Kaspersky Lab KASPERSKY ANTI-VIRUS-SMTP-GATEWAY 5.5 ADMINISTRATOR GUIDE

KASPERSKY LAB
Kaspersky® SMTP-Gateway 5.5 for
Linux/Unix
ADMINISTRATOR’S GUIDE

KASPERSKY® SMTP-GATEWAY 5.5 FOR LINUX/UNIX
Administrator’s Guide
© Kaspersky Lab
http://www.kaspersky.com
Revision date: July 2005

Contents
CHAPTER 1. KASPERSKY® SMTP-GATEWAY 5.5 FOR LINUX/UNIX...................... 6
1.1. What’s new in version 5.5 ..................................................................................... 7
1.2. Licensing policy ..................................................................................................... 8
1.3. Hardware and software requirements .................................................................. 8
1.4. Distribution kit ........................................................................................................ 9
1.5. Help desk for registered users ............................................................................ 10
1.6. Conventions......................................................................................................... 11
CHAPTER 2. APPLICATION STRUCTURE AND TYPICAL DEPLOYMENT
SCENARIOS .............................................................................................................. 12
2.1. Application architecture ....................................................................................... 12
2.2. The algorithm of application functioning ............................................................. 13
2.3. Typical deployment scenarios............................................................................. 15
2.3.1. Installing the application along corporate network perimeter ...................... 16
2.3.2. Installing the application inside your mail system........................................ 18
CHAPTER 3. INSTALLING THE APPLICATION......................................................... 20
3.1. Installing the application on a server running Linux ........................................... 20
3.2. Installing the application on a server running FreeBSD..................................... 21
3.3. Installation procedure .......................................................................................... 22
Step 1. Preparing the system ......................................................... 22
Step 2. Copying application files to destination directories
on your server .................................................................... 22
Step 3. Post-installation tasks ........................................................ 22
3.4. Configuring the application.................................................................................. 23
3.5. Installing the Webmin module to manage Kaspersky SMTP-Gateway ............ 25
CHAPTER 4. USING THE APPLICATION................................................................... 27
4.1. Updating the anti-virus databases ...................................................................... 27
4.1.1. Automatic updating of the anti-virus databases........................................... 29
4.1.2. Manual updating of the anti-virus databases............................................... 29
4.1.3. Creating a shared directory for storing and sharing database updates...... 30
4.2. Anti-virus protection of email traffic ..................................................................... 31

4 Kaspersky
®
SMTP-Gateway 5.5 for Linux/Unix
4.2.1. Creating groups of recipients/senders ......................................................... 31
4.2.2. General message processing algorithm ...................................................... 34
4.2.3. Main tasks..................................................................................................... 36
4.2.3.1. Deliver messages without changes ...................................................... 36
4.2.3.2. Delivery of clean or disinfected messages only.................................... 37
4.2.3.3. Removing infected attachments............................................................ 38
4.2.3.4. Replacement of infected attachments with standard notifications ....... 39
4.2.4. Additional tasks............................................................................................. 40
4.2.4.1. Block delivery of messages to recipients .............................................. 40
4.2.4.2. Deliver infected messages .................................................................... 41
4.2.4.3. Delivery of notifications to the sender, administrator and recipients.... 42
4.2.4.4. Additional filtering of objects by name and type.................................... 43
4.2.4.5. Backing up (quarantine, backup storage) ............................................. 44
4.2.4.6. Automatically add incoming and outgoing mail to archives.................. 45
4.3. Protection from hacker attacks and spam .......................................................... 46
4.4. Managing license keys........................................................................................ 47
4.4.1. Viewing information about license keys....................................................... 48
4.4.2. Renewing your license .................................................................................49
4.4.3. Removing a license key ............................................................................... 50
CHAPTER 5. ADVANCED APPLICATION SETTINGS .............................................. 51
5.1. Configuring anti-virus protection of mail traffic.................................................... 51
5.1.1. Scanning and disinfecting messages .......................................................... 51
5.1.2. Using the iChecker™ technology................................................................. 51
5.2. Setting up application timeouts ........................................................................... 52
5.3. Setting performance restrictions ......................................................................... 53
5.4. Setting up connection receiving interfaces ......................................................... 55
5.5. Setting up the routing table ................................................................................. 55
5.6. Checking the configuration file syntax ................................................................ 56
5.7. Syntax check in notification templates................................................................ 57
5.8. Work with backup storage and the quarantine directory.................................... 57
5.9. Management of application working queue........................................................ 59
5.10. Managing the application .................................................................................. 62
5.11. Control of application activity............................................................................. 63
5.12. Customizing date and time formats .................................................................. 64
5.13. Reporting options .............................................................................................. 64
5.14. Additional informational header fields in messages......................................... 66

Contents 5
CHAPTER 6. TESTING APPLICATION OPERABILITY ............................................. 67
6.1. Testing the application using Telnet ................................................................... 67
6.2. Testing the application using EICAR ..................................................................69
CHAPTER 7. UNINSTALLING THE APPLICATION ................................................... 71
CHAPTER 8. FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS................................................... 72
APPENDIX A. SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION ABOUT THE
PRODUCT 78
A.1. Distribution of the application files in directories ............................................... 78
A.2. Kaspersky SMTP-Gateway configuration file ................................................... 82
A.3. Use of external configuration files ..................................................................... 98
A.4. Control signals for the smtpgw component..................................................... 100
A.5. Control files....................................................................................................... 100
A.6. Application statistics......................................................................................... 101
A.7. Command line options for the smtpgw component ........................................ 106
A.8. Smtpgw return codes....................................................................................... 108
A.9. Command line options for licensemanager .................................................... 109
A.10. Licensemanager return codes......................................................................... 109
A.11. Keepup2date command line options .............................................................. 110
A.12. Keepup2date return codes .............................................................................. 110
A.13. Format of messages about template syntax check-up...................................111
A.14. Return codes for the kltlv utility........................................................................ 113
A.15. Command line options of the klmailq utility..................................................... 113
A.16. Command line options for the klmaila utility.................................................... 114
A.17. Return codes for the klmaila and klmailq utilities ............................................ 115
A.18. Format of messages about anti-virus scanning.............................................. 115
A.19. Notifications about actions applied to the message ....................................... 116
APPENDIX B. KASPERSKY LAB...................................................................... 119
B.1. Other Kaspersky Lab Products .......................................................................120
B.2. Contact Us........................................................................................................ 124
APPENDIX C. LICENSE AGREEMENT............................................................ 125

