Page 1

X8 MIG Welder
OPERATING MANUAL
Page 2

Contents
1 Read first.................................................................................................................... 4
1.1 Symbols..................................................................................................................................................................................... 4
2 X8 MIG Welder.......................................................................................................... 8
2.1 System introduction............................................................................................................................................................. 8
2.1.1 Introduction to WeldEye for welding procedure and qualification management....................... 9
2.2 System structure..................................................................................................................................................................10
2.2.1 X8 Power Source.................................................................................................................................................11
2.2.2 X8 Wire Feeder....................................................................................................................................................15
2.2.3 X8 MIG Guns........................................................................................................................................................ 20
2.2.4 Control Pad............................................................................................................................................................22
2.3 Installation..............................................................................................................................................................................25
2.3.1 Before installation...............................................................................................................................................25
2.3.2 Power Source installation................................................................................................................................ 26
2.3.3 Wire Feeder installation...................................................................................................................................34
2.3.4 Cables installation...............................................................................................................................................50
2.3.5 Control Pad installation....................................................................................................................................55
2.3.6 Welding gun installation..................................................................................................................................59
2.3.7 Lifting X8 MIG Welder......................................................................................................................................78
2.3.8 Purchasing and managing welding software.......................................................................................... 79
2.3.9 Optional accessories..........................................................................................................................................79
2.4 Operation............................................................................................................................................................................... 84
2.4.1 X8 MIG Welder control devices....................................................................................................................84
2.4.2 Preparing welding system for use.............................................................................................................101
2.4.3 How to use welding system........................................................................................................................ 110
2.5 Troubleshooting................................................................................................................................................................ 166
2.5.1 Error codes..........................................................................................................................................................170
2.6 Maintenance....................................................................................................................................................................... 170
2.6.1 Daily maintenance............................................................................................................................................171
2.6.2 Periodic maintenance of power source and wire feeder..................................................................173
2.6.3 Service workshops........................................................................................................................................... 174
2.7 Technical data.................................................................................................................................................................... 174
2.7.1 X8 Power Source 400 A / 400AMV....................................................................................................... 174
2.7.2 X8 Power Source 500 A / 500AMV....................................................................................................... 176
2.7.3 X8 Power Source 600 A / 600AMV....................................................................................................... 178
2.7.4 X8 Cooler.............................................................................................................................................................180
2.7.5 X8 Wire Feeder..................................................................................................................................................180
2.7.6 X8 Control Pad..................................................................................................................................................181
2.7.7 X8 MIG Gun 200-g.......................................................................................................................................... 182
2.7.8 X8 MIG Gun 300-g.......................................................................................................................................... 183
2.7.9 X8 MIG Gun 400-g.......................................................................................................................................... 184
2.7.10 X8 MIG Gun 420-w....................................................................................................................................... 185
2.7.11 X8 MIG Gun 520-w....................................................................................................................................... 186
2.7.12 X8 MIG Gun 600-w....................................................................................................................................... 187
2.7.13 X8 MIG Gun WS 420-w...............................................................................................................................189
ii
Page 3

2.8 Ordering codes..................................................................................................................................................................190
2.9 Disposal of unit.................................................................................................................................................................193
iii
Page 4

X8 MIG WELDER 1.1 Symbols
1 Read first
Kemppi takes special care in informing its customers about the safety of our products. We also mind the
environment and aspire to disposing of our products according to specified European Directives.
1.1 Symbols
Items in the manual that require particular attention, to minimize damage and personal harm, are indicated
with a three-level notification and warning system.
Convention Used for
Note:
Note text here.
Caution:
Caution text here.
Warning:
Warning text here.
Gives the user a piece of information of particular importance.
Describes a situation that may result in damage to the equipment or
system.
Describes a potentially dangerous situation that may result in personal
damage or fatal injury.
Kemppi symbols
Table 1: Kemppi symbols used in this documentation
Symbol Description
CE mark
EMC Class A
This symbol indicates that the waste of electrical and electronic equipment
must not be disposed as unsorted municipal waste and must be collected
separately. Contact an authorized representative of the manufacturer for
information concerning the decommissioning of your equipment.
Coolant input
OPERATING MANUAL | EN 4
©
KEMPPI | 2018-09-28
Page 5

X8 MIG WELDER 1.1 Symbols
Symbol Description
Coolant output
Gas input
Gas output
High voltage
#
'
8
!
Protective earth
1-MIG
DPulse MIG
Carbon arc gouging
MIG
MMA
5
Pulse MIG
%
OPERATING MANUAL | EN 5
©
KEMPPI | 2018-09-28
Page 6

X8 MIG WELDER 1.1 Symbols
Symbol Description
DProcess
WiseRoot+
,
WiseThin+
*
WiseFusion
+
WiseSteel
E
ŕ
P
S
R
T
WisePenetration+
Creep Start
Hot Start
Upslope
Crater Fill with Downslope
Crater Fill with Downlevel
U
OPERATING MANUAL | EN 6
©
KEMPPI | 2018-09-28
Page 7

X8 MIG WELDER 1.1 Symbols
Symbol Description
2T
Ö
4T
Õ
WP Switch
W
Touch Sense Ignition
Ɔ
O
User manual
OPERATING MANUAL | EN 7
©
KEMPPI | 2018-09-28
Page 8

X8 MIG WELDER 2.1 System introduction
2 X8 MIG Welder
These instructions describe the use of Kemppi's X8 MIG Welder, the top-class welding system for demanding
industrial use. The system consists of a power source, wire feeder, welding gun, Control Pad and various
welding software components and connectivity to Kemppi cloud services. Read the instructions through
carefully.
Disclaimer
While every effort has been made to ensure that the information contained in this guide is accurate and
complete, no liability can be accepted for any errors or omissions. Kemppi reserves the right to change the
specification of the product described at any time without prior notice. Do not copy, record, reproduce or
transmit the contents of this guide without prior permission from Kemppi.
2.1 System introduction
X8 MIG Welder is a multi-process welding equipment intended for demanding professional use in general or
heavy fabrication. The welding system is suitable for various MIG/MAG processes (MIG, 1-MIG, Pulse, DPulse,
WiseRoot+, WiseThin+ ) as well as MMA welding and gouging, cladding and brazing.
1. X8 Power Source 400/500/600
• Includes all the software, welding programs and memory channels for the welding system
• Connects to one or two X8 Wire Feeders
2. X8 Wire Feeder
• Operates with several wire spool types (some of which require an adapter)
• Connects to an external wire drum
OPERATING MANUAL | EN 8
©
KEMPPI | 2018-09-28
Page 9

X8 MIG WELDER 2.1 System introduction
• Contains a control panel for basic adjustment of welding parameters, memory channels and settings
3. X8 MIG Gun 200/300/400-g, 420/520/600-w, X8 MIG Gun WS 420-w
• Connects to the wire feeder with Kemppi Gun Adapter
• Gas-cooled models feature a rotating, changeable neck
• Remote control for selecting memory channels and adjusting settings (optional)
• Ergonomic pistol grip handle
4. X8 Cooler (optional)
• Optionally included in the power source delivery
• Can also be purchased separately
• Essential for welding with a current over 400 A
5. Control Pad
• Wireless remote interface for operating X8 MIG Welder
6. Interconnection Cable 70/95-w/-g (several options)
• Bundle of cables connecting the wire feeder to the power source
• Transfers the welding current, control signals, shielding gas and coolant from the power source to the
wire feeder
7. X8 Wheel Set (several options)
• The wheel set is included in the power source delivery
• The gas cylinder cart is optionally included in the power source delivery
8. My Fleet web service
• Cloud-based service for viewing and managing various information about your X8 MIG Welder
• Provides manufacturer's validation certificate
9. WeldEye (optional)
• Cloud-based service for creating and managing digital WPS documents and other welding-related
information
In addition:
• Several accessories (optional)
• Several welding software products (optional)
2.1.1 Introduction to WeldEye for welding procedure and qualification
management
Welding procedure and qualification management
WeldEye for Welding procedure and qualification management is a cloud-based tool for creating, managing
and storing various welding-related documents and qualification certificates. WeldEye is an end-to-end
solution for handling pWPS, WPQR and WPS documents as well as welder qualification certificates. The
software contains procedure and certificate templates to match all major welding standards. Together with its
integrated drawing tool, WeldEye is swift and easy to use.
The software enables you to keep track of qualification certificates and their expiration dates, and to easily
extend their validity. Revision history helps you track the changes made to the documents. With a flexible
search functionality, you can easily find the welding procedures, personnel, and certificates you need. You
OPERATING MANUAL | EN 9
©
KEMPPI | 2018-09-28
Page 10

X8 MIG WELDER 2.2 System structure
can print out documents or, for example, a list of welders with a certain qualification certificate. Attachments
can be added to any document.
Discover WeldEye – universal welding management software
WeldEye is your primary tool and storage space for keeping your welding-related documents in order.
There is even more to WeldEye than welding document management. WeldEye is a universal solution for
managing welding production. Fitting any size and type of organization that performs welding within the
requirements of international welding standards like ISO, ASME and AWS, WeldEye provides control in all
processes - including welding procedures, welder and inspector qualifications, documentation, reporting and
administration. Most importantly, you get 100% traceability for every weld you ever make.
WeldEye's modular structure is based on various useful functions that serve the needs of wide-ranging
industries and welding-related tasks:
Welding procedures
Includes the digital library and management of pWPS, WPQR and WPS templates according to the most
important welding standards.
Personnel and qualifications
Includes the management and renewal processes of all personnel - welders and inspectors - qualification
certificates.
Quality management
Includes quality verification functionalities with digital WPS and qualification compliance control against
automatically collected digital welding data.
Welding management
Includes document register functionalities and features for comprehensive welding project
documentation and management.
For more information on the full system and other modules, see www.weldeye.com.
2.2 System structure
The parts of X8 MIG Welder are in close co-operation with each other. The information transfer is efficient
and quick, and the different functions, for example, the use of displays, follow the same principles.
Caution:
Do not modify the welding equipment in any way, except for the changes and adjustments covered
in the manufacturer’s instructions.
OPERATING MANUAL | EN 10
©
KEMPPI | 2018-09-28
Page 11

