Page 1

BRUTE FORCE 750 4×4i
KVF 750 4×4
All Terrain Vehicle
Service Manual
Page 2

Page 3
Quick R eference Guide
General Information 1 j
Periodic Maintenance 2 j
Fuel System 3 j
Cooling System 4 j
Engine Top End 5 j
Converter System 6 j
Recoil Starter 7 j
Engine Lubrication System 8 j
This quick reference guide will assist
you in locating a desired topic or procedure.
•Bend the pages back to match the
black tab of the desired chapter number with the black tab on the edge at
each table of contents page.
•Refer to the sectional table of contents
for the exact pages to locate the specific topic required.
Engine Removal/Installation 9 j
Crankshaft/Transmission 10 j
Wheels/Tires 11 j
Final Drive 12 j
Brakes 13 j
Suspension 14 j
Steering 15 j
Frame 16 j
Electrical System 17 j
Appendix 18 j
Page 4

Page 5

BRUTE FORCE 750 4×4i
KVF 750 4×4
All Terrain Vehicle
Service Manual
All r ights reserved. No parts of this publication may be reproduced, stored in a retrieval system, or
transmitted in any form or by any means, electronic mechanical photocopying, recording or otherwise,
without the prior written permission of Quality Assurance Department/Consumer Products & Machinery
Company/Kawasaki Heavy Industries, Ltd., Japan.
No liability can be accepted for any inaccuracies or omissions in this publication, although every possible
care has been taken to make it as complete and accurate as possible.
The right is reserved to make changes at any time without prior notice and without incurring an obligation
to make such changes to products manufactured previously. See your dealer for the latest information on
product improvements incorporated after this publication.
All information contained in this publication is based on the latest product information available at the time
of publication. Illustrations and photographs in this publication are intended for reference use only and may
not depict actual model component parts.
© 2004 Kawasaki Heavy Industries, Ltd. Second Edition (1) : Jul. 6, 2004
Page 6
LIST OF ABBREVIATIONS
A
ABDC after bottom dead center
AC alternating current min minute(s)
ATDC after top dead center N newton(s)
BBDC before bottom dead center Pa pascal(s)
BDC bottom dead center PS horsepower
BTDC before top dead center psi pound(s) per square inch
°C degree(s) Celcius r revolution
DC direct current rpm revolution(s) per minute
F farad(s) TDC top dead center
°F degree(s) Fahrenheit TIR total indicator reading
ft foot, feet V volt(s)
g gram(s) W watt(s)
h hour(s) Ω ohm(s)
L liter(s)
ampere(s)
lb
m
pounds(s)
meter(s)
Read OWNER’S MANUAL before operating.
Page 7

EMISSION CONTROL INFORMATION
To protect the environment in which we all live, Kawasaki has incorporated crankcase emission
(1) and exhaust emission (2) control systems in compliance with applicable regulations of the
California Air Resources Board.
1. Crankcase Emission Control System
A sealed-type crankcase emission control system is used to eliminate blow-by gases. The blow
-by gases are led to the breather chamber through the crankcase. Then, it is led to the air cleaner.
Oil is separated from the gases while passing through the inside of the breather chamber from
the crankcase, and then returned back to the bottom of crankcase.
2. Exhaust Emission Control System
The exhaust emission control system applied to this engine family is engine modifications that
consist of a modified carburetor and an ignition system having optimum ignition timing characteristics.
The carburetor has been calibrated to provide lean air/fuel mixture characteristics and optimum
fuel economy with a suitable air cleaner and exhaust system.
A maintenance free ignition system provides the most favorable ignition timing and helps main-
tain a thorough combustion process within the engine which contributes to a reduction of exhaust
pollutants entering the atmosphere.
The Clean Air Act, which is the Federal law covering motor vehicle pollution, contains what is
commonly referred to as the Act’s " tampering provisions."
"Sec. 203(a) The following acts and the causing thereof are prohibited...
(3)(A) for any person to remove or render inoperative any device or element of design installed
on or in a motor vehicle or motor vehicle engine in compliance with regulations under this
title prior to its sale and delivery to the ultimate purchaser, or for any manufacturer or dealer
knowingly to remove or render inoperative any such device or element of design after such
sale and delivery to the ultimate purchaser.
(3)(B) for any person engaged in the business of repairing, servicing, selling, leasing, or trading
motor vehicles or motor vehicle engines, or who operates a f leet of m otor vehicles knowingly to remove or render inoperative any device or element of design installed on or in a
motor vehicle or motor vehicle engine in compliance with regulations under this title following its sale and delivery to the ultimate purchaser..."
NOTE
The phrase "remove or render inoperative any device or element of design" has been generally
○
interpreted a s follows :
1. Tampering does not include the temporary removal or rendering inoperative of devices or elements of design in o rder to perform maintenance.
2. Tampering could include:
a.Maladjustment of vehicle components such that the emission standards are ex-
ceeded.
b.Use of replacement parts or accessories which adversely affect the performance
or durability of the vehicle.
c.Addition of components or accessories that result in the vehicle exceeding the stan-
dards.
d.Permanently removing, disconnecting, or rendering inoperative any component or
element of design of the emission control systems.
WE RECOMMEND THAT ALL DEALERS OBSERVE THESE PROVISIONS OF FEDERAL LAW,
THEVIOLATIONOFWHICHISPUNISHABLEBYCIVILPENALTIESNOTEXCEEDING
$10,000 PER VIOLATION.
Page 8

PLEASE DO NOT TAMPER WITH NOISE CONTR OL SYSTEM
(US MODEL only)
To minimize the noise emissions from this product, Kawasaki has equipped it with effective
intake and exhaust silencing systems. They are designed to give optimum performance while
maintaining a low noise level. Please do not remove these systems, or alter them in any which
results in an increase in noise level.
Page 9

Foreword
This manual is designed primarily for use by
trained mechanics in a properly equipped shop.
However, it contains enough detail and basic information to make it useful to the owner who desires to perform his own basic maintenance and
repair work. A basic knowledge of mechanics,
the proper use of tools, and workshop procedures must be understood in order to carry out
maintenance and repair satisfactorily. Whenever the owner has insufficient experience or
doubts his ability to do the work, all adjustments, maintenance, and repair should be carried out only by qualified mechanics.
In order to perform the work efficiently and
to avoid costly mistakes, read the text, thoroughly familiarize yourself with the procedures
before starting work, and then do the work carefully in a clean area. Whenever special tools or
equipment are specified, do not use makeshift
tools or equipment. Precision measurements
can only be made if the proper instruments are
used, and the use of substitute tools may adversely affect safe operation.
For the duration of the warranty period,
we recommend that all repairs and scheduled
maintenance be performed in accordance with
this service manual. Any owner maintenance or
repair procedure not performed in accordance
with this manual may void the warranty.
To get the longest life out of your vehicle:
Follow the Periodic M aintenance Chart in the
•
Service Manual.
Be alert for problems and non-scheduled
•
maintenance.
Use proper tools and genuine Kawasaki Vehi-
•
cle parts. Special tools, gauges, and testers
that are necessary when servicing Kawasaki
vehicles are introduced by the Special Tool
Catalog or Manual. Genuine parts provided
as spare parts are listed in the Parts Catalog.
Follow the procedures in this manual care-
•
fully. Don’t take shortcuts.
Remember to keep complete records of main-
•
tenance and repair with dates and any new
parts installed.
How to Use This Manual
In this manual, the product is divided into
its major systems and these systems make up
the manual’s chapters. The Quick Reference
Guide shows you all of the product’s system
and assists in locating their chapters. Each
chapter in turn has its own comprehensive Table of Contents.
For example, if you want ignition coil information, use the Quick Reference Guide to locate
the Electrical System chapter. Then, use the
Table of Contents on the first page of the chapter to find the Ignition Coil section.
Whenever you see these WARNING and
CAUTION symbols, heed their instructions!
Always follow safe operating and maintenance
practices.
WARNING
This warning symbol identifies special
instructions or procedures which, if not
correctly followed, could result in per-
sonal injury, or loss of life.
CAUTION
This caution sym bol identifies special
instructions or procedures which, if not
strictly observed, could result in dam-
age to or destruction of equipment.
This m anual contains four more symbols (in
addition to WARNING and CAUTION) which will
help you distinguish different types of information.
NOTE
This note symbol indicates points of par-
○
ticular interest for more efficient and con-
venient operation.
Indicates a procedural step or work to be
•
done.
Indicates a procedural sub-step or how to do
○
the work of the procedural step it follows. It
also precedes the text of a NOTE.
Indicates a conditional step or what action to
take based on the results of the test or inspec-
tion in the procedural step or sub-step it fol-
lows.
In most chapters an exploded view illustration
of the system components follows the Table of
Contents. In these illustrations you will find the
instructions indicating which parts require specified tightening torque, oil, grease or a locking
agent during assembly.
Page 10

Page 11

GENERAL INFORMATION 1-1
General Information
Table of Contents
Before Servicing ..................................................................................................................... 1-2
Model Identification................................................................................................................. 1-7
General Specifications............................................................................................................ 1-8
Unit Conversion Table ............................................................................................................ 1-11
1
Page 12
1-2 GENERAL INFORMATION
Before Servicing
Before starting to perform an inspection service or carry out a disassembly and reassembly operation on a vehicle, read the precautions given below. To facilitate actual operations, notes, illustrations, photographs, cautions, and detailed descriptions have been included in each chapter wherever
necessary. This section explains the items that require particular attention during the removal and
reinstallation or disassembly and reassembly of general parts.
Especially note the following:
Battery Ground
Before completing any service on the vehicle, disconnect
the battery wires from the battery to prevent the engine from
accidentally turning over. Disconnect the ground wire (–)
first and then the positive (+). When completed with the
service, first connect the positive (+) wire to the positive
(+) terminal of the battery then the negative (–) wire to the
negative terminal.
Edges of Parts
Lift large or heavy parts wearing gloves to prevent injury
from possible sharp edges on the parts.
Solvent
Use a high-flush point solvent when cleaning parts. High
-flush point solvent should be used according to directions
of the solvent manufacturer.
Cleaning vehicle before disassembly
Clean the vehicle thoroughly before disassembly. Dirt or
other foreign materials entering into sealed areas during vehicle disassembly can cause excessive wear and decrease
performance of the vehicle.
Page 13
Before Servicing
Arrangement and Cleaning of Removed Parts
Disassembled parts are easy to confuse. Arrange the
parts according to the order the parts were disassembled
and clean the parts in order prior to assembly.
Storage of Removed Parts
After all the parts including subassembly parts have been
cleaned, store the parts in a clean area. Put a clean cloth
or plastic sheet over the parts to protect from any foreign
materials that may collect before re-assembly.
GENERAL INFORMATION 1-3
Inspection
Reuse of worn or damaged parts may lead to serious accident. Visually inspect removed parts for corrosion, discoloration, or other damage. Refer to the appropriate sections
of this manual for service limits on individual parts. Replace
the parts if any damage has been found or if the part is beyond its service limit.
Replacement Parts
Replacement Parts must be KAWASAKI genuine or
recommended by KAWASAKI. Gaskets, O-rings, Oil seals,
Grease seals, circlips or cotter pins must be replaced with
new ones whenever disassembled.
Assembly Order
In most cases assembly order is the reverse of disassembly, however, if assembly order is provided in this Service
Manual, follow the procedures given.
Page 14
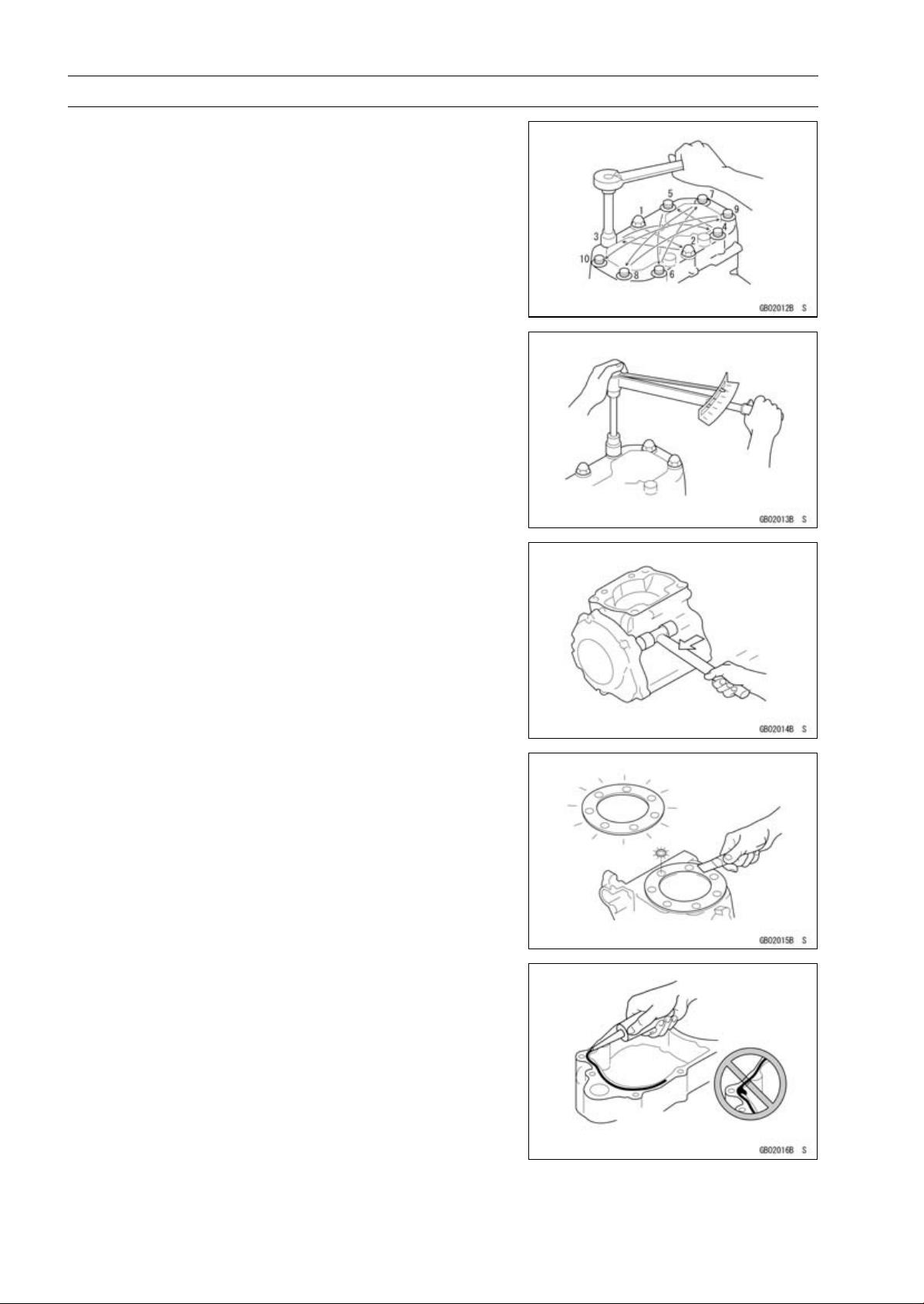
1-4 GENERAL INFORMATION
Before Servicing
Tightening Sequence
Generally, when installing a part with several bolts, nuts,
or screws, start them all in their holes and tighten them to
a snug fit. Then tighten them according to the specified sequence to prevent case warpage or deformation which can
lead to malfunction. Conversely when loosening the bolts,
nuts, or screws, first loosen all of them by about a quarter turn and then remove them. If the specified tightening
sequence is not indicated, tighten the fasteners alternating
diagonally.
Tightening Torque
Incorrect torque applied to a bolt, nut, or screw may
lead to serious damage. Tighten fasteners to the specified
torque using a good quality torque wrench.
Often, the tightening sequence is f ollowed twice initial
tightening and final tightening with torque wrench.
Force
Use common sense during disassembly and assembly,
excessive force can cause expensive or hard to repair damage. When necessary, remove screws that have a non
-permanent locking agent applied using an impact driver.
Use a plastic-faced mallet whenever tapping is necessary.
Gasket, O-ring
Hardening, shrinkage, or damage of both gaskets
and O-rings after disassembly can reduce sealing performance. Remove old gaskets and clean the sealing
surfaces thoroughly so that no gasket material or other
material remains. Install new gaskets and replace used
O-rings when re-assembling.
Liquid Gasket, Locking Agent
For applications that require Liquid Gasket or a
Non-Permanent Locking Agent, clean the surfaces so
that no oil residue remains before applying liquid gasket
or locking agent. Do not apply them excessively. Excessive application can clog oil passages and cause serious
damage.
Page 15
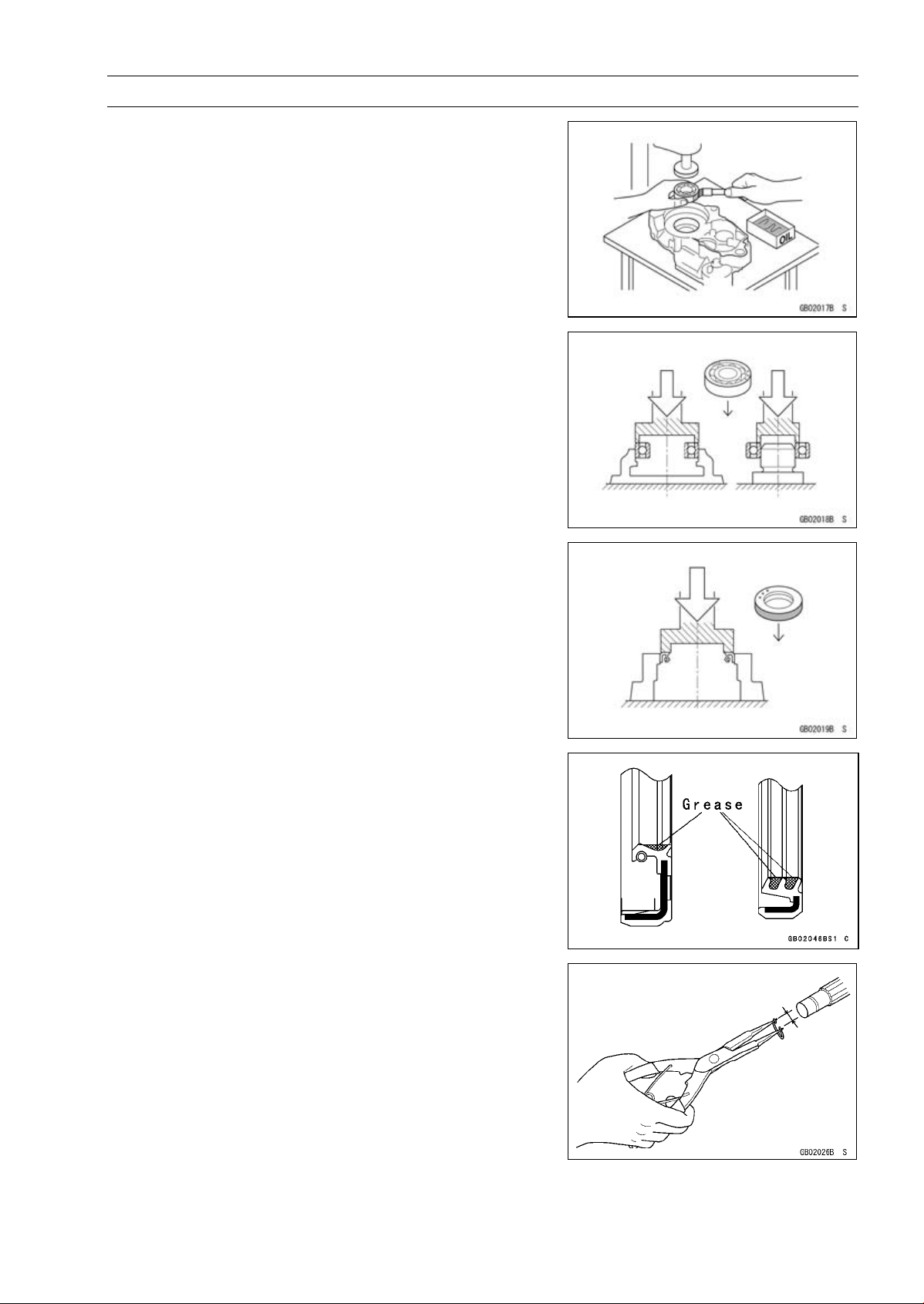
Before Servicing
Press
For items such as bearings or oil seals that must be
pressed into place, apply small amount of oil to the contact area. Be sure to maintain proper alignment and use
smooth movements when installing.
Ball Bearing and Needle Bearing
Do not remove pressed ball or needle unless removal is
absolutely necessary. Replace with new ones whenever
removed. Press bearings with the manufacturer and size
marks facing out. Press the bearing into place by putting
pressure on the correct bearing race as shown.
Pressing the incorrect race can cause pressure between
the inner and outer race and result in bearing damage.
GENERAL INFORMATION 1-5
Oil Seal, Grease Seal
Do not remove pressed oil or grease seals unless removal
is necessary. Replace with new ones whenever removed.
Press new oil seals with manufacture and size marks facing
out. Make sure the seal is aligned properly when installing.
Apply specified grease to the lip of seal before installing
the seal.
Circlips, Cotter Pins
Replace circlips or cotter pins that were removed with new
ones. Take care not to open the clip excessively when installing to prevent deformation.
Page 16
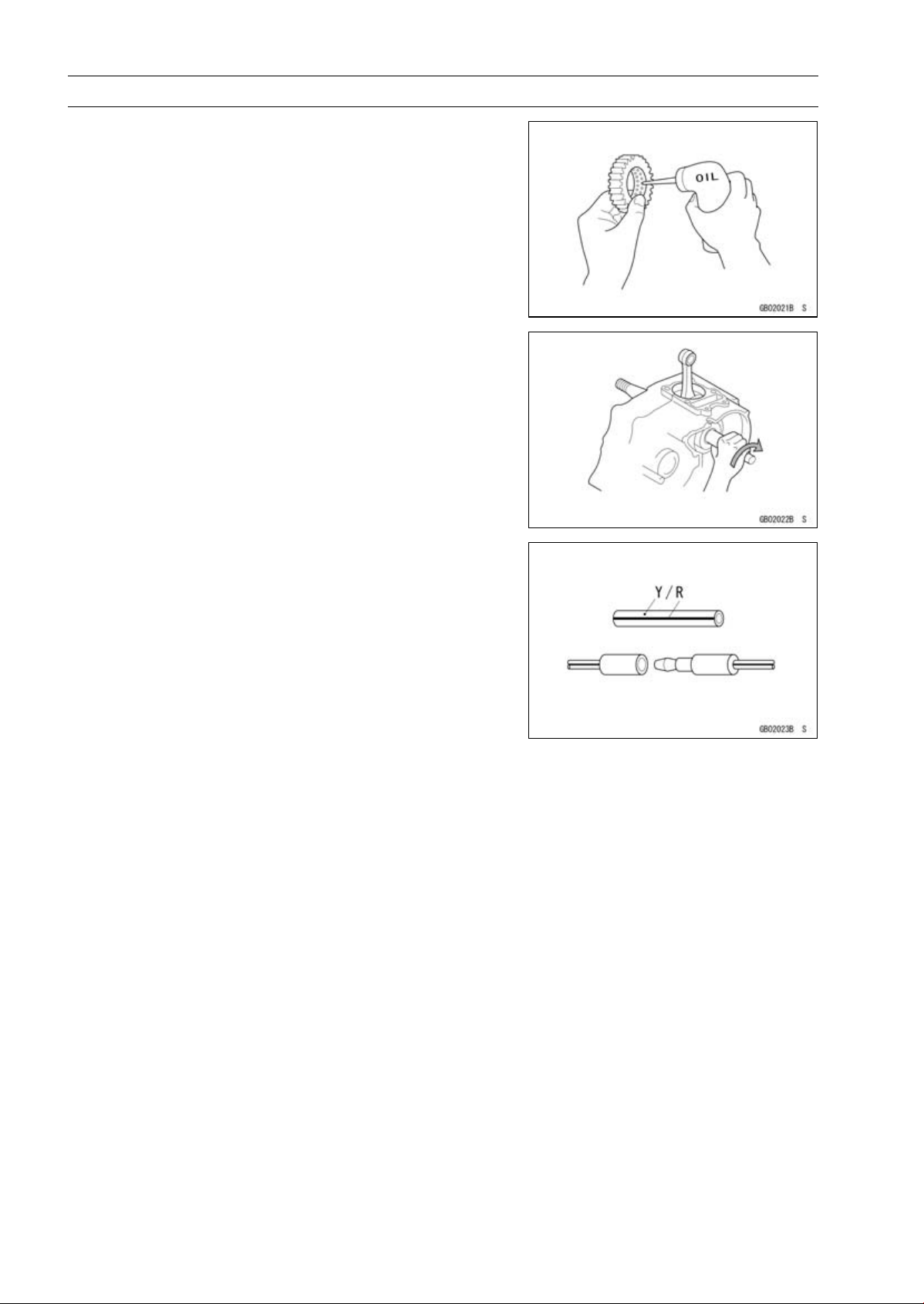
1-6 GENERAL INFORMATION
Before Servicing
Lubrication
It is important to lubricate rotating or sliding parts during
assembly to minimize wear during initial operation. Lubrication points are called out throughout this manual, apply
the specific oil or grease as specified.
Direction of Engine Rotation
When rotating the crankshaft by hand, the free play
amount of rotating direction will affect the adjustment. Rotate the crankshaft to positive direction (clockwise viewed
from output side).
Electrical Wires
A two-color wire is identified first by the primary color and
then the stripe color. Unless instructed otherwise, electrical
wires must be connected to those of the same color.
Page 17

