Page 1

SERVICE MANUAL
COMPACT COMPONENT SYSTEM
HX-Z1
Tentative
HX-Z1
HX-Z1
Contents
Safety precautions
Preventing static electricity
Important for laser products
Importance administering
point on the safety
Disassembly method
S
1-2
1-3
1-4
1-5
1-6
COMPACT
DIGITAL AUDIO
E
M
D
N
O
U
D
O
E
S
E
E
R
T
P
M
U
L
O
V
Area Suffix
J ------------------------- U.S.A.
C ----------------------- Canada
Adjustment method
1-24
Flow of functional operation
until TOC read (CD)
Maintenance of laser pickup
Replacement of laser pickup
Description of major ICs
1-29
1-30
1-30
1-31~41
COPYRIGHT 2002 VICTOR COMPANY OF JAPAN, LTD.
No.21088
Jun. 2002
1-1
Page 2
HX-Z1
1. This design of this product contains special hardware and many circuits and components specially for safety
purposes. For continued protection, no changes should be made to the original design unless authorized in
writing by the manufacturer. Replacement parts must be identical to those used in the original circuits. Services
should be performed by qualified personnel only.
2. Alterations of the design or circuitry of the product should not be made. Any design alterations of the product
should not be made. Any design alterations or additions will void the manufacturer`s warranty and will further
relieve the manufacture of responsibility for personal injury or property damage resulting therefrom.
3. Many electrical and mechanical parts in the products have special safety-related characteristics. These
characteristics are often not evident from visual inspection nor can the protection afforded by them necessarily
be obtained by using replacement components rated for higher voltage, wattage, etc. Replacement parts which
have these special safety characteristics are identified in the Parts List of Service Manual. Electrical
components having such features are identified by shading on the schematics and by ( ) on the Parts List in
the Service Manual. The use of a substitute replacement which does not have the same safety characteristics
as the recommended replacement parts shown in the Parts List of Service Manual may create shock, fire, or
other hazards.
4. The leads in the products are routed and dressed with ties, clamps, tubings, barriers and the like to be
separated from live parts, high temperature parts, moving parts and/or sharp edges for the prevention of
electric shock and fire hazard. When service is required, the original lead routing and dress should be
observed, and it should be confirmed that they have been returned to normal, after re-assembling.
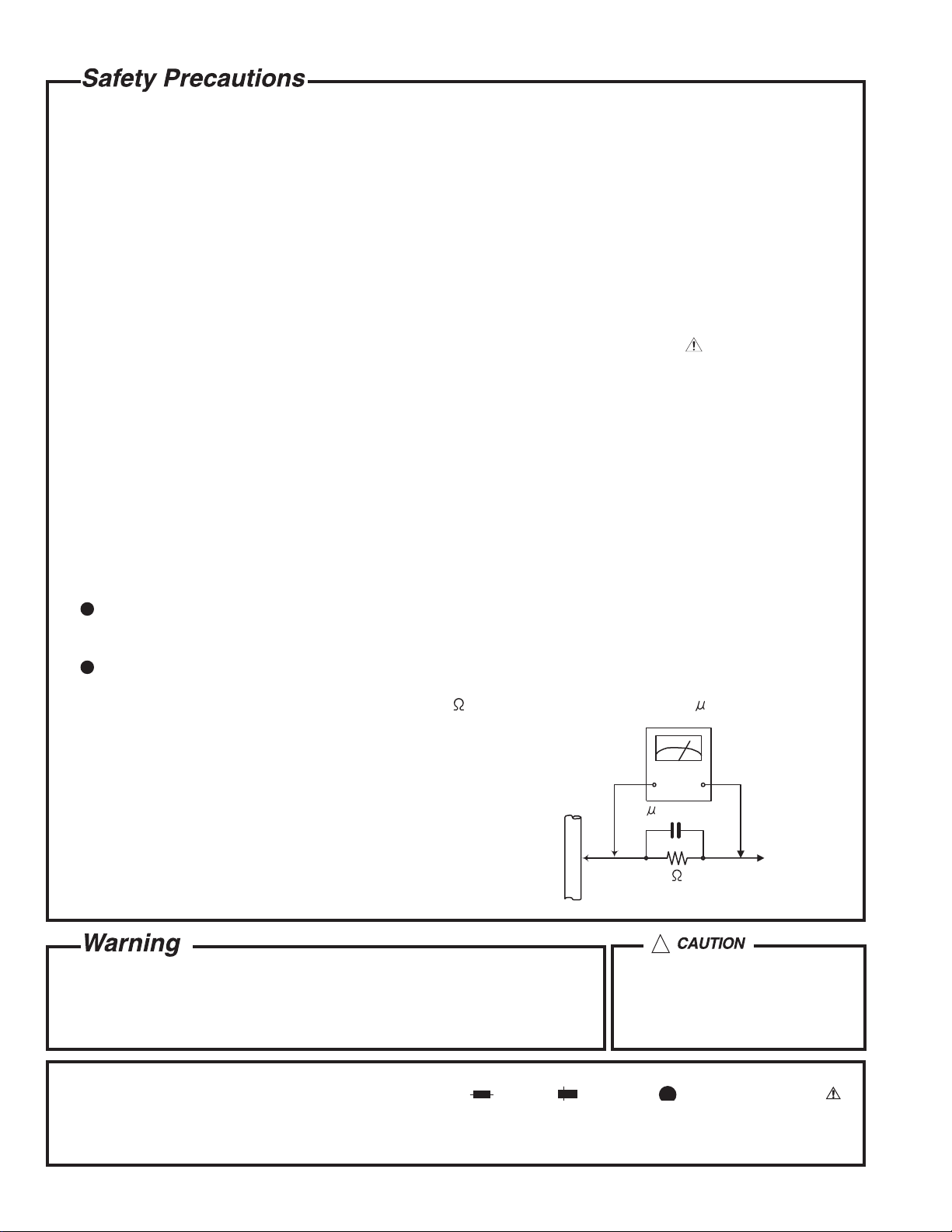
5. Leakage currnet check (Electrical shock hazard testing)
After re-assembling the product, always perform an isolation check on the exposed metal parts of the product
(antenna terminals, knobs, metal cabinet, screw heads, headphone jack, control shafts, etc.) to be sure the
product is safe to operate without danger of electrical shock.
Do not use a line isolation transformer during this check.
Plug the AC line cord directly into the AC outlet. Using a "Leakage Current Tester", measure the leakage
current from each exposed metal parts of the cabinet, particularly any exposed metal part having a return
path to the chassis, to a known good earth ground. Any leakage current must not exceed 0.5mA AC (r.m.s.).
Alternate check method
Plug the AC line cord directly into the AC outlet. Use an AC voltmeter having, 1,000 ohms per volt or more
sensitivity in the following manner. Connect a 1,500 10W resistor paralleled by a 0.15 F AC-type capacitor
between an exposed metal part and a known good earth ground.
Measure the AC voltage across the resistor with the AC
voltmeter.
Move the resistor connection to each exposed metal part,
particularly any exposed metal part having a return path to
the chassis, and meausre the AC voltage across the resistor.
Now, reverse the plug in the AC outlet and repeat each
measurement. Voltage measured any must not exceed 0.75 V
AC (r.m.s.). This corresponds to 0.5 mA AC (r.m.s.).
0.15 F AC TYPE
1500 10W
Good earth ground
AC VOLTMETER
(Having 1000
ohms/volts,
or more sensitivity)
Place this
probe on
each exposed
metal part.
!
1. This equipment has been designed and manufactured to meet international safety standards.
