Page 1

KASPERSKY LAB
Kaspersky KryptoStorage 1.0
Page 2

KASPERSKY KRYPTO S TORAGE 1.0
User Guide
Kaspersky Lab
http://www.kaspersky.com
Revision date: December, 2009
Page 3

Contents
CHAPTER 1. KASPERSKY KRYPTOSTORAGE OVERVIEW ...................................... 5
1.1. The Components of Kaspersky KryptoStorage .................................................... 6
1.2. Protected Objects ................................................................................................... 7
1.3. Rights of Access to Protected Objects .................................................................. 8
1.4. Password Recommendations. Using Password Hints ......................................... 8
CHAPTER 2. INSTALLING KASPERSKY KRYPTOSTORAGE ................................... 10
2.1. Hardware and Software Requirements ............................................................... 10
2.2. Installation ............................................................................................................. 11
2.3. Managing Licenses .............................................................................................. 13
2.4. Getting and Installing Licenses using an Activation Code .................................. 14
2.5. Updating the Product ............................................................................................ 16
CHAPTER 3. SYSTEM INTERFACE .............................................................................. 17
3.1. The Explorer Context Menu ................................................................................. 17
3.2. The Window of the Kaspersky KryptoStorage Manager .................................... 18
CHAPTER 4. PROTECTING DATA. USING PROTECTED OBJECTS ....................... 20
4.1. Protected Folders ................................................................................................. 20
4.1.1. Creating a Folder ......................................................................................... 21
4.1.2. Rules for Using Protected Folders .............................................................. 23
4.1.3. Attaching Protected Folders ........................................................................ 24
4.1.4. Detaching Protected Folders ....................................................................... 25
4.2. Protected Containers ............................................................................................ 25
4.2.1. Creating a Container .................................................................................... 25
4.2.2. Preparing a Container for Use ..................................................................... 28
4.2.3. Rules for Using Protected Containers ......................................................... 28
4.2.4. Attaching a Container .................................................................................. 28
4.2.5. Formatting a Container ................................................................................ 30
4.2.6. Detaching a Container ................................................................................. 31
4.2.7. Protecting Containers from Deletion ........................................................... 31
4.3. Protecting Disk Volumes and Removable Devices............................................. 31
4.3.1. Specific Features of Using Hard Disk Management Utilities ...................... 33
Page 4

4 Kaspersky KryptoStorage 1.0
4.3.2. Encrypting Disk Volumes and Removable Disks ....................................... 33
4.3.3. Interrupting Encryption ................................................................................. 35
4.3.4. Resuming Encryption ................................................................................... 36
4.3.5. Rolling back to the Unencrypted State ........................................................ 36
4.3.6. Decrypting Objects ....................................................................................... 37
4.3.7. Starting up Using Protected System Volume and/or Boot Volume ............ 37
4.3.8. Attaching the Protected Volumes of Hard Disks and Removable Devices 38
4.3.9. Detaching the Protected Volumes of Hard Disks and Removable Devices
................................................................................................................................ 39
4.3.10. Disk Recovery ............................................................................................ 39
4.4. Wiping Protected and Unprotected Objects ........................................................ 41
CHAPTER 5. CONFIGURING SUBSYSTEMS .............................................................. 42
CHAPTER 6. UNINSTALLING KASPERSKY KRYPTOSTORAGE ............................. 45
APPENDIX A. GLOSSARY ............................................................................................. 47
APPENDIX B. REFERENCE INFORMATION................................................................ 48
B.1. Contact Us ............................................................................................................ 48
B.2. License for the Windows Installer XML (WiX) Library ........................................ 48
Page 5

CHAPTER 1. KASPERSKY
KRYPTOSTORAGE OVERVIEW
Kaspersky KryptoStorage (hereafter Kaspersky KryptoStorage or the System) is a
system for the cryptographic protection of confidential data stored on PC from
unauthorized access.
The system is intended to protect the user’s confidential data against unauthorized
access and to prevent data leakage when the operating system saves system
information to disk or when the user’s files are not wiped.
Transparent encryption is used to encrypt information.
The transparent encryption is a mechanism which enables the storage of
information in the encrypted form inside of a protected object. The protected data
is processed in the following way: the data is automatically decrypted in RAM
when requested and the uploaded data is encrypted.
Data is encrypted with the 128-bit AES algorithm. The algorithm is approved by
the international cryptography community and represents a cryptographic
standard. AES is approved by the U.S. National Institute of Standards and
Technology (Standards and Technology (NIST) Federal Information Processing
Standards (FIPS) PUB 197 26.11.2001).
The cryptographic key is generated from the user’s password. Thereby the length
of this password can be limited by the local legal requirements.
The main functions of the System are listed below.
Protecting Data
With the System, you can:
create single protected NTFS virtual folders to store confidential data;
create protected virtual volumes (the protected containers) to store
confidential data;
protect all data on disk volumes, including the system and the boot
volumes, on Flash drives, and other USB Mass Storage devices;
Page 6
6 Kaspersky KryptoStorage 1.0
Component
Description
The components integrated
into the Explorer shell
Create protected objects; enable use of the
protected data, decrypting and wiping files and
folders.
Kaspersky KryptoStorage
manager
Enables activating the program, managing
licenses, configuring Kaspersky KryptoStorage
subsystems, creating protected objects,
recovering protected disks
The protection of system disk allows you to keep the following confidential:
RAM contents which are saved to a hard disk when the system
hibernates;
crash dump data which is saved to a hard disk when a fatal error
occurs;
data of temporary files and swap files.
Handling protected data
With the System, you can:
delimit access to protected information using password authorization;
store protected objects inside other protected objects with any nesting
depth;
prevent accidental or intended deletion of protected objects by limiting
access to these objects;
use protected folders, containers and volumes which are located on
the user’s computer;
move protected objects together with the physical carrier to another
computer where the System is installed. At the same time the objects
can be used;
wipe files and folders.
1.1. The Components of
Kaspersky KryptoStorage
The components of Kaspersky KryptoStorage are listed in the table.
Page 7
7 Kaspersky KryptoStorage 1.0
Component
Description
Kaspersky KryptoStorage
Help
A file containing .CHM help topics
1.2. Protected Objects
The protected objects are any objects encrypted with Kaspersky KryptoStorage
which are intended to store data.
There are the following types of protected objects.
A protected folder is a special NTFS folder created by a user on the user’s
computer with Kaspersky KryptoStorage. After the folder is attached using
Kaspersky KryptoStorage, you can use it as a common NTFS folder.
A protected container is a special file created by a user on the user’s
computer with Kaspersky KryptoStorage. After the container is attached
using Kaspersky KryptoStorage, you can use it as a virtual disk. Also,
container files can be copied, recorded to CD or DVD, emailed and moved
to another computer where the System is installed. At the same time the
containers can always be attached.
A protected volume is created by converting (encrypting) an existing hard
drive volume which contains data using Kaspersky KryptoStorage. This
operation also includes protecting the system and/or the boot volumes and
USB Mass Storage devices (Flash drives, USB storages, etc). After the
protected volume is attached using Kaspersky KryptoStorage, you can use
it as a common volume.
Attention!
All data placed to a created protected object is automatically protected, i.e.
encrypted. When you copy data from a protected object into an unprotected area,
the data is placed in the decrypted (unprotected) form.
Page 8
8 Kaspersky KryptoStorage 1.0
1.3. Rights of Access to
Protected Objects
A user must be authorized to access protected objects. It prevents unauthorized
operations on the objects.
The authorization is required to:
Attach protected objects;
Change password;
Decrypt volumes, interrupt and continue encrypting, decrypting and also
rolling the protected volumes back to a previous state.
To be authorized, you must type your password for accessing the protected.
Note:
If you type an incorrect password (for example, if you forgot the password), the
System displays the message that access is denied and a password hint, if you
specified the hint while selecting the password.
1.4. Password
Recommendations. Using
Password Hints
All protected objects are accessed upon authorization only. Password is the
mandatory authorization parameter. Follow the recommendations for selecting a
password:
a password should be made up of 7 characters or more;
a password can contain digits, English characters, space and special
characters («.», «,», «?», «!», «<», «>», «”», etc.);
it is highly advised to create a password which includes a combination
of upper- and lower-case alphabetic letters and digits.
You must not use in the password:
words found in a dictionary or set expressions;
any easy-to-guess sequence like: qwerty, 123456789, qazxsw, etc.
Page 9