Model Identification
KVF750-A1 Left Side View
GENERAL INFORMATION 1-7
KVF750-A1 Right Side View
The KVF750–B1 is a camouflage-surface-treated model and identical to the KVF750–A1, the base
model, in every other aspect: controls, features, and specifications.
Page 18
1-8 GENERAL INFORMATION
General Specifications
Items KVF750-A1, B1
Dimensions
Overall Length 2 192 mm (86.30 in.)
Overall Width 1 177 mm (46.34 in.)
Overall Height 1 249 mm (49.17 in.)
Wheelbase 1 283 mm (50.51 in.)
Ground Clearance: 269 mm (10.59 in.)
Seat Height 935 mm (36.81 in.)
Dry Mass 274 kg (604 lb), (EUR) 274.5 kg (605 lb)
Curb Mass:
Front 147.5 kg (325 lb), (EUR) 148 kg (326 lb)
Rear 149 kg (329 lb)
Fuel Tank Capacity 19.5 L (5.2 US gal)
Performance
Minimum Turning Radius 3.2 m (10.5 ft)
Engine
Type 4-stroke, SOHC, V2-cylinders
Cooling System Liquid-cooled
Bore and Stroke 85 × 66 mm (3.35 × 2.60 in.)
Displacement 749 mL (45.7 cu in.)
Compression Ratio 8.8 : 1
Maximum Horsepower 37.4 kW (50.9 PS) @6 500 r/min (rpm), (US) -
Maximum Torque 60.7 N·m (6.2 kgf·m, 45 ft·lb) @5 000 r/min (rpm)
Carburetion System Carburetor, Keihin CVKR-34
Starting System Electric Starter & Recoil Starter
Ignition System Digital DC-CDI
Timing A dvance Electronically advanced
Ignition Timing From 5° BTDC @1 150 r/min (rpm)
to 28° BTDC @5 000 r/min (rpm)
Spark Plug NGK CR7E, DENSO U22ESR-N
Cylinder Numbering Method Front to rear, 1-2
Firing Order 1-2
Valve Timing:
Inlet:
Open 20° BTDC
Close 44° ABDC
Duration 244°
Exhaust:
Open 44° BBDC
Close 20° ATDC
Duration 244°
Lubrication Aystem Forced lubrication (wet sump)
Page 19
General Specifications
Items KVF750-A1, B1
Engine oil:
Type
Viscosity SAE 10W-40
Capacity 2.6 L (2.75 US qt)
Drive Train
Primary Reduction System:
Type Belt converter
Reduction Ratio 3.122 ∼ 0.635
Transmission:
Type 2-speed and reverse
Gear Ratios:
Forward:
High
Low
Reverse 4.028 (16/12 × 18/16 × 29/18 × 20/12)
Final Drive System:
Type Shaft 2WD/4WD
Reduction Ratio 4.375 (35/8)
Overall Drive Ratio:
Forward:
High 42.32 ∼ 8.61
Low 66.02 ∼ 13.43
Reverse 55.01 ∼ 11 . 19
Front Final Gear Case Oil:
Type API SF or SG
Viscosity SAE10W-40
Capacity 0.40 L (0.42 US qt)
Rear Final Gear Case Oil:
Type
Capacity 0.72 L (0.76 US qt)
Frame
Type Double tubular
Caster (Rake Angle) 5.5°
Camber 0°
King Pin Angle 11°
Trail 28 mm (1.10 in.)
Tread:
Front 915 mm (36.23 in.)
Rear 875 mm (34.45 in.)
API SF or SG
API SH or SJ with JASO MA class
3.098 (30/26 × 29/18 × 20/12)
4.833 (36/20 × 29/18 × 20/12)
API SH or SJ with JASO MA class
MOBIL FLUID 424, CITGO TRANSGARD TRACTOR
HYDRAULIC FLUID, o r EXXON HYDRAUL 560
GENERAL INFORMATION 1-9
Page 20
1-10 GENERAL INFORMATION
General Specifications
Items KVF750-A1, B1
Front tire:
Type Tubeless
Size AT25 × 8 – 1 2
Rear tire:
Type Tubeless
Size AT25 × 10 – 12
Suspension:
Front:
Type Double Wishbone
Wheel Travel 171 mm (6.73 in.)
Rear:
Type Double Wishbone
Wheel Travel 200 mm (7.87 in.)
Brake:
Front Disc × 2
Rear Enclosed wet multi-plate
Parking Brake Enclosed wet multi-plate
Electrical Equipment
Battery 12 V 12 Ah
Headlight:
Type Semi-sealed beam
Bulb 12 V 40/40 W × 2
Tail/brake Light:
Bulb 12 V 5/21 W
Reverse Light:
Bulb
Alternator:
Type Three - phase AC
Rated Output 24.2 A, 14 V @6 000 r/min (rpm)
(EUR) 12V 10W
Specifications are subject to change without notice, and may not apply to every country.
US: United States Model
EUR: Europe Model
Page 21
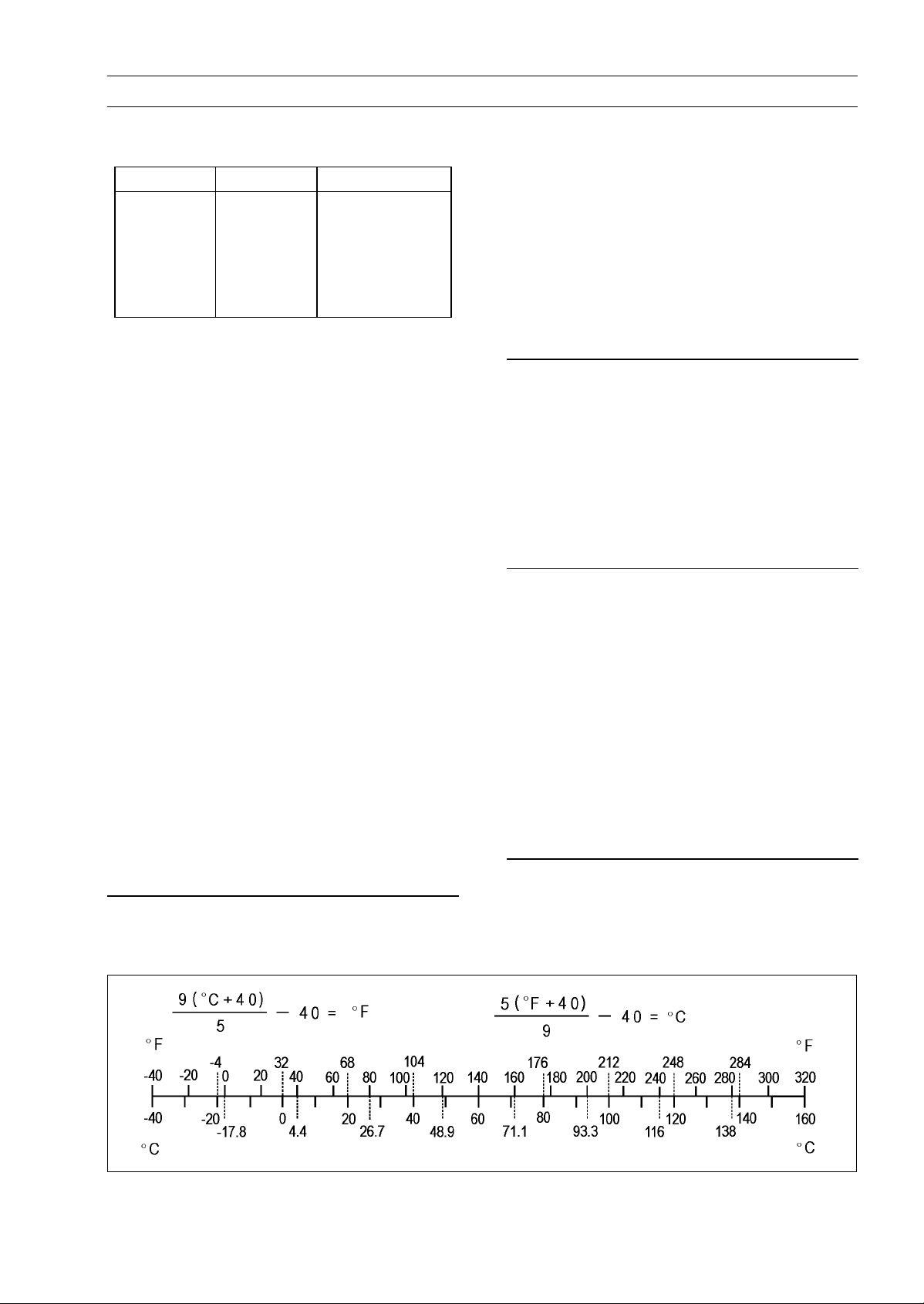
Unit Conversion Table
GENERAL INFORMATION 1-11
Prefixes for Units:
Prefix Symbol
mega M × 1 000 000
kilo k × 1 000
centi c ×0.01
milli m × 0.001
micro µ × 0.000001
Power
Units of Mass:
kg ×2.205=lb
g × 0.03527 = oz
Units of Volume:
L × 0.2642 = gal (US)
L × 0.2200 = gal (imp)
L×1.057=
L × 0.8799 =
L × 2.113 = pint (US)
L × 1.816 = pint (imp)
mL × 0.03381 = oz (US)
mL × 0.02816 = oz (imp)
mL × 0.06102 = cu in
qt (US)
qt (imp)
Units of Length:
km × 0.6214 = mile
m × 3.281 = ft
mm × 0.03937 = in
Units of Torque:
N·m × 0.1020 =
N·m × 0.7376 = ft·lb
N·m × 8.851 = in·lb
kgf·m × 9.807 = N·m
kgf·m × 7.233 = ft·lb
kgf·m
× 86.80 = in·lb
kgf·m
Units of Pressure:
kPa × 0.01020 = kgf/cm²
kPa × 0.1450 = psi
kPa × 0.7501 = cmHg
kgf/cm² × 98.07 = kPa
kgf/cm²
cmHg × 1.333 = kPa
× 14.22 = psi
Units of Speed:
km/h
× 0.6214 = mph
Units of Force:
N × 0.1020 = kg
N × 0.2248 = lb
kg ×9.807=N
kg ×2.205=lb
Units of Temperature
Units of Power:
kW × 1.360 =
kW × 1.341 = HP
PS × 0.7355 = kW
PS × 0.9863 = HP
PS
Page 22

Page 23

PERIODIC MAINTENANCE 2-1
Periodic Maintenance
Table of Contents
Periodic Maintenance Chart .............. 2-3
Torque and Locking Agent................. 2-5
Specifications .................................... 2-11
Special Tools ..................................... 2-13
Periodic Maintenance Procedures..... 2-14
Fuel System.................................... 2-14
Throttle Lever Free Play
Inspection .................................. 2-14
Throttle Lever Free Play
Adjustment ................................ 2-14
Choke Lever Free Play
Inspection .................................. 2-14
Choke Lever Free Play
Adjustment ................................ 2-15
Idle Speed Inspection .................. 2-15
Idle Speed Adjustment................. 2-16
Fuel System Cleanliness
Inspection .................................. 2-16
Air Cleaner Element Cleaning and
Inspection .................................. 2-17
Air Cleaner Draining..................... 2-17
Fuel Hose and Connection
Inspection .................................. 2-18
Fuel Hose Replacement .............. 2-18
Cooling System............................... 2-19
Radiator Cleaning ........................ 2-19
Radiator Hose and Connection
Inspection .................................. 2-20
Coolant Change........................... 2-20
Engine Top End .............................. 2-23
Valve Clearance Inspection ......... 2-23
Valve Clearance Adjustment ........ 2-24
Spark Arrester Cleaning............... 2-24
Converter System ........................... 2-25
Drive Belt Inspection .................... 2-25
Drive Belt Deflection Inspection... 2-25
Drive Belt Deflection Adjustment . 2-26
Actuator Lever (Engine Brake
Control Lever) Assembly
Inspection .................................. 2-27
Engine Lubrication System............. 2-27
Engine Oil Change....................... 2-27
Oil Filter Replacement ................. 2-28
Wheels/Tires................................... 2-28
Tire Inspection ............................. 2-28
Final Drive....................................... 2-29
2
Variable Differential Control Lever
Play Inspection.......................... 2-29
Variable Differential Control Lever
Play Adjustment ........................ 2-29
Front Final Gear Case Oil
Change...................................... 2-30
Rear Final Gear Case Oil Change 2-31
Universal Joint Lubrication........... 2-32
Brakes............................................. 2-32
Front Brake Pad Wear Inspection 2-32
Front Brake Hoses and
Connections Inspection............. 2-32
Front Brake Hose Replacement... 2-33
Brake Fluid Level Inspection........ 2-33
Brake Fluid Change ..................... 2-34
Front Brake Master Cylinder
Piston Assembly and Dust Seal
Replacement ............................. 2-34
Front Brake Caliper Piston Seal
and Dust Seal Replacement ..... 2-34
Rear Brake Plates Replacement.. 2-35
Rear Brake Lever Free Play
Inspection.................................. 2-35
Brake Pedal Free Play Inspection 2-35
Rear Brake Lever and Pedal Free
Play Adjustment ........................ 2-35
Steering .......................................... 2-36
Steering Inspection ...................... 2-36
Electrical System ............................ 2-36
Spark Plug Cleaning/Inspection ... 2-36
Spark Plug Gap Inspection .......... 2-36
Brake Light Switch Inspection...... 2-37
Brake Light Timing Adjustment .... 2-37
Drive Belt Failure Detection
System Inspection..................... 2-37
Joint Boots Inspection..................... 2-39
Front Axle/Knuckle Joint Boot
Inspection.................................. 2-39
Front Propeller Shaft Boot
Inspection.................................. 2-39
Tie-rod End Boot Inspection ........ 2-39
Rear Propeller Shaft Joint Boot
Inspection.................................. 2-39
Rear Axle/Stabilizer Joint Boot
Inspection.................................. 2-39
General Lubrication ........................ 2-40
Page 24