CHAPTER 1. KASPERSKY®
SMTP-GATEWAY 5.5 FOR
LINUX/UNIX
Kaspersky® SMTP-Gateway for Linux/Unix (hereinafter referred to as
Kaspersky SMTP-Gateway or the application) is designed for anti-virus
processing of SMTP mail traffic. The application is a full-featured mail relay
(compliant with IETF RFC internet standards) that runs under Linux, FreeBSD
and OpenBSD operating systems.
The application allows the user to:
• Scan email messages for viruses.
• Detect infected, suspicious, corrupted, and password-protected
attachments and message bodies.
• Perform anti-virus processing (including disinfection) of infected objects
revealed in email messages by scanning.
• Provide additional email traffic filtering by names, MIME types of
attachments, and apply certain processing rules to the filtered objects.
• Maintain archives of all email messages sent and/or received by the
application, if this is required by the internal security policy of the
company.
• Use the technology of DNS black lists (RBL) to filter spam.
• Compose "white" and "black" lists of senders/recipients for use by the
application while processing e-mail traffic.
• Enable restrictions for SMTP connections providing protection against
hacking attacks and preventing application use as an open mail relay for
unsolicited email messages.
• Limit the load on your server by configuring the application settings and
SMTP parameters.
• Notify senders, recipients, and the administrator about messages
containing infected, suspicious, or corrupted objects.
• Quarantine messages identified as spam or probable spam as well as
messages containing infected, suspicious, corrupted or passwordprotected objects.

Kaspersky® SMTP-Gateway 5.5 for Linux/Unix 7
• Update the anti-virus databases. The application retrieves updates from
the update servers of Kaspersky Lab.
The application detects and cures infected objects using the anti-virus
databases. During scans, the contents of each file are compared to the
sample code of known viruses contained in the database.
Please keep in mind that new viruses appear every day and
therefore we recommend maintaining the anti-virus databases
in an up-to-date state. New updates are made available on
Kaspersky Lab update servers every hour.
• Configure and manage Kaspersky SMTP-Gateway either from a remote
location using Webmin web-based interface, or locally, using standard OS
tools such as command line options, signals, by creating special
command files or by modifying the configuration file of the application.
• Monitor the anti-virus protection and view the statistics and application
logs.
1.1. What’s new in version 5.5
Version 5.5 of Kaspersky SMTP-Gateway has been enhanced with the following
additional features as compared with version 5.0:
• Access and routing rules are defined based not only on domain masks,
but on recipients address masks also.
• External files can be included into main configuration file.
• By administrator’s request the application can append to email messages
(as an extension header field) information about their scan status, antivirus software version, and the date of the anti-virus databases used for
scanning.
• By administrator’s request, the application can append to email messages
a disclaimer text generated according to a template defined by the
administrator. Different disclaimer messages may be specified for various
groups of recipients.
• Application working queue management (queue reviewing, message
removal from queue, scanning and sending a specified message ahead of
the general queue).
• Management of messages moved to quarantine, backup storage and to
archives of received and sent messages (attribute reviewing, message
removal, sending the isolated messages to their original recipients).
• An opportunity to restrict the application working queue size.

8 Kaspersky
• Support of the DNS Black List technology, an internal client for the DNS
service.
• Monitoring of application status (watсhdog process).
• Checking the syntax of the application configuration file and notification
templates.
®
SMTP-Gateway 5.5 for Linux/Unix
1.2. Licensing policy
The licensing policy for Kaspersky SMTP-Gateway includes a system of product
use limitations based on the following criteria:
• Number of users protected by the application
• Email traffic processed daily (MB/day).
Each type of licensing is also limited by a certain period (typically one year or two
years after the date of purchase).
You can purchase a license limited by one of the above criteria (for example, by
the daily mail traffic volume).
The application has slightly different configuration parameters, depending on the
type of license you have purchased. Thus, if the license is issued for a certain
number of users, you will have to create a list of addresses (domains) that will
be protected by the application against viruses. The application will notify the
administrator when the traffic volume reaches critical values or the number of
protected accounts is exceeded and hence the license is about to expire.
1.3. Hardware and software
requirements
Minimum system requirements for normal operation of Kaspersky SMTPGateway are as follows:
• Intel Pentium
• At least 128 МB of available RAM.
• At least 100 MB of available space on your hard drive to install the
application.
®
processor (Pentium III or Pentium 4 recommended).
Kaspersky® SMTP-Gateway 5.5 for Linux/Unix 9
Please note that the application working queue, quarantine
directory, and archives of incoming and outgoing email are
not included in the hard disk space required. If your network
security policy requires the use of the above features,
additional disk space will be needed.
• at least 500 MB of available space in the /tmp file system.
• One of the following operating systems:
• Red Hat Enterprise Linux Advanced Server 3
• Red Hat Linux 9.0
• Fedora Core 3
• SuSe Linux Enterprise Server 9.0
• SuSe Linux Professional 9.2
• Debian GNU/Linux 3.0r3
• Mandrake Linux 10.1
• FreeBSD 4.10 or 5.3
• OpenBSD 3.6.
• Perl interpreter, version 5.0 or higher (www.perl.org
to install the application.
• Webmin version 1.070 or higher (www.webmin.com
administration module.
) and the which utility
) to install the remote
1.4. Distribution kit
You can purchase the product either from our dealers (retail box) or at one of our
online stores (for example, www.kaspersky.com
The retail box contains:
• sealed envelope containing the installation CD with the product
• a copy of this Administrator’s Guide
• license key file bundled with the distribution package or recorded to a
special floppy disk
• License Agreement.
– follow the E-store link).

10 Kaspersky
®
SMTP-Gateway 5.5 for Linux/Unix
Before you unseal the envelope containing the CD, make sure you
have carefully read the License Agreement .
If you purchase our application online, you will download it from Kaspersky Lab's
website; the copy also contains this manual. Your license key is either included
in the installation package or will be sent to you by e-mail after payment.
The License Agreement constitutes a legal agreement between you and
Kaspersky Lab containing the terms and conditions under which you may use the
purchased software.
Please review the License Agreement carefully!
If you do not agree to the terms of the License Agreement, you may return the
box containing the software product to your dealer where you have purchased it
for a full refund provided that the envelope with the installation CD has not been
unsealed.
By opening the sealed envelope containing the installation CD, or by installing
the application, you confirm that you have accepted all the terms and conditions
of the License Agreement.
1.5. Help desk for registered users
Kaspersky Lab offers an extensive service package enabling registered
customers to boost the productivity of Kaspersky SMTP-Gateway .
If you purchase a license you will be provided with the following services for the
licensed period:
• new versions of this software product provided free of charge
• phone or email support on matters related to the installation,
configuration, and operation of the product you have purchased
• notifications about new software products from Kaspersky Lab, and about
new virus outbreaks. This service is provided to users who have
subscribed to the Kaspersky Lab e-mail newsletter service.
Kaspersky Lab does not give advice on the performance and use of
your operating system or other technologies.
Kaspersky® SMTP-Gateway 5.5 for Linux/Unix 11
1.6. Conventions
Various formatting conventions are used throughout the text of this document
depending on the purpose of a particular element. The table below lists the
formatting conventions used.
Style Meaning
Bold type
Note.
Attention!
In order to perform the
action,
1. Step 1.
2. …
Task, example
Solution
[key] – key purpose.
Text of information
messages and the command
line
Menu titles, menu items, window titles,
parts of dialog boxes, etc.
Additional information, notes.
Information requiring special attention.
Procedure description for user's steps
and possible actions.
Statement of a problem, example for
using the software features.
Solution to a defined problem.
Command line keys.
Text of configuration files, information
messages and the command line.

