Juniper SECURITY THREAT RESPONSE MANAGER 2008.2 R2 - INSTALLATION REV1, Security Threat Response Manager Installation Manual
Security Threat Response Manager
STRM Installation Guide
Release 2008.2 R2
Juniper Networks, Inc.
1194 North Mathilda Avenue
Sunnyvale, CA 94089
USA
408-745-2000
www.juniper.net
Part Number: 530-027290-01, Revision 1

Copyright Notice
Copyright © 2008 Juniper Networks, Inc. All rights reserved. Juniper Networks and the Juniper Networks logo are registered trademarks of Juniper
Networks Inc. in the United States and other countries. All other trademarks, service marks, registered trademarks, or registered service marks in this
document are the property of Juniper Networks or their respective owners. All specifications are subject to change without notice. Juniper Networks
assumes no responsibility for any inaccuracies in this document or for any obligation to update information in this document. Juniper Networks reserves
the right to change, modify, transfer, or otherwise revise this publication without notice.
FCC Statement
The following information is for FCC compliance of Class A devices: This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class A
digital device, pursuant to part 15 of the FCC rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection against harmful interference when the
equipment is operated in a commercial environment. The equipment generates, uses, and can radiate radio-frequency energy and, if not installed and
used in accordance with the instruction manual, may cause harmful interference to radio communications. Operation of this equipment in a residential
area is likely to cause harmful interference, in which case users will be required to correct the interference at their own expense. The following
information is for FCC compliance of Class B devices: The equipment described in this manual generates and may radiate radio-frequency energy. If it
is not installed in accordance with NetScreen’s installation instructions, it may cause interference with radio and television reception. This equipment has
been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class B digital device in accordance with the specifications in part 15 of the FCC rules. These
specifications are designed to provide reasonable protection against such interference in a residential installation. However, there is no guarantee that
interference will not occur in a particular installation. If this equipment does cause harmful interference to radio or television reception, which can be
determined by turning the equipment off and on, the user is encouraged to try to correct the interference by one or more of the following measures:
Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna. Increase the separation between the equipment and receiver. Consult the dealer or an experienced radio/TV
technician for help. Connect the equipment to an outlet on a circuit different from that to which the receiver is connected.
Caution: Changes or modifications to this product could void the user's warranty and authority to operate this device.
Disclaimer
THE SOFTWARE LICENSE AND LIMITED WARRANTY FOR THE ACCOMPANYING PRODUCT ARE SET FORTH IN THE INFORMATION PACKET
THAT SHIPPED WITH THE PRODUCT AND ARE INCORPORATED HEREIN BY THIS REFERENCE. IF YOU ARE UNABLE TO LOCATE THE
SOFTWARE LICENSE OR LIMITED WARRANTY, CONTACT YOUR JUNIPER NETWORKS REPRESENTATIVE FOR A COPY.
STRM Installation Guide
Release 2008.2 R2
Copyright © 2008, Juniper Networks, Inc.
All rights reserved. Printed in USA.
Revision History
September 2008—Revision 1
The information in this document is current as of the date listed in the revision history.
2
CONTENTS
ABOUT THIS GUIDE
Conventions 1
Technical Documentation 1
Contacting Customer Support 2
1 PREPARING FOR YOUR INSTALLATION
Deploying STRM 4
Additional Hardware Requirements 6
Additional Software Requirements 6
Browser Support 6
Preparing Your Network Hierarchy 6
Identifying Network Settings 7
Identifying Security Monitoring Devices and Flow Data Sources 8
Identifying Network Assets 9
2 INSTALLING STRM
Setting Up Appliances 11
Installing STRM Using Red Hat Enterprise 4.6 16
Installing Japanese Support 21
Accessing STRM 22
A SETTING UP RED HAT ENTERPRISE
Before You Begin 23
Configuring Network Parameters 24
Configuring Firewall Configuration 24
Configuring Disk Partitions 24
Installing Red Hat Enterprise 4
Update 6 25
Customizing Red Hat Upgrades 26
B CHANGING NETWORK SETTINGS
Changing Network Settings in an All-in-One Console 27
Changing the Network Settings of a Console in a Multi-System Deployment 28
Changing the Network Settings of a Non-Console in a Multi-System Deployment 31

INDEX
ABOUT THIS GUIDE
The STRM Installation Guide provides you with information on setting up STRM.
This guide assumes a working knowledge of networking and Linux systems.
