Page 1

Junos Space Network Management Platform
Published
2021-04-09
Monitoring and Troubleshooting Guide
Release
21.1
Page 2

Juniper Networks, Inc.
1133 Innovation Way
Sunnyvale, California 94089
USA
408-745-2000
www.juniper.net
Juniper Networks, the Juniper Networks logo, Juniper, and Junos are registered trademarks of Juniper Networks, Inc. in
the United States and other countries. All other trademarks, service marks, registered marks, or registered service marks
are the property of their respective owners.
Juniper Networks assumes no responsibility for any inaccuracies in this document. Juniper Networks reserves the right
to change, modify, transfer, or otherwise revise this publication without notice.
Junos Space Network Management Platform Monitoring and Troubleshooting Guide
21.1
Copyright © 2021 Juniper Networks, Inc. All rights reserved.
The information in this document is current as of the date on the title page.
ii
YEAR 2000 NOTICE
Juniper Networks hardware and software products are Year 2000 compliant. Junos OS has no known time-related
limitations through the year 2038. However, the NTP application is known to have some difficulty in the year 2036.
END USER LICENSE AGREEMENT
The Juniper Networks product that is the subject of this technical documentation consists of (or is intended for use with)
Juniper Networks software. Use of such software is subject to the terms and conditions of the End User License Agreement
(“EULA”) posted at https://support.juniper.net/support/eula/. By downloading, installing or using such software, you
agree to the terms and conditions of that EULA.
Page 3

Table of Contents
1
About the Documentation | vii
Documentation and Release Notes | vii
Documentation Conventions | vii
Documentation Feedback | x
Requesting Technical Support | x
Self-Help Online Tools and Resources | xi
Creating a Service Request with JTAC | xi
Overview
Overview | 2
iii
Monitoring Network Devices and Troubleshooting Software Issues with Junos Space Network
Management Platform | 2
Systems of Record | 3
System Snapshot | 3
Backup and Restore | 3
Maintenance Mode | 4
Audit Logs | 4
Jobs | 4
Secure Console | 5
Looking Glass | 5
Reports | 5
Junos Space Debug Utilities | 6
Overall System Condition and Fabric Load History Overview | 6
Overall System Condition | 6
Fabric Load History | 7
Active Users History | 8
Junos Space Network Management Platform Widgets | 9
Devices | 9
Device Templates | 9
CLI Configlets | 10
Images and Scripts | 10
Page 4

Reports | 10
2
Network Monitoring | 11
Configuration Files | 11
Jobs | 11
Role Based Access Control | 12
Audit Logs | 12
Administration | 12
Log Files and Debug Utilities
Troubleshooting Junos Space Network Management Platform Issues by Using Log
Files | 15
System Status Log File Overview | 15
System Status Log File | 15
Customizing Status Log File Content | 16
iv
Downloading System Log Files for a Junos Space Appliance | 16
Customizing Log Files to Download | 17
Junos Space Network Management Platform Log Files Overview | 17
Apache Web Server Log Files | 18
JBoss Application Server Log Files | 18
MySQL Database Log Files | 20
Node Management Agent Log Files | 20
Troubleshooting Log File Overview | 21
Downloading the Troubleshooting Log File in Server Mode | 22
Downloading the Troubleshooting Log File in Maintenance Mode | 25
Downloading Troubleshooting System Log Files Through the Junos Space CLI | 26
Downloading a System Log File by Using a USB Device | 26
Downloading System Log File by Using SCP | 28
Customizing Node System Status Log Checking | 31
Customizing Node Log Files to Download | 32
Troubleshooting Network Devices by Using Junos Space Debug Utilties | 33
Junos Space Debug Utilities Overview | 33
Device-Connection Debug Scripts | 34
getDeviceInfo.sh | 34
DeviceDebugInfoCollector.sh | 34
Page 5

getAllDeviceInfo.sh | 34
cleanupEditChannel.sh | 35
Device Import Scripts and Java Applications | 35
cleanupDeviceImportTables.sh | 35
DB-blob-reader.jar | 35
Job Management Scripts and Java Applications | 36
SystemLoadViewer.sh | 36
getJobThreadSump.sh | 36
JobInfoCollector.jar | 36
Usr/nma/bin/collectStuckJobLogFiles.pl | 36
HornetQ Scripts | 37
HornetQInfoProvider.sh | 37
HQMessageViewer.sh | 37
Compare.py | 37
v
Executing Device-Connection Debug Scripts | 38
Executing the Script to Collect Device-Connection Information | 38
Executing the Script to Collect Device Debug Information | 40
Executing the Script to Unlock the Device Configuration | 45
Executing the Script to Collect Node-Connection Information | 46
Executing Device Import Detail Script and Java Application | 52
Executing the Script to Delete Data from Device Import Tables | 52
Executing the Java Application to View Device XML | 53
Executing Job Management Scripts and Java Applications | 55
Executing the Java Application to Collect Job Information | 55
Executing the Script to View the Stack Trace of a Job | 59
Executing the Script to View Job Information on Nodes | 60
Executing HornetQ Scripts | 66
Executing the HornetQ Script to View all JBoss Queues | 66
Executing the HornetQ Script to List of Messages in a JBoss Queue | 68
Page 6

Troubleshooting Junos Space Platform Issues
3
Troubleshooting Login–Related Issues | 72
Troubleshooting the Not Able to Log In from the Junos Space Login Page Issue | 72
Troubleshooting Device Management–Related Issues | 74
Troubleshooting Device Discovery Failure | 74
Troubleshooting Device Data Collection Issue | 75
Troubleshooting Devices Discovered Twice Using the Device Discovery Workflow | 76
Troubleshooting Network Monitoring–Related Issues | 77
Troubleshooting the Network Monitoring Page Is Not Available Issue | 77
Troubleshooting DMI Schema–Related Issues | 78
Troubleshooting the Nondisplay of the DMI Schema Tree Issue | 78
vi
Page 7
About the Documentation
IN THIS SECTION
Documentation and Release Notes | vii
Documentation Conventions | vii
Documentation Feedback | x
Requesting Technical Support | x
Use this guide to know about the various features, such as Systems of Record, System Snapshot, Audit
Logs, Looking Glass, and so on, that you can use to monitor and troubleshoot devices; and also, know
about procedures to troubleshoot issues, such as login-related issues, device management-related issues,
DMI schema-related issues, and so on, in Junos Space Platform.
vii
Documentation and Release Notes
To obtain the most current version of all Juniper Networks®technical documentation, see the product
documentation page on the Juniper Networks website at https://www.juniper.net/documentation/.
If the information in the latest release notes differs from the information in the documentation, follow the
product Release Notes.
Juniper Networks Books publishes books by Juniper Networks engineers and subject matter experts.
These books go beyond the technical documentation to explore the nuances of network architecture,
deployment, and administration. The current list can be viewed at https://www.juniper.net/books.
Documentation Conventions
Table 1 on page viii defines notice icons used in this guide.
Page 8
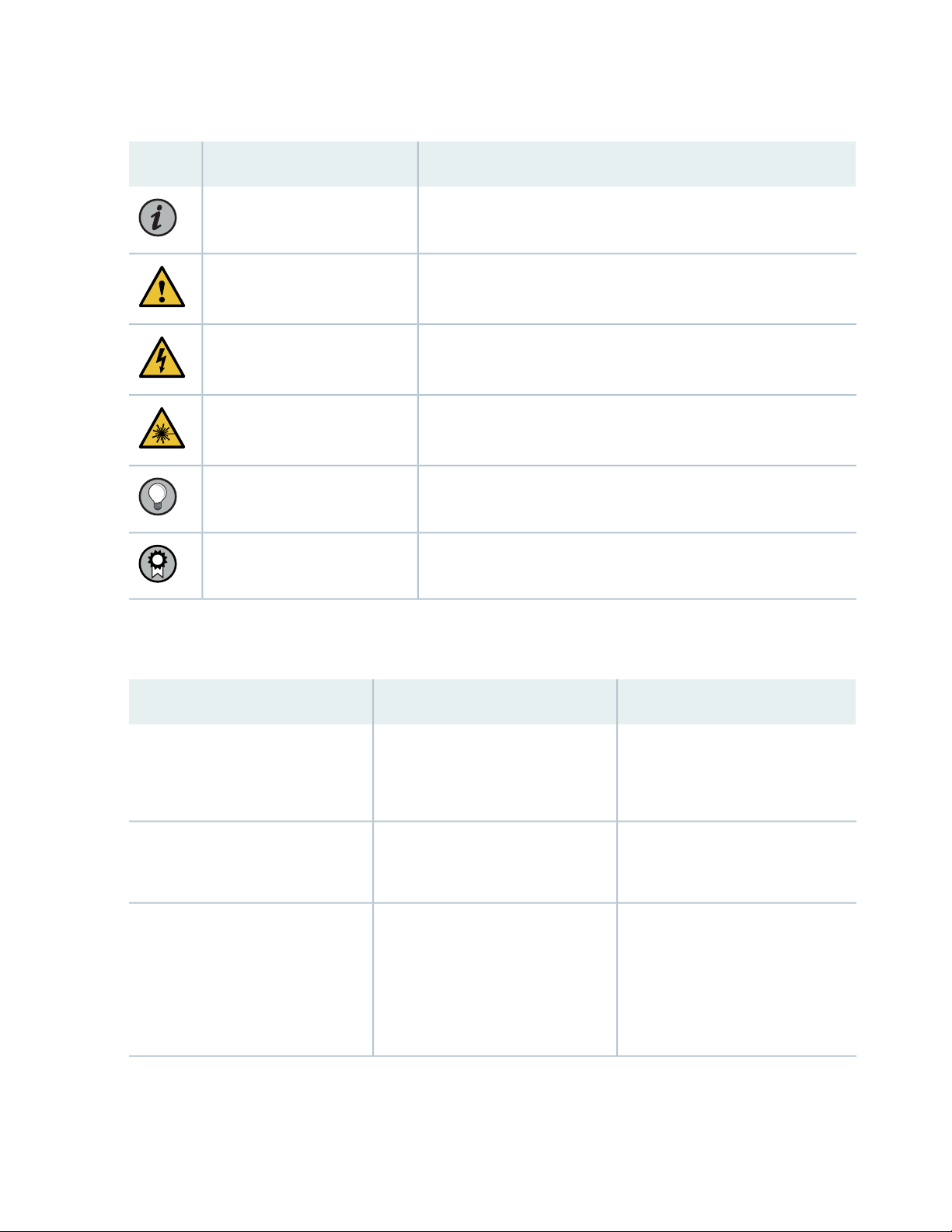
Table 1: Notice Icons
viii
DescriptionMeaningIcon
Indicates important features or instructions.Informational note
Caution
Indicates a situation that might result in loss of data or hardware
damage.
Alerts you to the risk of personal injury or death.Warning
Alerts you to the risk of personal injury from a laser.Laser warning
Indicates helpful information.Tip
Alerts you to a recommended use or implementation.Best practice
Table 2 on page viii defines the text and syntax conventions used in this guide.
Table 2: Text and Syntax Conventions
ExamplesDescriptionConvention
Fixed-width text like this
Italic text like this
Represents text that you type.Bold text like this
Represents output that appears on
the terminal screen.
Introduces or emphasizes important
•
new terms.
Identifies guide names.
•
Identifies RFC and Internet draft
•
titles.
To enter configuration mode, type
the configure command:
user@host> configure
user@host> show chassis alarms
No alarms currently active
A policy term is a named structure
•
that defines match conditions and
actions.
Junos OS CLI User Guide
•
RFC 1997, BGP Communities
•
Attribute
Page 9

Table 2: Text and Syntax Conventions (continued)
ix
ExamplesDescriptionConvention
Italic text like this
Text like this
< > (angle brackets)
| (pipe symbol)
Represents variables (options for
which you substitute a value) in
commands or configuration
statements.
Represents names of configuration
statements, commands, files, and
directories; configuration hierarchy
levels; or labels on routing platform
components.
variables.
Indicates a choice between the
mutually exclusive keywords or
variables on either side of the symbol.
The set of choices is often enclosed
in parentheses for clarity.
Configure the machine’s domain
name:
[edit]
root@# set system domain-name
domain-name
To configure a stub area, include
•
the stub statement at the [edit
protocols ospf area area-id]
hierarchy level.
The console port is labeled
•
CONSOLE.
stub <default-metric metric>;Encloses optional keywords or
broadcast | multicast
(string1 | string2 | string3)
# (pound sign)
[ ] (square brackets)
Indention and braces ( { } )
; (semicolon)
GUI Conventions
Indicates a comment specified on the
same line as the configuration
statement to which it applies.
Encloses a variable for which you can
substitute one or more values.
Identifies a level in the configuration
hierarchy.
Identifies a leaf statement at a
configuration hierarchy level.
rsvp { # Required for dynamic MPLS
only
community name members [
community-ids ]
[edit]
routing-options {
static {
route default {
nexthop address;
retain;
}
}
}
Page 10
Table 2: Text and Syntax Conventions (continued)
x
ExamplesDescriptionConvention
Bold text like this
> (bold right angle bracket)
Represents graphical user interface
(GUI) items you click or select.
Separates levels in a hierarchy of
menu selections.
In the Logical Interfaces box, select
•
All Interfaces.
To cancel the configuration, click
•
Cancel.
In the configuration editor hierarchy,
select Protocols>Ospf.
Documentation Feedback
We encourage you to provide feedback so that we can improve our documentation. You can use either
of the following methods:
Online feedback system—Click TechLibrary Feedback, on the lower right of any page on the Juniper
•
Networks TechLibrary site, and do one of the following:
Click the thumbs-up icon if the information on the page was helpful to you.
•
Click the thumbs-down icon if the information on the page was not helpful to you or if you have
•
suggestions for improvement, and use the pop-up form to provide feedback.
E-mail—Send your comments to techpubs-comments@juniper.net. Include the document or topic name,
•
URL or page number, and software version (if applicable).
Requesting Technical Support
Technical product support is available through the Juniper Networks Technical Assistance Center (JTAC).
If you are a customer with an active Juniper Care or Partner Support Services support contract, or are
Page 11

covered under warranty, and need post-sales technical support, you can access our tools and resources
online or open a case with JTAC.
JTAC policies—For a complete understanding of our JTAC procedures and policies, review the JTAC User
•
Guide located at https://www.juniper.net/us/en/local/pdf/resource-guides/7100059-en.pdf.
Product warranties—For product warranty information, visit https://www.juniper.net/support/warranty/.
•
JTAC hours of operation—The JTAC centers have resources available 24 hours a day, 7 days a week,
•
365 days a year.
Self-Help Online Tools and Resources
For quick and easy problem resolution, Juniper Networks has designed an online self-service portal called
the Customer Support Center (CSC) that provides you with the following features:
Find CSC offerings: https://www.juniper.net/customers/support/
•
Search for known bugs: https://prsearch.juniper.net/
•
xi
Find product documentation: https://www.juniper.net/documentation/
•
Find solutions and answer questions using our Knowledge Base: https://kb.juniper.net/
•
Download the latest versions of software and review release notes:
•
https://www.juniper.net/customers/csc/software/
Search technical bulletins for relevant hardware and software notifications:
•
https://kb.juniper.net/InfoCenter/
Join and participate in the Juniper Networks Community Forum:
•
https://www.juniper.net/company/communities/
Create a service request online: https://myjuniper.juniper.net
•
To verify service entitlement by product serial number, use our Serial Number Entitlement (SNE) Tool:
https://entitlementsearch.juniper.net/entitlementsearch/
Creating a Service Request with JTAC
You can create a service request with JTAC on the Web or by telephone.
Visit https://myjuniper.juniper.net.
•
Call 1-888-314-JTAC (1-888-314-5822 toll-free in the USA, Canada, and Mexico).
•
For international or direct-dial options in countries without toll-free numbers, see
https://support.juniper.net/support/requesting-support/.
Page 12

1
PART
Overview
Overview | 2
Page 13
CHAPTER 1
Overview
IN THIS CHAPTER
Monitoring Network Devices and Troubleshooting Software Issues with Junos Space Network Management
Platform | 2
Overall System Condition and Fabric Load History Overview | 6
Junos Space Network Management Platform Widgets | 9
2
Monitoring Network Devices and Troubleshooting Software Issues with Junos Space Network Management Platform
IN THIS SECTION
Systems of Record | 3
System Snapshot | 3
Backup and Restore | 3
Maintenance Mode | 4
Audit Logs | 4
Jobs | 4
Secure Console | 5
Looking Glass | 5
Reports | 5
Junos Space Debug Utilities | 6
Page 14

