Page 1

KASPERSKY LAB
Kaspersky® SMTP-Gateway 5.0 for
Linux/Unix
ADMINISTRATOR’S GUIDE
Page 2

KASPERSKY® SMTP-GATEWAY 5.0
FOR LINUX/UNIX
Administrator’s Guide
© Kaspersky Lab Ltd.
http://www.kaspersky.com
Revision date: August 2004
Page 3

Contents
CHAPTER 1. KASPERSKY® SMTP-GATEWAY 5.0..................................................... 6
1.1. Licensing policy ..................................................................................................... 7
1.2. Hardware and software requirements .................................................................. 7
1.3. Distribution kit ........................................................................................................ 8
1.4. Help desk for registered users .............................................................................. 9
1.5. Conventions........................................................................................................... 9
CHAPTER 2. APPLICATION DEPLOYMENT SCENARIOS...................................... 11
2.1. Application architecture ....................................................................................... 11
2.2. How Kaspersky SMTP-Gateway works ............................................................. 12
2.3. Typical deployment scenarios............................................................................. 14
2.3.1. Installing the application at the network perimeter....................................... 15
2.3.2. Installing the application inside your mail system........................................ 17
CHAPTER 3. INSTALLING KASPERSKY ANTI-VIRUS SMTP-GATEWAY.............. 19
3.1. Installing Kaspersky SMTP-Gateway under Linux............................................. 19
3.2. Installing KAV SMTP-Gateway on a server running FreeBSD or OpenBSD ... 20
3.3. Installation steps .................................................................................................. 21
3.4. Configuring Kaspersky SMTP-Gateway............................................................. 22
CHAPTER 4. UNINSTALLING KASPERSKY SMTP-GATEWAY .............................. 25
CHAPTER 5. USING KASPERSKY SMTP-GATEWAY APPLICATION.................... 26
5.1. Updating anti-virus database .............................................................................. 26
5.1.1. Automatic anti-virus database updating....................................................... 28
5.1.2. Manual updating of the anti-virus database................................................. 28
5.1.3. Creating a shared directory for storing and sharing database updates...... 29
5.2. Anti-virus protection of email traffic..................................................................... 30
5.2.1. Creating groups of recipients/senders ......................................................... 30
5.2.2. General message processing algorithm ...................................................... 33
5.2.3. Main tasks..................................................................................................... 35
5.2.3.1. Deliver messages without changes ...................................................... 35
5.2.3.2. Deliver only clean and disinfected messages....................................... 36
Page 4

4 Kaspersky
®
SMTP-Gateway 5.0
5.2.3.3. Delete infected attachments.................................................................. 37
5.2.3.4. Replace infected attachments with messages created using
templates................................................................................................. 38
5.2.4. Additional tasks............................................................................................. 38
5.2.4.1. Block messages delivery to recipients .................................................. 39
5.2.4.2. Deliver infected messages .................................................................... 40
5.2.4.3. Notify senders, administrator, and recipients........................................ 41
5.2.4.4. Filter messages by attachment types ................................................... 42
5.2.4.5. Backing up (quarantine, backup storage) ............................................. 43
5.2.4.6. Automatically add incoming and outgoing mail to archives.................. 44
5.3. Protection from hacker attacks and spam.......................................................... 45
5.4. Managing license keys........................................................................................ 46
5.4.1. Viewing information about license keys....................................................... 46
5.4.2. Renewing your license .................................................................................48
5.4.3. Removing a license key ............................................................................... 49
CHAPTER 6. ADVANCED SETTINGS ........................................................................ 50
6.1. Configuring anti-virus protection of mail traffic.................................................... 50
6.1.1. Scanning and disinfecting messages .......................................................... 50
6.1.2. iChecker technology ..................................................................................... 51
6.1.3. Setting up application timeouts .................................................................... 51
6.1.4. Setting performance restrictions .................................................................. 53
6.2. Setting up connection receiving interfaces ......................................................... 54
6.3. Setting up the routing table ................................................................................. 55
6.4. Managing the application .................................................................................... 56
6.5. Customizing date and time formats .................................................................... 58
6.6. Reporting options ................................................................................................ 58
CHAPTER 7. FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS................................................... 61
CHAPTER 8. TESTING APPLICATION OPERABILITY ............................................. 66
8.1. Testing the application using Telnet ................................................................... 66
8.2. Testing the application using EICAR ..................................................................68
APPENDIX A. SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION ABOUT THE PRODUCT......... 70
A.1. Location of the application files in directories..................................................... 70
A.2. Kaspersky SMTP-Gateway configuration file .................................................... 74
A.3. Control signals for the smtpgw component........................................................ 86
Page 5

Contents 5
A.4. Management files................................................................................................ 86
A.5. Application statistics............................................................................................ 87
A.6. Command line options for the smtpgw component ........................................... 92
A.7. Smtpgw return codes.......................................................................................... 93
A.8. Command line options for licensemanager ....................................................... 94
A.9. Kaspersky licensemanager return codes........................................................... 95
A.10. Keepup2date command line options ............................................................... 95
A.11. Keepup2date return codes ............................................................................... 96
A.12. Anti-virus scan information format.................................................................... 97
A.13. Messages about actions applied to the message ........................................... 98
APPENDIX B. KASPERSKY LAB............................................................................... 101
B.1. Other Kaspersky Lab Products ........................................................................ 102
B.2. Contact Us......................................................................................................... 106
APPENDIX C. LICENSE AGREEMENT .................................................................... 107
Page 6

CHAPTER 1. KASPERSKY
®
SMTP-GATEWAY 5.0
Kaspersky® SMTP-Gateway for Linux/Unix (hereinafter referred to as
Kaspersky SMTP-Gateway or the application) is designed for processing and
scanning SMTP mail traffic for viruses. The application is a full-featured mail
relay (compliant with IETF RFC internet standards) that runs under Linux,
FreeBSD and OpenBSD operating systems.
Kaspersky SMTP-Gateway allows to perform the following functions:
• Scan email traffic for viruses, including attached files and message
bodies.
• Detect infected, suspicious, corrupted, and password-protected at-
tachments and message bodies.
• Disinfect infected objects detected in email messages by scanning.
• Provide additional email traffic filtering by names and MIME types of
attachments and apply certain processing rules to the filtered objects.
• Maintain logs of all email messages sent and/or received by the application, if this is required by the internal security policy of the company;
• Provide protection against hacking attacks, block unwanted email
messages, provide the functions of an open mail relay of unsolicited
email messages;
• Limit the load on your server by configuring the application settings
and SMTP parameters.
• Notify senders, recipients, and the administrator of messages contain-
ing infected, suspicious, or corrupted objects.
• Automatically place infected, suspicious, and corrupted objects to the
quarantine or to the backup storage .
• Automatically update the anti-virus database from the Kaspersky
Lab’s update servers.
The application detects and disinfects infected objects using the anti-virus
database. During scans, the contents of each file are compared with the
sample code of known viruses contained in the database.
Page 7

Kaspersky® SMTP-Gateway 5.0 7
Remember that new viruses appear every day. To keep your
network constantly protected from the latest threats, we recommend that you update your anti-virus database every 3 hours.
• Configure and manage Kaspersky SMTP-Gateway either from a re-
mote location using Webmin web interface, or locally, using standard
OS tools such as command line options, signals, by creating special
command files or by modifying the configuration file of the application.
• Monitor the antivirus protection status and view the statistics and application logs.
1.1. Licensing policy
The licensing policy for Kaspersky SMTP-Gateway imposes limitations on the
use of the product by the following criteria:
• Number of users protected by the application
• Email traffic (MB/day)
Each type of licensing is also limited by a certain period (typically one year or two
years from the date of purchase).
You can purchase a license limited by one of the above criteria (for example, by
the daily mail traffic).
The application has slightly different configuration parameters, depending on the
type of license you have purchased. Thus, if the license is issued for a certain
number of users, you will have to create a list of addresses (domains) that will
be protected by Kaspersky SMTP-Gateway. If the license allows protection of
the limited amount of email traffic, the application can be configured to notify the
administrator when the traffic volume reaches critical values and hence the
license is about to expire.
1.2. Hardware and software
requirements
Minimum system requirements for normal operation of Kaspersky SMTPGateway are as follows:
• Hardware requirements:
• Intel Pentium® processor (Pentium III or Pentium 4 recom-
mended)
Page 8
8 Kaspersky
• at least 128 МB RAM
• 100 MB available space on your hard drive to install the appli-
cation
Note that the backup storage, quarantine, and logs of incoming
and outgoing mail are not included in the hard disk space required. If your network security policy requires the use of the
above features, extra disk space will be needed.
• at least 500 MB available space in the /tmp file system
• Software requirements:
• One of the following operating systems:
o Linux RedHat (version 7.3, 8.0 or 9.0), Linux SuSE (version
8.1, 8.2 or 9.0), or Linux Debian (version 3.0)
o FreeBSD versions 4.9 or 5.2.1
o OpenBSD version 3.4
• Perl interpreter, version 5.0 or higher (www.perl.org
the application.
• Webmin version 1.070 or higher (www.webmin.com
the remote administration module (optional).
®
SMTP-Gateway 5.0
) to install
) to install
1.3. Distribution kit
You can purchase Kaspersky SMTP-Gateway either from our dealers (retail
box) or online at one of our online stores (for example, www.kaspersky.com
follow the E-store link).
The retail box includes:
• a sealed envelope containing the installation CD
• a copy of this User Guide
• a license key file on the installation CD
• a license agreement
Before you unseal the envelope containing the CD, make sure you
have carefully read the license agreement.
If you buy the product online, you will download the installation file from the
Kaspersky Lab website. This installation file also includes this User Guide. The
–
Page 9

Kaspersky® SMTP-Gateway 5.0 9
license key will either be included into the distribution kit or will be sent to you by
email after receiving your payment.
The License Agreement is a legal agreement between you and the manufacturer
(Kaspersky Lab Ltd.) that stipulates the terms and conditions under which you
may use the anti-virus product you have purchased.
Carefully review the License Agreement!
If you do not agree to the terms of the License Agreement, you may return the
product to your Kaspersky Anti-Virus dealer for a full refund provided that the
envelope with the installation CD has not been unsealed.
By opening the sealed envelope containing the installation CD, or by installing
the application, you confirm that you have accepted all the terms and conditions
of the License Agreement.
1.4. Help desk for registered users
Kaspersky Lab offers an extensive service package enabling registered
customers to boost the productivity of Kaspersky
If you register and purchase a subscription you will be provided with the following
services for the period of your subscription:
• new versions of this anti-virus software product provided free of
charge;
• phone or email support on matters related to the installation, configuration, and operation of the product you have purchased;
• information about new Kaspersky Lab products and about new computer viruses (available to subscribers of the Kaspersky Lab’s newsletter).
Kaspersky Lab does not provide information related to operation and
use of operating systems or other technologies.
SMTP-Gateway.
1.5. Conventions
Various formatting conventions are used throughout the text of this document
depending on the purpose of a particular element. The table below lists the
formatting conventions used.
Page 10
10 Kaspersky
Convention Meaning
®
SMTP-Gateway 5.0
Bold font
Note.
Attention!
To do this,
1. Step 1.
2. …
Task or example
Solution
[option] – Function of the op-
tion
Text of information
messages and the command line
Menu titles, commands, window titles, dialog
elements, etc.
Additional information, notes
Critical information
Description of the sequence to actions to be
performed by the user
A task or an example of how to use the
product
A solution of the problem stated
Command line options
Text of configuration files, information
messages, and the command line.
Page 11

