Page 1
SERVICE MANUAL
MICRO COMPONENT SYSTEM
2203620034
UX-P55
COMPACT
DIGITAL AUDIO
CD-R/RW PLAYBACK
STANDBY / ON
DISPLAYDIMMER
AUTO
SOUND
FM MODE
PRESET
MODE
CD
CD
MULTI KEY
CANCEL
PTY
DISPLAY
/EON
MODE
AHB
VOLUME
PRO
RM-SUXP5R REMOTE CONTROL
MICRO COMPONENT SYSTEM UX·P55
STANDBY / ON
STANDBY/ON
SLEEP
MD/AUX
REPEATRANDOMPROG
FM/AM
TAPE
SET
AHB PRO
SOUND
PHONES
DIRECT OPERATING
FUNCTION
CD
/
TAPE
FM/AM
REC
AUTO REVERSE
MD/AUX
CLOCK
VOLUME
TIMER
REV.MODE
REC
SP-UXP55
CA-UXP55 SP-UXP55
Area Suffix
B ----------------------------- U.K.
E --------- Continental Europe
EN ------------ Norther Europe
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 Important Safety Precautions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
2 Disassembly method . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .6
3 Adjustment. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
4 Description of major ICs. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
COPYRIGHT © 2003 VICTOR COMPANY OF JAPAN, LTD.
No.22036
2003/4
Page 2
SECTION 1
Good earth ground
d
AC VOLTMETER
Important Safety Precautions
1.1 Safety Precautions
(1) This d esign of this product co ntains special hardware and
many circuits and components specially for safety purposes. For continued protection, no changes should be made
to the original design unless authorized in writing by the
manufacturer. Replacement parts must be identical to
those used in the original circuits. Services should be performed by qualified personnel only.
(2) Alterations o f the design or circuitry of the p roduct should
not be made. Any design alterations of the product should
not be made. Any design alterations or additions will void
the manufacturers warranty and will further relieve the
manufacture of responsibility for personal injury or property
damage resulting therefrom.
(3) Many electrical and mechanical parts in the products have
special safety-related characteristics. These characteristics are often not evident from visual inspection nor can the
protection afforded by them necessarily be obtained by using replacement components rated for higher voltage, wattage, etc. Replacement parts which have these special
safety characteristics are identified in the Parts List of Service Manual. Electrical components having such features
are identified by shading on the schematics and by ( ) on
the Parts List in the Service Manual. The use of a substitute
replacement which does not have the same safety characteristics as the recommended replacement parts shown in
the Parts List of Service Manual may create shock, fire, or
other hazards.
(4) The leads in the products are routed and dressed with ties,
clamps, tubings, barriers and the like to be separated from
live parts, high temperature parts, moving parts and/or
sharp edges for the prevention of electric shock and fire
hazard. When service is required, the origin al lead routing
and dress should be observed, and it should be confirmed
that they have been returned to normal, after reassembling.
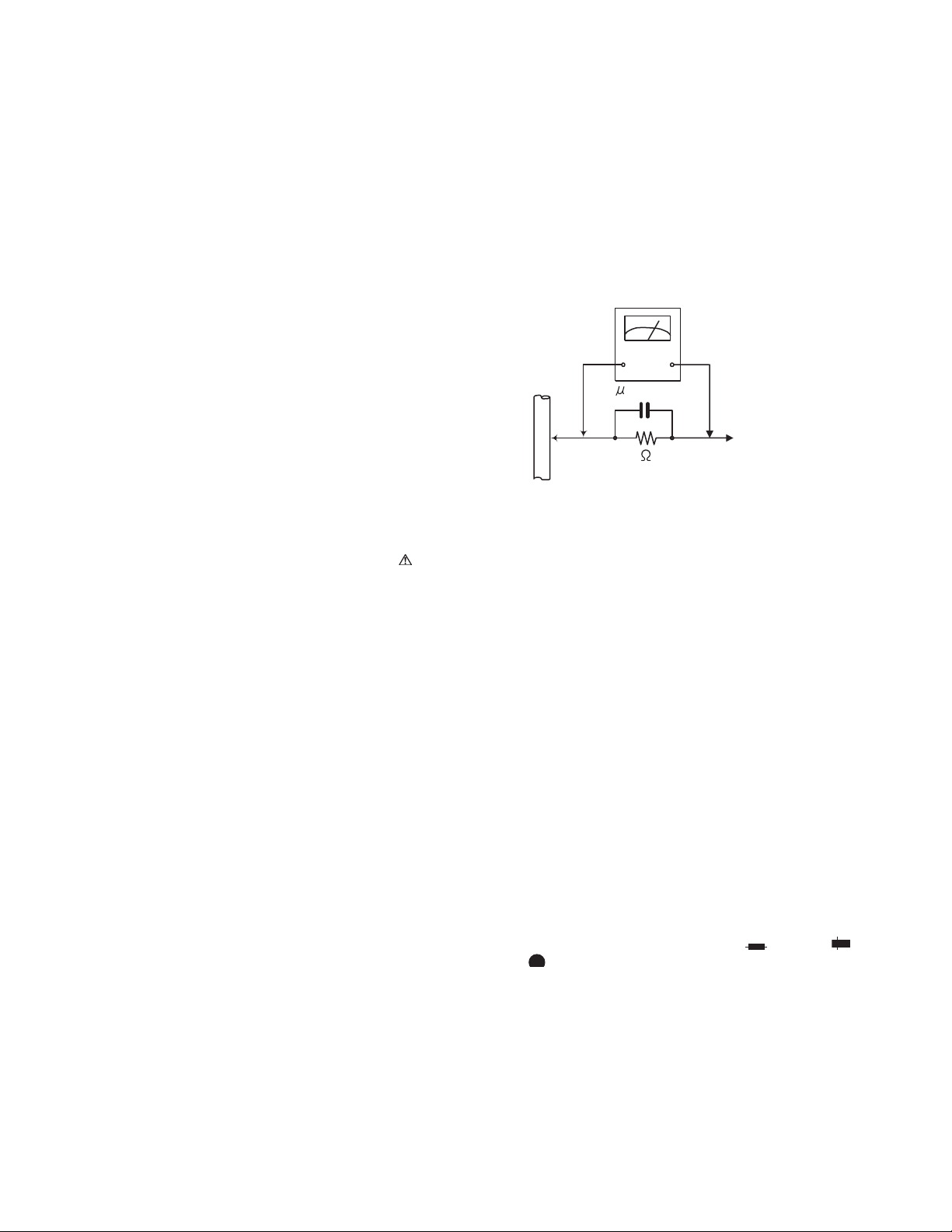
(5) Leakage shock hazard testing)
After reassembling the product, always perform an isolation check on the exposed metal parts of the product (antenna terminals, knobs, metal cabinet, screw heads,
headphone jack, control shafts, etc.) to be sure the product
is safe to operate without danger of electrical shock.Do not
use a line isolation transformer during this check.
• Plug the AC line cord directly into the AC outlet. Using a
"Leakage Current Tester", measure the leakage current
from each exposed metal parts of the cabinet, particularly any exposed metal part having a return path to the
chassis, to a known good earth ground. Any leakage current must not exceed 0.5mA AC (r.m.s.).
• Alternate check method
Plug the AC line cord directly into the AC outlet. Use an
AC voltmeter having, 1,000Ω per volt or more sensitivity
in the following manner. Connect a 1,500Ω 10W resistor
paralleled by a 0.15µF AC-type capacitor between an exposed metal part and a known good earth ground.
Measure the AC voltage across the resistor with the AC
1-2 (No.22036)
voltmeter.
Move the resistor connection to each exposed metal
part, particularly any exposed metal part having a return
path to the chassis, and measure the AC voltage across
the resistor. Now, reverse the plug in the AC outlet and
repeat each measurement. Voltage measured any must
not exceed 0.75 V AC (r.m.s.). This corresponds to 0.5µ
mA AC (r.m.s.).
(Having 1000
ohms/volts,
or more sensitivity)
0.15 F AC TYPE
Place this
probe on
1500 10W
1.2 Warning
(1) This equipment has been designed and manufactured to
meet international safety standards.
(2) It is the leg al responsibility of the repairer to ensure that
these safety standards are maintained.
(3) Repairs must be made in accordance with the relevant
safety standards.
(4) It is essential that safety critical components a re replaced
by approved parts.
(5) If mains voltage selector is provided, check setting for local
voltage.
1.3 Caution Burrs formed during molding may be left over on some parts
of the chassis.
Therefore, pay attention to such burrs in the case of preforming repair of this system.
1.4 Critical parts for safety
In regard with component parts appearing on the silk-screen
printed side (parts side) of the PWB diagrams, the parts that are
printed over with black such as the resistor ( ), diode ( )
and ICP ( ) or identified by the " " mark nearby are critical
for safety. When replacing them, be sure to use the parts of the
same type and rating as specified by the manufacturer.
(This regulation dose not Except the J and C version)
each expose
metal part.
Page 3