Use the following features of Junos Space Network Management Platform to monitor devices and
troubleshoot software issues:
Systems of Record
A network managed by Junos Space Platform contains two repositories of information about the devices
in the network: the devices themselves (each device defines and reports its official state) and the database
(which contains information that is reported by the device during device discovery). This is known as
systems of record.
The systems of record operate in the following two modes depending on where the repository of information
is stored:
Network as a system of record (NSOR)—By default, the network is the system of record (NSOR). In this
•
mode, when a user commits a change in the configuration of a network device, the commit operation
automatically triggers a report through the system log to Junos Space Platform.
Junos Space as a system of record (SSOR)—In this mode, when you perform any out-of-band commit
•
operation, Junos Space Platform receives a system log message from the device, but the values in the
Junos Space Platform database are not automatically changed or synchronized with the values on the
device. Instead, you can choose whether or not to overwrite the device's local changes by pushing the
accepted configuration to the device from the Junos Space Platform database. For more information
about systems of record in Junos Space Platform, see Systems of Record in Junos Space Overview.
3
System Snapshot
You can use the System Snapshot feature to create a snapshot of the current state of the Junos Space
system. The snapshot includes all persistent data on the hard disk including data in the database, system
and application configuration files, and application and Linux executables. You can roll back the Junos
Space system to a predefined state or an older release if the system reaches an unrecoverable error state
caused by undesirable behavior due to corruption of system files, interruption of critical processes, and
so on. The System Snapshot is a fabric-wide operation that maintains consistency of data across all nodes
in the fabric.
You can create a snapshot before a significant action is performed—for example, adding or deleting a Junos
Space node, installing a Junos Space application, and so on—because the action can precipitate the system
into an undesirable state. You can delete the snapshot after you have ascertained that the action was
performed successfully. For more information about system snapshots, see Creating a System Snapshot.
Backup and Restore
You use the Backup and Restore feature to back up (or schedule the backup of) and restore the data in
the Junos Space database. You can set up an hourly, daily, or weekly schedule. The database backup can
Page 15

be stored on the local Junos Space system or transferred to a remote system automatically using the Secure
Copy mechanism.
You can restore the backup in any of the following circumstances:
Junos Space data is corrupted and you need to replace the corrupted data with uncorrupted data.
•
Junos Space software is corrupted and unstable after a reinstallation or an upgrade and you need to
•
populate the Junos Space database with uncorrupted data.
For more information about backup and restore operations, see Backing Up and Restoring the Database
Overview.
Maintenance Mode
Maintenance mode is a mode in which you can perform database restore and debugging tasks while all
nodes in the fabric are shut down and the Junos Space Network Management Platform Web proxy is
running. You need to be an authorized Junos Space administrator to put the system into maintenance
mode. You can put the system into maintenance mode only after you initiate a restore task by using the
Backup and Restore feature.
4
The Junos Space system goes into maintenance mode in the following situations:
Junos Space Network Management Platform software goes down.
•
You initiate a restore operation by using the Backup and Restore feature.
•
You upgrade the Junos Space Network Management Platform software.
•
For more information about maintenance mode, see Maintenance Mode Overview.
Audit Logs
The Audit Logs workspace of Junos Space Platform displays the login history and tasks initiated by a local
or remote user. Through this workspace, you can track login history, view the list of device management
tasks, view the list of services that were provisioned on the device, and so on. However, tasks that are not
initiated by users, such as device-driven activities (for example, resynchronization of network elements),
and changes made from the Junos Space CLI are not recorded in audit logs. Audit logs can be used by
administrators to review events—for example, to identify which user accounts are associated with an event,
to determine the chronological sequence of events (that is, what happened before and during an event),
and so on. For more information about audit logs, see Junos Space Audit Logs Overview.
Jobs
You use the Jobs workspace of Junos Space Platform to monitor the status of jobs that are run in Junos
Space Platform and all Junos Space applications installed on Junos Space Platform. You can view the status
of the jobs on the Job Management page. A job is a user-initiated action that is performed on any object
Page 16

that is managed by Junos Space Platform, such as a device, service, or customer. Typical jobs in Junos
Space Network Management Platform include discovering devices, deploying services, prestaging devices,
and performing functional and configuration audits.
You can trigger jobs immediately or schedule jobs for a later date and time. Junos Space Platform maintains
a history of job statuses for all scheduled jobs. When a job is scheduled from a workspace, Junos Space
Platform assigns a job ID that serves to identify the job on the Job Management page. For more information
about jobs, see Jobs Overview.
Secure Console
The Secure Console feature on the Devices workspace provides a secure remote access connection to
managed and unmanaged devices. Secure Console initiates an SSH session from the Junos Space user
interface by using the SSH protocol. Secure Console is a terminal window embedded in Junos Space
Platform that eliminates the need for a third-party SSH client to connect to devices. Secure Console
provides additional security while connecting to your devices by initiating an SSH session from the Junos
Space server rather than from your Web browser. You can access the Secure Console feature either from
the Device Management page or the Secure Console page. For more information about Secure Console,
see Secure Console Overview.
5
Looking Glass
You use the Looking Glass feature from the Devices workspace to view device configurations by executing
basic CLI commands from the Junos Space user interface. You can execute these commands on multiple
devices and compare the configurations and runtime information of these devices. You can execute the
following types of commands by using Looking Glass: show, ping, test, and traceroute. The commands
that are supported and stored in the Junos Space Platform database are displayed on the Looking Glass
page. When you type the first few letters of the command, the suggestion list displays the commands that
are supported, are stored, and begin with the letters that you typed. For more information about Looking
Glass, see Looking Glass Overview.
Reports
With the Reports workspace of Junos Space Platform, you can generate customized reports for managing
the resources in your network. You can use these reports to gather device inventory details, job execution
details, user accounts, and audit trails. You first create a report definition to specify what information to
retrieve from the Junos Space Platform inventory database. You then use this report definition to generate,
export, and print the reports. Junos Space Platform provides some predefined categories to create report
definitions. You can combine multiple categories to create a report definition. By default, a predefined set
of attributes is included in a report definition. You can choose to add or remove the attributes according
to what information you want from the final generated report. You can group, sort, or filter data based on
specific attributes available with the report definition. For more information about reports, see Reports
Overview.
Page 17

Junos Space Debug Utilities
Junos Space debug utilities are a collection of scripts and Java applications to fetch details that cannot be
viewed on the JBoss CLI or from the Junos Space user interface. These scripts and Java applications are
stored at /var/log/space-debug/debug-utilities and categorized under deviceConnection, jobManagement,
deviceImport, and HornetQ directories. When you execute these scripts or Java applications, you can view
details such as device-connection or node-connection issues, device XMLs fetched from the Junos Space
Platform database, and jobs triggered and nodes that execute these jobs. For more information about
Junos Space debug utilities, see “Junos Space Debug Utilities Overview” on page 33.
RELATED DOCUMENTATION
Overall System Condition and Fabric Load History Overview | 6
Junos Space Network Management Platform Widgets | 9
6
Overall System Condition and Fabric Load History Overview
You can view the overall Junos Space system condition and fabric load from the Junos Space Network
Management Platform Dashboard or the Administration statistics page.
Overall System Condition
To calculate the overall Junos Space system condition, Junos Space Platform uses a formula based on
cluster health and node-function health:
Cluster health indicates the percentage of nodes in the fabric that are currently running.
•
For example, if only three nodes are reachable in a four-node fabric, cluster health is 75%.
Load-balancer health indicates the percentage of nodes (enabled for load balancing) that are running
•
the load-balancing process.
For example, if two nodes are enabled for load balancing and the load-balancing process is running on
only one node, the load-balancing health is 50%.
Database health indicates the percentage of nodes (enabled for database requests) that are running the
•
database process.
For example, if two nodes are enabled as the database server and the database process is running on
only one node, then database health is 50%.
Application-logic health indicates the percentage of nodes (enabled for application logic (DML and
•
business logic) that are running the application-logic process.
Page 18
For example, if three nodes are enabled for application logic and the application-logic process is running
on only two nodes, then application-logic health is 67%.
Junos Space Platform retrieves data on the nodes and the node functions that are running, and then applies
the following formula to determine the overall Junos Space system condition: Overall System Condition
= [(Number of Nodes Running) / (Number of Nodes in Fabric)] * [(Number of Nodes Running Load_Balancing
Process) / (Number of Nodes enabled for Load Balancing)] * [(Number of Nodes Running Database-Server
Process) / (Number of Nodes Enabled As Database Server)] * [(Number of Nodes Running Application-Logic
Process) / (Number of Nodes Enabled for Application Logic)]
The overall Junos Space system condition is expressed as a percentage. If we use the values in the preceding
examples in this formula, then the overall system condition would be calculated as: Overall System Condition
= 75% * 50%* 50% * 67% = 12.5%.
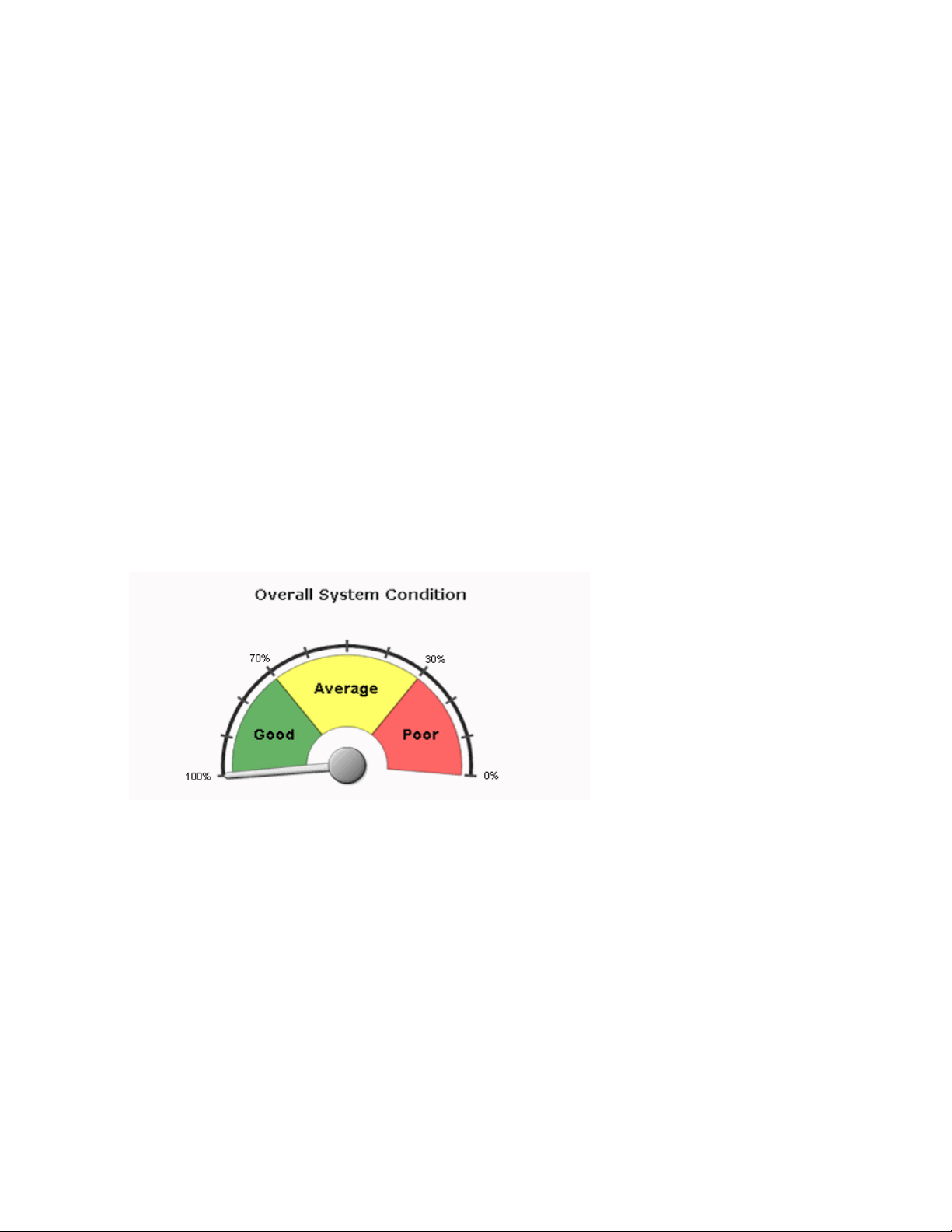
A value between 0 and 30% indicates that the system health is Poor, a value between 30% and 70%
indicates that the system health is average, and a value between 70% and 100% indicates that the system
health is good. The Overall System Condition chart displays the system health as shown in
Figure 1 on page 7
7
Figure 1: Overall System Condition Gauge
The overall system health indicates 0% (Poor) when any one of the following conditions is detected:
No nodes in the fabric are running.
•
No nodes enabled for load balancing are running the load-balancing process.
•
No nodes enabled for database requests are running the database process.
•
No nodes enabled for application logic are running the application-logic process.
•
Fabric Load History
The Fabric Load History chart, as shown in Figure 2 on page 8, displays the average CPU usage across
all nodes that are running in the fabric.
Page 19
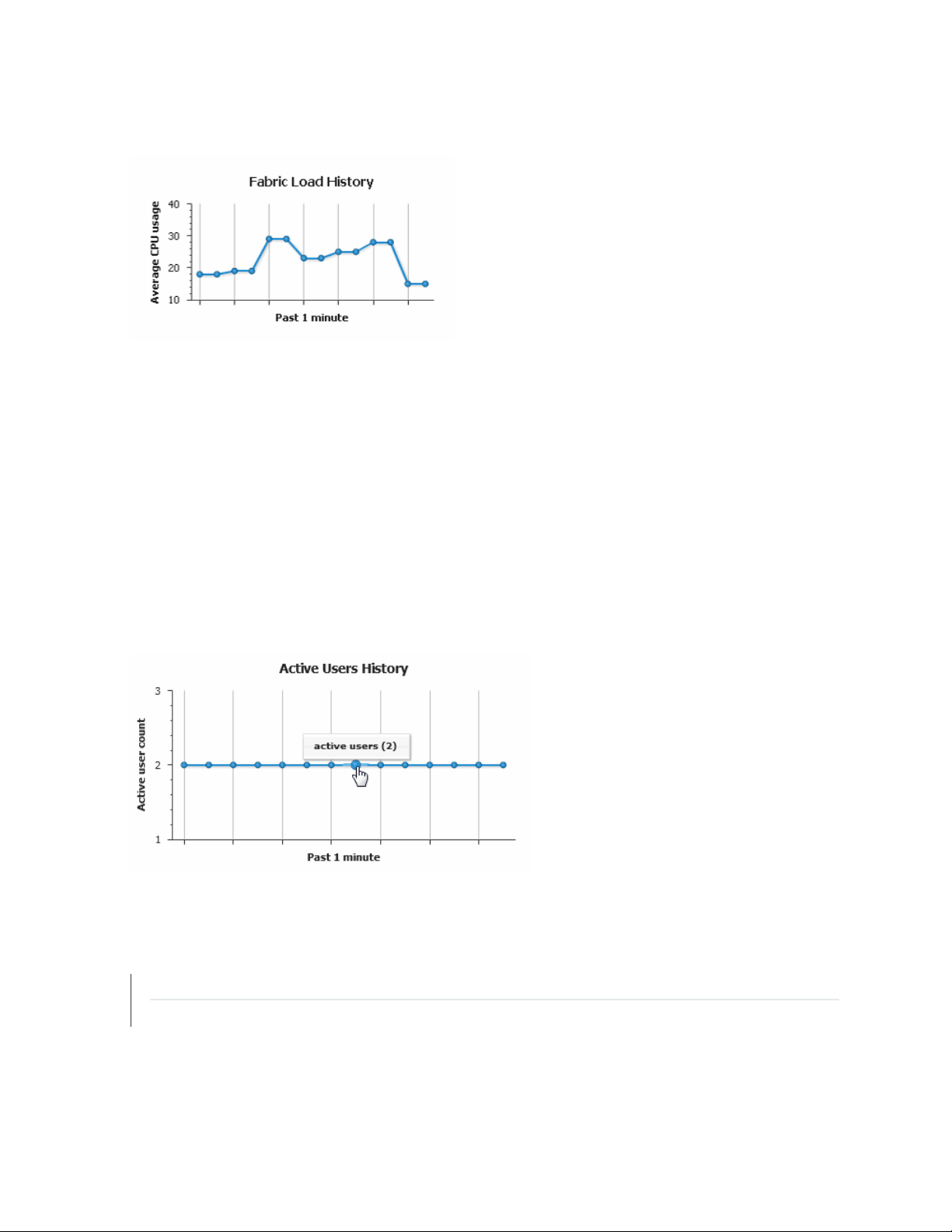
Figure 2: Fabric Load History Chart
Junos Space Platform uses the following formula to determine the fabric load: Fabric Load = (Total CPU
Usage for All Nodes Running) / (Number of Nodes Running)
For example, for a fabric with three nodes running and CPU usage of 80%, 30%, and 10%, respectively,
the fabric load is 40%.
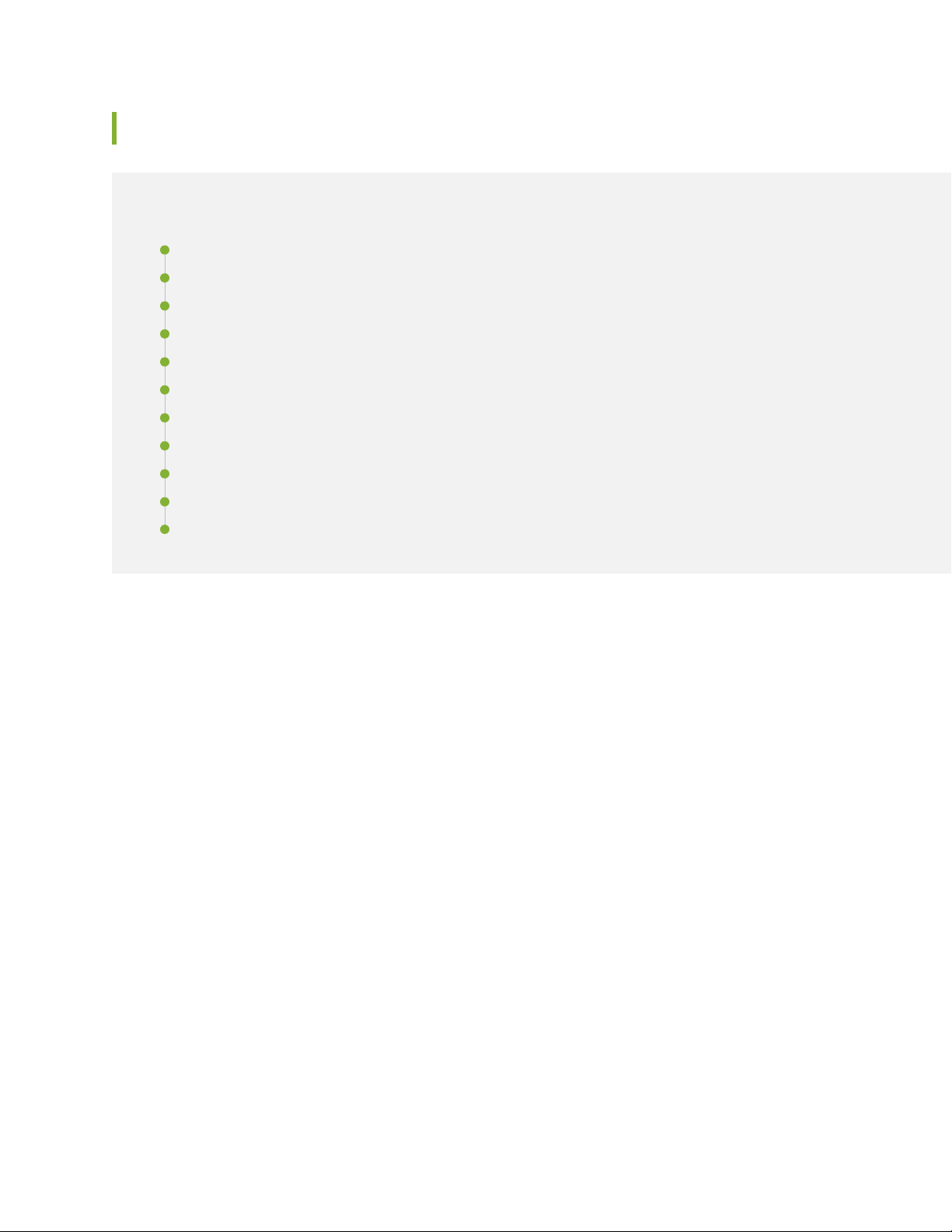
Active Users History
8
The Active Users History chart, as shown in Figure 3 on page 8, displays the number of active users in
the past one minute.
Figure 3: Active Users History Chart
RELATED DOCUMENTATION
Viewing the Junos Space Platform Dashboard
Viewing the Administration Statistics
Page 20
Junos Space Network Management Platform Widgets
IN THIS SECTION
Devices | 9
Device Templates | 9
CLI Configlets | 10
Images and Scripts | 10
Reports | 10
Network Monitoring | 11
Configuration Files | 11
Jobs | 11
Role Based Access Control | 12
Audit Logs | 12
9
Administration | 12
This topic presents a list of workspaces in Junos Space Network Management Platform and the widgets
that they display:
Devices
The Devices workspace displays the following widgets:
Device Count by Platform—Number of Juniper Networks devices added per device platform
•
Device Status—Percentage of devices with the UP, Down, or NA connection status
•
Device Count by OS—Number of devices running a particular Junos OS version
•
Device Count by Synchronization State—Device discovery targets that were discovered, failed, are
•
managed
For more information about these widgets, refer to the Viewing Device Statistics topic in the Junos Space
Network Management Platform Workspaces Feature Guide.
Device Templates
The Device Templates workspace displays the following widgets:
Template Status—Percentage of device templates with the Enabled and Need Review statuses
•
Page 21