2. It is the legal responsibility of the repairer to ensure that these safety standards are maintained.
3. Repairs must be made in accordance with the relevant safety standards.
4. It is essential that safety critical components are replaced by approved parts.
5. If mains voltage selector is provided, check setting for local voltage.
Burrs formed during molding may
be left over on some parts of the
chassis. Therefore, pay attention to
such burrs in the case of
preforming repair of this system.
In regard with component parts appearing on the silk-screen printed side (parts side) of the PWB diagrams, the
parts that are printed over with black such as the resistor ( ), diode ( ) and ICP ( ) or identified by the " "
mark nearby are critical for safety.
(This regulation does not correspond to J and C version.)
1-2
Page 3
HX-Z1
Preventing static electricity
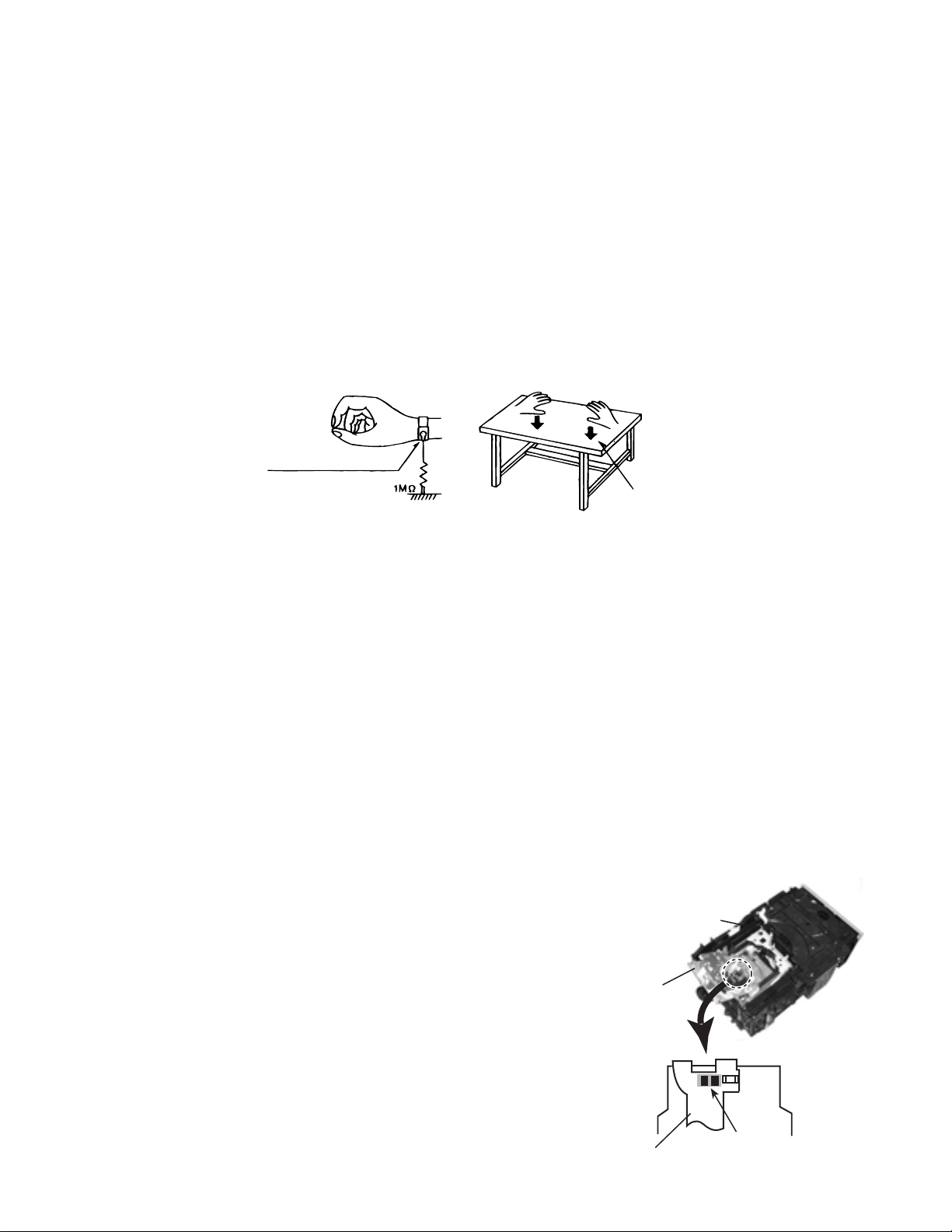
1. Grounding to prevent damage by static electricity
Electrostatic discharge (ESD), which occurs when static electricity stored in the body, fabric, etc. is discharged,
can destroy the laser diode in the traverse unit (optical pickup). Take care to prevent this when performing repairs.
2. About the earth processing for the destruction prevention by static electricity
In the equipment which uses optical pick-up (laser diode), optical pick-up is destroyed by the static electricity of
the work environment.
Be careful to use proper grounding in the area where repairs are being performed.
2-1 Ground the workbench
Ground the workbench by laying conductive material (such as a conductive sheet) or an iron plate over
it before placing the traverse unit (optical pickup) on it.
2-2 Ground yourself
Use an anti-static wrist strap to release any static electricity built up in your body.
(caption)
Anti-static wrist strap
Conductive material
(conductive sheet) or iron plate
3. Handling the optical pickup
1. In order to maintain quality during transport and before installation, both sides of the laser diode on the
replacement optical pickup are shorted. After replacement, return the shorted parts to their original condition.
(Refer to the text.)
2. Do not use a tester to check the condition of the laser diode in the optical pickup. The tester's internal power
source can easily destroy the laser diode.
4. Handling the traverse unit (optical pickup)
1. Do not subject the traverse unit (optical pickup) to strong shocks, as it is a sensitive, complex unit.
2. Cut off the shorted part of the flexible cable using nippers, etc. after replacing the optical pickup. For specific
details, refer to the replacement procedure in the text. Remove the anti-static pin when replacing the traverse
unit. Be careful not to take too long a time when attaching it to the connector.
3. Handle the flexible cable carefully as it may break when subjected to strong force.
4. It is not possible to adjust the semi-fixed resistor that adjusts the laser power. Do not turn it
Attention when traverse unit is decomposed
*Please refer to "Disassembly method" in the text for pick-up and how to
detach the CD traverse mechanism.
1. Remove the disk stopper and T. bracket on the CD changer mechanism
assembly.
2. Disconnect the harness from connector on the CD motor board.
3. CD traverse unit is put up as shown in Fig.1.
4. Solder is put up before the card wire is removed from connector CN601
on the CD servo control board as shown in Fig. 2.
(When the wire is removed without putting up solder, the CD pick-up
assembly might destroy.)
5. Please remove solder after connecting the card wire with CN601 when
you install picking up in the substrate.
CD changer
mechanism
assembly
CD traverse
unit
Flexible cable
Fig.1
Soldering
Fig.2
1-3
Page 4
HX-Z1
Important for laser products
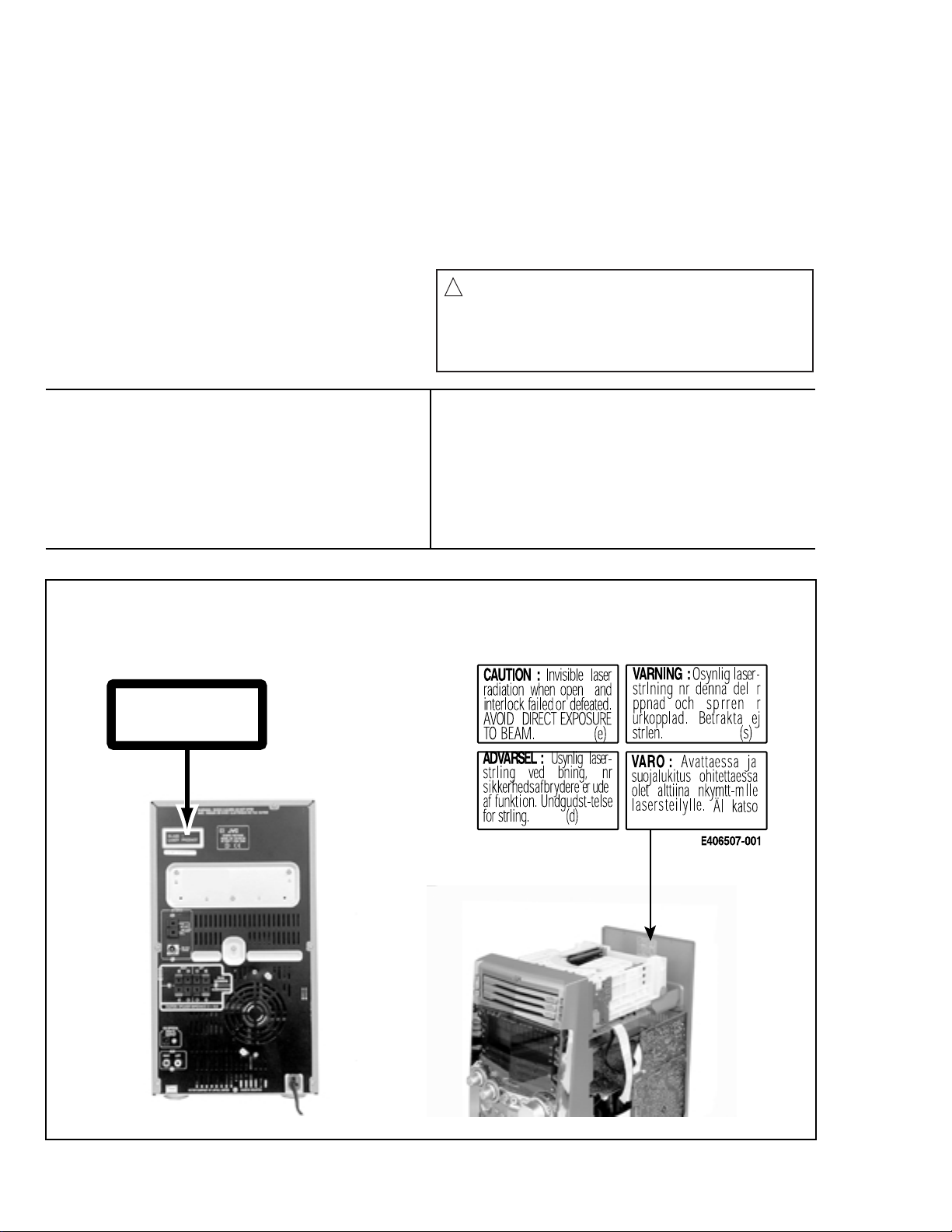
1.CLASS 1 LASER PRODUCT
2.DANGER : Invisible laser radiation when open and inter
lock failed or defeated. Avoid direct exposure to beam.
3.CAUTION : There are no serviceable parts inside the
Laser Unit. Do not disassemble the Laser Unit. Replace
the complete Laser Unit if it malfunctions.
4.CAUTION : The compact disc player uses invisible