CHAPTER 2. APPLICATION
STRUCTURE AND TYPICAL
DEPLOYMENT SCENARIOS
Correct application setup and its efficient operation require knowledge of its
structure and internal algorithms. It is also important for application deployment
within an existing corporate email system. This chapter contains a detailed
discussion of the application’s structure, architecture and operating principles as
well as typical scenarios of its deployment.
2.1. Application architecture
The review of the application functionality must be preceded by a description of
its internal architecture.
Kaspersky SMTP-Gateway is a full-featured Mail Transfer Agent (MTA) able to
receive and route email traffic scanning email messages for viruses.
Kaspersky SMTP-Gateway uses SMTP protocol commands (RFC 2821), Internet
message format (RFC 2822), MIME format (RFC 2045-2049, 2231, 2646), and
satisfies the requirements to mail relays (RFC 1123). In compliance with antispam recommendations (RFC 2505 standard), the application employs access
control rules for SMTP clients to prevent the use of this application as an open
relay. In addition, Kaspersky SMTP-Gateway supports the following SMTP
protocol extensions:
• Pipelining – enhances performance of servers supporting this mode of
operation (RFC 2920).
• 8-bit MIME Transport – processes national language characters code
tables (RFC 1652).
• Enhanced Error Codes – provides more informative explanations of
protocol errors (RFC 2034).
• DSN (Delivery Status Notifications) – decreases bandwidth usage and
provides more reliable diagnostics (RFC 1891, 3461-3464).
• SMTP Message Size – decreases the load and increases transfer rate
(RFC 1870).
Application structure and typical deployment scenarios 13
RFC documents mentioned above are available at:
http://www.ietf.org.
The application includes the following components:
• smtpgw – the main component – a full-featured mail relay with built-in
anti-virus protection.
• licensemanager – component for managing license keys (installation,
removal, viewing statistics).
• keepup2date – component that updates the anti-virus databases by
downloading the updates from the Kaspersky Lab’s update servers or a
local directory.
• Webmin module for remote administration of the application using a
web-based interface (optional installation). This component allows the
user to configure and manage the anti-virus database updates, specify
actions to be performed on the objects depending on their status and
monitor the results of the application’s operation.
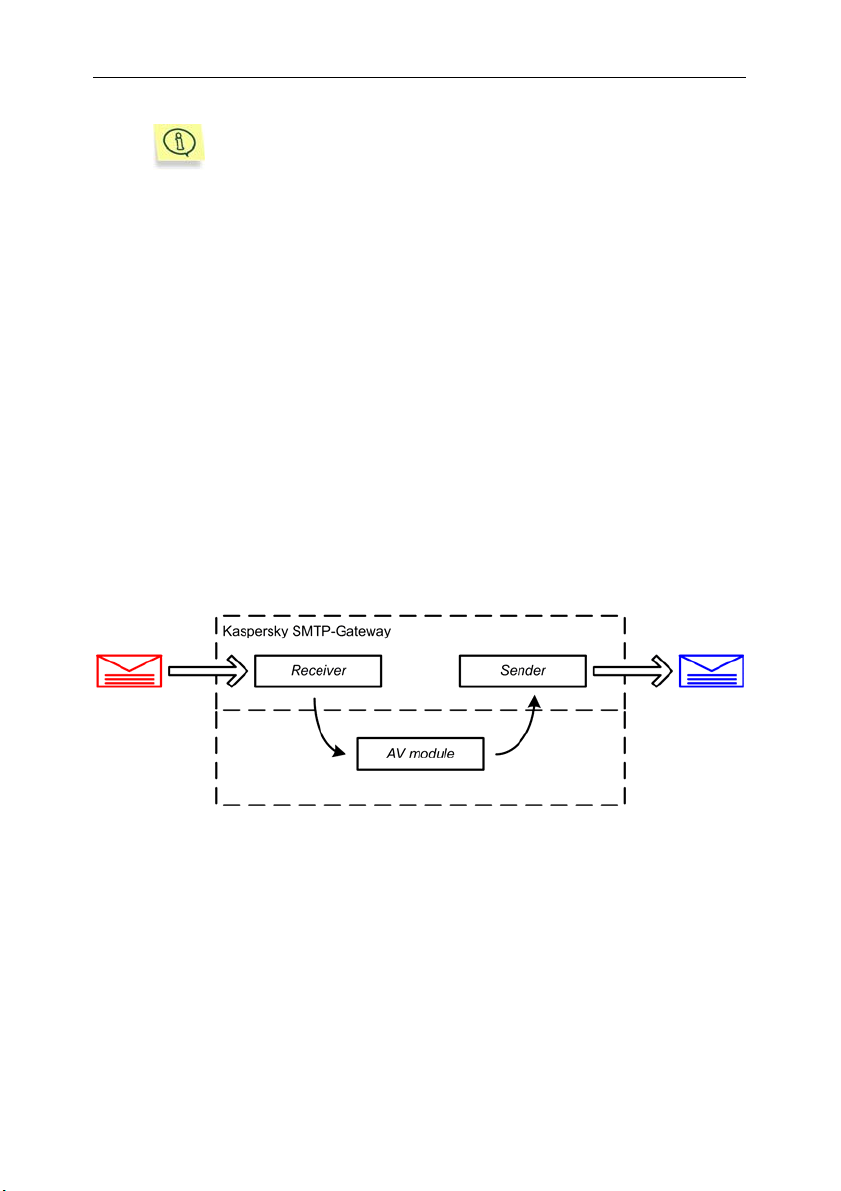
• The smtpgw component (see Fig.1), in its turn, consists of the following
modules: Receiver (incoming mail receiver), Sender (module for sending
scanned messages), and AV module (module implementing the anti-virus
scanning and processing.
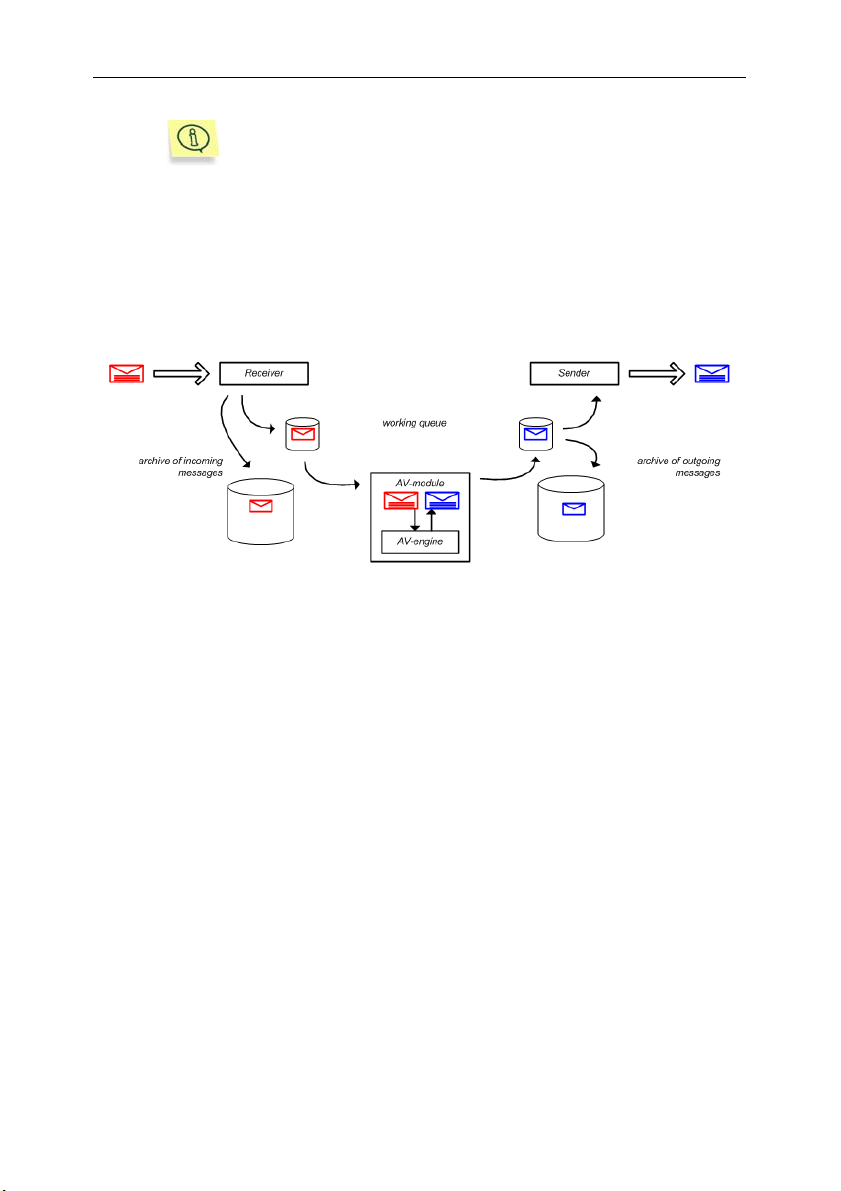
Figure 1. General architecture of Kaspersky SMTP-Gateway
2.2. The algorithm of application
functioning
The application works as follows (see Fig. 2):
1. The mail agent receives email messages via the SMTP protocol and
passes them to the Receiver module.
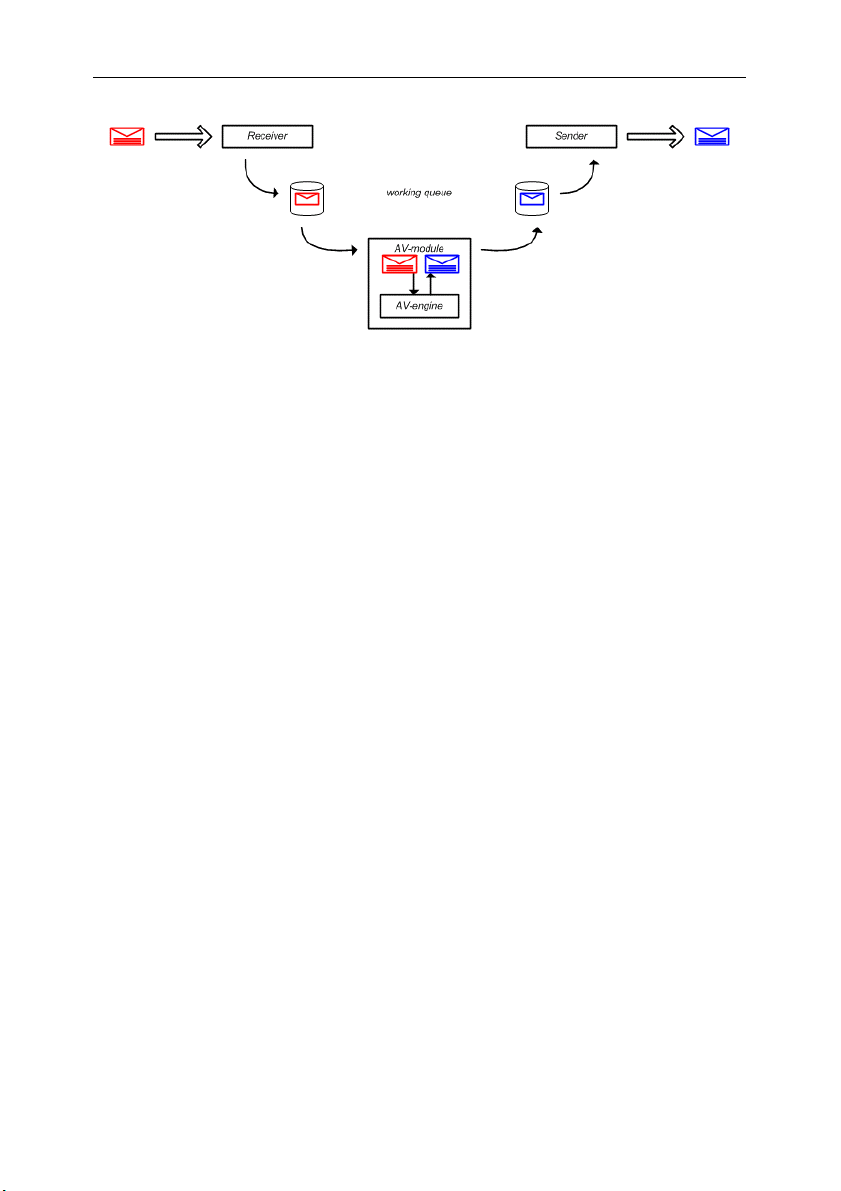
14 Kaspersky
Figure 2. The structure of Kaspersky SMTP-Gateway
®
SMTP-Gateway 5.5 for Linux/Unix
2. The Receiver module performs preliminary email processing using the
following criteria:
• presence of the sender’s IP address in the list of blocked and/or
trusted addresses including masks
• compliance with the access restrictions specified for SMTP
connections (see section 4.3 on p. 46)
• compliance of the email message size (as well as the mail
session in general and the total number of messages within the
session) with the limits specified in the application settings
• compliance of the number of open sessions (both from all IP
addresses and a single IP address) with the limits specified in
the application settings.
If the message satisfies the preliminary processing requirements, it is
sent to the working queue to be processed by the AV module.
3. The application disassembles each message received from the working
queue into individual components and passes them to the AV module
for analysis.
4. The AV module scans the objects and, if this option is enabled,
disinfects them, when necessary.
5. The application handles messages according to the status assigned to
each object during after the anti-virus scan (blocks message delivery,
deletes infected objects, replaces the original infected objects with
disinfected ones, adds messages to the quarantine directory, etc.).
6. If saving a backup copy in the backup storage or in the quarantine is
specified as the action to be performed on a message, the copy of the
scanned message will be saved in the backup storage or in the
quarantine concurrently with sending it to the ready-to-send queue
(depending on the message status).
Application structure and typical deployment scenarios 15
Message addition to backup or quarantine directory does not
block its delivery to the recipient. If you want to prevent its
delivery to end recipients, you have to specify an additional
action blocking it.
7. The Sender module receives each message from the ready-to-send
queue and transfers it via the SMTP protocol to the onward mail agent
to be delivered to local end users or rerouted to other mail servers.
8. If your network security policy requires logging of all outgoing email
traffic, a copy of each message will be automatically saved to the
archive of sent messages (see Fig. 3).
Figure 3. Saving messages to the archives of incoming/outgoing mail.
2.3. Typical deployment scenarios
Depending upon the network architecture, the following options for installation of
Kaspersky SMTP-Gateway are possible:
• Install the application at the network perimeter on the same computer with
your mail system (recommended for Sendmail, Postfix and Exim mail
systems).
• Install the application at the network perimeter on a dedicated server to
operate as an anti-virus filter (recommended for Sendmail, Postfix and
Exim mail systems).
• Install the application inside your existing mail system on the same
computer.
• Install the application inside your mail system on a dedicated server to
operate as an anti-virus filter.
The sections below discuss in detail the above scenarios and describe their
advantages.

