Juniper SECURITY THREAT RESPONSE MANAGER 2008.2 - EVENT CATEGORY CORRELATION REFERENCE GUIDE REV 1, Security Threat Response Manager Reference Manual
Page 1
Security Threat Response Manager
Event Category Correlation Reference
Guide
Release 2008.2
Juniper Networks, Inc.
1194 North Mathilda Avenue
Sunnyvale, CA 94089
USA
408-745-2000
www.juniper.net
Part Number: 530-025607-01, Revision 1
Page 2

Copyright Notice
Copyright © 2008 Juniper Networks, Inc. All rights reserved. Juniper Networks and the Juniper Networks logo are registered trademarks of Juniper
Networks Inc. in the United States and other countries. All other trademarks, service marks, registered trademarks, or registered service marks in this
document are the property of Juniper Networks or their respective owners. All specifications are subject to chang e without notice. Juniper Networks
assumes no responsibility for any inaccuracies in this document or for any obligation to update information in this document. Juniper Networks reserves
the right to change, modify, transfer, or otherwise revise this publicati on without notice.
FCC Statement
The following information is for FCC compliance of Class A devices: This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class A
digital device, pursuant to part 15 of the FCC rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection against harmful interference when the
equipment is operated in a commercial environment. The equipment generates, uses, and can radiate radio-frequency energy and, if not installed and
used in accordance with the instruction manual, may cause harmful interference to radio communications. Operation of this equipment in a residential
area is likely to cause harmful interference, in which case users will be required to correct the interference at their own expense. The following
information is for FCC compliance of Class B devices: The equipment described in this manual generates and may radiate radio-frequency energy. If it
is not installed in accordance with NetScreen’s installation instructions, i t may cause interference wi th radio and tele vision reception. This equip ment has
been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class B digital device in accordance with the specifications in part 15 of the FCC rules. These
specifications are designed to provide reasonable protection against such interference in a residential installation. However, there is no guarantee that
interference will not occur in a particular installation. If this equipmen t does cause harmful interference to radio or television reception, which can be
determined by turning the equipment off and on, the user is encouraged to try to correct the interference by one or more of the following measures:
Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna. Increase the separation between the equipme nt and receive r. Consult t he dealer o r an experienced ra dio/TV
technician for help. Connect the equipment to an outlet on a circuit different from that to which the receiver is connected.
Caution: Changes or modifications to this product could void the user's warrant y and authority to operate this device.
Disclaimer
THE SOFTWARE LICENSE AND LIMITED WARRANTY FOR THE ACCOMPANYING PRODUCT ARE SET FORTH IN THE INFORMATION PACKET
THAT SHIPPED WITH THE PRODUCT AND ARE INCORPORATED HEREIN BY THIS REFERENCE. IF YOU ARE UNABLE TO LOCATE THE
SOFTWARE LICENSE OR LIMITED WARRANTY, CONTACT YOUR JUNIPER NETWORKS REPRESENTATIVE FOR A COPY.
Event Category Correlation Reference guide
Release 2008.2
Copyright © 2008, Juniper Networks, Inc.
All rights reserved. Printed in USA.
Revision History
June 2008—Beta Draft
The information in this document is current as of the date listed in the revision history.
2
Page 3

CONTENTS
ABOUT THIS GUIDE
Conventions 1
Technical Documentation 1
Documentation Feedback 1
Requesting Support 2
EVENT CATEGORY CORRELATION
About Event Category Correlation 1
High-Level Event Categories 3
Event Correlation Processing 4
Additional Event Processing 14
Recon 14
DoS 16
Authentication 18
Access 23
Exploit 24
Malware 25
Suspicious Activity 26
System 30
Policy 33
CRE 34
Potential Exploit 34
SIM Audit 35
VIS Host Discovery 36
Application 36
Page 4

Page 5
ABOUT THIS GUIDE
The Event Category Correlation Reference Guide provides you with information on
how to investigate various types of sec u rity threats using the Offense Manager,
Event Viewer , or Flow V iewer. You can sort offenses by category (such as, exploit,
policy, or malware).
Conventions Table 1 lists conventions that are used throughout this guide.
Table 1 Icons
Icon Type Description
Information note Information that describes important features or
instructions.
Caution Information that alerts you to potential loss of
data or potential damage to an application,
system, device, or network.
Warning Information that alerts you to potential personal
injury.
Technical
Documentation
Documentation
Feedback
You can access technical documentation, technical notes, and release notes
directly from the Juniper networks Support Web site at
www.juniper.net/support/.
http://
We encourage you to provide feedback, comments, and suggestions so that we
can improve the documentation. Send your comments to
techpubs-comments@juniper.net, or fill out the documentation feedback form at
http://www.juniper.net/techpubs/docbug/docbugreport.html. If you are using e-mail, be
sure to include the following information with your comments:
• Document name
• Document part number
• Page number
• Software release version
STRM Event Category Correlation Reference Guide
Page 6

2 ABOUT THIS GUIDE
Requesting
Support
• Open a support case using the Case Management link at
http://www.juniper.net/support/ or call 1-888-314-JTAC (from the United States,
Canada, or Mexico) or 1-408-745-9500 (from elsewher e).
STRM Event Category Correlation Reference Guide
Page 7

EVENT CATEGORY CORRELATION
This document provides information on the types of event categories and the
processing of events. For example, the event category determines if events will
have an offense automatically created, real-time flow analysis, rate analysis, and
the default correlation tests performed. This document provides information on
event correlation including:
• About Event Category Correlation
• Recon
• DoS
• Authentication
• Access
• Exploit
• Malware
About Event
Category
Correlation
• Suspicious Activity
• System
• Policy
• CRE
• Potential Exploit
• SIM Audit
• VIS Host Discovery
• Application
An Event Processor processes events collected from one or more Event
Collector(s). Once received, the Event Processor correlates the information from
STRM and distributes to the appropriate Correlation Group for processing.
The Correlation Groups perform tests on the events to determine factors such as
vulnerability data, relevance of the targets, import ance, or credibility of the events.
The results of the Correlation Group tests appear as annotations in the Offense
Manager and Event Viewer. Also, custom rules are applied to additional events for
specific incident recognition. Once complete, the Event Processor stores the event
STRM Event Category Correlation Reference
Page 8
2 EVENT CATEGORY CORRELATION
in the Ariel database and, in some circumstances, performs real-time flow analysis
to determine the appropriate routing of the event.
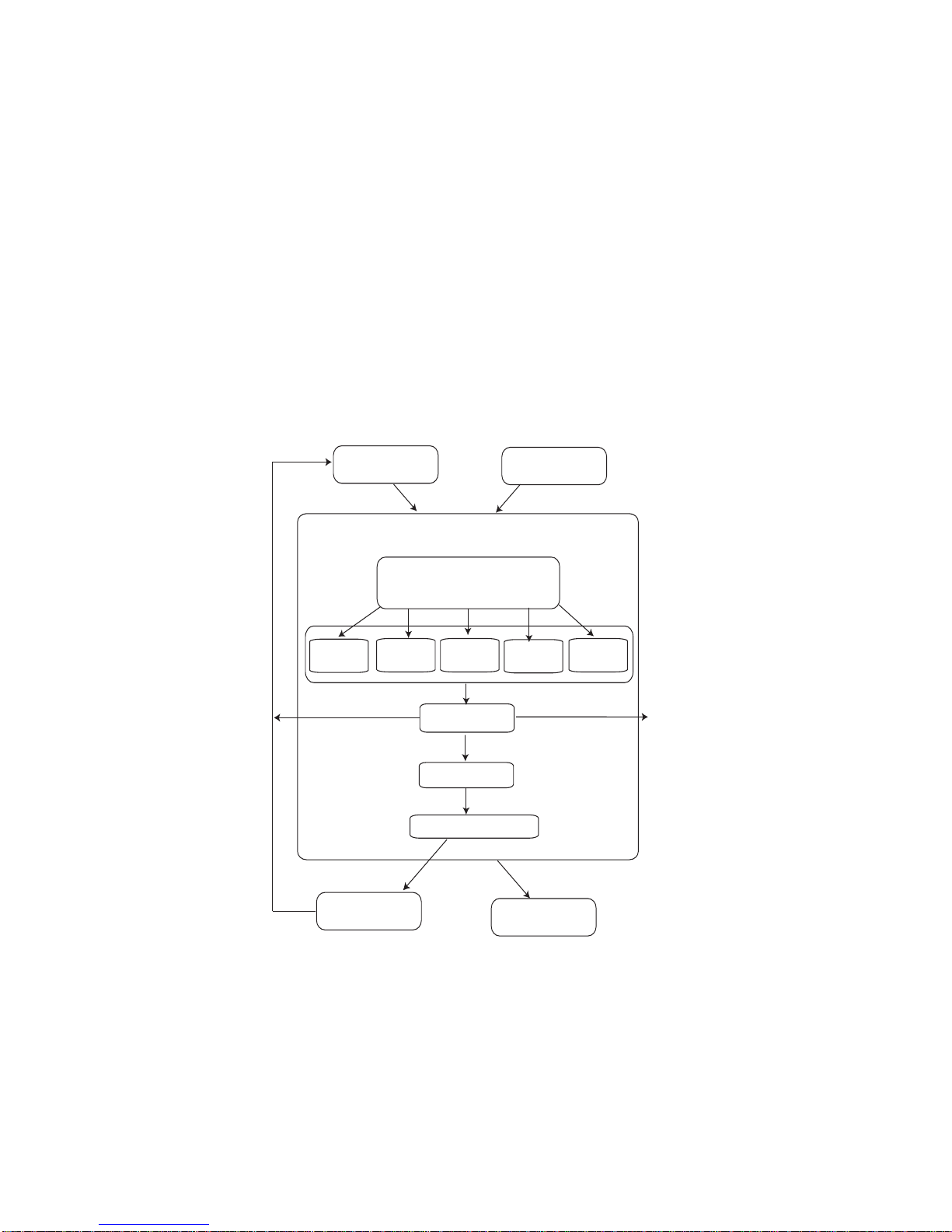
For example, Figure 2-1 provides a representation of the process within the Event
Processor for processing events. Once the Event Processor receives an event, the
Category Router determines the appropriate Correlation Group to apply tests to
the event. Once complete, the event is passed through the Custom Rules Engine
to determine the custom rules that apply to the event. The event is then passed
through the Ariel database for storage and the Flow Context and Routing
components to determine if real-time flow analysis should be performed and if the
event should automatically generate a new offense or become part of an existing
offense. If this is the case, the event is sent to the Magistrate. If real-time flow
analysis is requested of the event, a request is sent to the Classification Engine to
determine routing.
Events
Event Collector
Correlation
Group 1
Classification Engine
Correlation
Group 2
Events
Event Processor
Category Router
Correlation
Group 3
Custom Rules
Engine
Ariel DB Storage
Flow Context and Routing
Events
Correlation
Group 4
Event Collector
Correlation
Group 5
Magistrate
External Event
Exported to:
E-mail
Syslog
SNMP
Figure 2-1 Event Category Correlation Process
This section includes:
• High-Level Event Categories
• Event Correlation Processing
• Additional Event Processing
STRM Event Category Correlation Reference
Page 9

