driver Error : %ld, %s\n", errStatus,
err_message);
}
hpe1563_reset(vi);/* reset the digitizer */
hpe1563_close(vi);/* close the digitizer handle */
Keysight E8491B IEEE 1394 PC Link to VXI User Guide 45
Page 44

VXI Programming Using the IEEE 1394 Serial Bus Using this Chapter
exit(1);
}
return;
}
Comments
1 The maximum block transfer size allowed by the E1563A hpe1563_fetchAll_Q
function is 2,000 bytes.
2 This manual is included on the Keysight I_O Libraries CD. By viewing the
manual from the CD, you can cut and paste this program into your
development environment.
3 The section “Using E8491B Shared Memory” contains an example of block
data transfers using Keysight SICL.
Block Transfers using Keysight VISA
This program performs a block transfer of 60,000 readings using the
E1563A digitizer and the Keysight VISA function viMoveIn32.
// 1563visa.CPP - This program configures the E1563A digitizer using
its // VXIplug&play driver and then transfers a block of 60,000
readings from // the digitizer's FIFO memory to the computer using the
VISA viMoveIn32
// function.
#include "hpe1563.h"// include the driver header file
#include "visa.h"
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <windows.h>
// project files: 1563visa.cpp, hpe1563.lib, VISA.lib
// specify the addressing path
#define E1563 "VXI0::64::INSTR" // VXI addressing
// prototypes
void check(ViSession vi, ViStatus error);
void err_handler(ViSession vi, ViStatus err);
void main(void)
{
ViSession vi;
ViStatus errStatus, err;
ViInt32 rdgs[60000];
ViReal64 range;// range variable for reading conversions
ViInt16 *dataPtr;// pointer to cast readings to 16-bit integers
int i;
ViChar err_message[256];
// open a VXIplug&play device session and reset the digitizer
errStatus = hpe1563_init(E1563,0,1,&vi);
if( VI_SUCCESS > errStatus)
46 Keysight E8491B IEEE 1394 PC Link to VXI User Guide
Page 45

Using this Chapter VXI Programming Using the IEEE 1394 Serial Bus
{
hpe1563_error_message( vi, errStatus, err_message);
printf("Unable to open %s\n", E1563);
printf("hpe1563_init() returned error message %s\n",
err_message);
return;
}
// enable digitizer error detection
hpe1563_errorQueryDetect(vi, 1);
// set a 5s timeout period to allow functions to complete
errStatus = hpe1563_timeOut(vi, 5000);
check(vi, errStatus);
// configure the digitizer to take 60,000 post-trigger readings
// not to exceed 4V on channel 1
errStatus=hpe1563_configure(vi, 1, 4.0, 60000, 1);
check(vi, errStatus);
// set an immediate trigger
errStatus = hpe1563_trigEvent(vi, 1, hpe1563_TRIG_IMM, 0.0);
check(vi, errStatus);
// set the minimum sample period
errStatus = hpe1563_sampTim(vi, hpe1563_SAMP_TIM_MIN);
check(vi, errStatus);
// disable digitizer error detection
hpe1563_errorQueryDetect(vi, 0);
// initiate the digitizer
errStatus = hpe1563_initImm(vi);
// pause 78 ms (1.3e-6 * 60000) to allow readings to complete
Sleep (78);
// transfer the (60,000) readings from the digitizer using the VISA
// function viMoveIn32 - use the same session name (vi) opened for
// VXIplug&play
err = viMoveIn32(vi, VI_A16_SPACE, 0x08, 60000, (ViPUInt32)rdgs);
if(err < VI_SUCCESS) err_handler(vi, err);
// confirm readings transferred are valid
dataPtr = (ViInt16 *)rdgs;
// query digitizer reading range
errStatus = hpe1563_range_Q(vi, 1, &range);
printf("Reading samples are:\n\n");
for (i=0; i<10; i+=2)
{
printf("%lf\n\n",dataPtr[i]*range/32768);
}
// reset digitizer following the transfer
errStatus = hpe1563_reset(vi);
Keysight E8491B IEEE 1394 PC Link to VXI User Guide 47
Page 46

VXI Programming Using the IEEE 1394 Serial Bus Using this Chapter
// close the device session
hpe1563_close(vi);// Keysight VXIplug&play session
}
//************************************************************
// error checking routine
void check (ViSession vi, ViStatus errStatus)
{
ViInt32 inst_err;
ViChar err_message[256];
if(VI_SUCCESS > errStatus)
{
if(hpe1563_INSTR_ERROR_DETECTED == errStatus)
{
/* query instrument error */
hpe1563_dcl(vi);/* send a device clear */
hpe1563_error_query(vi, &inst_err, err_message);
/* display the error */
printf("Instrument Error : %ld, %s\n", inst_err, err_message);
}
else
{
/* get driver error message */
hpe1563_error_message(vi, errStatus, err_message);
/* display the error */
printf("E1563 Driver Error : %ld, %s\n", errStatus,
err_message);
}
hpe1563_reset(vi);/* reset the digitizer */
hpe1563_close(vi);/* close the digitizer handle */
exit(1);
}
return;
}
//*******************************************************************
*****
// Error handling function
void err_handler (ViSession vi, ViStatus err)
{
char buf[1024]={0};
viStatusDesc(vi,err,buf);
printf("ERROR = %s\n", buf);
return;
}
48 Keysight E8491B IEEE 1394 PC Link to VXI User Guide
Page 47

Using this Chapter VXI Programming Using the IEEE 1394 Serial Bus
Comments
1 A single instrument session opened with the hpe1563_init function can be
used by both Keysight VXIplug&play driver function calls and by Keysight
VISA function (i.e viMoveIn32) calls.
2 This manual is included on the Keysight I_O Libraries CD. By viewing the
manual from the CD, you can cut and paste this program into your
development environment.
3 The section “Using E8491B Shared Memory” contains an example of block
data transfers using Keysight SICL.
Keysight E8491B Triggering
The E8491B is capable of asserting, receiving, and routing trigger signals along
the VXI (mainframe) backplane trigger lines. In addition to the VXI backplane’s
eight TTL level trigger lines and two ECL level trigger lines, the E8491B can
receive and assert triggers on the faceplate ‘Trig In’ and ‘Trig Out’ connectors.
Table 3-1 summarizes the triggering parameters and capabilities of the
E8491B.
Table 0-1. Keysight E8491B Triggering Parameters.
Trigger Lines Trigger Levels Trigger Routing
TTLTRG7 - TTLTRG0
(VXI backplane)
ECLTRG1 - ECLTRG0
(VXI backplane)
Trig In Port*
(E8491B faceplate)
Trig Out Port*
(E8491B faceplate)
* The E8491B Trig In and Trig Out ports are configured using the Keysight I/O Libraries ‘I/O Config’ utility.
Trigger levels or pulses can be output
on any number of TTLTRG trigger lines.
Trigger levels or pulses can be output
on any number of ECLTRG trigger lines.
Input trigger levels are TTL, ECL,
CMOS, or programmable up to +30V.
Default assumes TTL low true signal.
Output trigger level is +5V (low true default) and can be pulled to +30V.
One TTLTRG trigger line can be routed to
one ECLTRG trigger line.
One ECLTRG trigger line can be routed to
one TTLTRG trigger line.
Input triggers can be routed to any number
of TTLTRG trigger lines and to any number
of ECLTRG trigger lines.
One TTLTRG or ECLTRG trigger line can be
routed to the Trig Out port
Using Triggers
The triggering functionality of the E8491B is accessed through the following
Keysight VISA and SICL functions:
Keysight E8491B IEEE 1394 PC Link to VXI User Guide 49
Page 48