1.5 Safety Precautions (U.K only)
(1) This design of this product contains special hardware and many circuits and components specially for safety purposes. For con-
tinued protection, no changes should be made to the original design unless authorized in writing by the manufacturer. Replacement parts must be identical to those used in the original circuits.
(2) A ny unauthorised design alterations or additions will void the manufacturer' s guarantee; furthermore the manufacturer cannot
accept responsibility for personal injury or property damage resulting therefrom.
(3) Essential safety critical components are identified by ( ) on the Parts List and by shading on the schematics, and must never
be replaced by parts other than those listed in the manual. Please not e however that many electrical and mechanical parts in
the product have special safety related characteristics. These characteristics are often not evident from visual inspection. Parts
other than specified by the manufacturer may not have the same safety characteristics as the recommended replacement parts
shown in the Parts List of the Service Manual and may create shock, fire, or other hazards.
(4) The leads in the products are routed and dressed with ties, clamps, tubings, barriers and the like to be separated from live parts,
high temperature parts, moving parts and/or sharp edges for the prevention of electric shock and fire hazard. When service is
required, the original lead routing and dress should be observed, and it shoul d be confirmed that they have been returned to
normal, after re-assembling.
1.5.1 Warning
(1) Service should be performed by qualified personnel only.
(2) This equipment has been designed and manufactured to meet international safety standards.
(3) It is the legal responsibility of the repairer to ensure that these safety standards are maintained.
(4) Repairs must be made in accordance with the relevant safety standards.
(5) It is essential that safety critical components are replaced by approved parts.
(6) If mains voltage selector is provided, check setting for local voltage.
Burrs formed during molding may be left over on some parts of the chassis. Therefore,
pay attention to such burrs in the case of preforming repair of this system.
(No.22036)1-3
Page 4
1.6 Preventing static electricity
Electrostatic discharge (ESD), which occurs when static electricity stored in the body, fabric, etc. is discharged, can destroy the laser
diode in the traverse unit (optical pickup). Take care to prevent this when performing repairs.
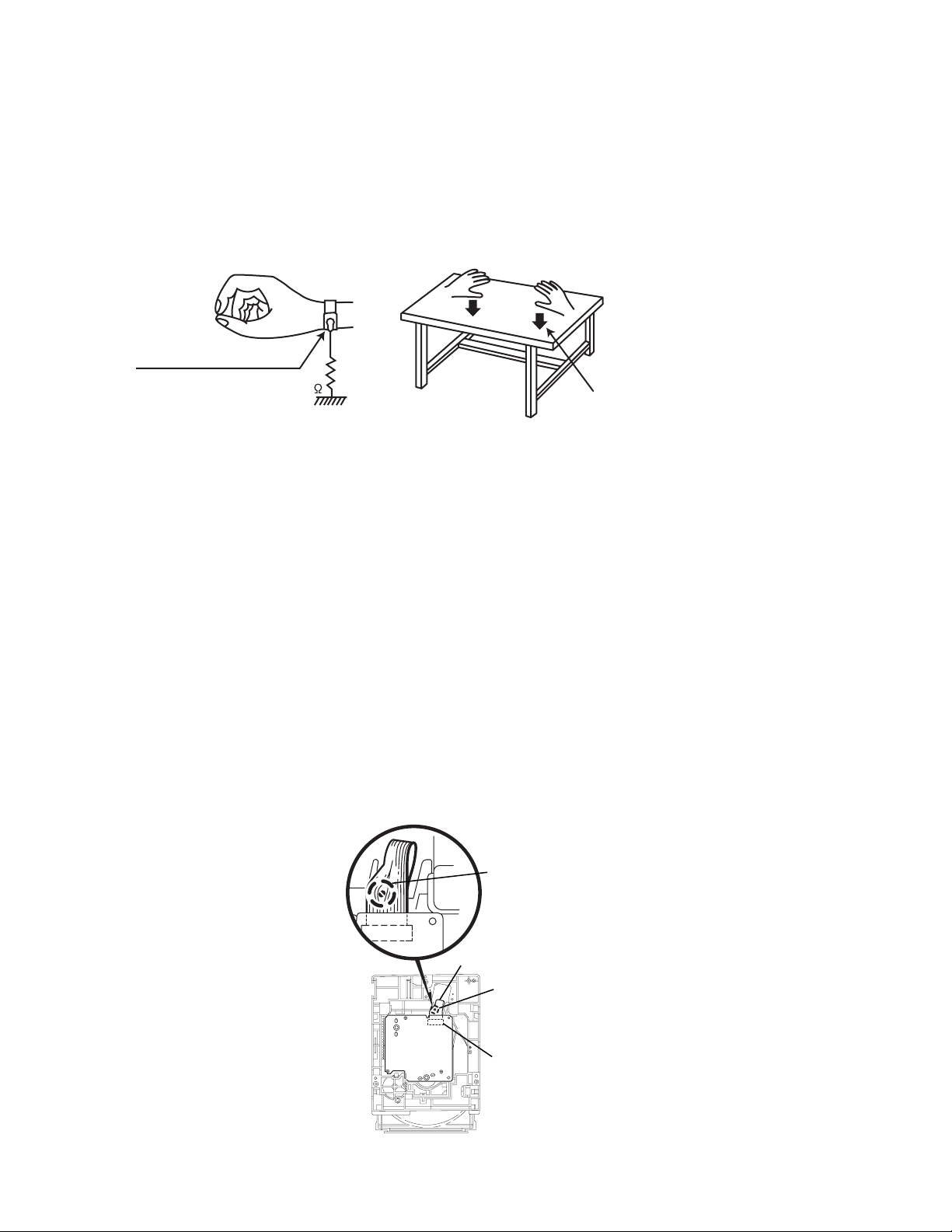
1.6.1 Grounding to prevent damage by static electricity
Static electricity in the work area can destroy the optical pickup (laser dio de) in devices such as CD players.
Be careful to use proper grounding in the area where repairs are being performed.
(1) Ground the workbench
Ground the workbench by laying conductive material (such as a conductive sh eet) or an iron plate over it before placing the
traverse unit (optical pickup) on it.
(2) Ground yourself
Use an anti-static wrist strap to release any static electricity built up in your body.
(caption)
Anti-static wrist strap
1M
Conductive material
(conductive sheet) or iron palate
(3) Handling the optical pickup
• In order to maintain quality during transport and before instal lation, both sides of the laser di ode on the replacement optica l
pickup are shorted. After replacement, return the shorted parts to their original condition.
(Refer to the text.)
• Do not use a tester to check the condition of the laser diode in the optical pickup. The tester's internal power source can easily
destroy the laser diode.
1.7 Handling the traverse unit (optical pickup)
(1) Do not subject the traverse unit (optical pickup) to strong shocks, as it is a sensitive, complex unit.
(2) Cut off the shorted part of the flexible cable using nippers, etc. after replacing the optical pickup. For specific details, refer to the
replacement procedure in the text. Remove the anti-static pin when replacing the traverse unit. Be careful not to take too long
a time when attaching it to the connector.
(3) Handle the flexible cable carefully as it may break when subjected to strong force.
(4) I t is not possible to adjust the semi-fixed resistor that adju sts the laser power. Do not turn it.
1.8 Attention when traverse unit is decomposed *Please refer to "Disassembly method" in the text for the CD pickup unit.
• Apply solder to the short land sections before the flexible wire is disconnected from the connector CN101 on the CD servo boar d.
(If the flexible wire is disconnected without applying solder, the CD pickup may be destroyed by static electricity.)
• In the assembly, be sure to remove solder from the short land sections after connecting the flexible wire.
1-4 (No.22036)
Flexible wire
Shorting round
Shorting round
CN601 on
mechanism
board
Page 5
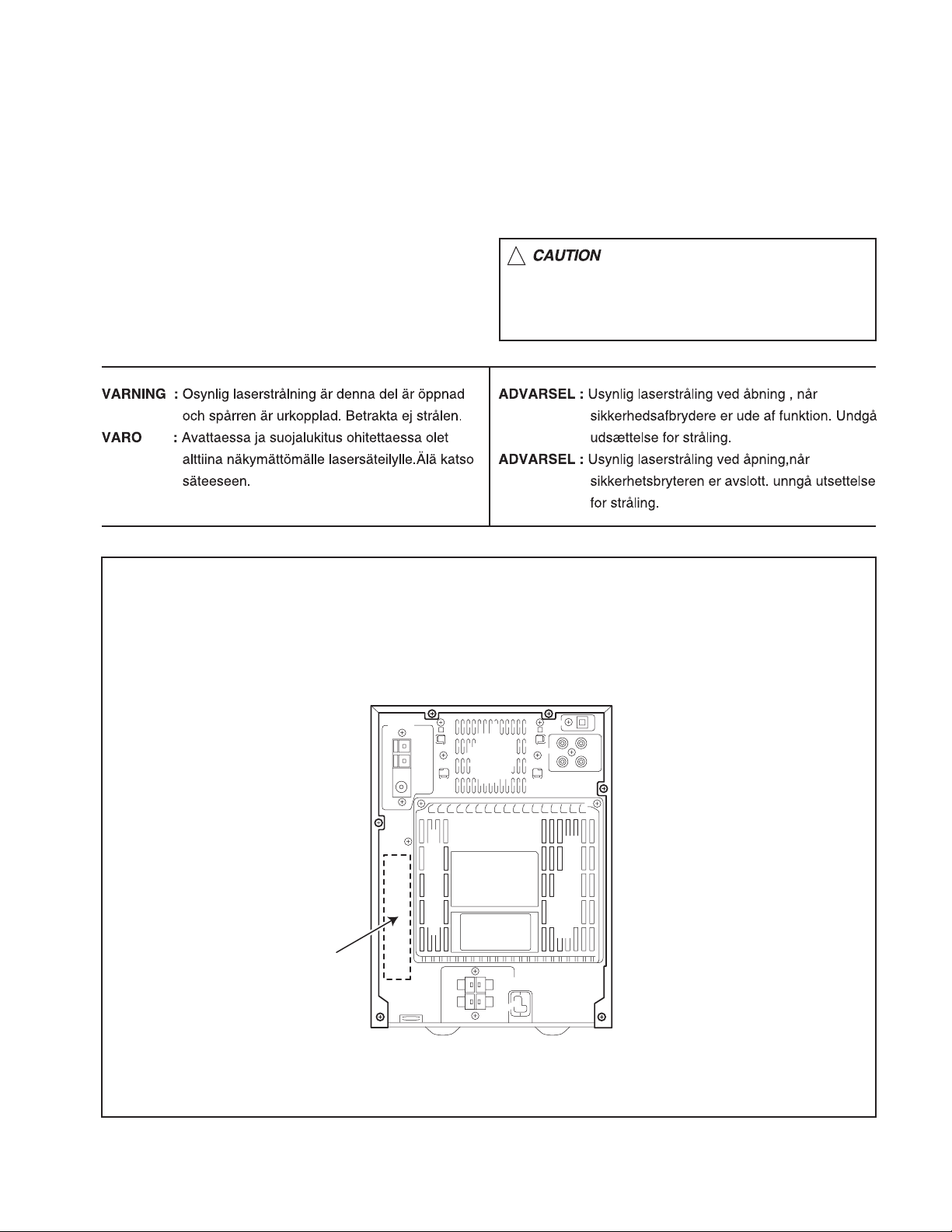
1.9 Important for laser products
1.CLASS 1 LASER PRODUCT
2.DANGER : Invisible laser radiation when open and inter
lock failed or defeated. Avoid direct exposure to beam.
3.CAUTION : There are no serviceable parts inside the
Laser Unit. Do not disassemble the Laser Unit. Replace
the complete Laser Unit if it malfunctions.
4.CAUTION : The compact disc player uses invisible laser
radiation and is equipped with safety switches which
prevent emission of radiation when the drawer is open and
the safety interlocks have failed or are de
feated. It is dangerous to defeat the safety switches.
5.CAUTION : If safety switches malfunction, the laser is able
to function.
6.CAUTION : Use of controls, adjustments or performance of
procedures other than those specified herein may result in
hazardous radiation exposure.
!
Please use enough caution not to
see the beam directly or touch it
in case of an adjustment or operation
check.
REPRODUCTION AND POSITION OF LABEL and PRINT
WARNING LABEL and PRINT
Caution
Label
(No.22036)1-5
Page 6
SECTION 2
A
A
A
A
Disassembly method
2.1 Main body
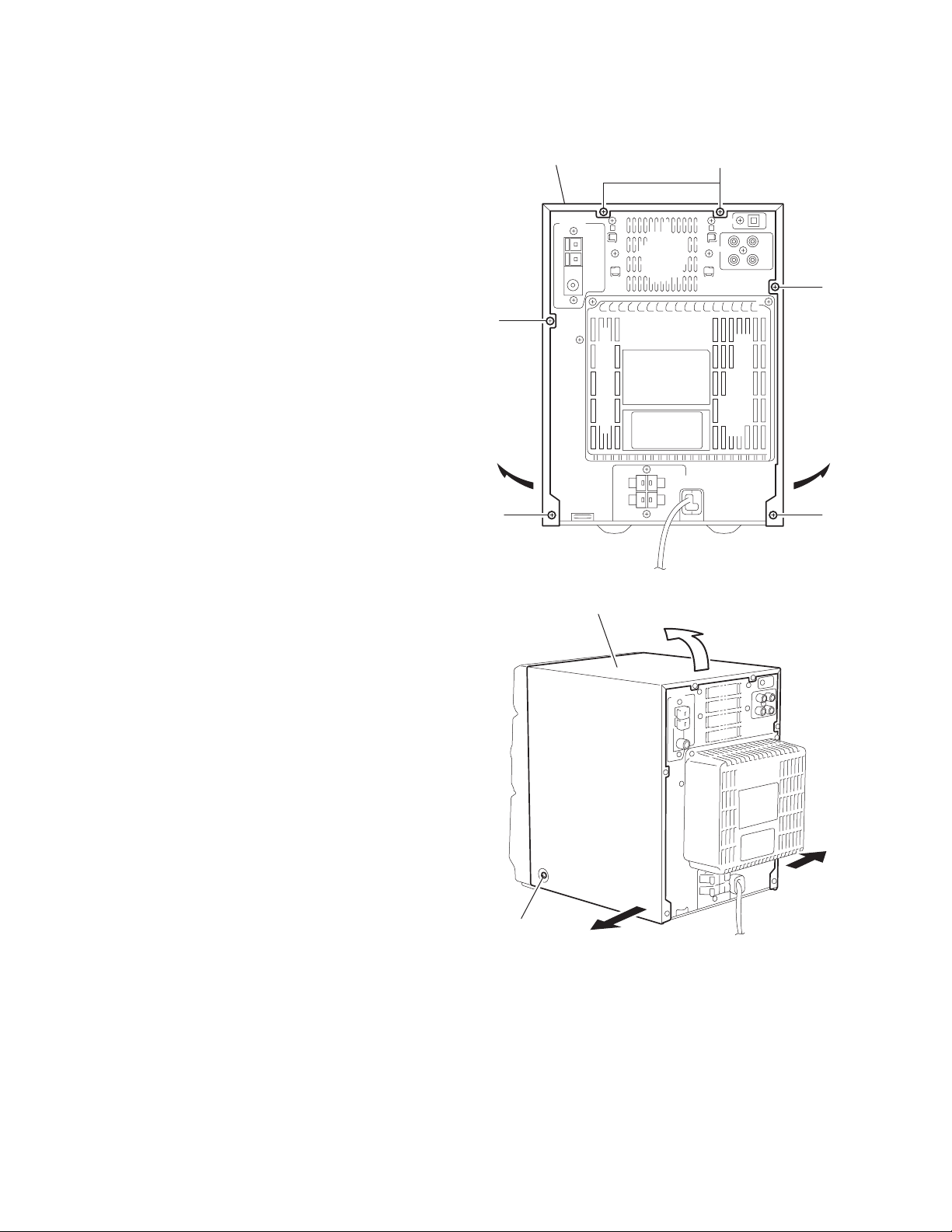
2.1.1 Removing the metal cover
(See Fig.1, 2)
(1) Remove the six screws A on the back of the body.
(2) Remove the two screws B on the side of the body.
(3) Pul l both side s of the meta l cover outward and lift the rear
part of the cover.
Metal cover
Metal cover
A
Fig.1
1-6 (No.22036)
B x 2
Fig.2
Page 7
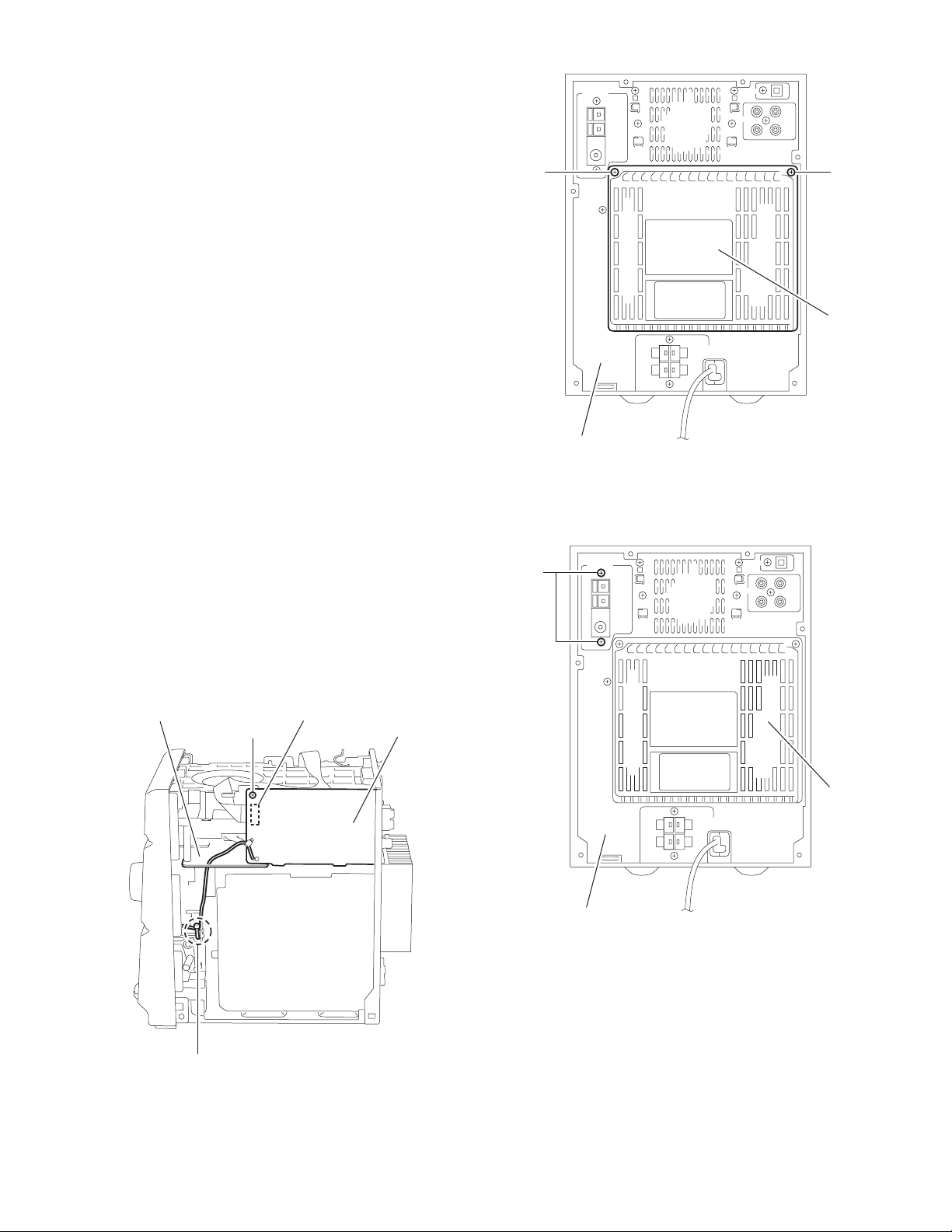
2.1.2 Removing the rear cover
r
r
(See Fig.3)
• Prior to performing the following procedure, remove the metal
cover.
(1) Remove the two screws C on the back of the body.
2.1.3 Removing the tuner board
(See Fig.4, 5)
• Prior to performing the following procedure, remove the metal