16 Kaspersky
The application, being a mail relay, does not include a local mail
delivery agent (MDA). Therefore, no matter which of the deployment
scenarios is used, a mail system (or mail systems) that delivers email
messages to the local users within the protected domains is required!
®
SMTP-Gateway 5.5 for Linux/Unix
2.3.1. Installing the application along
corporate network perimeter
The main advantage of this option is that it improves the overall performance of
your mail system because it minimizes the number of transfer cycles for email
messages.
In this case the existing corporate mail server has no connection to the Internet;
that means additional protection of your data. Moreover, demilitarized zones
(DMZ) may be set up.
To install the application and the mail system on the same server, the following
algorithm is provided to ensure their joint operation:
1. Configure all interfaces of Kaspersky SMTP-Gateway to listen on
port 25 for incoming email traffic from all IP addresses matching the
relevant MX records for the protected domain.
2. The application will scan email traffic and then transfer the
processed messages to the corporate mail system via a different
port (e.g., 1025).
You have to set up restrictions for the mail transfer agent
(MTA) receiving mail from Kaspersky SMTP-Gateway via port
1025 so that it accepts messages exclusively from Kaspersky
SMTP-Gateway. Otherwise, there will be an opportunity to
bypass the protection with a connection established directly
from external network through port 1025.
3. The mail system, configured to use a local interface, will deliver
messages to users.
The following steps are to be followed in order to install the application
and the mail system on the same server:
• Configure the application for mail receipt via port 25 on all network
interfaces of the server. In order to do this, specify the following value in
the [smtpgw.network] section of the configuration file:
ListenOn=0.0.0.0:25