About Event Category Correlation 3
High-Level Event
Categories
The high-level event categories include:
Table 2-1 High-Level Event Categories
Category Description
Recon Events relating to scanning a nd other techniqu es used to id entify
network resources, for example, network or host port scans.
DoS Events relating to Denial of Service (DoS) or Distributed Denial of
Service (DDoS) attacks against services or hosts, for example,
brute force network DoS attacks.
Authentication Events relating to authentication controls, group, or privilege
change, for example, log in or log out.
Access Events resulting from an attempt to access network resources,
for example, firewall accept or deny.
Exploit Events relating to application exploits and buffer overflow
attempts, for example, buffer overflow or web application
exploits.
Malware Events relating to viruses, trojans, back door attacks, or other
forms of hostile software. This may include a virus, trojan,
malicious software, or spyware.
Suspicious
Activity
The nature of the threat is unknown but behavior is suspicious
including protocol anomalies that potentially indicate evasive
techniques, for example, packet fragmentation or known IDS
evasion techniques.
System Events related to system changes, software installation, or status
messages.
Policy Events regarding corporate policy violations or misuse.
CRE Events generated from an offense or event rule. For more
information on creating custom rules, see the STRM
Administration Guide.
Potential Exploit Events relating to potential application exploits and buffer
overflow attempts.
SIM Audit Events relating to user interaction with the Console and STRM
Administration Console.
VIS Host
Discovery
Events relating to the host, ports, or vulnerabilities that the VIS
component discovers.
Application Events relating to application activity.
STRM Event Category Correlation Reference
Page 10

4 EVENT CATEGORY CORRELATION
Event Correlation
Processing
For each event category, the Correlation Group determines the correlation rules
(tests) that are performed on each event. Each test is performed and assigned a
value between 0 and 10. Once all tests are complete, all test results are weighted
and the data for the event is provided in the event viewer. Table 2-2 provides a list
of possible correlation rules (tests).
Table 2-2 Correlation Rules (Tests)
Rule Description
Relevance of the
day of the week
Determines the relevance of the day of the week for this event.
For example, if the event occurs on the weekend, an attack may
have a higher relevance.
Device credibility Credibility rating can be applied on a per device basis that allows
users to associate a credibility to a device based on the level of
trust for the device and the validity of the produced event. For
example, a highly tuned IDS in front of a key server may have a
credibility of 7 while an IDS outside the corporate network may
have a credibility of 3.
Event rate Determines if the event rate of this event type is greater than
normal. This is determined on a category by category basis.
Attacker Determines if the attacker is one of the configured assets.
Target Determines if the target is one of the configured assets.
Source port Determines if the source port is less than 1024. If the port is less
than 1024, the attacker may be attempting to fool a stateless
firewall.
Attacker age Determines the relative importance of how long the attacker has
been known to the system. If the attacker is new, the relevance of
this attacker increases.
Target age Determines the relative importance of how long the target has
been known to the system.
Remote attacker Determines the relative importance of the attacker network.
Remote target Determines the relative importance of the target network.
Target port Determines if the target port is included in the list of most
attacked ports provided by the incidents.org data.
Attacker risk Determine the overall risk assessment value for the attacker
based on the asset profile data.
Target risk Determine the overall risk assessment value for the target.
Time of the attack Determines the time of attack. For example, if the attack occurs
in the middle of the night, which is deemed to be a low traffic
time, this indicates a higher relevance of the attack .
Vulnerable
targeted port
If the port is open, determine if the targeted port is vulnerable to
the current exploit.
Vulnerable port Determines if the port is vulnerable to any type of atta ck or
exploit.
Open target port Determines if the target port is open.
STRM Event Category Correlation Reference
Page 11

About Event Category Correlation 5
Table 2-2 Correlation Rules (Tests) (continued)
Rule Description
Remote Target Determines if the target network is defined as a remote network
in STRM views.
Geographic
Location
Determines the relative importance of the geographic location of
the target.
Remote attacker Determines if the attacker network is defined as a remote
network in STRM views.
Attacker IP
address
Determines if the attacker IP address is included in the list of IP
addresses that are highlighted as suspicious in the Remote
Services View.
Attacker port Determines if the attacker port is included in the list of ports from
which attacks originate as provided by the incidents.org data.
Each low-level event category is processed by one of five event Correlation
Groups. This section provides information on the Correlation Groups including:
• Correlation Group 1
• Correlation Group 2
• Correlation Group 3
• Correlation Group 4
• Correlation Group 5
STRM Event Category Correlation Reference
Page 12

6 EVENT CATEGORY CORRELATION
Correlation Group 1
The Correlation Group 1 correlation model provides tests for the following traffic
types:
Table 2-3 Correlation Group 1 Tests
Traffic Type Correlation Rules (Tests)
Local-to-Local Correlation Group 1 performs the following tests for
Local-to-Local traffic:
• Relevance of the day of the week
• Device credibility
• Event rate
• Attacker
• Target
• Source port
• Target port
• Cross host
• Attacker age
• Target age
• Attacker network
• Target network
• Vulnerable targeted port
• Attacker risk
• Target risk
• Time of the attack
• Open target port
• Vulnerable port
Note: For test details, see
Table 2-2.
STRM Event Category Correlation Reference
Page 13

About Event Category Correlation 7
Table 2-3 Correlation Group 1 Tests (continued)
Traffic Type Correlation Rules (Tests)
Local-to-Remote Correlation Group 1 performs the following tests for
Local-to-Remote traffic:
• Relevance of the day of the week
• Device credibility
• Event rate
• Attacker
• Source port
• Target port
• Attacker age
• Attacker network
• Attacker risk
• Remote Target
• Geographic Location
• Time of the attack
Note: For test details, see
Table 2-2.
Remote-to-Local Correlation Group 1 performs the following tests for
Remote-to-Local traffic:
• Relevance of the day of the week
• Device credibility
• Event rate
• Target
• Source port
• Target age
• Attacker port
• Remote attacker
• Attacker IP address
• Geographic location
• Time of the attack
• Target network
• Target risk
• Open target port
• Vulnerable targeted port
• Vulnerable port
Note: For test details, see
Table 2-2.
STRM Event Category Correlation Reference
Page 14

8 EVENT CATEGORY CORRELATION
Correlation Group 2
The Correlation Group 2 correlation model provides tests for the following traffic
types:
Table 2-4 Correlation Group 2 Tests
Traffic Type Correlation Rules (Tests)
Local-to-Local Correlation Group 2 performs the following tests for
Local-to-Remote Correlation Group 2 performs the following tests for
Local-to-Local traffic:
• Relevance of the day of the week
• Device credibility
• Event rate
• Attacker
• Target
• Source port
• Attacker age
• Target age
• Attacker network
• Target port
• Attacker risk
• Target risk
• Time of the attack
• Open target port
Note: For test details, see
Table 2-2.
Local-to-Remote traffic:
• Relevance of the day of the week
• Device credibility
• Event rate
• Attacker
• Source port
• Target port
• Attacker age
• Attacker network
• Attacker risk
• Remote target
• Target
• Geographic location
• Time of the attack
Note: For test details, see
Table 2-2.
STRM Event Category Correlation Reference
Page 15

About Event Category Correlation 9
Table 2-4 Correlation Group 2 Tests (continued)
Traffic Type Correlation Rules (Tests)
Remote-to-Local Correlation Group 2 performs the following tests for
Remote-to-Local traffic:
• Relevance of the day of the week
• Device credibility
• Event rate
• Target
• Source port
• Target age
• Attacker port
• Target port
• Remote Attacker
• Attacker IP address
• Geographic location
• Time of the attack
• Target network
• Target risk
• Open target port
Note: For test details, see
Table 2-2.
STRM Event Category Correlation Reference
Page 16

10 EVENT CATEGORY CORRELATION
Correlation Group 3
The Correlation Group 3 correlation model provides tests for the following traffic
types:
Table 2-5 Correlation Group 3 Tests
Traffic Type Correlation Rules (Tests)
Local-to-Local Correlation Group 3 performs the following tests for
Local-to-Remote Correlation Group 3 performs the following tests for
Local-to-Local traffic:
• Relevance of the day of the week
• Device credibility
• Event rate
• Attacker
• Target
• Source port
• Attacker age
• Target age
• Attacker network
• Target network
• Target port
• Attacker risk
• Target risk
• Time of the attack
Note: For test details, see
Table 2-2.
Local-to-Remote traffic:
• Relevance of the day of the week
• Device credibility
• Event rate
• Attacker
• Source port
• Target port
• Attacker age
• Attacker network
• Attacker risk
• Geographic location
• Time of the attack
Note: For test details, see
Table 2-2.
STRM Event Category Correlation Reference
Page 17

About Event Category Correlation 11
Table 2-5 Correlation Group 3 Tests (continued)
Traffic Type Correlation Rules (Tests)
Remote-to-Local Correlation Group 3 performs the following tests for
Remote-to-Local traffic:
• Relevance of the day of the week
• Device credibility
• Event rate
• Target
• Source port
• Target age
• Attacker port
• Target port
• Attacker IP address
• Geographic location
• Time of the attack
• Target network
• Target risk
• Remote attacker
Note: For test details, see
Table 2-2.
STRM Event Category Correlation Reference
Page 18

12 EVENT CATEGORY CORRELATION
Correlation Group 4
The Correlation Group 4 correlation model provides tests for the following traffic
types:
Table 2-6 Correlation Group 4 Tests
Traffic Type Correlation Rules (Tests)
Local-to-Local Correlation Group 4 performs the following tests for
Local-to-Remote Correlation Group 4 performs the following tests for
Local-to-Local traffic:
• Relevance of the day of the week
• Device credibility
• Event rate
• Attacker
• Target
• Attacker age
• Target age
• Attacker network
• Target network
• Time of the attack
Note: For test details, see
Table 2-2.
Local-to-Remote traffic:
• Relevance of the day of the week
• Device credibility
• Event rate
• Attacker
• Attacker age
• Attacker network
• Remote Target
• Geographic location
• Time of the attack
Note: For test details, see
Table 2-2.
STRM Event Category Correlation Reference
Page 19

