Page 1

PLEASE READ AND FOLLOW THESE INSTRUCTIONS CAREFULLY
Ophthalmic and
Diagnostic Instruments
Instructions
Page 2

Contents
1.0 Ophthalmoscopes
2.0 Retinoscopes
3.0 Otoscopes
4.0 Keeler Handles
5.0 Charging Instructions for Keeler Rechargeable Handles
6.0 Cleaning and Sterilization Instructions
7.0 Warranty & Service
8.0 Ophthalmic & Diagnostic Accessories
Page 3
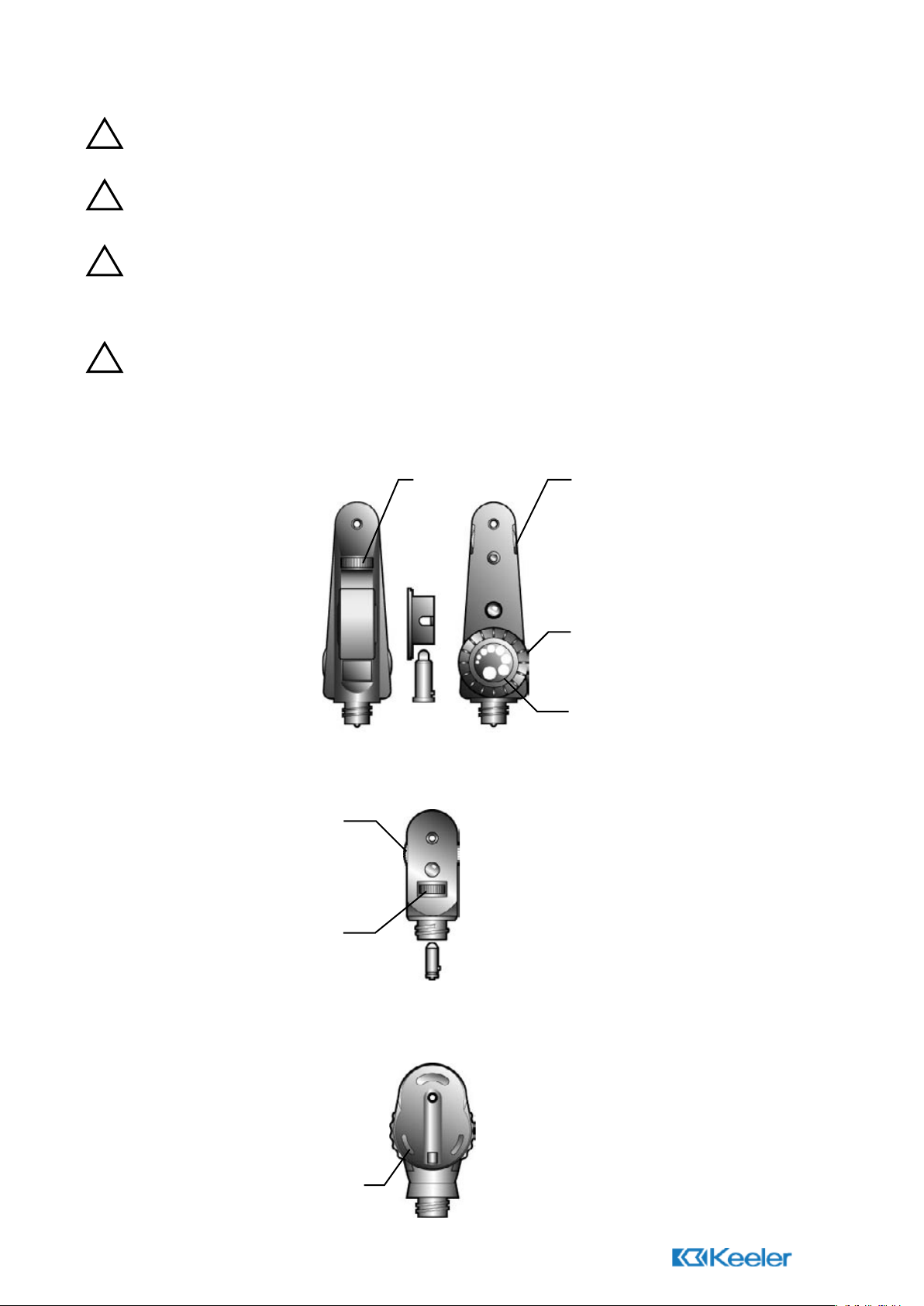
1.0 Ophthalmoscopes
Warning
This product must not be used in the presence of flammable gases.
