Page 1
E Series™ Broadband Services Routers
E120 and E320 Hardware Guide
Release 11.1.x
Juniper Networks, Inc.
1194 North Mathilda Avenue
Sunnyvale, California 94089
USA
408-745-2000
www.juniper.net
Published: 2010-03-25
Page 2

Juniper Networks, the Juniper Networks logo, JUNOS, NetScreen, ScreenOS, and Steel-Belted Radius are registered trademarks of Juniper Networks, Inc. in
the United States and other countries. JUNOSe is a trademark of Juniper Networks, Inc. All other trademarks, service marks, registered trademarks, or
registered service marks are the property of their respective owners.
Juniper Networks assumes no responsibility for any inaccuracies in this document. Juniper Networks reserves the right to change, modify, transfer, or
otherwise revise this publication without notice.
Products made or sold by Juniper Networks or components thereof might be covered by one or more of the following patents that are owned by or licensed
to Juniper Networks: U.S. Patent Nos. 5,473,599, 5,905,725, 5,909,440, 6,192,051, 6,333,650, 6,359,479, 6,406,312, 6,429,706, 6,459,579, 6,493,347,
6,538,518, 6,538,899, 6,552,918, 6,567,902, 6,578,186, and 6,590,785.
E Series™ Broadband Services Routers E120 and E320 Hardware Guide, Release 11.1.x
Copyright © 2010, Juniper Networks, Inc.
All rights reserved. Printed in USA.
Writing: Subash Babu Asokan, John Borelli
Editing: Ben Mann
Illustration: John Borelli
Cover Design: Edmonds Design
Revision History
April 2010—FRS JUNOSe 11.1.x
The information in this document is current as of the date listed in the revision history.
SOFTWARE LICENSE
The terms and conditions for using this software are described in the software license contained in the acknowledgment to your purchase order or, to the
extent applicable, to any reseller agreement or end-user purchase agreement executed between you and Juniper Networks. By using this software, you
indicate that you understand and agree to be bound by those terms and conditions.
Generally speaking, the software license restricts the manner in which you are permitted to use the software and may contain prohibitions against certain
uses. The software license may state conditions under which the license is automatically terminated. You should consult the license for further details.
For complete product documentation, please see the Juniper Networks Web site at www.juniper.net/techpubs.
ii ■
Page 3

END USER LICENSE AGREEMENT
READ THIS END USER LICENSE AGREEMENT (“AGREEMENT”) BEFORE DOWNLOADING, INSTALLING, OR USING THE SOFTWARE. BY DOWNLOADING,
INSTALLING, OR USING THE SOFTWARE OR OTHERWISE EXPRESSING YOUR AGREEMENT TO THE TERMS CONTAINED HEREIN, YOU (AS CUSTOMER
OR IF YOU ARE NOT THE CUSTOMER, AS A REPRESENTATIVE/AGENT AUTHORIZED TO BIND THE CUSTOMER) CONSENT TO BE BOUND BY THIS
AGREEMENT. IF YOU DO NOT OR CANNOT AGREE TO THE TERMS CONTAINED HEREIN, THEN (A) DO NOT DOWNLOAD, INSTALL, OR USE THE SOFTWARE,
AND (B) YOU MAY CONTACT JUNIPER NETWORKS REGARDING LICENSE TERMS.
1. The Parties. The parties to this Agreement are (i) Juniper Networks, Inc. (if the Customer’s principal office is located in the Americas) or Juniper Networks
(Cayman) Limited (if the Customer’s principal office is located outside the Americas) (such applicable entity being referred to herein as “Juniper”), and (ii)
the person or organization that originally purchased from Juniper or an authorized Juniper reseller the applicable license(s) for use of the Software (“Customer”)
(collectively, the “Parties”).
2. The Software. In this Agreement, “Software” means the program modules and features of the Juniper or Juniper-supplied software, for which Customer
has paid the applicable license or support fees to Juniper or an authorized Juniper reseller, or which was embedded by Juniper in equipment which Customer
purchased from Juniper or an authorized Juniper reseller. “Software” also includes updates, upgrades and new releases of such software. “Embedded
Software” means Software which Juniper has embedded in or loaded onto the Juniper equipment and any updates, upgrades, additions or replacements
which are subsequently embedded in or loaded onto the equipment.