About Event Category Correlation 13
Table 2-6 Correlation Group 4 Tests (continued)
Traffic Type Correlation Rules (Tests)
Remote-to-Local Correlation Group 4 performs the following tests for
Remote-to-Local traffic:
• Relevance of the day of the week
• Device credibility
• Event rate
• Target
• Target age
• Attacker port
• Remote attacker
• Geographic location
• Time of the attack
• Target network
• Vulnerable port
Note: For test details, see
Table 2-2.
Correlation Group 5
The Correlation Group 5 correlation model provides tests for the following traffic
types:
Table 2-7 Correlation Group 5 Tests
Traffic Type Correlation Rules (Tests)
Local-to-Local Correlation Group 5 performs the following tests for
Local-to-Local traffic:
• Relevance of the day of the week
• Device credibility
• Event rate
• Attacker
• Target
• Attacker network
• Target network
• Time of the attack
Note: For test details, see
Table 2-2.
STRM Event Category Correlation Reference
Page 20

14 EVENT CATEGORY CORRELATION
Table 2-7 Correlation Group 5 Tests (continued)
Traffic Type Correlation Rules (Tests)
Local-to-Remote Correlation Group 5 performs the following tests for
Remote-to-Local Correlation Group 5 performs the following tests for
Local-to-Remote traffic:
• Relevance of the day of the week
• Device credibility
• Event rate
• Attacker network
• Time of the attack
Note: For test details, see
Table 2-2.
Remote-to-Local traffic:
• Relevance of the day of the week
• Device credibility
• Event rate
• Target
• Target network
• Time of the attack
Note: For test details, see
Table 2-2.
Additional Event
Processing
Each event is processed using one of the following scenarios:
• Scenario 1 - Event information is forwarded to the Magistrate component by
automatically creating offenses. Even though offenses are created
automatically, no real-time flow analysis is performed. Events are stored in the
Event Processor.
• Scenario 2 - Events are stored in the Event Processor. Offenses are not
automatically created and no flow analysis is performed.
Recon The Recon category indicates events relating to scanning and other techniques
used to identify network resources. The associated low-level event categories
include:
Table 2-8 Recon Categories
Low Level Event
Category
Unknown Form of
Recon
Description
Indicates an unknown form of
reconnaissance.
Application Query Indicates reconnaissance to
applications on your system.
Severity Level
(0 to 10)
Event Correlation/
Processing
Additional Event
Processing
2 Correlation Group 2 Scenario 2
3 Correlation Group 2 Scenario 2
STRM Event Category Correlation Reference
Page 21

Table 2-8 Recon Categories (continued)
Recon 15
Low Level Event
Category
Description
Host Query Indicates reconnaissance to a
Severity Level
(0 to 10)
Event Correlation/
Processing
Additional Event
Processing
3 Correlation Group 2 Scenario 2
host in your network.
Network Sweep Indicates reconna issance on your
4 Correlation Group 2 Scenario 2
network.
Mail
Reconnaissance
Windows
Reconnaissance
Portmap / RPC
Request
Host Port Scan Indicates a scan occurred on the
Indicates reconnaissance on your
mail system.
Indicates reconnaissance for
windows.
Indicates reconnaissance on your
portmap or RPC request.
3 Correlation Group 2 Scenario 2
3 Correlation Group 2 Scenario 2
3 Correlation Group 2 Scenario 2
4 Correlation Group 2 Scenario 2
host’s ports.
RPC Dump Indicates Remote Procedure Call
3 Correlation Group 2 Scenario 2
(RPC) information is removed.
DNS
Reconnaissance
Misc
Reconnaissance
Indicates reconnaissance on the
DNS server.
Indicates a miscellaneous
reconnaissance event.
3 Correlation Group 2 Scenario 2
2 Correlation Group 2 Scenario 2
Event
Web
Reconnaissance
Database
Reconnaissance
ICMP
Reconnaissance
UDP
Reconnaissance
SNMP
Reconnaissance
Indicates web reconnaissance on
your network.
Indicates database
reconnaissance on your network.
Indicates reconnaissance on
ICMP traffic.
Indicates reconnaissance on
UDP traffic.
Indicates reconnaissance on
SNMP traffic.
3 Correlation Group 2 Scenario 2
3 Correlation Group 2 Scenario 2
3 Correlation Group 2 Scenario 2
3 Correlation Group 2 Scenario 2
3 Correlation Group 2 Scenario 2
ICMP Host Query Indicates an ICMP host query. 3 Correlation Group 2 Scenario 2
UDP Host Query Indicates a UDP host query. 3 Correlation Group 2 Scenario 2
NMAP
Indicates NMAP reconnaissance. 3 Correlation Group 2 Scenario 2
Reconnaissance
TCP
Reconnaissance
Unix
Reconnaissance
FTP
Indicates TCP reconnaissance on
3 Correlation Group 2 Scenario 2
your network.
Indicates reconnaissance on your
3 Correlation Group 2 Scenario 2
UNIX network.
Indicates FTP reconnaissance. 3 Correlation Group 2 Scenario 2
Reconnaissance
STRM Event Category Correlation Reference
Page 22

16 EVENT CATEGORY CORRELATION
DoS The DoS category indicates events relating to Denial Of Service (DoS) attacks
against services or hosts. The associated low-level event categories include:
Table 2-9 DoS Categories
Low Level Event
Category
Unknown DoS
Description
Indicates an unknown DoS attack. 8 Correlation Group 2 Scenario 2
Severity Level
(0 to 10)
Event Correlation/
Processing
Additional Event
Processing
Attack
ICMP DoS Indicates an ICMP DoS attack. 9 Correlation Group 2 Scenario 2
TCP DoS Indicates a TCP DoS attack. 9 Correlation Group 2 Scenario 2
UDP DoS Indicates a UDP DoS attack. 9 Correlation Group 2 Scenario 2
DNS Service DoS Indicates a DNS service DoS
8 Correlation Group 2 Scenario 2
attack.
Web Service DoS Indicates a web service DoS
8 Correlation Group 2 Scenario 2
attack.
Mail Service DoS Indicates a mail server DoS attack. 8 Correlation Group 2 Scenario 2
Distributed DoS Indicates a distributed DoS attack. 9 Correlation Group 2 Scenario 2
Misc DoS Indicates a miscellaneous DoS
8 Correlation Group 2 Scenario 2
attack.
Unix DoS Indicates a Unix DoS attack. 8 Correlation Group 2 Scenario 2
Windows DoS Indicates a Windows DoS attack. 8 Correlation Group 2 Scenario 2
Database DoS Indicates a database DoS attack. 8 Correlation Group 2 Scenario 2
FTP DoS Indicates an FTP DoS attack. 8 Correlation Group 2 Scenario 2
Infrastructure DoS Indicates a DoS attack on the
8 Correlation Group 2 Scenario 2
infrastructure.
Telnet DoS Indicates a Telnet DoS attack. 8 Correlation Group 2 Scenario 2
Brute Force Login Indicates access to your system
8 Correlation Group 2 Scenario 2
through unauthorized methods.
High Rate TCP
DoS
High Rate UDP
DoS
High Rate ICMP
DoS
Indicates a high rate TCP DoS
attack.
Indicates a high rate UDP DoS
attack.
Indicates a high rate ICMP DoS
attack.
8 Correlation Group 2 Scenario 2
8 Correlation Group 2 Scenario 2
8 Correlation Group 2 Scenario 2
High Rate DoS Indicates a high rate DoS attack. 8 Correlation Group 2 Scenario 2
Medium Rate TCP
DoS
Medium Rate UDP
DoS
Medium Rate
ICMP DoS
Indicates a medium rate TCP
attack.
Indicates a medium rate UDP
attack.
Indicates a medium rate ICMP
attack.
8 Correlation Group 2 Scenario 2
8 Correlation Group 2 Scenario 2
8 Correlation Group 2 Scenario 2
STRM Event Category Correlation Reference
Page 23

Table 2-9 DoS Categories (continued)
DoS 17
Low Level Event
Category
Description
Medium Rate DoS Indicates a medium rate DoS
Severity Level
(0 to 10)
Event Correlation/
Processing
Additional Event
Processing
8 Correlation Group 2 Scenario 2
attack.
Medium Rate DoS Indicates a medium rate DoS
8 Correlation Group 2 Scenario 2
attack.
Low Rate TCP
DoS
Low Rate UDP
DoS
Low Rate ICMP
DoS
Indicates a low rate TCP DoS
attack.
Indicates a low rate UDP DoS
attack.
Indicates a low rate ICMP DoS
attack.
8 Correlation Group 2 Scenario 2
8 Correlation Group 2 Scenario 2
8 Correlation Group 2 Scenario 2
Low Rate DoS Indicates a low rate DoS attack. 8 Correlation Group 2 Scenar io 2
Distributed High
Rate TCP DoS
Distributed High
Rate UDP DoS
Distributed High
Rate ICMP DoS
Distributed High
Rate DoS
Distributed Medium
Rate TCP DoS
Distributed Medium
Rate UDP DoS
Distributed Medium
Rate ICMP DoS
Distributed Medium
Rate DoS
Distributed Low
Rate TCP DoS
Distributed Low
Rate UDP DoS
Distributed Low
Rate ICMP DoS
Distributed Low
Rate DoS
High Rate TCP
Indicates a distributed high rate
8 Correlation Group 2 Scenario 2
TCP DoS attack.
Indicates a distributed high rate
8 Correlation Group 2 Scenario 2
UDP DoS attack.
Indicates a distributed high rate
8 Correlation Group 2 Scenario 2
ICMP DoS attack.
Indicates a distributed high rate
8 Correlation Group 2 Scenario 2
DoS attack.
Indicates a distributed medium
8 Correlation Group 2 Scenario 2
rate TCP DoS attack.
Indicates a distributed medium
8 Correlation Group 2 Scenario 2
rate UDP DoS attack.
Indicates a distributed medium
8 Correlation Group 2 Scenario 2
rate ICMP DoS attack.
Indicates a distributed medium
8 Correlation Group 2 Scenario 2
rate DoS attack.
Indicates a distributed low rate
8 Correlation Group 2 Scenario 2
TCP DoS attack.
Indicates a distributed low rate
8 Correlation Group 2 Scenario 2
UDP DoS attack.
Indicates a distributed low rate
8 Correlation Group 2 Scenario 2
ICMP DoS attack.
Indicates a distributed low rate
8 Correlation Group 2 Scenario 2
DoS attack.
Indicates a high rate TCP scan. 8 Correlatio n Gr ou p 2 Scenario 2
Scan
High Rate UDP
Indicates a high rate UDP scan. 8 Correlation Group 2 Scenario 2
Scan
High Rate ICMP
Indicates a high rate ICMP scan. 8 Correlation Group 2 Scenario 2
Scan
STRM Event Category Correlation Reference
Page 24