X8 MIG WELDER 2.2 System structure
5
7
1
6
42 3
Figure 1: A chart of the connections between the different parts of X8 MIG Welder
2.2.1 X8 Power Source
This section describes the structure of X8 Power Source.
Front
1. Indicator panel
2. Transportation handle
OPERATING MANUAL | EN 11
©
KEMPPI | 2018-09-28
Page 12

X8 MIG WELDER 2.2 System structure
6
2
3
3
2
4
4
8
5
5
9
7
10
1
11
12
3. USB connector
Connect a USB memory stick to upload the welding procedures (WPS) or Wise features to the power
source or update firmware if a wireless connection is unavailable.
4. Control Pad connector
Connect Control Pad to the power source with a cable to charge its battery or to use it in wired mode.
5. Front panel
6. Front panel latch
Pull to open the front panel and reveal the coolant container.
7. Coolant circulation button
Press to pump the coolant through the system.
Rear
1. Transportation handle
2. Welding current cable connectors (positive pole)
3. Earth return cable connectors (negative pole)
4. Measurement cable connectors
Connectors for wire feeder 1 on the left, wire feeder 2 on the right side of the power source.
5. Control cable connectors
Connectors for wire feeder 1 on the left, wire feeder 2 on the right side of the power source.
6. Ethernet connector
7. Power switch
8. Coolant outlet hose connector
9. Coolant inlet hose connector
10. Rear panel
11. Mains cable
OPERATING MANUAL | EN 12
©
KEMPPI | 2018-09-28
Page 13

X8 MIG WELDER 2.2 System structure
12. Strain relief holder
Indicator panel
1. Power indicator
The LED is green when the unit is on.
2. Voltage Reduction Device (VRD) indicator
The LED is green when VRD is switched on and the no-load voltage is under 35 V.
The LED blinks red when VRD is switched on and the no-load voltage is above 35 V.
The LED is off when VRD is switched off or during welding.
Note:
VRD is in use with MMA and Gouging modes only.
3. Overheat indicator
The LED is yellow when the unit is overheating.
Caution:
If the power source overheats, a thermal cutoff switches the unit off and does not allow it to be
used until it has cooled down.
4. Kemppi cloud connection
The LED is blue when the wire feeder or power source is connected to Kemppi cloud services.
The LED blinks blue when the wire feeder or power source is connecting to Kemppi cloud services.
5. Coolant level warning
The LED is yellow when the coolant level is too low.
6. Coolant temperature warning
The LED is yellow when the cooler is overheating.
Caution:
OPERATING MANUAL | EN 13
©
KEMPPI | 2018-09-28
Page 14

X8 MIG WELDER 2.2 System structure
7
1
4
2
3
65
If the coolant liquid overheats, a thermal cutoff switches the welding system off and does not
allow it to be used until the coolant liquid has cooled down.
7. Coolant circulation warning
The LED is green when the coolant circulation is working normally.
The LED is red when there is a problem in the coolant circulation.
The LED blinks green and red in turns when the circulation of the coolant liquid has been obstructed too
long.
Caution:
If the circulation of the coolant liquid is obstructed, a thermal cutoff switches the welding system
off. Check and fix the error before using the welding system again.
If the error was caused in an unsuccessful filling of the cooler, refill the cooler. In other cases, the
error disappears automatically in 30 seconds.
8. Wireless pairing button
To pair the wire feeder or power source with Control Pad, press the button. If the power source is
connected to wire feeder(s), the wire feeder(s) pairs with Control Pad. If the power source is not
connected to a wire feeder, the power source pairs with Control Pad.
The LED is blue when the wire feeder or power source is wirelessly connected to Control Pad.
The LED blinks blue when the wire feeder or power source is pairing with Control Pad.
Interconnection cable
1. Shielding gas hose
2. Coolant inlet hose
3. Coolant outlet hose
4. Welding current cable
5. Control cable
OPERATING MANUAL | EN 14
©
KEMPPI | 2018-09-28
Page 15

X8 MIG WELDER 2.2 System structure
6. Measurement cable
7. Strain relief pin
2.2.2 X8 Wire Feeder
This section describes the structure of X8 Wire Feeder.
Main parts
1. Top cover
Caution:
Keep the wire feeder top cover closed during welding to reduce the risk of injury or an electric
shock. Keep the top cover closed also at other times to keep the wire feeder insides clean.
2. Handle
Caution:
The handle is only intended for short distance manual carrying. Use Wire Feeder Hanger for
Boom for lifting or hanging the wire feeder.
3. Top cover latch
4. Cable cabinet door
5. Cable cabinet latch
6. Control panel
7. Strain relief
8. Strain relief latch
9. Gun holder mount
OPERATING MANUAL | EN 15
©
KEMPPI | 2018-09-28
Page 16

X8 MIG WELDER 2.2 System structure
15
12
13
14
1011
Figure 2: The warning sticker inside the wire feeder
10. Wire spool
11. Wire spool locking cover
12. Feed rolls
13. Pressure handle
14. Wire guide
15. Inside control buttons
OPERATING MANUAL | EN 16
©
KEMPPI | 2018-09-28
Page 17

X8 MIG WELDER 2.2 System structure
5
6
2
1
4
3
5
6
2
1
4
3
Control panel
The control panel on the front of the wire feeder enables easy control of the wire feeder's basic features.
Although Control Pad is the main control of the welding system, you can also use the wire feeder control
panel or the welding gun remote control.
The wire feeder control panel parts are:
1. Locking button
Press and hold for 2 seconds to lock or release the display and buttons.
2. Channel button
The button lights up blue, when the view is activated.
OPERATING MANUAL | EN 17
©
KEMPPI | 2018-09-28
Page 18

X8 MIG WELDER 2.2 System structure
3. Settings button
The button lights up orange, when the view is activated.
4. Left control knob
5. Right control knob
6. Left and right button
For more information on the use and features of the control panel, see Wire feeder views on page 96.
Control buttons on the inside
The wire feeder has control buttons inside the wire cabinet.
1. Wire retract button
Drive the filler wire backward with arc off.
2. Gas test button
Test the shielding gas flow, or flush out the remainder of the previous gas.
3. Wire inch button
Drive the filler wire forward with arc off.
Interconnection cable connectors
OPERATING MANUAL | EN 18
©
KEMPPI | 2018-09-28
Page 19

X8 MIG WELDER 2.2 System structure
1. Welding current
Supplies current from the power source to the wire feeder.
2. Shielding gas
Supplies shielding gas to the welding gun.
3. Measurement
Supplies the welding parameters measured during welding.
4. Control
Supplies data and operating voltage to the wire feeder.
5. Coolant outlet and inlet
Circulates coolant to and from the welding gun.
For information on the installation of the cables, see Cables installation on page 50.
External component connectors
1. Kemppi Gun Adapter
Connects to the welding gun.
Note:
The wire feeder is supplied with Kemppi Gun Adapter.
2. Subfeeder
Provides control to optional SuperSnake subfeeder or a motorized welding gun.
3. Remote control
Connects to remote control devices (Control Pad). Supplies power and data connection with 12 V voltage.
4. Voltage sensing
Connects to the welding piece and measures arc voltage in real time.
5. Coolant outlet
Delivers cold coolant to the welding gun.
6. Coolant inlet
Receives heated coolant from the welding gun.
OPERATING MANUAL | EN 19
©
KEMPPI | 2018-09-28
Page 20

X8 MIG WELDER 2.2 System structure
13
108
65 7 9
4
3
11212
1
2.2.3 X8 MIG Guns
Gas-cooled gun
1. Gas nozzle
2. Insulating bush
3. Contact tip
4. Contact tip adapter
5. Neck
6. Neck tightener
7. Work light
Press the trigger lightly to switch on the light.
8. Handle cover plate
Covers the handle if the remote control is not used.
9. Trigger
10. X8 Gun Remote Control
The remote control is an optional accessory.
11. Trigger on the pistol grip handle
OPERATING MANUAL | EN 20
©
KEMPPI | 2018-09-28
Page 21

X8 MIG WELDER 2.2 System structure
12. Pistol grip handle
Quick to attach and detach.
13. Kemppi Gun Connector
Water-cooled gun
1. Gas nozzle
2. Insulating bush
3. Contact tip
4. Contact tip adapter
5. Neck
6. Work light
Press the trigger lightly to switch on the light.
7. Handle cover plate
Covers the handle if the remote control is not used.
8. Trigger
9. X8 Gun Remote Control
The remote control is an optional accessory.
10. Trigger on the pistol grip handle
11. Pistol grip handle
Quick to attach and detach.
12. Kemppi Gun Connector
13. Coolant inlet hose
14. Coolant outlet hose
OPERATING MANUAL | EN 21
©
KEMPPI | 2018-09-28
Page 22

X8 MIG WELDER 2.2 System structure
6
7
8
9
5
4
1
2
4
3
6
7
8
9
5
4
1
2
4
3
2.2.4 Control Pad
This section describes the structure of Control Pad.
1. Power button
The button lights up orange, when you switch Control Pad on.
2. Left control knob
3. Right control knob
4. Left and right button
When the button lights up green, you can press the button to confirm an action.
5. Display
6. View buttons
7. Channel button
The button lights up blue, when the view is activated.
8. Menu button
The button lights up white, when the view is activated.
9. Settings button
The button lights up orange, when the view is activated.
OPERATING MANUAL | EN 22
©
KEMPPI | 2018-09-28
Page 23

X8 MIG WELDER 2.2 System structure
14
10
11
12
13
10. NFC reader
11. Barcode reader
12. ON/OFF button for NFC and barcode readers
The button also acts as a shortcut button for reading a barcode in any Control Pad view.
13. Loop for the carrying strap
14. Hook
When you connect or disconnect the charger, Control Pad shows you the charge level.
OPERATING MANUAL | EN 23
©
KEMPPI | 2018-09-28
Page 24

