Page 1

Juniper Networks Network
and Security Manager
NSMXpress and NSM3000 User Guide
Release
2010.4
Published: 2010-11-17
Revision 1
Copyright © 2010, Juniper Networks, Inc.
Page 2

Juniper Networks, Inc.
1194 North Mathilda Avenue
Sunnyvale, California 94089
USA
408-745-2000
www.juniper.net
This productincludes the Envoy SNMPEngine, developed by Epilogue Technology,an Integrated Systems Company.Copyright ©1986-1997,
Epilogue Technology Corporation. All rights reserved. This program and its documentation were developed at private expense, and no part
of them is in the public domain.
This product includes memory allocation software developed by Mark Moraes, copyright © 1988, 1989, 1993, University of Toronto.
This product includes FreeBSD software developed by the University of California, Berkeley, and its contributors. All of the documentation
and software included in the 4.4BSD and 4.4BSD-Lite Releases is copyrighted by the Regents of the University of California. Copyright ©
1979, 1980, 1983, 1986, 1988, 1989, 1991, 1992, 1993, 1994. The Regents of the University of California. All rights reserved.
GateD software copyright © 1995, the Regents of the University. All rights reserved. Gate Daemon was originated and developed through
release 3.0 by Cornell University and its collaborators. Gated is based on Kirton’s EGP, UC Berkeley’s routing daemon (routed), and DCN’s
HELLO routing protocol. Development of Gated has been supported in part by the National Science Foundation. Portions of the GateD
software copyright © 1988, Regents of the University of California. All rights reserved. Portions of the GateD software copyright © 1991, D.
L. S. Associates.
This product includes software developed by Maker Communications, Inc., copyright © 1996, 1997, Maker Communications, Inc.
Juniper Networks, Junos, Steel-Belted Radius, NetScreen, and ScreenOS are registered trademarks of Juniper Networks, Inc. in the United
States and other countries. The Juniper Networks Logo, the Junos logo, and JunosE are trademarks of Juniper Networks, Inc. All other
trademarks, service marks, registered trademarks, or registered service marks are the property of their respective owners.
Juniper Networks assumes no responsibility for any inaccuracies in this document. Juniper Networks reserves the right to change, modify,
transfer, or otherwise revise this publication without notice.
Products made or sold by Juniper Networks or components thereof might be covered by one or more of the following patents that are
owned by or licensed to Juniper Networks: U.S. Patent Nos. 5,473,599, 5,905,725, 5,909,440, 6,192,051, 6,333,650, 6,359,479, 6,406,312,
6,429,706, 6,459,579, 6,493,347, 6,538,518, 6,538,899, 6,552,918, 6,567,902, 6,578,186, and 6,590,785.
NSMXpress and NSM3000 User Guide
Copyright © 2010, Juniper Networks, Inc.
All rights reserved. Printed in USA.
Revision History
November 17, 2010—Revision 1
The information in this document is current as of the date listed in the revision history.
Copyright © 2010, Juniper Networks, Inc.ii
Page 3

END USER LICENSE AGREEMENT
READ THIS END USER LICENSE AGREEMENT (“AGREEMENT”) BEFORE DOWNLOADING, INSTALLING, OR USING THE SOFTWARE.
BY DOWNLOADING, INSTALLING, OR USING THE SOFTWARE OR OTHERWISE EXPRESSING YOUR AGREEMENT TO THE TERMS
CONTAINED HEREIN, YOU (AS CUSTOMER OR IF YOU ARE NOT THE CUSTOMER, AS A REPRESENTATIVE/AGENT AUTHORIZED TO
BIND THE CUSTOMER)CONSENT TO BE BOUNDBY THIS AGREEMENT.IF YOUDO NOTOR CANNOT AGREE TO THE TERMS CONTAINED
HEREIN, THEN (A) DO NOT DOWNLOAD, INSTALL, OR USE THE SOFTWARE, AND (B) YOU MAY CONTACT JUNIPER NETWORKS
REGARDING LICENSE TERMS.
1. The Parties. The parties to this Agreement are (i) Juniper Networks, Inc. (if the Customer’s principal office is located in the Americas) or
Juniper Networks (Cayman) Limited (ifthe Customer’sprincipal officeis located outsidethe Americas) (such applicable entitybeing referred
to herein as“Juniper”),and (ii) the person or organization thatoriginally purchasedfrom Juniperor an authorized Juniperreseller the applicable
license(s) for use of the Software (“Customer”) (collectively, the “Parties”).
2. The Software. In this Agreement, “Software” means the program modules and features of the Juniper or Juniper-supplied software, for
which Customer has paid the applicable license or support fees to Juniper or an authorized Juniper reseller, or which was embedded by
Juniper in equipment which Customer purchased from Juniper or an authorized Juniper reseller. “Software” also includes updates, upgrades
and new releases of such software. “Embedded Software” means Software which Juniper has embedded in or loaded onto the Juniper
equipment and any updates, upgrades, additions or replacements which are subsequently embedded in or loaded onto the equipment.
3. License Grant. Subject topayment of the applicablefees andthe limitations and restrictions set forth herein, Juniper grants toCustomer
a non-exclusive and non-transferable license, without right to sublicense, to use the Software, in executable form only, subject to the
following use restrictions:
a. Customer shall use Embedded Software solely as embedded in, and for execution on, Juniper equipment originally purchased by
Customer from Juniper or an authorized Juniper reseller.
b. Customer shall use the Software on a single hardware chassis having a single processing unit, or as many chassis or processing units
for which Customer has paid the applicable license fees; provided, however, with respect to the Steel-Belted Radius or Odyssey Access
Client software only, Customer shall use such Software on a single computer containing a single physical random access memory space
and containing any number of processors. Use of the Steel-Belted Radius or IMS AAA software on multiple computers or virtual machines
(e.g., Solaris zones) requires multiple licenses, regardless of whether such computers or virtualizations are physically contained on a single
chassis.
c. Product purchase documents, paper or electronic user documentation, and/or the particular licenses purchased by Customer may
specify limitsto Customer’s useof the Software. Suchlimits may restrictuse to amaximum numberof seats, registered endpoints, concurrent
users, sessions, calls, connections, subscribers, clusters, nodes, realms, devices, links, ports or transactions, or require the purchase of
separate licenses to use particular features, functionalities, services, applications, operations, or capabilities, or provide throughput,
performance, configuration, bandwidth, interface, processing, temporal, or geographical limits. In addition, such limits may restrict the use
of the Software to managing certain kinds of networks or require the Software to be used only in conjunction with other specific Software.
Customer’s use of the Software shall be subject to all such limitations and purchase of all applicable licenses.
d. For any trial copy of the Software, Customer’s right to use the Software expires 30 days after download, installation or use of the
Software. Customer may operate the Software after the 30-day trial period only if Customer pays for a license to do so. Customer may not
extend or create an additional trial period by re-installing the Software after the 30-day trial period.
e. The Global Enterprise Edition of the Steel-Belted Radius software may be used by Customer only to manage access to Customer’s
enterprise network. Specifically, service provider customers are expressly prohibited from using the Global Enterprise Edition of the
Steel-Belted Radius software to support any commercial network access services.
The foregoing license is not transferable or assignable by Customer. No license is granted herein to any user who did not originally purchase
the applicable license(s) for the Software from Juniper or an authorized Juniper reseller.
4. Use Prohibitions. Notwithstanding the foregoing, the license provided herein does not permit the Customer to, and Customer agrees
not to and shall not: (a) modify, unbundle, reverse engineer, or create derivative works based on the Software; (b) make unauthorized
copies of the Software (except as necessary for backup purposes); (c) rent, sell, transfer, or grant any rights in and to any copy of the
Software,in any form, toany thirdparty; (d)remove any proprietarynotices, labels,or marks on orin any copy of the Softwareor any product
in which the Software is embedded; (e) distribute any copy of the Software to any third party, including as may be embedded in Juniper
equipment sold inthe secondhand market; (f)use any ‘locked’ orkey-restricted feature,function, service, application, operation, orcapability
without first purchasing the applicable license(s) and obtaining a valid key from Juniper, even if such feature, function, service, application,
operation, or capability is enabled without a key; (g) distribute any key for the Software provided by Juniper to any third party; (h) use the
iiiCopyright © 2010, Juniper Networks, Inc.
Page 4

Software in any manner that extends or is broader than the uses purchased by Customer from Juniper or an authorized Juniper reseller; (i)
use Embedded Software on non-Juniper equipment; (j) use Embedded Software (or make it available for use) on Juniper equipment that
the Customer did not originally purchase from Juniper or an authorized Juniper reseller; (k) disclose the results of testing or benchmarking
of the Software to any third party without the priorwritten consent of Juniper; or (l) use the Software in any manner other than as expressly
provided herein.
5. Audit. Customer shall maintain accurate records as necessary to verify compliance with this Agreement. Upon request by Juniper,
Customer shall furnish such records to Juniper and certify its compliance with this Agreement.
6. Confidentiality. The Parties agree that aspects of the Software and associated documentation are the confidential property of Juniper.
As such, Customer shall exercise allreasonable commercial efforts to maintain the Software and associated documentation in confidence,
which at a minimum includes restricting access to the Software to Customer employees and contractors having a need to use the Software
for Customer’s internal business purposes.
7. Ownership. Juniper and Juniper’s licensors, respectively, retain ownership of all right, title, and interest (including copyright) in and to
the Software, associated documentation, and all copies of the Software. Nothing in this Agreement constitutes a transfer or conveyance
of any right, title, or interest in the Software or associated documentation, or a sale of the Software, associated documentation, or copies
of the Software.
8. Warranty, Limitation of Liability, Disclaimer of Warranty. The warranty applicable to the Software shall be as set forth in the warranty
statementthat accompaniesthe Software (the“Warranty Statement”).Nothing inthis Agreement shallgive riseto any obligation to support
the Software. Support services may be purchased separately. Any such support shall be governed by a separate, written support services
agreement. TO THE MAXIMUM EXTENT PERMITTED BY LAW, JUNIPER SHALL NOT BE LIABLE FOR ANY LOST PROFITS, LOSS OF DATA,
OR COSTSOR PROCUREMENTOF SUBSTITUTEGOODS ORSERVICES,OR FOR ANY SPECIAL,INDIRECT,OR CONSEQUENTIALDAMAGES
ARISING OUTOF THIS AGREEMENT,THE SOFTWARE,OR ANY JUNIPEROR JUNIPER-SUPPLIEDSOFTWARE. INNO EVENT SHALLJUNIPER
BE LIABLE FOR DAMAGES ARISING FROM UNAUTHORIZED OR IMPROPER USE OF ANY JUNIPER OR JUNIPER-SUPPLIED SOFTWARE.
EXCEPT AS EXPRESSLY PROVIDED IN THE WARRANTY STATEMENT TO THE EXTENT PERMITTED BY LAW, JUNIPER DISCLAIMS ANY
AND ALL WARRANTIES IN AND TO THE SOFTWARE (WHETHER EXPRESS, IMPLIED, STATUTORY, OR OTHERWISE), INCLUDING ANY
IMPLIED WARRANTY OF MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE, OR NONINFRINGEMENT. IN NO EVENT DOES
JUNIPER WARRANT THAT THE SOFTWARE, OR ANY EQUIPMENT OR NETWORK RUNNING THE SOFTWARE, WILL OPERATE WITHOUT
ERROR OR INTERRUPTION, OR WILL BE FREE OF VULNERABILITY TO INTRUSION OR ATTACK. In no event shall Juniper’s or its suppliers’
or licensors’ liability to Customer, whether in contract, tort (including negligence), breach of warranty, or otherwise, exceed the price paid
by Customer for the Software that gave rise to the claim, or if the Software is embedded in another Juniper product, the price paid by
Customer for such other product. Customer acknowledges and agrees that Juniper has set its prices and entered into this Agreement in
reliance upon the disclaimers of warranty and the limitations of liability set forth herein, that the same reflect an allocation of risk between
the Parties (including the risk that a contract remedy may fail of its essential purpose and cause consequential loss), and that the same
form an essential basis of the bargain between the Parties.
9. Termination. Any breach of this Agreement or failure by Customer to pay any applicable fees due shall result in automatic termination
of the license granted herein. Upon such termination, Customer shall destroy or return to Juniper all copies of the Software and related
documentation in Customer’s possession or control.
10. Taxes. All license fees payable under this agreement are exclusive of tax. Customer shall be responsible for paying Taxes arising from
the purchase of the license, or importation or use of the Software. If applicable, valid exemption documentation for each taxing jurisdiction
shall be provided to Juniper prior to invoicing, and Customer shall promptly notify Juniper if their exemption is revoked or modified. All
payments made by Customer shall be net of any applicable withholding tax. Customer will provide reasonable assistance to Juniper in
connection with such withholding taxes by promptly: providing Juniper with valid tax receipts and other required documentation showing
Customer’s payment of any withholding taxes; completing appropriate applications that would reduce the amount of withholding tax to
be paid; and notifying and assisting Juniper in any audit or tax proceeding related to transactions hereunder. Customer shall comply with
all applicable tax laws and regulations, and Customer will promptly pay or reimburse Juniper for all costs and damages related to any
liability incurred by Juniper as a result of Customer’s non-compliance or delay with its responsibilities herein. Customer’s obligations under
this Section shall survive termination or expiration of this Agreement.
11. Export. Customer agrees to comply with all applicable export laws and restrictions and regulations of any United States and any
applicable foreign agency or authority, and not to export or re-export the Software or any direct product thereof in violation of any such
restrictions, laws or regulations, or without all necessary approvals. Customer shall be liable for any such violations. The version of the
Software supplied to Customer may contain encryption or other capabilities restricting Customer’s ability to export the Software without
an export license.
Copyright © 2010, Juniper Networks, Inc.iv
Page 5

12. Commercial Computer Software. The Software is “commercial computer software” and is provided with restricted rights. Use,
duplication, or disclosure by the United States government is subject to restrictions set forth in this Agreement and as provided in DFARS
227.7201 through 227.7202-4, FAR 12.212, FAR 27.405(b)(2), FAR 52.227-19, or FAR 52.227-14(ALT III) as applicable.
13. Interface Information. To the extent required by applicable law, and at Customer's written request, Juniper shall provide Customer
with the interface information needed to achieve interoperability between the Software and another independently created program, on
payment of applicable fee, if any. Customer shall observe strict obligations of confidentiality with respect to such information and shall use
such information in compliance with any applicable terms and conditions upon which Juniper makes such information available.
14. Third Party Software. Any licensor of Juniper whose softwareis embedded in the Software and any supplier of Juniper whose products
or technology are embedded in (or services are accessed by) the Software shall be a third party beneficiary with respect to this Agreement,
and such licensor or vendor shall have the right to enforce this Agreement in itsown name asif it wereJuniper. In addition, certain thirdparty
software may be provided with the Software and is subject to the accompanying license(s), if any, of its respective owner(s). To the extent
portions of the Software are distributed under and subject to open source licenses obligating Juniper to make the source code for such
portions publicly available (such as the GNU General Public License (“GPL”) or the GNU Library General Public License (“LGPL”)), Juniper
will make such source code portions (including Juniper modifications, as appropriate) available upon request for a period of up to three
years from the date of distribution. Such request can be made in writing to Juniper Networks, Inc., 1194 N. Mathilda Ave., Sunnyvale, CA
94089, ATTN: General Counsel. You may obtain a copy of the GPL at http://www.gnu.org/licenses/gpl.html, and a copy of the LGPL
at http://www.gnu.org/licenses/lgpl.html .
15. Miscellaneous. This Agreement shall be governed by the laws of the State of California without reference to its conflicts of laws
principles. The provisions of the U.N. Convention for the International Sale of Goods shall not apply to this Agreement. For any disputes
arising under this Agreement, the Parties hereby consent to the personal and exclusive jurisdiction of, and venue in, the state and federal
courts within Santa Clara County, California. This Agreement constitutes the entire and sole agreement between Juniper and the Customer
with respect to the Software, and supersedes all prior and contemporaneous agreements relating to the Software, whether oral or written
(including any inconsistent terms contained in a purchase order), except that the terms of a separate written agreement executed by an
authorized Juniper representative and Customer shall govern to the extent such terms are inconsistent or conflict with terms contained
herein. No modification to this Agreement nor any waiver of any rights hereunder shall be effective unless expressly assented to in writing
by the party to be charged. If any portion of this Agreement is held invalid, the Parties agree that such invalidity shall not affect the validity
of the remainder of this Agreement. This Agreement and associated documentation has been written in the English language, and the
Parties agree that the English version will govern. (For Canada: Les parties aux présentés confirment leur volonté que cette convention de
même que tous les documents y compris tout avis qui s'y rattaché, soient redigés en langue anglaise. (Translation: The parties confirm that
this Agreement and all related documentation is and will be in the English language)).
vCopyright © 2010, Juniper Networks, Inc.
Page 6

