Page 1

PIO-32 Series
User’s Guide
A GREATER MEASURE OF CONFIDENCE
Page 2

WARRANTY
Hardware
Keithley Instruments, Inc. warrants that, for a period of one (1) year from the date of shipment (3 years for Models 2000,
2001, 2002, 2010 and 2700), the Keithley Hardware product will be free from defects in materials or workmanship. This
warranty will be honored provided the defect has not been caused by use of the Keithley Hardware not in accordance with
the instructions for the product. This warranty shall be null and void upon: (1) any modification of Keithley Hardware that
is made by other than Keithley and not approved in writing by Keithley or (2) operation of the Keithley Hardware outside
of the environmental specifications therefore.
Upon receiving notification of a defect in the Keithley Hardware during the warranty period, Keithley will, at its option,
either repair or replace such Keithley Hardware. During the first ninety days of the warranty period, Keithley will, at its
option, supply the necessary on site labor to return the product to the condition prior to the notification of a defect. Failure
to notify Keithley of a defect during the warranty shall relieve Keithley of its obligations and liabilities under this
warranty.
Other Hardware
The portion of the product that is not manufactured by Keithley (Other Hardware) shall not be covered by this warranty,
and Keithley shall have no duty of obligation to enforce any manufacturers' warranties on behalf of the customer. On those
other manufacturers’ products that Keithley purchases for resale, Keithley shall have no duty of obligation to enforce any
manufacturers’ warranties on behalf of the customer.
Software
Keithley warrants that for a period of one (1) year from date of shipment, the Keithley produced portion of the software or
firmware (Keithley Software) will conform in all material respects with the published specifications provided such Keithley
Software is used on the product for which it is intended and otherwise in accordance with the instructions therefore.
Keithley does not warrant that operation of the Keithley Software will be uninterrupted or error-free and/or that the Keithley
Software will be adequate for the customer's intended application and/or use. This warranty shall be null and void upon any
modification of the Keithley Software that is made by other than Keithley and not approved in writing by Keithley.
If Keithley receives notification of a Keithley Software nonconformity that is covered by this warranty during the warranty
period, Keithley will review the conditions described in such notice. Such notice must state the published specification(s)
to which the Keithley Software fails to conform and the manner in which the Keithley Software fails to conform to such
published specification(s) with sufficient specificity to permit Keithley to correct such nonconformity. If Keithley determines that the Keithley Software does not conform with the published specifications, Keithley will, at its option, provide
either the programming services necessary to correct such nonconformity or develop a program change to bypass such
nonconformity in the Keithley Software. Failure to notify Keithley of a nonconformity during the warranty shall relieve
Keithley of its obligations and liabilities under this warranty.
Other Software
OEM software that is not produced by Keithley (Other Software) shall not be covered by this warranty, and Keithley shall
have no duty or obligation to enforce any OEM's warranties on behalf of the customer.
Other Items
Keithley warrants the following items for 90 days from the date of shipment: probes, cables, rechargeable batteries, diskettes,
and documentation.
Items not Covered under Warranty
This warranty does not apply to fuses, non-rechargeable batteries, damage from battery leakage, or problems arising from
normal wear or failure to follow instructions.
Limitation of Warranty
This warranty does not apply to defects resulting from product modification made by Purchaser without Keithley's express
written consent, or by misuse of any product or part.
Page 3

Disclaimer of Warranties
EXCEPT FOR THE EXPRESS WARRANTIES ABOVE KEITHLEY DISCLAIMS ALL OTHER WARRANTIES,
EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING WITHOUT LIMITATION, ALL IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. KEITHLEY DISCLAIMS ALL WARRANTIES WITH
RESPECT TO THE OTHER HARDWARE AND OTHER SOFTWARE.
Limitation of Liability
KEITHLEY INSTRUMENTS SHALL IN NO EVENT, REGARDLESS OF CAUSE, ASSUME RESPONSIBILITY FOR
OR BE LIABLE FOR: (1) ECONOMICAL, INCIDENTAL, CONSEQUENTIAL, INDIRECT, SPECIAL, PUNITIVE OR
EXEMPLARY DAMAGES, WHETHER CLAIMED UNDER CONTRACT, TORT OR ANY OTHER LEGAL THEORY,
(2) LOSS OF OR DAMAGE TO THE CUSTOMER'S DATA OR PROGRAMMING, OR (3) PENALTIES OR PENALTY
CLAUSES OF ANY DESCRIPTION OR INDEMNIFICATION OF THE CUSTOMER OR OTHERS FOR COSTS, DAMAGES, OR EXPENSES RELATED TO THE GOODS OR SERVICES PROVIDED UNDER THIS WARRANTY.
Keithley Instruments, Inc.
Sales Offices: BELGIUM: Bergensesteenweg 709 • B-1600 Sint-Pieters-Leeuw • 02-363 00 40 • Fax: 02/363 00 64
CHINA: Yuan Chen Xin Building, Room 705 • 12 Yumin Road, Dewai, Madian • Beijing 100029 • 8610-6202-2886 • Fax: 8610-6202-2892
FINLAND: Tietäjäntie 2 • 02130 Espoo • Phone: 09-54 75 08 10 • Fax: 09-25 10 51 00
FRANCE: 3, allée des Garays • 91127 Palaiseau Cédex • 01-64 53 20 20 • Fax: 01-60 11 77 26
GERMANY: Landsberger Strasse 65 • 82110 Germering • 089/84 93 07-40 • Fax: 089/84 93 07-34
GREAT BRITAIN: Unit 2 Commerce Park, Brunel Road • Theale • Berkshire RG7 4AB • 0118 929 7500 • Fax: 0118 929 7519
INDIA: Flat 2B, Willocrissa • 14, Rest House Crescent • Bangalore 560 001 • 91-80-509-1320/21 • Fax: 91-80-509-1322
ITALY: Viale San Gimignano, 38 • 20146 Milano • 02-48 39 16 01 • Fax: 02-48 30 22 74
JAPAN: New Pier Takeshiba North Tower 13F • 11-1, Kaigan 1-chome • Minato-ku, Tokyo 105-0022 • 81-3-5733-7555 • Fax: 81-3-5733-7556
KOREA: 2FL., URI Building • 2-14 Yangjae-Dong • Seocho-Gu, Seoul 137-888 • 82-2-574-7778 • Fax: 82-2-574-7838
NETHERLANDS: Postbus 559 • 4200 AN Gorinchem • 0183-635333 • Fax: 0183-630821
SWEDEN: c/o Regus Business Centre • Frosundaviks Allé 15, 4tr • 169 70 Solna • 08-509 04 679 • Fax: 08-655 26 10
SWITZERLAND: Kriesbachstrasse 4 • 8600 Dübendorf • 01-821 94 44 • Fax: 01-820 30 81
TAIWAN: 1FL., 85 Po Ai Street • Hsinchu, Taiwan, R.O.C. • 886-3-572-9077• Fax: 886-3-572-9031
28775 Aurora Road • Cleveland, Ohio 44139 • 440-248-0400 • Fax: 440-248-6168
1-888-KEITHLEY (534-8453) • www.keithley.com
4/02
Page 4

The information contained in this manual is believed to be accurate and reliable. However, Keithley
Instruments, Inc., assumes no responsibility for its use; nor for any infringements or patents or other
rights of third parties that may result from its use. No license is granted by implication or otherwise
under any patent rights of Keithley Instruments, Inc.
KEITHLEY INSTRUMENTS, INC., SHALL NOT BE LIABLE FOR ANY SPECIAL, INCIDENTAL,
OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES RELATED TO THE USE OF THIS PRODUCT. THIS
PRODUCT IS NOT DESIGNED WITH COMPONENTS OF A LEVEL OF RELIABILITY THAT IS
SUITED FOR USE IN LIFE SUPPORT OR CRITICAL APPLICATIONS.
Refer to your Keithley Instruments license agreement and Conditions of Sale document for specific
warranty and liability information.
VIEWDAC and EASYEST LX are registered trademarks of Keithley Instruments, Inc. MetraByte is a
trademark of Keithley Instruments, Inc. All other brand and product names are trademarks or registered
trademarks of their respective companies.
© Copyright Keithley Instruments, Inc., 1994, 1998, 1999.
All rights reserved. Reproduction or adaptation of any part of this documentation beyond that permitted
by Section 117 of the 1976 United States Copyright Act without permission of the Copyright owner is
unlawful.
Keithley Instruments, Inc.
28775 Aurora Road, Cleveland, OH 44139
Page 5

PIO-32 Series
User’s Guide
Revision E - April, 2001
Part Number: 88170
Page 6

S
The following safety precautions should be observed before using this product and any associated instrumentation.
Although some instruments and accessories would normally be used with non-hazardous voltages, there are situations
where hazardous conditions may be present.
This product is intended for use by qualified personnel who recognize shock hazards and are familiar with the safety
precautions required to avoid possible injury. Read and follow all installation, operation, and maintenance information
carefully before using the product. Refer to the manual for complete product specifications.
If the product is used in a manner not specified, the protection provided by the product may be impaired.
The types of product users are:
Responsible body is the individual or group responsible for the use and maintenance of equipment, for ensuring that
the equipment is operated within its specifications and operating limits, and for ensuring that operators are adequately
trained.
Operators use the product for its intended function. They must be trained in electrical safety procedures and proper use
of the instrument. They must be protected from electric shock and contact with hazardous live circuits.
Maintenance personnel perform routine procedures on the product to keep it operating properly, for example, setting
the line voltage or replacing consumable materials. Maintenance procedures are described in the manual. The procedures explicitly state if the operator may perform them. Otherwise, they should be performed only by service personnel.
Service personnel are trained to work on live circuits, and perform safe installations and repairs of products. Only
properly trained service personnel may perform installation and service procedures.
Keithley products are designed for use with electrical signals that are rated Installation Category I and Installation
Category II, as described in the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) Standard IEC 60664. Most measurement, control, and data I/O signals are Installation Category I and must not be directly connected to mains voltage
or to voltage sources with high transient over-voltages. Installation Category II connections require protection for high
transient over-voltages often associated with local AC mains connections. Assume all measurement, control, and data
I/O connections are for connection to Category I sources unless otherwise marked or described in the Manual.
Exercise extreme caution when a shock hazard is present. Lethal voltage may be present on cable connector jacks or
test fixtures. The American National Standards Institute (ANSI) states that a shock hazard exists when voltage levels
greater than 30V RMS, 42.4V peak, or 60VDC are present.
age is present in any unknown circuit before measuring.
Operators of this product must be protected from electric shock at all times. The responsible body must ensure that
operators are prevented access and/or insulated from every connection point. In some cases, connections must be exposed to potential human contact. Product operators in these circumstances must be trained to protect themselves from
the risk of electric shock. If the circuit is capable of operating at or above 1000 volts,
may be exposed.
Do not connect switching cards directly to unlimited power circuits. They are intended to be used with impedance
limited sources. NEVER connect switching cards directly to AC mains. When connecting sources to switching cards,
install protective devices to limit fault current and voltage to the card.
Before operating an instrument, make sure the line cord is connected to a properly grounded power receptacle. Inspect
the connecting cables, test leads, and jumpers for possible wear, cracks, or breaks before each use.
afety Precautions
A good safety practice is to expect that hazardous volt-
no conductive part of the circuit
5/02
Page 7