3. License Grant. Subject to payment of the applicable fees and the limitations and restrictions set forth herein, Juniper grants to Customer a non-exclusive
and non-transferable license, without right to sublicense, to use the Software, in executable form only, subject to the following use restrictions:
a. Customer shall use Embedded Software solely as embedded in, and for execution on, Juniper equipment originally purchased by Customer from Juniper
or an authorized Juniper reseller.
b. Customer shall use the Software on a single hardware chassis having a single processing unit, or as many chassis or processing units for which Customer
has paid the applicable license fees; provided, however, with respect to the Steel-Belted Radius or Odyssey Access Client software only, Customer shall use
such Software on a single computer containing a single physical random access memory space and containing any number of processors. Use of the
Steel-Belted Radius or IMS AAA software on multiple computers or virtual machines (e.g., Solaris zones) requires multiple licenses, regardless of whether
such computers or virtualizations are physically contained on a single chassis.
c. Product purchase documents, paper or electronic user documentation, and/or the particular licenses purchased by Customer may specify limits to
Customer’s use of the Software. Such limits may restrict use to a maximum number of seats, registered endpoints, concurrent users, sessions, calls,
connections, subscribers, clusters, nodes, realms, devices, links, ports or transactions, or require the purchase of separate licenses to use particular features,
functionalities, services, applications, operations, or capabilities, or provide throughput, performance, configuration, bandwidth, interface, processing,
temporal, or geographical limits. In addition, such limits may restrict the use of the Software to managing certain kinds of networks or require the Software
to be used only in conjunction with other specific Software. Customer’s use of the Software shall be subject to all such limitations and purchase of all applicable
licenses.
d. For any trial copy of the Software, Customer’s right to use the Software expires 30 days after download, installation or use of the Software. Customer
may operate the Software after the 30-day trial period only if Customer pays for a license to do so. Customer may not extend or create an additional trial
period by re-installing the Software after the 30-day trial period.
e. The Global Enterprise Edition of the Steel-Belted Radius software may be used by Customer only to manage access to Customer’s enterprise network.
Specifically, service provider customers are expressly prohibited from using the Global Enterprise Edition of the Steel-Belted Radius software to support any
commercial network access services.
The foregoing license is not transferable or assignable by Customer. No license is granted herein to any user who did not originally purchase the applicable
license(s) for the Software from Juniper or an authorized Juniper reseller.
4. Use Prohibitions. Notwithstanding the foregoing, the license provided herein does not permit the Customer to, and Customer agrees not to and shall
not: (a) modify, unbundle, reverse engineer, or create derivative works based on the Software; (b) make unauthorized copies of the Software (except as
necessary for backup purposes); (c) rent, sell, transfer, or grant any rights in and to any copy of the Software, in any form, to any third party; (d) remove
any proprietary notices, labels, or marks on or in any copy of the Software or any product in which the Software is embedded; (e) distribute any copy of
the Software to any third party, including as may be embedded in Juniper equipment sold in the secondhand market; (f) use any ‘locked’ or key-restricted
feature, function, service, application, operation, or capability without first purchasing the applicable license(s) and obtaining a valid key from Juniper, even
if such feature, function, service, application, operation, or capability is enabled without a key; (g) distribute any key for the Software provided by Juniper
to any third party; (h) use the Software in any manner that extends or is broader than the uses purchased by Customer from Juniper or an authorized Juniper
reseller; (i) use Embedded Software on non-Juniper equipment; (j) use Embedded Software (or make it available for use) on Juniper equipment that the
Customer did not originally purchase from Juniper or an authorized Juniper reseller; (k) disclose the results of testing or benchmarking of the Software to
any third party without the prior written consent of Juniper; or (l) use the Software in any manner other than as expressly provided herein.
5. Audit. Customer shall maintain accurate records as necessary to verify compliance with this Agreement. Upon request by Juniper, Customer shall furnish
such records to Juniper and certify its compliance with this Agreement.
■ iii
Page 4

6. Confidentiality. The Parties agree that aspects of the Software and associated documentation are the confidential property of Juniper. As such, Customer
shall exercise all reasonable commercial efforts to maintain the Software and associated documentation in confidence, which at a minimum includes
restricting access to the Software to Customer employees and contractors having a need to use the Software for Customer’s internal business purposes.
7. Ownership. Juniper and Juniper’s licensors, respectively, retain ownership of all right, title, and interest (including copyright) in and to the Software,
associated documentation, and all copies of the Software. Nothing in this Agreement constitutes a transfer or conveyance of any right, title, or interest in
the Software or associated documentation, or a sale of the Software, associated documentation, or copies of the Software.