X8 MIG WELDER 2.2 System structure
When Control Pad is charging, green leds on the left side of the display indicate ongoing charging. The
lowest led turns red when the charge level is low.
OPERATING MANUAL | EN 24
©
KEMPPI | 2018-09-28
Page 25

X8 MIG WELDER 2.3 Installation
17
16
15
18
15. Charger cable port
A stopper shields the charger cable port.
16. Micro USB port
A cover shields the micro USB port and the USB cable port.
17. USB cable port
18. Combo cable port
Combo cable port transfers both data and power. A stopper shields the combo cable port.
2.3 Installation
Perform this installation procedure to prepare your X8 MIG Welder for use.
Read the instructions carefully and follow them closely.
2.3.1 Before installation
Make sure to acknowledge and follow the local and national requirements on installation and the use of high
voltage units.
Before installation, check the contents of the packages and make sure the parts are not damaged.
Before you remove the power source completely from its packaging, install the wheel set.
Before you install the power source on the site, see the following requirements regarding the mains cable
type and fuse rating.
Warning:
The mains cable must be installed by an authorized electrician.
OPERATING MANUAL | EN 25
©
KEMPPI | 2018-09-28
Page 26

X8 MIG WELDER 2.3 Installation
Warning:
Provided that the public low voltage short circuit power at the point of common coupling is higher
than or equal to 5.1 MVA, this equipment is compliant with IEC 61000-3-11 and IEC 61000-3-12 and
can be connected to public low voltage systems. It is the responsibility of the installer or user of the
equipment to ensure, by consultation with the distribution network operator if necessary, that the
system impedance complies with the impedance restrictions.
Table 2: Cable type and fuse rating requirements
High voltage version (380-460V) Multi-voltage version (220-230/380-460V)Unit amperage
Cable type Fuse rating Cable type Fuse rating
400 A 6 mm
500 A 6 mm
600 A 6 mm
2
2
2
25 A - -
32 A 16 mm
35 A 16 mm
2
2
63 A
63 A
2.3.2 Power Source installation
For power source cable connections, see Installing interconnection cable and Installing or replacing mains
cable. For operating the power source, see Preparing welding system for use.
2.3.2.1 Installing wheels
To have turning wheels in the front and the back, install the front wheel assembly to the front of the unit.
To have fixed wheels in the front, install the rear wheel assembly to the front of the unit. See also Installing
optional gas cylinder cart.
Proceed as follows:
Install the rear wheels:
Remove the packaging from the sides but leave the power source resting on the pallet.
1.
OPERATING MANUAL | EN 26
©
KEMPPI | 2018-09-28
Page 27

X8 MIG WELDER 2.3 Installation
1 2 3 4
Push the rear axle through the opening in the bottom of the rear side of the unit and set the axle in the
2.
middle.
Slide the two wheel spacers (1) onto the axle.
3.
Slide the two wheels (2) onto the axle.
4.
Slide the two washers (3) onto the axle.
5.
Slide the two retaining rings (4) on the axle, until they lock into the groove on the axle.
6.
Install the front wheels:
Push the front axle through the opening in the bottom of the front side of the unit and set the axle in
7.
the middle.
OPERATING MANUAL | EN 27
©
KEMPPI | 2018-09-28
Page 28

X8 MIG WELDER 2.3 Installation
21
Max. 20 Nm
Place the transportation handle over the ridge in the wheel assembly and align the holes in the wheel
8.
assembly with the ends of the axle.
Attach the front wheel assembly to the end of the axle with a bolt (1) and washer (2) from both sides.
9.
When the wheels are attached, lift the power source off the pallet.
10.
OPERATING MANUAL | EN 28
©
KEMPPI | 2018-09-28
Page 29

X8 MIG WELDER 2.3 Installation
Note:
If your setup includes X8 Gas Cylinder Cart, proceed to Installing optional gas cylinder cart.
2.3.2.2 Installing optional gas cylinder cart
To transport a larger gas cylinder with the power source, install X8 Gas Cylinder Cart. For detailed
instructions, see X8 Gas Cylinder Cart Mounting Instructions. If your setup does not include the gas cylinder
cart, proceed to Installing optional X8 Cooler.
Remove the packaging from the sides but leave the power source resting on the pallet.
1.
Attach a wheel set to the front of the unit.
2.
• To have turning wheels in the front and the back, install the front wheel assembly to the front of the
unit.
For more information, see Installing wheels on page 26.
• To have fixed wheels in the front, install the rear wheel assembly to the front of the unit.
For more information, see Installing wheels on page 26.
Attach the gas cylinder cart to the rear of the unit:
Push the axle through the opening in the bottom of the rear side of the unit.
3.
OPERATING MANUAL | EN 29
©
KEMPPI | 2018-09-28
Page 30

X8 MIG WELDER 2.3 Installation
4321
Attach the wheel set of the gas cylinder cart to the axle with a bolt (1) and washers (2, 3, 4) from both
4.
sides.
Insert cover plugs to the open ends of the wheel set.
5.
OPERATING MANUAL | EN 30
©
KEMPPI | 2018-09-28
Page 31

X8 MIG WELDER 2.3 Installation
3 2 1
Place the upper part of the gas cylinder cart on the wheel set, and push it down until the claw fastens
6.
over the transportation handle.
Attach the upper part of the gas cylinder cart to the wheel set with two bolts (1) and washers (2, 3) from
7.
both sides.
Attach the bottom of the gas cylinder cart to the wheel set with six bolts (1) and washers (2, 3).
8.
The gas cylinder cart bottom has two alternative settings (the lower setting described in the figure). The
higher setting gives a better ground clearance, but you must lift the gas cylinder higher.
OPERATING MANUAL | EN 31
©
KEMPPI | 2018-09-28
Page 32

X8 MIG WELDER 2.3 Installation
3 2 1
Max. 20 Nm
Place the gas cylinder on the cart.
9.
Fasten the straps in the cart around the gas cylinder.
10.
2.3.2.3 Installing optional X8 Cooler
If your setup does not include X8 Cooler, you can skip these instructions.
Caution:
X8 Cooler must be installed by authorized service personnel. Do not open the covers of X8 Power
Source.
OPERATING MANUAL | EN 32
©
KEMPPI | 2018-09-28
Page 33

X8 MIG WELDER 2.3 Installation
64 5
1
3
2
1. Front panel
2. Front panel latch
3. Coolant circulation button
4. Cooler
5. Coolant container
6. Connectors for the liquid cooling unit
Proceed as follows:
Detach the two screws in the front panel of the power source.
1.
OPERATING MANUAL | EN 33
©
KEMPPI | 2018-09-28
Page 34

X8 MIG WELDER 2.3 Installation
Pull the front panel outwards from the lower edge.
2.
Remove the lower left cover from the rear of the power source.
3.
Push the cooler inside the power source from the opening in the front.
4.
Note:
Do not use force, but make sure the connectors on the cooler and the power source are
properly connected.
Fill the coolant container with applicable coolant solution. For more information, see Filling cooler on
5.
page 103.
Attach the two screws in the front panel of the power source.
6.
2.3.2.4 Installing or replacing mains cable
The power source is supplied with a 5-meter mains cable without a plug installed.
Warning:
The mains cable must be installed by an authorized electrician.
For high voltage versions, install the 6 mm2 cable. For multi-voltage versions, install the 16 mm2 cable.
The mains cable includes the following wires:
1. Brown: L1
2. Black: L2
3. Grey: L3
4. Yellow-green: Protective earth
2.3.3 Wire Feeder installation
This chapter describes the wire feeder installation.
For wire feeder cable connections, see Installing interconnection cable. For information on operating the
wire feeder, see Wire feeder control panel on page 96.
Caution:
Welding quality and efficiency are greatly dependent on the consumable parts used on the wire
line. These include the wire guide tubes, feed rolls, wire liners, gas nozzles and contact tips. Always
ensure that you are using the correct consumable parts suitable for the filler wire size and material.
For more information, visit Kemppi consumable kit selection site at kitselect.kemppi.com.
2.3.3.1 Installing wire feeder
The installation of the Wire Feeder Rotating Plate and Double Wire Feeder Rotating Plate is identical, as is
installing one or two wire feeders.
Install the wire feeder on the power source with a Wire Feeder Rotating Plate. To install two wire feeders, use
a Double Wire Feeder Rotating Plate.
Note: To set up the system for double wire feeder configuration, you need certain assembly parts.
For more information, see Double wire feeder assembly parts.
Proceed as follows:
OPERATING MANUAL | EN 34
©
KEMPPI | 2018-09-28
Page 35

X8 MIG WELDER 2.3 Installation
Place the wire feeder rotating plate or double rotating plate on top of the power source, with the orange
1.
claw at the rear of the unit.
Pull the release lever at the front of the wire feeder rotating plate, and turn the top sideways to allow
2.
access to the bottom half.
Attach the bottom of the wire feeder rotating plate to the power source with four screws (1) and
3.
washers (2).
OPERATING MANUAL | EN 35
©
KEMPPI | 2018-09-28
Page 36

X8 MIG WELDER 2.3 Installation
2
1
5 Nm
With the control panel facing the same way as the power source front panel, place the wire feeder in the
4.
corresponding grooves on the wire feeder rotating plate.
Slide the wire feeder from front to back until the bar in the back of the unit locks to the orange claw at
5.
the back of the wire feeder rotating plate.
2.3.3.2 Installing welding gun holder
Install the welding gun holder to either side of the wire feeder.
OPERATING MANUAL | EN 36
©
KEMPPI | 2018-09-28
Page 37

X8 MIG WELDER 2.3 Installation
121
2
Proceed as follows:
Install the welding gun holder mount to the wire feeder with 2 screws going to the corresponding holes
1.
on the wire feeder upper cover hinge.
Attach the welding gun holder to the mount with 2 screws.
2.
2.3.3.3 Replacing feed rolls
Replace the feed rolls when the material and diameter of the filler wire changes.
Proceed as follows:
Open the top cover and lift the pressure handle.
1.
OPERATING MANUAL | EN 37
©
KEMPPI | 2018-09-28
Page 38