When installing equipment where access to the main power cord is restricted, such as rack mounting, a separate main
input power disconnect device must be provided, in close proximity to the equipment and within easy reach of the
operator.
For maximum safety, do not touch the product, test cables, or any other instruments while power is applied to the circuit under test. ALWAYS remove power from the entire test system and discharge any capacitors before: connecting
or disconnecting cables or jumpers, installing or removing switching cards, or making internal changes, such as installing or removing jumpers.
Do not touch any object that could provide a current path to the common side of the circuit under test or power line (earth)
ground. Always make measurements with dry hands while standing on a dry, insulated surface capable of withstanding the
voltage being measured.
The instrument and accessories must be used in accordance with its specifications and operating instructions or the
safety of the equipment may be impaired.
Do not exceed the maximum signal levels of the instruments and accessories, as defined in the specifications and operating information, and as shown on the instrument or test fixture panels, or switching card.
When fuses are used in a product, replace with same type and rating for continued protection against fire hazard.
Chassis connections must only be used as shield connections for measuring circuits, NOT as safety earth ground connections.
If you are using a test fixture, keep the lid closed while power is applied to the device under test. Safe operation requires the use of a lid interlock.
If or is present, connect it to safety earth ground using the wire recommended in the user documentation.
!
The symbol on an instrument indicates that the user should refer to the operating instructions located in the manual.
The symbol on an instrument shows that it can source or measure 1000 volts or more, including the combined
effect of normal and common mode voltages. Use standard safety precautions to avoid personal contact with these
voltages.
The
WARNING
associated information very carefully before performing the indicated procedure.
The
CAUTION
the warranty.
Instrumentation and accessories shall not be connected to humans.
Before performing any maintenance, disconnect the line cord and all test cables.
To maintain protection from electric shock and fire, replacement components in mains circuits, including the power
transformer, test leads, and input jacks, must be purchased from Keithley Instruments. Standard fuses, with applicable
national safety approvals, may be used if the rating and type are the same. Other components that are not safety related
may be purchased from other suppliers as long as they are equivalent to the original component. (Note that selected parts
should be purchased only through Keithley Instruments to maintain accuracy and functionality of the product.) If you
are unsure about the applicability of a replacement component, call a Keithley Instruments office for information.
To clean an instrument, use a damp cloth or mild, water based cleaner. Clean the exterior of the instrument only. Do
not apply cleaner directly to the instrument or allow liquids to enter or spill on the instrument. Products that consist
of a circuit board with no case or chassis (e.g., data acquisition board for installation into a computer) should never
require cleaning if handled according to instructions. If the board becomes contaminated and operation is affected,
the board should be returned to the factory for proper cleaning/servicing.
heading in a manual explains dangers that might result in personal injury or death. Always read the
heading in a manual explains hazards that could damage the instrument. Such damage may invalidate
Page 8

Table of Contents
Preface
Overview
1
Important Safety Instructions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-2
Supporting Software . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-3
Accessories . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-4
2
Functional Description
Input Circuitry . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-2
Output Circuitry . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-3
3
Setup and Installation
Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-1
Inventorying Required Installation Resources . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-2
Installing DriverLINX Software and Documentation . . . . . . . 3-3
Configuring Your Installation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-6
Preparing and Installing Your Board . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-7
Unpacking the Board . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-7
Setting the Base Address . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-8
Installing the Board . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-9
Checking Your Installation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-11
I/O Bit Tests . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-11
General Information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-11
Output Set Test . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-16
Input Read Test . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-21
4
Cabling and Wiring
Optional Cables . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-2
STP-37/FC Screw Terminal Panel . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-3
Typical Digital I/O Wiring . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-5
Connector Pin Assignments . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-6
Programming
5
i
Page 9

ii
Troubleshooting
6
Problem Isolation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-1
Identifying Symptoms and Possible Causes . . . . . . . . . . . 6-1
Testing the PIO-32 Series Board and Host Computer . . . . 6-4
Testing the Accessory Slot and I/O Connections . . . . . . . . 6-5
Technical Support . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-6
Specifications
A
B
Connector Pin Assignments
C
Register Maps
Index
List of Figures
Figure 2-1 General Layout of PIO-32 Series Boards . . . . . 2-1
Figure 2-2 Typical Input Circuit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-2
Figure 2-3 Typical Output Circuit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-3
Figure 3-1 Setting the Base Address . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-9
Figure 3-2 An AIO Panel example . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-12
Figure 3-3 DIO channel tab example . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-13
Figure 3-4 Configuring the digital I/O channels as
inputs and outputs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-15
Figure 3-5 Configuring channel 0 for output bit
pattern A . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-15
Figure 3-6 An AIO Panel example . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-17
Figure 3-7 Configuring the digital I/O channels as
inputs and outputs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-18
Figure 3-8 Configuring channel 0 for output bit
pattern A . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-19
Figure 3-9 Configuring channel 0 for output bit
pattern B . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-20
Figure 4-1 C-3200/C-32NN Optional Cables . . . . . . . . . . . 4-2
Figure 4-2 PIO-32 Series Board Cabled to Screw
Terminal Panels . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-3
Figure 4-3 STP-37/FC Mounting Holes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-4
Page 10

Figure 4-4 Typical Non-TTL Digital Input
Wiring Example . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-5
Figure 4-5 Typical Digital Output Control
Wiring Example . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-6
Figure 4-6 Pin Assignments for the C-3200 Cable 37-D
Connector, J1 Signals . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-7
Figure 4-7 Pin Assignments for the C-3200 Cable 37-D
Connector, J2 Signals . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-8
Figure 4-8 Pin Assignments for 40-Pin Ribbon Header,
J1 Signals . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-9
Figure 4-9 Pin Assignments for the 40-Pin Ribbon Header,
J2 Signals . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-10
Figure B-1 Pin Assignments for the C-3200 Cable 37-D
Connector, J1 Signals . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . B-3
Figure B-2 Pin Assignments for the C-3200 Cable 37-D
Connector, J2 Signals . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . B-4
Figure B-3 Pin Assignments for 40-Pin Ribbon Header
Connector, J1 Signals . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . B-5
Figure B-4 Pin Assignments for 40-Pin Ribbon Header
Connector, J2 Signals . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . B-6
List of Tables
Table 6-1 Troubleshooting Information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-2
Table A-1 PIO-32 Series Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A-1
Table B-1 37-D and 40-Pin Signals for Connectors
J1 and J2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . B-2
Table C-1 PIO-32 Series Register Map Summary . . . . . . . C-2
Table C-2 PIO-32I/O Register Map . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . C-3
Table C-3 PIO-32IN Register Map . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . C-3
Table C-4 PIO-32OUT Register Map . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . C-4
iii
Page 11

iv
Page 12

Preface
The
PIO-32 Series User’s Guide
program, and use the PIO-32 Series isolated, digital input and output
(I/O) boards. This guide serves data acquisition system designers,
engineers, technicians, programmers, scientists, and other users
responsible for setting up, cabling, wiring, and programming the PIO-32
Series boards. This guide assumes that you are familiar with data
acquisition and programming principles and with your particular
application.
The
PIO-32 Series User’s Guide
Section 1 briefly describes the features of the PIO-32 Series boards,
●
including descriptions of the supported software and accessories.
●
Section 2 describes in more detail the input and output circuitry.
●
Section 3 describes how to install the DriverLINX software and
documentation, how to unpack, set up, and install the board, and how
to configure and check the installation.
explains how to install, cable, wire,
is organized as follows:
●
Section 4 describes how to attach screw terminal panel accessories
and how to wire signals to the PIO-32 Series boards.
●
Section 5 briefly describes the need to program through the
DriverLINX interface—provided with your board—and tells how to
access the extensive DriverLINX documentation.
●
Section 6 explains how to troubleshoot problems that may arise with
the PIO-32 Series boards. It also explains how to obtain technical
assistance and repairs for the boards.
Appendix A lists the specifications for the PIO-32 Series boards.
●
v
Page 13

Appendix B lists the connector pin assignments.
●
Appendix C provides a register map, for background reference only
●
(you program the PIO-32 Series boards through the DriverLINX
interface, not at the register-level).
An index completes this guide.
vi
Page 14

1
Overview
The PIO-32 Series boards are part of a family of digital input and output
(I/O) boards designed for IBM
The software currently supplied with these boards requires the Windows
95/98/NT operating system and a compatible microprocessor (preferably
a Pentium microprocessor).
These boards provide a flexible interface for a variety of parallel I/O
devices, including instruments, displays, and control systems. The
members of the PIO-32 Series are as follows:
PIO-32I/O, which provides 16 digital inputs and 16 digital outputs
●
PIO-32IN, which provides 32 digital inputs
●
●
PIO-32OUT, which provides 32 digital outputs
The major features of all PIO-32 Series boards include the following:
●
Input level (if included) of 3.5VDC to 28VDC
Output relay contacts (if included), Form A, 0.75A at 30V RMS,
●
42.4V peak, 60VDC
®
PC series computers and compatibles.
®
●
Connections through on-board ribbon headers
High-density channel count
●
Only one slot required for the board
●
1-1
Page 15

Important Safety Instructions
Each PIO-32 Series board bears a warning symbol that corresponds to the
information in this section. Follow these steps when preparing to install
your PIO-32 board:
1. Read the warnings in this section.
2. When installing, cabling, and wiring your board, heed the warnings
marked on the board and described in this section, and follow the
instructions in Sections 3 and 4.
3. When using the board, do not exceed the ratings specified in
Appendix A.
Warning:
or 60VDC to any input or output on this board.
Live voltages can still be present on the board even when the computer is
turned off. To protect you and the circuit, covers are provided with the
PIO-32 Series boards. Though you can remove the covers to service the
PIO-32 Series boards,
removed!
Do not connect voltages greater than 30V RMS, 42.4V peak,
do not use these boards with the covers
In addition, disconnect all cables when servicing these boards.
1-2 Overview
Page 16

Supporting Software
DriverLINX software is supplied by Keithley with the PIO-32 Series
board. DriverLINX provides convenient interfaces to configure and set
I/O bits without register-level programming.
Most importantly, however, DriverLINX supports those programmers
who wish to create custom applications using Visual C/C++, Visual Basic,
or Delphi. DriverLINX accomplishes foreground and background tasks to
perform data acquisition. The software includes memory and data buffer
management, event triggering, extensive error checking, and context
sensitive online help.
More specifically, DriverLINX provides application developers a
standardized interface to over 100 services for creating foreground and
background tasks for the following:
Analog input and output
●
Digital input and output
●
●
Time and frequency measurement
Event counting
●
●
Pulse output
Period measurement
●
In addition to basic I/O support, DriverLINX also provides:
●
Built-in capabilities to handle memory and data buffer management
A selection of starting and stopping trigger events, including
●
pre-triggering, mid-point triggering and post-triggering protocols
●
Extensive error checking
●
Context-sensitive on-line help system
1-3
Page 17
Accessories
DriverLINX is essentially hardware independent, because its portable
APIs work across various operating systems. This capability eliminates
unnecessary programming when changing operating system platforms.
The optional accessories for the PIO-32 Series boards include screw
terminal panels (STPs) and cables (C-3200/C-32NN) that convert from
the ribbon headers on the board to the 37-D male cable connectors. The
C-3200 cables are 30 inches long; longer cables are available, C-32NN,
where NN is the number of feet added to the standard cable.
You can use STPs and cables to connect applications to the PIO-32 Series
boards. An STP-37/FC accessory is available that combines a 37-D
female receptacle, which directly mates to the 37-D male connector on
the optional C-3200 cable for the PIO-32 Series boards, and 37 screw
terminals in a protective case for desktop use.
Warning:
other STPs at voltages above 30V RMS, 42.4V peak, or 60VDC. These
accessories are rated for 30V RMS, 42.4V peak, or 60VDC maximum.
Use at higher voltages may result in shock hazard.
1-4 Overview
Do not use the STP-37/FC and C-3200/C-32NN accessories or
Page 18