laserradiation and is equipped with safety switches
whichprevent emission of radiation when the drawer is
open and the safety interlocks have failed or are de
feated. It is dangerous to defeat the safety switches.
VARNING : Osynlig laserstrålning är denna del är öppnad
och spårren är urkopplad. Betrakta ej strålen.
VARO : Avattaessa ja suojalukitus ohitettaessa olet
alttiina näkymättömälle lasersäteilylle.Älä katso
säteeseen.
5.CAUTION : If safety switches malfunction, the laser is able
to function.
6.CAUTION : Use of controls, adjustments or performance of
procedures other than those specified herein may result in
hazardous radiation exposure.
CAUTION
!
Please use enough caution not to
see the beam directly or touch it
in case of an adjustment or operation
check.
ADVARSEL : Usynlig laserstråling ved åbning , når
sikkerhedsafbrydere er ude af funktion. Undgå
udsættelse for stråling.
ADVARSEL : Usynlig laserstråling ved åpning,når
sikkerhetsbryteren er avslott. unngå utsettelse
for stråling.
REPRODUCTION AND POSITION OF LABELS
WARNING LABEL
CLASS 1
LASER PRODUCT
1-4
Page 5
Importance administering point on the safety
HX-Z1
Caution: For continued protection against risk of
fire, replace only with same type 2.5A/125V for
F103, 5A/125V for F001 and 6A/125V for F101, F102.
This symbolspecifies type of fast operating fuse.
Precaution: Pour evitisques de fer reux, remplacez
le fusible de surete de F103 comme le meme type
que 2.5A/125V, et 5A/125V pour F001 et 6A/125V
pour F101, F102.
Ce sont des fusibles suretes qui functionnes rapide.
^
1-5
Page 6
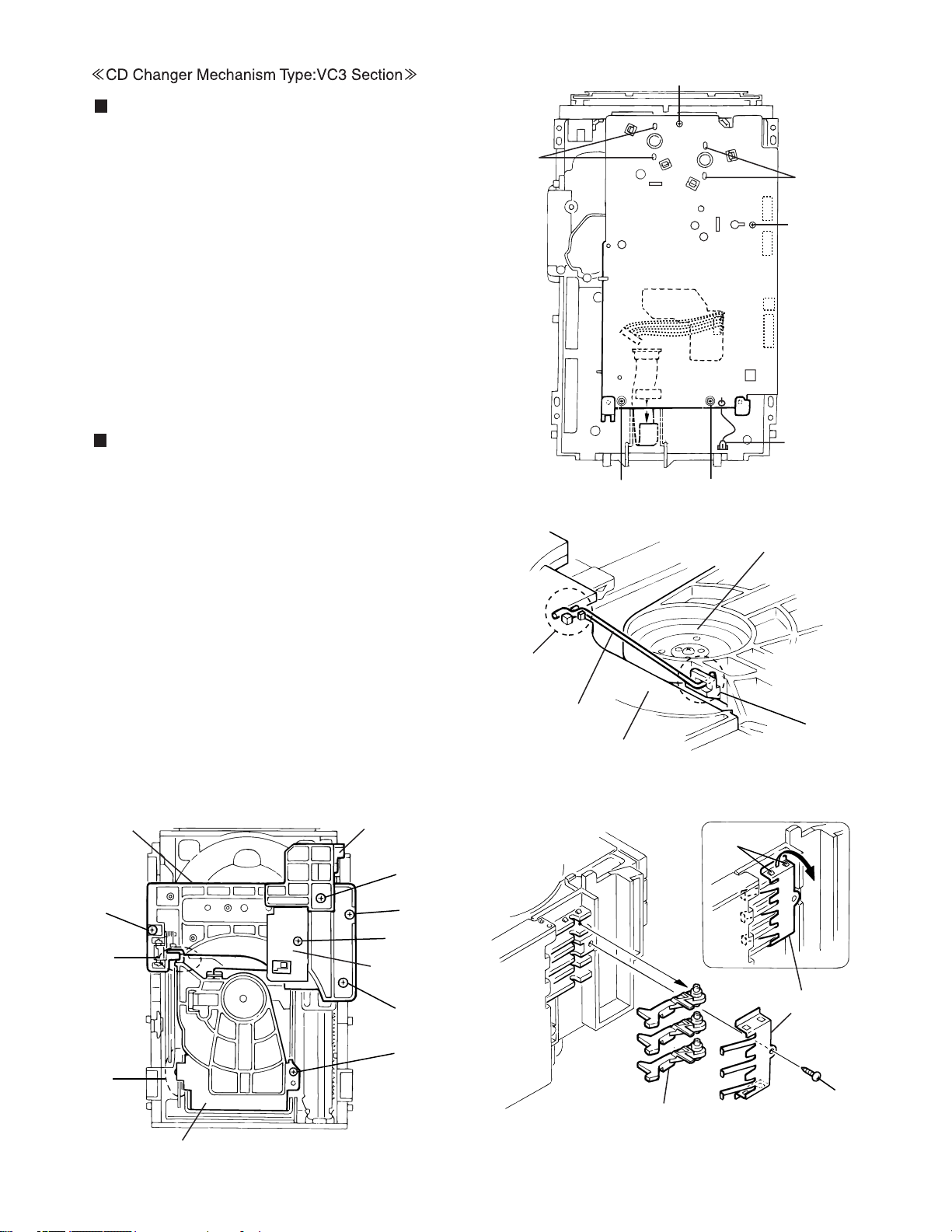
Removing the CD Servo control board
(See Fig.1)
1.Remove the metal cover.
2.Remove the CD changer mechanism assembly.
3.From bottom side the CD changer mechanism assembly,
remove the four screws A retaining the CD servo control
board.
4.Absorb the four soldered positions "a" of the right and
left motors with a soldering absorber.
5.Pull out the earth wire on the CD changer mechanism
assembly.
6.Disconnect the connector CN854 on the CD servo
control board.
7.Disconnect the card wire CN601 and the connector
CN801 on the CD servo control board.
HX-Z1
A
a
a
CN854
A
CN651
CD servo control board
CN652
CN801
CN601
CN151
Removing the CD tray assembly
(See Fig.2~4)
Remove the front panel assembly.
1.
Remove the CD changer mechanism assembly.
2.
Remove the CD Servo control board.
3.
Remove the screw B' retaining the lod stopper.
4.
From the T.bracket section "b" and clamper base
5.
section "c" , remove both of the edges fixing the
rod(See Fig.2 and 3).
Remove the screw B retaining the disc stopper
6.
(See Fig.3).
Remove the three screws C retaining the T.bracket
7.
(See Fig.3).
Remove the screw D retaining the clamper assembly
8.
(See Fig.3).
From the left side face of the chassis assembly, remove
9.
the one screw E retaining both of the return spring and
lock lever(See Fig. 4).
10.
By removing the pawl at the section "d" fixing the return
spring, dismount the return spring(See Fig.4).
11.
Remove the three lock levers(See Fig.4).
T.Braket
Disc stopper
B
Earth
wire
Fig.1
A
Clamper base
A
b
Rod
c
T.Braket
Fig.2
d
CC
B'
a
Lod stopper
(C/J version only)
C
D
b
Lock lever
Clamper ass'y
Fig.3
Fig.4
Return spring
E
1-15
Page 7
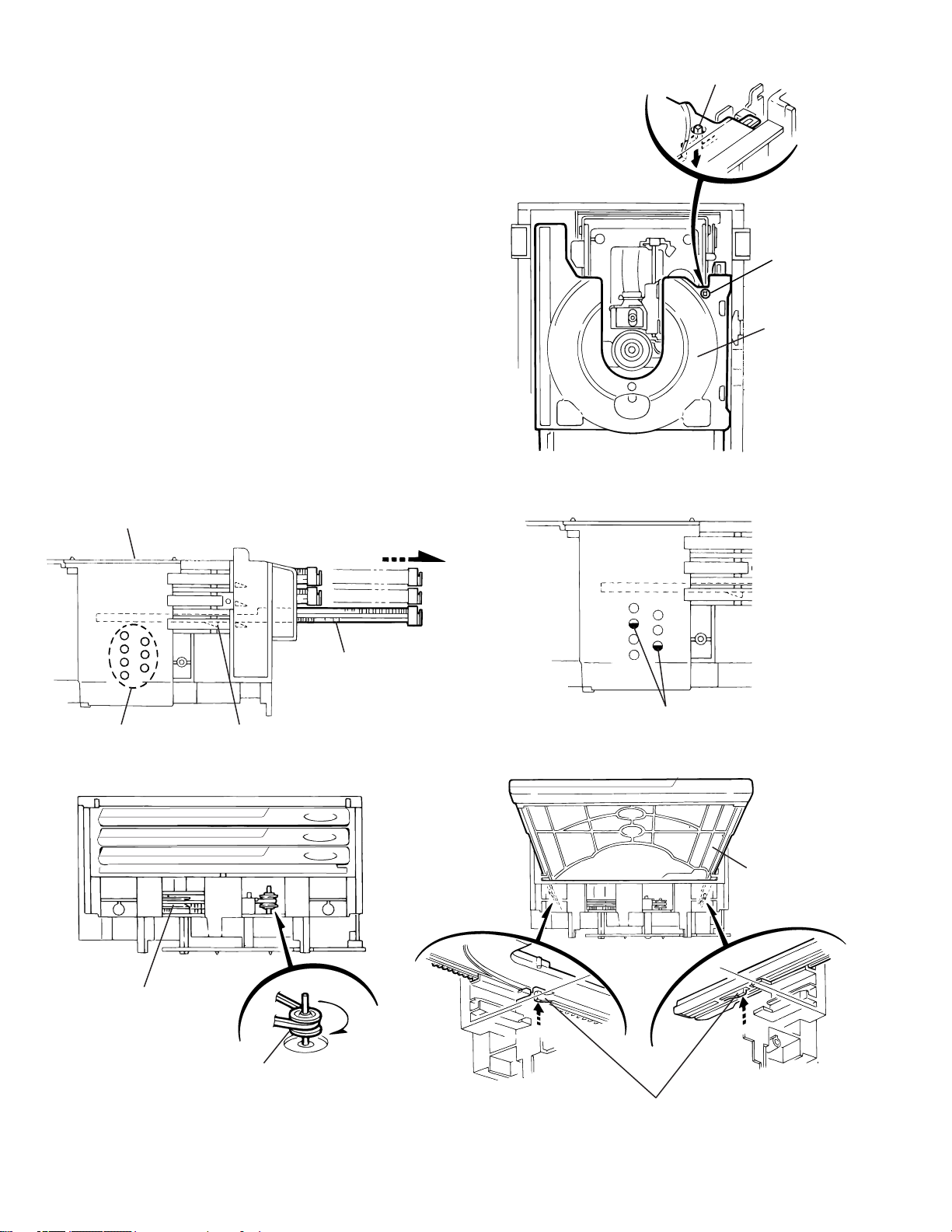
HX-Z1
11.
Check whether the lifter unit stopper has been caught
into the hole at the section "e" of CD tray assembly as
shown in Fig.5.
Make sure that the driver unit elevator is positioned as
12.
shown in Fig.6 from to the second or fifth hole on the
left side face of the CD changer mechanism assembly.
[Caution]
13.
14.
15.
Chassis assembly
In case the driver unit elevator is not at above
position, set the elevator to the position as
shown in Fig.7 by manually turning the pulley
gear as shown in Fig.8.
Manually turn the motor pulley in the clockwise
direction until the lifter unit stopper is lowered from the
section "e" of CD tray assembly(See Fig.8).
Pull out all of the three stages of CD tray assembly in
the arrow direction "f" until these stages stop
(See Fig.6).
At the position where the CD tray assembly has
stopped, pull out the CD tray assembly while pressing
the two pawls "g and g' " on the back side of CD tray
