
User Manual
Mesh2HT
Wireless Mesh Ethernet System
Mesh2HT Series

Mesh2HT User Manual
About This Users’ Guide
Intended Audience
This manual is intended for people who want to configure any of the Mesh2HT Series.
You will need a basic knowledge of TCP/IP and wireless topology.
Related Documentation
Quick Start Guide
The Quick Start Guide is designed to help you get up and running. It contains basic
information on setting up your individual Mesh2HT unit.
Technical Specification
The Technical specification is designed to provide you with all the technical specifications
related to the Mesh2HT units.
KBC Networks Website
Please refer to www.kbcnetworks.com for additional support documentation and product
certifications.
Feedback
We welcome all comments, questions and suggestions relating to our User Guides.
Please contact us on:
Americas: Europe, Middle East &
Africa
Technical Department
KBC Networks Ltd.
25691 Atlantic Ocean
Drive
Suite B3
Lake Forest
CA 92630
techsupport@kbcnetworks.com emeatechsupport@kbcnetworks.com apactechsupport@kbcnetworks.com
Thank you
Technical Department
KBC Networks Ltd.
Barham Court
Teston, Maidstone
Kent
ME18 5BZ
United Kingdom
APAC:
Technical Department
Manual-MESH2HT-Rev1311
Copyright © KBC Networks 2012 Page 2 of 59 www.kbcnetworks.com

Mesh2HT User Manual
Document Conventions
Warnings and Notes
These are how warnings and notes are shown is this Guide.
!Warning!
Warnings tell you about things that could harm you o
Note:
Notes tell you other important information or recommendations.
Example:
Examples are provided to help make the Mesh2HT set up straight forward.
Syntax Conventions
r your device.
The Mesh2HT units may be referred to as the ‘device’, the ‘product’ or the ‘system’ in
this guide.
<ENTER> denotes enter or return on your keyboard.
<*****> denotes that you need to select that option.
Manual-MESH2HT-Rev1311
Copyright © KBC Networks 2012 Page 3 of 59 www.kbcnetworks.com

Mesh2HT User Manual
Safety Warnings
!Warning! For your safety please read the following warning notices and
instructions.
Safety, Approvals and Regulatory Domain
Information
Safety Instruction
For your protection, please read and observe all safety instructions before operating this
system and keep this sheet and any additional instructions for future reference.
Installation and Use
OBSERVE WARNINGS: All warnings in the operating instructions should be carefully
followed. Do not make any modifications to the Mesh2HT unit, Power Injection Module
(PIM), or any other KBC Networks electronic device, as the unit(s) will no longer comply
with legal regulations and therefore void its warranty.
WATER AND MOISTURE: The Mesh2HT unit is weatherproof provided it is installed in
accordance to the mounting details listed in section 2.4.3. However, further protection
or housing is suggested for harsh environments, as moisture damage voids its warranty.
The PIMs used in this system are NOT weatherproof. None of the modules in this
system are waterproof and should never be submerged. Severe electrical shock,
personal injury or damage to the equipment may result.
POWER SOURCE: Connect the equipment to a power source only of the type
described on the operating instructions or as marked on the equipment. Excessive or
insufficient current or voltage can cause extended trouble-shooting or even damage
that could negate its warranty. The power supply cable should not be modified/extended
due to the ability to use up to 100m of power over Ethernet cable. In addition, Ethernet
cable running from the PIM to the WEM should be kept separated from high-voltage
cables and/or transformers.
ATTACHMENTS: Use only KBC Networks’ supplied or recommended Power Injection
Modules, Power Supplies, Cat5 Cables and weather seals and plugs.
WHEN NOT IN USE: Unplug the power if the equipment is left unattended or unused
for long periods of time or during lightning storms.
REPLACEMENT PARTS: When replacement parts are required, use only replacement
parts specified by KBC Networks. Unauthorized substitutions may result in damage to
the system and could void the warranty.
Manual-MESH2HT-Rev1311
Copyright © KBC Networks 2012 Page 4 of 59 www.kbcnetworks.com

Mesh2HT User Manual
FCC Required Information
Radio Frequency Interference Statement for Class B Digital Devices
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for an intentional
radiator, pursuant to Part 15, subpart C of the FCC Rules. This equipment generates,
uses and can radiate radio frequency energy. This equipment generates, uses, and can
radiate radio frequency energy. If not installed and used in accordance with the
instructions, it may cause harmful interference to radio communications. The limits are
designed to provide reasonable protection against such interference in residential
situations. However, there is no guarantee that interference will not occur in a particular
installation. If this equipment does cause interference to radio or television reception,
which can be determined by turning the equipment on and off, the user is encouraged
to try to correct the interference but on or more of the following measures:
• Re-orientate or relocate the receiving antenna of th
• Increase the separation between the equipment and the affected receiver.
• Connect the equipment and the affected receiver to power outlets on separate
circuits.
• Consult the dealer or an experienced radio/TV technician for assistance.
Shielded cables must be used with this unit to ensure compliance with Class B FCC
limits. Changes or modifications to this unit not expressly approved by the party
responsible for compliance could void the user’s authority to operate the equipment.
Changes or modifications not expressly approved by KBC could void the user’s authority
to operate the equipment.
e affected radio or television.
FCC Power Output Restrictions
The FCC does not require licensing to implement this device. License-free operation in
the industrial, scientific and medical band is documented in FCC Rules Part 15.247. It is
the responsibility of the individuals designing and implementing the radio system to
ensure compliance with any pertinent FCC Rules and Regulations. This device must be
professionally installed.
Exposure to Radio Frequency Fields
The Mesh2HT is designed to operate on the 5 GHz frequency band with up to 50 Watts
EIRP maximum transmit power. This level of RF energy is above the Maximum
Permissible Exposure (MPE) levels specified in FCC OET65:97-01. The following
precautions must be taken during installation of this equipment:
• The installed antenna must not be located in a manner that allows exposure of the
general population to the direct beam path of the antenna at a distance less than
20cm. Installation on towers, masts, or rooftops not accessible to the general
population is recommended or alternatively mount the antenna in a manner that
prevents any personnel from entering the area within 20cm from the front of the
antenna.
• It is recommended that the installer place radio frequency hazard warnings signs on
the barrier that prevents access to the antenna.
• During installation and alignment of the antenna, do not stand in front of the
antenna assembly.
• During installation and alignment of the antenna, do not handle or touch the front of
the antenna.
These simple precautions must be taken to prevent general population and installation
personnel from exposure to RF energy in excess of specified MPE levels.
Manual-MESH2HT-Rev1311
Copyright © KBC Networks 2012 Page 5 of 59 www.kbcnetworks.com

Mesh2HT User Manual
Industry Canada Restrictions
IC ID# 7849A-N523ESD
This Class A digital apparatus complies with Canadian ICES-003. To reduce potential
radio interference to other users, the antenna type and its gain should be so chosen that
the equivalent isotropically radiated power (E.I.R.P.) is not more than that permitted for
successful communication. This device complies with Industry Canada license-exempt
RSS standard(s).
Operation is subject to the following two conditions:
This device may not cause interference, and
This device must accept any interference, including interference that may cause
undesired operation of the device.
Cet appareil numérique de la classe A est confrome à la norme NMB-003 Canada. Pour
réduire le risque d’interférence aux autres utilisateurs, le type d’antenne et son gain
doivent être choisies de façon que la puissance isotrope rayonnée équivalente (PIRE) ne
dépasse pas ce qui est nécessaire
pour une communication réussie. Cet appareil est conforme à la norme RSS Industrie
Canada exempts de licence norme(s). Son fonctionnement est soumis aux deux
conditions suivantes:
17 Compliance
Cet appareil ne peut pas provoquer d’interférences et
Cet appareil doit accepter toute interférence, y compris les interférences qui peuvent
causer un mauvais fonctionnement du dispositif.
RF Exposure Warning
The antennas used for this transmitter must be installed to provide a separation distance
of at least 37.2 cm from all persons and must not be located or operating in conjunction
with any other antenna or transmitter.
Les antennes utilisées pour ce transmetteur doivent être installé en considérant une
distance de séparation de toute personnes d'au moins 37.2 cm et ne doivent pas être
localisé ou utilisé en conflit avec tout autre antenne ou transmetteur.
Manual-MESH2HT-Rev1311
Copyright © KBC Networks 2012 Page 6 of 59 www.kbcnetworks.com

Mesh2HT User Manual
CE Regulatory Statement
Class B ITE:
This is a Class B product. In a domestic environment this product may cause radio
interference in which case the user may be required to take adequate measures.
Declaration of Conformity:
KBC declares the following:
Product Name: Mesh2HT
Model No.: 802.11n station conforms to the following Product Standards:
This device complies with the Electromagnetic Compatibility Directive (89/336/EEC)
issued by the Commission of the European Community. Compliance with this directive
implies conformity to the following European Norms (in brackets are the equivalent
international standards.)
Electromagnetic Interference (Conduction and Radiation): EN 55022 (CISPR 22)
Electromagnetic Immunity: EN 55024 (IEC61000-4-2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 8, 11)
Low Voltage Directive: EN 60 950: 1992+A1: 1993+A2: 1993+A3: 1995+A4:
1996+A11: 1997.
CE Mark: following the provisions of the EC directive.
KBC also declares that:
The wireless card in this product complies with the R&TTE Directive (1999/5/EC) issued
by the Commission of the European Community. Compliance with this directive implies
conformity to the following:
EMC Standards: CE: EN 300 328-2, EN 300 826 (EN 301 489-17) EN 301 893.
CE marking on this product represents the product is
that are applicable to it.
This equipment may be operated in the following countries:
Great Britain and Northern Ireland, Austria, Belgium, Denmark, Finland, France,
Germany, Ireland, Italy, Netherlands, Norway, Portugal, Romania, Switzerland, Sweden
Installer Compliance Responsibility
Devices must be professionally installed and it is the professional installer's responsibility
to make sure the device is operated within local country regulatory requirements.
Dynamic Frequency Selection (DFS) & Transmit Power Control (TPC)
DFS and TPC are requirements of the ETSI standard EN301 893 V1.5.1, the European
Union’s harmonized radio standard for unlicensed devices operating in the 5150 – 5350
MHz and 5470 – 5725 MHz frequency bands. Radar detection is required when operating
on channels whose nominal bandwidth falls partly or completely within the frequency
ranges 5250 MHz to 5350 MHz or 5470 MHz to 5725 MHz. In addition devices using the
5600 – 5650 MHz band are subject to a 10 minute Channel Availability Check (CAC).
The following table shows how this can affect connection times for certain frequencies:
in compliance with all directives
Manual-MESH2HT-Rev1311
Copyright © KBC Networks 2012 Page 7 of 59 www.kbcnetworks.com
Mesh2HT User Manual
Frequency (MHz)
5500
5505
5510
5515
5520
5525
5530
5535
5540
5545
5550
5555
5560
5565
5570
5575
5580
5585
5590
5595
5600
5605
5610
5615
5620
5625
5630
5635
5640
5645
5650
5655
5660
5665
5670
5675
5680
5685
5690
5695
5700
Channel Bandwidth
5MHz 10MHz 20MHz 20/40MHz
2 mins 2 mins 2 mins 2 mins
2 mins
2 mins 2 mins
2 mins
2 mins 2 mins 2 mins
2 mins
2 mins 2 mins
2 mins
2 mins 2 mins 2 mins 2 mins
2 mins
2 mins 2 mins
2 mins
2 mins 2 mins 2 mins
2 mins
2 mins 2 mins
2 mins
2 mins 2 mins 2 mins 10 mins
2 mins
2 mins 2 mins
2 mins
10 mins 10 mins 10 mins
10 mins
10 mins 10 mins
10 mins
10 mins 10 mins 10 mins 10 mins
10 mins
10 mins 10 mins
10 mins
10 mins 10 mins 10 mins
10 mins
10 mins 10 mins
2 mins
2 mins 2 mins 2 mins 2 mins
2 mins
2 mins 2 mins
2 mins
2 mins 2 mins 2 mins
2 mins
2 mins 2 mins
2 mins
2 mins 2 mins
2 mins
Manual-MESH2HT-Rev1311
Copyright © KBC Networks 2012 Page 8 of 59 www.kbcnetworks.com