2
Functional Description
This section describes the general layout of the PIO-32 Series boards and
provides schematics of the typical input and output circuits.
The PIO-32 Series boards are channel-to-channel isolated and handle
digital voltages in a broader range than standard TTL levels. Optional
accessories for the board include screw terminal panels (STPs) and the
C-3200 cables. The C-3200 cables are 30-inches long; they let you route
the signals from 40-pin headers on the board through a slot in the rear
panel bracket to 37-D male connectors. You connect the 37-D connectors
to the optional STPs.
Figure 2-1 shows the general layout of PIO-32 Series boards. Note the
ribbon headers, labeled J1 and/or J2, on your board; these ribbon headers
provide 16 digital input or output channels each. The orientation of the
headers differs among the boards, as shown in Figure 2-1.
40-pin ribbon header
(orientation for IN and I/O boards)
pin 1
40-pin ribbon header
(orientation for OUT board only)
Figure 2-1. General Layout of PIO-32 Series Boards
pin 1
adapter plate
37-D connectors
(male pins)
C-3200
optional
cables
2 ft.
2-1
Page 19

Input Circuitry
The PIO-32I/O has 16 digital input channels and uses the J1 ribbon
header (channels 0 to 15). The PIO-32IN has 32 digital input channels
and uses the J1 and J2 ribbon headers (channels 0 to 31). Figure 2-2
shows each input channel schematically. You must limit the input voltage
to 28VDC and the input current to 15mA maximum. The positive input
signals are labeled PnP (where n is the bit number, 0 to 31); the negative
input signals are labeled P
nN (where n is the bit number, 0 to 31).
+5V
47kΩ
To HCT logic
(inverted logic)
2.0kΩ, 1/2W
28VDC and
15mA (maximum)
1/4 of ILQ-2
Figure 2-2. Typical Input Circuit
PnP
To ribbon header
input
PnN
2-2 Functional Description
Page 20
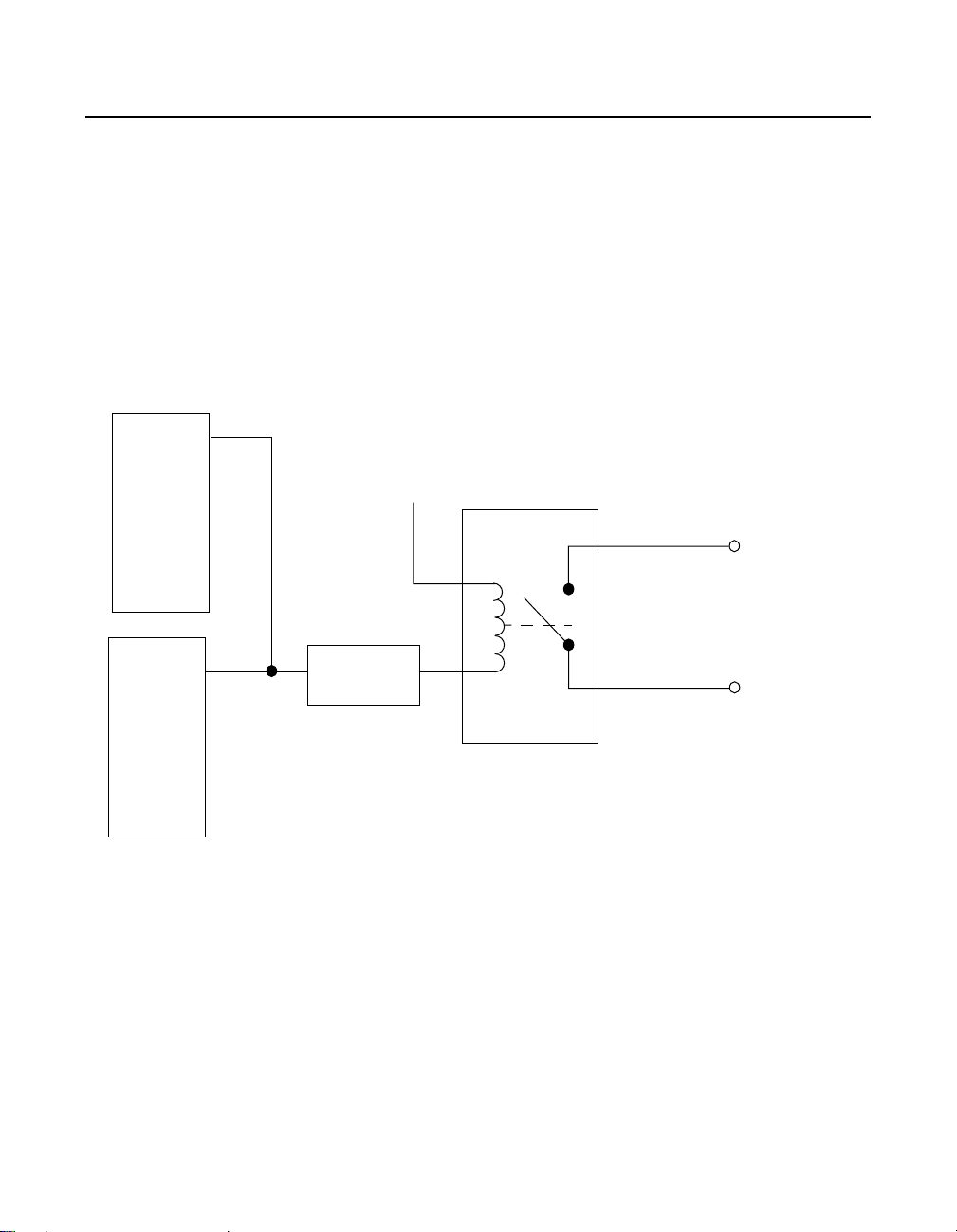
Output Circuitry
The PIO-32I/O has 16 digital output channels and uses the J2 ribbon
header (channels 16 to 31). The PIO-32OUT has 32 digital output
channels and uses the J1 and J2 ribbon headers (channels 0 to 31).
Figure 2-3 shows the output channels schematically. The output channels
are reed relays (form A) rated to 10W at 0.75A or 30V RMS, 42.4V peak,
or 60VDC maximum (resistive). The relay connections are not polarized
(positive or negative equivalent) and are labeled PnP and PnN (where n is
the bit number, 0 to 15).
1/8
74LS244
read
back
1/8
74LS273
data
register
+5V
1/2
relay driver
relay
Figure 2-3. Typical Output Circuit
2
To ribbon header
1
PnP
output
PnN
2-3
Page 21

Overview
3
Setup and Installation
Warning: The procedures in this section are intended for qualified
service personnel. Do not perform these procedures unless you are
qualified to do so.
This section describes the following:
● Inventorying installation resources.
● Installing the DriverLINX software needed to operate your PIO-32
board.
● Configuring the installation in software.
● Unpacking and inspecting the board, setting the base address of the
board, and then installing the board in your computer.
● Checking the installation.
If you encounter any problems with the board after installation, refer to
Section 6 for troubleshooting information.
3-1
Page 22

Note: Install the DriverLINX software before installing the PIO-32
board. Otherwise, the device drivers will be more difficult to install.
Inventorying Required Installation Resources
Before installing DriverLINX and the board, do the following:
1. Inventory your PIO-32 board’s configuration settings.
2. Determine the resources your PIO-32 board requires.
3. Inventory your computer’s resources already allocated to other
installed devices.
4. Determine whether your computer has sufficient resources for your
PIO-32 board.
5. Determine whether your PIO-32 board can use your computer’s free
resources.
Note: The DriverLINX Installation and Configuration Guide, Section 1,
amplifies the inventory process in checklist items 1-5. (Ignore the rest of
the checklist items for now.) To display this manual from your
DriverLINX PIO Series CD-ROM, open the Windows Explorer, then
double click on X:\Drvlinx4\Docs\Instconf.pdf, where X = the letter of
the CD-ROM drive. Acrobat Reader must already be installed on the other
system. If necessary, you can first install Acrobat Reader directly from the
CD-ROM by double clicking X:\Acrobat\setup.exe.
3-2 Setup and Installation
Page 23

Installing DriverLINX Software and Documentation
Note: Even if DriverLINX versions other than the PIO Series version are
already installed on your system, you must also install the PIO Series
DriverLINX version. In the process, some DriverLINX capabilities shared
by all boards may be upgraded (test utilities, for example).
This section discusses installation of drivers, interfaces, and
documentation. The component installation options provided by the
DriverLINX setup program are as follows:
● Install Drivers — This required component installs only the files you
need for configuring your hardware and running third-party
data-acquisition applications that require DriverLINX.
● Install Interfaces — This optional component installs the files and
example programs that you will need to develop custom applications
for DriverLINX using C/C++, Visual Basic, and Delphi.
● Install Documentation — This optional component installs
electronic documentation for DriverLINX that you can read, search,
and print using the Adobe Acrobat Reader.
● Install Acrobat — This optional component installs the Adobe
Acrobat Reader for the DriverLINX electronic documentation.
Install the DriverLINX software and board as follows:
1. Place the DriverLINX PIO Series CD-ROM in your drive and wait a
few seconds. On most systems, setup starts automatically. If not, run
the setup.exe file, found in the root directory of the CD-ROM.
A DriverLINX Browser Introduction screen appears. Thereafter, the
DriverLINX CD Navigator screen appears automatically after
waiting a few seconds or after clicking Next.
3-3
Page 24

Note: On the DriverLINX CD Navigator and other DriverLINX Browser
screens, place the cursor over a menu item to see an explanation. A star
next to a menu item means that it was selected previously.
Before continuing with this installation, Keithley suggests clicking Read
Me First on the DriverLINX CD Navigator and reviewing the brief
information that appears.
2. On the DriverLINX CD Navigator screen, click Install
DriverLINX. An Install These DriverLINX Components screen
appears.
3. Click Install Drivers, and then follow the series of on-screen
instructions. When done, the Install These DriverLINX Components
screen reappears.
4. If you do not plan to develop custom application software for your
PIO-32 Series board, then skip to Step 5. If you do plan to develop
custom application software, you must install DriverLINX
interfaces before writing the software. Install them now by clicking
Install Interfaces and following the series of on-screen
instructions. When done, the Install These DriverLINX Components
screen reappears.
5. Click Install Documentation and follow the series of on-screen
instructions. This step installs the manuals. When done, the Install
These DriverLINX Components screen reappears.
6. If Acrobat Reader is not already installed on your system, install it
now. You need Acrobat Reader to read the manuals, a section of
which you must access in step 9. Click on Install Acrobat and
follow the series of on-screen instructions. When done, the Install
These DriverLINX Components screen reappears.
7. Click Exit. Then, on the screen that appears saying “Thank you for
using DriverLINX,” click Done. The System Settings Changed
dialog box appears.
3-4 Setup and Installation
Page 25