VXI Programming Using the IEEE 1394 Serial Bus Using this Chapter
Asserting Triggers - Keysight VISA
viSetAttribute
VI_ATTR_TRIG_ID
VI_TRIG_TTL0 to VI_TRIG_TTL7
VI_TRIG_ECL0 to VI_TRIG_ECL1
viAssertTrigger
VI_TRIG_PROT_DEFAULT
Asserting Triggers - Keysight SICL
ivxitrigoff
ivxitrigon
ixtrig
I_TRIG_ALL
I_TRIG_TTL0 to I_TRIG_TTL7
I_TRIG_ECL0 to I_TRIG_ECL1
I_TRIG_EXT0 (specifies faceplate ‘Trig Out’ port)
Routing Triggers- Keysight SICL
ivxigettrigroute
ivxitrigroute
1
I_TRIG_ALL
I_TRIG_TTL0 to I_TRIG_TTL7
I_TRIG_ECL0 to I_TRIG_ECL1
I_TRIG_EXT0 (specifies faceplate ‘Trig Out’ and ‘Trig In’ ports)
1 Trigger routing is only available using the Keysight SICL ivxitrigroute function.
50 Keysight E8491B IEEE 1394 PC Link to VXI User Guide
Page 49

Using this Chapter VXI Programming Using the IEEE 1394 Serial Bus
Configuring the E8491B Trig In and Trig Out Ports
Configuration of the E8491B external ‘Trig In’ and ‘Trig Out’ ports is done through
the Keysight I/O Libraries’ ‘I/O Config’ utility. This portion of the utility is shown in
the following figure.
Figure 3-1 Configuring the Keysight E8491B External Trigger Ports.
When ‘External Trig In’ is selected, the faceplate ‘Trig In’ port is configured for the
trigger level and state (normally high or normally low) selected. When ‘External
Trig Out’ is selected, the faceplate ‘Trig Out’ port is configured for the state
(normally high or normally low) selected.
The ‘I/O Config’ help file associated with the E8491B interface
contains additional information on configuring the faceplate trigger
ports.
Note
Note
Triggering Example
The following program demonstrates how an external trigger received on the
faceplate ‘Trig In’ port is routed to TTL trigger lines on the VXI backplane.
// TRIGSICL.CPP - This program demonstrates how trigger signals are
// generated and routed using the E8491B. The program uses SICL
functions // to generate and route a trigger signal from the face
plate ‘Trig Out’
// port to VXI backplane trigger line TTLTRG4. The signal triggers the
// E1412 multimeter which then takes a burst of 10 readings.
Keysight E8491B IEEE 1394 PC Link to VXI User Guide 51
Page 50

VXI Programming Using the IEEE 1394 Serial Bus Using this Chapter
#include "sicl.h"
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
// project files: trigsicl.cpp, sicl32.lib
void main(void)
{
INST e8491; // E8491 SICL handle
INST e1412; // E1412 SICL handle
short i;
double dcv_rdgs[10];
// install SICL error handler
ionerror(I_ERROR_EXIT);
// open a (SICL) interface session to the E8491B
// open a (SICL) device session to the E1412
e8491 = iopen("vxi");
e1412 = iopen("vxi,24");
// set up trigger routing; rout a trigger from the faceplate 'Trig
In'
// port to VXI backplane TTL trigger line 4
ivxitrigroute(e8491, I_TRIG_EXT0, I_TRIG_TTL4);
// E1412 Multimeter configuration
// set a 50s timeout period for external trigger to occur
itimeout(e1412, 50000);
// configure the multimeter for DCV measurements
iprintf(e1412, "CONF:VOLT:DC 8.0\n");
// set the fastest aperture time
iprintf(e1412, "VOLT:DC:APER MIN\n");
// turn off the autozero function
iprintf(e1412, "ZERO:AUTO OFF\n");
// set the trigger source
iprintf(e1412, "TRIG:SOUR TTLT4\n");//trigger line 4
// set the sample count
iprintf(e1412, "SAMP:COUN 10\n");// 10 readings
// initiate the multimeter
iprintf(e1412, "INIT\n");
printf("Press 'Enter' to trigger the voltmeter\n");
getchar ();
// output a trigger pulse on the E8491B 'Trig Out' connector, the
// trigger is then input to the 'Trig In' connector via a jumper
wire
// and routed to TTL trigger line 4 which triggers the multimeter
ixtrig(e8491, I_TRIG_EXT0);
52 Keysight E8491B IEEE 1394 PC Link to VXI User Guide
Page 51

Using this Chapter VXI Programming Using the IEEE 1394 Serial Bus
// fetch the readings once the trigger is received
ipromptf(e1412, "FETC?\n", "%,10lf", dcv_rdgs);
// display the readings
for (i=0; i<10; i++)
{
printf("%lf\n", dcv_rdgs[i]);
}
// close the device sessions
iclose(e8491);// close SICL interface session
iclose(e1412);// close SICL device session
}
Comments
1 For demonstation purposes, the trigger signal output from the ‘Trig Out’ port
(ixtrig function) is routed to the ‘Trig In’ port using a jumper wire. The signal is
then routed to TTLTRG4 (ivxitrigroute function).
2 The external trigger routed to TTLTRG4 can also be routed to any or all of the
VXI backplane trigger lines.
3 When using the faceplate ‘Trig In’ and ‘Trig Out’ ports, notice that both ports
are specified using I_TRIG_EXT0.
In the program, ivxitrigroute(e8491s, I_TRIG_EXT0,
I_TRIG_TTL4)routes the trigger received on the faceplate ‘Trig In’ port
to backplane TTL trigger line 4. ixtrig(e8491s, I_TRIG_EXT0)
outputs a trigger pulse on the ‘Trig Out’ port which is connected by a
jumper wire to the ‘Trig In’ port.
4 This manual is included on the Keysight I/O Libraries CD. By viewing the
manual from the CD, you can cut and paste this program into your
development environment.
Keysight E8491B IEEE 1394 PC Link to VXI User Guide 53
Page 52

VXI Programming Using the IEEE 1394 Serial Bus Using this Chapter
E8491B
+V
DUT
" TRIG OUT "
SMB Connector
R
+ V = Pull Up Voltage (+ 30V M ax)
Outp ut Trigger State LH = Norm ally Low , High True
Outp ut Trigger State HL = Norm ally High, Low True (Default)
Trigger Pull Up
Trigger signals output from the E8491B ‘Trig Out’ port can be “pulled up” to
+30V as shown in Figure 3-2.
Figure 3-2 Using a Pull Up on the Keysight E8491B ‘Trig Out’ Port.
Using Keysight E8491B Shared Memory
The E8491B has 128 kBytes of shared (VME) memory. This memory is in the
E8491B’s A24 address space and is available to those VXI instruments capable of
mapping and accessing A24 memory. Shared memory is often used as a
temporary storage space for data transfers between the PC and VXI instruments.
Keysight instruments with the ability to store and receive data from shared
memory generally implement the SCPI (Standard Commands for Programmable
Instruments) MEMory:VME subsystem shown below:
MEMory:VME:SIZE
MEMory:VME:ADDRess
MEMory:VME:STATe
Corresponding Keysight VXIplug&play functions are:
hpexxxx_memVmeAddr
hpexxxx_memVmeSize
hpexxxx_memVmeStat
where xxxx is the instrument model number.
54 Keysight E8491B IEEE 1394 PC Link to VXI User Guide
Page 53