8. Warranty, Limitation of Liability, Disclaimer of Warranty. The warranty applicable to the Software shall be as set forth in the warranty statement that
accompanies the Software (the “Warranty Statement”). Nothing in this Agreement shall give rise to any obligation to support the Software. Support services
may be purchased separately. Any such support shall be governed by a separate, written support services agreement. TO THE MAXIMUM EXTENT PERMITTED
BY LAW, JUNIPER SHALL NOT BE LIABLE FOR ANY LOST PROFITS, LOSS OF DATA, OR COSTS OR PROCUREMENT OF SUBSTITUTE GOODS OR SERVICES,
OR FOR ANY SPECIAL, INDIRECT, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES ARISING OUT OF THIS AGREEMENT, THE SOFTWARE, OR ANY JUNIPER OR
JUNIPER-SUPPLIED SOFTWARE. IN NO EVENT SHALL JUNIPER BE LIABLE FOR DAMAGES ARISING FROM UNAUTHORIZED OR IMPROPER USE OF ANY
JUNIPER OR JUNIPER-SUPPLIED SOFTWARE. EXCEPT AS EXPRESSLY PROVIDED IN THE WARRANTY STATEMENT TO THE EXTENT PERMITTED BY LAW,
JUNIPER DISCLAIMS ANY AND ALL WARRANTIES IN AND TO THE SOFTWARE (WHETHER EXPRESS, IMPLIED, STATUTORY, OR OTHERWISE), INCLUDING
ANY IMPLIED WARRANTY OF MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE, OR NONINFRINGEMENT. IN NO EVENT DOES JUNIPER
WARRANT THAT THE SOFTWARE, OR ANY EQUIPMENT OR NETWORK RUNNING THE SOFTWARE, WILL OPERATE WITHOUT ERROR OR INTERRUPTION,
OR WILL BE FREE OF VULNERABILITY TO INTRUSION OR ATTACK. In no event shall Juniper’s or its suppliers’ or licensors’ liability to Customer, whether
in contract, tort (including negligence), breach of warranty, or otherwise, exceed the price paid by Customer for the Software that gave rise to the claim, or
if the Software is embedded in another Juniper product, the price paid by Customer for such other product. Customer acknowledges and agrees that Juniper
has set its prices and entered into this Agreement in reliance upon the disclaimers of warranty and the limitations of liability set forth herein, that the same
reflect an allocation of risk between the Parties (including the risk that a contract remedy may fail of its essential purpose and cause consequential loss),
and that the same form an essential basis of the bargain between the Parties.
9. Termination. Any breach of this Agreement or failure by Customer to pay any applicable fees due shall result in automatic termination of the license
granted herein. Upon such termination, Customer shall destroy or return to Juniper all copies of the Software and related documentation in Customer’s
possession or control.
10. Taxes. All license fees payable under this agreement are exclusive of tax. Customer shall be responsible for paying Taxes arising from the purchase of
the license, or importation or use of the Software. If applicable, valid exemption documentation for each taxing jurisdiction shall be provided to Juniper prior
to invoicing, and Customer shall promptly notify Juniper if their exemption is revoked or modified. All payments made by Customer shall be net of any
applicable withholding tax. Customer will provide reasonable assistance to Juniper in connection with such withholding taxes by promptly: providing Juniper
with valid tax receipts and other required documentation showing Customer’s payment of any withholding taxes; completing appropriate applications that
would reduce the amount of withholding tax to be paid; and notifying and assisting Juniper in any audit or tax proceeding related to transactions hereunder.
Customer shall comply with all applicable tax laws and regulations, and Customer will promptly pay or reimburse Juniper for all costs and damages related
to any liability incurred by Juniper as a result of Customer’s non-compliance or delay with its responsibilities herein. Customer’s obligations under this
Section shall survive termination or expiration of this Agreement.
11. Export. Customer agrees to comply with all applicable export laws and restrictions and regulations of any United States and any applicable foreign
agency or authority, and not to export or re-export the Software or any direct product thereof in violation of any such restrictions, laws or regulations, or
without all necessary approvals. Customer shall be liable for any such violations. The version of the Software supplied to Customer may contain encryption
or other capabilities restricting Customer’s ability to export the Software without an export license.
12. Commercial Computer Software. The Software is “commercial computer software” and is provided with restricted rights. Use, duplication, or disclosure
by the United States government is subject to restrictions set forth in this Agreement and as provided in DFARS 227.7201 through 227.7202-4, FAR 12.212,
FAR 27.405(b)(2), FAR 52.227-19, or FAR 52.227-14(ALT III) as applicable.
13. Interface Information. To the extent required by applicable law, and at Customer's written request, Juniper shall provide Customer with the interface
information needed to achieve interoperability between the Software and another independently created program, on payment of applicable fee, if any.
Customer shall observe strict obligations of confidentiality with respect to such information and shall use such information in compliance with any applicable
terms and conditions upon which Juniper makes such information available.