cover.
(1) Disconnect the card wire from connector CN1 on the tuner
board.
(2) Remove the screw D on the right side of the bod y.
(3) Remove the two screws E on the rear panel.
(4) Remove the b and bundling the wire and pull out the wire
through the hole of the CD-R board.
C
Rear panel
E
C
Rear cove
Fig.3
CD-R board
Band
D
Fig.4
CN 1
Tuner board
Rear cove
Rear panel
Fig.5
(No.22036)1-7
Page 8
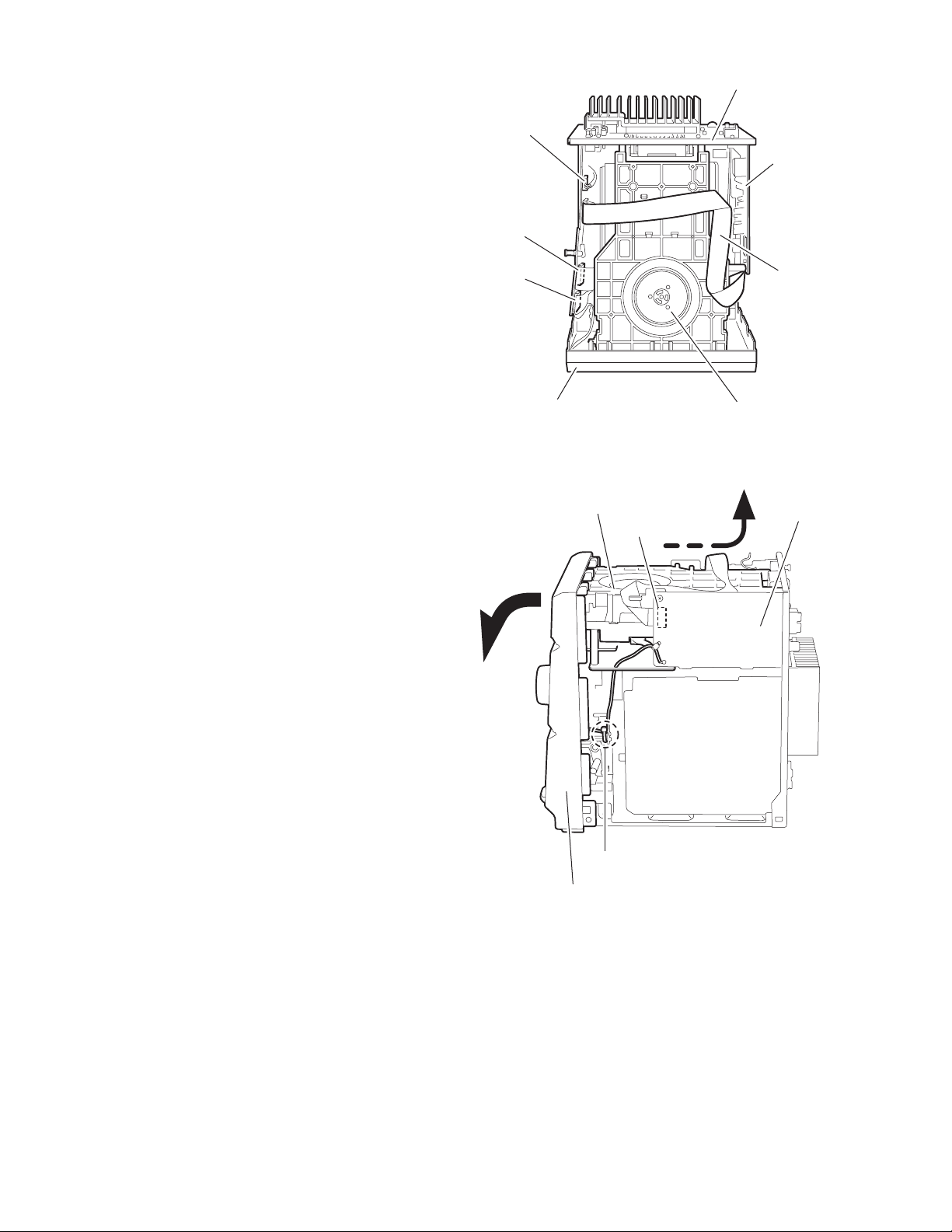
2.1.4 Removing the CD-R mechanism assembly
(See Fig.6 ~ 8)
• Prior to performing the following procedure, remove the metal
cover and the rear cover.
(1) Disconne ct the card wires from connector CN903, CN904
and the wire from CN905 on the main board on the upper
side of the body.
(2) Remove the screw D attaching the tuner board and the
CD-R mechanism on the right side of the body.
(3) Remove the two screws F attaching the rear panel and the
CD-R mechanism on the back of the body.
(4) Move the rea r part of the CD-R mechanism assembly up-
wards to disengage the two joints a and release fro m the
rear panel.
Pull the front panel toward the front and move the rear part
of the CD-R mechanism assembly upwards. Then pull out
the CD-R mechanism assembly from the fr on t p a ne l ba ckward.
REFERENCE:
To remove the CD-R mechanism assembly efficiently, disconnect the card wireconnecting the tuner board with the main
board in advance.
Main board
CN905
CN904
CN903
Front panel assembly
Rear panel
Tuner board
Card wires
CD-R mechanism assembly
Fig.6
2.1.5 Remove the rear panel
(See Fig.8 ~ 11)
• Prior to performing the following procedure, remove the metal
cover, rear cover and the CD-R mechanism assembly.
(1) Remove the seven screws G attaching the rear panel.
(2) Di sconnect the card wire from CN902 on the main board.
(3) Di sengage the lower two joints b on each side of the rear
panel using a screwdriver and remove the rear panel backward (The tuner board and the fan will be also detached.Remove them as needed).
2.1.6 Removing the fan
(See Fig.9 ~ 12)
• Prior to performing the following procedure, remove the metal
cover, the rear cover andthe CD-R mechanism assembly.
(1) Disconne ct the wire from connector CN908 on the main
board.
(2) Remove the two screws H on the back of the body.
(3) Move the fan upwards to disengage the four joints c and re-
lease from the rear panel.
CD-R mechanism
assembly
CN 1
Band
Front panel assembly
Fig.7
Tuner board
1-8 (No.22036)
Page 9
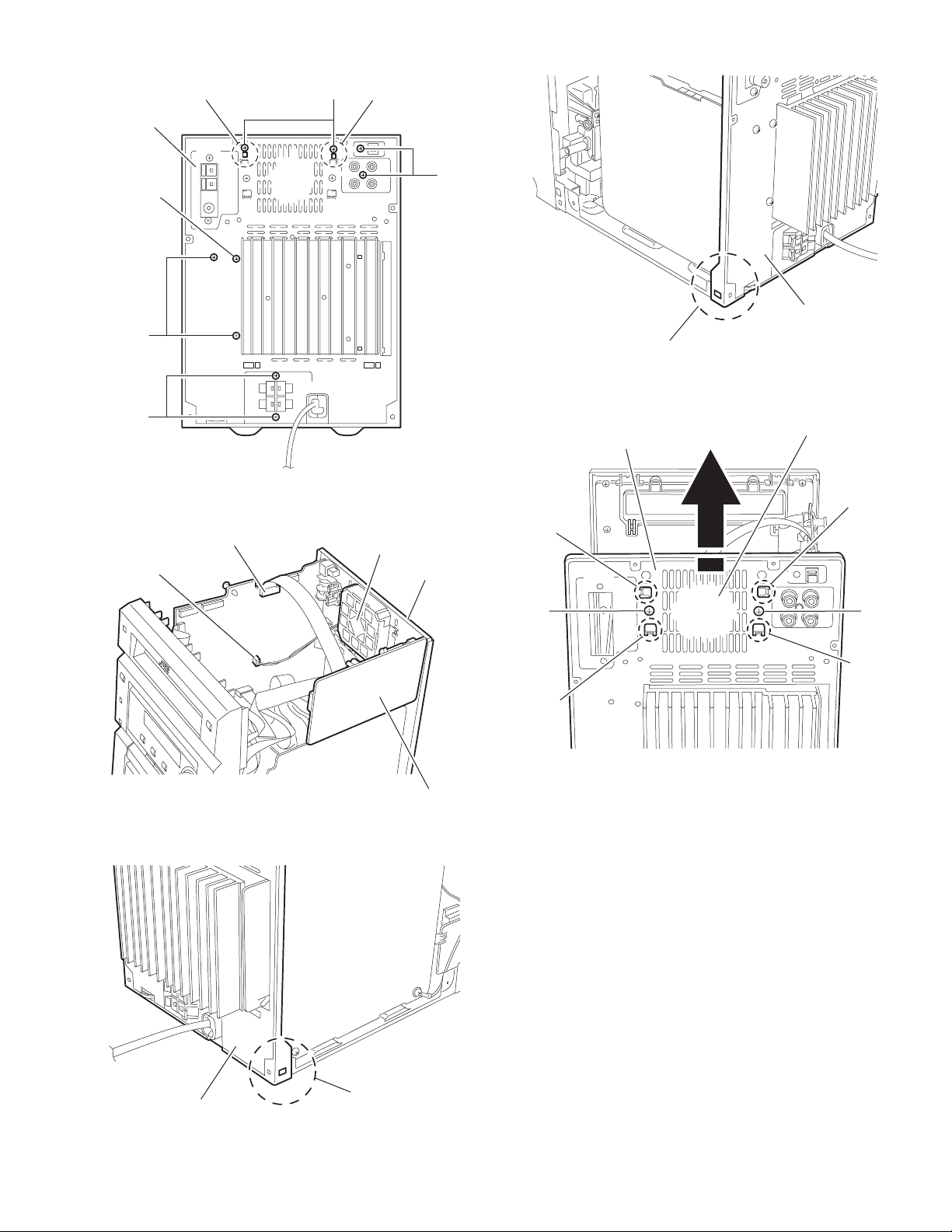
Rear panel
Joint a Joint a
F
G
G
G
Main board
CN908
CN902
Fig.8
Fan
G
Rear panel
Joint c
H
Rear panel
Rear panel
Joint b
Fig.11
Fan
Joint c
H
Rear panel
Joint c
Joint c
Fig.12
Tuner board
Fig.9
Joint b
Fig.10
(No.22036)1-9
Page 10
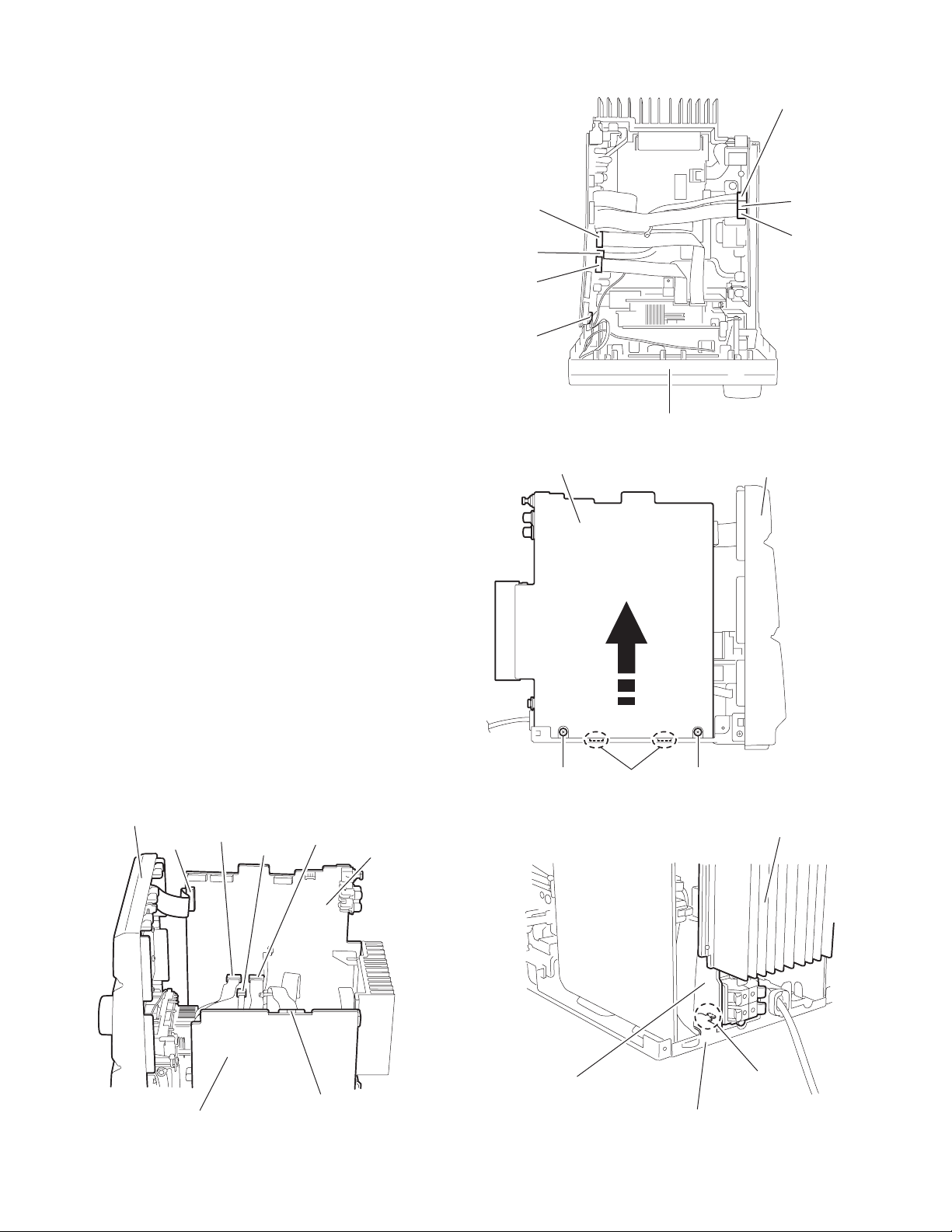
2.1.7 Removing the power amplifier board / power amplifier sub board / main board / heat sink
(See Fig.13 ~ 21)
• Prior to performing the following procedure, remove the metal
cover, the rear cover, the CD-R mechanism assembly and the
rear panel.
(1) Disconne ct the card wire from connector CN900, CN901,
CN933 and CN931 on the main board respectively.
(2) Di sconnect the wire from connector CN949, CN950 and
CN951 on the power supply board.
(3) Remove the two screws I on the right side of the body.
(4) Move the boards and heat sink assembly upwards and dis-
engage the joint d and the two joints e to release the power
amplifier board and the main board from the chassis (Refer
toFig.15 , 16).
Move the rear part of the board and heat sink assembly to
the right side.
CAUTION:
The wire extending from the lower side of the main board
is still connected with the body (Refer to Fig.17).
(5) Disco nnect the wire from connector CN906 on the lower
side of the main board (Refer to Fig.18).
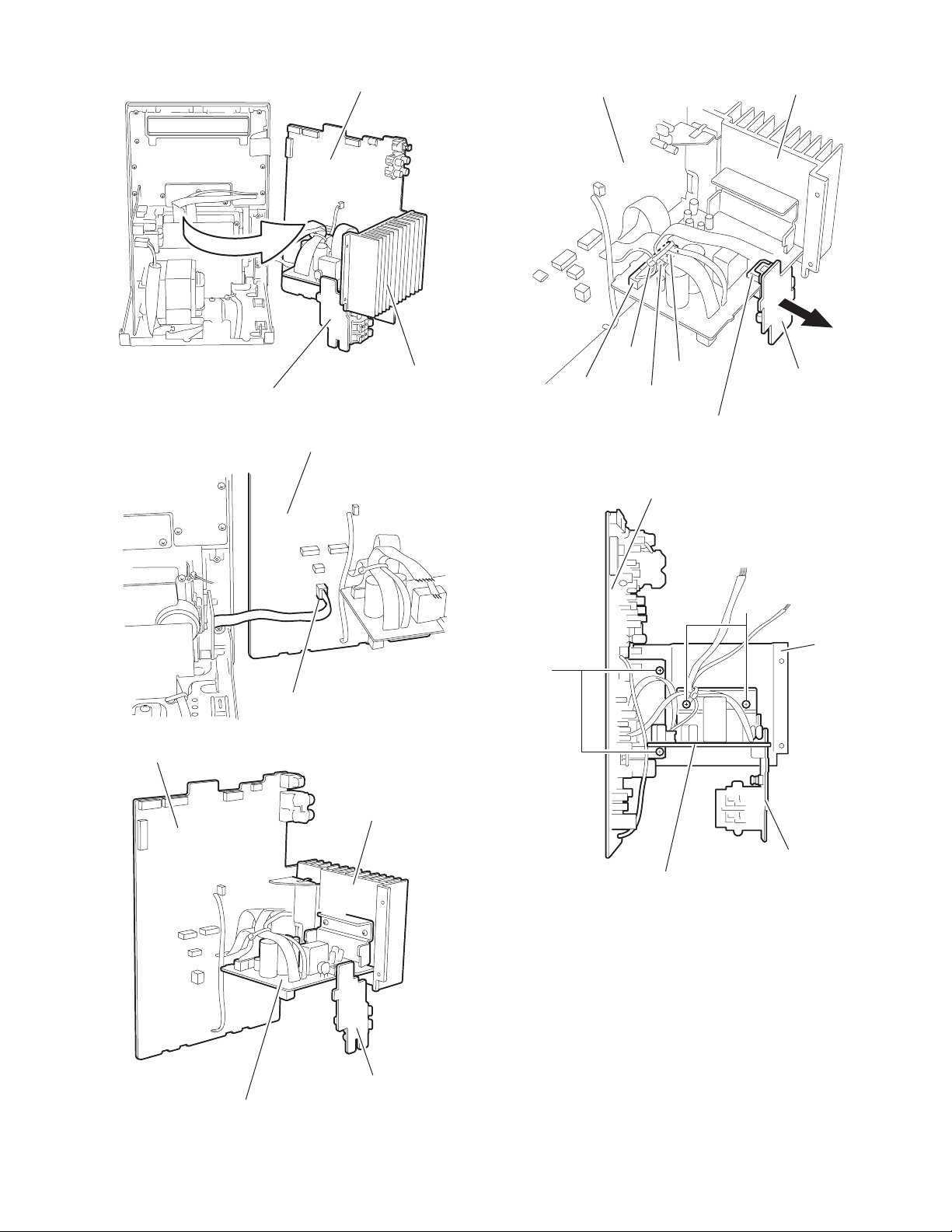
2.1.8 Removing the power amplifier board
(See Fig.19 ~ 21)
(1) Disconnect the power amplifier board from connector
CN941 on the power amplifier sub board.
2.1.9 Removing the power amplifier sub board
(See Fig.19 ~ 21)
(1) Disconne ct the two wires from connector CN944, CN9 45,
CN946 and CN947 on the power amplifier sub board.
(2) Remov e the two screws J attaching the power amplifier
sub board and the heat sink.
2.1.10 Removing the main board
(See Fig.19 ~ 21)
(1) Disconnect the wires from connector CN944, CN945,
CN946 and CN947 on the power amplifier sub board.
(2) Remo ve the two screws K attaching the main board and
the heat sink.
REFERENCE:
The power amplifier board, the power amplifier sub board, the
main board and the heat sink can be remove drespectively.
Front panel assembly
CN931
CN901
CN933
CN900
Main board
Main board
CN900
CN933
CN901
CN931
Main board
Power supply board
CN949
CN950
CN951
Front panel assembly
Fig.14
Front panel assembly
II
Joint e
Fig.15
Heat sink
Power supply board
1-10 (No.22036)
CN949 / CN950 / CN951
Fig.13
Power amplifier board
Joint d
Chassis
Fig.16
Page 11
Main board
Main board
Heat sink
Main board
Power amplifier board
Fig.17
Main board
CN906
Fig.18
Heat sink
K
CN944
CN945
CN947
CN946
Power amplifier sub board
CN941
Fig.20
Main board
Power amplifier board
J
Heat sink
Power amplifier sub board
Fig.19
Heat sink
Power amplifier board
Power amplifier
sub board
Fig.21
Power amplifier board
(No.22036)1-11
Page 12
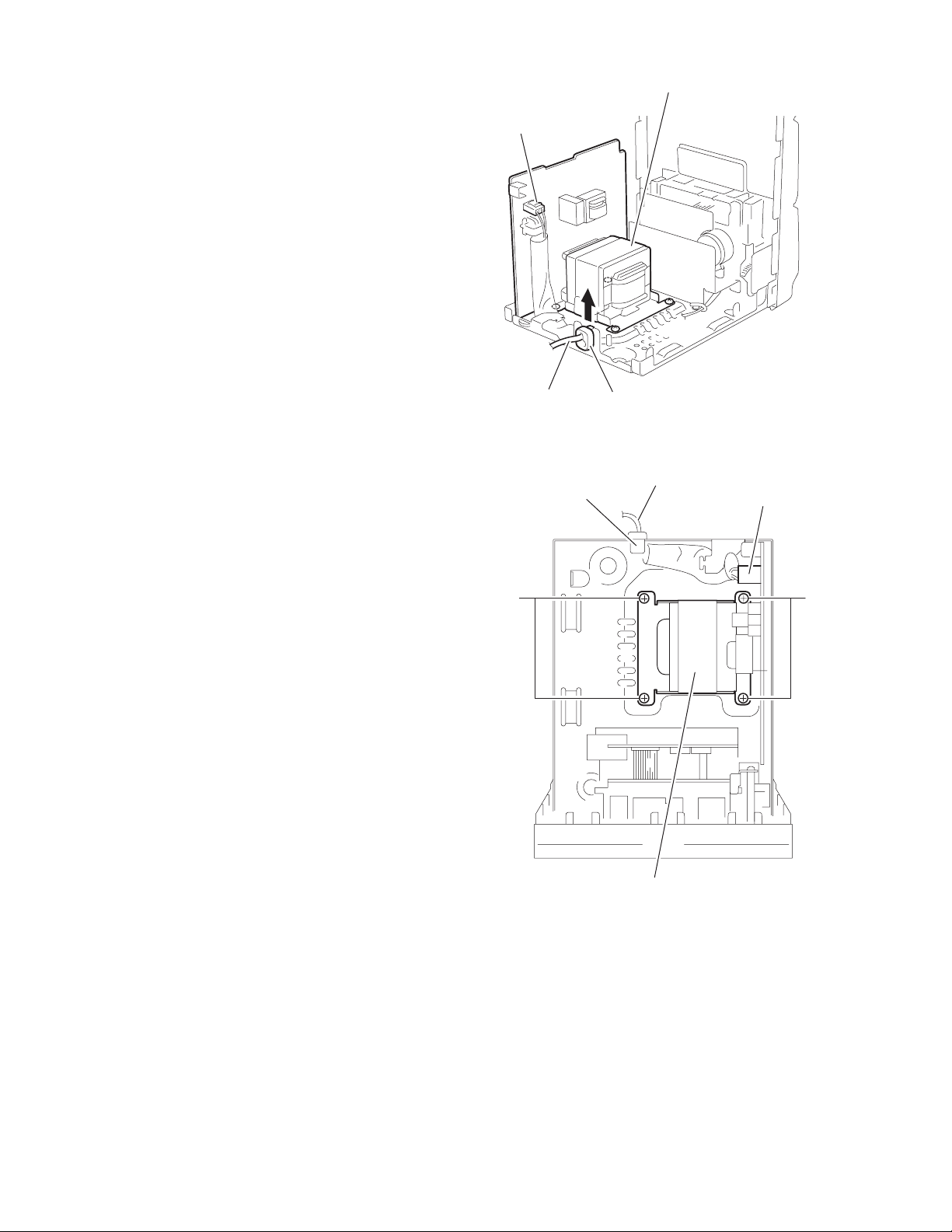
2.1.11 Removing the power transformer assembly
(See Fig.22, 23)
• Prior to performing the following procedure, remove the metal
cover, the rear cover, the CD-R mechanism assembly and the
rear panel.
• Remove the assembly consisting of the power amplifier board,
the power amplifier sub board and the main board fromthe
chassis incompletely (Refer to Fig.17).
(1) Remove the cord stopper upwards on the back of the body.
(2) Di sconnect the power cord from connector J1000 on the
board of the power transformer assembly .
(3) Remove the four screws L attaching the power transform-
er assembly.
Power transformer assembly
J1000
Power cord
Cord stopper
Cord stopper
Fig.22
Power cord
J1000
LL
1-12 (No.22036)
Power transformer assembly
Fig.23
Page 13
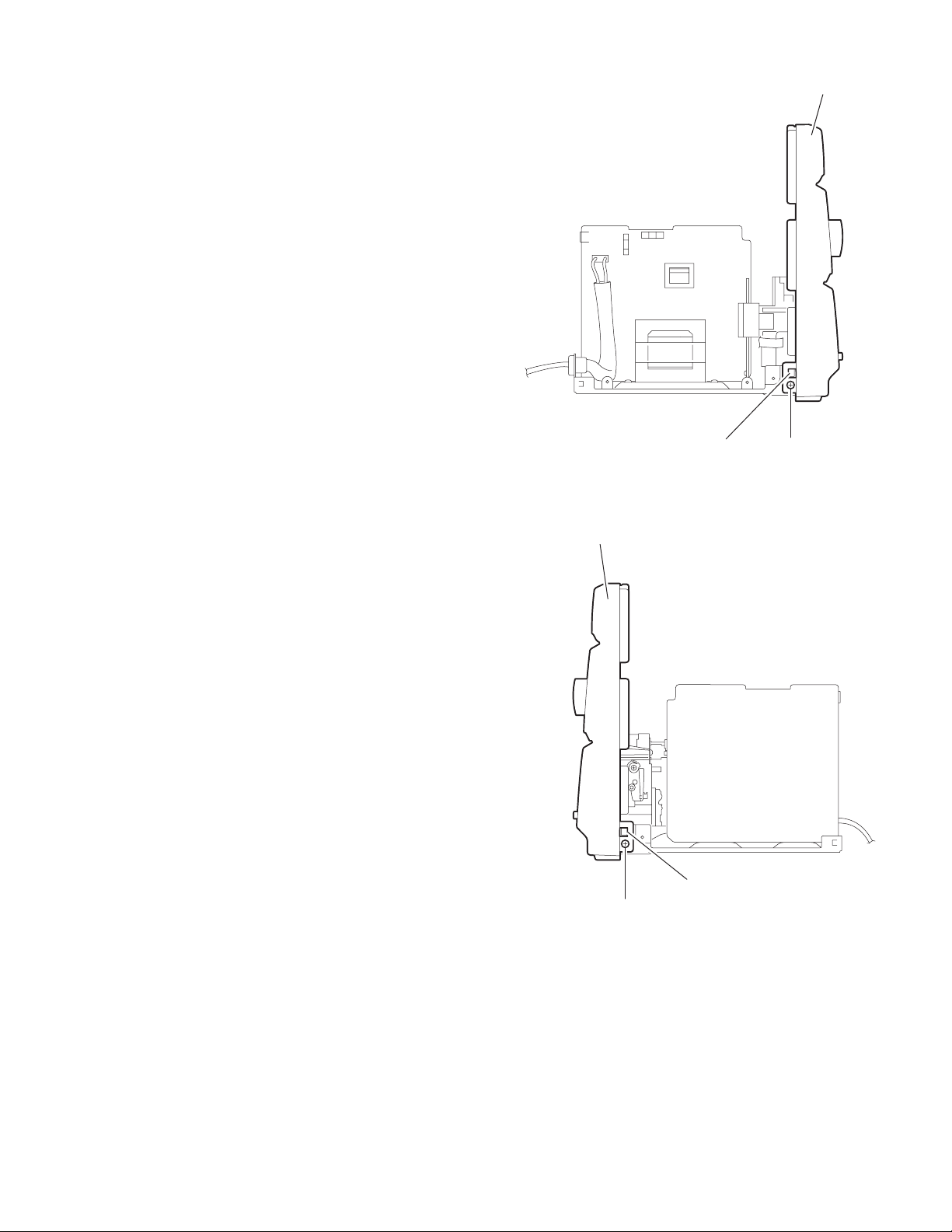
2.1.12 Removing the front panel assembly
(See Fig.24, 25)
• Prior to performing the following procedure, remove the metal
cover, the rear cover, the CD-R mechanism assembly and the
rear panel.
• Remove the assembly consisting of the power amplifier board,
the power amplifier sub board and the main board (Refer to
Fig.17, 18).
(1) Remove the two screws M on each lower side of the body.
(2) Disen gage the two joints f on each lowe r side of th e body
using a screwdriver andpull out the front panel assembly
toward the front.
Front panel assembly
Front panel assembly
M
Joint c
Fig.24
Joint c
Fig.25
M
(No.22036)1-13
Page 14