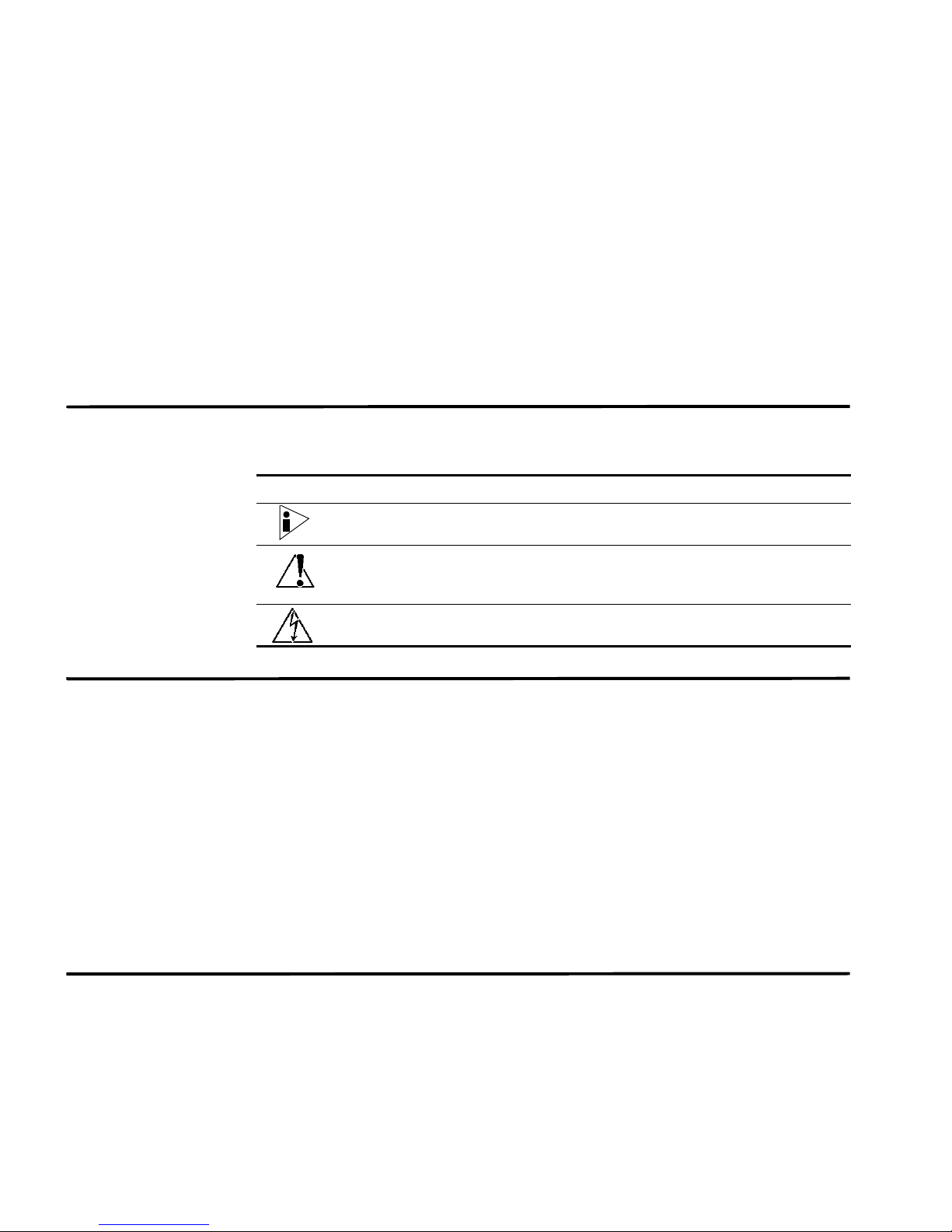
Conventions Table 1 lists conventions that are used throughout this guide.
Table 1 Icons
Icon Type Description
Information note Information that describes important features or
instructions.
Caution Information that alerts you to potential loss of
data or potential damage to an application,
system, device, or network.
Warning Information that alerts you to potential personal
injury.
Technical
Documentation
Contacting
Customer Support
You can access technical documentation, technical notes, and release notes
directly from the Qmmunity web site at https://support@juniper.net/. Once you
access the Qmmunity web site, locate the product and software release for which
you require documentation.
Your comments are important to us. Please send your e-mail comments about this
guide or any of the Juniper Networks documentation to:
documentation@Juniper.net.
Include the following information with your comments:
• Document title
• Page number
To help you resolve any issues that you may encounter when installing or
maintaining STRM, you can contact Customer Support as follows:
• Log a support request 24/7: https://support@juniper.net
For access to the Qmmunity web site, please contact Customer Support.