CHAPTER 2. APPLICATION
DEPLOYMENT SCENARIOS
This chapter contains a detailed discussion of the application’s architecture and
operating principles as well as typical scenarios of its deployment.
2.1. Application architecture
The review of the functionality of the application must be preceded by a
description of its internal architecture.
Kaspersky SMTP-Gateway is a full-featured Mail Transfer Agent (MTA) able to
receive and route email traffic scanning email messages for viruses. Kaspersky
SMTP-Gateway uses SMTP protocol options (RFC 2821), Internet message
format (RFC 2822), MIME format (RFC 2045-2049, 2231, 2646), and satisfies
the requirements to mail relays (RFC 1123). In accordance with anti-spam
recommendations (RFC 2505), the application uses its own relaying table to
prevent using of this application as an open relay. In addition, Kaspersky SMTP-
Gateway supports the following SMTP protocol extensions:
• Pipelining – Enhances performance of servers supporting this mode of
operation (RFC 2920).
• 8-bit MIME Transport – Processes national language characters code
tables (RFC 1652).
• Enhanced Error Codes – Provides more informative explanations of
protocol errors (RFC 2034).
• DSN (Delivery Status Notifications) – Decreases bandwidth usage and
provides more reliable diagnostics (RFC 1891, 3461-3464).
• SMTP Message Size Declaration – Decreases the load and increases
transfer rate (RFC 1870).
Kaspersky SMTP-Gateway includes the following components:
• smtpgw - the main component – a full-featured mail relay with in-built
anti-virus protection;
• licensemanager – component for managing license keys (installation,
removal, viewing statistics).
Page 12
12 Kaspersky
• keepup2date – components that updates the anti-virus database by
downloading the updates from the Kaspersky Lab’s update server.
• Webmin – a module for remote administration of the application using
a web interface (optional installation). This component allows to configure and manage the anti-virus database updates, specify actions to
be performed on the objects depending on their status and monitor
the results of the application’s operation.
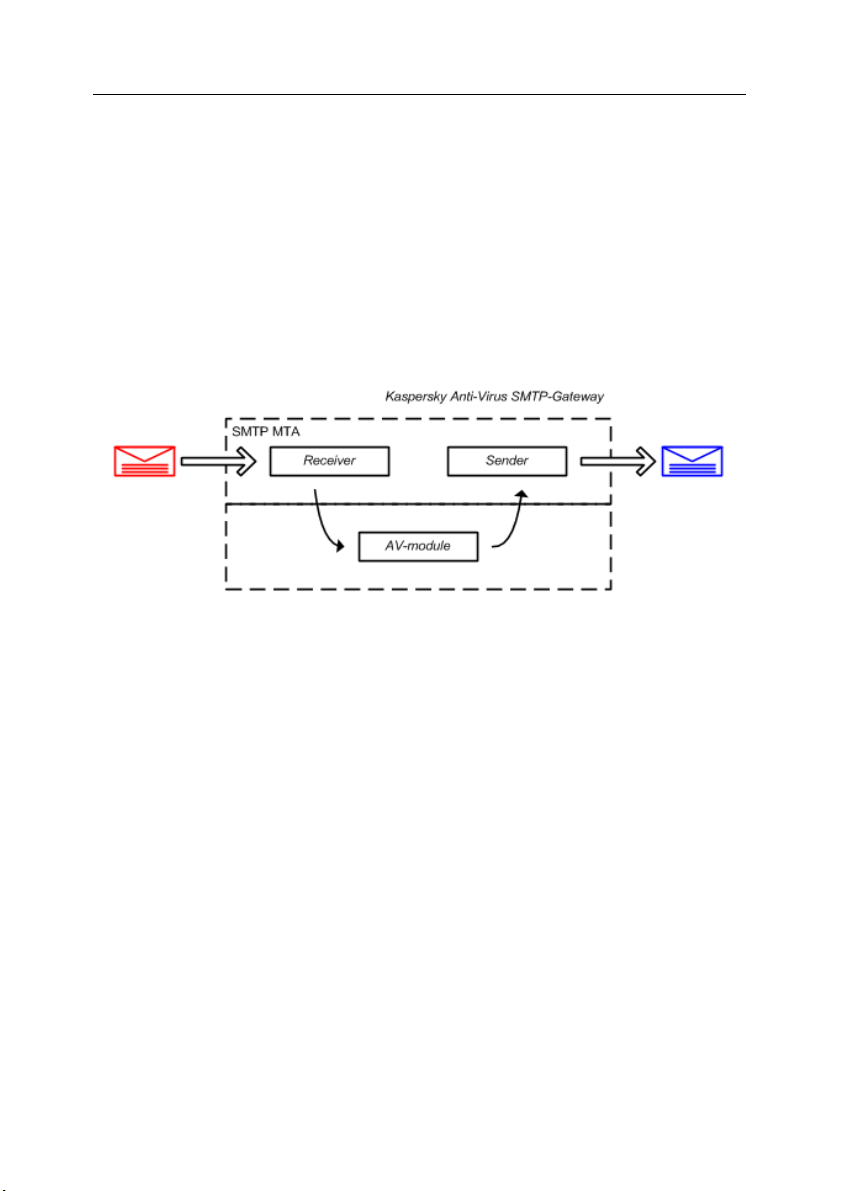
The smtpgw component (see Figure 1), in its turn, consists of the following
modules: Receiver (incoming mail receiver), Sender (module for sending
scanned messages), and AV module (module implementing the anti-virus
functionality).
Figure 1. Kaspersky SMTP-Gateway general architecture
®
SMTP-Gateway 5.0
The licensemanager components is used to manage license keys.
the keepup2date component updates the anti-virus database used for detecting
and disinfecting viruses.
2.2. How Kaspersky SMTP-Gateway
works
Kaspersky SMTP-Gateway works as follows (see Figure 2):
1. The mail agent receives email messages via the SMTP protocol and
passes them to the Receiver module.
2. The Receiver module performs the preliminary email processing using
the following criteria:
• presence of the sender’s IP address is in the list of blocked or
trusted addresses.
Page 13
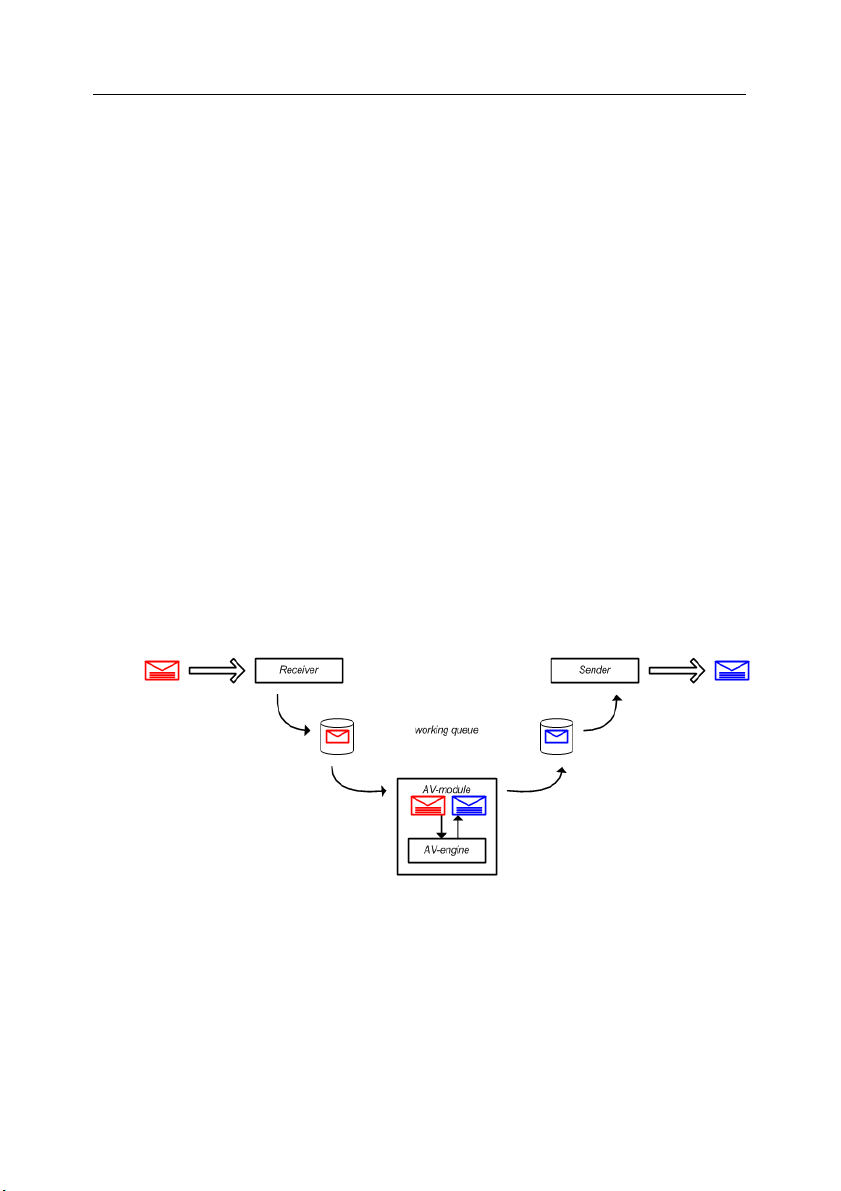
Application deployment scenarios 13
• compliance of the email message size (as well as the mail session and the total number of messages within the session) with
the specified limits specified in the application settings.
• compliance of the number of open sessions (from all IP addresses or a single IP address)with the specified limits specified
in the application settings.
If the message satisfies the preliminary processing, it is sent to the working
queue to be processed by the anti-virus engine.
3. The processing (scanning and disinfecting) procedure is as follows:
a. The AV module receives an object to be processed from the
working queue.
b. The AV module scans the object and, if this option is enabled,
disinfects it using the anti-virus database records. Then it passes
the scanned object to the ready-to-send message queue along with
the return code that indicates the object’s status.
c. The Sender module handles the object depending on the object’s
status, as defined by the settings stored in the configuration file.
4. Scanned messages together with the information on the scan and
disinfection results are transferred via the SMTP protocol to the onward
mail agent to be delivered to local end users or rerouted to other mail
servers.
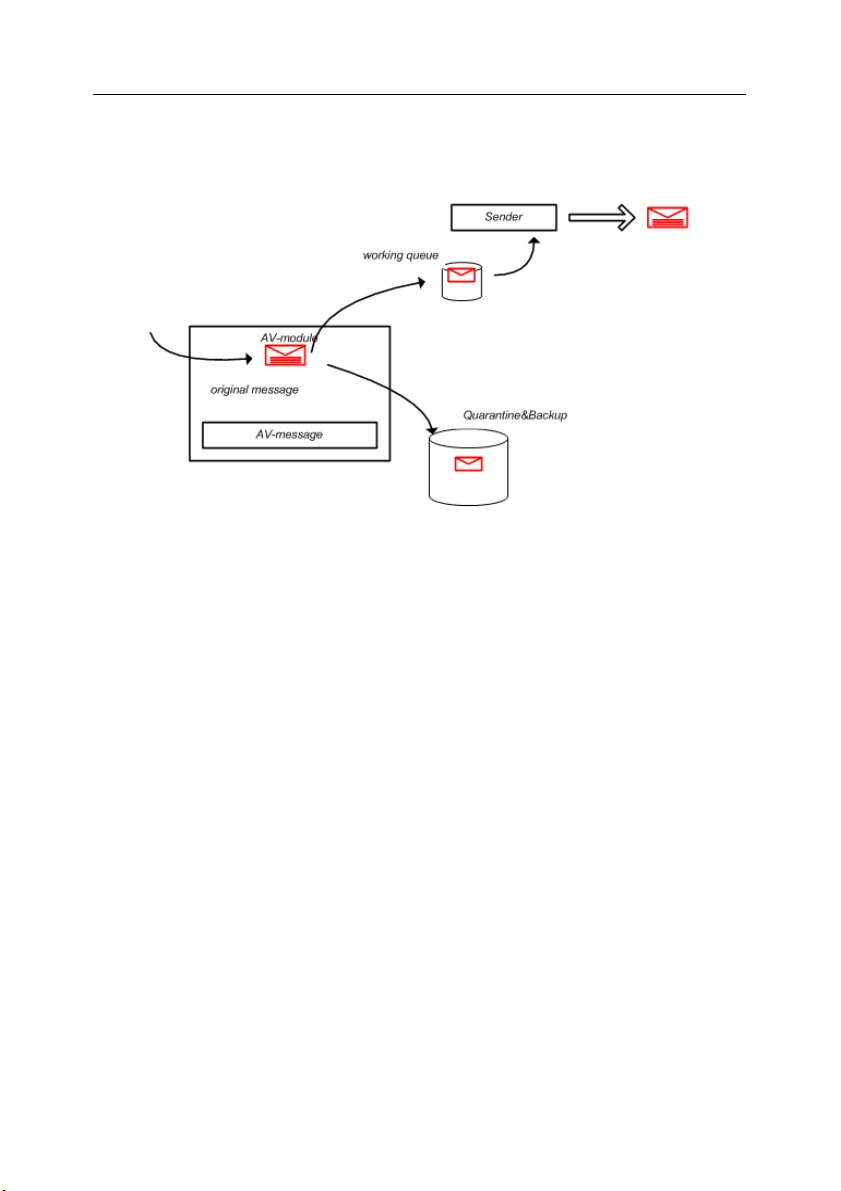
Figure 2. Kaspersky SMTP-Gateway working queue.
5. If saving a backup copy in the backup storage or in the quarantine is
specified as the action to be performed on a message (see Figure 3),
the copy of the scanned object will be saved in the backup storage or in
the quarantine concurrently with sending it to the ready-to-send queue
(depending on the message status).
Page 14
14 Kaspersky
®
SMTP-Gateway 5.0
6. If your network security policy requires logging of all outgoing e-mail
traffic, scanned messages will be automatically saved to the log
concurrently with sending them to the working queue.
Figure 3. Saving messages to the backup storage or the quarantine.
2.3. Typical deployment scenarios
Depending on the initial architecture of the mail server the following options of
Kaspersky Smtp-Gateway are provided:
• Install the application at the network perimeter on the same computer with
your mail system (recommended for Sendmail, Postfix and Exim mail systems).
• Install the application at the network perimeter on a dedicated server to
operate as an anti-virus filter (recommended for Sendmail, Postfix and
Exim mail systems).
• Install the application inside your existing mail system on the same com-
puter.
• Install the application inside your mail system on a dedicated server to
operate as an anti-virus filter.
The sections below discuss in detail the above scenarios and specify their
advantages.
Page 15

Application deployment scenarios 15
The application, being a mail relay, does not include a local delivery
agent. Therefore, no matter which of the deployment scenarios is used,
a mail system (or mail systems) that delivers e-mail messages to the
local users within the protected domains is required!
2.3.1. Installing the application at the
network perimeter
The advantage of this option is that it improves the overall performance of your
mail system because it minimizes the number of transfer cycles for email
messages.
Besides, in this case the existing mail server of the company has no connection
to the Internet, which enhances your data's security. In addition, demilitarized
zones (DMZ) may be set up.
To install the application and the mail system on the same server, the following
algorithm is provided to ensure their joint operation:
1. Configure all interfaces of Kaspersky SMTP-Gateway to listen on
port 25 for incoming email traffic.
2. The application will scan and process email traffic and then pass
the processed objects the mail system of the company via a
different port (for example port 1025).
3. The mail system, configured to use a local interface, will deliver
messages to users.
When implementing this deployment scenario the following settings must be
configured:
The following steps are to be followed in order to install the application
and the mail system on the same server:
• Configure the application for receiving mail via port 25 on all network interfaces of the server. In order to do this, specify the following value in
section [smtpgw.network] of the configuration file:
ListenOn=0.0.0.0:25
• Specify in the routing table transferring all scanned messages to the mail
system via port 1025. In order to do this, specify the following value in
section [smtpgw.network] of the configuration file:
ForwardRoute=company.com [host:1025]
Page 16
16 Kaspersky
®
SMTP-Gateway 5.0
where:company.com – protected company’s domain;
host – name of the mail server of the company.
• Change the settings of the existing mail system for receiving messages
from the application via port 1025. This will ensure receipt, anti-virus
scanning of all incoming mail messages and delivery of these messages
to the local users within the protected domains of the company.
• Specify the transferring of all messages received by the existing mail system via port 25 to the application. This will ensure anti-virus scanning of
all outgoing mail messages from the local users and delivery of such
messages to the internet.
• Specify the list of all local domains of the company by modifying the value
of parameter ProtectedDomains in section [smtpgw.network] of the
configuration file of the application (special symbols "*" and "?" can be
used). Mail messages for the specified domains will be scanned and licensed (a detailed description of the configuration file see section A.2,
page 74).
Application configuration for this deployment scenario will be implemented by default during the process installation.
The application operation algorithm, when the application is installed on a
dedicated server, is similar to operation on the same server, but the settings for
this scenario will differ.
When installing the application to a dedicated server, follow the below
instructions.
• Configure the application for receiving mail via port 25 on all network interfaces of the server. In order to do this, specify the following value in
section [smtpgw.network] of the configuration file:
ListenOn=0.0.0.0:25
• Specify in the routing table transferring all scanned messages to the mail
system via port 25. In order to do this, specify the following value in section [smtpgw.network] of the configuration file:
ForwardRoute=company.com [host:25]
where:company.com – protected company’s domain;
host – name of the mail server of the company.
• Specify the list of all local domains of the company by modifying the value
of parameter ProtectedDomains in section [smtpgw.network] (special
Page 17

Application deployment scenarios 17
symbols "*" and "?" can be used). Mail messages for the specified domains will be scanned and licensed.
This deployment scenario is the most convenient, especially if the installation of Kaspersky SMTP-Gateway is performed concurrently with
the deployment of the network and of the company’s mail system.
2.3.2. Installing the application inside your
mail system
If you install the application inside your mail system, the advantage is that the
information and settings for the anti-virus software installed on the server are not
available on the Internet. Besides, if the application is installed inside the mail
system on the dedicated server, this provides for the possibility to distribute the
load among several servers performing anti-virus scan.
The following algorithm is provided for joint operation of the application and the
mail system installed on the same server:
1. Duplicate your mail system and configure one of them to listen to port
25 and receive email messages via all available interfaces.
2. This mail system forwards all incoming messages through the local
interface via a different port (port 1025, for instance) to the application
for scanning.
3. The application scans the email messages for viruses and forwards
scanned and processed messages to the second mail system on a
different port (for example, port 1026).
4. The second mail system delivers email to the local users.
This deployment scenario is recommended if you are sure of the reliability of your mail system. The installation of the application will not
affect the stability of your mail system.
In general, installation on a dedicated server is similar to the above procedure.
Besides, when installing the application on a dedicated server, you can create
and run several copies of the application on different servers. This can help you
distribute the anti-virus processing load among several servers.
To implement this scenario:
Specify the list of all local domains of the company by modifying the value
of parameter ProtectedDomains in section [smtpgw.network] (special
Page 18

18 Kaspersky
®
symbols "*" and "?" can be used). Mail messages for the specified domains will be scanned and licensed.
Deploying Kaspersky SMTP-Gateway may require changes of all settings within the mail clients throughout the company so that all outgoing
mail messages will be delivered to the application that will pass the
messages to the external network after an anti-virus scan.
If the network includes a firewall or demilitarized zones (DMZ’s), it is
necessary to provide mail clients and internal and external networks
servers with access to the installed application to ensure joint operation
and routing of the mail traffic.
SMTP-Gateway 5.0
Page 19

CHAPTER 3. INSTALLING
KASPERSKY ANTI-VIRUS
SMTP-GATEWAY
Before installing Kaspersky SMTP-Gateway, it is necessary to:
• Make sure that your system meets the minimum system requirements
(see section 1.2 on page 7).
• Configure your Internet connection (optional; it is necessary for updating the anti-virus database).
• Log in to the system as root or as a privileged user.
3.1. Installing Kaspersky SMTPGateway under Linux
For servers running the Linux operating system, Kaspersky SMTP-Gateway is
distributed in three different installation packages, depending on the type of the
installation program for your OS.
You can use an rpm package to install Kaspersky SMTP-Gateway under Linux
Red Hat and Linux SuSe.
To install Kaspersky SMTP-Gateway from the rpm package, enter the
following in the command line:
rpm –i smtpgw-linux-5.0.x-yy.i386.rpm
If you are installing the application from the rpm package, after the files
have been copied to your server, run the postinstall.pl script to
perform post-installation configuration.
Under Linux Debian, Kaspersky SMTP-Gateway installation is performed from a
deb package.
To initiate installation of Kaspersky SMTP-Gateway from the deb
package, enter the following command in the command line:
dpkg –i smtpgw-linux-5.0.x.yy.deb
Page 20

20 Kaspersky
After you enter the command, Kaspersky SMTP-Gateway will be installed
automatically.
You can also use a universal distribution file for all Linux OS. Use this distribution
file if your Linux version does not support the rpm or deb formats or if your
network administrator does not wish to use (or cannot use) a built-in package
manager.
The universal Kaspersky SMTP-Gateway distribution file is supplied as an
archive (tar.gz).
To install Kaspersky SMTP-Gateway from the universal distribution
file, do the following:
1. Copy the archive of the distribution file to a file system directory on
your server.
2. Extract the archive using command
tar -xvf smtpgw-linux-5.0.x.yy.tar.gz
The archive contains the installer and the file tree of the application
distribution file that will be extracted by the above command.
3. Run the following installation script:
cd smtpgw-install
./install.sh
After you enter the command, Kaspersky SMTP-Gateway will be installed
automatically.
®
SMTP-Gateway 5.0
3.2. Installing KAV SMTP-Gateway
on a server running FreeBSD or
OpenBSD
The distribution file for installation of Kaspersky SMTP-Gateway on servers
running FreeBSD or OpenBSD OS is supplied as a pkg package.
Page 21

Installing Kaspersky Anti-Virus SMTP-Gateway 21
To initiate installation of Kaspersky SMTP-Gateway from a pkg pack-
age, enter the following in the command line:
pkg_add smtpgw-freebsd-4.x-5.0.x.yy.tgz
or:
pkg_add smtpgw-freebsd-5.x-5.0.x.yy.tgz
or:
pkg_add smtpgw-openbsd-3.4-5.0.x.yy.tgz
After you enter the command, Kaspersky SMTP-Gateway will be installed
automatically.
3.3. Installation steps
Installation errors can occur for a number of reasons. If an error message is displayed, make sure that your computer satisfies the minimum
system requirements listed in section 1.2 on page 7 and that you have
logged on to the system as a root.
To install the application on the server, follow the steps below:
Step 1. Preparing the system
At this stage, the system creates the system group and user account for the application. The default group is kavusers and the default user account is ka-
vuser. In future, the application will start under this user account (not root) to
provide additional security to your system.
Step 2. Copying application files to your server
The installer starts copying files to the installation directory on your server: A
detailed description of the directories to the application files will be copied, see
section A.1, page 70.
For Linux: /opt/kav/5.0/smtpgw
For OpenBSD and FreeBSD: /usr/local/share/kav/5.0/smtpgw
Step 3. Post-installation tasks
The post-installation configuration includes the following steps:
Page 22