Warning
This product should not be immersed in fluids.
Warning
Do not use if the product is damaged and periodically inspect visually for signs of
damage.
Warning
Federal law restricts this device to sale or order of a physician.
1.1 Specialist
1.2 Pocket
1.3 Standard
!
!
!
Graticule and
Filter Control
Lens Wheel
Pupilometer
Auxiliary
Lens Wheel
Lens
Wheel
Graticule and
Filter Control
Lens
Wheel
!
Page 4
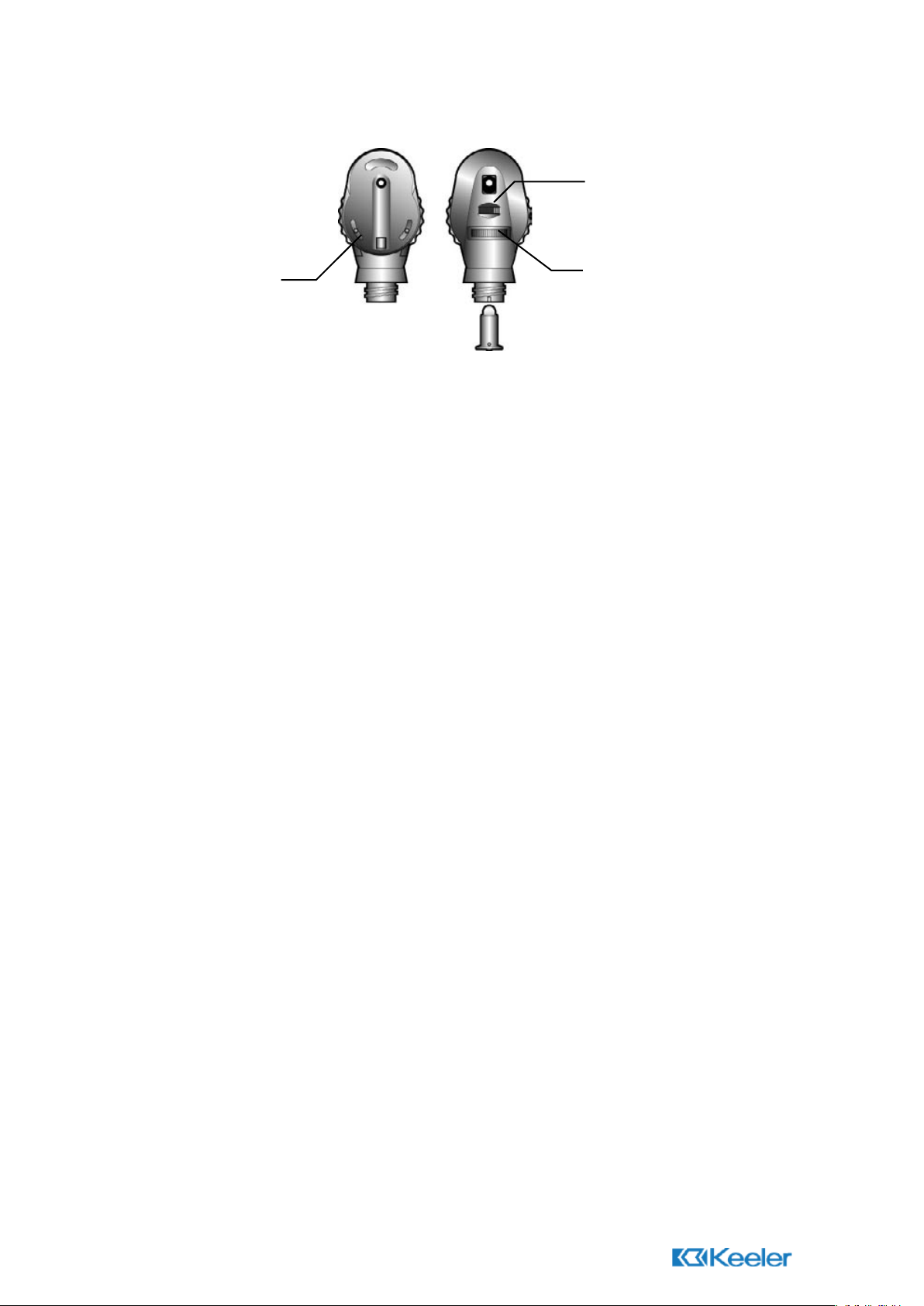
1.4 Practitioner / Professional
1.5 Lens Wheel
The lens wheel is rotated to select the required lens. Lens powers are displayed in the
viewing window as follows:
Black = (+) power lenses.