9 Kaspersky KryptoStorage 1.0
personal data: first and last names, addresses, passport numbers,
social security numbers, etc.
It is strongly advised not to reuse the passwords which you use to run
other programs (e-mail, databases, etc).
Attention!
If you lose the password to a protected object, the object’s contents cannot be
restored!
You can use password hints. A password hint is a character string which is
displayed in the special field. The password hint is specified by the user when the
user selects a password. If the hint has been specified and you type an incorrect
password, the System displays the hint after denying access to an object. The
password hint can contain certain information to help you recall your password.
Attention!
When you specify a password hint for your password, you must remember that the
password hint will be displayed to every user who tries to attach the object.
Therefore, the password hint must not contain the explicit description of your
password.
Page 10

CHAPTER 2. INSTALLING
KASPERSKY
KRYPTOSTORAGE
This chapter contains hardware and software requirements and describes how to
install and update the Product, and manage its licenses.
2.1. Hardware and Software
Requirements
Your computer must meet the following hardware and software requirements to
run Kaspersky KryptoStorage.
Hardware requirements:
processor Intel Celeron 1 GHz or higher;
RAM 256 MB;
10 MB free disk space to install the application.
Software requirements:
Any of the listed operating systems:
Microsoft Windows 2000 Professional (Service Pack 4 + all
updates);
Microsoft Windows XP (Service Pack 2);
Microsoft Windows Vista (Service Pack 1);
Microsoft Windows 7.
System supports operating systems on both x86 and x64 platforms.
Page 11

11 Kaspersky KryptoStorage 1.0
2.2. Installation
Attention!
You must have administrator rights to the computer to install Kaspersky
KryptoStorage.
The installation starts with the installation wizard. Each window contains a set of
buttons to control the installation process. The buttons provide the following
operations:
Next – accept the action and go to the next step of the installation
procedure.
Back – return to the previous step.
Cancel – cancel the installation.
See below the step-by-step description of the System installation procedure.
Step 1. Start the Installation
Insert the Kaspersky KryptoStorage setup disk into the CD-ROM drive or run the
installation file kksVVVen.exe.
The VVVV letters in the name of the installation file stand for the version of the
Product.
Note:
You can download an update of the Kaspersky KryptoStorage software product at
http://www.kaspersky.com/downloads.
The Welcome to the Kaspersky KryptoStorage Setup Wizard screen opens.
Click Next to proceed to the next step. Or click Cancel to cancel the installation.
Step 2. Accept License Agreement
You must accept the terms of the license agreement to continue the installation
and click Next.
Page 12

12 Kaspersky KryptoStorage 1.0
Step 3. Select the Installation Directory
The default path to the directory where Kaspersky KryptoStorage will be installed
is specified in the input field of the Destination Folder screen.
You can change the installation directory. Click Change… and select a directory in
the standard window for selecting the directory, or type the path to the directory in
the appropriate input field.
Click Next to proceed to the next step.
Step 4. Complete the Installation
After proceeding to the Ready to install Kaspersky KryptoStorage screen, click
Install, to install Kaspersky KryptoStorage.
Follow the installation wizard instructions to complete the installation of Kaspersky
KryptoStorage.
When the installation is complete, you will be asked to activate the product. You
can select one of the following options:
Activate 30-day trial version.
Activate full version.
To activate the full version, you must get and install a license using an activation
code. See information on the procedure for getting and using a license key in
Item 2.4 on Page 14. After the type of activation is selected, click Next.
Restart the computer to finish the installation. The corresponding notification is
displayed.
Attention!
It is strongly advised not to turn off computer’s power supply when restarting
(when Microsoft Windows is shutting down). It may cause an error while the
operating system is starting up.
If the power supply fails, keep hitting the F8 key when restarting. In the Windows
Advanced Options Menu, select the Last Known Good Configuration option.
After that, reinstall Kaspersky KryptoStorage.
Page 13
13 Kaspersky KryptoStorage 1.0
2.3. Managing Licenses
You must get and register a commercial license to make Kaspersky KryptoStorage
fully functional.
Note:
With the activated trial license, you can use the full-featured Kaspersky
KryptoStorage for 30 days. The password length is limited by 1 character.
When trial license expires, the functionality of the product is partially limited. You
can use the existing (protected) objects. Specifically, you can access your
information and decrypt the data. But you cannot create new protected objects, or
get technical assistance.
You can manage licenses using the Kaspersky KryptoStorage manager.
To run the Kaspersky KryptoStorage manager:
1. From the Start menu, select Programs ► Kaspersky KryptoStorage ►
Kaspersky KryptoStorage.
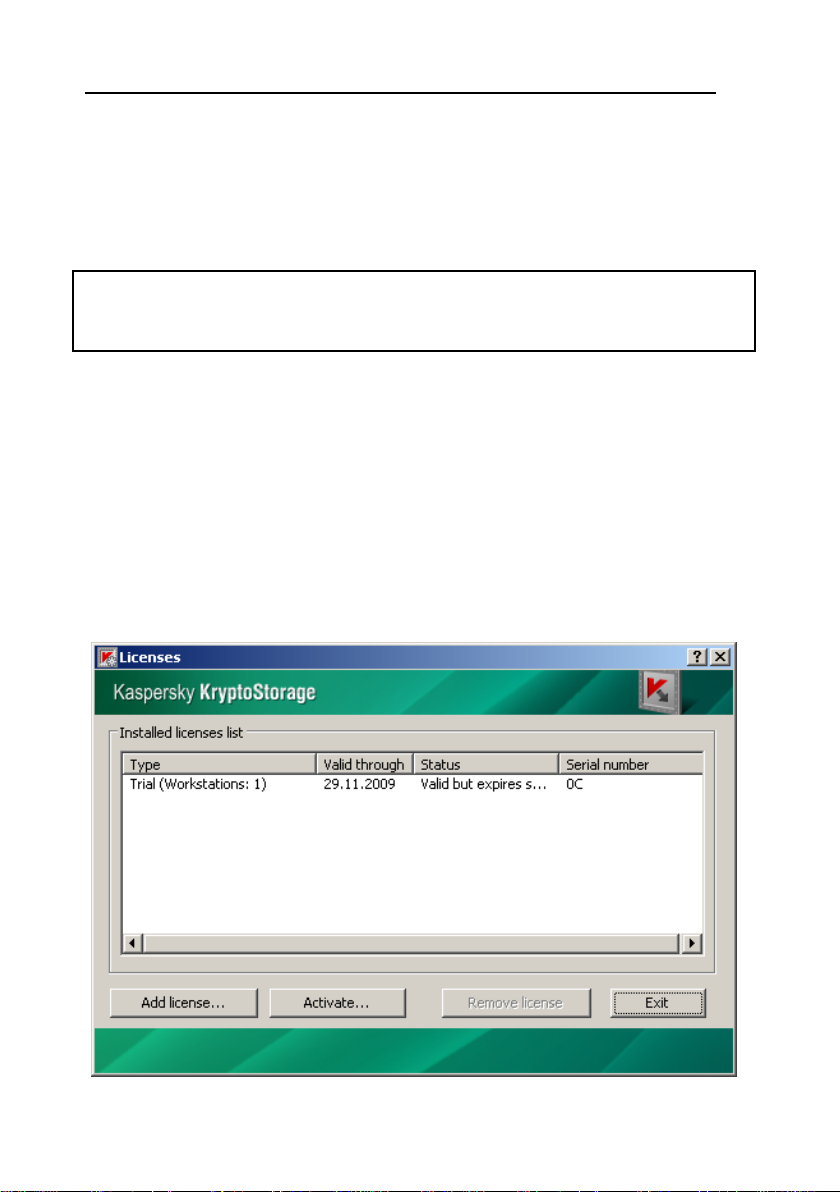
2. In the opened window, click Licenses.
The Licenses dialog window will be displayed (Figure 1).
Figure 1 Licenses
Page 14
14 Kaspersky KryptoStorage 1.0
This window contains a list of installed licenses and detailed information on each
license: type, serial number, current status and validity period.
To add a license to the list, click Add license…. In the opened dialog window,
specify the path to a license file and click Open.
Note:
The added license must be given to the same user who owns all other licenses in
the list. Otherwise you cannot add a license.
To remove a license from the list, select the license and click Remove license.
Note:
You cannot remove the Trial license from the license list.
Attention!
It is strongly not advised to remove the valid commercial license from the list.
Otherwise the functionality of the Product will be limited in a way similar to the
expired trial license.
To get and install a license using an activation code, click Activate…. Activating a
license using an activation code is covered in Item 2.4 on Page 14.
When you finish editing the list of installed licenses, click Exit to close the window.
2.4. Getting and Installing
Licenses using an Activation
Code
You can use an activation code to get and install a license while installing the
Product or after the Product is installed, when managing licenses (see Item 2.3 on
Page 13).
Attention!
When using an activation code, your computer must be connected to the Internet
to get a license from the license service.
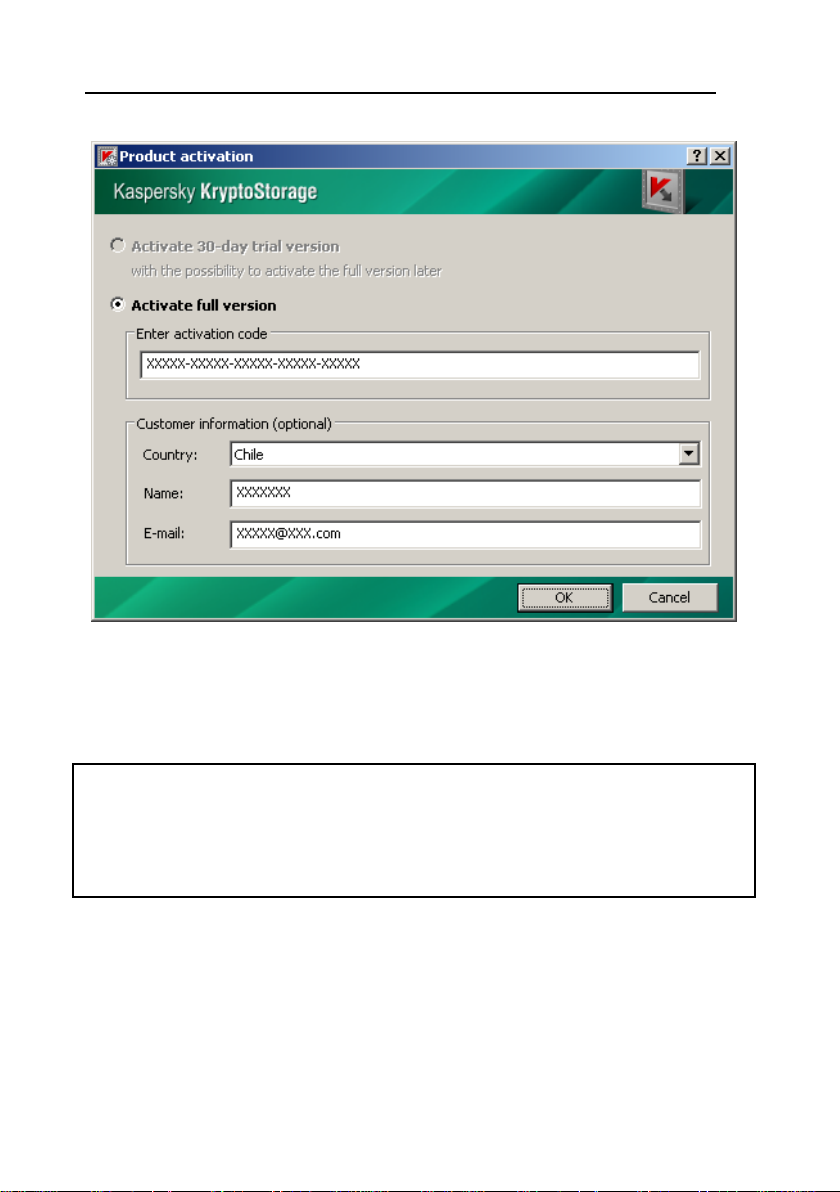
To get a license, type a product code consisting of five parts. Each part of the
code contains five characters (Figure 2). The code contains digits (except zero)
and upper-case English letters.
Page 15
15 Kaspersky KryptoStorage 1.0
Figure 2 Activating the Product
Then, in the customer information pane, specify your country. You can also
specify your name and e-mail address as additional information. Click ОК.
After that the license is acquired and installed automatically.
Attention!
Only one license is given for each activation code. Keep your product activation
code secret.
Copy the license file to another hard disk or removable device. This copy will be
needed to restore the System after a failure.
Page 16