Using this Chapter VXI Programming Using the IEEE 1394 Serial Bus
Locating E8491B Shared Memory
In order to use the E8491B shared memory, you must first locate the starting
address of the memory as mapped by the resource manager (see “Running the
Resource Manager” in Chapter 2). The address varies from system to system
depending on the number of devices that use A24 memory. The address can be
determined programatically using Keysight VISA or SICL, or by viewing the
resource manager output. Each method is described in the following sections.
Locating Shared Memory Using Keysight VISA
For Keysight VISA programs, the E8491B shared memory starting address is
obtained using the function:
viGetAttribute
and the VXI interface attribute:
VI_ATTR_MEM_BASE
The Keysight VISA version of the example “Storing Readings in Shared Memory”
demonstrates the use of this function and attribute.
Locating Shared Memory Using SICL
For SICL programs, the E8491B shared memory starting address is found using
the function:
ivxirminfo
This function fills the structure struct vxiinfo. The item within the structure
containing the starting address is memstart. The SICL version of the example
program showing the use of shared memory demonstrates the use of this
function and structure.
Locating Shared Memory by Viewing the Resource Manager Output
The third method of determining the E8491B’s shared memory starting address is
to view the resource manager output. “Viewing the Resource Manager Output” in
Chapter 2 describes how this is done using the ‘I/O Config’ utility. Figure 3-3
shows the section of the output that indicates A24 address mapping.
Another way to view the output is using the SICL ivxisc utility contained in the
<drive:>\siclnt\bin or sicl95\bin directory. This utility is an executable that is
used with the SICL logical unit number (see “Editing the E8491B Configuration”
in Chapter 2) to return the configuration output of the resource manager. Again,
Figure 3-3 shows a partial listing of the output.
Refer to Appendix B for additional information on using ivxisc and
for an example of the complete configuration output.
Keysight E8491B IEEE 1394 PC Link to VXI User Guide 55
Page 54

VXI Programming Using the IEEE 1394 Serial Bus Using this Chapter
starting address of E8491B shared
memory (hexadecimal)
Figure 3-3 Partial Listing of Resource Manager Output Showing Shared Memory Mapping.
Example Programs
The following examples show an application using the E8491B’s shared memory.
In the program, 8,000 readings are taken with the Keysight E1410 multimeter.
Because the E1410 has only enough memory to store 4,096 readings internally,
all 8,000 readings are stored in shared memory and then transferred to the PC.
Given the shared memory size of 128 kBytes and the E1410 storage format of
eight bytes/reading, up to 16,000 readings can be stored.
Figure 3-4 illustrates the reading transfers performed with the following
programs.
56 Keysight E8491B IEEE 1394 PC Link to VXI User Guide
Page 55

Using this Chapter VXI Programming Using the IEEE 1394 Serial Bus
DUT
Readings are taken and transferred from the
instrument to E8491B shared
the VXI backplane.
memory over
Readings are transferred in
blocks from shared memory
Figure 3-4 Storing Readings in Shared Memory.
Storing Readings in Shared Memory - Keysight VISA Example
This example uses the E1410 VXIplug&play driver to configure the multimeter,
take the readings, and store them in E8491B shared memory. Keysight VISA
functions are used to transfer the readings from shared memory to the PC.
// SHAR_VISA.CPP - This program demonstrates how to access the
// E8491B’s shared memory. The program stores readings taken
// by the E1410 multimeter in E8491B shared memory, and then
// transfers those readings from shared memory to the computer.
#include "hpe1410.h"// include the driver header file
#include "visa.h"
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <windows.h>
// project files: SHAR_VISA.cpp, hpe1410.lib, VISA32.lib
// specify the addressing path to the multimeter
#define E1410 "VXI0::24::INSTR" // E1410 path
#define E8491 "VXI0::0::INSTR" // E8491 path
// check for instrument errors
#define INSTR_ERROR 0xBFFC0D07
Keysight E8491B IEEE 1394 PC Link to VXI User Guide 57
Page 56

VXI Programming Using the IEEE 1394 Serial Bus Using this Chapter
// set up byte swap function for readings transferred from
// E8491B shared memory to the PC
#define SWAP_FLOAT64(rdgs) \
{ unsigned char src[8]; \
*((double *)src) = *((double *)rdgs); \
((unsigned char *) (rdgs))[0] = ((unsigned char*) (src))[7]; \
((unsigned char *) (rdgs))[1] = ((unsigned char*) (src))[6]; \
((unsigned char *) (rdgs))[2] = ((unsigned char*) (src))[5]; \
((unsigned char *) (rdgs))[3] = ((unsigned char*) (src))[4]; \
((unsigned char *) (rdgs))[4] = ((unsigned char*) (src))[3]; \
((unsigned char *) (rdgs))[5] = ((unsigned char*) (src))[2]; \
((unsigned char *) (rdgs))[6] = ((unsigned char*) (src))[1]; \
((unsigned char *) (rdgs))[7] = ((unsigned char*) (src))[0]; \
}
// prototypes
void check(ViSession vi, ViStatus error);
void err_handler(ViSession vi, ViStatus err);
void main(void)
{
ViSession vi, defaultRM, fw;
ViStatus errStatus, err;
unsigned long start_addr;// starting address of shared memory
ViReal64 rdgs[8000];// array for readings from shared memory
int i;
ViChar err_message[256];
// open a VXIplug&play device session and reset the multimeter
errStatus = hpe1410_init(E1410,0,1,&vi);
if( VI_SUCCESS > errStatus)
{
hpe1410_error_message( vi, errStatus, err_message);
printf("Unable to open %s\n", E1410);
printf("hpe1410_init() returned error message %s\n",
err_message);
return;
}
// open a VISA session to the E8491B
viOpenDefaultRM(&defaultRM);
viOpen(defaultRM,E8491, VI_NULL, VI_NULL, &fw);
// get E8491B shared memory base address
viGetAttribute(fw, VI_ATTR_MEM_BASE, &start_addr);
// enable multimeter error detection
hpe1410_errorQueryDetect(vi, 1);
// set a 5s timeout period to allow functions to complete
errStatus = hpe1410_timeOut(vi, 5000);
check(vi, errStatus);
// configure the multimeter for DCV measurements
errStatus = hpe1410_confVoltDc(vi);
check(vi, errStatus);
58 Keysight E8491B IEEE 1394 PC Link to VXI User Guide
Page 57