Mesh2HT User Manual
Environmental Restrictions of Wireless Devices
KBC products are engineered to the highest standards and designed to work in a variety
of wireless applications and environments. A wireless environment includes the site in
which the product is installed, the installation including power and cabling as well as any
extra materials that might be necessary to complete the wireless project. Due to the fact
that environments and installations differ from site to site, KBC cannot control the
variables required to ensure an ideal environment. Therefore, it is not possible to
guarantee a successful application based on a drawing, application note, distance
calculation, quote or other type of material that KBC may provide. Should a quote,
drawing, etc. be made available, it is based on the performance of the Mesh2HT product
in an ideal environment with clear line-of-sight, absence of interference and/or frequency
multi-path reflection. Therefore, KBC cannot be held responsible should the products not
operate as desired or should additional products be required to complete a project. In
addition, should a particular environment restrict the usage of the Mesh2HT in any way,
KBC offers a thirty (30) day return policy from date of shipment to the original purchaser
if goods are returned in an ‘as new’ condition.
RoHS / WEEE Compliance Statement
European Directive 2002/96/EC requires that the equipment bearing this symbol on the
product and/or its packaging must not be disposed of with unsorted municipal waste.
The symbol indicates that this product should be disposed of separately from regular
household waste streams. It is your responsibility to dispose of this and other electric
and electronic equipment via designated collection facilities appointed by the
government or local authorities. Correct disposal and recycling will help prevent potential
negative consequences to the environment and human health. For more detailed
information about the disposal of your old equipment, please contact your local
authorities, waste disposal service, or the shop where you purchased the product.
Instruction of Disassembly
Instruction of Disassembly of KBC Product (For EU Directive 2002/95/EECWEEE)
Tools required:
• No. 1 Phillips screwdriver
• No. 2 Phillips screwdriver
Steps for disassembly:
1. Remove Serial Label adhesive
2. Remove cover screws attaching top cover to radio module cavity.
3. Remove tightening screws for printed circuit board (PCB).
4. Take out all PCBs.
Note: W
Manual-MESH2HT-Rev1311
Copyright © KBC Networks 2012 Page 9 of 59 www.kbcnetworks.com
hen a product reaches the end of its life – return to KBC.

Mesh2HT User Manual
General Public License Statement
You may have received from KBC Networks products that contained – in part – free
software (software licensed in a way that ensures your freedom to run, copy, distribute,
study, change and improve the software). Such products include the Mesh2HT Series of
products.
As part of these products, KBC Networks may have distributed to you hardware and/or
software that contained a version of free software programs developed by the Free
Software Foundation, a separate not-for-profit organization without any affiliation to KBC
Networks. See http://www.gnu.org/philosophy/free-sw.html for more details. If KBC
Networks distributed any portions of these free software programs to you, you were
granted a license to that software under the terms of either the GNU General Public
License or GNU Lesser General Public License (“License”, copies of which are available
from http://www.gnu.org/licenses/licenses.html). The Licenses allow you to freely copy,
modify and redistribute that software without any other statement or documentation
from us.
For at least one (1) year from the date of distribution of the applicable product or
software, KBC Networks will provide to anyone who contacts us at the contact
information provided below, for a charge of no more than our cost of physically
performing source code distribution, a complete machine-readable copy of the complete
corresponding source code for the free software programs used in the version of the
programs that we distribute to you. The cost will be free if the delivery medium of the
machine-readable copy is through the Internet.
Contact information:
Email: techsupport@kbcnetworks.com
Tel: 949.297.4930
Address: 25691 Atlantic Ocean Drive Lake Forest, CA 92630
We ask for your understanding regarding expected delivery timelines:
• We will reply within 7 working days once the request
telephone.
• The default version sent will be the latest that we used in the firmware/programs.
Note: it may take longer if an older version is requested. The waiting time will not
exceed 2 weeks.
has been made via email or
Manual-MESH2HT-Rev1311
Copyright © KBC Networks 2012 Page 10 of 59 www.kbcnetworks.com

Mesh2HT User Manual
TABLE OF CONTENTS
ABOUT THIS USERS’ GUIDE .................................................................. 2
Related Documentation ................................................................................................................................ 2
DOCUMENT CONVENTIONS .................................................................. 3
Warnings and Notes ....................................................................................................................................... 3
SAFETY WARNINGS ....................................
........................................ 4
SAFETY, APPROVALS AND REGULATORY DOMAIN INFORMATION .................... 4
Safety Instruction .......................................................................................................................................... 4
FCC Required Information ........................................................................................................................... 5
Industry Canada Restrictions ..................................................................................................................... 6
CE Regulatory Statement ............................................................................................................................. 7
Environmental Restrictions of Wireless Devices ................................................................................... 9
ROHS/WEEE COMPLIANCE STATEMENT .................................................... 9
Instruction of Disassembly .......................................................................................................................... 9
GENERAL PUBLIC LICENSE STATEMENT ................................................. 10
1 OVERVIEW ................................................................................ 12
1.1 Introduction .......................................................................................................................................... 12
1.2 General Technical Specification............................................................................................................. 13
2 INSTALLATION ........................................................................... 18
2.1 Package Contents .................................................................................................................................. 18
2.2 Physical Connections ............................................................................................................................. 18
2.3 Basic Installation Method ..................................................................................................................... 20
3 GRAPHICAL USER INTERFACE ......................................................... 25
3.1 Accessing the Mesh2HT Graphical User Interface (GUI) ....................................................................... 25
3.2 Menu Options ....................................................................................................................................... 26
4 TROUBLESHOOTING .................................................................... 55
4.1 Visual Inspection ................................................................................................................................... 55
4.2 Test Cable Connections ......................................................................................................................... 56
4.3 GUI Tools ............................................................................................................................................... 56
4.4 KBC Technical Assistance ....................................................................................................................... 57
5 WARRANTY ...........................................
.................................... 58
5.1 Warranty Information ........................................................................................................................... 58
Manual-MESH2HT-Rev1311
Copyright © KBC Networks 2012 Page 11 of 59 www.kbcnetworks.com