X8 MIG WELDER 2.3 Installation
Push the collars on the mounting pins of the feed rolls up to pull the mounting pins off.
2.
OPERATING MANUAL | EN 38
©
KEMPPI | 2018-09-28
Page 39

X8 MIG WELDER 2.3 Installation
Note:
The mounting pins are different: The drive rolls' mounting pins have a circular mark on the
top, while the pressure rolls' mounting pins have no marks. The pressure rolls' mounting pins
have central axles attached to them, so the drive and pressure rolls' mounting pins cannot be
confused with each other.
Pull the drive rolls upwards (1) and the pressure rolls out of their slots (2).
3.
OPERATING MANUAL | EN 39
©
KEMPPI | 2018-09-28
Page 40

X8 MIG WELDER 2.3 Installation
1
2
Select the feed rolls according to the tables below.
4.
Wire feed rolls, plastic
Filler wire
material
Fe, Ss (Al, Mc,
Feed roll profile Filler wire
diameter (mm)
V-groove
0.6 W001045 W001046
Fc)
0.8−0.9 W001047 W001048
1.0 W000675 W000676
1.2 W000960 W000961
Feed roll
identification
Drive roll code Pressure roll
code
OPERATING MANUAL | EN 40
©
KEMPPI | 2018-09-28
Page 41

X8 MIG WELDER 2.3 Installation
Wire feed rolls, plastic
1.4 W001049 W001050
1.6 W001051 W001052
2.0 W001053 W001054
2.4 W001055 W001056
Fc, Mc (Fe) V-groove,
knurled
1.0 W001057 W001058
1.2 W001059 W001060
1.4−1.6 W001061 W001062
2.0 W001063 W001064
2.4 W001065 W001066
U-groove
1.0 W001067 W001068Al (Fc, Mc, Ss,
Fe)
1.2 W001069 W001070
OPERATING MANUAL | EN 41
©
KEMPPI | 2018-09-28
Page 42

X8 MIG WELDER 2.3 Installation
Wire feed rolls, plastic
1.6 W001071 W001072
Wire feed rolls, metal
Filler wire
material
Fe, Ss (Al, Mc,
Fc)
Feed roll profile Filler wire
diameter (mm)
V-groove
0.8−0.9 W006074 W006075
1.0 W006076 W006077
Feed roll
identification
See the text on
the roll
Drive roll code Pressure roll
code
1.2 W004754 W004753
1.4 W006078 W006079
Fc, Mc (Fe) V-groove,
knurled
1.0 W006080 W006081
1.2 W006082 W006083
1.4−1.6 W006084 W006085
2.0 W006086 W006087
Al (Fc, Mc, Ss,
U-groove
Fe)
Place the feed rolls back to their places. Align the cut on a drive roll's bottom with the pin on the drive
5.
1.0 W006088 W006089
1.2 W006090 W006091
1.6
W006092 W006093
shaft.
Reattach the mounting pins to lock the drive and pressure rolls to their places. Align one of the cuts on
6.
the bottom of the pressure rolls' mounting pin with the stud on the mount.
Lower the pressure handle on the feed rolls and close the top cover.
7.
OPERATING MANUAL | EN 42
©
KEMPPI | 2018-09-28
Page 43

X8 MIG WELDER 2.3 Installation
2
1
2.3.3.4 Replacing wire guides
The wire feed mechanism includes two wire guide tubes. Replace them when the filler wire diameter grows
or the material changes.
1. Inlet tube
Pull out the inlet tube and insert a new one. There is no additional locking.
2. Middle tube
A metal piece locks the middle wire guide tube in its place. Turn the piece aside to free the middle wire
guide tube for replacement. Turn it back to lock down the new middle wire guide tube.
2.3.3.5 Changing wire spool
Note:
Install the welding gun to the wire feeder before installing the wire spool.
Caution:
If you change the filler wire to a different diameter or material, change the feed rolls accordingly.
Proceed as follows:
Remove the wire spool:
OPERATING MANUAL | EN 43
©
KEMPPI | 2018-09-28
Page 44

X8 MIG WELDER 2.3 Installation
Open the top cover latch.
1.
Lift the top cover up.
2.
Cut and file the tip of the filler wire.
3.
Note:
The sharp cut tip of the filler wire may cause damage to the wire liner, if not filed.
Press Wire retract to pull back the remaining filler wire from the welding gun.
4.
Push the wire spool locking cover aside.
5.
Lift the wire spool from the wire feeder.
6.
Loosen and pull the wire spool brake halves apart.
7.
Install a new wire spool:
OPERATING MANUAL | EN 44
©
KEMPPI | 2018-09-28
Page 45

X8 MIG WELDER 2.3 Installation
Attach the wire spool brake halves to the new wire spool by pushing them together inside the wire
8.
spool. Tighten if necessary.
Note:
The spool brake is equipped with an optional wire tensioning feature, which keeps the wire feed
steady in short repeated welds and with heavy wire spools. To enable wire tensioning, attach
the spool brake hub to the wire spool so that the tightening knob is on the right, seen from the
front.
Lower the wire spool to its socket.
9.
Note:
Ensure that the wire spool is facing the right direction, the filler wire running from the top of the
spool to the feed rolls.
Lift the pressure handle off of the feed rolls.
10.
Install the filler wire:
OPERATING MANUAL | EN 45
©
KEMPPI | 2018-09-28
Page 46

X8 MIG WELDER 2.3 Installation
Release the pressure arms to move the feed rolls apart. This opens a gap between the feed rolls.
11.
Release the filler wire end from the spool and cut off any deformed section so that the end is straight.
12.
Note:
Ensure that the filler wire does not spill from the spool when it is released.
File the tip of the filler wire smooth.
13.
Caution:
Sharp edges on the filler wire tip may damage the wire liner.
Guide the filler wire through the inlet tube (A) and middle wire guide tube (B) to the outlet, which feeds
14.
the filler wire to the welding gun. Push the filler wire by hand inside the gun so that the wire reaches the
wire liner (about 20 cm).
Close the pressure arms so that the filler wire is locked between the feed rolls. Ensure that the filler wire
15.
sits in the feed roll grooves.
Lower the pressure handle on the feed rolls.
16.
Adjust the pressure of the feed rolls with the pressure adjustment wheels. The pressure is the same for
17.
both feed roll pairs.
The graduated scales on the pressure handle indicate the pressure applied to the feed rolls. Adjust the
pressure of the feed rolls according to the table below.
OPERATING MANUAL | EN 46
©
KEMPPI | 2018-09-28
Page 47

X8 MIG WELDER 2.3 Installation
Filler wire material Feed roll profile Filler wire diameter (mm) Adjustment (x100N)
Fe/Ss solid V-groove 0.8−1.0
≥ 1.2
1.5−2.0
2.0−2.5
Metal and flux cored V-groove, knurled ≥ 1.2 1.0−2.0
Self-shielded V-groove, knurled ≥ 1.6 2.0−3.0
Aluminium U-groove 1.0
1.2
1.4
≥ 1.6
0.5 1.0
1.0−1.5
1.5−2.0
2.0−2.5
Caution:
Excessive pressure flattens the filler wire and may damage coated or cored filler wires. Excessive
pressure also unnecessarily wears the feed rolls and increases gearbox load.
Press Wire inch to drive the filler wire to the welding gun's contact tip. To speed up the wire feed speed,
18.
turn the left control knob on the control panel.
Note:
The control panel shows how much the filler wire has run.
OPERATING MANUAL | EN 47
©
KEMPPI | 2018-09-28
Page 48

X8 MIG WELDER 2.3 Installation
Finalize the installation:
Select the shielding gas and attach the gas cylinder to the wire feeder.
19.
Press Gas test to flush the former shielding gas from the system.
20.
Note:
You can also use this button to test that the gases flow through the system properly.
Close the top cover.
21.
Wire spools
X8 MIG Welder has three different wire spool hub options available for different wire spools:
A. Standard spool
B. Spool hub for the small wire spool
Attach the extension pieces to the standard spool halves.
C. Spool hub for the wire spool with a large center hole
All parts are delivered with the wire feeder.
Loosen and pull the spool halves to detach them.
OPERATING MANUAL | EN 48
©
KEMPPI | 2018-09-28
Page 49

X8 MIG WELDER 2.3 Installation
2.3.3.6 Attaching interconnection cable to strain relief
To ease the installation of the interconnection cable and to prevent any unnecessary strain on the cable
connectors, attach both ends of the interconnection cable bundle to a strain relief.
Proceed as follows:
Attach the strain relief holder to the transportation handle at the rear of the power source. Fasten the
1.
strain relief holder with a bolt from below.
Take the power source end of the interconnection cable and insert the strain relief pin to the strain relief
2.
holder.
Note:
If the wire feeder is detached from the power source, insert the strain relief pin to the holder
from below.
Note:
If the wire feeder is on the power source, insert the strain relief pin to the holder from above.
OPERATING MANUAL | EN 49
©
KEMPPI | 2018-09-28
Page 50

X8 MIG WELDER 2.3 Installation
Insert the supplied locking pin through the hole in the strain relief pin.
3.
Route the cable bundle from the back of the power source and attach the strain relief in the other end of
4.
the cable to the left-hand side of the wire feeder. For more information, see .
2.3.4 Cables installation
For a detailed description of the power source and wire feeder cabling, see Installing interconnection cable.
For a full overview of the cabling, see Cabling diagram.
2.3.4.1 Installing interconnection cable
Install the interconnection cable first to the the wire feeder and then to the power source.
Proceed as follows:
OPERATING MANUAL | EN 50
©
KEMPPI | 2018-09-28
Page 51