Copyright © 2010, Juniper Networks, Inc.vi
Page 7

Table of Contents
About This Guide . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . xv
Objectives . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . xv
Audience . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . xv
Conventions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . xv
Documentation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . xvii
Documentation Feedback . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . xviii
Requesting Technical Support . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . xviii
Self-Help Online Tools and Resources . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . xix
Opening a Case with JTAC . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . xix
Part 1 Using the NSM Appliance
Chapter 1 Getting Started . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
About the NSM Appliances . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
Installation and Configuration Workflow . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
Hardware Installation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
NSM Appliance Ports . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
Installing the NSMXpress Hardware . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
Installing the NSM3000 Hardware . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
Initial Setup Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
Boot the NSM Appliance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
Set Up Your Appliance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
CLI Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
Web Interface Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
Chapter 2 Installing and Configuring NSM from the CLI . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Navigating the Menus . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
General Options . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Using nsm_setup . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Configuring the NSM Software . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Configuring a Regional Server . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
Configuring Typical Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
Configuring Custom Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
Configuring High Availability . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
Configuring Advanced Options . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
Configuring the Central Manager . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
Configuring High Availability . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
Configuring Advanced Options . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
Enabling and Configuring Remote Replication of the Database . . . . . . . 24
viiCopyright © 2010, Juniper Networks, Inc.
Page 8

NSMXpress and NSM3000 User Guide
Chapter 3 Configuring NSM from the Web Interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
Configuring Standard Configuration Options . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
Changing the Password . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
Setting Interface Options . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
Setting Routing Options . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
Changing the NSM Appliance Hostname . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
Adding DNS Servers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
Setting the System Time . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
Forwarding Local Status E-mails . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
Updating System Security . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
Saving Setup Options . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
The NSM Appliance Default Restoration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
Configuring the NSM Software . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
Configuring Basic Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
Configuring High Availability . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
Advanced Options . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
Enabling and Configuring Remote Replication of the Database . . . . . . . 37
Enabling and Configuring SRS (Regional Server Only) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
Installing NSM Software . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
Managing NSM Administration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
Changing the Superuser Password . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
Downloading NSM MIBS (Regional Server Only) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
Exporting Audit Logs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
Exporting Device Logs (Regional Server Only) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
Generating Reports (Regional Server Only) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
Modifying NSM Configuration Files . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
Backing Up the NSM Database . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
Changing the NSM Management IP . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
Scheduling Security Updates . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
Managing System Administration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
Rebooting or Shutting Down the NSM Appliance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
Changing the User Password . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
Configuring the Network . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
Network Interfaces . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
Routing and Gateways . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46
Hostname and DNS Clients . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46
Host Addresses . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47
Managing RADIUS Servers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47
Adding a RADIUS Server . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 48
Changing the Priority of RADIUS Servers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
Deleting a RADIUS Server . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
Editing RADIUS Server Parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
Monitoring with SNMP . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 50
SNMP Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 50
SNMP System Information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 51
SNMP Trap Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 52
Copyright © 2010, Juniper Networks, Inc.viii
Page 9

Table of Contents
Forwarding Syslog Messages . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 53
Viewing Syslog Receivers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 53
Adding and Configuring Syslog Receivers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 54
Editing Syslog Receiver Configurations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 56
Deleting Syslog Receivers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 56
Changing the System Time . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 56
Installing Updates . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 56
Managing Users . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 57
Creating New NSM Appliance Users . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 57
Deleting a User . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 58
Editing User Attributes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 59
Understanding User Profiles . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 59
Configuring the Web Interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 60
Maintaining NSM Appliances . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 61
Viewing System Statistics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 61
CPU . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 61
Log Rate . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 61
CPU Load . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 61
Memory Data . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 62
Network Data . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 62
Process Count . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 62
Disk Data . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 62
Tile All Graphs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 62
Upgrading the Recovery Partition . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 62
Troubleshooting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 63
Auditing User Operations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 63
Error Logs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 65
Network Utilities . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 66
Ping . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 66
Traceroute . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 67
Lookup . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 67
IP Subnet Calculator . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 68
Tech Support . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 68
Viewing System Information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 69
Part 2 Appendixes
Appendix A NSMXpress LEDs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 73
NSMXpress LEDs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 73
Part 3 Index
Index . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 77
ixCopyright © 2010, Juniper Networks, Inc.
Page 10

NSMXpress and NSM3000 User Guide
Copyright © 2010, Juniper Networks, Inc.x
Page 11

List of Figures
Part 1 Using the NSM Appliance
Chapter 1 Getting Started . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
Figure 1: Front Panel of NSMXpress . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
Figure 2: Rear Panel of NSM3000 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
Figure 3: Front Panel of NSM3000 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
Chapter 3 Configuring NSM from the Web Interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
Figure 4: Regional Server Configuration Main Menu . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
Figure 5: Central Manager Configuration Main Menu . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
Figure 6: High Availability Options . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
Figure 7: Shared Disk Options for Regional Servers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
Figure 8: Shared Disk Options for Central Managers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
Figure 9: HA Links Options . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
Figure 10: Redundant Links . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
Figure 11: HA Advanced Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
Figure 12: Advanced Options Menu . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
Figure 13: Remote Replication of Database Options . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
Figure 14: SRS Menu . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
Figure 15: Change Superuser Password . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
Figure 16: Download NSM MIBs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
Figure 17: Export Audit Logs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
Figure 18: Export Device Logs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
Figure 19: Generate Reports . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
Figure 20: NSM Configuration Files . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
Figure 21: Database Backup . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
Figure 22: Change Management IP . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
Figure 23: Schedule Security Updates . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
Figure 24: ReBoot or Shut Down . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
Figure 25: Change User Password . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
Figure 26: Network Interfaces Options . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
Figure 27: Network Interfaces . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46
Figure 28: Routes and Gateways . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46
Figure 29: DNS Client Options . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47
Figure 30: Host Address . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47
Figure 31: RADIUS Servers Dialog Box . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 48
Figure 32: Add RADIUS Server Dialog Box . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 48
Figure 33: Edit RADIUS Server Dialog Box . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 50
Figure 34: Configuring SNMP . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 51
Figure 35: Configuring SNMP System Information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 51
Figure 36: Configuring SNMP Traps . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 52
xiCopyright © 2010, Juniper Networks, Inc.
Page 12

NSMXpress and NSM3000 User Guide
Figure 37: Configuring a Syslog Receiver . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 55
Figure 38: NSMXpress Users Dialog Box . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 57
Figure 39: Create NSMXpress User Dialog Box . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 58
Figure 40: NSMXpress Users Dialog Box . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 58
Figure 41: Web Interface Access . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 61
Figure 42: System Statistics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 61
Figure 43: NSMXpress Actions Dialog Box . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 64
Figure 44: Search Results Dialog Box . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 65
Figure 45: Review Error Logs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 65
Figure 46: Error Log Detail . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 65
Figure 47: Network Utilities Options . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 66
Figure 48: Ping Utility . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 66
Figure 49: Traceroute Utility . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 67
Figure 50: Lookup Utility . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 68
Figure 51: IP Subnet Calculator . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 68
Figure 52: Juniper Tech Support . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 68
Figure 53: System Information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 69
Copyright © 2010, Juniper Networks, Inc.xii
Page 13

List of Tables
About This Guide . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . xv
Table 1: Notice Icons . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . xvi
Table 2: Text Conventions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . xvi
Table 3: Syntax Conventions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . xvii
Table 4: Network and Security Manager Publications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . xvii
Part 1 Using the NSM Appliance
Chapter 1 Getting Started . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
Table 5: Required Ports on an NSM Appliance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
Table 6: Ethernet Port LEDs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
Chapter 3 Configuring NSM from the Web Interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
Table 7: Viewing Syslog Receivers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 54
Table 8: NSM Appliance WebUI User Profiles and Permissions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 59
Part 2 Appendixes
Appendix A NSMXpress LEDs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 73
Table 9: NSMXpress LEDs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 73
xiiiCopyright © 2010, Juniper Networks, Inc.
Page 14

NSMXpress and NSM3000 User Guide
Copyright © 2010, Juniper Networks, Inc.xiv
Page 15
About This Guide
About This Guide contains the following sections:
•
Objectives on page xv
•
Audience on page xv
•
Conventions on page xv
•
Documentation on page xvii
•
Documentation Feedback on page xviii
•
Requesting Technical Support on page xviii
Objectives
Juniper Networks NSMXpress and NSM3000 are appliance versions of Network and
SecurityManager (NSM),a software application that centralizes control andmanagement
of your Juniper Networks devices. With NSM, Juniper Networks delivers integrated,
policy-based security and network management for network and security devices.
NSMXpress and NSM3000 run NSM 2010.4.
NSM appliances simplify the complexity of device administration by providing single,
integrated management interfaces that control device parameters. Each appliance is
preconfigured as either a regional server or central manager.
This guidedescribes how you can install NSM onto your NSM appliances. In addition, this
guide describes how to manage the appliance using the NSM command-line interface
(CLI) or the Web interface.
Audience
This guide is intended for system administrators responsible for the securityinfrastructure
of their organization. Specifically, this book provides procedures for firewall and VPN
administrators, network/security operations center administrators, and system
administrators responsible for user permissions on the network.
Conventions
The sample screens used throughout this guide are representations of the screens that
appear when you install and configure the NSM software. The actual screens you see
may differ.
xvCopyright © 2010, Juniper Networks, Inc.
Page 16

NSMXpress and NSM3000 User Guide
All examples show default file paths. If you do not accept the installation defaults, your
paths will vary from the examples.
Table 1 on page xvi defines notice icons used in this guide.
Table 1: Notice Icons
DescriptionMeaningIcon
Indicates important features or instructions.Informational note
Indicates a situation that might result in loss of data or hardware damage.Caution
Alerts you to the risk of personal injury or death.Warning
Table 2 on page xvi defines text conventions used in this guide.
Table 2: Text Conventions
Bold typeface like this
fixed-width font
Keynames linkedwith a plus (+) sign
Alerts you to the risk of personal injury from a laser.Laser warning
•
Represents commands and keywords
in text.
•
Represents keywords
•
Represents UI elements
Represents information as displayed on
the terminal screen.
keys simultaneously.
ExamplesDescriptionConvention
•
Issue the clock source command.
•
Specify the keyword exp-msg.
•
Click User Objects
user inputRepresents text that the user must type.Bold typeface like this
host1#
show ip ospf
Routing Process OSPF 2 with Router
ID 5.5.0.250
Router is an area Border Router
(ABR)
Ctrl + dIndicates that you must press two or more
Italics
The angle bracket (>)
•
Emphasizes words
•
Identifies variables
Indicates navigation paths through the UI
by clicking menu options and links.
•
The product supports two levels of
access, user and privileged.
•
clusterID, ipAddress.
Object Manager > User Objects > Local
Objects
Copyright © 2010, Juniper Networks, Inc.xvi
Page 17

Table 3 on page xvii defines syntax conventions used in this guide.
Table 3: Syntax Conventions
About This Guide
ExamplesDescriptionConvention
terminal lengthRepresent keywordsWords in plain text
mask, accessListNameRepresent variablesWords in italics
Words separated by the pipe ( | )
symbol
Words enclosed in brackets followed
by and asterisk ( [ ]*)
Documentation
Table 4 on page xvii describes documentation for NSM.
Table 4: Network and Security Manager Publications
Network and Security
Manager Installation Guide
variable to the left or right of this symbol. The
keywordor variable canbe optional or required.
can be entered more than once.
Represent required keywords or variables.Words enclosed in braces ( { } )
DescriptionBook
Describes the steps to install the NSM management system on a
single server or on separate servers. It also includes information on
how to install and run the NSMuser interface.This guideis intended
for IT administrators responsible for the installation or upgrade of
NSM.
diagnostic | lineRepresent a choice to select one keyword or
[ internal | external ]Represent optional keywords or variables.Words enclosed in brackets ( [ ] )
[ level1 | level2 | 11 ]*Represent optional keywords or variables that
{ permit | deny } { in |out } { clusterId
| ipAddress }
Network and Security
Manager Administration
Guide
Network and Security
Manager Configuring
ScreenOS Devices Guide
Describes how to use and configure key management features in
the NSM. Itprovides conceptual information, suggested workflows,
and examples. This guide is best used in conjunction with the NSM
Online Help,which provides step-by-step instructions for performing
management tasks in the NSM user interface (UI).
This guide is intended for application administrators or those
individuals responsible for owning the server and security
infrastructure and configuring the product for multiuser systems. It
is also intended for device configuration administrators, firewall
and VPN administrators, and network security operation center
administrators.
Describes NSM features related to device configuration and
management. It also explains how to configure basic andadvanced
NSM functionality, including deploying new device configurations,
managing security policies and VPNs, and general device
administration.
xviiCopyright © 2010, Juniper Networks, Inc.
Page 18
NSMXpress and NSM3000 User Guide
Table 4: Network and Security Manager Publications (continued)
DescriptionBook
Network and Security
Manager Online Help
Network and Security
Manager API Guide
Network and Security
Manager Release Notes
NSMXpress and NSM3000
User Guide
Documentation Feedback
We encourage you to provide feedback, comments, and suggestions so that we can
improve the documentation. You can send your comments to
techpubs-comments@juniper.net, or fill out the documentation feedback form at
https://www.juniper.net/cgi-bin/docbugreport/. If you are using e-mail, be sure to include
the following information with your comments:
Provides procedures for basic tasks in the NSM user interface. It
also includes a brief overview of the NSM system and a description
of the GUI elements.
Provides complete syntax and a description of the Simple Object
Access Protocol (SOAP) messaging interface to NSM.
Provides the latest information about features, changes, known
problems, resolved problems, and system maximum values. If the
information in the Release Notesdiffers from the information found
in the documentation set, follow the Release Notes.
Release Notes are included on the corresponding software CD and
are available on the Juniper Networks Website.
Describes how to set up andmanage an NSM appliance asa central
manager or regional server.
•
Document name
•
Document part number
•
Page number
•
Software release version (not required for Network Operations Guides [NOGs])
Requesting Technical Support
Technical productsupport isavailablethrough theJuniper Networks Technical Assistance
Center (JTAC). If you are a customer with an active J-Care or JNASC support contract,
or are covered under warranty, and need postsales technical support, you can access
our tools and resources online or open a case with JTAC.
•
JTAC policies—For a complete understanding of our JTAC procedures and policies,
review the JTAC User Guide located at
http://www.juniper.net/us/en/local/pdf/resource-guides/7100059-en.pdf .
•
Product warranties—For product warranty information, visit
http://www.juniper.net/support/warranty/ .
•
JTAC Hours of Operation —The JTAC centers have resources available 24 hours a day,
7 days a week, 365 days a year.
Copyright © 2010, Juniper Networks, Inc.xviii
Page 19

Self-Help Online Tools and Resources
For quick and easy problem resolution, Juniper Networks has designed an online
self-service portal called the Customer Support Center (CSC) that provides you with the
following features:
•
Find CSC offerings: http://www.juniper.net/customers/support/
•
Find product documentation: http://www.juniper.net/techpubs/
•
Find solutions and answer questions using our Knowledge Base: http://kb.juniper.net/
•
Download the latest versions of software and review release notes:
http://www.juniper.net/customers/csc/software/
•
Search technical bulletins for relevant hardware and software notifications:
https://www.juniper.net/alerts/
•
Join and participate in the Juniper Networks Community Forum:
http://www.juniper.net/company/communities/
•
Open a case online in the CSC Case Management tool: http://www.juniper.net/cm/
About This Guide
To verifyservice entitlement byproduct serial number,use our Serial Number Entitlement
(SNE) Tool: https://tools.juniper.net/SerialNumberEntitlementSearch/
Opening a Case with JTAC
You can open a case with JTAC on the Web or by telephone.
•
Use the Case Management tool in the CSC at http://www.juniper.net/cm/ .
•
Call 1-888-314-JTAC (1-888-314-5822 toll-free in the USA, Canada, and Mexico).
For international or direct-dial options in countries without toll-free numbers, visit us at
http://www.juniper.net/support/requesting-support.html
xixCopyright © 2010, Juniper Networks, Inc.
Page 20

NSMXpress and NSM3000 User Guide
Copyright © 2010, Juniper Networks, Inc.xx
Page 21

PART 1
Using the NSM Appliance
Part 1 contains the following chapters:
•
Getting Started on page 3
•
Installing and Configuring NSM from the CLI on page 13
•
Configuring NSM from the Web Interface on page 31
1Copyright © 2010, Juniper Networks, Inc.
Page 22

NSMXpress and NSM3000 User Guide
Copyright © 2010, Juniper Networks, Inc.2
Page 23