2-2 PERIODIC MAINTENANCE
Lubrication ................................... 2-40
Bolts and Nuts Tightening............... 2-41
Tightness Inspection .................... 2-41
Page 25
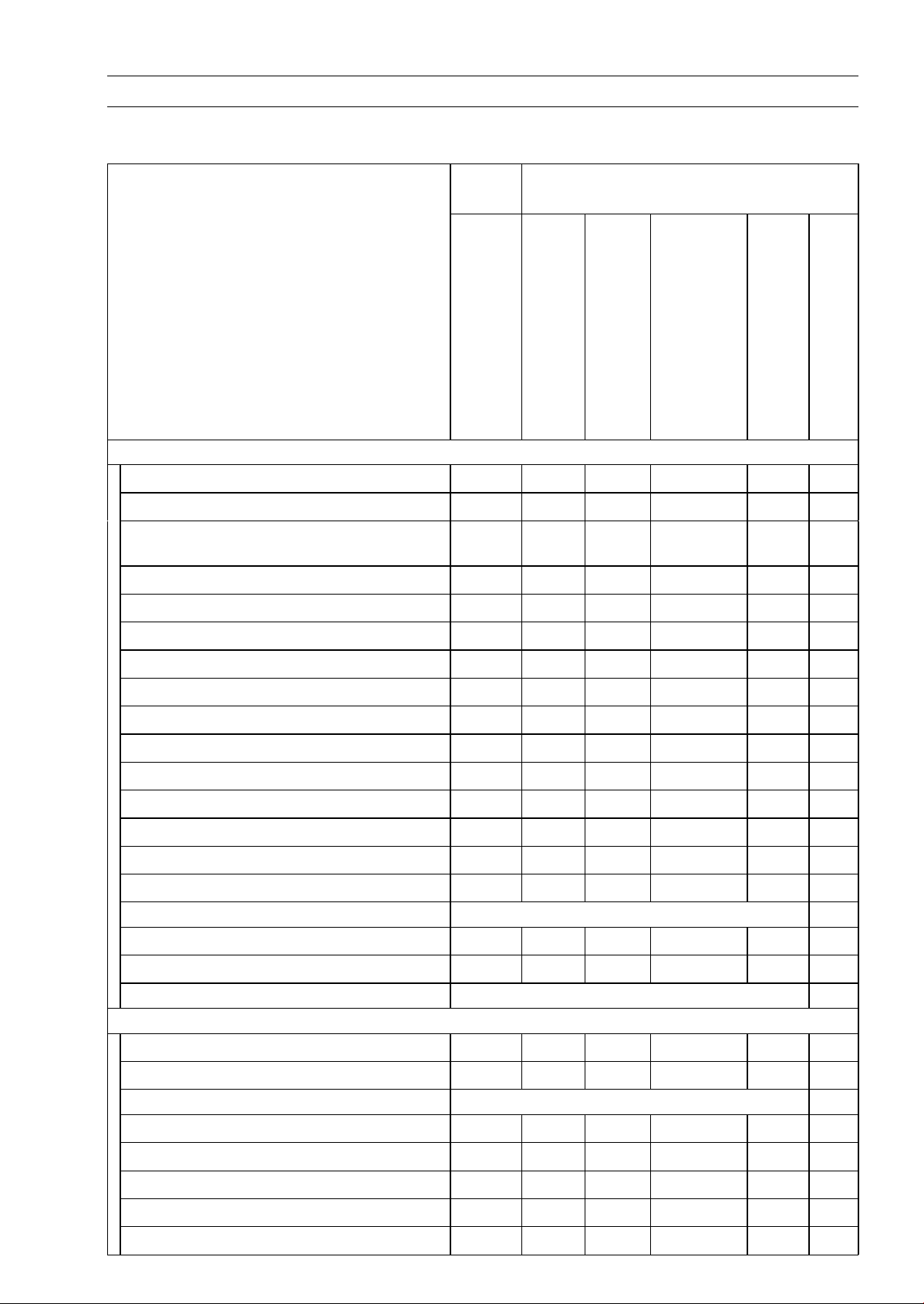
PERIODIC MAINTENANCE 2-3
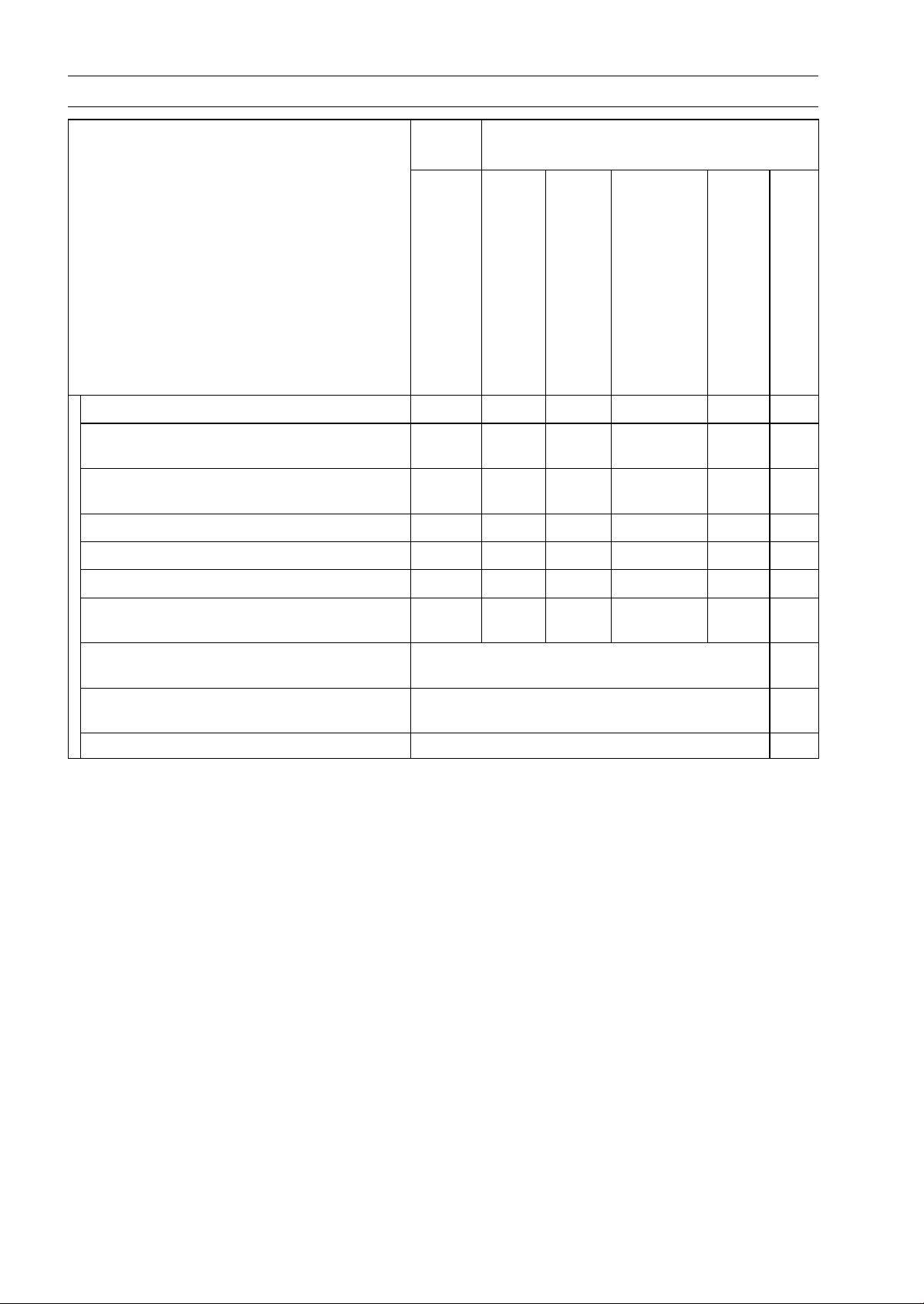
Periodic Maintenance Chart
The scheduled maintenance must be done in accordance with this chart to keep the vehicle in good
running condition. The initial maintenance is vitally important and must not be neglected.
FirstFREQUENCY
Service
Every
After 10
hrs. or
100 km
(60 mi.)
of use
OPERATION
ENGINE
Converter drive belt wear - inspect *
Converter drive belt deflection - inspect *
Drive belt failure detection system function
-inspect*
Engine brake control lever - inspect *
Air cleaner - inspect *
Throttle lever play - i nspect
Choke lever play - inspect
Idle speed - inspect
Valve clearance - inspect
Fuel system cleanliness - inspect *
Engine oil - change *
Oil filter - replace *
Spark plug - clean and gap
Spark arrester - clean
Fuel hoses and connections - inspect
Fuel hose - replace 4 years 2-18
• •
• •
• •
• •
• •
• •
• •
10
days or
200 km
(120
mi.) of
use
Regular Service
days, 1 700
Every
30
days or
600 km
(360
mi.) of
use
km (1 100
when belt
light turns
hrs of use)
whichever
comes first
•
Every 90
mi.) or
indicator
on (100
•
•
•
•
•
Every
year of
use
•
•
See
page
2-25
2-25
2-37
2-27
2-17
2-14
2-14
2-15
2-23
2-16
2-27
2-28
2-36
2-24
2-18
Radiator - clean*
Radiator hoses and connections - check*
Coolant - change*
CHASSIS
Joint boots - inspect *
Rear brake pedal and lever play - inspect *
Rear brake plates - replace * every 10 000 km (6 000 mi.) 2-35
Bolts and nuts - tighten
Front brake pad wear - inspect *
Brake light switch - inspect *
Steering - inspect
Differential control lever play - inspect
• •
•
2 years 2-20
• •
• •
• •
• •
• •
• •
• •
2-19
2-20
2-39
2-35
2-41
2-32
2-37
2-36
2-29
Page 26
2-4 PERIODIC MAINTENANCE
Periodic Maintenance Chart
FirstFREQUENCY
Service
Every
After 10
hrs. or
100 km
(60 mi.)
of use
OPERATION
Tire wear - inspect *
Front and rear final gear case oil - change
Rear propeller shaft universal joint
lubrication
General lubrication *
Front brake fluid level - inspect
Front brake fluid - change
Front brake hoses and connections inspect
Front brake master cylinder piston
assembly and dust seal - replace
Front brake caliper piston seal and dust
seal - replace
Front brake hose - replace 4 years 2-33
• •
• •
10
days or
200 km
(120
mi.) of
use
Regular Service
Every 90
days, 1 700
Every
30
days or
600 km
(360
mi.) of
use
km (1 100
mi.) or
when belt
indicator
light turns
on (100
hrs of use)
whichever
comes first
Every
year of
use
•
•
•
•
•
2 years 2-34
2 years 2-34
See
page
2-28
2-30
2-31
2-32
2-40
2-33
2-34
2-32
*: Service more frequently when operated in mud, dust, or other harsh riding conditions, or when
carrying heavy loads or pulling a trailer.
: Clean, adjust, lubricate, torque, or replace parts as necessary.
•
Page 27
PERIODIC MAINTENANCE 2-5
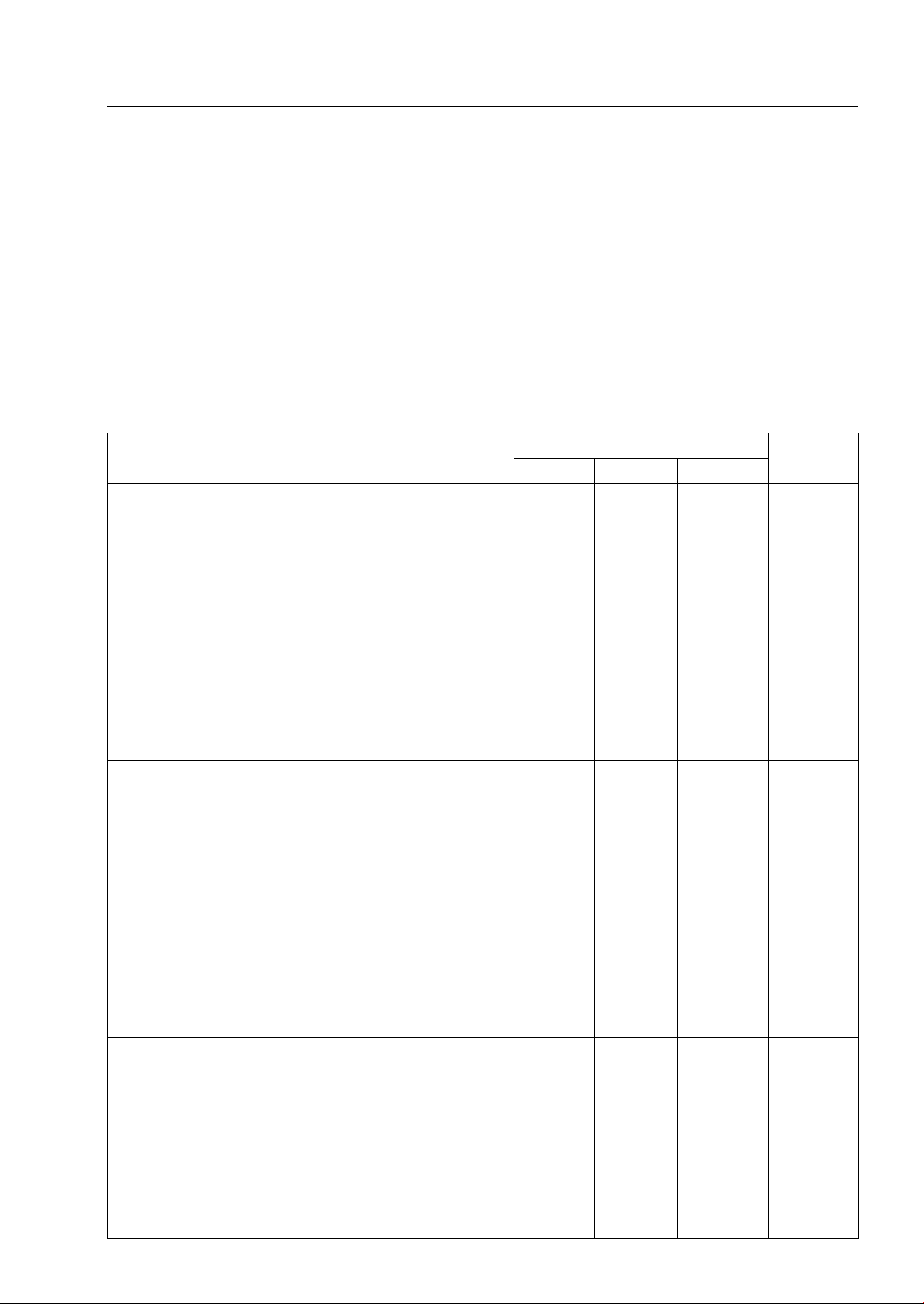
Torque and Lo cking Agent
The following tables list the t ightening torque for the major fasteners, and the parts requiring use of
a non-permanent locking agent or liquid gasket.
Letters used in the “Remarks” column mean:
AL: Tighten the two clamp bolts alternately t wo times to ensure even tightening torque.
L: Apply a non-permanent locking agent.
LB: Apply a non-permanent locking agent (Three Bond TB2471, Blue).
Lh: Left-hand Threads
MO: Apply molybdenum disulfide oil solution (mixture of the engine oil and molybdenum disulfide
grease in a weight ratio 10:1).
R: Replacement Parts
S: Follow the specific tightening sequence.
SS: Apply silicone sealant (Kawasaki Bond: 56019-120).
St: Stake the fasteners to prevent loosening.
TB: Apply a non-permanent locking agent (Three Bond TB1363A, Red).
Fastener
Fuel System
Idle Adjusting Screw Bracket Bolt 8.8 0.90 78 in·lb
Element Cover Screw 3.5 0.35 31 in·lb
Element Holder Screws 3.5 0.35 31 in·lb
Clamp Bracket Bolt 9.8 1.0 87 in·lb
Fuel Pump Mounting Nuts 7.8 0.80 69 in·lb
Fuel Tap Plate Screws 0.8 0.08 7in·lb
Fuel Tap Mounting Bolts 4.9 0.50 43 in·lb
Fuel Tap Cover Screws 9.8 1.0 87 in·lb
Fuel Tap Bracket Bolts 7.8 0.80 69 in·lb
Fuel Level Sensor Mounting Bolts 2.0 0.20 18 in·lb
Cooling System
Radiator Mounting Bolts 8.8 0.90 78 in·lb
Radiator Fan Switch 18 1.8 13
Radiator Fan Assembly Bolts 4.9 0.50 43 in·lb
Thermostat Housing Cover Bolts 8.8 0.90 78 in·lb
Coolant Temperature Warning Light Switch 6.9 0.70 61 in·lb SS
Air Bleeder Bolt 8.8 0.90 78 in·lb
Water Pump Cover Bolts 8.8 0.90 78 in·lb
Coolant Drain Plug 8.8 0.90 78 in·lb
Water Pump Impeller 7.8 0.80 69 in·lb
Water Pipe Mounting Bolts 8.8 0.90 78 in·lb
Engine Top End
Rocker Case Bolts 55 mm (2.2 in.)
Rocker Case Bolts 130 mm (5.1 in.) 9.8 1.0 87 in·lb S
Rocker Case Bolts 30 mm (1.2 in.) 9.8 1.0 87 in·lb S
Rocker Case Bolts 25 mm (1.0 in.) 9.8 1.0 87 in·lb S
Cylinder Head B olts (M10), first torque 25 2.5 18 S, MO
Cylinder Head Bolts (M10), final torque 49 5.0 36 S
Cylinder Head Bolts (M6) 9.8 1.0 87 in·lb
N·m kgf·m ft·lb
8.8 0.90 78 in·lb
Torque
Remarks
S
Page 28
2-6 PERIODIC MAINTENANCE
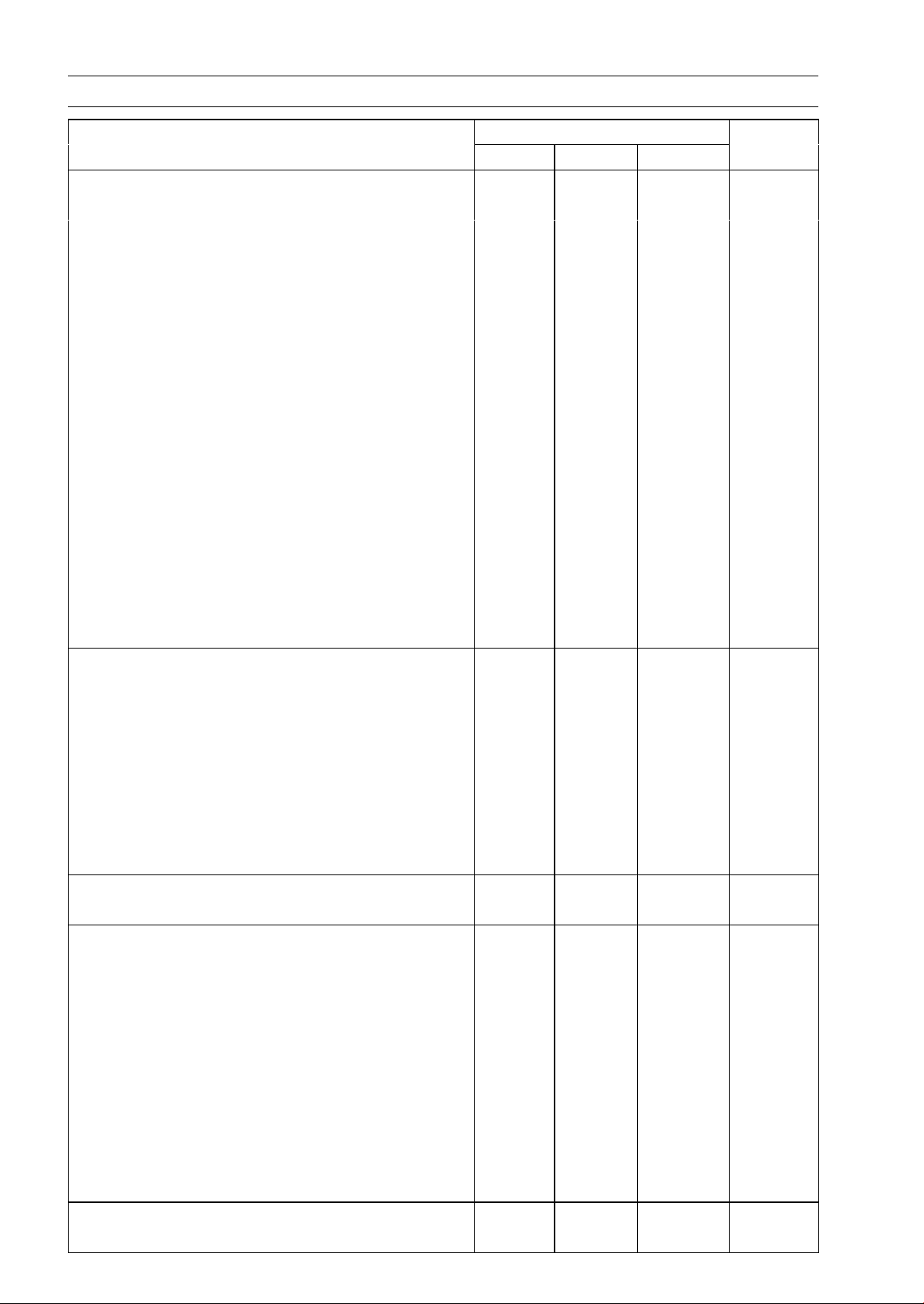
Torque and Locki ng Agent
Fastener
Valve Adjusting Cap Bolts 8.8 0.90 78 in·lb
Water Pipe Mounting Bolts 8.8 0.90 78 in·lb
Rocker Shaft Bolts 20 2.0 14
Valve Adjusting Screw Locknuts 12 1.2 104 in·lb
Chain Tensioner Mounting Bolts 8.8 0.90 78 in·lb
Chain Tensioner Cap Bolt 22 2.2 16
Position Plate Bolts 8.8 0.90 78 in·lb
Intermediate Shaft Chain Guide Bolts 8.8 0.90 78 in·lb
Intermediate Shaft Chain Tensioner Bolts 8.8 0.90 78 in·lb
Camshaft Splocket Bolts 12 1.2 104 in·lb L
Cylinder Bolts 40 mm (1.6 in.) 9.8 1.0 87 in·lb
Cylinder Bolts 30 mm (1.2 in.) 9.8 1.0 87 in·lb
Front Cylinder Camshaft Chain Guide Bolt 20 2.0 14
Rear Cylinder Camshaft Chain Guide Bolt 20 2.0 14
Exhaust Pipe Cover Bolts 8.8 0.90 78 in·lb
Muffler Clamp Bolts
Muffler Mounting First Nuts 15 1.5 11 S
Muffler Mounting Second Nuts 31 3.2 23 S
Muffler Cover Bolts 8.8 0.90 78 in·lb
Converter System
Drive Pulley Bolt 93 9.5 69 R, Lh
Driven Pulley Nut 93 9.5 69
Drive Pulley Cover Bolt 13 1.3 113 i n·lb
Ramp Waight Nuts 6.9 0.70 61 in·lb
Spider
JointDuctBolts 8.8 0.90 78 in·lb
Converter Cover Bolts 8.8 0.90 78 in·lb S
Engine Brake Actuator Mounting Bolts 8.8 0.90 78 in·lb
Recoil Starter
Recoil Starter Mounting Bolts 5.9 0.60 52 in·lb L
Engine Lubrication System
Oil Filter 18 1.8 13 R
Oil Pressure Switch 15 1.5 11 SS
Oil Pipe Bolts 8.8 0.90 78 in·lb
Engine Drain Plug 20 2.0 14
Oil Pressure Relief Valve 15 1.5 11 L
Oil Pump Bolts 8.8 0.90 78 in·lb
Chain Guide Bolts 8.8 0.90 78 in·lb
Oil Pump Drive Chain Tensioner Bolt 25 2.5 18
Oil Filter Mounting Bolts 25 2.5 18 L(15 mm)
Oil Pressure Switch Terminal Bolt 1.5 0.15 13 in·lb
Engine Removal/Installation
Engine Bracket Mounting Bolts 72 7.3 53
N·m kgf·m ft·lb
8.8 0.90 78 in·lb
275 28 203 Lh
Torque
Remarks
S
Page 29
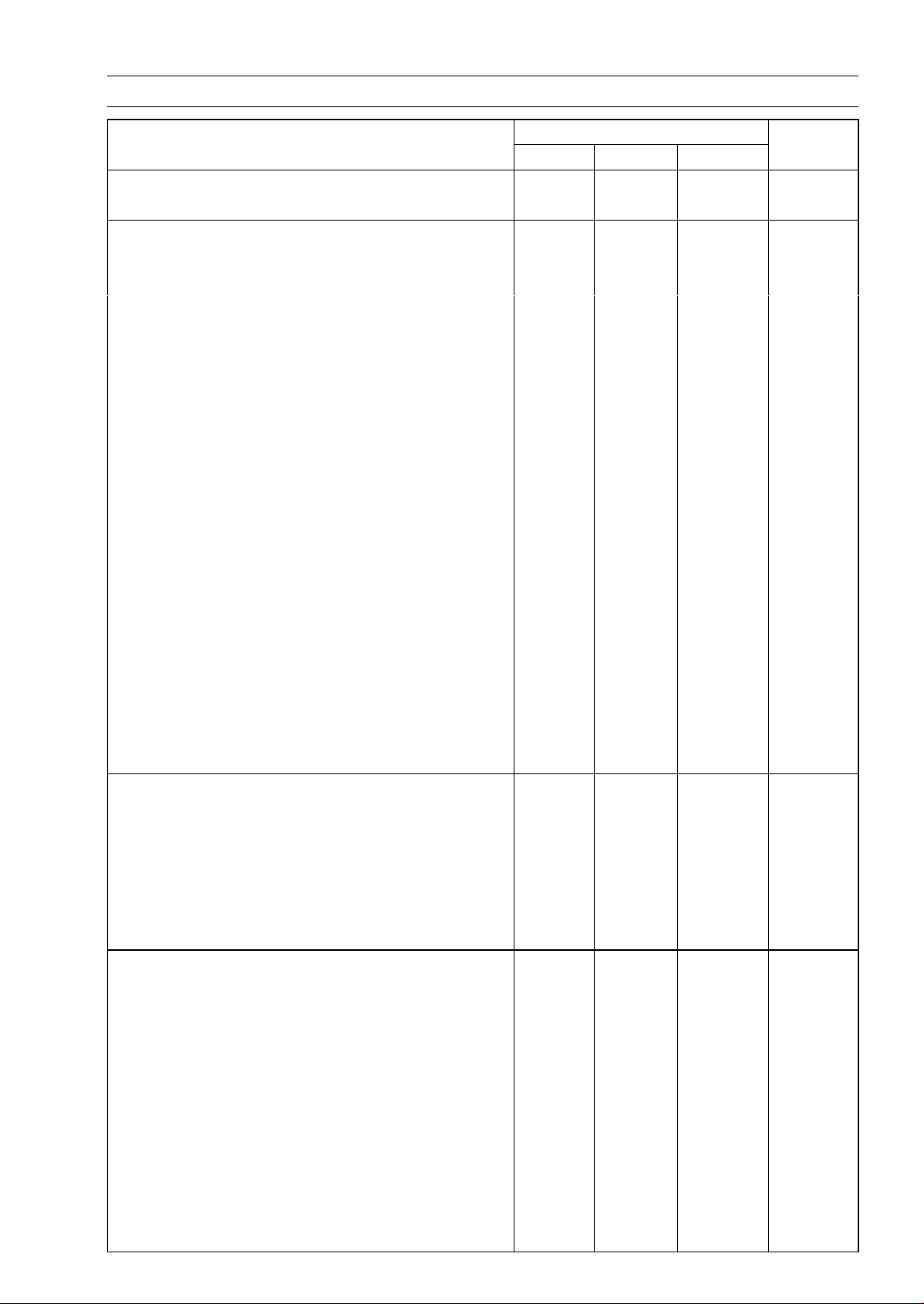
Torque and Lo cking Agent
PERIODIC MAINTENANCE 2-7
Fastener
Engine Mounting Bolt 62 6.3 46
Engine Mounting Nut 62 6.3 46
Crankshaft/Transmission
Connecting Rod Big End Cap Nuts 34 3.5 25 MO
Engine Drain Plug 20 2.0 14
Crankcase Bolts (M8) 75 mm (2.95 in.) 20 2.0 14 S
Crankcase Bolts (M8) 110 mm (4.33 in.) 20 2.0 14 S
Crankcase Bolt (M8) 110 m m (4.33 in.) 20 2.0 14 S, L(1)
Crankcase Bolts (M6) 40 mm (1.57 in.) 9.8 1.0 87 in·lb
Crankcase Bolts (M6) 65 mm (2.56 in.) 9.8 1.0 87 in·lb
Bearing Position Plate Screws 4.9 0.50 43 in·lb L
Grip Hold Nut 9.8 1.0 87 in·lb
Shift Lever Assembly Bracket Bolts 20 2.0 14
Tie-rod End Front Locknut 9.8 1.0 87 in·lb Lh
Tie-Rod End Rear Locknut 9.8 1.0 87 in·lb
Tie-rod End Nut 20 2.0 14
Shift Lever Assembly Nut 20 2.0 14
Tie-rod End Bolt 9.8 1.0 87 in·lb
Shift Shaft Positioning Bolt 25 2.5 18
Shift Shaft Spring Bolt 25 2.5 18 L
Shift Shaft Cover Bolts 8.8 0.90 78 in·lb
Tie-rod End Locknut 20 2.0 14
Neutral Position Switch 15 1.5 11
Reverse Position Switch 15 1.5 11
Wheel/Tires
Tie-rod Locknuts 37 3.8 27
Tie-rod End Nuts 42 4.3 31
Wheel Nuts (First Torque) 15 1.5 11 S
Wheel Nuts (Final Torque) 76 7.8 56 S
Front Axle Nuts 197 20 145
Rear Axle Nuts 265 27 195
Final Drive
(Output Bevel Gears)
Output Driven Bevel Gear Housing Bolts
Output Drive Bevel Gear Housing Bolts 26 2.7 20
Bearing Holder 137 14 101 L
Bevel Gear Holder Nut
Bearing Holder 11 8 12 87 L
Output Shaft Holder Nut 157 16 11 6 L
Rotor Mounting Bolts 12 1.2 104 in·lb
Output Drive Bevel Gear Cover Bolts 8.8 0.90 78 in·lb
(Front Final Gear Case)
Variable Differential Control Shift Shaft Lever Bolt
N·m kgf·m ft·lb
26 2.7 20
157 16 11 6 L
8.8 0.90 78 in·lb
Torque
Remarks
Page 30
2-8 PERIODIC MAINTENANCE
Torque and Locki ng Agent
Fastener
Front Final Gear Case Left Cover Bolts (M6) 9.8 1.0 87 in·lb L
Ring Gear Bolts 57 5.8 42 LB
Front Final Gear Case Center Cover Bolts (M6) 9.8 1.0 87 in·lb L
Front Final Gear Case Center Cover Bolts (M8) 24 2.4 17 L
Front Final Gear Case Oil Filler Cap 29 3.0 22
Pinion Gear Bearing Holder Nut 127 13 94 St
Pinion Gear Bearing Holder 137 14 101 L
Front Final Gear Case Coupling Nut 25 2.5 18
Front Final Gear Case O il Drain Plug 15 1.5 11
2WD/4WD Actuator Mounting Bolts
Variable Differential Control Cable Locknut 17 1.7 12
Variable Differential Control Lever Bolt – – – L
Front Final Gear Case Nuts 59 6.0 43
(Rear Final Gear Case)
Rear Final G ear Case Front Cover Bolts 24 2.4 17
Gasket Screws 13 0.13 11 in·lb
Pinion Gear Bearing Holder Nut 157 16 116 L
Pinion Gear Bearing Holder 137 14 101 L
Rear Final Gear Case Right Cover Bolts (M12) 93 9.5 69 L
Rear Final Gear Case Right Cover Bolts (M10) 49 5.0 36 L
Rear Final Gear Case Right Cover Bolts (M8) 24 2.4 17 L
Rear Final Gear Case Oil Filler Cap
Rear Final Gear Case Oil Drain Plug 13 1.3 113 in·lb
Bracket Bolts 59 6.0 43
Rear Final Gear Case Nuts
Brakes
Reservoir Cap Screws 1.5 0.15 13 in·lb
Brake Lever Pivot Bolt 6.0 0.60 53 in·lb
Brake Lever Pivot Bolt Locknut 6.0 0.60 53 in·lb
Master Cylinder Clamp Bolts 9.0 0.92 80 in·lb S
Bake Hose Banjo Bolt 25 2.5 18
Brake Caliper Mounting Bolts 25 2.5 18
Bleed Valves 5.4 0.55 48 in·lb
Brake Disc Mounting Bolts 37 3.8 27 L
Caliper Holder Shaft 17 1.7 13
Pad Mounting Bolts 17 1.7 13
Variable Differential Control Lever Bolt – – – L
Gasket Screws – – – L
Suspension
Front Shockabsorber M ounting Nuts 34 3.5 25
Front Suspension Arm Pivot Nuts 42 4.3 31
Front Knuckle Joint Nuts 29 3.0 22
Rear Shockabsorber Mounting Nuts 34 3.5 25
N·m kgf·m ft·lb
9.8 1.0 87 in·lb
29 3.0 22
72 7.3 53 TB
Torque
Remarks
L, S
Page 31