Red = (-) power lenses.
1.6 Auxiliary lens wheel
Swings in +/- 20 in one Dioptre step.*
*Professional only.
1.7 Specialist Auxiliary lens wheel
Rotate to align +10, +15, +30/ -10, -15, -30 Dioptre lenses.
1.8 Lens ranges
Specialist
+44D to –45D in single Dioptre steps.
Professional
+29D to –30D in single Dioptre steps.
Practitioner and Standard
+40D to –25D
Pocket
+20D to –20D
Auxiliary
Lens Wheel
Graticule
Control
Filter
Control
Page 5
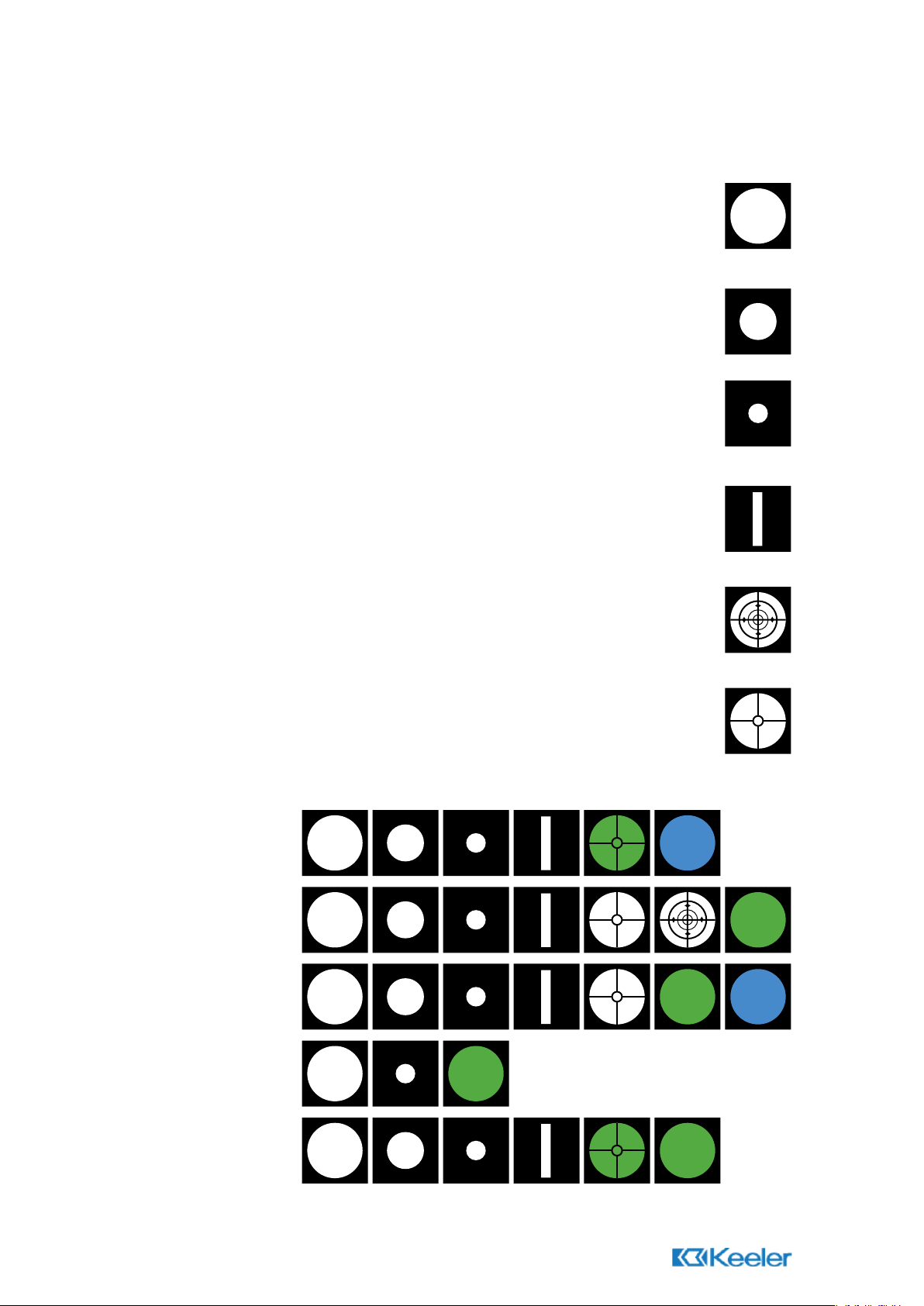
1.9 Graticule Control
The graticule control is used to select the required beam for examination. The choice of
graticules is as follows.