STRM Installation Guide

2 ABOUT THIS GUIDE
• Access Qmmunity and Self-Service support using e-mail: support@juniper.net
• Telephone assistance: 1.866.377.7000.
STRM Installation Guide

1
PREPARING FOR YOUR
I
NSTALLATION
This chapter provides information for when planning your STRM deployment
including:
• Deploying STRM
• Additional Hardware Requirements
• Additional Software Requirements
• Browser Support
• Preparing Your Network Hierarchy
• Identifying Network Settings
• Identifying Security Monitoring Devices and Flow Data Sources
• Identifying Network Assets
Your STRM deployment may consist of STRM installed on one or multiple
systems. You can use the STRM three-tier architecture to install any or all
components on a single server for small enterprises or distributed across multiple
servers for maximum performance and scalability in large enterprise
environments.
To ensure a successful STRM deployment, adhere to the recommendations in this
document.
STRM Installation Guide

4 PREPARING FOR YOUR INSTALLATION
Deploying STRM You can deploy STRM using STRM appliances or STRM software installed on
your own hardware. This section provides information on deploying STRM
including:
• STRM Components
A STRM appliance includes STRM software and a CentOS-4 operating system.
For further information on STRM appliances, see the Hardware Installation Guide.
STRM Components STRM components that may exist in your deployment include:
Note: For more information on each STRM component, see the STRM
Administration Guide.
• QFlow Collector - Passively collects traffic flows from your network through
span ports or network taps. The QFlow Collector also supports the collection of
external flow-based data sources, such as NetFlow. You can install a QFlow
Collector on your own hardware or use one of the QFlow appliances.
• Flow Processor - Normalizes flows sent from one or more QFlow Collector(s)
by consolidating, aggregating, and removing duplicate flows. The QFlow
Collector can also create superflows (aggregate flows) before the flows reach
the Classification Engine.
• Classification Engine - Analyzes flows to classify and identify all traffic in the
enterprise network into multiple objects.
• Console - Provides the interface for STRM. The Console provides real time
views, reports, alerts, and in-depth flow views of network traffic and security
threats. This Console is also used to manage distributed STRM deployments.
The Console is accessed from a standard web browser. When you access the
system, a prompt appears for a user name and password, which must be
configured during the installation process. You must also have Java installed.
For information on software requirements, see Additional Software
Requirements.
• Update Daemon - Stores the database and TopN data. Typically, the Update
Daemon is installed on the Console.
• Flow Writer - Stores the flow and asset profile data.
• Offense Resolution - Offense Resolution is a module that provides
enterprise-wide intrusion prevention for your network and includes Resolvers,
Resolutions and Resolver Agents.
• Event Collector - The Event Collector gathers events from local and remote
device sources. The Event Collector normalizes events and sends the
information to the Event Processor. Before being sent to the Event Processor,
the Event Collector bundles identical events to conserve system usage. During
this process, Magistrate risk factors map the events to the STRM Identification
System, and creates the bundles.
STRM Installation Guide

Additional Hardware Requirements 5
• Event Processor - Processes events collected from one or more Event
Collector(s). Once received, the Event Processor correlates the information
from STRM and distributes to the appropriate area, depending on the type of
event. The Event Processor also includes information gathered by STRM to
indicate any behavioral changes or policy violations for the event. Rules are
applied to the events that allow the Event Processor to process according to the
configured rules. Once complete, the Event Processor sends the events to the
Magistrate.
• Magistrate - Provides the core processing components. You can add one
Magistrate component for each deployment. The Magistrate provides views,
reports, alerts, and analysis of network traffic and security events. The
Magistrate processes the event against the defined custom rules to create an
offense. If no custom rules exist, the Magistrate uses the default rules to
process the event. An offense is an event that has been processed through
STRM using multiple inputs, individual events, and events combined with
analyzed behavior and vulnerabilities. Magistrate prioritizes the offenses and
assigns a magnitude value based on several factors, including number of
events, severity, relevance, and credibility.
Additional
Hardware
Requirements
Additional Software
Requirements
Before installing your STRM systems, make sure you have access to the additional
hardware components:
• Monitor and keyboard or a serial console
• To make sure that your STRM data is preserved during a power failure, we
highly recommend that all STRM appliances or systems running STRM
software storing data (such as, Consoles, Event Processors, or Flow
Processors) be equipped with a Uninterrupted Power Supply (UPS).