Template Definition Status—Percentage of device templates that are Published and Unpublished statuses
•
Template Count by Device Family—Number of device templates created per device family
•
For more information about these widgets, refer to the Viewing Device Template Statistics and Viewing
Template Definition Statistics topics in the Junos Space Network Management Platform Workspaces Feature
Guide.
CLI Configlets
The CLI Configlets workspace displays the following widgets:
CLI Configlet Count by Device Family—Number of CLI configlets created per device family
•
Configuration Viewer Count by Device Family—Number of configuration views per device family
•
For more information about these widgets, refer to the Viewing CLI Configlet Statistics and Viewing
Configuration Views Statistics topics in the Junos Space Network Management Platform Workspaces Feature
Guide.
10
Images and Scripts
The Images and Scripts workspace displays the following widgets:
Device Image Count by Platform Group—Number of device images per platform group
•
Device Images Count by Version—Number of device images created per Junos OS version
•
Number of Scripts by Type—Number of scripts created per script type. The script types are : Commit,
•
Op, and Event
Number of Jobs per Script Action—Number of jobs triggered by different script-related actions
•
For more information about these widgets, refer to the Viewing Statistics for Device Images and Scripts topic
in the Junos Space Network Management Platform Workspaces Feature Guide.
Reports
The Reports workspace displays the following widgets:
Report Definition Count by User—Number of report definitions created per user
•
Report Count by User—Number of reports created per user
•
For more information about these widgets, refer to the Viewing Report Statistics and Viewing Report Definition
Statistics topics in the Junos Space Network Management Platform Workspaces Feature Guide.
Page 22

Network Monitoring
The Network Monitoring workspace displays the following widgets:
Nodes with Pending Problems—Nodes with outstanding alarms
•
Nodes with Outages—Nodes that reported outages
•
Availability Over the Past 24 hours—Number and percentage availability of the network interfaces of
•
the devices that reported outages
Notification—Check for notifications sent to you, all Junos Space Platform users, and the on-call schedule
•
to fix outages.
Resource Graphs—Search for resource graphs. Resource graphs display data collected from managed
•
nodes throughout your network such as critical SNMP performance, response time, and so forth.
KSC Reports—Search for key SNMP customized (KSC) reports. KSC reports enable you to create and
•
view SNMP performance data using prefabricated graph types.
Quick Search—Search for nodes by node ID, node label, IP address, or the type of service whether ICMP
•
or SNMP.
11
For more information about these widgets, refer to the Network Monitoring Reports Overview topic in the
Junos Space Network Management Platform Workspaces Feature Guide.
Configuration Files
The Configuration Files workspace displays the following widgets:
Configuration File Count by Device Family—Number of configuration files per device family
•
Devices with most Frequently Revised Configuration Files—Devices whose configuration files have been
•
revised most number of times
For more information about these widgets, refer to the Viewing Configuration File Statistics topic in the
Junos Space Network Management Platform Workspaces Feature Guide.
Jobs
The Jobs workspace displays the following widgets:
Job Types—Percentage of all jobs of a particular type that are run
•
State of Jobs Run—Percentages of jobs that succeeded, are canceled, are in progress, or failed
•
Average Execution Time per Completed Job— Each bar in the Average Execution Time per Completed
•
Job bar chart represents a job type and the average execution time in seconds.
Page 23
For more information about these widgets, refer to the Viewing Statistics for Jobs topic in the Junos Space
Network Management Platform Workspaces Feature Guide.
Role Based Access Control
The Role Based Access Control workspace displays the following widget:
Number of Users Assigned by Role—Percentage and the number of users that are assigned to a role
•
For more information about these widgets, refer to Viewing User Statistics.
Audit Logs
The Audit Logs workspace displays the following widgets:
Audit Log Statistical Graph—Tasks that are performed and logged in all Junos Space applications over a
•
specific period of time
Top 10 Active Users in 24 hours—Top ten users who performed the most number of tasks over 24 hours
•
12
For more information about these widgets, refer to the Viewing Audit Log Statistics topic in the Junos Space
Network Management Platform Workspaces Feature Guide.
Administration
The Administration workspace displays the following widgets:
System Health—Junos Space system condition, load on the fabric, and active users.
•
System Alert Messages in the last 30 days—SMTP server alert messages categorized by application, and
•
when the error last occurred.
System Health Report—Health and performance of the Junos Space nodes in your Junos Space setup
•
and the processes on these nodes. Staring in Release 15.2R1, the Administration workspace displays
the System Health Report widget.
For more information about these widgets, refer to the Viewing the Administration Statistics topic in the
Junos Space Network Management Platform Workspaces Feature Guide.
Release History Table
DescriptionRelease
15.1R2
Staring in Release 15.2R1, the Administration workspace displays the System Health
Report widget.
Page 24
RELATED DOCUMENTATION
Overall System Condition and Fabric Load History Overview | 6
Junos Space Debug Utilities Overview | 33
13
Page 25

2
PART
Log Files and Debug Utilities
Troubleshooting Junos Space Network Management Platform Issues by Using Log
Files | 15
Troubleshooting Network Devices by Using Junos Space Debug Utilties | 33
Page 26

CHAPTER 2
Troubleshooting Junos Space Network Management Platform Issues by Using Log Files
IN THIS CHAPTER
System Status Log File Overview | 15
Junos Space Network Management Platform Log Files Overview | 17
Troubleshooting Log File Overview | 21
Downloading the Troubleshooting Log File in Server Mode | 22
Downloading the Troubleshooting Log File in Maintenance Mode | 25
Downloading Troubleshooting System Log Files Through the Junos Space CLI | 26
15
Customizing Node System Status Log Checking | 31
Customizing Node Log Files to Download | 32
System Status Log File Overview
The system writes a system log file for each fabric node to provide troubleshooting and monitoring
information. See “System Status Log File” on page 15.
The System Administrator can customize the information that is collected in the system log file. See
“Customizing Node System Status Log Checking” on page 31.
The System Administrator can download the latest log files for each fabric node when logged in to a Junos
Space Appliance. See “Downloading System Log Files for a Junos Space Appliance” on page 16.
In each operating mode, the System Administrator can customize the default log files that are downloaded
from a Junos Space Appliance. See “Customizing Node Log Files to Download” on page 32.
System Status Log File
Approximately once a minute, the system checks and writes a status log file SystemStatusLog for each
fabric node by default. Each log file consists of system status, such as the disk, CPU, and memory usage
information, as shown. Junos Space Network Management Platform writes each system status log file to
/var/log/SystemStatusLog
Page 27

2009-08-10 11:51:48,673 DEBUG [net.juniper.jmp.cmp.nma.NMAResponse] (Thread-110:)
Node IP: 192.0.2.0Filesystem 1K-blocks Used Available Use% Mounted
on
/dev/mapper/VolGroup00-LogVol00
79162184 15234764 59841252 21% /
Cpu(s): 8.7%us, 1.1%sy, 0.0%ni, 90.0%id, 0.1%wa, 0.0%hi, 0.0%si, 0.0%st
Mem: 3866536k total, 2624680k used, 1241856k free, 35368k buffers
Swap: 2031608k total, 941312k used, 1090296k free, 439704k cached
Customizing Status Log File Content
The System Administrator can customize the information that is written in a fabric node system status log
file. For more information, see “Customizing Node System Status Log Checking” on page 31.
Downloading System Log Files for a Junos Space Appliance
The System Administrator can download the latest log files for each fabric node when logged in to a Junos
Space Appliance. The system status log file and all other third-party log files are collected and compressed
in a troubleshooting file.
16
Table 3 on page 16 lists the files included in the troubleshoot file.
Table 3: Log Files included in the troubleshoot File
LocationDescription
/var/log/SystemStatusLogSystem status log files
/var/log/jboss/*JBoss log files
/var/tmp/jboss/debug/*Service-provisioning data files
/var/log/mysqld.logMySQL error log files
/var/log/httpd/*Log files for Apache, Node Management Agent (NMA), and
Webproxy
/var/log/watchdog/*Watchdog log files
/var/log/messages/*System messages
The System Administrator can download log files in each operation mode as follows:
Server mode (See “Downloading the Troubleshooting Log File in Server Mode” on page 22.)
•
Maintenance mode (See “Downloading the Troubleshooting Log File in Maintenance Mode” on page 25.)
•
Page 28

CLI mode (See “Downloading Troubleshooting System Log Files Through the Junos Space CLI” on
•
page 26.)
Customizing Log Files to Download
The System Administrator can also customize the log files to be downloaded for specific fabric nodes. For
more information about customizing node log files to download, see “Customizing Node Log Files to
Download” on page 32.
RELATED DOCUMENTATION
Customizing Node System Status Log Checking | 31
Customizing Node Log Files to Download | 32
Downloading the Troubleshooting Log File in Server Mode | 22
Downloading the Troubleshooting Log File in Maintenance Mode | 25
Downloading Troubleshooting System Log Files Through the Junos Space CLI | 26
17
Junos Space Network Management Platform Log Files Overview
IN THIS SECTION
Apache Web Server Log Files | 18
JBoss Application Server Log Files | 18
MySQL Database Log Files | 20
Node Management Agent Log Files | 20
Junos Space Network Management Platform log files contain useful information that help you to identify,
analyze, and troubleshoot issues related to Junos Space Network Management Platform. The software
components of Junos Space Network Management Platform—JBoss, Apache Web server, MySQL, and
CentOS—generate these log files.
Table 4 on page 18 lists log files related to the software components of Junos Space Network Management
Platform.
Page 29

Table 4: Junos Space Network Management Platform Log Files
Description of the Log FilesSoftware Component
Log files from the Apache Web server, NMA, and Web proxyApache Web server
Log files from JBoss, Junos Space core, and hosted Junos Space applicationsJBoss
Log files from MySQL serversMySQL
Linux-based system log messagesCentOS
Log files for system statuses and Junos Space and watchdog processesNode Management Agent
In addition to the log files related to software components, you can also refer to the /var/log/install.log
log file for information about Junos Space Platform upgrades and Junos Space application installations.
Apache Web Server Log Files
18
You can view the Apache Web server log files to view information related to HTTPS requests, Apache
modules, and CGI programs.
Table 5 on page 18 lists the Apache Web server log files.
Table 5: Apache Web Server Log Files
DescriptionLog File
Logs related to incoming HTTPS requests/var/log/httpd/access_log
Error logs for both Apache Web server modules and CGI programs/var/log/httpd/error_log
Error logs related to SSL certificates/var/log/httpd/ssl_error_log
JBoss Application Server Log Files
JBoss is used as an application server in Junos Space Network Management Platform. It provides a runtime
environment for plug-and-play Junos Space applications and supports standard packaging of pluggable
applications based on the .ear file format. It also supports hot plug-and-play deployment of Junos Space
applications when the system is fully operational.
JBoss provides three configuration options: minimal, default, and all. Junos Space Network Management
Platform specifies all as the default JBoss configuration option.
Table 6 on page 19 lists the JBoss directories.
Page 30

Table 6: JBoss Directories
JBoss DirectoryType of JBoss Directory
/usr/local/jbossHome directory
/var/log/jbossLog directory
/var/spool/jbossData directory
/var/tmp/jbosstmp directory
Table 7 on page 19 lists the JBoss log files available in the /var/log/jboss/servers/server1/ directory. You
can also refer to the console file available in the /var/log/jboss/ directory for console messages from
JBoss.
Table 7: Joss Log Files
DescriptionLog File Name
19
process-controller.log
host-controller.log
JBoss boot log fileboot.log
Console log fileconsole.log
Log file that contains records about starting and stopping services in
domain mode
Log file that contains information about the host controller that starts
and stops the application server
Service Provisioning application log fileprovisioning.log
JBoss Application server log fileserver.log
EJB transactions log filelong-jpa-txn.log
Network Activate log fileProvisioning.log
QoS Design log fileQos.log
Security Director log fileSD.log
The Junos Space Service Provisioning application stores XML data files in the /var/tmp/jboss/debug
directory for debugging purposes. Service request deployment, service functional audits, and any reported
deployment errors from the devices are captured and stored in these XML data files.
Page 31

MySQL Database Log Files
You use the MySQL database log files to view information related to the Junos Space Network Management
Platform database.
Table 8 on page 20 lists the MySQL database log files.
Table 8: MySQL Database Log Files
DescriptionLog File
Primary log file for MySQL-related procedures/var/log/mysqld.log
Log file for slow queriesvar/lib/mysql/log-slow-queries.log
Node Management Agent Log Files
A Node Management Agent (NMA) is a daemon that runs on every Junos Space node. An NMA manages
the configuration files for the software components of Junos Space Network Management Platform—JBoss,
MySQL, and Apache. An NMA also monitors the usage of system resources, such as CPU, memory, and
disk space, and the health of the other server processes.
20
Table 9 on page 20 lists the NMA log files.
Table 9: NMA Log Files
DescriptionLog File
Logs that contain information about operations executed on the NMA/var/log/nma.log
Error logs from NMA CGI scripts/var/log/httpd/error_log
/var/log/watchdog
/var/log/SystemStatusLog
Logs related to starting and stopping processes on Junos Space Network
Management Platform
Logs related to CPU, memory, and disk space usage by Junos Space
Network Management Platform
RELATED DOCUMENTATION
Troubleshooting Log File Overview | 21
Page 32