Mesh2HT User Manual
1 Overview
1.1 Introduction
This manual covers all the functions of the products that form KBC Networks’ Mesh2HT
series. Wireless mesh technology is primarily used in applications where redundant
wireless paths are created for critical connection uptime. The KBC Mesh2HT mesh nodes
are also designed for use in a wide range of other applications enabling wireless
connectivity where it is not practical or cost-effective or where it is beyond distance
limitations. They are designed for operating temperatures in non-environmentally
conditioned, outdoor applications. Mesh2HT has been specifically designed to transmit
constant streaming video but can also be used to send and receive standard Ethernet
data packets or to operate as a WiFi access point.
This manual will cover how to configure and manage the radios in order to create
numerous connectivity topologies. They can be configured into a ring for redundancy, a
line or star for repeating the signal along line-of-sight paths between nodes, or even
basic wireless structure such as a long range point to point wireless bridge. Other
topologies include multipoint receiving antennas, communicating to numerous
transmitting client devices including the WES2HT client or host/AP to a Mesh2HT client
radio. It is important to familiarize the installer with this manual to reduce configuration
error as Mesh systems can easily escalate to complex systems.
1.1.1 Mesh2HT
The KBC Networks’ Mesh2HT series is a wireless transmission system that operates in
the license-free 2.4GHz & 5GHZ bands and also in the 4.9GHz Public Safety band
(available in the USA & Canada). The units are provided with a range of antennas to suit
applications and will support a throughput of 230Mbps
Mesh2HT requires CAT6 or above Gigabit Ethernet cable.
2
thanks to MIMO technology.
Manual-MESH2HT-Rev1311
Copyright © KBC Networks 2012 Page 12 of 59 www.kbcnetworks.com
Mesh2HT User Manual
1.2 General Technical Specification
Mesh2HT Specification
Standards
IEEE 802.3 10BASE-T
IEEE 802.3u 100BASE-TX
IEEE 802.3x Full Duplex
IEEE 802.11a 5GHz
IEEE Standards
Radio
Frequency (MHz)
Frequency Operation
Power Output
Channel Capacity Selectable 5, 10, 20 or 20/40MHz
Modulation OFDM
Receive Sensitivity
(Tolerance ± 2dbm)
Antennas
5dBi
17dBi
IEEE 802.11b 2.4GHz
IEEE 802.11g 2.4GHz
IEEE 802.11y 4.9GHz US Public Safety
IEEE 802.11n MIMO
IEEE 802.11h ETSI DFS & TPC
IEEE 802.1D Spanning Tree
USA & Canada:
5745, 5765, 5785, 5805, 5825
Europe:
5500, 5520, 5540, 5560, 5580, 5600 5620,
5640, 5660, 5680, 5700
Auto-select
User static selectable
Dynamic Frequency Selection (ETSI DFS)
23dBm max1
Transmit Power Control (ETSI TPC)
MCS HT 20 HT 40
8 -97dBm -92dBm
9 -94dBm -90dBm
10 -92dBm -87dBm
11 -87dBm -84dBm
12 -84dBm -82dBm
13 -80dBm -78dBm
14 -79dBm -76dBm
15 -77dBm -74dBm
Omni-directional
Directional integrated patch
Dual polarization
Beamwidth:
Azimuth: Horizontal 30°, Vertical 33°
Elevation: Horizontal 17°, Vertical 17°
1
Territory specific.
Manual-MESH2HT-Rev1311
Copyright © KBC Networks 2012 Page 13 of 59 www.kbcnetworks.com
Mesh2HT User Manual
System
Data throughput2
(max values)
HT40
230Mbps
Latency < 60ms
Power
Power input (supplied by PIM)
24Vdc, 500mA
Reverse voltage protected
Power method Passive PoE
PoE cable spec 100m on 24AWG Cat5/5e/6/6e
Mechanical
Casing Weatherproof
Dimensions (Patch L x W x D)
170mm x 170mm x 40mm
6.7” x 6.7” x 1.58”
Weight 907g / 2lb
Installation Wall-mount or pole-mount
Environmental
Operating Temperature
Storage Temperature
-40° ~ +70°C / -40° ~ +158°F
-40° ~ +90°C / -40° ~ +194°F
Operating Humidity 5% to 95% non-condensing
Connectors
Antenna 4 x N-type female
10/100/1000 Electrical 1 x RJ45
Power
IEEE 802.af PoE or 24Vdc Passive PoE via
PIM
Approvals
FCC Part 15 subpart C Class B
IC ID# 7849A-N523ESD
CE Class B
EN 55024 (IEC61000-4-2,3,4,5,6,8,11) Electromagnetic Immunity
EN 55022 (CISPR 22)
EN 60 950: 1992+A1; 1993+A2;
1995+A4; 1996+A1; 1997
Electromagnetic Interference (Conduction
and Radiation)
Low Voltage Directive
EN 300 328-2
EN 300 826
EN 301 489-17
EN 301 893
R&TT Directive (1999/5/EC)
2
Assumes an ideal environment with maximum signal rates & within receive
sensitivity specification.
Manual-MESH2HT-Rev1311
Copyright © KBC Networks 2012 Page 14 of 59 www.kbcnetworks.com
Mesh2HT User Manual
R2 antennas
STP
Power Loss
1.2.1 Configuration Standards & Topology
1.2.1.1 Basic Mesh2HT Radio Overview
R1 antennas
Mesh2HT consists of two WiFi radios but one Ethernet LAN port. One
radio, Radio 1 or “R1” is default configured as a client while the second
radio (“R2”) is configured as an access point. When looking at the
Mesh2HT node chassis with the LAN port on the bottom of the case,
the two N-connector antenna ports on the top are for R1 and the two
adjacent to the LAN port and mounting block are the R2 ports. R1 and
R2 can be configured to their opposite nature (R1 converted to an AP,
R2 configured as a client) or to the same nature (both APs for
example). Regardless of R1 and R2 configurations, the two radios will
not associate with one another. In this manual, unless otherwise
noted, all diagrams and details will assume default configurations for
R1 and R2 nature configurations.
See section 3.2 and following for advanced set up details, the
following sections 1.1.1.2 – 1.1.1.3 provide an overview of the
topologies in which Mesh2HT nodes can operate.
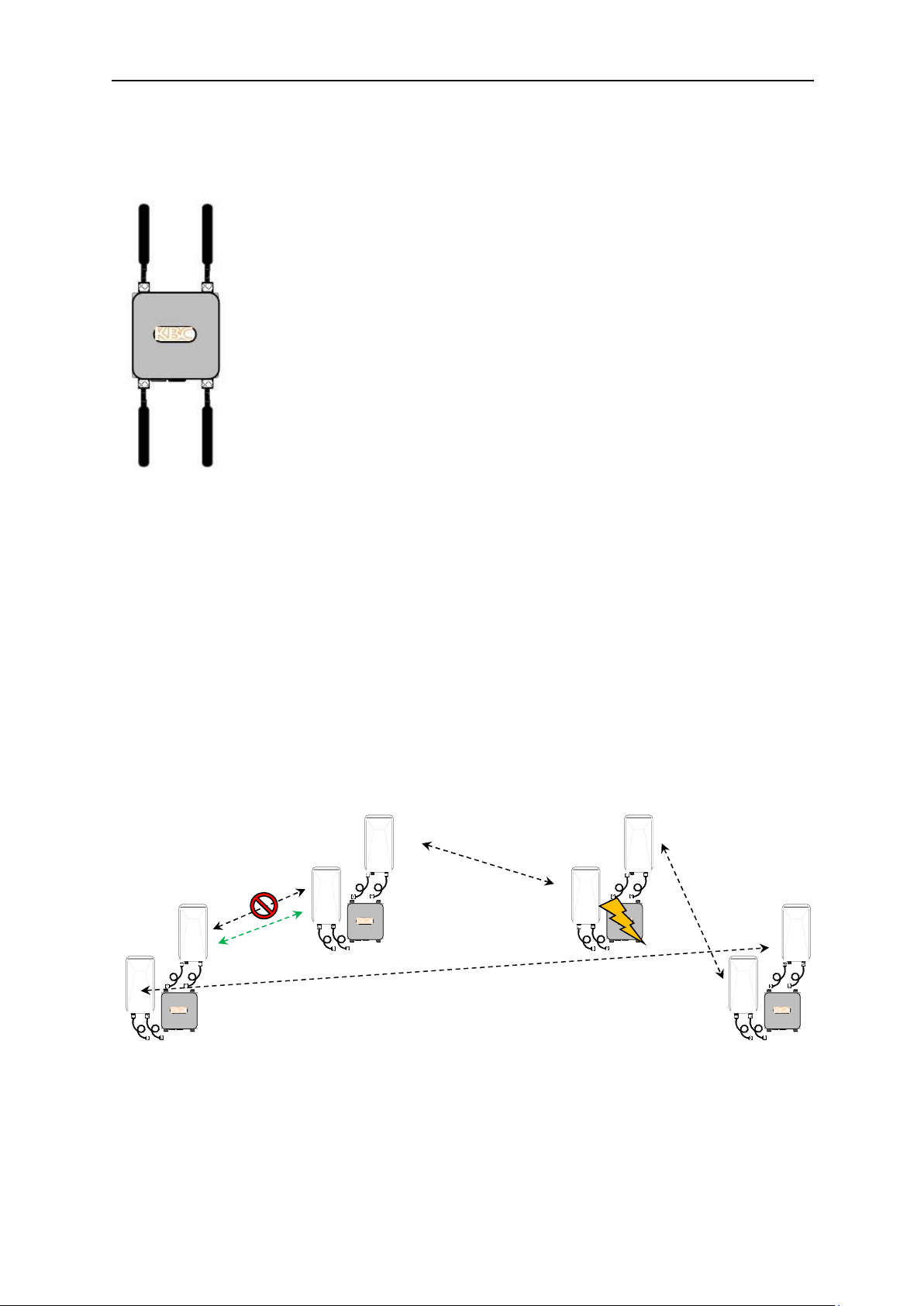
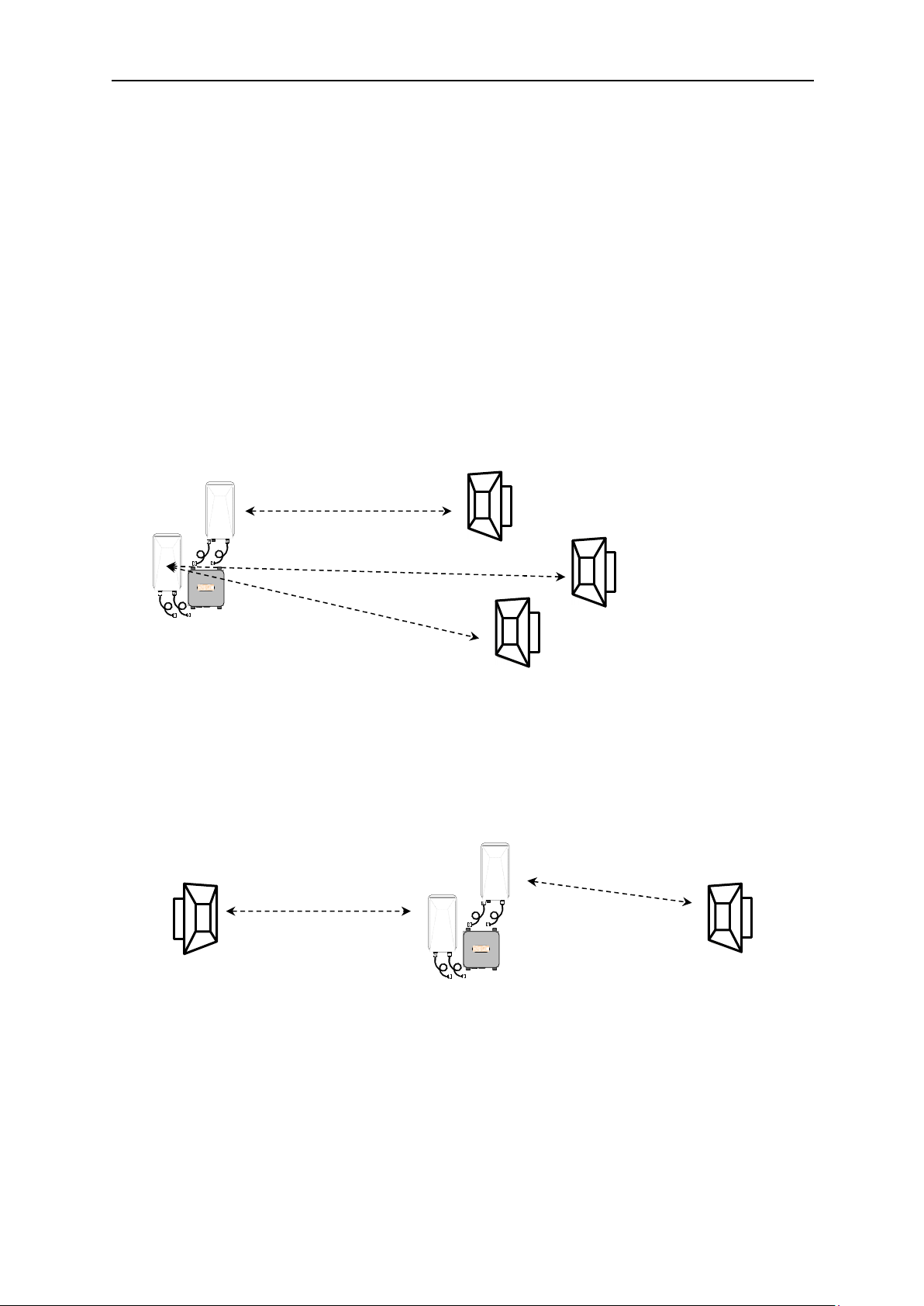
1.2.1.2 Mesh2HT Ring Topology
Mesh nodes are commonly configured with redundant paths to provide a second wireless
connection as an attempt to avoid critical downtime. Several Mesh topologies exist but
certain Mesh formats are most appropriate for systems transmitting constant video
streaming. If redundancy is required in a wireless video system, the ring topology using
directional antennas is recommended. Configuring several (i.e. three or more) Mesh2HTAA-Ox nodes into a ring will enable the remaining nodes to sustain connectivity in the
event one of the nodes in the ring loses connection. In order for any type of network
connection where data packets can route through multiple paths to any given point
resulting in a network loop, spanning tree protocol (STP) must be configured. STP
essentially “breaks” one path to eliminate the loop and routes packets along the
remaining connection of the network.
STP opens
link
Mesh2HT nodes shown with optional directional
patchantennas. Kit comes with omni-directional antennas.
Since the wireless connection is still established where STP has avoided routing the data,
STP will then restructure the connection should another portion of the ring be disturbed
and is no longer a part of the ring network. Mesh2HT contains an STP function
eliminating the need for a managed switch with STP as part of the wireless network.
Manual-MESH2HT-Rev1311
Copyright © KBC Networks 2012 Page 15 of 59 www.kbcnetworks.com
Mesh2HT User Manual
Other Mesh topologies exist. The complexity of the other Mesh formats can escalate
quickly. While providing numerous paths available may create various back up options,
the latency due to increased spanning tree protocol decisions to avoid network looping
can make the simple ring format the most advantageous for redundant wireless video
systems.
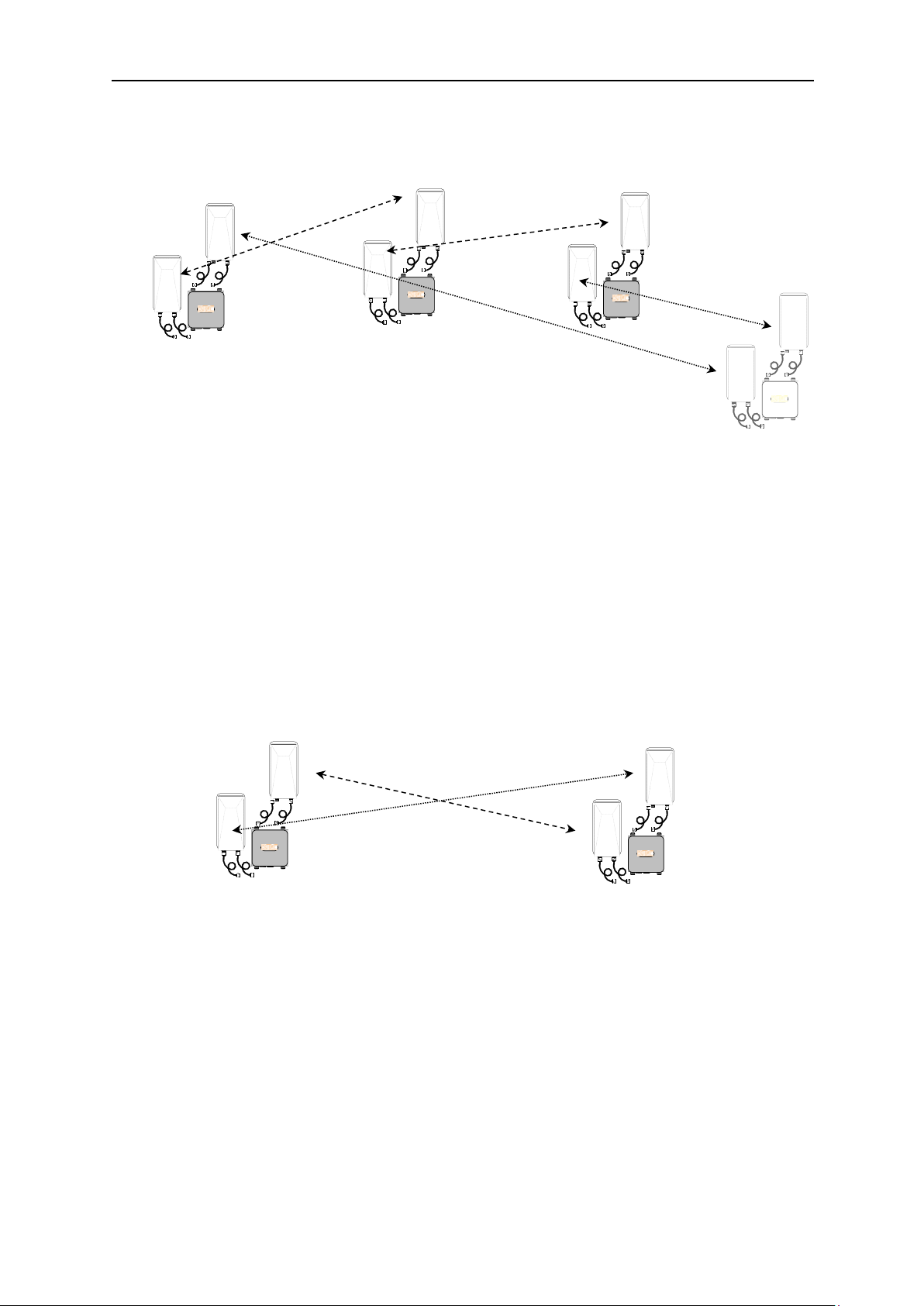
1.2.1.3 Other Available Topologies
Another basic wireless topology in which Mesh nodes can be configured is one where
multiple remote sites transmit to one receive location. Using the Mesh2HT radios in this
configuration allows for integration with other KBC wireless systems (Mesh2HT product
line) or future expansion. Below are some diagrams showing other ways to configure the
Mesh2HT radios. Some topologies also include point to point linear designs.
Connecting Mesh2HT to Mesh 2HT
The Mesh2HT AP/host can connect to a Mesh2HT client and the Mesh2HT client can
connect to a Mesh2HT AP/host.
WESII-AA-C*
Host
MESH2HT-AA** mesh node
WESII-AC-C*
Client
WESII-AC-C*
Client
Configuring Mesh2HT as a Repeater Point
Mesh2HT can integrate with Mesh2HT where the remote and head end units are
Mesh2HT and the repeater node is Mesh2HT.
WESII-AC-C*
Client
MESH2HT-AA** Mesh node
WESII-AB-**
MP Host
Manual-MESH2HT-Rev1311
Copyright © KBC Networks 2012 Page 16 of 59 www.kbcnetworks.com
Mesh2HT User Manual
I
f line of sight path exists
Configuring Mesh2HT Nodes for Available Future Expansion Deployment
If all transmit locations contain Mesh nodes and the topology of the wireless connection
is linear point to point, then one or more of the radios will be available for future use.
Radio enabled when new
node is deployed
Configuring as Redundant Point-to-Point Backhaul Link
When two nodes are connected to one another in a point-to-point ring, R1 would connect
to R2 of the second node while R1 of the second node connects to R2 of the first node.
Since this format is a loop, spanning tree protocol is used to break one of the two
connections. Redundancy is recommended to be established by configuring in three or
more node clusters as opposed to one point-to-point ring in two nodes. This type of
“linear loop” is only beneficial if one link quality drops below a certain threshold while the
other link signal strength is still well above the designated threshold. The diagram below
shows this type of setup:
Established
RF link
Link stopped by STP
available if other link falls
below an RSSI threshold
Frequencies should be static set to opposite
ends of available frequency band
Future
Mesh2HT
node
Manual-MESH2HT-Rev1311
Copyright © KBC Networks 2012 Page 17 of 59 www.kbcnetworks.com
Mesh2HT User Manual
3 4
5
8
9 10
11
2 Installation
2.1 Package Contents
• Mesh2HT RF module
• One mid-span compliant power injector module
• One 24Vdc, 500mA PSU
• Wall- or pole-mount bracket and assembly kit
• Quick Start Guide
Consult the Quick Start Guide for the exact list of components for the particular part
number ordered. Please contact you dealer or distributor if a part is missing or damaged
within 10 days of receiving the products.
2.2 Physical Connections
1 1
2.2.1 Rear View
1. R1 antenna ports
2
. R2 antenna ports
3. Signal and status LEDs
4. Power & network LEDs
(See section 2.2.4 for description)
5. Mounting direction arrow
6. Device serial number
7. Product series Info
8. FCC Part 15 Statement
9. LAN port (RJ45)
10. Mounting block
11. Reset to default button
7
2 2
6
2.2.2 Bottom View
1. R2 antenna ports
2. LAN port
3. Mounting block base
4. Reset to default button
(Remove Screw and insert small
screw driver)
1 1 2 3
4
Manual-MESH2HT-Rev1311
Copyright © KBC Networks 2012 Page 18 of 59 www.kbcnetworks.com