22 Kaspersky
• Configuring the smtpgw component (see section 3.4 page 22).
• Installing and registering the license key.
• If you have no license key at the time of installation (for example, if
you purchased the application via the Internet and have not received
the license key yet), you can activate the application after installation
before its first use. For details see section 5.4, page 46. Note that if
the license key is not installed, the anti-virus database cannot be updated and the smtpgw component cannot be run during the installation process. You will have to do it manually, after the key is installed.
• Configuring the keepup2date component.
• Updating the anti-virus database.
You must install the anti-virus database before using the application. The procedure of detecting and disinfecting viruses relies on
the use of the anti-virus database records that contain description
of viruses known at the moment and the methods of disinfecting
these viruses. Anti-virus scanning and processing of email messages cannot be performed without the anti-virus database.
• Installing the Webmin module.
The Webmin module for remotely managing the application can be installed
correctly only if the Webmin application is located in the default directory. After Webmin is installed, you will receive detailed instructions on how to configure the module to work with the application.
• Running the smtpgw component.
®
SMTP-Gateway 5.0
If, after installation, Kaspersky SMTP-Gateway has not started working
as required, check the configuration settings. Pay special attention to
the port number you specified for receiving mail traffic. You may also
view the application log file.
After you properly complete these steps, a corresponding message on the server
console will appear.
3.4. Configuring Kaspersky SMTPGateway
Immediately after the files have been copied to your server, system configuration
process will start. Depending on the package manager you use, the configuration
process will either be started automatically or (if the package manager does not
Page 23

Installing Kaspersky Anti-Virus SMTP-Gateway 23
allow the use of interactive scripts, such as rpm), some additional actions will
have to be performed by the administrator.
If you are using the rpm installation package, enter the following command to start configuration after the files are copied to your server:
/opt/kav/5.0/smtpgw/setup/postinstall.pl
The configuration process includes the following tasks:
• Setting up (by the administrator) of the server name that will be used
to identify the application in the SMTP-protocol commands when creating the DNS and notifications (the [smtpgw.network] section,
Hostname parameter). Enter the host name using the following format: <*.*>.
• Setting up the domain name that will be used to:
• Assign the Postmaster address ([smtpgw.network] section,
Postmaster parameter)
• Assign the sender’s return address for notifications
([smtpgw.options] section, NotifyFromAdress parameter)
• Define the administrator’s address ([smtpgw.options] section,
AdminNotifyAddress parameter)
• Allow incoming mail to this domain ([smtpgw.options] section,
Rule parameter).
Enter the domain name using the following format: <*.*>.
• Defining the interface and port that listens to the incoming email traffic
( [smtpgw.network] section, ListenOn parameter). Type the port
name and the IP address in the format <x.х.х.x:y>, where:
x.х.х.x is the IP address, and
y is the port number.
• Specifying local network identifiers ([smtpgw.access] section, Rule
parameter). This value is used to assign rules for message delivery
and processing, for example, rules specific for your organization concerning mail processing, or blocking email messages from external
servers, etc. Specify the values using the following formats:
<x.х.х.x>, <x.х.х.x/y.y.y.y>, or <x.х.
х.x/y>, where:
x.х.х.x is the IP address, and
y.y.y.y or y is the subnet mask.
Page 24

24 Kaspersky
®
SMTP-Gateway 5.0
• Specifying the server to which all processed messages will be forwarded ([smtpgw.forward] section, the ForwardRoute parameter).
Type the host name in the format <x.х.х.x:z>, where:
x.х.х.x is the IP address, and
z is the port number.
• Modifying the application configuration file
If all the above steps have been successfully completed, the configuration file will
have all settings that are required to start working with the application.
After the system is installed and configured, it is recommended that you
check the settings for Kaspersky SMTP-Gateway and test its performance. For more details, see Chapter 8 on page 66.
Page 25

Installing Kaspersky Anti-Virus SMTP-Gateway 25
CHAPTER 4. UNINSTALLING
KASPERSKY SMTPGATEWAY
To uninstall Kaspersky SMTP-Gateway, you should have root privileges. If you
are currently logged under a user account with lesser privileges, log on as a
root.
The uninstallation process will automatically stop the application!
When you are uninstalling Kaspersky SMTP-Gateway, the application will be
stopped, and all files and directories created during installation will be deleted.
However, files and directories created or modified by the administrator, such as
the application configuration file, notification templates, and the quarantine and
backup directories, archives of received and sent messages, anti-virus
databases, license key file, will remain.
There are several different ways to run the uninstall procedure, depending on the
package manager you used. Below is a detailed discussion of these options:
If you installed the application from the rpm package, type the following
string to uninstall Kaspersky SMTP-Gateway:
rpm -e <package_name>
If you installed the application from the deb package, type the following
string to uninstall Kaspersky SMTP-Gateway:
dpkg -r <package_name>
If you installed the application from the universal package (tar.gz),
type the following string to uninstall Kaspersky SMTP-Gateway:
/opt/kav/5.0/smtpgw/setup/uninstall.pl
If you installed the application from the pkg package, type the
following string to uninstall Kaspersky SMTP-Gateway:
pkg_delete <package_name>
After the application has been successfully removed from your server, you will
see a corresponding message on your screen.
Page 26

CHAPTER 5. USING KASPERSKY
SMTP-GATEWAY
APPLICATION
Using Kaspersky SMTP-Gateway, you can build a comprehensive anti-virus
protection system for email messages transferred through the mail server of your
organization.
The anti-virus protection system is based on the performance of tasks that
represent major functionality of the application.
All tasks implemented by the application may be divided into two major groups:
1. Anti-virus protection of email messages.
2. Updating of the anti-virus database used to detect and disinfect
infected objects.
Each of the above groups include more specific tasks. In this chapter, we will
discuss tasks that the administrator can combine and enhance depending on the
needs of his/her organization.
This guide contains a description of how to locally configure and start tasks from
the command line. Issues related to starting and managing tasks from remote
computers using the Webmin application are not considered in this document.
In all examples below, it is assumed that the administrator has completed all required post-installation tasks and the application operates
correctly.
5.1. Updating anti-virus database
The application detects viruses and disinfect infected objects based on the antivirus database records that contain description of all viruses known at the
moment and the methods used to disinfect objects infected by this viruses.
The keepup2date module is included into the architecture of KasperskySMTP-
Gateway to provide various types of updates. The source of updates are
Kaspersky Lab’s update servers, such as:
http://downloads1.kaspersky-labs.com/updates/
http://downloads2.kaspersky-labs.com/updates/
Page 27
Using Kaspersky SMTP-Gateway application 27
ftp://downloads1.kaspersky-labs.com/updates/, etc.
The updcfg.xml file included in the installation package lists the URLs of all
available Kaspersky Lab’s update servers.
To update the anti-virus database or application modules, the keepup2date
component first selects an address from the list of update servers and tries to
download updates from this server. If the server is currently unavailable, the
application connects to another server, trying to download updates. After the
database has been successfully updated, a command specified as the value of
parameter PostUpdateCmd in section [updater.options] of the configuration
file will be executed. By default, this command will automatically restart the
application; it is not recommended to alter this command.
All settings of the keepup2date component are stored in the [updater.*]
sections of the configuration file.
If your network has a complicated structure, we recommend that you download
updates from Kaspersky Lab’s update servers every three hours and place them
to a network directory. To keep other networked computers constantly updated,
configure the local computers to copy the updates from this directory. For
detailed instructions on how to implement this updating scenario, see
section 5.1.3 on page 29.
We urgently recommend that you set the application to update your
anti-virus database every 3 hours!
You can also configure the updating process to run at a certain time by using the
cron utility (see section 0 on page 27) or manually, from the command line (see
section 5.1.2 no page 28).
All Kaspersky Lab’s applications that have the keepup2date component
can be automatically updated.
: view the list of all Kaspersky Lab’s applications that can be up-
Task
dated.
Solution
: in order to implement this task, enter in the command line:
keepup2date –i
This will print to the screen the list that includes the names of all Kaspersky Lab’s
applications that include the keepup2date component as well as their application
ID’s.
Page 28

28 Kaspersky
®
SMTP-Gateway 5.0
5.1.1. Automatic anti-virus database
updating
You can schedule the application to automatically update the anti-virus database
using the cron program.
Task
: Configure the application to automatically update your anti-virus
database every day at 07.00 a.m. An update server should be selected
from the updcfg.xml file. Only errors encountered in the component
operation should be recorded in the system log. Keep a general log of
all task executions. Output no information to the console.
Solution
1. In the configuration file, specify the appropriate values for the
2. Edit the file that sets the rules for the cron process (crontab –e) by
For Linux:
For FreeBSD and OpenBSD:
: To accomplish the above tasks, do the following:
following parameters, for example:
[updater.options]
KeepSilent=yes
[updater.report]
Append=yes
ReportLevel=1
entering the following string for the root user:
0 7 * * * /opt/kav/5.0/smtpgw/bin/keepup2date
0 7 * * *
/usr/local/share/kav/5.0/smtpgw/bin/keepup2date
5.1.2. Manual updating of the anti-virus
database
You can start updating your anti-virus database from the command line at any
time.
Page 29
Using Kaspersky SMTP-Gateway application 29
: To start updating of the database and save updating results in the
Task
/tmp/updatesreport.log file.
Solution
user that have the rights of a privileged user) and enter in the command
line:
#keepup2date –l /tmp/updatesreport.log
If you need to update the anti-virus database on several server, it may be more
convenient to download the updates from an update server once, save them to a
shared directory, and then update the databases on other computers from this
directory.
Task
/home/kavuser/bases
or empty, update the database from Kaspersky Lab’s update servers.
Save the results to file /tmp/updatesreport.log.
Solution
user that have the rights of a privileged user) and do the following:
1. In the application configuration file, enter the appropriate values for
2. Enter the following string in the command line:
: To accomplish the task, log in as a root user (or as any other
: Start the updating of the anti-virus database from the
shared directory. If this directory is inaccessible
: To accomplish the task, log in as a root user (or as any other
the following parameters:
[updater.options]
UpdateServerUrl=/home/kavuser/bases
UseUpdateServerUrl=yes
UseUpdateServerUrlOnly=no
#keepup2date –l /tmp/updatesreport.log
You can accomplish these or similar tasks remotely using the Webmin
remote administration module.
5.1.3. Creating a shared directory for
storing and sharing database
updates
To update the anti-virus databases correctly on local computers from the shared
directory, you need to create in this directory a file structure that is similar to that
Page 30

30 Kaspersky
of Kaspersky Lab’s update servers. This is a complicated task that deserves a
detailed explanation.
: Create a shared local directory from which the local computers
Task
will be able to update the anti-virus database.
®
SMTP-Gateway 5.0
Solution
user that have the rights of a privileged user) and do the following:
1. Create a local directory.
2. Run the keepup2date component as follows:
3. Allow local computers on your network to access this directory.
: To accomplish this task, log in as a root user (or as any other
keepup2date –u rdir
where rdir is the full path to the directory created.
5.2. Anti-virus protection of email
traffic
Anti-virus filtering of mail traffic is the most main task of Kaspersky SMTPGateway.
The application is used to protect users against infected messages, and to
deliver only clean or disinfected messages, along with information on scanning
results for every message.
Additional filtration of messages by names and attachment types decrease the
load on the server when scanning email traffic for viruses. This represents only a
part of the application’s functionality. There is an extended discussion of the
application’s functionality below, in the sections describing specific protection
tasks.
All smtpgw settings are located in the [smtpgw.*] sections of the application configuration file.
5.2.1. Creating groups of
recipients/senders
Recipients/Senders group is defined as pairs of recipient/sender email
addresses. A particular email message may be assigned to a particular group
Page 31

Using Kaspersky SMTP-Gateway application 31
depending on whether this group contains either the sender’s or the recipient’s
address from commands MAIL FROM and RCPT TO.
The administrator can specify individual rules for processing each mail messages
depending on the recipients/senders group. Therefore it is particularly important
that the addresses are associated with the correct groups.
The application searches through the list of addresses for a specific address. If it
finds a matching combination of the sender/recipient addresses, the rules
defined for this group will be applied to the email message.
The anti-virus functionality of Kaspersky SMTP-Gateway depends on
the configuration file settings. You can make configuration changes to
the file either locally or remotely (using the Webmin remote administration module).
The configuration file contains the description of [smtpgw.policy] section that
implicitly defines the policy group that determines the default email messages
processing rules.
All settings specified in this section and the section itself are mandatory.
The policy group does not contain the names of senders and recipients. Rules
defined in the policy, are applied to all messages, except those that belong to
other groups explicitly described as sections [smtpgw.group:group_name].
All parameters in sections [smtpgw.group:group_name] are optional. If a
parameter value in such section is not specified, it will be taken from section
[smtpgw.policy]
If a configuration file included into the application installation package is used,
then the mail messages will be processed as per the following rules (defined by
the policy group).
• Scan all messages.
• Deliver only clean messages to the recipients.
• Messages that could not be disinfected, suspicious, corrupted, pro-
tected messages that caused errors, must be deleted
• Notify recipients and the group administrator about infected, disinfected, suspicious, corrupted or protected messages that caused errors.
You can change the parameters of the policy group or create new groups. If you
would like to process email messages belonging to different groups of
recipients/senders using different rules, you will have to create several distinct
groups.
Page 32

32 Kaspersky
To create a new group of addresses:
®
SMTP-Gateway 5.0
1. Create section [smtpgw.group:group_name] in the configuration
file.
2. In the Senders and Recipients fields, specify sender and recipient
addresses (masks of addresses) separated with commas.
To define masks, use the "*" and "?" symbols.
If you do not define the Recipients OR Senders parameters, the default value will be "
*@*"
It is required to set at least one of parameters Senders
or Recipients.
If you added other groups to the configuration file, the application will process
messages from these groups as follows:
1. The application first compares the message address(es) with
addresses in the groups created by the administrator. If the
recipient/senders addresses pair is found in a specific group, the
rules for this group will be applied to the message.
If the sender/recipient address matches the addresses of several
groups, the application will use the rules for the first of these groups.
2. If the message addresses do not match any group, created by the
administrator, the message will be processed according to the rules
described in the policy group.
If a message has several recipients that belong to different groups, virtual copies of the initial message will be created to match the number of
such groups. Each copy will be processed individually according to the
rules specified by the particular group.
Figure 4 shows the sequence of actions performed by Kaspersky SMTP-
Gateway with a received email message.
Page 33

Using Kaspersky SMTP-Gateway application 33
Figure 4. Message processing
5.2.2. General message processing
algorithm
In this section, we describe how Kaspersky SMTP-Gateway processes email
messages. When the server receives an email message AV-module:
1. determines the group this message belongs to.
2. if the message has multiple recipients that belong to different
groups, before further anti-virus scan is performed, the application
creates virtual copies of this message to match the number of
groups and applies different rules to each of such copies.
3. using a built-in MIME format identifier (MIME, RFC822, UUE), the
application divides the message into elements, such as message
body, attachments, etc.
4. if the application is configured to filter objects by name and/or
attachment type, it applies the specified filtering rules for this
message. If the message meets the filter conditions, the object will
be assigned status Filtered and will not be subjected to further
anti-virus scanning.
Page 34

34 Kaspersky
®
SMTP-Gateway 5.0
5. Then each of the received objects will be sent to the anti-virus
engine that processes the received object and returns it with the
status assigned to it.
A message may be assigned one of the following statuses in the
process of checking:
o Clear – Message is clean.
o Infected – Message is infected and cannot be disinfected
or disinfection has not been attempted.
o Disinfected – Infected object has been successfully disin-
fected.
o Suspicious – Object is suspected of being infected by an
unknown virus or by a new modification of a known virus
o Protected – Scanning failed because the message is
password-protected (for instance, it’s an archive)
o Error – Object is corrupted or an error occurred during the
scan.
6. Depending on the object status, the application performs an action
as specified in the settings for this group (basic actions).
7. After the anti-virus scan of all components of the message and
performing actions on these components, actions will be performed
on the message as a whole (additional actions).
The tasks that can be performed with objects are of the following two types:
• Basic actions:
• Deliver messages without changes (see para 5.2.3 page 35).
• Deliver only clear or disinfected messages (see 5.2.3.2
page 36).
• Delete infected attachments (see para 5.2.3.3 page 37).
• Replace infected attachments with messages created using
templates (see section 5.2.3.4 ob page 38).
• Additional actions:
• Block messages delivery to the recipients (see section 5.2.4 on
page 38).
• Deliver all messages, including infected messages (see section 5.2.4.2 on page 40).
Page 35

Using Kaspersky SMTP-Gateway application 35
• Create and send alerts to the sender, administrator, and recipient (see section 5.2.4.3 on page 41).
• Quarantine infected messages or place it to the backup storage
(see section 5.2.4.5 on page 43).
Examples of these actions are presented below.
5.2.3. Main tasks
The tasks considered in this section implement the core of the Kaspersky
SMTP-Gateway anti-virus functionality.
The configuration file included into the installation package by default implements
e-mail processing rules that are optimal for most of cases.
5.2.3.1. Deliver messages without changes
Tasks
:
• Scan for viruses all incoming and outgoing traffic on the
server;
• Deliver all messages to recipients, regardless of message
status;
• Notify senders, recipients, and administrator about infected,
suspicious, and corrupted email messages and about objects
the application failed to scan.
Solution
In the [smtpgw.group:] section of the configuration file assign
parameter values as follows:
: To implement the above tasks, do the following:
Check=yes
BlockMessage=
ActionDisinfected=pass
ActionInfected=pass
ActionSuspicious=pass
ActionProtected=pass
ActionError=pass
ActionFiltered=pass
Page 36

36 Kaspersky
®
SMTP-Gateway 5.0
NotifyAdmin=disinfected, infected, suspicious,
protected, error, filtered
NotifyRecipient=disinfected, infected, suspicious, protected, error, filtered
NotifySender=disinfected, infected, suspicious,
protected, error, filtered
5.2.3.2. Deliver only clean and disinfected
messages
Task
:
• Scan for viruses all incoming and outgoing email messages
on the server and disinfect all infected messages;
• Delete infected messages the application failed to disinfect;
• Deliver disinfected messages to recipients;
• Notify senders, recipients, and administrator about infected,
suspicious, and corrupted email messages and about objects
the application failed to scan; attach unchanged infected
messages to notifications sent to the administrator.
Solution
: To implement the above tasks, do the following:
1. In the [smtpgw.ave] section of the configuration file assign
parameter value as follows:
Cure=yes
2. In the [smtpgw.policy] section of the configuration file assign
parameter values as follows:
Check=yes
BlockMessage=infected, suspicious, protected, error, filtered
ActionDisinfected=cure
ActionInfected=remove
ActionSuspicious=remove
ActionProtected=remove
ActionError=remove
ActionFiltered=remove
Page 37