Torque and Lo cking Agent
PERIODIC MAINTENANCE 2-9
Fastener
Stabilizer Holder Bolts 23 2.3 17
Stabilizer Joint Nuts 48 4.8 35
Rear Suspension Arm Pivot Nuts 48 4.8 35
Rear Knuckle Mounting Nuts 48 4.8 35
Steering
Handlebar Holder Bolts 29 3.0 22 S
Steering Stem Clamp Bolts 25 2.5 18
Tie-rod End Nuts 42 4.3 31
Tie-rod Locknuts 37 3.8 27
Steering Stem Bearing Joint Bolts 23 2.3 17 L
Steering Stem Bottom End Nut 62 6.3 46
Front Knuckle Joint Nuts 29 3.0 22
Master Cylinder Clamp Bolts 9.0 0.92 80 in·lb
Variable Differential Control Lever Bolt – – – L
Frame
Front Guard Bolts 37 3.8 27
Front Carrier Bolts, L=50 mm (2.0 in.) 25 2.5 18
Front Carrier Bolts, L=70 mm (2.8 in.) 25 2.5 18
Front Carrier Bracket Bolts 32 3.3 24
Rear Carrier Bolts, L=14 mm (0.6 in.) 54 5.5 40
Rear Carrier Bolts, L=41 mm (1.6 in.) 54 5.5 40
Rear Carrier Bracket Bolts
Footboard Bracket Bolts 37 3.8 27
Hitch Bracket Bolts 82 8.3 60
Electrical System
Starter Motor Mounting Bolts 8.8 0.90 78 in·lb
Starter Motor Terminal Nut 4.9 0.50 43 in·lb
Starter Motor Terminal Locknut
Starter Motor Bolts 4.9 0.50 43 in·lb
Starter Motor Clutch Bolts 34 3.5 25 L
Alternator Stator Bolts 13 1.3 113 in·lb
Crankshaft Sensor Mounting Bolts 5.9 0.60 52 in·lb
Alternator Cover Plugs 18 1.8 13
Alternator Rotor Bolt 127 13 94
Alternator Cover Bolts 8.8 0.90 78 in·lb
Spark Plugs 13 1.3 113 in·lb
2WD/4WD Actuator Mounting Bolts 9.8 1.0 87 in·lb L,S
Engine Brake Actuator Mounting Bolts 8.8 0.90 78 in·lb
Forward/Reverse Detectring Sensor Mounting Bolt 15 1.5 11
Speed Sensor Mounting Bolt 8.8 0.90 78 in·lb
Neutral Position Switch 15 1.5 11
Reverse Position Switch 15 1.5 11
Ignition Coil Mounting Bolts 8.8 0.90 78 in·lb
N·m kgf·m ft·lb
42 4.3 31
6.9 0.70 61 in·lb
Torque
Remarks
Page 32