Mesh2HT User Manual
1
2
2.2.3 Power Injector Module (PIM)
Note: The Power Injector Modules are not weatherproof units and must be protected
from moisture.
1. Power – Power supply input
2. OUT – Connect to the Mesh2HT unit
Powe r
POE +
3. IN – Connect to the Ethernet device
OUT
IN
Local Power
Remote Pow er
PIM Top View
3
PIM Side View (Power and Output)
PIM Side View (Input)
Note: The Power injector is not required if connecting to an 802.3af PoE switch. If the
PIM is used, 24Vdc must be used.
2.2.4 RF Module LED Description
1. Signal Strength Indicator – 40 RSSI
If this LED is illuminated, the signal strength for R1 is > 40
2. Signal Strength Indicator – 30 RSSI
If this LED is illuminated, the signal strength for R1 is 30 ~ 39
3. Signal Strength Indicator – 20 RSSI
If this LED is illuminated, the signal strength for R1 is 20 ~ 29
4. Signal Strength Indicator – 10 RSSI
If this LED is illuminated, the signal strength for R1 is < 19
5. Not Used
6. Ethernet Link Activity
7. Power
Note: The RSSI LEDs pertain to the signal strength of radio 1 (R1). If not illuminated,
R1 is not connected or is not being used.
Manual-MESH2HT-Rev1311
Copyright © KBC Networks 2012 Page 19 of 59 www.kbcnetworks.com

Mesh2HT User Manual
Default Password:
admin
2.3 Basic Installation Method
2.3.1 Bench Test Set Up
KBC Networks recommends that all equipment be bench tested before being installed on
site. Four straight through Ethernet cables are required. Refer to any applicable
provided documentation for LAN IP addresses or R1 / R2 custom configurations.
1. Remove the Mesh2HT module, power supply unit (PSU) and power injector modules
(PIM) from the box. Connect a straight through cable from “In” on the PIM to a laptop or
PC LAN port. Connect another Ethernet cable from “Out” on the same PIM to the
Mesh2HT LAN port.
2. Verify that the static IP address on the laptop is set to the 192.168.1.x subnet (refer
to provided documentation for exact IP per serial number) and open a web browser to
access the Mesh2HT on its 192.168.1.10 default IP address.
Default User Name: admin
3. Enter the default user ID and password (admin / admin) to access the GUI. Disable
any other Network Interface connection including the laptop/PC WiFi access that is not
being used to access the Mesh2HT node.
4. For all deployments outside of North America, select the Basic Wireless menu and
choose the country for the appropriate regulatory domain. Click “Apply Settings” and
then “Save” next to “Save Configuration Changes”. North American firmware units do not
provide an alternate option for country code.
Note: It is the sole responsibility of the installer of the KBC Networks’ Mesh2HT
equipment to ensure that the correct country code is selected to comply with the RF
regulatory requirements of the country in which the equipment is installed. KBC
Networks accepts no liability for incorrect selection.
5. To set the Mesh2HT radios to a specific channel manually, select R2 Basic Wireless Set
Up and select one of the available frequencies and apply/save changes. When selecting a
channel on site, first click “Interference Analyzer” to determine available frequencies in
the environment.
6. R1 is default set as a client while R2 is configured as an access point (AP). R1 and R2
should also remain as two separate SSIDs. Three nodes can be configured in a ring using
configurations such as:
Manual-MESH2HT-Rev1311
Copyright © KBC Networks 2012 Page 20 of 59 www.kbcnetworks.com

Mesh2HT User Manual
4 5
R1 Configuration:
Client
SSID: KBC-Mesh2HT-3
R1 Configuration:
Client
SSID: KBC-Mesh2HT-1
R1 Configuration:
Client
SSID: KBC-Mesh2HT-2
R2 Configuration:AP
SSID: KBC-MESH2HT-1
Channel: 5745 MHz
R2 Configuration:AP
SSID: KBC-MESH2HT-2
Channel: 5805 MHz
R2 Configuration:AP
SSID: KBC-MESH2HT-3
Channel: 5825 MHz
ote: Channels and SSIDs shown as examples only.
N
2.3.2 Pole and Wall-mount Assembly
Mesh2HT nodes come with a hardware kit for mounting to a pole/mast that is no more
than 3 inches in diameter. The node itself does not require antenna alignment if using
the omni-directional antennas. If using the 17 dBi directional patch antennas, see
section 4.1.1.2 for alignment.
2.3.2.1 Mounting Kit Parts Included
1
2
A
7
3
B C
6
Note: Diagram is shown with part #6 inserted
8
between parts B and C using a longer bolt (part
#3). Bolt #3 and washer #6 are supplied
separately in the Mesh2HT box since the preassembled mounting kit is sufficient for most
applications. The star washer and longer bolt
allow for finer up/down alignment angles.
10
9
Manual-MESH2HT-Rev1311
Copyright © KBC Networks 2012 Page 21 of 59 www.kbcnetworks.com

Mesh2HT User Manual
A B C D E
Item
A 1 Mounting Base
B 1 Left/Right Swivel Bracket
C 1 Up/Down Swivel Bracket &
1 1 U-bolt
2 1 Mast Clamp
3 1 2” Phillips Hex Head 8x30 Screw
4 1 Lock Washer
5 1 1.5” Hex Head 8x30 Bolt
6 1 Star Washer
7 3 Flat Washer
8 3 Hex Nut
9 1 1/4” Lock Washer
10 1 1/4”-20 Phillips Pan Head Screw
Qty Description
Mesh2HT Mounting Platform
2.3.2.2 Mounting Kit Procedure
• Remove all packaging material
• All parts are pre-assembled and ready for mounting.
For more fine-tuned alignment,
see next step. Otherwise skip to bullet point 4 below.
• Up/Down Alignment offers one position when using the pre-fabricated channel lock
grooves on parts B and C. Directional antennas may require additional up/down
alignment angles than are allowed on the pre-fabricated grooves. To achieve different
angles, remove the bolt which connects parts B & C and separate. Insert the longer
bolt through part B and add star washer. Re-connect part C and tighten.
• Remove U-Bolt and attach to the pole/mast, re-attach
washers and nuts for secure
tight mount positioning.
• Attach Mesh2HT to part C using screw and lock washer
• If using the omni-directional antennas no further mounting steps are needed. If also
mounting directional antennas, use procedure as noted under section 4.1.1.2
• When in the best position tighten all mounts for protection against anything that can
knock the antennas/Mesh2HT out of desired positioning.
2.3.3 Strain Relief Assembly
• Insert A into the large tightening knob (B)
• Thread piece C to the end of A. Do not tighten completely until connected to the
Mesh2HT LAN port and power is confirmed.
• Insert the rubber grommet (D) into the open end of C
• Attach E to threaded portion of C. As E is tightened
, the grommet will squeeze against
the Ethernet cable jacket. Leave E loose enough for the cable to wiggle slightly.
Manual-MESH2HT-Rev1311
Copyright © KBC Networks 2012 Page 22 of 59 www.kbcnetworks.com

