Page 1

Release
Published
2021-04-22
Notes
Junos®OS 20.2R1 Release Notes
SUPPORTED ON
ACX Series, EX Series, Junos Fusion Enterprise, Junos Fusion Provider Edge, JRR Series,
•
MX Series, NFX Series, PTX Series, QFX Series, and SRX Series
SOFTWARE HIGHLIGHTS
Retain the authentication session based on DHCP or SLAAC snooping entries (EX Series)
•
Rest API support for EX2300, EX2300-MP, EX3400, EX4300, EX4300-MP, EX4600,
•
EX4650, and EX9200
TI-LFA SRLG protection for IS-IS (MX Series and PTX Series)
•
MX Series Virtual Chassis support for the ephemeral database (MX Series)
•
Change the default re-merge behavior on the P2MP LSP (MX Series)
•
BGP-LU over SR-MPLS and IS-IS segment routing underlay
•
Support for Layer 2 circuit, Layer 2 VPN, and VPLS services with BGP labeled unicast (MX
•
Series and EX Series)
Packet capture of unknown application traffic (NFX Series, SRX Series, and vSRX)
•
Safe search enhancement for Web filtering (SRX Series and vSRX)
•
Encrypted traffic analysis
•
Support for Application Quality of Experience (AppQoE) (SRX4600)
•
Page 2

IN FOCUS GUIDE
Use this new guide to quickly learn about the most important Junos OS features and how
•
you can deploy them in your network.
Day One+
Use this new setup tool to get your Junos OS up and running in three quick steps.
•
Page 3

Release Notes: Junos®OS Release 20.2R1 for
the ACX Series, EX Series, Junos Fusion, JRR
Series, MX Series, NFX Series, PTX Series, QFX
Series, and SRX Series
1
22 April 2021
Contents
Introduction | 12
Junos OS Release Notes for ACX Series | 12
What's New | 13
Hardware | 13
Authentication, Authorization, and Accounting | 18
Class of Service (CoS) | 18
EVPN | 18
Interfaces and Chassis | 19
Juniper Extension Toolkit (JET) | 20
Junos Telemetry Interface | 20
MPLS | 20
Multicast | 21
Network Management and Monitoring | 21
Routing Policy and Firewall Filters | 22
What's Changed | 23
Class of Service (CoS) | 23
General Routing | 23
Juniper Extension Toolkit (JET) | 24
Network Management and Monitoring | 24
Page 4

Known Limitations | 25
General Routing | 25
Open Issues | 28
General Routing | 28
Platform and Infrastructure | 31
Resolved Issues | 31
General Routing | 32
Interfaces and Chassis | 33
Layer 2 Ethernet Services | 33
MPLS | 33
Routing Protocols | 33
VPNs | 33
Documentation Updates | 34
Migration, Upgrade, and Downgrade Instructions | 34
2
Upgrade and Downgrade Support Policy for Junos OS Releases | 35
Junos OS Release Notes for EX Series | 35
What's New | 36
What’s New in Release 20.2R1-S1 | 37
What’s New in Release 20.2R1 | 37
What's Changed | 44
Class of Service (CoS) | 45
General Routing | 45
Juniper Extension Toolkit (JET) | 45
Network Management and Monitoring | 46
Known Limitations | 46
EVPN | 47
Infrastructure | 47
Open Issues | 47
Authentication and Access Control | 48
EVPN | 48
Infrastructure | 48
Interfaces and Chassis | 48
Layer 2 Ethernet Services | 48
Layer 2 Features | 49
Page 5

Platform and Infrastructure | 49
Routing Protocols | 51
Resolved Issues | 51
Authentication and Access Control | 52
EVPN | 52
High Availability (HA) and Resiliency | 52
Infrastructure | 52
Interfaces and Chassis | 52
Junos Fusion Enterprise | 53
Junos Fusion Satellite Software | 53
Layer 2 Ethernet Services | 53
Layer 2 Features | 53
MPLS | 53
Platform and Infrastructure | 53
3
Routing Protocols | 55
User Interface and Configuration | 55
Documentation Updates | 56
Migration, Upgrade, and Downgrade Instructions | 56
Upgrade and Downgrade Support Policy for Junos OS Releases | 57
Junos OS Release Notes for JRR Series | 57
What's New | 58
Layer 2 Features | 58
What's Changed | 59
Known Limitations | 59
Open Issues | 60
Resolved Issues | 60
General Routing | 60
Documentation Updates | 61
Migration, Upgrade, and Downgrade Instructions | 61
Upgrade and Downgrade Support Policy for Junos OS Releases | 62
Junos OS Release Notes for Junos Fusion for Enterprise | 62
What’s New | 63
What's Changed | 64
Known Limitations | 64
Page 6

Open Issues | 65
Resolved Issues | 65
Resolved Issues: Release 20.2R1 | 65
Documentation Updates | 66
Migration, Upgrade, and Downgrade Instructions | 66
Basic Procedure for Upgrading Junos OS on an Aggregation Device | 67
Upgrading an Aggregation Device with Redundant Routing Engines | 69
Preparing the Switch for Satellite Device Conversion | 69
Converting a Satellite Device to a Standalone Switch | 71
Upgrade and Downgrade Support Policy for Junos OS Releases | 71
Downgrading Junos OS | 71
Junos OS Release Notes for Junos Fusion Provider Edge | 72
What's New | 73
Hardware | 74
4
Junos Fusion | 74
What's Changed | 75
Known Limitations | 75
Open Issues | 75
Resolved Issues | 76
Fusion for Provider Edge | 76
Documentation Updates | 77
Migration, Upgrade, and Downgrade Instructions | 77
Basic Procedure for Upgrading an Aggregation Device | 78
Upgrading an Aggregation Device with Redundant Routing Engines | 80
Preparing the Switch for Satellite Device Conversion | 81
Converting a Satellite Device to a Standalone Device | 82
Upgrading an Aggregation Device | 85
Upgrade and Downgrade Support Policy for Junos OS Releases | 85
Downgrading from Junos OS Release 20.1 | 85
Page 7

Junos OS Release Notes for MX Series | 86
What's New | 87
What’s New in Release 20.2R1-S1 | 88
What’s New in Release 20.2R1 | 88
What's Changed | 113
Class of Service (CoS) | 113
General Routing | 113
Juniper Extension Toolkit (JET) | 114
Network Management and Monitoring | 114
Services Applications | 115
Software-Defined Networking (SDN) | 115
Known Limitations | 116
General Routing | 116
Infrastructure | 118
5
Interfaces and Chassis | 118
MPLS | 118
Platform and Infrastructure | 118
Open Issues | 119
Class of Service (CoS) | 119
EVPN | 120
Forwarding and Sampling | 120
General Routing | 120
High Availability (HA) and Resiliency | 124
Interfaces and Chassis | 124
Layer 2 Ethernet Services | 125
MPLS | 125
Network Management and Monitoring | 126
Platform and Infrastructure | 126
Routing Protocols | 127
VPNs | 127
Resolved Issues | 128
Application Layer Gateways (ALGs) | 129
Class of Service (CoS) | 129
EVPN | 129
Page 8

Forwarding and Sampling | 130
General Routing | 130
High Availability (HA) and Resiliency | 138
Infrastructure | 138
Interfaces and Chassis | 138
Intrusion Detection and Prevention (IDP) | 139
J-Web | 139
Junos Fusion for Enterprise | 139
Junos Fusion Satellite Software | 139
Layer 2 Ethernet Services | 139
Layer 2 Features | 140
MPLS | 140
Platform and Infrastructure | 141
Routing Policy and Firewall Filters | 142
6
Routing Protocols | 142
Services Applications | 144
Subscriber Access Management | 144
VPNs | 144
Documentation Updates | 145
Advanced Subscriber Management Provider | 145
Migration, Upgrade, and Downgrade Instructions | 146
Basic Procedure for Upgrading to Release 20.2R1 | 147
Procedure to Upgrade to FreeBSD 11.x-based Junos OS | 147
Procedure to Upgrade to FreeBSD 6.x-based Junos OS | 150
Upgrade and Downgrade Support Policy for Junos OS Releases | 151
Upgrading a Router with Redundant Routing Engines | 152
Downgrading from Release 20.2R1 | 152
Junos OS Release Notes for NFX Series | 153
What’s New | 153
Application Security | 154
High Availability | 155
Interfaces | 155
What's Changed | 155
What’s Changed in Release 20.2R1 | 156
Page 9

Known Limitations | 156
High Availability | 157
Platform and Infrastructure | 157
Open Issues | 157
High Availability | 158
Interfaces | 158
Platform and Infrastructure | 158
Virtual Network Functions (VNFs) | 159
Resolved Issues | 159
Application Security | 160
High Availability | 160
Interfaces | 160
Mapping of Address and Port with Encapsulation (MAP-E) | 160
Platform and Infrastructure | 160
7
Virtualized Network Functions (VNFs) | 161
Documentation Updates | 161
Migration, Upgrade, and Downgrade Instructions | 162
Upgrade and Downgrade Support Policy for Junos OS Releases | 162
Basic Procedure for Upgrading to Release 20.2 | 162
Junos OS Release Notes for PTX Series | 164
What's New | 165
High Availability (HA) and Resiliency | 165
Interfaces and Chassis | 166
Juniper Extension Toolkit (JET) | 166
Junos Telemetry Interface | 167
MPLS | 170
Network Management and Monitoring | 170
Routing Policy and Firewall Filters | 172
Routing Protocols | 172
System Logging | 173
What's Changed | 173
General Routing | 174
Juniper Extension Toolkit (JET) | 174
Network Management and Monitoring | 174
Page 10

Known Limitations | 175
General Routing | 175
Routing Protocols | 176
Open Issues | 176
General Routing | 176
Interfaces and Chassis | 177
MPLS | 177
Routing Protocols | 177
Resolved Issues | 178
General Routing | 178
Infrastructure | 180
Layer 2 Ethernet Services | 180
MPLS | 180
Routing Protocols | 180
8
Documentation Updates | 181
Migration, Upgrade, and Downgrade Instructions | 181
Basic Procedure for Upgrading to Release 20.2 | 181
Upgrade and Downgrade Support Policy for Junos OS Releases | 184
Upgrading a Router with Redundant Routing Engines | 185
Junos OS Release Notes for the QFX Series | 185
What's New | 186
What’s New in Release 20.2R1-S1 | 187
What’s New in Release 20.2R1 | 189
What's Changed | 211
Class of Service | 211
General Routing | 211
Interfaces and Chassis | 212
Junos Extension Toolkit | 212
Network Management and Monitoring | 212
Known Limitations | 213
Class of Service (CoS) | 213
General Routing | 213
Layer 2 Ethernet Services | 214
Page 11

Open Issues | 214
Class of Service (CoS) | 215
EVPN | 215
General Routing | 215
High Availability (HA) and Resiliency | 218
Infrastructure | 218
Interfaces and Chassis | 218
Layer 2 Ethernet Services | 218
Layer 2 Features | 218
Platform and Infrastructure | 219
Routing Protocols | 219
Virtual Chassis | 219
Resolved Issues | 220
Resolved Issues: 20.2R1 | 220
9
Documentation Updates | 225
Migration, Upgrade, and Downgrade Instructions | 226
Upgrading Software on QFX Series Switches | 226
Installing the Software on QFX10002-60C Switches | 229
Installing the Software on QFX10002 Switches | 229
Upgrading Software from Junos OS Release 15.1X53-D3X to Junos OS Release
15.1X53-D60, 15.1X53-D61.7, 15.1X53-D62, and 15.1X53-D63 on QFX10008 and
QFX10016 Switches | 230
Installing the Software on QFX10008 and QFX10016 Switches | 232
Performing a Unified ISSU | 236
Preparing the Switch for Software Installation | 237
Upgrading the Software Using Unified ISSU | 237
Upgrade and Downgrade Support Policy for Junos OS Releases | 239
Junos OS Release Notes for SRX Series | 240
What’s New | 241
Application Security | 242
Authentication and Access Control | 243
Flow-Based and Packet-Based Processing | 243
General Packet Radio Switching (GPRS) | 243
Intrusion Detection and Prevention (IDP) | 243
Junos Telemetry Interface | 244
Page 12

Juniper Extension Toolkit (JET) | 245
J-Web | 245
Juniper Sky ATP | 246
Logical Systems and Tenant Systems | 246
Multicast | 247
Network Address Translation (NAT) | 247
Network Management and Monitoring | 248
Platform and Infrastructure | 249
Port Security | 249
Security | 249
Software Installation and Upgrade | 250
Unified Threat Management (UTM) | 250
What's Changed | 251
Application Security | 252
10
Flow-Based and Packet-Based Processing | 254
Juniper Extension Toolkit (JET) | 254
Juniper Sky ATP | 255
Network Management and Monitoring | 255
VPNs | 255
Known Limitations | 257
Authentication and Access Control | 258
Flow-Based and Packet-Based Processing | 258
J-Web | 258
Routing Policy and Firewall Filters | 258
VPNs | 258
Open Issues | 259
Flow-Based and Packet-Based Processing | 259
J-Web | 259
Routing Policy and Firewall Filters | 260
VPNs | 260
Resolved Issues | 261
Application Layer Gateways (ALGs) | 261
Authentication and Access Control | 261
Flow-Based and Packet-Based Processing | 261
Page 13

Intrusion Detection and Prevention (IDP) | 263
J-Web | 263
Layer 2 Ethernet Services | 263
Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) | 263
Network Address Translation (NAT) | 263
Network Management and Monitoring | 263
Platform and Infrastructure | 264
Routing Policy and Firewall Filters | 264
Routing Protocols | 264
Unified Threat Management (UTM) | 264
VPNs | 264
Documentation Updates | 265
Migration, Upgrade, and Downgrade Instructions | 266
Upgrade and Downgrade Support Policy for Junos OS Releases and Extended End-Of-Life
Releases | 266
11
Upgrading Using ISSU | 267
Licensing | 267
Compliance Advisor | 268
Finding More Information | 268
Documentation Feedback | 268
Requesting Technical Support | 270
Self-Help Online Tools and Resources | 270
Creating a Service Request with JTAC | 271
Revision History | 271
Page 14

Introduction
Junos OS runs on the following Juniper Networks®hardware: ACX Series, EX Series, Junos Fusion, JRR
Series, M Series, MX Series, NFX Series, PTX Series, QFabric systems, QFX Series, and SRX Series, T Series.
These release notes accompany Junos OS Release 20.2R1 for the ACX Series, EX Series, Junos Fusion,
JRR Series, MX Series, NFX Series, PTX Series, QFX Series, and SRX Series. They describe new and changed
features, limitations, and known and resolved problems in the hardware and software.
In Focus guide—We have a document called In Focus that provides details on the most important features
•
for the release in one place. We hope this document will quickly get you to the latest information about
Junos OS features. Let us know if you find this information useful by sending an e-mail to
techpubs-comments@juniper.net.
Important Information:
•
Upgrading Using ISSU on page 267
•
12
Licensing on page 267
•
Compliance Advisor on page 268
•
Finding More Information on page 268
•
Documentation Feedback on page 268
•
Requesting Technical Support on page 270
•
Junos OS Release Notes for ACX Series
IN THIS SECTION
What's New | 13
What's Changed | 23
Known Limitations | 25
Open Issues | 28
Resolved Issues | 31
Documentation Updates | 34
Migration, Upgrade, and Downgrade Instructions | 34
Page 15

These release notes accompany Junos OS Release 20.2R1 for the ACX Series. They describe new and
changed features, limitations, and known and resolved problems in the hardware and software.
You can also find these release notes on the Juniper Networks Junos OS Documentation webpage, located
at https://www.juniper.net/documentation/product/en_US/junos-os.
What's New
IN THIS SECTION
Hardware | 13
Authentication, Authorization, and Accounting | 18
Class of Service (CoS) | 18
EVPN | 18
13
Interfaces and Chassis | 19
Juniper Extension Toolkit (JET) | 20
Junos Telemetry Interface | 20
MPLS | 20
Multicast | 21
Network Management and Monitoring | 21
Routing Policy and Firewall Filters | 22
Learn about new features introduced in the Junos OS main and maintenance releases for ACX Series
routers.
Hardware
New ACX710 Universal Metro Routers (ACX Series)—In Junos OS Release 20.2R1, we introduce the
•
ACX710 router. The ACX710 is a compact 1-U router that provides system throughput of up to 320
Gbps through the following port configurations:
Twenty-four 10GbE or 1GbE ports (ports 0 through 23) that operate at 10-Gbps speed when you use
•
small form-factor pluggable plus (SFP+) transceivers or at 1-Gbps speed when you use small form-factor
pluggable (SFP) optics. Ports 0 through 15 also support 1000 Mbps speeds when you use tri-rate SFP
optics. Ports 16 through 23 support 100 Mbps and 1000 Mbps speeds when you use tri-rate SFP
optics.
Page 16