Wide Angle
Illuminates the largest area of fundus for the best possible general diagnosis
through a dilated pupil.
Intermediate
Permits easier access through an undilated pupil in peripheral examination.
Particularly useful in paediatric examination.
Macular
Designed specifically for viewing the macular area of the fundus. Reduces
pupillary reaction and improves patient comfort.
Slit
Used primarily to determine retinal elevations and depressions but may also be
used to assess anterior chamber depth.
Glaucoma
Projects a graticule onto the retina to assess the optic disc/cup ratio as an aid to
glaucoma diagnosis and monitoring.
Fixation Cross
Projects a graticule on to the retina for assessment of the degree and direction
of eccentric fixation. This is particularly useful when examining children.
The Graticule Range for each ophthalmoscope is as follows.
Specialist
Professional
Practitioner
Standard
Pocket
Page 6
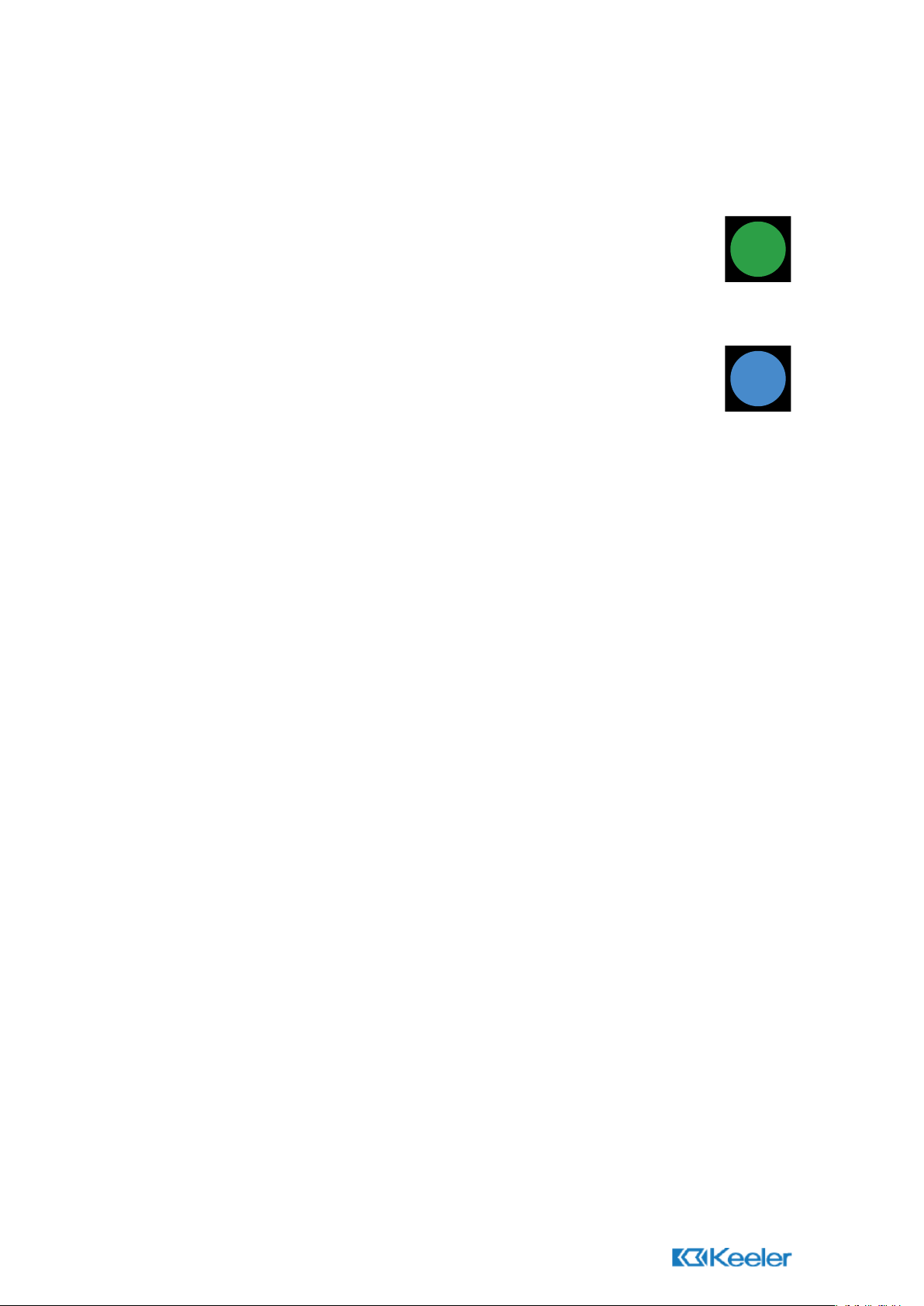
1.10 Filter Control *
The filter control is used to select the required filter.
(*Professional/Practitioner/Standard only.)
1.11 Filter Applications
Red Free (Green filter)
Is used to examine the blood vessels in fine detail. The green filter blocks red
rays showing blood vessels as black against a dark green background. This filter
is particularly useful for diabetic retinopathy.
Cobalt Blue *
Is used in conjunction with flourescein dye for the detection and examination of
corneal scars and abrasions.
(*Practitioner and Specialist only).
1.12 Pupillometer *
Hold the pupillometer adjacent to the patients eye to estimate pupil size. 1=1mm. The
range is 1mm to 8mm.
(*Applies to Specialist only.)
1.13 Precautions when using ophthalmoscopes
The intensity of light directed into the patients eye should be limited to the minimum
level necessary for diagnosis.
It is well established that exposure to the eye to intense light sources for extended
periods of time poses a risk of retinal photic injury. Many Ophthalmic instruments
illuminate the eye with intense light. The decision about the intensity of light level used