8. On the System Settings Changed dialog box, click No. (The system
will be rebooted and configured later under “Configuring Your
Installation.”) The screen returns to the Windows desktop.
9. Print out one section of a DriverLINX manual that you will briefly
review later during system configuration. Proceed as follows:
a. In the Start menu under Programs
→ DriverLINX, click
On-line Manuals. A menu document appears
b. In the menu document, scroll until you find the major category
Configuration.
c. Under Configuration click Hardware References. A list of
documents appears.
d. In the list of documents, click Keithley PIO Series. Acrobat
Reader opens and the manual entitled Using DriverLINX with
Your Hardware—Keithley PIO Series appears.
e. Print the following section from the Using DriverLINX with
Your Hardware—Keithley PIO Series manual: “Configuring the
PIO Series.”
Note: If your data acquisition system is not connected to a printer, you
can display and print the Using DriverLINX with Your Hardware—
Keithley PIO Series manual sections from another system, directly from
the CD-ROM (without installing anything). To display the manual, open
the Windows Explorer, then double click on
X:\Drvlinx4\Docs\Notes\kmbpio.pdf, where X = the letter of the
CD-ROM drive. Acrobat Reader must already be installed on the other
system. If necessary, you can first install Acrobat Reader directly from the
CD-ROM by double clicking X:\Acrobat\setup.exe.
10. Continue with the next section, “Configuring Your Installation.”
3-5
Page 26

Configuring Y our Installation
1. Locate and briefly review the manual section, “Configuring the PIO
Series,” that you printed earlier during step 9 of “Installing
DriverLINX Software and Documentation.” Reviewing this section
will help prepare you to input information and select options when
configuring your installation.
Note: Be sure to note and follow all configuration differences between
installations for Windows NT and Windows 95/98.
2. Reboot your computer. The DriverLINX Plug and Play Wizard
appears on your screen automatically at the end of the boot cycle.
Note: If you do not run the DriverLINX Plug and Play Wizard now, it
will not reappear during the current computer session, although it may
appear after a subsequent reboot. If you wish to configure your board
sometime later, you can start the Plug and Play Wizard manually from a
batch file. In the Windows Explorer, double click
X:\Drvlinx4\Help\kmbpio.bat, where X is the letter of the drive on which
DriverLINX is installed.
3. On the Plug and Play Wizard, click Wizard and follow the series of
on-screen instructions that appear. The wizard will first lead you
through the steps of installing your hardware—from a software
viewpoint—and configuring it.
Note: If your operating system is Windows NT, use Windows NT
Diagnostics to find the free resources that the Plug and Play Wizard asks
you to assign. However, if your board requires an interrupt, to reliably
find a free ISA interrupt you may need to: 1) configure your computer as
having a non-Plug and Play operating system, using BIOS setup, and then
2) individually assign the interrupt to the ISA bus.
4. Continue with the next section, “Preparing and Installing Your
Board.”
3-6 Setup and Installation
Page 27

Preparing and Installing Your Board
Caution: Ensure that the computer is turned OFF before installing or
removing a board. Installing or removing a board while power is ON can
damage your computer, the board, or both.
Handle the board in a static-controlled workstation; wear a grounded
wrist strap. Discharge static voltage differences between the wrapped
board and the handling environment before removing the board from its
protective wrapper. Failure to discharge static electricity before and
during handling may damage semiconductor circuits on the board.
Handle the board using the mounting bracket. Do not touch the circuit
traces or connector contacts when handling the board.
Unpacking the Board
To prevent any damage to your PIO-32 Series board, perform the
following steps when unpacking the board:
1. Remove the wrapped PIO-32 Series board from its outer shipping
carton.
2. Making sure your computer is turned OFF but grounded, hold the
wrapped board in one hand while placing your other hand firmly on
the metal portion of the computer chassis; this discharges any static
electricity.
3. Carefully remove the board from its anti-static wrapping material.
You may store the wrapping material for future use.
4. Inspect the board for signs of damage. If any damage is apparent,
arrange to return the board to the factory; refer to Section 6 for more
information.
5. Check the remaining contents of your package against the packing
list to ensure that your order is complete. Immediately report any
missing items to the factory.
3-7
Page 28

6. Once you have determined that the board is acceptable, set the base
address. The next section explains how to set the base address.
Setting the Base Address
Note: Before setting the base address switches, check the different
requirements for Windows 95/98 and Windows NT. Refer to “Configuring
the PIO Series” in Using DriverLINX with Your Hardware—Keithley PIO
Series manual, which you printed in step 9 of “Installing the DriverLINX
Software.”
The base address is the only item you need to set on the PIO-32 Series
boards. The PIO-32 Series boards normally use a block of eight I/O
addresses. The factory default base address is 300h. If 300h was assigned
to the board when you ran the DriverLINX Plug and Play Wizard, you do
not need to set the address switch. Otherwise, reconfigure the base
address switch (labeled BASE ADDRESS on the board) to conform to the
base address assigned when you ran the Wizard.
The base address switch block contains eight switches, labeled 1 through
8. Switch 1 corresponds to the most significant bit (MSB) of the base
address (A9); switch 7 corresponds to the least significant bit (LSB) of the
base address (A3). Switch 8 is reserved.
You place a switch in the ON position (logic 0) by sliding the switch
toward the top (numbered side) of the switch block. You place a switch in
the OFF position (logic 1) by sliding the switch toward the bottom
(unnumbered side) of the switch block. Figure 3-1 illustrates the setting
for a base address of 300h; switches 1 and 2 are in the OFF position and
switches 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, and 8 are in the ON position (A9 and A8 are logic 1,
A7 through A3 are logic 0).
3-8 Setup and Installation
Page 29

BASE
ADDRESS
O
N
Figure 3-1. Setting the Base Address
Write down the base address for each board; you will need the base
address when you program the board. See Section 5 for information on
register level programming.
Proceed next to “Installing the Board.”
Installing the Board
1 2 3 4 5 6 7
A9 A8 A7 A6 A5 A4 A3 A2
8
Before installing the PIO-32 Series board in the host computer, ensure
that the base address switches are set appropriately.
Warning: Do not connect voltages greater than 30V RMS, 42.4V peak,
or 60VDC to any input or output on this board.
Live voltages can still be present on the board even when the computer is
turned off. To protect you and the circuit, Keithley provides covers with
the PIO-32 Series boards. Though you can remove the covers to service
the PIO-32 Series boards, do not use these boards with the covers
removed! In addition, disconnect all cables when servicing these boards.
Caution: Installing or removing a board with the power ON can cause
damage to your board and/or computer.
3-9
Page 30

To install the board, perform the following steps:
1. Turn power to the computer and all attached equipment OFF.
2. Remove the computer chassis cover.
3. Select an available slot appropriate to the length of the board.
4. Loosen and remove the screw at the top of the blank adapter plate,
and then slide the plate up and out to remove.
5. If you are installing your own cables or the optional
C-3200/C-32NN ribbon cables, decide how to run the cables. Note
that the strain relief on the C-3200/C-32NN 40-pin connector may
need to be removed for clearance or to allow the cable to run in the
correct direction. Decide on the folds and orientation of the cables
but do not install them yet.
6. Insert and secure the board connector in the selected slot.
7. Route your cables or the C-3200/C-32NN cables from the outside of
the chassis through the slot in the adapter plate and connect them to
the appropriate 40-pin header. Fold the ribbon cable so that it does
not interfere with other boards in the chassis.
8. Replace the computer chassis cover.
9. Plug in all cords and cables not already connected.
10. Continue with the next section, “Checking Your Installation.”
3-10 Setup and Installation
Page 31

Checking Y our Installation
The ability to start the DriverLINX AIO Panel utility, which is available
after you install DriverLINX, verifies that DriverLINX and the board are
installed and configured satisfactorily.
You can also test the functions of the PIO-32 board, without needing to
write an application program, by connecting appropriate digital signals
and observing the responses with the DriverLINX AIO Panel.
After you configure and check your installation, you can attach
accessories as needed and wire the appropriate signals to the board. Refer
to Section 4 for instructions.
I/O Bit Tests
General Information
1. Start the AIO Panel as follows:
a. In the Start menu, click Programs.
b. Find the DriverLINX ➧ Test Panels folder, under which you
should find the AIO Panel entry.
3-11
Page 32

c. Click on the AIO Panel entry. The Analog I/O Panel should
appear, similar to the example in Figure 3-2. (If you have other
DriverLINX devices installed in addition to the digital
input/output card you are testing, they will also be listed. In that
case, select the desired digital I/O card and the proper device
number before proceeding.)
Figure 3-2. An AIO Panel example
Note: The “Driver Selection” column will show the actual DriverLINX
driver(s) you have installed.
3-12 Setup and Installation
Page 33

2. On the AIO Control Panel, click the DIO tab.
Figure 3-3. DIO channel tab example
3-13
Page 34

Note: The on-screen digital I/O controller works as follows:
● Channels 0 to 15 refer to the 8-bit general-purpose registers of
your digital input-output card. (Depending on which card is
used, the number of valid 8-bit registers will vary.) Bits
displayed on the Digital Input Panel and the Digital Output
Panel are numbered 0-7 for every channel. Refer elsewhere in
this manual for a description of the available ports and their
direction.
● Invalid channels and settings appear as dark gray squares. For
example:
- Non-existent channels always appear as dark gray squares.
- Channels configured as inputs will appear as dark gray
squares on the output panel.
● Valid channels and settings appear as white squares when OFF
and green squares when ON. (When the manual is printed in
black and white, valid channels and settings appear as white
squares when OFF and as light gray squares when ON.)
● The two-digit numeric displays under Input Bits and Output
Bits show the hexadecimal values of the adjacent bit patterns.
● To configure a valid channel either for input or output, use the
Digital Channel Configuration Panel. Click on either the
Input or Output square below the channel number. Note: this
selection will be disabled for channels which are fixed as input
or output by hardware design.
● To turn ON output-channel bits, use the Digital Output Panel.
First select the channel number of the bits to be turned on by
clicking on the appropriate square under Channels. Then, turn
ON a bit by clicking the appropriate square under Output Bits.
Turn OFF a bit in the same way.
● To read an input-channel bit, use the Digital Input Panel. First
select the channel number to be checked by clicking the
appropriate square under Channels. Then, read the numbered
bit under Input Bits. OFF input bits appear as black dots and
ON input bits appear as green dots. (When the manual is
printed in black and white, OFF input bits appear as black dots
and ON input bits appear as light gray dots.)
3-14 Setup and Installation
Page 35

3. Under Digital I/O Configuration Panel, configure channels as
shown in Figure 3-4. (Actual channels available will vary according
to your hardware.)
KEITHLEY
Channel Configuration
0
Input
Output
123456789101112131415
Digital I/O Configuration Panel
Figure 3-4. Configuring the digital I/O channels as inputs and outputs
Note: For clarity when the manual is printed in black and white, the
control colors in Figure 3-4 and subsequent drawings will be shown as
follows:
Color on
Illustration
Actual Panel Function
BLACK DARK GRAY Invalid
WHITE LIGHT GRAY OFF
GRAY GREEN ON
4. In the Digital Output Panel under Channels, click on a channel
(here, channel 0) as shown in Figure 3-5.
KEITHLEY
Channels
1234567
0
8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15
Figure 3-5. Configuring channel 0 for output bit pattern A
5. In the Digital Output Panel under Output Bits, set the bits of the
channel as desired as shown in Figure 3-5. (Click on each bit
position to turn it ON or OFF.)
Digital Output Panel
Output Bits
765 43210
55
3-15
Page 36