Four 100GbE ports (ports 0 through 3) that support quad small form-factor pluggable 28 (QSFP28)
•
transceivers. You can channelize these ports into four 25-Gbps interfaces using breakout cables and
channelization configuration. These ports also support 40-Gbps speed when you use quad small
form-factor pluggable plus (QSFP+) optics. You can channelize these 40-Gbps ports into four 10-Gbps
interfaces using breakout cables and channelization configuration. [See Channelize Interfaces on
ACX710 Routers.]
The ACX710 router is a DC-powered device that is cooled using a fan tray with five high-performance
fans to cool the chassis.
To install the ACX710 router hardware and perform initial software configuration, routine maintenance,
and troubleshooting, see the ACX710 Universal Metro Router Hardware Guide.
Table 1 on page 14 summarizes the ACX710 features supported in Junos OS Release 20.2R1.
Table 1: Features Supported by the ACX710 Routers
DescriptionFeature
14
Class of service (CoS)
DHCP
EVPN
Firewalls and policers
Standard CoS feature support, including configuring classification,
•
rewrite, shaping, buffering, and scheduling parameters for traffic
management. [See CoS on ACX Series Routers Features Overview.]
DHCP server, DHCP client, and DHCP relay configuration for IPv4
•
and IPv6 services. [See Understanding DHCP Client Operation on ACX
Series.]
EVPN-VPWS. [See Overview of VPWS with EVPN Signaling
•
Mechanisms EVPN-VPWS with flexible cross-connect (FXC).]
EVPN-VPWS with flexible cross-connect (FXC). [See Overview of
•
Flexible Cross-Connect Support on VPWS with EVPN.]
EVPN with ELAN services over MPLS. [See EVPN Overview.]
•
Configure firewall filters on packets (families such as bridge domain,
•
IPv4, IPv6, CCC, and MPLS) based on packet match conditions. Along
with the match conditions, actions such as count, discard, log, syslog,
policer are performed on the packets that match the filter. You can
configure policers and attach them to a firewall term. [See Standard
Firewall Filter Match Conditions and Actions on ACX Series Routers
Overview.]
Page 17
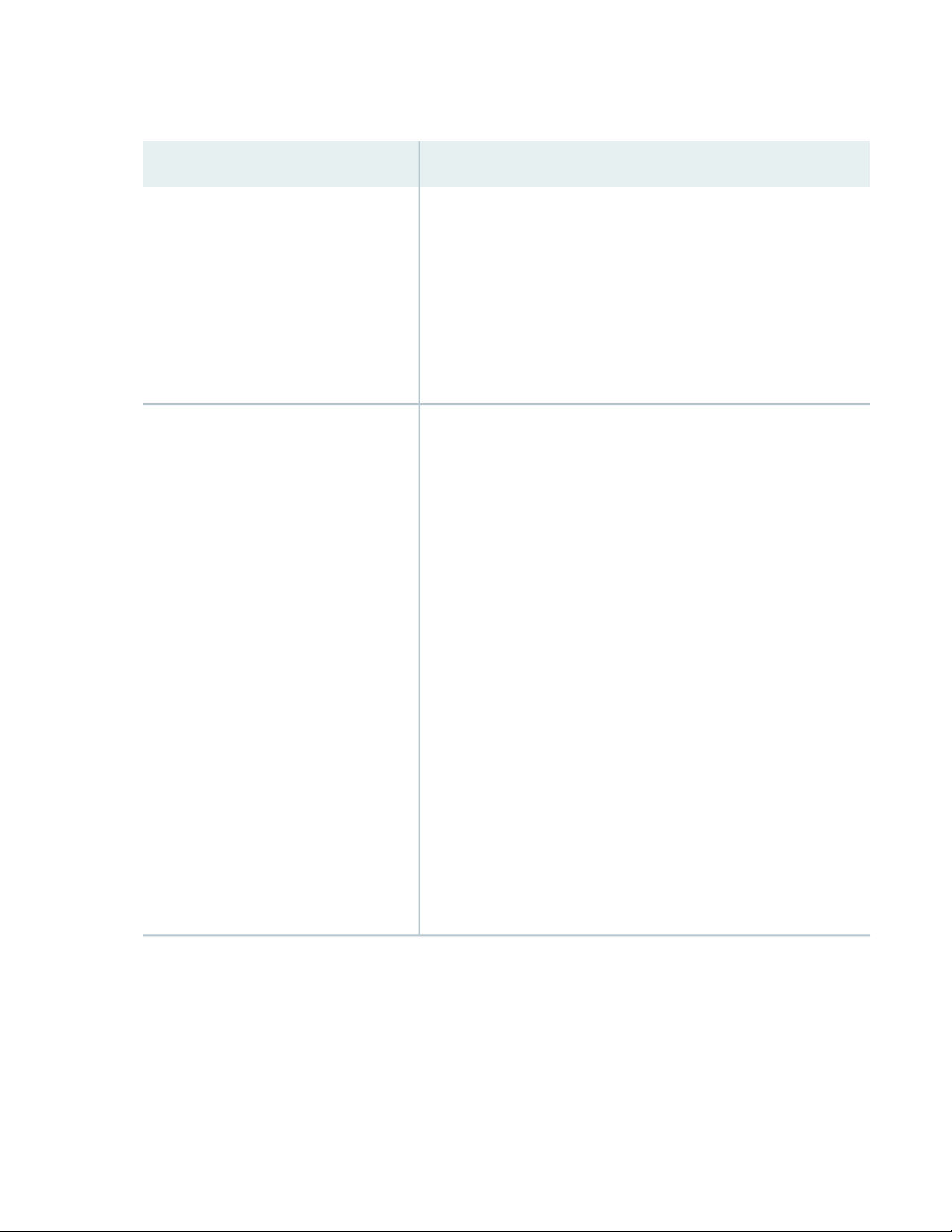
Table 1: Features Supported by the ACX710 Routers (continued)
DescriptionFeature
15
High availability (HA) and resiliency
Layer 2 features
VRRP protocol support with Broadcom’s DNX chipset. [See
•
Understanding VRRP Overview.]
Configure alarm input and output, manage FRUs, and monitor
•
environment. The router also supports field-replaceable unit (FRU)
management and environmental monitoring. [See alarm-port.]
Platform resiliency to handle failures and faults of the components
•
such as fan trays, temperature sensors, and power supplies. The router
also supports firmware upgrade for FPGA and U-boot. [See show
chassis alarms and show system firmware.]
Layer 2 support: bridging, bridge domain with no vlan-id, with vlan-id
•
none, or with single vlan-id, single learning domain support,.Q-in-Q
service for bridging, MAC limit feature support, no local switching
support for bridge domain, and E-LINE from a bridge with no MAC
learning. [See Layer 2 Bridge Domains on ACX Series Overview.]
Layer 2 support for bridge interfaces for vlan-map push operation,
•
swap operation, pop operation, and swap-swap operation. [See Layer
2 Bridging Interfaces Overview.]
Layer 2 support for control protocols (L2CP): RSTP, MSTP, LLDP,
•
BPDU guard/protection, loop protection, root protection, Layer 2
protocol tunneling, storm control, IRB interface, LAG support with
corresponding hashing algorithm, E-LINE, E-LAN, E-ACCESS, and
E-Transit service over L2/Bridge with the following AC interface types:
Port, VLAN, Q-in-Q, VLAN range and VLAN list. [See Layer 2 Control
Protocols on ACX Series Routers.]
Layer 2 circuit cross-connect (L2CCC) support for Layer 2 switching
•
cross-connects. You can leverage the hardware support available for
cross-connects on the ACX710 device with the Layer 2 local switching
functionality using certain models. With this support, you can provide
the EVP and EVPL services. [See Configuring MPLS for Switching
Cross-Connects.]
Reflector function support in RFC 2544. [See RFC 2544-Based
•
Benchmarking Tests Overview.]
Page 18
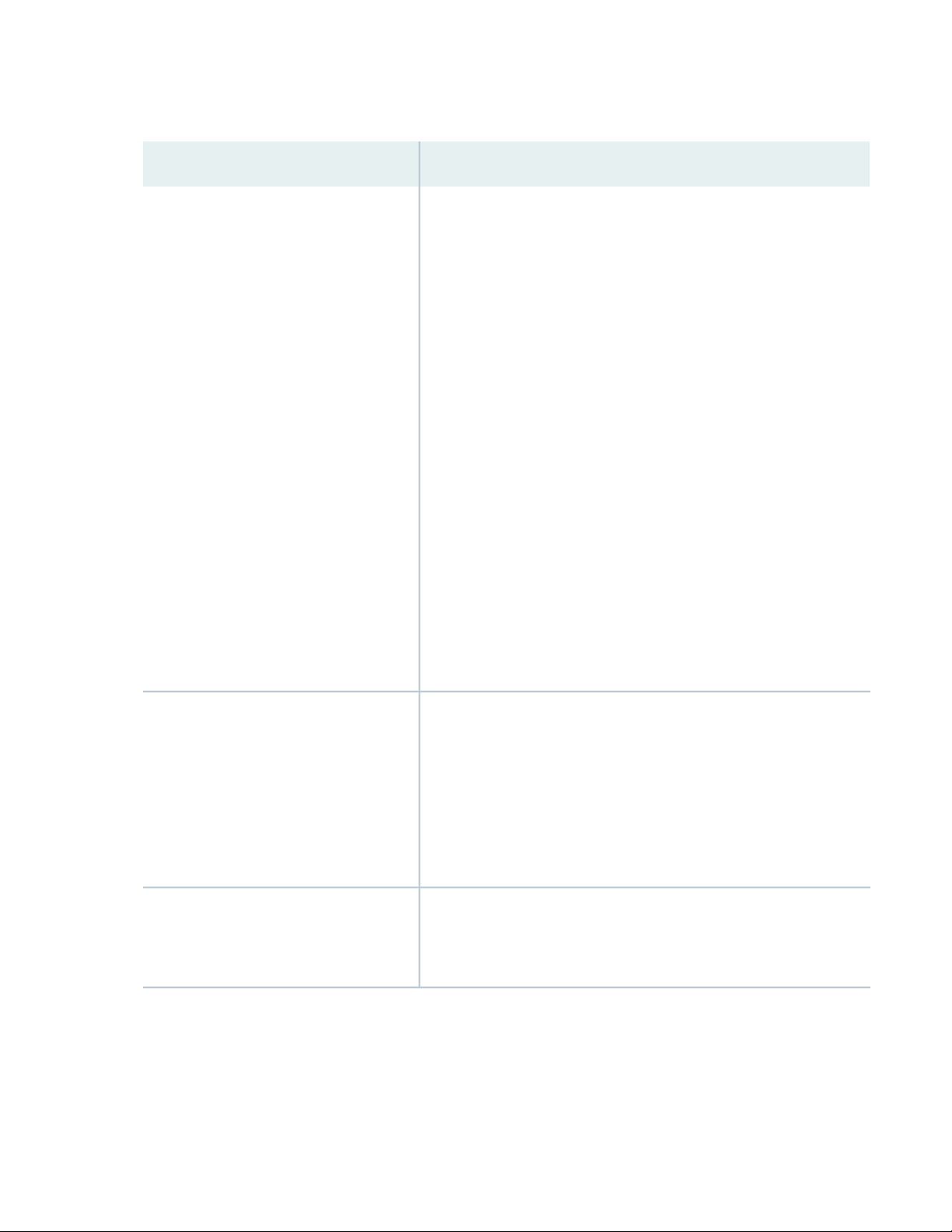
Table 1: Features Supported by the ACX710 Routers (continued)
DescriptionFeature
16
Layer 3 features
Layer 3 VPN and Layer 3 IPv6 VPN Provider Edge router (6VPE)
•
support over MPLS. The router uses MPLS as a transport mechanism
with support for label-switching router (LSR), label edge routers (LERs),
and pseudowire services. These protocols are also supported: ECMP,
OSPF, IS-IS, and BGP. [See Understanding Layer 3 VPNs.]
Basic Layer 3 services over segment routing infrastructure. The
•
segment routing features supported are: segment routing with OSPF
through MPLS, segment routing with IS-IS through MPLS, segment
routing traffic engineering (SR-TE), segment routing global block (SRGB)
range label used by source packet routing in networking (SPRING),
anycast segment identifiers (SIDs) and prefix SIDs in SPRING, and
segment routing with topology independent (TI)-loop-free alternate
(LFA) provides fast reroute (FRR) backup paths corresponding to the
post-convergence path for a given failure. [See Segment Routing LSP
Configuration.]
Enhanced timing and synchronization support using Synchronous
•
Ethernet with ESMC and BITS-Out. [See Synchronous Ethernet
Overview and synchronization (ACX Series).]
Supports full-mesh VPLS domain deployment. The router supports
•
interworking of both BGP as well as LDP-based VPLS. BGP can be
used only for auto-discovery of the VPLS PEs, while LDP signaling for
VPLS connectivity. [See Introduction to VPLS.]
MPLS
Multicast
Supports the Path Computation Element Protocol (PCEP). You can
•
configure the PCEP implementation for both RSVP-TE and segment
routing label-switched paths (LSPs). [See PCEP Configuration.]
Support for MPLS fast reroute (FRR) and unicast reverse-path
•
forwarding (uRPF). [See fast-reroute (Protocols MPLS) and Guidelines
for Configuring Unicast RPF on ACX Series Routers.]
Provides MPLS ping and traceroute support. [See MPLS Connectivity
•
Verification and Troubleshooting Methods.]
Multicast support for IPv4 and IPv6 PIM-SM, SSM, IGMP snooping
•
and proxy support, IGMP, IGMPv1/v2/v3 snooping, IGMP snooping
support for LAG, global multicast support, MLD, and multicast support
on IRB. [See Multicast Overview.]
Page 19

Table 1: Features Supported by the ACX710 Routers (continued)
DescriptionFeature
17
Network management and monitoring
OAM
System management
TWAMP support. [See Two-Way Active Measurement Protocol on
•
ACX Series.]
NETCONF sessions over TLS. [See NETCONF Sessions over Transport
•
Layer Security (TLS).]
Support for adding custom YANG data models to the Junos OS schema
•
[See Understanding the Management of Non-Native YANG Modules
on Devices Running Junos OS.]
Secure boot support in U-boot phase to authenticate and verify the
•
loaded software image while also preventing software-based attack.
[See Software Installation and Upgrade Guide.]
IEEE 802.3ah standard for operation, administration, and management
•
(OAM) connectivity fault management (CFM), BFD, and the ITU-T
Y.1731 standard for Ethernet service OAM. [See IEEE 802.1ag OAM
Connectivity Fault Management Overview.]
Zero-touch provisioning (ZTP) can automate the provisioning of the
•
device configuration and software image. [See Software Installation
and Upgrade Guide.]
Page 20
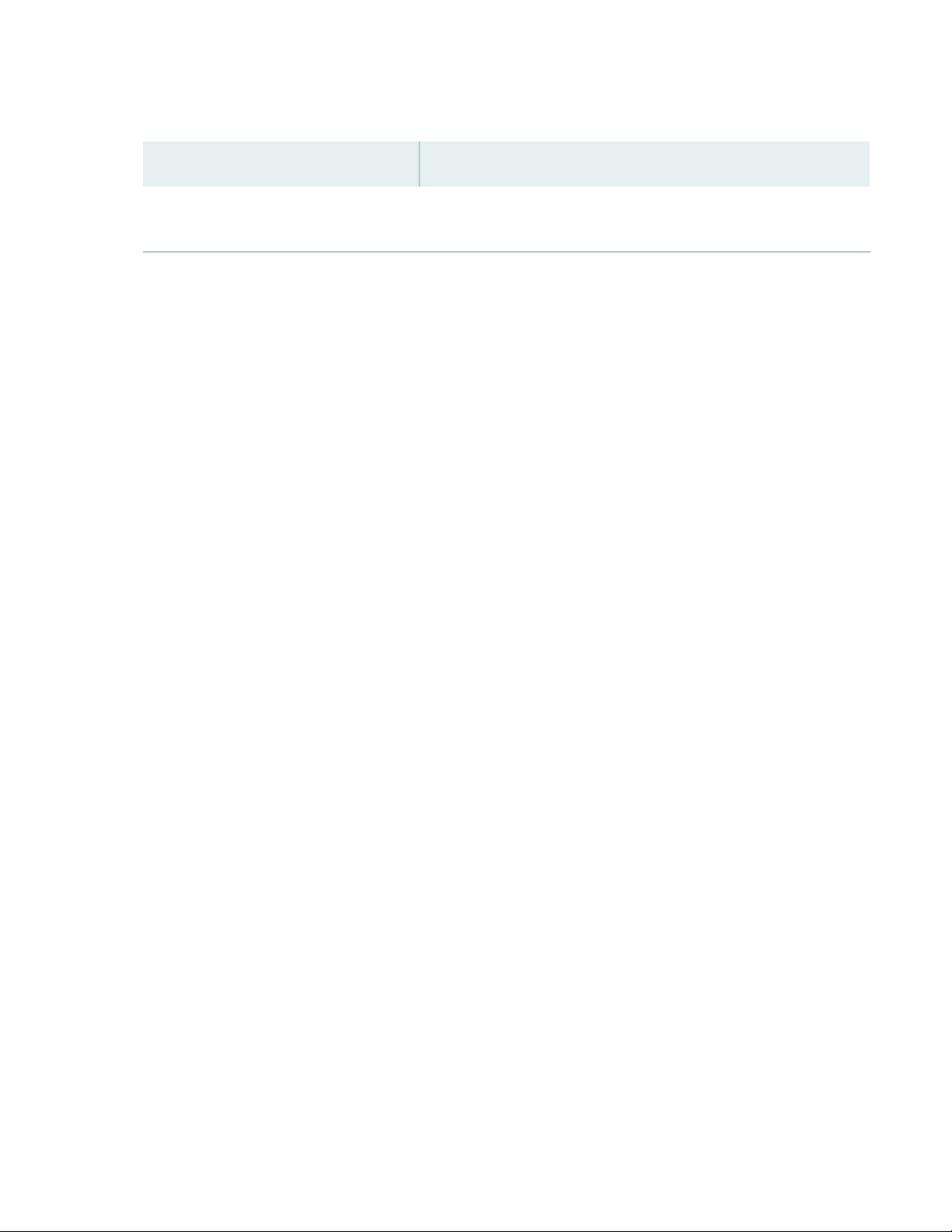
Table 1: Features Supported by the ACX710 Routers (continued)
DescriptionFeature
To view the hardware compatibility matrix for optical interfaces, transceivers, and DACs supported across all platforms,
see the Hardware Compatibility Tool.
Authentication, Authorization, and Accounting
Support for LDAP authentication and authorization over TLS (ACX710)— Starting in Junos OS Release
•
20.2R1, we support LDAP authentication and authorization for Junos OS user login. Through the use
of LDAP over TLS (LDAPS), we’ve implemented the LDAP authentication and authorization support for
Junos OS user login user by providing TLS security between the device running Junos OS (which is the
LDAPS client) and the LDAPS server.
To enable LDAPS support, you can configure the ldaps-server option at the [edit system
authentication-order] hierarchy level. LDAPS ensures the secure transmission of data between a client
and a server with better privacy, confidentiality, data integrity and higher scalability.
18
[See Understanding LDAP Authentication over TLS.]
Class of Service (CoS)
Support for hierarchical class of service (HCoS) (ACX5448)—Starting with Junos OS Release 20.2R1,
•
ACX5448 devices support up to four levels of hierarchical scheduling (physical interfaces, logical interface
sets, logical interfaces, and queues). By default, all interfaces on the ACX5448 use port-based scheduling
(eight queues per physical port). To enable hierarchical scheduling, set hierarchical-scheduler at the [edit
interfaces interface-name] hierarchy level.
[See Hierarchical Class of Service in ACX Series Routers.]
EVPN
Noncolored SR-TE LSPs with EVPN-MPLS (ACX5448, EX9200, MX Series, and vMX)—Starting in Junos
•
OS Release 20.2R1, ACX5448, EX9200, MX Series, and vMX routers support noncolored static segment
routing-traffic engineered (SR-TE) label-switched paths (LSPs) with an EVPN-MPLS core network and
the following Layer 2 services running at the edges of the network:
E-LAN
•
EVPN-ETREE
•
EVPN-VPWS with E-Line
•
Without color, all LSPs resolve using a BGP next hop only.
Page 21

The Juniper Networks routers support noncolored SR-TE LSPs in an EVPN-MPLS core network with
the following configurations:
EVPN running in a virtual switch routing instance
•
Multihoming in active/active and active/standby modes
•
The Juniper Networks routers also support noncolored SR-TE LSPs when functioning as a Data Center
Interconnect (DCI) device that handles EVPN Type 5 routes.
[See Static Segment Routing Label Switched Path.]
Interfaces and Chassis
Port speeds and channelization (ACX710 routers)—Starting in Junos OS Release 20.2R1, you can
•
configure multiple speeds and interface channelization on our new ACX710 router. The router has 28
ports, which support the following speeds:
Ports 0 through 23 on PIC 0 support 1-Gbps speed (with SFP transceivers) and 10-Gbps speed (with
•
SFP+ transceivers).
19
Ports 0 through 3 on PIC 1 support the default 100-Gbps speed (with QSFP28 transceivers) or the
•
configured 40-Gbps speed (with QSFP+ transceivers). You can use the set chassis fpc slot-number pic
pic-number port port-number speed speed CLI command and breakout cables to channelize each:
100-Gbps port into four 25-Gbps interfaces
•
40-Gbps port into four 10-Gbps interfaces
•
[See Channelize Interfaces on ACX710 Routers.]
Ethernet OAM and BFD support (ACX710)—Starting in Junos OS Release 20.2R1, the ACX710 routers
•
support IEEE 802.3ah standard for Operation, Administration, and Maintenance (OAM) connectivity
fault management (CFM), BFD, and the ITU-T Y.1731 standard for Ethernet service OAM.
[See Introduction to OAM Connectivity Fault Management (CFM).]
Alarm port configuration, FRU management, and environmental monitoring (ACX710)—Starting in Junos
•
OS Release 20.2R1, you can configure the alarm port on the ACX710 router. You can use the alarm
input to connect the router to external alarm sources such as security sensors so that the router receives
alarms from these sources and displays those alarms. You can use the alarm output to connect the router
to an external alarm device that gives audible or visual alarm signals based on the configuration. You
can configure three alarm inputs and one alarm output by using the alarm-port statement at the [edit
chassis] hierarchy level. You can view the alarm port details by using the show chassis craft-interface
command.
The ACX710 also supports FRU management and environmental monitoring.
Page 22

[See alarm-port.]
Multichassis link aggregation groups, configuration synchronization, and configuration consistency
•
check (ACX5448 routers)—Starting in Junos OS Release 20.2R1, multichassis link aggregation (MC-LAG)
includes support of Layer 2 circuit functionality with ether-ccc and vlan-ccc encapsulations.
MC-LAG enables a client device to form a logical LAG interface using two switches. MC-LAG provides
redundancy and load balancing between the two switches, multihoming support, and a loop-free Layer
2 network without running spanning-tree protocols (STPs).
[See Multichassis Link Aggregation Features, Terms, and Best Practices.]
Juniper Extension Toolkit (JET)
JET Clang toolchain supports cross-compiling JET applications for use on ARM platforms
•
(ACX710)—Starting in Junos OS Release 20.2R1, you can use the Clang toolchain to compile JET
applications written in C, Python, or Ruby to run on the ARM architecture as well as Junos OS with
FreeBSD and upgraded FreeBSD. The Clang toolchain for ARM is included in the JET software bundle.
After you have downloaded the JET software bundle, you can access the Clang toolchain at
/usr/local/junos-jet/toolchain/llvm/. Use the mk-arm,bsdx command to use the Clang toolchain to
compile your application.
20
[See Develop On-Device JET Applications.]
Python 3 support for JET (ACX Series, EX Series, MX Series, PTX Series, QFX Series, and SRX
•
Series)—Starting in Junos OS Release 20.2R1, Junos OS can use Python 3 to execute JET scripts. To
enable unsigned JET Python applications that support Python 3 to run on devices running Junos OS,
use the set system scripts language python3 command.
[See language (Scripts), Develop Off-Device JET Applications, and Develop On-Device JET Applications.]
Junos Telemetry Interface
•
Network instance (policy) statistics and OpenConfig configuration enhancements on JTI (ACX1100,
ACX2100, ACX5448, ACX6360, EX4300, MX240, MX480, MX960, MX10003, PTX10008, PTX10016,
QFX5110, and QFX10002)—Junos OS Release 20.2R1 provides enhancements to support the OpenConfig
data models openconfig-local-routing.yang and openconfig-network-instance.yang.
[See Mapping OpenConfig Routing Policy Commands to Junos Configuration and Mapping OpenConfig
Network Instance Commands to Junos Operation.]
MPLS
Support for MPLS ping and traceroute for segment routing (ACX Series, MX Series, and PTX
•
Series)—Starting in Junos OS Release 20.2R1, we extend the MPLS ping and traceroute support for all
Page 23