in any procedure must be made on a case by case basis. In each case, the clinician must
take a risk benefit judgement about the intensity of light to be used. Use of insufficient
intensity may result in inadequate visualization and in adverse effects more serious than
a retinal photic injury. Further, despite all efforts taken to minimize the risk of retinal
damage, damage may still occur. Retinal photic injury is a possible complication of the
need to use bright light to clearly visualize ocular structures during delicate ophthalmic
surgical procedures.
While no visible retinal photic lesions have been identified for ophthalmic instruments, it
is recommended that illumination levels be set to the minimum level necessary to perform
the diagnostic function. Young children and persons with diseased eyes may be at higher
risk. The risk may also be increased if the person being examined has had any exposure
with the same instrument or any other ophthalmic instrument using an intense visible
light source during the previous 24 hours. This will apply particularly if the eye has been
exposed to retinal photography.
The time to reach a potential optical radiation hazard for this device is 3 minutes when
the instrument is being operated at maximum intensity and maximum aperture. This
time is for a cumulative exposure in a day. It should be noted that there is a safety factor
Page 7

of about 10 built into the safety guidelines. Hence, for a source with continuous light
output, if the exposure time is 100s, photoretinitis might be expected for an exposure
time of 10 x 100s = 1000s (about 17 minutes).
Complies with EN ISO 15004:1997
Ophthalmic instruments - Fundamental Requirements and test methods .
Practitioner / Standard / Professional / Specialist only
Page 8

2.0 Retinoscopes
Warning
Keeler Professional Retinoscopes contain strong magnets. Pacemakers and magnetically
stored data will be affected or damaged by magnets.
Warning
Strong magnetic fields may influence or distort sensitive electronic or mechanical test
instruments. Very sensitive devices may even be destroyed. Always keep magnets at a safe
distance from such devices.