Using this Chapter VXI Programming Using the IEEE 1394 Serial Bus
// turn off autorange, set a 30V DCV range
errStatus = hpe1410_voltDcRang(vi, 0, 30);
check(vi, errStatus);
// set a 10 us aperture time
errStatus = hpe1410_voltDcAper(vi, 10.0e-6);
check(vi, errStatus);
// set 8000 readings
errStatus = hpe1410_sampCoun(vi, 8000);
check(vi, errStatus);
// store the readings in E8491B shared memory
// specify the E8491B shared memory base address
errStatus = hpe1410_memVmeAddr(vi, start_addr);
check(vi, errStatus);
// specify the amount of memory required
// (8000 readings * 8 bytes/reading)
errStatus = hpe1410_memVmeSize(vi, 64000);
check(vi, errStatus);
// enable the readings to be stored
errStatus = hpe1410_memVmeStat(vi, 1);
// disable multimeter error detection
hpe1410_errorQueryDetect(vi, 0);
// initiate the multimeter to take the readings
errStatus = hpe1410_initImm(vi);
// pause 30s to allow readings to complete
Sleep (30000);
// transfer the 8,000 readings (64,000 bytes) from the multimeter
using
// the VISA function viMoveIn8
err = viMoveIn8(fw, VI_A24_SPACE, 0, 64000, (ViPUInt8)rdgs);
if(err < VI_SUCCESS) err_handler(fw, err);
// swap the bytes once they are transferred from shared memory
for (i=0;i<7999;i++)
{
SWAP_FLOAT64(&rdgs[i]);
}
// print some readings to verify the transfer was successful
for (i=0; i<10; i++)
{
printf("%lf\n", rdgs[i]);
}
// close the device sessions
hpe1410_close(vi); // close E1410 session
viClose(fw); // close E8491 session
}
Keysight E8491B IEEE 1394 PC Link to VXI User Guide 59
Page 58

VXI Programming Using the IEEE 1394 Serial Bus Using this Chapter
//**********************************************************
// error checking routine
void check (ViSession vi, ViStatus errStatus)
{
ViInt32 inst_err;
ViChar err_message[256];
if(VI_SUCCESS > errStatus)
{
if(INSTR_ERROR == errStatus)
{
// query instrument error
hpe1410_dcl(vi);// send a device clear
hpe1410_error_query(vi, &inst_err, err_message);
// display the error
printf("Instrument Error : %ld, %s\n", inst_err, err_message);
}
else
{
// get driver error message
hpe1410_error_message(vi, errStatus, err_message);
// display the error
printf("E1410 Driver Error : %ld, %s\n", errStatus,
err_message);
}
hpe1410_reset(vi);// reset the multimeter
hpe1410_close(vi);// close the multimeter handle
exit(1);
}
return;
}
//**************************************************************
// Error handling function
void err_handler (ViSession vi, ViStatus err)
{
char buf[1024]={0};
viStatusDesc(vi,err,buf);
printf("ERROR = %s\n", buf);
return;
}
Comments
1 1. Because of the E1410 multimeter data storage format (eight bytes /
reading), the readings are transferred from shared memory to the PC in bytes.
Therefore, it is necessary to swap each byte in order to re-construct the
60 Keysight E8491B IEEE 1394 PC Link to VXI User Guide
Page 59

Using this Chapter VXI Programming Using the IEEE 1394 Serial Bus
reading. Depending on the storage formats of your particular instruments,
swapping may not be necessary.
2 2. This manual is included on the Keysight I/O Libraries CD. By viewing the
manual from the CD, you can cut and paste this program into your
development environment.
Storing Readings in Shared Memory - SICL Example
This example uses the E1410 VXIplug&play driver to configure the multimeter,
take the readings, and store them in E8491B shared memory. SICL functions are
used to transfer the readings from shared memory to the PC.
// SHAR_SICL.CPP - This program demonstrates how to access the
// E8491B’s shared memory. The program stores readings taken by
// the E1410 multimeter in E8491B shared memory, and then
// transfers those readings from shared memory to the computer.
#include "sicl.h"
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <windows.h>
// project files: SHAR_SICL.cpp, SICL32.lib
// set up byte swap function for readings transferred from
// E8491B shared memory to the PC
#define SWAP_FLOAT64(rdgs) \
{ unsigned char src[8]; \
*((double *)src) = *((double *)rdgs); \
((unsigned char *) (rdgs))[0] = ((unsigned char*) (src))[7]; \
((unsigned char *) (rdgs))[1] = ((unsigned char*) (src))[6]; \
((unsigned char *) (rdgs))[2] = ((unsigned char*) (src))[5]; \
((unsigned char *) (rdgs))[3] = ((unsigned char*) (src))[4]; \
((unsigned char *) (rdgs))[4] = ((unsigned char*) (src))[3]; \
((unsigned char *) (rdgs))[5] = ((unsigned char*) (src))[2]; \
((unsigned char *) (rdgs))[6] = ((unsigned char*) (src))[1]; \
((unsigned char *) (rdgs))[7] = ((unsigned char*) (src))[0]; \
}
void main(void)
{
INST e8491; // handle for SICL session to E8491
INST e1410; // handle for SICL session to E1410
struct vxiinfo info; // structure for data returned by
ivxirminfo
unsigned long start_addr; // starting address of shared memory
double rdgs[8000]; // array for readings from shared
memory
short i;
unsigned long map; // memory map space
// install SICL error handler
ionerror(I_ERROR_EXIT);
Keysight E8491B IEEE 1394 PC Link to VXI User Guide 61
Page 60

VXI Programming Using the IEEE 1394 Serial Bus Using this Chapter
// open a (SICL) interface session to the E8491B
// open a (SICL) device session to the E1410
e8491 = iopen("vxi");
e1410 = iopen("vxi,24");
// read the VXI resource manager information in order to determine
// the E8491B shared memory starting address
ivxirminfo(e8491, 0, &info);
start_addr = info.memstart;
// convert address from pages to an address
start_addr = (start_addr*256);
// map E8491B memory space for transfer of readings from
// E8491B shared memory to the computer
map = imapx(e8491, I_MAP_SHARED, 0, 1);
// set a 5s timeout period to allow functions to complete
itimeout(e8491, 5000);
itimeout(e1410, 5000);
// configure the multimeter for DCV measurements
iprintf(e1410, "CONF:VOLT:DC 30.0\n");
// set a 10 us aperture time
iprintf(e1410, "VOLT:APER 10.0e-6\n");
// set 8000 readings
iprintf(e1410, "SAMP:COUN 8000\n");
// store the readings in E8491B shared memory
// specify the E8491B shared memory base address
iprintf(e1410, "MEM:VME:ADDR %d\n", start_addr);
// specify the amount of memory required
// (8000 readings * 8 bytes/reading)
iprintf(e1410, "MEM:VME:SIZE 64000\n");
// enable the reading to be stored
iprintf(e1410, "MEM:VME:STAT 1\n");
// initiate the multimeter to take the readings
iprintf(e1410, "INIT\n");
// pause 30s to allow readings to complete and to transfer
// to shared memory
Sleep (30000);
// transfer the (8000) readings from the multimeter using the SICL
// function iblockmovex - the parameters are id, source handle,
source
// offset, source width, source increment, destination handle,
destination
// offset, destination width, destination increment, count, and
swap
62 Keysight E8491B IEEE 1394 PC Link to VXI User Guide
Page 61

Using this Chapter VXI Programming Using the IEEE 1394 Serial Bus
iblockmovex(e8491, map, 0, 8, 1, 0, (unsigned long) rdgs, 8, 1,
64000, 0);
// swap the bytes once they are transferred from shared memory
for (i=0;i<7999;i++)
{
SWAP_FLOAT64(&rdgs[i]);
}
// print some readings to verify the transfer was successful
for (i=0; i<10; i++)
{
printf("%lf\n", rdgs[i]);
}
// unmap memory
iunmapx(e8491, map, I_MAP_SHARED, 0, 1);
// close the device sessions
iclose(e8491);// close SICL interface session
iclose(e1410);// close SICL device session
}
Comments
1 Because of the E1410 multimeter data storage format (eight bytes / reading),
the readings are transferred from shared memory to the PC in bytes.
Therefore, it is necessary to swap each byte in order to re-construct the
reading. Depending on the storage formats of your particular instruments,
swapping may not be necessary.
2 This manual is included on the Keysight I/O Libraries CD. By viewing the
manual from the CD, you can cut and paste this program into your
development environment.
Keysight E8491B IEEE 1394 PC Link to VXI User Guide 63
Page 62