14. Third Party Software. Any licensor of Juniper whose software is embedded in the Software and any supplier of Juniper whose products or technology
are embedded in (or services are accessed by) the Software shall be a third party beneficiary with respect to this Agreement, and such licensor or vendor
shall have the right to enforce this Agreement in its own name as if it were Juniper. In addition, certain third party software may be provided with the
Software and is subject to the accompanying license(s), if any, of its respective owner(s). To the extent portions of the Software are distributed under and
subject to open source licenses obligating Juniper to make the source code for such portions publicly available (such as the GNU General Public License
(“GPL”) or the GNU Library General Public License (“LGPL”)), Juniper will make such source code portions (including Juniper modifications, as appropriate)
available upon request for a period of up to three years from the date of distribution. Such request can be made in writing to Juniper Networks, Inc., 1194
N. Mathilda Ave., Sunnyvale, CA 94089, ATTN: General Counsel. You may obtain a copy of the GPL at http://www.gnu.org/licenses/gpl.html, and
a copy of the LGPL at http://www.gnu.org/licenses/lgpl.html.
15. Miscellaneous. This Agreement shall be governed by the laws of the State of California without reference to its conflicts of laws principles. The provisions
of the U.N. Convention for the International Sale of Goods shall not apply to this Agreement. For any disputes arising under this Agreement, the Parties
hereby consent to the personal and exclusive jurisdiction of, and venue in, the state and federal courts within Santa Clara County, California. This Agreement
constitutes the entire and sole agreement between Juniper and the Customer with respect to the Software, and supersedes all prior and contemporaneous
iv ■
Page 5

agreements relating to the Software, whether oral or written (including any inconsistent terms contained in a purchase order), except that the terms of a
separate written agreement executed by an authorized Juniper representative and Customer shall govern to the extent such terms are inconsistent or conflict
with terms contained herein. No modification to this Agreement nor any waiver of any rights hereunder shall be effective unless expressly assented to in
writing by the party to be charged. If any portion of this Agreement is held invalid, the Parties agree that such invalidity shall not affect the validity of the
remainder of this Agreement. This Agreement and associated documentation has been written in the English language, and the Parties agree that the English
version will govern. (For Canada: Les parties aux présentés confirment leur volonté que cette convention de même que tous les documents y compris tout
avis qui s'y rattaché, soient redigés en langue anglaise. (Translation: The parties confirm that this Agreement and all related documentation is and will be
in the English language)).
■ v
Page 6

vi ■
Page 7

Table of Contents
About the Documentation xiii
E Series and JUNOSe Documentation and Release Notes ..............................xiii
Audience ......................................................................................................xiii
E Series and JUNOSe Text and Syntax Conventions ......................................xiii
Obtaining Documentation .............................................................................xv
Documentation Feedback ..............................................................................xv
Requesting Technical Support ........................................................................xv
Self-Help Online Tools and Resources ....................................................xvi
Opening a Case with JTAC ......................................................................xvi
Part 1 Product Overview
Chapter 1 E120 and E320 Overview 3
System Description .........................................................................................3
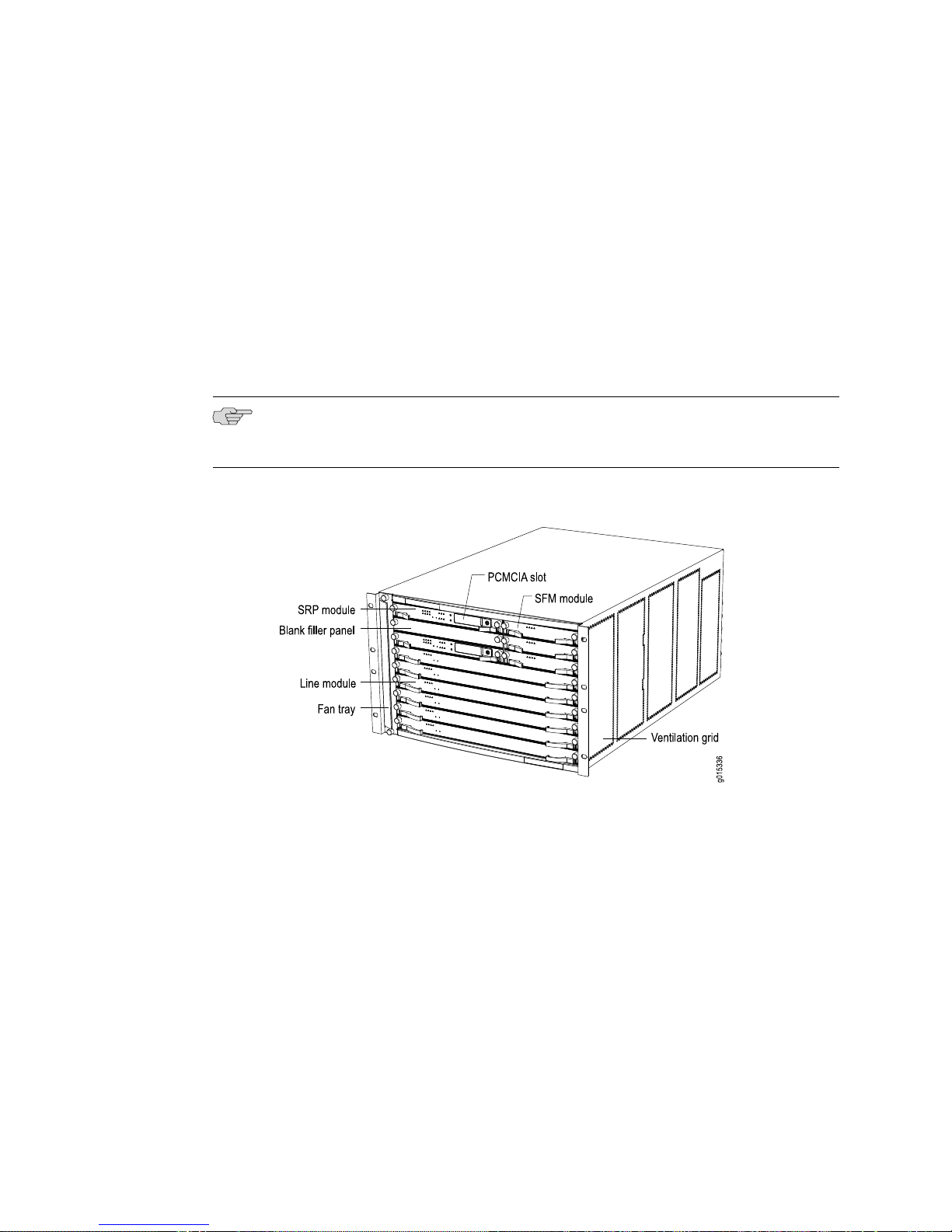
Chassis Overview ............................................................................................3
E320 Model ..............................................................................................4
E120 Model ..............................................................................................6
E120 and E320 Modules ..................................................................................7
SRP Module ..............................................................................................7
Module Details ....................................................................................8
Nonvolatile Storage ............................................................................9
SFM Module ..............................................................................................9
Fabric Slices .....................................................................................10
SRP IOA ..................................................................................................10
Module Details ..................................................................................10
Line Modules ..........................................................................................11
Packet Classification .........................................................................12
I/O Adapters ...........................................................................................12
Network Management Tools ..........................................................................13
CLI Management .....................................................................................13
SNMP MIB Management .........................................................................13
Redundancy Features ....................................................................................14
SRP Modules ...........................................................................................14
NVS Cards ........................................................................................14
Power .....................................................................................................14
Fans ........................................................................................................14
Table of Contents ■ vii
Page 8

E120 and E320 11.1.x Hardware Guide
Part 2 Initial Installation
Chapter 2 Unpacking and Inspecting the Router 19
Before You Begin ...........................................................................................19
Unpacking the Router ....................................................................................19
Inspecting Router Components and Accessories ...........................................20