types segment routing--traffic engineering (SR-TE) tunnels, including static segment routing tunnels,
BGP-SR-TE tunnels, and PCEP tunnels.
We also support the following features:
FEC validation support, as defined in RFC 8287, for paths consisting of IGP segments. Target FEC
•
stack contains single or multiple segment ID sub-TLVs. This involves validating IPv4 IGP-Prefix Segment
and IGP-Adjacency Segment ID FEC-stack TLVs.
ECMP traceroute support for all types of SR-TE paths.
•
We do not support the following:
Ping and traceroute for SR-TE tunnel for non-enhanced-ip mode.
•
OAM for IPv6 prefix.
•
BFD
•
[See traceroute mpls segment-routing spring-te and ping mpls segment routing spring-te.]
21
Multicast
Support for IPv6 multicast using MLD (ACX5448)—Starting with Junos OS Release 20.2R1, ACX5448
•
routers support Multicast Listener Discovery (MLD) snooping with MLDv1 and MLDv2 for both any
source multicast and SSM. Support for MLD snooping in EVPN was introduced in Junos OS Release
19.4R2.
MLD snooping for IPv6 is used to optimize Layer 2 multicast forwarding. It works by checking the MLD
messages sent between hosts and multicast routers to identify which hosts are interested in receiving
IPv6 multicast traffic, and then forwarding the multicast streams to only those VLAN interfaces that are
connected to the interested hosts (rather than flooding the traffic to all interfaces). You can enable or
disable MLD snooping per VLAN at the [edit protocols mld-snooping vlan vlan-ID] hierarchy level. Note,
however, that you cannot use ACX Series routers to connect to a multicast source.
[See Understanding MLD Snooping, Understanding MLD, and Overview of Multicast Forwarding with
IGMP or MLD Snooping in an EVPN-MPLS Environment.]
Network Management and Monitoring
NETCONF sessions over TLS (ACX710)—Starting in Junos OS Release 20.2R1, ACX710 routers support
•
establishing Network Configuration Protocol (NETCONF) sessions over Transport Layer Security (TLS)
to manage devices running Junos OS. TLS uses mutual X.509 certificate-based authentication and
provides encryption and data integrity to establish a secure and reliable connection. NETCONF sessions
over TLS enable you to remotely manage devices using certificate-based authentication and to more
easily manage networks on a larger scale than when using NETCONF over SSH.
[See NETCONF Sessions over Transport Layer Security (TLS).]
Page 24
Python 3 support for YANG scripts (ACX Series, EX Series, MX Series, PTX Series, QFX Series, and SRX
•
Series)—Starting in Junos OS Release 20.2R1, Junos OS uses Python 3 to execute YANG action and
translation scripts that are written in Python. Junos OS does not support using Python 2.7 to execute
YANG Python scripts as of this release.
[See Understanding Python Automation Scripts for Devices Running Junos OS.]
Support for port mirroring (ACX5448)—Starting in Junos OS Release 20.2R1, you can use analyzers to
•
mirror copies of packets to a configured destination. Mirroring helps in debugging network problems
and also in defending the network against attacks. You can mirror all ingress traffic to a configured port
(or port list), using a protocol analyzer application that passes the input to mirror through a list of ports
configured through the logical interface. You configure the analyzer at the [edit forwarding-options
analyzer] hierarchy level.
Configuration guidelines and limitations:
Maximum of four default analyzer sessions
•
LAGs supported as mirror output; a maximum of eight child members
•
22
Not supported:
•
Egress mirroring
•
Mirroring on IRB, Virtual Chassis, or management interfaces
•
Nondefault analyzers
•
[See show forwarding-options analyzer.]
Routing Policy and Firewall Filters
Support for firewall filters and policers (ACX710)—Starting with Junos OS Release 20.2R1, the ACX710
•
router supports configuring firewall filters on packets (families such as bridge domain, IPv4, IPv6, CCC,
and MPLS) based on packet match conditions. Along with the match conditions, actions such as count,
discard, log, syslog, and policer are performed on the packets that match the filter. You can configure
policers and attach them to a firewall term.
[See Standard Firewall Filter Match Conditions and Actions on ACX Series Routers Overview.]
SEE ALSO
What's Changed | 23
Known Limitations | 25
Open Issues | 28
Resolved Issues | 31
Page 25
Documentation Updates | 34
Migration, Upgrade, and Downgrade Instructions | 34
What's Changed
IN THIS SECTION
Class of Service (CoS) | 23
General Routing | 23
Juniper Extension Toolkit (JET) | 24
Network Management and Monitoring | 24
23
Learn about what changed in Junos OS main and maintenance releases for ACX Series routers.
Class of Service (CoS)
We’ve corrected the output of the show class-of-service interface | display xml command. Output of
•
the following sort: <container> <leaf-1> data </leaf-1><leaf-2>data </leaf-2> <leaf-3> data</leaf-3>
<leaf-1> data </leaf-1> <leaf-2> data </leaf-2> <leaf-3> data </leaf-3> </container> will now appear
correctly as <container> <leaf-1> data </leaf-1><leaf-2>data </leaf-2> <leaf-3>
data</leaf-3></container> <container> <leaf-1> data </leaf-1> <leaf-2> data </leaf-2> <leaf-3> data
</leaf-3> </container>.
General Routing
Support for full inheritance paths of configuration groups to be built into the database by default (ACX
•
Series, EX Series, MX Series, PTX Series, QFX Series, and SRX Series)—Starting with Junos OS Release
20.2R1, the persist-groups-inheritance option at the [edit system commit] hierarchy level is enabled by
default. To disable this option, use no-persist-groups-inheritance.
[See commit (System).]
New major alarms (ACX-710) —We have introduced the following major alarms:
•
PTP No Foreign Master—Indicates that the external Precision Time Protocol (PTP) master is not sending
•
announce packets.
PTP Sync Fail—Indicates that the PTP lock-status is not in Phase Aligned state.
•
Page 26

Chassis Loss of all Equipment Clock Synch References—Indicates that both the primary and secondary
•
SyncE references have failed and the chassis PLL is in holdover.
Chassis Loss of Equipment Clock Synch Reference 1—Indicates that the primary SyncE reference has
•
failed, and no secondary SyncE reference is configured or present.
Chassis Loss of Equipment Clock Synch Reference 2—Indicates that you have configured at least two
•
or more SyncE sources and the secondary SyncE source has failed.
NOTE: These alarms get cleared when the system recovers from the error condition.
See show chassis alarms.
Juniper Extension Toolkit (JET)
PASS keyword required for Python 3 JET applications (ACX Series, EX Series, MX Series, PTX Series,
•
QFX Series, and SRX Series)—If you are writing a JET application using Python 3, include the PASS
keyword in the Exception block of the script. Otherwise, the application throws an exception when you
attempt to run it.
24
[See Develop Off-Device JET Applications and Develop On-Device JET Applications.]
Updates to IDL for RIB service API bandwidth field (ACX Series, EX Series, MX Series, PTX Series, QFX
•
Series, and SRX Series)—The IDL for the RouteGateway RIB service API has been updated to document
additional rules for the bandwidth field. You must set bandwidth only if a next hop has more than one
gateway, and if you set it for one gateway on a next hop, you must set it for all gateways. If you set
bandwidth when there is only a single usable gateway, it is ignored. If you set bandwidth for one or
more gateways but not all gateways on a next hop, you see the error code
BANDWIDTH_USAGE_INVALID.
[See Juniper EngNet.]
Network Management and Monitoring
Junos OS only supports using Python 3 to execute YANG Python scripts (ACX Series, EX Series, MX
•
Series, PTX Series, QFX Series, and SRX Series)—Starting in Junos OS Release 20.2R1, Junos OS uses
Python 3 to execute YANG action and translation scripts that are written in Python. In earlier releases,
Junos OS uses Python 2.7 to execute these scripts.
[See Understanding Python Automation Scripts for Devices Running Junos OS.]
SEE ALSO
What's New | 13
Page 27
Known Limitations | 25
Open Issues | 28
Resolved Issues | 31
Documentation Updates | 34
Migration, Upgrade, and Downgrade Instructions | 34
Known Limitations
IN THIS SECTION
General Routing | 25
25
Learn about known limitations in this release for ACX Series routers.
For the most complete and latest information about known Junos OS defects, use the Juniper Networks
online Junos Problem Report Search application.
General Routing
If Layer 2 VPN sessions have the OAM control-channel option set to router-alert-label, the
•
no-control-word option in the Layer 2 VPN should not be used for BFD sessions to come up. PR1432854
The time consumed on 1-Gigabit performance is not equal to that on 10-Gigabit performance.
•
Compensation is done to bring the mean value under class A but the peak-to-peak variations are high
and can go beyond 100 ns. It has a latency variation with peak-to-peak variations of around 125–250
ns without any traffic (for example, 5–10 percent of the mean latency introduced by each phy which is
of around 2.5us). PR1437175
On the ACX710 router, variable amount of time is taking to reflect the TWAMP packets. Because of
•
this, the packet latency is not uniform. PR1477329
On the ACX710 router, as per current design and BCOM input, load balancing does not work on any
•
packet which is injected from host path. PR1477797
On the ACX710 router, OSPF neighbors are not learned via VPLS connections because the vlan-tags
•
outer vlan-id1 inner vlan-id2 statement is not supported in VPLS routing instance. PR1477957
On the ACX710 router, sequential increment of both SRC and DST MAC do not provide better load
•
balance as per HASH result. PR1477964
Page 28

On the ACX710 router, load balancing does not happen based on inner IP address when MPLS labelled
•
traffic is received on NNI interface. PR1478945
On the ACX710 router, for TCP protocol as well as for non-TCP protocol, loss-priority medium-low is
•
not supported. PR1479164
For ethernet-vpls encapsulation, if both DST IP and SRC IP are identically varied at the same octet, then
•
hashing might not happen and leads to undefined behavior in load balancing on the ACX710 router.
PR1479767
For bridge LB with vlan-bridge encapsulation, if both SRC IP and DST IP are incremented or decremented
•
by the same order (such as DIP = 10.1.1.1 (increment by 1 upto 100) and SIP = 20.2.3.1 (increment by
1 upto 100), then hashing does not happen on the ACX710 router. PR1479986
For vlan-ccc encapsulation, if both SRC IP and DST IP are incremented or decremented by the same
•
order (such as DIP = 10.1.1.1 (increment by 1 upto 100) and SIP = 20.2.3.1 (increment by 1 upto 100),
then hashing does not happen on the ACX710 router. PR1480228
On the ACX710 router, the input packet statistics for the show interfaces command represents the
•
input packets at the MAC. The error packets which get dropped by MAC and that do not reach PHY will
not be accounted. PR1480413
26
Fragmentation or reassembly is not supported on ACX710 platforms due to the lack of hardware support.
•
PR1481867
On ACX5448 and ACX710 routers, each traffic stream is measured independently per port. Storm control
•
is initiated only if one of the streams exceeds the storm control level. For example, if you set a storm
control level of 100 Megabits and the broadcast and unknown unicast streams on the port are each
flowing at 80 Mbps, storm control is not triggered. PR1482005
On the ACX710 router, RFC2544 reports high latency and throughput loss when the packet size is 64
•
bytes at 100 percent line rate on the ASIC. The ASIC has low threshold value due to which packets are
moved to DRAM from SRAM. When packets are moved to DRAM, high latency and packet drop are
observed. PR1483370
On the ACX710 router, VRRP over aggregated Ethernet interface is not supported. PR1483594
•
On the ACX710 router, traffic loss is seen for segment routing, if protection (FRR) is enabled for 128
•
IPv6 prefix route. PR1484234
Counters for PCS bit errors are not supported because of hardware limitations. Hence "Bit errors" and
•
"Errored blocks" are not supported on an ACX710. PR1484766
If any queue is configured with high priority, it is expected that accuracy of traffic distribution might
•
vary for normal queues because of chip limitation. PR1485405
For Layer 3 VPN configuration, sequential increment of both SRC IP and DST IP address would not
•
provide better load balance as per hash result on the ACX710 router. PR1486406
On the ACX710 router, double tagged interfaces implicit normalization to VLAN ID none is not supported.
•
PR1486515
Page 29
On the ACX710 router, double tagged interfaces implicit normalization to VLAN ID none, ingress VLAN
•
map operation, and pop-pop are not supported. PR1486520
On the ACX710 router, packet priority at egress is derived from the internal priority. This internal priority
•
is derived from the outer VLAN priority at ingress. Thus, the exiting packet retains the same priority as
the ingress outer VLAN priority. PR1486571
When you add or delete a configuration or a LAG member link flaps, configuration updates happen for
•
all other members of the LAG too. This results in transient traffic drop on the ACX710 devices. PR1486997
On the ACX710 router, double tagged ELMI and LLDP PDUs are dropped when L2PT is enabled for
•
these protocols on the ingress interface. These PDUs are supposed to be untagged/native VLAN tagged
and hence the drop. PR1487931
On the ACX710 router, VLAN map operations like swap/swap does not work because the vlan-tags
•
outer vlan-id1 inner vlan-id2 statement is not supported in VPLS routing instance. PR1488084
On the ACX710 router, whenever the 100-Gigabit Ethernet interface is disabled, the alarm is not shown
•
in the jnxDomMib jnxDomCurrentLaneWarnings and jnxDomCurrentLaneAlarms. PR1489940
On the ACX710 router, in case of Layer 2 circuit, load balancing does not occur based on inner MAC
•
address when MPLS labelled traffic is received on an NNI interface. PR1490441
27
On the ACX710 router, unable to scale 1000 CFM sessions at 3 ms intervals; an error message is observed.
•
PR1495753
On ACX5448 routers, aggregated Ethernet LACP toggles with host path traffic with MAC rewrite
•
configuration enabled. PR1495768
The traceroute mpls ldp command does not work in case explicit-null is configured. It does not affect
•
data path traffic. PR1498339
On the ACX710 router, the convergence time for the traffic to switch over from the primary to the
•
secondary link during link flap could be expected to be around 60 to 200 ms with the basic link aggregation
configuration. PR1499965
The maximum FIB route scale supported in an ACX710 router are as below:
•
FIB IPv6 route scale - 80,000
FIB IPv4 route scale - 170,000
If routes are added above this scale, an error indicating lpm route add failure is reported. PR1515545
SEE ALSO
What's New | 13
What's Changed | 23
Open Issues | 28
Page 30
Resolved Issues | 31
Documentation Updates | 34
Migration, Upgrade, and Downgrade Instructions | 34
Open Issues
IN THIS SECTION
General Routing | 28
Platform and Infrastructure | 31
28
Learn about open issues in this release for ACX Series routers.
For the most complete and latest information about known Junos OS defects, use the Juniper Networks
online Junos Problem Report Search application.
General Routing
Policer discarded packets are marked as color black. Black color is used to discard the packets in the
•
pipeline. These packets are not really enqueued into the queues (VoQs) in hardware. The hardware
queue statistics shows this as discarded. However today, both actual-enqueued and the discarded counts
are shown as queue-stats in software. This is a software queue-statistics show issue. PR1414887
DHCP clients are not able to scale to 96,000. PR1432849
•
Protocols get forwarded when using non-existing SSM map source address in IGMPv3 instead of pruning.
•
PR1435648
Memory leaks are expected in this release. PR1438358
•
When there is a failure of the I2C daemon, core files are generated on ACX5448. PR1455928
•
On ACX5048 routers, the egress queue statistics are not working for the aggregated Ethernet interfaces.
•
PR1472467
On ACX710 routers, VPLS OAM sessions are detected with error( remote defect indication sent by some
•
MEPs) after changing VLANs. PR1478346
On ACX710 routers, initial few packet drop is observed after changing ALT port cost for RSTP. PR1482566
•
On ACX710 routers, VRRP over dual tagged interface is not supported. PR1483759
•
Page 31

Issue is seen during unified ISSU to Junos OS Releases 20.2. Unified ISSU is completed, but the Packet
•
Forwarding Engine does not function. Because of this, forwarding is affected. PR1483959
On ACX710 routers, FEC of channel 0 in a channelized 25-Gigabit Ethernet interface is set to None
•
while channels 1, 2, and 3 have FEC74 as the default value for 100G LR4 optics. The desired FEC value
can be set through the CLI command set interfaces et-x/y/z: channel no gigether-options fec fec value.
PR1488040
Queue statistics are not as expected after you configure physical interface and logical interface shaping
•
with transmit-rate and scheduler-map. PR1488935
Port mirroring is not supported on ACX6360-OR. PR1491789
•
On ACX710 routers, the ping mpls l2ckt/l2vpn command does not work if the no-control-word statement
•
is configured. PR1492963
On ACX710 routers, the ping mpls l2circuit command does not work if explicit-null is configured. It
•
does not affect data path traffic. PR1494152
On ACX710 routers, high convergence is seen with EVPN-ELAN service in a scaled scenario during FRR
•
switchover. With 150 EVPN-ELAN session, the switchover can go as high as ~200 msec with aggregated
Ethernet in the core. PR1497251
29
When the NETCONF session is established over an outbound SSH connection, the high rate of pushing
•
the configuration to an ephemeral database might result in flapping of the outbound SSH connection
or a memory leak issue. PR1497575
The local link speed parameter under the autonegotiation information displays configured speed instead
•
of negotiated speed. However, the link partner speed indicates the negotiated speed. When speed is
not configured, the local link speed is not displayed with reboot or Packet Forwarding Engine restart. It
is displayed when the speed is configured and later deleted. PR1499012
On ACX710 routers with an EVPN-VPWS and EVPN-FXC circuits, Layer 3 VPN destination reachable
•
over composite next hop (this is enabled using CLI set routing-options forwarding-table
chained-composite-next-hop ingress l3vpn) does not get HW FRR behavior (less than 50 ms convergence).
The traffic convergence dependents on control plane convergence. PR1499483
I2C errors and SFP toxic message might be seen during boot, if the port with copper SFP is disabled
•
before reboot. These I2C errors do not flood and see during boot, then they stop. Even though SFP toxic
message is seen, there is no functional impact. PR1501332
On ACX710 routers, if we configure DHCP option 012 host-name in DHCP server and the actual base
•
configuration file also has the host-name in it, then overwriting of the base configuration file's host-name
with the DHCP option 012 host-name is happening. PR1503958
On the ACX6360 platform, the core file core-ripsaw-node-aftd-expr is generated and you are unable
•
to back trace the file. PR1504717
On ACX710 routers, in case the following steps are done for PTP:
•
1. One or two port as source for chassis synchronization and both PTP and SyncE locked.
Page 32

2. Disable both Logical Interfaces.
3. Restart clksyncd.
4. Rollback 1 chassis does not lock again.
This can be recovered by deleting PTP configuration, restart clksyncd, and reconfiguring the PTP post
this operation. PR1505405
MPLS LSP check is failing while verifying basic lsp_retry_limit. Reset the src_address of the LSP to 0 (if
•
src_address is not configured) whenever it changes its state from up to down. So when the ingress LSP
goes to down state, reset it to 0. The script is failing because the script is checking for src_address to be
present for the ingress lSP session. PR1505474
In a PTP environment, some vendor devices act as slave expecting announce messages at an interval of
•
-3 (8pps) from upstream master device. Currently, announce messages are configured in a range of 0 to
3. To support -3 requirement, a hidden CLI statement set protocol ptp master announce-interval -3 is
introduced. In a network or design where you have this requirement, you can configure the hidden CLI
or the regular CLI which is in the range of 0 to 3. Both the CLI statements are mutually exclusive, commit
error is expected if both are configured. This new change is applicable to all ACX platforms except
ACX5000 line of routers. PR1507782
30
On ACX710 routers, unexpected delay counter values are seen under show ptp statistics detail when
•
upstream master stops sending the PTP packets. PR1508031
On ACX710 routers, if the ukern is restarted with the chassis-control restart command, the state of the
•
PTP lock status on the Routing Engine will transition between holdover/acquiring/phase locked. The
clock data is displayed accordingly. Once the Packet Forwarding Engine is up and running after restart,
clock data is stable and correct. During the time the Packet Forwarding Engine is not up, the clock display
is inconsistent but eventually it becomes valid once the Packet Forwarding Engine is up and the clock
is created and announce packets are being generated. PR1508385
On ACX710 routers, the Packet Forwarding Engine might crash and the FPC might remain down. This
•
issue occurs when the PTP is configured and removed, and then the router is rebooted. This issue
happens when the DMA in QAX device goes in bad state when host bound PTP traffic is pumped and
router rebooted. This causes the router to crash and it does not come up. PR1509402
On ACX710 routers, EXP re-marking is supported only for a single MPLS label packet. PR1509627
•
On ACX710 routers, local repair can be in seconds (>50 ms) during FRR convergence. If explicit NULL
•
is configured on the PHP node and on the PHP node of the backup path, the link failure is observed at
PHP node. Global repair resumes the traffic flow. PR1515512
On ACX710 routers, whenever EVPN core link is flapped, the following errors might be seen for a few
•
seconds LOG: Err] dnx_nh_indr_bcm_nh_install: BCM L3 Egress create object failed for:Indirect nh
2097905 (-4:Invalid parameter), LOG: Err] ACX_L2_CFG_FAILED: ACX Error
(L2):dnx_l2alm_get_gport_from_ifl_index : Failed to get hw nh index for evpn ifl 270533361, LOG: Err]
ACX_PFE_ERROR: dnx_l2alm_add_mac_table_entry_in_hw: Get port from ifl failed ifl index 270533361.
PR1515516
Page 33

On ACX710 routers, the L2ALD process might restart unexpectedly during interface flaps. PR1517074
•
On ACX710 routers, CFMD memory leak is observed for scaled configurations involving IPv4 and IPv6
•
logical interfaces with operations like deactivate, activate logical interfaces, and restart FPCs etc. This
memory leak can lead to CFMD core file generation. PR1517775
On ACX710 routers with trirate copper SFP, the interface speed in CLI is seen as 10-Gbps intermittently
•
when the configurations are deleted. PR1518111
On ACX5448 and ACX5448-D routers, Packet Forward Engine memory exhaustion is reported because
•
of continuous IPv6 neighbor flaps. PR1519372
On ACX710 routers, delete chassis alarm-port does not delete the alarm port configuration and show
•
chassis craft-interface command displays the old configuration. PR1520326
Platform and Infrastructure
The CFM REMOTE MEP does not come up after configuration or remains in Start state. PR1460555
•
31
SEE ALSO
What's New | 13
What's Changed | 23
Known Limitations | 25
Resolved Issues | 31
Documentation Updates | 34
Migration, Upgrade, and Downgrade Instructions | 34
Resolved Issues
IN THIS SECTION
General Routing | 32
Interfaces and Chassis | 33
Layer 2 Ethernet Services | 33
MPLS | 33
Routing Protocols | 33
VPNs | 33
Page 34