18 EVENT CATEGORY CORRELATION
Table 2-9 DoS Categories (continued)
Low Level Event
Category
Description
Severity Level
(0 to 10)
Event Correlation/
Processing
Additional Event
Processing
High Rate Scan Indicates a high rate scan. 8 Correlation Group 2 Scenario 2
Medium Rate TCP
Scan
Medium Rate UDP
Scan
Medium Rate
ICMP Scan
Indicates a medium rate TCP
scan.
Indicates a medium rate UDP
scan.
Indicates a medium rate ICMP
scan.
8 Correlation Group 2 Scenario 2
8 Correlation Group 2 Scenario 2
8 Correlation Group 2 Scenario 2
Medium Rate Scan Indicates a medium rate scan. 8 Correlation Group 2 Scenario 2
Low Rate TCP
Indicates a low rate TCP scan. 8 Correlation Group 2 Scenario 2
Scan
Low Rate UDP
Indicates a low rate UDP scan. 8 Correlation Group 2 Scenario 2
Scan
Low Rate ICMP
Indicates a low rate ICMP scan. 8 Correlation Group 2 Scenario 2
Scan
Low Rate Scan Indicates a low rate scan. 8 Correlation Group 2 Scenario 2
VoIP DoS Indicates a VoIP DoS attack 8 Correlation Group 2 Scenario 2
Authentication The authentication category indicates events relating to authentication and access
controls. The associated low-level event categories include:
Table 2-10 Authentication Categories
Low Level Event
Category
Unknown
Description
Indicates unknown authentication 1 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
Severity Level
(0 to 10)
Event Correlation/
Processing
Additional Event
Processing
Authentication
Host Login
Succeeded
Indicates the host login was
successful.
1 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
Host Login Failed Indicates the host login failed. 3 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
Misc Login
Succeeded
Misc Login Failed Indicates that login sequence
Indicates that the login sequence
succeeded.
1 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
3 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
failed.
Privilege
Escalation Failed
Privilege
Escalation
Indicates that the privileged
escalation failed.
Indicates that the privilege
escalation succeeded.
3 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
1 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
Succeeded
Mail Service Login
Succeeded
Indicates that the mail service
login succeeded.
1 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
STRM Event Category Correlation Reference
Page 25

Table 2-10 Authentication Categories (continued)
Authentication 19
Low Level Event
Category
Mail Service Login
Failed
Auth Server Login
Failed
Auth Server Login
Succeeded
Web Service Login
Succeeded
Web Service Login
Failed
Admin Login
Successful
Admin Login
Failure
Suspicious
Username
Description
Indicates that the mail service
login failed.
Indicates that the authentication
server login failed.
Indicates that the authentication
server login succeeded.
Indicates that the web service
login succeeded.
Indicates that the web service
login failed.
Indicates the administrative login
was successful.
Indicates the administrative login
failed.
Indicates that a user attempted to
access the network using an
Severity Level
(0 to 10)
Event Correlation/
Processing
Additional Event
Processing
3 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
3 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
1 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
1 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
3 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
1 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
3 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
4 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
incorrect username.
Login with
username/
password defaults
Indicates that a user accessed the
network using the default
username and password.
4 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
successful
Login with
username/
password defaults
failed
FTP Login
Succeeded
Indicates that a user was
unsuccessful accessing the
network using the default
username and password.
Indicates that the FTP login was
successful.
4 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
1 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
FTP Login Failed Indicates that the FTP logi n failed. 3 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
SSH Login
Succeeded
Indicates that the SSH login was
successful.
1 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
SSH Login Failed Indicates that the SSH login failed. 2 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
User Right
Assigned
Indicates that user access to
network resources was
1 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
successfully granted.
User Right
Removed
Indicates that user access to
network resources was
1 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
successfully removed.
Trusted Domain
Added
Indicates that a trusted domain
was successfully added to your
1 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
deployment.
Trusted Domain
Removed
Indicates that a trusted domain
was removed from your
1 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
deployment.
STRM Event Category Correlation Reference
Page 26

20 EVENT CATEGORY CORRELATION
Table 2-10 Authentication Categories (continued)
Low Level Event
Category
System Security
Access Granted
System Security
Access Removed
Description
Indicates that system security
access was successfully granted.
Indicates that system security
access was successfully removed.
Policy Added Indicates that a policy was
Severity Level
(0 to 10)
Event Correlation/
Processing
Additional Event
Processing
1 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
1 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
1 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
successfully added.
Policy Change Indicates that a policy was
1 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
successfully changed.
User Account
Added
User Account
Changed
Password Change
Failed
Indicates that a user account was
successfully added.
Indicates a change to an existing
user account.
Indicates that an attempt to
change an existing password
1 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
1 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
3 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
failed.
Password Change
Succeeded
User Account
Removed
Group Member
Added
Group Member
Removed
Group Added Indicates that a group was
Indicates that a password change
was successful.
Indicates that a user account was
successfully removed.
Indicates that a group member
was successfully added.
Indicates that a group member
was removed.
1 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
1 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
1 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
1 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
1 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
successfully added.
Group Changed Indicates a change to an existing
1 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
group.
Group Removed Indicates a group was re mo ved. 1 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
Computer Account
Added
Computer Account
Changed
Computer Account
Removed
Remote Access
Login Succeeded
Indicates a computer account has
been successfully added.
Indicates a change to an existing
computer account.
Indicates a computer account has
been successfully removed.
Indicates that access to the
network using a remote login was
1 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
1 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
1 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
1 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
successful.
Remote Access
Login Failed
Indicates that an attempt to
access the network using a
3 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
remote login failed.
STRM Event Category Correlation Reference
Page 27

Table 2-10 Authentication Categories (continued)
Authentication 21
Low Level Event
Category
General
Authentication
Description
Indicates that the authentication
processes was successful
Successful
General
Authentication
Indicates that the authenticating
process failed.
Failed
Telnet Login
Succeeded
Indicates that the telnet login was
successful.
Telnet Login Failed Indicates that the telnet login
failed.
Suspicious
Password
Indicates that a user attempted to
login using a suspicious
password.
Samba Login
Successful
Samba Login
Failed
Auth Server
Session Opened
Indicates a user successfully
logged in using Samba.
Indicates user login failed using
Samba.
Indicates that a communication
session with the authentication
server was started.
Auth Server
Session Closed
Indicates that a communication
session with the authentication
server was closed.
Firewall Session
Closed
Indicates that a firewall session
was closed.
Host Logout Indicates that a host successfully
logged out.
Misc Logout Indicates that a user successfully
logged out.
Auth Server
Logout
Indicates that the process to log
out of the authentication server
was successful.
Web Service
Logout
Indicates that the process to log
out of the web service was
successful.
Admin Logout Indicates that the administrative
user successfully logged out.
FTP Logout Indicates that the process to log
out of the FTP service was
successful.
SSH Logout Indicates that the process to log
out of the SSH session was
successful.
Severity Level
(0 to 10)
Event Correlation/
Processing
Additional Event
Processing
1 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
3 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
1 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
3 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
4 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
1 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
3 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
1 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
1 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
1 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
1 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
1 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
1 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
1 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
1 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
1 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
1 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
STRM Event Category Correlation Reference
Page 28

22 EVENT CATEGORY CORRELATION
Table 2-10 Authentication Categories (continued)
Low Level Event
Category
Remote Access
Logout
Description
Indicates that the process to log
out using remote access was
Severity Level
(0 to 10)
Event Correlation/
Processing
Additional Event
Processing
1 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
successful.
Telnet Logout Indicates that the process to log
1 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
out of the Telnet session was
successful.
Samba Logout Indicates that the process to log
1 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
out of Samba was successful.
SSH Session
Started
Indicates that the SSH login
session has been initiated on a
1 Correlation Group 5 Scenario 2
host.
SSH Session
Finished
Admin Session
Started
Indicates the termination of an
SSH login session on a host.
Indicates that a login session has
been initiated on a host by an
1 Correlation Group 5 Scenario 2
1 Correlation Group 5 Scenario 2
administrative or privileged user.
Admin Session
Finished
Indicates the termination of an
administrator or privileged users
1 Correlation Group 5 Scenario 2
login session on a host.
VoIP Login
Succeeded
VoIP Login Failed Indicates an unsuccessful attempt
Indicates a successful VoIP
service login
1 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
1 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
to access VoIP service.
VoIP Logout Indicates a user logout, 1 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
VoIP Session
Initiated
VoIP Session
Terminated
Database Login
Succeeded
Database Login
Failure
Indicates the beginning of a VoIP
session.
Indicates the end of a VoIP
session.
Indicates a successful database
login.
Indicates that a database login
attempt failed.
1 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
1 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
1 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
3 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
STRM Event Category Correlation Reference
Page 29

Access 23
Access The access category indicates events relating to authentication and access
controls. The associated low-level event categories include:
Table 2-11 Access Categories
Low Level Event
Category
Unknown Network
Communication
Description
Indicates an unknown network
communication event.
Event
Firewall Permit Indicates access to the firewall
was permitted.
Firewall Deny Indicates access to the firewall
was denied.
Flow Context
Response
Indicates events from the
Classification Engine in response
to a SIM request.
Misc Network
Communication
Indicates a miscellaneous
communications event.
Event
IPS Deny Indicates Intrusion Prevention
Systems (IPS) denied traffic.
Firewall Session
Opened
Firewall Session
Closed
Dynamic Address
Translation
Indicates the firewall session has
been opened.
Indicates the firewall session has
been closed.
Indicates that dynamic address
translation was successful.
Successful
No Translation
Group Found
Indicates that no translation
group has been found.
Misc Authorization Indicates that access was
granted to a miscellaneous
authentication server.
ACL Permit Indicates that an ACL was
permitted access.
ACL Deny Indicates that an ACL was
denied access.
Access Permitted Indicates that access was
permitted.
Access Denied Indicates that access was
denied.
Session Opened Indicates that a session was
opened
Session Closed Indicates that a session was
closed.
Severity Level
(0 to 10)
Event Correlation/
Processing
Additional Event
Processing
3 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
0 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
4 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
5 No event
Scenario 2
pass-through
3 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
4 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
0 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
0 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
0 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
2 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
2 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
0 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
4 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
0 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
4 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
1 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
1 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
STRM Event Category Correlation Reference
Page 30