assembly(See Fig.9). In this case, it is easy to pull out
the assembly when it is pulled out first from the stage
CD tray assembly.
Stopper
e
CD tray
assembly
Fig.5
Refer to Fig.7
Pulley gear
Pawl
Fig.6
CD tray assembly
g
CD
CD
CD
f
Drive unit of elevator
Fig.7
3
2
1
CD tray assembly
1-16
Motor pulley
Fig.8
Pawl ,
g
Fig.9
g'
Page 8
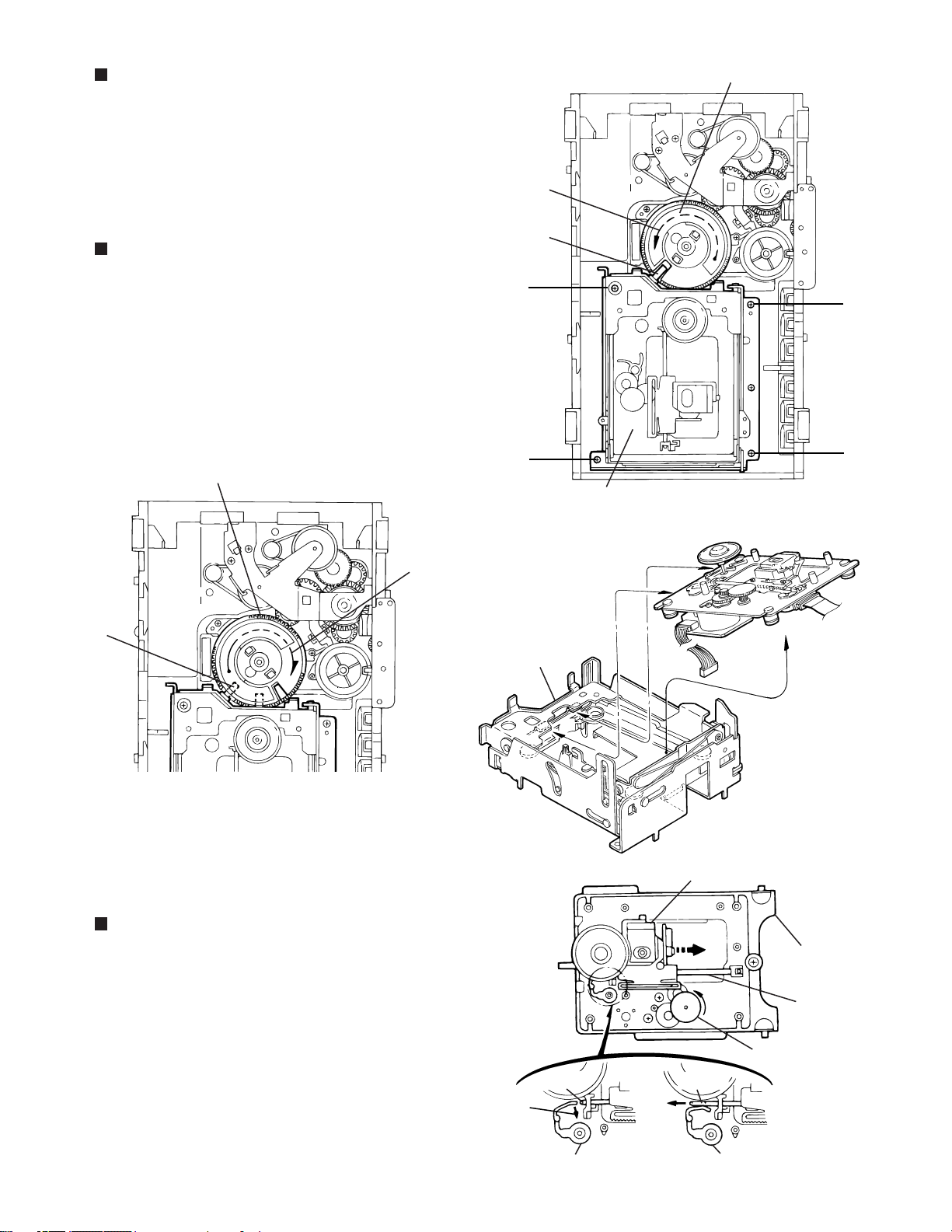
HX-Z1
Removing the CD loading mechanism
assembly(See Fig.10)
1.2.While turning the cams R1 and R2 assembly in the
arrow direction "h" ,align the shaft "i" of the CD loading
mechanism assembly to the position shown in Fig.10.
Remove the four screws F retaining the CD loading
mechanism assembly.
Removing the CD traverse mechanism
(See Fig.11 and 12 )
For dismounting only the CD traverse mechanism
1.
without removing the CD loading mechanism assembly,
align the shaft "j" of the CD loading mechanism
assembly to the position shown Fig.11 while turning the
cam R1 and R2 assembly in the arrow direction "k" .
By raising the CD loading mechanism assembly in the
2.
arrow direction "l", remove the assembly from the lifter
unit
Cam R1, R2 assembly
Cams R1, R2 assembly
Arrow
h
i
F
F
CD loading mechanism assembly
Fig.10
F
F
CD traverse mechanism
Arrow
k
j
Fig.11
Removing the CD pick unit
(See Fig.13 )
1.
Move the cam gear in the arrow direction "m" . Then,
the CD pickup unit will be moved in the arrow direction
"n" .
According to the above step, shift the CD pickup unit to
2.
the center position.
While pressing the stopper retaining the shaft in the
3.
arrow direction "o" , pull out the shaft in the arrow
direction "p".
After dismounting the shaft from the CD pickup unit,
4.
remove the CD pickup unit
Lifter unit
o
Stopper
Shaft
Fig.12
CD Pickup unit
n
m
Shaft
p
Stopper
Fig.13
Arrow
CD loading
mechanism
Shaft
Cam gear
l
1-17
Page 9
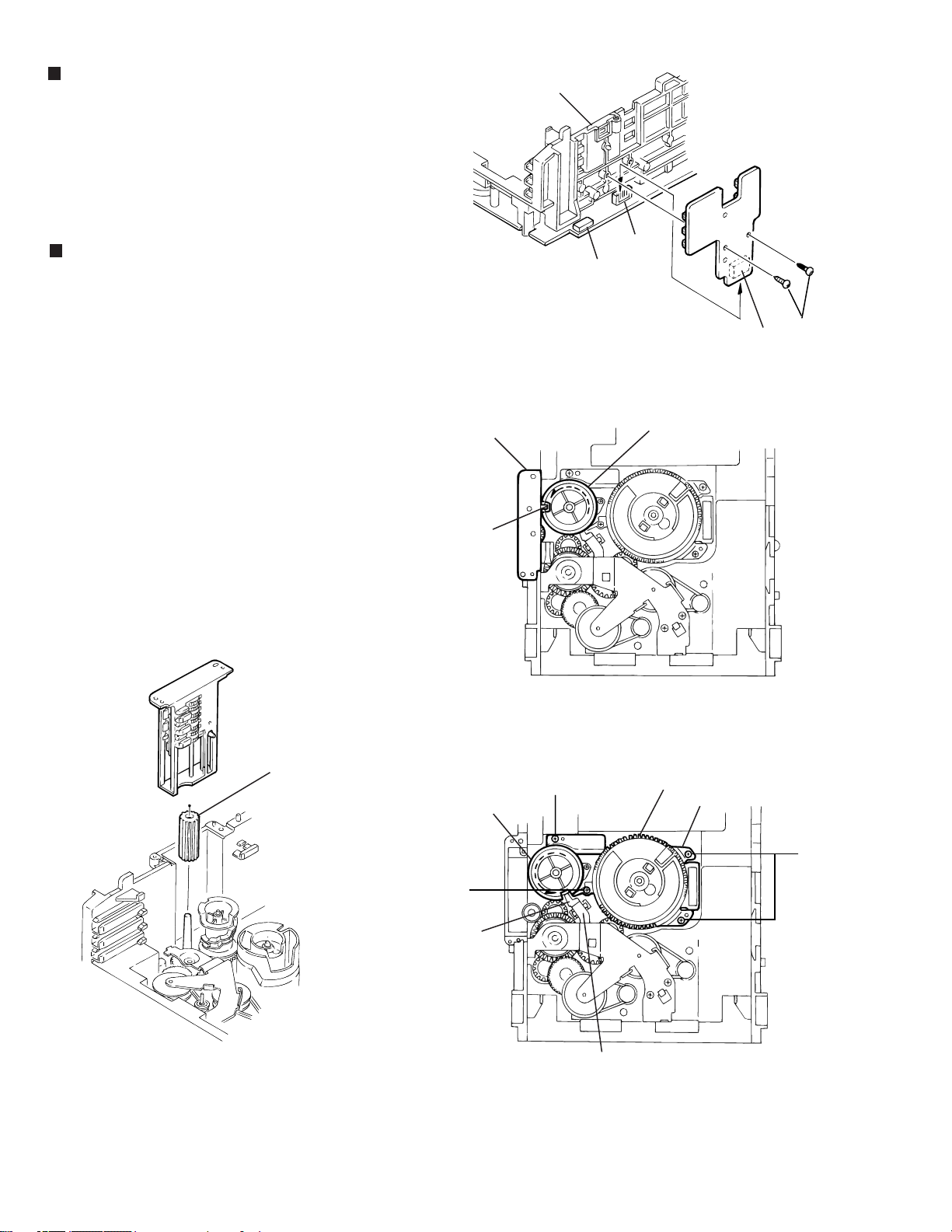
HX-Z1
Removing the try select switch board
(See Fig.14)
1.2.Remove the two screws G retaining the tray select
switch board.
Disconnect the tray select switch board from connector
CN804 on the CD servo control board.
Removing the cam unit
(See Fig.15 ~17 )
1.
Remove the CD loading mechanism assembly.
2.
While turning the cam gear "q", align the Paul "r"
position of the drive unit to the notch position(Fig.16) on
the cam gear "q".
Pull out the drive unit and cylinder gear(See Fig.17).
3.
While turning the cam gear "q", align the Paul "s"
4.
position of the select lever to the notch position(Fig.18)
on the cam gear "q".
Remove the four screws H retaining the cam unit(cam
5.
gear "q" and cams R1/R2 assembly)(See Fig.18).
Chassis assembly
Drive unit
CN851
CN854
Fig.14
Cam gear
Tray select
switch board
CN804
q
G
Drive unit
Cylinder gear
r
Cam gear
H
s
Fig.15
H
q
Cams R1, R2 assembly
Cam unit
J
1-18
Fig.16
Select lever
Fig.17
Page 10
HX-Z1
Fig.18
Fig.20
Fig.19
Fig.21
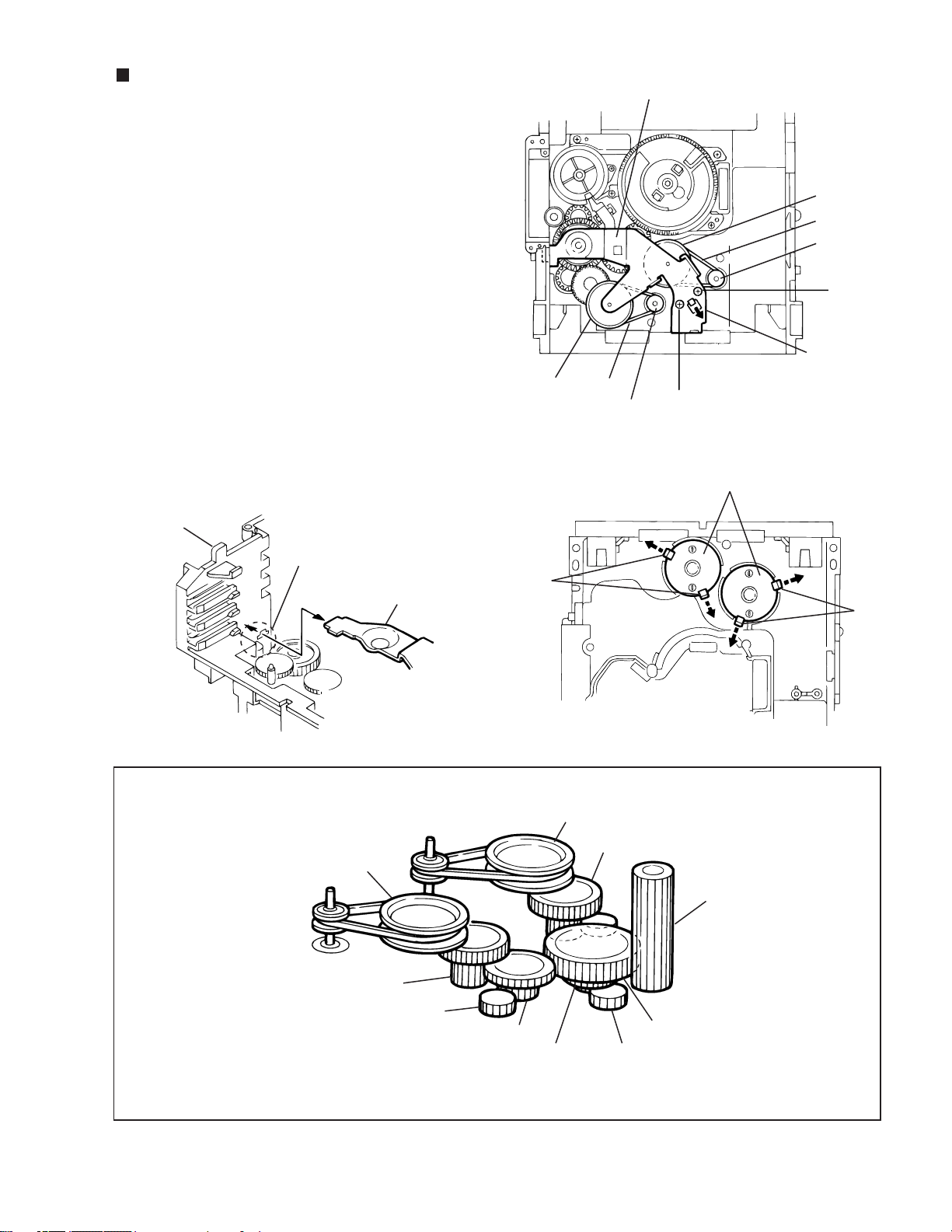
[Note]
When the chassis assembly is turned over under
the conditions wherein the gear bracket and belt
have been removed, then the pulley gear as well
as the gear, etc. constituting the gear unit can
possibly be separated to pieces. In such a case,
assemble these parts by referring to the assembly
and configuration diagram in Fig. 21.
Removing the actuator motor and belt
(See Fig.18~21)
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
Remove the two screws I retaining the gear bracket
(See Fig.18).
While pressing the pawl "t" fixing the gear bracket in the
arrow direction, remove the gear bracket
(See Fig.18).
From the notch "u section" on the chassis assembly
fixing the edge of gear bracket, remove and take out the
gear bracket(See Fig. 19).
Remove the belts respectively from the right and left
actuator motor pulleys and pulley gears(See Fig. 18).
After turning over the chassis assembly, remove the
actuator motor while spreading the four pawls "v" fixing
the right and left actuator motors in the arrow
direction(See Fig. 20).
Pulley gear
Belt
Motor pulley
Belt
Pulley gear
Motor pulley
Gear bracket
t
I
I
Pawl
v
Actuator motor
v
Chassis assembly
u
Gear bracket
Pulley gear
Gear B
Cylinder gear
Gross gear U
Gear C
Gross gear L
Select gear
Gear B
Gear C
Pulley gear
Assembly and Configuration Diagram
1-19
Page 11