Output Set Test
The output set test checks whether logic levels measured at all output pins
agree with output bit patterns set by software, using a DriverLINX
graphical interface (AIO Panel).
Note: This test is performed without user circuits being connected to the
outputs.
Perform the output set test as follows:
6. In the Digital Input Panel under Channels, click on a channel to
select it and display the logical state of its input lines.
1. Ready the following equipment:
● A digital voltmeter (DVM) or a digital multimeter (DMM) set
to measure voltages, or a logic probe capable of reading TTL
logic levels.
● A suitable accessory and cable for the board being tested.
2. Turn OFF the host computer.
3. Connect the cable and accessory to your board.
4. Turn ON the host computer and boot Windows 95/98/NT.
5. Click the Windows 95/98/NT Start tab.
3-16 Setup and Installation
Page 37

6. Start the AIO Panel as follows:
a. In the Start menu, click Programs.
b. Find the DriverLINX ➧ Test Panels folder, under which you
should find the AIO Panel entry.
c. Click on the AIO Panel entry. The Analog I/O Panel should
appear, similar to the example in Figure 3-6. (If you have other
DriverLINX devices installed in addition to the digital
input/output card you are testing, they will also be listed. In that
case, select the desired digital I/O card and the proper device
number before proceeding.)
Figure 3-6. An AIO Panel example
3-17
Page 38

7. On the AIO Panel, click the DIO tab.
Note: To read an input-channel bit, use the Digital Input Panel. First,
select the channel number to be checked by clicking the appropriate
square under Channels. Then, read the numbered bit under Input Bits.
OFF input bits appear as black dots and ON input bits appear as green
dots. (When the manual is printed in black and white, OFF input bits
appear as black dots and ON input bits appear as light gray dots.) Further
information about this panel, how to make changes, and how to interpret
displays, is given in “I/O Bit Tests” of this section.
8. Under Digital I/O Configuration Panel, configure the output
channels to be tested as shown in Figure 3-7. (Actual output
channels will vary according to your hardware.)
KEITHLEY
Channel Configuration
0
Input
Output
123456789101112131415
Digital I/O Configuration Panel
Figure 3-7. Configuring the digital I/O channels as inputs and outputs
Note: In Figure 3-7 and subsequent drawings of digital I/O controller
panels, the squares below invalid channels are colored black instead of
dark gray—for clarity when the manual is printed in black and white.
3-18 Setup and Installation
Page 39

9. In the Digital Output Panel under Channels, click on an output
channel (channel 0 in this example) as shown in Figure 3-8.
KEITHLEY
Channels
1234567
0
8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15
Figure 3-8. Configuring channel 0 for output bit pattern A
10. In the Digital Output Panel under Output Bits, set the bits of
channel 0 for bit pattern A as shown in Figure 3-8.
11. Measure the voltage between signal ground and each bit of the
output port with a DMM or DVM. Make measurements at the
cabled mating connector of your accessory.
12. Each bit set to ON in the AIO Panel should output a logic-high signal at the corresponding I/O terminal, reading typically about
4 volts (minimum of 2.2 volts) at a DMM/DVM. Each bit set to
OFF in the AIO Panel should output a logic-low signal at the corresponding I/O terminal, reading typically about 0 volts (maximum of
0.8 volts) at a DMM/DVM. Do one of the following:
Digital Output Panel
Output Bits
765 43210
55
Note: The typical values shown are valid for boards with TTL
compatible outputs. For boards with relay outputs (REL-16, PDISO-8,
and PIO-32) the output will be a relay contact closure. For boards with
open collector outputs (PIO-HV) use a pull up resistor to an appropriate
voltage to detect output state. Refer to the hardware description in this
user’s guide for more details on the output’s electrical specification.
● If the bit patterns set on the AIO Panel do not agree with the
logic levels measured at the I/O terminals, the board is not
functioning properly. Stop here, and determine why.
● If the bit patterns set on the AIO Panel agree with the logic
levels measured at the I/O terminals, then repeat steps 9, 10, and
11 for remaining output channels.
3-19
Page 40

13. In the Digital Output Panel under Channels, click on the output
channel to test (channel 0 in this example) as shown in Figure 3-9.
KEITHLEY
Channels
1234567
0
8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15
Figure 3-9. Configuring channel 0 for output bit pattern B
14. In the Digital Output Panel under Output Bits, set the bits of
channel 0 for bit pattern B as shown in Figure 3-9.
15. Measure the voltage between signal ground and each bit of the
output port with a DMM or DVM. Make measurements at the
STA-50 terminals or the cabled mating connector that is connected
to the selected CONN-3160-D1 50-pin connector.
16. Again, each bit set to ON in the AIO Panel should output a logichigh signal at the corresponding I/O terminal, reading typically
about 4 volts (minimum of 2.2 volts) at a DMM/DVM. Each bit set
to OFF in the AIO Panel should output a logic-low signal at the
corresponding I/O terminal, reading typically about 0 volts
(maximum of 0.8 volts) at a DMM/DVM.
Digital Output Panel
Output Bits
76 5 43 2 1 0
AA
Note: The typical values shown are valid for boards with TTL
compatible outputs. For boards with relay outputs (REL-16, PDISO-8,
and PIO-32) the output will be a relay contact closure. For boards with
open collector outputs (PIO-HV) use a pull up resistor to an appropriate
voltage to detect output state. Refer to the hardware description in this
user’s guide for more details on the output’s electrical specification.
● If the bit patterns set on the AIO Panel do not agree with the
logic levels measured at the I/O terminals, the board is not
functioning properly. Stop here, and determine why.
3-20 Setup and Installation
Page 41

17. Repeat steps 13, 14, and 15 for additional output channels.
Input Read Test
A similar test of input circuitry can be performed by applying an input
signal of suitable type to each input line and verifying that the appropriate
input indicator changes state. Refer to the hardware description in this
user’s guide for more details on the input’s electrical specifications.
● If the bit patterns set on the AIO Panel do agree with the logic
levels measured at the I/O terminals, and you have performed an
output set test for all ports, the board is functioning properly.
3-21
Page 42

4
Cabling and Wiring
Warning: The procedures in this section are intended for qualified
service personnel. Do not perform these procedures unless you are
qualified to do so.
After installing your PIO-32 Series boards, you can attach accessories
and wire the appropriate signals to the board. This section includes the
following information about cabling and wiring the PIO-32 Series boards:
● Description and illustration of the optional C-3200/C-32NN cables
for the PIO-32 Series boards
● Description and illustration of cabling the boards to an STP-37/FC
screw terminal panel
● Examples of typical digital I/O wiring
● Connector pin assignments
Caution: Before you make any connections to a PIO-32 Series board,
make sure that power to your computer and any accessories attached to
the PIO-32 Series board are OFF.
4-1
Page 43

Optional Cables
Warning: Do not use the C-3200/C-32NN cables at voltages above
30V RMS, 42.4V peak, or 60VDC. These cables are rated for 30V RMS,
42.4V peak, or 60VDC maximum. Use at higher voltages may result in
insulation breakdown and shock hazard.
To connect the PIO-32 Series boards to screw terminal panel accessories
or other equipment, you need additional cables. You have the option of
providing your own cables or purchasing two C-3200/C-32NN cables.
The C-3200/C-32NN cables have a 40-pin ribbon connector at one end
and a 37-pin, D-type male connector at the other end. Use the 40-pin
connectors to bring the cables through the board’s rear adapter plate slot
to the headers on the board. You use the 37-D connector to attach
equipment or to wire a screw terminal panel. Figure 4-1 shows the C-3200
and C-32NN cables. Note that the C-3200 cable is 30-inches long while
the C-32NN cable has NN extra feet of cable (NN being the number of
feet added to the standard cable).
40-pin ribbon
connector
pin 1
removeable strain relief
30 in./NN feet
Figure 4-1. C-3200/C-32NN Optional Cables
4-2 Cabling and Wiring
pin 1
37-D male
connector
Page 44

STP-37/FC Screw Terminal Panel
Warning: Do not use the STP-37/FC and C-3200/C-32NN accessories or
other screw terminal panels at voltages above 30V RMS, 42.4V peak, or
60VDC. These accessories are rated for 30V RMS, 42.4V peak, or
60VDC maximum. Use at higher voltages may result in shock hazard.
Using the screw terminals on the STP-37/FC, you can easily connect your
applications to the PIO-32 Series boards with your own cables or with the
optional C-3200/C-32NN cables. Figure 4-2 shows the PIO-32 Series
board cabled to two STP-37/FC screw terminal panels. Labeled from 1
to 37, the screw terminals correspond directly to the numbers of the
pins on the C-3200/C-32NN cable 37-D connectors (not the 40-pin
ribbon header).
Screw Terminal Panels
STP-37/FC
PIO-32 Series board
C-3200/C-32NN
cables
Figure 4-2. PIO-32 Series Board Cabled to Screw Terminal Panels
Caution: Keithley recommends that you always use the STP-37/FC with
your wiring
your wiring
a case and cover. Figure 4-3 shows the mounting holes for the STP-37/FC
without the case.
4-3
Page 45

0.20 in.
0.81
in.
4.79 in.
4.400 in.
2.84 in.
1.250
in.
for rubber feet
(4 holes)
Figure 4-3. STP-37/FC Mounting Holes
mounting holes
(0.125 in. DIA)
pin 1
mounting holes
(0.125 in. DIA)
pin 1
4-4 Cabling and Wiring
Page 46

Typical Digital I/O Wiring
This section provides a typical non-TTL digital input wiring example for
the PIO-32IN board and a typical digital output control wiring example
for the PIO-32OUT board.
In the digital input example shown in Figure 4-4, the PIO-32IN board
monitors the presence of non-TTL signals. If no signal is present, the
input value is 0; if a non-TTL signal is present, the input value is 1. The
polarity matters for a digital input.
push button
+
R
28V
–
LOAD
Positive (+)
PIO-32IN
Negative (-)
Figure 4-4. Typical Non-TTL Digital Input Wiring Example
4-5
Page 47

In the digital output example shown in Figure 4-5, the PIO-32OUT board
is used to control the on and off state of a device. The polarity does not
matter in this example.
R
LOAD
Power
Supply
Figure 4-5. Typical Digital Output Control Wiring Example
Connector Pin Assignments
If you are using the C-3200/C-32NN cables, note that the pin assignments
for the 37-D connector and the 40-pin ribbon header are numbered
differently. Figure 4-6 on page 4-7 shows the 37-D cable connector and its
pin assignments for the J1 signals; Figure 4-7 on page 4-8 shows this
connector and its pin assignments for the J2 signals. Figure 4-8 on page
4-9 shows the 40-pin ribbon header and its pin assignments for the J1
signals; Figure 4-9 on page 4-10 shows the ribbon header and its pin
assignments for the J2 signals. Refer to Appendix B for more information
on these pin assignments.
Positive (+)
PIO-32OUT
Negative (-)
Note: The positive input signals are labeled PnP (where n is the bit
number, 0 to 31); the negative input signals are labeled PnN (where n is
the bit number, 0 to 31).
4-6 Cabling and Wiring
Page 48