If You Detect or Suspect Damage ..................................................................21
Contacting Juniper Networks .........................................................................21
The Next Step ................................................................................................21
Chapter 3 Installing the Router 23
Before You Begin ...........................................................................................23
Freestanding Installation ...............................................................................23
Rack-Mounted Installation .............................................................................25
Installation Guidelines .............................................................................25
Preparing the Equipment Racks ..............................................................26
Installing the Router ................................................................................26
The Next Step ................................................................................................26
Chapter 4 Installing Modules 27
Overview .......................................................................................................27
Slot Numbering .......................................................................................30
IOA Slot Combinations ............................................................................32
Module Combinations .............................................................................34
IOAs Requiring SFPs ...............................................................................35
Proper Handling of ES2 4G LMs ..............................................................35
ES2 10G Uplink Line Modules .................................................................36
Managing Modules Using the Software ...................................................36
Order of Installation ................................................................................36
Hot-Swapping Modules ...........................................................................37
Protecting Modules and Slots ..................................................................37
Required Tools and Safety Items .............................................................38
Safety Guidelines ...........................................................................................38
Installing an SRP Module or SFM Module ......................................................38
Installing an IOA Shelf ...................................................................................40
Installing a Line Module or an IOA ................................................................41
Removing Modules and IOAs ........................................................................42
Installing and Removing SFPs .......................................................................44
Installing SFPs .........................................................................................44
Removing SFPs .......................................................................................45
The Next Step ................................................................................................46
viii ■ Table of Contents
Page 9
Table of Contents
Chapter 5 Cabling the Router 47
Cabling Overview ..........................................................................................47
Required Tools, Wires, and Cables ................................................................48
Cabling the SRP IOA ......................................................................................49
Network Timing Ports .............................................................................50
Management Ports ..................................................................................51
Connecting to the Network ...............................................................51
Connecting to a Console Terminal ....................................................51
Cabling IOAs .................................................................................................51
LC Duplex Connectors ............................................................................52
SFPs ........................................................................................................52
Cabling the Router for Power ........................................................................52
Task 1: Turn Off All Router Power ..........................................................54
Task 2: Connect the Grounding Cables ....................................................54
Task 3: Connect the Power Cables ..........................................................55
The Next Step ................................................................................................56
Chapter 6 Powering Up the Router 57
Before You Power Up the System ..................................................................57
Powering Up .................................................................................................57
Initialization Sequence ............................................................................58
Status LEDs ...................................................................................................58
Powering Down .............................................................................................59
The Next Step ................................................................................................59
Chapter 7 Accessing E Series Routers 61
Setting Up Management Access .....................................................................61
Console Port Setup ........................................................................................61
Using HyperTerminal ..............................................................................62
Connecting Directly to the Router ...........................................................62
Assigning an IP Address ..........................................................................63
Telnet Setup ..................................................................................................64
SNMP ............................................................................................................65
The Next Step ................................................................................................66
Part 3 Hardware Maintenance, Replacement, and Troubleshooting
Procedures
Chapter 8 Maintaining the Router 69
Required Tools and Items ..............................................................................69
Storing Modules and Components .................................................................69
Table of Contents ■ ix
Page 10