24 EVENT CATEGORY CORRELATION
Table 2-11 Access Categories (continued)
Low Level Event
Category
Description
Session Reset Indicates that a session was
reset.
Session Terminated In dicates that a session was
terminated.
Session Denied Indicates that a session was
denied.
Session in Progress Indicates that a session is
currently in progress.
Session Delayed Indicates that a session was
delayed.
Session Queued Indicates that a session was
queued.
Session Inbound Indicates that a session is
inbound.
Session Outbound Indicates that a session is
outbound.
Unauthorized
Access Attempt
Indicates that an unauthorized
access attempt was detected.
Severity Level
(0 to 10)
Event Correlation/
Processing
Additional Event
Processing
3 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
4 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
5 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
1 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
3 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
1 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
1 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
1 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
1 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
Exploit The exploit category indicates events where a communication or access has
occurred. The associated low-level event categories include:
Table 2-12 Exploit Categories
Low Level Event
Category
Unknown Exploit
Attack
Description
Indicates an unknown exploit
attack.
Buffer Overflow Indicates a buffer overflow. 9 Correlation Group 1 Scenario 2
DNS Exploit Indicates a DNS exploit. 9 Correlation Group 1 Scenario 2
Telnet Exploit Indicates a Telnet exploit. 9 Correlation Group 1 Scenario 2
Linux Exploit Indicates a Linux exploit. 9 Correlation Group 1 Scenario 2
Unix Exploit Indicates a Unix exploit. 9 Correlation Group 1 Scenario 2
Windows Exploit Indicates a Windows exploit. 9 Correlation Group 1 Scenario 2
Mail Exploit Indicates a mail server exploit. 9 Correlation Group 1 Scenario 2
Infrastructure
Exploit
Indicates an infrastructure
exploit.
Misc Exploit Indicates a miscellaneous
exploit.
Web Exploit Indic at es a web exp lo i t. 9 Correlation Group 1 Scenario 2
Severity Level
(0 to 10)
Event Correlation/
Processing
Additional Event
Processing
9 Correlation Group 1 Scenario 2
9 Correlation Group 1 Scenario 2
9 Correlation Group 1 Scenario 2
STRM Event Category Correlation Reference
Page 31

Table 2-12 Exploit Categories (continued)
Malware 25
Low Level Event
Category
Description
Session Hijack Indicates a session in your
Severity Level
(0 to 10)
Event Correlation/
Processing
Additional Event
Processing
9 Cor re l at io n Gr ou p 2 Scenar io 2
network has been interceded.
Worm Active Indicates an active worm. 10 Correlation Group 1 Scenario 2
Password
Guess/Retrieve
Indicates that a user has
requested access to their
9 Cor re l at io n Gr ou p 2 Scenar io 2
password information from the
database.
FTP Exploit Indicates an FTP exploit. 9 Correlation Gr ou p 1 Scen ar io 2
RPC Exploit Indicates an RPC exploit. 9 Correlation Group 1 Scenario 2
SNMP Exploit Indicates an SNMP exploit. 9 Correlation Gr ou p 1 Scen ar io 2
NOOP Exploit Indicates an NOOP exploit. 9 Correlation Group 1 Scenar io 2
Samba Exploit Indicates an Samba exploit. 9 Correlation Group 1 Scenario 2
Database Exploit Indicates a database exploit. 9 Correlation Group 1 Scenario 2
SSH Exploit Indicates an SSH exploit. 9 Correlation Group 1 Scenario 2
ICMP Exploit Indicates an ICMP exploit. 9 Correlation Group 1 Scenario 2
UDP Exploit Indicates a UDP exploit. 9 Correlation Grou p 1 Scen ar io 2
Browser Exploit Indicates an exploit on your
9 Cor re l at io n Gr ou p 1 Scenar io 2
browser.
DHCP Exploit Indicates a DHCP exploit 9 Correlation Group 1 Scenario 2
Remote Access
Exploit
ActiveX Exploit Indicates an exploit through an
Indicates a remote access
exploit
9 Cor re l at io n Gr ou p 1 Scenar io 2
9 Cor re l at io n Gr ou p 1 Scenar io 2
ActiveX application.
SQL Injection Indicates that an SQL injection
9 Cor re l at io n Gr ou p 1 Scenar io 2
has occurred.
Malware The malicious software (malware) category indicates events relating to application
exploits and buffer overflow attempts. The associated low-level event categories
include:
Table 2-13 Malware Categories
Low Level Event
Category
Unknown Malware Indicates an unknown virus. 4 Correlation Group 2 Scenario 2
Backdoor Detected Indicates that a backdoor to the
Hostile Mail
Attachment
Malicious Software Indicates a virus. 6 Correlation Group 2 Scenario 2
Description
system has been detected.
Indicates a hostile mail
attachment.
Severity Level
(0 to 10)
Event Correlation/
Processing
9 Correlation Group 2 Scenario 2
6 Correlation Group 2 Scenario 2
STRM Event Category Correlation Reference
Additional Event
Processing
Page 32

26 EVENT CATEGORY CORRELATION
Table 2-13 Malware Categories (continued)
Low Level Event
Category
Hostile Software
Download
Description
Indicates a hostile software
download to your network.
Virus Detected Indicates a virus has been
detected.
Misc Malware Indicates miscellaneous
malicious software
Trojan Detected Indicates a trojan has been
detected.
Spyware Detected Indicates spyware has been
detected on your system.
Content Scan Indicates that an attempted scan
of your content has been
detected.
Content Scan
Failed
Content Scan
Successful
Content Scan in
Progress
Indicates that a scan of your
content has failed.
Indicates that a scan of your
content was successful.
Indicates that a scan of your
content is currently in progress.
Keylogger Indicates that a key logger has
been detected.
Severity Level
(0 to 10)
Event Correlation/
Processing
Additional Event
Processing
6 Correlation Group 2 Scenario 2
8 Correlation Group 2 Scenario 2
4 Correlation Group 2 Scenario 2
7 Correlation Group 2 Scenario 2
6 Correlation Group 2 Scenario 2
3 Correlation Group 2 Scenario 2
8 Correlation Group 2 Scenario 2
3 Correlation Group 2 Scenario 2
3 Correlation Group 2 Scenario 2
7 Correlation Group 2 Scenario 2
Suspicious Activity The suspicious activity category indicates events relating to viruses, trojans, back
door attacks, and other forms of hostile software. The associated low-level event
categories include:
Table 2-14 Suspicious Categories
Low Level Event
Category
Unknown
Suspicious Event
Suspicious Pattern
Detected
Content Modified By
Firewall
Invalid Command or
Data
Description
Indicates an unknown suspicious
event.
Indicates a suspicious pattern
has been detected.
Indicates that content has been
modified by the firewall.
Indicates an invalid command or
data.
Suspicious Packet Indicates a suspicious packet. 3 Correlation Group 2 Scenario 2
Suspicious Activity Indicates suspicious activity. 3 Correlation Group 2 Scenario 2
STRM Event Category Correlation Reference
Severity Level
(0 to 10)
Event Correlation/
Processing
Additional Event
Processing
3 Correlation Group 2 Scenario 2
3 Correlation Group 2 Scenario 2
3 Correlation Group 2 Scenario 2
3 Correlation Group 2 Scenario 2
Page 33

Table 2-14 Suspicious Categories (continued)
Suspicious Activity 27
Low Level Event
Category
Suspicious File
Description
Indicates a suspicious file name. 3 Correlation Group 2 Scenario 2
Severity Level
(0 to 10)
Event Correlation/
Processing
Additional Event
Processing
Name
Suspicious Port
Indicates suspicious port activity. 3 Correlation Group 2 Scenario 2
Activity
Suspicious Routing Indicates suspicious routing. 3 Correlation Group 2 Scenario 2
Potential Web
Vulnerability
Unknown Evasion
Event
Indicates potential web
vulnerability.
Indicates an unknown evasion
event.
3 Correlation Group 2 Scenario 2
5 Correlation Group 2 Scenario 2
IP Spoof Indicates an IP spoof. 5 Correlation Group 2 Scenario 2
IP Fragmentation Indicates IP fragmentation. 3 Correlation Group 2 Scenario 2
Overlapping IP
Fragments
Indicates overlapping IP
fragments.
5 Correlation Group 2 Scenario 2
IDS Evasion Indicates an IDS evasion. 5 Correlation Group 2 Scenario 2
DNS Protocol
Anomaly
FTP Protocol
Anomaly
Mail Protocol
Anomaly
Routing Protocol
Anomaly
Web Protocol
Anomaly
SQL Protocol
Anomaly
Executable Code
Detected
Misc Suspicious
Event
Indicates a DNS protocol
anomaly.
Indicates an FTP protocol
anomaly.
Indicates a mail protocol
anomaly.
Indicates a routing protocol
anomaly.
Indicates a web protocol
anomaly.
Indicates an SQL protocol
anomaly.
Indicates that an executable code
has been detected.
Indicates a miscellaneous
suspicious event.
3 Correlation Group 2 Scenario 2
3 Correlation Group 2 Scenario 2
3 Correlation Group 2 Scenario 2
3 Correlation Group 2 Scenario 2
3 Correlation Group 2 Scenario 2
3 Correlation Group 2 Scenario 2
5 Correlation Group 2 Scenario 2
3 Correlation Group 2 Scenario 2
Information Leak Indicates an information leak. 1 Correlation Group 2 Scenario 2
Potential Mail
Vulnerability
Potential Version
Vulnerability
Potential FTP
Vulnerability
Potential SSH
Vulnerability
Potential DNS
Vulnerability
Indicates a potential vulnerability
in the mail server.
Indicates a potential vulnerability
in the STRM version.
Indicates a potential FTP
vulnerability.
Indicates a potential SSH
vulnerability.
Indicates a potential vulnerability
in the DNS server.
4 Correlation Group 2 Scenario 2
4 Correlation Group 2 Scenario 2
4 Correlation Group 2 Scenario 2
4 Correlation Group 2 Scenario 2
4 Correlation Group 2 Scenario 2
STRM Event Category Correlation Reference
Page 34