2.1.13 Removing the display board / switch board
(See Fig.26 ~ 28)
• Prior to performing the following procedure, remove the front
panel assembly.
(1) Pul l out the VOLUME knob on the front panel.
(2) Remove the eleven screws N on the back of the front panel
and remove the display board with the switch board.
(3) Remove the three screws O attaching the switch board to
the LCD holder.
(4) If necessary, unsolder the wire connected to connector
FW931 on the display board and FW931 on the switch
board.
Front panel assembly
VOLUME knob
N
N
Switch board
Display board
N
N
Fig.26
Display board
FW931
O
Fig.27
Fig.28
NN
Switch board
1-14 (No.22036)
Page 15

2.1.14 Removing the headphone board
(See Fig.29)
• Prior to performing the following procedure, remove the front
panel assembly.
(1) Remove the screw P on the back of the front panel.
(2) If necessary, remove the band bundling the wire extending
from the headphone board and the display board.
2.1.15 Removing the cassette mechanism assembly
(See Fig.29, 30)
• Prior to performing the following procedure, remove the front
panel assembly.
(1) P ress the EJCT button on the front panel to open the cas-
sette door.
(2) Remove the four screws Q on the back of the front panel.
2.1.16 Removing the LED board
(See Fig.30 ~ 32)
• Prior to performing the following procedure, remove the front
panel assembly.
(1) P ress the EJCT button on the front panel to open the cas-
sette door.
(2) Remove the cassette holder in the direction of the arrow.
(3) Release the two joint hooks g engaging the LED board with
the cassette door.
Display board
Front panel assembly
Cassette door
EJCT button
Fig.30
Q
Cassette mechanism assembly
Fig.29
Q
P
Headphone board
Cassette door holder
Fig.31
LED board
Hooks g
Cassette door
Fig.32
(No.22036)1-15
Page 16