Mesh2HT User Manual
RJ45
Connector
• Slide Ethernet cable through the assembled strain relief unit before crimping on the
RJ45 connector.
• Strip cable and configure color code (see section 2.
4.5). Use one of the LAN port
weather protection seal stickers – two are provided.
2.3.4 Configuring the Cable
• Determine the length of cable that will be required and where the PIM will be located.
Note: The total length of cable from the Mesh2HT to the Ethernet device cannot exceed
100m (325 feet), however, the PIM can be located anywhere along the overall 100m of
cable. KBC Networks recommends shielded Ethernet cables for the cable connecting the
PIM to the Mesh2HT unit. Any cable exposed to the elements should also be outdoor
rated.
• Slide the weatherproof connector over the cable jacket before crimping the connector.
See section 2.3.3 for the strain relief assembly instructions. If needed, see below for
color-code standards to configure the correct type of Ethernet cable.
Ethernet standard straight-through cable configurations used must be configured to one
of the Ethernet standards (568-A or 568-B) in order for the Mesh2HT system to operate
efficiently. Any deviation from one of the two standard configurations can lead to
undesired activity.
Pin out for color codes 568-A and 568-B:
568-A 568-B
1- Green/White 1- Orange/White
2- Solid Green 2- Solid Orange
3- Orange/White 3- Green/White
4- Solid Blue 4- Solid Blue
5- Blue/White 5- Blue/White
6- Solid Orange 6- Solid Green
7- Brown/White 7- Brown/White
8- Solid Brown 8- Solid Brown
A cable configured with the 568-A color code on one end and the 568-B color code on
the other end is an Ethernet standard crossover cable.
• Connect the RJ45 connector into the Mesh2HT’s LAN port. Slide the strain relief back
up the cable to the threaded portion on the LAN port of the device and screw it into
the host/AP or client and tighten.
• Tighten the clamping nut until the Ethernet cable is secured in the connector. The
weatherproof strain relief should be tight to the case but the rubber grommet opening
should remain loose enough for the cable to wiggle slightly. This will allow for
condensation release.
Manual-MESH2HT-Rev1311
Copyright © KBC Networks 2012 Page 23 of 59 www.kbcnetworks.com

Mesh2HT User Manual
2.3.5 Establishing a Link
For each Mesh2HT radio in the system, carry out the following steps:
• The R1 and R2 default Configurations are:
- R1: client, SSID= KBC-Mesh2HT-2; HT20/40
- R2: AP, SSID= KBC-Mesh2HT-1; Auto-select frequency, HT20/40
• A second node configured under default settings will connect (assuming clear line of
sight, no interference and within range). In order to connect several nodes or more
particular wireless design may be necessary requiring specific re-configuration. KBC
Tech Support can assist with configuration settings. Care with regard to radio settings
is advised.
• In most applications, R1 of one node will connect to
recommended that R1 is configured as a client and R2 is configured as an AP.
• Verify the antenna alignment (if applicable) and LED status. RSSI LEDs will reflect the
signal strength status of R1 only. See section 2.4.4 for applicable LED activity.
• If using the PIM, ensure that the green power LED is illuminated. The Mesh2HT unit’s
power LED should be green provided the cable into the LAN port is seated properly.
Note: The RSSI figures can be used to fine tune alignment see section 4.1.1.2
R2 of another, etc. It is
2.3.6 Locating Software Tools
A tool for RF connection set up, trouble-shooting and maintenance is recommended to
download and run from a site use laptop. Search online for a locating tool that will scan
all devices within a given subnet. The scanning tool would not be designed by or for KBC
Networks or KBC Networks products but many of these tools have been tested with KBC
Networks products. KBC Networks cannot be held responsible for any possible malicious
attacks due to online software downloads. For queries regarding the recommended
software tool, please contact KBC technical support.
Manual-MESH2HT-Rev1311
Copyright © KBC Networks 2012 Page 24 of 59 www.kbcnetworks.com

Mesh2HT User Manual
Default Password:
admin
3 Graphical User Interface
3.1 Accessing the Mesh2HT Graphical User Interface (GUI)
The Mesh2HT series provides a web browser based configuration system accessible by
either connecting directly to the Mesh2HT RF module through the PIM, via a Mesh2HT AP
connection to a client PC/laptop or over the Mesh2HT wireless connection.
3.1.1 Connecting to the Mesh2HT GUI using a PC
Mesh2HT can be powered via an 802.3af PoE switch or use the supplied 24VAC PSU
connected to the provided power injector module. If using the PIM, connect a straightthrough Ethernet cable from a computer’s LAN port to the “In” port on the PIM. Connect
a second straight-through Ethernet cable from the “Out” port on the PIM to the Mesh2HT
node. Connect the PSU to the PIM and verify the green LED illuminates on the PIM. The
right two green LEDs (Power and Network) of the Mesh2HT unit should also light up
indicating power and link activity (see section 2.2.4 for expected LED status). Due to
various port types, a crossover Ethernet cable may be required between the Ethernet
device and the “In” port on the PIM. KBC Networks recommends a crossover cable be
available during set up, troubleshooting and maintenance of the system.
3.1.2 Accessing the GUI via a Web Browser
The computer used to access the Mesh2HT GUI must be set to a static IP address on the
same subnet as the Mesh2HT unit. The Mesh2HT default configuration is on the
192.168.1.x subnet (refer to provided documentation for exact IP per unit Serial
Number) therefore the computer must also be set to a 192.168.1.x IP address if the unit
is still on its factory set configurations.
Default User Name: admin
Once the computer’s IP address is confirmed, open a web browser such as MS Internet
Explorer
of the web browser. If the IP is correct and the link activity is established, the browser
will prompt you to enter the user ID and password. The ID and password is “admin” /
“admin” (case sensitive).
®
or Mozilla Firefox®. Type in the node IP address in the address bar at the top
Manual-MESH2HT-Rev1311
Copyright © KBC Networks 2012 Page 25 of 59 www.kbcnetworks.com

Mesh2HT User Manual
3.2 Menu Options
The Mesh2HT has the following menu options:
DIAGNOSTICS
• Status
• Services
• System
• Topology
NETWORK
• Basic Network
ASIC NETWORK
B
• Radio 1
• Radio 2
ADVANCED WIRELESS
• Radio 1
• Radio 2
Manual-MESH2HT-Rev1311
Copyright © KBC Networks 2012 Page 26 of 59 www.kbcnetworks.com

Mesh2HT User Manual
3.2.1 DIAGNOSTICS
3.2.1.1 Status
The initial page displayed on the web browser GUI is the ‘Status’ screen.
Manual-MESH2HT-Rev1311
Copyright © KBC Networks 2012 Page 27 of 59 www.kbcnetworks.com

Mesh2HT User Manual
The individual sections and description are:
3.2.1.2 Status: Main
The ‘MAIN’ screen shows the Uptime, the host name and System Time information.
Uptime: This shows the number of hours and minutes since the last reboot or when
the system was initially powered up.
Host Name: This displays the chosen name of the device as set in the ‘SYSTEM’ menu.
3.2.1.3 Status: VERSION
he ‘Version’ screen shows the firmware version information.
T
Firmware Version: This is the firmware version on the Mesh2HT unit.
3.2.1.4 Status: LAN SETTING
The ‘LAN Setting screen shows the LAN MAC, Mode, IP Address, Gateway IP Address and
LAN cable information. These are set in the ‘NETWORK: Basic Network’ menu option.
LAN MAC: this is the unit’s own MAC address for the Ethernet LAN side of the device.
There are three MAC address per Mesh2HT unit; the radios also have their own MAC
addresses, these can be found under the Radio 1 and Radio 2 tabs.
Manual-MESH2HT-Rev1311
Copyright © KBC Networks 2012 Page 28 of 59 www.kbcnetworks.com

Mesh2HT User Manual
MODE: this shows whether the unit is either set to a static IP address or DHCP in the
‘Basic Network’ menu.
IP ADDRESS: this is the IP address of the unit. The address show above is the default
IP address for the unit.
GATEWAY IP ADDRESS: this is the Gateway IP address shown under the Basic
Network setting menu. If access is required to the Mesh2HT unit from outside of the
network then this could be the router address. This needs to be a pingable address on
the network for the Topology function to work correctly.
LAN cable: this shows whether there is a LAN cable connected or not.
3.2.1.5 Status : Radio 1 & Radio 2 Tabs
Details of the Mesh2HT unit accessed are recorded and appear on this status information
page. If either Radio 1 (R1) or Radio 2 (R2) is connected to another Mesh2HT, Mesh2HT
or other device, its MAC address and other link details will also appear. This page assists
in providing critical details needed for wireless link set up, trouble-shooting and/or
maintenance.
Client/Station Radio 1 tab:
Host/AP Radio 2 tab:
Manual-MESH2HT-Rev1311
Copyright © KBC Networks 2012 Page 29 of 59 www.kbcnetworks.com

Mesh2HT User Manual
Wireless Mode: This shows whether the radio is either set as a station WDS (Mesh2HT
client) or access point WDS (Mesh2HT host). As a default, Radio 1 is configured as a
client and Radio 2 is an host/AP.
Note: Host/APs and clients are pre-set in the factory and cannot be changed.
MAC: Each Ethernet device has a unique MAC (Media Access Control) address. This
number should be used to track and reference the Mesh2HT units.
LOCAL AP SSID: This displays the SSID (Service Set Identifier) chosen on the ‘BASIC
WIRELESS’ interface page. Each radio within one particular node should be assigned an
individual SSID.
TX CCQ:
Channel Width:
Frequency: This displays the frequency used for the host/AP to connect to the client.
The client will connect via the host/AP frequency selection based on either MAC address
lock and/or SSID.
Security: This displays the encryption method selected on the ‘BASIC WIRELESS’
interface page.
Ack Timeout:
Refresh: This button refreshes the “bytes”, “packets” and “errors” information as well
statistics from the connected client(s).
Antenna Alignment:
When a host radio and client radio are connected the client radio portion of the Status
page displays an alignment tool button. When using external directional antennas, the
Mesh2HT antennas need to be aligned to their respective mate. This tool can be used to
Manual-MESH2HT-Rev1311
Copyright © KBC Networks 2012 Page 30 of 59 www.kbcnetworks.com

Mesh2HT User Manual
identify the optimal mounting alignment.
Connected Stations: the number of connected devices is shown in parenthesis. When
R1 is connected to R2 of another Mesh2HT, Mesh2HT-AB series product or Mesh2HT-AA
series single point host/AP, the MAC address(es), Signal Strength(s), TX Rate(s), TX
CCQ(s), RX Rate(s) and Channel Width(s) will also be displayed. These are used to
identify if the signal strength and data rates are sufficient for a wireless connection
needed for a constant stream of video. In the screen shot below the important details
are highlighted and defined:
Note: A
client radio will show this section as ‘CONNECTED AP’ but will display all of the
same information for the AP radio connected to the client radio.
MAC Address: connected station / AP MAC address.
Signal Strength: This is the RSSI (Received Signal Strength Indication) ranging from 0-
100. The RSSI is the measure of the strength of the RF connection between radios. The
RSSI number in the screen shot above is ‘93’ with the numbers within the parenthesis
showing the RSSI’s for the vertical (92) and horizontal (91) portions of the radio (i.e. the
2x2 function of the MIMO). The vertical and horizontal RSSI figures can be used if two
separate directional antennas require individual alignment. Certain variables exist by
which this indicator is established. If line of sight, interference or other adverse site
specific conditions exist, the RSSI will be limited to a much lower number on the 0-100
scale. The RSSI in the above screen shot was attained when the radios were in very
close proximity on a bench test. When distance is increased between the radios and
other variables are introduced the number will drop significantly from the high numbers
shown. A reasonable RSSI for average deployments will be in the 40 to 50 range. A bare
minimum RSSI that KBC Networks recommends to maintain an RF link for constant
streaming video is no less than 20. If max TX and RX rates are established at lower
RSSIs then the system is performing as optimally as possible in a harsh RF environment.
Tx / Rx Rates: The rate of transmission and reception is auto-negotiated with the
opposite radio in the RF connection. The system attempts to establish a link at the
maximum rate of 162Mbps (in 40 MHz bandwidth) however, if the environment restricts
a connection at the maximum rate, the radios will attempt connection at the next lower
rate. It will continue to auto-negotiate the rate until a connection can be established.
Tx CCQ: Transmission client Connection Quality – this value, shown as a percentage,
shows how effective the transmitted bandwidth being used is compared to the theoretical
maximum bandwidth.
Manual-MESH2HT-Rev1311
Copyright © KBC Networks 2012 Page 31 of 59 www.kbcnetworks.com