Learn which issues were resolved in the Junos OS main and maintenance releases for ACX Series routers.
For the most complete and latest information about known Junos OS defects, use the Juniper Networks
online Junos Problem Report Search application.
General Routing
Drift messages in ACX2200, which is a PTP hybrid (PTP + Synchronous Ethernet) device. PR1426910
•
ACX5448-D interfaces support: The input bytes value for the show interfaces extensive command is
•
not at par with older ACX Series or MX Series devices. PR1430108
On an ACX5448 device, DHCP packets are not transparent over Layer 2 circuit. PR1439518
•
On an ACX5048 device, SNMP polling stops after the link is flapped or the SFP transceiver is replaced,
•
and ACX_COS_HALP(acx_cos_gport_sched_set_strict_priority:987): Failed to detach logs might be
seen. PR1455722
ACX5448-D and ACX5448-M devices do not display airflow information and temperature sensors as
•
expected. PR1456593
32
Unable to get shared buffer count as expected. PR1468618
•
Loss of manageability on ACX6360-OX platform when its disk gets full. PR1470217
•
ERP might not come up properly when MSTP and ERP are enabled on the same interface. PR1473610
•
On an ACX710 device, MPLS packet load balancing is done without hashing enabled. PR1475363
•
FPC might continuously crash after deactivating or activating loopback filter or reboot the system after
•
configuring the loopback filter. PR1477740
The dcpfe core file is generated when disabling or enabling MACsec through Toby scripts. PR1479710
•
Link does not come up when a 100-Gigabit Ethernet port is channelized into four port 25-Gigabit Ethernet
•
interfaces. PR1479733
Memory utilization enhancement on ACX platforms to reduce the memory foot print. PR1481151
•
On ACX5448 devices, dnx_nh_mpls_tunnel_install logs are seen. PR1482529
•
ACX AUTHD process memory usage is 15 percent. PR1482598
•
FPC crash is seen on ACX5448 platform. PR1485315
•
On an ACX5448 device, Layer 2 VPN with interface ethernet-ccc input-vlan-map/output-vlan-map can
•
cause traffic to be discarded silently. PR1485444
On the ACX710 router, VPLS flood group results in IPv4 traffic drop after core interface flap. PR1491261
•
On the ACX710 routers, LSP (primary and standby) does not Act/Up after routing or rpd restart.
•
PR1494210
During speed mismatch, QSFP28/QSFp+ optics/cables might or might not work. PR1494600
•
Page 35

ACX710 BFD sessions are in initialization state with CFM scale of 1000 on reboot or chassis control
•
restart. PR1503429
On an ACX500-i router, SFW sessions are not getting updated on ms- interfaces. PR1505089
•
On an ACX710 router, wavelength changed from CLI does not take effect in tunable optics. PR1506647
•
PIC slot might be shut down in less than 240 seconds due to the over-temperature start time is handled
•
incorrectly. PR1506938
BFD flaps with the error ACX_OAM_CFG_FAILED: ACX Error (oam):dnx_bfd_l3_egress_create : Unable
•
to create egress object after random time interval. PR1513644
Interfaces and Chassis
The status of the MC-AE interface might be shown as unknown when you add the subinterface as part
•
of the VLAN on the peer MC-AE node. PR1479012
33
Layer 2 Ethernet Services
Member links state might be asychronized on a connection between a PE device and a CE device in an
•
EVPN active/active scenario. PR1463791
MPLS
BGP session might keep flapping between two directly connected BGP peers because of the incorrect
•
TCP-MSS in use. PR1493431
Routing Protocols
The BGP route target family might prevent route reflector from reflecting Layer 2 VPN and Layer 3 VPN
•
routes. PR1492743
VPNs
The Layer 2 circuit neighbor might be stuck in RD state at one end of the MG-LAG peer. PR1498040
•
The rpd core files are generated while disabling Layer 2 circuit with connection protection, backup
•
neighbor configuration, and Layer 2 circuit trace logs enabled. PR1502003
SEE ALSO
Page 36

What's New | 13
What's Changed | 23
Known Limitations | 25
Open Issues | 28
Documentation Updates | 34
Migration, Upgrade, and Downgrade Instructions | 34
Documentation Updates
There are no errata or changes in Junos OS Release 20.2R1 documentation for ACX Series routers.
SEE ALSO
34
What's New | 13
What's Changed | 23
Known Limitations | 25
Open Issues | 28
Resolved Issues | 31
Migration, Upgrade, and Downgrade Instructions | 34
Migration, Upgrade, and Downgrade Instructions
IN THIS SECTION
Upgrade and Downgrade Support Policy for Junos OS Releases | 35
This section contains the upgrade and downgrade support policy for Junos OS for ACX Series routers.
Upgrading or downgrading Junos OS might take several minutes, depending on the size and configuration
of the network.
For information about software installation and upgrade, see the Installation and Upgrade Guide.
Page 37

Upgrade and Downgrade Support Policy for Junos OS Releases
Support for upgrades and downgrades that span more than three Junos OS releases at a time is not
provided, except for releases that are designated as Extended End-of-Life (EEOL) releases. EEOL releases
provide direct upgrade and downgrade paths—you can upgrade directly from one EEOL release to the
next EEOL release even though EEOL releases generally occur in increments beyond three releases.
You can upgrade or downgrade to the EEOL release that occurs directly before or after the currently
installed EEOL release, or to two EEOL releases before or after. For example, Junos OS Releases 19.3,
19.4, and 20.1 are EEOL releases. You can upgrade from Junos OS Release 19.3 to Release 19.4 or from
Junos OS Release 19.3 to Release 20.1.
You cannot upgrade directly from a non-EEOL release to a release that is more than three releases ahead
or behind. To upgrade or downgrade from a non-EEOL release to a release more than three releases before
or after, first upgrade to the next EEOL release and then upgrade or downgrade from that EEOL release
to your target release.
For more information about EEOL releases and to review a list of EEOL releases, see
https://www.juniper.net/support/eol/junos.html.
35
For information about software installation and upgrade, see the Installation and Upgrade Guide.
SEE ALSO
What's New | 13
What's Changed | 23
Known Limitations | 25
Open Issues | 28
Resolved Issues | 31
Documentation Updates | 34
Junos OS Release Notes for EX Series
IN THIS SECTION
What's New | 36
What's Changed | 44
Page 38

Known Limitations | 46
Open Issues | 47
Resolved Issues | 51
Documentation Updates | 56
Migration, Upgrade, and Downgrade Instructions | 56
These release notes accompany Junos OS Release 20.2R1 for the EX Series. They describe new and
changed features, limitations, and known and resolved problems in the hardware and software.
You can also find these release notes on the Juniper Networks Junos OS Documentation webpage, located
at https://www.juniper.net/documentation/product/en_US/junos-os.
36
What's New
IN THIS SECTION
What’s New in Release 20.2R1-S1 | 37
What’s New in Release 20.2R1 | 37
Learn about new features introduced in this release for EX Series Switches.
NOTE: The following EX Series switches are supported in Release 20.2R1: EX2300, EX2300-C,
EX3400, EX4300, EX4600, EX4650, EX9200, EX9204, EX9208, EX9214, EX9251, and EX9253.
Page 39

What’s New in Release 20.2R1-S1
Software Installation and Upgrade
Zero touch provisioning (ZTP) with IPv6 support (EX3400, EX4300, QFX5100 and QFX5200 switches,
•
MX-Series routers)—Starting in Junos OS Release 20.2R1-S1, ZTP supports the DHCPv6 client. During
the bootstrap process, the device first uses the DHCPv4 client to request for information regarding
image and configuration file from the DHCP server. The device checks the DHCPv4 bindings sequentially.
If there is a failure with one of the DHCPv4 bindings, the device will continue to check for bindings until
provisioning is successful. If there are no DHCPv4 bindings, however, the device will check for DHCPv6
bindings and follow the same process as for DHCPv4 until the device can be provisioned successfully.
Both DHCPv4 and DHCPv6 clients are included as part of the default configuration on the device.
The DHCP server uses DHCPv6 options 59 and 17 and applicable suboptions to exchange ZTP-related
information between itself and the DHCP client.
NOTE: Only HTTP and HTTPS transport protocols are supported EX3400, EX4300, QFX5100,
and QFX5200 devices.
37
[See Zero Touch Provisioning.]
What’s New in Release 20.2R1
Authentication, Authorization, and Accounting
Retain the authentication session based on DHCP or SLAAC snooping entries (EX2300, EX3400, and
•
EX4300)—Starting in Junos OS Release 20.2R1, you can configure the authenticator to check for a
DHCP, DHCPv6, or SLAAC snooping entry before terminating the authentication session when the MAC
address ages out. If a snooping entry is present, the authentication session for the end device with that
MAC address remains active. This ensures that the end device will be reachable even if the MAC address
ages out.
[See Authentication Session Timeouts.]
EVPN
802.1X authentication with EVPN-VXLAN (EX4300-48MP and EX4300-48MP Virtual Chassis)—Starting
•
in Junos OS Release 20.2R1, EX4300-48MP switches that act as access switches can use 802.1X
authentication to protect an EVPN-VXLAN network from unauthorized end devices. EX4300-48MP
switches support the following 802.1X authentication features on access and trunk ports:
Access ports: single, single-secure, and multiple supplicant modes
•
Trunk ports: single and single-secure supplicant modes
•
Guest VLAN
•
Page 40

Server fail
•
Server reject
•
Dynamic VLAN
•
Dynamic firewall filters
•
RADIUS accounting
•
Port bounce with Change of Authorization (CoA) requests
•
MAC RADIUS client authentication
•
Central Web Authentication (CWA) with redirect URL
•
Captive portal client authentication
•
Flexible authentication with fallback scenarios
•
[See 802.1X Authentication.]
Support for firewall filtering on EVPN-VXLAN traffic (EX4300-MP)—Starting with Junos OS Release
•
20.2R1, you can configure firewall filters and policers on the VXLAN traffic in an EVPN network
(EVPN-VXLAN traffic). You set the rules that the devices uses to accept or discard packets by defining
the terms for a firewall filter. For filters that you would apply to a port or VLAN, configure firewall filters
at the [edit firewall family ethernet-switching] hierarchy level. For filters that you would apply to an
IRB interface, configure firewall filters at the [edit firewall family inet] hierarchy level. After a firewall
filter is defined, you can then apply it at an interface.
38
[See Firewall Filtering and Policing Support for EVPN-VXLAN.]
Noncolored SR-TE LSPs with EVPN-MPLS (ACX5448, EX9200, MX Series, and vMX)—Starting in Junos
•
OS Release 20.2R1, ACX5448, EX9200, MX Series, and vMX routers support noncolored static segment
routing-traffic engineered (SR-TE) label-switched paths (LSPs) with an EVPN-MPLS core network and
the following Layer 2 services running at the edges of the network:
E-LAN
•
EVPN-ETREE
•
EVPN-VPWS with E-Line
•
Without color, all LSPs resolve using a BGP next hop only.
The Juniper Networks routers support noncolored SR-TE LSPs in an EVPN-MPLS core network with
the following configurations:
EVPN running in a virtual switch routing instance
•
Multihoming in active/active and active/standby modes
•
The Juniper Networks routers also support noncolored SR-TE LSPs when functioning as a Data Center
Interconnect (DCI) device that handles EVPN Type 5 routes.
Page 41

[See Static Segment Routing Label Switched Path.]
MAC filtering, storm control, and port mirroring support in EVPN-VXLAN overlay networks
•
(EX4300-48MP)—Starting with Junos OS Release 20.2R1, EX4300-48MP switches support the following
features in an EVPN-VXLAN overlay network:
MAC filtering
•
Storm control
•
Port mirroring and analyzers
•
[See MAC Filtering, Storm Control, and Port Mirroring Support in an EVPN-VXLAN Environment.]
Layer 2 and 3 families, encapsulation types, and VXLAN on the same physical interface (EX4600)—Starting
•
in Junos OS Release 20.2R1, you can configure and successfully commit the following on a physical
interface of an EX4600 switch in an EVPN-VXLAN environment:
Layer 2 bridging (family ethernet-switching) on any logical interface unit number (unit 0 and any
•
nonzero unit number).
VXLAN on any logical interface unit number (unit 0 and any nonzero unit number).
•
39
Layer 2 bridging (family ethernet-switching and encapsulation vlan-bridge) on different logical interfaces
•
(unit 0 and any nonzero unit number).
Layer 3 IPv4 routing (family inet) and VXLAN on different logical interfaces (unit 0 and any nonzero
•
unit number).
For these configurations to be successfully committed and work properly, you must specify the
encapsulation flexible-ethernet-services configuration statements at the physical interface level—for
example, set interfaces xe-0 /0/5 encapsulation flexible-ethernet-services.
[See Understanding Flexible Ethernet Services Support With EVPN-VXLAN.]
Page 42

High Availability (HA) and Resiliency
Support for failover configuration synchronization for the ephemeral database (EX Series, MX Series,
•
MX Series Virtual Chassis, PTX Series, and QFX Series)—Starting in Junos OS Release 20.2R1, when
you configure the commit synchronize statement at the [edit system] hierarchy level in the static
configuration database of an MX Series Virtual Chassis or dual Routing Engine device, the backup Routing
Engine will synchronize both the static and ephemeral configuration databases when it synchronizes its
configuration with the master Routing Engine. This happens, for example, when a backup Routing Engine
is newly inserted, comes back online, or changes mastership. On a dual Routing Engine system, the
backup Routing Engine synchronizes both configuration databases with the master Routing Engine. In
an MX Series Virtual Chassis, the master Routing Engine on the protocol backup synchronizes both
configuration databases with the master Routing Engine on the protocol master.
[See Understanding the Ephemeral Configuration Database.]
Juniper Extension Toolkit (JET)
Python 3 support for JET (ACX Series, EX Series, MX Series, PTX Series, QFX Series, and SRX
•
Series)—Starting in Junos OS Release 20.2R1, Junos OS can use Python 3 to execute JET scripts. To
enable unsigned JET Python applications that support Python 3 to run on devices running Junos OS,
use the set system scripts language python3 command.
40
[See language (Scripts), Develop Off-Device JET Applications, and Develop On-Device JET Applications.]
Junos OS XML, API, and Scripting
Support for Rest API (EX2300, EX2300-MP, EX3400, EX4300, EX4300-MP, EX4600, EX4650, and
•
EX9200)—Starting in Release 20.2R1, Junos OS supports the REST API on EX2300, EX2300-MP, EX3400,
EX4300, EX4300-MP, EX4600, EX4650, and EX9200 switches. The REST API enables you to securely
connect to the Junos OS devices, execute remote procedure calls (RPC) commands, use REST API explorer
GUI to conveniently experiment with any of the REST APIs, and use a variety of formatting and display
options including JavaScript Object Notation (JSON).
[See REST API Guide.]
Junos Telemetry Interface
•
Network instance (policy) statistics and OpenConfig configuration enhancements on JTI (ACX1100,
ACX2100, ACX5448, ACX6360, EX4300, MX240, MX480, MX960, MX10003, PTX10008, PTX10016,
QFX5110, and QFX10002)—Junos OS Release 20.2R1 provides enhancements to support the OpenConfig
data models openconfig-local-routing.yang and openconfig-network-instance.yang.
[See Mapping OpenConfig Routing Policy Commands to Junos Configuration and Mapping OpenConfig
Network Instance Commands to Junos Operation.]
•
Support for OpenConfig configuration model version 4.0.1 for BGP with JTI (EX2300, EX3400, EX4300,
EX4600, and EX9200)— Junos OS Release 20.2R1 provides support for the OpenConfig version 4.0.1
data models openconfig-bgp-neighbor.yang and openconfig-bgp-policy.yang using Junos telemetry
Page 43

interface (JTI) and remote procedure call (gRPC) services. Using JTI and gRPC services, you can stream
telemetry statistics to an outside collector.
The following major resource paths are supported with gRPC and JTI:
/network-instances/network-instance/protocols/protocol/bgp/global/
•
/network-instances/network-instance/protocols/protocol/bgp/global/afi-safis/afi-safi/
•
/network-instances/network-instance/protocols/protocol/bgp/neighbors/neighbor/
•
/network-instances/network-instance/protocols/protocol/bgp/peer-groups/peer-group/
•
[See Guidelines for gRPC and gNMI Sensors (Junos Telemetry Interface and OpenConfig Data Model
Version.]
•
Support for OpenConfig configuration model version 1.0.0 for local routing with JTI (EX2300, EX3400,
EX4300, EX4600, and EX9200)— Junos OS Release 20.2R1 provides support for the OpenConfig version
1.0.0 data model openconfig-local-routing.yang using Junos telemetry interface (JTI) and remote
procedure call (gRPC) services. Using JTI and gRPC services, you can stream telemetry statistics to an
outside collector.
41
The following major resource paths are supported with gRPC and JTI:
/local-routes/static-routes/static/
•
/local-routes/local-aggregates/aggregate/
•
[See Guidelines for gRPC and gNMI Sensors (Junos Telemetry Interface and OpenConfig Data Model
Version.]
•
Packet Forwarding Engine and Routing Engine sensor support with JTI (EX2300, EX2300-MP, and
EX3400)—Starting in Junos OS Release 20.2R1, you can use Junos telemetry interface (JTI) with remote
procedure call (gRPC) services to export Packet Forwarding Engine statistics and Routing Engine statistics
from EX2300, EX2300-MP, and EX3400 switches to an outside collector. These statistics can also be
exported through UDP (native) sensors.
Supported Packet Forwarding Engine sensors are:
Sensor for CPU (ukernel) memory (resource path /junos/system/linecard/cpu/memory/)
•
Sensor for firewall filter statistics (resource path /junos/system/linecard/firewall/)
•
Sensor for physical interface traffic (resource path /junos/system/linecard/interface/)
•
Sensor for logical interface traffic (resource path /junos/system/linecard/interface/logical/usage/).
•
Not supported on EX2300 or 2300-MP switches.
Sensor for software-polled queue-monitoring statistics (resource path /junos/system/linecard/
•
qmon-sw/). Not supported on EX2300 or 2300-MP switches.
Supported Routing Engine sensors are:
Page 44

Sensor for LACP state export (resource path /lacp/)
•
Sensor for chassis environmentals export (resource path /junos/system/components/component/)
•
Sensor for chassis components export (resource path /components/)
•
Sensor for LLDP statistics export (resource path /lldp/interfaces/interface[name='name’]/)
•
Sensor for BGP peer information export (resource path /network-instances/network-instance/
•
protocols/protocol/bgp/). Not supported on EX2300 or 2300-MP switches.
Sensor for RPD task memory utilization export (resource path /junos/task-memory-information/)
•
Sensor network discovery ARP table state (resource path /arp-information/)
•
Sensor for network discovery NDP table state (resource path /nd6-information/)
•
[See Understanding OpenConfig and gRPC and gNMI on Junos Telemetry Interface, sensor (Junos
Telemetry Interface), and Guidelines for gRPC and gNMI Sensors (Junos Telemetry Interface.]
Multicast
Static multicast route leaking for VRF and virtual router instances (EX4650 and QFX5120-48Y)—Starting
•
with Junos OS Release 20.2R1, you can configure the switch to statically share (leak) IPv4 multicast
routes for IGMPv3 (S,G) traffic among different virtual router or virtual routing and forwarding (VRF)
instances. You can only leak static multicast routes per group, not per source and group. The destination
prefix length must be 32.
42
To configure multicast route leaking to the VRF or virtual router instance routing-instance-name, configure
the next-table routing-instance-name.inet.0 statement at the [edit routing-instances routing-instance-name
routing-options static route destination-prefix/32] hierarchy level.
[See Understanding Multicast Route Leaking for VRF and Virtual Router Instances.]
Multicast-only fast reroute (MoFRR) (EX4650 and QFX5120-48Y)—Starting in Junos OS Release 20.2R1,
•
you can configure MoFRR to minimize multicast packet loss in PIM domains when link failures occur.
With MoFRR enabled, the switch maintains primary and backup traffic paths, forwarding traffic from
the primary path and dropping traffic from the backup path. If the primary path fails, the switch can
quickly start forwarding the backup path stream (which becomes the primary path). The switch creates
a new backup path if it detects available alternative paths. MoFRR applies to all multicast (S,G) streams
by default, or you can configure a policy for the (S,G) entries where you want MoFRR to apply.
[See Understanding Multicast-Only Fast Reroute.]
Network Management and Monitoring
Python 3 support for YANG scripts (ACX Series, EX Series, MX Series, PTX Series, QFX Series, and SRX
•
Series)—Starting in Junos OS Release 20.2R1, Junos OS uses Python 3 to execute YANG action and
translation scripts that are written in Python. Junos OS does not support using Python 2.7 to execute
YANG Python scripts as of this release.
[See Understanding Python Automation Scripts for Devices Running Junos OS.]
Page 45