2-10 PERIODIC MAINTENANCE
Torque and Locki ng Agent
Fastener
N·m kgf·m ft·lb
Radiator Fan Switch 18 1.8 13
Coolant Temperature Warning Light Switch 6.9 0.70 61 in·lb SS
Oil Pressure Switch 15 1.5 11 SS
Oil Pressure Switch Terminal Bolt 1.5 0.15 13 in·lb
Regulator/Rectifier M ounting Bolts 8.8 0.90 78 in·lb
Fuel Level Sensor Mounting Bolts 2.0 0.20 18 in·lb
The tables below, relating tightening torque to thread diameter, lists the basic torque for the bolts
and nuts. Use this table for only the bolts and nuts which do not require a specific torque value. All of
the values are for use with dry solvent-cleaned threads.
Torque
Remarks
Basic Torque for General Fasteners of Engine Parts
Threads dia. Mark of Torque
mm (in.) bolt head N·m kgf·m ft·lb
6 (0.24) 9T 12 ∼ 15 1.2 ∼ 1.5 104 ∼ 130 in·lb
6 (0.24) 7T 7.8 ∼ 9.8 0.8 ∼ 1.0 69 ∼ 87 in·lb
6 (0.24) 4T 3.9 ∼ 4.9 0.4 ∼ 0.5 35 ∼ 43 in·lb
8 (0.31) 7T 18 ∼ 22 1.8 ∼ 2.2 13 ∼ 16
8 (0.31) 4T 10 ∼ 14 1.0 ∼ 1.4 87 ∼ 122 in·lb
10 (0.39)
10 (0.39)
5 (0.20) 4T 2.2 ∼ 2.6 0.22 ∼ 0.27 19 ∼ 23 in·lb
7T 39 ∼ 44 4.0 ∼ 4.5 29 ∼ 33
4T 20 ∼
24
2.0
∼ 2.4
14 ∼
17
Basic Torque for General Fasteners of Frame Parts
Threads dia. Torque
mm (in.) N·m kgf·m ft·lb
5 (0.20) 3.4 ∼ 4.9 0.35 ∼ 0.5 30 ∼ 43 in·lb
6 (0.24) 5.9 ∼ 7.8 0.6 ∼ 0.8 52 ∼ 69 in·lb
8 (0.31) 14 ∼ 19 1.4 ∼ 1.9 10.0 ∼ 13.5
10 (0.39) 25 ∼ 34 2.6 ∼ 3.5 19.0 ∼ 25
12 (0.47) 44 ∼ 61 4.5 ∼ 6.2 33 ∼ 45
14 (0.55) 73 ∼ 98 7.4 ∼ 10.0 54 ∼ 72
16 (0.63)
18 (0.71)
20 (0.79) 225 ∼ 325 23 ∼ 33 165 ∼ 240
115 ∼ 155 11.5 ∼ 16.0 83 ∼ 115
165 ∼ 225 17.0 ∼ 23.0 125 ∼ 165
Page 33

PERIODIC MAINTENANCE 2-11
Specifications
Item Standard Service Limit
Fuel System
Throttle Lever Free Play 2 ∼ 3 mm (0.08 ∼ 0.12 in.) –––
Choke Lever Free Play about 3 mm (0.12 in.) –––
Idle Speed 1 150 ± 50 r/min (rpm) –––
Air Cleaner Element Oil High-quality foam air filter oil
Cooling System
Coolant:
Type (Recommended) Permanent type antifreeze –––
Color Green –––
Mixed Ratio Soft water 50%, Coolant 50% –––
Freezing Point −35°C (−31°F) –––
Total Amount 2.2 L (2.3 US qt.) –––
Engine Top End
Valve Clearance:
Exhaust 0.20 ∼ 0.25 mm (0.0079 ∼ 0.0098 in.) –––
Inlet 0.10 ∼ 0.15 m m (0.0039 ∼ 0.0059 in.) –––
Converter System
Belt Width 29.7 ∼ 30.3 mm (1.169 ∼ 1.193 in.) 28.0 mm (1.102 in.)
Belt Deflection 22 ∼ 27 mm (0.87 ∼ 1.06 in.) –––
Actuator Lever Guide Shoe Wear
Engine Lubrication System
Engine Oil:
Type API SF or SG –––
Viscosity SAE10W-40 –––
Capacity 2.1 L (2.2 US qt) –––
Wheels/Tires
Tire Tread Depth:
Front ––– 3 mm (0.12 in.)
Rear –––
Standard tire:
Front AT 25 × 8-12 –––
Rear AT 25 × 10-12 –––
–––
API SH or SJ with JASO MA class –––
(When filter is not removed)
2.2 L (2.3 US qt) –––
(When filter is removed)
2.6 L (2.7 US qt) –––
(When engine is completely dry)
DUNLOP, KT191, Tubeless
DUNLOP, KT195, Tubeless –––
–––
6 mm (0.24 in.)
4 mm (0.16 in.)
–––
Page 34

2-12 PERIODIC MAINTENANCE
Specifications
Item Standard Service Limit
Final Drive
Front Final Gear Case:
Gear Case Oil:
Type API SF or SG –––
API SH or SJ of JASO MA class –––
Viscosity SAE 10W-40 –––
Oil Level Filler opening bottom –––
Capacity 0.40 L (0.42 US qt) –––
Rear Final Gear Case:
Gear Case Oil:
Type
Oil level Filler opening bottom –––
Capacity 0.72 L (0.76 US qt) –––
Brakes
Front Brake Fluid:
Type DOT 3 or DOT 4 –––
Front Disc Brake:
Pad Lining Thickness 4mm(0.16in.) 1 mm (0.04 in.)
Rear Brake Lever, Pedal and
Cables:
Rear Brake Lever Free Play 1 ∼ 2 mm (0.04 ∼ 0.08 in.) –––
Brake Pedal Free Play 15 ∼ 25 mm (0.6 ∼ 1.0 in.) –––
Electrical System
Spark Plug Gap 0.7 ∼ 0.8 mm (0.028 ∼ 0.032 in.) –––
Rear Brake Light Switch Timing
MOBIL Fluid 424, CITGO
TRANSGARD TRACTOR
HYDRAULIC FLUID, or EXXON
HYDRAUL 560
ON after 10 mm (0.4 in.) of pedal
travel
–––
–––
Page 35

Special Tools
PERIODIC MAINTENANCE 2-13
Oil Filter Wrench:
57001-1249
Carburetor Drain Plug Wrench, Hex 3:
57001-1269
Flywheel & Pulley Holder:
57001-1343
Filler Cap Driver:
57001-1454
Pulley Holder Attachment:
57001-1472
Page 36

2-14 PERIODIC MAINTENANCE
Periodic Maintenance Procedures
Fuel System
Throttle Lever Free Play Inspection
Check that the throttle lever [A] moves smoothly from full
•
open to close, and the throttle closes quickly and completely in all steering positions by the return spring.
If the throttle lever does not return properly, check the
throttle cable routing, lever free play, and cable damage.
Then lubricate the throttle cable.
Run the engine at the idle speed, and turn the handlebar
•
all the way to the right and left to ensure that the idle speed
does not change.
If the idle speed increases, check the throttle lever free
play and the cable routing.
Stop the engine and check the throttle lever free play [B].
•
If the free play is not within the specified range, adjust the
cable.
Throttle Lever Free Play
Standard: 2 ∼ 3 mm (0.08 ∼ 0.12 in.)
Throttle Lever Free Play Adjustment
Remove the handle cover (see Multifunction Meter Unit
•
Removal in the Electrical System chapter).
Slide the rubber cover off the adjuster at the throttle case.
•
Loosen the locknut [A] and turn the throttle cable upper
•
adjuster [B] until the cable has proper amount of play.
Tighten the locknut and reinstall the rubber cover.
•
If the free play cannot be adjusted by using the upper cable adjuster, remove the left side cover (see Frame chapter) and then use t he cable adjusting nuts [A] at the lower
end of the throttle cable and make the necessary free
play.
Choke Lever Free Play Inspection
Check if the choke lever [A] returns properly and if the
•
inner cable slides smoothly.
Make sure that the choke lever returns to its released po-
•
sition all the way.
To determine the amount of choke cable play at the lever,
•
pull the choke lever to the left until feeling the operation of
the lever tough; the amount of choke lever is equivalent
to that of cable play.
The proper amount of play ranges about 3 mm (0.12 in.)
•
at the choke lever.
If the free play is not within the specified range, adjust the
cable.
ChokeLeverFreePlay[B]
Standard: about 3 mm (0.12 in.)
Page 37

Periodic Maintenance Procedures
Choke Lever Free Play Adjustment
Remove:
•
Handlebar Cover Screws [A]
Remove:
•
Handlebar Cover Screws [A]
Handlebar Cover Front [B]
PERIODIC MAINTENANCE 2-15
Loosen the locknut [A] of the choke cable.
•
Turn the adjuster [B] until the cable has proper amount of
•
play.
Tighten the l ocknut securely.
•
Idle Speed Inspection
Start the engine and warm it up thoroughly.
•
With the engine idling, turn the handlebar to both sides to
•
check for any changes in the idle speed.
If handlebar movement changes the idle speed, the throttle cable may be improperly adjusted incorrectly routed,
or damaged. Be sure to correct any of these conditions
before riding.
WARNING
Operation with improperly adjusted, incorrectly
routed, or damaged cables could result in an unsafe riding condition.
Check idle speed with a suitable tachometer.
•
If the idle speed is out of the specified range, adjust it (see
Idle Speed Adjustment).
Idle Speed
Standard: 1 150 ± 50 r/min (rpm)
Page 38

2-16 PERIODIC MAINTENANCE
Periodic Maintenance Procedures
Idle Speed Adjustment
Start the engine and warm it up thoroughly.
•
Turn the idle adjusting screw [A] until the idle speed is
•
correct.
Open and close the throttle a few times to make sure that
○
the idle speed is within the specified range.
Fuel System Cleanliness Inspection
WARNING
Gasoline is extremely flammable and can be explosive under certain conditions. Turn the ignition
switch O FF. Do not smoke. Make sure the area is
well-ventilated and free from any source of flame
or sparks; this includes any appliance with a pilot
light.
Remove the check valve [A] at the end of the carburetor
•
overflow hose [B].
Run the lower end of the carburetor overflow hose to a
•
suitable container.
Turn out the carburetor drain plugs [A] a few turns and
•
drain the fuel system.
Special Tool - Carburetor Drain Plug Wrench, Hex 3 [B] :
57001-1269
Check to see if water or dirt com es out.
•
Tighten the drain plugs.
•
If any water or dirt appears during the above inspection,
clean the fuel system (carburetor, fuel pump, fuel tank,
fuel hose).
Page 39

Periodic Maintenance Procedures
Air Cleaner Element Cleaning and Inspection
NOTE
In dusty areas, the element should be cleaned more
○
frequently than the recommended interval.
After riding through rain or muddy terrains, the element
○
should be cleaned immediately.
Also, if there is a break in the element m aterial or any
○
other damage to the element, replace the element with
a new one.
WARNING
Clean the element in a well-ventilated area, and
take care that there are no sparks or flame anywhere near the working area; this includes any
appliance with a pilot light. Because of the danger
of highly flammable liquids, do not use gasoline or
a low-flash point solvent to clean the foam element.
Remove the air cleaner element (see Fuel System chap-
•
ter).
PERIODIC MAINTENANCE 2-17
Clean the element [A] in a bath of high-flash point solvent.
•
Squeeze it dry in a clean towel [A]. Do not wring the ele-
•
ment or blow it dry; the element can be damaged.
Inspect the element for damage.
•
If it is torn, punctured, or hardened, replace it.
After cleaning, saturate the element with a high-quality
•
foam-air-filter oil, squeeze out the excess oil, then wrap
it in a clean rag and squeeze it as dry as possible. Be
careful not to tear the element.
Air Cleaner Draining
If any water or oil accumulates in the tube, drain it by
•
taking off the tube plug [A]. After draining, be sure to install
the tube plug and clamp firmly.
Page 40

2-18 PERIODIC MAINTENANCE
Periodic Maintenance Procedures
Fuel Hose and Connection Inspection
The fuel hoses are designed to be used throughout the
○
vehicle life without any maintenance, however, if the vehicle is not properly handled, the pressure inside the fuel
line can cause fuel to leak [A] or the hose to burst. Check
the fuel hose.
Replace the fuel hose if any fraying, cracks [B] or bulges
[C] are noticed.
Check that the hoses are securely connected and clamps
•
are installed correctly.
When installing the fuel hoses, route the hoses according
•
to Cable, Wire, and Hose Routing section in the Appendix
chapter.
When installing the fuel hoses, avoid sharp bending, kink-
•
ing, flattening or twisting, and route the fuel hoses with a
minimum of bending so that the fuel flow will not be obstructed.
Replace the hose if it has been sharply bent or kinked.
Fit the fuel hose [A] onto the fitting fully and install the
•
plate clamp [B] beyond the raised rib [C].
1 ∼ 2 mm (0.0039 ∼ 0.0078 in.) [D]
The hose end must reach the fillet [E] or be as near as
○
possible to the step [F].
Fit the fuel pump inlet hoses onto the Y-joint fully until
○
each end of the inlet hose touches the second raised rib.
Fuel Hose Replacement
WARNING
Gasoline is extremely flammable and can be explosive under certain conditions. Turn the ignition
switch O FF. Do not smoke. Make sure the area is
well ventilated and free from any source of flame
or sparks; this includes any appliance with a pilot
light.
Remove:
•
Right Side Cover (see Frame chapter)
Electric Parts Case (see Frame chapter)
Rear Fender (see Frame chapter)
Turn the fuel tap to the ON position.
•
Page 41

Periodic Maintenance Procedures
Remove:
•
Clamps [A]
Fuel Hoses [B]
Replace the fuel hoses with new ones.
•
When installing the fuel hose, route the hose according
•
to Cable, Wire, and Hose Routing section in Appendix
chapter.
When installing the fuel hose, avoid sharp bending, kink-
•
ing, flattening or twisting, and route the fuel hose w ith a
minimum of bending so that the fuel flow will not be obstructed.
Fit the fuel hose onto the pipe fully and install the clamps
•
beyond the raised r ib (see Fuel Hose and Connection Inspection).
PERIODIC MAINTENANCE 2-19
Cooling System
Radiator Cleaning
CAUTION
Clean the radiator screen and the radiator in accordance with the P eriodic Maintenance Chart.
In dusty areas, they should be cleaned more frequently than the recommended interval. After
riding through muddy terrains, the radiator screen
and the radiator should be cleaned immediately.
Remove:
•
Front Guard (see Frame chapter)
Front Fender (see Frame chapter)
Radiator Screen Mounting Screws [A]
Radiator Screen [B]
Clean the radiator screen in a bath of tap water, and then
•
dry it with compressed air or by shaking it.
Clean the radiator.
•
CAUTION
When cleaning the radiator w ith steam cleaner, be
careful of the following to prevent radiator damage.
Keep the steam gun away more than 0.5 m (20 in.)
from the radiator core [A].
Hold the steam gun perpendicular to the core surface.
Run the steam gun following the core fin direction.
Page 42

2-20 PERIODIC MAINTENANCE
Periodic Maintenance Procedures
Radiator Hose and Connection Inspection
The high pressure inside the radiator hose can cause
○
coolant to leak [A] or the hose to burst if the line is not
properly maintained. Visually inspect the hoses for signs
of deterioration. Squeeze the hoses. A hose should not
be hard and brittle, nor should i t be soft or swollen.
Replace the hose if any fraying, cracks [B] or bulges [C]
are noticed.
Check that the hoses are securely connected and clamps
•
are tightened correctly.
Coolant Change
WARNING
To avoid burns, do not remove the radiator cap or
try to change the coolant when the engine is still
hot. Wait until it cools down.
Coolant on tires will make them slippery and can
cause an accident and injury. Immediately wash
away any coolant that spills on the frame, engine,
or wheels.
Since coolant is harmful to the human body, do not
use for drinking.
Remove:
•
Left Footboard (see Frame chapter)
Front Fender (see Frame chapter)
Radiator Cover Screws [A] and Collars
Remove:
•
Radiator Cover Screws [A] and Collars
Radiator Cover [B]
Page 43

Periodic Maintenance Procedures
Remove:
•
Clamp [A]
Reserve Tank Screws [B]
Reserve Tank [C] with Hose
Remove the reserve tank cap, and pour the coolant into
•
a container.
Place a container under the drain plug [A] at the bottom
•
of the water pump [B], then remove the drain plug.
PERIODIC MAINTENANCE 2-21
Remove the radiator cap [A] in two steps. First turn the
•
cap counterclockwise to the first step. Then push and turn
it further in the same direction and remove the cap.
The coolant will drain from the radiator and engine.
•
Place a container under the drain plug [A] at the front
•
cylinder, then remove the drain plug.
Place a container under the drain plug [A] at the rear cylin-
•
der, then remove the drain plug.
Page 44

2-22 PERIODIC MAINTENANCE
Periodic Maintenance Procedures
Tighten the drain plug.
•
Torque - Coolant Drain Plug: 8.8 N·m (0.90 kgf·m, 78 in·lb)
Support the vehicle on a stand or the jack so that the front
•
wheels are off the ground. This makes air bleeding easier.
Fill the r adiator up to the radiator filler neck [A] with
•
coolant.
NOTE
Pour in the coolant slowly so that the air in the engine
○
and radiator can escape.
CAUTION
Soft or distilled water must be used with the antifreeze in the cooling system.
If hard water is used in the system, it causes scale
accumulation in the water passages, considerably
reducing the efficiency of the cooling system.
Water and Coolant Mixture Ratio (when shipping)
Soft Water: 50%
Coolant: 50%
Freezing Point:
Total Amount:
−35°C (−31°F)
2.2 L (2.3 US qt)
NOTE
Choose a suitable mixture ratio by referring to the
○
coolant manufacturer’s directions.
Bleed the air from the cooling system as follows.
•
Start t he engine with the r adiator cap removed and run it
○
until no more air bubbles [A] can be seen in the coolant.
Tap the radiator hoses to force any air bubbles caught
○
inside.
Stop the engine and add coolant up to the radiator filler
○
neck.
Install the radiator cap.
•
Remove the reserve tank cap.
•
Fill the reserve tank up to the F mark [A] with coolant and
•
install the cap.
Start the engine, warm it up thoroughly until the radiator
•
fan turns on and then stop the engine.
Check the coolant level in the reserve tank after the en-
•
gine cools down.
If the coolant level is lower than the low level line, add
coolant to the full level line.
CAUTION
Do not add more coolant above the full level line.
Page 45

Periodic Maintenance Procedures
Engine Top E nd
Valve Clear ance Inspection
NOTE
Check the valve clearance only when the engine is cold
○
(at room temperature).
Remove:
•
Left Side Cover (see Frame chapter)
Battery Case (see Frame chapter)
Valve Adjusting Caps [A]
Recoil Starter (see Recoil Starter chapter)
Remove the timing inspection plug [A].
•
Special Tool - Filler Cap Driver [B]: 57001-1454
PERIODIC MAINTENANCE 2-23
Turn the crankshaft counterclockwise with a wrench on
•
the alternator rotor bolt until “T-F” mark [A] on the alternator rotor aligns with the notch [B] as shown: the end of
the compression stroke in the front cylinder head.
Measure the clearance for all four valves, one at a time
•
between the end of the valve stem and the adjusting
screw [A] with the thickness gauge [B].
Valve Clearance (when cold)
Exhaust:
Inlet:
If the valve clearance is not correct, adjust it (see Valve
Clearance Adjustment).
0.20 ∼ 0.25 mm (0.0079 ∼ 0.0098 in.)
0.10 ∼ 0.15 mm (0.0039 ∼ 0.0059 in.)
Page 46