Mesh2HT User Manual
Channel Width: The selected bandwidth from “BASIC WIRELESS” is shown. Other
options include HT5, HT10 and HT20. The larger the bandwidth the lower number of
channel options available to use.
Local AP Statistics: The transmitted and received data packets over the RF connection
are recorded and viewable here. Any error will also be captured. The refresh button will
update the transmission statistics.
Local AP Errors: Any additional error and/or collision in the wireless traffic when a host
is connected to a client or group of clients will be captured and displayed in this section
helping to identify the loss of data over the wireless link.
3.2.1.6 Status: More Status (Pull Down Menu)
The pull down menu for More Status is a quick link tool to various services diagnostic
tools. Each of the following is also covered under section 3.2.2 below.
Ping Utility:
Use to ping from within the Mesh2HT node interface.
ARP Table:
View the ARP Table. The ARP table is view only.
Bridge Table:
Select to view the wireless bridge table. Details described under section 3.2.2.4.
Manual-MESH2HT-Rev1311
Copyright © KBC Networks 2012 Page 32 of 59 www.kbcnetworks.com

Mesh2HT User Manual
3.2.2 Services
The ‘Services’ menu is where the tools to set-up trouble-shooting and maintenance are
found.
Manual-MESH2HT-Rev1311
Copyright © KBC Networks 2012 Page 33 of 59 www.kbcnetworks.com

Mesh2HT User Manual
3.2.2.1 Services: SPANNING TREE PROTOCOL (STP) SET UP
If the Mesh2HT topology involves redundant paths where there are loops in the network,
Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) must be enabled. Each node can be manually set as the
Root Bridge in order to identify the link STP will break. The lower the root priority, the
greater the significance of the link as it pertains to STP. If kept to default configurations,
STP will decide the broken link based on a few variables (which determine the highest
root priority number). When another previously established link goes down for some
reason, STP will then enable the link it broke in order to avoid the loop.
3.2.2.2 Services: PING WATCHDOG
The ping watchdog serves as an option to perform an automatic power cycle if the unit
loses connection to a particular IP address. As soon as the system can no longer ping an
IP on the network under the conditions for which it is set, the unit will reboot. When
enabled the system will begin pinging the IP entered after the given interval and will
function as configured. It must be configured to wait for a particular number of nonresponses (typically five) before rebooting. It will reboot then try the ping again. In the
example below (a picture of the default configurations) the unit will start to ping
192.168.1.1 after 60 seconds. Each ping can be set to the desired interval between
pings adding to or subtracting from the amount of time elapsed before failure responses
create the need for a reboot.
Note: t
he ping watch dog should never be used with a device that obtains its IP via
DHCP, it should only be used with devices using static IP addresses.
The main purpose for a ping watchdog is a quick solution to re-connect the RF link in the
event interference, a network issue or where some other site specific adverse condition
locks up a Mesh2HT node. Rebooting the device can clear ARP (Address Resolution
Protocol) tables or resolve other network issues that might have forced the unit to lock
up. Rebooting may temporarily solve the issue but may not address an actual network or
other site specific condition. The tool gives the ability to re-establish a wireless
connection and streaming video in the event the unit loses the RF link to its mate radio.
Though this tool limits down time it may only mask the greater environmental problems
at the site. KBC Networks recommends trouble-shooting all system and connection
issues before resorting to the ping watchdog tool.
Note: If the IP selected is not on the network, is not pow
ered up or some other issue
exists, the unit enabled with ping watchdog will continue to reboot until ping watchdog is
disabled. Please disable or reset the watchdog to a different IP in the event the
configured IP is known to be unreachable.
Manual-MESH2HT-Rev1311
Copyright © KBC Networks 2012 Page 34 of 59 www.kbcnetworks.com

Mesh2HT User Manual
3.2.2.3 Services: NETWORK PING
The network ping tool enables an IP address to be to be pinged from within the Mesh2HT
unit which can help to confirm an Ethernet cable connection between the Mesh2HT unit
and the Ethernet device it is connected to. This tool can ping any IP on the network
given that the wireless unit has an established connection either wirelessly or over cable.
Select the ‘Ping Utility’ button and the following screen will appear.
Insert the IP address under ‘Destination IP/HOST’. The packet count & size can be
changed to a desired number of ping attempts and length of packet. If ‘continuous’ is
selected, the ping attempts will continue until ‘Stop’ button below is clicked. Continuous
pings will determine when a device has reconnected after either being rebooted or
having left the network.
The sample IP above is a valid IP on the 192.168.1 subnet on the network. All five
attempts replied indicating that the connection to 192.168.1.15 from the Mesh2HT unit
which performed the ping is established.
3.2.2.4 Services: BRIDGE TABLE
The Bridge Table displays the MAC addresses of connected devices to the node. The table
will indicate whether the device is local to the node or if it is connected via the RF
connection through one of the WiFi radios.
Manual-MESH2HT-Rev1311
Copyright © KBC Networks 2012 Page 35 of 59 www.kbcnetworks.com

Mesh2HT User Manual
3.2.2.5 Services: Auto-Reboot
The Mesh2HT can be set to reboot automatically. This can be performed at a scheduled
time each day or after a given amount of time of operation.
By Hour
By selecting the ‘By Hour’ option, a number of hours can be inserted and the unit will
reboot after the particular number of hours of operation. It will quickly soft reboot and
will be available for reconnection. If its mate Mesh2HT is active, it will reconnect
automatically.
By Time
Insert the time (according to the internal Mesh2HT clock) at which the system will
reboot.
Note: t
he internal clock cannot be set to match real time.
Manual-MESH2HT-Rev1311
Copyright © KBC Networks 2012 Page 36 of 59 www.kbcnetworks.com

Mesh2HT User Manual
3.2.2.6 Services: SNMP SETUP
The system is compatible with SNMP version 2.
3.2.2.7 Services: NTP SETUP
Use this section to set the system to network time protocol. The node must be connected
to the web for NTP set up to take place. Each node connected via the wireless Mesh link
can also be set to the same NTP by using the identical NTP server and gateway IP.
Select the time zone of the node deployment and click the ‘Enable NTP client’ check box
and select from the pull down menu for ‘Known Time Server’. Ensure that all nodes
connected are using the same Known Time Server. Select <Apply> and <Save Changes>
to initiate the NTP Set Up.
3.2.2.8 Services: TELNET SERVER
Telnet is default enabled for port 23, the default standard for Telnet. If desired for
security reasons, this option can be disabled. Telnet allows unit configuration settings
and readings through command line without the use of the embedded webpages.
Manual-MESH2HT-Rev1311
Copyright © KBC Networks 2012 Page 37 of 59 www.kbcnetworks.com

Mesh2HT User Manual
3.2.2.9 Services: SYSTEM LOG
When enabled the system will begin logging connection status to the configured IP using
Telnet via the default log port 514. Results are viewed in Telnet.
3.2.3 System Configuration
The ‘System’ page allows certain configuration and upgrade changes to be performed to
the Mesh2HT system. KBC Networks recommends using the configuration backup to save
the settings of each unit once any custom configurations are complete.
Manual-MESH2HT-Rev1311
Copyright © KBC Networks 2012 Page 38 of 59 www.kbcnetworks.com

Mesh2HT User Manual
New password
example
:
“KBC
12345
”
3.2.3.1 System: FIRMWARE UPGRADE
To upgrade the Mesh2HT firmware, follow the procedures below:
1. Contact KBC Networks to get a firmware upgrade emailed to you.
2. Connect an Ethernet cable from the PIM attached to the Mesh2HT RF module to the
PC.
3. Access the Mesh2HT unit web browser interface and click on “SYSTEM”
4. Click on “Browse”
5. Search for the file in the location where it was saved (under step 1 above)
6. Click “UPGRADE” and the software will walk you through the remainder of the apply
and reboot process.
3.2.3.2 System: HOST NAME
In this menu option the unit can be given a customized name, this is then displayed in
the ‘Status’ page.
Example: If a Mesh2HT node is at camera # 2 the host name co
uld be ‘Camera 2’ or the
position of the camera such as ‘Lot 1’.
The host name is for identification purposes only; the node does not search for a mate
Mesh2HT by its name. The default is ‘AP’.
3.2.3.3 System: ADMINISTRATIVE ACCOUNT
This menu option is used to change the default administrator username and password.
The default settings for both of these are ‘admin’.
1. Insert the new administrator username.
2. Insert the existing password.
3. Choose a new password and enter it in the ‘New Password’ field
4. Confirm the new password in the “Verify New Password” field.
5. Click <Apply>.
6. Click <Save> next to ‘Save configuration changes’.
After changing the administrator username and password names the system will prompt
another request to insert the new password and administrator username. Enter the new
administrator name and password created in order to re-access the interface and
continue with any other configuration changes. Restoring to defaults will return the
username and password to “admin” / “admin” see section 3.2.3.5. for default settings.
The admin username can also be changed, it does
not need to be “admin” to change the password.
If default configuration, “admin”
Manual-MESH2HT-Rev1311
Copyright © KBC Networks 2012 Page 39 of 59 www.kbcnetworks.com

Mesh2HT User Manual
3.2.3.4 System: DEVICE MAINTENANCE
In this menu option the unit can be soft rebooted or reset to defaults.
Reboot: this performs a re-boot to the unit.
Reset to defaults: in this menu option the unit can be soft re-booted or reset to
defaults.
The default configurations are as follows:
LAN Configuration: 192.168.1.10
255.255.255.0
No Gateway IP
Interface Access Username: admin
Interface Access password: admin
Hostname: AP
Local AP-ESSID: KBC-Mesh2HT-2 (Radio 1)
KBC-Mesh2HT-1 (Radio 1)
ountry Code: USA, Canada (North America)
C
Select Country (all other countries)
Wireless Profile: NA (IEEE802.11n & IEEE802.11a)
NG (IEEE802.11n & IEEE802.11g)
NY (IEEE802.11n & IEEE802.11y)
Channel Spectrum Width: 20/40M
Channel-Frequency: set to auto-select
Transmit Power: 23 dBm (North America)
19 dBm (all other countries)
Local AP WPA Cipher: AES
Local AP Pre-shared Key: 11111111
Long Range Parameters: Enabled
RSSI LEDs: LED1=10; LED2=20; LED3=30; LED4=40
Note: i
f configurations (such as a LAN configuration or username/password) are lost, the
unit may need to be restored to defaults using the hard reset button on the bottom of
the unit case. If a restore is required, delete the old saved configuration file and create a
new one.
Manual-MESH2HT-Rev1311
Copyright © KBC Networks 2012 Page 40 of 59 www.kbcnetworks.com

Mesh2HT User Manual
3.2.4 Topology
The system mapping capability of the topology page enables end users to view system
configuration and health all on one page. Mesh2HT topology shows the links between
different station/clients and host/APs. System mapping supports dynamic changes in the
network so as the network changes it learns the new topology and updates this on the
topology webpage. In order to show an actual mapping topology, one network device
that is able to reply Ping (or a Mesh2HT unit), shall be configured with IP address
192.168.1.1
Along with system mapping, the topology view also displays all node information; this
can be viewed by holding your mouse over a particular node and radio. Node hover over
will display following node information:
• Node IP address
• Bridge MAC address
• Root bridge information
• Gateway information
• Radio up/down status
• Radio host/client role
• Connected peer information
Manual-MESH2HT-Rev1311
Copyright © KBC Networks 2012 Page 41 of 59 www.kbcnetworks.com