VXI Programming Using the IEEE 1394 Serial Bus Using this Chapter
64 Keysight E8491B IEEE 1394 PC Link to VXI User Guide
Page 63

Keysight E8491B IEEE 1394 PC Link to VXI
Configuration and User Guide
4 IEEE 1394 Fundamentals and
Interface Overview
Using this Chapter
This chapter contains reference information on the IEEE 1394 Serial Bus, the data
transfer protocol, and on the related hardware. The contents of the chapter
include:
IEEE 1394 Topology and Terminology page 66
IEEE 1394 Data Transfer Protocol page 69
OHCI-Compatible Host Adapter and Interface Cable page 71
The Keysight E8491B PC to VXI Interconnect page 72
The Keysight I/O Libraries page 74
65
Page 64

IEEE 1394 Fundamentals and Interface Overview Using this Chapter
parent chil d
child
VXI mai nframe 1 VXI mai nframe 3
VXI mainframe 2
PC w/ IEEE 1394- to-PCI
host adapter
HP E84 91A IEEE 1 394
to VXI inter connect
root
node
branch
node
leaf
node
leaf
node
hop
hop
hop
IEEE 1394 Topology and Terminology
Optimizing the IEEE 1394 bus must include an understanding of the topology
and terms associated with its use. Figure 4-1 shows a VXI system consisting of a
PC and three VXI mainframes - interconnected with the IEEE 1394 bus.
Figure 4-1 IEEE 1394 Topology and Terms.
66 Keysight E8491B IEEE 1394 PC Link to VXI User Guide
The terms shown in Figure 4-1 are defined in the following table.
Page 65

Using this Chapter IEEE 1394 Fundamentals and Interface Overview
Table 0-2. Definition of Terms.
Host Adapter Links the computer’s PCI bus to the IEEE 1394 interface. To use a host adapter,
computers must be PCI Rev. 2.0 compliant.
E8491B
1394-to-VXI
Interconnect
Root Node Each device (E8491B) on the bus is a “node.” In VXI systems, the PC is always
Branch Node A branch node has IEEE 1394 cables connected to two or more ports. In Figure
Leaf Node A leaf node has a single IEEE 1394 cable connected to it.VXI mainframes 2 and
Parent A node (E8491B) is a parent if it is physically connected closer to the root than
Child A node (E8491B) is a child if it is farther from the root than an adjacent node. In
Hop A hop is a IEEE 1394 cable link between nodes. There can be no more than 16
Links the IEEE 1394 interface to the VXI backplane. Provides the backplane’s
clock and trigger resources.
the root node having cycle master and bus master capabilities.
1, VXI mainframe 1 is a branch node because of the 1394 cables connecting it
to the PC (root node) and to VXI mainframe 3 on its right.
3 are leaf nodes.
an adjacent node. In Figure 1, VXI mainframe 1 is a parent node because it is
closer to the root than VXI mainframe 3.
Figure 1, VXI mainframe 3 is a child node because it is farther from the root
than VXI mainframe 1.
A node with a single IEEE 1394 cable connected to it (leaf node) is always a
child (VXI mainframe 2).
hops between any two nodes. In the diagram above, there is a maximum of
three hops between nodes. The distance between any two nodes cannot
exceed 72m.
Features of the IEEE 1394 Bus
The following features of the IEEE 1394 bus apply to all bus applications
including VXI systems.
– Daisy-chain or branching configurations are allowed. There can be no
closed loops (i.e. more than one connection between any two devices).
– Up to 63 devices (including 16 E8491Bs) are allowed per bus segment.
One host adapter represents one bus segment.
– There is a maximum of 16 hops between any two devices. The bus cable
length cannot exceed 72 meters between any two devices.
– Live/hot connections. A VXI mainframe anywhere in the configuration can
be turned on/off without affecting the other mainframes. The IEEE 1394
bus automatically reconfigures itself any time a VXI mainframe (or other
device) is added or removed. It is best to do this however, if there are no
data transactions taking place elsewhere in the system.
Keysight E8491B IEEE 1394 PC Link to VXI User Guide 67
Page 66

IEEE 1394 Fundamentals and Interface Overview Using this Chapter
Optimizing the Configuration
I/O performance is impacted slightly by the hardware configuration.The VXI
mainframe closest to the PC (root node) has the highest priority. For example, if
instruments in VXI mainframes 1 and 3 (Figure 4-1) contend for the bus at the
same time, the root node will grant mainframe 1 access to the bus first. However,
the bus’s fair arbitration protocol (covered in the next section) ensures that each
device has equal access to the bus and that devices closer to the root are not
continually granted the bus.
68 Keysight E8491B IEEE 1394 PC Link to VXI User Guide
Page 67

Using this Chapter IEEE 1394 Fundamentals and Interface Overview
VXI mainframe 1 VXI mainframe 3
VXI mainframe 2
block transfer
data packet
data packet
data packet
data pa cket
data pa cket
data pa cket
block transfer
arb
seq
data
packet
ack
arb
seq packet
data
ack
arb
seq
data
packet
ack
mainfr ame 1 or 2 mainfr ame 1 or 2 mainfr ame 3
subact ion 1 subacti on 2 subactio n 3
Fairness Interval
n
subact ion gaps
arbitration rest gap arbi tration ga p
F I
n-1 n+1
F I
IEEE 1394 Data Transfer Protocol
Data transfer over the IEEE 1394 bus can be either asynchronous or
1
isochronous
. Keysight’s IEEE 1394 based VXI systems use asynchronous data
transfers and a “fair arbitration” protocol to ensure each VXI mainframe has equal
access to the bus. Figure 4-2 illustrates the concepts of asynchronous data
transfers and fair arbitration.
Figure 4-2 IEEE 1394 Data Transfer Protocol.
1 Isochronous data transfers broadcast variable amounts of data at regular intervals with no
acknowledgement. Isochronous and Asynchronous data transfers can occur on the same bus.
Keysight E8491B IEEE 1394 PC Link to VXI User Guide 69
Page 68

IEEE 1394 Fundamentals and Interface Overview Using this Chapter
Asynchronous Data Transfers
During an asynchronous data transfer, a variable amount of data is transferred to
an explicit address in real time, and an acknowledgement is returned. Data is
transferred across the IEEE 1394 bus in packets called “subactions.” An
asynchronous subaction is made up of three parts:
– arbitration sequence - the period when a device requests control of the
bus in order to transmit a data packet.
– data packet - the data packet consists of a data prefix that contains
information about the transaction, the data itself (e.g. VXI instrument
commands), and a data end signal. The maximum packet size is 2 kByte for
400 Mbit adapters such as the adapter supplied with the E8491B.
– acknowledgement - a code returned by the (addressed) data destination
indicating the action taken by the receiver.
The periods between subactions are called subaction gaps. The subaction gap
allows devices that have not had control of the bus during the current “fairness
interval” to arbitrate for control.
Fair Arbitration Protocol
The fair arbitration protocol is based on the fairness interval shown in Figure 2. A
fairness interval consists of one or more subactions in which data packets are
transferred over the bus. A fairness interval is as follows:
1 The interval begins when devices (E8491B’s) arbitrate for control of the bus.
2 When a device is granted control, it transfers its data packet and is then
disabled from arbitrating until the next fairness interval.
3 A subaction gap occurs after the previous data packet is transferred. During
this period, remaining devices arbitrate for the bus. The next device granted
the bus transfers its data packet and is then disabled from arbitrating until the
next fairness interval.
4 The fairness interval ends after each device has had an opportunity to access
to the bus and the arbitration reset gap, which is longer than the subaction
gap, occurs. The arbitration reset gap re-enables each device for arbitration
during the next fairness interval.
VXI Data Transfers
To take advantage of the IEEE 1394 data transfer protocol, large amounts of data
should be transferred between VXI instruments and the PC using block transfers.
During a block transfer, data is divided into the packets described previously; the
number of packets depends on the amount of data and whether a 200 Mbit or
400 Mbit host adapter is used. Compared to protocols that transfer data one
byte or one word at a time, transfer speed between the instrument and the PC is
increased because the IEEE 1394 protocol overhead is associated with the
70 Keysight E8491B IEEE 1394 PC Link to VXI User Guide
Page 69