2-24 PERIODIC MAINTENANCE
Periodic Maintenance Procedures
Then, turn the crankshaft counterclockwise with a
•
wrench on the alternator rotor bolt until “T-R” mark [A] on
the alternator rotor aligns with the notch [B] as shown:
the end of the compression stroke in the rear cylinder
head.
Measure the clearance for all four valves, one at a time
•
between the end of the valve stem and the adjusting
screw with the thickness gauge.
Valve Clearance (when cold)
Exhaust: 0.20 ∼ 0.25 mm (0.0079 ∼ 0.0098 in.)
Inlet:
If the valve clearance is not correct, adjust it (see Valve
Clearance Adjustment).
Valve Clearance Adjustment
Remove the valve adjusting caps.
•
Loosen the locknut and turn the adjusting screw until the
•
clearance is correct.
Hold the adjusting screw [A] from turning and tighten the
•
locknut [B].
Torque - Valve Adjusting Screw Locknuts: 12 N·m (1.2
Recheck the clearance.
•
If the clearance is incorrect, repeat the adjustment procedure.
If the clearance is correct, perform the adjustment procedure on the other valve.
0.10 ∼ 0.15 mm (0.0039 ∼ 0.0059 in.)
kgf·m, 104 in·lb)
Spark Arrester Cleaning
WARNING
To avoid burns, wear gloves while cleaning the
spark arrester. Since the engine must be run during this procedure, the muffler will become hot.
Remove the drain plug [A] on the muffler.
•
In an open area away from combustible materials, start
•
the engine w ith the transmission in neutral.
Raise and lower engine speed while tapping on the muf-
•
fler with a rubber mallet until carbon particles are purged
from the muffler.
WARNING
Do not run t he engine in a closed area. Exhaust
gases contain carbon m onoxide; a colorless, odorless, poisonous gas. Breathing exhaust gas leads
to carbon monoxide poisoning, asphyxiation, and
death.
Stop the engine.
•
Install the drain plug.
•
Page 47

Periodic Maintenance Procedures
Converter System
Drive Belt Inspection
Inspection of the drive belt is required at least every 90
days of vehicle use (average 12 mile/day) not to exceed 1
700 km (1 100 mile) or belt indicator light turn on (100 hours
of use) counted by the hour meter. More frequent inspection
is necessary if the vehicle is subjected to hard usage.
WARNING
Neglect, abuse, or failure to maintain the transmis-
sion can result in a severely worn or damaged drive
belt locking up the transmission and wheels. This
can cause the operator to lose control and have an
accident resulting in injury or death.
Remove the torque converter cover (see Converter Sys-
•
tem chapter).
Measure the width [A] of the belt at several locations with
•
a pair of suitable straightedges [B] as shown.
If any measurements exceed the service limit, replace the
belt.
PERIODIC MAINTENANCE 2-25
Belt Width
Standard: 29.7 ∼ 30.3 mm (1.169 ∼ 1.193 in.)
Service Limit: 28.0 mm (1.102 in.)
Check the belt [A] for abnormal wear [B].
•
Measure the width [C] of the belt at abnormal wear point.
○
If any measurements exceed 0.5 mm (0.02 in.), replace
the belt.
When using the belt of large abnormal wear, the drive belt
○
failure detection switch could be activated.
Check the belt for cracks, breaks, or peeling.
•
If necessary, replace t he belt with a new one.
Belt [A]
Crack [B]
Broken [C]
Peeling [D]
NOTE
Whenever the belt is replaced, inspect the drive and the
○
driven pulleys.
Drive Bel t Deflection Inspection
Remove the torque converter cover (see Converter Sys-
•
tem chapter).
Put the transmission in neutral and rotate the driven pulley
•
by hand to make sure the belt is shifted all the way to the
top of the driven pulley.
Page 48

2-26 PERIODIC MAINTENANCE
Periodic Maintenance Procedures
Measure the belt deflection [A] as shown:
•
Place a straightedge [B] on top of the belt between the
○
drive pulley [ C] and the driven pulley [D].
Use a ruler to push the belt away from the straightedge.
○
Push hard, but with no more force than 59 N (6 kgf, 13 lb).
Belt Deflection
Standard: 22 ∼ 27 mm (0.87 ∼ 1.06 in.)
If the belt deflection is not within the specified range, adjust the deflection by adding or removing spacers on the
fixed sheave of the driven pulley.
When adjusting the deflection, less is better than more.
•
Less deflection will maintain better performance for more
time as the belt width decreases by normal wear, which
causes the deflection to increase with usage.
Drive Belt Deflection Adjustment
Disassemble the driven pulley (see Converter System
•
chapter).
If the belt deflection is more than 27 m m (1.06 in.), remove
the spacers to decrease it.
The rule-of-thumb is: 0.1 mm (0.004 in.) change in spacer
○
thickness equals about 1.3 mm (0.051 in.) change in belt
deflection.
If the adjustment cannot be done within the specified
range even if the shim is removed, replace the drive belt.
If the belt deflection is less t han 22 mm (0.87 in.), add the
spacers [A] to increase it.
The rule-of-thumb is: 0.1 mm (0.004 in.) change in spacer
○
thickness equals about 1.6 mm (0.063 in.) change in belt
deflection.
NOTE
When using the plural spacers, install the thick spacer
○
to the movable sheave side and thin spacer to the fixed
sheave side.
Spacers
Part No. Thickness
92026-0034
92026-1569
92026-1617
92026-1565
92026-1570 1.4 mm (0.055 in.)
0.3 mm (0.012 in.)
0.6 mm (0.024 in.)
0.8 mm (0.032 in.)
1.0 mm (0.039 in.)
Page 49

Periodic Maintenance Procedures
Assemble the driven pulley (see Converter System chap-
•
ter).
With the transmission in neutral, rotate the driven pulley
•
to allow the belt to return to the top of the sheaves before
measuring the belt deflection.
Measure the belt deflection again and repeat the above
•
procedures until it is within the standard range.
Using the flywheel & pulley holder and pulley holder at-
•
tachment, tighten the driven pulley nut.
Special Tools - Flywheel & Pulley Holder: 57001-1343
Pulley Holder Attachment: 57001-1472
Torque - Driven Pulley Nut: 93 N·m (9.5 kgf·m, 69 ft·lb)
Actuator Lever (Engine Brake Control Lever) Assembly Inspection
Measure the width [A] of the plastic guide shoe [B] of the
•
actuator lever assembly.
If the guide contact area width is greater than the service
limit, replace t he actuator lever assembly.
PERIODIC MAINTENANCE 2-27
Actuator Lever Guide Shoe
Service Limit: 6 mm (0.24 in.)
Engine Lubrication System
Engine Oil Change
Support the vehicle so that it is level side to side and front
•
to back after warming up the engine.
Remove the engine drain plug [A] to drain the oil.
•
The oil in the filter can be drained by removing the f ilter
○
(see Oil Filter Change).
Replace the drain plug gasket with a new one.
•
Tighten:
•
Torque - Engine Drain Plug: 20 N·m (2.0 kgf·m, 14 ft·lb)
Pour in the specified type and amount of oil.
•
Engine Oil
Type: API SF or SG
API SH or SJ with JASO MA class
Viscosity: SAE 10W-40
Amount: 2.1 L (2.2 US qt)
(When filter is not removed)
2.2 L (2.3 US qt)
(When filter is removed)
2.6 L (2.7 US qt)
(When engine is completely dry)
NOTE
Although 10W-40 engine oil is the recommended oil
○
for most conditions, the oil viscosity may need to be
changed to accommodate atmospheric conditions in
your riding area.
Page 50

2-28 PERIODIC MAINTENANCE
Periodic Maintenance Procedures
Oil Filter Replacement
Drain the engine oil.
•
Remove the oil filter [A] with the oil filter wrench [B].
•
Special Tool - Oil Filter Wrench: 57001-1249
Replace the filter with a new one.
•
When installing the oil filter, be careful of the following.
•
Apply oil to the gasket [A] before installation.
○
Tighten the filter with the oil filter wrench.
○
Special Tool - Oil Filter Wrench: 57001-1249
Torque - Oil Filter: 18 N·m (1.8 kgf·m, 1 3 ft·lb)
Pour in the specified type and amount of oil.
○
Wheels/Tires
Tire Inspection
Examine the tire for damage and wear.
•
If the tire is cut or cracked, replace it.
Lumps or high spots on the tread or sidewalls indicate
○
internal damage requiring tire replacement.
Remove any foreign objects from the tread. After re-
○
moval, check for leaks with a soap and water s olution.
Measure the tread depth at the center of the tread with a
•
depth gauge [A]. Since the tire may wear unevenly, take
measurements at several places.
If any measurements are less than the service limit, replace the tire.
Tire Tread Depth
Service Limit:
Front: 3 mm (0.12 in.)
Rear: 4 mm (0.16 in.)
Standard Tire
Front: AT 25 × 8 - 12
DUNLOP, KT191, Tubeless
Rear: AT 25 × 10 - 12
DUNLOP, KT195, Tubeless
Page 51

Periodic Maintenance Procedures
Final Drive
Variable Differential Control Lever Play Inspection
Pull the variable differential control lever [A] towards the
•
handlebar grip [B] with a spring scale until it reads 30 N
(3 kgf, 7 lb) of force.
The differential control in the front final gear case must be
○
locked, then the clearance [C] between the control lever
and grip should be 20 mm (0.8 in.).
If the clearance is not the specified length, adjust the ca-
ble.
Differential Control Lever Lock Position Length
Standard: 20 mm (0.8 in.)
Variable Differential Control Lever Play Adjustment
Remove:
•
Handlebar Cover Screws [A]
PERIODIC MAINTENANCE 2-29
Remove:
•
Handlebar Cover Screws [A]
Handlebar Cover Front [B]
Loosen the locknut [A] of t he differential control cable.
•
Turn the adjuster [B] until the cable has proper amount of
•
play.
Tighten the l ocknut securely.
•
Page 52

2-30 PERIODIC MAINTENANCE
Periodic Maintenance Procedures
Front Final Gear Case Oil Change
Warm up the oil by running the vehicle so that the oil will
•
pick up any sediment and drain easily. Then stop the
vehicle.
Park the vehicle so that it is level, both side-to-side and
•
front-to-rear.
Remove the front side cover (see Frame chapter).
•
Place an oil pan beneath the front final gear case and
•
remove the drain plug [A].
WARNING
When draining or filling the final gear case, be careful that no oil gets on the tire or rim. Clean off any
oil that inadvertently gets on them with a high-flash
point solvent.
After the oil has completely drained out, install the drain
•
plug with a new aluminum gasket, and tighten it.
Torque - Oil Drain Plug: 15 N·m (1.5 kgf·m, 11 ft·lb)
Fill the gear case up to the bottom of filler opening with
•
the oil specified below.
Front Final Gea r Case Oil
Type: API SF or SG
APISHorSJwithJASOMAclass
Viscosity: SAE 10W-40
Capacity: 0.40 L (0.42 US qt)
NOTE
Depending on the atmospheric temperature of your rid-
○
ing area, the engine oil viscosity should be changed according to the chart.
Be sure the O-ring [A] is in place, and tighten the filler cap
•
[B].
Apply grease to the O-ring.
○
Torque - Oil Filler Cap: 29 N·m (3.0 kgf·m, 22 ft·lb)
Page 53

Periodic Maintenance Procedures
Rear Final Gear Case Oil Change
Warm up the oil by running the vehicle so that the oil will
•
pick up any sediment and drain easily. Then stop the
vehicle.
Park the vehicle so that it is level, both side-to-side and
•
front-to-rear.
Place an oil pan beneath the rear final gear case and
•
remove the drain plug [A].
WARNING
When draining or filling the final gear case, be care-
ful that no oil gets on the tire or rim because oil will
deteriorate the tire. Clean off any oil that inadver-
tently gets on them with a high-flash point solvent.
After the oil has completely drained out, install the drain
•
plug with a new aluminum gasket.
Torque - Oil Drain Plug: 13 N·m (1.3 kgf·m, 113 in·lb)
Fill the final gear case up to the bottom of filler opening
•
with the oil specified below.
PERIODIC MAINTENANCE 2-31
Final Gear Case Oil
Type: MOBIL FLUID 424,
CITGO TRANSGARD TRACTOR
HYDRAULIC FLUID or EXXON HYDRAUL
560
Capacity: 0.72 L (0.76 US qt)
Do not use mixing the above oils.
○
Be sure the O-ring [A] is in place, and tighten the filler cap
•
[B].
Apply grease to the O-ring.
○
Torque - Oil Filler Cap: 29 N·m (3.0 kgf·m, 22 ft·lb)
Page 54

2-32 PERIODIC MAINTENANCE
Periodic Maintenance Procedures
Universal Joint Lubrication
Remove:
•
Rear Propeller Shaft (see Final Drive chapter)
Force grease into the grease nipples [A] until the grease
•
comes out from the nipple, and wipe off any excess
grease.
[B] Grease Gun
Brakes
Front Brake Pad Wear Inspection
Check the lining thickness [A] of the pads in each caliper.
•
If the lining thickness of either pad is less than the service
limit [B], replace both pads in the caliper as a set.
Pad Lining Thickness
Standard: 4 mm (0.16 in.)
Service Limit: 1 mm (0.04 in.)
Front Brake Hoses and Connections Inspection
Inspect the brake hose and fittings for deterioration,
•
cracks and signs of leakage.
Thehighpressureinsidethebrakelinecancausefluidto
○
leak [A] or the hose to burst if the line is not properly maintained. Bend and twist the rubber hose while examining
it.
Replace the hose if any cracks [B] or bulges [C] are noticed.
Tighten any loose fittings.
•
Page 55

Periodic Maintenance Procedures
Front Brake Hose Replacement
Pump the brake fluid out of the line as explained in the
•
Brake Fluid Change.
Remove the banjo bolts at both ends of the brake hose,
•
and pull the hose off the vehicle.
Immediately wipe up any brake fluid that spills.
•
CAUTION
Brake fluid quickly ruins painted surfaces; any
spilled fluid should be completely w ashed away
immediately.
Use a new flat washer for each side of the hose fittings.
•
Install the new brake hose in its place (see Appendix
•
chapter), and tighten the banjo bolts.
Torque - Brake Hose Banjo Bolts: 25 N·m (2.5 kgf·m, 18
ft·lb)
Brake Fluid Level Inspection
Position the reservoir horizontal, and check that the fluid
•
level in the reservoir is higher than the lower level line [A].
If the fluid level is lower than the lower level line, check
for fluid leakage of the brake line, and add the fluid as
follows:
PERIODIC MAINTENANCE 2-33
Remove the reservoir cap, and fill the reservoir to the up-
○
per level line [A] in the reservoir with the same type and
brand of the fluid that is already in the reservoir. And then
install the reservoir cap.
WARNING
Change the fluid in the brake line completely if the
fluid must be refilled but the type and brand of the
fluid that is already in the reservoir are unidentified.
Tighten:
•
Torque - Reservoir Cap Screws: 1.5 N·m (0.15 kgf·m, 13
in·lb)
Page 56

2-34 PERIODIC MAINTENANCE
Periodic Maintenance Procedures
Brake Fluid Change
Remove the reservoir cap and the rubber cap on the bleed
•
valve.
Attach a clear plastic hose to the bleed valve on the
•
caliper, and run the other end of the hose into a container.
Fill the reservoir with new brake fluid.
•
Change the brake fluid as follows:
•
Open the bleed valve [A].
○
Apply the brake lever and hold it [B].
○
Close the bleed valve [C].
○
Release the brake lever [D].
○
Check the fluid level in the reservoir often, replenishing it
•
as necessary.
NOTE
If the fluid in the reservoir runs completely out any time
○
during fluid changing, air will enter the line, and the system must be bled.
Repeat this operation until fresh brake fluid comes out into
•
the plastic hose or the color of the fluid changes.
WARNING
Do not mix t wo brands of fluid. Change the brake
fluid in the brake line completely if the brake fluid
must be refilled but the type and brand of the brake
fluid that is already in the reservoir are not known.
Tighten:
•
Torque - Bleed Valves: 5.4 N·m (0.55 kgf·m, 48 in·lb)
Apply the brake lever forcefully for a few seconds, and
•
check for fluid leakage around the fittings.
If necessary, bleed the air from the brake line (see Brake
Line Air Bleeding section in Brakes chapter).
WARNING
If the brake lever has a soft or "spongy feeling"
when it is applied, there might be air in the brake
line or the brake may be defective. S ince it is dangerous to operate the vehicle under such conditions, bleed the air from the brake line immediately.
Front Brake Master Cylinder Piston Assembly and
Dust Seal Replacement
Refer to the Master Cylinder section in the Brakes chap-
•
ter f or Front Brake Master Cylinder Piston Assembly and
Dust Seal Replacement.
Front Brake Caliper Piston Seal and Dust Seal Replacement
Refer to the Caliper section in the Brakes chapter for Front
•
Brake Caliper Piston Seal and Dust Seal Replacement.
Page 57

Periodic Maintenance Procedures
Rear Brake Plates Replacement
Replace the steel plates and friction plates in accordance
•
with the specified interval (see Rear Final Gear Case sec-
tion in the Final Drive chapter).
Rear Brake Lever Free Play Inspection
Check the rear brake lever free play [A].
•
Pull the rear brake lever lightly until the brake is applied.
○
If the play is incorrect, adjust it.
Rear Brake Lever Free Play
Standard: 1 ∼ 2mm(0.04∼ 0.0 8 in.)
Brake Pedal Free Play Inspection
Check the brake pedal free play [A].
•
Depress the brake pedal lightly by hand until the brake is
○
applied.
If the free play is incorrect, adjust it.
PERIODIC MAINTENANCE 2-35
Brake Pedal Free Play
Standard: 15 ∼ 25 mm (0.6 ∼ 1.0 in.)
Rear Brake Lever and Pedal F ree Play Adjustment
NOTE
Since the rear brake lever and pedal free play adjust-
○
ments affect each other, make them at the same time.
Rear Brake Lever:
Loosen the knurled locknut [A] and turn the adjuster [ B]
•
at the rear brake lever in as far as it will go.
Tighten the locknut.
•
Turn the brake lever adjuster [A] at the rear end of the
•
brake cable until the rear brake lever has the correct
amount of play.
Brake Pedal:
Turn the brake pedal adjuster [B] at the rear end of the
•
brake cable until the brake pedal has the correct amount
of play.
Operate the pedal a few times to see that it returns to its
•
rest position immediately upon release.
Rotate the rear wheels to check for brake drag.
•
Check braking effectiveness.
•
If there is any doubt as to the conditions of the brake,
check the brake parts for wear or damage.
Page 58

2-36 PERIODIC MAINTENANCE
Periodic Maintenance Procedures
Steering
Steering Inspection
Turn the handlebar left and right, and check the steering
•
action.
If the steering action is not smooth, or if the steering binds
or catches before the stop, lubricate the steering stem
bearing.
NOTE
The cables and wires will have some effect on the steer-
○
ing action which must be taken into account.
Check the steering action again.
•
If steering stem bearing lubrication does not remedy the
problem, inspect the steering stem for straightness, steering stem clamps, and tie-rod bearings.
If you feel looseness, or if the steering rattles as it turns,
check the tightness of the steering bolts and nuts.
Tighten loose bolts and nuts to the specified torque (see
•
Steering chapter), and check the steering action again.
If the steering action does not change by tightening the
bolts and nuts, inspect the steering stem clamps, steering stem bearings, tie-rod bearings, and steering knuckle
joints.
Electrical System
Spark Plug Cleaning/Inspection
Remove the spark plug (see Electrical System chapter).
•
Clean the spark plug, preferably in a sandblasting device,
•
and then clean off any abrasive particles. The plug may
also be cleaned using a wire brush or other suitable tool.
If the spark plug electrodes are corroded or damaged,
or if the insulator is cracked, replace the plug. Use the
standard spark plug or its equivalent.
Spark Plug Gap Inspection
Measure the gap [A] with a wire-type thickness gauge.
•
If the gap is incorrect, carefully bend the side electrode
[B] with a suitable tool to obtain the correct gap.
Spark Plug Gap
0.7 ∼ 0.8 mm (0.028 ∼ 0.032 in.)
Page 59