16 Kaspersky KryptoStorage 1.0
2.5. Updating the Product
You can download updates of the Kaspersky KryptoStorage software product at
http://www.kaspersky.com/downloads.
To update the Product to a newer version, run the setup program of the update.
Note:
You cannot update an older version to an earlier version. To install an earlier
version, you must first uninstall the existing version of the Product (see Chapter 6
on Page 45).
Page 17

CHAPTER 3. SYSTEM
INTERFACE
This chapter describes the user interface of the System.
3.1. The Explorer Context Menu
You can access functions of the System using Windows Explorer context menu.
To open the Kaspersky KryptoStorage menu:
1. Select the necessary object (a folder, a container, or a volume) and rightclick it.
2. In the opened context menu, select the item Kaspersky KryptoStorage
(see Figure 3).
This menu item contains a submenu which depends on the type of object
and whether the object is protected or not.
Figure 3 The Kaspersky KryptoStorage menu
Page 18

18 Kaspersky KryptoStorage 1.0
To create a protected folder or container:
Right-click any place in the opened folder or on the desktop and from the
opened context menu select New ► Kaspersky KryptoStorage Folder
or New ► Kaspersky KryptoStorage Container.
3.2. The Window of the
Kaspersky KryptoStorage
Manager
To run the Kaspersky KryptoStorage manager,
from the Start menu, select Programs ► Kaspersky KryptoStorage ►
Kaspersky KryptoStorage.
The window of the manager will be opened (Figure 4).
Figure 4 The manager window
Page 19

19 Kaspersky KryptoStorage 1.0
With the manager you can:
Create protected folders (Item 4.1.1 on Page 21)
Create protected containers (Item 4.2.1 on Page 25)
Encrypt volumes (Item 4.3.2 on Page 33)
Configure subsystems (Chapter 5 on Page 42)
Use Explorer to open the object in a new window after attaching
Manage licenses and activate the product (see Item 2.3 on Page 13)
Recover disks (Item 4.3.10 on Page 39)
Page 20

CHAPTER 4. PROTECTING
DATA. USING PROTECTED
OBJECTS
This chapter describes how to use the following protected objects:
Protected folders (Item 4.1 on Page 20).
Protected containers (Item 4.2 on Page 25).
Protected hard disk volumes and removable media (see Item 4.3 on
Page 31).
4.1. Protected Folders
You can create a protected folder only if the following conditions are met:
You can use the protected folders if Kaspersky KryptoStorage is installed
on the computer and the Protected folders subsystem is running (for more
information about the subsystem, see Chapter 5 on Page 42). The
subsystem is running by default.
A device (a hard disk or a removable media) where you create a protected
folder must be write-enabled. The user who creates the protected folder
must have privileges for creating folders.
A protected folder can be created only in the NTFS file system.
You cannot create a new Kaspersky KryptoStorage folder inside of another
Kaspersky KryptoStorage folder.
A protected folder cannot be created in an EFS-protected folder (an
encrypting file system, which is included into the Microsoft Windows OS);
A folder must have a full name which does not exceed 255 characters.
Page 21

21 Kaspersky KryptoStorage 1.0
4.1.1. Creating a Folder
Attention!
Before starting, read about the specific features of creating protected folders
(Item 4.1 on Page 20).
You can create a protected folder on a hard disk or removable media. Moreover, a
protected folder can be created inside of another protected object (a volume or
protected container).
Note:
If a folder is created inside of any other protected object, you must attach this
object prior to creating the folder.
To create a protected folder:
1. Complete one of the following steps:
Right-click any place in an opened folder or on the desktop and from
the opened context menu select New ► Kaspersky KryptoStorage
Folder.
Run the Kaspersky KryptoStorage manager: from the Start menu
select Programs ► Kaspersky KryptoStorage► Kaspersky
KryptoStorage. In the opened window of the manager, click Create a
protected folder….
After that, the Create protected folder dialog window will be displayed
(Figure 5).
Page 22