Warning
Do not use Keeler Retinoscopes in ambient temperatures above 30°C.
Warning
Federal law restricts this device to sale or order of a physician.
2.1 Professional Combi Retinoscope
Warning
The bulb should be replaced as indicated in previous diagrams
2.2 Focussing and axis control Professional Combi Retinoscope (Streak)
The vergence is altered by sliding the focussing control up and down as indicated. In the
top position the effect is a concave mirror. Mid position produces a streak behind the
patient. The mid position is used to determine the presence and axis of any astigmatism.
In the bottom position the effect is a divergent plane mirror effect. Refraction is normally
performed between the mid position and the bottom position.
The focussing and axis control can be rotated continuously in any direction.
2.3 Focussing and axis control Professional Combi Retinoscope (Spot).
The vergence is altered by sliding the focussing control up and down as indicated.
For all positions the effect is a plane mirror effect.
!
!
!
Aperture
Control
Focussing
and Axis
Control
Brow Rest
!
!
Page 9

2.4 Brow Rest
The Keeler retinoscope is supplied with a choice of brow rests to accommodate spectacle
wearers. To interchange the brow rest disconnect and attach as indicated.
2.5 Aperture Control
The aperture control has two positions. To change from the large to the small aperture
slide the control from left to right as indicated.
3.0 Otoscopes
Warning
Disposable speculae should not be used for insufflation testing.
Five permanent Speculae are provided with each Otoscope/Set. The diameters are as
follows: 2.5, 3.5, 4.5, 5.5 & 8mm. These are attached to the Otoscope head. As shown in
diagrams below.
Warning
Federal law restricts this device to sale or order of a physician.
3.1 Standard / Pocket
3.2 Fibre Optic
!
!
Page 10

3.3 Practitioner
3.4 Deluxe
3.5 Disposable Speculae *
Disposable speculae can be fitted to the Standard, Practitioner, Fibre Optic and Pocket
Otoscopes.
The disposable speculae is attached as shown on above.
3.6 Pneumatic Testing *
An insufflation tube can be fitted to your Otoscope to enable you to carry out pneumatic
testing.
For Practitioner, Standard, Pocket & Fibre Optic Otoscopes attach the insufflation adaptor
into port. The insufflation tube can then be attached to this. An Insufflation adaptor is
also available for Practitioner as shown on above.
3.7 Minor surgical Procedures
Should you wish to use surgical instruments such for minor procedures the following
notes may be of assistance.
3.8 Standard & Pocket Otoscopes
The magnifier can be removed to allow the introduction of surgical instruments.
3.9 Fibre Optic/Practitioner
The Fibre Optic magnifier can be moved to one side or removed completely to aid the
introduction of surgical instruments.
3.10 Deluxe Otoscope
The Deluxe magnifier may be swung to the side to aid the introduction of surgical
instruments. The magnifier can also be rotated clockwise to bring the focus closer to the
end of the specula.
Page 11

4.0 Keeler Handles
Warning
When connecting instrument heads to handles please check that the voltage of the bulb
in the instrument corresponds with the voltage of the handle.
Warning
Please ensure that the control is in the off position when the examination has been
completed.
Warning
Dry cell batteries should be removed if your instrument is not to be used for long periods.
Warning
Only Keeler rechargeable batteries (3.6v - 0.7Ah Ni-Cd) should be used with Keeler
rechargeable handles.
Warning
For indoor use only (protect against moisture)
4.1 Pocket
!
!
!
!
!
2x AA or
MN 1500
Page 12

4.2 C Size
4.3 Connection of the instrument heads to the handle
The connection between the instrument head to the handle is a screw
thread. To connect our instrument head connect as shown and rotate in
clockwise direction. Ensure the connection between the head and handle is
positive.
4.4 Compatibility
The Keeler Specialist, Professional, Standard and Practitioner
Ophthalmoscopes and Keeler Retinoscopes are compatible with Keeler Vista
2.8v and 3.6v Keeler handles.
4.5 On/Off brightness control
To switch the instrument on, rotate the brightness control as indicated to the right.
To switch off the instrument, rotate the brightness control as indicated to the left.
Keeler C sizes Handles have a power indicator. This will show if the instrument is on or
off.
Red = on Silver = off.