28 EVENT CATEGORY CORRELATION
Table 2-14 Suspicious Categories (continued)
Low Level Event
Category
Potential SMB
Vulnerability
Potential Database
Vulnerability
IP Protocol
Anomaly
Suspicious IP
Address
Invalid IP Protocol
Usage
Description
Indicates a potential SMB
(Samba) vulnerability.
Indicates a potential vulnerability
in the database.
Indicates a potential IP protocol
anomaly
Indicates a suspicious IP address
has been detected.
Indicates an invalid IP protocol
misuse.
Severity Level
(0 to 10)
Event Correlation/
Processing
Additional Event
Processing
4 Correlation Group 2 Scenario 2
4 Correlation Group 2 Scenario 2
3 Correlation Group 2 Scenario 2
2 Correlation Group 2 Scenario 2
2 Correlation Group 2 Scenario 2
Invalid Protocol Indicates an invalid protocol. 4 Correlation Group 2 Scenario 2
Suspicious Window
Events
Suspicious ICMP
Activity
Potential NFS
Vulnerability
Potential NNTP
Vulnerability
Indicates a suspicious event with
a screen on your desktop.
Indicates suspicious ICMP
activity.
Indicates a potential Network File
System (NFS) vulnerability.
Indicates a potential Network
News Transfer Protocol (NNTP)
2 Correlation Group 2 Scenario 2
2 Correlation Group 2 Scenario 2
4 Correlation Group 2 Scenario 2
4 Correlation Group 2 Scenario 2
vulnerability.
Potential RPC
Vulnerability
Potential Telnet
Vulnerability
Potential SNMP
Vulnerability
Illegal TCP Flag
Combination
Suspicious TCP
Flag Combination
Indicates a potential RPC
vulnerability.
Indicates a potential Telnet
vulnerability on your system.
Indicates a potential SNMP
vulnerability.
Indicates an invalid TCP flag
combination has been detected.
Indicates a potentially invalid
TCP flag combination has been
4 Correlation Group 2 Scenario 2
4 Correlation Group 2 Scenario 2
4 Correlation Group 2 Scenario 2
5 Correlation Group 2 Scenario 2
4 Correlation Group 2 Scenario 2
detected.
Illegal ICMP
Protocol Usage
Indicates an invalid use of the
ICMP protocol has been
5 Correlation Group 2 Scenario 2
detected.
Suspicious ICMP
Protocol Usage
Indicates a potentially invalid use
of the ICMP protocol has been
4 Correlation Group 2 Scenario 2
detected.
Illegal ICMP Type Indicates an invalid ICMP type
5 Correlation Group 2 Scenario 2
has been detected.
Illegal ICMP Code Indicates an invalid ICMP code
5 Correlation Group 2 Scenario 2
has been detected.
STRM Event Category Correlation Reference
Page 35

Table 2-14 Suspicious Categories (continued)
Suspicious Activity 29
Low Level Event
Category
Suspicious ICMP
Type
Suspicious ICMP
Code
Description
Indicates a potentially invalid
ICMP type has been detected.
Indicates a potentially invalid
ICMP code has been detected.
TCP port 0 Indicates a TCP packet using a
reserved port (0) for source or
destination.
UDP port 0 Indicates a UDP packets using a
reserved port (0) for source or
destination.
Hostile IP Indicates the use of a known
hostile IP address.
Watch list IP Indicates the use of an IP
address from a watch list of IP
addresses.
Known offender IP Indicates the use of an IP
address of a known offender.
RFC 1918 (private) IPIndicates the use of an IP
address from a private IP address
range.
Potential VoIP
Vulnerability
Indicates a potential VoIP
vulnerability.
Blacklist Address Indicates that an IP address is on
the black list.
Watchlist Address Indicates that the IP address is
on the list of IP addresses being
monitored.
Darknet Address Indicates that the IP address is
part of a darknet.
Botnet Address Indicates that the address is part
of a botnet.
Suspicious Address Indicates that the IP address
should be monitored.
Severity Level
(0 to 10)
Event Correlation/
Processing
Additional Event
Processing
4 Correlation Group 2 Scenario 2
4 Correlation Group 2 Scenario 2
4 Correlation Group 2 Scenario 2
4 Correlation Group 2 Scenario 2
4 Correlation Group 2 Scenario 2
4 Correlation Group 2 Scenario 2
4 Correlation Group 2 Scenario 2
4 Correlation Group 2 Scenario 2
4 Correlation Group 2 Scenario 2
8 Correlation Group 2 Scenario 2
7 Correlation Group 2 Scenario 2
5 Correlation Group 2 Scenario 2
7 Correlation Group 2 Scenario 2
5 Correlation Group 2 Scenario 2
STRM Event Category Correlation Reference
Page 36

30 EVENT CATEGORY CORRELATION
System The system category indicates that the nature of threat is unknown but the
behavior is suspicious including protocol anomalies potentially indicating evasive
techniques. The associated low-level event categories include:
Table 2-15 System Categories
Low Level Event
Category
Unknown System
Event
Description
Indicates an unknown system
event.
Severity Level
(0 to 10)
Event Correlation/
Processing
Additional Event
Processing
1 Correlation Group 5 Scenario 2
System Boot Indicates a system boot. 1 Correlation Group 5 Scenario 2
System
Configuration
System Halt Indicates the system has been
Indicates a change in the
system configuration.
1 Correlation Group 5 Scenario 2
1 Correlation Group 5 Scenario 2
halted.
System Failure Indicates a system failure. 6 Correlation Group 5 Scenario 2
System Status Indicates any informatio n eve nt . 1 Correlation Group 5 Scenario 2
System Error Indicates a system error. 3 Correlation Group 5 Scenario 2
Misc System Event Indicates a miscellaneous
1 Correlation Group 5 Scenario 2
system event.
Service Started Indicates system services have
1 Correlation Group 5 Scenario 2
started.
Service Stopped Indicates system services have
1 Correlation Group 5 Scenario 2
stopped.
Service Failure Indicates a system failure. 6 Correlation Group 5 Scenario 2
Successful Registry
Modification
Indicates that a modification to
the registry has been
1 Correlation Group 5 Scenario 2
successful.
Successful
Host-Policy
Modification
Successful File
Modification
Successful Stack
Modification
Successful
Application
Modification
Successful
Configuration
Modification
Successful Service
Modification
Failed Registry
Modification
Indicates that a modification to
the host policy has been
successful.
Indicates that a modification to a
file has been successful.
Indicates that a modification to
the stack has been successful.
Indicates that a modification to
the application has been
successful.
Indicates that a modification to
the configuration has been
successful.
Indicates that a modification to a
service has been successful.
Indicates that a modification to
the registry has failed.
1 Correlation Group 5 Scenario 2
1 Correlation Group 5 Scenario 2
1 Correlation Group 5 Scenario 2
1 Correlation Group 5 Scenario 2
1 Correlation Group 5 Scenario 2
1 Correlation Group 5 Scenario 2
1 Correlation Group 5 Scenario 2
STRM Event Category Correlation Reference
Page 37

Table 2-15 System Categories (continued)
System 31
Low Level Event
Category
Failed Host-Policy
Modification
Failed File
Modification
Failed Stack
Modification
Failed Application
Modification
Failed Configuration
Modification
Failed Service
Modification
Description
Indicates that a modification to
the host policy has failed.
Indicates that a modification to a
file has failed.
Indicates that a modification to
the stack has failed.
Indicates that a modification to
an application has failed.
Indicates that a modification to
the configuration has failed.
Indicates that a modification to
the service has failed.
Registry Addition Indicates that an new item has
Severity Level
(0 to 10)
Event Correlation/
Processing
Additional Event
Processing
1 Correlation Group 5 Scenario 2
1 Correlation Group 5 Scenario 2
1 Correlation Group 5 Scenario 2
1 Correlation Group 5 Scenario 2
1 Correlation Group 5 Scenario 2
1 Correlation Group 5 Scenario 2
1 Correlation Group 5 Scenario 2
been added to the registry.
Host-Policy Created Indicates that a new entry has
1 Correlation Group 5 Scenario 2
been added to the registry.
File Created Indicates that a new has been
1 Correlation Group 5 Scenario 2
created in the system.
Application Installed Indicates that a new application
1 Correlation Group 5 Scenario 2
has been installed on the
system.
Service Installed Indicates that a new service has
1 Correlation Group 5 Scenario 2
been installed on the system.
Registry Deletion Indicates that a registry entry
1 Correlation Group 5 Scenario 2
has been deleted.
Host-Policy Deleted Indicates that a host policy entry
1 Correlation Group 5 Scenario 2
has been deleted.
File Deleted Indicates that a file has been
1 Correlation Group 5 Scenario 2
deleted.
Application
Uninstalled
Service Uninstalled Indicates that a service has
Indicates that an application has
been uninstalled.
1 Correlation Group 5 Scenario 2
1 Correlation Group 5 Scenario 2
been uninstalled.
System Informational Indicates system information. 3 Correlation Group 5 Sc en ar io 2
System Action Allow Indicates that an attempted
3 Correlation Group 5 Scenario 2
action on the system has been
authorized.
System Action Deny Indicates that an attempted
4 Correlation Group 5 Scenario 2
action on the system has been
denied.
Cron Indicates a crontab message. 1 Correlation Group 5 Scen ar io 2
STRM Event Category Correlation Reference
Page 38