NETCONF sessions over outbound HTTPS (EX Series, MX Series, PTX1000, PTX3000, PTX5000,
•
PTX10001, PTX10002, PTX10008, PTX10016, QFX Series, SRX1500, SRX4100, SRX4200, SRX4600,
SRX5400, SRX5600, SRX5800, and vSRX)—Starting in Junos OS Release 20.2R1, the Junos OS with
upgraded FreeBSD software image includes a Juniper Extension Toolkit (JET) application that supports
establishing a NETCONF session using outbound HTTPS. The JET application establishes a persistent
HTTPS connection with a gRPC server over a TLS-encrypted gRPC session and authenticates the
NETCONF client using an X.509 digital certificate. A NETCONF session over outbound HTTPS enables
you to remotely manage devices that might not be accessible through other protocols, for example, if
the device is behind a firewall.
[See NETCONF Sessions over Outbound HTTPS.]
Routing Policy and Firewall Filters
Support for MPLS firewall filter on loopback interface (EX4650, QFX5120-32C, and
•
QFX5120-48Y)—Starting with Junos OS Release 20.2R1, you can apply an MPLS firewall filter to a
loopback interface on a Label switching router (LSR). For example, you can configure an MPLS packet
with ttl=1 along with MPLS qualifiers such as label, exp, and Layer 4 tcp/udp port numbers. Supported
actions include accept, discard, and count.
43
You configure this feature at the [edit firewall family mpls] hierarchy level. You can only apply a loopback
filters on family mpls in the ingress direction.
[See Overview of MPLS Firewall Filters on Loopback Interface.]
Routing Protocols
Support for Layer 2 circuit, Layer 2 VPN, and VPLS services with BGP labeled unicast (MX Series,
•
EX9204, EX9208, EX9214, EX9251, and EX9253 devices)—Starting with Junos OS Release 20.2R1, MX
Series, EX9204, EX9208, EX9214, EX9251, and EX9253 devices support BGP PIC Edge protection for
Layer 2 circuit, Layer 2 VPN, and VPLS (BGP VPLS, LDP VPLS and FEC 129 VPLS) services with BGP
labeled unicast as the transport protocol. BGP PIC Edge using the BGP labeled unicast transport protocol
helps to protect traffic failures over border nodes (ABR and ASBR) in multi-domain networks. Multi-domain
networks are typically used in metro-aggregation and mobile backhaul networks designs.
A prerequisite for BGP PIC Edge protection is to program the Packet Forwarding Engine (PFE) with
expanded next-hop hierarchy.
To enable BGP PIC Edge protection, use the following CLI configuration statements:
Expand next-hop hierarchy for BGP labeled unicast family:
•
[edit protocols]
user@host#set bgp group group-name family inet labeled-unicast nexthop-resolution
preserve-nexthop-hierarchy;
Page 46

BGP PIC for MPLS load balance nexthops:
•
[edit routing-options]
user@host#set rib routing-table-name protect core;
Fast convergence for Layer 2 circuit and LDP VPLS:
•
[edit protocols]
user@host#set l2circuit resolution preserve-nexthop-heirarchy;
Fast convergence for Layer 2 VPN, BGP VPLS, and FEC129:
•
[edit protocols]
user@host#set l2vpn resolution preserve-nexthop-heirarchy;
[See Load Balancing for a BGP Session.]
44
SEE ALSO
What's Changed | 44
Known Limitations | 46
Open Issues | 47
Resolved Issues | 51
Documentation Updates | 56
Migration, Upgrade, and Downgrade Instructions | 56
What's Changed
IN THIS SECTION
Class of Service (CoS) | 45
General Routing | 45
Juniper Extension Toolkit (JET) | 45
Network Management and Monitoring | 46
Page 47

Learn about what changed in this release for EX Series Switches.
Class of Service (CoS)
We've corrected the output of the "show class-of-service interface | display xml" command. Output of
•
the following sort: <container> <leaf-1> data </leaf-1> <leaf-2> data </leaf-2> <leaf-3> data </leaf-3>
<leaf-1> data </leaf-1> <leaf-2> data </leaf-2> <leaf-3> data </leaf-3> </container> to will now appear
correctly as: <container> <leaf-1> data </leaf-1> <leaf-2> data </leaf-2> <leaf-3> data </leaf-3>
</container> <container> <leaf-1> data </leaf-1> <leaf-2> data </leaf-2> <leaf-3> data </leaf-3>
</container>
General Routing
Support for full inheritance paths of configuration groups to be built into the database by default (ACX
•
Series, EX Series, MX Series, PTX Series, QFX Series, and SRX Series)—Starting with Junos OS Release
20.2R1, the persist-groups-inheritance option at the [edit system commit] hierarchy level is enabled by
default. To disable this option, use no-persist-groups-inheritance.
45
[See commit (System).]
Juniper Extension Toolkit (JET)
PASS keyword required for Python 3 JET applications (ACX Series, EX Series, MX Series, PTX Series,
•
QFX Series, and SRX Series)—If you are writing a JET application using Python 3, include the PASS
keyword in the Exception block of the script. Otherwise, the application throws an exception when you
attempt to run it.
[See Develop Off-Device JET Applications and Develop On-Device JET Applications.]
Updates to IDL for RIB service API bandwidth field (ACX Series, EX Series, MX Series, PTX Series, QFX
•
Series, and SRX Series)—The IDL for the RouteGateway RIB service API has been updated to document
additional rules for the bandwidth field. You must set bandwidth only if a next hop has more than one
gateway, and if you set it for one gateway on a next hop, you must set it for all gateways. If you set
bandwidth when there is only a single usable gateway, it is ignored. If you set bandwidth for one or
more gateways but not all gateways on a next hop, you see the error code
BANDWIDTH_USAGE_INVALID.
[See Juniper EngNet.]
Page 48

Network Management and Monitoring
Junos OS only supports using Python 3 to execute YANG Python scripts (ACX Series, EX Series, MX
•
Series, PTX Series, QFX Series, and SRX Series)—Starting in Junos OS Release 20.2R1, Junos OS uses
Python 3 to execute YANG action and translation scripts that are written in Python. In earlier releases,
Junos OS uses Python 2.7 to execute these scripts.
[See Understanding Python Automation Scripts for Devices Running Junos OS.]
SEE ALSO
What's New | 36
Known Limitations | 46
Open Issues | 47
Resolved Issues | 51
46
Documentation Updates | 56
Migration, Upgrade, and Downgrade Instructions | 56
Known Limitations
IN THIS SECTION
EVPN | 47
Infrastructure | 47
Learn about known limitations in this release for EX Series. For the most complete and latest information
about known Junos OS defects, use the Juniper Networks online Junos Problem Report Search application.
Page 49

EVPN
When only one link is present between the leaf devices and it goes down resulting in a silent drop in
•
traffic. PR1480847
Infrastructure
Depending on the actual traffic pattern and the order in which the MACs are learned, the actual MAC
•
DB scale may vary. This is due to the way the MACs are internally stored in the hardware. PR1485319
On EX-4300MP, 9000 IPv6 MC routes can be installed. If you try to add more IPv6 MC routes, error
•
messages will be seen. PR1493671
SEE ALSO
What's New | 36
47
What's Changed | 44
Open Issues | 47
Resolved Issues | 51
Documentation Updates | 56
Migration, Upgrade, and Downgrade Instructions | 56
Open Issues
IN THIS SECTION
Authentication and Access Control | 48
EVPN | 48
Infrastructure | 48
Interfaces and Chassis | 48
Layer 2 Ethernet Services | 48
Layer 2 Features | 49
Platform and Infrastructure | 49
Routing Protocols | 51
Page 50

Learn about open issues in Junos OS Release 20.2R1 for EX Series switches. For the most complete and
latest information about known Junos OS defects, use the Juniper Networks online Junos Problem Report
Search application.
Authentication and Access Control
When a 802.1X session terminates, an event denoting the same was not logged in single supplicant
•
mode. As fix, a new event DOT1XD_USR_SESSION_DISCONNECTED is logged consistently whenever
a session terminates irrespective of supplicant mode. DOT1XD_AUTH_SESSION_DELETED events still
get generated too but only for multiple and single-secure supplicant modes (as per design). PR1512724
On EX2300/EX3400/EX4300 that supports Private-Vlan and dot1x platforms, the authenticated dot1x
•
client in the isolated (secondary vlan) is not cleared when the authenticated PVLAN is deleted. PR1516341
EVPN
In all platforms with VXLAN Static VTEP tunnels scenario (including Static VXLAN without EVPN), after
•
Routing Engine switchover or restart of l2-learning, if you create a new VTEP interface, the interface
may not work. PR1520078
48
Infrastructure
qmon-sw sensor is not supported in EX3400. PR1506710
•
The IP communication between directly connected interfaces on EX4600 TVP platforms would fail. This
•
issue only might occur in this special scenario and it might have traffic/service impact. PR1515689
Interfaces and Chassis
On GRES, VSTP port cost on aggregated Ethernet interfaces might get changed, leading to topology
•
change. PR1174213
The same IP address could be configured on different logical interfaces from different physical interfaces
•
in the same routing instance (including master routing instance), but only one logical interface was
assigned with the identical address after commit. There was no warning during the commit, only syslog
messages indicating incorrect configuration. PR1221993
Layer 2 Ethernet Services
If forward-only is set within dhcp-reply in a Juniper Networks device as a DHCP relay agent, the DHCP
•
DECLINE packets that are broadcast from the DHCP client are dropped and not forwarded to the DHCP
server. PR1429456
Page 51

In a DHCP relay scenario, if the device (DHCP relay) receives a request packet with option 50 where
•
the requested IP address matches the IP address of an existing subscriber session, such request packet
would be dropped. In such a case, the subscriber might need more time to get IP address assigned. The
subscriber might also remain in this state until its lease expires if it has previously bound with the address
in the option 50. PR1435039
Sometimes image upgrade through ZTP may fail due to not having enough space on EX3400. Below kb
•
article talks about how to free up the space : KB31198. PR1515013
Layer 2 Features
GARPs were being sent whenever there was a MAC (fdb) operation (add or delete). This is now updated
•
to send GARP when the interface is up and l3 interface attached to the VLAN. PR1192520
On QFX5000/EX46xx, if forwarding-options enhanced-hash-key hash-params is not configured and if
•
the hash function and pre-process for LAG is the same on ingress nodes and QFX5K/EX46xx, egress
traffic imbalance might be observed when ECMP or LAG is used. It might cause traffic congestion
unexpectedly. PR1514793
49
Platform and Infrastructure
EX3400/EX2300 upgrade may fail due to space and the system generates the following messages:
•
/usr/libexec/ui/package: /var/tmp/mchassis-install.tgz: no such filePR1440122
On EX9208 switches, 33 percent degradation in MAC learning rate is seen in Junos OS Release 19.3R1
•
while comparing with Junos OS Release 18.4R1. PR1450729
On EX4300 platforms configured with ERP, after multiple devices reboot/restart at the same time, ERP
•
might not revert back to the IDLE state. This issue might be seen in situations where the ERP node-id
is not configured manually and after the restart, the default node-id (switch base MAC address) might
get reset to 00:00:00:00:00:00, effectively causing multiple devices to have the same node-id. PR1461434
On MX series platforms, when a route's next-hop is an IRB interface with lt- as the underlying L2 interface,
•
it is not getting programmed on PFE, resulting in packet drop. PR1494594
Chassis connection dropped often in AD-2 while when dot1x clients connect/disconnect. The issue is
•
seen when dot1x clients connect/disconnect. PR1513274
After GRES, interfaces may flap due to which DHCP bindings may be lost. PR1515234
•
Craftd messages are generated on MX10003 and MX204 platforms. These platforms do not have a craft
•
interface. Hence these errors are expected, and can safely be ignored. When Craftd daemon tries to
open the device, it fails with a junk char in the fatal error message because the error no is not mapped
to a string in the kernel code. The following messages are seen: Feb 20 01:49:38 MX craftd[xxxx]: craftd
detected platform mx10002 Feb 20 01:49:38 MX craftd[xxxx]: LIBJSNMP_SA_IPC_REG_ROWS:
Page 52

ns_subagent_register_mibs: registering 1 rows Feb 20 01:49:38 MX craftd[xxxx]: fatal error, failed to
open smb device: ,JÎÈ"" PR1359929
On an EX9208 switch, a few xe- interfaces are going down with the error if_msg_ifd_cmd_tlv_decode
•
ifd xe-0/0/0 #190 down with ASIC Error. PR1377840
Unicast RPF check in strict mode might not work properly. PR1417546
•
On the EX9214 device, if the MACsec-enabled link flaps after reboot, the error errorlib_set_error_log():
•
err_id(-1718026239) is observed. PR1448368
In overall commit time, the evaluation of mustd constraints is taking 2 seconds more than usual. This is
•
because the persist-group-inheritance feature has been made a default feature in the latest Junos OS
releases. Eventually, this feature helps improve the subsequent commit times for scaled configurations
significantly. The persist-group-inheritance feature is useful in customer scenarios where groups and
nested groups are used extensively. In those scenarios, the group inheritance paths are not built every
time, thus subsequent commits are faster. This issue is seen only with a QFX platform or other low end
devices. PR1457939
On EX4300 switches, when packets entering a port exceed a size of 144 bytes, they might get dropped
•
in very few cases. PR1464365
50
While verifying Last-change op-state value through XML, rpc-reply message is inappropriate. PR1492449
•
When the NETCONF session is established over outbound ssh, the high rate of pushing the configuration
•
to the ephemeral DB might result in flapping of the outbound SSH connection or a or memory leak issue.
PR1497575
EX4300-48MP-EX4300-VC: This issue is very rarely seen and is Virtual Chassis specific. For the issue
•
to get triggered, the Lag IRB interface where OSPF is stuck should be present in the Standby switch.
The problem state is recovered by rebooting the master and switch is not seen again. PR1498903
On EX4300/EX3400/EX2300 Virtual-Chassis with NSB and xSTP enabled, the continuous traffic loss
•
might be observed while doing GRES. PR1500783
LLDP packets are not acquired when native-vlan configured is same as tagged vlan-id. PR1504354
•
On EX/QFX virtual-chassis setup, when LLDP is configured along with the PVLAN and the interface is
•
connected to the backup or linecard member port, LLDP might not work on the other end of Virtual
Chassis. PR1511073
35 seconds delay is added in reboot time from Junos OS Release 20.2R1 release compared to Release
•
19.4R2. PR1514364
Memory leak is seen in 'dot1xd' daemon when no 'dot1x' is configured. Memory leak is seen for the
•
allocation while creating socket from 'dot1xd' daemon to 'authd' daemon. If 'authd' is not running ,
'dot1xd' daemon tries to connect to 'authd' periodically and every time it was allocating memory for
string "/var/run/authd_control" for socket creation. The memory does not free in this scenario and we
see memory leak for string "/var/run/authd_control". There will be no service impact to other
services/daemons other than dot1x. PR1515972
Page 53

Routing Protocols
ECDSA256+SHA256 is not used for software integrity checking. PR1504211
•
On 48 port (2 units), partial packet drops may be seen when unicast stream is configured. PR1520059
•
SEE ALSO
What's New | 36
What's Changed | 44
Known Limitations | 46
Resolved Issues | 51
Documentation Updates | 56
Migration, Upgrade, and Downgrade Instructions | 56
51
Resolved Issues
IN THIS SECTION
Authentication and Access Control | 52
EVPN | 52
High Availability (HA) and Resiliency | 52
Infrastructure | 52
Interfaces and Chassis | 52
Junos Fusion Enterprise | 53
Junos Fusion Satellite Software | 53
Layer 2 Ethernet Services | 53
Layer 2 Features | 53
MPLS | 53
Platform and Infrastructure | 53
Routing Protocols | 55
User Interface and Configuration | 55
Page 54

This section lists the issues fixed in Junos OS Release 20.2R1 for EX Series switches.
For the most complete and latest information about known Junos OS defects, use the Juniper Networks
online Junos Problem Report Search application.
Authentication and Access Control
EX2300-48MP: Client did not receive captive-portal success page by downloading the ACL parameter
•
as Authentication failed. PR1504818
EVPN
The ESI of IRB interfaces does not get updated after an autonomous-system number change if the
•
interface is down. PR1482790
The VXLAN function might be broken due to a timing issue after the change in PR 1495098. PR1502357
•
52
High Availability (HA) and Resiliency
Kernel core files on backup Routing Engine might cause traffic drop if multicast-mac is configured on
•
IRB interface. PR1467847
Infrastructure
Memory leak leads to kernel crash (vmcore) due to SNMP polling. PR1482379
•
Kernel core files might be observed if you deactivate the daemon on EX2300/EX3400 platforms.
•
PR1483644
The fxpc process might crash when configuring scaled configuration with 4093 VLANs. PR1493121
•
Interfaces and Chassis
The following FRU with no connection arguments is observed after MX Series Virtual Chassis local or
•
global switchover: fru_send_msg Global FPC x. PR1428254
The MC-LAG configuration-consistency ICL configuration might fail after committing some changes.
•
PR1459201
Executing commit might hang up due to a stuck dcd process. PR1470622
•
A stale IP address might be seen after a specific order of configuration changes under a logical-systems
•
scenario. PR1477084
Traffic might get dropped as the next hop points to ICL even though the local MC-LAG is up. PR1486919
•
Page 55

Junos Fusion Enterprise
SDPD core files found: vfpc_all_eports_deletion_complete vfpc_dampen_fpc_timer_expiry. PR1454335
•
Loop detection might not work on extended ports in Junos fusion scenarios. PR1460209
•
Junos Fusion Satellite Software
Temperature sensor alarm is seen on EX4300 in a Junos fusion scenario. PR1466324
•
Layer 2 Ethernet Services
Member links state might be asychronized on a connection between PE and CE devices in an EVPN
•
active/active scenario. PR1463791
Issues with DHCPv6 relay processing Confirm and Reply packets. PR1496220
•
53
Layer 2 Features
The LLDP function might fail when a Juniper device connects to a non-Juniper one. PR1462171
•
EX4650/QFX5120: QinQ: The third VLAN tag is not pushed onto the stack and SWAP is being done
•
instead. PR1469149
Traffic might be affected if composite next hop is enabled. PR1474142
•
MPLS
BGP session might keep flapping between two directly connected BGP peers because of the wrong
•
TCP-MSS in use. PR1493431
Platform and Infrastructure
The IRB traffic might get dropped after mastership switchover. PR1453025
•
The switch might not be able to learn MAC addresses with dot1x and interface-mac-limit configured.
•
PR1470424
EX4300: Input firewall filter attached to isolated or community VLANs not matching 802.1p bits on the
•
VLAN header. PR1478240
MAC learning under bridge-domain stops after an MC-LAG interface flap. PR1488251
•
The NSSU upgrade might fail on EX4300 switches due to a storage issue in the /var/tmp directory.
•
PR1494963
Page 56

On the EX4300 device, high CPU load due to receipt of specific IPv4 packets is observed. PR1495129
•
Traffic loss might be seen with framing errors or runts if MACsec is configured on EX4300. PR1502726
•
The MAC Pause frames will be incrementing in the Receive direction if half-duplex mode on 10-Mbps
•
or 100-Mbps speed is configured. PR1452209
Link up delay and traffic drop might be seen on mixed SP L2/L3 and EP L2 type configurations. PR1456336
•
MAC addresses learned on RTG may not be aged out after the aging time. PR1461293
•
RTG link faces nearly 20 seconds down during backup node rebooting. PR1461554
•
The jdhcpd process might consume high CPU and no further subscribers can be brought up if there are
•
more than 4000 DHCP relay clients in the MAC move scenario. PR1465277
FPCs might get disconnected from the EX3400 Virtual Chassis briefly after a reboot or an upgrade.
•
PR1467707
Traffic loss might be seen with framing errors or runts if MACsec is configured on EX4600 or QFX5100
•
platforms. PR1469663
SSH session closes while checking for the show configuration | display set command for both local and
•
nonlocal users. PR1470695
54
The shaping of CoS does not work after reboot. PR1472223
•
CoS 802.1p bits rewrite might not happen in Q-in-Q mode. PR1472350
•
DSCP marking might not work as expected if the fixed classifiers are applied to interfaces on QFX5000
•
or EX4600 platforms. PR1472771
ERP might not come up properly when MSTP and ERP are enabled on the same interface. PR1473610
•
The RIPv2 packets forwarded across a Layer 2 circuit connection might be dropped. PR1473685
•
On EX4300, the output of show security macsec statisitics shows high values incorrectly. PR1476719
•
EX3400 me0 interface might remain down. PR1477165
•
The dhcpd process may crash in a Junos fusion environment. PR1478375
•
Trio based linecard might crash when there is bulk route update failure in a corner case. PR1478392
•
TFTP installation from loader prompt may not succeed on the EX Series devices. PR1480348
•
ARP request packets for an unknown host might get dropped in remote PE in EVPN-VXLAN scenario.
•
PR1480776
On EX2300 switches, SNMP traps are not generated when the MAC addresses limit threshold is reached.
•
PR1482709
Incorrect frame length of 132 bytes might be displayed in the packet header. PR1487876
•
Virtual Chassis ports might go down in a mixed Virtual Chassis setup of QFX5100-24Q-2P/EX4300 and
•
EX4600/EX4300. PR1489985
Page 57

DHCP binding fails while you verify DHCPv4 snooping functionality with P-VLAN with a firewall to
•
block or allow certain IPv4 packets. PR1490689
On the EX2300 device, high CPU load due to the receipt of specific multicast packets on Layer 2 interface
•
is observed. PR1491905
Traffic loss could be observed in a mixed-Virtual Chassis setup of QFX5100 and EX4300. PR1493258
•
Traffic loss could be seen in an MC-LAG scenario on QFX5120 and EX4650. PR1494507
•
The fxpc process might crash when renumbering the primary member ID value of the EX2300 or EX3400
•
Virtual Chassis. PR1497523
Traffic might get dropped if AE member interface is deleted/added or a SFP of the AE member interface
•
is unplugged/plugged. PR1497993
On EX4650 switches, the firewall filter might not get applied. PR1499647
•
The isolated VLAN from radius is not deleted when the interface flaps. PR1506427
•
Routing Protocols
55
BGP IPv4/IPv6 convergence and RIB install and delete time is degraded in Junos OS Releases 19.1R1,
•
19.2R1, 19.3R1, and 19.4R1. PR1414121
MUX State in LACP interface does not go to collecting and distributing and remains attached after
•
enabling the ae interface. PR1484523
FPC might go to "NotPrsnt" state after upgrading with non-TVP image in VC/VCF setup. PR1485612
•
The BGP route-target family might prevent RR from reflecting Layer 2 VPN and Layer 3 VPN routes.
•
PR1492743
On the EX4300-MP and EX4600 devices, high CPU load due to receipt of specific Layer 2 frames in
•
EVPN-VXLAN deployment. PR1495890
Firewall filter could not work in certain conditions in an Virtual Chassis setup. PR1497133
•
Packets drop might be seen when multicast MAC with static ARP is configured on one IRB interface.
•
PR1489374
User Interface and Configuration
umount: unmount of /.mount/var/val/chroot/packages/mnt/jweb-ex32-d2cf6f6b failed: Device busy
•
message is seen when Junos OS is upgraded with the validate option. PR1478291
On the EX2300 and EX3400 devices, installing J-Web application package might fail. PR1513612
•
Page 58