2x c or
MN 1500
Rechargable
Battery
Blue Cap Red Cap
Off Half On On
Page 13

4.6 Handle Identification
Keeler C size and pocket handles are colour coded to allow you to distinguish between
a dry cell battery handle (2.8v) and a rechargeable handle (3.6v). The handles are colour
coded as follows:
Blue base = 2.8v. for dry cell batteries.
Red base = 3.6v for rechargeable batteries.
Keeler bulbs are colour coded in the same way.
Blue base = 2.8v. for dry cell batteries.
Red base = 3.6v for rechargeable batteries.
Please ensure when replacing batteries and bulbs that the voltage corresponds to the
handle.
Dispose of old batteries safely.
4.7 Inserting/Replacing Batteries
Unscrew battery cap, insert batteries and replace battery cap as shown.
The following dry cell batteries should be used:
Keeler Pocket Handle – 2 x 1.5v AA size dry cell batteries – Duracell MN 1500 or
equivalent.
Keeler C size handle – 2 x 1.5v C size batteries. – Duracell MN 1400 or equivalent.
Please note Keeler rechargeable handles are normally supplied complete with a
rechargeable battery.
(3.6v - 0.7Ah Ni-Cd)
4.8 Upgrade from Battery to Rechargeable Handles.
Your Keeler 2.8 v C Size Handle (blue base) dry cell battery handle can be upgraded to a
3.6v (red base) rechargeable handle. For part numbers required please see the accessory
section
Please note the bulb in your instrument will also need to be upgraded from 2.8v to 3.6 v.
Contact Keeler for details on +44 (0) 1753 857177 or fax +44 (0) 1753 827145.
Page 14

5.0 Charging Instructions for Keeler Rechargeable Handles
Warning
Do not attempt to charge Non-Rechargeable batteries.
5.1 Battery Conditioning
Your Keeler rechargeable batteries need to be conditioned to ensure you achieve the
maximum life from the product. Follow the conditioning instructions as indicated.
Step 1
Fully charge your new Keeler rechargeable battery. This will take approx.15 hours.
Step 2
Use the instrument WITHOUT RECHARGING UNTIL THE BATTERY IS COMPLETELY EMPTY.
Step 3
Once empty recharge the battery until full. This will take approx. 15 hours.
Repeat step 1, 2 and 3 three times. i.e. fully charge and discharge the battery three times
to complete the conditioning process.
Once you have conditioned your batteries as described above you may place your
instrument in the charger when not in use between examinations.
5.2 Charger Compatibility
Keeler Rechargeable Handles can be used in the following Keeler chargers:
Vista range of chargers (single, double, mobile)
Keeler Mini charger
Keeler Duo charger.
Please ensure you are using one of the power supplies listed
5.3 Non Keeler Chargers
Warning
Only charge your Keeler handle from a charger providing 65 mA current limited.
Keeler rechargeable handles can be used with most other chargers. To charge the
instrument in a non Keeler charger first ensure that the charging rate from the non
Keeler charger is 65 mA current limited. Then remove the centre of the base cap, using a
coin. Your Keeler handle can now be charged from another manufactures charger.
5.4 Replacing the bulb
Warning
Care should be taken when handling halogen bulbs. Halogen bulbs can shatter if
scratched or damaged.
The bulb should be replaced as indicated in previous diagrams
Switch off the instrument and allow the bulb to cool before attempting to replace it.
!
!
!
Page 15

Only Keeler bulbs can be used in the instrument for which they are designed. Ensure the
replacement matches the bulb being replaced.
Ensure the replacement bulb is the correct voltage. See base of bulb Blue = 2.8v for dry
cell battery handles Red = 3.6v for rechargeable handles.
6.0 Cleaning and Sterilization Instructions
Warning
Plastic reusable Speculae will degrade if exposed to ultra-violet light, dry heat or gamma
irradiation. These methods of sterilization must not be used.
Only manual non-immersion cleaning as described below should be used for the direct
ophthalmoscope, retinoscope, otoscope heads and handles.
1. Wipe the external surface with a clean absorbent, non-shedding cloth dampened
with a water/detergent solution (2% detergent by volume) or water/isopropyl
alcohol solution (70% IPA by volume). Avoid optical surfaces.
2. Ensure that excess solution does not enter the instrument. Use caution to ensure cloth
is not saturated with solution.