HX-Z1
Removing the cams R1/R2 assembly
and cam gear q(See Fig.22)
Remove the slit washer fixing the cams R1 and R2
1.
assembly.
By removing the two pawls "w" fixing the cam R1,
2.
separate R2 from R1.
Remove the slit washer fixing the cam gear "q".
3.
Pull out the cam gear "q" from the C.G. base assembly.
4.
Removing the C.G. base assembly
(See Fig.22 and 23)
Remove the three screws J retaining the C.G. base
assembly.
[Caution]
To reassemble the cylinder gear, etc.with the
cam unit (cam gear and cans R1/R2 assembly),
gear unit and drive unit, align the position of the
pawl "x" on the drive unit to that of the notch on
the cam gear "q". Then, make sure that the
gear unit is engaged by turning the cam gear
"q" (See Fig. 24).
Slit washer
Cam gear q
J
Slit washer
Cam R2
Pawl
w
Cam R1
Cam switch board
C.G. base assembly
Pawl
w
Notch
Pawl
x
Cylinder
gear
Drive unit
Fig.22
Cam gear q
Cam R1, R2 assembly
Gear unit
Gear bracket
Fig.23
1-20
Page 12

HX-Z1
<Cassette mechanism section>
Removing the playback / recording &
eraser head (See Fig. 1 ~ 3)
1.
While shifting the trigger arms seen on the right side
of the head mount in the arrow direction, turn the
flywheel R in counterclockwise direction until the
head mount has gone out with a click (See Fig. 1).
2.
When the flywheel (R) is rotated in counterclockwise
direction, the playback / recording & eraser head will
be turned in counterclockwise direction from the
position in Fig. 2 to that in Fig. 3.
3.
At this position, disconnect the flexible P.C. board
(outgoing from the playback / recording & eraser
head) from the connector CN31 on the head
amplifier & mechanism control P.C. board.
4.
Remove the flexible P.C. board from the chassis
base.
5.
Remove the spring a from behind the playback /
recording & eraser head.
Head mount
Flexible board
Cassette mechanism
Flywheel (R)
Trigger arm
Fig. 1
Playback / recording &
eraser head
Spring a
Trigger arm
6.
Loosen the reversing azimuth screw retaining the
playback / recording & eraser head.
7.
Take out the playback / recording & eraser head from
the front of the head mount.
8.
The playback / recoring & eraser head should also
be removed similarly according to steps 1 to 7 above.
Reassembling the playback / recording &
eraser head (See Fig.2, 3)
1.
Reassemble the playback head from the front of the
head mount to the position as shown in Fig. 3.
2.
Fix the reversing azimuth screw.
3.
Set the spring 1 from behind the playback / recording
& eraser head.
4.
Attach the flexible P.C. board to the chassis base, as
shown in Fig. 3.
5.
The playback / recording & eraser head should also
be reassembled similarly to step 1 to 4 above.
CN31
Head amplifier & mechanism
control P.C. board
Fig. 2
Playback / recording & eraser head
Spring 1
Head amplifier & mechanism control
P.C. board
Fig. 3
Flywheel (R)
Reversing azimuth screw
Head mount
Flexible
board
1-21
Page 13