37-D Cable Connector, J1 Signals
P0N Pin 19
P0P Pin 18
P1N Pin 17
P1P Pin 16
P2N Pin 15
P2P Pin 14
P3N Pin 13
P3P Pin 12
P12N Pin 11
P12P Pin 10
P13N Pin 9
P13P Pin 8
P14N Pin 7
P14P Pin 6
P15N Pin 5
P15P Pin 4
- Pin 3
- Pin 2
+5V Pin 1
Pin 37 P7N
Pin 36 P7P
Pin 35 P6N
Pin 34 P6P
Pin 33 P5N
Pin 32 P5P
Pin 31 P4N
Pin 30 P4P
Pin 29 P11N
Pin 28 P11P
Pin 27 P10N
Pin 26 P10P
Pin 25 P9N
Pin 24 P9P
Pin 23 P8N
Pin 22 P8P
Pin 21 -
Pin 20 GROUND
Figure 4-6. Pin Assignments for the C-3200 Cable 37-D Connector, J1 Signals
4-7
Page 49

37-D Cable Connector, J2 Signals
P16N Pin 19
P16P Pin 18
P17N Pin 17
P17P Pin 16
P18N Pin 15
P18P Pin 14
P19N Pin 13
P19P Pin 12
P28N Pin 11
P28P Pin 10
P29N Pin 9
P29P Pin 8
P30N Pin 7
P30P Pin 6
P31N Pin 5
P31P Pin 4
- Pin 3
- Pin 2
+5V Pin 1
Pin 37 P23N
Pin 36 P23P
Pin 35 P22N
Pin 34 P22P
Pin 33 P21N
Pin 32 P21P
Pin 31 P20N
Pin 30 P20P
Pin 29 P27N
Pin 28 P27P
Pin 27 P26N
Pin 26 P26P
Pin 25 P25N
Pin 24 P25P
Pin 23 P24N
Pin 22 P24P
Pin 21 -
Pin 20 GROUND
Figure 4-7. Pin Assignments for the C-3200 Cable 37-D Connector, J2 Signals
4-8 Cabling and Wiring
Page 50

40-Pin Ribbon Header, J1 Signals
- Pin 39
P0N Pin 37
P0P Pin 35
P1N Pin 33
P1P Pin 31
P2N Pin 29
P2P Pin 27
P3N Pin 25
P3P Pin 23
P12N Pin 21
P12P Pin 19
P13N Pin 17
P13P Pin 15
P14N Pin 13
P14P Pin 11
P15N Pin 9
P15P Pin 7
- Pin 5
- Pin 3
+5V Pin 1
Pin 40 Pin 38 Pin 36 P7N
Pin 34 P7P
Pin 32 P6N
Pin 30 P6P
Pin 28 P5N
Pin 26 P5P
Pin 24 P4N
Pin 22 P4P
Pin 20 P11N
Pin 18 P11P
Pin 16 P10N
Pin 14 P10P
Pin 12 P9N
Pin 10 P9P
Pin 8 P8N
Pin 6 P8P
Pin 4 Pin 2 GROUND
Figure 4-8. Pin Assignments for 40-Pin Ribbon Header, J1 Signals
4-9
Page 51

40-Pin Ribbon Header, J2 Signals
- Pin 39
P16N Pin 37
P16P Pin 35
P17N Pin 33
P17P Pin 31
P18N Pin 29
P18P Pin 27
P19N Pin 25
P19P Pin 23
P28N Pin 21
P28P Pin 19
P29N Pin 17
P29P Pin 15
P30N Pin 13
P30P Pin 11
P31N Pin 9
P31P Pin 7
- Pin 5
- Pin 3
+5V Pin 1
Pin 40 Pin 38 Pin 36 P23N
Pin 34 P23P
Pin 32 P22N
Pin 30 P22P
Pin 28 P21N
Pin 26 P21P
Pin 24 P20N
Pin 22 P20P
Pin 20 P27N
Pin 18 P27P
Pin 16 P26N
Pin 14 P26P
Pin 12 P25N
Pin 10 P25P
Pin 8 P24N
Pin 6 P24P
Pin 4 Pin 2 GROUND
Figure 4-9. Pin Assignments for the 40-Pin Ribbon Header, J2 Signals
4-10 Cabling and Wiring
Page 52

5
Programming
You do not program the registers of your PIO-32 Series board directly
through Windows 95/98/NT. Instead, you program register changes
through the application programming interface (API) of DriverLINX.
DriverLINX is provided on the CD-ROM that comes with your board and
should now be installed on your system. (Refer to Section 3.) Using
DriverLINX, you can program the board in Visual C/C++, Visual Basic,
and Delphi.
DriverLINX features are summarized in Section 1. For detailed
information about DriverLINX in general and about programming with
DriverLINX specifically, refer to your DriverLINX documentation.
Note: To access the DriverLINX documents on-line, Acrobat Reader
(version 3.0 or greater) must be installed on your computer.
To access the DriverLINX documentation after you have installed it on
your computer, do the following:
1. Click the Windows 95/98/NT Start tab.
2. In the Start menu, click Programs.
3. Find the DriverLINX folder, under which you should find the
On-line Manuals entry.
4. Click on the On-line Manuals entry. The DriveLINX Printable
Documentation table of contents opens via Acrobat reader.
5. Scroll through the DriverLINX Printable Documentation table of
contents and find the document or document category that you want.
5-1
Page 53

6. Click on the wanted document or document category. Either the
selected document appears or a list of documents that fit the selected
category appears.
7. If a list appears, click on the title of the document that you want. The
desired document appears.
To access the DriverLINX documentation from the CD-ROM that came
with your board, do the following:
1. In Windows Explorer, double click on X:\Drvlinx4\Docs\Toc.pdf,
where X is the drive letter of your CD-ROM drive. The DriveLINX
Printable Documentation table of contents opens via Acrobat reader.
2. Scroll through the DriveLINX Printable Documentation table of
contents and find the document or document category that you want.
3. Click on the wanted document or document category. Either the
selected document appears or a list of documents that fit the selected
category appears.
4. If a list appears, click on the title of the document that you want. The
desired document appears.
5-2 Programming
Page 54

Warning: The procedures in this section are intended for qualified
service personnel. Do not perform these procedures unless you are
qualified to do so.
If your PIO-32 Series board is not operating properly, use the information
in this section to help you isolate the problem. If the problem appears
serious enough to require technical support, refer to page 6-6 for
information on how to contact an applications engineer.
Problem Isolation
6
Troubleshooting
If you encounter a problem with a PIO-32 Series board, use the
instructions in this section to isolate the cause of the problem before
calling Keithley Technical Support.
Identifying Symptoms and Possible Causes
Use the troubleshooting information in Table 6-1 to try to isolate the
problem. Table 6-1 lists general symptoms and possible solutions for
problems with PIO-32 Series boards.
6-1
Page 55

Table 6-1. Troubleshooting Information
Symptom Possible Cause Possible Solution
Board does not
respond
Intermittent
operation
DriverLINX is not installed
correctly or the combined
DriverLINX/board installation is
not properly configured.
Base address is incorrect. Make sure that no other system resource
The board is incorrectly aligned
in the accessory slot.
The board is damaged. Contact the Keithley Applications
The most common cause of this
problem is that the I/O bus speed
is in excess of 8 MHz.
Vibrations or loose connections
exist.
Reinstall and/or reconfigure DriverLINX
if necessary. Refer to page 3-3 and to
“Configuring the PIO Series” in the
manual Using DriverLINX With Your
Hardware—Keithley PIO Series.
is using the specified base address and
that the board base address setting
matches the software setting.
Reconfigure the base address, if
necessary. Refer to page 3-8 for
instructions on setting the base address.
Check installation.
Engineering Department; see page 6-6.
Reduce I/O bus speed to a maximum of
8 MHz (to change the I/O bus speed, run
BIOS setup). See the documentation for
your computer for instructions on
running BIOS setup.
Cushion source of vibration and tighten
connections.
The board is overheating. Check environmental and ambient
temperature. See the documentation for
your computer for specifications.
Electrical noise exists. Provide better shielding or reroute
wiring.
6-2 Troubleshooting
Page 56

Table 6-1. Troubleshooting Information (cont.)
Symptom Possible Cause Possible Solution
Data appears to be
invalid
Computer does not
boot.
The most common cause of this
problem is that the I/O bus speed
is in excess of 8 MHz.
An open connection exists. Check wiring to screw terminal.
Another system resource is using
the specified base address.
Polarity of input current reversed. Check wiring for proper use of positive
Outputs not indicating proper
level.
Board not seated properly. Check that the board is properly
The base address setting of the
PIO-32 board conflicts with that
of another system resource.
Reduce I/O bus speed to a maximum of
8 MHz (to change the I/O bus speed, run
BIOS setup). See the documentation for
your computer for instructions on
running BIOS setup.
Reconfigure the base address of the
PIO-32 Series board; refer to page 3-8
for more information. Check the I/O
assignments of other system resources
and reconfigure, if necessary.
and negative connections.
Check that the circuit is complete (are
both relay connections used?).
You may need to apply pull-up resistors
for the external source
installed.
Verify that the base address settings of
your system resources are unique.
The power supply of the host
computer is too small to handle
all the system resources.
Check the needs of all system resources
and obtain a larger power supply.
If your board is not operating properly after using the information in
Table 6-1, continue with the next two sections to further isolate the
problem.
6-3
Page 57

Testing the PIO-32 Series Board and Host Computer
To isolate the problem to the PIO-32 Series board or to the host computer,
perform the following steps.
Warning: Do not connect voltages greater than 30V RMS, 42.4V peak,
or 60VDC to any input or output on this board.
Live voltages can still be present on the board even when the computer is
turned off. To protect you and the circuit, Keithley provides covers with
the PIO-32 Series boards. Though you can remove the covers to service
the PIO-32 Series boards, do not use these boards with the covers
removed! In addition, disconnect all cables when servicing these boards.
1. Turn the power to the host computer OFF, and remove power
connections to the computer.
Caution: Removing a board with the power ON can cause damage to
your board and/or computer.
2. Unplug the accessory connector(s) or cable(s) from the PIO-32 Series
board(s), keeping the connections intact on the accessory board(s).
3. Remove the PIO-32 Series board(s) from the computer and visually
check for damage. If a board is obviously damaged, refer to page 6-6
for information on returning the board.
4. With the PIO-32 Series board(s) out of the computer, check the
computer for proper operation. Power up the computer and perform
any necessary diagnostics.
At this point, if you have another PIO-32 Series board that you know is
functional, you can test the slot and I/O connections using the instructions
in the next section. If you do not have another board, refer to the
instructions on page 6-6 before calling Keithley Applications
Engineering.
6-4 Troubleshooting
Page 58