Periodic Maintenance Procedures
Brake Light Switch Inspection
Turn on the ignition switch.
•
Check the operation of the rear brake light switch by de-
•
pressing the brake pedal.
If it does not as specified, adjust the brake light timing.
Brake Light Timing
Standard: On after about 10 mm (0.4 in.) of pedal
travel [A]
Brake Light Timing Adjustment
Remove the right hootboard (see Frame chapter).
•
Adjust the brake light switch [A] up or down. To change
•
the switch position, turn the adjusting nut [B].
CAUTION
To avoid damaging the electrical connections in-
side the switch, be sure that the switch body does
not turn during adjustment.
PERIODIC MAINTENANCE 2-37
Drive Belt Failure Detection System Inspection
Remove:
•
Seat (see Frame chapter)
Check the drive belt failure detection system according to
•
following chart.
Page 60

2-38 PERIODIC MAINTENANCE
Periodic Maintenance Procedures
Page 61

Periodic Maintenance Procedures
Joint Boots Inspection
Front Axle/Knuckle Joint Boot Inspection
Visually inspect the front axle joint boots [A].
•
If the joint boot is torn, worn, deteriorated, or leaks grease,
replace the joint boot or front axle assembly (see Final
Drive chapter).
Visually inspect the knuckle joint boots [B].
•
If the joint boot is torn, worn, deteriorated, or leaks
grease, replace the knuckle (see Steering Knuckle sec-
tion in Steering chapter).
Front Propeller Shaft Boot Inspect ion
Visually inspect the boots [A] of the front propeller shaft.
•
If damage, tear or deterioration is found, replace the boots
(see Front Propeller Shaft section in Final Drive chapter).
PERIODIC MAINTENANCE 2-39
Tie-rod End Boot Inspection
Visually inspect the tie-rod end boots [A] of the tie-rods.
•
If the boot is torn, w orn, deteriorated, or leaks grease,
replace the tie-rod end (see Steering chapter).
Rear Propeller Shaft Joint Boot Inspection
Visually inspect the boots [A] of the rear propeller shaft.
•
If the joint boot is torn, worn, or deteriorated, replace the
joint boot and check the propeller shaft (see Rear Pro-
peller Shaft section in Final Drive chapter).
Rear Axle/Stabilizer Joint Boot Inspection
Visually inspect the rear axle joint boots [A].
•
If the joint boot is torn, worn, deteriorated, or leaks grease,
replace the joint boot or rear axle assembly (see Final
Drive chapter).
Visually inspect the stabilizer joint boots [B].
•
If the joint boot is torn, worn, deteriorated, or leaks grease,
replace the stabilizer joint (see Suspension chapter).
Page 62

2-40 PERIODIC MAINTENANCE
Periodic Maintenance Procedures
General Lubrication
Lubrication
Before lubricating each part, clean off any rusty spots with
•
rust remover and wipe off any grease, oil, dirt, or grime.
Lubricate the points listed below with indicated lubricant.
•
NOTE
Whenever the vehicle has been operated under
○
wet or rainy conditions, or especially after using a
high-pressure spray water, perform the general lubrication.
Cables: Lubricate with Cable Lubricant
Brake Cables
Throttle Cable
Choke Cables
Variable Differential Control Cable
Lubricate the cables by seeping the oil between the cable
•
and housing.
The c able may be lubricated by using a pressure cable
○
luber with an aerosol cable lubricant.
With the cable disconnected at the both ends, the cable
•
should move freely [A] within the cable housing.
If cable movement is not free after lubricating, if the cable
is frayed [B], or if the cable housing is kinked [C], replace
the cable.
Points: Lubricate with Grease.
Throttle Inner Cable Ends [A]
Choke Cable Lower End
Brake Cable Ends
Variable Differential Control Cable Ends
Page 63

Periodic Maintenance Procedures
Slide Points: Lubricate with Grease.
Brake Lever
Brake Pedal Pivot Shaft
Throttle Lever Shaft
Bolts and Nuts Tightening
Tightness Inspection
Check the tightness of the bolts and nuts listed here in
•
accordance with the Periodic Maintenance Chart. Also,
check to see that each cotter pin is in place and in good
condition.
If there are loose fasteners, retorque them to the speci-
fied torque following the specified tightening sequence.
Refer to the appropriate chapter for torque specifications.
If torque specifications are not listed in the appropriate
chapter, see the Basic Torque Table (see Torque and
Locking Agent). For each fastener, first loosen it by 1/2
turn, then tighten it.
If cotter pins are damaged, replace them with new ones.
Bolts, Nuts, and Fasteners to be checked
Wheels:
Front Axle Nuts and Cotter Pins
Rear Axle Nuts and Cotter Pins
Wheel Nuts
Brakes:
Front Brake Master Cylinder Clamp Bolts
Brake Lever Pivot Bolt
Brake Lever Pivot Nut
Front Brake Caliper Mounting Bolts
Brake Pedal Cotter Pin
Steering/Suspension:
Handlebar Clamp Bolts
Stem Clamp Bolts
Stem Bearing Housing Bolts
Tie-rod End Nuts and Cotter Pins
Tie-rod Adjusting Sleeve Locknuts
Shock Absorber Mounting Bolts and Nuts
Suspension Arm Pivot Bolts
Steering Knuckle Pivot Nuts and Cotter Pins
Engine:
Engine Mounting Bolts
Engine Mounting Bracket Bolts
Exhaust Pipe Holder Nuts
Muffler Mounting Bolts
Muffler Clamp Bolt
Front Final Drive:
Gear Case Bracket Bolts
Others:
Footboard Mounting Bolts
Throttle Mounting Bolts
Carrier Mounting Bolts
PERIODIC MAINTENANCE 2-41
Page 64

Page 65

Fuel System
Table of Contents
Exploded View................................... 3-2
Specifications .................................... 3-6
Special Tools ..................................... 3-7
Throttle Lever and Cable ................... 3-8
Throttle Lever Free Play
Inspection .................................. 3-8
Throttle Lever Free Play
Adjustment ................................ 3-8
Throttle Case
Removal/Disassembly............... 3-8
Throttle Case
Assembly/Installation ................ 3-8
Throttle Cable Installation ............ 3-9
Throttle Case Inspection .............. 3-9
Throttle Cable Lubrication and
Inspection .................................. 3-9
Choke Lever and Cable..................... 3-10
Choke Lever Free Play
Inspection .................................. 3-10
Choke Lever Free Play
Adjustment ................................ 3-10
Choke Lever and Cable Removal 3-10
Choke Lever and Cable
Installation ................................. 3-11
Choke Cable Lubrication and
Inspection .................................. 3-11
Carburetor ......................................... 3-12
Idle Speed Inspection .................. 3-12
Idle Speed Adjustment................. 3-12
Pilot Screw Adjustment ................ 3-12
Service Fuel Level Inspection ...... 3-12
Service Fuel Level Adjustment .... 3-14
Carburetor Synchronization
Inspection .................................. 3-14
FUEL SYSTEM 3-1
3
Carburetor Synchronization
Adjustment ................................ 3-15
Fuel System Cleanliness
Inspection.................................. 3-15
Carburetor Removal..................... 3-15
Carburetor Installation.................. 3-17
Carburetor Disassembly .............. 3-17
Carburetor Assembly ................... 3-19
Carburetor Separation ................. 3-20
Carburetor Joining ....................... 3-20
Carburetor Cleaning..................... 3-21
Carburetor Inspection .................. 3-22
Air Cleaner......................................... 3-24
Air Cleaner Elem ent Removal...... 3-24
Air Cleaner Element Installation... 3-24
Air Cleaner Element Cleaning and
Inspection.................................. 3-24
Air C leaner Housing Removal...... 3-24
Air C leaner Housing Installation... 3-26
Fuel Tank........................................... 3-28
Fuel Tank Removal ...................... 3-28
Fuel Tank Installation ................... 3-29
Fuel Tank Cleaning ...................... 3-30
Fuel Tap Removal ........................ 3-30
Fuel Tap Installation ..................... 3-30
Fuel Tap Inspection ...................... 3-31
Fuel Tap Cleaning ........................ 3-32
Fuel Pump ......................................... 3-33
Fuel Pump Removal .................... 3-33
Fuel Pump Removal .................... 3-33
Fuel Pump Installation ................. 3-34
Fuel Pump Inspection .................. 3-34
Page 66

3-2 FUEL SYSTEM
Exploded View
Page 67

Exploded View
FUEL SYSTEM 3-3
No. Fastener
Torque
N·m kgf·m ft·lb
1 Idle Adjusting Screw Bracket Bolt 8.8 0.90 78 in·lb
2. Choke Lever
3. Choke Cable
4. Throttle Cable
5. Throttle Lever
6. Jet Needle
7. Pilot Jet
8. Main Jet
9. Needle Jet
10. Pilot Screw
11. Pr i m ing P ump
12. Air Tem perature Sensor
G: Apply grease.
O: Apply engine oil.
CA: Canada Model
Remarks
Page 68

3-4 FUEL SYSTEM
Exploded View
Page 69

Exploded View
FUEL SYSTEM 3-5
No. Fastener
Torque
N·m kgf·m ft·lb
1 Element Cover Screw 3.5 0.35 31 in·lb
2 Element Holder Screws 3.5 0.35 31 in·lb
3 Clamp Bracket Bolt 9.8 1.0 87 in·lb
4 Fuel Pump Mounting Nuts 7.8 0.80 69 in·lb
5 Fuel Tap Plate Screws 0.8 0.08 7in·lb
6 Fuel Tap Mounting Bolts 4.9 0.50 43 in·lb
7 Fuel Tap Cover Screws 9.8 1.0 87 in·lb
8 Fuel Tap Bracket Bolts 7.8 0.80 69 in·lb
9 Fuel Level Sensor Mounting Bolts 2.0 0.20 18 in·lb
10. Fuel Pump
11. I nsert the fuel breather tube end into the hole of the right frame.
AD: Apply adhesive agent.
G: Apply grease.
R: Replacement Part
W: Apply water or soap and water solution.
Remarks
Page 70

3-6 FUEL SYSTEM
Specifications
Item Standard Service Limit
Throttle Case and Cable
Throttle Lever Free Play 2 ∼ 3 mm (0.08 ∼ 0.12 in.) –––
Choke Lever and Cable
Choke Lever Free Play about 3 mm (0.12 in.) –––
Carburetor
Make/Type KEIHIN, CVKR-34 –––
Main Jet:
Front #152 –––
Rear #158 –––
Main Air Jet #70 –––
Needle Jet #6 –––
Jet Needle:
Front NFKK –––
Rear NFKL –––
Pilot Jet #38 –––
Pilot Air Jet #100 –––
Pilot Screw 2 1/4 turns out –––
Carburetor Synchronization vacuum less than 2.7 kPa (2 cmHg) difference
between carburetors
Starter Jet #82 –––
Idle Speed 1 150 ±50 r/min (rpm) –––
Service Fuel Level:
Front 20.4 ±1 mm (0.80 ±0.04 in.) below
the punch mark
Rear
Float Height 2.9±1mm(0.11±0.04in.) –––
Optional Parts:
Main Jet:
*Altitude
0 ∼ 1 200 m (0 ∼ 3 900 ft):
Front #152 (92063-1331) –––
Rear #158 (92063-1344) –––
1 200 ∼ 2 500 m (3 900 ∼ 8 200 ft):
Front #145 (92063-1017) –––
Rear #152 (92063-1331) –––
2 500 ∼ 3 500 m (8 200 ∼ 11 500 ft):
Front #142 (92063-1016) –––
Rear #148 (92063-1324) –––
3 500 ∼ 4 500 m (11 500 ∼ 14 800 ft):
Front #135 (92063-1014) –––
Rear #140 (92063-1013) –––
Air Cleaner
Air Cleaner Element Oil High-quality foam air filter oil –––
19.5 ±1 mm (0.77 ±0.04 in.) below
the punch mark
–––
–––
–––
*: Refer to pg. 6-27 for high altitude setting in the converter system.
Page 71

Special Tools
FUEL SYSTEM 3-7
Fuel Level Gauge:
57001-1017
Pilot Screw Adjuster, A:
57001-1239
Carburetor Drain Plug Wrench, Hex 3 :
57001-1269
Vacuum Gauge:
57001-1369
Page 72

3-8 FUEL SYSTEM
Throttle Lever and Cable
Throttle Lever Free Play Inspection
Refer to the Throttle Lever Free Play Inspection in the
•
Periodic Maintenance chapter.
Throttle Lever Free Play Adjustment
Refer to the Throttle Lever Free Play Adjustment in the
•
Periodic Maintenance chapter.
Throttle Case Removal/Disassembly
Remove the throttle case screws [A] and pull the case
•
open.
Slide the cable adjuster dust cover out of place.
•
Remove the rubber cover [A].
•
Pull the cable tip [A] out of the throttle lever catch with the
•
throttle lever opened.
Loosen the locknut [B] and unscrew the adjuster [C].
•
Disassemble the throttle case as follows:
•
Remove the throttle lever screw [D], lockwasher, and flat
○
washer, and lift the throttle lever [E] and return spring from
the case.
Pull the throttle control lever [F] out of the case.
○
Throttle Case Assembly/Installation
Lubricate the throttle case and cable before assembly/in-
•
stallation.
Be certain that the return spring is correctly installed on
•
the throttle lever [A].
Page 73

Throttle Lever and Cable
Swing the throttle control lever so that the carburetor throt-
•
tle valve is fully open. Turn the throttle limiter screw [A]
until it is spaced about 1 mm (0.04 in.) [B] away from the
throttle lever stop [C]. Tighten the locknut [D].
NOTE
Refer to the Owner’s Manual for the function of the throt-
○
tle limiter and adjustment procedure of it.
WARNING
Operation with an improperly assembled throttle
case could result in an unsafe riding condition.
Check the throttle lever free play (see Throttle Lever Free
•
Play Inspection in Periodic Maintenance chapter).
Throttle Cable Installation
Lubricate the throttle cable before installation.
•
Route the cable correctly according to the Appendix chap-
•
ter.
WARNING
FUEL SYSTEM 3-9
Operation with an improperly adjusted, incorrectly
routed, or damaged cable could result in an unsafe
riding condition.
Check the throttle cable (see Throttle Lever Free Play In-
•
spection in Periodic Maintenance chapter).
Throttle Case Inspection
With the throttle cable disconnected from the throttle
•
lever, the lever should move freely and return smoothly
by spring.
If the lever is heavy, disassemble the throttle case, clean
and lubricate the throttle case.
Examine the lever and case for cracks. Replace the case
•
assembly if it is cracked.
Throttle Cable Lubrication and Inspection
Whenever the throttle cable is removed or in accordance
•
with the Periodic Maintenance Chart in the Periodic Maintenance chapter, lubricate the cable .
Refer to the General Lubrication in the Periodic Mainte-
•
nance chapter for the cable lubrication and inspection.
Page 74

3-10 FUEL SYSTEM
Choke Lever and Cable
Choke Lever Free Play Inspection
Refer to the Choke Lever Free Play Inspection in the Pe-
•
riodic Maintenance chapter.
Choke Lever Free Play Adjustment
Refer to the Choke Lever Free Play Adjustment in the
•
Periodic Maintenance chapter.
Choke Lever and Cable Removal
Remove the air cleaner housing (see Air Cleaner Housing
•
Removal).
Remove the carburetor from the carburetor holder (see
•
Carburetor Removal).
Remove the screws [A] and holder plates [B] from both
•
carburetors.
Pull out the starter plungers.
•
Hold the starter plunger springs compressed, and free the
•
choke cable lower ends [A] from the plungers [B].
Remove:
•
Choke Lever Mounting Screw [A], Plane Washer, and
Wave Washer
Switch Case Mounting Screws [B]
Free the choke cable upper end [A] from the choke lever
•
[B].
Page 75

Choke Lever and Cable
Pull off the retaining clip [A].
•
Fit the cable end [A] in the grommet [B], and free the cable
•
from the switch case.
Pull the cable out of the vehicle.
•
FUEL SYSTEM 3-11
Choke Lever and Cable Installa tion
Lubricate the choke cable before installation.
•
Install the wave washer, plane washer and screw in that
•
order.
Route the choke cable according to the Appendix chapter.
•
WARNING
Operation with an incorrectly routed, or damaged
cable could result in an unsafe riding condition.
Choke Cable Lubrication and Inspection
Whenever the choke cable is removed or in accordance
•
with the Periodic Maintenance chart i n the Periodic Maintenance chapter, lubricate the cable.
Refer to the General Lubrication in the Periodic Mainte-
•
nance chapter for the cable lubrication and inspection
Page 76

3-12 FUEL SYSTEM
Carburetor
Idle Speed Inspection
Refer to the Idle Speed Inspection in the Periodic Main-
•
tenance chapter.
Idle Speed Adjustment
Refer to the Idle Speed Adjustment in the Periodic Main-
•
tenance chapter.
Pilot Screw Adjustment
Adjust the pilot screw if necessary.
•
Remove the air cleaner cover (see Frame chapter).
•
Turn the carburetor pilot screw [A] all the way in until it
•
seats lightly.
Special Tool - Pilot Screw Adjuster, A: 57001-1239 [B]
CAUTION
Do not overtighten the pilot screw or the carburetor
body will be damaged and require replacement.
Back the pilot screw out the specified number of turns.
•
Carburetor Pilot Screw Setting
Standard: 2 1/4 turns out
Service Fuel Level Inspection
WARNING
Gasoline is extremely flammable and can be explosive under certain conditions. Turn the ignition
switch O FF. Do not smoke. Make sure the area is
well ventilated and free from any source of flame
or sparks; this includes any appliance with a pilot
light.
Park the vehicle on a level surface.
•
Remove:
•
Side Covers (see Frame chapter)
Throttle Link Case Cover
Carburetor Drain Hose
Page 77

Carburetor
Connect two suitable hoses [A] to the fuel level gauge [B]
•
and the float chamber of the carburetors.
Special Tool - Fuel Level Gauge: 57001-1017
Mark the additional graduation [C] 15 mm (0.59 in.) higher
•
than the top graduation [D].
Hold the gauge so that the additional graduation is placed
•
slightly higher than the punch mark [E].
[F] Front Carburetor
[G] Rear Carburetor
Run the engine at idle speed.
•
Loosen the carburetor drain screw.
•
Special Tool - Carburetor Drain Plug Wrench, Hex 3:
57001-1269
Wait until the fuel level in the gauge settles.
•
Hold the gauge vertically and lower it slowly so that the
•
additional graduation aligns with punch mark.
NOTE
Do not align the additional graduation on the gauge
○
lower than the punch mark. If it is lowered and then
raised, the gauge will show a fluid level that is higher
than the actual level, which will require a remeasurement.
FUEL SYSTEM 3-13
Read the fuel level [ H].
•
If the fuel level is incorrect, adjust it.
Fuel Level
Standard:
Front 20.4 ±1 mm (0.80 ±0.04 in.) below the
punch mark
Rear 19.5 ±1 mm (0.77 ±0.04 in.) below the
punch mark
Stop the engine.
•
Tighten the drain screw.
•
Repeat the same procedure for the other carburetor.
•
Page 78