HX-Z1
Removing the head amplifier & mechanism
control board (See Fig. 4)
1.
Remove the cassette mechanism assembly.
2.
After turning over th cassette mechanism assembly,
remove the three screws A retaining the head
amplifier & mechanism control board.
3.
Disconnect the connector CN32 on the board
including the connector CN1 on the reel pulse P.C.
board.
4.
When necessary, remove the 4 pin parallel wire
soldered to the main motor.
Removing the main motor assembly
(See Fig.4 ~ 6)
1.
Remove the two screws B retaining the main motor
assembly (See Fig. 4 and 4a).
2.
While raising the main motor, remove the capstan
belt from the motor pulley (See Fig. 4a).
A
Head amplifier &
mechanism control
board
Flexible board
Capstan belt
CN32
CN31
A
Main motor
assembly
A
Belt
Main motor
assembly
B
B
4pin parallel wire
Main motor
assembly
Fig. 4
CAUTION:
Capstan
belt
Be sure to handle the capstan belt so
carefully that this belt will not be stained
by grease and other foreign matter.
Moreover, this belt should be hanged
while referring to the capstan belt
hanging method in Fig. 5 and 6.
Mechanism motor
assembly
Motor
pulley
Fig. 5
Main motor
assembly
Flywheel
Capstan belt
Motor
pulley
Fig. 4a
Motor pulley
Fig. 6
1-22
Page 14

Removing the flywheel (See Fig. 7, 8)
1.
Remove the head amplifier & mechanism control P.C.
board.
2.
Remove the main motor assembly.
3.
After turning over the cassette mechanism, remove
the two slit washers and fixing the capstan shafts R
and L, and pull out the flywheel (R) and (L)
respectively from behind the cassette mechanism.
HX-Z1
Flywheel (R) Flywheel (L)
Flywheel R Flywheel L
Fig. 8
Removing the reel pulse P.C. board and
solenoid (See Fig. 9)
1.
Remove the five pawls a to e reattaining the reel
pulse board.
2.
From the surface of the reel pulse board parts,
remove the two pawls f and g retaining the solenoid.
a b c d e
g
f
Solenoid
Capstan shaft (R)
Slit washer
Capstan shaft (L)
Slit washer
Fig. 7
Reel pulse board
Fig. 9
1-23
Page 15

HX-Z1
Adjustment method
Measurement Instruments Required for
Adjustment
1. Low frequency oscillator
This oscillator should have a capacity to output
0dBs to 600 at an oscillation frequency of
50Hz-20kHz.
2. Attenuator impedance : 600
3. Electronic voltmeter
4. Distortion meter
5. Frequency counter
6. Wow & flutter meter
7. Test tape
VTT703L : Head azimuth
VT712 : Tape speed and running unevenness
(3kHz)
VT724 : Reference level (1kHz)
8. Blank tape
TYPE : AC-225
TYPE : AC-514
9. Torque gauge : For play and back tension
FWD(TW2111A), REV(TW2121a) and
FF/REW(TW2231A)
10. Test disc: CTS-1000
Measurement conditions
Power supply voltage
AC120V (60Hz) : Ver.J,C
Reference output : Speaker : 0.775V/4
: Headphone : 0.077V/32
Reference frequency and
input level ------------------------------ 1kHz, AUX : -8dBs
Measurement output terminal ------- at Speaker J3002
Load resistance --------------------------- 4
Radio Input signal
AM frequency --------------------------------------- 400Hz
AM modulation ---------------------------------------- 30%
FM frequency --------------------------------------- 400Hz
FM frequency deviation ------------------------ 22.5kHz
Tuner section
FM Band cover: 87.5 108MHz
MW Band cover: 522 1,629kHz
LW Band cover: 144 288kHz
Voltage applied to tuner +B : DC5.7V
VT : DC 12V
Reference measurement
output 26.1mV(0.28V)/3
Input positions AM : Standard loop antenna
FM : TP1 (hot) and TP2 (GND)
Standard measurement position of volume
Function switch to Tape
Beat cut switch to Cut
Super Bass/Active hyper Bass to OFF
Bass Treble to Center
Adjustment of main volume to reference output
VOL : 28
Precautions for measurement
1. Apply 30pF and 33k to the IF sweeper output
side and 0.082 F and 100k in series to the
sweeper input side.
2. The IF sweeper output level should be made as
low as possible within the adjustable range.
3. Since the IF sweeper is a fixed device, there is no
need to adjust this sweeper.
4. Since a ceramic oscillator is used, there is no need
to perform any MIX adjustment.
5. Since a fixed coil is used, there is no need to adjust
the FM tracking.
6. The input and output earth systems are separated.
In case of simultaneously measuring the voltage in
both of the input and output systems with an
electronic voltmeter for two channels, therefore, the
earth should be connected particularly carefully.
7. In the case of BTL connection amp., the minus
terminal of speaker is not for earthing. Therefore, be
sure not to connect any other earth terminal to this
terminal. This system is of an BTL system.
8. For connecting a dummy resistor when measuring
the output, use the wire with a greater code size.
9. Whenever any mixed tape is used, use the band
pass filter (DV-12).
1-24
Page 16

<<
Arrangement of Adjusting Position
HX-Z1
>>
Cassette mechanism section
Head azimuth
adjusting screw
(Forward side)
Cassette AMP board
VR37
C308
R314
MOTOR SPEED
VR37
L301
B155
VR31
BIAS ADJ
VR31
Head azimuth
adjusting screw
(Reverse side)
MB
PBRAGPBL
RECRAGRECL
MS
SW8V
MG
1
CN34
C307
R313
C310
R315
C314
Q302
R327
C317
C319
C221
B112
C313
C121
L303
C316
R310
R335
B198
R353
Q305
C106
Q103
R305
R303
R122
Q101
C103
B163
Q321
R221
10
B156
C303
R115
R108
R101
B157
C113
R110
R109
R102
C110
1
C108
C104
9
R301
R121
C107
B151
R112
R111
B152
C102
R107
C302
R103
1
C301
C111
B164
C306
Cassette mechanism section (Back side)
Head azimuth
adjusting screw
(Forward side)
Playback/Recording &
eraser head
R304
C109
B158
8
B106
C101
6
B166
R116
R212
R211
C211
R216
9
IC32
9
C201
B101
CN33
B109B108
C209
R342
C213
R210
R209
C207
B159
16
B102
R341
C208
R207
B200
1
B110
CN31
1
R208
R340
R205
R105
C105
B160
NC
R343
C305
C206
R345
R201
1IC31
TAP
C304
B113
RRE
C202
C210
Q331
SOL
C375
C205
R215
C203
B161
R339
C334
R106
R206
R204
R203
B153
R104
R222
C204
B168
PHO5VMG
R202
C333
C332
PLA
R375
Q201
Q203
C331
Q372
R331
B167
FRE
R371
C376
10
70u
Q375
CN32
R376
R372
R373
B162
C371
16
1
C374
R338
B
E
D375
Q376
B
Q371
E
R337
R336
9
IC33
8
Head azimuth
adjusting screw
(Reverse side)
1-25
Page 17

HX-Z1
Tape Recorder Section
Items
Confirmation
of head angle
Measurement
conditions
Test tape
: VTT703L (8kHz)
Measurement output
terminal
: Speaker terminal
Speaker R
(Load resistance: 4 )
: Headphone terminal
Measurement method
1 Playback the test tape VTT703L (8kHz)
2 With the recording & playback mechanism,
adjust the head azimuth screw so that the
forward and reverse output levels become
maximum. After adjustment, lock the head
azimuth at least by half turn.
3 In either case, this adjustment should be
performed in both the forward and reverse
directions with the head azimuth screw.
Confirmation
of tape speed
Test tape
: VT712 (3kHz)
Measurement output
terminal
: Headphone terminal
Adjust VR37 so that the frequency counter
reading becomes 2,940~3,090Hz when
playing back the test tape VT712 (3kHz) with
playback and recording mechanism after
ending forward winding of the tape.
Reference Values for Confirmation Items
Standard
Values
Maximum
output
Tape speed
of deck
: 2,940 ~
3,090Hz
Adjusting
positions
Adjust the head
azimuth screw
only when the
head has been
changed.
VR37
Items
Difference
between the
forward and
reverse speed
Measurement
conditions
Test tape
: VT712 (3kHz)
Measurement output
terminal
: Speaker terminal
Speaker R
(Load resistance: 4 )
Measurement output
terminal
: Headphone
Wow & flutter Test tape
: VT712 (3kHz)
Measurement output
terminal
: Headphone terminal
Measurement method
Standard
Values
When the test tape VT712 (3kHz) has been
played back with the recording and playback
mechanism at the beginning of forward
winding, the frequency counter reading of the
difference between both of the mechanism
should be 6.0Hz or less.
When the test tape VT712 (3kHz) has been
played back with the recording and playback
mechanism at the beginning of forward
winding, the frequency counter reading of
wow & flutter should be 0.25% or less
(WRMS).
6.0Hz or
less
0.25% or
less
(WRMS)
Adjusting
positions
Head azimuth
screw
1-26
Page 18