3. Surfaces should be carefully hand-dried using a clean non-shedding dry cloth.
4. Safely dispose of used cleaning materials.
The cleaning and sterilization of reusable speculum, metal tongue depressor, nasal
dilator, laryngeal and post natal mirrors can be accomplished as follows:
a. Manually clean all surfaces of the units using a suitable brush and water/detergent
solution (2% detergent by volume). Ensure that hinged versions of specula are
cleaned in both open and closed positions. Ensure all crevices are accessed. Solution
can be heated to no more than 35°C.
b. Carefully examine to ensure that all visible contamination has been removed.
c. Safely dispose of used cleaning materials.
d. Sterilize using a validated steam sterilizer complying to BS 3970 or equivalent
standard. Operating cycle condition as below: 134 - 138°C sterilizing temperature at
2.25 bar operating pressure for minimum of 3 minutes hold time.
e. Inspect for any visible damage prior to use.
f. Nominal life of 400 sterilization cycles for reusable Speculum.
5. Disposable Speculae - use once only and dispose of safely.
!
Page 16

7.0 Warranty & Service
Your Keeler diagnostic ophthalmic instruments are guaranteed for 3 years and will be
replaced or repaired free of charge subject to the following,
1. Any fault that is due to faulty manufacture.
2. The instrument has been used in compliance with these instructions.
3. Proof of purchase accompanies any claim
Please note bulbs and batteries are not covered by this warranty statement.
No user serviceable parts. All preventative maintenance and servicing must only be
performed by authorized Keeler representatives.
8.0 Ophthalmic & Diagnostic Accessories
Pack of two Ophthalmoscope bulbs - 2.8v Xenon 1011-P-7106
Pack of two Ophthalmoscope bulbs - 3.6v Xenon 1011-P-7114
Pack of two Pocket Ophthalmoscope bulbs - 2.8v Halogen 1011-P-7050
Pack of two Standard, Deluxe Otoscope bulbs - 2.8v Halogen 1015-P-7031
Pack of two Standard, Deluxe Otoscope bulbs - 3.6v Halogen 1015-P-7023
Pack of two Practitioner, Fibre Optic Otoscope bulbs - 2.8v 1015-P-7066
Pack of two Practitioner, Fibre Optic Otoscope bulbs - 3.6v 1015-P-7058
Pack of two Professional Streak Retinoscope bulbs - 2.8v 1013-P-7008
Pack of two Professional Streak Retinoscope bulbs - 3.6v 1013-P-7009
Pack of two Professional Spot Retinoscope bulbs - 2.8v 1013-P-7006
Pack of two Professional Spot Retinoscope bulbs - 3.6v 1013-P-7007
Pocket Battery 2.8v 1901-P-5380
Battery Handle 2.8v 1901-P-1064
Rechargeable Handle complete with battery 3.6v 1911-P-1084
Rechargeable Battery 3.6v 1919-P-7069
Mini Charger 1911-P-1148
Duo Charger 1941-P-1202
Airtight Chamber with Lens for Pocket & Standard Otoscopes 1501-P-7117
Viewing lens for Practitioner Otoscope 1513-P-7034
Pneumatic Testing Adaptor for Practitioner, Fibre Optic, Standard & Pocket Otoscope 1514-P-7028
Pneumatic Testing Adaptor for ‘old type’ Standard & PocketOtoscopes 1501-P-7133
Insufflator bulb for all Otoscopes 1599-P-7245
Bulb extractor for Deluxe, Medic Lux, Standard & PocketOtoscopes 1599-P-7237
3x Magnifier for Deluxe Otoscope 1531-P-5016
Page 17

MANUFACTURED IN THE UK BY:
Keeler Limited
Clewer Hill Road
Windsor
Berkshire SL4 4AA
England
Tel: +44 (0)1753 857177
Fax: +44 (0)1753 827145
FREEPHONE: 0800 521 251
DISTRIBUTED BY:
Keeler Instruments Inc.
456 Parkway
Broomall
PA 19008, USA
Toll Free: 1 800 523 5620
Tel: 610 353 4350
Fax: 610 353 7814
As part of our policy of continued product improvement we reserve the right to alter and/
or amend specifications at any time without prior notice.
EP59-19009 Issue A
 Loading...
Loading...