2.2 Cassette mechanism assembly
r
2.2.1 Removing the playback/recording & eraser head
(See Fig.1 to 3)
(1) While shifting the trigger arm seen on the right side of the
head mount in the arrow direction, turn the flywhee l (R) in
counterclockwise direction until the head mount has gone
out with a click (See Fig.1).
(2) When the flywheel (R) is rotated in counterclockwise direc-
tion, the playback/recording &erase head will be turned in
counterclockwise direction from the position in Fig.2 to that
in Fig.3.
(3) At this position, disconnect the flexible wire (outgoing from
the playback/recording &erase head) from the connector
CN31 on the head amplifier & mechanism control board.
(4) Remove the flexible wire from the fixing point b on the
chassis base.
(5) Re move the spring a from behind the playback/recording
&erase head.
(6) Loosen the reversing azimuth screw A retaining the play-
back/recording &erase head.
(7) Take out the playback/recording &erase head from the
front of the head mount.
2.2.2 Reassembling the playback/recording & eraser head
(1) Reassemble the playback/recording & eraser head from
the front of the head mount to the position as shown in
Fig.3.
(2) Fix the reversing azimuth screw A.
(3) Atta ch the spring a from behind the playback/recording &
eraser head.
(4) Atta ch the flexible wire to th e fixing point b on the chassis
base.
(5) Attach the flexible wire (outgoing from the playback/record-
ing & eraser head) to the connector CN31 on the head am-
plifier & mechanism control board.
Head (R/P,Erase)
Flexible wire
Head amp & Mecha
control board
Head (R/P,Erase)
spring a
flexible wire
fixing point b
Head amp & Mechanism
control board
BB
spring a
trigger arm
CN31
fixing point b
Fig.1
CN31
Head amp & mechanism
control board
Fig.2
fly wheel(R)
REV
azimuth screw
head mount
belt
A
flexible wire
CN32
CN31
Main motor
assembly
C
C
B
4pin flat wire
Main moto
assembly
Fig.3
1-16 (No.22036)
Page 17

2.2.3 Removing the head amplifier & mechanism control
board
(See Fig.4 and 5)
(1) Remove the flexib le wire from the connector CN31 on the
head amplifier & mechanism control board on the rear of
the cassette mechanism assembly.
(2) Remove the th ree screws B retai ning th e he ad amplifier &
mechanism control board.
(3) Disconn ect the connector CN 32 on the head amplifier &
mechanism control board from the connector CN1 on the
reel pulse board, and remove the head amplifier & mechanism control board.
Note:
When necessary, remove the 4 pin parallel wire soldered to
the main motor.
2.2.4 Removing the main motor
(See Fig.4 to 7)
• Prior to the following procedure, it is not necessary to remove
the head amplifier & mechanism control board.
(1) Remove the two screws C retaining the main motor.
(2) While raising the main motor, remove the capstan belt from
the motor pulley.
CAUTION:
Be sure to handle the capstan belt so carefully that this belt will
not be stained by grease and so on. Moreover, this belt should
be hanged while referring to the capstan belt h anging method
in Fig. 6 and 7.
main motor assembly
capstan belt
motor pully
Fig.4
main motor assembly
motor pully
capstan belt
Fig.5
main motor assembly
fly wheel
capstan belt
Fig.6
motor pully
fly wheel (R)
capstan
shaft (R)
slit washer d slit washer c
Fig.7
fly wheel (L)
capstan shaft (L)
(No.22036)1-17
Page 18

2.2.5 Removing the flywheel
(See Fig.8 and 9)
• Prior to the following procedure, remove the head amplifier
&mechanism control board.
• Prior to the following procedure, remove the main motor as-
sembly.
(1) Remov e the slit washers c and d fixing the capstan shafts
(L) and (R) from the front of the cassette mechanism assembly. And pull out the flywheels (L) and (R) respectively
from the rear of the cassette mechanism assembly in the
arrow direction. Then, remove the flywheels (L) and (R).
fly wheel (L)fly wheel (R)
Fig.8
Cassette mechanism
Fly wheel(R)
Head mount
2.2.6 Removing the reel pulse board and solenoid
(See Fig.10)
• Prior to the following procedure, remove the head amplifier &mechanism control board.
• Prior to the following procedure, remove the main motor assembly.
(1) Remo ve one screw D attaching the reel pulse board.
(2) Remove the five fixing points e attaching the reel pulse board respectively in the arrow direction.
(3) From th e front of the cassette mechanism assembly, push the two fixing points f retaining the solenoid in the arrow dire ction,
and remove the solenoid.
Note:
When reassembly, make sure that the fixing point g of the solenoid is attached properly.
fixing point e fixing point e fixing point e
Reel pulse board
fixing point f
Trigger arm
Fig.9
1-18 (No.22036)
fixing point g
z
solenoid
Fig.10
Page 19