X8 MIG WELDER 2.3 Installation
Connect the interconnection cable to the wire feeder:
Lift the cable cabinet latch to reveal the connectors.
1.
Connect the welding current cable to the wire feeder. Push the cable as far as it goes and turn the
2.
connector clockwise to tighten the cable to its place.
Caution:
Tighten the welding current cable as much as you can by hand. If the welding current cable
connection is loose, it may overheat.
Push the shielding gas hose towards the shielding gas hose connector base until it locks down.
3.
Attach the strain relief to the slot on the wire feeder.
4.
Lock the strain relief latch to secure the strain relief.
5.
Connect the control cable to the connector. Rotate the collar clockwise to lock it in place.
6.
Connect the measurement cable to the connector. Rotate the collar clockwise to lock it in place.
7.
If you have the optional cooler, pull the cover over the cooling water hoses' slot to remove it.
8.
OPERATING MANUAL | EN 51
©
KEMPPI | 2018-09-28
Page 52

X8 MIG WELDER 2.3 Installation
Connect the cooling water hoses to the slot.
9.
Close and lock the cable cabinet door.
10.
Note:
When connecting the cables to the wire feeder, route the cables neatly so that the cable cabinet
door closes properly.
Connect the interconnection cable to the power source:
OPERATING MANUAL | EN 52
©
KEMPPI | 2018-09-28
Page 53

X8 MIG WELDER 2.3 Installation
Connect the welding current cable to the plus (+) side connector (1) on the power source.
11.
The interconnection cable crosses from the wire feeder to the power source connector diagonally.
Note:
If two wire feeders are connected to a power source, connect the interconnection cable upright:
from the wire feeder on the left to the connector (1) on the left.
Connect the earth return cable to the minus (-) side connector (2).
12.
Connect the measurement cable to the measurement cable connector (4).
13.
Connect the control cable to the control cable connector (3) on the same side as the measurement
14.
cable.
If the water cooler is present, use the red connector (5) for the hose that goes to the cooler.
15.
If the water cooler is present, use the blue connector (6) for the hose that comes from the cooler.
16.
If you need shielding gas, connect the shielding gas hose to the gas cylinder.
17.
The power source can be connected to two wire feeders at the same time.
Caution:
Ensure that you have connected and tightened all the cables properly.
2.3.4.2 Cabling diagram
Connect the interconnection cables to power source and wire feeder. The figure below shows the cables with
colors to facilitate the identification.
OPERATING MANUAL | EN 53
©
KEMPPI | 2018-09-28
Page 54

X8 MIG WELDER 2.3 Installation
Figure 3: Interconnection cabling for power source and wire feeder
Table 3: Color codes
Welding current cable
Shielding gas hose
Control cable
Measurement cable
Coolant input and output hoses
OPERATING MANUAL | EN 54
©
KEMPPI | 2018-09-28
Page 55

X8 MIG WELDER 2.3 Installation
Earth return cable
2.3.5 Control Pad installation
This chapter describes the control pad installation.
For information on operating Control Pad, see Control Pad on page 84.
2.3.5.1 Wireless connection
Control Pad connects wirelessly to X8 Wire Feeder. If there are two wire feeders in the system, choose which
one to connect to. Control Pad can be connected to X8 Power Source in applications where no wire feeder is
needed, such as stick welding or gouging.
To set up a wired connection between Control Pad and the power source or the wire feeder, see Wired
connection on page 57.
If Control Pad is not connected, you see this info message on the display.
Proceed as follows:
To connect Control Pad wirelessly to a wire feeder or power source:
1.
a) Press the wireless pairing button on the power source indicator panel.
OPERATING MANUAL | EN 55
©
KEMPPI | 2018-09-28
Page 56

X8 MIG WELDER 2.3 Installation
The led on the power source begins to blink when it is searching for Control Pad.
The serial numbers of the nearby available wire feeders or power sources appear on Control Pad's
display.
Note:
When there are wire feeders connected to the welding system, pressing the wireless pairing
button allows you to connect Control Pad to a wire feeder. When there are no wire feeders
connected to the system, Control Pad allows you to connect to a power source.
Figure 4: Connecting to wire feeder Figure 5: Connecting to power source
b) Move focus to select the connection and press the green button.
Note:
OPERATING MANUAL | EN 56
©
KEMPPI | 2018-09-28
Page 57

X8 MIG WELDER 2.3 Installation
The connection list shows the serial numbers of the available wire feeders and a power
source. Check the serial number on the device rating plate.
A connection forms between the wire feeder or power source and Control Pad. The led on the power
source lights up permanently.
Note:
Once you have created the connection, Control Pad tries to reconnect if you take it out of the
connection distance. Select Disconnect on Control Pad to disconnect the connection.
You can also connect Control Pad to the wire feeder through the wire feeder control panel if the wire
2.
feeder is far from the power source.
a) Go to Settings > Wireless devices > Connect.
The wire feeder connects automatically to Control Pad.
If the buttons of the power source and wire feeder are unreachable:
3.
a) Go to Settings > WirelessDevicesAvailable in Control Pad.
b) Move focus to a wire feeder or a power source.
c) Press the green button.
2.3.5.2 Wired connection
Control Pad makes a wired connection with X8 Power Source and X8 Wire Feeder. Connect Control Pad to a
wired connection, when wireless connection is unavailable.
Proceed as follows:
To make a wired connection between Control Pad and the power source:
1.
a) Plug the combo cable to the Control Pad connector of the power source.
The connector is marked with a Control Pad icon.
OPERATING MANUAL | EN 57
©
KEMPPI | 2018-09-28
Page 58

X8 MIG WELDER 2.3 Installation
b) Plug the combo cable to the combo cable port on the bottom of Control Pad.
To make a wired connection between Control Pad and the wire feeder:
2.
a) Plug the combo cable to the remote control connector of the wire feeder.
The connector is marked with a Control Pad icon.
b) Plug the combo cable to the combo cable port on the bottom of Control Pad.
Note:
Use mainly the external charger to charge Control Pad.
2.3.5.3 Suspending Control Pad
Control Pad has a hook, which you can use to suspend it on the welding machine or other suitable place.
Control Pad also has a loop in each corner, which you can use for the carrying strap.
OPERATING MANUAL | EN 58
©
KEMPPI | 2018-09-28
Page 59

X8 MIG WELDER 2.3 Installation
2.3.6 Welding gun installation
2.3.6.1 Preparing and connecting welding gun
X8 MIG Gun has been preassembled by the manufacturer: the wire liner, contact tip and gas nozzle are
premounted. To start using the gun, proceed as follows:
Check that the wire liner, contact tip and gas nozzle are suitable for the job. Change if needed. If your
1.
setup includes a gas-cooled gun, you can also change the neck.
Attach the pistol grip handle, if suitable for the job.
2.
Attach X8 Gun Remote Control, if suitable for the job (optional accessory).
3.
Connect the welding gun to the wire feeder: Push the welding gun connector into the wire feeder gun
4.
adapter, and hand-tighten the collar.
OPERATING MANUAL | EN 59
©
KEMPPI | 2018-09-28
Page 60

X8 MIG WELDER 2.3 Installation
Note:
X8 MIG Guns connect to X8 Wire Feeder with Kemppi Gun Adapter that enables, among other
things, accurate measurement of the actual arc voltage and the usage of the remote control.
Therefore, X8 MIG Guns are only compatible with X8 Wire Feeder.
If your setup includes a water-cooled gun, connect the cooling hoses to the wire feeder. The coolant
5.
inlet hose is marked with blue and the coolant outlet hose with red color.
Dress the sharp filler wire tip before loading to improve wire loading and to lengthen consumables'
6.
lifetime.
Press the Wire inch button to load the filler wire.
7.
OPERATING MANUAL | EN 60
©
KEMPPI | 2018-09-28
Page 61

X8 MIG WELDER 2.3 Installation
Trim the excess filler wire at a slight angle to improve ignition.
8.
Check the gas flow rate.
9.
The welding gun is now ready for use. When not using the gun, keep it in the welding gun holder on the wire
feeder.
2.3.6.2 Replacing consumable parts of welding gun
Select a suitable contact tip, gas nozzle, neck and wire liner according to the job. See also how to change the
feed rolls of the wire feeder accordingly: Replacing feed rolls on page 37.
Standard delivery set of consumable parts
The tables below list the consumable parts that are delivered with the welding gun. To find other compatible
parts for various materials, use Kemppi's Consumable Kit Selector at kitselect.kemppi.com.
Gas-cooled guns
X8 MIG Gun 200-g (3.5m) X8301203500
X8 MIG Gun 200-g (5.0m) X8301205000
X8 MIG Gun 300-g (3.5m) X8301303500
X8 MIG Gun 300-g (5.0m) X8301305000
Contact tip W012132
Contact tip adapter W011483
Gas nozzle W011478
Wire guide tube SP011868
X8 MIG Gun 200-g (3.5m) X8301203500
X8 MIG Gun 300-g (3.5m) X8301305000
Wire liner W012361
X8 MIG Gun 200-g (5.0m) X8301205000
X8 MIG Gun 300-g (5.0m) X8301305000
Wire liner W012362
OPERATING MANUAL | EN 61
©
KEMPPI | 2018-09-28
Page 62

X8 MIG WELDER 2.3 Installation
X8 MIG Gun 400-g (3.5m) X8301403500
X8 MIG Gun 400-g (5.0m) X8301405000
Contact tip W012134
Contact tip adapter W011483
Gas nozzle W011472
Wire guide tube SP011869
X8 MIG Gun 400-g (3.5m) X8301403500
Wire liner W012361
X8 MIG Gun 400-g (5.0m) X8301405000
Wire liner W012362
Water-cooled guns
X8 MIG Gun 420-w (3.5m) X8300423500
X8 MIG Gun 420-w (5.0m) X8300425000
Contact tip W012132
Contact tip adapter W011483
Gas nozzle W011478
Liner guide tube SP011868
X8 MIG Gun 420-w (3.5m) X8300423500
Wire liner W013628
X8 MIG Gun 420-w 5.0m X8300425000
Wire liner W013632
X8 MIG Gun 520-w (3.5m) X8300523500
X8 MIG Gun 520-w (5.0m) X8300525000
Contact tip W012134
Contact tip adapter W011483
Gas nozzle W011472
Liner guide tube SP011869
X8 MIG Gun 520-w (3.5m) X8300523500
Wire liner W013628
X8 MIG Gun 520-w (5.0m) X8300525000
Wire liner W013632
OPERATING MANUAL | EN 62
©
KEMPPI | 2018-09-28
Page 63