22 Kaspersky KryptoStorage 1.0
Figure 5 Creating a protected folder
2. In this window, specify parameters for the created protected folder:
Select folder. Select a folder in which the protected folder will be
located. By default, if the protected folder in created using the Explorer
context menu, then the folder of the menu is specified, if the folder is
created using the manager, the My Documents folder of the current
user’s profile is specified. You can specify different folders.
Protected folder name. Specify the name of the protected folder.
Note:
While using the protected folders, you can change the names of the
folders using the tools of the operating system.
Password, Confirm, Password hint. Specify a password to access
the protected folder and a hint for your password (optional). You will
need these parameters to access the folder.
Note:
See password and hint recommendations in Item 1.4 on Page 8.
Page 23

23 Kaspersky KryptoStorage 1.0
3. When all necessary parameters are specified, click OK.
A protected folder is created. When the folder is created, it is attached and is
ready for use.
4.1.2. Rules for Using Protected
Folders
While using the protected folders, you must consider the following rules:
All files and folders which are located inside a protected folder are
encrypted and they are protected objects too.
You can do any operations on a protected folder (reading, writing,
renaming, archiving, removing and etc.) only when the folder is
attached.
An attached folder can be accessed by any user or software
who/which uses the same computer locally under the account of the
user who attached the object. The System prohibits network access to
protected folders.
Note:
It is advised to detach a protected folder after you have finished
using it.
Copies and moved files and folders are protected only by the objects
which they are placed inside.
Note:
Copies and moved files and folders are not protected when they are
placed into objects which are not protected by the System.
The System does not support the following operations on the protected
folders and their contents: moving to the Recycle Bin, moving within
one volume of files and folders which contain files.
Note:
If you move a folder which contains files within a volume, the source
folder remains unchanged. An empty folder which has the same
name as the source folder will be created in the target place. This
folder is protected by the object which it is placed inside.
Page 24

24 Kaspersky KryptoStorage 1.0
Some file managers, for example, Total Commander, can delete the
source objects after copying if files or folders are moved within a
volume. In this case you can move the objects, but the moved files
and folders will be protected by the objects which they are placed
inside.
You can move unprotected folders containing protected subfolders
within a volume to unprotected folders. In this case, protected objects
do not have to be attached and at the same time their properties
remain.
An unprotected folder containing protected subfolders can be moved to
the Recycle Bin if all protected objects are attached.
Note:
You can delete or restore a folder which is moved to the Recycle
Bin. When restoring the folder, all protected objects of the folder will
be attached. After you restart the computer or log off the system, you
cannot delete the folder which is moved to the Recycle Bin but you
can restore it. When restoring, all protected objects of the folder will
be detached. With Microsoft Windows Vista and Microsoft Windows
7, you can delete the folder from the Recycle Bin after restarting the
Windows or logging out.
Total Commander cannot move an unprotected folder containing
protected subfolders to the Recycle Bin.
4.1.3. Attaching Protected Folders
You can use a protected folder (reading, writing, renaming, copying, deleting and
etc.) only if the folder is attached.
To attach a folder:
1. Select a protected folder to attach.
2. Right-click the selected folder and from the opened context menu select
Kaspersky KryptoStorage ► Attach folder.
3. In the opened dialog window, type the password to access the protected
folder.
4. Click OK.
Page 25

25 Kaspersky KryptoStorage 1.0
4.1.4. Detaching Protected Folders
When you detach a protected folder, the folder is transited to the state in which it
cannot be used until you attach it again.
Attention!
Before detaching a folder, save all changes and complete using the folder. These
steps are needed because some applications can retain access to the data until all
operations with the data are completed.
To detach a protected folder:
1. Select a protected folder to detach.
2. Right-click the selected object and from the opened context menu select
Kaspersky KryptoStorage ► Detach folder.
The System requires more time to detach several protected objects
simultaneously. In some emergency situations, you may need to detach all
protected objects simultaneously. For this purpose you must save the changes
and restart or shut down the computer. After that, all protected objects will be
detached. You can detach all protected folders by logging off the system.
4.2. Protected Containers
A device (a hard disk or a removable disk) where you create a protected container
must be write-enabled. The user who creates the container must have privileges
for creating files.
Creating protected containers on CD/DVD disks is not supported. At the same
time, you can use CD/DVD disks to store the created protected containers.
You can use the protected containers if Kaspersky KryptoStorage is installed on
your computer and the Protected containers subsystem is running.
4.2.1. Creating a Container
Attention!
Before starting, read about the specific features of creating protected containers
(Item 4.2 on Page 25).
You can create containers on a hard disk or removable media. Moreover, a
protected container can be created inside other protected object (a volume,
removable device, folder or protected container).
Page 26

26 Kaspersky KryptoStorage 1.0
Note:
If a container is created inside any other protected object, you must attach this
object prior to creating the container.
To create a container:
1. Complete one of the following steps:
Right-click any place in an opened folder or on the desktop and from
the opened context menu select New ► Kaspersky KryptoStorage
Container.
Run the Kaspersky KryptoStorage manager: click Start and from the
Start menu select Programs ► Kaspersky KryptoStorage►
Kaspersky KryptoStorage. In the opened window of the manager,
click Create a protected container….
After that, the Create protected container dialog window will be
displayed (Figure 6).
Figure 6 Creating a protected container
Page 27

27 Kaspersky KryptoStorage 1.0
2. In this window, specify parameters for the created protected container:
Select folder. Select a folder in which the file of the protected
container will be located. By default, if the container is created using
the Explorer context menu, then the folder of the menu is specified, if
the container is created using the window of the manager, the My
Documents folder of the current user’s profile is specified. You can
specify different folders.
Protected container name. The name and extension of the container
file.
The default extension of the container file name is .kde (when
Kaspersky KryptoStorage is installed, the files with this extension are
registered in the operating system as the Kaspersky KryptoStorage
Containers). The operating system displays the files as the icon .
If you specify any other extension which is not registered in the
operating system instead of .kde, the container file will be displayed
as a file of unknown format.
Notes:
Attaching container files of the .kde extension somewhat differs
from attaching container files of any other extension (see Item 4.2.4
on Page 28).
While using these files, you can change the names and extensions
of the containers using the tools of the operating system.
Container size. The size of the volume. The size is specified in
megabytes.
Password, Confirm, Password hint. Specify a password to access
the protected container and a hint for your password (optional). You
will need these parameters to access the container
Note:
See password and hint recommendations in Item 1.4 on Page 8.
3. When all necessary parameters are specified, click OK.
When the protected container is created, you will be asked to attach the container
(Item 4.2.4 on Page 28) and format it (Item 4.2.5 on Page 30).
Page 28

28 Kaspersky KryptoStorage 1.0
4.2.2. Preparing a Container for Use
To prepare a container for use, you must:
1. Attach the container (Item 4.2.4 on Page 28).
2. Format the volume to which the protected container is attached
(Item 4.2.5 on Page 30).
4.2.3. Rules for Using Protected
Containers
You can use the contents of a protected container only after the container is
attached.
Attention!
You can attach and use the protected containers if Kaspersky KryptoStorage is
installed on your computer and the Protected containers subsystem is running.
An attached container is not protected and available to all users who work at this
computer. Therefore, you must detach a protected object after you finish using it.
While using a protected container, remember that all files and folders which are
located inside the container are encrypted and they are protected objects too.
However, if you move the objects outside the container, the objects become
unprotected.
4.2.4. Attaching a Container
You can use the contents of a protected container only after the container is
attached.
To attach a protected container:
1. Select a protected container.
2. Right-click the selected container and from the opened context menu
select Kaspersky KryptoStorage ► Attach container.
Note:
If the extension of a container file is .kde (displayed as the icon .),
you can attach the container by double clicking it.
Page 29

29 Kaspersky KryptoStorage 1.0
3. In the opened dialog window, type the password to access the protected
container.
4. Click OK.
The system displays the dialog window Container parameters (Figure 7).
Figure 7. Specifying parameters of a protected container
5. In the opened dialog window specify the parameters to attach the
container:
Mount point. Select a mount point for the protected container. A
mount point can be a logical disk (you can specify any free character of
volume).
Mount mode. Specify the parameters for attaching the container
(grayed out if the container is not formatted yet):
Mount in read-only mode. If the check-box is selected, all
contents of the protected container are available only for reading.
Adding or deleting data are not permitted.
Note:
The check-box is selected automatically and cannot be cleared if
the container file has the Read-only attribute.
Microsoft Windows 2000 does not support the Read-only mode for
the NTFS-formatted protected containers.
Mount as removable disk. By default, a protected container can
be attached as a removable disk (it is displayed in the list of
removable devices in My Computer). However, if you clear the
check-box, the protected container is attached as a fixed disk (it is
displayed in the fixed disk list in My Computer).
Page 30