Troubleshooting Log File Overview
The troubleshooting log file is a zip or tar package that contains the log files generated by different software
components of Junos Space Network Management Platform and service provisioning data files.
You can download the troubleshooting log file from the Junos Space user interface in sever mode, by
accessing the Junos Space Appliance URL in maintenance mode, or from the Junos Space Appliance console
in CLI mode. The troubleshooting log file is downloaded as a zip package in server mode and maintenance
mode, and as a tar package in CLI mode.
Server mode (See “Downloading the Troubleshooting Log File in Server Mode” on page 22.)
•
Maintenance mode (See “Downloading the Troubleshooting Log File in Maintenance Mode” on page 25.)
•
CLI mode (See “Downloading Troubleshooting System Log Files Through the Junos Space CLI” on
•
page 26.)
You need to be assigned the system administrator role to download the troubleshooting log file in server
mode and maintenance mode.
21
Junos Space Network Management Platform automatically names the troubleshooting zip package in the
troubleshoot_yyyy-mm-dd_hh-mm-ss.zip format. The date and time is represented in the Coordinated
Universal Time (UTC) format. For example, troubleshoot_2010-04-01_11-25-12.zip.
Table 10 on page 21 lists the files in this zip package.
Table 10: List of Log Files in the Troubleshooting Log File
LocationDescription
/var/log/jboss/*JBoss log files
/var/tmp/jboss/debug/*Service provisioning data files
/var/log/mysqld.logMYSQL error log file
/var/log/httpd/*Apache, NMA, and Webproxy log files
/var/log/watchdog/*Watchdog log file
/var/log/messages/*Linux system messages
RELATED DOCUMENTATION
/var/log/SystemStatusLogCPU, RAM, and disk statistics (during past 24 hours)
Page 33

Junos Space Network Management Platform Log Files Overview | 17
Downloading the Troubleshooting Log File in Server Mode | 22
Downloading the Troubleshooting Log File in Maintenance Mode | 25
Downloading Troubleshooting System Log Files Through the Junos Space CLI | 26
Downloading the Troubleshooting Log File in Server Mode
You download the troubleshooting log file in Server mode when you want to view the contents of the
troubleshooting log file and fix issues. You need to have the privileges of a System Administrator to
download the troubleshooting log file.
Before you download the troubleshooting log file in Server mode:
Ensure that you check the available disk space on the Junos Space node. The Lack Of Space error message
•
is displayed if the disk space is insufficient.
22
Ensure that a troubleshooting log download job you triggered earlier is not in progress. An error message
•
is displayed if you trigger another troubleshooting log download job while a previous download job is
in progress.
NOTE: On a multinode setup, the troubleshooting log file is stored at the following location on
the Junos Space node that completes the job: /var/cache/jboss/space-logs. You cannot download
the troubleshooting log file if this node goes down.
To download the troubleshooting log file in Server mode:
1. On the Junos Space Network Management Platform user interface, select Administration > Space
Troubleshooting.
The Space Troubleshooting page is displayed.
Page 34

2. Select whether to download the troubleshooting log file now or later.
To download the troubleshooting log file now:
•
i. Click Download.
The Collect Junos Space Logs Job Information dialog box is displayed.
ii. Click OK in the dialog box.
You can download the troubleshooting log file from the Job Management page.
iii. Double-click the ID of the troubleshooting log collection job on the Job Management page.
The Job Details dialog box is displayed.
iv. Click the Download link to access the troubleshoot_yyyy-mm-dd_hh-mm-ss.zip file in your
browser.
The filename of the troubleshoot zip file includes the server Coordinated Universal Time (UTC)
date and time. For example, troubleshoot_2010-04-01_11-25-12.zip.
23
If you are using Mozilla Firefox: In the Opening troubleshoot zip dialog box, click Save file,
•
then click OK to save the zip file to your computer using the Firefox Downloads dialog box.
If you are using Internet Explorer: From the File Download page, click Save and select a directory
•
on your computer where you want to save the troubleshoot_yyyy-mm-dd_hh-mm-ss.zip file.
NOTE: If the download job failed, the Job Details dialog box displays the reason the
job failed.
Table 11 on page 23 lists the files included in the troubleshoot_yyyy-mm-dd_hh-mm-ss.zip file.
Table 11: Log Files in the Troubleshooting Log File and Their Location
LocationLog File Description
/var/log/SystemStatusLogSystem status log file
/var/log/jboss/*JBoss log files
/var/tmp/jboss/debug/*Service provisioning data files
/var/log/mysqld.logMySQL error log file
/var/log/httpd/*Apache Web Server, NMA, and Web proxy log files
Page 35

Table 11: Log Files in the Troubleshooting Log File and Their Location (continued)
Watchdog log files /var/log/watchdog/*
/var/log/messages/*Linux system log messages
–CPU, RAM, or disk statistics (for the past 24 hours)
/var/log/jbossHeap and CPU Profiling Agent (HPROF) files
To download the troubleshooting log file later:
•
i. Select the Schedule at a later time option button.
ii. Enter the date in the Date field in the DD/MM/YYYY format.
iii. Enter the time in the Time field in the hh:mm format.
24
iv. Click Download.
The troubleshooting log download job is triggered at the scheduled time. You can view the status
of the scheduled job on the Job Management page.
TIP: When you contact Juniper Technical Assistance Center, describe the problem
you encountered and provide the troubleshoot_yyyy-mm-dd_hh-mm-ss.zip file to the
JTAC representative.
3. Click Close to return to the Administration statistics page.
RELATED DOCUMENTATION
System Status Log File Overview | 15
Customizing Node System Status Log Checking | 31
Customizing Node Log Files to Download | 32
Downloading the Troubleshooting Log File in Maintenance Mode | 25
Downloading Troubleshooting System Log Files Through the Junos Space CLI | 26
Page 36

Downloading the Troubleshooting Log File in Maintenance Mode
Maintenance Mode is a special mode that an administrator can use to perform system recovery or debugging
tasks while all nodes in the fabric are shut down and the Web proxy is running.
The administrator can download the troubleshoot_yyyy-mm-dd_hh-mm-ss.zip file from Maintenance Mode.
The troubleshoot zip file includes the server Coordinated Universal Time (UTC) date and time. For example,
troubleshoot_2010-04-01_11-25-12.zip.
To download the troubleshooting log file in maintenance mode, perform the following steps:
1. Connect to a Junos Space Appliance in maintenance mode by using the Junos Space Appliance URL.
For example:
https://<ipaddress>/maintenance
Where ipaddress is the address of the Junos Space Appliance.
25
The Maintenance Mode page appears.
2. Click the click here to log in link. The login dialog box appears.
3. Log in to maintenance mode by using the authorized login name and password.
4. Click OK. The Maintenance Mode Actions menu appears.
5. Click Download Troubleshooting Data and Logs. The file download dialog box appears.
6. Click Save to download the troubleshoot_yyyy-mm-dd_hh-mm-ss.zip file to the connected computer.
7. Click Log Out and Exit from Maintenance Mode.
RELATED DOCUMENTATION
Maintenance Mode Overview
System Status Log File Overview | 15
Customizing Node System Status Log Checking | 31
Customizing Node Log Files to Download | 32
Downloading the Troubleshooting Log File in Server Mode | 22
Downloading Troubleshooting System Log Files Through the Junos Space CLI | 26
Page 37

Downloading Troubleshooting System Log Files Through the Junos Space CLI
IN THIS SECTION
Downloading a System Log File by Using a USB Device | 26
Downloading System Log File by Using SCP | 28
If a Junos Space node is Up, the administrator can log in to the Junos Space node and download system
status logs for each fabric node by using the Secure Copy Protocol (SCP). If the Junos Space node is Down
but you can log in to the console of a Junos Space Appliance, you can download system status logs to a
USB drive.
26
The Retrieve Logs utility collects all system log files in the /var/log subdirectory and creates a compressed
TAR file (extension *.tgz). For more information about the log files that are written, see “System Status
Log File Overview” on page 15.
This topic includes the following sections:
Downloading a System Log File by Using a USB Device
Using the Retrieve Logs > Save to USB Device command, the administrator can download system status
logs to a connected USB device if the Junos Space node is Down and you can log in to the console.
Before you begin, ensure that the USB device is connected to the Junos Space Appliance.
Page 38

1. Log in to the Junos Space Appliance using the administrator username (admin) and password.
The Junos Space Settings Menu appears, as shown.
Junos Space Settings Menu
1> Change Password
2> Change Network Settings
3> Change Time Options
4> Retrieve Logs
5> Security
6> (Debug) run shell
Q> Quit
R> Redraw Menu
Choice [1-6,QR]:
27
2. Type 4 at the prompt.
The Retrieve Logs submenu appears.
Choice [1-6,AQR]: 4
1> Save to USB Device
2> Send Using SCP
A> Apply changes
M> Return to Main Menu
R> Redraw Menu
Choice [1-2,AMR]:
3. Type 1.
The following message is displayed: This process will retrieve the log files on all cluster members and
combine them into a .tar file. Once the file is created, you can copy the files onto a USB drive. Continue?
[y/n]
4. Type y to continue.
You are prompted to enter the administrator password.
5. Enter the administrator password.
Page 39

The system downloads the log files from all the nodes in the fabric and combines them into a .tar file.
After the file is created, the file is coped to the USB device and a message similar to the following is
displayed: Copying 20090827-1511-logs.tar to USB drive.
NOTE: If the USB device is not ready, the following message appears: Log collection complete
If USB key is ready, press "Y". To abort, press "N".
6. After the files are copied, unmount the USB and eject it from the Junos Space Appliance.
Downloading System Log File by Using SCP
Using the Junos Space CLI Retrieve Logs > SCP command, the administrator can download system status
logs to a specific location.
To download system status logs by using SCP, perform the following steps:
28
1. Log in to the Junos Space node using the administrator username (admin) and password.
The Junos Space Settings Menu appears, as shown.
Junos Space Settings Menu
1> Change Password
2> Change Network Settings
3> Change Time Options
4> Retrieve Logs
5> Security
6> (Debug) run shell
Q> Quit
R> Redraw Menu
Choice [1-6,QR]:
2. Type 4 at the prompt.
The Retrieve Logs submenu appears.
Choice [1-6,AQR]: 4
1> Save to USB Device
2> Send Using SCP
Page 40

A> Apply changes
M> Return to Main Menu
R> Redraw Menu
Choice [1-2,AMR]:
3. Type 2.
The following confirmation message is displayed:
This process will retrieve the log files on all cluster members and combine them into a .tar file. Once
the file is created, you will be asked for a remote scp server to transfer the file to. Continue? [y/n]
4. Type y to continue.
You are prompted to enter the administrator password.
29
5. Enter the administrator password.
A message indicating that the log files are being collected is displayed. The process retrieves the log
files on all cluster members and combines them into a .TAR file. This might take a few minutes to
complete.
After this is completed, you are prompted to enter the IP address of the remote server.
6. Enter the IP address of the SCP server to which to transfer the file.
NOTE:
Depending on whether the Junos Space fabric is configured with only IPv4 addresses or
•
both IPv4 and IPv6 addresses, Junos Space Platform allows you to enter an IPv4 address
or either an IPv4 or IPv6 address respectively for the SCP server.
The IPv4 and IPv6 addresses that you use must be valid addresses. Refer to
•
http://www.iana.org/assignments/ipv4-address-space for the list of restricted IPv4
addresses and http://www.iana.org/assignments/ipv6-address-space for the list of restricted
IPv6 addresses.
7. Enter the remote SCP user.
8. Enter the directory on the remote SCP server where the log file should be stored; for example,
/root/tmplogs.
The remote server information that you entered is displayed. The following is a sample:
Page 41

Remote scp IP: 192.0.2.0
Remote scp user: root
Remote scp path: /root/tmplogs
Is this correct? [y/n]
9. If the SCP server information is correct, type y.
If you are connecting to the SCP server for the first time, a message is displayed asking you to confirm
that you want to continue. The following is a sample message:
The authenticity of host '192.0.2.0 (192.0.2.0)' can't be established.
RSA key fingerprint is 01:70:4c:47:9e:1e:84:fc:69:3c:65:99:6d:e6:88:87.
Are you sure you want to continue connecting (yes/no)? yes
NOTE: If the SCP server information is incorrect or if you want to modify the SCP server
information, type n at the prompt, and modify the SCP server information as explained in the
preceding steps.
30
10. Type y to continue.
You are prompted to enter the password.
11. Enter the password for the SCP server.
If the credentials are correct, the file is transferred to the SCP server.
RELATED DOCUMENTATION
Maintenance Mode Overview
System Status Log File Overview | 15
Customizing Node System Status Log Checking | 31
Customizing Node Log Files to Download | 32
Downloading the Troubleshooting Log File in Server Mode | 22
Downloading the Troubleshooting Log File in Maintenance Mode | 25
Page 42

Customizing Node System Status Log Checking
You customize the system status checking for a fabric node to ensure that all necessary information is
written to the /var/log/SystemStatusLog log file. You must have the privileges of a System Administrator
to customize the system status checking. You customize the system status checking by modifying the
fabric node Perl script in /usr/nma/bin/writeLogCronJob.
To customize system status checking for a fabric node, modify the writeSystemStatusLogFile sub-function
in writeLogCronJob as shown:
sub writeSystemStatusLogFile{
my $err = 0;
my $logfile = $_[0];
$err = system("date >> $logfile");
$err = system("df /var >> $logfile");
$err = system("top -n 1 -b | grep Cpu >> $logfile");
$err = system("top -n 1 -b | grep Mem: >> $logfile");
$err = system("top -n 1 -b | grep Swap: >> $logfile");
31
***<Add additional system command here that you want to print out in the
SystemStatusLog file>***
if ($err == 0 ) { print "write log to $logfile successfully\n";
} else { print "cannot write log to $logfile\n";
}
return $err;
}
RELATED DOCUMENTATION
System Status Log File Overview | 15
Customizing Node Log Files to Download | 32
Downloading the Troubleshooting Log File in Server Mode | 22
Downloading the Troubleshooting Log File in Maintenance Mode | 25
Downloading Troubleshooting System Log Files Through the Junos Space CLI | 26
Page 43

Customizing Node Log Files to Download
You customize the log files downloaded for a fabric node to ensure that you download all the necessary
log files. You must have the privileges of a System Administrator to customize the log files. You customize
the log files you want to download by modifying the Perl script in /var/www/cgi-bin/getLogFiles.
Modify the getLogFiles Perl script zip command as shown:
. . .
system("zip –r $logFileName /var/log/jboss/* /var/tmp/jboss/debug/ /var/log/mysqld.log
/var/log/httpd/* /var/log/watchdog /var/log/messages /var/log/SystemStatusLog >
/dev/null");
. . .
RELATED DOCUMENTATION
32
System Status Log File Overview | 15
Customizing Node System Status Log Checking | 31
Downloading the Troubleshooting Log File in Server Mode | 22
Downloading the Troubleshooting Log File in Maintenance Mode | 25
Downloading Troubleshooting System Log Files Through the Junos Space CLI | 26
Page 44

CHAPTER 3
Troubleshooting Network Devices by Using Junos Space Debug Utilties
IN THIS CHAPTER
Junos Space Debug Utilities Overview | 33
Executing Device-Connection Debug Scripts | 38
Executing Device Import Detail Script and Java Application | 52
Executing Job Management Scripts and Java Applications | 55
Executing HornetQ Scripts | 66
33
Junos Space Debug Utilities Overview
IN THIS SECTION
Device-Connection Debug Scripts | 34
Device Import Scripts and Java Applications | 35
Job Management Scripts and Java Applications | 36
HornetQ Scripts | 37
Compare.py | 37
Junos Space debug utilities allow you to debug issues related to Junos Space nodes and devices managed
by Junos Space Network Management Platform and view details about jobs scheduled on Junos Space
Network Management Platform. Junos Space debug utilities are a collection of scripts and Java applications
stored at /var/log/space-debug/debug-utilities. These scripts and Java applications are organized under
the following categories: deviceConnection, jobManagement, deviceImport, and HornetQ. You can save
the output of the scripts at a custom location. By default, the output of the scripts is stored at the location
where the scripts are stored.
Page 45