SEE ALSO
What's New | 36
What's Changed | 44
Known Limitations | 46
Open Issues | 47
Documentation Updates | 56
Migration, Upgrade, and Downgrade Instructions | 56
Documentation Updates
There are no errata or changes in Junos OS Release 20.2R1 documentation for EX Series switches.
56
SEE ALSO
What's New | 36
What's Changed | 44
Known Limitations | 46
Open Issues | 47
Resolved Issues | 51
Migration, Upgrade, and Downgrade Instructions | 56
Migration, Upgrade, and Downgrade Instructions
IN THIS SECTION
Upgrade and Downgrade Support Policy for Junos OS Releases | 57
This section contains the upgrade and downgrade support policy for Junos OS for EX Series switches.
Upgrading or downgrading Junos OS can take several hours, depending on the size and configuration of
the network. For information about software installation and upgrade, see the Installation and Upgrade
Guide.
Page 59

Upgrade and Downgrade Support Policy for Junos OS Releases
Support for upgrades and downgrades that span more than three Junos OS releases at a time is not
provided, except for releases that are designated as Extended End-of-Life (EEOL) releases. EEOL releases
provide direct upgrade and downgrade paths—you can upgrade directly from one EEOL release to the
next EEOL release even though EEOL releases generally occur in increments beyond three releases.
You can upgrade or downgrade to the EEOL release that occurs directly before or after the currently
installed EEOL release, or to two EEOL releases before or after. For example, Junos OS Releases 19.3,
19.4, and 20.1 are EEOL releases. You can upgrade from Junos OS Release 19.3 to Release 19.4 or from
Junos OS Release 19.3 to Release 20.1.
You cannot upgrade directly from a non-EEOL release to a release that is more than three releases ahead
or behind. To upgrade or downgrade from a non-EEOL release to a release more than three releases before
or after, first upgrade to the next EEOL release and then upgrade or downgrade from that EEOL release
to your target release.
For more information about EEOL releases and to review a list of EEOL releases, see
https://support.juniper.net/support/eol/software/junos/.
57
SEE ALSO
What's New | 36
What's Changed | 44
Known Limitations | 46
Open Issues | 47
Resolved Issues | 51
Documentation Updates | 56
Junos OS Release Notes for JRR Series
IN THIS SECTION
What's New | 58
What's Changed | 59
Known Limitations | 59
Open Issues | 60
Page 60

Resolved Issues | 60
Documentation Updates | 61
Migration, Upgrade, and Downgrade Instructions | 61
These release notes accompany Junos OS Release 20.2R1 for the JRR Series. They describe new and
changed features, limitations, and known and resolved problems in the hardware and software.
You can also find these release notes on the Juniper Networks Junos OS Documentation webpage, located
at https://www.juniper.net/documentation/product/en_US/junos-os.
What's New
58
IN THIS SECTION
Layer 2 Features | 58
Learn about new features introduced in Junos OS Release 20.2R1 for JRR Series Route Reflectors.
Layer 2 Features
Support for Link Layer Discovery Protocol (JRR200)—Starting in Junos OS Release 20.2R1, JRR Series
•
devices support Link Layer Discovery Protocol (LLDP) is supported both on the management port em0
and on the WAN ports em2 through em9. LLDP is a link-layer protocol defined in IEEE 802.1AB that
allows network devices to advertise their identity, capabilities, and configuration to other devices on
the LAN.
[See Understanding LLDP.]
SEE ALSO
What's Changed | 59
Known Limitations | 59
Page 61

Open Issues | 60
Resolved Issues | 60
Documentation Updates | 61
Migration, Upgrade, and Downgrade Instructions | 61
What's Changed
There are no changes in behavior and syntax in Junos OS Release 20.2R1 for JRR Series Route Reflectors.
SEE ALSO
What's New | 58
Known Limitations | 59
59
Open Issues | 60
Resolved Issues | 60
Documentation Updates | 61
Migration, Upgrade, and Downgrade Instructions | 61
Known Limitations
There are no known limitations JRR Series in Junos OS Release 20.2R1 for JRR Series Route Reflectors.
SEE ALSO
What's New | 58
What's Changed | 59
Open Issues | 60
Resolved Issues | 60
Documentation Updates | 61
Migration, Upgrade, and Downgrade Instructions | 61
Page 62
Open Issues
There are no open issues in Junos OS 20.2R1 Release for JRR Series Route Reflectors.
SEE ALSO
What's New | 58
What's Changed | 59
Known Limitations | 59
Resolved Issues | 60
Documentation Updates | 61
Migration, Upgrade, and Downgrade Instructions | 61
60
Resolved Issues
IN THIS SECTION
General Routing | 60
Learn about resolved issues for JRR Series in Junos OS 20.2R1 Release.
For the most complete and latest information about known Junos OS defects, use the Juniper Networks
online Junos Problem Report Search application.
General Routing
USB install image is not working for JRR200 platform. PR1471986
•
Link state of virtual em interfaces in Junos OS might not reflect the true link status of corresponding
•
physical interfaces in the Linux host. PR1492087
SEE ALSO
What's New | 58
Page 63

What's Changed | 59
Known Limitations | 59
Open Issues | 60
Documentation Updates | 61
Migration, Upgrade, and Downgrade Instructions | 61
Documentation Updates
There are no errata or changes in Junos OS Release 20.2R1 documentation for JRR200 Route Reflectors.
SEE ALSO
What's New | 58
61
What's Changed | 59
Known Limitations | 59
Open Issues | 60
Resolved Issues | 60
Migration, Upgrade, and Downgrade Instructions | 61
Migration, Upgrade, and Downgrade Instructions
IN THIS SECTION
Upgrade and Downgrade Support Policy for Junos OS Releases | 62
This section contains the upgrade and downgrade support policy for Junos OS for the JRR Series Route
Reflector. Upgrading or downgrading Junos OS might take several minutes, depending on the size and
configuration of the network.
For information about software installation and upgrade, see the JRR200 Route Reflector Quick Start and
the Installation and Upgrade Guide.
Page 64

Upgrade and Downgrade Support Policy for Junos OS Releases
Support for upgrades and downgrades that span more than three Junos OS releases at a time is not
provided, except for releases that are designated as Extended End-of-Life (EEOL) releases. EEOL releases
provide direct upgrade and downgrade paths—you can upgrade directly from one EEOL release to the
next EEOL release even though EEOL releases generally occur in increments beyond three releases.
You can upgrade or downgrade to the EEOL release that occurs directly before or after the currently
installed EEOL release, or to two EEOL releases before or after. For example, Junos OS Releases 19.3,
19.4, and 20.1 are EEOL releases. You can upgrade from Junos OS Release 19.3 to Release 19.4 or from
Junos OS Release 19.3 to Release 20.1.
You cannot upgrade directly from a non-EEOL release to a release that is more than three releases ahead
or behind. To upgrade or downgrade from a non-EEOL release to a release more than three releases before
or after, first upgrade to the next EEOL release and then upgrade or downgrade from that EEOL release
to your target release.
For more information about EEOL releases and to review a list of EEOL releases, see
https://www.juniper.net/support/eol/junos.html.
62
SEE ALSO
What's New | 58
What's Changed | 59
Known Limitations | 59
Open Issues | 60
Resolved Issues | 60
Documentation Updates | 61
Junos OS Release Notes for Junos Fusion for Enterprise
IN THIS SECTION
What’s New | 63
What's Changed | 64
Page 65

Known Limitations | 64
Open Issues | 65
Resolved Issues | 65
Documentation Updates | 66
Migration, Upgrade, and Downgrade Instructions | 66
These release notes accompany Junos OS Release 20.2R1 for the Junos fusion for enterprise. They describe
new and changed features, limitations, and known and resolved problems in the hardware and software.
You can also find these release notes on the Juniper Networks Junos OS Documentation webpage, located
at https://www.juniper.net/documentation/product/en_US/junos-os.
63
What’s New
There are no new features or enhancements to existing features in Junos OS Release 20.2R1 for Junos
fusion for enterprise.
NOTE: For more information about the Junos fusion for enterprise features, see the Junos fusion
for enterprise User Guide.
SEE ALSO
What's Changed | 64
Known Limitations | 64
Open Issues | 65
Resolved Issues | 65
Documentation Updates | 66
Migration, Upgrade, and Downgrade Instructions | 66
Page 66

What's Changed
There are no changes in behavior of Junos OS features and changes in the syntax of Junos OS statements
and commands in Junos OS Release 20.2R1 for Junos fusion for enterprise.
SEE ALSO
What's New | 63
Known Limitations | 64
Open Issues | 65
Resolved Issues | 65
Documentation Updates | 66
Migration, Upgrade, and Downgrade Instructions | 66
64
Known Limitations
There are no known behaviors, system maximums, and limitations in hardware and software in Junos OS
Release 20.2R1 for Junos fusion for enterprise.
For the most complete and latest information about known Junos OS problems, use the Juniper Networks
online Junos Problem Report Search application.
SEE ALSO
What's New | 63
What's Changed | 64
Open Issues | 65
Resolved Issues | 65
Documentation Updates | 66
Migration, Upgrade, and Downgrade Instructions | 66
Page 67

Open Issues
There are no known issues in hardware and software in Junos OS Release for 20.2R1 Junos fusion for
enterprise.
For the most complete and latest information about known Junos OS defects, use the Juniper Networks
online Junos Problem Report Search application.
SEE ALSO
What's New | 63
What's Changed | 64
Known Limitations | 64
Resolved Issues | 65
Documentation Updates | 66
65
Migration, Upgrade, and Downgrade Instructions | 66
Resolved Issues
IN THIS SECTION
Resolved Issues: Release 20.2R1 | 65
Learn which issues were resolved in the Junos OS main and maintenance releases for Junos fusion for
enterprise.
For the most complete and latest information about known Junos OS defects, use the Juniper Networks
online Junos Problem Report Search application.
Resolved Issues: Release 20.2R1
Observing duplicate ECID values for cluster and extended ports on member ports of same cluster.
•
PR1408947
The SDPD process generates a core file at vfpc_all_eports_deletion_complete
•
vfpc_dampen_fpc_timer_expiry. PR1454335
Page 68

Loop detection might not work on extended ports in a Junos fusion scenario. PR1460209
•
The temperature sensor alarm is seen on EX4300 in a Junos fusion scenario. PR1466324
•
SEE ALSO
What's New | 63
What's Changed | 64
Known Limitations | 64
Open Issues | 65
Documentation Updates | 66
Migration, Upgrade, and Downgrade Instructions | 66
66
Documentation Updates
There are no errata or changes in Junos OS Release 20.2R1 for documentation for Junos fusion for
enterprise.
SEE ALSO
What's New | 63
What's Changed | 64
Known Limitations | 64
Open Issues | 65
Resolved Issues | 65
Migration, Upgrade, and Downgrade Instructions | 66
Migration, Upgrade, and Downgrade Instructions
IN THIS SECTION
Basic Procedure for Upgrading Junos OS on an Aggregation Device | 67
Upgrading an Aggregation Device with Redundant Routing Engines | 69
Page 69

Preparing the Switch for Satellite Device Conversion | 69
Converting a Satellite Device to a Standalone Switch | 71
Upgrade and Downgrade Support Policy for Junos OS Releases | 71
Downgrading Junos OS | 71
This section contains the procedure to upgrade or downgrade Junos OS and satellite software for a Junos
fusion for enterprise. Upgrading or downgrading Junos OS and satellite software might take several hours,
depending on the size and configuration of the Junos fusion for enterprise topology.
Basic Procedure for Upgrading Junos OS on an Aggregation Device
When upgrading or downgrading Junos OS for an aggregation device, always use the junos-install package.
Use other packages (such as the jbundle package) only when so instructed by a Juniper Networks support
representative. For information about the contents of the junos-install package and details of the installation
process, see the Installation and Upgrade Guide.
67
NOTE: Before upgrading, back up the file system and the currently active Junos OS configuration
so that you can recover to a known, stable environment in case the upgrade is unsuccessful.
Issue the following command:
user@host> request system snapshot
The installation process rebuilds the file system and completely reinstalls Junos OS. Configuration
information from the previous software installation is retained, but the contents of log files might
be erased. Stored files on the routing platform, such as configuration templates and shell scripts
(the only exceptions are the juniper.conf and ssh files), might be removed. To preserve the stored
files, copy them to another system before upgrading or downgrading the routing platform. See
the Junos OS Administration Library.
To download and install Junos OS:
1. Using a Web browser, navigate to the Download Software URL on the Juniper Networks webpage:
https://www.juniper.net/support/downloads/
2. Log in to the Juniper Networks authentication system using the username (generally your e-mail address)
and password supplied by Juniper Networks representatives.
Page 70

3. Select By Technology > Junos Platform > Junos fusion to find the software that you want to download.
4. Select the release number (the number of the software version that you want to download) from the
Version drop-down list on the right of the page.
5. Select the Software tab.
6. Select the software package for the release.
7. Review and accept the End User License Agreement.
8. Download the software to a local host.
9. Copy the software to the routing platform or to your internal software distribution site.
10. Install the new junos-install package on the aggregation device.
68
NOTE: We recommend that you upgrade all software packages out of band using the console
because in-band connections are lost during the upgrade process.
Customers in the United States and Canada, use the following commands, where n is the spin number.
user@host> request system software add validate reboot source/package-name.n.tgz
All other customers, use the following commands, where n is the spin number.
user@host> request system software add validate reboot source/package-name.n-limited.tgz
Replace source with one of the following values:
/pathname—For a software package that is installed from a local directory on the router.
•
For software packages that are downloaded and installed from a remote location:
•
ftp://hostname/pathname
•
http://hostname/pathname
•
scp://hostname/pathname (available only for Canada and U.S. version)
•
The validate option validates the software package against the current configuration as a prerequisite
to adding the software package to ensure that the router reboots successfully. This is the default
behavior when the software package being added is a different release.
Page 71

Adding the reboot command reboots the router after the upgrade is validated and installed. When the
reboot is complete, the router displays the login prompt. The loading process might take 5 to 10 minutes.
Rebooting occurs only if the upgrade is successful.
Upgrading an Aggregation Device with Redundant Routing Engines
If the aggregation device has two Routing Engines, perform a Junos OS installation on each Routing Engine
separately to minimize disrupting network operations as follows:
1. Disable graceful Routing Engine switchover (GRES) on the master Routing Engine and save the
configuration change to both Routing Engines.
2. Install the new Junos OS release on the backup Routing Engine while keeping the currently running
software version on the master Routing Engine.
3. After making sure that the new software version is running correctly on the backup Routing Engine,
switch over to the backup Routing Engine to activate the new software.
69
4. Install the new software on the original master Routing Engine that is now active as the backup Routing
Engine.
For the detailed procedure, see the Installation and Upgrade Guide.
Preparing the Switch for Satellite Device Conversion
There are multiple methods to upgrade or downgrade satellite software in your Junos fusion for enterprise.
See Configuring or Expanding a Junos fusion for enterprise.
For satellite device hardware and software requirements, see Understanding Junos fusion for enterprise
Software and Hardware Requirements.
Use the following command to install Junos OS on a switch before converting it into a satellite device:
user@host> request system software add validate reboot source/package-name
NOTE: The following conditions must be met before a Junos switch that is running Junos OS
Release 14.1X53-D43 can be converted to a satellite device when the action is initiated from
the aggregation device:
The switch running Junos OS can be converted only to SNOS 3.1 and later.
•
Either the switch must be set to factory-default configuration by using the request system
•
zeroize command, or the following command must be included in the configuration: set chassis
auto-satellite-conversion.
Page 72

When the interim installation has completed and the switch is running a version of Junos OS that is
compatible with satellite device conversion, perform the following steps:
1. Log in to the device using the console port.
2. Clear the device:
[edit]
user@satellite-device# request system zeroize
NOTE: The device reboots to complete the procedure for resetting the device.
If you are not logged in to the device using the console port connection, your connection to the device
is lost after you enter the request system zeroize command.
If you lose connection to the device, log in using the console port.
70
3. (EX4300 switches only) After the reboot is complete, convert the built-in 40-Gbps QSFP+ interfaces
from Virtual Chassis ports (VCPs) into network ports:
user@satellite-device> request virtual-chassis vc-port delete pic-slot 1 port port-number
For example, to convert all four built-in 40-Gbps QSFP+ interfaces on an EX4300-24P switch into
network ports:
user@satellite-device> request virtual-chassis vc-port delete pic-slot 1 port 0
user@satellite-device> request virtual-chassis vc-port delete pic-slot 1 port 1
user@satellite-device> request virtual-chassis vc-port delete pic-slot 1 port 2
user@satellite-device> request virtual-chassis vc-port delete pic-slot 1 port 3
This step is required for the 40-Gbps QSFP+ interfaces that will be used as uplink interfaces in a Junos
fusion topology. Built-in 40-Gbps QSFP+ interfaces on EX4300 switches are configured into VCPs by
default, and the default settings are restored after the device is reset.
After this initial preparation, you can use one of three methods to convert your switches into satellite
devices—autoconversion, manual conversion, or preconfiguration. See Configuring or Expanding a Junos
fusion for enterprise for detailed configuration steps for each method.
Page 73

Converting a Satellite Device to a Standalone Switch
If you need to convert a satellite device to a standalone device, you must install a new Junos OS software
package on the satellite device and remove it from the Junos fusion topology. For more information, see
Converting a Satellite Device to a Standalone Device.
Upgrade and Downgrade Support Policy for Junos OS Releases
Support for upgrades and downgrades that span more than three Junos OS releases at a time is not
provided, except for releases that are designated as Extended End-of-Life (EEOL) releases. EEOL releases
provide direct upgrade and downgrade paths—you can upgrade directly from one EEOL release to the
next EEOL release even though EEOL releases generally occur in increments beyond three releases.
You can upgrade or downgrade to the EEOL release that occurs directly before or after the currently
installed EEOL release, or to two EEOL releases before or after. For example, Junos OS Releases 19.3,
19.4, and 20.1 are EEOL releases. You can upgrade from Junos OS Release 19.3 to Release 19.4 or from
Junos OS Release 19.3 to Release 20.1.
71
You cannot upgrade directly from a non-EEOL release to a release that is more than three releases ahead
or behind. To upgrade or downgrade from a non-EEOL release to a release more than three releases before
or after, first upgrade to the next EEOL release and then upgrade or downgrade from that EEOL release
to your target release.
For more information about EEOL releases and to review a list of EEOL releases, see
https://www.juniper.net/support/eol/junos.html
Downgrading Junos OS
Junos fusion for enterprise is first supported in Junos OS Release 16.1, although you can downgrade a
standalone EX9200 switch to earlier Junos OS releases.
NOTE: You cannot downgrade more than three releases.
For more information, see the Installation and Upgrade Guide.
To downgrade a Junos fusion for enterprise from Junos OS Release 20.2, follow the procedure for upgrading,
but replace the 20.2 junos-install package with one that corresponds to the appropriate release.
SEE ALSO
What's New | 63
Page 74
What's Changed | 64
Known Limitations | 64
Open Issues | 65
Resolved Issues | 65
Documentation Updates | 66
Junos OS Release Notes for Junos Fusion Provider Edge
IN THIS SECTION
72
What's New | 73
What's Changed | 75
Known Limitations | 75
Open Issues | 75
Resolved Issues | 76
Documentation Updates | 77
Migration, Upgrade, and Downgrade Instructions | 77
These release notes accompany Junos OS Release 20.2R1 for fusion for provider edge. They describe new
and changed features, limitations, and known and resolved problems in the hardware and software.
You can also find these release notes on the Juniper Networks Junos OS Documentation webpage, located
at https://www.juniper.net/documentation/product/en_US/junos-os.
Page 75

What's New
IN THIS SECTION
Hardware | 74
Junos Fusion | 74
Learn about new features introduced in this release for Junos fusion for provider edge.
73
Page 76

Hardware
Support for QFX5110 as a satellite device in a Junos fusion for provider edge on a GNF(MX480 and
•
MX960)—With Junos Node Slicing, you can create guest network functions (GNFs), partitions where an
aggregation device can be configured. The aggregation device on a GNF supports a maximum of 10
satellite devices. Starting in Junos OS Release 20.2R1, Junos OS supports QFX5110 switches as satellite
devices in Junos fusion for provider edge on a GNF.
[See Understanding Junos Fusion Provider Edge Software and Hardware Requirements and Junos Node
Slicing Overview.]
Junos Fusion
MPC10E and MPC11E interoperability with Junos fusion for provider edge (MX240, MX480, MX960,
•
MX2010, and MX2020)—Starting in Junos OS Release 20.2R1, Junos OS supports using the MPC10E
and MPC11E alongside other MPC line cards in the same MX Series router chassis that has been
configured with Junos fusion for provider edge. The line cards can coexist in the same router chassis,
and the router passes traffic between the devices connected to the MPC10E/MPC11E and the satellite
devices that are connected to other MPC line cards through the switch fabric. You cannot use
MPC10E/MPC11E in Junos fusion, which means you cannot connect satellite devices to ports on the
MPC10E/MPC11E line cards.
74
Junos fusion does not support hyper mode. To support Junos fusion in an MX Series router where
MPC10E/MPC11E coexists with other MPC line cards, use the set forwarding-options no-hyper-mode
statement. In addition, you must also use an FPC slot ID in the range of 160—252 for the satellite device
interfaces. To configure the FPC slot ID, use the set chassis satellite-management fpc slot-id statement.
[See Junos Fusion Provider Edge Overview.]
SEE ALSO
What's Changed | 75
Known Limitations | 75
Open Issues | 75
Resolved Issues | 76
Documentation Updates | 77
Migration, Upgrade, and Downgrade Instructions | 77
Page 77