E120 and E320 11.1.x Hardware Guide
Cleaning the System ......................................................................................70
Upgrading NVS Cards on SRP Modules ..........................................................70
Upgrading a System That Contains One SRP Module ..............................71
Upgrading a System That Contains Two SRP Modules ............................71
Replacing an NVS Card ..................................................................................72
Replacing Fan Trays ......................................................................................73
Removing an E320 Fan Tray ...................................................................74
Installing an E320 Fan Tray ....................................................................74
Installing an Air Filter ....................................................................................75
Replacing a Power Distribution Unit ..............................................................76
Chapter 9 Troubleshooting 79
Diagnosing Problems ....................................................................................79
Initialization Sequence ............................................................................79
Troubleshooting Power Failures ....................................................................80
Understanding Status LEDs to Troubleshoot ..................................................80
LED Identification ...................................................................................80
LED Activity ............................................................................................83
Monitoring Temperatures of Modules ............................................................85
Resetting Line Modules and SRP Modules .....................................................86
Double-Bit Errors on SRP Modules .................................................................86
Detecting Double-Bit Errors ....................................................................87
Fixing Double-Bit Errors ..........................................................................87
Part 4 Appendixes
Appendix A System Specifications 91
E120 Broadband Services Router Specifications ............................................91
E320 Broadband Services Router Specifications ............................................93
Router Power Requirements .........................................................................94
Appendix B Installation Guidelines and Requirements 97
Your Preinstallation Responsibilities ..............................................................97
Environmental Requirements ........................................................................97
Regulatory Compliances ................................................................................98
Safety Guidelines ...........................................................................................98
Equipment Rack Requirements .....................................................................99
Mechanical Requirements .......................................................................99
Space Requirements .............................................................................100
Proper Rack Installation ........................................................................100
Cabling Recommendations ..........................................................................101
Product Reclamation and Recycling Program ..............................................102
x ■ Table of Contents
Page 11
Table of Contents
Hardware Compliance .................................................................................103
Federal Communications Commission (FCC) Statement .......................103
FCC Requirements for Consumer Products ...........................................104
Food and Drug Administration, Center for Devices and Radiological
Health ............................................................................................104
Canadian Department of Communications Radio Interference
Regulations .....................................................................................104
Réglement sur le brouillage radioélectrique du ministère des
communications .............................................................................104
Industry Canada Notice CS-03 ..............................................................104
Avis CS-03 d'Industrie Canada ..............................................................105
D.O.C. Explanatory Notes: Equipment Attachment Limitations ............106
Notes explicatives du ministère des Communications: limites visant les
accessoires .....................................................................................106
EC Declaration of Conformity ...............................................................107
Voluntary Control Council for Interference (VCCI) Statement for
Japan ..............................................................................................107
Appendix C Cable Pinouts 109
SRP IOA ......................................................................................................109
Appendix D Contacting Customer Support and Returning Hardware 113
Contacting Customer Support ......................................................................113
Return Procedure ........................................................................................113
Locating Component Serial Numbers ..........................................................114
Information You Might Need to Supply to JTAC ...........................................115
Tools and Parts Required ............................................................................116
Returning Products for Repair or Replacement ...........................................116
Packing Instructions for Returning a Chassis .........................................116
Appendix E Declaration of Conformity 119
Declaration of Conformity – E120 Broadband Services Router ....................119
Declaration of Conformity – E320 Broadband Services Router ....................120
Part 5 Index
Index ...........................................................................................................123
Table of Contents ■ xi
Page 12

E120 and E320 11.1.x Hardware Guide
xii ■ Table of Contents
Page 13
About the Documentation
■ E Series and JUNOSe Documentation and Release Notes on page xiii
■ Audience on page xiii
■ E Series and JUNOSe Text and Syntax Conventions on page xiii
■ Obtaining Documentation on page xv
■ Documentation Feedback on page xv
■ Requesting Technical Support on page xv
E Series and JUNOSe Documentation and Release Notes
For a list of related JUNOSe documentation, see
http://www.juniper.net/techpubs/software/index.html .