Testing the Accessory Slot and I/O Connections
When you are sure that the computer is operating properly, test the
computer accessory slot and I/O connections using another PIO-32 Series
board that you know is functional. To test the computer accessory slot and
the I/O connections, follow these steps:
1. Remove computer power again, and install a PIO-32 Series board that
you know is functional. Do not make any I/O connections.
2. Apply computer power and check operation with the functional
PIO-32 Series board in place. This test checks the computer accessory
slot. If you are using more than one PIO-32 Series board, check the
other slots you are using.
3. If the accessory slots are functional, check the I/O connections.
Connect the accessory boards, one at a time, and check operation.
4. If operation is normal, the problem is in the PIO-32 Series board(s)
originally in the computer. Try the PIO-32 Series board(s) one at a
time in the computer to determine which is faulty. Use the
troubleshooting information in the next section to try to isolate the
problem.
5. If you cannot isolate the problem, refer to the next section for
instructions on getting technical support.
6-5
Page 59

Technical Support
Before returning any equipment for repair, call the Keithley Hardware
Applications Engineering Department at:
1-888-KEITHLEY
Monday - Friday, 8:00 a.m. - 5:00 p.m., Eastern Time
An applications engineer will help you diagnose and resolve your
problem over the telephone. Please make sure that you have the following
information available before you call:
PIO-32 Series Model I/O IN OUT
board Serial # _____________________
Computer Manufacturer _____________________
Revision code (4 digits) _____________________
Base address setting _____________________
CPU type _____________________
Clock speed (MHz) _____________________
Math coprocessor Yes No
Amount of RAM _____________________
Video system _____________________
BIOS type _____________________
Operating system DOS version _____________________
Windows version _____________________
Windows mode _____________________
Software package Name _____________________
Version _____________________
Invoice/order # _____________________
Compiler Language _____________________
(if applicable) Manufacturer _____________________
Version _____________________
6-6 Troubleshooting
Page 60

Accessories STP-37/FC _____________________
STA-U _____________________
C-3200/C-32NN cables _____________________
Other _____________________
Type _____________________
If a telephone resolution is not possible, the applications engineer will
issue you a Return Material Authorization (RMA) number and ask you to
return the equipment. Include the RMA number with any documentation
regarding the equipment.
When returning equipment for repair, include the following information:
● Your name, address, and telephone number.
● The invoice or order number and date of equipment purchase.
● A description of the problem or its symptoms.
● The RMA number on the outside of the package.
Repackage the equipment, using the original anti-static wrapping, if
possible, and handling it with ground protection. Ship the equipment to:
ATTN: RMA #_______
Repair Department
Keithley Instruments, Inc.
28775 Aurora Road
Cleveland, Ohio 44139
Telephone 1-888-KEITHLEY
FAX (440) 248-6168
Notes: If you are submitting your equipment for repair under warranty,
you must include the invoice number and date of purchase.
To enable Keithley to respond as quickly as possible, you must include
the RMA number on the outside of the package.
6-7
Page 61

Specifications
This appendix provides a table of the specifications for the PIO-32 Series
boards. In Table A-1, the abbreviation N/A means not applicable.
Table A-1. PIO-32 Series Specifications
Feature Attribute PIO-32I/O PIO-32IN PIO-32OUT
A
Digital
Output
Channels 16 0 32
Contact Type Rhodium plated
(Form A, normally
open contacts)
Contact
Rating
Contact
Resistance
Contact Life 10
Operation
Time
Release Time 1.0 ms N/A 1.0 ms
10W at 0.75A or
30V RMS, 42.4V
peak, or 60VDC
maximum (resistive)
100mΩ (maximum,
initial)
7
operations at
rated load; 109 at low
level
1.0 ms N/A 1.0 ms
N/A Rhodium plated
(Form A, normally
open contacts)
N/A 10W at 0.75A or
30V RMS, 42.4V
peak, or 60VDC
maximum (resistive)
N/A 100mΩ (maximum,
initial)
N/A 10
7
operations at
rated load; 109 at low
level
A-1
Page 62

Table A-1. PIO-32 Series Specifications (cont.)
Feature Attribute PIO-32I/O PIO-32IN PIO-32OUT
Digital Input Channels 16 32 0
Type Optoisolator Optoisolator N/A
Input
Resistor
Input High
(Min.)
Input High
(Max.)
Input Low 0.8VDC or open 0.8VDC or open N/A
Response
Frequency
Power
Consumption
Environment Operating
Mechanical Length 13.3 in. (Full slot) 9.0 in. 13.3 in. (Full slot)
+5 VDC
(typical)
Temperature
Storage
Temperature
Humidity 0 to 90%
Height 4.25 in. 4.25 in. 4.25 in.
2.0kΩ, 1/2W 2.0kΩ, 1/2W N/A
3.5VDC, 1.25mA 3.5VDC, 1.25mA N/A
28VDC, 15mA 28VDC, 15mA N/A
<3.0kHz <3.0kHz N/A
0.8A + 22mA per
active relay (max.)
0° to 50°C0° to 50°C0° to 50°C
-20° to 70°C -20° to 70°C -20° to 70°C
noncondensing
0.5A 1.0A + 22mA per
active relay (max.)
0 to 90%
noncondensing
0 to 90%
noncondensing
Depth 0.75 in. 0.75 in. 0.75 in.
Weight 10 oz. 6 oz. 12 oz.
Board
Connector
Type
Board
Connector
Mate
A-2 Specifications
2 x 40-pin ribbon
3M #2540-6002UG
2 x 40-pin ribbon
3M #3417-7000
2 x 40-pin ribbon
3M #2540-6002UG
2 x 40-pin ribbon
3M #3417-7000
2 x 40-pin ribbon
3M #2540-6002UG
2 x 40-pin ribbon
3M #3417-7000
Page 63

B
Connector Pin Assignments
This appendix provides a table of the connector pin assignments for the
37-D and 40-pin ribbon connectors and of the signals for the J1 and J2
connectors of the PIO-32 Series boards. In addition, this appendix
contains the same pin assignment figures for these connectors as shown in
Section 4. For instructions on cabling accessories and wiring signals to
your PIO-32 Series board, see Section 4.
In Table B-1, note that input and output signals are paired as PnP and PnN
(where n is the bit number, 0 to 15). The P suffix represents the positive
side and the N suffix the negative side. Connector J1 is associated with
signals for bits 0 to 15, and connector J2 is associated with signals for bits
16 to 31.
B-1
Page 64

Table B-1. 37-D and 40-Pin Signals for Connectors J1 and J2
37-D
Pins
1 1 +5V +5V 20 2 GROUND GROUND
2 3 - - 21 4 - -
3 5 - - 22 6 P8P P24P
4 7 P15P P31P 23 8 P8N P24N
5 9 P15N P31N 24 10 P9P P25P
6 11 P14P P30P 25 12 P9N P25N
7 13 P14N P30N 26 14 P10P P26P
8 15 P13P P29P 27 16 P10N P26N
9 17 P13N P29N 28 18 P11P P27P
10 19 P12P P28P 29 20 P11N P27N
11 21 P12N P28N 30 22 P4P P20P
12 23 P3P P19P 31 24 P4N P20N
13 25 P3N P19N 32 26 P5P P21P
14 27 P2P P18P 33 28 P5N P21N
Ribbon
Pins
PIO-32 J1
Signals
PIO-32 J2
Signals
37-D
Pins
Ribbon
Pins
PIO-32 J1
Signals
PIO-32 J2
Signals
15 29 P2N P18N 34 30 P6P P22P
16 31 P1P P17P 35 32 P6N P22N
17 33 P1N P17N 36 34 P7P P23P
18 35 P0P P16P 37 36 P7N P23N
19 37 P0N P16N - 38 - -
-39 - -
-40 - -
B-2 Connector Pin Assignments
Page 65

Figure B-1 shows the pin assignments for the 37-D cable connector, J1
signals. Figure B-2 on page B-4 shows the pin assignments for the 37-D
cable connector, J2 signals. Figure B-3 on page B-5 shows the pin
assignments for the 40-in ribbon header, J1 signals. Figure B-4 on page
B-6 shows the pin assignments for the 40-pin ribbon header, J2 signals.
Note: The positive input signals are labeled PnP (where n is the bit
number, 0 to 31); the negative input signals are labeled PnN (where n is
the bit number, 0 to 31).
C-3200 Cable 37-D Cable Connector, J1 Signals
P0N Pin 19
P0P Pin 18
P1N Pin 17
P1P Pin 16
P2N Pin 15
P2P Pin 14
P3N Pin 13
P3P Pin 12
P12N Pin 11
P12P Pin 10
P13N Pin 9
P13P Pin 8
P14N Pin 7
P14P Pin 6
P15N Pin 5
P15P Pin 4
- Pin 3
- Pin 2
+5V Pin 1
Pin 37 P7N
Pin 36 P7P
Pin 35 P6N
Pin 34 P6P
Pin 33 P5N
Pin 32 P5P
Pin 31 P4N
Pin 30 P4P
Pin 29 P11N
Pin 28 P11P
Pin 27 P10N
Pin 26 P10P
Pin 25 P9N
Pin 24 P9P
Pin 23 P8N
Pin 22 P8P
Pin 21 -
Pin 20 GROUND
Figure B-1. Pin Assignments for the C-3200 Cable 37-D Connector, J1 Signals
B-3
Page 66

C-3200 Cable 37-D Cable Connector, J2 Signals
P16N Pin 19
P16P Pin 18
P17N Pin 17
P17P Pin 16
P18N Pin 15
P18P Pin 14
P19N Pin 13
P19P Pin 12
P28N Pin 11
P28P Pin 10
P29N Pin 9
P29P Pin 8
P30N Pin 7
P30P Pin 6
P31N Pin 5
P31P Pin 4
- Pin 3
- Pin 2
+5V Pin 1
Pin 37 P23N
Pin 36 P23P
Pin 35 P22N
Pin 34 P22P
Pin 33 P21N
Pin 32 P21P
Pin 31 P20N
Pin 30 P20P
Pin 29 P27N
Pin 28 P27P
Pin 27 P26N
Pin 26 P26P
Pin 25 P25N
Pin 24 P25P
Pin 23 P24N
Pin 22 P24P
Pin 21 -
Pin 20 GROUND
Figure B-2. Pin Assignments for the C-3200 Cable 37-D Connector, J2 Signals
B-4 Connector Pin Assignments
Page 67

40-Pin Ribbon Header Connector, J1 Signals
- Pin 39
P0N Pin 37
P0P Pin 35
P1N Pin 33
P1P Pin 31
P2N Pin 29
P2P Pin 27
P3N Pin 25
P3P Pin 23
P12N Pin 21
P12P Pin 19
P13N Pin 17
P13P Pin 15
P14N Pin 13
P14P Pin 11
P15N Pin 9
P15P Pin 7
- Pin 5
- Pin 3
+5V Pin 1
Pin 40 Pin 38 Pin 36 P7N
Pin 34 P7P
Pin 32 P6N
Pin 30 P6P
Pin 28 P5N
Pin 26 P5P
Pin 24 P4N
Pin 22 P4P
Pin 20 P11N
Pin 18 P11P
Pin 16 P10N
Pin 14 P10P
Pin 12 P9N
Pin 10 P9P
Pin 8 P8N
Pin 6 P8P
Pin 4 Pin 2 GROUND
Figure B-3. Pin Assignments for 40-Pin Ribbon Header Connector, J1 Signals
B-5
Page 68