Using this Chapter IEEE 1394 Fundamentals and Interface Overview
External
IEEE 1394
Connectors
12 VDC
Power Connector
fairness interval and with each packet, rather than with each byte or word
transferred. Thus, transfer speeds (bits/second) over the IEEE 1394 bus increase
as the amount of data transferred (block size) increases.
OHCI-Compatible Host Adapter and Interface Cable
The OHCI-compatible PCI-to-IEEE 1394 host adapter is a PC plug-in card1
capable of transferring data at up to 400 MBits/second. The adapter has three
external IEEE 1394 ports. Each OHCI adapter represents one bus segment
capable of supporting up to 63 nodes. If required, the OHCI adapter can supply
12V with a maximum total current of 0.5A to all three 1394 ports for IEEE 1394
devices that require power.The layout of a typtical adapter is shown below.
Figure 4-3 Layout of a Typical OHCI PCI-to-IEEE 1394 Host Adapter.
The interface cable supplied with the host adapter has two power wires and two
signal twisted-pairs. A cross-section of the cable and the cable connector is
shown in Figure 4-4.
1 In the future, IEEE 1394 will be a standard port on selected PCs.
Keysight E8491B IEEE 1394 PC Link to VXI User Guide 71
Page 70

IEEE 1394 Fundamentals and Interface Overview Using this Chapter
135
246
6.1 mm
power wires
shields
signal pair wires
connector
PIN #
COMMENT
1
cable pow er
2
cable ground
3/4
strobe on receive,
data on transmit
5/6
data on receive,
strobe on transmit
Figure 4-4 Cross-section of the IEEE 1394 Cable.
The power wires route power from the host adapter to devices (nodes) on the
bus, whether the devices are turned on or off. Since each device in the system
acts as a repeater, the power supplied to a device that is turned off enables
signals to be transferred across that device. This maintains signal continuity
throughout the system.
The Keysight E8491B PC to VXI Interconnect
The E8491B is a VXI C-size device (Figure 4-5) normally installed in mainframe
slot 0. With a logical address of 0, the E8491B functions as the mainframe’s
resource manager via software included with the I_O libraries. The E8491B has
128 kBytes of shared RAM and contains many of the clock and triggering
features found on the Keysight E1406A Command Module - a VXI resource
manager/slot 0 device common in many GPIB-based systems. A VXI mainframe
with the E8491B in slot 0 can also be powered on/off at any time without
affecting other mainframes in the system.
72 Keysight E8491B IEEE 1394 PC Link to VXI User Guide
The E8491B IEEE 1394 interconnect links the VXI backplane to the IEEE 1394
bus. However, the E8491B and the IEEE 1394 bus do not extend the (VXI)
backplane between frames in multi-frame VXI systems. This means that the
multimeter and multiplexers in a VXI scanning multimeter for example, must be
installed in the same mainframe. Devices sharing the VXI Local bus must also be
installed in the same mainframe VXI Local bus.
Page 71

Using this Chapter IEEE 1394 Fundamentals and Interface Overview
IEEE
IEEE 1394 Ports
HP E8491B
Reset
internally and distributed over the
address in multi-frame VXI
systems.
Used to identify the interconnect
uted from an external source.
vices, or the triggers can be distrib-
VXI backplane and to external de-
Configuration Label
VXI
The E8491B is capable of sourcing
TTL level triggers and receiving
specified levels up to +30V.
Trigger signals can be generated
TTL, CMOS, ECL, or user
the mainframe's VXI backplane.
VXI - indicates data traffic across
instrument self-test.
SYSFAIL - asserted during a VXI
over the IEEE 1394 bus
IEEE-1394 - indicates data traffic
self-test.
or the E8491B is performing a
was detected in the HP E8491B,
Failed - a hardware failure
Trigger Ports
SYSFAIL
Annunciators
Failed
Resets the HP E8491B and all instruments
in the mainframe. Re-runs the resource
mainframe and can also be routed to
signal is distributed to every slot in the
received from an external source. The
clock is internally generated or can be
mainframe's slot 0 device. This TTL level
The E8491B is capable of sourcing and
receiving the VXI system's 10 MHz clock.
The system clock (CLK10) is one of the
external devices.
VXI resources provided by the
manager.
Trig Out
Reset Button
which minimize the number of hops.
Each port is identical and any port or
System Clock Ports
Three ports allow tree topologies
IEEE 1394 Ports
combination of ports can be used.
Trig In
Clk Out
Clk In
A
VXI
1394
B
C
Figure 4-5 The Keysight E8491B IEEE 1394 to VXI Interconnect.
Keysight E8491B IEEE 1394 PC Link to VXI User Guide 73
Page 72
IEEE 1394 Fundamentals and Interface Overview Using this Chapter
Development Environment
(C/C++, Visual BASIC, HP VEE)
Drivers
HP VXI plug&play Instrument
HP VISA / HP SICL
Host Adapter Drivers
VXI Instruments
HP Universal Instrument
Drivers
HP I_O Libraries
Using the Keysight E8491B with the Keysight E1406 Command Module
Though not a common configuration, the E1406 command module can be used
in the same mainframe as the E8491 to provide GPIB access to instruments. In
this configuration, however, the E8491B must be the mainframe’s resource
manager. See the section titled “Alternate Configurations” in Chapter 2, page
<Blue>24.
The Keysight I/O Libraries
The software required to use the IEEE 1394 interface in a VXI system is contained
in the Keysight I/O Libraries and Keysight VXIplug&play Drivers. The software
supports the Windows 95 and Windows NT platforms.
The software “stack” shown below shows the relationship of the VXIplug&play
drivers to Keysight VISA/ SICL, to the host adapter drivers, and to the VXI
instruments. Notice that Keysight’s implementation of the IEEE 1394 interface
requires Keysight VISA and will not work with the VISA supplied by other
vendors.
Figure 4-6 System Software and Drivers.
Most application programs are written using the instruments’ VXIplug&play
drivers. The plug&play driver functions make subsequent calls to the VISA
74 Keysight E8491B IEEE 1394 PC Link to VXI User Guide
functions and so on. Message-based instruments can be programmed at the
Keysight VISA / SICL level by embedding SCPI commands in the Keysight VISA /
SICL functions.
Page 73

Using this Chapter IEEE 1394 Fundamentals and Interface Overview
Keysight E8491B IEEE 1394 PC Link to VXI User Guide 75
Page 74

IEEE 1394 Fundamentals and Interface Overview Using this Chapter
76 Keysight E8491B IEEE 1394 PC Link to VXI User Guide
Page 75