CHAPTER 1
Getting Started
This version of the NSM appliance comes preconfigured as a regional server or central
manager.
This chapter contains the following sections:
•
About the NSM Appliances on page 3
•
Hardware Installation on page 4
•
Initial Setup Configuration on page 8
About the NSM Appliances
NSMXpress and NSM3000 are appliance versions of Network and Security Manager
(NSM) and run NSM 2010.4. NSM appliances simplify the complexity of network
administrationby providing single, integrated management interfaces thatcontrol device
parameters.
These robust hardware management systems install in minutes with full high availability
(HA) support, making it easy to scale and deploy. Enterprise customers with limited
resources can benefit significantly from NSM appliances because it eliminates the need
to have dedicated resources for maintaining anetwork and security management solution.
NSM appliances make it easy for administrators to control device configuration, network
settings, and security policy settings for multiple families of Juniper Networks devices
including:
•
IDP Series IntrusionDetection and PreventionAppliances andFirewall and VPN devices
running ScreenOS.
•
Devices running Junos OS, such as J Series Services Routers, SRX Series Services
Gateways, EX Series Ethernet Switches, M Series Multiservice Edge Routers, and MX
Series Ethernet Services routers.
•
SA Series SSL VPN Appliances
•
IC Series Unified Access Control Appliances
For a complete list of supported device families and platforms, see the Network and
Security Manager Administration Guide.
Up to 10 administrators can log into an NSM appliance concurrently.
3Copyright © 2010, Juniper Networks, Inc.
Page 24

NSMXpress and NSM3000 User Guide
Installation and Configuration Workflow
This guide explains the steps for installing and configuring an NSM appliance and for
configuring NSM.
1. Install the NSM appliance hardware.
2. Set up the NSM appliance using the serial port.
3. Configure the NSM appliance software using either the CLI or the Web interface.
4. Configure the NSM software which is preinstalled in the NSM appliance, with
site-specific parameters.
Hardware Installation
We recommend that you install the NSM appliance on your LAN to ensure that it can
communicate withyour applicable resources,such asauthentication servers, DNSservers,
internal Web servers through HTTP/HTTPS, external Web sites through HTTP/HTTPS
(optional), the Juniper update server via HTTP, Network File System (NFS) file servers
(optional), and client/server applications (optional).
NSM Appliance Ports
NOTE: If you decide to install an NSM appliance in your DMZ, ensure that it
can connect to your internal resources.
Table 5 on page 5 provides required port information on the NSM appliances.
Copyright © 2010, Juniper Networks, Inc.4
Page 25

Table 5: Required Ports on an NSM Appliance
Chapter 1: Getting Started
Depends on
ConfigurationInternetLANDescriptionPortDirection
NoNoYesSSH command-line management22In
443
8443
7800
7808
7802
7803
7804
22Out
23
NoNoYesWeb interface for administrator
login
YesYesLANWebinterfacefor listening for NSM
API messages.
NoYesYesConnections from managed
devices to the NSM appliance
NoNoYesConnections from the NSM GUI
Client to NSM
YesNoYesHeartbeat between peers in anHA
cluster
YesYesYesConnections from managed IDP
devices to NSM
YesYesYesConnections from devices running
Junos, Secure Access devices, or
Infranet Controller devices
NoYesYesSSH connection to new managed
device
YesNoYesTelnet connection to new
managed device
For more information on ports, refer to the Network and Security Manager Installation
Guide.
Installing the NSMXpress Hardware
Follow these steps to unpack the NSMXpress appliance and connect it to your network.
80
123
NoNoYesDNS lookups53
YesYesNoSystem Security Updates from
Juniper Networks
YesNoYesShared Disk portmap lookup111
YesYesYesNetworkTime Protocol (NTP) time
synchronization
YesNoYesShared Disk NFS connection2049
5Copyright © 2010, Juniper Networks, Inc.
Page 26

NSMXpress and NSM3000 User Guide
To install NSMXpress:
1. Place the shipping container on a flat surface and remove the hardware components
with care.
2. Remove the NSMXpress device from the shipping container and place it on a flat
surface.
3. Mount NSMXpress in your server rack using the attached mounting brackets.
4. Plug the power cord into the AC receptacle on the rear panel.
If your NSMXpress contains two power supplies, plug a power cord into each AC
receptacle.
5. Plug the other end of the power cord into a wall socket.
If yourNSMXpress containstwo power supplies, plug each power cord intoa separate
power circuit to ensure that the NSMXpress continues to receive power if one of the
power circuits fails.
6. Plug the Ethernet cable into the port marked ETH0 on the front panel. See Figure 3
on page 8.
Figure 1: Front Panel of NSMXpress
7. Plug the null modem serial cable into the console port. See Figure 3 on page 8.
This cable was shipped with your NSMXpress. If you do not have this cable, use any
other null modem serial cable.
8. Push the power button in the upper left corner of the front panel.
The green LED below the power button turns on. The NSMXpress hard disk LED turns
on whenever the appliance reads data from or writes data toan NSMXpresshard disk.
The internal port uses two LEDs to indicate the LAN connection status, which is
described in Table 6 on page 6.
Hardware installation is now complete. The next step is to set up the software, as
described in “Initial Setup Configuration” on page 8.
Table 6 on page 6 provides LED information for the Ethernet ports.
Table 6: Ethernet Port LEDs
LED2LED 1LAN Status
OffOff10 Mbps connection
Copyright © 2010, Juniper Networks, Inc.6
Page 27
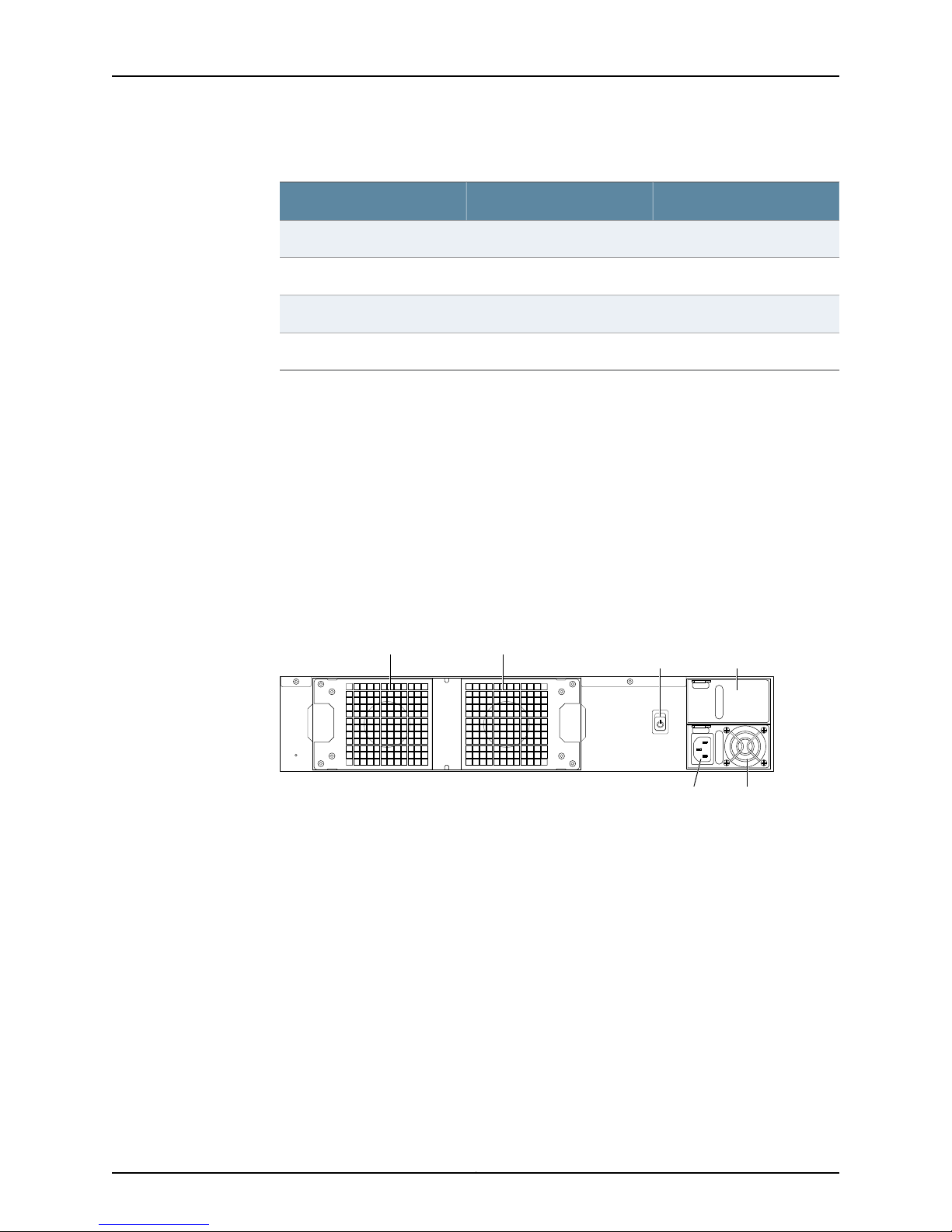
Table 6: Ethernet Port LEDs (continued)
g040042
Power
supply
AC Power
supply
receptacle
AC Power Blank power
supply tray
switch
Fan 0 Fan 1
Installing the NSM3000 Hardware
Follow these steps to unpack the NSM3000 appliance and connect it to your network.
To install NSM3000:
1. Place the shipping container on a flat surface and remove the hardware components
with care.
Chapter 1: Getting Started
LED2LED 1LAN Status
OffGreen100 Mbps connection
OffOrange1000 Mbps connection
BlinkingOrange, Green, or OffData is being transferred
OffOffNo connection
2. Remove the NSM appliance from the shipping container and place it on a flatsurface.
3. Mount the NSM appliance in your server rack using the attached mounting brackets.
4. Plug the power cord into the AC receptacle on the rear panel.
Figure 2: Rear Panel of NSM3000
If your NSM appliance contains two power supplies, plug a power cord into each AC
receptacle.
5. Plug the other end of the power cord into a wall socket.
If your NSM appliance contains two power supplies, plug each power cord into a
separate power circuit to ensure that the NSM appliance continues to receive power
if one of the power circuits fails.
6. Plug the Ethernet cable into the port marked ETH0 on the front panel.
7Copyright © 2010, Juniper Networks, Inc.
Page 28
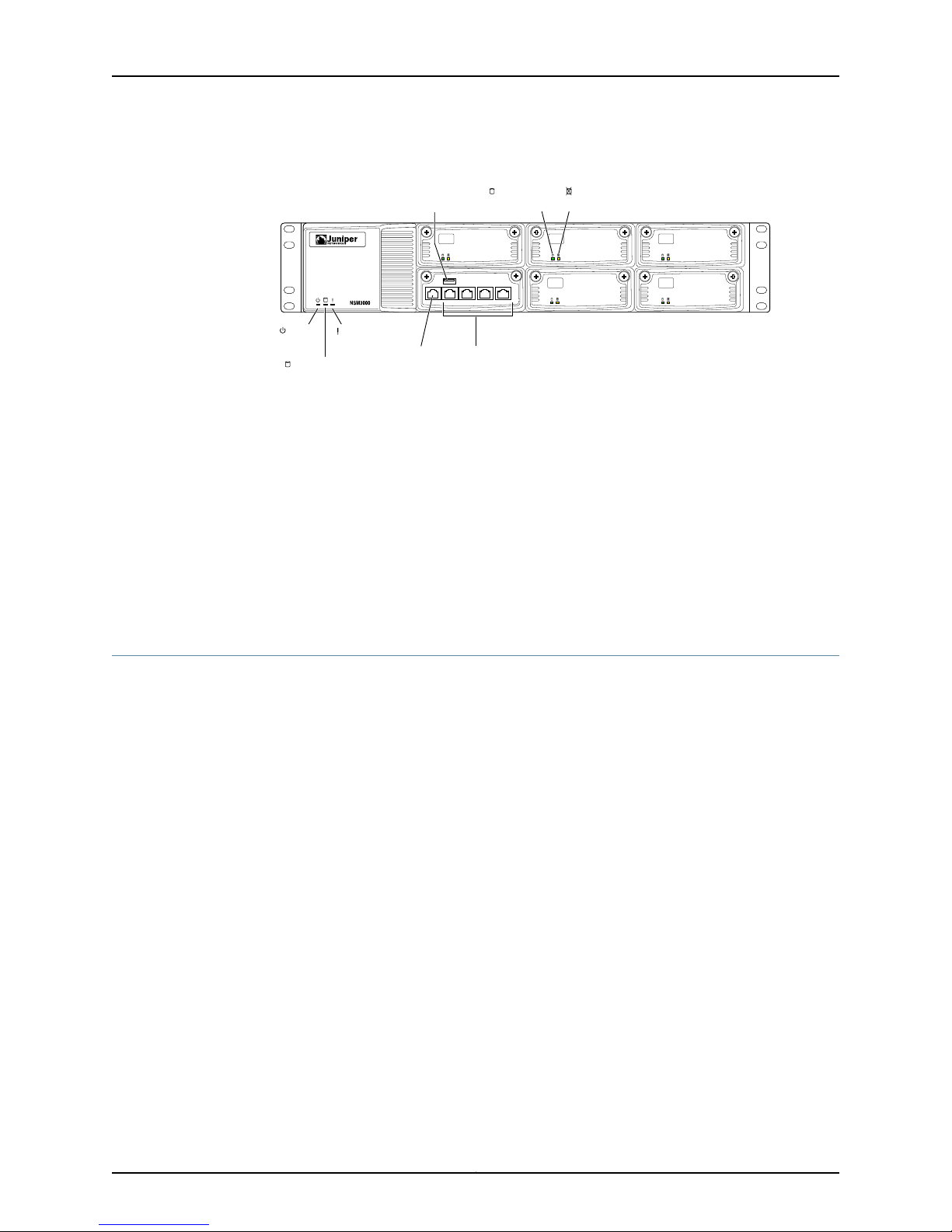
CONSOLE ETH3 ETH2 ETH1 ETH0
g040041
Power
LED
Hardware
LED
Hard disk LED
Console
port
Ethernet
ports
USB
port
Hard disk
Activity LED
Hard disk
Failure LED
NSMXpress and NSM3000 User Guide
Figure 3: Front Panel of NSM3000
7. Plug the null modem serial cable into the console port.
This cable was shipped with your NSM3000. If you do not have this cable, use any
other null modem serial cable.
8. Push the power button in the upper left corner of the front panel.
The green LED below the power button turns on. The NSM3000 hard disk LED turns
on whenever the appliance reads data from or writes data to an NSM3000 hard disk.
The internal port uses twoLEDs to indicate theLAN connectionstatus, which is described
in Table 6 on page 6.
Table 6 on page 6 provides LED information for the Ethernet ports.
Initial Setup Configuration
When you first turn on an unconfigured NSM appliance, you need to enter basic network
and machine information through the serial console to make your appliance accessible
to the network. After entering these settings, you can continue configuring the appliance
using the CLI or the Web interface. You are not prompted for the initial setup information
again.
This section describes the requiredserial console setupand the tasks you need to perform
when connecting to your NSM appliance for the first time:
•
Boot the NSM Appliance on page 8
•
Set Up Your Appliance on page 9
Boot the NSM Appliance
To configure the NSM appliance for the first time, you must attach your NSM appliance
to a console terminal running an emulation utility such as HyperTerminal.
1. Configure a console terminal or terminal emulation utility to use the following serial
connection parameters:
•
9600 bits per second
•
8-bit no parity (8N1)
Copyright © 2010, Juniper Networks, Inc.8
Page 29

Chapter 1: Getting Started
•
1 stop bit
•
No flow control
2. Connect the terminal or laptop to the null modem serial cable plugged into the NSM
appliance console port.
3. Turn on the NSM appliance.
When the NSM appliance is powered on, the serial console displays diagnostic
information before proceeding to the boot countdown. When complete, the serial
console displays the login prompt terminal emulator.
NSMXpress.juniper.net login:
4. Enter admin as your default login name.
5. Enter abc123 as your default password.
6. Change your default password when prompted. Enter the default password first,
followed by your new password. All passwords are case-sensitive.
Set Up Your Appliance
This section provides the minimuminformation necessary tomake your appliance active
on the network.
To set up your appliance either as a regional server or a central manager, follow these
steps:
1. Enter the IP address for interface eth0 and press Enter.
2. Enter the subnet mask for interface eth0 and press Enter.
3. Enter the default route or default gateway address for interface eth0 and press Enter.
Applying changes...
Re-loading database
ip_tables: (C) 2000–2002 Netfilter core team
ip_tables: (C) 2000–2002 Netfilter core team
ip_tables: (C) 2000–2002 Netfileter core team
Done!
Your NSMXpress is now active on the network.
To configure your system via a web browser, connect to:
https://10.150.43.205/administration
To configure your system via command line, type:
nsm_setup
For operation of NSM server, switch to user “nsm”.
Please consult NSM product documentation for details.
[admin@NSMXpress ~]$
9Copyright © 2010, Juniper Networks, Inc.
Page 30