3.1 Adjustment method
V
SECTION 3
Adjustment
Measurement Instruments Required for
Adjustment
1. Low frequency oscillator
This oscillator should have a capacity to output
0dBs to 600 at an oscillation frequency of
50Hz-20kHz.
2. Attenuator impedance : 600
3. Electronic voltmeter
4. Distortion meter
5. Frequency counter
6. Wow & flutter meter
7. Test tape
VT703L : Head azimuth
VT712 : Tape speed and running unevenness
(3kHz)
VT724 : Reference level (1kHz)
8. Blank tape
TYPE : AC-225
TYPE : AC-514
9. Torque gauge : For play and back tension
FWD(TW2111A), REV(TW2121a) and
FF/REW(TW2231A)
10. Test disc: CTS-1000
Measurement conditions
Power supply voltage
AC 230V ~ , 50Hz
Reference output : Speaker : 0.775V/4
: Headphone : 0.077V/32
Reference frequency and
input level ------------------------------ 1kHz, AUX : -8dBs
Measurement output terminal ------- at Speaker J3002
Load resistance --------------------------- 4
Radio Input signal
AM frequency --------------------------------------- 400Hz
AM modulation ---------------------------------------- 30%
FM frequency --------------------------------------- 400Hz
FM frequency deviation ------------------------ 22.5kHz
Tuner section
FM tuning range: 87.5MHz~108.00MHz
AM tuning range: 522kHz~1,629kHz
Voltage applied to tuner +B : DC5.7V
VT : DC 12
Reference measurement
output 26.1mV(0.28V)/3
Input positions AM : Standard loop antenna
FM : TP1 (hot) and TP2 (GND)
Standard measurement position of volume
Function switch to Tape
Beat cut switch to Cut
Super Bass/Active hyper Bass to OFF
Bass Treble to Center
Adjustment of main volume to reference output
VOL : 28
Precautions for measurement
1. Apply 30pF and 33k to the IF sweeper output
side and 0.082 F and 100k in series to the
sweeper input side.
2. The IF sweeper output level should be made as
low as possible within the adjustable range.
3. Since the IF sweeper is a fixed device, there is no
need to adjust this sweeper.
4. Since a ceramic oscillator is used, there is no need
to perform any MIX adjustment.
5. Since a fixed coil is used, there is no need to adjust
the FM tracking.
6. The input and output earth systems are separated.
In case of simultaneously measuring the voltage in
both of the input and output systems with an
electronic voltmeter for two channels, therefore, the
earth should be connected particularly carefully.
7. In the case of BTL connection amp., the minus
terminal of speaker is not for earthing. Therefore, be
sure not to connect any other earth terminal to this
terminal. This system is of an BTL system.
8. For connecting a dummy resistor when measuring
the output, use the wire with a greater code size.
9. Whenever any mixed tape is used, use the band
pass filter (DV-12).
(No.22036)1-19
Page 20

3.2 Cassette mechanism section
Head angle
azimuth screw
(foward)
Mechanism control P.C. board
Motor speed
VR37
BIAS adjustment
VR31
L301
VR37
VR31
R314
C308
B155
R315
R327
Head angle
azimuth screw
(reverse)
MB
PBRAGPBL
RECRAGRECL
MS
SW8V
MG
1
CN34
C307
R313
C310
C314
Q302
C317
C319
C221
B112
C313
C316
C121
L303
R310
R335
C106
Q103
R305
Q305
B198
R353
R303
R122
Q101
C103
B163
Q321
R221
10
B156
C303
R115
B157
R108
R101
C113
R110
R109
R102
C110
C104
R301
R121
1
C108
C107
9
B151
R112
R111
C102
R107
B152
C302
R103
1
C301
C111
C306
B164
R304
C109
B158
8
B106
C101
6
B166
R116
R212
R211
C211
R216
Head angle
azimuth screw
(foward)
CN31
Recording and play head/Erase head
9
9
IC32
C201
B109B108
C209
B101
CN33
R342
C213
R210
R209
C207
B159
16
B102
R341
C208
R207
1
B110
CN31
B200
1
R205
R208
B160
R340
R105
C105
NC
R343
C305
C206
R345
R201
1IC31
TAP
C304
B113
C202
C210
Q331
RRE
C375
C205
B161
R215
R339
C203
C334
R106
R206
5VMGSOL
R204
R203
B153
R104
R222
C204
B168
PHO
R202
C333
C332
R375
Q201
PLA
Q203
C331
Q372
R331
B167
FRE
R371
C376
10
70u
Q375
E
CN32
R376
D375
Q376
Q371
E
R372
R373
C374
B162
C371
R338
R337
16
1
R336
9
8
IC33
Head angle
azimuth screw
(reverse)
B
B
1-20 (No.22036)
Page 21

3.3 Mechanism section
Item
Mesurement
condition
Confirmation of angle of head Tape speed confirmation
Test tape: VT703L (8kHz)
Measurement output terminal:
Speaker terminal
Mesurement
procedure
1.Test tape VT703L (8kHz) is played.
2.It is adjusted that becomes an output
that both are the maximum on a forward
side and a reverse side with the screw
for the azimuth adjustment.
3.This adjustment is adjusted respectively
with the adjustment screw for the forward
side and the adjustment screw for a
reverse side.
Standard
value
Adjustment
position
3.4 Reference and standard value of confirmation matter
The maximum output
Only when the head is exchanged,
adjusts.
Test tape: VT712 (3kHz)
Measurement output terminal:
Speaker terminal or headphone terminal
Test tape VT712(3kHz) of the forward is
reproduced by finishing rolling , and
adjusted for the display of the frequency
counter to become 2,940-3,090Hz by
VR37.
2,940 ~ 3,090Hz
VR37
Item
Mesurement
condition
Mesurement
procedure
Standard
value
Adjustment
position
Forward/reverse tape speed difference Wow & flutter
Test tape: VT712 (3kHz)
Measurement output terminal: Speaker terminal or headphone terminal
Both reverse must forward/reproduce, and
the speed difference must be 6.0Hz or
less as for finish wrapping of test tape
VT712 (3kHz).
6.0Hz or less
Both reverse must forward/reproduce,
and each wow & flutter must be 0.25%
(WRMS) or less as for begin to wrap of
test tape VT712 (3kHz).
0.25% or less (WRMS)
VR31
(No.22036)1-21
Page 22

3.5 Electric adjustment
Item
Mesurement
condition
Mesurement
procedure
Standard
value
Adjustment
position
Recording BIAS adjustment
Forward or reverse
Test tape: AC-514 TYPE and
AC-225 TYPE
Measurement output terminal:
Recording and headphone terminal
1.Test tape (AC-514 TYPE ,AC-225
TYPE )is installed, and makes to
recording/pose.
2.Connects in the head for the recording
and to connect 100 with the series and
to measure the current of the bias,
connects with VTVM.
3.The pose is released after sets and the
recording begins. It is adjusted that the
current of the bias reaches the following
value by VR31 for L side at this time and
VR32 for R side.
4.0 (TYPE )and4.20 (TYPE )
AC-225: 4.20
AC-514: 4.0
VR31
Recording reproduction
frequency characteristic
Standard frequency: 1kHz/10kHz
(Srandard: -20dB)
Test tape: AC-514 TYPE
Measurement input terminal: OSC IN
1.Test tape (AC-514 TYPE )is installed,
and makes to recording/pose.
2.Records the recording's releasing the
pose, beginning, and repeating 1kHz
and 10kHz of a standard frequency from
the frequency transmitter.
3.VR31 for L side and VR32 for R side are
adjusted so that the recorded part may
be reproduced and there is a difference
between 1kHz and 10kHz in 1dB }2dB,
and the recording is repeated again.
Output difference
1kHz/10kHz:-1dB 2dB
3.6 Electric characteristic confirmation
Item
Mesurement
condition
Forward or reverse
Test tape: AC-514 TYPE
Measurement terminal:
Current of recording bias Deletion current (standard value)
BIAS TP on P.C.board
Mesurement
procedure
1. It is confirmed that BIAS1 and 2 are
switched, and the frequency changes.
2.Test tape (AC-514 TYPE ) is installed,
and recording/makes to the pose.
3.It is confirmed that it is BIAS TP on the
substrate and the frequency is 100Hz
6kHz.
Standard
value
Adjustment
position
100kHz 6kHz
Forward or reverse
State of recording
Test tape: AC-514 TYPE and
AC-225TYPE
Measurement terminal:
Erase head's both ends
1.Test tape (AC-514 TYPE )is installed,
and makes to recording/pose.
2.The pose is released and after sets in
the state of the recording, 1W is
confirmed, and connects with the series,
and the deletion current is confirmed
from erase head's both ends to the
erase head.
TYPE : 120mA
TYPE : 75mA
1-22 (No.22036)
Page 23

3.7 Flow of functional operation until TOC read (CD)
Power ON
Power Key
Slider turns REST
SW ON.
Automatic tuning
of TE offset
Check Point
Check that the voltage at the pin 5
of CN801 is 0V?
VREF
Tracking error waveform at TOC reading
pin 20 of
IC601(TE)
Approx
1.7V
Tracking
servo
Disc start
to rotate
off
Automatic measurement
of TE amplitude and
automatic tuning of
TE balance
Approx.1sec
Tracking
servo ON
Disc to be
braked to stop
TOC reading
finishes
500mv/div
2ms/div
Fig.1
Laser ON
Detection of disc
Automatic tuning of
Focus offset
Automatic measurement of
Focus S-curve amplitude
Disc is rotated
Focus servo ON
(Tracking servo ON)
Automatic measurement of
Tracking error amplitude
Automatic tuning of
Tracking error balance
Check that the voltage at the
pin2 of IC601 is 4.4V?
Confirm that the Focus error
S-cuve, ie at the pin23 of
IC601 is approx.2Vp-p
Confirm that the siganl from
pin 5,6 of IC801 is a 2V
accelerated pulse with approx.
700ms.
Confirm the waveform of
the Tracking error signal
at the pin20 of IC601
(See fig-1)
Automatic tuning of
Focus error balance
Automatic tuning of
Focus error gain
Automatic tuning of
Tracking error gain
TOC reading
Play a disc
Confirm the eye-pattern
at the lead of TP1
(No.22036)1-23
Page 24

3.8 Maintenance of laser pickup (CD)
(1) Cl eaning the pick up lens
Before you replace the pick up, please try to clean the lens
with a alcohol soaked cotton swab.
(2) Life of the laser diode
When the life of the laser diode has expired, the following
symptoms will appear.
• The level of RF output (EFM output : ampli tude of eye
pattern) will below.
3.9 Replacement of laser pickup (CD)
Turn off the power switch and, disconnect the
power cord from the ac outlet.
Replace the pickup with a normal one.(Refer
to "Pickup Removal" on the previous page)
Is the level of
RFOUT under
1.25V 0.22Vp-p?
NO
Replace it.
YES
O.K
(3) Semi-fixed resistor on the APC PC board
The semi-fixed resistor on the APC printed circuit board
which is attached to the pickup is used to adjust the laser
power. Since this adjustment should be performed to
match the characteristics of the whole optical block, do not
touch the semi-fixed resistor.
If the laser power is lower than the specified value, the laser diode is almost worn out, and the laser pickup should
be replaced.
If the semi-fixed resistor is adjusted while the pickup is
functioning normally, the laser pickup may be damaged
due to excessive current.
Plug the power cord in, and turn the power on.
At this time, check that the laser emits for
about 3seconds and the objective lens moves
up and down.
Note: Do not observe the laser beam directly.
Play a disc.
Check the eye-pattern at TP1.
Finish.
1-24 (No.22036)
Page 25

4.1 AN22000A-W (IC601) : RF head amp.
• Terminal layout
ACBDPDF
323130292827262524232221201918
123456789
LD
PD
VCC
RFN
RFOUT
PDE
RFIN
TBAL
FBAL
GCTRL
FEOUT
10111213141516
ARF
CEA
CAGC
3TOUT
FEN
TEN
BDO
CBDO
• Block diagram
32
31
30
29
27
28
RFOUT
RF_EQ
AMP
AMP
AMP
AMP17GCA BCA
+
-
624754 8
RFIN
AGC
NRFDET
GCA BCA
GCA BCA
GCA BCA
11 12
BDO
SUBT
SUBT
SECTION 4
Description of major ICs
• Pin function
Pin
Symbol I/O Function
TEOUT
TEBPF
OFTR
COFTR
VDET
VREF
17
GND
RFDET
13 14
OFTR
3TENV
VDET
9
10
15
22
-
+
-
+
-
+
23
21
20
19
18
2
LD
No.
1 PD I APC Amp. input terminal
2 LD O APC Amp. output terminal
3 VCC - Power supply terminal
4 RFN I RF adder Amp. inverti ng input terminal
5 RFOUT O RF adder Amp. output terminal
6 RFIN I AGC input terminal
7 CAGC I Input terminal for AGC loop filter capacitor
8 ARF O AGC output terminal
9 CEA I Capacitor connecting terminal
10 3TOUT O 3 TENV output terminal
11 CBDO I Capacitor connecting terminal for envelope
12 BDO O BDO output terminal
13 COFTR I Capacitor connecting terminal for envelope
14 OFTR O OFTR output terminal
15 NRFDET O NRFDET output terminal
16 GND - Ground
17 VREF O VREF output terminal
18 VDET O VDET output terminal
19 TEBPF I VDET output terminal
20 TEOUT O TE Amp. output terminal
21 TEN I TE Amp. inverting input terminal
22 FEN I FE Amp. inverting input terminal
23 FEOUT O FE Amp. output terminal
24 GCTL O GCTL & APC terminal
25 FBAL O FBAL control terminal
26 TBAL O TBAL control terminal
27 E I Tracking signal input terminal 1
28 F I Tracking sign al input terminal 2
29 D I Focus signal input terminal 4
30 B I Focus signal input terminal 3
31 C I Focus signal input terminal 2
32 A I Focus signal input terminal 1
for HPF-Amp.
detection on the darkness side
detection on the light side
GCTL26TBAL
25 16 3
FBAL
PD
1
(No.22036)1-25
Page 26