Using Kaspersky SMTP-Gateway application 37
NotifyAdmin=infected, suspicious, protected,
error, filtered
NotifySender=infected, suspicious, protected,
error, filtered
NotifyRecepient=infected, suspicious, protected,
error, filtered
5.2.3.3. Delete infected attachments
:
Task
• Scan for viruses all incoming and outgoing email on the
server and disinfect all infected messages;
• Deliver only clean and disinfected messages;
• Delete infected, corrupted, or password protected attach-
ments upon detection and deliver the message without these
attachments.
Solution
1. In the [smtpgw.ave] section of the configuration file assign parameter
value as follows:
Cure=yes
2. In the [smtpgw.policy] section of the configuration file assign
parameter values as follows:
Check=yes
BlockMessage=
ActionDisinfected=cure
ActionInfected=remove
ActionSuspicious=remove
ActionProtected=remove
ActionError=remove
ActionFiltered=remove
NotifyAdmin=
NotifySender=
NotifyRecepient=
: To implement the above tasks, do the following:
Page 38

38 Kaspersky
®
SMTP-Gateway 5.0
5.2.3.4. Replace infected attachments with
messages created using templates
Task:
• Scan for viruses all incoming and outgoing email on the
server and disinfect all infected messages;
• Deliver only disinfected messages;
• Replace infected, suspicious, corrupted, or password pro-
tected attachments with a standard message and deliver the
email message without attachments.
Solution
1. In the [smtpgw.ave] section of the configuration file assign parameter
value as follows:
Cure=yes
2. In the [smtpgw.policy] section of the configuration file assign
parameter values as follows:
Check=yes
BlockMessage=
ActionDisinfected=cure
ActionInfected=placeholder
ActionSuspicious=placeholder
ActionProtected=placeholder
ActionError=placeholder
ActionFiltered=placeholder
NotifyAdmin=
NotifySender=
NotifyRecepient=
: To configure the above tasks, do the following:
5.2.4. Additional tasks
A discussion of additional tasks help understand enhanced functionality of the
application. The examples below help the administrator tune up the application
for performing particular tasks to extend the functionality of the application and to
Page 39

Using Kaspersky SMTP-Gateway application 39
tailor the application for the conditions and requirements of a particular
organization.
5.2.4.1. Block messages delivery to recipients
Sometimes, the administrator needs block delivery of certain messages to the
recipients.
For example, a message that may contain important information, that needs to
be saved, is flagged as suspicious. This important information may be corrupted
or lost during disinfection. In this case, it is recommended that you block this
message and send it to Kaspersky Lab for expert analysis.
Task:
• Scan for viruses all incoming and outgoing email on the
server;
• Block infected, suspicious, corrupted, and password protected messages and those the application failed to scan;
• Notify senders, recipients, and administrator about blocked,
disinfected, deleted, suspicious, and corrupted email messages and about objects the application failed to scan; add
unchanged infected messages to notifications sent to the
administrator.
Solution
In the [smtpgw.policy] section of the configuration file assign
parameter values as follows:
: To implement the above tasks, do the following:
ActionDisinfected=cure
ActionInfected=remove
ActionSuspicious=remove
ActionProtected=remove
ActionError=remove
ActionFiltered=remove
BlockMessage=disinfected, infected, suspicious,
protected, error, filtered
NotifyAdmin=disinfected, infected, suspicious,
protected, error, filtered
NotifySender=disinfected, infected, suspicious,
protected, error, filtered
Page 40

40 Kaspersky
®
SMTP-Gateway 5.0
NotifyRecepient=disinfected, infected, suspicious, protected, error, filtered
5.2.4.2. Deliver infected messages
In some situations you may wish to deliver all messages, including infected ones,
to certain groups of users.
Task:
• Scan for viruses all incoming and outgoing email on the
server
• Deliver all messages, including infected ones, to users from
the urgent group, adding notifications that these messages
are possibly infected
Solution
: To implement the above task, do the following:
Create group urgent (section [smtpgw.group:urgent]) and assign
parameter values as follows:
ActionDisinfected=pass
ActionInfected=pass
ActionSuspicious=pass
ActionProtected=pass
ActionError=pass
ActionFiltered=pass
BlockMessage=
NotifyAdmin=
NotifyRecipient=disinfected, infected,
suspicious,protected, error, filtered
NotifySender=
Page 41

Using Kaspersky SMTP-Gateway application 41
5.2.4.3. Notify senders, administrator, and
recipients
Task:
• Scan for viruses all incoming and outgoing email on the
server and disinfect all infected messages;
• Deliver to the recipients only disinfected messages;
• Notify senders, recipients, and administrator about blocked,
disinfected, deleted, suspicious, and corrupted messages
and about objects the application failed to scan; attach unchanged infected messages to notifications sent to the administrator.
Solution
1. In the [smtpgw.ave] section of the configuration file assign the
2. In the [smtpgw.policy] section of the configuration file assign the
: To implement the above task, do the following:
following parameter value:
Cure=yes
following parameter values:
ActionDisinfected=cure
ActionInfected=pass
ActionSuspicious=pass
ActionProtected=pass
ActionError=pass
ActionFiltered=pass
BlockMessage=infected, suspicious, protected, error, filtered
NotifyAdmin=disinfected, infected, suspicious,
protected, error, filtered
NotifyRecipient=disinfected, infected, suspicious, protected, error, filtered
NotifySender=disinfected, infected, suspicious,
protected, error, filtered
Page 42

42 Kaspersky
®
SMTP-Gateway 5.0
5.2.4.4. Filter messages by attachment types
There are types of files, such as exe files, in which infection is highly probable.
To avoid problems, we recommend that you configure the application to filter
email by name and/or attachment types and save such objects in a separate
directory.
There are objects that cannot be infected with viruses. To reduce the load on the
server during the anti-virus scan of the email messages we recommend that you
specify the types and/or the names of such attachments so that the application
does not scan them.
Filtering of objects is performed using name masks (parameters
IncludeByName, ExcludeByName) and types (parameters IncludeByType,
ExcludeByType) in sections [smtp.policy] or [smtp.group:group_name] of
the application configuration file.
Task:
• Scan all group email messages for viruses;
• Filter email with exe attachments and block the delivery of
email messages, containing such files;
• Notify senders, recipients, and administrators about exe attachments deleted, infected, corrupted, or blocked messages
and about objects the application failed to scan; add unchanged infected messages to notifications sent to the administrator.
Solution
: To implement the above task, do the following:
In the [smtpgw.policy] section of the configuration file assign
parameter values as follows:
IncludeByName=*.exe
ActionDisinfected=cure
ActionInfected=pass
ActionSuspicious=pass
ActionProtected=pass
ActionError=pass
ActionFiltered=pass
BlockMessage=infected, suspicious, protected, error
Page 43

Using Kaspersky SMTP-Gateway application 43
NotifyAdmin=infected, suspicious, protected,
error, filtered
NotifyRecipient=infected, suspicious, protected,
error, filtered
NotifySender=infected, suspicious, protected,
error, filtered
5.2.4.5. Backing up (quarantine, backup storage)
You can configure Kaspersky SMTP-Gateway to move messages with certain
statuses to a separate storage, such as quarantine or backup storage.
This feature may be used, for example, if an infected attachment that contain
important data was detected by the anti-virus scan. A disinfection attempt may
corrupt the data. The message can also be isolated in a separate storage and
then sent to Kaspersky Lab for analysis. Our experts will possibly be able to
disinfect the file and save the integrity of data.
Scanned objects flagged as Infected are moved to the quarantine directory. Other messages that you suspect are infected, and those the
application failed not scan, are copied into the backup storage.
Task:
• Scan all email messages for viruses and disinfect all infected
email messages;
• Deliver to the recipients only disinfected messages;
• Move suspicious objects detected during the scan to quaran-
tine directory /tmp/suspicious;
• Notify senders, recipients, and administrators about deleted,
infected, cured, corrupted, or blocked messages and about
objects the application failed to scan; attach unchanged infected messages to notifications sent to the administrator.
Solution
1. In the [smtpgw.ave] section of the configuration file assign
2. In the [smtpgw.policy] section of the configuration file assign
: To implement the above task, do the following:
parameter value as follows:
Cure=yes
parameter value as follows:
Page 44

44 Kaspersky
®
ActionDisinfected=cure
ActionInfected=remove
ActionSuspicious=remove
ActionProtected=remove
ActionError=remove
ActionFiltered=remove
BlockMessage=infected, suspicious, protected, error, filtered
NotifyAdmin=disinfected, infected, suspicious,
protected, error, filtered
NotifyRecipient=disinfected, infected, suspicious, protected, error, filtered
NotifySender=disinfected, infected, suspicious,
protected, error, filtered
SaveInQB=suspicious
BackupPath=/tmp/suspicious
QuarantinePath=/tmp/suspicious
5.2.4.6. Automatically add incoming and
outgoing mail to archives
SMTP-Gateway 5.0
If the security policy of your network includes archiving email traffic processed by
the server, you can set the application to automatically add email messages to
archives. If necessary the administrator can view all files in archives and delete
them permanently from the server.
If the auto archiving option is enabled, copied of the following messages will be
archived:
• All incoming messages, including infected, without additionally notifying the administrator. Archiving of such messages is enabled when
the path to the archive directory is specified as the value of the
IncomingArchivePath parameter in section [smtpgw.path]) of the
application configuration file.
• Outgoing messages, including those delivered to recipients, blocked
because of a virus, and notifications generated by the application. Archiving of such messages is enabled when the path to the archive directory is specified as the value of the OutgoingArchivePath pa-
rameter in section [smtpgw.path]) of the application configuration file.
Page 45

Using Kaspersky SMTP-Gateway application 45
Before you enable this option, make sure that there is enough space in
your server’s file system to accommodate the archive.
Do not forget to periodically purge this directory to remove old messages and compress necessary files (the purging frequency depends
on the mail traffic intensity within your network).
5.3. Protection from hacker attacks
and spam
To provide highest level of security to your mail system, we recommend that you
modify the Kaspersky SMTP-Gateway configuration file to extend the anti-virus
functionality of the application. To protect your server from hacker attacks or, for
example, to prevent spam being relayed through your server, configure the
following options:
• DenyUnresolvedConnect in the [smtpgw.access] section of the ap-
plication configuration file. This parameter defines the application response to an attempt to start an SMTP session from a host if it cannot
be defined by the IP address. If the parameter is set to true (DenyUn-
resolvedConnect=true), the application will try to determine the
name of the host that requested the mail connection. If the host name
cannot be determined, the application will close the mail session.
• DenyUnresolvedMailfrom in the [smtpgw.access] section of the
configuration file. This parameter limits reception of messages from IP
addresses that are not explicitly specified in your DNS settings. If this
option is enabled (DenyUnresolvedMailfrom=true), the application
will try to determine the IP address of the MX-record of the domain
contained in the sender address. If the IP address cannot be determined, messages are not sent or received from this IP address.
• Rule in the [smtpgw.access] section of the configuration file. This pa-
rameter limits the routing of messages via the application from certain
IP addresses only to some authorized domains. The value of this parameter is critical for preventing using the application as an open mail
relay.
A detailed discussion of the syntax of these command is provided in the
description of the configuration file (see A.2, page 74)
Page 46

46 Kaspersky
®
SMTP-Gateway 5.0
5.4. Managing license keys
The right to use Kaspersky SMTP-Gateway is determined by the license key.
The key is included in the product’s distribution kit and entitles you to use the
application from the day you have purchased it and installed the key.
Kaspersky SMTP-Gateway will not work without a license key!
After the license expires, the functionality of the application will still be preserved
except for the possibility to update the anti-virus database. You will still be able to
scan email messages for viruses and disinfect infected objects, but you will be
unable to use database issued after your license expiration date. Therefore, we
cannot guarantee you 100% reliable protection against new viruses that have
appeared after your license expired.
In order to protect your computer against new viruses, we recommend that you
renew the license for the use of Kaspersky SMTP-Gateway.
The license key gives you the right to use the application It contains all
information related to the license you have purchased, including the type of
license, license expiry date, information about dealers, etc.
In addition to the right to use the application during the license period, you will
have the following benefits:
• twenty-four-hour technical support
• updates of the anti-virus database every three hours
• up-to-date information about new virus threats
Therefore, it is very important to periodically check the information contained in
the license key and keep track of its expiry date.
5.4.1. Viewing information about license
keys
You can view information about the installed license keys in the reports of the
smtpgw component. Each time the component starts, sptpgw loads the license
key information and displays it in the report.
A more detailed information about the status of the license keys may be obtained
using licensemanager, a special component of the application.
Page 47

Using Kaspersky SMTP-Gateway application 47
All information about keys may be viewed either on the server’s console, or
remotely from any networked computer that has access to the Webmin remote
administration module.
To view information about installed license keys:
Type the following string in the command line:
#licensemanager –s
In the server console, you will see information similar to the following:
Kaspersky license manager. Version 5.0.0.0/RELEASE
Copyright (C) Kaspersky Lab. 1998-2003.
Active key info:
Product name: Kaspersky Anti-Virus 5 Business Optimal
1 month
Key file 00053BC3.key
Type: Commercial
Expiration date: 17-11-2003, expires in 60 days
Serial: 02B1-000454-00053BC
Additional key info:
Product name: Kaspersky Anti-Virus 5 Business Optimal
1 month
Key file 00053E3D.key
Type: Commercial
Expiration date: expired
Serial: 02B1-000454-00053E3
To view information about a license key:
Type, for example, the following string in the command line:
#licensemanager -k 00053E3D.key
where 00053E3D.key is the name of the license key file.
In the server console, you will see information similar to the following:
Kaspersky license manager. Version
5.0.0.0/RELEASE
Copyright (C) Kaspersky Lab. 1998-2003.
Page 48

48 Kaspersky
®
SMTP-Gateway 5.0
Product name: Kaspersky Anti-Virus 5 Business Optimal 1 month
Creation date: 23-07-2003
Expiration date: 21-11-2003
Serial 02B1-000454-00053E3
Type: Commercial
Lifespan: 30
5.4.2. Renewing your license
Renewal of the license for Kaspersky SMTP-Gateway will give you the right to
re-enable full product functionality. Besides, additional services listed in section
5.4 on page 46 will be resumed.
The license term depends on the product you bought and the type of the license
you purchased. The license for Kaspersky SMTP-Gateway is usually issued for
one year.
To renew the license for Kaspersky SMTP-Gateway:
Contact the company that sold you the product and renew your license
for Kaspersky SMTP-Gateway.
or:
Purchase a license directly from Kaspersky Lab. Write a letter of request to the Sales Department of our company at
sales@kaspersky.com
(www.kaspersky.com), section Products Æ Renew Your License. After your payment is received, we will send a license key to the email address indicated in the corresponding field of your license renewal form.
After you have purchased the license key, you will have to copy it to the directory
specified as the value of the LicensePath parameter in section [path] of the
application configuration file and to install it using the licensemanager utility.
or fill in the corresponding form on our website
To install a new license key:
The licensemanager module is used with the –a option to install new
licenses as follows
#licensemanager -a 00053E3D.key
Page 49

Using Kaspersky SMTP-Gateway application 49
where 00053E3D.key is the name of the license key file.
In the server console, you will see information similar to the following:
Kaspersky license manager. Version 5.0.0.0/RELEASE
Copyright (C) Kaspersky Lab. 1998-2003.
Key file 00053E3D.key is successfully registered
We recommend that you update the anti-virus database after the installation.
If you want to install a new license key before the current license key expires,
you can add it as a backup license key. The backup key will be activated
immediately after the previous one expires. The term of validity for the backup
key starts from the activation date. You can install only one backup key.
The backup key is installed in the same way as the main license key. You can
view information about installed the active and the backup keys from the server
console together with information about the current key.
5.4.3. Removing a license key
To remove the current license key:
Enter the following string in the command line:
#licensemanager –da
In the server console, you will see the following:
Kaspersky license manager. Version 5.0.0.0/RELEASE
Copyright (C) Kaspersky Lab. 1998-2003.
Active key was successfully removed
To remove a backup key:
Type the following string in the command line:
#licensemanager –dr
In the server console, you will see the following information:
Kaspersky license manager. Version 5.0.0.0/RELEASE
Copyright (C) Kaspersky Lab. 1998-2003.
Page 50

CHAPTER 6. ADVANCED
SETTINGS
This chapter discusses in detail the advanced settings of Kaspersky SMTPGateway. In contrast to main settings (see section 5.2 on page 30) that provide
the application functionality, advanced settings can be configured optionally at
the administrator’s discretion.
6.1. Configuring anti-virus protection
of mail traffic
All mail traffic anti-virus protection settings are grouped in section
[smtpgw.ave] of the application configuration file.
The server mail traffic anti-virus protection settings requires that you set up rules
to be used for processing infected objects depending on its type.
If parameters ScanArchives and ScanMailBases are set to true, the application
will also scan archives and mail databases respectively.
6.1.1. Scanning and disinfecting messages
By default, the application only scans your email traffic for viruses. If a virus is
detected, the application can delete such infected object, rename it, block
messages, deliver message containing such object and/or send notifications to
the sender, recipient, and administrator. To enable disinfection, set the Cure
parameter to true.
To have Kaspersky SMTP-Gateway disinfect infected messages, specify the
following:
• Cure=true – disinfect an infected object. If disinfection has
been successful, the object is assigned the Cure status.
Page 51