NSMXpress and NSM3000 User Guide
To complete the setup process using the CLI, go to “CLI Configuration” on page 10. To
complete the setup process usingthe Webinterface, go to “Web Interface Configuration”
on page 11.
CLI Configuration
To finish initial setup from the CLI, use the following steps. If you are logged in, enter
nsm_setup at the command prompt.
If you are not logged on, follow these steps:
1. Enter your admin username, and then press Enter.
2. Enter your password and then press Enter.
Juniper NSMXpress OS build 2.105498
NSM 2010.4Kernel 2.6.9–55.0.2.ELsmp on an i686
NSMXpress.Juniper.net login: admin
Password:
Last login: Tue May 27 17:20:25 on ttyS0
Run NSMXpress system setup? [y/N]
3. Enter y to run the system setup program from the CLI.
NOTE: These values are not case-sensitive. However, the uppercase N
indicates it is the default value. Any keystroke, including Enter but not y
or Y, accepts the default value.
4. Go to “Installing and Configuring NSM from the CLI” on page 13 for information about
how to install and configure NSM on your NSM appliance from the CLI.
NSM Appliance Users
An NSM appliance has three user levels. All users log in as the “admin” user. To use the
command line to administer NSM, change tothe “nsm”user. For advancedadministration,
change to the “root” user.
The following users are available to manage an appliance.
•
“admin” user—Logs into the NSM appliance setup program and changesto “nsm” user
or “root” user from the command line.
•
“nsm” user—Administers NSM services. To change to the “nsm” user from the “admin”
user, go to the $ prompt, enter sudo su - nsm for the $ nsm prompt, then enter the
“admin” password you set when logging into the NSM appliance. To return to the
“admin” user, enter exit at the $ prompt.
•
“root” user—Administers advanced system settings. To change to “root” user from the
“admin” user, go to the $ prompt, enter sudosu - root for the # root prompt, then enter
the “admin” password you set when logging into the NSM appliance. To return to the
“admin” user, enter exit from the # prompt.
Copyright © 2010, Juniper Networks, Inc.10
Page 31

Chapter 1: Getting Started
Web Interface Configuration
To finish initial setup from a Web interface, use the following steps.
1. Copy the URL (starting with https://) from the terminal emulator after installing the
NSM appliance:
Your NSMXpress is now active on the network.
To configure your system via a web browser, connect to:
https//10.150.43.205/administration
2. Open a Web browser and paste the URL into the address text box.
3. Press Enter to open the NSM appliance login page.
4. Enter the admin user name and password and then click Login.
5. See “Configuring NSM from the Web Interface” on page 31 for details about how to
install and configure NSM on your NSM appliance from the Web interface.
11Copyright © 2010, Juniper Networks, Inc.
Page 32

NSMXpress and NSM3000 User Guide
Copyright © 2010, Juniper Networks, Inc.12
Page 33

CHAPTER 2
Installing and Configuring NSM from the
CLI
This chapter describes how to install and configure NSM on your NSM appliance from
the command-line interface (CLI). It contains the following sections:
•
Navigating the Menus on page 13
•
Configuring the NSM Software on page 15
•
Configuring a Regional Server on page 16
•
Configuring the Central Manager on page 21
•
Configuring Standard Configuration Options on page 25
•
The NSM Appliance Default Restoration on page 29
Navigating the Menus
As youconfigure NSM on your NSM appliance, the following standard navigational menu
options are available to you. This section provides information on general options you
can use during setup and configuration. These options include:
•
General Options on page 13
•
Using nsm_setup on page 14
General Options
The NSM Configuration Main Menu has the following options:
NSM Configuration Main Menu
1> Management IP [10.150.43.205]
The IP address on this server that will be
used for management
2> NSM 'super' password []
Password for 'super' user
3> GUI server one-time password []
Password to initiate authentication
between HA peers and to Central Manager.
This password must be the same for all
NSM servers in this installation.
13Copyright © 2010, Juniper Networks, Inc.
Page 34

NSMXpress and NSM3000 User Guide
4> NSM License type []
Specify a license file, or select "Base Install"
to use the built-in limited device license.
A> Apply settings
C> Cancel all changes and quit
R> Redraw menu
Choice [1-4,A,C,R]:
To select an option, enter the number at the prompt and then press Enter. The following
options are available on most menus:
•
Numbered Options—Enter setting options by number (1, 2, and so on) to access
individual parameters or open menus.
•
Apply settings—Enter A to apply and save any modifications you have made and take
you out of the setup program.
•
Cancel all changes and quit—Enter C to leave the setup program without saving any
changes you made since you last saved.
Using nsm_setup
•
Redraw menu—Enter R to redraw the screen text.
•
Main Menu/Return to Main Menu—Enter M to return to the main menu. This option is
last on most menus.
•
Quit—Enter Q to exit from the setup program. You will be prompted to save or cancel
any changes you made since you last saved:
Q> Quit
R> Redraw menu
Choice [1–9,Q,R]: Q
After initial setup, you can cancel out of the setup program and later return to it. Follow
these steps to return to the NSMappliance setup program. The steps in this procedure
assume the NSMappliance is connected to a computer running a terminal emulation
program. If not, see “Initial Setup Configuration” on page 8 for details.
NOTE: Run nsm_setup with your “admin” user login only. Do not run
nsm_setup as an “nsm” user.
To return to the setup program after the initial setup:
1. Turn on the NSM appliance and wait for the login prompt:
Juniper NSMXpress NSM 2010.4Kernel 2.6.9–42.0.8.ELsmp on an i686
NSMXpress.juniper.net logon: admin
Password:
Las Login: Tue May 17 09:43:50 on tty50
Run NSMXpress system setup? [y/N] N
Copyright © 2010, Juniper Networks, Inc.14
Page 35

Chapter 2: Installing and Configuring NSM from the CLI
To start system setup manually, type:
nsm_setup
for operation of NSM server, switch to user “nsm”.
Please consult NSM product documentation for details.
[admin@NSMXpress ~]$
2. Log in using your “admin” user name and password.
3. Enter nsm_setup at the prompt.
4. Enter your password and press Enter.
5. From the Settings menu:
•
For a regional server, enter 9, and then enter 1 to display the NSM Configuration
Main Menu for typical settings, or enter 2 for custom settings.
•
For a central manager, enter 9 to display the Configuration Main Menu.
Configuring the NSM Software
After you log in as an “admin” user, an initial setup script walks you through additional
configurationsystemsettings before finalizing theNSM installation. This section describes
that setup process.
The steps in this procedure assume you:
•
Have completed all appropriate steps in “Getting Started” on page 3.
•
Have a console terminal or terminal emulation utility running.
•
See the following command output in the emulation utility window:
Your NSMXpress is now active on the network.
To configure your system via a web browser, connect to:
https://10.150.43.205/administration
To configure your system via command line, type:
nsm_setup
For operation of NSM server, switch to user “nsm”
Please consult NSM product documentation for details.
[admin@NSMXpress “]$
Your NSM appliance comes preconfigured as a regional server or a central manager, as
described in the following sections:
•
Configuring a Regional Server on page 16
•
Configuring the Central Manager on page 21
15Copyright © 2010, Juniper Networks, Inc.
Page 36

NSMXpress and NSM3000 User Guide
Configuring a Regional Server
For details onusing the general setupmenu items,see “Navigating the Menus”on page13.
To configure the regional server, select one of the following options by number:
•
Typical Settings—Enter 1 to select typical settings. This option provides a simplified
menu to install a regional server. When using these options neither HA nor statistical
report server (SRS) can be in use.
•
Custom Settings—Enter 2 to select custom settings. This option provides full access
to all configuration options including HA and SRS for regional server.
The following sections provide details of these options:
•
Configuring Typical Settings on page 16
•
Configuring Custom Settings on page 17
Configuring Typical Settings
This section describes the options that are available for a typical installation for the
regional server:
NSM Configuration Main Menu
1> Management IP [10.150.43.205]
The IP address on this server that will be
used for management
2> NSM 'super' password []
Password for 'super' user
3> GUI server one-time password []
Password to initiate authentication
between HA peers and to Central Manager.
This password must be the same for all
NSM servers in this installation.
4> NSM License type []
Specify a license file, or select "Base Install"
to use the built-in limited device license.
A> Apply settings
C> Cancel all changes and quit
R> Redraw menu
Choice [1-4,A,C,R]:
You have the following options:
•
Management IP—Enter 1 to select interface eth0 or eth1 as the primary IP address for
your management server. Once configured, the setup program displays the IP address
for the interface you selected.
•
NSM ‘super’ password—Enter 2 to specify an NSM super password. This password
must be at least eight characters long and is case-sensitive. This password is used by
Copyright © 2010, Juniper Networks, Inc.16
Page 37

the NSM superuser (also referred to as the NSM administrator). This user has the
highest level of privilege in NSM.
•
GUI Server one-time password—Enter 3 to specify this password. This password
authenticates this server to its peers in a high-availability configuration, and to the
central manager.
•
NSM License type [Base Install]—Enter 4 to specify the license option. Enter Base
Install to use the built-in limited device license for as many as 25 devices. This option
is the default. Otherwise, enter the filename of the license file you purchased from
Juniper Networks that permits you to manage more than 25 devices.
For additional details about NSM licensing, see the Network and Security Manager
Installation Guide.
Configuring Custom Settings
This section describes the custom options that are available for a regional server
configuration. The custom options include the typical options described in the previous
section as well as the following two options:
5> Menu: High Availability [Off]
Chapter 2: Installing and Configuring NSM from the CLI
6> Menu: Advanced Options
You have the following options:
•
High Availability—Enter 5 to open a menu to configure HA.
•
AdvancedOptions—Enter 6to open a menuof additionalconfigurableoptions, including
the port number for receiving messages through the NSM API, remote database
replication details, and the Statistical Report Server (SRS).
The following sections provide details about these options:
•
Configuring High Availability on page 17
•
Configuring Advanced Options on page 19
Configuring High Availability
NOTE: When installing NSM regional server in a high availability configuration
with a shared disk, you must first revert the system to factory default values
using the boot menu. See “The NSM Appliance Default Restoration” on
page 29 for details.
The following options are available to configure high availability (HA) on the regional
server.
•
High Availability—Enter 1 to turn HA on or off.
•
Primary Status—Enter 2to specifythe NSMappliance aseither theprimary or secondary
server. At the next prompt, enter y for the primary server.Enter n for a secondary server.
•
HA Remote IP—Enter 3 to specify the IP address for the HA peer in the HA cluster.
17Copyright © 2010, Juniper Networks, Inc.
Page 38

NSMXpress and NSM3000 User Guide
•
HA Link Failure Detection IP—Enter 4 to specify the IP address of a machine outside
the HA cluster that you can ping to verify connection status.
•
HA Inter-server password—Enter 5 to specify the heartbeat password used between
the primary and secondary servers.
•
Menu: Shared Disk—Enter 6 to open a menu to help you configure a shared disk. NSM
appliances support shared disks with NFS only. Because of the data-intensive nature
of NSM, we recommend gigabit speed links (1000 Mbps) for shared disk usage. For
more information on options available to you for custom settings, refer to the Network
and Security Manager Installation Guide.
1> Shared Disk: Gui Server [n]
If 'y', data directory for GUI Server is a shared disk partition
2> Shared Disk: Device Server [n]
If 'y', data directory for Device Server is a shared disk partition
3> Shared Disk Source (NFS) []
Source of shared disk, e.g. /dev/sdc1 or server:/share
4> Shared Disk NFS Mount Options [rw]
Options when mounting shared disk e.g. rw, intr, tcp, soft, timeo=2
5> Return to High Availability menu
•
Menu: HA Links—Enter 7 to open a menu to help you configure the second HA link in
the HA cluster. Use the items in this menu to set up a redundant link for the HA cluster.
If you are going to use a second link, you need to set the IP address for eth1 before
configuring this setting (see “Setting Interface Options” on page 26 for more
information). Setting a redundant link is optional. For more information on options
available to you for custom settings, refer to the Network and Security Manager
Installation Guide.
If you configure HA with just one heartbeat link, then device management traffic and
data replication traffic both usethat link.If youconfigure two links, device management
traffic uses the first link and data replication uses the second.
If the HA link count is set to 1, the only options available are to set the HA link count
and to return to the High Availability menu. If the HA link count is set to 2, all options
are available.
1> HA Link count [2]
Number of heartbeat links between the Primary and SecondaryServers.
2> HA Link 2 Local IP []
IP address for this machine's secondary heartbeat link
3> HA Link 2 Remote IP []
IP address for the peer's secondary heartbeat link
4> HA Remote Replication IP []
IP address used for remote HA replications
5> Return to High Availability Menu
Copyright © 2010, Juniper Networks, Inc.18
Page 39

Chapter 2: Installing and Configuring NSM from the CLI
•
Menu: HA Advanced Settings—Enter 8 to open a menu to configure HA advanced
settings. For more information on options available to you for custom settings, refer
to the Network and Security Manager Installation Guide.
1> HA Heartbeat Frequency [15]
Time interval in seconds between heartbeat messages (Default is 15
seconds)
2> HA Heartbeat Failure Threshold [4]
Number of missing heartbeat messages before automatic switchover
occurs (Default is 4 missing messages)
3> HA Data Replication Timeout [1800]
Rsync Command Replication Timeout (Default is 1800 seconds)
4> Return to high Availability menu
Configuring Advanced Options
The Advanced Options menu provides the following configuration options:
Menu: Advanced Options
1> https port for NBI service [8443]
The port number to listen for NBI
(Default is 8443)
2> Menu: Remote Replication of Database [Off]
3> Menu: SRS [Off]
M> Main Menu
R> Redraw menu
Choice [1-3,M,R]:
You have the following options:
•
https portfor NBIservice—Enter 1 to change the port number for listeningfor messages
for the NSM API. In response to the prompt, enter a value in the range 1025 through
65535. Any number outside this range returns an error message. The default value is
8443.
•
Menu: Remote Replication of Database—Enter 2 to display a menu of options for
configuring thetime of day to take the backup, the location of the backup, and timeout
value.
•
Menu: SRS—Enter 3 to open a menu to configure Statistical Report Server (SRS).
The following sections provide details about configuring remote backup and SRS:
•
Enabling and Configuring Remote Replication of the Database on page 20
•
Enabling and Configuring the Statistical Report Server on page 20
19Copyright © 2010, Juniper Networks, Inc.
Page 40

NSMXpress and NSM3000 User Guide
Enabling and Configuring Remote Replication of the Database
On the Advanced Options menu, enter 2 to open a menu that allows you to mirror the
daily backup to an external server. You can toggle it on or off. After you turn it on, use the
menu options to configure this option:
1> Remote Replication of Database [n]
If 'y', local backups will be sent to a remote backup machine
2> Hour of day to Replicate Database [02]
Hour to start a backup
3> Remote backup IP [ ]
IP address of a remote backup machine
4> Remote Replication Timeout (seconds) [1800]
Rsync Command Backup Timeout (seconds)
(Default is 1800 seconds)
The screen always shows the current status of the remote backup database. If no status
exists, the option has not yet been configured.
•
Remote Replication of Database—Enter 1 to turn remote replication on or off. At the
next prompt, enter y to change the state.
•
Hour of day to Replicate Database—Enter 2 to start the backup at the specified time.
The valid range is 00-23.
•
Remote Backup IP—Enter 3 to specify the IP address of the remote backup machine.
Backup information is copied to the /var/netscreen/dbbackup directory on the remote
server. The “nsm” user must exist on both servers and you must establish an SSH trust
relationship. See the Network and Security Manager Installation Guide for details.
•
Remote Replication Timeout—Enter 4 to time out the remote backup. The valid range
is 1-65535 seconds.
Enabling and Configuring the Statistical Report Server
The following options are available to configure the statistical report server (SRS):
NOTE: SRS must be installed on a separate server from NSM.
1> SRS [n]
Statistical Report Server will be used with this GUI Server
2> SRS DB IP []
Database server IP address
3> SRS DB Type [pgsql]
Database Type
4> SRS Database Name [netscreen]
Database name
5> SRS DB Owner Name [netscreen]
Database user name
Copyright © 2010, Juniper Networks, Inc.20
Page 41