4.2 BA15218F-XE (IC904) : Dual operation amplifier
• Pin layout
OUT1 1
-IN1 2
+IN1 3
VEE 4
• Block diagram
Vcc
-IN
+IN
1
2
R1
Q5
Q1
Q2
D1
Q3 Q4
8 Vcc
7 OUT2
6 -IN2
5 +IN2
C2
Q9
R5
Q6
Q8
Q10
Q7
R7
Q11
R6
Q12
R8
Q18Q13
OTHER
CH
Q19
Q17Q16
VEE
C1
R3R2
R4
Q14 Q15Q114
R9
OUTPUT
1-26 (No.22036)
Page 27

4.3 GP1U261X (IC933) : Receiver
•Pin layout
Vout
GND
Vcc
• Block diagram
4.4 KIA78S06P-T (IC932) : Regulator
•Pin layout
1 2 3
• Block diagram
B.P.F.LimiterAmp
Demodulator
Integrator
Comparator
GND Vcc Vout
3 INPUT
Z1
Q14
R9
Q16
R11 R10
Q1
R1
Q2 Q7
Q4
Q3
Q6
R2
R3
Q8
C1
Q5
R4
Q9
Q10
Q11
Q12
R8
Q13
R7R5R6
1 OUTPUT
2 COMMON
(No.22036)1-27
Page 28

4.5 L4909 (IC910) : Regulator
A
• Pin layout
1234 56789101112131415
• Block diagram
EN1
EN2
EN3
OC
TRIG
GND
THERMAL
SHUTDOWN
6
7
9
5
4
8
ENABLE
CONTROL
OVER
CURRENT
CHECK
REFERENCE
GENERATOR
REG1
REG2
REG3
• Pin functions
Pin No. Symbol Function
1 FB1 REG1 feedback voltage input
2 VO1 REG1 output voltage
3 VINA Input DC supply voltage
4 TRIG Trigger for external SCR (crowbar protection)
5 OC Over current warning output
6 EN1 REG1 enable input
7 EN2 REG2 enable input
8 GND Analog ground
9 EN3 REG3 enable input
10 FB3 REG3 feedback voltage input
11 VO3 REG3 output voltage
12 N.C. Not connected
13 VINB Input DC supply voltage
14 VO2 REG2 output voltage
15 FB2 REG2 feedback voltage input
REF
REF+20%
REG1
REG2
REG3
3,13
14
15
11
10
VIN
VINB
2
VO1
1
FB1
VO2
FB2
VO3
FB3
1-28 (No.22036)
Page 29

4.6 LA1838 (IC1) : FM AM IF amp & detector, FM MPX decoder
• Block Diagram
30
ALC
BUFF
FM
S-METER
FM IF
1
29
AM
OSC
S-CLRVE
PM
DET
2
28
REG
AM
MIX
SD
COMP
AM/FM
IF-BUFF
3
27
FM
RF.AMP
AM IF
4
26
AGC
AM
S-METER
GND
5
DET
25
TUNING
DRIVE
6
24
STEREO
DRIVE
7
22
23
P-DET
VCC
89
21
DECODER
ANIT-BIRDIE
VCO
384KHz
10
20
STEREO
5N
SW
FF
38k
11
18
19
MUTE
FF
/
19k
2
12 13
FF
19k
17 16
/LS
14
PILOT
DET
15
• Pin Function
Pin No. Symbol I/O Function
1 FM IN I This is an input terminal of FM IF signal.
2 AM MIX O This is an out put terminal for AM mixer.
3 FM IF I Bypass of FM IF
4 AM IF I Input of AM IF Signal.
5 GND - This is the device gro und terminal.
6
7
TUNED
STEREO
O When the set is tunning,this terminal becomes "L".
O Stereo indicator output. Stereo "L", Mono: "H"
8 VCC - This is the powe r sup ply terminal.
9 FM DET - FM detect transformer.
10 AM SD - This is a terminal of AM ceramic filter.
11 FM VSM O Adjust FM SD sensitivity.
12 AM VSM O Adjust AM SD sensitivity.
13 MUTE I/O When the signal of IF REQ of IC 121(LC721 31) appe ar, the signal of FM/AM IF output. //Muting
control input.
14
15
FM/AM
MONO
/ST
I Change over the FM/AM input. "H" :FM, "L" : AM
O Stereo : "H", Mono: "L"
16 L OUT O Left channel signal output.
17 R OUT O Right channel signal output.
18 L IN I Input terminal of the Left channel post AMP.
19 R IN I Input terminal of the Right channel post AMP.
20 RO O Mpx Right channel signal output.
21 LO O Mpx Left channel signal output.
22 MPX IN I Mpx input terminal
23 FM OUT O FM detection output.
24 AM DET O AM detection output.
25 AM AGC I T his is an AGC voltage input terminal for AM
26 AFC - This is an output terminal of voltage for FM-AFC.
27 AM RF I AM RF signal input.
28 REG O Register value between pin 26 and pin28 besides the frequency width of the input signal.
29 AM OSC - This is a terminal of AM Local oscillation circuit.
30 OSC BUFFER O AM Local oscillation Signal output.
(No.22036)1-29
Page 30

4.7 LA6541-X (IC801) : BTL driver
• Pin layout & Block diagram
Vcc Vref Vin4 Vg4 Vo8 Vo7
24 23
22
21
11k
ohm
20
19
Gnd
Vcc
Vo6 Vo5 Vg3 Vin3 Cd Res
18
17 16
15
14
13
11k
ohm
- +
- +
Level
shift
Level
shift
B T L
driver
B T L
driver
11k
ohm
1
Vcc Mute Vin1 Vg1 Vo1 Vo2 Vo3 Vo4 Vg2 Vin2 Reg
2
3456
Gnd
789101112
• Pin function
Pin No. Symbol Description
1 Vcc Power supply (Shorted to pin 24)
2 Mute All BTL amplifier outputs ON/OFF
3 Vin1 BTL AMP 1 input pin
4 Vg1 BTL AMP 1 input pin (For gain adjustment)
5 Vo1 BTL AMP 1 input pin (Non inverting side)
6 Vo2 BTL AMP 1 input pin (Inverting side)
7 Vo3 BTL AMP 2 input pin (Inverting side)
8 Vo4 BTL AMP 2 input pin (Non inverting side)
9 Vg2 BTL AMP 2 input pin (For gain adjustment)
10 Vin2 BTL AMP 2 input pin
11 Reg Out External transistor collector (PNP) connection. 5V power supply output
12 Reg In External transistor (PNP) base connection
13 Res
Reset output
14 Cd Reset output delay time setting (Capacitor connected externally)
15 Vin3 BTL AMP 3 input pin
16 Vg3 BTL AMP 3 input pin (For gain adjustment)
17 Vo5 BTL AMP 3 output pin (Non inverting side)
18 Vo6 BTL AMP 3 output pin (Inverting side)
19 Vo7 BTL AMP 4 output pin (Inverting side)
20 Vo8 BTL AMP 4 output pin (Non inverting side)
21 Vg4 BTL AMP 4 output pin (For gain adjustment)
22 Vin4 BTL AMP 4 output pin
23 Vref Level shift circuit's reference voltage application
24 Vcc Power supply (Shorted to pin 1)
B T L
driver
B T L
driver
Level
shift
Level
shift
11k
ohm
out
RESET
Regulator
Reg
In
1-30 (No.22036)
Page 31

4.8 LC72136N (IC2) : PLL frequency synthesizer
•Pin layout
1
XT
FM/AM
CE
DI
CLOCK
DO
FM/ST/VCO
AM/FM
SDIN
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
22
21
20
19
18
17
16
15
14
13
12
XT
GND
LPFOUT
LPFIN
PD
VCC
FMIN
AMIN
IFCONT
IFIN
• Block diagram
1
22
16
15
3
4
5
6
17
21
1/2
C
2B
I/F
Power
on
Reset
Reference
Swallow Counter
Swallow Counter
Programmable
Data Shift Register & Latch
7821113
• Pin function
Pin
Symbol I/O Function
No.
1 XT I X'tal oscillator connect (75kHz)
2FM
/AM O LOW:FM mode
3 CE I When data output/input for 4pin(input)
and 6pin(output): H
4 DI I Input for receive the serial data from
controller
5 CLOCK I Sync signal input use
6 DO O Data output for Controller Output port
7 FM/ST/VCO O Low: MW mode
8AM
/FM O Open state after the power on reset
9 LW I/O Input/output port
10 MW I/O Input/output port
11 SDIN I/O Data input/output
12 IFIN I IF counter signal input
Driver
1/16,1/17 4bit
1/16,1/17 4bit
12bit
DriverS
Phase
Detector
Charge Pump
Unlock
Detector
Universal
Counter
Pin
Symbol I/O Function
No.
18
19
20
12
13 IFCONT O IF signal output
14 - Not use
15 AMIN I AM Local OSC signal output
16 FMIN I FM Local OSC signal input
17 VCC - Power suplly(VDD=4.5-5.5V)
When power ON:Reset circuit move
18 PD O PLL charge pump output (H: Local
OSC frequency Height than Reference
frequency.L: Low Agreement: Height
impedance)
19 LPFIN I Input for active lowpassfilter of PLL
20 LPFOUT O Output for active lowpassfilter of PLL
21 GND - Connected to GND
22 XT
I X'tal oscillator(75KHz)
(No.22036)1-31
Page 32

4.9 LC75345M-X (IC901) : E.volume
• Pin layout
CL
VDD
ROPOUT
36 35 34 33 32 31 30 29 28 27 26 25 24 23 22 21 20 19
DI
CE
VSS
RINM
RINP
LINM
LOPOUT
ROOUT
RSB
LINP
LOUT
RBASS2
RBASS1
LSB
LBASS2
RTRE
RVRIN
LTRE
LBASS1
RSELOR5R4
L5
LVRIN
LSELO
R3
L4
R2
L3
R1
L2
Vref
181716151413121110987654321
L1
• Block diagram
14
L5
15
L4
16
L3
17 18
L2
L1
19
Vref
20
R1
21
R2
22 23
R3
R4
24
R5
LSELO
13
LVRIN
12
LTRE
11
LVref
RVref
CONTROL
CIRCUIT
LOGIC
CIRCUIT
CONTROL
CIRCUIT
LBASS1
10
LBASS2
9
LSB
8
CCB
INTERFACE
LOUT
7
6
LINP
5
LINM
LOPOUT
34
VSS
2
CE
1
DI
36
CL
35
VDD
34
ROPOUT
33
RINM
32
RINP
1-32 (No.22036)
25
RESLO
26
RVRIN
27
RTRE
28
RBASS1
29
RBASS2
30
RSB
31
ROUT
Page 33

• Pin function
Pin No. Symbol Function
1 DI Serial data and clock input pin for control.
2 CE Chip enable pin.
3 VSS Ground pin.
4 LOPOUT Output pin of general-purpose operation amplifier.
5 LINM Non-inverted input pin of general-purpuse operation amplifier.
6 LINP Non-inverted input pin of general-purpuse operation amplifier.
7 LOUT ATT + equalizer output pin.
8 LSB Capacitor and resistor connection pin comprising filters for bass and super-bass band.
9 LBASS2 Capacitor and resistor connection pin comprising filters for bass and super-bass band.
10 LBASS1 Capacitor and resistor connection pin comprising filters for bass and super-bass band.
11 LTRE Capacitor and resistor connection pin comprising treble band fil ter.
12 LVRIN Volume input pin.
13 LSELO Input selector output pin.
14 L5 Input signal pin.
15 L4 Input signal pin.
16 L3 Input signal pin.
17 L2 Input signal pin.
18 L1 Input signal pin.
19 Vref 0.5 x VDD voltage generation block for analog ground.
20 R1 Input signal pin.
21 R2 Input signal pin.
22 R3 Input signal pin.
23 R4 Input signal pin.
24 R5 Input signal pin.
25 RSELO Input selector output pin.
26 RVRIN Volume input pin.
27 RTRE Capacitor connection pin comprising treble band filter.
28 RBASS1 Capacitor and resistor connection pin comprising filter for bass and super-bass band.
29 RBASS2 Capacitor and resistor connection pin comprising filter for bass and super-bass band.
30 RSB Capacitor and resistor connection pin comprising filte r for bass and super-bass band .
31 ROUT ATT + equalizer output pin.
32 RINP Non inverted input pin of general-purpose operation amplifier.
33 RINM Non inverted input pin of general purpose operation amplifier.
34 ROPOUT Output pin of gen eral-purpose operation amplifier.
35 VDD Supply pin.
36 CL Serial data and clock input pin for control.
(No.22036)1-33
Page 34