32 EVENT CATEGORY CORRELATION
Table 2-15 System Categories (continued)
Low Level Event
Category
Description
Cron Status Indicates a crontab status
Severity Level
(0 to 10)
Event Correlation/
Processing
Additional Event
Processing
1 Correlation Group 5 Scenario 2
message.
Cron Failed Indicates a crontab failure
4 Correlation Group 5 Scenario 2
message.
Cron Successful Indicates a crontab success
1 Correlation Group 5 Scenario 2
message.
Daemon Indicates a daemon message. 1 Correlation Group 5 Scenario 2
Daemon Status Indicates a daemon status
1 Correlation Group 5 Scenario 2
message.
Daemon Failed Indicates a daemon failure
4 Correlation Group 5 Scenario 2
message.
Daemon Successful Indicates a daemon success
1 Correlation Group 5 Scenario 2
message.
Kernel Indicates a kernel message. 1 Correlation Group 5 Scenario 2
Kernel Status Indicates a kernel status
1 Correlation Group 5 Scenario 2
message.
Kernel Failed Indicates a kernel failure
Correlation Group 5 Scenario 2
message.
Kernel Successful Indicates a kernel successful
1 Correlation Group 5 Scenario 2
message.
Authentication Indicates an authentication
1 Correlation Group 5 Scenario 2
message.
Information Indicates an informational
2 Correlation Group 5 Scenario 2
message.
Notice Indicates a notice message. 3 Correlation Group 5 Scenario 2
Warning Indicates a warning message. 5 Correlation Group 5 Scenario 2
Error Indicates an error message. 7 Correlation Group 5 Scenario 2
Critical Indicates a critical message. 9 Correlation Group 5 Scenario 2
Debug Indicates a debug message. 1 Correlation Group 5 Scenario 2
Messages Indicates a generic message. 1 Correlation Group 5 Scenario 2
Privilege Access Indicates that privilege access
3 Correlation Group 5 Scenario 2
was attempted.
STRM Event Category Correlation Reference
Page 39

Policy 33
Policy The policy category indicates events relating to system changes, software
installation, or status messages. The associated low-level event categories
include:
Table 2-16 Policy Categories
Low Level Event
Category
Unknown Policy
Violation
Description
Indicates an unknown policy
violation.
Web Policy Violation Indicates a web policy
violation.
Remote Access
Policy Violation
IRC/IM Policy
Violation
Indicates a remote access
policy violation.
Indicates an instant
messenger policy violation.
P2P Policy Violation Indicates a Peer-to-Peer (P2P)
policy violation.
IP Access Policy
Violation
Application Policy
Violation
Database Policy
Violation
Network Threshold
Policy Violation
Indicates an IP access policy
violation.
Indicates an application policy
violation.
Indicates a database policy
violation.
Indicates a network threshold
policy violation.
Porn Policy Violation Indicates a porn policy
violation.
Games Policy
Violation
Indicates a games policy
violation.
Misc Policy Violation Indicates a miscellaneous
policy violation.
Compliance Policy
Violation
Indicates a compliance policy
violation.
Mail Policy Violation Indicates a mail policy
violation.
IRC Policy Violation Indicates an IRC policy
violation
IM Policy Violation Indicates a policy violation
related to instant messaging
(IM) activities.
VoIP Policy Violation Indicates a VoIP policy
violation
Severity Level
(0 to 10)
Event Correlation/
Processing
Additional Event
Processing
2 Correlation Group 4 Scenario 2
2 Correlation Group 4 Scenario 2
2 Correlation Group 4 Scenario 2
2 Correlation Group 4 Scenario 2
2 Correlation Group 4 Scenario 2
2 Correlation Group 4 Scenario 2
2 Correlation Group 4 Scenario 2
2 Correlation Group 4 Scenario 2
2 Correlation Group 4 Scenario 2
2 Correlation Group 4 Scenario 2
2 Correlation Group 4 Scenario 2
2 Correlation Group 4 Scenario 2
2 Correlation Group 4 Scenario 2
2 Correlation Group 4 Scenario 2
2 Correlation Group 4 Scenario 2
2 Correlation Group 4 Scenario 2
2 Correlation Group 4 Scenario 2
STRM Event Category Correlation Reference
Page 40

34 EVENT CATEGORY CORRELATION
CRE The CRE category indicates events generated from a custom offense or event
rule. The associated low-level event categories include:
Table 2-17 CRE Category
Low Level Event
Category
Description
Unknown CRE Event Indicates an unknown custom
rules engine event.
Single Event Rule
Match
Event Sequence Rule
Match
Cross-Offense Event
Sequence Rule Match
Indicates a single event rule
match.
Indicates an event sequence
rule match.
Indicates a cross-offense
event sequence rule match.
Offense Rule Match Indicates an offense rule
match.
Severity Level
(0 to 10)
Event Correlation/
Processing
5 No event
pass-through
5 No event
pass-through
5 No event
pass-through
5 No event
pass-through
5 No event
pass-through
Additional Event
Processing
Scenario 1
Scenario 1
Scenario 1
Scenario 1
Scenario 1
Potential Exploit The Potential Exploit category indicates events relating to potential application
exploits and buffer overflow attempts. The associated low-level event categories
include:
Table 2-18 Potential Exploit Category
Low Level Event
Category
Unknown Potential
Exploit Attack
Description
Indicates a potential
exploitative attack has been
detected.
Potential Buffer
Overflow
Indicates a potential buffer
overflow has been detected.
Potential DNS Exploit Indicates a potentially
exploitative attack through the
DNS server has been
detected.
Potential Telnet
Exploit
Indicates a potentially
exploitative attack through
Telnet has been detected.
Potential Linux Exploit Indicates a potentially
exploitative attack through
Linux has been detected.
Potential Unix Exploit Indicates a potentially
exploitative attack through
Unix has been detected.
Potential Windows
Exploit
Indicates a potentially
exploitative attack through
Windows has been detected.
Severity Level
(0 to 10)
Event Correlation/
Processing
Additional Event
Processing
7 Correlation Group 1 Scenar io 2
7 Correlation Group 1 Scenar io 2
7 Correlation Group 1 Scenar io 2
7 Correlation Group 1 Scenar io 2
7 Correlation Group 1 Scenar io 2
7 Correlation Group 1 Scenar io 2
7 Correlation Group 1 Scenar io 2
STRM Event Category Correlation Reference
Page 41

Table 2-18 Potential Exploit Category (continued)
SIM Audit 35
Low Level Event
Category
Description
Potential Mail Exploit Indicates a potentially
exploitative attack through
mail has been detected.
Potential Infrastructure
Exploit
Indicates a potential
exploitative attack on the
system infrastructure has
been detected.
Potential Misc Exploit Indicates a potentially
exploitative attack has been
detected.
Potential Web Exploit Indicates a potentially
exploitative attack through the
web has been detected.
Potential Botnet
connection
Indicates a potentially
exploitative attack using
Botnet has been detected.
Potential worm activity Indicates a potentially
exploitive attack using worm
activity has been detected.
Severity Level
(0 to 10)
Event Correlation/
Processing
Additional Event
Processing
7 Correlation Group 1 Scenario 2
7 Correlation Group 1 Scenario 2
7 Correlation Group 1 Scenario 2
7 Correlation Group 1 Scenario 2
6 Correlation Group 1 Scenario 2
6 Correlation Group 1 Scenario 2
SIM Audit The SIM Audit events category indi cates events related to user interaction with the
Console and the Administration Console. User logins and configuration changes
will generate events that are sent to the Event Collector, which correlates with
other security events from the network. The associated low-level event categories
include:
Table 2-19 SEM Audit Event Category
Low Level Event
Category
SIM User
Authentication
SIM Configuration
Change
Description
Indicates a user login or
logout on the Console.
Indicates that a user has
made a change to the SIM
configuration or deployment.
SIM User Action Indicates that a user has
initiated a process in the SIM
module. This may include
starting a backup process or
generated a report.
Severity Level
(0 to 10)
Event Correlation/
Processing
Additional Event
Processing
5 Correlation Group 5 Scenario 2
3 Correlation Group 5 Scenario 2
3 Correlation Group 5 Scenario 2
STRM Event Category Correlation Reference
Page 42

36 EVENT CATEGORY CORRELATION
VIS Host Discovery When the VIS component discovers and stores new hosts, ports, or vulnerabilities
detected on the network, the VIS component generates events. These events are
sent to the Event Collector to be correlated with other security events.
The associated low-level event categories include:
Table 2-20 VIS Host Discovery Category
Low Level Event
Category
New Host Discovered Indicates that the VIS
New Port Discovered Indicates that the VIS
New Vuln Discovered Indicates that the VIS
New OS Discovered Indicates that the VIS
Bulk Host Discovered Indicates that the VIS
Description
component has detected a
new host.
component has detected a
new open port.
component has detected a
new vulnerability.
component has detected a
new operating system on a
host.
component has detected
many new hosts in a short
period of time.
Severity Level
(0 to 10)
3 Correlation Group 5 Scenar io 2
3 Correlation Group 5 Scenar io 2
3 Correlation Group 5 Scenar io 2
3 Correlation Group 5 Scenar io 2
3 Correlation Group 5 Scenar io 2
Event Correlation/
Processing
Additional Event
Processing
Application The Application category indicates events relating to application activity, such as
e-mail or FTP activity. The associated low-level event categories include:
Table 2-21 Application Category
Low Level Event
Category Description
Mail Opened Indicates that an e-mail
connection was established.
Mail Closed Indicates that an e-mail
connection was closed.
Mail Reset Indicates that an e-mail
connection was reset.
Mail Terminated Indicates that an e-mail
connection was terminated.
Mail Denied Indicates that an e-mail
connection was denied.
Severity Level
(0 to 10)
1 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
1 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
3 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
4 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
4 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
STRM Event Category Correlation Reference
Event Correlation/
Processing
Additional Event
Processing
Page 43

Table 2-21 Application Category (continued)
Application 37
Low Level Event
Category
Description
Mail in Progress Indicates that an e-mail
connection is being
attempted.
Mail Delayed Indicates that an e-mail
connection was delayed.
Mail Queued Indicates that an e-mail
connection was queued.
Mail Redirected Indicates that an e-mail
connection was redirected.
FTP Opened Indicates that an FTP
connection was opened.
FTP Closed Indicates that an FTP
connection was closed.
FTP Reset Indicates that an FTP
connection was reset.
FTP Terminated Indicates that an FTP
connection was terminated.
FTP Denied Indicates that an FTP
connection was denied.
FTP In Progress Indicates that an FTP
connection is currently in
progress.
FTP Redirected Indicates that an FTP
connection was redirected.
HTTP Opened Indicates that an HTTP
connection was established.
HTTP Closed Indicates that an HTTP
connection was closed.
HTTP Reset Indicates that an HTTP
connection was reset.
HTTP Terminated Indicates that an HTTP
connection was terminated.
HTTP Denied Indicates that an HTTP
connection was denied.
HTTP In Progress Indicates that an HTTP
connection is currently in
progress.
HTTP Delayed Indicates that an HTTP
connection was delayed.
HTTP Queued Indicates that an HTTP
connection was queued.
Severity Level
(0 to 10)
Event Correlation/
Processing
Additional Event
Processing
1 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
4 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
3 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
1 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
1 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
1 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
3 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
4 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
4 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
1 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
3 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
1 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
1 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
3 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
4 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
4 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
1 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
3 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
1 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
STRM Event Category Correlation Reference
Page 44