Keysight E8491B IEEE 1394 PC Link to VXI
Configuration and User Guide
A Specifications
The following specifications define the operating and performance
characteristics of the Keysight E8491B.
Interface Characteristics
Operating System Windows 95
Controllers PC based
I/O Library SICL / VISA
Windows NT
Backplane PCI
Interface IEEE 1394
Maximum I/O Speed*
* 200 MHz Pentium PC
/
400 MHz Selectron Host
Languages C/C++, Visual Basic, Keysight VEE, LabView
16-bit: 1.76 MBytes/s to PC
2.50 MBytes/s to E8491B
32 bit: 1.0 MByte/s to PC
1.0 MByte/s to E8491B
77
Page 76

Specifications
VXI Characteristics
General
VXI Device Type Message-based commander
Data transfer bus n/a
Slot 0 functionality Yes
Resource Manager Functionality Yes
MXIbus Resource Manager Yes
Size C
Slots 1
Connectors P1 / P2
Shared Memory 128 kBytes
VXI busses TTL trigger bus, ECL trigger bus
C-size compatibility n/a
CLK 10
Clk In
Input TTL
Frequency Stability 100 ppm
Duty Cycle 50% ± 5%
Clk Out
Output TTL
Frequency Stability 100 ppm
Duty Cycle 50% ± 5%
External Trigger Input
Connector SMB (on faceplate)
Levels TTL, CMOS, ECL, 0 to +33V
Programmable Threshold Range 0 to +30V
Programmable Threshold Accuracy ± 0.4V
Threshold Sensitivity (hysteresis) 0.5 Vpp maximum
0.1 Vpp minimum
Input Load 50 pf, 55 kohms
78 Keysight E8491B IEEE 1394 PC Link to VXI User Guide
Page 77

Maximum Rate 2 MHz
Minimum Pulse Width 200 ns
External Trigger Output
Connector SMB (on faceplate)
Levels nominal pull up to + 5V
Maximum External Pull Up + 30V
Specifications
Trigger Delays
Cooling
Sink Current 10 mA @ V
ol
150 mA @ V
Maximum delay from TTLTRG to ECLTRG 60 ns
Maximum delay from ECLTRG to TTLTRG 60 ns
Maximum delay from Trig In port to
300ns
ECLTRG or TTLTRG
Maximum delay from TTLTRG or ECLTRG
100 ns
to Trig Out port
Watts / slot 20W
P mm H
0 0.10
2
Air flow liters / s 2.0
< 0.4V or
< 1.0V
ol
Power Supply Loading
I
(amps) IDM (amps)
PM
+5V 2.5 0.001
+12V 0.35 0.050
-12V 0.015 0.001
+24V 0.0 0.0
-24V 0.0 0.0
-5.2V 0.180 0.001
-2V 0.360 0.001
Keysight E8491B IEEE 1394 PC Link to VXI User Guide 79
Page 78

Specifications
80 Keysight E8491B IEEE 1394 PC Link to VXI User Guide
Page 79

Keysight E8491B IEEE 1394 PC Link to VXI
Configuration and User Guide
B Editing the Keysight E8491B
Resource Manager Configuration
Introduction
The resource manager functionality provided through the Keysight E8491B
configures your VXI system based on rules specified by the VXI standard. The
configuration can be viewed or modified through the configuration files and
utility f unctions outlined in this appendix.
Configuration File Overview
Configuration files (.cf extension) are placed in the <drive:>\siclnt\defaults or \
sicl95\defaults directory when the Keysight I/O Libraries are installed. Except
where noted, the following files can be edited from the Keysight I/O Libraries’
‘I/O Config’ utility (Figure B-1) as shown on the following pages. When editing a
file, note the following:
1 Add your entry(ies) below the commented (lines).
2 The first column must contain an entry. Any number of spaces can separate
remaining entries on the line.
81
Page 80

Editing the Keysight E8491B Resource Manager Configuration Introduction
1. From the I_O Libraries
program group, click I_O
2. Select the configured
E8491B interface and
then click Edit. This
brings up the window
(partial view) in Figure
Figure B-1 Editing Configuration Files from the ‘I/O Config’ Utility.
82 Keysight E8491B IEEE 1394 PC Link to VXI User Guide
Page 81
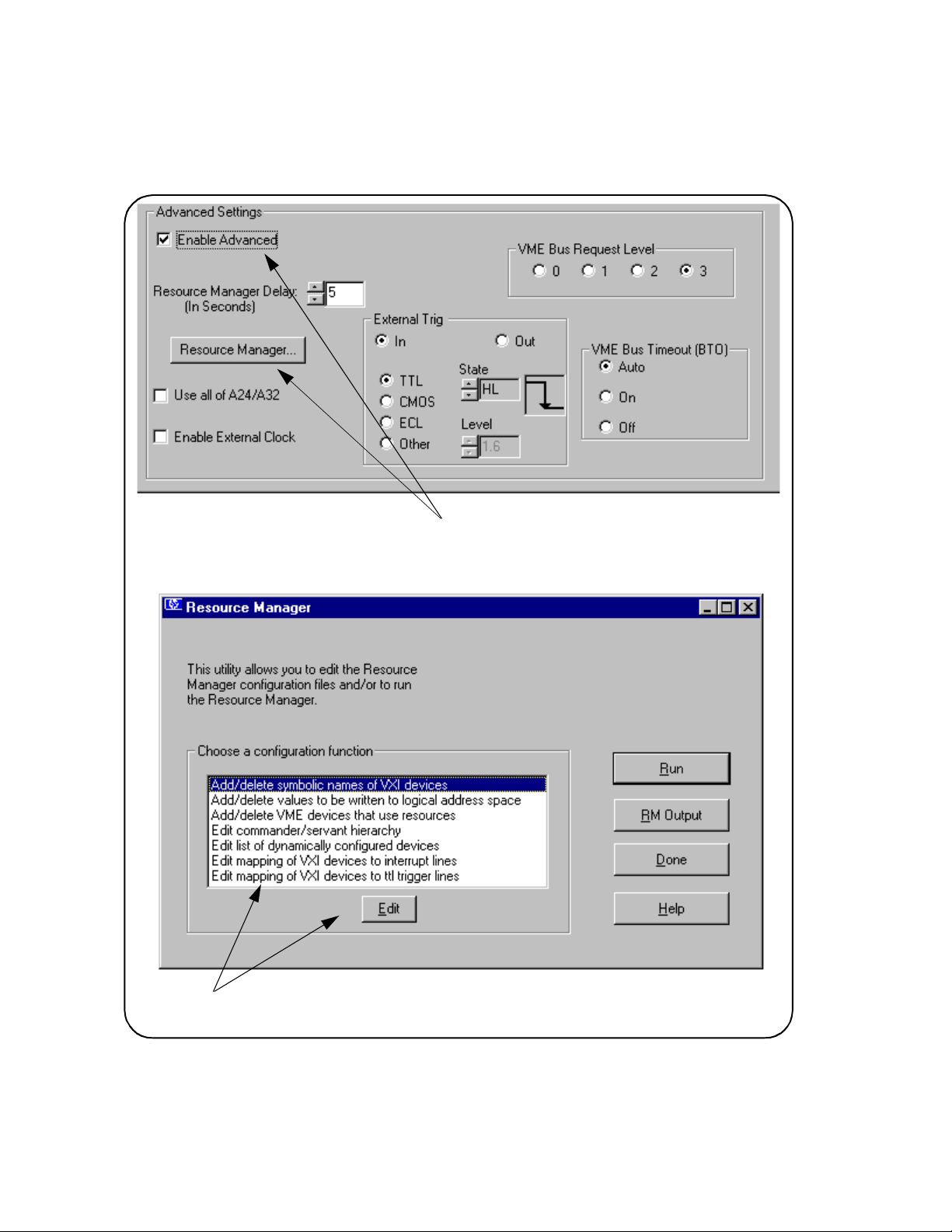
Introduction Editing the Keysight E8491B Resource Manager Configuration
3. Check Enable Advanced and
then click Resource Manager...
4. Select the portion of the
configuration to edit and then
Figure B-2 Editing Configuration Files from the ‘I/O Config’ Utility (cont’d).
Keysight E8491B IEEE 1394 PC Link to VXI User Guide 83
Page 82