If the information in the latest release notes differs from the information in the
documentation, follow the JUNOSe Release Notes.
To obtain the most current version of all Juniper Networks® technical documentation,
see the product documentation page on the Juniper Networks website at
http://www.juniper.net/techpubs/.
Audience
This guide is intended for experienced system and network specialists working with
Juniper Networks E Series Broadband Services Routers in an Internet access
environment.
E Series and JUNOSe Text and Syntax Conventions
Table 1 on page xiv defines notice icons used in this documentation.
E Series and JUNOSe Documentation and Release Notes ■ xiii
Page 14

E120 and E320 11.1.x Hardware Guide
Table 1: Notice Icons
Table 2 on page xiv defines text and syntax conventions that we use throughout the
E Series and JUNOSe documentation.
DescriptionMeaningIcon
Indicates important features or instructions.Informational note
Indicates a situation that might result in loss of data or hardware damage.Caution
Alerts you to the risk of personal injury or death.Warning
Alerts you to the risk of personal injury from a laser.Laser warning
Table 2: Text and Syntax Conventions
Represents commands and keywords in text.Bold text like this
Bold text like this
Fixed-width text like this
Represents text that the user must type.
Represents information as displayed on your
terminal’s screen.
Italic text like this
Emphasizes words.
■
Identifies variables.
■
Identifies chapter, appendix, and book
■
names.
Plus sign (+) linking key names
keys simultaneously.
Syntax Conventions in the Command Reference Guide
ExamplesDescriptionConvention
Issue the clock source command.
■
Specify the keyword exp-msg.
■
host1(config)#traffic class low-loss1
host1#show ip ospf 2
Routing Process OSPF 2 with Router
ID 5.5.0.250
Router is an Area Border Router
(ABR)
There are two levels of access: user and
■
privileged.
clusterId, ipAddress.
■
Appendix A, System Specifications
■
Press Ctrl + b.Indicates that you must press two or more
terminal lengthRepresents keywords.Plain text like this
| (pipe symbol)
xiv ■ E Series and JUNOSe Text and Syntax Conventions
mask, accessListNameRepresents variables.Italic text like this
diagnostic | lineRepresents a choice to select one keyword
or variable to the left or to the right of this
symbol. (The keyword or variable can be
either optional or required.)
Page 15
Table 2: Text and Syntax Conventions (continued)
About the Documentation
ExamplesDescriptionConvention
[ internal | external ]Represent optional keywords or variables.[ ] (brackets)
[ ]* (brackets and asterisk)
that can be entered more than once.
Represent required keywords or variables.{ } (braces)
Obtaining Documentation
To obtain the most current version of all Juniper Networks technical documentation,
see the Technical Documentation page on the Juniper Networks Web site at
http://www.juniper.net/.
To download complete sets of technical documentation to create your own
documentation CD-ROMs or DVD-ROMs, see the Offline Documentation page at
http://www.juniper.net/techpubs/resources/cdrom.html
Copies of the Management Information Bases (MIBs) for a particular software release
are available for download in the software image bundle from the Juniper Networks
Web site athttp://www.juniper.net/.
Documentation Feedback
[ level1 | level2 | l1 ]*Represent optional keywords or variables
{ permit | deny } { in | out }
{ clusterId | ipAddress }
We encourage you to provide feedback, comments, and suggestions so that we can
improve the documentation to better meet your needs. Send your comments to
techpubs-comments@juniper.net, or fill out the documentation feedback form at
https://www.juniper.net/cgi-bin/docbugreport/. If you are using e-mail, be sure to include
the following information with your comments:
■ Document or topic name
■ URL or page number
■ Software release version
Requesting Technical Support
Technical product support is available through the Juniper Networks Technical
Assistance Center (JTAC). If you are a customer with an active J-Care or JNASC support
contract, or are covered under warranty, and need post-sales technical support, you
can access our tools and resources online or open a case with JTAC.