Electrical Performance
HX-Z1
Items
Adjustment of
recording bias
current
(Reference
Value)
Adjustment of
recording and
playback
frequency
characteristics
Measurement
conditions
Mode: Forward or
reverse mode
Recording mode
Test tape
: AC-514 to TYPE
and AC-225 to
TYPE
Measurement output
terminal
: Both recording and
headphone terminals
Reference frequency
: 1kHz and 10kHz
(REF.: -20dB)
Test tape
: AC-514 to TYPE
Measurement input
terminal
: OSC IN
Measurement method
Standard
Values
1 With the recording and playback
mechanism, load the test tapes (AC-514 to
TYPE
and AC-225 to TYPE ), and set
the mechanism to the recording and
pausing condition in advance.
2 After connecting 100
in series to the
recorder head, measure the bias current
with a valve voltmeter at both of the
terminals.
3 After resetting the [PAUSE] mode, start
recording. At this time, adjust VR31 for Lch
and VR32 for Rch so that the recording
bias current values become 4.0
A (TYPE
) and 4.20 A (TYPE ).
1 With the recording and playback
mechanism, load the test tapes (AC-514 to
TYPE
), and set the mechanism to the
recording and pausing condition in
advance.
2 While repetitively inputting the reference
frequency signal of 1kHz and 10kHz from
OSC IN, record and playback the rape.
3 While recording and playback the test tape
in TYPE , adjust VR31 for Lch and VR32
for Rch so that the output deviation
between 1kHz and 10kHz becomes
-1dB 2dB.
AC-225
: 4.20
A
AC-514
: 4.0 A
Output
deviation
between
1kHz and
10kHz
: -1dB 2dB
Adjusting
positions
VR31
VR31
Reference Values for Electrical Function Confirmation Items
Items
Recording
bias
frequency
Measurement
conditions
Forward or reverse
Test tape
: TYPE (AC-514)
Measurement
terminal : BIAS TP on
P.C. board
Measurement method
1 While changing over to and from BIAS 1
and 2, confirm that the frequency is
changed.
2 With the recording and playback
mechanism, load the test tape.
(AC-514 to TYPE ), and set the
mechanism to the recording and pausing
condition in advance.
3 Confirm that the BIAS TP frequency on the
P.C. board is 100kHz 6kHz.
Eraser
current
(Reference
value)
Forward or reverse
Recording mode
Test tape
: AC-514 to TYPE
and AC-225 to
TYPE
Measurement
terminal : Both of the
eraser head terminals
1 While recording and playback mechanism,
load the test tapes (AC-514 to TYPE
and AC-225 to TYPE ), and set the
mechanism to the recording and pausing
conditions in advance.
2 After setting to the recording conditions,
connect 1W in series to the eraser head on
the recording and playback mechanism
side, and measure the eraser current from
both of the eraser terminals.
Standard
Values
100 kHz
6 kHz
TYPE
: 120 mA
TYPE
: 75 mA
Adjusting
positions
1-27
Page 19

HX-Z1
Extension code connecting method
CD servo
control board
CN651
Main board
CN661
1-28
Page 20

Flow of functional operation until TOC read
Power ON
Play Key
Slider turns REST
SW ON.
Automatic tuning
of TE offset
Confirm that the voltage at the pin5
of CN801 is "H"\"L"\"H".
HX-Z1
Check Point
Tracking error waveform at TOC reading
Approx.3sec
Tracking
servo
off states
Automatic measurement
of TE amplitude and
automatic tuning of
TE balance
VREF
pin 25 of
IC601(TE)
Approx
1.8V
Disc states
to rotate
Tracking
servo
on states
Disc to be
braked to stop
TOC reading
finishes
500mv/div
2ms/div
Fig.1
Laser ON
Detection of disc
Automatic tuning of
Focus offset
Automatic measurement of
Focus S-curve amplitude
Disc is rotated
Focus servo ON
(Tracking servo ON)
Automatic measurement of
Tracking error amplitude
Automatic tuning of
Tracking error balance
Check that the voltage at the
pin40 of IC651 is + 5V?
Confirm that the Focus error
S-cuve signal at the pin28 of
IC651 is approx.2Vp-p
Confirm that the signal from
pin24 IC651 is 0V as a
accelerated pulse during
approx.400ms.
Confirm the waveform of
the Tracking error signal.
at the pin 25 of IC601 (R604)
(See fig-1)
Automatic tuning of
Focus error balance
Automatic tuning of
Focus error gain
Automatic tuning of
Tracking error gain
TOC reading
Play a disc
Confirm the eys-pattern
at the lead of TP1
1-29
Page 21

HX-Z1
Maintenance of laser pickup
(1) Cleaning the pick up lens
Before you replace the pick up, please try to
clean the lens with a alcohol soaked cotton
swab.
(2) Life of the laser diode
When the life of the laser diode has expired,
the following symptoms will appear.
1. The level of RF output (EFM output : ampli
tude of eye pattern) will below.
Is the level of
RFOUT under
1.25V 0.22Vp-p?
YES
O.K
NO
Replace it.
Replacement of laser pickup
Turn off the power switch and, disconnect the
power cord from the ac outlet.
Replace the pickup with a normal one.(Refer
to "Pickup Removal" on the previous page)
Plug the power cord in, and turn the power on.
At this time, check that the laser emits for
about 3seconds and the objective lens moves
up and down.
Note: Do not observe the laser beam directly.
Play a disc.
Check the eye-pattern at TP1.
Finish.
(3) Semi-fixed resistor on the APC PC board
The semi-fixed resistor on the APC printed circuit board which is attached to the pickup is used to adjust the laser
power. Since this adjustment should be performed to match the characteristics of the whole optical block, do not
touch the semi-fixed resistor.
If the laser power is lower than the specified value, the laser diode is almost worn out, and the laser pickup should
be replaced.
If the semi-fixed resistor is adjusted while the pickup is functioning normally, the laser pickup may be damaged
due to excessive current.
1-30
Page 22

Description of major ICs
BU2092 (IC642) : Port expander
1.Pin Layout
HX-Z1
Vss
DATA
CLOCK
LCK
Q0
Q1
Q2
Q3
Q4
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
CONTROL
CIRCUIT
12BIT SHIFT RESISTER
12BIT STRAGE RESISTER
OUTPUT BUFFER(OPEN DRAIN)
18
17
16
15
14
13
12
11
10
Vdd
OE
Q11
Q10
Q9
Q8
Q7
Q6
Q5
2.Pin function
Pin No.
1
2
3
4
5~16
17
18
Symbol
Vss
DATA
CLOCK
LCK
Q0~Q11
OE
Vdd
I/O
-
I
I
I
O
I
-
Function
Connect to GND
Serial Data input
Shift Clock of Data
Latch Clock of Data
Parallel Data Output
Latch Data L H
OUTPUT ON OFF
Output Enable
Power Supply
1-31
Page 23

HX-Z1
BH3874AKS (IC434) : Audio sound processor
1.
Pin
layout
48 ~ 33
49
~
64
1 ~ 16
2. Block diagram
VFC1
-9dB
47INLD
INLC
45
INLB
43
INLA
INRA
INRB
INRC
INRD
RECR
41
42
44
46
48
-9dB
52
MODE SELECTOR
VFC2
MIC
11dB
+
-
+
-
11dB
+
-
+
19dB
+
+
-
32
~
17
+
+
DPLR2
DPLR1
DPLL2
+
+
EFFECT
-
+
DPLL1
+
+
F2L2
F2L1
F1L2
F1L1
5 BAND EQ
5 BAND EQ
F3L1
F3L2
F4L1
F4L2
F5L
-30dB~-
RECL
PS1
PS2
0~30dB
+
10K
-
+
10K
+
L-R
+
+
+
L+R
+
PS
PS
10.5Hz
HPFL1
+
HPFL2
HPP
VCA
HPFL3
1918171563 64 3 4 7 8 11 1258576059626151565553
BASS1
FILTER
26252423
Vcc
1
Vcc
2
+
+
-
+
+
-
VCC
30
-
+
FILTER
28
GND
54
OUTL
32
BASS5
27
CAP
29
OUTR
31
BASS4
BASS3
BASS2
DET
10.5Hz
10.5Hz
10.5Hz
DET
DET
MPX
HPP
DIGITAL
CONTROL
SCK
35
SI
34
DET
10.5Hz
DET
ALC
33
STEPC
1-32
22K
40 36 37 38 39 1 2 5 6 9 10 13 14 16 20 21 22 50 49
BPNF
C
B
A
F1R1
BPOUT
F1R2
F2R1
F2R2
F3R1
F3R2
F4R1
F4R2
F5R
HPFR1
HPFR2
HPFR3
ALCB
ALCC
Page 24