Advanced settings 51
6.1.2. iChecker technology
While performing anti-virus scan, the application may use iChecker technology
(parameter UseIChecker section [smtpgw.ave]) that eliminates the need to scan
identical objects each time they are detected in the flow of email messages and,
if possible, perform only one comparison with the existing data.
The object (file) anti-virus scan algorithm will be changed as follows:
When a message is scanned for the first time (if it has been flagged as Clean),
data about the message (name, checksum, date, etc) is saved to the iChecker
database. The database path is defined by the ICheckerDBFilename option in
the [smtpgw.options] section.
Next time the message is sent to the AV module for scanning
first looks for this file in the iChecker database by name. If it finds a match, the
current object is compared with the database record. If the current status of the
object and its description in the database are fully identical, then the object is
considered to remain unchanged and is not scanned for viruses.
To have the application use the iChecker technology, set the UseI-
Checker parameter in the [smtpgw.ave] section to true.
, the application
6.1.3. Setting up application timeouts
All timeout settings are located in the [smtpgw.timeouts] section of the
application configuration file.
By setting up various timeouts, the administrator can:
• Limit the maximum period after which the application will attempt to
deliver outgoing messages that have not been sent yet (Maximal-
BackoffTime parameter, in seconds).
• Define the time between attempts to deliver outgoing messages that
have not been sent yet (MinimalBackoffTime parameter, in seconds).
• Specify the interval (in days) during which the application will try to deliver a message with the frequency defined by the MinimalBack-
offTime parameter (MaximalQueueLifetime option). After this period
elapses, the unsent message will be removed from the ready-to-send
queue. If necessary, a DSN message on the initial message delivery
failure will be generated.
Page 52

52 Kaspersky
®
SMTP-Gateway 5.0
• Define the timeout for refreshing the MX record in the application
cache (MXCacheRefreshPeriod option, in seconds). During this period of time the application will not perform DNS-inquiries on the domains information on which is stored by MX-records.
• Determine the time for storing information about hosts with unresolved
name (parameter UnresolvedCacheRefreshPeriod). After an unsuccessful attempt to determine the name of the application host, no repeated attempts will be made to connect to such host or to determine
the name o such host during this period of time.
• Specify timeouts for intercepting various network operations (for the
Sender and Receiver modules), such as:
• Network reading timeout (ReadTimeout option). The default
value specified in the configuration file of the application is the
optimal value for most cases and it is not recommended to alter
it.
• Network writing timeout (WriteTimeout option). The default
value specified in the configuration file of the application is the
optimal value for most cases and it is not recommended to alter
it.
• Specify timeouts used by the application to send messages:
• Maximum time for receiving data from the remote server when
establishing an SMTP session (SendingInitialTimeout option).
• Maximum time to start a mail session (command HELO/EHLO)
(SendingHelloTimeout option).
• Timeout for waiting for the response from the remote server to
the MAIL FROM command (SendingMailTimeout option).
• Timeout for defining the recipient (RCPT TO command) (SendingRcptTimeout option).
• Timeout for initiating data transfer (DATA command) (SendingDataInitiationTimeout option, in seconds).
• Timeout for stopping the data transfer (CRLF.CRLF sequence)
by the remote server (SendingDataTerminationTimeout option).
• Timeout for quitting the current mail session (QUIT command)
(SendingQuitTimeout option).
• Specify timeouts used by the application to receive messages:
Page 53

Advanced settings 53
• Timeout for starting the DATA command (ReceivingDataInitia-
tionTimeout option).
• Timeout for stopping the DATA transfer by the remote server
(ReceivingDataTerminationTimeout option).
• Timeout for waiting for commends HELO/EHLO, MAIL FROM,
RCPT TO, QUIT of the remote server (SendingDataInitiation-
Timeout option).
6.1.4. Setting performance restrictions
Kaspersky SMTP-Gateway provides the administrator with the possibility to
setup certain limits when working with the application. In some cases, this may
help reduce the load on your server, increase performance, prevent spam
relaying through your server. In addition, using network restrictions, it is possible
to prevent and fight some types of attacks, such as DOS attacks aimed at
paralyzing your mail server with huge volumes of mail traffic.
You can find restriction settings in the [smtpgw.limits] section of the
application configuration file.
You can set the following restrictions:
• Number of objects concurrently processed by one module (for the re-
ceiver, sender, and AV modules; the IncomingSessions, Out-
goingSessions, and AntiviralSessions options, respectively).
• Maximum number of message hops (MaximalIncomingHops option).
Set this parameter to avoid looping due to incorrect configuration of
the routing table.
• Limit the maximum message size received at the server (MaximalIncomingMessageSize option) and the total number of messages re-
ceived during one mail session (MaximalIncomingMessagesPerSession option).
• Limit the number of recipients of a single message (MaximalIncoming-RcptsPerMessage option). This parameter restricts spam which
is addressed to your users.
• Maximum size of a single mail session (MaximalIncomingSessionSize option).
• Maximum number of simultaneous connections from one and the
same IP (or host) that are processed by the receiver and by the
Page 54

54 Kaspersky
sender (parameters MaximalIncomingSessionsPerlP and MaximalOutgoingSessionsPerHost)
If the mail traffic at your server exceeds the specified limits, we recommend that you:
• Limit the number of objects simultaneously processed by the anti-virus
kernel (AntiviralSessions parameter) and the number of hops for a
single message (MaximalIncomingMessageSize option). This in-
creases application performance and message processing speed
If your server has a low-speed Internet connection, the following actions
are recommended:
• Decrease the number of objects simultaneously processed by the Receiver and Sender modules (IncomingSessions and OutgoingSes-
sions options).
• Decrease the maximum number of incoming messages received during one session (MaximalIncomingMessagesPerSession option).
®
SMTP-Gateway 5.0
6.2. Setting up connection receiving
interfaces
The set of interface and ports, used by the application to receive the
connections, is defined by ListenOn parameter in section [smptgw.network] of
the application configuration file. By default, Kasperksy STMPT-Gateway listens
for connection on port 25 using all available interfaces.
If a particular interface is to be used rather than all available interfaces or if it is
necessary to use a port other than 25, additional settings configuration must be
performed.
Configure the application to wait for connection on port 1025 of interface 192.168.0.1:
In order to do this, modify the value of parameter ListenOn, section
[smtpgw.network] as follows:
ListenOn=192.168.0.1:1025
In order to use several particular interfaces, create several ListenOn parameter
records in the configuration file.
Page 55

Advanced settings 55
Configure the application to wait for connection on port 25, interfaces
192.168.0.1 и 10.0.0.1
In order to do this, modify the value of parameter ListenOn, section
[smtpgw.network] as follows:
ListenOn=192.168.0.1:25
ListenOn=10.0.0.1:25
6.3. Setting up the routing table
The application does not include a local agent used message delivery, therefore
all incoming mail messages must be transferred to the local host that is equipped
with such agent.
The rules for transferring (routing) are set by the ForwardRoute parameter
section [smtpgw.forward] of the application configuration file.
This parameter is specified using one of the following formats:
ForwardRoute=recipient_domain_suffix recipient
ForwardRoute=recipient_domain_suffix recipient:port
ForwardRoute=recipient_domain_suffix [recipient]
ForwardRoute=recipient_domain_suffix [recipient:port]
where:
recipient_domain_suffix – the address of the recipient of the
messages (special symbols "*" and "?" can be used; if the parameter is
assigned value any, then any recipient’s address may be used);
recipient:port – is the delivery point (IP address or host name,
port).
For example, if you create the following record in section [smtpgw.forward]
ForwardRoute=domain.com [localhost:1025]
then all mail messages to domain.com will be sent to port 1025 of the local host
after having been scanned for viruses
If several routing rules must be specified, create several copies of parameter
ForwardRoute in the configuration file. For example, record created in section
[smtpgw.forward]
ForwardRoute=domain1.com [localhost:1025]
ForwardRoute=domain2.com [somehost.somedomain.com]
ForwardRoute=domain3.com otherdomain.com
Page 56

56 Kaspersky
®
SMTP-Gateway 5.0
will mean the following processing rules:
• forward all email messages for domain domain1.com to port 1025 of the
local host after the messages have been scanned for viruses
• forward all email messages for domain domain2.com to port 25 of host
somehost.somedomain.com after the messages have been scanned for
viruses
• forward all email messages for domain domain3.com to MX-host of do-
main otherdomain.com after the messages have been scanned for viruses (the domain will be determined at the time the message is sent)
• forward all other messages to the corresponding MX-hosts after they
have been scanned for viruses
When determining the routing rules the first record will be used out
of those where the domain matches the messages recipient
domain.
6.4. Managing the application
When the application works in the operating mode, you can manage the
application using scripts, signals, and special files.
This section describes how to manage the application using scripts (about
management options using signals, see section A.3 on page 86; about using
files, see A.4 on page 86).
If you use Linux distribution package (except for installations made using the tar.gz package), to run the management script, enter the following string in the command line:
/etc/kav/init.d/smtpgw <action>
or use the link:
/etc/init.d/smtpgw <action>
If you use FreeBSD, to run the management script, enter the following:
/usr/local/etc/rc.d/smtpgw.sh <action>
Page 57

Advanced settings 57
For OpenBSD, to run the management script, enter the following string:
/usr/local/share/kav/5.0/smtpgw/setup/smtpgw.sh <action>
where the <action> parameter can take one of the following values:
Parameter Value
start
stop
restart
reload
reloadbases
status
stats
recv-on
recv-off
send-on
send-off
avir-on
avir-off
Start the application.
Stop the application.
Stop and then start the application.
Reinitialize the application and reload the antivirus database and the configuration file
Reload the anti-virus database.
Request the application status.
Request the application statistics.
Start the Receiver task.
Stop the Receiver task.
Start the Sender task.
Stop the Sender task.
Start the anti-virus scan task.
Stop the anti-virus scan task.
Page 58

58 Kaspersky
®
SMTP-Gateway 5.0
6.5. Customizing date and time
formats
Kaspersky SMTP-Gateway generates reports for every component. This
information always contains the date and time of creation.
By default, Kaspersky SMTP-Gateway displays the date and time according to
the strftime standard:
%H:%M:%S – Date format
%d/%m/%y – Time format
The administrator can customize how the time and date are displayed in the
[locale] section of the application configuration file. You can choose one of the
following formats:
%I:%M:%S %P – Display time in 12-hour format (TimeFormat parameter).
%y/%m/%d and %m/%d/%y – Display date (DateFormat parameter) as
yy/mm/dd and mm/dd/yy, respectively.
6.6. Reporting options
The performance of the sptpgw component is recorded in the report file that is
output into the application log file in the plain text format (LogFilename option in
the [smtpgw.options] section) or in the system log (syslog). The data is not
logged if the LogFilename option is not defined (LogFilename=).
To customize the output data, change the report detail level (LogLevel option in
the [smtpgw.options] section).
Report detail level is a number that defines the level of reported detail for
application performance data. Each subsequent level of detail contains all the
details from the previous level and adds new reporting parameters.
The table below lists possible report detail levels.
Page 59

Advanced settings 59
Lev
el
Level description
Fatal errors F only information on fatal errors that
Letter symbol
Value
result in termination of the
application due to a failure to
perform a certain action. For
example, the component is infected,
a scan error occurred, errors
activating database updates or
license keys.
1 Errors E information about other errors that
may or may not lead to application
shutdown, for example, file scan
errors.
2 Warning W information about errors that may
lead to the application shutdown
(license key expiration warning, outof-disk-space warning, etc.)
3 Info, Notice I important information messages,
such as whether a component is
enabled or disabled, the path to the
configuration file, latest changes in
scan area, database updates,
license keys, summary statistics.
4 Activity A
messages on files scanning
according to the report detail level
9 Debug D debugging messages, for example,
the content of the configuration file.
Information about fatal errors are always displayed, regardless of the report
detail level. The optimal level for the component operation is level 4, which is
also the default level.
Information messages may be divided into the following types:
• Messages about the actions applied to the e-mail message
Page 60

60 Kaspersky
®
SMTP-Gateway 5.0
• Other messages (component start, loading anti-virus database, return
code, etc.)
• Messages about system event
The output format for each of the detail level listed above is as follows:
[date time detail_level] envelope-id: MESSAGE for messages
about the actions applied to the e-mail message;
[date time detail_level]: MESSAGE for all other types of messages,
where:
• [date time detail_level] – is the parameter that contains the
date and the time (in the format specified by the administrator in the [lo-
cale]) section and the first letter of the report detail level.
• envelope-id – e-mail message identifier in the working queue of the
application, to which the e-mail message corresponds.
• MESSAGE – message text that may have different format depending on
the type of the message.
For text of messages containing information about the actions applied to the email message see A.13, page 98.
Page 61

CHAPTER 7. FREQUENTLY
ASKED QUESTIONS
This chapter contains a detailed discussion of questions most frequently asked
by our users regarding the installation, configuration and operation of Kaspersky
SMTP-Gateway.
Question: Why does Kaspersky SMTP-Gateway cause a decrease in
my computer performance and impose a considerable load on the
processor?
The process of virus detection is a computationally intensive mathematical problem requiring structural analysis, checksum calculation and
mathematical data conversions. Processor time is therefore the main
resource consumed by the anti-virus software, and each new virus
added to the anti-virus database increases the overall scanning time.
That is a necessary sacrifice for the security and safety of your data.
Other anti-virus products speed up the scan process by excluding from
their databases both viruses that are less easily detectable or less frequent in the geographic location of the anti-virus vendor, and file formats that require complicated analysis (e.g. PDF files). By contrast,
Kaspersky Lab believes that the purpose of its anti-virus applications is
to establish real and complete anti-virus security for its users. We believe that "partial-protection" is worse than no protection at all, since it
forces users to resort to personal precautions.
Kaspersky SMTP-Gateway gives its users maximum protection. Experienced users can, of course, accelerate anti-virus scanning process to
the detriment of overall security by disabling the scanning of various file
types, but we do not recommend doing so to users who want the best
possible protection.
To ensure maximum user protection, Kaspersky SMTP-Gateway recognizes more than 40 types of archives and installation packages, and can
detect viruses in more than 350 different file formats. This is essential
for anti-virus security because harmful executable code may be hidden
inside files of any recognizable format. However, despite the daily
growth in the number of viruses detected by Kaspersky SMTP-Gateway
(approximately 30 new viruses daily) and the ever increasing number of
recognized file formats, each version of our product functions faster
than the previous one. This is achieved through the use of new unique
technologies, such as iChecker™ and i-Stream™, developed at
Kaspersky Lab. Each file is checked for viruses only once, during the
Page 62

62 Kaspersky
first scan. During subsequent scans the file is not scanned for viruses
provided that it has remained unchanged since the last scan. Thus, the
anti-virus application performance increases dramatically after the first
file scanning.
®
SMTP-Gateway 5.0
Question
: Do I need a license key ? Will the application work without it?
Kaspersky SMTP-Gateway will not work without a properly installed license key.
If you haven’t yet made a decision whether you wish to buy Kaspersky
SMTP-Gateway, we can provide you with a trial key, which will work for
a period of either two weeks or one month. The key will be disabled
when this period expires.
Question
: What happens when my license expires?
After expiration of the license, Kaspersky SMTP-Gateway will still work,
but it will not be able to use update anti-virus database The application
will still disinfect infected objects, but while doing so, it will use old antivirus database.
The anti-virus database updating from the Kaspersky Lab’s update
servers, using the update component, will not available. Even if you
copy the anti-virus database without using this component, the application will not be able to use this database.
Therefore we cannot guarantee your protection against new virus infections.
Question: My application does not function.
What should I do?
First, check whether a solution to your problem is described in this
document, particularly in this section, or at our site (Services Æ For
customers Æ Technical Support Æ Online support).
In addition, we recommend that you apply for support to the dealer from
whom you purchased Kaspersky SMTP-Gateway, or write to the Technical Support Service (support@kaspersky.com
) or at the address con-
tained in the license key information.
The following will facilitate prompt processing of your inquiry:
Page 63

Frequently asked questions 63
1. Please indicate in the subject of your message, the operating system of your server, the name of the component you are having
problems with, and briefly describe the problem. For example:
Linux, Webmin, no access to settings of the licensed users’ list.
2. Please use plain text messages. Avoid sending messages in
HTML format as it is hard to read.
3. At the beginning of the message specify the exact version of your
operating system and Kaspersky SMTP-Gateway installation
package, and provide the name of your license key file.
4. Describe your problem briefly but comprehensibly. Please keep in
mind that the Support team has no information about your problem
when your letter just arrives, and they will be able to help you only
if they understand it completely and manage to reproduce it.
5. Please compress the following data into one archive, and send it to
the Technical Support Service:
• all configuration files of your mail agent (MTA);
• mail system log file;
• logs of the respective components of your application
• your license key file.
6. Make sure that if any of the following is present in your system it is
mentioned in your message:
• SCSI controller;
• a very old or a brand new CPU, or a multiprocessor configura-
tion;
• RAM below 64 Mb or above 2 Gb.
7. Indicate the approximate amount of daily traffic and load peaks, if
they exist.
Question
A hacker may be able to download the anti-virus databases from the
Kaspersky Lab's site and copy them to the anti-virus database storage
directory, but the Kaspersky SMTP-Gateway will not use them in its operation!
Every anti-virus database has a unique signature verified by Kaspersky
SMTP-Gateway while accessing the database. If the signature does not
: Can a hacker deliberately replace the anti-virus databases?
;
Page 64