30 Kaspersky KryptoStorage 1.0
6. When the parameters are specified, click OK.
If you attach a container which has not been formatted yet, you will be asked to
format the container. Click Yes to start the formatting (see Item 4.2.5 on Page 30).
4.2.5. Formatting a Container
Attention!
While formatting a disk to which a protected container is attached, all data inside
the container is deleted.
A user of a protected container can format an attached container in a way similar
to formatting of a disk. The container is formatted using the standard tools of
Microsoft Windows. When specifying parameters for formatting, consider the
following:
You should not attach the container in the read-only mode.
To format a container to FAT or FAT32 in Microsoft Windows 2000, you
must attach the container as a removable disk (when attaching the
container, select the Mount as removable disk check box).
If you do a full format, the file of a protected container will have the size
specified while creating the container.
If you do a quick format and select the FAT, FAT32 or exFAT file systems,
the size of a protected container is minimized and it increases while you fill
the container with data. This feature saves free disk space.
If you do a quick format and select the NTFS file system, then the container
file will have the size which you specify when creating the container.
Note:
Regardless of the formatting type, the size of a protected container which is
mounted as a virtual disk is always equal to the size specified while creating the
container. But the size of the container file can change.
Attention!
When using a container whose file size increases while you fill it with data, the
volume containing the file of the protected container may run out of free space. In
this case you will be asked to save data in another place. If the volume where you
want to save the data is not protected, the data will not be protected either. If you
place the data to the protected area (on other protected volume or removable
device), the data is protected as an object placed within a protected area.
Page 31

31 Kaspersky KryptoStorage 1.0
4.2.6. Detaching a Container
Before detaching a container, you must complete all operations on objects of the
container (files, folders, protected sub-containers).
To detach a protected container:
1. Select a volume to which the protected container is attached or the file of
the protected container.
2. Right-click the selected object and from the opened context menu select
Kaspersky KryptoStorage ► Detach container.
The System requires more time to detach several protected objects
simultaneously. In some emergency situations, you may need to detach all
protected objects simultaneously. For this purpose you must save the changes
and restart or shut down the computer. After that, all protected objects will be
detached.
4.2.7. Protecting Containers from
Deletion
A protected container is a standard file which can be deleted by any user. To
prevent the unauthorized deletion of a protected container, you can place the
container file into a protected folder or protected volume.
Attention!
This kind of protection requires the Kaspersky KryptoStorage system to be
installed on your computer.
4.3. Protecting Disk Volumes and
Removable Devices
You can encrypt disk volumes (including the system and the boot volumes) and
other Mass Storage devices.
Encrypted disk volumes and removable devices have the following features:
If you encrypt the system or the boot volume, you must authorize prior to
loading the operating system to access the protected volume (for more
details, see Item 4.3.7 on Page 37).
Page 32

32 Kaspersky KryptoStorage 1.0
Moreover, if you encrypt the system volume of a hard disk using
Kaspersky KryptoStorage, you protect the crash damp file as well as the
RAM data which is saved to the system disk when the system hibernates.
If you encrypt the system volume, you prevent the leak of confidential
data through the system information which is saved on the hard disk.
You can use a protected disk or a removable device only if Kaspersky
KryptoStorage is installed on the computer and the Protected volumes
subsystem is running (see Chapter 5 on Page 42). If the subsystem is
disabled, the unprotected data on an encrypted disk or a removable disk
cannot be accessed. The operating system displays this volume as an
unformatted volume or a volume containing errors. If the system and/or
the boot volume of a hard disk is encrypted, the manager does not allow
disabling the Protected volumes subsystem.
It is not advised to use Kaspersky KryptoStorage on computers where
several operating systems are installed, to protect the disk volumes
which are used to load the installed operating systems.
The System’s data on all encrypted volumes of a physical media
(physical hard disk, Flash disk, etc) is stored in the root directory of the
first volume of the physical media in the iwcs.bin file. If the volume
containing iwcs.bin is formatted or if iwcs.bin is removed, replaced
or corrupted, you can lose access to all protected volumes of the physical
media. If the Protected volumes subsystem is running on the computer
where Kaspersky KryptoStorage is installed (see Chapter 5 on Page 42),
the System protects the iwcs.bin file from removal or modification.
Therefore, it is not advised to disable the Protected volumes subsystem if
some volumes are encrypted. If you need to format the volume
containing iwcs.bin, you must decrypt all volumes of the physical
media, format the volume and then encrypt the volumes again.
There are some limitations for encrypting disk volumes and removable disks:
You can encrypt hard disk volumes and removable storages only if the
sector size of a device is 512 bytes (the standard sector size of the
majority of devices of this kind).
Encrypting dynamic volumes is not supported.
You can encrypt only local disks. Encrypting network disks is not
supported.
You cannot simultaneously encrypt\decrypt\re-encrypt several volumes of
a hard disk. But you can simultaneously use the volumes of different
disks.
You can encrypt the hard disk volume where Kaspersky KryptoStorage is
installed only if the volume is the system or/and the boot volume.
Page 33

33 Kaspersky KryptoStorage 1.0
The encryption is allowed if the volume which you want to encrypt is
write-enabled.
You can start encrypting a removable disk if the removable disk is not
used by any programs. You can use the files on the removable disk while
the removable disk is being encrypted.
In Windows 7, if you physically attach a protected removable USB device,
the operating system reports that the device is not formatted and does
not allow the access to the device till the device is attached by means of
the System (see Item 4.3.8 on Page 38).
The System does not support the direct encryption of CD/DVD disks. At
the same time, you can use CD/DVD disks to store protected containers
(see Item 4.2 on Page 25).
4.3.1. Specific Features of Using Hard
Disk Management Utilities
Some utilities allow you to change the size of disk volumes. Do not change sizes
of hard disk volumes protected with Kaspersky KryptoStorage. It may lead to data
loss.
If you need to change the size of a volume, you must first decrypt all protected
volumes, reallocate free disk space and then encrypt the volumes again.
4.3.2. Encrypting Disk Volumes and
Removable Disks
Attention!
Before encrypting, read about the rules of encrypting disk volumes and removable
devices (see item 4.3 on Page 31).
Disk volumes and removable devices are encrypted in the background mode.
Consequently, you can continue using the device while the encryption process is
running.
If necessary, the encryption process can be interrupted (Item 4.3.3 on Page 35).
You can resume the encryption later (see Item 4.3.4 on Page 36), or cancel it (see
Item 4.3.5 on Page 36).
Page 34

34 Kaspersky KryptoStorage 1.0
Note:
When a computer hibernates or goes into Standby mode, the encryption process
is automatically interrupted. After the computer returns from Hibernation or
Standby mode, you can resume the encryption or cancel it.
To encrypt a disk volume or a removable disk:
1. Complete one of the following steps:
In the Explorer, select an object (a volume of a hard disk or a
removable disk) to encrypt. Right-click the selected object and from the
opened context menu select Kaspersky KryptoStorage ► Encrypt
volume.
Run the Kaspersky KryptoStorage manager: from the Start menu
select Programs ► Kaspersky KryptoStorage► Kaspersky
KryptoStorage. In the opened window select Encrypt volume…,
specify a volume which must be protected and click OK.
As the result, the dialog window Encrypt volume will be displayed
(Figure 8).
Figure 8 Protecting a volume
2. In this window, specify the parameters of the volume:
Volume name. Specify the name of the volume which will be
protected. You can specify a different volume by clicking Select
volume.
Page 35