The following scripts and Java applications are available for debugging:
Device-Connection Debug Scripts
IN THIS SECTION
getDeviceInfo.sh | 34
DeviceDebugInfoCollector.sh | 34
getAllDeviceInfo.sh | 34
cleanupEditChannel.sh | 35
The device-connection debug scripts stored at /var/log/space-debug/debug-utilities/deviceConnection/
fetch and display device-connection information from DeviceDataMatrix. DeviceDataMatrix is a memory
data structure in the Junos Space Network Management Platform database that stores device-connection
information. You can also view this information through JConsole or JMXTerm.
34
The following are the device-connection debug scripts:
getDeviceInfo.sh
getDeviceInfo.sh is a script to collect device-connection information for a single device. The script output
displays the device ID (as stored in the Junos Space Platform database), IP address of the device, IP address
of the Junos Space node to which the device is currently connected, status of the edit flag on the device,
SSH control channel number, number of channels opened from the device, and details of the open channels.
DeviceDebugInfoCollector.sh
DeviceDebugInfoCollector.sh is a script to execute frequently used Junos OS debug commands on a
device. When you execute this script, SSH connections are initiated to the device from the Junos Space
node you specified. The script output displays the list of active management daemon (MGD) processes on
the device, active SSH daemon (SSHD) processes on the device, active SSH connections to Junos Space
Platform from the device, and all active SSH connections from the device. You can also view additional
details about each of these processes and SSH connections.
getAllDeviceInfo.sh
getAllDeviceInfo.sh is a script to collect device-connection information about all devices that are connected
to a Junos Space node. The script output displays the device ID (as stored in the Junos Space Platform
database), IP address of the device, IP address of the Junos Space node to which the device is currently
connected, status of the edit flag on the device, SSH control channel number, number of channels opened
from the device, and details of the open channels about all devices that are connected to a Junos Space
node. On a multinode setup, you can also collect this information for all Junos Space nodes.
Page 46
cleanupEditChannel.sh
cleanupEditChannel.sh is a script to unlock the device configuration on the device. Junos Space Platform
sets a lock when you deploy a configuration from Junos Space Platform or Junos Space applications. You
use this script to unlock the device configuration if the previous deployments were erroneous and you are
currently unable to deploy the configuration from Junos Space Platform. You enter the variable false to
unlock the device configuration.
For more information about executing device-connection debug scripts, see “Executing Device-Connection
Debug Scripts” on page 38.
Device Import Scripts and Java Applications
IN THIS SECTION
cleanupDeviceImportTables.sh | 35
DB-blob-reader.jar | 35
35
The device import scripts and Java applications stored at
/var/log/space-debug/debug-utilities/deviceImport/ clear the device import tables and fetch device
inventory information or device configuration in XML format.
The following are the device import scripts and Java applications:
cleanupDeviceImportTables.sh
cleanupDeviceImportTables.sh is a script to clean data from device import tables. You can execute the
script to fix data errors during a device resynchronization process. You need to manually resynchronize
the device with the Junos Space Platform database from the user interface after you execute the script.
DB-blob-reader.jar
DB-blob-reader.jar is a Java application to collect the device information XML or interface information
XML. When you execute this application, the information from the XML is written to the
DB-blob-reader-result.txt file. This information can be useful for debugging device resynchronization
issues. You can modify the MySQL query in the DB-blob-reader.properties file and fetch information
based on that MySQL query. You can specify the following in the DB-blob-reader.properties file: device
ID (as stored in the Junos Space Platform database) and name of the RPC, device configuration, or interface.
For more information about executing device import scripts and Java applications, see “Executing Device
Import Detail Script and Java Application” on page 52.
Page 47

Job Management Scripts and Java Applications
IN THIS SECTION
SystemLoadViewer.sh | 36
getJobThreadSump.sh | 36
JobInfoCollector.jar | 36
Usr/nma/bin/collectStuckJobLogFiles.pl | 36
The job management scripts and Java applications stored at
/var/log/space-debug/debug-utilities/jobManagement/ fetch information about jobs executed from the
Junos Space nodes. You can also view the output of the scripts through JConsole or JMXTerm.
The following are the job management scripts and Java applications:
36
SystemLoadViewer.sh
SystemLoadViewer.sh is a script to collect information about available memory on all Junos Space nodes
and the jobs triggered on these nodes. The script output displays information such as the memory on the
nodes, number of root jobs and subjobs on each of the nodes, type of job (root job or subjob), state of the
job (running, queued, or stopped), name of the job, queue name of the job, the time the job was created,
and the time the job was modified. The script output also displays the top five processes that consume
CPU and memory when the script is executed.
getJobThreadSump.sh
getJobThreadSump.sh is a script to view the stack trace of a specific job. You can also view the script
output through JConsole or JMXTerm.
JobInfoCollector.jar
JobInfoCollector.jar is a Java application to execute SQL queries and collect information about jobs. You
can construct the SQL query in the JobInfoCollector.properties file. This file contains a default example
query. The application can also display the hierarchy of a subjob (input as the parent job ID) and list of jobs
that are currently unscheduled. You can also input a SQL query to obtain information about jobs.
For more information about executing job management scripts and Java applications, see “Executing Job
Management Scripts and Java Applications” on page 55.
Usr/nma/bin/collectStuckJobLogFiles.pl
Usr/nma/bin/collectStuckJobLogFiles.pl is a script to collect all the troubleshooting logs and threats at
the time of a job getting stuck. This Auto Gathering tool monitors and identifies the stuck job once added
to crontab as required. Stuck jobs are the ones that are in pending or under progress for more than forty
five minutes. Once the tool identifies such jobs, it collects all the logs and thread dump from the server,
Page 48

saves them in /var/tmp/stuckJobLogFiles_<timestamp>.tgz location, notifies the user via e-mail with details
such as file name, file location, node, and so on.
HornetQ Scripts
IN THIS SECTION
HornetQInfoProvider.sh | 37
HQMessageViewer.sh | 37
The HornetQ scripts stored at /var/log/space-debug/debug-utilities/hornetQ/ display the list of all JBoss
queues, of messages in a specific JBoss queue, or of jobs that are to be executed by a specific JBoss queue.
You can also view the script output through JConsole or JMXTerm.
37
The following are the HornetQ scripts:
HornetQInfoProvider.sh
HornetQInfoProvider.sh is a script to collect details about all HornetQ queues. The script output also lists
details such as consumer-count, message-count, and scheduled-count.
HQMessageViewer.sh
HQMessageViewer.sh is a script to view the list of messages in a specific JBoss queue. The script output
displays the job ID and job operation name. You can view the jobs that are queued to be executed by a
specific JBoss queue.
For more information about executing HornetQ scripts, see “Executing HornetQ Scripts” on page 66.
Compare.py
RELATED DOCUMENTATION
Junos Space Network Management Platform Log Files Overview | 17
Monitoring Network Devices and Troubleshooting Software Issues with Junos Space Network
Management Platform | 2
Page 49

Executing Device-Connection Debug Scripts
IN THIS SECTION
Executing the Script to Collect Device-Connection Information | 38
Executing the Script to Collect Device Debug Information | 40
Executing the Script to Unlock the Device Configuration | 45
Executing the Script to Collect Node-Connection Information | 46
You execute the device-connection debug scripts to view information about device-connection issues
related to Junos Space nodes and devices connected to these nodes. Device-connection scripts are stored
at the following location: /var/log/space-debug/debug-utilities/deviceConnection. When you execute
these scripts, the output is stored as .txt files at the same location. You can also specify a custom path to
store the output. The following sections list the steps to execute the scripts to collect information about
device-connection issues.
38
Executing the Script to Collect Device-Connection Information
You execute the getDeviceInfo.sh script to collect device-connection information of a device.
To execute the script to collect device-connection information:
1. Log in to the CLI of the Junos Space node.
2. Enter the administrator username and password at the Junos Space login prompt and press Enter.
The default username is admin and the default password is abc123.
The Junos Space Settings Menu is displayed.
3. Enter 6 (if you are using a hardware appliance) or 7 (if you are using a virtual appliance) at the Junos
Space Settings Menu prompt to run shell commands.
You are prompted to enter your password.
The following is a sample output from a virtual appliance:
admin@10.206.41.183's password:
Last login: Mon Aug 17 06:17:58 2015 from 10.206.41.42
Page 50

Welcome to the Junos Space network settings utility.
Initializing, please wait
Junos Space Settings Menu
1> Change Password
2> Change Network Settings
3> Change Time Options
4> Retrieve Logs
5> Security
6> Expand VM Drive Size
7> (Debug) run shell
A> Apply changes
Q> Quit
R> Redraw Menu
39
Choice [1-7,AQR]: 7
4. Type the administrator password and press Enter.
The shell prompt appears.
5. Type cd /var/log/space-debug/debug-utilities/deviceConnection at the shell prompt and press Enter.
6. (Optional) To view the list of debug scripts, type ls and press Enter.
The list of device-connection debug scripts is displayed.
7. Type ./getDeviceInfo.sh<device-IP address> and press Enter—for example, ./getDeviceInfo.sh
10.206.33.17.
The output of this command is saved to the DeviceInfo-<device-IP address>.txt file in the same directory.
The following is a sample output:
-----------------------------------------------------------Time of execution: Wed Jul 15 05:45:26 UTC 2015
-----------------------------------------------------------Device Id: 131153 Device Ip: 10.206.33.17
Node id: 10.206.41.57
Connection state: Connected
Page 51

Connection changed at: 07/14/2015 17:35:04
EditFlag : false
EditChannel num:0
SSH ctrl channel num: 4
Max channels allowed: 32
Number of channels opened: 4
------------------------------------------------------Channel details:
Channel Id: 1
Seq num: 11
Channel state: CHANNEL_STATE_UNUSE
Channel type: Netconf
------------------------------------------------------Channel Id: 2
Seq num: 14
Channel state: CHANNEL_STATE_UNUSE
Channel type: Netconf
------------------------------------------------------Channel Id: 3
Seq num: 22
Channel state: CHANNEL_STATE_OPEN
Channel type: Syslog
------------------------------------------------------Channel Id: 4
Seq num: 24
Channel state: CHANNEL_STATE_UNUSE
Channel type: Netconf
-------------------------------------------------------
40
8. (Optional) To save node connection information at a custom output location, type
./getDeviceInfo.sh<device-IP address> <output-file-path> and press Enter.
You can use the information from the .txt file to debug device-connection issues.
Executing the Script to Collect Device Debug Information
You execute the DeviceDebugInfoCollector.sh script to collect information about the connections and
processes on a device.
To execute the script to collect device debug information:
1. Log in to the CLI of the Junos Space node.
2. Enter the administrator username and password at the Junos Space login prompt and press Enter.
Page 52

The default username is admin and the default password is abc123.
The Junos Space Settings Menu is displayed.
3. Enter 6 (if you are using a hardware appliance) or 7 (if you are using a virtual appliance) at the Junos
Space Settings Menu prompt to run shell commands.
You are prompted to enter your password.
4. Type the administrator password and press Enter.
The shell prompt appears.
5. Type cd /var/log/space-debug/debug-utilities/deviceConnection at the shell prompt and press Enter.
6. (Optional) To view the list of debug scripts, type ls.
The list of device-connection debug scripts is displayed.
41
7. Type ./DeviceDebugInfoCollector.sh<device-IP address><device-username><node-VIP address> and
press Enter—for example, ./DeviceDebugInfoCollector.sh 10.206.32.107 user1 10.206.41.57..
8. Enter the device password.
The output from this command is saved to the DeviceDebugInfo-<device-IP address>.txt file in the
same directory.
The following is a sample output:
Time of execution: Wed Jul 15 07:43:43 UTC 2015
========================================================================================================
List of MGD processes on the device : (Command Executed - ps auxwww | sed -n
"1p; /sed -n/d; /mgd/p;")
========================================================================================================
USER PID %CPU %MEM VSZ RSS TT STAT STARTED TIME COMMAND
user1 1841 0.0 0.0 41132 236 ?? S Fri12AM 0:10.15 /usr/sbin/mgd
-N
user1 2310 0.0 0.0 41180 220 ?? S Fri12AM 0:06.62 mgd: (mgd)
(user1) (mgd)
user1 2367 0.0 0.0 41180 220 ?? S Fri12AM 0:06.67 mgd: (mgd)
(user1) (mgd)
user1 2424 0.0 0.0 41188 220 ?? S Fri12AM 0:06.54 mgd: (mgd)
(keybased) (mgd)
user1 4243 0.0 0.1 41180 520 ?? S 12:27AM 0:02.90 mgd: (mgd)
(user1) (mgd)
user1 7662 0.0 0.1 41180 520 ?? S 2:29AM 0:02.84 mgd: (mgd)
Page 53

(user1) (mgd)
user1 8595 0.0 0.2 41192 1664 ?? Is 4:09AM 0:00.07 mgd: (mgd)
(user1)/dev/ttyp2 (mgd)
user1 9065 0.0 0.0 41192 136 ?? Is 4:39AM 0:00.05 mgd: (mgd)
(user1)/dev/ttyp1 (mgd)
user1 10295 0.0 0.1 41180 520 ?? S 6:12AM 0:02.67 mgd: (mgd)
(user1) (mgd)
user1 11557 0.0 0.1 41180 520 ?? S 8:03AM 0:02.66 mgd: (mgd)
(user1) (mgd)
user1 15817 0.0 0.1 41180 520 ?? S 3:26PM 0:02.34 mgd: (mgd)
(user1) (mgd)
user1 18495 0.0 0.1 41180 520 ?? S 8:16PM 0:02.13 mgd: (mgd)
(user1) (mgd)
user1 18549 0.0 0.1 41180 520 ?? S 8:20PM 0:02.13 mgd: (mgd)
(user1) (mgd)
user1 18907 0.0 0.1 41180 520 ?? S 8:22PM 0:02.14 mgd: (mgd)
(user1) (mgd)
user1 19574 0.0 3.3 41180 25220 ?? S 8:38PM 0:02.11 mgd: (mgd)
(user1) (mgd)
user1 20290 0.0 0.6 41172 4876 ?? Is 9:46PM 0:00.10 mgd: (mgd)
(user1)/dev/ttyp0 (mgd)
user1 20794 0.0 3.3 41180 25228 ?? S 9:52PM 0:02.06 mgd: (mgd)
(user1) (mgd)
user1 21861 0.0 0.0 41180 220 ?? S Fri09PM 0:05.93 mgd: (mgd)
(user1) (mgd)
user1 50416 0.0 0.1 41180 520 ?? S Sun08AM 0:04.53 mgd: (mgd)
(user1) (mgd)
user1 63963 0.0 0.1 41180 520 ?? S Sun08PM 0:04.06 mgd: (mgd)
(user1) (mgd)
user1 84282 0.0 0.1 41180 520 ?? S Mon10AM 0:03.55 mgd: (mgd)
(user1) (mgd)
=================================================================================================================
List of active sshd processes on the device : (Command Executed - ps auxwww |
sed -n "1p; /sed -n/d; /sshd/p;")
=================================================================================================================
USER PID %CPU %MEM VSZ RSS TT STAT STARTED TIME COMMAND
user1 20972 1.7 0.4 7684 2916 ?? Ss 10:11PM 0:00.15 sshd:
user1@notty (sshd)
user1 1944 0.0 0.1 7784 692 ?? Ss Fri12AM 1:00.95 sshd:
user1@notty (sshd)
user1 2354 0.0 0.1 7816 700 ?? Ss Fri12AM 1:00.21 sshd:
user1@notty (sshd)
user1 2378 0.0 0.1 7820 700 ?? Ss Fri12AM 1:00.39 sshd:
keybased@notty (sshd)
42
Page 54

user1 3907 0.0 0.1 7784 772 ?? Ss 12:27AM 0:10.47 sshd:
user1@notty (sshd)
user1 5334 0.0 0.0 7676 320 ?? Is 1:25AM 0:00.30 sshd:
user1@ttyp1 (sshd)
user1 5361 0.0 0.1 7676 476 ?? Is 1:26AM 0:00.25 sshd:
user1@ttyp2 (sshd)
user1 7649 0.0 0.1 7784 776 ?? Ss 2:29AM 0:07.62 sshd:
user1@notty (sshd)
user1 10284 0.0 0.1 7784 468 ?? Ss 6:11AM 0:02.11 sshd:
user1@notty (sshd)
user1 11544 0.0 0.1 7784 776 ?? Ss 8:03AM 0:04.69 sshd:
user1@notty (sshd)
user1 15806 0.0 0.1 7784 788 ?? Ss 3:26PM 0:03.38 sshd:
user1@notty (sshd)
user1 18484 0.0 0.1 7784 792 ?? Ss 8:16PM 0:02.99 sshd:
user1@notty (sshd)
user1 18538 0.0 0.1 7784 776 ?? Ss 8:20PM 0:03.47 sshd:
user1@notty (sshd)
user1 18896 0.0 0.1 7796 784 ?? Ss 8:22PM 0:02.89 sshd:
user1@notty (sshd)
user1 19561 0.0 0.4 7784 2924 ?? Ss 8:38PM 0:02.41 sshd:
user1@notty (sshd)
user1 20272 0.0 0.4 7684 2900 ?? Is 9:46PM 0:00.26 sshd:
user1@ttyp0 (sshd)
user1 20783 0.0 0.4 7796 2932 ?? Ss 9:52PM 0:00.52 sshd:
user1@notty (sshd)
user1 21820 0.0 0.1 7800 696 ?? S Fri09PM 0:47.90 sshd:
user1@notty (sshd)
user1 50401 0.0 0.1 7784 776 ?? Ss Sun08AM 0:36.25 sshd:
user1@notty (sshd)
user1 63919 0.0 0.1 7796 784 ?? Ss Sun08PM 0:34.21 sshd:
user1@notty (sshd)
user1 84233 0.0 0.1 7784 776 ?? Ss Mon10AM 0:20.37 sshd:
user1@notty (sshd)
==============================================================================================================================
List of open SSH connections to 10.206.41.57 from the device : (Command Executed
- netstat -tln | egrep "Pro|\.7804"; netstat -tln | grep "\.22"). Please note
that of the listed connections, one is opened by this debug script to collect
the debug information from the device
==============================================================================================================================
Proto Recv-Q Send-Q Local Address Foreign
Address (state)
tcp4 0 0 10.206.32.107.22
10.206.41.57.43098 ESTABLISHED
43
Page 55