Chapter 2: Installing and Configuring NSM from the CLI
6> SRS DB Owner Password []
Database password
You have the following options:
•
SRS—Enter 1 to turn the statistical report server on or off. At the next prompt, enter y
to turn it on or n to turn it off. If you turn it on, the SRS will be used with the GUI Server.
•
SRS DB IP—Enter 2 to specify the IP address for the server on which you have installed
the SRS database server.
•
SRS DB Type—Enter 3 to specify the database type. The options are pgsql (default),
oracle, and mssql.
•
SRS Database Name—Enter 4 to specify the name of the SRS database on the SRS
server. The default value for this option is netscreen.
•
SRS DB Owner Name—Enter 5 to specify the name of the SRS database owner. The
default value for this option is netscreen.
•
SRS DB Owner Password—Enter 6 to specifythe ownerpasswordfor theSRS database.
At least eight characters are required. The password is case-sensitive.
Click Submit to save the options and return to the NSM Configuration Main Menu.
Configuring the Central Manager
For details about using the general setup menu items, see “Navigating the Menus” on
page 13.
This sectiondescribes the options that are available for acentral managerconfiguration.
The central manager main menu options are:
NSM Configuration Main Menu
1> Management IP [10.150.43.205]
The IP address on this server that will be
used for management
2> NSM 'super' password []
Password for 'super' user
3> GUI server one-time password []
Password for authentication between
HA peers and to all Regional Servers
4> Menu: High Availability [Off]
5> Menu: Advanced Options
A> Apply settings
C> Cancel all changes and quit
R> Redraw menu
Choice [1-5,A,C,R]:
You have the following options:
21Copyright © 2010, Juniper Networks, Inc.
Page 42

NSMXpress and NSM3000 User Guide
•
Management IP—Enter 1 to select interface eth0 or eth1 as the primary IP address for
your management server. Once configured, the setup program displays the IP address
for the interface you selected.
•
NSM super password—Enter 2 to specify an NSM “super” password. This password
must be at least eight characters long and is case-sensitive. This password is used by
the NSM superuser (also referred to as the NSM administrator). This user has the
highest level of privileges in NSM.
•
GUI Server one-time password—Enter 3 to specify this password. This password
authenticates this server to its peer in a high-availability configuration, and to regional
servers.
•
Menu: HighAvailability—Enter 4 to opena menuto configure HA. See “Configuring High
Availability” on page 22.
•
Menu: Advanced Options—Enter 5 to open a menu of additional options, including the
port number for receiving messages through the NSM API, and remote database
replication details.
The following sections provide procedures for configuring HA and advanced options:
•
Configuring High Availability on page 22
•
Configuring Advanced Options on page 24
Configuring High Availability
To configure high availability (HA), from the NSM Configuration Main menu, enter 4. The
NSM appliance displays the High Availability menu:
1> High Availability [n]
Whether to enable HA on this server or not
2> Primary Status [y]
If 'y', this machine is a Primary Server
and if 'n' this machine is a Secondary
Server
3> HA Remote IP []
IP address for the peer's primary
heartbeat link
4> HA Link Failure Detection IP []
IP address outside the HA cluster
5> HA Inter-server password []
Shared password for heartbeat
6> Menu: Shared Disk [Off]
7> Menu: HA Links
8> Menu: HA Advanced Settings
The following options are available to configure HA.
Copyright © 2010, Juniper Networks, Inc.22
Page 43

Chapter 2: Installing and Configuring NSM from the CLI
•
High Availability—Enter 1 to turn HA on or off.
•
Primary Status—Enter 2 to set the NSM appliance as either the primary or secondary
server. At the next prompt, enter y for a primary server; enter n for a secondary server.
•
HA Remote IP—Enter 3 to set the IP address for the HA peer in the HA cluster.
•
HA Link Failure Detection IP—Enter 4 to set the IP address of a computer outside the
HA cluster that you can ping to verify connection status.
•
HA Inter-server password—Enter 5 to set the heartbeat password used between the
primary and secondary servers.
•
Menu: Shared Disk—Enter 6 to open the Shared Disk menu.
The options in this menu help you configure a shared disk. NSM supports shared disk
via NFS only. Due to the data-intensive nature of NSM, we recommend gigabit speed
links (1000 Mbps) for shared disk use. For more information on custom settings, refer
to the Network and Security Manager Installation Guide.
1> Shared Disk: Gui Server [n]
If 'y', data directory for GUI Server
is a shared disk partition
2> Shared Disk Source (NFS) []
Source of shared disk, e.g. /dev/sdc1
or server:/share
3> Shared Disk NFS Mount Options []
Options when mounting shared disk
e.g. rw,intr,tcp,soft,timeo=2
4> Return to High Availability menu
•
Menu: HA Links—Enter 7 to open the HA Links menu.
The options in this menu help you configure the second HA link in the HA cluster. If you
are going to use a second link, you needto set the IP address for eth1 before configuring
this setting (see“Setting Interface Options” on page26 for details). Setting aredundant
link is optional. For more information on options available to you for custom settings,
refer to the Network and Security Manager Installation Guide.
If the HA link count is set to 1, the only options available are to set the HA link count
and to return to the High Availability menu. If the HA link count is set to 2, all options
are available.
1> HA Link count [2]
Number of heartbeat links between the Primary and Secondary
Server.
2> HA Link 2 Local IP []
IP address for this machine's secondary heartbeat link
3> HA Link 2 Remote IP []
IP address for the peer's secondary heartbeat link
4> HA Remote Replication IP []
IP address used for remote HA replications
5> Return to High Availability menu
23Copyright © 2010, Juniper Networks, Inc.
Page 44

NSMXpress and NSM3000 User Guide
•
Menu: HA Advanced Settings—Enter 8 to open the HA Advanced Settings menu. For
more information about HA advanced settings, refer to the Network and Security
Manager Installation Guide.
1> HA Heartbeat Frequency [15]
Time interval in seconds between heartbeat messages (Default is 15
seconds)
2> HA Heartbeat Failure Threshold [4]
Number of missing heartbeat messages before automatic switchover
occurs (Default is 4 missing messages)
3> HA Data Replication Timeout [1800]
Rsync Command Replication timeout (Default is 1800 seconds)
4> Return to High Availability menu
Configuring Advanced Options
To configure advanced options, from the NSM Configuration Main menu, enter 5. The
NSM appliance displays the Advanced Options menu:
Menu: Advanced Options
1> https port for NBI service [8443]
The port number to listen for NBI
(Default is 8443)
2> Menu: Remote Replication of Database [Off]
M> Main Menu
R> Redraw menu
Choice [1-2,M,R]:
You have the following options:
•
https portfor NBIservice—Enter 1 to change the port number for listeningfor messages
for the NSM API. In response to the prompt, enter a value in the range 1025 through
65535. Any number outside this range returns an error message. The default value is
8443.
•
Menu: Remote Replication of Database—Enter 2 to display a menu of options for
configuring thetime of day to take the backup, the location of the backup, and timeout
value. See “Enabling and Configuring Remote Replication of the Database”on page24.
Enabling and Configuring Remote Replication of the Database
On the Advanced Options menu, enter 2 to open a menu that allows you to mirror the
daily backup to an external server. You can toggle it on or off. After you turn it on, use the
menu options to configure this option:
1> Remote Replication of Database [n]
If 'y', local backups will be sent to a remote backup machine
2> Hour of day to Replicate Database [02]
Hour to start backup
Copyright © 2010, Juniper Networks, Inc.24
Page 45

Chapter 2: Installing and Configuring NSM from the CLI
3> Remote Backup IP []
IP address of a remote backup machine
4> Remote Replication Timeout (seconds) [1800]
Rsync Command Backup Timeout (seconds)
(Default is 1800 seconds)
The screen always shows the current status of the remote backup database. If no status
exists, the option has not yet been configured.
•
Remote Replication of Database—Enter 1 to turn remote replication on or off. At the
next prompt, enter y to change the state.
•
Hour of day to Replicate Database—Enter 2, and then specify the hour to start the
backup. The valid range is 00 through 23.
•
Remote Backup IP—Enter 3 to specify the IP address of the remote backup server.
Backup information is copied to the /var/netscreen/dbbackup directory on the remote
server. The “nsm” user must exist on both servers and you must establish an SSH trust
relationship. See the Network and Security Manager Installation Guide for details.
•
Remote Replication Timeout—Enter 4 to change the timeout period for the remote
backup. The valid range is 1 through 65535 seconds.
Configuring Standard Configuration Options
After the initial setup, continue configuring typical options, including the following tasks.
Follow the setup prompts on the main menu to set or modify these options. Your
configuration options (with the exception of any password changes) will not take effect
until you apply the changes.
Run nsm_setup to access these options on the NSM appliance Settings Menu:
•
Changing the Password on page 25
•
Setting Interface Options on page 26
•
Setting Routing Options on page 26
•
Changing the NSM Appliance Hostname on page 27
•
Adding DNS Servers on page 27
•
Setting the System Time on page 27
•
Forwarding Local Status E-mails on page 28
•
Updating System Security on page 28
•
Saving Setup Options on page 29
Changing the Password
To change your password:
1. On the NSM appliance Settings Menu, enter 1 at the prompt.
2. Enter y when prompted to change the password for an “admin” user.
25Copyright © 2010, Juniper Networks, Inc.
Page 46

NSMXpress and NSM3000 User Guide
3. Type the new password and press Enter.
4. Retype the new password and press Enter.
Your password is changed and the setup program returns you to the NSM appliance
Settings menu.
Setting Interface Options
The NSM appliance has twoports labeled ETH0and ETH1.During initial setup, youspecify
the eth0interfaceoptions. Use this menu to set interface options for eth1or modify either
interface.
To set or modify interface options:
1. On the NSM appliance Settings menu, enter 2 at the prompt. The menu shows the
existing status of each interface.
NOTE: If you are going to use a second link, you need to configure an IP
address for eth1 before configuring this setting.
2. Set or modify options for one of the interfaces by selecting one ofthe following options:
•
1 to modify eth0.
•
2 to set or modify eth1.
3. Make the following selection for interface options by selecting one of the following
options:
•
1 to change the IP address and return to the NSM appliance Settings menu.
•
2 to go to the next step.
4. Make the following selection for physical parameters (such as interface speed) by
selecting one of the following options:
•
1 to set the autonegotiate option and return to the main menu.
•
2 to set the physical parameters manually and go to the next step.
5. Select the interface speed by entering one of the following options:
•
1 for 10 Mbps and go to the next step.
•
2 for 100 Mbps and go to the next step.
•
3 for 1000 Mbps and go to the next step.
6. Enter1 for fullduplex or2 for half duplex, and then return to theNSM applianceSettings
menu.
Setting Routing Options
To set or modify routing options:
Copyright © 2010, Juniper Networks, Inc.26
Page 47

1. On the NSM appliance Settings menu, enter 3 at the prompt.
2. Enter one of the following options:
•
1 to change default gateway options.
Follow the prompts to change the IP address of the default gateway and return to
the NSM appliance Settings menu.
•
2 to change the static routing options.
Follow the prompts to add a new static route and return to the NSM appliance Settings
menu.
Changing the NSM Appliance Hostname
To change the hostname:
1. On the NSM appliance Settings menu, enter 4 at the prompt.
2. Enter y at the verification prompt to continue.
3. Enter the new hostname and press Enter to return to the Settings menu.
Chapter 2: Installing and Configuring NSM from the CLI
Adding DNS Servers
You can add up to three DNS servers. Enter each one using dotted decimal notation.
Each additionreturns you to the main menu. If youwant to add more DNS servers, repeat
the following procedure.
To add the DNS servers:
1. On the NSM appliance Settings menu, enter 5 at the prompt.
2. Enter 1 to add a name server.
3. When prompted, enter the new nameserver in dotted decimal notation.
Setting the System Time
You can change time zones or the Network Time Protocol (NTP) configuration. The
default time zone is set for Pacific Standard Time (PST)/Pacific Daylight Time (PDT).
Select time zones in the following order:
•
NOTE: If a hostname consisting of 4 or more labels is changed to a different
hostname, also with 4 or more labels, the previous hostname alias might
remain in the /etc/hosts file. This condition can be corrected by manually
editing the /etc/hosts file.
Continent or ocean
•
Country
•
Region
27Copyright © 2010, Juniper Networks, Inc.
Page 48

NSMXpress and NSM3000 User Guide
To change time options:
1. On the NSM appliance Settings menu, enter 6 at the prompt.
2. Enter 1 to change the time zone.
Follow the prompts to find the time zone you want based on the options listed earlier.
The final selection returns you to the NSM appliance Settings menu.
3. Enter 2 to set NTP servers.
NTP servers automatically set the system clock based on external time sources.
4. Enter one of the following values at the prompt:
•
•
NOTE: NTP is disabled by default. We recommend that you enable this
option to ensure that the time is always accurate.
1 to enable or disable NTP.
2 to add an NTP server.
The remaining numbered options allow you to remove an NTP server from the list.
5. Follow the prompts to enable, set, or delete the NTP servers and return to the NSM
appliance Settings menu.
Forwarding Local Status E-mails
You can use this option to forward all local root e-mail messages to an e-mail address.
You can add an unlimited number of e-mail addresses in addition to mailing lists to help
manage large numbers of recipients.
To set the Forward Local Status:
1. On the NSM appliance Settings menu, enter 7 at the prompt.
2. Enter 1 to add or change the recipient.
3. Enter 2 to remove the recipient.
Updating System Security
Systemsecurity updates are NSM appliance operating system-level patches that protect
the system against any futurereported security vulnerabilities. The NSMappliance checks
for new updates daily by connecting to Juniper Networks.
To manage system security updates:
1. On the NSM appliance Settings menu, enter 8 at the prompt.
2. Enter one of the following values to select the option:
•
1 to check for and install security updates now.
•
2 to enable or disable automatic security updates.
Copyright © 2010, Juniper Networks, Inc.28
Page 49

Saving Setup Options
Chapter 2: Installing and Configuring NSM from the CLI
•
3 to check for and install the latest available NSM appliance version.
•
4 to set the proxy for security update check.
3. Follow the prompts to managesecurity updates, and then return to the NSM appliance
Settings menu.
Beforeyou configure the regionalserver orthe central manager, theNSM applianceopens
the Apply Change submenu. If you quit out of a menu after making changes, The NSM
appliance also opens this screen and prompts you to save your changes. Updates are
enabled by default.
Select a change to cancel it:
1> IP Change: eth1 is 192.168.1.78 / 255.255.255.0
2> Add route: 192.168.0.0 /255.255.0.0 —> eth1 : [192.168.1.254]
3> DNS add: 192.168.2.2
4> Enable NTP
5> Security updates: automatic check Disabled
A> Apply all changes
B> Make more changes
C> Cancel all changes and quit
R> Redraw menu
Choice [1–5,A,M,C,R]:
You have three options for saving changes:
•
At the prompt, enter one of the following menu options:
•
A to apply all the new changes.
•
M to make more changes before configuring the regional server or the central
manager.
•
C to cancel all new changes and quit the NSM appliance setup program. After you
cancel a change, the Change Apply submenu reappears.
•
Enter the number next to a displayed change to cancel only the selected change.
•
Highlight one of the options you modified and delete it.
The NSM Appliance Default Restoration
When you reinstall the NSM appliance, it is completely reimaged. No user data remains
on the system. If you want to preserve your database, back it up before reinstalling.
To reinstall an NSM appliance, use the following procedure. The steps in the procedure
assume the NSM appliance is connected to the computer with a null-modem cable. If
not, refer to the section “Initial Setup Configuration” on page 8 for details.
To reinstall the NSM appliance configuration:
29Copyright © 2010, Juniper Networks, Inc.
Page 50

NSMXpress and NSM3000 User Guide
1. Turn on the NSM appliance.
2. Press any key while the Booting NSMXpress countdown scrolls through the screen to
access the boot menu:
3. Use the arrow keys to select Re-Install current-version-number, and then press Enter:
Press any key to enter the menu
Booting NSMXPress
Booting NSMXpress
Booting NSMXpress
Booting NSMXpress
Booting NSMXpress
Booting NSMXpress
in 4 seconds...
NSMXpress
Rescue
Re-Install <current—version—number>
Re-Install <previous-version-number>
Rescue Boot from Secondary Drive
NOTE: If you have not updated the recovery partition through the Web
UI, only the Re-install option (option to install the previous version) is
displayed.
4. Read the paragraph, and then press Enter.
Booting 'Re-Install'
Using this option will completely erase your appliance and load the factory
default image. No data recovery is possible after re-installing. To confirm
erase and re-install, type “erase” as the password prompt. To abort and
boot
into Rescue mode, just hit <Enter> at the password prompt. Press any key.
5. Enter erase at the prompt to erase the disk. This task will take a few minutes.
When reinstallation is finished, you are prompted to login.
Copyright © 2010, Juniper Networks, Inc.30
Page 51