35 Kaspersky KryptoStorage 1.0
Password, Confirm, Password hint. Specify the password to access
the protected volume and a hint for your password (optional). You will
need these parameters to access the volume
Note:
See password and hint recommendations in Item 1.4 on Page 8.
3. When all necessary parameters are specified, click OK.
After that, the System starts encrypting the object. From this moment the
volume (removable disk) is a protected object.
Attention!
If the system and/or the boot volume is encrypted, then you must be authorized
prior to loading the operating system (for more details, see Item 4.3.7 on
Page 37). Authorization is required every time you start or restart the computer
and also when the computer returns from hibernation or Standby mode.
4.3.3. Interrupting Encryption
In some cases you may need to interrupt the encryption manually or the
encryption is interrupted due to a fatal error (for example, when the computer’s
power is unexpectedly turned off). You can resume the encryption later.
Attention!
A volume (a removable disk) is a protected object regardless of whether it is fully
protected or partially. Consequently, if you interrupt the encryption, you can use
the volume (or the removable device) only after attaching it (successful
authorization). At the same time, if the encryption is not completed some data on
the volume remains unencrypted.
To interrupt the encryption process:
1. Select an object which is being encrypted.
2. Complete one of the following steps:
In the dialog window displaying progress of the encryption, click Stop.
Right-click the selected object and in the opened context menu select
Kaspersky KryptoStorage ► Stop.
3. In the opened dialog window, type the Password to access the protected
object. Click OK.
The encryption process is interrupted. The protected disk (removable device)
remains attached and you can continue using it.
Page 36

36 Kaspersky KryptoStorage 1.0
4.3.4. Resuming Encryption
An object is safely protected only after the encryption process is completed. If you
interrupt the encryption for some reason, some data remains unprotected. You
can continue encrypting using a special function.
To resume the encryption:
1. Select an object which is partially encrypted.
2. If necessary, attach the protected object (Item 4.3.8 on Page 38).
3. Right-click the selected object and from the opened context menu, select
Kaspersky KryptoStorage ► Continue volume encryption.
4. In the opened dialog window, type the Password to access the protected
object. Click OK.
The encryption process resumes. The protected disk (removable device) remains
attached and you can continue using it.
4.3.5. Rolling back to the Unencrypted
State
If you interrupt the encryption, you can cancel it and roll the object back to the
unprotected state.
To cancel the encryption and roll back to the unprotected state:
1. Select an object which is partially encrypted.
2. If necessary, attach the protected object (Item 4.3.8 on Page 38).
3. Right-click the selected object and from the opened context menu select
Kaspersky KryptoStorage ► Rollback volume encryption.
4. In the opened dialog window type the Password to access the protected
object. Click OK.
After that, the roll back process starts. The protected disk (removable device)
remains attached and you can continue using it.
Page 37

37 Kaspersky KryptoStorage 1.0
4.3.6. Decrypting Objects
This operation is available only if the object (a disk volume or a removable device)
is attached (for more information about how to attach a protected object, see
Item 4.3.8 on Page 38).
Note:
You can decrypt only one volume of a physical disk. Several protected volumes
are decrypted one-by-one.
To decrypt an object:
1. Select an object to decrypt.
2. Right-click the selected object and from the opened context menu select
Kaspersky KryptoStorage ► Decrypt volume.
3. In the opened dialog window, type the Password to access the protected
object. Click OK.
Disk volumes and removable devices are decrypted in the background mode.
Consequently, you can continue using the volume while the decryption process is
running.
If necessary, you can interrupt the decryption. The canceling of the decryption
process is identical to the canceling encryption (Item 4.3.3 on Page 35).
Decryption can be resumed later. Resuming decryption is identical to resuming
encryption (Item 4.3.4 on Page 36).
Moreover, you can cancel the decryption and roll the object back to the previous
state. The procedure of rolling back is identical to rolling back to the unencrypted
state (Item 4.3.5 on Page 36). After you cancel the decryption, the object remains
encrypted.
4.3.7. Starting up Using Protected
System Volume and/or Boot Volume
If a system and/or a boot volume is protected with Kaspersky KryptoStorage, you
must attach the volume to load the operating system. To attach a protected
volume, you must be authorized prior to loading the system.
To attach a protected system and/or boot volume:
type your Password to access the protected object.
Page 38

38 Kaspersky KryptoStorage 1.0
Note:
If the system and the boot volumes are located on different volumes on your
computer and the both volumes are protected, you must attach each volume.
After that, a user must be authorized. If the authorization is successful the
operating system, installed on a protected volume, starts up.
Note:
If you type an incorrect password while authorizing, the System displays the
notification that the password is incorrect and a password hint, if you specified it
while selecting the password. You will be asked to type your password again. If
you have not specified the password hint, you must restart the computer using the
<CTRL+ALT+DEL> key combination to repeat the authorization.
4.3.8. Attaching the Protected
Volumes of Hard Disks and Removable
Devices
You can use a protected volume (reading, writing, renaming, copying, deleting and
etc.) only if the object is attached.
To attach a protected volume of a hard disk or a removable storage:
1. Select a protected volume to attach.
2. Right-click the selected object and from the opened context menu select
Kaspersky KryptoStorage ► Attach volume.
3. In the opened dialog window, type the password to access the protected
volume. Click OK.
If the object is attached, it is not protected and available to all users who use this
computer. Therefore, it is advised to detach the object after using it.
Page 39

39 Kaspersky KryptoStorage 1.0
4.3.9. Detaching the Protected
Volumes of Hard Disks and Removable
Devices
When you detach a protected object, the object is transited to the state in which it
cannot be used until you attach it again.
Attention!
Before detaching an object, save all changes and finish using the object.
You cannot detach a protected system and/or boot volume while using it.
To detach a protected volume of a hard disk or a removable storage:
1. Select a protected object (a disk volume or a removable storage) to
detach.
2. Right-click the selected file or folder and from the opened context menu
select Kaspersky KryptoStorage ► Detach volume.
The System requires more time to detach several protected objects
simultaneously. In some emergency situations, you may need to detach all
protected objects simultaneously. For this purpose you must save the changes
and restart or shut down the computer. After that, all protected objects (including
the system and/or the boot volumes) will be detached.
4.3.10. Disk Recovery
Attention!
You must have administrator rights to the computer to use the disk recovery
feature.
From the window of the Kaspersky KryptoStorage manager, you can access a
feature which cleans the space on a hard disk, Flash drives, USB mass storage
devices used by protected volumes when the access to the volumes cannot be
recovered.
You may need to delete the data on a protected volume without decrypting it,
when:
You have lost the access keys to the protected volume and consequently
cannot attach or decrypt it.
Page 40

40 Kaspersky KryptoStorage 1.0
The protected volume is formatted without using Kaspersky KryptoStorage
and its subsystem Protected volumes. As a consequence, all of the data of
this volume is lost, but the record made by the System that the volume
exists on the disk still remains. You can access this volume on a computer
where Kaspersky KryptoStorage is installed and the Protected volumes
subsystem is running after you delete the information about protection. For
example, you may need to access the volume if unencrypted data is written
to the volume after the volume has been formatted.
The size of a protected volume is changed (see Item 4.3.1 on Page 33). As
a consequence, the size allocated by the System does not correspond to
the real size of the protected volume.
You cannot access the abovementioned protected volumes, if the Protected
volumes (see Chapter 5 on Page 42) subsystem is running on a computer where
Kaspersky KryptoStorage is installed. Moreover, the space allocated for the
volumes on a disk cannot be used. With the feature, you can make this space
available for use including for use by Kaspersky KryptoStorage.
You must complete the following steps before using the recovery feature:
1. Complete all operations on encrypting, re-encrypting and decrypting
volumes of the physical disk.
2. Detach the protected volumes of the physical disk whose information you
want to delete from the System using the recovery feature.
Attention!
Be attentive when selecting a protected volume. After the System’s information
about the protected volume is deleted, the data on this volume cannot be
decrypted. Therefore, if the volume is encrypted, it will look like an unformatted
volume.
To make the disk space used by a protected volume available:
1. Run the Kaspersky KryptoStorage manager. From the Start menu, select
Programs ► Kaspersky KryptoStorage ► Kaspersky KryptoStorage.
2. In the window of the Kaspersky KryptoStorage manager, click Disk
recovery.
3. In the Disk recovery window, select a protected volume to delete
System’s information about it. Right-click the selected volume and from
the opened context menu select Delete information about encrypted
area.
Page 41