tcp4 0 0 10.206.32.107.22
10.206.41.57.33080 ESTABLISHED
=================================================================================================================
List of open SSH connections on the device : (Command Executed - netstat -tln
| egrep "Pro|\.7804"; netstat -tln grep "\.22")
=================================================================================================================
Proto Recv-Q Send-Q Local Address Foreign
Address (state)
tcp4 0 0 10.206.32.107.58052
10.206.41.46.7804 SYN_SENT
tcp4 0 0 10.206.32.107.53398
10.206.41.192.7804 ESTABLISHED
tcp4 0 0 10.206.32.107.22
10.206.41.57.43098 ESTABLISHED
tcp4 0 0 10.206.32.107.22
10.206.41.62.60026 ESTABLISHED
tcp4 0 0 10.206.32.107.22
10.206.155.85.62406 ESTABLISHED
tcp4 0 0 10.206.32.107.22
10.206.41.143.39926 ESTABLISHED
tcp4 0 0 10.206.32.107.22
10.207.70.104.36730 ESTABLISHED
tcp4 0 0 10.206.32.107.22
10.206.41.171.52993 ESTABLISHED
tcp4 0 0 10.206.32.107.22
10.206.41.33.45765 ESTABLISHED
tcp4 0 0 10.206.32.107.22
10.206.41.211.50000 ESTABLISHED
tcp4 0 0 10.206.32.107.22
10.206.41.57.33080 ESTABLISHED
tcp4 0 0 10.206.32.107.22
10.206.41.156.49032 ESTABLISHED
tcp4 0 0 10.206.32.107.22
10.206.40.4.38068 ESTABLISHED
tcp4 0 0 10.206.32.107.22
10.206.41.240.61583 ESTABLISHED
tcp4 0 0 10.206.32.107.22
10.206.41.240.61569 ESTABLISHED
tcp4 0 0 10.206.32.107.22
10.206.41.149.60804 ESTABLISHED
tcp4 0 0 10.206.32.107.22
10.206.41.235.59358 ESTABLISHED
tcp4 0 0 10.206.32.107.22
10.206.41.231.34530 ESTABLISHED
44
Page 56

tcp4 0 0 10.206.32.107.22
10.206.41.221.48186 ESTABLISHED
tcp4 0 0 10.206.32.107.22
10.205.56.82.41163 ESTABLISHED
tcp4 0 0 10.206.32.107.22
10.161.11.161.42174 ESTABLISHED
tcp4 0 0 10.206.32.107.22
10.206.41.71.47831 ESTABLISHED
9. (Optional) To save device debug connection information at a custom output location, type
./DeviceDebugInfoCollector.sh<device-IP address> <device-username> <node-VIP address>
<output-file-path> and press Enter..
You can use the information from the .txt file to debug issues related to the connections and processes
on the device.
45
Executing the Script to Unlock the Device Configuration
You execute the cleanupEditChannel.sh script to unlock the device configuration.
To execute the script to unlock the device configuration:
1. Log in to the CLI of the Junos Space node.
2. Enter the administrator username and password at the Junos Space login prompt and press Enter.
The default username is admin and the default password is abc123.
The Junos Space Settings Menu is displayed.
3. Enter 6 (if you are using a hardware appliance) or 7 (if you are using a virtual appliance) at the Junos
Space Settings Menu prompt to run shell commands.
You are prompted to enter your password.
4. Type the administrator password and press Enter.
The shell prompt appears.
5. Type cd /var/log/space-debug/debug-utilities/deviceConnection at the shell prompt and press Enter.
6. (Optional) To view the list of debug scripts, type ls and press Enter.
Page 57

The list of device-connection debug scripts is displayed.
7. Type ./cleanupEditChannel.sh <device-IP address>false and press Enter—for example,
./cleanupEditChannel.sh 10.206.33.17 false.
You can modify the configuration on the device from the Junos Space user interface.
Executing the Script to Collect Node-Connection Information
You execute the getAllDeviceInfo.sh script to collect information about devices connected to a Junos
Space node. You can also execute the script to collect information about devices connected to all the
nodes in your Junos Space setup.
To execute the script to collect node-connection information:
1. Log in to the CLI of the Junos Space node.
2. Enter the administrator username and password at the Junos Space login prompt and press Enter.
46
The default username is admin and the default password is abc123.
The Junos Space Settings Menu is displayed.
3. Enter 6 (if you are using a hardware appliance) or 7 (if you are using a virtual appliance) at the Junos
Space Settings Menu prompt to run shell commands.
You are prompted to enter your password.
4. Type the administrator password and press Enter.
The shell prompt appears.
5. Type cd /var/log/space-debug/debug-utilities/deviceConnection at the shell prompt and press Enter.
6. (Optional) To view the list of debug scripts, type ls and press Enter.
7. Type ./getAllDeviceInfo.sh <node-VIP address> and press Enter—for example, ./getAllDeviceInfo.sh
10.206.41.57.
The output from this command is saved to the DeviceInfoOutput.txt file in the same directory.
The following is a sample output:
-----------------------------------------------------------Time of execution: Wed Jul 15 05:35:21 UTC 2015
Page 58

-----------------------------------------------------------Device Id: 131129 Device Ip: 10.206.32.107
Node id: 10.206.41.57
Connection state: Connected
Connection changed at: 07/14/2015 17:35:04
EditFlag : false
EditChannel num:0
SSH ctrl channel num: 6
Max channels allowed: 32
Number of channels opened: 6
------------------------------------------------------Channel details:
Channel Id: 1
Seq num: 10
Channel state: CHANNEL_STATE_UNUSE
Channel type: Netconf
------------------------------------------------------Channel Id: 2
Seq num: 16
Channel state: CHANNEL_STATE_UNUSE
Channel type: Netconf
------------------------------------------------------Channel Id: 3
Seq num: 21
Channel state: CHANNEL_STATE_OPEN
Channel type: Syslog
------------------------------------------------------Channel Id: 4
Seq num: 23
Channel state: CHANNEL_STATE_UNUSE
Channel type: Netconf
------------------------------------------------------Channel Id: 5
Seq num: 110
Channel state: CHANNEL_STATE_UNUSE
Channel type: Netconf
------------------------------------------------------Channel Id: 6
Seq num: 112
Channel state: CHANNEL_STATE_UNUSE
Channel type: Netconf
------------------------------------------------------=======================================================
Device Id: 131153 Device Ip: 10.206.33.17
47
Page 59

Node id: 10.206.41.57
Connection state: Connected
Connection changed at: 07/14/2015 17:35:04
EditFlag : false
EditChannel num:0
SSH ctrl channel num: 4
Max channels allowed: 32
Number of channels opened: 4
------------------------------------------------------Channel details:
Channel Id: 1
Seq num: 11
Channel state: CHANNEL_STATE_UNUSE
Channel type: Netconf
------------------------------------------------------Channel Id: 2
Seq num: 14
Channel state: CHANNEL_STATE_UNUSE
Channel type: Netconf
------------------------------------------------------Channel Id: 3
Seq num: 22
Channel state: CHANNEL_STATE_OPEN
Channel type: Syslog
------------------------------------------------------Channel Id: 4
Seq num: 24
Channel state: CHANNEL_STATE_UNUSE
Channel type: Netconf
------------------------------------------------------=======================================================
Device Id: 131233 Device Ip: 127.0.0.1
Node id: 10.206.41.57
Connection state: Connected
Connection changed at: 07/14/2015 17:35:17
EditFlag : false
EditChannel num:0
SSH ctrl channel num: 13
Max channels allowed: 32
Number of channels opened: 7
------------------------------------------------------Channel details:
Channel Id: 1
Seq num: 26
48
Page 60

Channel state: CHANNEL_STATE_UNUSE
Channel type: Netconf
------------------------------------------------------Channel Id: 2
Seq num: 27
Channel state: CHANNEL_STATE_UNUSE
Channel type: Netconf
------------------------------------------------------Channel Id: 3
Seq num: 28
Channel state: CHANNEL_STATE_OPEN
Channel type: Syslog
------------------------------------------------------Channel Id: 4
Seq num: 102
Channel state: CHANNEL_STATE_UNUSE
Channel type: Netconf
------------------------------------------------------Channel Id: 5
Seq num: 103
Channel state: CHANNEL_STATE_UNUSE
Channel type: Netconf
------------------------------------------------------Channel Id: 6
Seq num: 113
Channel state: CHANNEL_STATE_UNUSE
Channel type: Netconf
------------------------------------------------------Channel Id: 7
Seq num: 114
Channel state: CHANNEL_STATE_UNUSE
Channel type: Netconf
------------------------------------------------------=======================================================
Device Id: 131149 Device Ip: 10.206.40.1
Node id: 10.206.41.57
Connection state: Connected
Connection changed at: 07/14/2015 17:35:03
EditFlag : false
EditChannel num:0
SSH ctrl channel num: 5
Max channels allowed: 32
Number of channels opened: 5
-------------------------------------------------------
49
Page 61

Channel details:
Channel Id: 1
Seq num: 9
Channel state: CHANNEL_STATE_UNUSE
Channel type: Netconf
------------------------------------------------------Channel Id: 2
Seq num: 15
Channel state: CHANNEL_STATE_UNUSE
Channel type: Netconf
------------------------------------------------------Channel Id: 3
Seq num: 20
Channel state: CHANNEL_STATE_UNUSE
Channel type: Netconf
------------------------------------------------------Channel Id: 4
Seq num: 25
Channel state: CHANNEL_STATE_OPEN
Channel type: Syslog
------------------------------------------------------Channel Id: 5
Seq num: 29
Channel state: CHANNEL_STATE_UNUSE
Channel type: Netconf
------------------------------------------------------=======================================================
Device Id: 131121 Device Ip: 10.206.32.186
Node id: 10.206.41.57
Connection state: Connected
Connection changed at: 07/14/2015 17:35:03
EditFlag : false
EditChannel num:0
SSH ctrl channel num: 3
Max channels allowed: 32
Number of channels opened: 6
------------------------------------------------------Channel details:
Channel Id: 1
Seq num: 8
Channel state: CHANNEL_STATE_UNUSE
Channel type: Netconf
------------------------------------------------------Channel Id: 2
50
Page 62

Seq num: 17
Channel state: CHANNEL_STATE_UNUSE
Channel type: Netconf
------------------------------------------------------Channel Id: 3
Seq num: 18
Channel state: CHANNEL_STATE_OPEN
Channel type: Syslog
------------------------------------------------------Channel Id: 4
Seq num: 19
Channel state: CHANNEL_STATE_UNUSE
Channel type: Netconf
------------------------------------------------------Channel Id: 5
Seq num: 109
Channel state: CHANNEL_STATE_UNUSE
Channel type: Netconf
------------------------------------------------------Channel Id: 6
Seq num: 111
Channel state: CHANNEL_STATE_UNUSE
Channel type: Netconf
------------------------------------------------------=======================================================
51
8. (Optional) To save node connection information at a custom output location, type ./getAllDeviceInfo.sh
<node-VIP address> <output-file-path> and press Enter.
9. (Optional) To view connection information across all nodes, type ./getAllDeviceInfo.sh ALL-NODES
and press Enter.
You can use the information from the .txt file to debug issues related to devices connected to a single or
multiple Junos Space nodes.
RELATED DOCUMENTATION
Junos Space Debug Utilities Overview | 33
Monitoring Network Devices and Troubleshooting Software Issues with Junos Space Network
Management Platform | 2
Page 63

Executing Device Import Detail Script and Java Application
IN THIS SECTION
Executing the Script to Delete Data from Device Import Tables | 52
Executing the Java Application to View Device XML | 53
You execute the device import script to delete data from device import tables. You execute the
DB-blob-reader.jar Java application to view device information in XML format. Device import script and
Java application are stored at the following location: /var/log/space-debug/debug-utilities/deviceImport.
When you execute the Java application, the output is stored as a .txt file at the same location. The following
sections list the steps to execute the script to delete device import details and Java application to view
device information.
52
Executing the Script to Delete Data from Device Import Tables
You execute the cleanupDeviceImportTables.sh script to delete data from device import tables.
To execute the script to delete data from device import tables:
1. Log in to the CLI of the Junos Space node.
2. Enter the administrator username and password at the Junos Space login prompt and press Enter.
The default username is admin and the default password is abc123.
The Junos Space Settings Menu is displayed.
3. Enter 6 (if you are using a hardware appliance) or 7 (if you are using a virtual appliance) at the Junos
Space Settings Menu prompt to run shell commands.
You are prompted to enter your password.
The following is a sample output from a virtual appliance:
admin@10.206.41.183's password:
Last login: Mon Aug 17 06:17:58 2015 from 10.206.41.42
Welcome to the Junos Space network settings utility.
Initializing, please wait
Page 64

Junos Space Settings Menu
1> Change Password
2> Change Network Settings
3> Change Time Options
4> Retrieve Logs
5> Security
6> Expand VM Drive Size
7> (Debug) run shell
A> Apply changes
Q> Quit
R> Redraw Menu
Choice [1-7,AQR]: 7
53
4. Type the administrator password and press Enter.
The shell prompt appears.
5. Type cd /var/log/space-debug/debug-utilities/deviceImport at the shell prompt and press Enter.
6. (Optional) To view the list of device import scripts and Java applications, type ls and press Enter.
7. Type ./cleanupDeviceImportTables.sh <device-name> and press Enter. For example:
./cleanupDeviceImportTables.sh jboss netscreen build_db ABC123
Warning: Using a password on the command line interface can be insecure.
Device id from ABC123 is :XXXXX
Warning: Using a password on the command line interface can be insecure.
Finished cleaning up the import related tables for device ABC123
Executing the Java Application to View Device XML
You execute the DB-blob-reader.jar application to view the device XML information.
Ensure that you have updated the MySQL query in the DB-blob-reader.properties file before executing
the Java application. The file also contains an example configuration.
Page 65

To execute the Java application and view a device XML:
1. Log in to the CLI of the Junos Space node.
2. Enter the administrator username and password at the Junos Space login prompt and press Enter.
The default username is admin and the default password is abc123.
The Junos Space Settings Menu is displayed.
3. Enter 6 (if you are using a hardware appliance) or 7 (if you are using a virtual appliance) at the Junos
Space Settings Menu prompt to run shell commands.
You are prompted to enter your password.
4. Type the administrator password and press Enter.
The shell prompt appears.
54
5. Type cd /var/log/space-debug/debug-utilities/deviceImport at the shell prompt and press Enter.
6. (Optional) To view the list of device import scripts and Java applications, type ls and press Enter.
7. Type /usr/bin/java -jar DB-blob-reader.jar and press Enter.
8. Enter the database username.
9. Enter the database password.
The output from this command is saved to the DB-blob-reader-result.txt file in the same directory.
You can view the output of the query you entered in the DB-blob-reader.properties file.
RELATED DOCUMENTATION
Junos Space Debug Utilities Overview | 33
Monitoring Network Devices and Troubleshooting Software Issues with Junos Space Network
Management Platform | 2
Page 66

Executing Job Management Scripts and Java Applications
IN THIS SECTION
Executing the Java Application to Collect Job Information | 55
Executing the Script to View the Stack Trace of a Job | 59
Executing the Script to View Job Information on Nodes | 60
You execute job management scripts and Java applications to view information about jobs triggered from
Junos Space nodes. The JobInfoCollector.jar Java application and the job management scripts are stored
at the following location: /var/log/space-debug/debug-utilities/jobManagement. When you execute the
JobInfoCollector.jar Java application and job management scripts, the output is stored as .txt files at the
same location. You can also specify a custom path to store the output. The following sections list the steps
to execute the scripts to collect information about jobs.
55
Executing the Java Application to Collect Job Information
You execute the JobInfoCollector.jar application to collect job information. Ensure that you have updated
the MySQL query in the JobInfoCollector.properties file before executing the Java application. The file
also contains an example configuration.
To execute the Java application to collect job information:
1. Log in to the CLI of the Junos Space node.
2. Enter the administrator username and password at the Junos Space login prompt and press Enter.
The default username is admin and the default password is abc123.
The Junos Space Settings Menu is displayed.
3. Enter 6 (if you are using a hardware appliance) or 7 (if you are using a virtual appliance) at the Junos
Space Settings Menu prompt to run shell commands.
You are prompted to enter your password.
The following is a sample output from a virtual appliance:
admin@10.206.41.183's password:
Last login: Mon Aug 17 06:17:58 2015 from 10.206.41.42
Page 67

Welcome to the Junos Space network settings utility.
Initializing, please wait
Junos Space Settings Menu
1> Change Password
2> Change Network Settings
3> Change Time Options
4> Retrieve Logs
5> Security
6> Expand VM Drive Size
7> (Debug) run shell
A> Apply changes
Q> Quit
R> Redraw Menu
56
Choice [1-7,AQR]: 7
4. Type the administrator password and press Enter.
The shell prompt appears.
5. Type cd /var/log/space-debug/debug-utilities/jobManagement at the shell prompt and press Enter.
6. (Optional) To view the list of job management scripts and Java applications, enter ls and press Enter.
7. Type /usr/bin/java -jar JobInfoCollector.jar and press Enter.
The following options will be displayed:
Please select an option from below:
1. Display job parent-children hierarchy
2. Filter from job data
3. Display jobs not yet picked up by Job Dispatcher
8. Type 1, 2, or 3 to select an option.
9. Enter the database username.
Page 68