CHAPTER 3
Configuring NSM from the Web Interface
This chapter describes how to configure NSM from the NSM appliance Web interface. It
contains the following sections:
•
Configuring the NSM Software on page 31
•
Managing NSM Administration on page 39
•
Managing System Administration on page 44
•
Maintaining NSM Appliances on page 61
•
Troubleshooting on page 63
•
Viewing System Information on page 69
Configuring the NSM Software
After logging in as an “admin” user, an initial setup script walks you through additional
configurationsystemsettings before finalizing theNSM installation. This chapter describes
that setup process.
Your NSM appliance comes preconfigured as a regional server or a central manager.
Most installation and configuration steps in this section are identical for both types of
server. All exceptions are noted.
After logging into the NSM appliance Web interface, you have the following installation
options:
•
Configuring Basic Settings on page 31
•
Configuring High Availability on page 34
•
Advanced Options on page 36
•
Installing NSM Software on page 39
Configuring Basic Settings
To install the regional server or central manager software using the minimum
requirements:
1. Complete all appropriate steps in “Getting Started” on page 3.
2. Enter the https://<ip>/administration URL for your appliance in a Web browser. See
“Web Interface Configuration” on page 11 for details.
31Copyright © 2010, Juniper Networks, Inc.
Page 52

NSMXpress and NSM3000 User Guide
3. Log in to the Web interface. The System Info page opens.
4. Click theInstall NSM Regional Server link to viewthe Install NSMRegional Server page
(see Figure 4 on page 32) or click the Install NSM Central Manager link to view the
Install NSM Central Manager page (see Figure 5 on page 33) as the case may be.
Figure 4: Regional Server Configuration Main Menu
NOTE: The “admin” user default username is admin and the password is
the one you created in Step 6 of “Boot the NSM Appliance” on page 8.
Copyright © 2010, Juniper Networks, Inc.32
Page 53

Chapter 3: Configuring NSM from the Web Interface
Figure 5: Central Manager Configuration Main Menu
5. Enter the primary IP address of your management server for eth0 (the default).
You can use the default IP address next to the first radio button or select the second
radio button and then enter a different IP address.Each IP address youadd (in addition
to the default IP address) will be available in the drop-down list after you click the
second radio button.
6. Enter the NSM superuser password in the top text box, and then reenter it in the text
box below it.
This password must be at least eight characters long and is case-sensitive. This
password is used by the NSM superuser (also referred to as the NSM administrator).
This user has the highest level of privileges in NSM.
7. Enter the GUI Server one-time password in the top text box, and then reenter it in the
text box below it. This password is used to authenticate this NSM server with other
NSM servers with which it communicates. Regional servers use this password to
authenticate peer servers in an HA configuration and to authenticate the central
manager. The central manager uses this password to authenticate its peer server in
an HA configuration and any regional servers it manages. NSM servers must have the
same GUI Server one-time password, or the authentication will fail.
8. Select the license option. (This option is available only for regional servers.)
a. Select Base Install to use the built-in limited device license for as many as 25
devices.
b. Click Upload license file to upload the license file you generated using the Juniper
License Management System (LMS), which permits you to manage more than 25
devices. This license file must be located on your local hard drive.
33Copyright © 2010, Juniper Networks, Inc.
Page 54

NSMXpress and NSM3000 User Guide
See the Network and Security Manager installation Guide for more information about
NSM licensing.
9. Click Submit to save any changes, and then click Install to install the software.
Configuring High Availability
To configure high availability (HA) settings:
1. On the NSM Configuration Main Menu, click Menu next to High Availability to access
HA options. See Figure 6 on page 34.
Figure 6: High Availability Options
2. Use the High Availability option to turn HA on (y) or off (n). The default is off.
3. Use the Primary Status option to set your NSM appliance as either the primary or
secondary server in the HA cluster. If you select y, it is the primary server (the default).
If you select n, it is the secondary server.
4. Use the HA Remote IP option to enter the IP address for the HA peer in the HA cluster.
5. Use the HA Link Failure Detection IP option to enter the IP address of a computer
outside the HA cluster that you can ping to verify connection status.
6. Use the HA Inter-server password option to enter the heartbeat password used
between the primary and secondary servers.
7. Click Submit to save the changes.
8. (Optional) Click Menu next to Shared Disk (see Figure 6 on page 34) to configure a
shared disk for regional servers (see Figure 7 on page 35) or for central managers (see
Figure 8 on page 35).
Copyright © 2010, Juniper Networks, Inc.34
Page 55

Chapter 3: Configuring NSM from the Web Interface
Figure 7: Shared Disk Options for Regional Servers
Figure 8: Shared Disk Options for Central Managers
The NSM appliance supports shared disk via NFS only. Due to the data-intensive
nature of NSM, we recommend gigabit speed links (1000 Mbps) for shared disk use.
For moreinformation about customsettings, refer to the Network and Security Manager
Installation Guide.
9. (Optional) Click Menu next to HA Links (see Figure 6 on page 34) to configure the
second link in the HA cluster (see Figure 9 on page 35).
Figure 9: HA Links Options
Use the options in this menu to set up a redundant link for the HA cluster. If you are
going to use a second link, you need to set the IP address for eth1 before configuring
this setting (see“Configuring theNetwork” on page 45 for details). Settinga redundant
link is optional. For more information about custom settings, refer to the Network and
Security Manager Installation Guide.
If you configure HA with just one heartbeat link, then device management traffic and
data replication traffic both usethat link.If youconfigure two links,device management
traffic uses the first link and data replication uses the second.
35Copyright © 2010, Juniper Networks, Inc.
Page 56

NSMXpress and NSM3000 User Guide
If you set the HA link count to 2, an expanded menu appears to configure the second
link as shown below:
Figure 10: Redundant Links
10. (Optional) Click Menu next to HA Advanced Settings (see Figure 6 on page 34) to
configure HA advanced settings (see Figure 11 on page 36).
For moreinformation about customsettings, refer to the Network and Security Manager
Installation Guide.
Advanced Options
Figure 11: HA Advanced Settings
11. Click Submit to save the HA options and return to the NSM Configuration Main Menu.
To display the Advanced Options menu, on the NSM Configuration Main Menu, select
Menu next to Advanced Options. The Advanced Options menu appears as shown in
Figure 12 on page 36.
Figure 12: Advanced Options Menu
Advanced installation options include:
Copyright © 2010, Juniper Networks, Inc.36
Page 57

Chapter 3: Configuring NSM from the Web Interface
•
https port for NBI service—Allows you to configure a port to listen for messages for the
NSM API. By default, this value is 8443. You can configure it to any port number from
1025 to 65535.
•
Remote Replication of Database—Mirrors the daily backup to an external server. You
can toggle iton or off. After you turn it on,use themenu optionsto configure this option.
•
SRS Enabled Options (regional server only)—Opens a menu to enable and configure
Statistical Report Server (SRS). These options enable the NSM appliance to interface
with SRS. You can toggle it on or off. When it is on, a menu with additional options is
available.
NOTE: SRS must be installed on a separate server from NSM.
The following sections provide details about the remote replication and SRS options:
•
Enabling and Configuring Remote Replication of the Database on page 37
•
Enabling and Configuring SRS (Regional Server Only) on page 38
Enabling and Configuring Remote Replication of the Database
To configure remote replication of database settings:
1. On the Advanced Options menu, click Menu next to Remote Replication of Database
(see Figure 6 on page 34) to configure daily backups (see Figure 13 on page 37).
Figure 13: Remote Replication of Database Options
2. Use the Remote Replication of Database option to turn remote replication on (y) or
off (n). The default is off.
3. Use the Hour of day to Replicate Database option to start the backup. The valid range
(in hours) is 00-23. The default is 2 AM.
4. Use the Remote Backup IP option to enter the IP address of the remote backup server.
Backup information is copied to the/var/netscreen/dbbackup directory on theremote
server. The“nsm” user must exist on both servers and youmust establishan SSH trust
relationship. See the Network and Security Manager Installation Guide, for details.
37Copyright © 2010, Juniper Networks, Inc.
Page 58

NSMXpress and NSM3000 User Guide
5. Use the Remote Replication Timeout option to set up a timeout for Rsync. The valid
range (in seconds) is 1-65535. The default is 1800 seconds.
6. Click Submit to save the options and return to the main menu or continue with the
other advanced installation options.
Enabling and Configuring SRS (Regional Server Only)
(This option is not available on a central manager.) To configure statistical report server
(SRS) settings:
1. On the Advanced Options menu, click Menu next to SRS (see Figure 6 on page 34)
to open the SRS menu (see Figure 14 on page 38).
Figure 14: SRS Menu
2. Use the SRS options to turn SRS on (y) or off (n). The default is off. If you turn on this
feature, the server is used with the GUI Server.
3. Use the SRS DB IP option to enter the IP address for the server on which you have
installed the SRS database server.
4. Use the SRS DB Type option to select the database type. The values are pgsql (the
default), oracle, or mssql.
5. Use the SRS Database Name option to enter the name of the SRS database. The
default value is netscreen. To enter another name, click the radio button next to the
blank text box and enter the name in the text box.
6. Use the SRS DB Owner Name option to enter the owner’s name of the SRS database.
The default value is netscreen. To enter another name, click the radio button next to
the blank text box and enter the name in the text box.
Copyright © 2010, Juniper Networks, Inc.38
Page 59

7. Use the SRS DB Owner Password option to enter the SRS database password. The
password requires a minimum of eight characters and is case-sensitive. Reenter the
password in the second text box.
8. Click Submit to save the options and return to the NSM Configuration Main Menu.
Installing NSM Software
After you submit all your configuration options, click Install to install the NSM software
on your NSM appliance. Installation takes a few minutes. A status indicator shows the
progress of the installation. Wait until installation is finished before continuing to use the
Web interface.
Managing NSM Administration
Expand NSM Administration in the left navigation tree to access the options described
in this section. These options are available only after installing NSM.
The following sections explain how to use each of the NSM Administration options:
Chapter 3: Configuring NSM from the Web Interface
•
Changing the Superuser Password on page 39
•
Downloading NSM MIBS (Regional Server Only) on page 40
•
Exporting Audit Logs on page 40
•
Exporting Device Logs (Regional Server Only) on page 40
•
Generating Reports (Regional Server Only) on page 41
•
Modifying NSM Configuration Files on page 41
•
Backing Up the NSM Database on page 42
•
Changing the NSM Management IP on page 43
•
Scheduling Security Updates on page 43
Changing the Superuser Password
To change the superuser password, select NSM Administration > NSM Super User
Password. See Figure 15 on page 39.
Figure 15: Change Superuser Password
39Copyright © 2010, Juniper Networks, Inc.
Page 60

NSMXpress and NSM3000 User Guide
Downloading NSM MIBS (Regional Server Only)
To download any available MIBs, select NSM Administration > Download NSM MIBS,
and then click Download MIB. See Figure 16 on page 40. This option is not available on
the central manager.
Figure 16: Download NSM MIBs
Exporting Audit Logs
To export audit logs, select NSM Administration > Export Audit Logs. See Figure 17 on
page 40.
Figure 17: Export Audit Logs
To export an audit log to a csv file, select csv in the drop-down list box, and then enter
the csv file name in the text box.
To export an audit log to a system log server, select syslog in the drop-down list box,
and then enter the server IP address, if it is not the local host.
Exporting Device Logs (Regional Server Only)
To export device logs, select NSM Administration > Export Device Logs. See Figure 18
on page 40. This option is not available on the central manager.
Figure 18: Export Device Logs
Copyright © 2010, Juniper Networks, Inc.40
Page 61

Generating Reports (Regional Server Only)
To generate reports, select NSM Administration > Generate Reports. See Figure 19 on
page 41. This option is not available on the central manager.
Figure 19: Generate Reports
Chapter 3: Configuring NSM from the Web Interface
NOTE: The user is an NSM administrator and not an NSM appliance user.
Enter a user name as domain/user, such as global/super.
Modifying NSM Configuration Files
To manuallyedit the GuiSrv.cfg,DevSvr.dfg and HaSvr.cfg files, select NSM Administration
> Modify NSM Configuration Files. The example in Figure 20 on page 42 shows the
option to modify the GuiSvr.cfg file.
41Copyright © 2010, Juniper Networks, Inc.
Page 62

NSMXpress and NSM3000 User Guide
Figure 20: NSM Configuration Files
Backing Up the NSM Database
To configurebackups of the NSMdatabase,select NSM Administration > NSM Database
Backup link under NSM Administration. See Figure 21 on page 43.
NOTE: If you subsequently change the NSM appliance configuration by using
the nsm-setup utility, all manual changes to the configuration files are lost.
Copyright © 2010, Juniper Networks, Inc.42
Page 63

Figure 21: Database Backup
Chapter 3: Configuring NSM from the Web Interface
Changing the NSM Management IP
To change the IP address of the NSM management server, select NSM Administration
> NSM Management IP link under NSM Administration. See Figure 22 on page 43.
Figure 22: Change Management IP
Scheduling Security Updates
To schedulesecurity updates, select NSM Administration > Schedule Security Updates.
See Figure 23 on page 44.
43Copyright © 2010, Juniper Networks, Inc.
Page 64

NSMXpress and NSM3000 User Guide
Figure 23: Schedule Security Updates
Managing System Administration
Use the options on the System Administration menu to perform the tasks described in
the following sections:
•
Rebooting or Shutting Down the NSM Appliance on page 44
•
Changing the User Password on page 45
•
Configuring the Network on page 45
•
Managing RADIUS Servers on page 47
•
Monitoring with SNMP on page 50
•
Forwarding Syslog Messages on page 53
•
Changing the System Time on page 56
•
Installing Updates on page 56
•
Managing Users on page 57
•
Configuring the Web Interface on page 60
Rebooting or Shutting Down the NSM Appliance
To reboot or shut down the NSM appliance, select System Administration > Bootup
and Shutdown, and then click either Reboot System or Shutdown System. See Figure
24 on page 44.
Figure 24: ReBoot or Shut Down
Copyright © 2010, Juniper Networks, Inc.44
Page 65

Changing the User Password
To change the user password, select System Administration > Change User Password,
fill out the form shown in Figure 25 on page 45, and then click Change.
Figure 25: Change User Password
Configuring the Network
To access optionsthat allow you to configure thenetwork, select System Administration
> Network Configuration.The Network Configurationwindow appears as shown in Figure
26 on page 45.
Chapter 3: Configuring NSM from the Web Interface
Figure 26: Network Interfaces Options
The following sections describeeach ofthe optionsavailablein the Network Configuration
window:
•
Network Interfaces on page 45
•
Routing and Gateways on page 46
•
Hostname and DNS Clients on page 46
•
Host Addresses on page 47
Network Interfaces
Use this option to manage the network interfaces. See Figure 27 on page 46.
45Copyright © 2010, Juniper Networks, Inc.
Page 66

NSMXpress and NSM3000 User Guide
Figure 27: Network Interfaces
Routing and Gateways
Use this option to configure andmanage routes and gateways. SeeFigure 28 on page 46.
Figure 28: Routes and Gateways
Hostname and DNS Clients
Use this option to configure and manage hostnames and DNS clients. See Figure 29 on
page 47.
Copyright © 2010, Juniper Networks, Inc.46
Page 67

Chapter 3: Configuring NSM from the Web Interface
Figure 29: DNS Client Options
Host Addresses
Use this option to manage host addresses, See Figure 30 on page 47.
Figure 30: Host Address
Managing RADIUS Servers
The NSM appliance WebUI supports authentication of users defined in the RADIUS
servers, in addition to authentication of locally defined admin users.
When a user logs into the NSM appliance using the WebUI, the software first checks the
UNIX user database and then the WebUI user database to authenticate the user. If the
user is not a locally defined admin user, thesoftware contacts theRADIUS servers added
to the RADIUS server list in the Web UI to authenticate the user. The RADIUS servers are
contactedin the order of priority set in the RADIUS server list. If any of the RADIUS servers
authenticates the user, the user is logged in with the privileges that are associated with
the user profile. If none of the servers authenticates the user, the user login fails.
NOTE: The NSM appliance must be configured as a RADIUS client on a
RADIUS server so that the RADIUS server responds to authentication requests
from the appliance. Select any Juniper Make or Model in the Make/Model
field while adding an NSM appliance as a RADIUS client. You will need to
update the Juniper dictionary file (juniper.dct) in the RADIUS server with the
Juniper defined Vendor-Specific Attribute (VSA) for the NSM
appliance:ATTRIBUTE Juniper-Nsmxpress-Profile Juniper-VSA(6, string) r
. You also need to add NSM appliance users with their associateduser profiles
(SysAdmin,NSMAdmin, Operator, Guest), to the RADIUS database. For more
details see Steel-Belted Radius Documentation.
NOTE: You need System Administration or NSM Administration permission
to manage RADIUS servers in the NSM appliance WebUI.
47Copyright © 2010, Juniper Networks, Inc.
Page 68