64 Kaspersky
correspond to the one assigned at the Kaspersky Lab, or the date of the
database is later than that of the license expiry, Kaspersky SMTPGateway will not use it.
Question: The application cannot be started, the Sender task does not
work, etc. What should I do?
If, due to incorrect settings, the number of running processes (threads)
exceeds the maximum number permitted by the system, the application
performance may be affected or your system will freeze. To solve this
problem, decrease the number of concurrently active incoming and outgoing mail sessions and the number of objects scanned simultaneously
by the anti-virus module (AntiviralSessions, IncomingSessions, and
OutgoingSessions parameters in the [smtpgw.limits] section of the
application configuration file).
This problem can be also solved by limiting the stack size. To limit the
size, enter the following string in the command line:
>ulimit –s
The maximum stack size will be displayed on the console. Set the new
value equal to the quarter of the current value by doing the following:
>ulimit –s <number>
where <number> is a new maximum stack size.
®
SMTP-Gateway 5.0
Question: What should I do to make man pages of the application available by the command man <name>?
To make application man pages available using man <name> command after each restart of your system, do the following:
o For Debian Linux, SuSE Linux distributions, the following line
should be added to /etc/manpath.config file:
MANDATORY_MANPATH /opt/kav/5.0/smtpgw/man
o For RedHat Linux distributions, the following line should be
added to /etc/man.config file:
MANPATH /opt/kav/5.0/smtpgw/man
o For OpenBSD distributions the following line in /etc/man.conf
file:
_default /usr/{share,X11R6,X11,contrib,gnu,\
local}/{man,man/old}/
Page 65

Frequently asked questions 65
should be modified like:
_default /usr/{share,X11R6,X11,contrib,gnu,\
local}/{man,man/old,share/kav/5.0/smtpgw/man}/
o For FreeBSD distributions the following line should be added
to /etc/manpath.config file:
MANDATORY_MANPATH \
/usr/local/share/kav/5.0/smtpgw/man
Page 66

CHAPTER 8. TESTING
APPLICATION OPERABILITY
After you install and configure Kaspersky SMTP-Gateway, it is recommended
that you test its operability by using the following two methods:
• Telnet program,
• EICAR test virus
8.1. Testing the application using
Telnet
To test the application operation using Telnet it is necessary to:
1. Configure the connection to the server and the application using
Telnet. Enter the following string:
telnet <host address with smtpgw> <port>
where the host address and port are values set in the [smtpgw.network] section
for the ListenOn option during the installation.
2. After the connection is established, wait for a response from the
smtpgw component. You will see the following information:
220 smtpgw.company.com ESMTP
where smtpgw.company.com is the name of the server being
tested
3. To confirm the connection to the server, type the following
command:
EHLO <user>
You will see the following information (or similar information):
250- smtpgw.company.com hello user [127.0.0.1]
250-ENHANCEDSTATUSCODES
250-PIPELINING
250-8BITMIME
Page 67

Testing application operability 67
250-SIZE 10485760
250 DSN
where:
smtpgw.company.com is the name of the server being tested
user is the client host name
[127.0.0.1] is the client IP address.
In the terminal line, enter:
MAIL FROM:<sender address>
You will see the following message:
250 2.1.0 OK
Type the following line:
RCPT TO:<recipient_address>
You will see the following:
250 2.1.0 OK
Type the command:
DATA
You will see the following:
354 Start mail input; end with <CRLF>.<CRLF>
In the command line, type:
Subject: test
test
You will see the following string:
250 2.1.0 OK
4. If the response is 250 2.1.0 OK, the test message has been
successfully accepted by the server. After this, the message must
be scanned for viruses and then sent to the recipient in accordance
with the routing table. It is recommended that you check message
delivery. To verify the results, view the application statistics. One
message will have been added to the totals of scanned and sent
messages.
Page 68

68 Kaspersky
®
SMTP-Gateway 5.0
8.2. Testing the application using
EICAR
This test "virus" has been developed by (The European Institute for
Computer Anti-Virus Research) specifically for the purpose of verification of the
anti-virus software operation.
The test "virus" IS NOT A VIRUS and contains no code that may harm your
computer. However, most products of anti-virus vendors identify it as a virus.
Never use real viruses to test the operation of your anti-virus application!
The test "virus" can be downloaded from the official site of EICAR at:
http://www.eicar.org/anti_virus_test_file.htm
can create a test "virus" manually. To do so enter the line below in any text editor
and save the file as eicar.com:
X5O!P%@AP[4\PZX54(P^)7CC)7}$EICAR-STANDARD-ANTIVIRUS-TESTFILE!$H+H*
The file that you downloaded from the EICAR site or created in a text editor as
described above, contains the body of a standard test "virus". The anti-virus
application will detect it, flag it as Infected and perform the specified action for
objects with this status.
To test the application's response to other types of objects, modify the body of
the standard test "virus" by adding one of the prefixes below (see Table 1).
You can verify the proper operation of Kaspersky SMTP-Gateway using modifications of the EICAR "virus" only if your anti-virus databases
was last updated on or after October 24, 2003, or has the cumulative
updates for October 2003.
. If you have no Internet access, you
Page 69

Testing application operability 69
Table 1. Test "virus" modifications
Prefix Object type
No prefix,
standard test
"virus"
CORR–
SUSP–
WARN–
ERRO–
CURE–
DELE–
Infected. An error occurs during disinfection. The object will
then be deleted.
Corrupted.
Suspicious (unknown virus code).
Suspicious (modified code of a known virus).
Error when scanning the object.
Infected. The object will be disinfected and the text in the
infected file will be changed to CURED.
Infected. The object will be deleted automatically.
The first column of the table contains the prefixes that should be added to the
beginning of the line in the standard test "virus" file (e.g. DELE–
X5O!P%@AP[4\PZX54(P^)7CC)7}$EICAR-STANDARD-ANTIVIRUS-TESTFILE!$H+H*).
After adding a prefix to the test “virus”, save it to a file with another name, for
example eicar_dele.com; assign names to all the modified “viruses” in the same
manner.
The second column contains the types of objects identified by the anti-virus
application after you added a prefix. The actions for each type of object are
defined by the application's settings customized by the administrator.
Page 70

APPENDIX A. SUPPLEMENTARY
INFORMATION ABOUT THE
PRODUCT
The default distribution kit of Kaspersky SMTP-Gateway includes the
configuration file containing all necessary parameters of the application’s
operation. This appendix contains a detail description each section of the
parameters provided in the file. If a parameter has a default value, it will be
specified.
A.1. Location of the application files
in directories
After the installation of Kaspersky Anti-Virus SMTP-Gateway is complete, the
application files will be located in the following directories, provided that default
paths have been accepted during the installation:
Linux distribution kit:
/opt/kav/5.0/smtpgw/ – main application directory. This directory includes:
/opt/kav/5.0/smtpgw/bin/ – directory containing application components' ex-
ecutable files of the application components:
smtpgw – executable file of the main application (anti-virus protection)
component;
keepup2date – executable file of the Kaspersky KeepUp2Date compo-
nent responsible for updating the anti-virus database;
licensemanager – executable file of the Kaspersky License component.
/opt/kav/5.0/smtpgw/setup/ – directory containing scripts and executable
files used during the installation and removal of the application.
/etc/kav/init.d/ – directory containing scripts used for controlling the application.
/etc/kav/5.0/smtpgw/ – directory containing the default application configuration
file smtpgw.conf;
/var/db/kav/5.0/smtpgw/ – directory containing application data:
/var/db/kav/5.0/smtpgw/bases/ – directory containing the anti-virus da-
tabases and the configuration file updcfg.xml of the KeepUp2Date
component;
Page 71

Appendix A 71
/var/db/kav/5.0/smtpgw/bases.backup – directory where the
KeepUp2Date component saves the anti-virus database that are
up-to-date until the next update:
/var/db/kav/5.0/smtpgw/licences – directory where the license key files
are installed;
/var/db/kav/5.0/smtpgw/patches/ – directory where the updates of the
application components are saved;
/var/db/kav/5.0/smtpgw/quarantine/ – the default quarantine directory;
/var/db/kav/5.0/smtpgw/backup/ – the default backup storage directory;
/var/db/kav/5.0/smtpgw/arch_in/ – default directory for storing the ar-
chive of all received email messages;
/var/db/kav/5.0/smtpgw/arch_out/ – default directory for storing the ar-
chive of all sent email messages;
/var/db/kav/5.0/smtpgw/stat/ – default directory for storing the statistics
file;
/var/db/kav/5.0/smtpgw/templates/ – directory where the default applica-
tion templates are installed:
notify.tmpl – notification messages template;
placeholder.tmpl – template used for replacing an infected object
with a message.
/var/db/kav/5.0/smtpgw/ichecker/ – default directory for storing the work-
ing file of the iChecker database.
/var/spool/kav/5.0/smtpgw/ – default directory for storing the working queue of
messages;
/var/log/kav/5.0/smtpgw – the default directory for storing log files.
/opt/kav/5.0/smtpgw/man – the default directory containing application manual
pages.
FreeBSD distribution kit:
/usr/local/share/kav/5.0/smtpgw/ – main application directory into which the ap-
plication is installed. This directory includes:
/usr/local/share/kav/5.0/smtpgw/bin/ – directory containing application com-
ponents' executable files:
smtpgw – executable file of the main (anti-virus protection) component;
keepup2date – executable file of the Kaspersky KeepUp2Date compo-
nent responsible for updating the anti-virus database;
licencemanager – executable file of the component responsible for deal-
ing with licensing issues.
/usr/local/share/kav/5.0/smtpgw/setup/ – directory containing scripts and ex-
ecutable files used during the installation, initial configuration and removal of the application.
Page 72

72 Kaspersky
®
SMTP-Gateway 5.0
/usr/local/etc/rc.d/ – directory containing scripts used for controlling the applica-
tion.
/etc/kav/5.0/smtpgw/ – directory containing the default application configuration
file smtpgw.conf;
/var/db/kav/5.0/smtpgw/ – directory containing application data:
/var/db/kav/5.0/smtpgw/bases/ – directory where the anti-virus database
and updcfg.xml – configuration file of the KeepUp2Date component
are installed
/var/db/kav/5.0/smtpgw/bases.backup – directory where the
KeepUp2Date component saves the anti-virus database that are
up-to-date until the next update;
/var/db/kav/5.0/smtpgw/licences – directory where the license key files
are installed;
/var/db/kav/5.0/smtpgw/patches/ – directory where the updates of the
application components are saved;
/var/db/kav/5.0/smtpgw/quarantine/ – the default quarantine directory;
/var/db/kav/5.0/smtpgw/backup/ – the default backup storage directory;
/var/db/kav/5.0/smtpgw/arch_in/ – default directory for storing the ar-
chive of all received email messages;
/var/db/kav/5.0/smtpgw/arch_out/ – default directory for storing the ar-
chive of all sent email messages;
/var/db/kav/5.0/smtpgw/stat/ – default directory for storing the statistics
file;
/var/db/kav/5.0/smtpgw/templates/ – directory where the default applica-
tion templates are installed:
notify.tmpl – notification messages template;
placeholder.tmpl – template for replacing an infected object with a
message.
/var/db/kav/5.0/smtpgw/ichecker/ – default directory for storing the work-
ing file of the iChecker database.
/var/spool/kav/5.0/smtpgw/ – default directory for storing the working queue of
messages;
/var/log/kav/5.0/smtpgw – the default directory for storing log files.
/usr/local/share/kav/5.0/smtpgw/man – the default directory containing applica-
tion manual pages.
OpenBSD distribution kit:
/usr/local/share/kav/5.0/smtpgw/ – main application directory into which the ap-
plication is installed. This directory includes:
/usr/local/share/kav/5.0/smtpgw/bin/ – directory containing application com-
ponents' executable files:
Page 73

Appendix A 73
smtpgw – executable file of the main (anti-virus protection) component;
keepup2date – executable file of the Kaspersky KeepUp2Date compo-
nent responsible for updating the anti-virus database;
licencemanager – executable file of the component responsible for deal-
ing with licensing issues.
/usr/local/share/kav/5.0/smtpgw/setup/ – directory containing scripts and ex-
ecutable files used during the installation, initial configuration and removal of the application.
/etc/kav/5.0/smtpgw/ – – directory containing the default application configu-
ration file smtpgw.conf;
/var/db/kav/5.0/smtpgw/ – directory containing application data:
/var/db/kav/5.0/smtpgw/bases/ – directory where the anti-virus da-
tabase and updcfg.xml – configuration file of the KeepUp2Date
component are installed;
/var/db/kav/5.0/smtpgw/bases.backup – directory where the
KeepUp2Date component saves the anti-virus database that are
up-to-date until the next update;
/var/db/kav/5.0/smtpgw/licences – directory where the license key files
are installed;
/var/db/kav/5.0/smtpgw/patches/ – directory where the updates of the
application components are saved;
/var/db/kav/5.0/smtpgw/quarantine/ – the default quarantine directory.
/var/db/kav/5.0/smtpgw/backup/ – the default backup storage directory;
/var/db/kav/5.0/smtpgw/arch_in/ – default directory for storing the ar-
chive of all received email messages;
/var/db/kav/5.0/smtpgw/arch_out/ – default directory for storing the ar-
chive of all sent email messages;
/var/db/kav/5.0/smtpgw/stat/ – default directory for storing the statistics
file;
/var/db/kav/5.0/smtpgw/templates/ – directory where the default applica-
tion templates are installed:
notify.tmpl – notification messages template;
placeholder.tmpl – template for replacing an infected object with a
message.
/var/db/kav/5.0/smtpgw/ichecker/ – default directory for storing the work-
ing file of the iChecker database.
/var/spool/kav/5.0/smtpgw/ – default directory for storing the working
queue of messages;
/var/log/kav/5.0/smtpgw – the default directory for storing log files.
Page 74

74 Kaspersky
/usr/local/share/kav/5.0/smtpgw/man – directory containing application
manual pages.
®
SMTP-Gateway 5.0
A.2. Kaspersky SMTP-Gateway
configuration file
The Kaspersky SMTP-Gateway default installation package includes
smtpgw.conf file that contains configuration settings for the application.
This configuration file is divided into sections that describe parameters/options of
the operation of a separate application functional groups.
Each section is described the following way: first line – the heading [section
name], the line containing the description of the parameter
parameter=description, default value. The description of the section of the
configuration file is completed by the header of the next section.
The configuration file for binary settings that may accept true|false
values may also accept equivalent values: yes|no, y|n or 1|0.
The options described as “required parameters” are critical for the application. Without these parameters, the configuration file is invalid!
The [path] section contains options that define the path to the critical files,
without which the application will not work:
BasesPath – Full path to the anti-virus database. Required parameter.
LicensePath – Full path to the license key directory. Required parameter.
The [locale] section contains date and time formats:
DateFormat – Format used by the components to display date in the report
(strftime).
You can alter the time format to 12 hour format (a.m., p.m.),
enter the string: %I:%M:%S %P
TimeFormat – Format used by the components to display time in the report
(strftime)
You can change the date format to be displayed in e-mail messages, for example, %y/%m/%d or %m/%d/%y.
Page 75

Appendix A 75
The [smtpgw.access] section includes the following options used to control the
access of SMTP clients:
DenyUnresolvedConnect=true|false – Defines the rules for connecting to
SMTP clients whose hosts are not listed in DNS records. The default
value is false. To reject such connections, set the option to true.
DenyUnresolvedMailfrom=true|false – Defines the rules for receiving
messages from recipients whose hosts are not explicitly listed in DNS
records in the MAIL FROM field (SMTP command). The default value is
false. To reject receiving messages from such SMTP clients, set the
option to true.
Rule – this option is presented in the form of a table (list of parameters) that
defines rules for relaying messages via the application. Each rule is de-
fined by a line of the following format:
Rule=rule from address_or_mask to recipient_domain
where:
– determines whether the client shall be granted access (values
rule
are: allow or deny);
address_or_mask
(value’s format x.x.x.x or x.x.x.x/x.x.x.x or x.x.x.x/y);
recipient_domain
"*" and "?" can be used). Value “any” stands for the name of any do-
main.
When selecting rules from the list the first rule matching the pair ad-
dress_or_mask / recipient_domain will apply.
– determines the senders’ IP-address or mask
– determines the recipient’s domain (special symbols
The [smtpgw.ave] section contains options for scanning messages for viruses:
Cure=true|false – Disinfect infected objects. The default value is false. To
enable this mode, set the option to true.
ScanArchives= true|false – Scan archives. The default value is true. To
disable this mode, set the option to false.
ScanMailBases= true|false – Scan mail databases. The default value is
true. To disable this mode, set the option to false.
ScanTimeout=0 … 3600 – Time (in seconds) during which an anti-virus
scan module can process a single object. If the scan time exceeds the
limit, the object is assigned the Error status (scan error).
UseIChecker=true – Use iChecker technology to scan for viruses. The de-
fault value is true. To disable the mode, set the parameter to false.
Page 76