10. Enter the database password.
11. The inputs displayed depend on the option you selected.
If you selected option 1, you need to enter the parent job ID.
Enter a job ID.
•
The output from this command is saved to the JobHierarchy-<job-ID>.txt file in the same directory.
The following is a sample output if you selected 1:
=====Job details for 491529 =====
NODE: 10.206.41.57
STARTTIMESTAMP: 17 Jul 2015 17:51:00 GMT
JOBSTATE: Done
JOBSTATUS: Success
ENDTIMESTAMP: 17 Jul 2015 17:52:15 GMT
CHILDCOUNT: 2
57
Child job details:
ID || NODE || STARTTIMESTAMP || JOBSTATE || JOBSTATUS || ENDTIMESTAMP ||
CHILDCOUNT ||
491530 | 10.206.41.57 | 17 Jul 2015 17:51:01 GMT | Done | Success | 17 Jul
2015 17:51:13 GMT | 0 |
491531 | 10.206.41.57 | 17 Jul 2015 17:51:01 GMT | Done | Success | 17 Jul
2015 17:51:13 GMT | 0 |
If you selected option 2, you need to enter a MySQL query.
Page 69

Enter a MySQL query—for example, mostate=’Failure’.
•
This query filters the jobs that failed. The following is a sample output if you selected 2:
ID || NAME || NODE || STARTTIMESTAMP || JOBSTATE || JOBSTATUS || ENDTIMESTAMP
||
196608 | Discover Network Elements-196608 | 10.206.41.184 | 10 Aug 2015
10:44:48 GMT | Done | Failure | 10 Aug 2015 10:48:47 GMT |
196624 | Discover Network Elements-196624 | 10.206.41.184 | 10 Aug 2015
10:49:52 GMT | Done | Failure | 10 Aug 2015 10:49:58 GMT |
196643 | Mail User Password-196643 | 10.206.41.184 | 10 Aug 2015 14:11:21
GMT | Done | Failure | 10 Aug 2015 14:11:21 GMT |
196649 | Mail User Password-196649 | 10.206.41.184 | 11 Aug 2015 02:39:18
GMT | Done | Failure | 11 Aug 2015 02:39:18 GMT |
196650 | Mail User Password-196650 | 10.206.41.184 | 11 Aug 2015 02:39:18
GMT | Done | Failure | 11 Aug 2015 02:39:18 GMT |
196660 | Sync Files-196660 | 10.206.41.187 | 11 Aug 2015 11:54:13 GMT | Done
| Failure | 11 Aug 2015 11:54:46 GMT |
360448 | Resync Network Elements-360448 | 10.206.41.184 | 11 Aug 2015 18:06:07
GMT | Done | Failure | 11 Aug 2015 18:06:08 GMT |
360449 | Discover Network Elements-360449 | 10.206.41.187 | 11 Aug 2015
18:12:43 GMT | Done | Failure | 11 Aug 2015 18:13:16 GMT |
58
If you selected option 3, the list of unscheduled jobs is saved to the UnscheduledJobs.txt file in the
same directory.
Page 70

The following is a sample output if you selected 3:
•
ID || NAME || JOBSTATE || PARENTJOBID ||
393501 | ND Discovery-393501 | Done | 0 |
393858 | Backup Configuration Files-393858 | Done | 0 |
720906 | ND Discovery-720906 | Done | 0 |
721067 | Backup Configuration Files-721067 | Done | 0 |
721884 | Backup Configuration Files-721884 | Done | 0 |
1048659 | Backup Configuration Files-1048659 | Done | 0 |
1182260 | Enable Script-1182260 | InProgress | 0 |
1182413 | Execute Script-1182413 | InProgress | 0 |
1183914 | Backup Configuration Files-1183914 | Done | 0 |
1184310 | Delete Device-1184310 | Done | 0 |
1189992 | Stage Script-1189992 | InProgress | 0 |
1190105 | Update Network Element-1190105 | InProgress | 0 |
1442231 | Backup Configuration Files-1442231 | Done | 0 |
1442232 | -1442232 | InProgress | 1184310 |
1442233 | -1442233 | InProgress | 1184310 |
1442234 | -1442234 | InProgress | 1184310 |
1442235 | -1442235 | InProgress | 1184310 |
1442236 | -1442236 | InProgress | 1184310 |
1442237 | -1442237 | InProgress | 1184310 |
1442238 | -1442238 | InProgress | 1184310 |
1442239 | -1442239 | InProgress | 1184310 |
1442240 | -1442240 | InProgress | 1184310 |
1445400 | Generate SD LR Report-1445400 | Scheduled | 0 |
1445528 | Cloud Infrastructure Event Purge-1445528 | Scheduled | 0 |
1445602 | Policy Hits Collection-1445602 | Scheduled | 0 |
1903749 | useraccounts-1903749 | Done | 0 |
59
You can view the hierarchy of a subjob (input as the parent job ID), list of jobs that are currently unscheduled,
or the output based on the query you entered in the JobInfoCollector.properties file.
Executing the Script to View the Stack Trace of a Job
You execute the getJobThreadDump.sh script to view the stack trace of a job.
To execute the script to view the stack trace of a job:
1. Log in to the CLI of the Junos Space node.
2. Enter the administrator username and password at the Junos Space login prompt and press Enter.
The default username is admin and the default password is abc123.
Page 71

The Junos Space Settings Menu is displayed.
3. Enter 6 (if you are using a hardware appliance) or 7 (if you are using a virtual appliance) at the Junos
Space Settings Menu prompt to run shell commands.
You are prompted to enter your password.
4. Type the administrator password and press Enter.
The shell prompt appears.
5. Type cd /var/log/space-debug/debug-utilities/jobManagement at the shell prompt and press Enter.
6. (Optional) To view the list of job management scripts and Java applications, type ls and press Enter.
7. Type ./getJobThreadDump.sh <job-ID> and press Enter.
The output from this command is saved to the JobThreadDump-<job-ID>.txt file in the same directory.
60
8. (Optional) To save the stack trace of the job at a custom output location, type ./getJobThreadDump.sh
<job-ID> <output-file-path> and press Enter.
Executing the Script to View Job Information on Nodes
You execute the SystemLoadViewer.sh script to view job information on a node.
To execute the script to view job information on a node:
1. Log in to the CLI of the Junos Space node.
2. Enter the administrator username and password at the Junos Space login prompt and press Enter.
The default username is admin and the default password is abc123.
The Junos Space Settings Menu is displayed.
3. Enter 6 (if you are using a hardware appliance) or 7 (if you are using a virtual appliance) at the Junos
Space Settings Menu prompt to run shell commands.
You are prompted to enter your password.
4. Type the administrator password and press Enter.
The shell prompt appears.
5. Type cd /var/log/space-debug/debug-utilities/jobManagement at the shell prompt and press Enter.
Page 72

6. (Optional) To view the list of job management scripts and Java applications, type ls and press Enter.
7. Type ./SystemLoadViewer.sh and press Enter.
The output from this command is saved to the ./SystemLoadInfo.txt file in the same directory. The
following is a sample output from the command:
-----------------------------------------------------------Time of execution: Mon Jul 20 06:54:14 UTC 2015
------------------------------------------------------------
=====================NODE SUMMARY======================
Node IP: 10.206.41.35
Maximum JVM memory: 2040528896
Estimated memory usage per node: 40465
Reserved memory size: 20000000
(Available Memory = Maximum JVM memor - Estimated memory usage per node - Reserved
memory)
Available Memory:2020488431
Number of first root jobs on this node:1
Number of next root jobs on this node:0
Number of sub jobs on this node:0
------------------------------------------===========================================
Node load statistics:
===========================================
Resource Id:autoresync-group:132832:user1@host:0360471000000000008G
Type:autoresync-group
SubType:132832
Context type:FIRST_ROOT_JOB
State:RUNNING
Queue:
Node IP:10.206.41.35
Creation Time:2015-07-20 06:54:13.166
Last modification time:2015-07-20 06:54:13.166
Estimated Memory:40465
===========================================
============================SYSTEM LOAD SUMMARY FOR LOCAL
NODE=============================
Filesystem 1K-blocks Used Available Use% Mounted on
/dev/mapper/jmpvgnocf-lvvar
52772604 2584204 47373632 6% /var
======Command executed: LINES=20 COLUMNS=120 top -n 2 -b -c | tail -n
+22==================
top - 06:54:18 up 3 days, 19:01, 2 users, load average: 1.24, 0.88, 0.82
61
Page 73

Tasks: 271 total, 2 running, 268 sleeping, 0 stopped, 1 zombie
Cpu(s): 42.2%us, 23.5%sy, 0.5%ni, 32.7%id, 0.3%wa, 0.1%hi, 0.7%si, 0.0%st
Mem: 7937672k total, 7827836k used, 109836k free, 539116k buffers
Swap: 8193140k total, 132684k used, 8060456k free, 1246572k cached
PID USER PR NI VIRT RES SHR S %CPU %MEM TIME+ COMMAND
30383 user1 20 0 83616 24m 2508 S 36.8 0.3 0:02.16 /usr/bin/perl
/var/www/cgi-bin/secure/resourceMonitoring
4204 jboss 20 0 4081m 2.7g 14m S 27.6 36.0 395:59.73
/usr/lib/jvm/java-1.7.0-openjdk-1.7.0.79.x86_64/jre/bin/jav
31240 user1 20 0 124m 15m 2448 S 7.6 0.2 0:00.23 perl -e use
lib("/usr/nma/lib"); use NmaUtil; print NmaUtil
31251 user1 20 0 72016 14m 2384 R 6.9 0.2 0:00.21 perl -e use
lib("/usr/nma/lib"); use NmaDb; print NmaDb::ge
30719 mysql 16 -4 2936m 744m 6628 S 3.6 9.6 62:17.79 /usr/sbin/mysqld
--basedir=/usr --datadir=/var/lib/mysql -32329 opennms 25 5 3446m 877m 21m S 3.0 11.3 164:35.59
/usr/lib/jvm/jre-1.7.0-openjdk.x86_64/bin/java -Djava.endor
3120 user1 20 0 84612 21m 2460 S 1.0 0.3 13:51.23 /usr/bin/perl
/usr/bin/jmp-sync
30651 user1 20 0 12896 1436 952 R 1.0 0.0 0:00.07 top -n 2 -b -c
13332 user1 20 0 154m 9824 4480 S 0.7 0.1 26:56.92 /usr/sbin/snmpd
-Lsd -Lf /dev/null -p /var/run/snmpd.pid -a
18186 postgres 20 0 268m 12m 9252 S 0.7 0.2 0:00.38 postgres: opennms
opennms 127.0.0.1(55330) idle
2589 jboss 20 0 924m 197m 10m S 0.3 2.5 6:11.24 java -D[Host
Controller] -Dorg.jboss.boot.log.file=/var/log
15335 apache 23 3 141m 4936 3012 S 0.3 0.1 0:00.62 /usr/sbin/httpd
======Command executed: COLUMNS=120 top -n 1 -b -c | egrep
'(mysqld|java|postgres)'========
4204 jboss 20 0 4081m 2.7g 14m S 1.9 36.0 395:59.74
/usr/lib/jvm/java-1.7.0-openjdk-1.7.0.79.x86_64/jre/bin/jav
32329 opennms 25 5 3446m 877m 21m S 1.9 11.3 164:35.60
/usr/lib/jvm/jre-1.7.0-openjdk.x86_64/bin/java -Djava.endor
2556 jboss 20 0 527m 47m 9800 S 0.0 0.6 4:44.43 java -D[Process
Controller] -server -Xms32m -Xmx128m -XX:Ma
2589 jboss 20 0 924m 197m 10m S 0.0 2.5 6:11.24 java -D[Host
Controller] -Dorg.jboss.boot.log.file=/var/log
2886 postgres 20 0 268m 10m 7524 S 0.0 0.1 0:00.10 postgres: opennms
opennms 127.0.0.1(55289) idle
2888 postgres 20 0 268m 10m 7580 S 0.0 0.1 0:00.08 postgres: opennms
opennms 127.0.0.1(55290) idle
2889 postgres 20 0 268m 10m 8040 S 0.0 0.1 0:00.15 postgres: opennms
opennms 127.0.0.1(55291) idle
62
Page 74

2891 postgres 20 0 268m 12m 9352 S 0.0 0.2 0:00.31 postgres: opennms
opennms 127.0.0.1(55292) idle
2893 postgres 20 0 267m 10m 7612 S 0.0 0.1 0:00.09 postgres: opennms
opennms 127.0.0.1(55293) idle
2895 postgres 20 0 267m 8968 6548 S 0.0 0.1 0:00.03 postgres: opennms
opennms 127.0.0.1(55294) idle
3507 jboss 20 0 528m 47m 9856 S 0.0 0.6 4:51.80 java -D[Process
Controller] -server -Xms32m -Xmx128m -XX:Ma
3561 jboss 20 0 566m 143m 10m S 0.0 1.8 5:43.77 java -D[Host
Controller] -Dorg.jboss.boot.log.file=/var/log
5570 postgres 20 0 266m 4680 2784 S 0.0 0.1 0:00.01 postgres: opennms
opennms 127.0.0.1(36280) idle
5572 postgres 20 0 266m 4688 2792 S 0.0 0.1 0:00.01 postgres: opennms
opennms 127.0.0.1(36281) idle
5573 postgres 20 0 266m 4676 2780 S 0.0 0.1 0:00.01 postgres: opennms
opennms 127.0.0.1(36282) idle
5575 postgres 20 0 266m 4684 2788 S 0.0 0.1 0:00.01 postgres: opennms
opennms 127.0.0.1(36283) idle
5578 postgres 20 0 266m 4696 2800 S 0.0 0.1 0:00.00 postgres: opennms
opennms 127.0.0.1(36284) idle
5579 postgres 20 0 266m 4688 2792 S 0.0 0.1 0:00.01 postgres: opennms
opennms 127.0.0.1(36285) idle
5581 postgres 20 0 266m 4680 2784 S 0.0 0.1 0:00.00 postgres: opennms
opennms 127.0.0.1(36286) idle
5583 postgres 20 0 266m 4676 2780 S 0.0 0.1 0:00.01 postgres: opennms
opennms 127.0.0.1(36287) idle
5586 postgres 20 0 266m 4680 2784 S 0.0 0.1 0:00.00 postgres: opennms
opennms 127.0.0.1(36288) idle
5587 postgres 20 0 266m 4676 2780 S 0.0 0.1 0:00.01 postgres: opennms
opennms 127.0.0.1(36289) idle
5590 postgres 20 0 266m 4692 2796 S 0.0 0.1 0:00.00 postgres: opennms
opennms 127.0.0.1(36290) idle
5591 postgres 20 0 266m 4692 2796 S 0.0 0.1 0:00.00 postgres: opennms
opennms 127.0.0.1(36291) idle
5593 postgres 20 0 266m 4696 2800 S 0.0 0.1 0:00.00 postgres: opennms
opennms 127.0.0.1(36292) idle
5595 postgres 20 0 266m 4680 2784 S 0.0 0.1 0:00.00 postgres: opennms
opennms 127.0.0.1(36293) idle
5597 postgres 20 0 266m 4676 2780 S 0.0 0.1 0:00.01 postgres: opennms
opennms 127.0.0.1(36294) idle
5599 postgres 20 0 266m 4684 2788 S 0.0 0.1 0:00.00 postgres: opennms
opennms 127.0.0.1(36295) idle
5601 postgres 20 0 268m 10m 8172 S 0.0 0.1 0:00.14 postgres: opennms
opennms 127.0.0.1(36296) idle
63
Page 75

5603 postgres 20 0 268m 10m 7376 S 0.0 0.1 0:00.07 postgres: opennms
opennms 127.0.0.1(36297) idle
5605 postgres 20 0 267m 9.8m 7228 S 0.0 0.1 0:00.05 postgres: opennms
opennms 127.0.0.1(36298) idle
5607 postgres 20 0 267m 9972 7132 S 0.0 0.1 0:00.06 postgres: opennms
opennms 127.0.0.1(36299) idle
5609 postgres 20 0 268m 10m 8252 S 0.0 0.1 0:00.20 postgres: opennms
opennms 127.0.0.1(36300) idle
5611 postgres 20 0 268m 11m 8848 S 0.0 0.2 0:00.21 postgres: opennms
opennms 127.0.0.1(36301) idle
8123 postgres 20 0 268m 10m 8160 S 0.0 0.1 0:00.14 postgres: opennms
opennms 127.0.0.1(56849) idle
17000 user1 20 0 2299m 68m 8072 S 0.0 0.9 6:32.60 ./jre/bin/java
-Djava.compiler=NONE -cp /usr/StorMan/RaidMa
18186 postgres 20 0 268m 12m 9256 S 0.0 0.2 0:00.38 postgres: opennms
opennms 127.0.0.1(55330) idle
18187 postgres 20 0 268m 11m 8800 S 0.0 0.2 0:00.18 postgres: opennms
opennms 127.0.0.1(55331) idle
18188 postgres 20 0 268m 10m 7484 S 0.0 0.1 0:00.09 postgres: opennms
opennms 127.0.0.1(55332) idle
18190 postgres 20 0 268m 10m 7800 S 0.0 0.1 0:00.10 postgres: opennms
opennms 127.0.0.1(55333) idle
20287 postgres 20 0 266m 4680 2784 S 0.0 0.1 0:00.00 postgres: opennms
opennms 127.0.0.1(36339) idle
20289 postgres 20 0 266m 4676 2780 S 0.0 0.1 0:00.00 postgres: opennms
opennms 127.0.0.1(36340) idle
20291 postgres 20 0 266m 4684 2788 S 0.0 0.1 0:00.00 postgres: opennms
opennms 127.0.0.1(36341) idle
20297 postgres 20 0 266m 4680 2784 S 0.0 0.1 0:00.00 postgres: opennms
opennms 127.0.0.1(36342) idle
20298 postgres 20 0 266m 4676 2780 S 0.0 0.1 0:00.00 postgres: opennms
opennms 127.0.0.1(36343) idle
20301 postgres 20 0 267m 7448 5228 S 0.0 0.1 0:00.01 postgres: opennms
opennms 127.0.0.1(36344) idle
20306 postgres 20 0 267m 7804 5548 S 0.0 0.1 0:00.01 postgres: opennms
opennms 127.0.0.1(36345) idle
20308 postgres 20 0 267m 9660 6872 S 0.0 0.1 0:00.06 postgres: opennms
opennms 127.0.0.1(36346) idle
20311 postgres 20 0 268m 10m 7692 S 0.0 0.1 0:00.14 postgres: opennms
opennms 127.0.0.1(36347) idle
22848 postgres 20 0 266m 4684 2788 S 0.0 0.1 0:00.00 postgres: opennms
opennms 127.0.0.1(56892) idle
22850 postgres 20 0 266m 4680 2784 S 0.0 0.1 0:00.01 postgres: opennms
opennms 127.0.0.1(56893) idle
64
Page 76