Application structure and typical deployment scenarios 17
• Specify in the routing table transfer of all scanned messages to the mail
system via port 1025. In order to do this, specify the following value in the
[smtpgw.forward] section of the application configuration file:
ForwardRoute=*@company.com [host:1025]
where: *@company.com is the mask for recipient addresses
host – name of the your corporate mail server.
• Change the settings of the existing mail system for receiving messages
from the application via port 1025. This will ensure receipt of all incoming
mail messages and delivery of these messages to the local users within
the protected domains of the company.
• Set up the existing mail system to transfer all messages it receives to the
application via port 25. This will ensure anti-virus scanning of all outgoing
mail messages from the local users.
• Specify the list of all corporate local domains as a value for the
ProtectedDomains option in the [smtpgw.network] section of the
application configuration file ("*" and "?" wildcards can be used). Mail
messages for the specified domains will be scanned.
Application configuration for this deployment scenario will be
implemented by default during the installation process.
The operation algorithm of the application, when the latter is installed on a
dedicated server, is identical to its operation on the same server with an email
system, but the settings for this scenario will differ. IP address of the server,
where the application is installed must be included in MX records corresponding
to the protected domain.
In order to install the application on a dedicated server:
• Configure the application for mail receipt via port 25 on all network
interfaces of the server. In order to do this, specify the following value in
the [smtpgw.network] section of the application configuration file:
ListenOn=0.0.0.0:25
• Specify in the routing table transfer of all scanned messages to the mail
system via port 25. In order to do this, specify the following value in the
[smtpgw.forward] section of the application configuration file:
ForwardRoute=*@company.com [host:25]
where: *@company.com is the mask for recipient addresses
host – name of the your corporate mail server.