Mesh2HT User Manual
Link Color
RSSI Range
If any parameter eg. IP address , node name , SSID etc. changes then topology reports
updates accordingly.
Note: Only KBC Network nodes are shown on the topology page.
If any node goes down within the network then it is shown in red after 100 seconds
(default). If it then remains down for more than 200 seconds (default) the node entry
will be removed from topology view. When the node is reconnected to the network it will
be added back to the topology.
Link connection lines are shown in different colors, these represent different ranges of
RSSI and makes it easy to identify weak RF links.
Dark green 40dBm and above
Light green 40dBm to 30dBm
Yellow 30dBm to 20dBm
Orange 20dBm to 10dBm
Red 10dBm and lower
Hashed Indicated STP blocked port
The Mesh2HT system mapping tool works with STP enabled as well as STP disabled. The
Root bridge is shown by a green dot and if the Root bridge is lost then this is shown as a
red dot. All wired links are shown as black lines.
Maps can be imported as a background in either JPEG or GIF format. Nodes can then be
moved around on the uploaded map to show them in their physical locations.
If you double click on a node then the embedded UI can be accessed.
The Refresh button can be used to refresh the topology page manually however it is
automatically refreshed every 60 seconds.
The following browsers are supported:
• Firefox version 21 or later
• Internet Explorer: 9.0, 8.0
• Safari: 5.1.5, 5.1.7
.2.4.1 System Topology Setup
3
Step 1: All nodes within the network need to have a gateway address set on the
NETWORK - Basic Network page. This gateway must be a ping-able network device that
is connected to any one of the system node’s Ethernet port. It does not have to be an
actual gateway just a pingable device – for setting up this can be the PC you are
connected to, you will also need to turn off the firewall on the PC too. The system
Manual-MESH2HT-Rev1311
Copyright © KBC Networks 2012 Page 42 of 59 www.kbcnetworks.com

Mesh2HT User Manual
network device
mapping uses ping to the gateway as a mechanism for a low bandwidth means to
confirm system connectivity. If the system map were to be viewed from outside the
network, then this will be an actual gateway.
ep 2: Once the Mesh2HT system can been configured and properly connected, a
St
generic system map will be drawn like the one below:
Set this to a pingable
Manual-MESH2HT-Rev1311
Copyright © KBC Networks 2012 Page 43 of 59 www.kbcnetworks.com

Mesh2HT User Manual
Note: a router symbol is used to represent the gateway. At this point, all nodes have the
same gateway IP address which is set to the gateway shown connected to the Node 1
Step 3: A background image can be uploaded by selecting the <Browse> button and
uploading the desired background image.
Note: the image size is limited to 120kB and must be in a JPEG or GIF format. The
topology page will auto size to fit the uploaded image
Step 4: Once an image has been selected, select the <Upload>
button. It will take
approximately 20 seconds to upload and render the background image.
Step 5: Move the Mesh2HT nodes around on the page to represe
nt their physical
locations as shown below:
Manual-MESH2HT-Rev1311
Copyright © KBC Networks 2012 Page 44 of 59 www.kbcnetworks.com

Mesh2HT User Manual
Step 6: Once the image has been loaded and the nodes moved, select <Save> to store
the page configurations in nonvolatile memory.
Note: The mouse hover over feature will display details for the radio as shown below:
Note: Each node has 2 radios and details for each radio ar
e displayed separately.
Hovering the pointer over the top half of the node will render details for Radio1 and the
bottom half will display details for Radio2.
3.2.5 NETWORK
3.2.5.1 Basic Network
The ‘Basic Network’ menu option allows the LAN IP, subnet mask and Gateway IP to be
set as either static IPs on the network or configured automatically by a DHCP server.
Manual-MESH2HT-Rev1311
Copyright © KBC Networks 2012 Page 45 of 59 www.kbcnetworks.com

Mesh2HT User Manual
3.2.5.2 Basic Network: LOCAL AREA NETWORK
LAN Configuration example from the host/AP (Default Configuration):
LAN Mode: This can be set to either DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) or
Static to allow the LAN IP, subnet mask and Gateway IP to be set as either static IPs on
the network or configured automatically.
If Static is selected enter the LAN IP, Netmask and Gateway IP using an available IP on
the network. KBC Networks recommends obtaining valid unused IPs from the network
administrator if the units will reside on the network. The Mesh2HT units can connect
independently from the network structure and are not required to be configured as static
IPs within the network subnet.
If DHCP is selected the LAN configuration will be set dynamically according to the
network availability. When DHCP is selected, the IP Address, Netmask and Gateway IP
configuration area will be grayed out to prohibit custom LAN settings being entered as
they will be obtained through the network. Once DHCP is saved an IP searching tool will
be required to determine the Mesh2HT unit IP address. A locator tool which shows the
hostname can be used to distinguish the IP from other IP addresses on the network.
Manual-MESH2HT-Rev1311
Copyright © KBC Networks 2012 Page 46 of 59 www.kbcnetworks.com

Mesh2HT User Manual
3.2.5.3 Basic Network: Bandwidth Control
The Mesh2HT system can control throughput into the LAN port to the radio as well as out
of the radio to the LAN port based on desired throughput configurations. Default setting
is 1 Mbps for each selection.
3.2.6 BASIC WIRELESS: Radio 1 & Radio 2
Channel frequency selection and bandwidth options are set within the Basic Wireless
menu option. The host/AP will connect to a client provided that the SSID, MAC Lock (if
applicable) and Country Code settings are the same.
3.2.6.1 BASIC WIRELESS SETTINGS
This menu option shows the default settings.
The default setting Radio 1 is a client/station.
Manual-MESH2HT-Rev1311
Copyright © KBC Networks 2012 Page 47 of 59 www.kbcnetworks.com

Mesh2HT User Manual
The default setting for Radio 2 is an access point/host.
Manual-MESH2HT-Rev1311
Copyright © KBC Networks 2012 Page 48 of 59 www.kbcnetworks.com

Mesh2HT User Manual
Wireless Mode: this can be either a client/station or access point/host. In the AP/host
mode the unit will connect with remote radios from Mesh2HT nodes which are
configured as clients assuming that SSID, Spectrum Width and Country Code matches.
Local AP-ESSID: This is the area in which the SSID is configured if a custom SSID is
desired.
Hide SSID: If the SSID should not be broadcast for other clients to see it can be hidden
by selecting this box. The AP’s MAC address will still appear in AP lists but will not show
the SSID.
Country Code: Select the country in which the system will be deployed. The radio will
then transmit under the legal operation for that particular regulatory domain. Any
restricted channels will no longer be available for static selection and power output will
also be tailored to the regulations of the local country. If using an external antenna, use
only the power output regulated per dB gain of the antenna.
Note: A
Country Code selection is not required for North America.
Wireless Profile: Depending on the unit you have purchased this will be either:
‘NA’ to show that the system is working to IEEE802.11a and IEEE 802.11n (5Ghz
operation and using MIMO technology).
‘NG’ to show that the system is working to IEEE802.11g and IEEE802.11n specifications
(2.4GHz operation and using MIMO technology).
‘NY’ to show that the system is working to IEEEE802.11y and IEEEE802.n specifications
(4.9GHz operation and using MIMO technology).
Channel Spectrum Width: Channel availability is based on the spectrum width. With
larger spectrum width comes additional throughput capability. With less spectrum width,
more channels are available, however with less throughput and there is a greater chance
of frequency bleed-over.
Manual-MESH2HT-Rev1311
Copyright © KBC Networks 2012 Page 49 of 59 www.kbcnetworks.com

Mesh2HT User Manual
Below is a chart to show the potential throughput based on spectrum width:
MCS
Index
Spatial
Streams
Modulation
Type
Coding
Rate
Data Rate (Mbps)
20 MHz Channel 40 MHz Channel
800 ns
GI
400 ns
GI
800 ns
GI
400 ns
GI
8 2 BPSK 1/2 13.00 14.40 27.00 30.00
9 2 QPSK 1/2 26.00 28.90 54.00 60.00
10 2 QPSK 3/4 39.00 43.30 81.00 90.00
11 2 16-QAM 1/2 52.00 57.80 108.00 120.00
12 2 16-QAM 3/4 78.00 86.70 162.00 180.00
13 2 64-QAM 2/3 104.00 115.60 216.00 240.00
14 2 64-QAM 3/4 117.00 130.00 243.00 270.00
15 2 64-QAM 5/6 130.00 144.40 270.00 300.00
Where:
MCS: Modulation and Coding Scheme
Spatial Streams: all Mesh2HT radios are 2x2
Modulation Types:
BPSK= Binary Phase-Shift Keying
QPSK= Quadrature Phase-Shift Keying
QAM= Quadrature Amplitude Modulation
Coding Rate: Useful proportion of the data-stream
Channel Frequency:
Automatic: This facility is only on the host/AP. To do this select the Basic Wireless
option and ensure that the ‘Auto’ box next to the Channel-Frequency is ticked. The
frequencies available to be automatically selected will be based on both the Country
Code and Spectrum Width chosen.
Manual setting: the frequency can also be selected manually, this is necessary if there
are more than one Mesh2HT links on a site. It is recommended that an Interference
Analyzer survey is conducted to determine which frequencies are the least congested to
use. See the Interference Analyzer section below for details.
Setting the Host / AP frequency:
On the host/AP radio in the Basic Wireless: Radio 2 (default is Radio 2) option use the
drop down menu to choose a unique frequency for the link you are setting up.
Frequencies available will depend on the Country Code & Spectrum Width selected. Once
a frequency has been chosen, select <Apply Settings>.
Note: o
n the EMEA firmware versions you can choose whether to include the 5600 –
5650MHz band. If these frequencies are included, the link connection time can increase
to 10 minutes due to Dynamic Frequency Selection (DFS) regulations see page 8.
Manual-MESH2HT-Rev1311
Copyright © KBC Networks 2012 Page 50 of 59 www.kbcnetworks.com

Mesh2HT User Manual
Setting the Client / Station frequency:
The client obtains its frequency from its connected host/AP. To ensure that a particular
client connects to a certain host/AP, the SSID, Country Code and Channel Width setting
need to be the same as the host/AP unit to which the unit wishes to connect to.
Interference Analyzer: The ‘Interference Analyzer’ facility is located on the host/AP
and can be used to determine whether there are other pieces of equipment in the vicinity
using the same frequencies as the Mesh2HT units are using. By carrying out an
interference analyzer survey, congested channels can be avoided when selecting
channels manually.
Note: S
urveys to detect interference should only be conducted when directly connected
to the host/AP, if connected to the host/AP via the client over a wireless link, the link will
be disconnected.
To carry out a frequency site survey select <Interference Analyzer>. The Interference
Analyzer is only found on the host/AP and is only available if a channel width of either
20M or 20/40MHz is selected.
Example: In the example, the 5GHz frequency band is shown wi
th green color bars to
indicate the other APs that are in the environment. As the color bar becomes larger it
changes from green to red to indicate the stronger RSSI of other equipment and greater
chance for interference if operating on that channel. You can hover your mouse over to
see the other APs using those frequencies.
Manual-MESH2HT-Rev1311
Copyright © KBC Networks 2012 Page 51 of 59 www.kbcnetworks.com

Mesh2HT User Manual
Transmit Power: the Transmit Power option allows the output power to be adjusted.
There is no default setting since different regions require different levels. It is often
advisable to reduce this for short distance links. The picture below shows the power
output options:
The maximum transmit power available is 23dBm in North American and 19dBm in other
countries. Please check legal requirements according to the local regulatory domain for
use with high gain parabolic, patch sector or other antenna types.
If higher gain antennas are required, please consult KBC Networks.
Note: I
t is the responsibility of the user to operate the system under the local regulatory
domain requirements. KBC Networks recommends researching the regulations prior to
deploying a license-free wireless system.
3.2.6.2 Basic Wireless: Local AP
The Local AP section is used to configure the host/AP radio as an access point in order to
connect using a laptop/PC via WiFi connection. This section is also used for the preshared key connection data for an AP radio and client radio to connect. If the pre-shared
key and other encryption details do not match, the two radios will not connect. For any
device (including a laptop/tablet/phone) to obtain access via WiFi AP, it must be
configured to the security (WPA2) and cipher type (AES is default configuration)
selected. The SSID will appear in the computer’s available APs list unless ‘Hide SSID’ is
selected. Once the Mesh2HT host/AP is selected the WPA Pre-shared Key must be
entered as the AP password. The default configuration is 11111111 but it can be set to
any desired pre-shared key.
3.2.7 ADVANCED WIRELESS: Radio 1 & Radio 2
This section can be used to alter the long range parameters of the link, this is necessary
Manual-MESH2HT-Rev1311
Copyright © KBC Networks 2012 Page 52 of 59 www.kbcnetworks.com