41 Kaspersky KryptoStorage 1.0
4.4. Wiping Protected and
Unprotected Objects
Files and folders which you delete with the standard operations can be restored
using special utilities. Consequently, the data stored in the deleted object can be
accessed by unauthorized persons. This problem is solved by wiping.
Wiping is available both for protected and unprotected objects.
Attention!
When a folder is wiped, its subfolders and all files in its subfolders will be deleted
A protected folder can be wiped only after attaching.
A protected container can be wiped only after detaching.
To wipe a file or folder:
1. Select an object (a file, folder or protected container) to wipe.
2. Right-click the selected object and from the opened context menu select
Kaspersky KryptoStorage ► Wipe.
3. In the opened confirmation window click Yes.
Page 42

42 Kaspersky KryptoStorage 1.0
Subsystem
Purpose
Protected volumes
Protects volumes of a hard disk and
removable devices
Protected containers
Creates protected containers, allows
for the use of the protected containers
Protected folders
Creates protected folders, allows for
the use of the protected folders
CHAPTER 5. CONFIGURING
SUBSYSTEMS
Kaspersky KryptoStorage consists of three subsystems which protect objects of
specific types. The purposes of the subsystems are described in the table.
The Kaspersky KryptoStorage manager is intended to configure the subsystems
included in Kaspersky KryptoStorage.
To open the window of the Kaspersky KryptoStorage manager, from the Start
menu, select Programs ► Kaspersky KryptoStorage► Kaspersky
KryptoStorage.
The window containing data on the Kaspersky KryptoStorage subsystems which
are installed on your computer is displayed (Figure 9).
Page 43

43 Kaspersky KryptoStorage 1.0
Figure 9 Configuring Kaspersky KryptoStorage subsystems
To the right of the subsystem’s name there is the Autorun field. If the check-box
in the field is selected, the autorun of the subsystem is enabled.
After Kaspersky KryptoStorage is installed, the autorun option is enabled for all
subsystems. However, you can change the autorun parameters of each
subsystem:
to disable autorun, clear the Autorun check-box;
to enable autorun, select the Autorun check-box.
Note:
The autorun settings come into effect after you restart the computer.
When disabling the autorun option of the subsystems, you must consider the
operating specifics of the Kaspersky KryptoStorage subsystems. The table
describes the consequences which arise from disabling the subsystems.
Page 44

44 Kaspersky KryptoStorage 1.0
Subsystem
The result of disabling the subsystem
Protected volumes
The operating system identifies protected volumes as
unformatted volumes. The contents are encrypted.
The functions of the System for using disk volumes and
removable devices are not available.
Note: You cannot disable the subsystem if the system
and/or the boot volumes are protected.
Protected containers
The contents of protected containers cannot be used.
The contents are encrypted.
The functions of the System for using the protected
containers are not available
Protected folders
The protected files and folders in these folders can be
deleted from the computer by any user.
The contents of files are encrypted; you can view only
the structure of subfolders.
The functions of the System for using protected files and
folders are not available.
Page 45

45 Kaspersky KryptoStorage 1.0
CHAPTER 6. UNINSTALLING
KASPERSKY
KRYPTOSTORAGE
If Kaspersky KryptoStorage is uninstalled it means that all subsystems are
disabled for all protected objects (see Chapter 5 on Page 42):
The protected files and folders in these folders can be deleted from the
computer by any user. The contents of files are encrypted; you can view
only the structure of subfolders.
The containers remain protected, but you cannot use them because the
containers cannot be attached.
The disk volumes and removable devices remain protected. However,
you cannot access the data stored on the devices because they cannot
be attached.
Attention!
The operating system displays these objects as the unformatted objects and when
you try to access a protected object, you are prompted to format the objects. Once
the object formatting is done all data is deleted. Therefore, if the object contains
important data, you must cancel the formatting.
The System must not be removed if the system and/or the boot volume of hard
disk is protected. If you uninstall the System, the operating system cannot be
loaded and consequently the data stored on the disk cannot be accessed.
Before uninstalling the System, complete the preliminary steps:
Decrypt the system and/or the boot volumes, non-system volumes and
removable disks.
Attach the protected containers and folders and copy the contents of
these containers and folders to unprotected hard disks and removable
media.
Attention!
You must have administrator rights to the computer to uninstall Kaspersky
KryptoStorage.
Kaspersky KryptoStorage is uninstalled using Microsoft Windows standard tools.
Page 46

46 Kaspersky KryptoStorage 1.0
To uninstall Kaspersky KryptoStorage:
1. Open the Add or Remove programs tool. To do this, from the Start
menu select Settings ► Control Panel. In the control panel, double-click
the Add or Remove Programs icon.
2. In the Add or Remove Programs window, select Kaspersky
KryptoStorage and click Remove.
You must restart the computer to finish uninstalling the System.
Page 47

47 Kaspersky KryptoStorage 1.0
Confidential data
The data with restricted access. Confidential data can be accessed by
the users on a need-to-know basis.
Kaspersky KryptoStorage
A system which is intended to cryptographically protect confidential
information stored on a user’s computer from unauthorized access.
Password
A combination of characters which is used to access the contents of a
protected object. A user must keep the password secret.
Protected container
A file of a specific format which is displayed by the System as a virtual
volume. Data is located in the file.
Protected object
Protected objects are any objects which are intended for storing data
and are encrypted with Kaspersky KryptoStorage.
Protection of information
Preventive measures to limit access of users (user groups) to
information.
Transparent encryption
A mechanism which enables storage of information in the encrypted
form inside of a protected object. The protected data is processed in
the following way: the data is automatically decrypted in RAM when
requested and the uploaded data is encrypted.
Wiping of an object
A function of wiping files and folders which deletes the name of an
object from the file system as well as wipes the contents of the deleted
object.
APPENDIX A. GLOSSARY
Page 48

48 Kaspersky KryptoStorage 1.0
Technical support
Please find the technical support information at
http://support.kaspersky.com/
Helpdesk: http://support.kaspersky.com/helpdesk
General information
WWW: http://www.kaspersky.com
E-mail: info@kaspersky.com
APPENDIX B. REFERENCE
INFORMATION
B.1. Contact Us
If you have any questions, comments, or suggestions, please refer them to one of
our distributors or directly to Kaspersky Lab. We will be glad to assist you in any
matters related to our product by phone or via email. Rest assured that all of your
recommendations and suggestions will be thoroughly reviewed and considered.
B.2. License for the Windows
Installer XML (WiX) Library
Kaspersky KryptoStorage uses the Windows Installer XML (WiX) 3.0 library,
Copyright (c) 2005-2008 Microsoft Corporation under the license CPL 1.0
Distribution kit: http://sourceforge.net/projects/wix/
This Appendix contains the license text for Windows Installer XML (WiX) Library
version 3.0 Copyright (c) 2005-2008 Microsoft Corporation.
Note:
The license text is copied from the source:
http://www.opensource.org/licenses/cpl1.0.php.
Page 49

49 Kaspersky KryptoStorage 1.0
Common Public License Version 1.0
THE ACCOMPANYING PROGRAM IS PROVIDED UNDER THE TERMS OF
THIS COMMON PUBLICLICENSE ("AGREEMENT"). ANY USE,
REPRODUCTION OR DISTRIBUTION OF THE PROGRAMCONSTITUTES
RECIPIENT'S ACCEPTANCE OF THIS AGREEMENT.
1. DEFINITIONS
"Contribution" means:
a) in the case of the initial Contributor, the initial code and documentation
distributed under this Agreement, and
b) in the case of each subsequent Contributor:
i) changes to the Program, and
ii) additions to the Program;
where such changes and/or additions to the Program originate from and
are distributed by that particular Contributor. A Contribution 'originates'
from a Contributor if it was added to the Program by such Contributor itself
or anyone acting on such Contributor's behalf. Contributions do not include
additions to the Program which: (i) are separate modules of software
distributed in conjunction with the Program under their own license
agreement, and (ii) are not derivative works of the Program.
"Contributor" means any person or entity that distributes the Program.
"Licensed Patents " mean patent claims licensable by a Contributor which are
necessarily infringed by the use or sale of its Contribution alone or when combined
with the Program.
"Program" means the Contributions distributed in accordance with this Agreement.
"Recipient" means anyone who receives the Program under this Agreement,
including all Contributors.
2. GRANT OF RIGHTS
a) Subject to the terms of this Agreement, each Contributor hereby grants
Recipient a non-exclusive, worldwide, royalty-free copyright license to
reproduce, prepare derivative works of, publicly display, publicly perform,
distribute and sublicense the Contribution of such Contributor, if any, and
such derivative works, in source code and object code form.
Page 50