X8 MIG WELDER 2.3 Installation
Changing wire liner (gas-cooled gun)
Caution:
Use the correct wire liner. The tip of the filler wire may damage an incorrect liner.
Lay the welding gun cable straight on a flat surface.
1.
Loosen the neck tightener by rotating it half a turn, and remove the neck.
2.
Remove the guide nut from the tip of the sleeve.
3.
Remove the sleeve and pull out the liner. Make sure the cone and the seal slide out with the liner.
4.
OPERATING MANUAL | EN 63
©
KEMPPI | 2018-09-28
Page 64

X8 MIG WELDER 2.3 Installation
1 2
Load the new liner through the welding gun connector as far as it goes. Check that you have pushed the
5.
liner far enough: the liner must be visible at the tip of the gun.
OPERATING MANUAL | EN 64
©
KEMPPI | 2018-09-28
Page 65

X8 MIG WELDER 2.3 Installation
1 2 3
Assemble the cone (1), seal (2) and sleeve (3) (supplied with the new liner) over the liner protruding from
6.
the welding gun connector. Tighten the sleeve as tight as possible with a spanner.
Cut the excessive liner leaving 1 - 2 mm. Use side cutting pliers for spiral liner and carpet knife for DL
7.
Chili liner.
OPERATING MANUAL | EN 65
©
KEMPPI | 2018-09-28
Page 66

X8 MIG WELDER 2.3 Installation
1-2 mm
Attach the guide nut at the tip of the sleeve.
8.
Re-assemble the neck and tighten the neck tightener to secure.
9.
Changing neck (gas-cooled gun)
You can change the neck without tools.
Turn the neck tightener half a turn counter-clockwise to loosen it, and pull the neck out.
1.
OPERATING MANUAL | EN 66
©
KEMPPI | 2018-09-28
Page 67

X8 MIG WELDER 2.3 Installation
Push in the new neck and turn the neck tightener half a turn clockwise to secure it. Make sure you push
2.
the neck deep enough: When the neck is correctly inserted, the groove on the neck is completely hidden
under the neck tightener.
Note:
You can rotate the neck into different positions without loosening the neck tightener.
Changing gas nozzle (gas-cooled gun)
Screw the gas nozzle into its place.
OPERATING MANUAL | EN 67
©
KEMPPI | 2018-09-28
Page 68

X8 MIG WELDER 2.3 Installation
Changing contact tip (gas-cooled gun)
Remove the contact tip.
1.
Replace the contact tip adapter / gas diffuser, if needed. Screw in and hand-tighten the new adapter as
2.
tight as possible (no tool is needed). Make sure there is no gap between the contact tip adapter and the
black plastic bushing.
Note:
It is important to tighten the adapter properly to enable a tight connection of the contact tip to
the gun.
OPERATING MANUAL | EN 68
©
KEMPPI | 2018-09-28
Page 69

X8 MIG WELDER 2.3 Installation
Screw in a new contact tip and tighten it with an appropriate tool. Some thread grooves on the contact
3.
tip remain visible when the contact tip is properly connected to the gun.
Changing wire liner (water-cooled gun)
Caution:
Use the correct wire liner. The tip of the filler wire may damage an incorrect liner.
Lay the welding gun cable straight on a flat surface.
1.
OPERATING MANUAL | EN 69
©
KEMPPI | 2018-09-28
Page 70

X8 MIG WELDER 2.3 Installation
Remove the guide nut from the tip of the sleeve.
2.
Remove the sleeve and pull out the liner together with the cone .
3.
OPERATING MANUAL | EN 70
©
KEMPPI | 2018-09-28
Page 71

X8 MIG WELDER 2.3 Installation
Load the new liner through the welding gun connector as far as it goes The liner should be just visible, a
4.
couple of millimeters from the tip of the gun.
Note:
Make sure the liner is properly inside the contact tip adapter before you cut the liner at the
connector end.
OPERATING MANUAL | EN 71
©
KEMPPI | 2018-09-28
Page 72

X8 MIG WELDER 2.3 Installation
1 2
Assemble the cone (1) and sleeve (2) (supplied with the liner) over the liner protruding from the welding
5.
gun connector. Tighten the sleeve with a spanner to secure.
OPERATING MANUAL | EN 72
©
KEMPPI | 2018-09-28
Page 73

X8 MIG WELDER 2.3 Installation
1-2 mm
Cut the excessive liner leaving 1 - 2 mm. Use side cutting pliers for spiral liner and carpet knife for DL
6.
Chili liner.
Attach the guide nut at the tip of the sleeve.
7.
OPERATING MANUAL | EN 73
©
KEMPPI | 2018-09-28
Page 74

X8 MIG WELDER 2.3 Installation
Changing gas nozzle (water-cooled gun)
Screw the gas nozzle into its place.
Changing contact tip (water-cooled gun)
Remove the contact tip.
1.
OPERATING MANUAL | EN 74
©
KEMPPI | 2018-09-28
Page 75

X8 MIG WELDER 2.3 Installation
Replace the contact tip adapter/gas diffuser , if needed. Screw in and hand-tighten the new adapter as
2.
tight as possible (no tool is needed).
Note:
It is important to tighten the adapter properly to enable a tight connection of the contact tip to
the gun.
Screw in a new contact tip and tighten it properly with a tool. Some thread grooves on the contact tip
3.
remain visible when the contact tip is properly connected to the gun.
OPERATING MANUAL | EN 75
©
KEMPPI | 2018-09-28
Page 76

X8 MIG WELDER 2.3 Installation
2.3.6.3 Installing pistol grip handle
The pistol grip handle is suitable for all X8 MIG Guns. The handle improves the ergonomics of many welding
positions.
To attact the pistol grip handle, align the grooves and pull the handle forward to attach the front side (1),
and then push the handle back to snap-lock it into its place (2).
To detach the pistol grip handle, press the lock button at the back of the handle.
2.3.6.4 Installing remote control
X8 Gun Remote Control is an optional accessory for X8 MIG Gun.
OPERATING MANUAL | EN 76
©
KEMPPI | 2018-09-28
Page 77

X8 MIG WELDER 2.3 Installation
TORX 20
For operation instructions, see Gun remote control on page 99.
Unscrew the two screws that attach the cover to the gun.
1.
Remove the protective cover from the gun by pushing it forwards and lifting it up.
2.
Remove the interface card that covers the connectors.
3.
Note:
Store the interface card in case you want to remove the remote control later. If you remove the
remote control, re-mount the interface and the cover on the gun.
Attach the remote control by pushing it down and backwards into its place so that the connectors align.
4.
OPERATING MANUAL | EN 77
©
KEMPPI | 2018-09-28
Page 78

X8 MIG WELDER 2.3 Installation
Screw in the two screws.
5.
2.3.7 Lifting X8 MIG Welder
If you need to lift X8 MIG Welder, pay special attention to the safety measures. Follow the local regulations.
Warning:
Do not lift the welder with the gas cylinder.
Proceed as follows:
OPERATING MANUAL | EN 78
©
KEMPPI | 2018-09-28
Page 79

X8 MIG WELDER 2.3 Installation
Loop two lifting straps through the handle at the front and two straps through the handle at the back of
1.
the power source.
Caution:
Place the straps as close to the power source as possible.
Lift steadily straight up.
2.
2.3.8 Purchasing and managing welding software
You can purchase Kemppi welding software licenses to X8 MIG Welder. Installed licenses can be viewed with
Control Pad.
For more information, visit www.kemppi.com.
2.3.9 Optional accessories
X8 MIG Welder has several accessories to facilitate its use and improve welding quality.
Wire Drum Kit
To use the wire drum kit, drill a hole at the back of X8 Wire Feeder's transparent cover.
OPERATING MANUAL | EN 79
©
KEMPPI | 2018-09-28
Page 80

X8 MIG WELDER 2.3 Installation
Wire Feeder Hanger for Boom
The wire feeder hanger for boom facilitates welding where it is difficult to bring the full X8 MIG Welder
welding system. The hanger allows more fluent transitions in constricted spaces.
Caution:
Do not hang the wire feeder from the handle. Use the wire feeder hanger for boom instead.
OPERATING MANUAL | EN 80
©
KEMPPI | 2018-09-28
Page 81

X8 MIG WELDER 2.3 Installation
Wire Feeder Counterbalance Arm
The wire feeder counterbalance arm reduces the weight of the cable bundle over the working area.
Proceed as follows:
OPERATING MANUAL | EN 81
©
KEMPPI | 2018-09-28
Page 82

X8 MIG WELDER 2.3 Installation
1. Lock the rotating plate to its position.
2. Adjust the length of the arm. Tighten the screws to lock to position.
3. Turn to adjust the tension of the counterbalance spring.
4. Turn to adjust the damping of the up and down movement.
Wire Feeder Cabinet Heater
The wire feeder cabinet heater prevents moisture from condensing inside the wire feeder cabinet so that the
wire spool stays dry.
Double Wire Feeder Rotating Plate
The double wire feeder rotating plate allows the use of two wire feeders on one power source.
OPERATING MANUAL | EN 82
©
KEMPPI | 2018-09-28
Page 83

X8 MIG WELDER 2.3 Installation
X8 Cable Rack
The cable rack holds the interconnection cable during transportation or storage.
Note:
This is an alternative accessory for the gas cylinder cart. Both cannot be installed at the same time.
X8 Accessory Tray
The accessory rack holds the small parts and tools needed for welding. Install it on the side of the welding
machine.
OPERATING MANUAL | EN 83
©
KEMPPI | 2018-09-28
Page 84