Mesh2HT User Manual
for wireless link lengths exceeding 1.6km/1mile and also to alter the value of the signal
strengths of the RSSI LEDs located on the back of the Mesh2HT units.
3.2.7.1 ADVANCED WIRELESS: LONG RANGE PARAMETERS
I tis recommended that for all links over 1.6km/1mile the long range parameters must
be set. In the example below, the Mesh2HT unit is configured for a 1600m/1 mile
connection. Both host/AP and client units must be configured for the distance
parameters:
Manual-MESH2HT-Rev1311
Copyright © KBC Networks 2012 Page 53 of 59 www.kbcnetworks.com

Mesh2HT User Manual
When setting the long range parameters, first set the distance in metres, and then press
<Calculate>. This will refresh the slot time, ACK and CTS timeout values. Once these
fields have been updated, press <Apply Settings> then <Save>.
3.2.7.2 Advanced Wireless: OTHER SETTINGS
Noise Immunity:
Signal Strength Indicator (RSSI):
The following are the default RSSI LED configurations. These parameters can be changed
to any desired RSSI (0 through 100).
Note: t
he RSSI LED indicators are only associated to Radio 1.
Manual-MESH2HT-Rev1311
Copyright © KBC Networks 2012 Page 54 of 59 www.kbcnetworks.com

Mesh2HT User Manual
4 Troubleshooting
4.1 Visual Inspection
If the Mesh2HT antennas can be accessed, the status LEDs can be investigated to
determine if there is an obvious answer to the problem.
4.1.1 LED Status
If the Link Activity LED is not illuminated then the Mesh2HT RF Module does not sense
an established cable link from the Ethernet device through the PIM to the Mesh2HT unit.
Check all cables and connectors as well as connections into and out of the PIM. For
instance, if the “Data In” side of the PIM is connected to the Mesh2HT, the device will
receive its power but the Link Activity LED will not be on.
If all four of the RSSI LEDs are not lit then radio 1 link may be unsatisfactory or is not
used. If one or more of the RSSI LEDs are lit but some are not illuminated then the link
may be obstructed, channel selection is needed or alignment is necessary. If connecting
long range, visit the “Long Range Parameters” in the GUI for the host/AP and client and
insert the approximate distance in meters. See section 3.2.6.1.
4.1.1.1 Increasing Signal Strength
In some cases a suitable RSSI can only be achieved by using the external directional
antennas. The external antennas are a much higher gain antenna than the supplied
omni-directional antennas.
4.1.1.2 External Directional Antenna Alignment
Alignment is recommended and in some cases, critical, for directional antennas. KBC
external directional antennas come with the same hardware kit as the kit supplied with
the Mesh2HT node. Below is the recommended procedure for alignment:
• Assemble the mounting kit (see section 2.3.2.1 for d
• Attach the directional antenna to the antenna base plate piece of the mounting arm.
• Keep left/right and up/down swivel pieces just loose enough to move in the desired
direction.
• Access the Mesh2HT node user interface to which the antenna is connected and view
the status information page for the particular radio’s signal strength to be adjusted.
Radio 1 uses the top antenna ports and Radio 2 uses the lower two ports.
• If the radio in question is an access point, view the “CONNECTED STATIONS” section
of the status information detail and note the signal strength indication. The number
outside of the parenthesis is the important number. As the alignment process is
carried through, the higher the signal strength (or RSSI), the more fine-tuned the
alignment has become. The RSSI LEDs on the node case will reflect the Radio 1 RSSI
figure as configured on the Advanced Wireless screen.
• To align the antenna, face the plastic white portion which has the KBC logo in the
direction of its configured mate. Move the antenna downward slightly and refresh the
status information page to see the impact of alignment upon the RSSI. Refresh the
browser a few more times before moving the antenna again. Continue moving the
antenna downward and refreshing the browser until the RSSI is significantly lower
than the best position found. Return the antenna upward to the position of the
strongest signal.
• Tighten the up/down alignment piece and perform the
left/right alignment to find the over-all strongest RSSI.
etails) and fix to a pole or mast.
same procedure for the
Manual-MESH2HT-Rev1311
Copyright © KBC Networks 2012 Page 55 of 59 www.kbcnetworks.com

Mesh2HT User Manual
up / down
Side view of mounting assembly with pivot points shown.
Note: F
or fine-tuned up/down alignment the loner bolt and star washer should be used.
L / R
4.2 Test Cable Connections
4.2.1 Determine Link Activity
Obtain an IP locating device and search for the Mesh2HT node address. First attempt to
locate and/or ping the locally connected Mesh2HT device then attempt to ping the
remote Mesh2HT node. If the pings reply then the link is established to the local unit. If
the ping does not reply or the GUI is not accessible for the remote Mesh2HT antenna
then access the GUI for the local device and try the ping from within the Mesh2HT.
Note: T
subnet as the LAN address of the Mesh2HT node. The Windows Firewall may need to be
disabled as well.
he computer used for ping requests must be set to a static IP on the same
4.2.2 Test Wireless Device over Cable (without the Mesh2HT)
A bench test is always recommended to test the wirelessly connected devices over a
cable connected link. This verifies that the devices in line with the Mesh2HT are
operating. In addition, a test with the Mesh2HT in line while transmitting in a sterile
environment will help to ensure that the wireless system is working properly.
4.3 GUI Tools
See section 3 for the diagnostic tools available. Contact KBC Networks for technical
assistance.
Manual-MESH2HT-Rev1311
Copyright © KBC Networks 2012 Page 56 of 59 www.kbcnetworks.com

Mesh2HT User Manual
4.4 KBC Technical Assistance
Technical Support Availability
KBC offers technical support over the phone or by e-mail to all KBC integrators, dealers
and end users of the Mesh products.
NORTH AMERICA
Our technical support hotline is available during regular US west coast business hours,
Monday through Friday on all non-major holiday business days. KBC will follow up on all
electronic inquiries before the end of the following business day.
+1 888-366-4276: Monday – Friday 10am-8pm Eastern (7am-5pm Pacific) (Toll-free)
techsupport@kbcnetworks.com: 24hr availability, response time varies
HAWAII & ALASKA / GUAM, PR & OTHER US TERRITORIES
+1 949-297-4930: Monday – Friday 7am-5pm Pacific Time
techsupport@kbcnetworks.com: 24hr availability, response time varies
Note: the toll free 888# does not work from Alaska
CENTRAL / SOUTH AMERICA
latamtechsupport@kbcnetworks.com: 24hr availability, response time varies
ASIA
apactechsupport@kbcnetworks.com: 24hr availability, response time varies
SOUTH PACIFIC / PACIFIC ISLANDS
apactechsupport@kbcnetworks.com: 24hr availability, response time varies
EUROPE
+44(0)1622 618787: Monday – Friday 9am-5pm UK time
emeatechsupport@kbcnetworks.com: 24hr availability, response time varies
AFRICA & MIDDLE EAST
emeatechsupport@kbcnetworks.com: 24hr availability, response time varies
Technical support is offered in English; however, KBC Networks has worldwide
representatives who can provide technical support in many local languages.
Note: technical assistance is available after having read through this manual.
Comprehension of terms and topics will assist in trouble-shoot procedures.
Manual-MESH2HT-Rev1311
Copyright © KBC Networks 2012 Page 57 of 59 www.kbcnetworks.com

Mesh2HT User Manual
5 Warranty
5.1 Warranty Information
KBC extends the following LIMITED WARRANTY to the original owner/purchaser of this
product as follows:
- Five years from the date of initial sale for Ethernet switches.
- Two years from the date of initial sale for all wireless and other network products.
- Five years from the date of initial sale for all fiber products.
2) If, within the specified warranty period, this product, or any part or portion thereof,
shall prove upon examination by KBC, to be defective in material or workmanship, KBC
will repair or replace such part or portion at KBC’s option. The warranty period on the
repaired or replaced part or portion of this product shall be limited to the unexpired term
of the original warranty. The buyer shall be responsible for all shipping and
transportation of the product to KBC for any performance under this warranty.
3) Conditions and Exceptions:
a) Any accident to this product, any misuse or abuse, alternation, use in modified form,
or any attempt to repair this product shall void this warranty. These conditions to the
warranty include, but are not limited to, incorrect power connections, physical damage
due to mechanical shock, exposure to moisture, and circuit modification.
b) SHOULD THIS PRODUCT PROVE DEFECTIVE FOLLOWING PURCHASE, THE BUYER,
NOT THE MANUFACTURER, DISTRIBUTOR, OR RETAILER, ASSUMES THE ENTIRE COST
OF ALL SERVICING OR REPAIR, EXCEPT AS OTHERWISE PROVIDED BY THE TERMS OF
THIS WARRANTY.
c) FOR BREACH OF ANY WRITTEN OR IMPLIED WARRANTY ON THIS PRODUCT, THE
BUYER IS LIMITED TO THE FOLLOWING DAMAGES. (1) THE COST OF LABOR TO REPAIR
OR REPLACE DEFECTIVE PARTS OR PORTIONS OF THIS PRODUCT, AND (2) THE COST OF
THE REPAIRED OR REPLACE PARTS OR PORTIONS OF THIS PRODUCT.
d) NO OTHER EXPRESSED OR IMPLIED WARRANTIES HAVE BEEN MADE OR WILL BE
MADE ON BEHALF OF KBC WITH RESPECT TO THE SALE, REPAIR, INSTALLATION,
OPERATION, OR REPLACEMENT OF THIS PRODUCT. KBC DISCLAIMS ANY IMPLIED
WARRANTY OF MERCHANTABILITY OF THIS PRODUCT OR ITS FITNESS FOR ANY
PURPOSE, AND THE BUYER AGREES THAT THIS PRODUCT IS SOLD “AS IS” AND THAT
THE ENTIRE RISK OF QUALITY AND PERFORMANCE OF THIS PRODUCT IS WITH THE
BUYER, EXCEPT AS OTHERWISE PROVIDED BY THE TERMS OF THIS WARRANTY.
e) Some states/jurisdictions do not allow exclusions or limitations of incidental or
consequential damages, or limitations on how long an implied warranty lasts, so the
above exclusions or limitations may not apply to you.
f) If you do not wish to be bound by any of the provisions in this warranty, please return
the product(s) immediately.
4) Contact your dealer regarding return authorizations for out of warranty repairs and
any further product information.
This warranty does not apply in Australia.
Manual-MESH2HT-Rev1311
Copyright © KBC Networks 2012 Page 58 of 59 www.kbcnetworks.com

data delivered
KBC Networks North America.
25691 Atlantic Ocean Drive
Mesh2HT User Manual
Suite 3B
Lake Forest, CA 92630
U.S.A
Phone: 1 949 297 4930
Fax: 1 949 297 4933
Email: info@kbcnetworks.com
KBC Networks Ltd. EMEA
KBC Networks Ltd.
Barham Court
Teston, Maidstone
Kent, ME18 5BZ
United Kingdom
Phone: +44(0)1622 618787
Email: emeainfo@kbcnetworks.com
Asia Office
BC Networks
K
Phone: +65 97475123
Email: apacinfo@kbcnetworks.com
Web: www.kbcnetworks.com
Manual-MESH2HT-Rev1311
Copyright © KBC Networks 2012 Page 59 of 59 www.kbcnetworks.com
 Loading...
Loading...