18 Kaspersky
• Specify the list of all corporate local domains as a value for the
ProtectedDomains option in the [smtpgw.network] section of the
application configuration file ("*" and "?" wildcards can be used). Mail
messages for the specified domains will be scanned.
This deployment scenario is the most convenient one, especially if the
installation of Kaspersky SMTP-Gateway is performed at the same time
with the deployment of the network and of the company’s mail system.
®
SMTP-Gateway 5.5 for Linux/Unix
2.3.2. Installing the application inside your
mail system
If the application is installed inside your mail system, there is no access from
outside to the information about the application running on the server and its
configuration. Besides, if the application is installed inside the mail system on a
dedicated server, this provides for the possibility to distribute the load among
several servers performing anti-virus scanning.
The following algorithm is provided for joint operation of the application and the
mail system installed on the same server:
1. Duplicate your mail system and configure one of the copies to listen
on port 25 and receive email messages via all available interfaces.
2. This mail system forwards all incoming messages through the local
interface via a different port (port 1025, for instance) to the
application for anti-virus scanning.
3. The application scans the email messages for viruses and forwards
scanned and processed messages to the second mail system
copy, which receives mail on a different port (e.g., port 1026).
4. The second mail system delivers email to the local users.
This deployment scenario is recommended if you are sure of the
reliability of your mail system. The installation of the application will not
affect the stability of your mail system.
Application setup on a dedicated server is similar to the above procedure.
Besides, when installing the application on a dedicated server, you can create
and run several copies of the application on different servers. This can help you
distribute the anti-virus processing load among several servers.
To implement this scenario of application deployment, specify the list of all
corporate local domains as a value for the ProtectedDomains option in the
[smtpgw.network] section of the application configuration file ("*" and "?"
wildcards can be used). Mail messages for the specified domains will be
scanned.

Application structure and typical deployment scenarios 19
Deploying Kaspersky SMTP-Gateway may require changes of the
settings for the mail clients throughout the company so that all outgoing
mail messages are delivered to the application, which will transfer the
messages to the external network after an anti-virus scan.
If the network includes installed firewalls or demilitarized zones
(DMZ’s), it is necessary to provide mail clients and internal and external
networks servers with access to the installed application to ensure joint
operation and routing of the mail traffic.

CHAPTER 3. INSTALLING THE
APPLICATION
Before installing Kaspersky SMTP-Gateway, it is necessary to:
• Make sure that your system meets the hardware and software
requirements (see section 1.3 on p. 8).
• Configure your Internet connection. The application distribution package
does not contain the anti-virus databases. They have to be retrieved from
the update servers of Kaspersky Lab before you start using the
application.
• Log on to the system as root or as a privileged user.
3.1. Installing the application on a
server running Linux
For servers running the Linux operating system, Kaspersky SMTP-Gateway is
distributed in three different installation packages, depending on the type of your
Linux distribution.
You can use an rpm package to install the application under Red Hat Linux and
SuSE Linux.
To initiate installation of Kaspersky SMTP-Gateway from the rpm
package, enter the following in the command line:
# rpm –i smtpgw-linux-<version_number>.i386.rpm
If you are installing the application from the rpm package, after the files
have been copied to your server, run the postinstall.pl script to perform
post-installation configuration. By default, the postinstall.pl script is
located in the /opt/kav/5.5/smtpgw/setup/ directory.
In Debian Linux, the installation is performed from a deb package.
To initiate installation of Kaspersky SMTP-Gateway from the deb
package, enter the following command in the command line:
# dpkg –i smtpgw-linux-<version_number>.deb
After you enter the command, the application will be installed automatically.

Installing the application 21
You can also use a universal distribution file for all Linux OS. Use this distribution
file if your Linux version does not support the rpm or deb formats or if your
administrator does not wish to use (or cannot use) a built-in package manager.
The universal Kaspersky SMTP-Gateway distribution file is supplied as an
archive (tar.gz).
To initiate installation of Kaspersky SMTP-Gateway from the universal
distribution file, do the following:
1. Copy the archive of the distribution file to a directory within the file
system of your server.
2. Extract the archive using the following command:
# tar zxvf smtpgw-linux-<version_number>.tar.gz
The archive contains the installer and the file tree of the application
files that will be extracted by the above command.
3. Run the following installation script:
# cd <package_directory>
# ./install.sh
After you enter the command, the application will be installed automatically.
The procedure of application setup under Mandrake Linux distributions
has some peculiarities. You might have to perform some additional
actions to ensure correct functioning of the application in such systems
(please see Chapter 8 on p. 72 for details).
3.2. Installing the application on a
server running FreeBSD
The distribution file for installation of Kaspersky SMTP-Gateway on servers
running FreeBSD OS is supplied as a pkg package.
To initiate installation of Kaspersky SMTP-Gateway from a pkg
package, enter the following in the command line, depending upon the
version of your FreeBSD distribution:
# pkg_add smtpgw-freebsd-4.x-<version_number>.tgz
or:
# pkg_add smtpgw-freebsd-5.x-<version_number>.tgz
or:
# pkg_add smtpgw-openbsd-3.4--<version_number>.tgz

22 Kaspersky
After you enter the command, the application will be installed automatically.
®
SMTP-Gateway 5.5 for Linux/Unix
3.3. Installation procedure
Installation errors can occur for a number of reasons. If an error
message is displayed, make sure that your computer satisfies the
hardware and software requirements (see section 1.3 on p. 8 and that
you have logged into the system as a root.
To install the application on the server, follow the steps below:
Step 1. Preparing the system
At this stage, the system creates the system group and user account for the
application. The default group is kavusers and the default user account is
kavuser. In future, the application will start under this user account (not root) to
provide additional security for your system.
Step 2. Copying application files to destination directories
on your server
The installer starts copying the application files to the destination directories on
your server. For a detailed description of the directories where the application
files will be copied, see section A.1 on p. 78.
If you installed the application from an rpm package, then you should
run the postinstall.pl script (present by default in the
/opt/kav/5.5/smtpgw/setup/ directory) to perform the following steps.
Step 3. Post-installation tasks
The post-installation configuration includes the following steps:
• Configuring the smtpgw component (see section 3.4 on p. 23).
• Installing and registering the license key.
If you have no license key at the time of installation (for example, if you
purchased the application via the Internet and have not received the
license key yet), you can activate the application after installation before
its first use. For details see section 4.4 on p. 47. Please note that if the
license key is not installed, the anti-virus databases cannot be updated
and the smtpgw component cannot be started during the installation
process. You will have to do it manually, after the key is installed.