76 Kaspersky
®
SMTP-Gateway 5.0
The [smtpgw.forward] section contains the following options for relaying
messages through the application:
ForwardRoute – Routing table containing message routing options. It ex-
plicitly defines the mail server for specified domains to which the appli-
cation will send messages that should be sent to listed domains. The
values include the domain mask (special symbols "*" and "?" can be
used). and the name / IP address of the mail server the application will
connect to send email. If the default port 25 is already being used by
another application, another port number should be specified.
The [smtpgw.limits] section includes options that limit application functionality
when mail traffic scan is performed:
AntiviralSessions =10.. 1024 – Defines the number of concurrently running
anti-virus sessions (it is not recommended to increase the value of this
parameter, except for the cases when the application is overloaded).
The default value is 10.
IncomingSessions =1…1024 – Maximum number of open incoming ses-
sions. The default value is 100.
OutgoingSessions =1…1024 – Maximum number of open outgoing ses-
sions. The default value is 20.
MaximalIncomingHops=1…100 – Maximum number of intermediate hosts
for a single message. The default value is 20.
MaximalIncomingMessageSize=64…204800 – Maximum size (Kb) of an
incoming message. The default value is 10240.
MaximalIncomingMessagesPerSession=1…1024 – Maximum number of
messages that can be received during one mail session. The default
value is 100.
MaximalIncomingRcptsPerMessage=1…1024 – Maximum number of re-
cipients of a single message. The default value is 100.
MaximalIncomingSessionSize=64…2048000 – Maximum size (KB) of in-
coming messages transferred within a single mail session. The default
value is 10240.
MaximalIncomingSessionsPerIP=1…1024 – Maximum number of open
connections for receiving messages from a single IP address. The
maximum value is 4.
MaximalOutgoingSessionsPerHost=1…1024 – Maximum number of si-
multaneous connections for sending messages to a single host. The
maximum value is 4.
Page 77

Appendix A 77
The [smtpgw.network] section includes options applications network settings:
ListenOn – this option is presented as a table (list of values) that defines in-
terfaces and ports used by the Receiver module to receive email traffic.
The default value is "0.0.0.0:25" (all available interfaces, port 25).
Hostname – Host name that identifies the server where the application is
installed. Required parameter.
Postmaster– Mail address used as the <postmaster> address. Required
parameter.
ProtectedDomains– The list of domains that require scanning and licensing
(special symbols "*" and "?" can be used). Required parameter.
The [smtpgw.options] contains the application settings not included in other
sections:
LogFilename – Full name of the log-file where results of smtpgw
component operation are written in the text format. If parameter value is
an empty string (LogFilename=), operation information is not logged.
Information can also be written to system log (LogFilename=syslog).
LogLevel =1…9 – Application work report detail level. The default value: 4.
StatFilename– Name and path to the file that stores the performance statis-
tics. The default value: /var/db/kav/5.0/smtpgw/smtpgw.stat.
ICheckerDBFilename – Name of and path to the database file that stores
the information about the messages scanned using the iChecker tech-
nology. The default value: /var/db/kav/5.0/smtpgw/smtpgw.sfdb
PrependReceived=true|false – If this option is enabled, the smtpgw com-
ponent will add the Received: header to scanned messages. The de-
fault value is true (the header will be added).
DSNTemplate – Name of and the path to the file used as a template for De-
livery Status Notification messages. Required parameter.
DSNEntireMessage=true|false – If this option is enabled, the original mes-
sage will be entirely included in the corresponding DSN messages.
Otherwise, the DSN message will contain only the header of the original
message. The default value: false.
DSNOnRelaying = true|false – An option used for generating a DSN mes-
sage upon successful delivery of a message. The default value is:
false.
AVStatistics – Full name of a file or a socket to which the application’s anti-
virus statistical data will be logged. If parameter value is an empty string
(AVStatistics=), anti-virus statistical data will not be logged.
DropMailformedMail = true|false – An option that determines the delivery
of removal of mail messages that do not meet the RFC standards. The
default value: false. This also includes an attempt to make the message
Page 78

78 Kaspersky
®
SMTP-Gateway 5.0
compliant with the standards, after which certain actions as per the con-
figuration file settings will be performed. If the option is set to true, then
the messages that do not comply with the standards, will not be deliv-
ered.
The [smtpgw.path] section contains paths to archives, management files and
the working queue of the application:
IncomingArchivePath – Path to the directory where the archive with all in-
coming messages is stored. If the option is set to an empty string or if
the option is excluded altogether, then the received messages will not
be archived.
OutgoingArchivePath – Path to the directory where the archive with all
outgoing messages is stored. If the option is set to an empty string or if
the option is excluded altogether, then the sent messages will not be
archived.
QueuePath – Path to the directory that stores the working queue of objects
to be processed by the application. Required parameter.
ControlPath – Path to the application management files. Required parame-
ter.
The [smtpgw.timeouts] section contains application timeout options:
MaximalBackoffTime=60…64800 – Maximum period of time (in seconds)
that must elapse before the application will try to send an undelivered
message next time. The default value: 21600.
MinimalBackoffTime=64…64800– Minimum time (in seconds) that must
elapse before the application will try to send an undelivered message
next time. The default value: 1800.
Please pay attention that the value, set for UnreachableCacheRe-
freshPeriod parameter, should be less than MinimalBackoffTime.
Otherwise, a situation could occur when a repeated attempt to send
message will take place in a period of time less than Unreachable-
CacheRefreshPeriod, the application will find information about unreachable host in cache and will not attempt to send such a message.
MaximalQueueLifetime=1…14 – Period (in days) during which the applica-
tion will try to send a message that was not delivered. If the message
could not be delivered during the specified time, it will be deleted and a
notification about failed delivery will be generated. The default value: 5.
MXCacheRefreshPeriod=60…64800
– Period of time (in seconds) for stor-
ing information about MX-records. Upon a DNS request, the application
defines MX records and, provided that the lifetime of these records
(TTL, defined in DNS) exceeds the value of MXCacheRefreshPeriod,
the application caches them for the period=TTL. During this time, the
Page 79

Appendix A 79
application will not send DNS requests about the domains whose MX
records have been cached. The default value: 1200.
UnreachableCacheRefreshPeriod=60…64800
storing information about unavailable hosts. If an attempt to connect to
a remote host fails, this information will be stored in the cache during
the period specified as the value for UnreachableCacheRefreshPe-
riod. During this period, the application will not try to connect to this
host. The default value is 1200.
UnresolvedCacheRefreshPeriod=60…64800
storing information about hosts not listed in DNS. Within the specified
time, the application will not try to connect to this host. The default value
is 1200.
ReadTimeout=1…1200
the Receiver module. The default value is 120.
WriteTimeout=1…1200
the Sender module. The default value is 120.
ReceivingCommandTimeout=1…1200
SMTP-protocol commands: HELO/EHLO, MAIL FROM, RCPT TO (first
such command) and QUIT SMTP protocol from a host. The default
value is 300.
ReceivingDataInitiationTimeout=1…2400
command DATA of the SMTP protocol from a remote host. Note that
the timeout for the first command RCPT TO is defined by the above pa-
rameter, whereas all the subsequent RCPT TO commands must be
transferred by the client during the time specified as ReceivingDataIni-
tiationTimeout. The default value is 600.
ReceivingDataTerminationTimeout=1…7200
terminating data transfer (CRLF.CRLF sequences). The default value is
300.
SendingInitialTimeout=1.1200 – Timeout (in seconds) for waiting for the
response from a remote server when establishing an SMTP session.
The default value is 300.
SendingHelloTimeout=1…1200
response from a remote server to the HELO/EHLO command of the
SMTP protocol. The maximum value is 300.
SendingMailTimeout=1…1200 – Timeout (in seconds) for waiting for the
response from a remote server to the MAIL FROM command. The de-
fault value is 300.
SendingRcptTimeout=1…1200 – Timeout (in seconds) for waiting for the
response from a remote server to the RCPT TO command of the SMTP
protocol. The default value is 300.
– Timeout (in seconds) for reading network data by
– Timeout (in seconds) for writing network data by
– Timeout (in seconds) for waiting
– Timeout (in seconds) for waiting for the
– Period (in seconds) for
– Period (in seconds) for
– Timeout (in seconds) for
– Timeout (in seconds) for
Page 80

80 Kaspersky
®
SMTP-Gateway 5.0
SendingDataInitiationTimeout=1…2400– Timeout (in seconds) for waiting
for the response from a remote server to the DATA command of the
SMTP protocol. The default value is: 600.
SendingDataTerminationTimeout=1…7200 – Timeout (in seconds) for
termination of the data transfer (CRLF.CRLF sequences). The default
value is 300.
SendingQuitTimeout=1…1200
– Timeout (in seconds) for waiting for the
response from a remote server to the QUIT command of the SMTP pro-
tocol. The default value is: 300.
The [smtpgw.policy] section contains the default settings for processing email
messages:
Check=true|false – Defines the anti-virus scanning mode for all mail mes-
sages included into the particular group of recipients/senders. To dis-
able the mode (i.e., configure the application to bypass the scanning of
messages), set the option to false. Required parameter.
AdminNotifyAddress – an email address to which the application will send
notifications to the administrator regarding the scan results for mes-
sages included into this group. Required parameter.
NotifyFromAddress – email address from which the application will send
notifications regarding the scan results for messages of this group. Re-
quired parameter.
BackupPath – Path to the backup storage folder. Required parameter.
QuarantinePath – Path to the quarantine folder. Required parameter.
IncludeByName – Defines masks for filtering by the attachment name. The
application will filter the objects if their names match the specified
masks and do not match the masks used to define exclusions from
scanning. If the parameter is not defined, the application will use the
value <*> – any name.
ExcludeByName – Defines masks for filtering out attachment names. Ob-
jects, whose names do not match these masks and match the masks
used to define inclusions into scanning, will be filtered.
IncludeByMime – Defines masks for filtering by MIME type. The application
will filter the objects if their names match the specified masks and do
not match the masks used to define exclusions from scanning. If this
parameter is not defined, the application will use the value <*> – any
type.
ExcludeByMime – Defines masks for filtering out MIME types. The applica-
tion will filter the objects whose names do not match these masks and
match the masks used to define inclusions into scanning.
NotifyAdminTemplate – Path to the template file used to generate notifica-
tions to be sent to the administrator. Required parameter.
Page 81

Appendix A 81
NotifyRecipientTemplate – Path to the template file used to generate noti-
fications to be sent to the recipient. Required parameter.
NotifySenderTemplate – Path to the template file used to generate notifica-
tions to be sent to the sender. Required parameter.
PlaceholderTemplate – Path to the file the content of which is used to re-
place infected attached objects. Required parameter.
ActionDisinfected=cure|pass|remove|placeholder – Actions to be applied
to disinfected objects. Required parameter.
ActionInfected=pass|remove|placeholder – Actions to be applied to in-
fected objects. Required parameter.
ActionSuspicious=pass|remove|placeholder – Actions to be applied to
objects that are suspected of being infected with an unknown virus. Re-
quired parameter.
ActionProtected=pass|remove|placeholder – Actions to be applied to ob-
jects that the application has failed to scan because they are password-
protected. Required parameter.
ActionError=pass|remove|placeholder – Actions to be applied to objects
the application failed to scan because of a scan error. Required pa-
rameter.
ActionFiltered=cure|pass|remove|placeholder – Actions to be applied to
objects filtered by name or MIME type. Required parameter.
BlockMessage=disinfected, infected, suspicious, protected, error, fil-
tered | all | none – List of statuses assigned to objects based on the
scan results. Original messages with these statuses are blocked. Re-
quired parameter.
NotifyAdmin=disinfected, infected, suspicious, protected, error, filtered
| all | none – List of statuses assigned to objects based on the scan re-
sults. When these statuses are assigned, the application sends notifica-
tions to the administrator. Required parameter.
NotifyRecipient=disinfected, infected, suspicious, protected, error, fil-
tered | all | none – List of statuses assigned to objects based on the
scan results. When these statuses are assigned, the application sends
notifications to the recipient of the original email message. Required pa-
rameter.
NotifySender=disinfected, infected, suspicious, protected, error, fil-
tered | all | none – List of statuses assigned to objects based on the
scan results. When these statuses are assigned, the application sends
notifications to the sender of the original email message. Required pa-
rameter.
SaveInQB=disinfected, infected, suspicious, protected, error, filtered |
all | none – List of statuses assigned to objects based on the scan re-
sults. The objects with these statuses will be moved to the quarantine or
to the backup directory. Required parameter.
Page 82

82 Kaspersky
®
SMTP-Gateway 5.0
The [smtpgw.group:group_name] section contains the settings for processing
email messages for particular groups of recipients/senders:
Check=true|false – Defines the anti-virus scanning mode for all mail mes-
sages included into the particular group of recipients/senders. The de-
fault value is: true. To disable the mode (i. e., configure the application
to bypass the scanning of messages), set the option to false. Required
parameter.
Senders – Masks of addresses of the senders of an e-mail message. Enter
masks as Senders=mask (one mask per line). You can use the "*" and
"?" symbols (for example, Senders=*@mycompany.com). If this op-
tion is not defined, the value is considered to be "
*@*" (all addresses).
Recipients – Masks of addresses of the recipients of an e-mail message.
Enter masks as Recipient=mask (one mask per line). You can use the
"*" and "?" symbols (for example, Recipients=*@mycompany.com). If
this option is not defined, the value is considered to be "*@*" (all ad-
dresses)
It is required to set at least one of parameters Senders or Recipients.
.
AdminNotifyAddress – an email address to which the application will send
notifications to the administrator regarding the scan results for mes-
sages included into this group. If this message is not defined, the value
of the same parameter from section [smtpgw.policy] will be used.
NotifyFromAddress – email address from which the application will send
notifications regarding the scan results for messages of this group. If
this message is not defined, the value of the same parameter from sec-
tion [smtpgw.policy] will be used.
BackupPath – Path to the backup storage folder. If this message is not de-
fined, the value of the same parameter from section [smtpgw.policy]
will be used.
QuarantinePath – Path to the quarantine folder. If this parameter is not
specified, the application will use the path defined for the quarantine file
specified in the [smtpgw.policy] section.
IncludeByName – Defines masks for filtering by the attachment name. The
application will filter the objects if their names match the specified
masks and do not match the masks used to define exclusions from
scanning. If this option is not defined, the application will use the value
<*> (any name).
ExcludeByName – Defines masks for filtering out attachment names. The
application will filter the objects whose names do not match these
masks and match the masks used to define inclusions into scanning.
Page 83

Appendix A 83
IncludeByMime – Defines masks for filtering by MIME type. The application
will filter the objects if their names match the specified masks and do
not match the masks used to define exclusions from scanning. If this
option is not defined, the application will use the value <*> – any type.
ExcludeByMime – Defines masks for filtering out MIME types. The applica-
tion will filter the objects whose names do not match these masks and
match the masks used to define inclusions into scanning.
NotifyAdminTemplate – Path to the template file used to generate notifica-
tions to be sent to the administrator. If this parameter is not defined, the
value of the same parameter from section [smtpgw.policy] will be
used.
NotifyRecipientTemplate – Path to the template file used to generate noti-
fications to be sent to the recipient. If this parameter is not defined, the
value of the same parameter from section [smtpgw. policy] will be
used.
NotifySenderTemplate – Path to the template file used to generate notifica-
tions to be sent to the sender. If this parameter is not defined, the value
of the same parameter from section [smtpgw. policy] will be used.
PlaceholderTemplate – Path to the file the content of which is used to re-
place infected attached objects. If this message is not defined, the value
of the same parameter from section [smtpgw.policy] will be used.
ActionDisinfected=cure|pass|remove|placeholder – Actions to be applied
to disinfected objects. The default value is: cure.
ActionInfected=cure|pass|remove|placeholder – Actions to be applied to
infected objects. If this parameter is not defined, the value of the same
parameter from section [smtpgw. policy] will be used.
ActionSuspicious=pass|remove|placeholder – Actions to be applied to
objects that are suspected of being infected with an unknown virus. If
this parameter is not defined, the value of the same parameter from
section [smtpgw. policy] will be used.
ActionProtected=pass|remove|placeholder – Actions to be applied to ob-
jects that the application has failed to scan because they are password-
protected. If this parameter is not defined, the value of the same pa-
rameter from section [smtpgw. policy] will be used.
ActionError=pass|remove|placeholder – Actions to be applied to objects
the application failed to scan because of a scan error. If this parameter
is not defined, the value of the same parameter from section [smtpgw.
policy] will be used.
ActionFiltered=pass|remove|placeholder – Actions to be applied to ob-
jects filtered by name or MIME type. If this parameter is not defined, the
value of the same parameter from section
[smtpgw. policy] will be
used.
Page 84

84 Kaspersky
®
SMTP-Gateway 5.0
BlockMessage=disinfected, infected, suspicious, protected, error, fil-
tered | all | none – List of statuses assigned to objects based on the
scan results. Original messages with these statuses are blocked. If this
parameter is not defined, the value of the same parameter from section
[smtpgw. policy] will be used.
NotifyAdmin=disinfected, infected, suspicious, protected, error, filtered
| all | none – List of statuses assigned to objects based on the scan re-
sults. When these statuses are assigned, the application sends notifica-
tions to the administrator. If this parameter is not defined, the value of
the same parameter from section [smtpgw. policy] will be used.
NotifyRecipient=disinfected, infected, suspicious, protected, error, fil-
tered | all | none – List of statuses assigned to objects based on the
scan results. When these statuses are assigned, the application sends
notifications to the recipient of the original email message. If this pa-
rameter is not defined, the value of the same parameter from section
[smtpgw. policy] will be used.
NotifySender disinfected, infected, suspicious, protected, error, filtered
| all | none – List of statuses assigned to objects based on the scan re-
sults. When these statuses are assigned, the application sends notifica-
tions to the sender of the original email message. If this parameter is
not defined, the value of the same parameter from section [smtpgw.
policy] will be used.
SaveInQB disinfected, infected, suspicious, protected, error, filtered |
all | none – List of statuses assigned to objects based on the scan re-
sults. The objects with these statuses will be moved to the quarantine or
to the backup directory. If this parameter is not defined, the value of the
same parameter from section [smtpgw. policy] will be used.
The [updater.path] section contains the paths to directories and files required
for the keepup2date component to work:
BackUpPath – Path to the existing directory that stores the archive of the
anti-virus database during updating. Required parameter.
UploadPatchPath– Path to the existing directory that stores application
patches.
DiffUtilPath – Path to the executable file of the component (kavapplydiff).
Required parameter.
The [updater.options] section contains various parameters of the keepup2date
component operation:
KeepSilent=true|false – Defines display options for the report of the com-
ponent work. If set to true, the reports from are not displayed. The de-
fault value is: false.
Page 85