Editing the Keysight E8491B Resource Manager Configuration Introduction
The names.cf Configuration File
The names.cf file is a database that contains a list of symbolic names to assign
VXI devices that have been configured. The ivxirm utility reads the model id
number from the VXI device and the ivxisc utility uses that information and this
file to print out the VXI device symbolic name. If you add a new VXI device to
your system that is not currently in the database, you may want to add an entry
to this file.
This file is edited by selecting “Add/delete symbolic names of VXI devices” in the
Resource Manager window (Figure B-2).
The oride.cf Configuration File
The oride.cf file contains values to be written to logical address space for
register-based instruments. This data is written to A16 address space after the
resource manager runs, but before the system’s resources are released. This can
be used for custom configuration of register-based instruments every time the
resource manager runs.
This file is edited by selecting “Add/delete values to be written to logical address
space” in the Resource Manager window (Figure B-2).
The vmedev.cf Configuration File
The vmedev.cf file contains a list of VME devices that use resources in the VXI
card cage. Since the resource manager is unable to detect VME devices, the
resource manager uses this information to determine such things as the slot
number where the VME device is located, what type (A16, A24, or A32) and how
much memory it uses, and what interrupt lines it uses. Additionally, the resource
manager verifies that multiple resources aren’t allocated. This file is also used by
the ivxisc utility to print out information about the devices.
This file is edited by selecting “Add/delete VME devices that use resources” in the
Resource Manager window (Figure B-2).
The cmdrsrvt.cf Configuration File
The cmdrsrvt.cf file contains a commander/servant hierarchy other than the
default for the VXI system. The resource manager will set up the
commander/servant hierarchy according to the commander’s logical addresses
and the servant area switch. However, you can use this file to override the default
based on the commander’s servant area. This file should only contain changes
from the default.
This file is edited by selecting “Edit commander/servant hierarchy” in the
Resource Manager window (Figure B-2).
84 Keysight E8491B IEEE 1394 PC Link to VXI User Guide
Page 83

Introduction Editing the Keysight E8491B Resource Manager Configuration
The dynamic.cf Configuration File
The dynamic.cf file contains a list of VXI devices to be dynamically configured.
You only need to add entries to this file if you want to override the default
dynamic configuration assignment by the resource manager. Normally, if you
have a dynamically configurable device and the logical address is set at 255, the
resource manager will assign the first available address. However, if a
dynamically configurable device has an entry in this file, the resource manager
will assign the address listed in the file.
This file is edited by selecting “Edit list of dynamically configured devices” in the
Resource Manager window (Figure B-2).
The irq.cf Configuration File
The irq.cf file is a database that maps specific interrupt lines to VXI interrupt
handlers. If you have non-programmable interrupters and you want the
interrupters to be recognized by a VXI interrupt handler, you must make an entry
in this file. Additionally, if you have programmable interrupters and you want
them to be recognized by a device other than what’s assigned by the resource
manager (the commander of that device), you can make an entry in this file to
override the default. Keep in mind that not all VXI devices need to use interrupt
lines and not all interrupt lines need to be assigned. Note that any interrupt lines
assigned in this file cannot also be assigned in the vmedev.cf configuration file.
This file is edited by selecting “Edit mapping of VXI devices to interrupt lines” in
the Resource Manager window (Figure B-2).
The ttltrig.cf Configuration File
The ttltrig.cf file contains the mapping of VXI devices to TTL trigger lines in
extended VXI systems. If you have a MXI-extended (multiple-mainframe) system
and you are sending / receiving triggers between mainframes, you must map the
TTL trigger line to the logical address of the device asserting the trigger. This file
is only used for extended VXI systems.
This file is edited by selecting “Edit mapping of VXI devices to TTL trigger lines”
in the Resource Manager window (Figure B-2).
The vximanuf.cf Configuration File
The vximanuf.cf file contains a database that cross references the VXI
manufacturer id numbers and the name of the manufacturer. The ivxirm utility
reads the manufacturer id number from the VXI device. The ivxisc utility then
uses that number and this file to print out the name of the manufacturer. If you
add a new VXI device from a vendor that is not currently in the file, you may want
to add an entry to the file.
This file can not be edited using ‘I/O Config’.
Keysight E8491B IEEE 1394 PC Link to VXI User Guide 85
Page 84

Editing the Keysight E8491B Resource Manager Configuration Introduction
The vximodel.cf Configuration File
The vximodel.cf file contains a database that lists a cross reference of
manufacturer id, model id, and VXI device names. The ivxirm utility reads the
model id number from the VXI device and the ivxisc utility uses that information
and this file to print out the VXI device model. If you add a new VXI device to your
system that is not currently in this database, you may want to add an entry to this
file.
This file can not be edited using ‘I/O Config’.
Utility Function Overview
Within the <drive:>\siclnt\bin or \sicl95\bin directory are utility functions that
view the resource manager output (ivxisc) and which clear the
E8491B interface (iclear) and run the resource manager (if the iproc utility is
running).
Using ivxisc
The ivxisc function is used to view the resource manager output. ivxisc is
executed from the Windows command (DOS) prompt (..\siclnt\bin or \sicl95\bin
directory) as:
ivxisc vxi<logical unit>
where <logical unit> is the value from the ‘Logical Unit’ window in the
Keysight I/O Libraries ‘I/O Config’ utility. An example of the output produced by
ivxisc is shown in Figures B-3 and B-4.
86 Keysight E8491B IEEE 1394 PC Link to VXI User Guide
Page 85

Introduction Editing the Keysight E8491B Resource Manager Configuration
Figure B-3 Output of ivxisc.
Keysight E8491B IEEE 1394 PC Link to VXI User Guide 87
Page 86

Editing the Keysight E8491B Resource Manager Configuration Introduction
Figure B-4 Output of ivxisc (cont’d).
Using iclear
The iclear function is used to clear the interface (E8491B) or individual
message-based instruments in the VXI mainframe. iclear is executed from the
DOS command prompt (..\siclnt\bin or \sicl95\bin directory) as:
iclear <SICL interface name, [logical address]>
SICL interface name is the name (vxi) listed in the ‘I/O Config’ SICL
Interface Name window. logical address is the address of the
message-based VXI instrument to be cleared.
If a logical address is not specified, the (E8491B) interface is cleared and the
resource manager is started.
88 Keysight E8491B IEEE 1394 PC Link to VXI User Guide
Page 87

Page 88

This information is subject to change
without notice.
© Keysight Technologies, 1999-2019
Printed in Malaysia
Edition 3, August 2019
*E8491-90001*
E8491-90001
www.keysight.com
 Loading...
Loading...