22852 postgres 20 0 266m 4676 2780 S 0.0 0.1 0:00.00 postgres: opennms
opennms 127.0.0.1(56894) idle
22858 postgres 20 0 266m 6388 4312 S 0.0 0.1 0:00.01 postgres: opennms
opennms 127.0.0.1(56895) idle
22860 postgres 20 0 268m 10m 7452 S 0.0 0.1 0:00.11 postgres: opennms
opennms 127.0.0.1(56896) idle
22863 postgres 20 0 268m 10m 7968 S 0.0 0.1 0:00.22 postgres: opennms
opennms 127.0.0.1(56897) idle
22864 postgres 20 0 267m 7608 5368 S 0.0 0.1 0:00.02 postgres: opennms
opennms 127.0.0.1(56898) idle
22866 postgres 20 0 268m 10m 7528 S 0.0 0.1 0:00.13 postgres: opennms
opennms 127.0.0.1(56899) idle
29715 user1 16 -4 13052 1068 1064 S 0.0 0.0 0:00.11 /bin/sh
/usr/bin/mysqld_safe --datadir=/var/lib/mysql --pid
30719 mysql 16 -4 2936m 744m 6628 S 0.0 9.6 62:17.79 /usr/sbin/mysqld
--basedir=/usr --datadir=/var/lib/mysql -31064 postgres 20 0 265m 17m 16m S 0.0 0.2 0:32.35
/usr/pgsql-9.4/bin/postmaster -p 5432 -D /var/lib/pgsql/9.4
31072 postgres 20 0 119m 1728 868 S 0.0 0.0 0:03.28 postgres: logger
process
31074 postgres 20 0 265m 42m 41m S 0.0 0.5 0:39.87 postgres:
checkpointer process
31075 postgres 20 0 265m 7304 6368 S 0.0 0.1 0:05.45 postgres: writer
process
31076 postgres 20 0 265m 6076 5156 S 0.0 0.1 0:53.84 postgres: wal writer
process
31077 postgres 20 0 265m 2688 1496 S 0.0 0.0 0:12.46 postgres: autovacuum
launcher process
31078 postgres 20 0 119m 2056 924 S 0.0 0.0 0:58.40 postgres: stats
collector process
31304 user1 20 0 61220 768 664 S 0.0 0.0 0:00.00 egrep
(mysqld|java|postgres)
65
8. (Optional) To save job information about a node at a custom output location, enter
./SystemLoadViewer.sh <output-file-path>.
You can view information such as the memory on the nodes, number of root jobs and subjobs on each of
the nodes, and so on.
RELATED DOCUMENTATION
Junos Space Debug Utilities Overview | 33
Page 77

Monitoring Network Devices and Troubleshooting Software Issues with Junos Space Network
Management Platform | 2
Executing HornetQ Scripts
IN THIS SECTION
Executing the HornetQ Script to View all JBoss Queues | 66
Executing the HornetQ Script to List of Messages in a JBoss Queue | 68
You execute HornetQ scripts to fetch details about all queues from the JBoss CLI or view the list of
messages on a specific queue. HornetQ scripts are stored at the following location:
/var/log/space-debug/debug-utilities/HornetQ. When you execute these scripts, the output is stored as
.txt files at the same location. You can also specify a custom path to store the output. The following sections
list the steps to execute the scripts to fetch details about queues from the JBoss CLI.
66
Executing the HornetQ Script to View all JBoss Queues
You execute the HornetQInfoProvider.sh script to view all the JBoss queues.
To execute the script to view all JBoss queues:
1. Log in to the CLI of the Junos Space node.
2. Enter the administrator username and password at the Junos Space login prompt and press Enter.
The default username is admin and the default password is abc123.
The Junos Space Settings Menu is displayed.
3. Enter 6 (if you are using a hardware appliance) or 7 (if you are using a virtual appliance) at the Junos
Space Settings Menu prompt to run shell commands.
You are prompted to enter your password.
The following is a sample output from a virtual appliance:
admin@10.206.41.183's password:
Last login: Mon Aug 17 06:17:58 2015 from 10.206.41.42
Page 78

Welcome to the Junos Space network settings utility.
Initializing, please wait
Junos Space Settings Menu
1> Change Password
2> Change Network Settings
3> Change Time Options
4> Retrieve Logs
5> Security
6> Expand VM Drive Size
7> (Debug) run shell
A> Apply changes
Q> Quit
R> Redraw Menu
67
Choice [1-7,AQR]: 7
4. Type the administrator password and press Enter.
The shell prompt appears.
5. Type cd /var/log/space-debug/debug-utilities/hornetQ at the shell prompt and press Enter.
6. (Optional) To view the list of HornetQ scripts, type ls and press Enter.
7. Type ./HornetQInfoProvider.sh and press Enter.
The output from this command is saved to the HornetQInfo.txt file in the same directory. The following
sample output displays one of the JBoss queues:
-----------------------------------------------------------Time of execution: Tue Jul 21 05:58:23 UTC 2015
-----------------------------------------------------------==============================10.206.41.57===============================
{
"outcome" => "success",
"result" => [
{
Page 79

"address" => [
("subsystem" => "messaging"),
("hornetq-server" => "default"),
("jms-queue" => "timeOutQueue")
],
"outcome" => "success",
"result" => {
"consumer-count" => 15,
"dead-letter-address" => "jms.queue.DLQ",
"delivering-count" => 0,
"durable" => true,
"entries" => ["queue/timeOutQueue"],
"expiry-address" => undefined,
"message-count" => 0L,
"messages-added" => 0L,
"paused" => false,
"queue-address" => "jms.queue.timeOutQueue",
"scheduled-count" => 0L,
"selector" => undefined,
"temporary" => false
}
},
68
8. (Optional) To save the list of all JBoss queues at a custom output location, type
./getDeviceInfo.sh<output-file-path> and press Enter.
You can view all the JBoss queues.
Executing the HornetQ Script to List of Messages in a JBoss Queue
You execute the HornetQInfoProvider.sh script to view the list of messages in a JBoss queue.
To execute the script to view the list of messages in a JBoss queue:
1. Log in to the CLI of the Junos Space node.
2. Enter the administrator username and password at the Junos Space login prompt and press Enter.
The default username is admin and the default password is abc123.
The Junos Space Settings Menu is displayed.
3. Enter 6 (if you are using a hardware appliance) or 7 (if you are using a virtual appliance) at the Junos
Space Settings Menu prompt to run shell commands.
Page 80

You are prompted to enter your password.
The following is a sample output from a virtual appliance:
admin@10.206.41.183's password:
Last login: Mon Aug 17 06:17:58 2015 from 10.206.41.42
Welcome to the Junos Space network settings utility.
Initializing, please wait
Junos Space Settings Menu
1> Change Password
2> Change Network Settings
3> Change Time Options
4> Retrieve Logs
5> Security
6> Expand VM Drive Size
7> (Debug) run shell
69
A> Apply changes
Q> Quit
R> Redraw Menu
Choice [1-7,AQR]: 7
4. Type the administrator password and press Enter.
The shell prompt appears.
5. Type cd /var/log/space-debug/debug-utilities/hornetQ at the shell prompt and press Enter.
6. (Optional) To view the list of HornetQ scripts, type ls and press Enter.
7. Type ./HornetQMessageViewer.sh<queue-name>—for example,
./HornetQMessageViewer.shResyncJobDispatcherQueue.
The output from this command is saved to the <queue-name>-messages.txt file in the same directory.
The following sample output displays the list of messages in a JBoss queue named
ResyncJobDispatcherQueue.
Page 81

-----------------------------------------------------------Time of execution: Tue Jun 2 16:13:51 PDT 2015
-----------------------------------------------------------[{"consumerName":"ServerConsumer [id=0, filter=null, binding=LocalQueueBinding
[address=jms.queue.ResyncJobDispatcherQueue,
queue=QueueImpl[name=jms.queue.ResyncJobDispatcherQueue, postOffice=PostOfficeImpl
[server=HornetQServerImpl::serverUUID=d2f96781-0972-11e5-9e84-69e3a4c4a918]]@3ead3529]]",
"elements":[{"timestamp":1433286830611,
"userID":"ID:0780c666-097d-11e5-9e84-69e3a4c4a918",
"messageID":37172,
"JobOperationName":"executeResyncDevices",
"expiration":0,
"address":"jms.queue.ResyncJobDispatcherQueue",
"priority":4,
"JobId":196669,
"__HQ_CID":"077f8de2-097d-11e5-9e84-69e3a4c4a918",
"durable":false,"type":2}]}]
70
8. (Optional) To save the list of all messages at a custom output location, type
./HornetQMessageViewer.sh<queue-name> <output-file-path> and press Enter.
You can view the list of messages in a specific JBoss queue.
RELATED DOCUMENTATION
Junos Space Debug Utilities Overview | 33
Monitoring Network Devices and Troubleshooting Software Issues with Junos Space Network
Management Platform | 2
Page 82

3
PART
Troubleshooting Junos Space Platform
Issues
Troubleshooting Login–Related Issues | 72
Troubleshooting Device Management–Related Issues | 74
Troubleshooting Network Monitoring–Related Issues | 77
Troubleshooting DMI Schema–Related Issues | 78
Page 83

CHAPTER 4
Troubleshooting Login–Related Issues
IN THIS CHAPTER
Troubleshooting the Not Able to Log In from the Junos Space Login Page Issue | 72
Troubleshooting the Not Able to Log In from the Junos Space Login Page Issue
72
Problem
Description: You cannot login to Junos Space Network Management Platform from the Junos Space login
page. The login page displays a message stating the possible cause of the issue.
Cause
You may not be able to log in from the Junos Space login page for one of the following reasons:
You entered an incorrect username, password, or both.
•
The following message is displayed on the login page: The username or password is incorrect
Your account is locked because you exceeded the maximum number of login attempts
•
The following message is displayed on the login page: The account is Locked. You can’t Log in
NOTE: By default, your account is locked out after four unsuccessful login attempts.
Solution
If you have entered incorrect login credentials, verify and enter the correct login credentials.
•
If your account is locked
•
1. Try logging in from another system.
2. Contact the administrator to unlock your user account.
Page 84

NOTE: Your user account is automatically unlocked in 24 hours.
RELATED DOCUMENTATION
Troubleshooting Device Discovery Failure | 74
73
Page 85

CHAPTER 5
Troubleshooting Device Management–Related Issues
IN THIS CHAPTER
Troubleshooting Device Discovery Failure | 74
Troubleshooting Device Data Collection Issue | 75
Troubleshooting Devices Discovered Twice Using the Device Discovery Workflow | 76
Troubleshooting Device Discovery Failure
74
Problem
Description: Devices are not discovered to Junos Space Network Management Platform.
Symptoms: The devices you tried to discover to Junos Space Network Management Platform are not listed
on the Device Management page.
The device discovery job for devices discovered through a device discovery profile, listed on the Job
Management page fails.
Cause
You cannot discover devices to Junos Space Network Management Platform for one of the following
reasons:
You provided an incorrect password to access the device through the Device Discovery Profile workflow.
•
You provided an incorrect private key or passphrase during the Device Discovery Profile workflow
•
The device is not reachable.
•
You provided incorrect SNMP settings for the device in the Device Discovery workflow.
•
Solution
If you entered an incorrect password, modify the device discovery profile by reentering the password
•
and rediscover the device by using the Device Discovery Profile workflow.
If you uploaded an incorrect private key or passphrase, modify the device discovery profile by uploading
•
the correct private key and passphrase and rediscover the device by using the Device Discovery Profile
workflow.
Page 86

If the device you are trying to discover is not reachable, add the correct route to the device. For more
•
information about adding a route to the device, refer to the appropriate device configuration guide.
If you entered incorrect SNMP settings for the device, you can do one of the following:
•
Modify the device discovery profile by clearing the Use SNMP check box on the Network Management
•
Platform > Devices > Device Discovery Profiles > Modify Device Discovery Profile > Specify Probes
page and rediscover the device.
Modify the device discovery profile by adding the correct SNMP details on the Network Management
•
Platform > Devices > Device Discovery Profiles > Modify Device Discovery Profile > Specify Probes
page and rediscover the device.
NOTE: Ensure that SNMP is enabled on the device. For more information about enabling
SNMP on the device, refer to the appropriate device configuration guide.
75
RELATED DOCUMENTATION
Troubleshooting Device Data Collection Issue | 75
Troubleshooting Device Data Collection Issue
Problem
Description: The device on Junos Space Network Management Platform displays the Managed status but
the device is not able to collect data.
Cause
A device cannot collect data even though the status of the device is Managed for one of the following
reasons:
You have not updated the SNMP settings of the device. You may have chosen to skip updating the
•
SNMP details when you discovered the device to Junos Space Network Management Platform.
You have not selected the device interfaces for data collection.
•
Solution
If you have not updated the SNMP settings of the device, update the SNMP settings on the Network
•
Management Platform > Network Monitoring > Admin page.
If you have not selected the device interfaces for data collection:
•
Page 87

1. Select the device on the Network Management Platform > Network Monitoring > Admin > Configure
SNMP Data Collection per Interface page.
2. In the Collect column, select Collect or Default from the drop-down list corresponding to the
interfaces.
RELATED DOCUMENTATION
Troubleshooting Device Discovery Failure | 74
Troubleshooting Devices Discovered Twice Using the Device Discovery Workflow
Problem
Description: Using the Device Discovery Profile workflow, devices are discovered twice to Junos Space
Network Management Platform.
76
Cause
You are using the ping-only method to discover devices to Junos Space Network Management Platform.
Solution
Select the SNMP check box on the Network Management Platform > Devices > Device Discovery Profile
> Create Device Discovery Profile > Specify Probes when discovering devices using the Device Discovery
Profile workflow. Enabling the SNMP option ensures that Junos Space Network Management Platform
checks the serial number of the devices during the discovery process. This prevents the discovery process
from adding duplicate instances of the devices to Junos Space Network Management Platform.
RELATED DOCUMENTATION
Troubleshooting Device Discovery Failure | 74
Page 88

CHAPTER 6
Troubleshooting Network Monitoring–Related Issues
IN THIS CHAPTER
Troubleshooting the Network Monitoring Page Is Not Available Issue | 77
Troubleshooting the Network Monitoring Page Is Not Available Issue
Problem
Description: You can navigate to all other workspaces but the Network Monitoring workspace is not
accessible.
77
Cause
The Network Monitoring service has stopped unexpectedly.
Solution
Restart the Network Monitoring service. To restart the Network Monitoring service:
1. Navigate to the Network Management .Platform > Administration > Applications page.
2. Right-click Network Management Platform and select Manage Services from the Actions menu.
3. Select Network Monitoring, then select the Restart Service icon.
RELATED DOCUMENTATION
Troubleshooting Device Discovery Failure | 74
Page 89

CHAPTER 7
Troubleshooting DMI Schema–Related Issues
IN THIS CHAPTER
Troubleshooting the Nondisplay of the DMI Schema Tree Issue | 78
Troubleshooting the Nondisplay of the DMI Schema Tree Issue
Problem
Description: The DMI schema tree is not displayed.
78
Symptoms: On the Create Template Definition page, you cannot navigate the DMI schema tree or the
hierarchy of configuration options on the left.
Cause
The DMI schema is defective or corrupt.
If the topmost node (Configuration) cannot be opened to reveal the hierarchy, the schema was corrupted
during transition. (Use the grep command to search for SchemaMgr ERROR in the server.log file.)
NOTE: One defective schema does not affect other schemas, which are still available for use.
Solution
Use your own compressed TAR file. This does not require you to restart JBoss. Ensure that the Enable
Schema Overwrite check box is selected when you update the schema. For instructions to add or update
a DMI schema , see Adding Missing DMI Schemas or Updating Outdated DMI Schemas by Using the Update
Schema Menu in the Junos Space Network Management Platform Workspaces User Guide.
For instructions to create your own compressed TAR file, see Creating a Compressed TAR File for Updating
DMI Schema in the Junos Space Network Management Platform Workspaces User Guide.
RELATED DOCUMENTATION
Page 90

Monitoring Network Devices and Troubleshooting Software Issues with Junos Space Network
Management Platform | 2
79
 Loading...
Loading...