X8 MIG WELDER 2.4 Operation
2.4 Operation
Follow these operating instructions carefully to have full advantage of your X8 MIG Welder and to minimize
the risk of malfunctions.
2.4.1 X8 MIG Welder control devices
Welding with X8 MIG Welder can be controlled through three different control panels, which offer slightly
different features for adjusting the welding parameters.
The actual features vary according to the functions and usability of the control panel.
2.4.1.1 Control Pad
Control Pad is a window to X8 MIG Welder: Control Pad shows you all the settings and licenses installed in
the welding system.
You can adjust the welding parameters and their values remotely with the one-knob navigation, and connect
Control Pad to any X8 MIG Welder nearby.
Navigation
Above the display, Control Pad has three view buttons. Press these buttons to change the view on Control
Pad's display. Press the Menu button twice to open the View menu.
Use the knobs under the display to move in the display and to adjust the values. When there is a green light
in the center of the knob, the knob also functions as a push button.
OPERATING MANUAL | EN 84
©
KEMPPI | 2018-09-28
Page 85

X8 MIG WELDER 2.4 Operation
Figure 6: The View menu
In the Welding view, adjust the welding power with the left knob and the fine tuning with the right knob. In
most welding processes, this secondary parameter is voltage.
In all other views, move up and down in the menus with the right knob. Press the green button in the center
of the knob to open an item.
If you need to perform a reversing action, such as Cancel or Default, press the green button to accept.
Header and footer
Control Pad's header displays the serial number of the welding machine, the selected wire feeder, and the
name of the user:
There is an instruction on the footer above the knob, when the knob has a specific function. A green circle in
the footer prompts the push of the button on the control knob. The adjustable parameter or value in focus is
highlighted with orange.
OPERATING MANUAL | EN 85
©
KEMPPI | 2018-09-28
Page 86

X8 MIG WELDER 2.4 Operation
Figure 7: Control Pad display with the Adjust
footer
Figure 8: Control Pad display with the Select footer
If the selection of the toggle button comes into effect right away, the footer command is Close. If the change
comes into effect after pressing the green button, the footer command is OK.
Control Pad views
There are three main views on Control Pad display: Channel (memory channels), Welding, and Settings.
Toggle between the views with the view buttons. The View menu inside Welding opens, when you press the
Menu button again in the Welding view.
Figure 9: The Channel button
Figure 10: The Menu button
OPERATING MANUAL | EN 86
©
KEMPPI | 2018-09-28
Page 87

X8 MIG WELDER 2.4 Operation
Figure 11: The Settings button
Welding view
In the Welding view, you can:
• See an overview of the settings of the selected welding program
• Adjust the main parameters (welding power and fine tuning)
Depending on the selected welding process, function and program, some or all of the following information
is shown:
1. Memory channel, its number and the welding program
The first row shows the memory channel's name.
The second row shows the welding program's name, which consists of the filler wire material and
diameter and the shielding gas.
If you have modified the welding settings, the channel number tilts to the right. To save changes, press
and hold the Channel button until the number returns to its normal position.
2. Operation mode of the welding gun (trigger logic)
2T, 4T or WP Switch. For more information, see Trigger logic functions on page 133.
3. Touch sense ignition
Option for smooth ignition with less spatter.
OPERATING MANUAL | EN 87
©
KEMPPI | 2018-09-28
Page 88

X8 MIG WELDER 2.4 Operation
4. Upslope
The selected start and stop logics.
5. Estimated welding current
6. Estimated plate material thickness
7. Wire feed speed
8. Serial number of the power source, wire feeder's number (1 or 2) and user name
9. Welding process
10. Hot start
The selected start and stop logics.
11. Crater fill
The selected start and stop logics.
12. Voltage
13. Voltage/Fine tuning
Adjust the welding power with the left control knob.
Fine tune the secondary welding parameter with the right control knob. The adjustable secondary parameter
varies according to the welding process and function.
The welding power graph shows with grey raster pattern the area, where the selected values result in
globular transfer.
Figure 12: Raster pattern in the wire feed arc
In DPulse, WP Switch and DProcess, you can adjust two value sets: the first level and the second power level.
Press the left green button to toggle between them. Adjust the values with the control knobs. The other
power level is shown with gray line on the wire feed speed diagram.
OPERATING MANUAL | EN 88
©
KEMPPI | 2018-09-28
Page 89
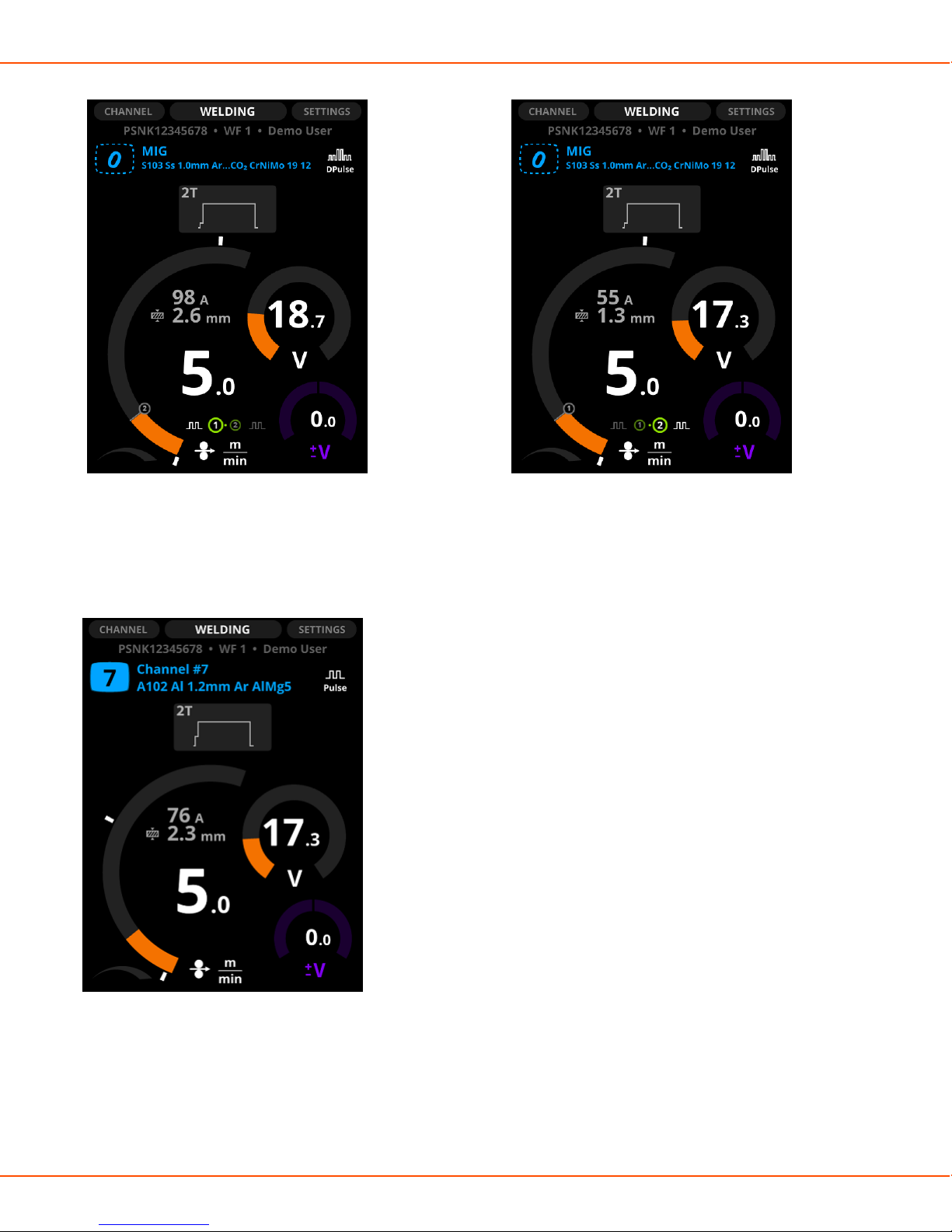
X8 MIG WELDER 2.4 Operation
Figure 13: Toggling DPulse (1) Figure 14: Toggling DPulse (2)
You can specify the minimum and maximum values of the wire feed speed. They are displayed as white
stoppers beside the wire feed speed diagram.
Figure 15: The minimum and maximum stoppers
The value range of the welding power and voltage graphs specified by the Welding Procedure Specification
(WPS) are displayed with a green arc between the stoppers. The stoppers are by default at the top and
bottom of the specified WPS area, but you can adjust them to your preferences: to narrow the area or to
weld outside the specified area.
OPERATING MANUAL | EN 89
©
KEMPPI | 2018-09-28
Page 90

X8 MIG WELDER 2.4 Operation
Figure 16: The minimum and maximum stoppers for WPS
If you adjust the wire feed speed or voltage to a level outside the WPS range, the parameter graph turns red
and a warning symbol appears on the display.
Note:
If you have installed WeldEye, it saves the data as unsuitable use, even if the welding job requires
such values.
Figure 17: Values outside the range specified by WPS
OPERATING MANUAL | EN 90
©
KEMPPI | 2018-09-28
Page 91

X8 MIG WELDER 2.4 Operation
Settings view
Settings displays all the welding parameters and other settings of the selected program. The contents under
the titles are collapsed by default. Press the green button to expand the columns. There are two modes, Basic
and Advanced. This section describes the Settings view in the Advanced mode.
Figure 18: The Settings view menu in the Advanced mode
For more information on welding programs, see Welding programs in Control Pad on page 93.
DPulse menu
With the DPulse process in a welding program, Settings features an additional menu, DPulse.
For more information, see Standard MIG welding processes in X8 MIG Welder on page 119.
DProcess menu
If the welding program includes the DProcess process, the DProcess menu appears in the Settings view.
For more information, see Standard MIG welding processes in X8 MIG Welder on page 119.
Wise feature menu
Wise feature displays the Wise features available for use with the welding program.
For more information, see Wise features on page 127.
Trigger logic menu
Trigger logic displays the trigger logic options: 2T, 4T and WP Switch.
For more information, see Trigger logic functions on page 133.
OPERATING MANUAL | EN 91
©
KEMPPI | 2018-09-28
Page 92