Appendix A 85
PostUpdateCmd – Defines the command that will be executed immediately
after the anti-virus database updating is successfully completed. The
value, set in configuration file, included in application distribution kit, will
start automatic reloading of the updated anti-virus database. You are
not advised to change the value of this parameter.
UseUpdateServerUrl=true|false – Use the URL specified by Update-
ServerUrl to update the database. The default value is: false.
UseUpdateServerUrlOnly=true|false – Use only the URL specified by Up-
dateServerUrl to update the database. If this option is set to false, if
updating from the UpdateServerUrl address fails, the application will
use a different address from the list of update servers. The default value
is: true.
UpdateServerUrl= http://url/ | ftp://url/ | smb://url/ | /local_path/ – Defines
the path to be used to update the database from a shared directory.
RegionSettings – Defines the user regional code used to update the data-
base from the nearest Kaspersky Lab's update server.
ConnectTimeout – Network timeout (in seconds) for the database update. If
updating is not completed during the specified time, the application will
try to download updates from a different server from the list of Kasper-
sky Lab’s update servers. The default value is: 20.
UseProxy true|false – Use a proxy-server to connect to one of Kaspersky
Lab’s update servers. If the parameter value is no – proxy server will
not be used. If the parameter value is
true proxy server address, de-
fined by ProxyAddress parameter, will be taken. If the value of
ProxyAddress parameter is not defined the value of http_proxy envi-
ronmental variable will be taken. If the value of environmental variable is
not defined proxy server will not be used. The default value is true.
ProxyAddress – The address of proxy server, used for connection. Pa-
rameter is set as: http://username:password@url:port. Username
and/or password can be absent in proxy server address. If the address
is not defined its value is taken from http_proxy environmental vari-
able.
PassiveFtp=true|false – Use passive FTP to download updates. The de-
fault value is: false.
The [updater.report] section contains report output options for the keepup2date
component:
ReportFilename – Name of the log file that will store the component per-
formance report. If the option is set to syslog, the component saves the
report to the system log. The default value is:
TEMP_PATH/keepup2date.log, where TEMP_PATH – the value of the
environmental variable TMP, if TMP is omitted – the value of TEMP,
and if TEMP is omitted– directory/tmp.
Page 86

86 Kaspersky
ReportLevel=1…9 –component performance report detail level. The default
value is: 4.
Append=true|false – Append a new component performance report to the
end of the existing report file. If this option is set to false, the previous
report will be overwritten with the new report when the file is open. The
default value is: true.
®
SMTP-Gateway 5.0
A.3. Control signals for the
smtpgw
component
You can manipulate the application using the special control signals listed in the
Table below:
TERM
QUIT
INT
HUP
Stop the application (see section 6.2 on page 54).
Restarts the application and reloads the configuration file, allowing
new settings to take effect.
A.4. Management files
Under Linux/Unix platforms, you can manage an application by creating special
management files:
.c_stats
.c_recv_on
.c_recv_off
Display application status statistics.
Start the Receiver module.
Stop the Receiver module.
.c_avir_on
.c_avir_off
.c _send_on
.c_send_off
Start the anti-virus scan module.
Stop the anti-virus scan module.
Start the Sender module.
Stop the Sender module.
Page 87

Appendix A 87
.c_db_reload
To initiate an action, create a file with the corresponding name in the directory
specified as the value for the ControlPath parameter in the [smtpgw.path]
section. The application will periodically check this directory for known
management files, execute the corresponding command from this file, and then
deletes the file.
Application restart with anti-virus database reloading.
A.5. Application statistics
Following the administrator's command, the application logs its performance
statistics (from the moment of application startup till its current state) to a text file,
which name is specified by the StatFileName option in the [smtpgw.options]
section of configuration file.
This txt file contains a set of lines in the following format:
parameter_name=parameter_value
The table below lists the names and values of the application status parameters.
Parameter name: Value:
time_initialized
time_processing
mta_received_messages
Time of the server initialization
Server operation time (in seconds).
Number of incoming messages successfully
received by the server since its initialization
mta_received_bytes
mta_received_recipients
mta_sent_messages
mta_sent_bytes
Number of bytes successfully received by
the server since its initialization.
Number of recipients of incoming messages
successfully received by the server since its
initialization.
Number of outgoing messages successfully
sent by the server since its initialization.
Number of bytes successfully sent by the
server since its initialization.
Page 88

88 Kaspersky
®
SMTP-Gateway 5.0
mta_sent_recipients
mta_stored_messages_current
mta_incoming_connections_total
mta_incoming_connections_curre
nt
mta_incoming_connections_maxi
mum
mta_incoming_connection_errors
mta_incoming_connections_refus
ed_total
mta_incoming_connections_refus
ed_for_relaying
Number of recipients of outgoing messages
successfully sent by the server since its
initialization.
Number of queued messages (at the
moment the report was generated).
Number of incoming connections to the
server since its initialization.
Number of simultaneous incoming
connections to the server at the moment
the report was generated.
Maximum number of incoming connections
to the server since its initialization.
Number of incoming connection errors
since the server initialization.
Total number of rejected incoming
connections to the server since its
initialization.
Total number of incoming connections
rejected by the server since the server
initialization based on the relaying rules.
mta_incoming_connections_refus
ed_for_connections_limit
mta_incoming_connections_refus
ed_for_connections_limit
mta_outgoing_connections_total
Number of incoming connections rejected
by the server since its initialization due to
the limit on the number of simultaneous
incoming connections.
Number of incoming connections rejected
by the server since its initialization due to
the limit on the number of simultaneous
incoming connections from a single IP
address.
Number of outgoing connections from the
server since its initialization.
Page 89

Appendix A 89
mta_outgoing_connections_curre
nt
mta_outgoing_connections_maxi
mum
mta_outgoing_connection_errors
mta_outgoing_connections_failed
_total
mta_outgoing_connections_failed
_through_cache
mta_routing_queries_total
mta_dns_queries_total
mta_dns_queries_through_cache
Number of simultaneous outgoing
connections at the moment the report was
generated.
Maximum number of outgoing connections
from the server since the server
initialization.
Number of outgoing connection errors since
the server initialization.
Total number of rejected outgoing
connections from the server since its
initialization.
Total number of outgoing connections that
were rejected since the server initialization
because information about the host was
found in the cache of unavailable hosts.
Total number of routing queries since the
server initialization.
Total number of DNS queries since the
server initialization.
Number of cached DNS queries since the
server initialization.
mta_dns_queries_failed
mta_receivings_refused_total
mta_receivings_refused_for_mes
sage_size_limit
mta_receivings_refused_for_sessi
on_size_limit
Number of failed DNS queries since the
server initialization.
Total number of incoming connections
rejected by the server since its initialization.
Total number of incoming connections
rejected by the server because of the
message size since server startup.
Number of incoming messages rejected by
the server since its initialization because of
the session size limit.
Page 90

90 Kaspersky
®
SMTP-Gateway 5.0
mta_receivings_refused_for_hops
_limit
mta_receivings_refused_for_mes
sages_per_session_limit
mta_sendings_failed_total
mta_sendings_failed_for_messag
e_size_limit
mta_sendings_failed_for_8bitmim
e
mta_malformed_messages
mta_dsn_generated
Number of incoming messages rejected by
the server since its initialization because of
the limit on the number of hops.
Number of incoming messages rejected by
the server since its initialization because of
the limited number of messages per
session.
Total number of outgoing rejected
messages since its initialization.
Number of outgoing rejected messages
because of the size limit (since its
initialization).
Number of outgoing rejected messages
since the server initialization because the
remote server does not support 8BITMIME
SMTP protocol extension.
Number of malformed incoming messages
received since the server initialization.
Number of generated DSN messages since
the server initialization.
antiviral_checking_sessions_curr
ent
antiviral_checking_sessions_maxi
mum
antiviral_checked_objects_total
antiviral_checked_objects_throug
h_ichecker
antiviral_checked_objects_infecte
d
Number of anti-virus sessions at the
moment of generating the report.
Maximum number of anti-virus scanning
sessions since the server initialization.
Total number of scanned objects since
server initialization.
Number of clean objects scanned using
iChecker since server initialization.
Number of infected objects that cannot be
disinfected since the server initialization.
Page 91

Appendix A 91
antiviral_checked_objects_disinfe
cted_objects
antiviral_checked_objects_suspic
ious_objects
antiviral_checked_objects_protect
ed_objects
antiviral_checked_objects_filtered
_objects
antiviral_check_checked_objects_
error
antiviral_infected_objects
antiviral_checked_messages_tota
l
antiviral_checked_messages_bloc
ked
antiviral_checked_messages_mo
dified
Number of disinfected objects since the
server initialization.
Number of suspicious objects detected
since the server initialization.
Number of protected objects not subject to
scan since the server initialization.
Number of filtered objects since the server
initialization.
Number of scan errors that occurred since
the server initialization.
Number of objects that could not be
disinfected since the server initialization.
Total number of scanned e-mail messages
since the server initialization.
Number of blocked messages since the
server initialization.
Number of modified messages since the
server initialization.
antiviral_notifications_generated_
for_sender
antiviral_notifications_generated_
for_recipients
antiviral_notifications_generated_
for_admin
task_sender_running
task_receiver_running
Number of sender notifications generated
since the server initialization.
Number of recipient notifications generated
since the server initialization.
Number of administrator notifications
generated since the server initialization.
Status of the Sender module– 0 stopped, 1
running.
Status of the Receiver module– 0 stopped,
1 running.
Page 92

92 Kaspersky
®
SMTP-Gateway 5.0
task_antivirus_running
Status of the AV module – 0 stopped, 1
running.
A.6. Command line options for the
smtpgw
The configuration file parameters can be redefined using command line options,
when you are launching the application from the command line. The Table below
contains a detailed discussion of the command line options.
Help options:
–?
or
--help
–V
or
--version
Configuration options:
component
Display reference information about the command line
options available for the particular component on the
console and quit stop the component.
Display the application version on the console and stop the
component.
–с
or
--conf–file= <path_to_the_file
>
–d
or
--no–daemon
–p
or
--pid–file=<path_to_the_file>
Use the alternative configuration file
<path_to_the_file>.
Do not run the component as a daemon
process.
Use the alternative pid file <path_to_the_file>.
Page 93

Appendix A 93
–n
or
--no–pid–file
–u
or
--user=<user_name>
–o
or
--no-change-owner
A.7. Smtpgw
The smtpgw component may return any of the following return codes:
0
1
30
The component started successfully.
Error in command line options.
A critical system error occurred during the application operation.
Do not use the pid file.
Define the user <user_name> as the owner of
the process.
Do not change the user-owner of the process.
return codes
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
The PID file already exists.
The PID file cannot be created.
Unable to run the daemon process for the application.
The UID and GID of the owner of the process cannot be changed.
The signal handler cannot be identified.
IOS could not be closed.
IOS could not be rerouted.
Error initialization the anti-virus kernel.
Page 94

94 Kaspersky
®
SMTP-Gateway 5.0
49
50
51
55
64
65
66
67
70
Error initializing the debug information display (trace) module.
Error loading anti-virus database.
The anti-virus database date stamp is not within the license key
validity period.
Error matching the network name with the socket (bind).
License data is missing or no license key was found using the path
specified in the configuration file.
The configuration file cannot be loaded.
Error in the configuration file
Error initializing the log file.
Component executable file is corrupted.
A.8. Command line options for
licensemanager
Help options:
–h
Command line options for managing license keys:
–s
–c (–y)
<path_to_file>
–k <path_to_file>
Display reference information about the command line options available for
the particular component on the console and stop the component.
Display information about all installed license keys on the
console.
Use the alternative configuration file <path_to_file>.
Display information about the current key being used in
the console.
Page 95

Appendix A 95
–a <path_to_file>
–d <a|r>
A.9.
Kaspersky licensemanager
Install the key file.
Delete the main current/additional key file.
return codes
Kaspersky licensemanager may return any of the following return codes:
0
30
64
65
70
A.10.
The component operation was successfully completed.
Critical system error.
Licensing error.
Error reading the configuration file.
The component executable file is corrupted.
Keepup2date
command line
options
Help options:
–h
–v
–p <id>
–i
Display reference information about the command line options
available for the particular component on the console and stop the
component.
Display the application version on the console and stop the
component.
Display the application ID on the console.
Display a list of all installed Kaspersky Lab’s applications on the
console.
Page 96

96 Kaspersky
Options for managing license keys:
–c <path_to_file> Use the alternative configuration file <path_to_file>.
License key works only if one Kaspersky Lab application
is installed on the server, or if the updated application is
defined by –p key (otherwise, system message about
several installed applications will be displayed).
–u<path_to_file> Copy the update to the local directory <path_to_file>.
®
SMTP-Gateway 5.0
–b <path>
–t <path> Use the directory <path> to store temporary files.
Report generation options:
–l <path_to_file> Log work results in file <path_to_file>.
A.11.
The keepup2date component may return any of the following return codes:
0
1
10
30 The PostUpdaterCmd command could not be executed after the
60
Keepup2date
The anti-virus database does not need updating.
The anti-virus database was updated successfully.
A critical error occurred; updating was interrupted.
database was updated.
License information is missing or no license key was found using the
path specified in the configuration file.
When updating, create a backup copy of the current antivirus database in the directory <path>.
return codes
75
The configuration file cannot be loaded or there is an error in
configuration file parameters.
Page 97

Appendix A 97
A.12. Anti-virus scan information
format
The application provide for a possibility to view separate statistical data of the
anti-virus component of the application.
In order to create a file that will contain these statistical data about the AV-
module, specify the value for option AVStatistics=file name|TCP-socket in
section [smtpgw.options] of the configuration file, where the information on
each processed object will be stored.
Each line in the statistics file created will contain data about one scanned object
using the following format:
Time\tSize\tSender\tRecipients\tStatus\tVirusList\tIP
\tMessage-id
Values for each of the parameters are listed in the table below. If the parameter
is optional, the corresponding field in the report line may remain blank.
Symbolic name Value Note
Time Record creation time
Size Record size
Sender Sender’s e-mail address
Recipients Recipient’s e-mail address.
Only a small number of
addresses can be listed
Status List of statuses after the
anti-virus scan
VirusList List of viruses Optional
IP IP-address of the host from
which the message was
received
Message-id Message ID. Optional
Optional
Page 98

98 Kaspersky
All information in the statistics file is logged after the anti-virus scan of email
message is performed.
If, for some reason, the output of the report about the processed object is not
possible (for example, the statistics server is not available), the information about
the object will not be logged.
®
SMTP-Gateway 5.0
A.13. Messages about actions
applied to the message
Messages added to the log file, may be different depending on the action
performed.
When a message is delivered, the following line is added to the report
file:
envelope-id: RECEIVED, from=<...>, nrcpt=...,
size=..., client=[...], helo=<...>,
message_id=<message id>, flags=...
where:
envelope-id – message identifier in the application’s working queue.
from – value received from the MAIL FROM command.
nrcpt – number of the recipients of this e-mail message (received
from the RCPT TO command(s)).
size – message size.
client – IP address of the client’s host.
helo – client’s domain name, received from HELLO/EHLO command.
message_id – message ID.
flags – flag(s), that have the following meanings:
E – used ESMTP.
D – client requested DSN-confirmations.
where:
When a message is scanned for viruses, the following line is added to
the log file:
envelope-id: SCANNED, group=<...>, nrcpt=...,
status="...", srcid=..., names="..."
envelope-id – message identifier in the application’s working queue.
Page 99

Appendix A 99
group – the name of the group of the recipients (or group policy) to
which this message belongs.
nrcpt – the number of recipients of this e-mail message (out of recipi-
ents that belong to this group).
status – status assigned to the message based on the anti-virus scan
results.
srcid – original message ID.
names – names of viruses, if detected, divided by ", ".
When generating system notifications the following line will be added to
the log file:
envelope-id: CREATED,
notify=<admin|recipient|sender>, nrcpt=..., size=...,
srcid=...
where:
envelope-id – message identifier in the application’s working queue.
notify – to whom the notification will be delivered (possible values are
admin, recipient, sender).
nrcpt – the number of recipients of this e-mail message.
size – message size.
srcid – original message ID.
where:
When a copy of the e-mail message is created (for the delivery of this
message to different groups of recipients) the following line will be
added to the log file:
envelope-id: SPLITTED, domain=<...>, nrcpt=...,
srcid=...
envelope-id – message identifier in the application’s working queue.
domain –name of the domain for which a copy of the original message
was created.
nrcpt – the number of recipients of this e-mail message (out of recipi-
ents that belong to this group).
srcid – original message ID.
Page 100

100 Kaspersky
When the e-mail message is delivered, the following line will be added
to the log file:
envelope-id: DELIVERED, rcpt=<...>, server=...,
size=..., status=sent|failed
where:
envelope-id – message identifier in the application’s working queue.
rcpt – address of the message recipient.
server – ip-address and name of the server where the message is
delivered.
size – message size.
status – delivery status, poossible values are:
sent – message was successfully devivered.
failed – message was not delivered.
When the e-mail message is blocked, the following line will be added to
the log file.
envelope-id: BLOCKED, rcpt=..., size=...
where:
envelope-id – message identifier in the application’s working queue.
®
SMTP-Gateway 5.0
rcpt – address of the message recipient.
size – message size.
 Loading...
Loading...