What's Changed
There are no changes in the behavior of Junos OS features or in the syntax of Junos OS statements and
commands in this release for Junos fusion for provider edge.
SEE ALSO
What's New | 73
Known Limitations | 75
Open Issues | 75
Resolved Issues | 76
Documentation Updates | 77
Migration, Upgrade, and Downgrade Instructions | 77
75
Known Limitations
There are no known behaviors, system maximums, and limitations in hardware and software in Junos OS
Release 20.2R1 for Junos fusion for provider edge.
For the most complete and latest information about known Junos OS defects, use the Juniper Networks
online Junos Problem Report Search application.
SEE ALSO
What's New | 73
What's Changed | 75
Open Issues | 75
Resolved Issues | 76
Documentation Updates | 77
Migration, Upgrade, and Downgrade Instructions | 77
Open Issues
There are no known issues in the Junos OS Release 20.2R1 for Junos fusion for provider edge.
Page 78

For the most complete and latest information about known Junos OS defects, use the Juniper Networks
online Junos Problem Report Search application.
SEE ALSO
What's New | 73
What's Changed | 75
Known Limitations | 75
Resolved Issues | 76
Documentation Updates | 77
Migration, Upgrade, and Downgrade Instructions | 77
Resolved Issues
76
IN THIS SECTION
Fusion for Provider Edge | 76
This section lists the issues fixed in the Junos OS Release 20.2R1 for Junos fusion for provider edge.
For the most complete and latest information about known Junos OS defects, use the Juniper Networks
online Junos Problem Report Search application.
Fusion for Provider Edge
On the EX4300 devices in the Junos fusion scenario, the temperature sensor alarm is observed.
•
PR1466324
SEE ALSO
What's New | 73
What's Changed | 75
Known Limitations | 75
Page 79

Open Issues | 75
Documentation Updates | 77
Migration, Upgrade, and Downgrade Instructions | 77
Documentation Updates
There are no errata or changes in Junos OS Release 20.2R1 documentation for Junos fusion for provider
edge.
SEE ALSO
What's New | 73
What's Changed | 75
77
Known Limitations | 75
Open Issues | 75
Resolved Issues | 76
Migration, Upgrade, and Downgrade Instructions | 77
Migration, Upgrade, and Downgrade Instructions
IN THIS SECTION
Basic Procedure for Upgrading an Aggregation Device | 78
Upgrading an Aggregation Device with Redundant Routing Engines | 80
Preparing the Switch for Satellite Device Conversion | 81
Converting a Satellite Device to a Standalone Device | 82
Upgrading an Aggregation Device | 85
Upgrade and Downgrade Support Policy for Junos OS Releases | 85
Downgrading from Junos OS Release 20.1 | 85
Page 80

This section contains the procedure to upgrade Junos OS, and the upgrade and downgrade policies for
Junos OS for Junos fusion for provider edge. Upgrading or downgrading Junos OS might take several
hours, depending on the size and configuration of the network.
Basic Procedure for Upgrading an Aggregation Device
When upgrading or downgrading Junos OS, always use the jinstall package. Use other packages (such as
the jbundle package) only when so instructed by a Juniper Networks support representative. For information
about the contents of the jinstall package and details of the installation process, see the Installation and
Upgrade Guide.
NOTE: Before upgrading, back up the file system and the currently active Junos OS configuration
so that you can recover to a known, stable environment in case the upgrade is unsuccessful.
Issue the following command:
user@host> request system snapshot
78
The installation process rebuilds the file system and completely reinstalls Junos OS. Configuration
information from the previous software installation is retained, but the contents of log files might
be erased. Stored files on the routing platform, such as configuration templates and shell scripts
(the only exceptions are the juniper.conf and ssh files), might be removed. To preserve the stored
files, copy them to another system before upgrading or downgrading the routing platform. See
the Installation and Upgrade Guide.
The download and installation process for Junos OS Release 20.2R1 is different from that for earlier Junos
OS releases.
1. Using a Web browser, navigate to the Download Software URL on the Juniper Networks webpage:
https://www.juniper.net/support/downloads/
2. Log in to the Juniper Networks authentication system by using the username (generally your e-mail
address) and password supplied by Juniper Networks representatives.
3. Select By Technology > Junos Platform > Junos fusion to find the software that you want to download.
4. Select the release number (the number of the software version that you want to download) from the
Version drop-down list to the right of the page.
5. Select the Software tab.
Page 81

6. Select the software package for the release.
7. Review and accept the End User License Agreement.
8. Download the software to a local host.
9. Copy the software to the routing platform or to your internal software distribution site.
10. Install the new jinstall package on the aggregation device.
NOTE: We recommend that you upgrade all software packages out-of-band using the console,
because in-band connections are lost during the upgrade process.
Customers in the United States and Canada, use the following commands.
For 64-bit software:
•
79
NOTE: We recommend that you use 64-bit Junos OS software when implementing Junos
fusion for provider edge.
user@host> request system software add validate reboot
source/jinstall64-20.2R1.SPIN-domestic-signed.tgz
For 32-bit software:
•
user@host> request system software add validate reboot
source/jinstall-20.2R1.SPIN-domestic-signed.tgz
All other customers, use the following commands.
For 64-bit software:
•
NOTE: We recommend that you use 64-bit Junos OS software when implementing Junos
fusion for provider edge.
user@host> request system software add validate reboot
source/jinstall64-20.2R1.SPIN-export-signed.tgz
Page 82
For 32-bit software:
•
user@host> request system software add validate reboot
source/jinstall-20.2R1.SPIN-export-signed.tgz
Replace source with one of the following values:
/pathname—For a software package that is installed from a local directory on the router.
•
For software packages that are downloaded and installed from a remote location:
•
ftp://hostname/pathname
•
http://hostname/pathname
•
scp://hostname/pathname (available only for the Canada and U.S. version)
•
The validate option validates the software package against the current configuration as a prerequisite
for adding the software package to ensure that the router reboots successfully. This is the default
behavior when the software package being added is for a different release.
80
Adding the reboot command reboots the router after the upgrade is validated and installed. When the
reboot is complete, the router displays the login prompt. The loading process might take 5 to 10 minutes.
Rebooting occurs only if the upgrade is successful.
NOTE: After you install a Junos OS Release 20.2R1 jinstall package, you cannot return to the
previously installed software by issuing the request system software rollback command. Instead,
you must issue the request system software add validate command and specify the jinstall
package that corresponds to the previously installed software.
Upgrading an Aggregation Device with Redundant Routing Engines
If the aggregation device has two Routing Engines, perform a Junos OS installation on each Routing Engine
separately as follows to minimize disrupting network operations:
1. Disable graceful Routing Engine switchover (GRES) on the master Routing Engine and save the
configuration change to both Routing Engines.
2. Install the new Junos OS release on the backup Routing Engine while keeping the currently running
software version on the master Routing Engine.
Page 83

3. After making sure that the new software version is running correctly on the backup Routing Engine,
switch over to the backup Routing Engine to activate the new software.
4. Install the new software on the original master Routing Engine that is now active as the backup Routing
Engine.
For the detailed procedure, see the Installation and Upgrade Guide.
Preparing the Switch for Satellite Device Conversion
Satellite devices in a Junos fusion topology use a satellite software package that is different from the
standard Junos OS software package. Before you can install the satellite software package on a satellite
device, you first need to upgrade the target satellite device to an interim Junos OS software version that
can be converted to satellite software. For satellite device hardware and software requirements, see
Understanding Junos fusion Software and Hardware Requirements
NOTE: The following conditions must be met before a standalone switch that is running Junos
OS Release 14.1X53-D43 can be converted to a satellite device when the action is initiated from
the aggregation device:
81
The switch can be converted to only SNOS 3.1 and later.
•
Either the switch must be set to factory-default configuration by using the request system
•
zeroize command, or the following command must be included in the configuration: set chassis
auto-satellite-conversion.
Customers with EX4300 switches, use the following command:
user@host> request system software add validate reboot
source/jinstall-ex-4300-14.1X53-D43.3-domestic-signed.tgz
Customers with QFX5100 switches, use the following command:
user@host> request system software add reboot
source/jinstall-qfx-5-14.1X53-D43.3-domestic-signed.tgz
When the interim installation has completed and the switch is running a version of Junos and OS on one
line that is compatible with satellite device conversion, perform the following steps:
1. Log in to the device by using the console port.
2. Clear the device:
Page 84

[edit]
user@satellite-device# request system zeroize
NOTE: The device reboots to complete the procedure for resetting the device.
If you are not logged in to the device by using the console port connection, your connection to the
device is lost after you enter the request system zeroize command.
If you lose your connection to the device, log in using the console port.
3. (EX4300 switches only) After the reboot is complete, convert the built-in 40-Gbps QSFP+ interfaces
from Virtual Chassis ports (VCPs) into network ports:
user@satellite-device> request virtual-chassis vc-port delete pic-slot 1 port port-number
For example, to convert all four built-in 40-Gbps QSFP+ interfaces on an EX4300-24P switch into
network ports:
82
user@satellite-device> request virtual-chassis vc-port delete pic-slot 1 port 0
user@satellite-device> request virtual-chassis vc-port delete pic-slot 1 port 1
user@satellite-device> request virtual-chassis vc-port delete pic-slot 1 port 2
user@satellite-device> request virtual-chassis vc-port delete pic-slot 1 port 3
This step is required for the 40-Gbps QSFP+ interfaces that will be used as uplink interfaces in a Junos
fusion topology. Built-in 40-Gbps QSFP+ interfaces on EX4300 switches are configured into VCPs by
default, and the default settings are restored after the device is reset.
After this initial preparation, you can use one of three methods to convert your switches into satellite
devices—autoconversion, manual conversion, and preconfiguration. See Configuring Junos fusion for
provider edge for detailed configuration steps for each method.
Converting a Satellite Device to a Standalone Device
If you need to convert a satellite device to a standalone device, you must install a new Junos OS software
package on the satellite device and remove the satellite device from the Junos fusion topology.
Page 85

NOTE: If the satellite device is a QFX5100 switch, you need to install a PXE version of Junos
OS. The PXE version of Junos OS is software that includes pxe in the Junos OS package name
when it is downloaded from the Software Center—for example, the PXE image for Junos OS
Release 14.1X53-D43 is named install-media-pxe-qfx-5-14.1X53-D43.3-signed.tgz . If the
satellite device is an EX4300 switch, you install a standard jinstall-ex-4300 version of Junos OS.
The following steps explain how to download software, remove the satellite device from Junos fusion, and
install the Junos OS software image on the satellite device so that the device can operate as a standalone
device.
1. Using a Web browser, navigate to the Junos OS software download URL on the Juniper Networks
webpage:
https://www.juniper.net/support/downloads
2. Log in to the Juniper Networks authentication system by using the username (generally your e-mail
address) and password supplied by Juniper Networks representatives.
83
3. Select By Technology > Junos Platform > Junos fusion from the drop-down list and select the switch
platform series and model for your satellite device.
4. Select the Junos OS Release 14.1X53-D30 software image for your platform.
5. Review and accept the End User License Agreement.
6. Download the software to a local host.
7. Copy the software to the routing platform or to your internal software distribution site.
8. Remove the satellite device from the automatic satellite conversion configuration.
If automatic satellite conversion is enabled for the satellite device’s member number, remove the
member number from the automatic satellite conversion configuration. The satellite device’s member
number is the same as the FPC slot ID.
[edit]
user@aggregation-device# delete chassis satellite-management auto-satellite-conversion
satellite member-number
For example, to remove member number 101 from Junos fusion:
[edit]
Page 86

user@aggregation-device# delete chassis satellite-management auto-satellite-conversion
satellite 101
You can check the automatic satellite conversion configuration by entering the show command at the
[edit chassis satellite-management auto-satellite-conversion] hierarchy level.
9. Commit the configuration.
To commit the configuration to both Routing Engines:
[edit]
user@aggregation-device# commit synchronize
Otherwise, commit the configuration to a single Routing Engine:
[edit]
user@aggregation-device# commit
84
10. Install the Junos OS software on the satellite device to convert the device to a standalone device.
[edit]
user@aggregation-device> request chassis satellite install URL-to-software-package fpc-slot
member-number
For example, to install a PXE software package stored in the /var/tmp directory on the aggregation
device onto a QFX5100 switch acting as the satellite device using FPC slot 101:
[edit]
user@aggregation-device> request chassis satellite install
/var/tmp/install-media-pxe-qfx-5-14.1X53-D43.3-signed.tgz fpc-slot 101
For example, to install a software package stored in the var/tmp directory on the aggregation device
onto an EX4300 switch acting as the satellite device using FPC slot 101:
[edit]
user@aggregation-device> request chassis satellite install
/var/tmp/jinstall-ex-4300-14.1X53-D30.3-domestic-signed.tgz fpc-slot 101
The satellite device stops participating in the Junos fusion topology after the software installation starts.
The software upgrade starts after this command is entered.
Page 87

11. Wait for the reboot that accompanies the software installation to complete.
12. When you are prompted to log back into your device, uncable the device from the Junos fusion topology.
See Removing a Transceiver from a QFX Series Device or Remove a Transceiver, as needed. Your device
has been removed from Junos fusion.
NOTE: The device uses a factory-default configuration after the Junos OS installation is
complete.
Upgrading an Aggregation Device
When you upgrade an aggregation device to Junos OS Release 20.2R1, you must also upgrade your satellite
device to Satellite Device Software version 3.1R1.
85
Upgrade and Downgrade Support Policy for Junos OS Releases
Support for upgrades and downgrades that span more than three Junos OS releases at a time is not
provided, except for releases that are designated as Extended End-of-Life (EEOL) releases. EEOL releases
provide direct upgrade and downgrade paths—you can upgrade directly from one EEOL release to the
next EEOL release even though EEOL releases generally occur in increments beyond three releases.
You can upgrade or downgrade to the EEOL release that occurs directly before or after the currently
installed EEOL release, or to two EEOL releases before or after. For example, Junos OS Releases 19.3,
19.4, and 20.1 are EEOL releases. You can upgrade from Junos OS Release 19.3 to Release 19.4 or from
Junos OS Release 19.3 to Release 20.1.
You cannot upgrade directly from a non-EEOL release to a release that is more than three releases ahead
or behind. To upgrade or downgrade from a non-EEOL release to a release more than three releases before
or after, first upgrade to the next EEOL release and then upgrade or downgrade from that EEOL release
to your target release.
For more information about EEOL releases and to review a list of EEOL releases, see
https://www.juniper.net/support/eol/junos.html.
Downgrading from Junos OS Release 20.1
To downgrade from Release 20.1 to another supported release, follow the procedure for upgrading, but
replace the 20.1 jinstall package with one that corresponds to the appropriate release.
Page 88

NOTE: You cannot downgrade more than three releases.
For more information, see the Installation and Upgrade Guide.
SEE ALSO
What's New | 73
What's Changed | 75
Known Limitations | 75
Open Issues | 75
Resolved Issues | 76
Documentation Updates | 77
86
Junos OS Release Notes for MX Series
IN THIS SECTION
What's New | 87
What's Changed | 113
Known Limitations | 116
Open Issues | 119
Resolved Issues | 128
Documentation Updates | 145
Migration, Upgrade, and Downgrade Instructions | 146
These release notes accompany Junos OS Release 20.2R1 for the MX Series. They describe new and
changed features, limitations, and known and resolved problems in the hardware and software.
You can also find these release notes on the Juniper Networks Junos OS Documentation webpage, located
at https://www.juniper.net/documentation/product/en_US/junos-os.
Page 89

What's New
IN THIS SECTION
What’s New in Release 20.2R1-S1 | 88
What’s New in Release 20.2R1 | 88
Learn about new features introduced in the Junos OS main and maintenance releases for MX Series routers.
87
Page 90
What’s New in Release 20.2R1-S1
Software Installation and Upgrade
Zero touch provisioning (ZTP) with IPv6 support (EX3400, EX4300, QFX5100 and QFX5200 switches,
•
MX-Series routers)—Starting in Junos OS Release 20.2R1-S1, ZTP supports the DHCPv6 client. During
the bootstrap process, the device first uses the DHCPv4 client to request for information regarding
image and configuration file from the DHCP server. The device checks the DHCPv4 bindings sequentially.
If there is a failure with one of the DHCPv4 bindings, the device will continue to check for bindings until
provisioning is successful. If there are no DHCPv4 bindings, however, the device will check for DHCPv6
bindings and follow the same process as for DHCPv4 until the device can be provisioned successfully.
Both DHCPv4 and DHCPv6 clients are included as part of the default configuration on the device.
The DHCP server uses DHCPv6 options 59 and 17 and applicable suboptions to exchange ZTP-related
information between itself and the DHCP client.
NOTE: Only HTTP and HTTPS transport protocols are supported EX3400, EX4300, QFX5100,
and QFX5200 devices.
88
[See Zero Touch Provisioning.]
What’s New in Release 20.2R1
Class of Service (CoS)
Support for rewrite rules on a per-customer basis on MPC10 and MPC11 (MX Series)—Starting in Junos
•
OS Release 20.2R1, we support creating rewrite rules on a per-customer basis on MPC10 and MPC11
cards. You can create rewrite rules on a per-customer basis through a policy map. You define policy
maps at the [edit class-of-service policy-map] hierarchy level, and assign the policy map to a customer
through a firewall action, an ingress interface, or a routing policy.
[See Assigning Rewrite Rules on a Per-Customer Basis Using Policy Maps Overview.]
EVPN
IPv4 unicast VXLAN encapsulation optimization (MX240, MX480, MX960, MX2008, MX2010, MX2020,
•
MX10003, MX10008, and MX10016)—Starting in Junos OS Release 20.2R1, by default, the listed MX
Series routers optimize the IPv4 unicast VXLAN encapsulation process for the following tunnel types:
PIM-based VXLAN
•
EVPN-VXLAN
•
Static VXLAN
•
The optimized encapsulation process results in an increased throughput rate for IPv4 unicast packets
between 512 to 1500 bytes in size.
Page 91

The optimization feature does not support the following:
EVPN Type-5 tunnels, which are already optimized
•
Forwarding table filters
•
[See Understanding VXLANs.]
EVPN on MPLS-over-UDP tunnels (MX Series and vMX)—Starting in Junos OS Release 20.2R1, Junos
•
OS supports an EVPN network with MPLS-over-UDP tunnels. EVPN uses indirect next hop while
MPLS-over-UDP tunnels use tunnel composite next hop (TCNH) in resolving routes in the routing table.
In Junos OS releases before Release 20.2R1, indirect next hops for EVPN traffic on MPLS-over-UDP
tunnels resolve into unicast next hops. With this release, the indirect next hops for EVPN traffic on
MPLS-over-UDP tunnels will resolve into TCNH.
[See EVPN Overview and Example: Configuring Next-Hop-Based MPLS-Over-UDP Dynamic Tunnels.]
Support for inline performance monitoring services on EVPN (MX Series)—Starting in Junos OS Release
•
20.2R1, you can enable inline performance monitoring services on an EVPN network. With inline
performance monitoring, you can configure a greater number of performance monitoring sessions. Inline
performance monitoring applies only to delay measurements and synthetic loss measurements. You
must also enable both enhanced IP network services and enhanced CFM mode in the device.
89
To enable inline performance monitoring, include the following statements:
hardware-assisted-pm and hardware-assisted-keepalives enable statements at the [edit protocols
•
oam ethernet connectivity-fault-management performance-monitoring] hierarchy level.
enhanced-ip statement at the [edit chassis network-services] hierarchy level.
•
enhanced-cfm-mode statement at the [edit protocols oam ethernet connectivity-fault-management]
•
hierarchy level.
[See Connectivity Fault Management Support for EVPN and Layer 2 VPN Overview.]
Noncolored SR-TE LSPs with EVPN-MPLS (ACX5448, EX9200, MX Series, and vMX)—Starting in Junos
•
OS Release 20.2R1, ACX5448, EX9200, MX Series, and vMX routers support noncolored static segment
routing-traffic engineered (SR-TE) label-switched paths (LSPs) with an EVPN-MPLS core network and
the following Layer 2 services running at the edges of the network:
E-LAN
•
EVPN-ETREE
•
EVPN-VPWS with E-Line
•
Without color, all LSPs resolve using a BGP next hop only.
The Juniper Networks routers support noncolored SR-TE LSPs in an EVPN-MPLS core network with
the following configurations:
EVPN running in a virtual switch routing instance
•
Multihoming in active/active and active/standby modes
•
Page 92