X8 MIG WELDER 2.4 Operation
Start and stop logic menu
Start and stop logic displays several options. For more information, see Start and stop functions on page
134.
Parameters
The parameters available vary according to the welding process used:
• Wire feed speed
In addition to wire feed speed, you can adjust the minimum and maximum values of wire feed speed here.
• Voltage
• Fine tuning
• Dynamics
• Pulse current percent
• Start power
• Start level
• Stop power
For more information, see the description of the processes.
System settings
The options under System settings are:
1. Water cooling
Set water cooling ON, OFF or on AUTO.
In ON mode, the water cooling is continuous. In OFF mode, the water cooling is fully stopped. In AUTO
mode, the water cooling is on when needed.
2. Sub feeder selection
Select the sub feeder you are using and its length, or the motorized gun.
3. WF Motor warning level
Select a limit for the welding current. The system warns you, if the value exceeds the limit.
4. Voltage display mode
Select the welding voltage: terminal or arc voltage.
5. Safe wire inch
Set the Safe wire inch ON or OFF. If the Safe wire inch is ON, the wire feeder feeds maximum 5 cm of the
wire, if the arc does not ignite until then. If the Safe wire inch is OFF, the wire feeder feeds maximum 5 m
of the wire. This is to prevent the wire from hitting the welder.
6. Voltage reduction device (VRD)
Switch VRD ON or OFF if you are using MMA or gouging process. VRD reduces the maximum unloaded
open circuit voltage across the output terminals of the welding machine to a safe voltage.
7. Factory reset
Restore the settings back to factory default settings.
Panel settings
Panel settings display Control Pad's mechanical settings:
OPERATING MANUAL | EN 92
©
KEMPPI | 2018-09-28
Page 93

X8 MIG WELDER 2.4 Operation
1. PIN lock
Lock Control Pad with a 4-digit PIN code. When PIN lock is on, PIN code is required every time when
Control Pad is turned on. PIN lock does not prevent welding.
2. Change PIN code
Change the 4-digit PIN code.
3. Language
Choose the language out of 13 options.
4. Basic/Advanced mode
(User interface mode)
5. Brightness
Brightness of the display in percents.
6. Power usage
The settings available are Minimum, Economic and Normal.
Welding programs in Control Pad
Select the mode in Settings > Mode. Then select one of the welding programs in Welding program.
The MMA and GOUGING modes have one welding program each, and you can adjust their settings in
Parameters.
Figure 19: The Welding program menu in Settings
You can use the filters under Welding program to filter the welding programs on the selection list. You can
also select the needed welding program without using the filters.
The parameters available in Settings vary according to the selected welding process and the Basic/Advanced
mode.
Welding program menu
The filters under Welding program are:
OPERATING MANUAL | EN 93
©
KEMPPI | 2018-09-28
Page 94

X8 MIG WELDER 2.4 Operation
1. Material
Select the material of the welding piece.
2. Wire material
3. Wire diameter
4. Shielding gas
5. Type
Select welding/brazing or cladding.
6. Process
7. Polarity
Not available for all materials.
Which polarity is in use. If the polarity is positive (+), connect the + side to the wire feeder.
8. Welding program
After filtering, this column displays the suitable welding programs.
Channel view
Welding parameters are stored in the memory channels. The memory channel displays the same information
of the welding parameters as the Welding view. To take a channel into use, move the focus to it. Each user
has their own memory channels.
Figure 20: The Channel view
To adjust the welding parameters of the channel in focus, press the Menu or Settings button. When you
adjust a parameter, the number of the memory channel tilts to the right to indicate a difference from the
saved settings.
A WPS defines a range of values for welding parameters. If a WPS is used to create a memory channel, the
parameters are set in the middle of the range.
OPERATING MANUAL | EN 94
©
KEMPPI | 2018-09-28
Page 95

X8 MIG WELDER 2.4 Operation
View menu
In the Welding view, press the Menu button again to see the list of the available additional views.
Figure 21: The list of the additional views
The View menu displays the following views:
1. Welding
Press to return to the Welding view.
2. Weld data
Displays information on the last welds.
3. WPS
For more information on WPSs, see Using digital WPSs on page 137.
4. Licenses
Displays the licenses installed into the welding system.
5. Error log
Displays the error occurred previously and its point of time. Select the error and press the green button
to view the details.
6. Date & time
Set the date, time and the time zone.
7. System
Displays information on the welding system.
8. Cloud services
Connect to Kemppi cloud services.
OPERATING MANUAL | EN 95
©
KEMPPI | 2018-09-28
Page 96

X8 MIG WELDER 2.4 Operation
2.4.1.2 Wire feeder control panel
The control panel of the wire feeder has a one-knob navigation and push buttons for selecting parameters or
values. You can, for example, adjust the welding parameters and save settings on memory channels.
Wire feeder navigation
The three main views on the wire feeder display are the same as in Control Pad: Channel, Welding, and
Settings.
Note:
You can press the Power button to lock the wire feeder and avoid starting welding accidentally.
The wire feeder has a memory channels button on the left and the Settings button on the right side of the
display. Press these buttons to change the view on the wire feeder's display. Press the button again to return
to the Welding view.
Use the knobs under the display to move focus in the display and to adjust the values. When there is a green
light in the center of the knob, the knob also functions as a push button.
In the Welding view, adjust the welding power with the left knob and the fine tuning with the right knob. In
most welding processes, this secondary parameter is voltage.
In all other views, move up and down in the menus with the right knob. Press the green button in the center
of the knob to open an item.
Wire feeder views
Welding view
In the Welding view, you can:
• See an overview of the settings of the selected welding program
• Adjust the main parameters (welding power and fine tuning)
OPERATING MANUAL | EN 96
©
KEMPPI | 2018-09-28
Page 97

X8 MIG WELDER 2.4 Operation
1. Memory channel
2. Welding power
The unit of the parameter varies according to the welding process.
3. Voltage
Note:
Not all processes have this parameter.
4. Fine tuning
The unit of the parameter varies according to the welding process.
5. Applied settings displayed in symbols
For more information on symbols, see Kemppi symbols.
Adjust the welding power with the left control knob.
Note:
The welding parameter shown is Wire feed speed, Current or Plate Thickness.
Fine tune the secondary welding parameter with the right control knob. The adjustable secondary parameter
varies according to the welding process and function.
Memory Channels view
Welding parameters are stored in the memory channels. The memory channel displays the same information
of the welding parameters as the Welding view. Each user has their own memory channels.
Press the Channel button on the left to see the Channel view. A menu of the memory channels appears on
the left side of the display. To take a channel into use, move focus to it with the right control knob. A tilted
number of the memory channel indicates that the parameters of the original memory channel have been
modified.
To save a modified channel, press and hold the Channel button or press Save on the green button of the
right knob.
Settings view
For more information on wire feeder's settings, see Wire feeder settings view on page 97.
Wire feeder settings view
You can adjust the selected memory channel or the settings of the wire feeder through the Settings view.
Press the Settings button to access the wire feeder settings. When the settings view is open, the Settings
button lights up orange.
Modify the parameters with the right knob. Press the green button in the center of the knob to select and
turn the right knob to adjust a parameter.
Table 4: Wire feeder settings
Trigger Change the welding gun trigger mode (2T/4T).
OPERATING MANUAL | EN 97
©
KEMPPI | 2018-09-28
Page 98

X8 MIG WELDER 2.4 Operation
WP Switch ON/OFF Switch the WP Switch feature ON or OFF.
Dynamics Adjust the dynamics setting for MIG, 1-MIG, Pulse,
DPulse and WiseThin+.
DPulse and WP Switch also have a Dynamics2
setting for adjusting the second level dynamics.
Touch sense ignition Switch the optimized ignition feature ON or OFF.
Hot start Switch the HotStart feature ON or OFF.
Crater fill Switch the crater fill feature ON or OFF.
Weld data Shows you the information on the latest weld.
Press the green button on the right knob to view
more information.
Device information Shows you the serial number and software versions
of the welding system.
Press the green button on the right knob to view
more information.
Wireless devices Press the Connect button on the right to set a
wireless connection to Control Pad.
OPERATING MANUAL | EN 98
©
KEMPPI | 2018-09-28
Page 99

X8 MIG WELDER 2.4 Operation
2 1
2
3
2.4.1.3 Gun remote control
With the remote control, you can select memory channels and WPSs, and adjust wire feed speed, fine tuning
and dynamics.
Figure 22: Control buttons of the remote control
1. Channel button
2. Arrow buttons
3. Adjustment roll
The remote control has two views: Channel view and Settings view. Use the Channel button to move
between the views.
Figure 23: Moving between Channel view and Settings view
Selecting a memory channel or WPS
In the Channel view, use the arrow buttons to move between the channels. There are two kinds of channels:
OPERATING MANUAL | EN 99
©
KEMPPI | 2018-09-28
Page 100

X8 MIG WELDER 2.4 Operation
• Memory channels. The view shows the number of the memory channel, the name of the welding program,
and the process symbol.
• WPS channels. The view shows the WPS name and the pass name. If the WPS covers several passes, use
the arrow buttons to move between the passes.
Figure 24: Channel view: memory channel and WPS channel
Adjusting welding parameters
In the Settings view, you can view and adjust wire feed speed, fine tuning and dynamics. Use the arrow
buttons to move between the parameters. Use the adjustment roll to adjust the parameter value.
Figure 25: Parameters in the Settings view
You can save the changes in the channel by pressing and holding the channel button for more than 3
seconds.
Example
To select a channel and adjust its settings, proceed as follows:
Press the Channel button to open the Channel view.
1.
Browse the channels with the arrow buttons until you find the channel you want to use.
2.
Press the Channel button to open the Settings view.
3.
OPERATING MANUAL | EN 100
©
KEMPPI | 2018-09-28
 Loading...
Loading...