38 EVENT CATEGORY CORRELATION
Table 2-21 Application Category (continued)
Low Level Event
Category
Description
HTTP Redirected Indicates that an HTTP
connection was redirected.
HTTP Proxy Indicates that an HTTP
connection is being proxied.
HTTPS Opened Indicates that an HTTPS
connection was established.
HTTPS Closed Indicates that an HTTPS
connection was closed.
HTTPS Reset Indicates that an HTTPS
connection was reset.
HTTP Terminated Indicates that an HTTPS
connection was terminated.
HTTPS Denied Indicates that an HTTPS
connection was denied.
HTTPS In Progress Indicates that an HTTPS
connection is currently in
progress.
HTTPS Delayed Indicates that an HTTPS
connection was delayed.
HTTPS Queued Indicates that an HTTPS
connection was queued.
HTTPS Redirected Indicates that an HTTPS
connection was redirected.
HTTPS Proxy Indicates that an HTTPS
connection is proxied.
SSH Opened Indicates than an SSH
connection was established.
SSH Closed Indicates that an SSH
connection was closed.
SSH Reset Indicates that an SSH
connection was reset.
SSH Terminated Indicates that an SSH
connection was terminated.
SSH Denied Indicates that an SSH session
was denied.
SSH In Progress Indicates that an SSH session
is currently in progress.
RemoteAccess
Opened
Indicates that a remote
access connection was
established.
Severity Level
(0 to 10)
Event Correlation/
Processing
Additional Event
Processing
1 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
1 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
1 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
1 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
4 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
4 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
4 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
1 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
3 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
3 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
3 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
1 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
1 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
1 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
3 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
3 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
4 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
1 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
1 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
STRM Event Category Correlation Reference
Page 45

Table 2-21 Application Category (continued)
Application 39
Low Level Event
Category
Description
RemoteAccess Closed Indicates that a remote
access connection was
closed.
RemoteAccess Reset Indicates that a remote
access connection was reset.
RemoteAccess
Terminated
Indicates that a remote
access connection was
terminated.
RemoteAccess
Denied
Indicates that a remote
access connection was
denied.
RemoteAccess In
Progress
Indicates that a remote
access connection is currently
in progress.
RemoteAccess
Delayed
Indicates that a remote
access connection was
delayed.
RemoteAccess
Redirected
Indicates that a remote
access connection was
redirected.
VPN Opened Indicates that a VPN
connection was opened.
VPN Closed Indicates that a VPN
connection was closed.
VPN Reset Indicates that a VPN
connection was reset.
VPN Terminated Indicates that a VPN
connection was terminated.
VPN Denied Indicates that a VPN
connection was denied.
VPN In Progress Indicates that a VPN
connection is currently in
progress.
VPN Delayed Indicates that a VPN
connection was delayed
VPN Queued Indicates that a VPN
connection was queued.
VPN Redirected Indicates that a VPN
connection was redirected.
RDP Opened Indicates that an RDP
connection was established.
RDP Closed Indicates that an RDP
connection was closed.
Severity Level
(0 to 10)
Event Correlation/
Processing
Additional Event
Processing
1 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
3 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
4 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
4 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
4 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
3 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
3 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
1 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
1 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
3 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
4 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
4 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
1 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
3 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
3 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
3 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
1 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
1 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
STRM Event Category Correlation Reference
Page 46

40 EVENT CATEGORY CORRELATION
Table 2-21 Application Category (continued)
Low Level Event
Category
Description
RDP Reset Indicates that an RDP
connection was reset.
RDP Terminated Indicates that an RDP
connection was terminated.
RDP Denied Indicates that an RDP
connection was denied.
RDP In Progress Indicates that an RDP
connection is currently in
progress.
RDP Redirected Indicates that an RDP
connection was redirected.
FileTransfer Opened Indicates that a file transfer
connection was established.
FileTransfer Closed Indicates that a file transfer
connection was closed.
FileTransfer Reset Indicates that a file transfer
connection was reset.
FileTransfer
Terminated
Indicates that a file transfer
connection was terminated.
FileTransfer Denied Indicates that a file transfer
connection was denied.
FileTransfer In
Progress
Indicates that a file transfer
connection is currently in
progress.
FileTransfer Delayed Indicates that a file transfer
connection was delayed.
FileTransfer Queued Indicates that a file transfer
connection was queued.
FileTransfer
Redirected
Indicates that a file transfer
connection was redirected.
DNS Opened Indicates that a DNS
connection was established.
DNS Closed Indicates that a DNS
connection was closed.
DNS Reset Indicates that a DNS
connection was reset.
DNS Terminated Indicates that a DNS
connection was terminated.
DNS Denied Indicates that a DNS
connection was denied.
Severity Level
(0 to 10)
Event Correlation/
Processing
Additional Event
Processing
3 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
4 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
4 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
1 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
3 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
1 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
1 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
3 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
4 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
4 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
1 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
3 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
3 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
3 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
1 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
1 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
5 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
5 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
5 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
STRM Event Category Correlation Reference
Page 47

Table 2-21 Application Category (continued)
Application 41
Low Level Event
Category
Description
DNS In Progress Indicates that a DNS
connection is currently in
progress.
DNS Delayed Indicates that a DNS
connection was delayed.
DNS Redirected Indicates that a DNS
connection was redirected.
Chat Opened Indicates that a chat
connection was opened.
Chat Closed Indicates that a chat
connection was closed.
Chat Reset Indicates that a chat
connection was reset.
Chat Terminated Indicates that a chat
connection was terminated.
Chat Denied Indicates that a chat
connection was denied.
Chat In Progress Indicates that a chat
connection is currently in
progress.
Chat Redirected Indicates that a chat
connection was redirected.
Database Opened Indicates that a database
connection was established.
Database Closed Indicates that a database
connection was closed.
Database Reset Indicates that a database
connection was reset.
Database Terminated Indicates that a database
connection was terminated.
Database Denied Indicates that a database
connection was denied.
Database In Progress Indicates that a database
connection is currently in
progress.
Database Redirected Indicates that a database
connection was redirected.
SMTP Opened Indicates that an SMTP
connection was established.
SMTP Closed Indicates that an SMTP
connection was closed.
Severity Level
(0 to 10)
Event Correlation/
Processing
Additional Event
Processing
1 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
5 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
4 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
1 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
1 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
3 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
3 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
3 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
1 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
1 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
1 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
1 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
5 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
5 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
5 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
1 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
3 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
1 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
1 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
STRM Event Category Correlation Reference
Page 48

42 EVENT CATEGORY CORRELATION
Table 2-21 Application Category (continued)
Low Level Event
Category
Description
SMTP Reset Indicates that an SMTP
connection was reset.
SMTP Terminated Indicates that an SMTP
connection was terminated.
SMTP Denied Indicates that an SMTP
connection was denied.
SMTP In Progress Indicates that an SMTP
connection is currently in
progress.
SMTP Delayed Indicates that an SMTP
connection was delayed.
SMTP Queued Indicates that an SMTP
connection was queued.
SMTP Redirected Indicates that an SMTP
connection was redirected.
Auth Opened Indicates that an authorization
server connection was
established.
Auth Closed Indicates that an authorization
server connection was closed.
Auth Reset Indicates that an authorization
server connection was reset.
Auth Terminated Indicates that an authorization
server connection was
terminated.
Auth Denied Indicates that an authorization
server connection was
denied.
Auth In Progress Indicates that an authorization
server connection is currently
in progress.
Auth Delayed Indicates that an authorization
server connection was
delayed.
Auth Queued Indicates that an authorization
server connection was
queued.
Auth Redirected Indicates that an authorization
server connection was
redirected.
P2P Opened Indicates that a Peer-to-Peer
(P2P) connection was
established.
Severity Level
(0 to 10)
Event Correlation/
Processing
Additional Event
Processing
3 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
5 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
5 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
1 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
3 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
3 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
3 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
1 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
1 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
3 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
4 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
4 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
1 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
3 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
3 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
2 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
1 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
STRM Event Category Correlation Reference
Page 49

Table 2-21 Application Category (continued)
Application 43
Low Level Event
Category
Description
P2P Closed Indicates that a P2P
connection was closed.
P2P Reset Indicates that a P2P
connection was reset.
P2P Terminated Indicates that a P2P
connection was terminated.
P2P Denied Indicates that a P2P
connection was denied.
P2P In Progress Indicates that a P2P
connection is currently in
progress.
Web Opened Indicates that a web
connection was established.
Web Closed Indicates that a web
connection was closed.
Web Reset Indicates that a web
connection was reset.
Web Terminated Indicates that a web
connection was terminated.
Web Denied Indicates that a web
connection was denied.
Web In Progress Indicates that a web
connection is currently in
progress.
Web Delayed Indicates that a web
connection was delayed.
Web Queued Indicates that a web
connection was queued.
Web Redirected Indicates that a web
connection was redirected.
Web Proxy Indicates that a web
connection was proxied.
VoIP Opened Indicates that a Voice Over IP
(VoIP) connection was
established.
VoIP Closed Indicates that a VoIP
connection was closed.
VoIP Reset Indicates that a VoIP
connection was reset.
VoIP Terminated Indicates that a VoIP
connection was terminated.
Severity Level
(0 to 10)
Event Correlation/
Processing
Additional Event
Processing
1 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
4 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
4 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
3 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
1 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
1 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
1 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
4 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
4 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
4 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
1 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
3 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
1 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
1 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
1 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
1 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
3 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
3 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
STRM Event Category Correlation Reference
Page 50

44 EVENT CATEGORY CORRELATION
Table 2-21 Application Category (continued)
Low Level Event
Category
Description
VoIP Denied Indicates that a VoIP
connection was denied.
VoIP In Progress Indicates that a VoIP
connection is currently in
progress.
VoIP Delayed Indicates that a VoIP
connection was delayed.
VoIP Redirected Indicates that a VoIP
connection was redirected.
Suspicious Protocol
Usage
Indicates that suspicious
protocol usage was detected.
Severity Level
(0 to 10)
Event Correlation/
Processing
Additional Event
Processing
3 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
1 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
3 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
3 Correlation Group 3 Scenario 2
5 Correlation Group 2 Scenario 2
STRM Event Category Correlation Reference
 Loading...
Loading...