Before installing STRM, make sure you have Java Runtime Environment installed
on your system. You can download Java version 1.5.0_15 at the following web
site: http://java.com/.
Browser Support You must have a browser installed on your client system to access the STRM
interface. STRM supports the following web browsers:
- Microsoft Internet Explorer 6.0/7.0
- Firefox 2.0
Preparing Your
Network Hierarchy
STRM uses the network hierarchy to understand your network traffic and provide
you with the ability to view network activity for your entire deployment. STRM
supports any network hierarchy that can be defined by a range of IP addresses.
STRM Installation Guide
6 PREPARING FOR YOUR INSTALLATION
You can create your network based on many different variables, including
geographical or business units. For example, your network hierarchy may include
corporate IP address ranges (internal or external), physical departments or areas,
mails servers, and web servers.
Once you define the components you wish to add to your network hierarchy and
install STRM, you can then configure the network hierarchy using the STRM
interface. For each component you wish to add to your network hierarchy, use the
following table to indicate each component in your network map.
At a minimum, we recommend that you define objects in the network hierarchy for:
• Internal/external Demilitarized zone (DMZ)
• VPN
• All internal IP address space (for example, 0.0.0.0/8)
• Proxy servers
• Network Address Translation (NAT) IP address range
• Server Network subnets
• Voice over IP (VoIP) subnets
Identifying Network
Settings
Table 1-1 Network Hierarchy
Description Name IP/CIDR Value Weight
For more information, see the STRM Administration Guide - Setting Up STRM,
Creating Your Network Hierarchy.
Before you install STRM, you must have the following information for each system
you wish to install:
• Hostname
• IP address
• Network Mask address
• Subnet Mask
• Default Gateway
• Primary DNS Server
• Secondary DNS Server (Optional)
• Public IP address for networks using Network Address Translation (NAT)
STRM Installation Guide
Identifying Security Monitoring Devices and Flow Data Sources 7
• E-mail Server
• NTP Server (Console only) or Time server
Identifying Security
Monitoring Devices
and Flow Data
Sources
Table 1- 2 Devices
Product
Device
Type
QTY
Name/
Version
STRM can collect and correlate events received from external sources such as
security equipment (for example, firewalls, VPNs, or IDSs) and host or application
security logs, such as, window logs. Device Support Modules (DSMs) and QFlow
Collectors allows you to integrate STRM with this external data.
STRM automatically discovers sensor devices that are sending syslog messages
to an Event Collector. Any sensor devices that are automatically discovered by
STRM appear in the Sensor Devices window within the STRM Administration
Console. For more information, see Chapter 4 Using the Deployment Editor of the
STRM Administration Guide.
Non-syslog based information sources must be added to your deployment
manually. For more information, see the Managing Sensor Devices Guide. For
each device you wish to add to your deployment, record the device in Ta bl e 1 -2 .
Link
Speed
& Type
Msg
Level
Avg Log
Rate
(Event/Sec)
No. of
Users
Network
Location
Geographic
Location
Credibility
(0 to 10)
Where:
• Link Speed & Type indicates the maximum network link (in Kbps) for firewall,
router, and VPN devices. Record the primary application of the host system, for
example, e-mail, anit-virus, domain controller, or a workstation.
• Msg Level indicates the message level you wish to log. For example, critical,
informational, debug.
• No. of Users indicates the maximum number of hosts/users using or being
served by tis device.
• Network Location indicates whether this device is located on the Internet
DMZ, Intranet, or Extranet DMZ.
• Geographic Location indicates if the device is located on the same LAN as
STRM or sending logs over the WAN identified in the Link Speed & Type
column.
STRM Installation Guide
8 PREPARING FOR YOUR INSTALLATION
• Credibility indicates the integrity of an event or offense as determined by the
credibility rating from source devices. Credibility increases as multiple sources
report the same event.
Identifying Network
Assets
STRM can learn about your network and server infrastructure based on flow data.
The Server Discovery function uses STRM’s Asset Profile database to discover
many types of servers.
Defining certain additional server and IP address types also improves tuning
results. Ta bl e 1 -3 provides a list of possible servers. When identified, see the
STRM Users Guide for information on defining severs within STRM. If your
network includes a large number of servers, you can use CIDR or IP subnet
addresses within the server networks category.
Table 1-3 Asset Identification
Server IP Address(es) QTY Name
NAT Address Range
Vulnerability Scanners
Network Management
Servers
Proxy Servers
Virus Definition and
Other Update Servers
Windows Server
Networks, such as,
domain controllers or
exchange servers
STRM Installation Guide