The Juniper Networks routers also support noncolored SR-TE LSPs when functioning as a Data Center
Interconnect (DCI) device that handles EVPN Type 5 routes.
[See Static Segment Routing Label Switched Path.]
Layer 3 gateway in an EVPN-MPLS environment (MPC10 and MPC11 line cards with MX240, MX480,
•
and MX960)—Starting in Junos OS Release 20.2R1, the supported MX Series routers with MPC10 and
MPC11 line cards can act as a default Layer 3 gateway for an EVPN instance (EVI), which can span a set
of routers. In this role, the MX Series routers can perform inter-subnet forwarding. With inter-subnet
forwarding, each subnet represents a distinct broadcast domain.
The Layer 3 gateway supports the following features:
IRB interfaces through which the default gateway routes IPv4 and IPv6 traffic from one bridge domain
•
to another [See Example: Configuring EVPN with IRB Solution.]
Dynamic list next hop [See Configuring Dynamic List Next Hop.]
•
EVPN proxy ARP and ARP suppression, and proxy NDP and NDP suppression on IRB interfaces [See
•
EVPN Proxy ARP and ARP Suppression, and Proxy NDP and NDP Suppression.]
90
The substitution of a source MAC address with a proxy MAC address in an ARP or NDP reply [See
•
ARP and NDP Request with a Proxy MAC Address.]
Data center interconnectivity using EVPN Type 5 routes [See EVPN Type-5 Route with MPLS
•
encapsulation for EVPN-MPLS.]
Multihoming in an EVPN-MPLS environment (MPC10 and MPC11 line cards with MX240, MX480, and
•
MX960)—Starting in Junos OS Release 20.2R1, you can multihome a customer edge (CE) device to two
or more provider edge (PE) devices (the supported MX Series routers with MPC10 and MPC11 line
cards) in an EVPN-MPLS network. We support the following multihoming features:
Single-active and all-active modes
•
The configuration of an Ethernet segment identifier (ESI) per interface
•
Preference-based designated forwarder election
•
[See EVPN Multihoming Overview.]
EVPN-VXLAN (MPC10 and MPC11 line cards with MX2010, MX2020)—Starting in Junos OS Release
•
20.2R1, the MX2010 and MX2020 routers with MPC10 and MPC11 line cards installed support the
following EVPN-VXLAN features:
Layer 2 VXLAN
•
Multihoming with active/active and active/standby modes, an Ethernet segment identifier (ESI) per
•
interface, and preference-based designated forwarder (DF) election
MAC pinning, MAC move, MAC limiting, and MAC aging
•
QoS
•
Page 93

DHCP and DHCP relay
•
Prevention of broadcast, unknown unicast, and multicast (BUM) traffic loops when a leaf device is
•
multihomed to more than one spine device
Layer 3 VXLAN
•
IRB interfaces
•
IPv6 over IRB interfaces
•
Support for OSPF, IS-IS, BGP, and static routing over IRB interfaces
•
Proxy ARP and ARP suppression, and proxy NDP and NDP suppression with and without IRB
•
interfaces
IPv6 underlay
•
Virtual machine traffic optimization (VMTO) for ingress traffic
•
Data Center Interconnect (DCI)
•
Nonpure and pure EVPN Type-5 routes
•
91
High availability
•
Nonstop active routing (NSR)
•
Graceful Routing Engine switchover (GRES)
•
Graceful restart from a routing process restart or Routing Engine switchover without NSR enabled
•
Operations and management
•
Core isolation feature
•
Ping over EVPN Type-5 tunnel
•
Static VXLAN
•
Overlay ping and traceroute
•
[See EVPN User Guide.]
High Availability (HA) and Resiliency
Support for VRRP on the MPC11 (MX2010 and MX2020)—Starting in Junos OS Release 20.2R1, VRRP
•
is supported on the MPC11 line card. All VRRP features are supported.
[See Understanding VRRP.]
LACP inline support during unified ISSU for multivendor networks (MX104, MX240, MX480, MX960,
•
and MX10003)—Starting with Junos OS Release 20.2R1, unified ISSU supports LACP interoperability
with other vendor devices for fast periodic interval sessions. LACP sessions in full-scale scenarios with
interoperability will no longer experience timeouts during unified ISSU.
Page 94

Use the set protocols lacp ppm inline command to enable LACP inline support.
[See Getting Started with Unified In-Service Software Upgrade.]
Support for failover configuration synchronization for the ephemeral database (EX Series, MX Series,
•
MX Series Virtual Chassis, PTX Series, and QFX Series)—Starting in Junos OS Release 20.2R1, when
you configure the commit synchronize statement at the [edit system] hierarchy level in the static
configuration database of an MX Series Virtual Chassis or dual Routing Engine device, the backup Routing
Engine will synchronize both the static and ephemeral configuration databases when it synchronizes its
configuration with the master Routing Engine. This happens, for example, when a backup Routing Engine
is newly inserted, comes back online, or changes mastership. On a dual Routing Engine system, the
backup Routing Engine synchronizes both configuration databases with the master Routing Engine. In
an MX Series Virtual Chassis, the master Routing Engine on the protocol backup synchronizes both
configuration databases with the master Routing Engine on the protocol master.
[See Understanding the Ephemeral Configuration Database.]
Support for VRRP on the MPC10 and MPC11 (MX240, MX480, and MX960)—Starting in Junos OS
•
Release 20.2R1, VRRP is supported on the MPC11 and MPC10 line cards. All VRRP features are supported.
92
[See Understanding VRRP.]
Unsupported hardware for unified ISSU (MX240, MX480, MX960, MX10003, and PTX3000)—The
•
following cards do not support unified ISSU upgrading to Junos OS Release 20.2R1:
MPC7E-MRATE
•
MPC8E with MRATE MIC
•
MPC9E with MRATE MIC
•
MPC10E-10C-MRATE
•
MPC10E-15C-MRATE
•
PTX5000 with 24-Port 10-Gigabit Ethernet, 40-Gigabit Ethernet PIC with QSFP+ or 15-Port 10-Gigabit,
•
40-Gigabit Ethernet, 100-Gigabit Ethernet PIC with QSFP28
MX10003 with QSFP28 Ethernet TIC
•
Interfaces and Chassis
Transparent forwarding of CFM packets over VPLS (MX Series)—In Junos OS Release 20.2R1 and later,
•
MX Series router supports VLAN transparency for connectivity fault management (CFM) packets over
Virtual private LAN service (VPLS). If the incoming CFM packets have more vlan-tags than the configured
interface vlan-tags, then CFM PDU is treated transparent. In the earlier Junos OS releases, CFM frame
filtering was applied on all CFM PDU including on CFM PDU that had more number of tags than the
interface configuration.
We do not support the following on MX Series routers:
Transparency for tagged CFM PDU incoming on untagged interface.
•
Page 95

Transparency for untagged CFM PDU on interface with native VLAN configuration.
•
[See Example: Configuring Ethernet CFM over VPLS.]
Support for 400-Gbps port speed (MX240, MX480, and MX960)—In Junos OS Release 20.2R1, you can
•
configure port speed of 400-Gbps for MPC10E (MPC10E-10C-MRATE and MPC10E-15C-MRATE) on
MX240, MX480, and MX960 routers. Use the QSFP56-DD optics to configure 400-Gbps port speed
on:
MPC10E-10C-MRATE: Port 4 of the MPC
•
MPC10E-15C-MRATE: Port 4 of the MPC
•
[See Port Speed.]
Support for monitoring link degradation (MX Series routers with MPC10E)—Starting in Junos OS
•
Release 20.2R1, you can monitor link degradation of the 10-Gigabit Ethernet interfaces, 40-Gigabit
Ethernet interfaces, and 100-Gigabit Ethernet interfaces on the MPC10E (MPC10E-15C-MRATE and
MPC10E-10C-MRATE) line cards. Link degradation monitoring enables you to monitor the quality of
physical links on interfaces and take corrective action when the link quality degrades beyond a certain
value.
93
To enable your device to monitor the links, use the link-degrade-monitor statement at the [edit interfaces
interface-name] hierarchy level.
[See Link Degrade Monitoring Overview.]
Targeted broadcast support (MPC10E and MX2K-MPC11E)—Starting in Junos OS Release 20.2R1, you
•
can configure targeted broadcast on broadcast interfaces on the MPC10E and MX2K-MPC11E line
cards. Targeted broadcast enables a broadcast packet, destined for a remote network, to transit across
networks until the destination network is reached. In the destination network, the packet is broadcast
as a normal broadcast packet. This feature is useful when the Routing Engine is flooded with packets to
process. You can configure targeted broadcast to forward the packets to :
Both the egress interface and the Routing Engine.
•
Egress interface only.
•
To configure targeted broadcast on an interface, include the targeted-broadcast statement at the [edit
interfaces interface-name unit logical-unit-number family inet] hierarchy level.
[See Understanding Targeted Broadcast.]
Juniper Extension Toolkit (JET)
RIB service APIs support dynamic next-hop interface binding (MX Series, PTX Series, and vMX)—Starting
•
in Junos OS Release 20.2R1, programmed RIB routes react to Up, Down, Add, and Delete events for
direct next-hop interfaces. When all direct next-hop interfaces are unusable, the route becomes inactive.
This prevents traffic from being dropped and keeps inactive routes from being propagated through the
network.
Page 96

This feature applies to all routes programmed using the rib_service JET API where an interface is
configured as a direct next hop, including interfaces that are part of a flexible tunnel. It also applies to
tunnels configured with the flexible_tunnel_service JET API.
To disable this feature, use edit routing-options programmable-rpd rib-service
dynamic-next-hop-interface disable.
[See rib-service (programmable-rpd), Juniper Extension Toolkit Developer Guide, and Juniper Engineering
Network website.]
Python 3 support for JET (ACX Series, EX Series, MX Series, PTX Series, QFX Series, and SRX
•
Series)—Starting in Junos OS Release 20.2R1, Junos OS can use Python 3 to execute JET scripts. To
enable unsigned JET Python applications that support Python 3 to run on devices running Junos OS,
use the set system scripts language python3 command.
[See language (Scripts), Develop Off-Device JET Applications, and Develop On-Device JET Applications.]
Junos Telemetry Interface
•
Network instance (policy) statistics and OpenConfig configuration enhancements on JTI (ACX1100,
ACX2100, ACX5448, ACX6360, EX4300, MX240, MX480, MX960, MX10003, PTX10008, PTX10016,
QFX5110, and QFX10002)—Junos OS Release 20.2R1 provides enhancements to support the OpenConfig
data models openconfig-local-routing.yang and openconfig-network-instance.yang.
94
[See Mapping OpenConfig Routing Policy Commands to Junos Configuration and Mapping OpenConfig
Network Instance Commands to Junos Operation.]
•
ON-CHANGE BGP peer information statistics support for JTI (MX960, MX2008, MX2010, MX2020,
PTX1000, PTX5000, PTX10000, QFX5100, and QFX5200)—Junos OS Release 20.2R1 provides BGP
peer sensor support using Junos telemetry interface (JTI) and remote procedure call (gRPC) services or
gRPC Network Management Interface (gNMI) services. ON_CHANGE statistics are sent to an outside
collector.
The following resource paths are supported:
/network-instances/network-instance/protocols/protocol/bgp/neighbors/neighbor/afi-safis/afi-safi/
•
state/active (ON_CHANGE)
/network-instances/network-instance/protocols/protocol/bgp/neighbors/neighbor/afi-safis/afi-safi/
•
state/prefixes (ON_CHANGE)
/network-instances/network-instance/protocols/protocol/bgp/neighbors/neighbor/afi-safis/afi-safi/
•
state/prefixes/received (ON_CHANGE)
/network-instances/network-instance/protocols/protocol/bgp/neighbors/neighbor/afi-safis/afi-safi/
•
state/prefixes/sent (ON_CHANGE)
/network-instances/network-instance/protocols/protocol/bgp/neighbors/neighbor/afi-safis/afi-safi/
•
state/prefixes/rejected (ON_CHANGE)
Page 97

/network-instances/network-instance/protocols/protocol/bgp/neighbors/neighbor/state/admin-state
•
(ON_CHANGE)
/network-instances/network-instance/protocols/protocol/bgp/neighbors/neighbor/state/
•
established-transitions (ON_CHANGE)
/network-instances/network-instance/protocols/protocol/bgp/neighbors/neighbor/state/
•
last-established (ON_CHANGE)
/network-instances/network-instance/protocols/protocol/bgp/neighbors/neighbor/state/messages/
•
received/notification (stream)
/network-instances/network-instance/protocols/protocol/bgp/neighbors/neighbor/messages/
•
received/update (stream)
/network-instances/network-instance/protocols/protocol/bgp/neighbors/neighbor/state/messages/
•
sent/notification (stream
/network-instances/network-instance/protocols/protocol/bgp/neighbors/neighbor/state/messages/
•
sent/update (stream)
95
/network-instances/network-instance/protocols/protocol/bgp/neighbors/neighbor/state/
•
session-state (ON_CHANGE)
/network-instances/network-instance/protocols/protocol/bgp/neighbors/neighbor/state/
•
supported-capabilities (ON_CHANGE)
/network-instances/network-instance/protocols/protocol/bgp/transport/state/local-address
•
(ON_CHANGE)
/network-instances/network-instance/protocols/protocol/bgp/transport/state/remote-address
•
(ON_CHANGE)
/network-instances/network-instance/protocols/protocol/bgp/transport/state/remote-port
•
(ON_CHANGE)
[See Guidelines for gRPC and gNMI Sensors (Junos Telemetry Interface).]
Telemetry support for LDP and MLDP traffic statistics (MX Series and PTX Series)—Starting in Junos
•
OS Release 20.2R1, the following LDP and multipoint LDP native sensors are added for the Junos
telemetry interface:
/junos/services/ldp/label-switched-path/ingress/usage/
•
/junos/services/ldp/label-switched-path/transit/usage/
•
/junos/services/ldp/p2mp/interface/receive/usage/
•
/junos/services/ldp/p2mp/interface/transmit/usage/
•
/junos/services/ldp/p2mp/label-switched-path/usage/
•
You must enable telemetry streaming with the sensor-based-stats option at the [edit protocols ldp
traffic-statistics] hierarchy level.
Page 98

The show ldp traffic-statistics command is enhanced to display upstream LDP traffic statistics and to
display multipoint LDP traffic statistics per interface.
On PTX Series routers, this feature is not supported for the following variants:
PTX3000 and PTX5000 with the RE-DUO-C2600-16G Routing Engine
•
PTX10003
•
PTX10008 with the PTX10K-LC1201-36CD line card
•
FPC2 line cards do not support ingress multipoint LDP statistics.
•
[See sensor (Junos Telemetry Interface).]
gRPC telemetry support for LDP and MLDP traffic statistics (MX Series)—Starting in Junos OS Release
•
20.2R1, gRPC support is available to export LDP and multipoint LDP traffic statistics. You can use the
following resource paths to export sensor data:
LDP LSP transit
•
traffic—/mpls/signaling-protocols/ldp/lsp-transit-policies/lsp-transit-policy/state/counters
96
LDP LSP ingress
•
traffic—/mpls/signaling-protocols/ldp/lsp-ingress-policies/lsp-ingress-policy/state/counters
Multipoint LDP traffic—/mpls/signaling-protocols/ldp/p2mp-lsps/p2mp-lsp/state/counters
•
Multipoint LDP egress traffic
•
per-interface—/mpls/signalling-protocols/ldp/p2mp-interfaces/p2mp-interface/state/counters
Multipoint LDP ingress traffic
•
per-interface—/mpls/signalling-protocols/ldp/p2mp-interfaces/p2mp-interface/
[See Guidelines for gRPC and gNMI Sensors (Junos Telemetry Interface).]
•
JTI sensor support for Packet Forwarding Engine and Routing Engine sensors (MX Series Virtual Chassis
and MX Series routers with dual Routing Engines)—Junos OS Release 20.2R1 extends Junos telemetry
interface (JTI) sensor support for all Packet Forwarding Engine and Routing Engine sensors currently
supported on MX Series routers to include MX routers with dual Routing Engines or MX Series Virtual
Chassis. The level of sensor support currently available for MX Series routers applies, whether through
streaming or ON_CHANGE statistics export, using UDP, remote procedure call (gRPC) services or gRPC
Network Management Interface (gNMI) services. Additionally, JTI operational mode commands will
provide details for all Routing Engines and MX Series Virtual Chassis, too.
[See Guidelines for gRPC and gNMI Sensors (Junos Telemetry Interface).]
•
JTI sensor support for standby Routing Engine statistics (MX480, MX960, MX10003, MX2010, and
MX2020)—Junos OS Release 20.2R1 provides Junos telemetry interface (JTI) sensor support for standby
Routing Engine statistics using remote procedure call (gRPC) services. This feature is supported on both
single chassis and virtual chassis unless otherwise indicated. Use this feature to better track the state
of software components running on a standby Routing Engine. Statistics exported to an outside collector
Page 99

through the following sensors (primarily under subscriber management) provide a more complete view
of the system health and resiliency state:
Chassis role (backup or master) sensor /junos/system/subscriber-management/chassis and /junos/
•
system/subscriber-management/chassis[chassis-index=chassis-index] (for specifying an index for an
MX Series Virtual Chassis)
Routing Engine status and GRES notification sensor /junos/system/subscriber-management/chassis/
•
routing-engines/routing-engine and /junos/system/subscriber-management/chassis/routing-engines/
routing-engine[re-index=RoutingEngineIndex] (to specify an index number for a specific Routing Engine)
Subscriber management process sensor /junos/system/subscriber-management/chassis/
•
routing-engines/process-status/subscriber-management-processes/subscriber-management-process
and /junos/system/subscriber-management/chassis/routing-engines/process-status/
subscriber-management-processes/subscriber-management-process[pid=ProcessIdentifier] (to specify
a PID for a specific process)
Per Routing Engine DHCP binding statistics for server or relay sensor /junos/system/
•
subscriber-management/chassis/routing-engines/routing-engine/dhcp-bindings/
dhcp-element[dhcp-type-name=RelayOrServer/v4] and /junos/system/subscriber-management/
chassis/routing-engines/routing-engine/dhcp-bindings/dhcp-element[dhcp-type-name=RelayOrServer/
v6]
97
Virtual Chassis port counter sensor /junos/system/subscriber-management/chassis/
•
virtual-chassis-ports/virtual-chassis-port and /junos/system/subscriber-management/chassis/
virtual-chassis-ports/virtual-chassis-port[vcp-interface-name=vcp-interface-port-string] (to specify
the interface name). This resource path is only supported on a virtual chassis.
[See Guidelines for gRPC and gNMI Sensors (Junos Telemetry Interface) and Understanding OpenConfig
and gRPC on Junos Telemetry Interface.]
•
CPU statistics support on JTI (MX960, MX2010, MX2020, PTX1000, PTX5000, PTX10000, QFX5100,
and QFX5200)—Junos OS Release 20.2R1 supports streaming various CPU statistics and process
parameters using remote procedure call (gRPC) or gRPC Network Management Interface (gNMI) services
and Junos telemetry interface (JTI). You can stream CPU usage per process (statistics are similar to output
from the show system process detail operational mode command), as well as CPU usage per Routing
Engine core.
This feature supports the private data model openconfig-procmon.yang.
To stream statistics to an outside collector, include the following resource paths in a gRPC or gNMI
subscription:
Individual process level information (resource path /system/processes/process/)
•
Individual Routing Engine core information (resource path /components/component/cpu/)
•
[See Guidelines for gRPC and gNMI Sensors (Junos Telemetry Interface).]
Page 100

•
TARGET_DEFINED subscription mode support with JTI (MX5, MX10, MX40, MX80, MX104, MX150,
MX204, MX240, MX480, MX960, MX2008, MX2010, MX2020, MX10003, MX10008, and
MX10016)—Junos OS Release 20.2R1 adds support for TARGET-DEFINED mode for subscriptions made
using gRPC Network Management Interface (gNMI) services.
Using a gNMI subscription, an external collector stipulates how sensor data should be delivered:
STREAMING mode periodically streams sensor data from the DUT at a specified interval.
•
ON_CHANGE mode sends updates for sensor data from the DUT only when data values change.
•
Newly supported TARGET_DEFINED mode (submode 0) instructs the DUT to select the relevant mode
•
(STREAMING or ON_CHANGE) to deliver each element (leaf) of sensor data to the external collector.
When a subscription for a sensor with submode 0 is sent from the external collector to the DUT, the
DUT responds, activating the sensor subscription so that periodic streaming does not include any of
the ON_CHANGE updates. However, the DUT will notify the collector whenever qualifying
ON_CHANGE events occur.
[See Understanding OpenConfig and gRPC and gNMI on Junos Telemetry Interface.]
98
•
Packet Forwarding Engine sensor support with INITIAL_SYNC on JTI (MX960, MX2008, MX2010,
MX2020, PTX1000, PTX5000, PTX10000 line of routers, QFX5100, and QFX5200)—Starting in Junos
OS Release 20.2R1, you can use Junos telemetry interface (JTI) and gRPC Network Management Interface
(gNMI) services to export Packet Forwarding Engine statistics from devices to an outside collector using
gNMI submode INITIAL_SYNC. When an external collector sends a subscription request for a sensor
with INITIAL_SYNC (gnmi-submode 2), the host sends all supported target leaves (fields) under that
resource path at least once to the collector with the current value. This is valuable because:
The collector has a complete view of the current state of every field on the device for that sensor
•
path.
Event-driven data (ON_CHANGE) is received by the collector at least once before the next event is
•
seen. In this way, the collector is aware of the data state before the next event happens.
Packet Forwarding Engine sensors that contain zero counter values (zero-suppressed) that normally
•
do not show up in streamed data are sent, ensuring that all fields from each line card (also referred to
as source) are known to the collector.
NOTE: ON_CHANGE data is not available for native (UDP) Packet Forwarding Engine Sensors.
INITIAL_SYNC submode requires that at least one copy to be sent to the collector; however, sending
more than one is acceptable.
INITIAL_SYNC submode is supported for the following sensors:
Sensor for CPU (ukernel) memory (resource path /junos/system/linecard/cpu/memory/)
•
Sensor for firewall filter statistics (resource path /junos/system/linecard/firewall/)
•
 Loading...
Loading...