3. Pin function
Pin NO. Name Function
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
F1R1
F1R2
F2L1
F2L2
F2R1
F2R2
F3L1
FAL2
F3R1
F3R2
F4L1
F4L2
F4R1
F4R2
F5L
F5R
HPFL1
HPFL2
HPFL3
HPFR1
HPFR2
HPFR3
BASS1
BASS2
BASS3
BASS4
BASS5
FILTER
CAP
VCC
OUTR
OUTL
STEPC
Rch GREQ f1 filter setting pin
Rch GREQ f1 filter setting pin
Lch GREQ f2 filter setting pin
Lch GREQ f2 filter setting pin
Rch GREQ f2 filter setting pin
Rch GREQ f2 filter setting pin
Lch GREQ f3 filter setting pin
Lch GREQ f3 filter setting pin
Rch GREQ f3 filter setting pin
Rch GREQ f3 filter setting pin
Lch GREQ f4 filter setting pin
Lch GREQ f4 filter setting pin
Rch GREQ f4 filter setting pin
Rch GREQ f4 filter setting pin
Lch GREQ f5 filter setting pin
Rch GREQ f5 filter setting pin
Lch high-pass filter setting pin
Lch high-pass filter setting pin
Lch high-pass filter setting pin
Rch high-pass filter setting pin
Rch high-pass filter setting pin
Rch high-pass filter setting pin
Dynamic bass filter setting pin
Dynamic bass filter setting pin
Dynamic bass filter setting pin
Dynamic bass filter setting pin
Biamp output pin
VCC/2 pin
ALC trap frequency setting pin
Power supply pin
Rch output pin
Lch output pin
Time conatant attachment for
switching shook protection
Pin NO.
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
Name Function
SI
SCK
A
B
C
BPOUT
BPNF
INLA
INRA
INLB
INRB
INLC
INRC
INLD
INRD
ALCC
ALCR
RECL
REOR
VFC1
GND
VFC2
MIC
DPLL1
DPLL2
DPLR1
DPLR2
PS1
PS2
F1L1
F1L2
Serial data larch receiving pin
Serial clook receiving pin
Parallel data receiving pin
Parallel data receiving pin
Parallel data receiving pin
Output pin for spectrum analyzer
Spectrum analyzer level setting pin
Lch input pin A
Rch input pin A
Lch input pin B
Rch input pin B
Lch input pin C
Rch input pin C
Lch input pin D
Rch input pin D
Time constant of ALC setting pin
ALC level setting pin
Lch RECOUT output pin
Rch RECOUT output pin
Vocal fade filter setting pin
Ground pin
Vocal fade filter setting pin
Input pin for microphone
Lch output pin for DPL
Lch input pin for DPL
Rch output pin for DPL
Rch input pin for DPL
Surround setting pin
Surround setting pin
Lch GREQ f1 filter setting pin
Lch GREQ f1 filter setting pin
HX-Z1
1-33
Page 25

HX-Z1
KIA7805API (IC360) : Regulator
1.
Pin
layout
1 2 3
2.Block diagram
1.VCC
2.GND
3.OUTPUT
1
INPUT
Z1
R1
Q12
R12
R11
R13
Q13
Q2
Q18
R18
R4
R22
Q11
Q1
Q17
R2
R3
Q3
Q4
R5
Q14
Q6
R19
R7
Q5
R6
C1
Q9
Q7
R8
R17
Q19
R26
Q11-1
R10
R9
Q8
Q10
Q15
R15
R14
Q16
R16
R20
R21
3
OUTPUT
2 COMMON (GND)
1-34
Page 26

KIA7808API (IC303) : Regulator
1.
Pin
layout
1.VCC
2.GND
3.OUTPUT
1 2 3
2.Block diagram
1
HX-Z1
INPUT
Z1
R1
Q12
R12
R11
R13
Q13
Q2
Q18
R18
R4
R22
Q11
Q1
Q17
R2
R3
Q3
Q4
R5
Q14
Q6
R19
R7
Q5
R6
C1
Q9
Q7
R8
R17
Q19
R26
Q11-1
R10
R9
Q8
Q10
Q15
R15
R14
Q16
R16
R20
R21
3
OUTPUT
2 COMMON (GND)
1-35
Page 27

HX-Z1
KIA7812API (IC240) : Regulator
1.
Pin
layout
1.VCC
2.GND
3.OUTPUT
1 2 3
2.Block diagram
1
INPUT
Z1
R1
Q12
R12
R11
R13
Q13
Q2
Q18
R18
R4
R22
Q11
Q1
Q17
R2
R3
Q3
Q4
R5
Q14
Q6
R19
R7
Q5
R6
C1
Q9
Q7
R8
R17
Q19
R26
Q11-1
R10
R9
Q8
Q10
Q15
R15
R14
Q16
R16
R20
R21
3
OUTPUT
2 COMMON (GND)
1-36
Page 28

KIA7042AP-T (IC830) : Regulator
HX-Z1
1. Pin layout
2. Block diagram
1 2 3
1.VCC
2.GND
3.OUT
NJM4580D (IC501, IC502, IC571) : LPF, Mic and H.phone amp.
1. Pin layout
A OUT
1
+
8
V
2. Block diagram
+
V
INPUT
+
A -IN
A +IN
V
2
A
3
-
4
(TOP VIEW)
B
7
6
5
B OUT
B -IN
B +IN
OUTPUT
-
V
1-37
Page 29

HX-Z1
GP1U271XK (IC951) : Receiver for remote
+
–
Amp.
Limiter Integrator Comparator
STK402-050 (IC602) : 2ch AF power amp.
Pin
layout
1.
B.P.F
Demodulator
GND
VCC Vout
1 ~ 15
2.Block diagra
4
R1
1
2
TR3
R2
8
TR7
TR4
C1
TR5
TR2TR1
D1
R3
R4
R5
R6
TR8
TR6
R7
TR9
TR10
R8
TR12
TR13
R9
R13
TR1E
C2
R15R14
R11
R12
R10
TR16
R14
1-38
9
SUB
151411106712513
Page 30

STK402-010 (IC701) : 2ch AF power amp.
Pin
layout
1.
1 ~ 18
HX-Z1
2.Block diagra
R1 C1
14
TR3
15
16
TR5
R2
TR2TR1
TR4
D2
C2
D1
R4
R5
TR6
R6
R3
TR7
R7
TR8
TR9
TR10
13 18 17
D12R13
TR11TR12
TR16
TR19
TR20
TR18
C12
R14
R15
R16
TR17
R17
R11C11
TR13TR14
TR15
R12
TR41
TR51
D41
D51
R41
Comparator
Comparator
R51
D42
SUB
D53
D52
1
3
D43
2
7
5
4
6
12
9 8 11 10
1-39
Page 31

HX-Z1
UPD784975AGF303 (IC810) : Main micon
1.
Pin
layout
100 ~ 81
1
~
30
31 ~ 50
80
~
51
2. Pin function
Pin NO. Name Function
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
AVDD
SPIDTI
MSI
MPX
H/P
KEY1
KEY2
KEY3
VOL-
VOL+
SLCPLAY
SLCKEY
PHOTO A
AVSS
VSS1
X1
X2
VDD1
IC(VPP)
VC3RESET
M STAT
KCMND
RDS DATA
RDS CK
BUZZER
REMIN
SMUTE
SLCCE
CK
DATA OUT
DATA I N
SM-
SM+
ECHO1
ECHO2
I/O
AD VDD, same as VDD1
SPI analog input
I
Music scan input
I
Tuner stereo indicator
I
I
SW vol IC btw bi-amp & dyn & off relay
I
Key 1 input
I
Key 2 input
I
Key 3 input
I
Volume decrease
I
Volume increase
I
SLC detect play
I
SLC key input
I
SLC photo A
-
AD VDD, same as VSS1
-
GND
I
Oscillation
-
Oscillation
-
-
Connect to VSS1
I/O
VC3 reset
I/O
VC3 status input
I/O
VC3 KCMND(serial data)
I/O
RDS data
INT
RDS clock
I/O
Buzzer on
INT
Remocon input
I/O
System mute
I/O
SLC chip enable
I/O
SLC / tuner clock
I/O
SLC / tuner data out
I/O
Tuner data in
I/O
Soundmode reverse
I/O
Soundmode forward
I/O
Echo 1 data
I/O
Echo 2 data
Pin NO.
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62~78
79
80
81~84
85~100
Name Function
SPI A
SPI B
SPI C
PBMUTE
VSS0
VDD0
RESET
INH
LATCH
VOLCK
VOLDA
RELAY
POUT
ECON
PRT
AUXMUTE
TUCE
EXTDA
EXTCK
EXTCE
OEEXT
VOLLED
FSEARCH
RSEARCH
S21~S5
VDD2
VLOAD
S4~S1
G16~G1
I/O
I/O
SPI A data
I/O
SPI B data
I/O
SPI C data
I/O
Playback mute
-
I
Micom reset
I/O
Back-up mode detect
I/O
Latch for vol IC
I/O
Volume clock
I/O
Volume data
I/O
Relay out
I/O
Power on
I/O
Ecology mode
I/O
Protector in
O
Auxmute
O
Tuner chip enable
O
Available pin
O
Available pin
O
External IC data
O
External IC clock
O
External IC strobe
O
Output enable for external IC
I/O
Volume led
I/O
Forward skip
I/O
Reverse skip
I/O
FL segment
I/O
I/O
Negative power supply(-30V)
I/O
FL segment
I/O
FL display grid
1-40
Page 32

HX-Z1
KIA7809API (IC305) :
1.Pin layout
1 2 3
2.Block diagram
Regulator
1.INPUT
2.COMMON
3.OUTPUT
R22
R17
R23
1
INPUT
Z1
R1
Q12
R12
R11
R13
Q13
Q2
Q18
R18
R4
Q11
Q1
Q17
R2
R3
Q3
Q4
R5
Q14
Q6
R19
R7
Q5
R6
C1
Q9
Q7
R8
Q19
Q11-1
R10
R9
Q8
Q10
Q15
R15
R14
Q16
R16
R20
R21
3
OUTPUT
2 COMMON (GND)
1-41
Page 33

HX-Z1
HX-Z1
VICTOR COMPANY OF JAPAN, LIMITED
AUDIO & COMUNICATION BUSINESS DIVISION
PERSONAL & MOBILE NETWORK BUSINESS UNIT. 10-1,1chome,Ohwatari-machi,Maebashi-city,371-8543,Japan
1-42
(No.21088)
Printed in Japan
200206
 Loading...
Loading...