40-Pin Ribbon Header Connector, J2 Signals
- Pin 39
P16N Pin 37
P16P Pin 35
P17N Pin 33
P17P Pin 31
P18N Pin 29
P18P Pin 27
P19N Pin 25
P19P Pin 23
P28N Pin 21
P28P Pin 19
P29N Pin 17
P29P Pin 15
P30N Pin 13
P30P Pin 11
P31N Pin 9
P31P Pin 7
- Pin 5
- Pin 3
+5V Pin 1
Pin 40 Pin 38 Pin 36 P23N
Pin 34 P23P
Pin 32 P22N
Pin 30 P22P
Pin 28 P21N
Pin 26 P21P
Pin 24 P20N
Pin 22 P20P
Pin 20 P27N
Pin 18 P27P
Pin 16 P26N
Pin 14 P26P
Pin 12 P25N
Pin 10 P25P
Pin 8 P24N
Pin 6 P24P
Pin 4 Pin 2 GROUND
Figure B-4. Pin Assignments for 40-Pin Ribbon Header Connector, J2 Signals
B-6 Connector Pin Assignments
Page 69

C
Register Maps
Note: Address maps are provided here only for background reference
purposes. You do not program registers directly in Windows 95/98/NT.
Instead, you program register changes through the application
programming interface (API) of DriverLINX, which is provided on the
CD-ROM that comes with your board. Refer to the DriverLINX
documentation that is installed on your system. (If it is not yet installed,
you can find it on the CD-ROM in the X:\DrvLINX4\Docs and
X:\DrvLINX4\Docs\Notes folders, where X is the drive letter of the
CD-ROM drive.)
The PIO-32 Series boards contain four 8-bit registers. To maintain
compatibility with the PIO-12 products, which use an 8255
Programmable Peripheral Interface integrated circuit, the four registers
are at base addresses +0h, +1h, +4h, and +5h. Base addresses +2h, +3h,
+6, and +7h are not used. Reads or writes to these locations are ignored;
the ports are not software configurable.
C-1
Page 70

Table C-1 summarizes the PIO-32 Series register maps.
Table C-1. PIO-32 Series Register Map Summary
Base 8255 Port PIO-32IN PIO-32OUT PIO-32I/O
+0h Port A Read Readback/Write Read
+1h Port B Read Readback/Write Read
+2h Port C (not used) N/A N/A N/A
+3h Control Register (fixed) N/A N/A N/A
+4h Port A Read Readback/Write Readback/Write
+5h Port B Read Readback/Write Readback/Write
+6h Port C (not used) N/A N/A N/A
+7h Control Register (fixed) N/A N/A N/A
Table C-2 lists the register map for the PIO-32I/O board; Table C-3 lists
the register map for the PIO-32IN board; and Table C-4 lists the register
map for the PIO-32OUT board.
Notes: In each table, the abbreviation BA is for the Base Address.
For input port bits: 0 = no current through optoisolator,
1 = current > 1.25mA (voltage > 3.5V)
For output port bits: 0 = relay is not activated (open)
1 = relay is activated (closed
C-2 Register Maps
Page 71

Table C-2. PIO-32I/O Register Map
BA Write Bits Read Bits
7654321076543210
Not Used Input Port
+0h--------P7P6P5P4P3P2P1P0
Not Used Input Port
+1h--------P15P14P13P12P11P10P9P8
Output Port Readback Port
+4h P23 P22 P21 P20 P19 P18 P17 P16 P23 P22 P21 P20 P19 P18 P17 P16
Output Port Readback Port
+5h P31 P30 P29 P28 P27 P26 P25 P24 P31 P30 P29 P28 P27 P26 P25 P24
Table C-3. PIO-32IN Register Map
BA Write Bits Read Bits
7654321076543210
Not Used Input Port
+0h--------P7P6P5P4P3P2P1P0
Not Used Input Port
+1h--------P15P14P13P12P11P10P9P8
Not Used Input Port
+4h--------P23P22P21P20P19P18P17P16
Not Used Input Port
+5h--------P31P30P29P28P27P26P25P24
C-3
Page 72

Table C-4. PIO-32OUT Register Map
BA Write Bits Read Bits
7654321076543210
Output Port Readback Port
+0h P7 P6 P5 P4 P3 P2 P1 P0 P7 P6 P5 P4 P3 P2 P1 P0
Output Port Readback Port
+1h P15 P14 P13 P12 P11 P10 P9 P8 P15 P14 P13 P12 P11 P10 P9 P8
Output Port Readback Port
+4h P23 P22 P21 P20 P19 P18 P17 P16 P23 P22 P21 P20 P19 P18 P17 P16
Output Port Readback Port
+5h P31 P30 P29 P28 P27 P26 P25 P24 P31 P30 P29 P28 P27 P26 P25 P24
C-4 Register Maps
Page 73

Numerics
37-D cable connector, J2 signals B-4
40-pin ribbon header, J1 signals B-5
40-pin ribbon header, J2 signals 4-10, B-6
40-pin ribbon header/cable connector, J1
signals 4-9
8255 Programmable Peripheral Interface
integrated circuit C-1
A
accessories 1-4, 4-1
Applications Engineering Department 6-6
B
base address
setting 3-8
board
grounding during handling to protect 3-7
handling 3-7
installing 3-9
unpacking 3-7
connecting a screw terminal panel 4-3
connections 1-1
connector pin assignments 4-6, B-1
connectors 4-2
covers for boards 1-2, 3-9, 6-4
D
default base address 3-8
digital input
specifications A-2
wiring example 4-5
digital output
specifications A-1
wiring example 4-6
documentation, DriverLINX
accessing 3-5, 5-1
installing 3-3
documentation, this manual, installing 3-3
DriverLINX
configuring 3-6
description 1-3
documentation, accessing 3-5, 5-1
documentation, installing 3-3
installing 3-3
programming 5-1
C
cable removal 1-4
cables 2-1, 4-2, 4-6
cabling and wiring 4-1
checking the installation 3-11
circuitry
input 2-2
output 2-3
computer resources
determination for installation 3-2
configuring
DriverLINX 3-6
installation 3-6
F
features 1-1
functional description 2-1
G
grounding
handling to protect board 3-7
to protect board 3-7
X-1
Page 74

H
N
high voltages 1-2, 4-3
I
I/O bit tests 3-11
general information 3-11
input read test 3-21
output set test 3-16
important safety instructions 1-2
input circuitry 2-2
input current limit 2-2
input level 1-1
input voltage limit 2-2
installation
checking 3-11
configuring 3-6
resource inventory 3-2
installing
board 3-9
documentation 3-3
software, DriverLINX 3-3
interfaces
installing for applications 3-3
L
layout, general 2-1
M
Manuals, DriverLINX
accessing 5-1
manuals, DriverLINX
accessing 3-5
installing 3-3
maps, register C-1
mounting holes diagram (STP-37/FC) 4-4
non-TTL digital input wiring 4-5
O
output circuitry 2-3
output relay contacts 1-1
overview 1-1
P
pin assignments 4-6, B-1
PIO-12 boards C-1
PIO-32 Series cable 4-2
PIO-32I/O
features 1-1
input circuitry 2-2
output circuitry 2-3
register map C-3
specifications A-1
PIO-32IN
features 1-1
input circuitry 2-2
register map C-3
specifications A-1
PIO-32OUT
features 1-1
output circuitry 2-3
register map C-4
specifications A-1
precautions, installation
board 3-7
DriverLINX before board 3-2
problem isolation 6-1
programming
base address setting 3-9
DriverLINX 5-1
overview 1-3
registers 5-1
X-2 Index
Page 75

R
registers
maps C-1
programming 5-1
relay connections 2-3
resources, installation, inventory 3-2
returning equipment 6-7
RMA number 6-7
routing signals 2-1
S
safety instructions 1-2
schematics
input circuitry 2-2
output circuitry 2-3
screw terminal panel (STP) 1-4, 4-3
setting the base address 3-8
setup and installation 3-1
shock hazard 1-2, 1-4, 3-9, 4-3, 6-4
signal labels 2-2, 4-6, B-3
signals, routing 2-1
software, DriverLINX
description 1-3
installing 3-3
programming 5-1
specifications A-1
STP See screw terminal panel
STP-37/FC screw terminal panel 1-4, 4-3
supporting software 1-3
switch block, base address 3-8
T
technical support 6-6
37-D cable connector, J1 signals 4-7
37-D cable connector, J2 signals 4-8
troubleshooting 6-1
typical digital I/O wiring 4-5
U
unpacking the board 3-7
W
warning symbol 1-2
warranty repairs 6-7
wiring signals 4-1
X-3
Page 76

Specifications are subject to change without notice.
All Keithley trademarks and trade names are the property of Keithley Instruments, Inc. All other trademarks and
trade names are the property of their respective companies.
Keithley Instruments, Inc. 28775 Aurora Road • Cleveland, Ohio 44139 • 440-248-0400 • Fax: 440-248-6168
1-888-KEITHLEY (534-8453) • www.keithley.com
Sales Offices: BELGIUM: Bergensesteenweg 709 • B-1600 Sint-Pieters-Leeuw • 02-363 00 40 • Fax: 02/363 00 64
CHINA:
Yuan Chen Xin Building, Room 705 • 12 Yumin Road, Dewai, Madian • Beijing 100029 • 8610-6202-2886 • Fax: 8610-6202-2892
FINLAND: Tietäjäntie 2 • 02130 Espoo • Phone: 09-54 75 08 10 • Fax: 09-25 10 51 00
FRANCE: 3, allée des Garays • 91127 Palaiseau Cédex • 01-64 53 20 20 • Fax: 01-60 11 77 26
GERMANY: Landsberger Strasse 65 • 82110 Germering • 089/84 93 07-40 • Fax: 089/84 93 07-34
GREAT BRITAIN: Unit 2 Commerce Park, Brunel Road • Theale • Berkshire RG7 4AB • 0118 929 7500 • Fax: 0118 929 7519
INDIA: Flat 2B, Willocrissa • 14, Rest House Crescent • Bangalore 560 001 • 91-80-509-1320/21 • Fax: 91-80-509-1322
ITALY: Viale San Gimignano, 38 • 20146 Milano • 02-48 39 16 01 • Fax: 02-48 30 22 74
JAPAN:
New Pier Takeshiba North Tower 13F • 11-1, Kaigan 1-chome • Minato-ku, Tokyo 105-0022 • 81-3-5733-7555 • Fax: 81-3-5733-7556
KOREA: 2FL., URI Building • 2-14 Yangjae-Dong • Seocho-Gu, Seoul 137-888 • 82-2-574-7778 • Fax: 82-2-574-7838
NETHERLANDS: Postbus 559 • 4200 AN Gorinchem • 0183-635333 • Fax: 0183-630821
SWEDEN: c/o Regus Business Centre • Frosundaviks Allé 15, 4tr • 169 70 Solna • 08-509 04 679 • Fax: 08-655 26 10
SWITZERLAND: Kriesbachstrasse 4 • 8600 Dübendorf • 01-821 94 44 • Fax: 01-820 30 81
TAIWAN: 1FL., 85 Po Ai Street • Hsinchu, Taiwan, R.O.C. • 886-3-572-9077• Fax: 886-3-572-9031
© Copyright 2001 Keithley Instruments, Inc.
Printed in the U.S.A.
4/02
 Loading...
Loading...