Installing the application 23
• Configuring the keepup2date component.
• Installation (updating) of the anti-virus databases.
You must install the anti-virus databases before using the
application. The procedure of detecting and disinfecting viruses
relies on the use of the anti-virus database records that contain
description of viruses known at the moment and the methods of
disinfecting these viruses. Anti-virus scanning and processing of
email messages cannot be performed without the anti-virus
database.
• Installing the Webmin module.
The Webmin module for remote management of the application can be
installed correctly only if the Webmin application is located in the default
directory. After the module is installed, you will receive detailed
instructions on how to configure it to work with the application.
• Launching the smtpgw component.
If, after installation, Kaspersky SMTP-Gateway has not started working
as required, check the configuration settings. Pay special attention to
the port number you specified for receiving mail traffic. You may also
view the application log file.
After you properly complete these steps, a corresponding message on the server
console will appear as soon as the installation procedure is over.
3.4. Configuring the application
Immediately after the files have been copied to your server, system configuration
process will start. Depending on the package manager you use, the configuration
process will either be started automatically or (if the package manager does not
allow the use of interactive scripts, such as rpm), some additional actions will
have to be performed by the administrator. All settings are stored in the
smtpgw.conf file installed by default in the /etc/kav/5.5/smtpgw/ directory.
If you are using the rpm installation package, enter the following
command to start configuration after the files are copied to your server:
# /opt/kav/5.5/smtpgw/setup/postinstall.pl
The configuration procedure includes the following tasks:
• Setting up (by the administrator) of the server name that will be used to
identify the application in the SMTP commands when creating the DSN
and notifications (the Hostname parameter in the [smtpgw.network]

24 Kaspersky
®
SMTP-Gateway 5.5 for Linux/Unix
section). Full domain name of the server must be specified as the
parameter value.
• Setting up the domain name that will be used to:
• Assign the Postmaster address ([smtpgw.network] section,
Postmaster parameter)
• Assign the sender’s return address for notifications
([smtpgw.options] section, NotifyFromAdress parameter)
• Define the administrator’s address ([smtpgw.options] section,
AdminNotifyAddress parameter)
• Allow incoming mail to this domain ([smtpgw.options] section,
RelayRule parameter).
• Defining the interface and port to listen to the incoming email traffic
([smtpgw.network] section, ListenOn parameter). Type the port name
and the IP address in the <x.x.x.x:z> format, where:
x.x.x.x is the IP address, and
z is the port number.
• Specifying local network identifiers ([smtpgw.access] section,
RelayRule parameter). This value is used to assign rules for message
delivery and processing, for example, rules specific for your organization
concerning mail processing, or blocking email messages from specified
domains, etc. Enter the values using the following formats: <x.x.x.x> or
<x.x.x.x/y.y.y.y>, or <x.x.x.x/y>,where:
x.x.x.x is the IP address, and
y.y.y.y or y is the subnet mask.
• Specifying (when necessary) the server to which all processed messages
will be forwarded ([smtpgw.forward] section, the ForwardRoute
parameter). Type the host name in the format: <x.x.x.x:z>, where:
x.x.x.x is the IP address, and
z is the port number.
• Specifying the proxy server name ([updater.options] section,
ProxyAddress parameter). This option is necessary for computers
connected to the Internet via a proxy server.
• Modifying the application configuration file.
If all the above steps have been successfully completed, the configuration file will
contain all settings that are required to start working with the application.

Installing the application 25
After the system is installed and configured, it is recommended that you
check the settings for Kaspersky SMTP-Gateway and test its
performance. For more details, see Chapter 6 on p. 67.
3.5. Installing the Webmin module to
manage Kaspersky SMTPGateway
The activity of Kaspersky SMTP-Gateway can be controlled remotely via a web
browser using Webmin.
Webmin is a program, which simplifies administration of Linux/Unix systems. The
software is based on modular structure and supports connection of new modules
as well as development of your own customized ones. You can obtain additional
information about Webmin and download its distribution package from the official
program web site at: www.webmin.com
If the default settings have been used, then you can access Webmin from your
web browser using HTTP / HTTPS to connect to port 10000 as soon as the
program installation is finished.
In order to install the Webmin module to control Kaspersky SMTPGateway:
1. Use your web browser to access Webmin with the privileges of its
administrator.
2. Select the Webmin Configuration tab in the program menu, and
then proceed to the Webmin Modules section.
3. Select the From Local File option in the Install Module section
and click
(see Figure 4).
.
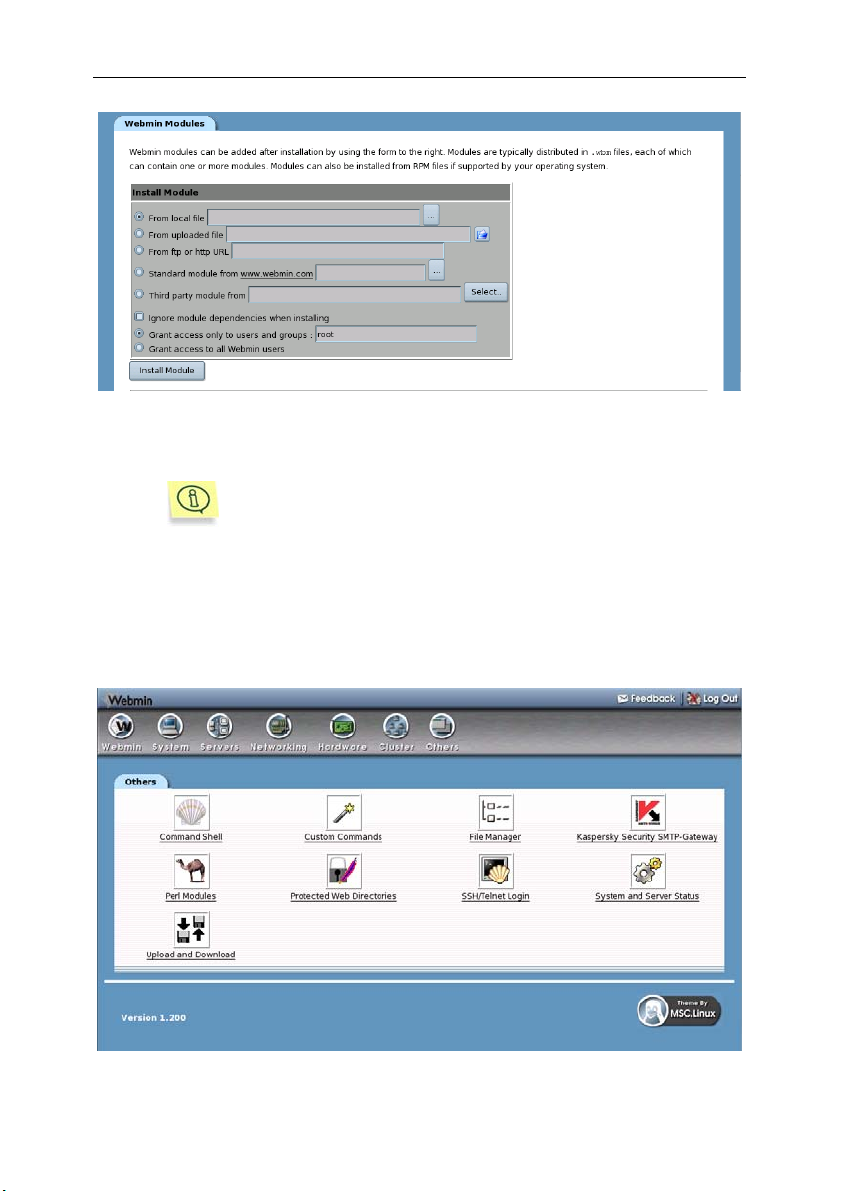
26 Kaspersky
Figure 4. Install Module section
®
SMTP-Gateway 5.5 for Linux/Unix
4. Enter the path to the Webmin module of the product and click ОК.
Webmin module is located in the kavsmtpgw.wbm file
installed by default to the /opt/kav/5.5/smtpgw/setup/ directory
(in Linux distributions) or the
/usr/local/share/kav/5.5/smtpgw/setup directory (for FreeBSD
and OpenBSD distributions).
If the Webmin module is installed successfully, you will see a corresponding
message on the display.
You can access the settings of Kaspersky SMTP-Gateway by clicking its icon
within the Others tab (see Figure 5).
Figure 5. The icon of Kaspersky SMTP-Gateway in the Others tab