50 Kaspersky KryptoStorage 1.0
b) Subject to the terms of this Agreement, each Contributor hereby grants
Recipient a non-exclusive, worldwide, royalty-free patent license under
Licensed Patents to make, use, sell, offer to sell, import and otherwise
transfer the Contribution of such Contributor, if any, in source code and object
code form. This patent license shall apply to the combination of the
Contribution and the Program if, at the time the Contribution is added by the
Contributor, such addition of the Contribution causes such combination to be
covered by the Licensed Patents. The patent license shall not apply to any
other combinations which include the Contribution. No hardware per se is
licensed hereunder.
c) Recipient understands that although each Contributor grants the licenses to
its Contributions set forth herein, no assurances are provided by any
Contributor that the Program does not infringe the patent or other intellectual
property rights of any other entity. Each Contributor disclaims any liability to
Recipient for claims brought by any other entity based on infringement of
intellectual property rights or otherwise. As a condition to exercising the rights
and licenses granted hereunder, each Recipient hereby assumes sole
responsibility to secure any other intellectual property rights needed, if any.
For example, if a third party patent license is required to allow Recipient to
distribute the Program, it is Recipient's responsibility to acquire that license
before distributing the Program.
d) Each Contributor represents that to its knowledge it has sufficient copyright
rights in its Contribution, if any, to grant the copyright license set forth in this
Agreement.
3. REQUIREMENTS
A Contributor may choose to distribute the Program in object code form under its
own license agreement, provided that:
a) it complies with the terms and conditions of this Agreement; and
b) its license agreement:
i) effectively disclaims on behalf of all Contributors all warranties and
conditions, express and implied, including warranties or conditions of title
and non-infringement, and implied warranties or conditions of
merchantability and fitness for a particular purpose;
ii) effectively excludes on behalf of all Contributors all liability for damages,
including direct, indirect, special, incidental and consequential damages,
such as lost profits;
iii) states that any provisions which differ from this Agreement are offered
by that Contributor alone and not by any other party; and
iv) states that source code for the Program is available from such
Contributor, and informs licensees how to obtain it in a reasonable manner
on or through a medium customarily used for software exchange.
Page 51

51 Kaspersky KryptoStorage 1.0
When the Program is made available in source code form:
a) it must be made available under this Agreement; and
b) a copy of this Agreement must be included with each copy of the Program.
Contributors may not remove or alter any copyright notices contained within the
Program.
Each Contributor must identify itself as the originator of its Contribution, if any, in a
manner that reasonably allows subsequent Recipients to identify the originator of
the Contribution.
4. COMMERCIAL DISTRIBUTION
Commercial distributors of software may accept certain responsibilities with
respect to end users, business partners and the like. While this license is intended
to facilitate the commercial use of the Program, the Contributor who includes the
Program in a commercial product offering should do so in a manner which does
not create potential liability for other Contributors. Therefore, if a Contributor
includes the Program in a commercial product offering, such Contributor
("Commercial Contributor") hereby agrees to defend and indemnify every other
Contributor ("Indemnified Contributor") against any losses, damages and costs
(collectively "Losses") arising from claims, lawsuits and other legal actions brought
by a third party against the Indemnified Contributor to the extent caused by the
acts or omissions of such Commercial Contributor in connection with its
distribution of the Program in a commercial product offering. The obligations in this
section do not apply to any claims or Losses relating to any actual or alleged
intellectual property infringement. In order to qualify, an Indemnified Contributor
must: a) promptly notify the Commercial Contributor in writing of such claim, and
b) allow the Commercial Contributor to control, and cooperate with the
Commercial Contributor in, the defense and any related settlement negotiations.
The Indemnified Contributor may participate in any such claim at its own expense.
For example, a Contributor might include the Program in a commercial product
offering, Product X. That Contributor is then a Commercial Contributor. If that
Commercial Contributor then makes performance claims, or offers warranties
related to Product X, those performance claims and warranties are such
Commercial Contributor's responsibility alone. Under this section, the Commercial
Contributor would have to defend claims against the other Contributors related to
those performance claims and warranties, and if a court requires any other
Contributor to pay any damages as a result, the Commercial Contributor must pay
those damages.
Page 52

52 Kaspersky KryptoStorage 1.0
5. NO WARRANTY
EXCEPT AS EXPRESSLY SET FORTH IN THIS AGREEMENT, THE PROGRAM
IS PROVIDED ON AN "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR
CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, EITHER EXPRESS OR IMPLIED INCLUDING,
WITHOUT LIMITATION, ANY WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF TITLE, NONINFRINGEMENT, MERCHANTABILITY OR FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR
PURPOSE. Each Recipient is solely responsible for determining the
appropriateness of using and distributing the Program and assumes all risks
associated with its exercise of rights under this Agreement, including but not
limited to the risks and costs of program errors, compliance with applicable laws,
damage to or loss of data, programs or equipment, and unavailability or
interruption of operations.
6. DISCLAIMER OF LIABILITY
EXCEPT AS EXPRESSLY SET FORTH IN THIS AGREEMENT, NEITHER
RECIPIENT NOR ANY CONTRIBUTORS SHALL HAVE ANY LIABILITY FOR
ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT, INCIDENTAL, SPECIAL, EXEMPLARY, OR
CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES (INCLUDING WITHOUT LIMITATION LOST
PROFITS), HOWEVER CAUSED AND ON ANY THEORY OF LIABILITY,
WHETHER IN CONTRACT, STRICT LIABILITY, OR TORT (INCLUDING
NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE) ARISING IN ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE OR
DISTRIBUTION OF THE PROGRAM OR THE EXERCISE OF ANY RIGHTS
GRANTED HEREUNDER, EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH
DAMAGES.
7. GENERAL
If any provision of this Agreement is invalid or unenforceable under applicable law,
it shall not affect the validity or enforceability of the remainder of the terms of this
Agreement, and without further action by the parties hereto, such provision shall
be reformed to the minimum extent necessary to make such provision valid and
enforceable.
If Recipient institutes patent litigation against a Contributor with respect to a patent
applicable to software (including a cross-claim or counterclaim in a lawsuit), then
any patent licenses granted by that Contributor to such Recipient under this
Agreement shall terminate as of the date such litigation is filed. In addition, if
Recipient institutes patent litigation against any entity (including a cross-claim or
counterclaim in a lawsuit) alleging that the Program itself (excluding combinations
of the Program with other software or hardware) infringes such Recipient's
patent(s), then such Recipient's rights granted under Section 2(b) shall terminate
as of the date such litigation is filed.
Page 53

53 Kaspersky KryptoStorage 1.0
All Recipient's rights under this Agreement shall terminate if it fails to comply with
any of the material terms or conditions of this Agreement and does not cure such
failure in a reasonable period of time after becoming aware of such
noncompliance. If all Recipient's rights under this Agreement terminate, Recipient
agrees to cease use and distribution of the Program as soon as reasonably
practicable. However, Recipient's obligations under this Agreement and any
licenses granted by Recipient relating to the Program shall continue and survive.
Everyone is permitted to copy and distribute copies of this Agreement, but in order
to avoid inconsistency the Agreement is copyrighted and may only be modified in
the following manner. The Agreement Steward reserves the right to publish new
versions (including revisions) of this Agreement from time to time. No one other
than the Agreement Steward has the right to modify this Agreement. IBM is the
initial Agreement Steward. IBM may assign the responsibility to serve as the
Agreement Steward to a suitable separate entity. Each new version of the
Agreement will be given a distinguishing version number. The Program (including
Contributions) may always be distributed subject to the version of the Agreement
under which it was received. In addition, after a new version of the Agreement is
published, Contributor may elect to distribute the Program (including its
Contributions) under the new version. Except as expressly stated in Sections 2(a)
and 2(b) above, Recipient receives no rights or licenses to the intellectual property
of any Contributor under this Agreement, whether expressly, by implication,
estoppel or otherwise. All rights in the Program not expressly granted under this
Agreement are reserved.
This Agreement is governed by the laws of the State of New York and the
intellectual property laws of the United States of America. No party to this
Agreement will bring a legal action under this Agreement more than one year after
the cause of action arose. Each party waives its rights to a jury trial in any
resulting litigation.
 Loading...
Loading...