NSMXpress and NSM3000 User Guide
The following sections explain how to manage a RADIUS server.
•
Adding a RADIUS Server on page 48
•
Changing the Priority of RADIUS Servers on page 49
•
Deleting a RADIUS Server on page 49
•
Editing RADIUS Server Parameters on page 49
Adding a RADIUS Server
To add a RADIUS server:
1. Select System Administration > RADIUSManagement. TheRADIUS Servers dialog box
appears listing the RADIUS Servers that have been added. See Figure 31 on page 48.
Figure 31: RADIUS Servers Dialog Box
2. Click Add to add a RADIUS Server to the WebUI. The Add RADIUS Server dialog box
appears. See Figure 32 on page 48.
Figure 32: Add RADIUS Server Dialog Box
3. Configure the following parameters in the Add RADIUS Server dialog box:
a. Name: The name of the user to be authenticated by the RADIUS server
b. Server address: The IP address or the hostname of the RADIUS Server.
c. Shared secret: The shared secret the NSM appliance and the RADIUS server use
for secure authentication.
d. Auth Port: The RADIUS authentication software port. (We recommend UDP port
1812)
Copyright © 2010, Juniper Networks, Inc.48
Page 69

Chapter 3: Configuring NSM from the Web Interface
e. Acct Port: The RADIUS accounting software port. (We recommend UDP port 1813)
f. Disconnect/CoA port: The change of authorization or disconnect port.
g. Timeout (sec): Automatic time out in second(s) of the RADIUS access-request
after which the request is retransmitted, if applicable. Enter a value between 1 and
10 seconds.
h. Retries: The number of times the RADIUS access-request must be retransmitted
for RADIUS authentication. Enter a value between 1 and 5.
4. Click Add. The RADIUS Servers dialog box appearswith the RADIUS Serveryou added
listed.
Changing the Priority of RADIUS Servers
To change the priority of RADIUS servers:
1. Select System Administration > RADIUSManagement. TheRADIUS Servers dialog box
appears listing the RADIUS Servers that have been added.
2. To increase the priority of a RADIUS server, select the check box next to the name of
the server whose priority you want to increase, and click Move Up.
To decrease the priority of a RADIUS server, select the check box next to the name of
the server whose priority you want to decrease, and click Move Down.
Deleting a RADIUS Server
To delete a RADIUS server:
1. Select System Administration > RADIUSManagement. TheRADIUS Servers dialog box
appears listing the RADIUS Servers that have been added.
2. Select the check box next to the name of the server you want to delete, and click
Delete Selected.
NOTE: You need System Administration permissions to delete RADIUS
servers.
Editing RADIUS Server Parameters
To edit the parameters of a RADIUS server:
1. Select System Administration > RADIUSManagement. TheRADIUS Servers dialog box
appears listing the RADIUS Servers that have been added.
2. Select the name of the server whose properties you want to edit. The Edit RADIUS
Server dialog box appears. See Figure 33 on page 50.
49Copyright © 2010, Juniper Networks, Inc.
Page 70

NSMXpress and NSM3000 User Guide
Figure 33: Edit RADIUS Server Dialog Box
3. Edit the parameters you want to change and click Save.
Monitoring with SNMP
You can configure your NSM appliance for SNMP monitoring from a network operations
server. The server can then issue periodic SNMP Get instructions to return the status of
the NSM appliance.
You configure SNMP on the NSM appliances with access credentials for either SNMP
v2c or SNMP v3. NSM appliances support read-only access to the System Descriptor
(sysDescr) and Host Resource MIB.
This section provides instructions for configuring NSMappliances for SNMP monitoring.
You must provide access credentials for the SNMP server, a list of IP addresses from
which logon requests will be accepted, and the trap conditions to be reported to the
SNMP server.
To configure SNMP monitoring of your NSM appliance, select System Administration >
SNMP Monitoring. TheSNMP window appears.This window containsthe tabsdescribed
in the following sections:
•
SNMP Configuration on page 50
•
SNMP System Information on page 51
•
SNMP Trap Configuration on page 52
SNMP Configuration
To configure SNMP:
1. Select System Administration > SNMP Monitoring.
2. Select the SNMP Config tab, which is shown in Figure 34 on page 51.
Copyright © 2010, Juniper Networks, Inc.50
Page 71

Chapter 3: Configuring NSM from the Web Interface
Figure 34: Configuring SNMP
3. Select the version of SNMP to be used, either v2c or v3.
4. Provide authentication information:
•
If you selected SNMP v2c, enter a username.
•
If you selected SNMP v3, enter a username and password.
The password must be at least 8 characters long.
The NSM appliancesimplement a singleusername andpassword,which is effective
only for SNMP communication and is not related to any other username and
password used on the NSM appliance.
5. To limit SNMP Get requests to specific servers, select Only, and then enter the IP
addresses of the permitted servers.
6. Click Save.
SNMP System Information
To configure SNMP system information:
1. Select System Administration > SNMP Monitoring.
2. Select the System Info tab, which is shown in Figure 35 on page 51.
Figure 35: Configuring SNMP System Information
3. Enter the following information, with is required for any SNMP-managed device:
•
Contact—Contact information for the appliance.
•
Location—Location of the appliance.
51Copyright © 2010, Juniper Networks, Inc.
Page 72

NSMXpress and NSM3000 User Guide
•
4. Click Save.
SNMP Trap Configuration
To configure SNMP trap conditions:
1. Select System Administration > SNMP Monitoring.
2. Select the SNMP Traps tab, which is shown in Figure 36 on page 52.
Figure 36: Configuring SNMP Traps
Description—A brief description of the appliance.
3. In the Manager IP field, enter the IP address of the SNMP management server.
4. Select from the following trap conditions:
•
Disk space low
Enter the percentage of free disk space below which SNMP issues a trap.
•
Memory low
Enter the percentage of free memory below which SNMP issues a trap.
•
CPU high
Enter the percentage of CPU use over which SNMP issues a trap.
•
NSM start/stop
•
Admin Logon/Logoff
•
External IP unreachable
Enter the IP address of the required device.
5. Click Save.
Copyright © 2010, Juniper Networks, Inc.52
Page 73

Forwarding Syslog Messages
The NSM appliances provide a simple mechanism for configuring syslog messaging
between the NSM appliance and a syslog receiver running rsyslog, syslog-NG, or basic
syslog.This mechanismsimplifies choosingsyslog receivers, data sources ofthe messages
you want to log, and the message transport used.
For thetype ofmessage transport, you can chooseamong TCP, SSL,and UDP. For rsyslog
or syslog-NG implementations use TCP or SSL. SSL adds security to TCP; if you select
SSL, the NSMappliance creates a secure tunnel to the syslog receiver. UDP messaging
is available for basic syslog implementations.
The following sections provide procedures for managing syslog message forwarding:
•
Viewing Syslog Receivers on page 53
•
Adding and Configuring Syslog Receivers on page 54
•
Editing Syslog Receiver Configurations on page 56
•
Deleting Syslog Receivers on page 56
Chapter 3: Configuring NSM from the Web Interface
Viewing Syslog Receivers
To view the syslog receivers configured on your NSM appliance, follow these steps:
1. Select System Administration > Syslog Forwarding. The Syslog Forwarding window
appears. Figure 37 on page 55 shows an example.
53Copyright © 2010, Juniper Networks, Inc.
Page 74

NSMXpress and NSM3000 User Guide
2. View the configured syslog receivers in the table in the top portion of the window.
Table 7 on page 54 describes the fields.
Table 7: Viewing Syslog Receivers
DescriptionField
Receiver
A nameprovided bythe network administratorto identify the syslog
receiver
The IP address of the syslog receiverIP Address
The protocol used for forwarding messages: UDP, TCP, SSLType
The data sources configured for forwardingData sources
The system logs configured to be sent to this receiver.System
The Device Server logs configured to be sent to this receiver.Device Server
The GUI Server logs configured to be sent to this receiver.GUI Server
The HA Server logs configured to be sent to this receiver.HA Server
Adding and Configuring Syslog Receivers
To add and configure a syslog receiver, follow these steps:
1. Select System Administration > Syslog Forwarding.
2. In the Data Sources section, select the syslog facility for each GUI Server log, Device
Server log, and HA Server log. The syslog facility is a field included in the syslog
message to help identify the data source.
3. Click Save.
4. Click Add new Receiver.
The syslog receiver configuration window appears as shown in Figure 37 on page 55.
Copyright © 2010, Juniper Networks, Inc.54
Page 75

Chapter 3: Configuring NSM from the Web Interface
Figure 37: Configuring a Syslog Receiver
5. In the Name field, enter a namefor the syslog receiver. This is the name thatthe syslog
receiver will be known by within NSM.
6. In the IP field, Enter the IP address of the syslog receiver.
7. In the Transport field, select the type of syslog receiver:
•
Select UDP for basic syslog implementations.
•
Select TCP for rsyslog or syslog-NG implementations.
55Copyright © 2010, Juniper Networks, Inc.
Page 76

NSMXpress and NSM3000 User Guide
•
•
•
8. Click Save to save and apply the configuration.
Editing Syslog Receiver Configurations
To edit a syslog receiver configuration, follow these steps:
1. Select System Administration > Syslog Forwarding.
2. In the Syslog Receivers window, click the name of the syslog receiver you want to edit.
The syslog receiver configuration window appears for the selected recevier.
Select SSL to create a secure tunnel to a syslog receiver in rsyslog or syslog-NG
implementations.
In the System Logs section of the Data Sources table, select the sources of data
from whichsystemmessages will be forwarded to the syslog receiver. These sources
can include NSM appliance system messages, package updates, and mail logs.
In the NSM section of the Data sources table, select each GUI Server log, Device
Server log, and HA Server log to be forwarded to the syslog receiver.
3. Make the desired changes to the configuration.
4. Click Save to save and apply your edits to the configuration of this syslog receiver.
Deleting Syslog Receivers
To delete a syslog receiver configuration, follow these steps:
1. Select System Administration > Syslog Forwarding.
2. In the Syslog Receivers window, check the box next to each syslog receiver you want
to delete.
3. Click Delete selected receivers.
The NSM appliance deletes the selected syslog receivers and any secure tunnels
configured for their use.
Changing the System Time
To set the system time, select System Administration > System Time. From the System
Time window, you can perform the following functions:
•
Set or change the system time.
•
Set the time zone.
•
Configure an NTP server to synchronize the system time with an external clock.
Installing Updates
Select System Administration > System Update to perform the following tasks:
•
Check for updates and install them.
•
Enable or disable automatic updates.
Copyright © 2010, Juniper Networks, Inc.56
Page 77

Managing Users
Chapter 3: Configuring NSM from the Web Interface
•
Install a new NSM appliance version.
•
Add or modify proxy settings for the Yum server.
The NSM appliance WebUI allows you to create multiple users with role-based access
control to the WebUI. You can create a user in the WebUI and associate the user to a
predefined user profile. You can also map a user created in the NSM appliance OS to a
predefined user profile in the WebUI. However, this user profile is only applicable to the
local OS user in the WebUI.
NOTE: You need System Administration permission to create users.
This topic contains the following sections:
•
Creating New NSM Appliance Users on page 57
•
Deleting a User on page 58
•
Editing User Attributes on page 59
•
Understanding User Profiles on page 59
Creating New NSM Appliance Users
To create a local OS user:
1. Select System Administration > User Management. The NSMXpress Users dialog box
appears listing all NSMXpress users. See Figure 38 on page 57.
Figure 38: NSMXpress Users Dialog Box
2. Click Create a new NSMXpress User. The Create NSMXpress user dialog box appears.
See Figure 39 on page 58.
57Copyright © 2010, Juniper Networks, Inc.
Page 78

NSMXpress and NSM3000 User Guide
Figure 39: Create NSMXpress User Dialog Box
3. Enter the user name in the Username text box.
4. Select Unix authentication from the Password drop-down list. The Password and
Confirm Password text boxes are then disabled since the password is fetched from
the local OS.
5. From the User Profile drop-down list box, select the userprofile you want to associate
with the local user in the WebUI.
6. Click Submit. The NSMXpress Users dialog box appears with the new NSM appliance
user listed.
To create a WebUI user:
1. Select System Administration > User Management. The NSMXpress Users dialog box
appears listing all the NSM appliance users. See Figure 40 on page 58.
2. Click Create a new NSMXpress User. The Create NSMXpress user dialog box appears.
3. Enter a user name in the Username text box.
4. Select Set to from the password drop-down list and enter the password you want to
set in the password text box.
5. Reenter the password in the Confirm Password text box.
6. Select the user profile you want to associate with this user from the User Profile
drop-down list box.
7. Click Submit. The NSMXpress Users dialog box appears with the new NSM appliance
user listed.
Deleting a User
To delete a user:
1. Select System Administration > User Management. The NSMXpress Users dialog box
appears listing all NSM appliance users.
2. Select the check box next to the name of the user you want to delete and click Delete
Selected. Click Delete User in the Delete Users confirmation dialog box that appears.
NOTE: You cannot delete admin users or change their user profiles.
Copyright © 2010, Juniper Networks, Inc.58
Page 79

Chapter 3: Configuring NSM from the Web Interface
Editing User Attributes
To edit user attributes:
1. Select System Administration > User Management. The NSMXpress Users dialog box
appears, with all the NSM appliance users listed.
2. Click on the name of the user whose attributes you want to edit. The Edit NSMXpress
Users dialog box appears.
3. Edit the parameters you want to change and click Submit. You can change the
password and the user profile.
Understanding User Profiles
NSM appliances provide four predefined user profiles that allow you to implement
role-based access control over the NSM appliance WebUI. A user created via the WebUI
or in the RADIUS server can be associated with any one of the following profiles:
•
System Administrator—System Administrators are superusers who have full access
to all the modules in the NSM appliance WebUI.
•
NSM Administrator—NSM Administratorshave access toNSM Administration, RADIUS
Management, Maintenance and Troubleshooting modules.
•
Network Operator—Network Operators have access to Network Utilities and Report
Generation Modules.
•
Guest User—Guest Users have readaccess to System Informationand System Statistics
modules.
When a user logs in, the NSM appliance modules are displayed or hidden based on the
user profile and the permissions associated with the profile. For more details about user
profiles and permissions, see Table 8 on page 59.
Table 8: NSM Appliance WebUI User Profiles and Permissions
System
AdministratorNSM Appliance Modules
System Administration
NSM
Administrator
Network
Operator
Guest User
NoNoNoYesBootup and Shutdown
NoNoNoYesChange User Password
NoNoNoYesNetwork Configuration
NoNoYesYesRADIUS Management
NoNoNoYesSNMP Monitoring
NoNoNoYesSyslog Forwarding
NoNoNoYesSystem Time
59Copyright © 2010, Juniper Networks, Inc.
Page 80

NSMXpress and NSM3000 User Guide
Table 8: NSM Appliance WebUI User Profiles and Permissions (continued)
NSM Administration
System
AdministratorNSM Appliance Modules
NSM
Administrator
Network
Operator
Guest User
NoNoNoYesSystem Update
NoNoNoYesUser Management
NoNoNoYesWebUI Configuration
NoNoYesYesChange NSM Super User Password
NoNoYesYesDownload NSM MIBs
NoYesYesYesExport Audit Logs
NoYesYesYesExport Device Logs
NoYesYesYesGenerate Reports
NoNoYesYesNSM Configuration Files
NoNoYesYesNSM Database Backup
Maintenance
Troubleshooting
Configuring the Web Interface
To specify which NSM client computers can access the NSM appliance through the Web
interface, select System Administration > WebUI Configuration. The Allowed IP
Addresses window appears as shown in Figure 41 on page 61.
NoNoYesYesNSM Management IP
NoNoYesYesSchedule Security Updates
YesYesYesYesSystem Statistics
NoNoYesYesAction Audit Logs
NoYesYesYesError Logs
NoYesYesYesNetwork Utilities
NoYesYesYesTech Support
YesYesYesYesSystem Information
Copyright © 2010, Juniper Networks, Inc.60
Page 81

Figure 41: Web Interface Access
Maintaining NSM Appliances
The Maintaining section of the NSM appliance navigation tree allows you to perform the
tasks described in the following sections:
•
Viewing System Statistics on page 61
•
Upgrading the Recovery Partition on page 62
Viewing System Statistics
Chapter 3: Configuring NSM from the Web Interface
To view system statistics, select System Administration > Maintenance > System
Statistics. The system Statistics window appears as shown in Figure 42 on page 61.
Figure 42: System Statistics
CPU
Select CPU to view graphs that monitor the CPU activity hourly, daily, weekly, monthly,
or on a customizable basis.
Log Rate
Select lograte to view graphs that monitor the log rate hourly, daily, weekly, monthly, or
on a customizable basis.
CPU Load
Select Load to view graphs that monitor the CPU load hourly, daily, weekly, monthly, or
on a customizable basis.
61Copyright © 2010, Juniper Networks, Inc.
Page 82