3-14 FUEL SYSTEM
Carburetor
Service Fuel Level Adjustment
WARNING
Gasoline is extremely flammable and can be explosive under certain conditions. Turn the ignition
switch to OFF. Do not smoke. Make sure the area
is well-ventilated and free from any source of flame
or sparks; this includes any appliance with a pilot
light.
Remove the carburetors, and drain the fuel.
•
Remove the float chamber.
•
Remove the screw [A].
•
Slide out the pivot pin [B] and remove the float [C].
•
Bend the tang [A] on the float arm very slightly to change
•
the float height.
Float Height
Standard: 2.9 ±1 mm (0.11 ±0.04 in.)
Measure the float height [A] from the mating surface [B]
○
of float by tilting the carburetor so that the tang of the float
[C] just touches the needle rod [D]. At this time, the float
valve [E] rod must not be depressed.
Increasing the float height lowers the fuel level and de-
○
creasing the float height raises the fuel level.
Assemble the carburetor and recheck the fuel level.
•
If the fuel level cannot be adjusted by this method, the
float or the float valve is damaged.
Carburetor Synchronization Inspection
Remove:
•
Side Covers (see Frame chapter)
Throttle Link Case Cover
Check idle speed.
•
Remove the front vacuum hose [A ] and install the vacuum
•
hose for vacuum gauge.
Page 79

Carburetor
Remove the rear vacuum hose [A] and install the vacuum
•
hose for vacuum gauge.
Connect:
•
Vacuum Gauge [A]
Special Tool - Vacuum Gauge: 57001-1369
Connect the fuel hose of a suitable fuel tank [B] to the
•
carburetor.
Start the engine and read the intake vacuum of each car-
•
buretor when idling.
If the vacuum is out of the specified range, adjust it.
FUEL SYSTEM 3-15
Carburetor Synchronization Vacuum
Standard: Less than 2.7 kPa (2 cmHg) difference
between c arburetors
Carburetor Synchronization Adjustment
Turn the adjust screw [A] to synchronize the carburetors.
•
If the carburetor synchronization cannot be obtained by
using the adjusting screw, check for dirt or blockage, and
then check the pilot screw settings.
Special Tool - Pilot Screw Adjuster, A: 57001-1239
Check the carburetor synchronization again.
•
NOTE
Do not turn the pilot screws carelessly during carburetor
○
synchronization. You may cause poor running at low
engine speed.
Check idle speed.
•
Fuel System Cleanliness Inspection
Refer to the Fuel System Cleanliness Inspection in the
•
Periodic Maintenance chapter.
Carburetor Removal
WARNING
Gasoline is extremely flammable and can be explosive under certain conditions. Turn the ignition
switch OFF. Do not smoke. Make sure the area is
well ventilated and free from any source of flame
or sparks; this includes any appliance with a pilot
light.
Page 80

3-16 FUEL SYSTEM
Carburetor
Remove:
•
Air Cleaner Housing (see Air Cleaner Housing Removal)
Drain the fuel from the carburetors.
•
Remove:
•
Fuel Hose [A ]
Heater and Ground Lead Connectors [B]
Remove:
•
Screws [A] and Throttle Link Case Cover [B]
Remove:
•
Locknut [A]
Throttle Cable Lower End [B]
Loosen the carburetor clamp screws [C].
•
Remove the carburetor out of the frame.
•
Remove:
•
Screw [A]
Holder Plate [B]
Remove:
•
Starter Plunger [A]
Page 81

Carburetor
Remove:
•
Screw [A]
Holder Plate [B]
Starter Plunger
Carburetor Insta llation
Confirm the groove of the carburetor holder [A] fits on the
•
projection [B] of the cylinder head.
Check fuel leakage from the carburetors.
•
WARNING
Fuel spilled from the carburetors is hazardous.
Adjust the idle speed (see Idle Speed Adjustment in Pe-
•
riodic Maintenance chapter).
Check the throttle cable (see Throttle Lever Free Play In-
•
spection in Periodic Maintenance chapter).
FUEL SYSTEM 3-17
Carburetor Disassembly
Remove the carburetors (see Carburetor Removal).
•
WARNING
Gasoline is extremely flammable and can be explosive under certain conditions. Turn the ignition
switch to OFF. Do not smoke. Make sure the area
is well-ventilated and free from any source of flame
or sparks; this includes any appliance with a pilot
light.
NOTE
The carburetors c an be disassembled in the joined
○
state.
Page 82

3-18 FUEL SYSTEM
Carburetor
Remove the upper chamber cover [A], spring [B], and vac-
•
uum piston [C].
CAUTION
During carburetor disassembly, be careful not to
damage the diaphragm. Never use a sharp edge to
remove the diaphragm.
Remove the jet needle [D] from the vacuum piston. These
•
can be detached together with the spring seat [E].
Do not remove the pilot screw if possible, synchronization
○
of the carburetors is necessary if pilot screws are removed
(see Pilot Screw Adjustment).
Remove:
•
Screws [A]
Float Chamber [B]
Remove:
•
Screw [A]
Float Pivot Pin [B], Float [C], and Float Needle Valve
Pilot Jet [D]
Main Jet [E]
Starter Jet [F]
Remove:
•
Screws [A]
Coasting Enricher Cover [B]
Page 83

Carburetor
Remove:
•
Diaphragm [A]
O-ring [B]
Carburetor Assembly
WARNING
Fuel spilled from the carburetors is hazardous.
CAUTION
Do not apply force to the jet or overtighten it, or
this could damage the jet or the carburetor body,
requiring replacement.
FUEL SYSTEM 3-19
Install the float valve needle in the valve seat and hook
•
the needle hanger [A] onto the float tang.
Insert the float pivot pin [B] into the pivot post and the float.
•
Tighten the screw [C].
•
Set the float to the standard height (see Service Fuel
•
Level Adjustment).
Insert the jet needle [A] into the hole i n the center of the
•
vacuum piston [B], and place the spring seat [C] over the
needle.
Slip the needle through the hole in the center of the vac-
•
uum piston, and put the spring seat [A] on t he top of the
needle. Turn the seat so that it does not block the hole
[B] at the bottom of the vacuum piston.
After installing the upper chamber cover, check that the
•
vacuum piston slides up and down smoothly without binding in the carburetor bore.
Page 84

3-20 FUEL SYSTEM
Carburetor
Fit the projection [A] of the vacuum piston diaphragm in
•
the recess [B] of the body.
After installing the upper chamber cover, check to make
•
sure that the vacuum piston moves smoothly in the carburetor body.
Carburetor Separation
Remove:
•
Carburetor (see Carburetor Removal)
Screws [A]
Fuel Hose Fittings [B]
Remove:
•
Cotter Pins [A], Collars and Washers
Link Arm [ B]
Remove:
•
Link Case Screws [A]
Link Case [B]
Separate the Carburetors.
•
Carburetor Joining
Install link case and tighten link case screws.
•
Apply grease to the link pins [A].
•
Install the link arm as shown.
•
Washers [B]
Collars [C]
Link Arm [ D]
Cotter Pins [E]
Bend the ends of the cotter pins.
•
Install the fuel hose fittings, and tighten the screws.
•
Page 85

Carburetor
Visually synchronize the throttle (butterfly) valves.
•
Check to see that all throttle valves open and close
○
smoothly without binding when turning the pulley.
Visually check the clearance [A] between the throttle
○
valve and the carburetor bore in each carburetor.
If there is a difference between two carburetors, turn the
balance adjusting screw [A] to obtain the same clearance.
Install the carburetors (see Carburetor Installation).
•
Adjust the synchronization (see Synchronization Adjust-
•
ment).
FUEL SYSTEM 3-21
Carburetor Cleaning
WARNING
Clean the carburetor in a well-ventilated area and
take care that there are no sparks or flame anywhere near the working area; this includes any appliance with a pilot light. Because of the danger
of highly flammable liquids, do not use gasoline or
low-flash point solvents to clean the carburetor.
CAUTION
Do not use compressed air on an assembled carburetor, the f loat m ay be crushed by the pressure, and
the vacuum piston diaphragm may be dam aged.
Remove as many rubber or plastic parts from the
carburetor as possible before cleaning the carburetor with a cleaning solution. This will prevent damage or deterioration of the parts.
The carburetor body has plastic parts that cannot be removed. Do not use a strong carburetor
cleaning solution which could attack these parts;
instead, use a mild high-flash point cleaning solution safe for plastic parts.
Do not use wire or any other hard instrument to
clean carburetor parts, especially jets, as they may
be damaged.
Page 86

3-22 FUEL SYSTEM
Carburetor
Disassemble the carburetor and clean all the metal parts
•
in a carburetor cleaning solution.
Rinse the parts in water and dry them with compressed
•
air.
Blow through the air and fuel passages with compressed
•
air.
Remove the float valve, spray cleaning solution from the
•
valve seating surface into the fuel passage, and clean the
strainer (press-fitted) with compressed air [A].
Assemble the carburetor (see Carburetor Assembly).
•
Carburetor Inspection
WARNING
Gasoline is extremely flammable and can be explosive under certain conditions. Turn the ignition
switch O FF. Do not smoke. Make sure the area is
well ventilated and free from any source of flame
or sparks; this includes any appliance with a pilot
light.
Remove the carburetor (see Carburetor Removal).
•
Before disassembling the carburetors, check the fuel level
•
(see Fuel Level Inspection).
Turn the throttle cable pulley [A] to check that the throttle
•
butterfly valves [B] move smoothly and return back with
the spring tension.
If the t hrottle valves do not move smoothly, replace the
carburetor.
Page 87

Carburetor
Disassemble the carburetors (see Carburetor Disassem-
•
bly).
Clean the carburetor (see Carburetor Cleaning).
•
Check the vacuum piston diaphragm [A], and the O-rings
•
[B] on the float bowl, pilot screw, coasting enricher, and
starter plunger cap.
If any of the diaphragm or O-rings are not in good condition, replace them.
FUEL SYSTEM 3-23
Check the plastic tip [A] of the float valve needle. It should
•
be smooth, without any grooves, scratches, or tears.
If the plastic tip is damaged [C], replace the float valve [B].
Push the rod [D] in the other end of the float valve needle
•
and then release it [E].
If it does not spring out, replace the float valve.
Check the tapered portion [A] of the pilot screw [B] for
•
wear or damage.
If the pilot screw is worn or damaged on the tapered portion, it will prevent the engine from idling smoothly. Replace it.
Check that the vacuum piston moves smoothly in t he car-
•
buretor body. The surface of the piston must not be excessively worn.
If the vacuum piston does not move smoothly, or if it is
very loose in the carburetor body, replace both the body
and the vacuum piston.
Page 88

3-24 FUEL SYSTEM
Air Cleaner
Air Cleaner Element Removal
Remove:
•
Seat (see Frame chapter)
Clips [A]
Air Cleaner Housing Cap [B]
Remove:
•
Element Cover Screw [A]
Element Cover [B]
Element [C]
After removing the element, stuff pieces of lint-free, clean
•
cloth i nto the air cleaner ducts to keep dirt out of the carburetor and engine.
WARNING
If dirt or dust is allowed to pass through into the
carburetors, the throttle may become stuck, possibly causing an accident.
CAUTION
If dirt gets through into the engine, excessive engine wear and possibly engine damage will occur.
Air Cleaner Element Installation
Install:
•
Element
Element Cover
Tighten:
•
Torque - Element Cover Screw: 3.5 N·m (0.35 kgf·m, 31
in·lb)
Air Cleaner Element Cleaning and Inspection
Refer to the Air Cleaner Element Cleaning and Inspection
•
in the Periodic Maintenance chapter.
Air Cleaner Housing Removal
Remove:
•
Side Covers (see Frame chapter)
Air Cleaner Housing Cap
Air Cleaner Element (see Air Cleaner Element Removal)
Page 89

Air Cleaner
Remove:
•
Screws [A]
Element Holder [B]
Spark Arrester [C]
Remove:
•
Screw [A]
Air Intake Duct [B]
Air Cleaner Housing Bolt [C]
FUEL SYSTEM 3-25
Remove:
•
Air Cleaner Housing Bolt [A]
Loosen the clamp screws [A].
•
Remove:
•
Breather Hose [A]
Page 90

3-26 FUEL SYSTEM
Air Cleaner
Remove:
•
Screw [A]
Carburetor Breather Tank [B]
Air Cleaner Housing [C]
Air Cleaner Housing Installation
Fit the projection [A] of the housing in the groove [B] of
•
the joint duct [C] (front and rear), and tighten the clamp
screws.
Install:
•
Dust Seal [A]
Air Cleaner Housing Cover [B]
[C] Inside
Install the air cleaner housing and joint duct on the carbu-
•
retor.
Install:
•
Breather Hose and Clamp
Carburetor Breather Tank
Fit the joint duct on the fitting of the carburetor securely
•
and tighten the clamp screws.
Tighten the air cleaner housing bolts.
•
Install the spark arrester [A] so that the swelling faces
•
upward.
Page 91

Air Cleaner
Apply the soap and water solution over the trim seal [A].
•
Install:
•
Element Holder
Tighten:
•
Torque - Element Holder Screws: 3.5 N·m (0.35 kgf·m, 31
in·lb)
Install:
•
Element (see A ir Cleaner Element Installation)
FUEL SYSTEM 3-27
Page 92

3-28 FUEL SYSTEM
Fuel Tank
Fuel Tank Removal
Remove:
•
Electrical Parts Case (see Frame chapter)
Rear Fender (see Frame chapter)
Storage Case [A] (Optional Part)
Check Valve Hose [B]
Remove:
•
Two Right Footboard Bolts [A]
Insert a thin driver [A] in the clamp [B] to clear its stopper,
•
and slide the clamp forward.
Move the main harness [A] inside as shown.
•
Remove:
•
Fuel Level Sensor Lead Connector [B]
Vacuum Hose [C]
Fuel Hose [D ]
Bolts [E]
Damper Bracket Bolt [F]
Damper Bracket [G]
Remove:
•
Fuel Tank [A] with Tank Case [B]
Page 93

Fuel Tank
Fuel Tank Installation
Check the insulators [A] on the tank case.
•
If the insulators are damaged or deteriorated, replace
them.
Check the rubber dampers [A] on the frame as shown.
•
If the dampers are damaged or deteriorated, replace
them.
FUEL SYSTEM 3-29
Install the fuel tank with case, and tighten the bolts.
•
Check the damper [A] on the damper bracket [B].
•
If the damper is damaged or deteriorated, replace it.
Tighten the damper bracket bolt.
•
Install the check valve so that the arrow [A] faces fuel tank.
•
[B] Black Color
[C] Blue Color
Install:
•
Hose [A]
Clamps [B]
Page 94

3-30 FUEL SYSTEM
Fuel Tank
Install:
•
Vacuum Hose [A] and Clamp [B]
Fuel Level Sensor Lead Connector
Install the removed parts.
•
Fuel Tank Cleaning
Remove the fuel tank and drain it (see Fuel Tank Re-
•
moval).
Pour some high-flash point solvent into the fuel tank and
•
shake the tank to remove dirt and fuel deposits.
WARNING
Clean the tank in a well-ventilated area, and take
care that there is no spark or flame anywhere
near the working area; this includes any appliance
with a pilot light. B ecause of the danger of highly
flammable liquids, do not use gasoline or low-flash
point solvents to clean the tank. A fire or explosion
could result.
Pour the solvent out the tank.
•
Dry the tank with compressed air.
•
Install the fuel tank (see Fuel Tank Installation).
•
Fuel Tap Removal
Remove:
•
Fuel Pump (see Fuel Pump Removal)
Fuel Tap Mounting Bolts [A]
Vacuum Hose [B]
Fuel Tap [C]
Fuel Tap Installation
Be sure the O-ring [A] is in good condition to prevent leak-
•
age.
Page 95

Fuel Tank
Connect the fuel hoses to the fuel tap as follows.
•
Vacuum Hose [A]
Fuel Pump Hose [B]
Be sure to clamps [C] the fuel hoses to prevent leakage.
•
Fuel Tap Inspection
Check the fuel tap filter screen [A] for any breaks or dete-
•
rioration.
If the filter screen has any break or is deteriorated, it may
allow dirt to reach the carburetor, causing poor running.
Replace the fuel tap.
FUEL SYSTEM 3-31
If the fuel tap leaks, replace the damaged gasket [A] or
O-rings [B].
Apply grease to the lever [A].
•
Tighten:
•
Torque - Fuel Tap Plate Screws [A]: 0.8 N·m (0.08 kgf·m, 7
in·lb)
Page 96

3-32 FUEL SYSTEM
Fuel Tank
Fuel Tap Cleaning
Remove:
•
Fuel Tap (see Fuel Tap Removal)
Clean the fuel tap filter screen in a high-flash point sol-
•
vent.
WARNING
Clean the tap in a well-ventilated area, and take care
that there is no spark or flame anywhere near the
working area; this includes any appliance with a pilot light. Because of the danger of highly flammable
liquids, do not use gasoline or low-flash point solvents to clean the tap. A fire or explosion could result.
Pour high-flash point solvent through the tap in PRI posi-
•
tion.
Dry the fuel tap with compressed air.
•
Install t he fuel tap (see Fuel Tap Installation).
•
Page 97

Fuel Pump
Fuel Pump Removal
CAUTION
Never drop the fuel pump, especially on a hard surface. Such a shock to the pump can damage it.
WARNING
Gasoline is extremely flammable and can be explosive under certain conditions. Make sure the area
is well-ventilated and free from any source of flame
or sparks; this includes any appliance with a pilot
light. Do not smoke. Turn the ignition switch OFF.
Disconnect the battery (-) terminal.
To make fuel spillage minimum, draw the fuel out
from the fuel tank when the engine is cold. Be
prepared for fuel spillage; any spilled fuel must be
completely wiped up immediately.
Fuel Pump Removal
Remove:
•
Electrical Parts Case (see Frame chapter)
Bolts [A]
Fuel Hose [B]
FUEL SYSTEM 3-33
Remove:
•
Vacuum Hose [A]
Fuel Hose [B]
Remove:
•
Nuts [A] and Washers
Fuel Pump [B ]
Page 98

3-34 FUEL SYSTEM
Fuel Pump
Fuel Pump Installation
Install:
•
Bracket [A]
Fuel Pump [B]
Washers [ C] and Nuts [D]
Install:
•
Vacuum Hose [A]
Fuel Hose (Carburetor Side) [B]
Clamps [C]
Install:
•
Fuel Hose (Fuel Tap Side) [A]
Clamp [B]
Bolts [C]
Removed Parts
Fuel Pump Inspection
Remove the fuel pump (see Fuel Pump Removal).
•
If the hose connection areas [A] of the fittings are damaged, replace the fuel pump.
Blow the air to the outlet fitting [A], and make sure does
•
not flow the blown air from the inlet fitting [B].
If the fuel pump does not operate as described, replace it
with a new one.
Page 99

Fuel Pump
Inhale the air to the inlet fitting [A], and make sure does
•
not inhale the blown air from the outlet fitting [B].
If the fuel pump does not operate as described, replace it
with a new one.
FUEL SYSTEM 3-35
Page 100

 Loading...
Loading...