4.10 MN662748RPMFA (IC651) : Digital servo & Digital signal processor
A
R
• Pin layout
20 ~ 1
• Block diagram
LRCKIN(MSEL)
BCLK(SSEL)
SRDATAIN
(PSEL)
IOSEL
CLVS
CRC
BLKCK
CLDCK
SBCK
SUBC
DEMPH
RESY
FLAG6(RESY)
SSEL
SQCK
SUBQ
AVDD2
AVDD2
PCK
EFM
PLLF
DSLF
IREF
DRF
ARF
RSEL
PSEL
MLD
MCLK
MDATA
CK384(EFM)
VCOF
BYTCK
SMCK
FCLK
CSEL
MSEL
X2
X1
ÊSTAT
21
~
40
SUB
CODE
BUFFER
DSL.
PLL
VCO
ITUNING
GENERATION
PITCH
CONTROL
41 ~ 60
DIGITAL
DEEMPHSIS
VCO
80
~
61
8TIMES
OVER SAMPUNC
DIGITAL FILTER
EFM
DEMODULATION
SYNC
INTERPOLATION
SUBCODE
DEMODULATION
MICRO
COMPUTER
INTERFACE
A/D
COVERTER
1BIT
DAC
LOGIC
S
16k
SRAM
CIRC
ERROR
CORRECTION
DEINTERLEVE
CLV
SERVO
INPUT
PEM
(R)
PEM
(L)
D/A
CONVERTER
OUTPUT
DIGITAL
AUDIO
INTERFASE
DIGITAL
AUDIO
INTERFASE
INTER POLATION
SOFT MUTING DIGITAL
ATTENUATION
PEAK DETECTIVE
AUTO CUE
PORT
SERVO
TIMING GENERATOR
AVSS1
AVDD1
OUTR
OUTL
FLAG
IPFLAG
TX
ECM
PC
LRCK
SRDAT
BCLK
DMUTE
TRKV
KICK
VREF
TRVST
ECS
TVD
TRD
FOD
TBAL
FBAL
TOFS
TES
/TLOCK
/FLOCK
PLAY
LDON
WVEL
SENSE
1-34 (No.22036)
D
/
D
V
V
V
S
D
D
S
D
D
1
/
R
V
T
S
S
E
T
S
S
1
T
F
E
R
T
F
E
E
N
V
T
R
C
R
S
B
V
D
D
O
E
T
/
R
F
D
E
O
F
T
Page 35

• Pin function
Pin No. Symbol I/O Function
1 BCLK O Not used
2 LRCK O Not used
3 SRDATA O Not used
4 DVDD1 - Power supply (Digital)
5 DVSS1 - Connected to GND
6 TX O Digital audio interface output
7 MCLK I CPU command clock signal input
(Data is latched at signal's rising
point)
8 MDATA I CPU command data inp ut
9 MLD I CPU command load signal input
10 SENSE O Sense signal output
11 FLOCK O Focus lock signal output Active :Low
12 TLOCK O Tracking lock signal output Active
:Low
13 BLKCK O sub-code/block/clock signal output
14 SQCK I Outside clock for sub-code Q resister
input
15 SUBQ O Sub-code Q -code output
16 DMUTE Connected to GND
17 STATUS O "Status signal
(CRC,CUE,CLVS,TTSTOP,ECLV,EC
LV,SQOK)"
18 RST I Reset signa l input (L:Reset)
19 SMCK - Not used
20 PMCK - Not used
21 TRV O Traverse enforced output
22 TVD O Traverse drive output
23 PC - Not used
24 ECM O Spindle motor drive signal (Enforced
mode output) 3-State
25 ECS O "Spindle motor drive signal (Servo er-
ror signal output)"
26 KICK O Kick pulse output
27 TRD O Tracking drive output
28 FOD O Focus drive output
29 VREF I "Reference voltage input pin for D/A
output block (TVD,FOD,FBA,TBAL)"
30 FBAL O Focus Balance adjust signal output
31 TBAL O Tracking Balance adjust signal output
32 FE I Focus error signal input (Analog in-
put)
33 TE I Tracking error signal input (Analog in-
put)
34 RF ENV I RF envelope signal input (Analog in-
put)
35 VDET I Vibration detect signal input (H:de-
tect)
36 OFT I Off track signal input (H:off track)
37 TRCRS I Track cross signal input
Pin No. Symbol I/O Function
38 RFDET I RF detect signal input (L:detect)
39 BDO I BDO input pin (L:detect)
40 LDON I Laser ON signal output (H:on)
42 TES O Tracking error shunt signal output
(H:shunt)
41 PLAY - Not used
43 WVEL - Not used
44 ARF I RF signal input
45 IREF I Reference current input pin
46 DRF I Bias pin for DSL
47 DSLF I/O Loop filter pin for DSL
48 PLLF I/O Loop filter pin for PLL
49 VCOF - Not used
50 AVDD2 - Power supply (Analog)
51 AVSS2 - Connected to GND (Analog)
52 EFM - Not used
53 PCK - Not used
54 PDO - Not used
55 SUBC - Not used
56 SBCK - Not used
57 VSS - "Connected to GND (for X'tal oscilla-
tion circuit)"
58 XI I Input of 16.9344MHz X'tal oscillation
circuit
59 X2 O Output of X'tal oscillation circuit
60 VDD - Power supply (for X'tal oscillation cir-
cuit)
61 BYTCK - Not used
62 CLDCK - Not used
63 FLAG - Not used
64 IPPLAG - Not used
65 FLAG - Not used
66 CLVS - Not used
67 CRC - Not used
68 DEMPH - Not used
69 RESY - Not used
70 IOSEL - pull up
71 TEST - pull up
72 AVDD1 - Power supply (Digital)
73 OUT L O Lch audio output
74 AVSS1 - Connected to GND
75 OUT R O Rch audio output
76 RSEL - pull up
77 CSEL - Connected to GND
78 PSEL - Connected to GND
79 MSEL - Connected to GND
80 SSEL - Pull up
(No.22036)1-35
Page 36

4.11 LA72723(IC3): RDS demodulation
/
• Pin layout
VREF
MPXIN
Vdda
Vssa
FLOUT
CIN
TES
XOUT
• Block Diagram
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
+5V
Vdda
Vssa
MPXIN
TEST
RDS-ID/READY
16
RDCL
15
RDDA
14
RST
13
MODE
12
Vddd
11
Vssd
10
XIN
9
REFERENCE
VOLTAGE
ANTI ALIASING
FILTER
TEST
VREF
57kHz
(SCF)
BPF
FLOUT
SMOOTHING
FILTER
CLK(4.332MHz)
OSC
VREF
CIN
+
PLL
(57kHz)
-
CLOCK
RECOVERY
(1187.5Hz)
DATA
DECODER
RAM
(128-bits)
RDS-ID
DETECT
Vddd
Vssd
RDDA
RDCL
MODE
RST
RDS-ID
READY
+5V
XIN
XOUT
• Pin functions
Pin No. Symbol I/O Function
1 VREF O Reference voltage output (Vdda/2)
2 MPXIN I Baseband (multiplexed) signal input
3 Vdda - Analog power supply (+5V)
4 Vssa - Analog ground
5 FLOUT O Subcarrier input (filter output)
6 CIN I Subca rrier input (comparator inp ut)
7 TEST I Test input
8 XOUT O Crystal oscillator output (4.332MHz)
9 XIN I Crystal oscillator input (exeternal referen c e input)
10 Vssd - Digtal ground
11 Vddd - Digtal power supply
12 MODE I Read mode setting (0:ma ster, 1:slave)
13 RST I RDS-ID/RAM reset (positive polarity)
14 RDDA O RDS data output
15 RDCL I/O RDS clock output (master mode)/RDS clock input (slave mode)
16 RDS-ID/READY O RDS-ID/READY output (negative polarity)
1-36 (No.22036)
Page 37

4.12 LB1641 (IC801) : DC motor driver
•Pin layout •Truth table
Input Output Mode
IN1 IN2 OUT1 OUT2
0000 Brake
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
GND OUT1 P1
VZ IN1 IN2
VCC1
VCC2 P2
10
OUT2
1 0 1 0 CLOCKWISE
0 1 0 1 COUNTER-CLOCKWISE
1100 Brake
4.13 NJU6433FG1 (IC934) : LCD driver
• Pin layoout • Pin function
49
3348
32
Pin
No.
Symol Function
1~50 SEG1~SEG50 Se gment output terminal for LCD.
51,52 OSC1,OSC2 CR oscillating terminal.
53 VDD Power supply terminal for inside.
54 Vss G ND level.
55 VLCD Power supply terminal for LCD drive.
56 CE Chip enable.
64
17
1
16
57 SCL Serial data transmission clock terminal.
58 DATA Serial data input terminal.
59 MODE Mode-setting-signal input terminal.
60 INH Display-off control signal input terminal.
61~44 COM4~COM1 Commo n output terminal for LCD.
• Block diagram
VDD
Vss
VLCD
INH
OSC1
OSC2
CE
DATA
MODE
SCL
COMMON
DRIVER
DIVIDING
CIRCUIT
OSC
COM1
INPUT
SELECTING
CIRCUIT
COM4
SEG50
MSB LSB
SHIFT REGISTOR 4
50bit
DECORDER
LATCH CIRCUIT/SEGMENT DRIVER
MSB LSB
SHIFT REGISTOR 3
50bit
SHIFT RESISTOR
CONTROL CIRCUIT
MSB LSB
SHIFT REGISTOR 2
50bit
INPUT CHANGING CIRCUIT
MSB LSB
SHIFT REGISTOR 1
50bit
SEG1
(No.22036)1-37
Page 38

4.14 UPD780055GC-045 (IC931) : Micon
• Pin layout
60 ~ 41
40
61
~
~
80
21
1 ~ 20
• Pin function
Pin No. Symbol I/O Function
1 SAFETY0 I Irregular voltage detection 0
2 REST/OP_SW/CL_SW I REST/CLOSE switch detect port
3 SCD I CD safety voltage detect port
4 AVSS - GND
5NC-Not use
6NC-Not use
7 AVREF1 - Reference voltage
8 SUBQ/RDDA I Q-code data input port
9NC-Not use
10 SQCK O Q-code serial clock
11 STAT I Status input port
12 MDATA O Data input port
13 MCLK O Data clock
14 RST O Reset
15 MLD O Command ready signal
16 MUTE O Mute control port
17 SDATA/VOLDA O Serial data / Volume data
18 SCK/VOLCK O Serial clock / Volume clock
19 FLAG - Not use
20 CLOSE I Door close switch input port
21 OPEN I Door open switch input port
22 FCD O CD Function ('H'=CD)
23 NC - Not use
24 NC - Not use
25 VOLCE O Volumn Chip Enable
26 NC - Not use
27 LINEMUTE O Line mute
28 PBMUTE O Playback mute
29 SMUTE O System mute
30 SPKMUTE O Speaker mute
31 AHB O AHB control
32 POUT O Power On/Off ('H'=Power On)
33 VSS - GND
34 PROTECTOR O Protector
35 MODEL1 I MODEL setting
36 MODEL2 I MODEL setting
1-38 (No.22036)
Page 39

Pin No. Symbol I/O Function
37 NC - Not use
38 NC - Not use
39 NC - Not use
40 LEDRV O LED indicate Reverse
41 LEDREC O LED indicate REC
42 LEDFR O LED indicate Forward
43 STTA O Tape strobe
44 DATA O LCD data
45 MODE O LCD data mode control
46 SCL O LCD serial clock
47 NC - Not use
48 PHOTO I Tape end detection
49 INH O LCD driver inhibit ('L' at end of transmission)
50 LCDCE - LCD chip enable
51 DIMMER - Dimmer control
52 VOL+ I Volumn plus
53 LEDCTL O Power standby LED control
54 BASS- I Bass minus
55 VOL- I Volumn minus
56 BASS+ I Bass plus
57 TUST/CE O Tuner PLL strobe
58 FTUNER O T uner function ('H'=TUNER)
59 BUP O Back up power detect ('H'=BACKUP)
60 RESET - Reset signal
61 REM I Remote control input
62 RDSCK I RDS clock
63 MPX I FM stereo detection ('L' =STEREO)
64 NC - Not use
65 +BCTL - Not use
66 BLKCL I Block clock input port
67 VSS0 - GND
68 VDD - Power supply
69 X2 - Not use
70 X1 - Not use
71 IC - GND
72 XT2 - Not use
73 XT1 - Not use
74 AVDD - Power supply
75 AVREF0 - Reference voltage
76 SAFETY1 I Irregular voltage detection 1
77 TAPE0 I Tape Switch 0
78 TAPE1 I Tape Switch 1
79 KEY0 I Unit Key input 1
80 KEY1 I Unit Key input 0
(No.22036)1-39
Page 40

4.15 TDA7294 (IC940,IC941) : Audio amp.
• Pin layout
• Block diagram
15
14
13
12
11
10
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
BOOTSTRAP
-Us (POWER)
OUT
+Us (POWER)
N.C.
N.C.
MUTE
STAND-BY
-Us (SIGNAL)
+Us (SIGNAL)
BOOTSTRAP
N.C.
SUR
NON INUERTING INPUT
INVERTING INPUT
STAND-BY GND
+Vs
BOOTSTRAP
IN+
IN-
BIPOLAR
TRANSCONDUCTANCE
INPUT STAGE
LEVEL SHIFTING
STAGE
OUTPUT
-Vs
MOS CUTPUT STAGEMOS GHAIN &
SHORT CIRCUIT
PROTECTION
1-40 (No.22036)
Page 41

(No.22036)1-41
Page 42

VICTOR COMPANY OF JAPAN, LIMITED
AV & MULTIMEDIA COMPANY AUDIO/VIDEO SYSTEMS CATEGORY 10-1,1chome,Ohwatari-machi,Maebashi-city,371-8543,Japan
(No.22036)
Printed in Japan
WPC
 Loading...
Loading...