NSMXpress and NSM3000 User Guide
Memory Data
Select Memory to view graphs that monitor the memory activity hourly, daily, weekly,
and monthly.
Network Data
Select either eth0 or eth1 to view graphs that monitor network activity hourly, daily,
weekly, and monthly.
Process Count
SelectProcess to view graphs thatmonitor thenumber of processes hourly, daily, weekly,
and monthly.
Disk Data
Select Disk to view graphs that monitor the file system disk space usage hourly, daily,
weekly, and monthly.
Tile All Graphs
Select Tile all graphs to display all the statistical graphs for the system in one window.
Upgrading the Recovery Partition
The recovery partition contains all files necessary to perform a clean installation of the
NSM appliance OS and its applications with default settings. It provides a last-resort
recovery mechanism. When the NSM appliance is shipped from the factory, the recovery
partition files match the version of the NSM appliance OS with factory default settings.
Using the Recovery Upgrade option, you can make the current version of the NSM
appliance available for recovery, displacing the existing files in the recovery partition. The
factorydefaultrecoveryfiles are retained as analternativerecoverychoice. Other versions
are deleted.
Recovery upgrade uses two sets of packages to create a set of files from which you can
perform a clean installation. One set makes up the NSM appliance OS, the other a set
of upgrade script packages. Both sets are usually retained in the local file system. The
NSM appliance OS set can also be downloaded from the Juniper Networks software
repository.
The recovery upgrade process is split into a preparation phase and an upgrade phase. In
the preparation phase, the NSM appliance assembles a copy of the current version of
the image files in a temporary workspace. In the upgrade phase, the NSM appliance
replaces the old recovery image files, and installs the current version of the image files
from the temporary workspace into the recovery partition. By splitting the process into
two phases, the NSM appliance minimizes the period of vulnerability while the upgrade
itself takes place.
To upgrade the recovery partition, follow these steps:
Copyright © 2010, Juniper Networks, Inc.62
Page 83

Chapter 3: Configuring NSM from the Web Interface
1. Select System Administration > Maintenance > Update Recovery Partition.
If thenew recovery partition files havealready been prepared,then the Upgrade screen
appears. Proceed with the upgrade phase as described in step 5.
If the upgrade files have not yet been prepared, the Upgrade Preparation window
appears. Proceed with the preparation phase in step 2.
2. Enter the location of the NSM appliance Regional server or Central Manager upgrade
zip file, downloadedfrom theJuniper CustomerSupport Center when upgrading NSM,
on the local file system.
3. If the NSM appliance Offline server upgrade file is available on the local file system,
enter its location and name of the file in the System upgrade source field. If the NSM
appliance offline server upgrade file is not available on the local file system and the
appliance has access to the Juniper Update site, select Online.
4. Click Prepare System.
The Preparation Progress screen shows the progress of the operation.
Errors are reported if the required files are unavailable, disk space is not sufficient, or
the previous version files are invalid.
5. In theUpgrade window, enterthe adminWeb UI password andthen clickStart Update.
Troubleshooting
Use the options in the Troubleshooting section to access the following information and
utilities:
•
Auditing User Operations on page 63
•
Error Logs on page 65
•
Network Utilities on page 66
•
Tech Support on page 68
Auditing User Operations
You can audit all user operations performed in an NSM appliance. Users with System
Administrator and NSM administrator permissions can view all Actions Logs in the NSM
appliance.
When preparation is completed, the Upgrade window appears.
The upgrade process usually takes less than one minute.
CAUTION: Do not interrupt the upgrade process. If you do, your NSM
appliance might not boot normally.
To view Action Audit Logs:
1. Select Troubleshooting > Action Audit Logs. The NSMXpress Actions Log dialog box
appears. See Figure 43 on page 64.
63Copyright © 2010, Juniper Networks, Inc.
Page 84

NSMXpress and NSM3000 User Guide
Figure 43: NSMXpress Actions Dialog Box
2. Select the Action Audit Logs that you want to view:
•
Actions by NSMXpress Users: Select the By any user check box to select actions by
all users. Select the By user check box and choose a username from the drop-down
list to specify actions by a particular user. Select By any user except and choose a
username from the drop-down list to exclude actions by a specific user.
•
Actions by User Profile : Select the By any profile check box to select actions by all
user profiles. Select the By profile check box and choose a profile from the
drop-down list to specify actions by a specific user profile. Select By any profile
except and choose a profile from the drop-down list to exclude actions by a user
profile.
•
Actions by authentication mechanism: Select the By any authentication check box
to select actions by all authentication mechanisms. Select the By authentication
check box and choose an authentication mechanism from the drop-down list to
specify actions bya specificauthentication mechanism. SelectBy any authentication
except and choose a profile from the drop-down list to exclude actions by an
authentication mechanism.
•
Actionsin module: Select theIn any module check boxto select actions in all modules.
Select the In module check box and choose a module from the drop-down list to
specify actions in a particular module.
•
Actions on dates: Select the At any time check box to select actions at any time.
Selectthe For today only check boxto select today’s actions.Select the For yesterday
only check box to select yesterday’s actions. Select the During the last week check
box to select last week’s actions. Select the Between check box and enter the start
date and end date in the drop-down list to view actions within the specified time
period.
3. Click Search. The Search Results dialog box appears with the result of your query. See
Figure 44 on page 65.
Copyright © 2010, Juniper Networks, Inc.64
Page 85

Error Logs
Chapter 3: Configuring NSM from the Web Interface
Figure 44: Search Results Dialog Box
To review error logs, select Troubleshooting > Error Logs. Figure 45 on page 65 shows
an example,
Figure 45: Review Error Logs
To view details of an individual error log, select the file you want to view and click View.
Figure 46 on page 65 shows sample error log details.
Figure 46: Error Log Detail
65Copyright © 2010, Juniper Networks, Inc.
Page 86

NSMXpress and NSM3000 User Guide
Network Utilities
To access basic network utilities (ping, traceroute, and nslookup) for TCP/IP Networking,
select Troubleshooting > Network Utilities. These tools also provide an IP subnet
calculator. SeeFigure 47 on page 66.
Figure 47: Network Utilities Options
Ping
Ping is a tool for checking network connectivity. The NSM appliance prompts you with
questions so you can focus your search.
Figure 48 on page 66 shows an example.
Figure 48: Ping Utility
How Many Packets
Enter the number of packets this ping command will send. The default is 5. The values
range from 1-99.
Packet Size
Enter the packetsize (inbytes)this pingcommand willsend. The default is 56. The values
range from 1-9999.
How Many Sec Between Sending Each Packet
Enter how much time (in seconds) ping should wait between sending each packet.
Patterns to Send (Hex)
The data sent by ping contains a hexadecimal pattern. If you leave this option blank, ping
will fill it with random data. This option is useful if you do not have problems with
connectivity itself but with data loss.
Copyright © 2010, Juniper Networks, Inc.66
Page 87

Chapter 3: Configuring NSM from the Web Interface
Verbosity Output
The NSM appliance lists the ICMP packets (otherthan ECHO_Response) that have been
received.
Numeric Output Only
Check thisoption if you do not want any attempts tobe made to look up symbolic names
for host addresses.
Bypass Routing Tables
If the hostis not a directly attached network, an error is returned. This option can be used
to ping a local host through an interface that has no route through it.
Traceroute
Traceroute is a tool to print the route a packet takes to a network host. See Figure 49 on
page 67.
Figure 49: Traceroute Utility
Lookup
Use the lookup tool to obtain the IP address from a hostname and the hostname from
an IPaddress (seeFigure 50on page 68).The querytype drop-downlist contains several
types of records found in the DNS database. Enter a nameserver or select the default. If
you choose the default, nslookup usesthe serveron whichthe NSMappliance is installed.
NOTE: The only required field is Hostname. The value can be either a
hostname or an IP address.
67Copyright © 2010, Juniper Networks, Inc.
Page 88

NSMXpress and NSM3000 User Guide
Figure 50: Lookup Utility
IP Subnet Calculator
Use the IP subnet calculator to calculate the netmask for a TCP/IP-network. You can
calculate a netmask by class and subnet bits or by the number of hosts (see Figure 51
on page 68). When you calculate a netmask by the number of hosts, the NSM appliance
returns the smallest network available.
Tech Support
Figure 51: IP Subnet Calculator
To getcontact information forJuniper Networks technicalsupport, selectTroubleshooting
> Tech Support. To help analyze problems, select a detail type in the drop-down list box,
and then click Run Tech-Support Script. The NSM appliance creates a file you can
download and send to Juniper Networks technical support. See Figure 52 on page 68.
Figure 52: Juniper Tech Support
Copyright © 2010, Juniper Networks, Inc.68
Page 89

Viewing System Information
Use the System Information menu item to display information about the server, including
CPU load and memory use, as shown in Figure 53 on page 69.
Figure 53: System Information
Chapter 3: Configuring NSM from the Web Interface
69Copyright © 2010, Juniper Networks, Inc.
Page 90

NSMXpress and NSM3000 User Guide
Copyright © 2010, Juniper Networks, Inc.70
Page 91

PART 2
Appendixes
•
NSMXpress LEDs on page 73
71Copyright © 2010, Juniper Networks, Inc.
Page 92

NSMXpress and NSM3000 User Guide
Copyright © 2010, Juniper Networks, Inc.72
Page 93

APPENDIX A
NSMXpress LEDs
This appendix describes the LEDs on the NSMXpress appliance.
•
NSMXpress LEDs on page 73
NSMXpress LEDs
The front panel of the NSMXpress appliance has the following LEDs:
•
Power LED
•
Hard Disk LED
•
Hardware LED
•
Hard Disk Tray LEDs
Table 9 on page 73 describes their states.
Table 9: NSMXpress LEDs
UnlitPower
Green
On steadily
ConditionColorLED
The appliance is not receiving
power.
The appliance is receiving
power.
No hard disk activity.UnlitHard Disk
Hard disk activity.Blinking yellow
Normal operation.UnlitHardware
A fan has failed.Blinking fast (1/sec)
A power supply has failed.Blinking slow (4/sec)
Warning that the system is
overheating and is about to
power off.
73Copyright © 2010, Juniper Networks, Inc.
Page 94

NSMXpress and NSM3000 User Guide
Table 9: NSMXpress LEDs (continued)
Hard Disk Tray LEDs
Hard disk activityBlinking greenHard Disk Activity LED
Hard disk failureOn steadily(Red)Hard Disk Failure LED
NOTE: This is applicable for
NSM 3000 RAID
configurations and not for
non-RAID configurations
(NSMXpress/NSMCM).
NOTE: For information on LAN LEDs, see Table 6 on page 6
Hard disk recovery or rebuildBlinking red
Copyright © 2010, Juniper Networks, Inc.74
Page 95

PART 3
Index
•
Index on page 77
75Copyright © 2010, Juniper Networks, Inc.
Page 96

NSMXpress and NSM3000 User Guide
Copyright © 2010, Juniper Networks, Inc.76
Page 97

Index
A
admin user.................................................................................10
Advanced Options menu
central manager......................................................24, 36
regional server..........................................................19, 36
Apply Change menu..............................................................29
audit logs, exporting..............................................................40
B
backup........................................................................................42
C
central manager
configuring with CLI........................................................21
configuring with Web interface..................................31
CLI, configuring NSMXpress from...............................10, 13
configuration files, editing....................................................41
console port................................................................................6
console terminal, configuring...............................................8
CPU load.....................................................................................61
CPU use.......................................................................................61
customer support.................................................................xviii
contacting JTAC............................................................xviii
D
database
backing up.........................................................................42
remote replication of......................................20, 24, 37
default gateway
address..................................................................9, 26, 46
default gateway, address........................................9, 26, 46
defaults, restoring...................................................................29
device logs, exporting...........................................................40
DevSvr.cfg file............................................................................41
disk usage..................................................................................62
DMZ................................................................................................4
DNS client.................................................................................46
DNS server.................................................................................27
documentation
comments on................................................................xviii
E
e-mail, forwarding..................................................................28
enterprise customers...............................................................3
error logs....................................................................................65
eth0
activity................................................................................62
configuring........................................................................26
IP address............................................................................9
LED.........................................................................................6
subnet mask.......................................................................9
eth1
activity................................................................................62
configuring........................................................................26
LED.........................................................................................6
Ethernet cable............................................................................6
Ethernet port
cabling..................................................................................6
configuring........................................................................26
LED.........................................................................................6
external clock....................................................................28, 56
G
GUI Server one-time password.............................17, 22, 33
GuiSvr.cfg file.............................................................................41
H
HA Advanced Settings menu...............................19, 24, 36
HA Links menu............................................................18, 23, 35
hardware components............................................................5
hardware installation...............................................................6
HaSvr.cfg file..............................................................................41
heartbeat, configuring.............................................18, 23, 35
high availability
central manager, configuring..............................22, 34
regional server, configuring...................................17, 34
High Availability menu
central manager..............................................................22
regional server...................................................................17
host address..............................................................................47
hostname............................................................................27, 46
77Copyright © 2010, Juniper Networks, Inc.
Page 98

NSMXpress and NSM3000 User Guide
I
interfaces, configuring...................................................26, 45
IP address, configuring............................................................9
IP subnet calculator...............................................................68
L
LEDs...............................................................................................6
license, NSM........................................................................17, 33
log rate.........................................................................................61
lookup utility..............................................................................67
M
management IP
central manager......................................................22, 33
changing............................................................................43
regional server...........................................................16, 33
manuals
comments on................................................................xviii
memory usage.........................................................................62
MIBs.............................................................................................40
mounting brackets....................................................................6
N
NBI See NSM API
network activity.......................................................................62
network utilities
IP subnet calculator......................................................68
lookup.................................................................................67
ping.....................................................................................66
traceroute..........................................................................67
network, configuring..............................................................45
northbound interface See NSM API
NSM
configuration files, editing...........................................41
installing............................................................................39
updating............................................................................56
NSM API
port for central manager.............................................24
port for regional server...........................................19, 37
NSM appliances Settings menu........................................25
NSM Configuration Main Menu
central manager..............................................................21
regional server..................................................................16
NSM license.........................................................................17, 33
nsm user......................................................................................10
nsm_setup utility......................................................................14
NTP server..........................................................................28, 56
null modem serial cable.........................................................6
P
password
admin user........................................................................25
GUI server, one-time.........................................17, 22, 33
heartbeat.............................................................18, 23, 34
NSM, central manager.................................................22
super user, central manager...............................33, 39
super user, regional server............................16, 33, 39
user......................................................................................45
ping utility..................................................................................66
ports, required by NSMXpress..............................................4
power cord...................................................................................6
primary server, configuring.....................................17, 23, 34
process count...........................................................................62
R
reboot..........................................................................................44
Recovery Partition
preparing...........................................................................63
upgrading..........................................................................62
regional server
configuring with CLI.......................................................16
configuring with Web interface..................................31
custom settings................................................................17
typical settings, configuring........................................16
reinstallation.............................................................................29
Remote Replication of Database menu...........20, 24, 37
reports..........................................................................................41
root user......................................................................................10
routing
default gateway......................................................26, 46
static............................................................................26, 46
S
secondary server, configuring................................17, 23, 34
security, updating............................................................28, 43
Shared Disk menu.....................................................18, 23, 34
shutdown...................................................................................44
SNMP
authentication................................................................50
configuring........................................................................50
monitoring NSM appliances with............................50
system information for..................................................51
trap configuration..........................................................52
SRS See Statistical Report Server
SSH.................................................................................................5
static routing.....................................................................26, 46
Statistical Report Server menu..................................20, 38
Statistical Report Server, configuring......................20, 38
Copyright © 2010, Juniper Networks, Inc.78
Page 99

subnet calculator....................................................................68
subnet mask, configuring.......................................................9
sudo su - nsm............................................................................10
support, technical See technical support
syslog
forwarding.........................................................................53
receivers, adding.............................................................54
receivers, configuring....................................................54
receivers, deleting..........................................................56
receivers, editing.............................................................56
receivers, viewing...........................................................53
system information................................................................69
system logs...............................................................................65
system statistics......................................................................61
system time........................................................................27, 56
T
technical support...................................................................68
contacting JTAC............................................................xviii
tiling.............................................................................................62
time zone............................................................................28, 56
time, setting.......................................................................27, 56
traceroute utility......................................................................67
trap conditions, SNMP..........................................................52
troubleshooting.......................................................................63
Index
U
URL, Web interface...................................................................11
user
admin, nsm, root.............................................................10
W
Web interface
configuring.......................................................................60
login URL.............................................................................11
Web interface configuration
configuration......................................................................11
Web login.....................................................................................11
Y
Yum server.................................................................................57
79Copyright © 2010, Juniper Networks, Inc.
Page 100

NSMXpress and NSM3000 User Guide
Copyright © 2010, Juniper Networks, Inc.80
 Loading...
Loading...