CHAPTER 4. USING THE
APPLICATION
Using Kaspersky SMTP-Gateway, you can build a comprehensive anti-virus
protection system for email messages transferred through the mail server of your
organization.
The anti-virus protection system is based on the performance of tasks that
represent major functionality of the application.
The tasks implemented by Kaspersky SMTP-Gateway may be divided into three
major groups:
1. Updates of the databases used for anti-virus scanning and
disinfection of objects.
2. Anti-virus protection of email traffic.
Each of the above groups includes more specific tasks. In this chapter, we will
discuss the most typical tasks that the administrator can combine and enhance
depending on the needs of his/her organization.
This guide contains a description of how to locally configure and start tasks from
the command line. Issues related to starting and managing tasks from remote
computers using the Webmin application are not discussed in this document.
In all examples below, it is assumed that the administrator has
completed all required post-installation tasks and the application
operates correctly.
4.1. Updating the anti-virus
databases
Kaspersky SMTP-Gateway uses the anti-virus databases during scanning of
email traffic and disinfection of infected objects; they contain descriptions of all
currently known viruses and the methods of disinfection for objects affected by
those viruses.
The keepup2date component is included into Kaspersky SMTP-Gateway to
provide for software updates. The updates are retrieved from the update servers
of Kaspersky Lab, e.g.:
http://downloads1.kaspersky-labs.com/
http://downloads2.kaspersky-labs.com/

28 Kaspersky
®
SMTP-Gateway 5.5 for Linux/Unix
ftp://downloads1.kaspersky-labs.com/ etc.
The updcfg.xml file included in the installation package lists the URLs of all
available update servers.
The keepup2date component supports NTLM and Basic authentication
for connections through a proxy server.
To update the anti-virus databases, the keepup2date component selects an
address from the list of update servers and tries to download updates from that
server. If the server is currently unavailable, the application connects to another
server, trying to download updates. After a successful update, a command
specified as the value of the PostUpdateCmd parameter in the
[updater.options] section of the configuration file will be executed. By default,
this command will automatically restart the application. The restart is necessary
to make the application use the updated databases. Incorrect modification of that
parameter may prevent the application from using the updated databases or
even stop its functioning altogether.
All settings of the keepup2date component are stored in the [updater.*]
sections of the configuration file.
If your network has a complicated structure, we recommend that you download
updates from Kaspersky Lab’s update servers every hour and place them in a
network directory. To keep other networked computers constantly updated,
configure the local computers to copy the updates from that directory. For
detailed instructions on how to implement this updating scenario, see
section 4.1.3 on p. 30.
We strongly recommend that you set up the keepup2date component to
update the databases every hour!
The updating process can be scheduled to run automatically using the cron
utility (see section 4.1.1 on p. 29) or started manually from the command line by
the administrator (see section 4.1.2 on p. 29). Starting the keepup2date
component requires root user privileges.
All Kaspersky Lab’s applications that include keepup2date can be
automatically updated by the component.
Task: view the list of all Kaspersky Lab’s applications that can be
updated.
Solution: in order to perform this task, enter in the command line:
# keepup2date –i
Using the application 29
This will print to the screen a list of all Kaspersky Lab applications
including the keepup2date component, with their Application IDs.
4.1.1. Automatic updating of the anti-virus
databases
You can schedule regular automatic updates for the anti-virus databases using
the cron utility.
Task
: Configure the application to update automatically your anti-virus
databases every hour. An update server should be selected from the
updcfg.xml file by default. Only errors occurring in the component
operation should be recorded in the system log. Keep a general log of
all task starts. Output no information to the console.
Solution: to perform the above task, do the following:
1. In the application configuration file, specify the following values for
the parameters below:
[updater.options]
KeepSilent=true
[updater.report]
Append=true
ReportLevel=1
2. Edit the file that sets the rules for the cron process (crontab –e) by
entering the following string for the root user (or any other
privileged user), add the following line:
In Linux:
0 * * * * /opt/kav/5.5/smtpgw/bin/keepup2date
In FreeBSD:
0 * * * *
/usr/local/share/kav/5.5/smtpgw/bin/keepup2date
4.1.2. Manual updating of the anti-virus
databases
You can start updating your anti-virus databases from the command line at any
time.

30 Kaspersky
Task
If you need to update the anti-virus databases on several servers, it may be more
convenient to download the updates from an update server once, save them to a
shared directory, and then update the databases on other computers from that
directory. Please see section 4.1.3 on p. 30 for details related to creation of a
shared directory for updates.
: start updating of the anti-virus databases, save updating results in
the /tmp/updatesreport.log file.
Solution
privileged user) and enter in the command line:
# keepup2date –l /tmp/updatesreport.log
Task
/home/kavuser/bases
or empty, update the databases from Kaspersky Lab’s update servers.
Save the results to the /tmp/updatesreport.log file.
Solution
privileged user) and do the following:
1. Mount the network directory containing the database updates to the
2. In the application configuration file, specify the following values for
3. Enter the following in the command line:
: to accomplish the task, log in as the root (or any other
: start the updating of the anti-virus databases from the
shared directory. If the directory is inaccessible
: to accomplish the task, log in as the root (or any other
/home/kavuser/bases local directory.
the parameters below:
[updater.options]
UpdateServerUrl=/home/kavuser/bases
UseUpdateServerUrl=true
UseUpdateServerUrlOnly=false
# keepup2date –l /tmp/updatesreport.log
®
SMTP-Gateway 5.5 for Linux/Unix
You can accomplish these or similar tasks remotely using the Webmin
remote administration module.
4.1.3. Creating a shared directory for
storing and sharing database
updates
To update the anti-virus databases correctly on local computers from the shared
directory, you need to reproduce in that directory a file structure that is similar to
 Loading...
Loading...