■ JTAC policies—For a complete understanding of our JTAC procedures and policies,
review the JTAC User Guide located at
http://www.juniper.net/customers/support/downloads/7100059-EN.pdf .
Obtaining Documentation ■ xv
Page 16

E120 and E320 11.1.x Hardware Guide
■ Product warranties—For product warranty information, visit
http://www.juniper.net/support/warranty/ .
■ JTAC hours of operation—The JTAC centers have resources available 24 hours a
day, 7 days a week, 365 days a year.
Self-Help Online Tools and Resources
For quick and easy problem resolution, Juniper Networks has designed an online
self-service portal called the Customer Support Center (CSC) that provides you with
the following features:
■
Find CSC offerings: http://www.juniper.net/customers/support/
■
Search for known bugs: http://www2.juniper.net/kb/
■
Find product documentation: http://www.juniper.net/techpubs/
■ Find solutions and answer questions using our Knowledge Base:
http://kb.juniper.net/
■ Download the latest versions of software and review release notes:
http://www.juniper.net/customers/csc/software/
■ Search technical bulletins for relevant hardware and software notifications:
https://www.juniper.net/alerts/
■ Join and participate in the Juniper Networks Community Forum:
http://www.juniper.net/company/communities/
■
Open a case online in the CSC Case Management tool: http://www.juniper.net/cm/
To verify service entitlement by product serial number, use our Serial Number
Entitlement (SNE) Tool: https://tools.juniper.net/SerialNumberEntitlementSearch/
Opening a Case with JTAC
You can open a case with JTAC on the Web or by telephone.
■
Use the Case Management tool in the CSC at http://www.juniper.net/cm/ .
■ Call 1-888-314-JTAC (1-888-314-5822 toll-free in the USA, Canada, and Mexico).
For international or direct-dial options in countries without toll-free numbers, see
http://www.juniper.net/support/requesting support.html .
xvi ■ Requesting Technical Support
Page 17

Part 1
Product Overview
■ E120 and E320 Overview on page 3
Product Overview ■ 1
Page 18

E120 and E320 11.1.x Hardware Guide
2 ■ Product Overview
Page 19
Chapter 1
E120 and E320 Overview
This chapter provides introductory information about the Juniper Networks E120
and E320 Broadband Services Routers. It contains the following sections:
■ System Description on page 3
■ Chassis Overview on page 3
■ E120 and E320 Modules on page 7
■ Network Management Tools on page 13
■ Redundancy Features on page 14
System Description
E Series routers are modular, carrier-class networking devices that deliver
performance, reliability, and service differentiation to both enterprise and residential
Internet users. The E120 router and E320 router are next-generation, high-capacity
additions to the E Series product family offering high-port density and high bandwidth
in a fully redundant system, supporting evolving IP-based broadband services. The
E120 router supports the same services as the E320 router, but with smaller capacity
and scaling capabilities for smaller configurations.
Chassis Overview
The routers utilize the same JUNOSe™ software architecture and provide a single IP
entry point into the service provider network with the same IP-based protocols and
services that are available on existing E Series products. They address a wide range
of edge applications, including subscriber management (including 802.11 hotspots),
video on demand, Voice over IP (VoIP), Metro Ethernet, customer circuit aggregation,
virtual private networks (VPNs), and wholesale services.
E Series routers offer the complete edge solution for IP-optimized carriers.
Two models are available:
■ E120 router
■ E320 router
Both models use the same software and share a system architecture and common
components:
System Description ■ 3
Page 20
E120 and E320 11.1.x Hardware Guide
■ Switch route processors (SRPs)—Perform system management, routing table
calculations maintenance, forwarding table computations, and other control
plane functions
■ Switch fabric modules (SFMs)—Create a distributed shared memory switching
fabric
■ Line modules (LMs)—Are frame processing and forwarding engines for IOAs
■ Input/output adapter (IOA)—Provide the physical connection to the network via
10–Gigabit Ethernet, Ethernet, ATM, and Packet over SONET (PoS) interfaces
■ Power modules—Distribute redundant power feeds through the system to all
components
E320 Model
A fully configured E320 router consists of 2 switch route processors (SRPs), 3 switch
fabric modules (SFMs), 12 line modules, and up to 2 I/O adapters (IOAs) per line
module. See Figure 1 on page 5 and Figure 2 on page 5.
An IOA shelf (bracket) can be installed on a slot-by-slot basis to create an upper IOA
bay and lower IOA bay, enabling you to use up to two IOAs in the same slot. This
architecture enables you to combine different IOA types in the same slot and to
support oversubscribed configurations.
NOTE: The routers illustrated in this book might look different than your router due
to configuration variations.
4 ■ Chassis Overview
Page 21
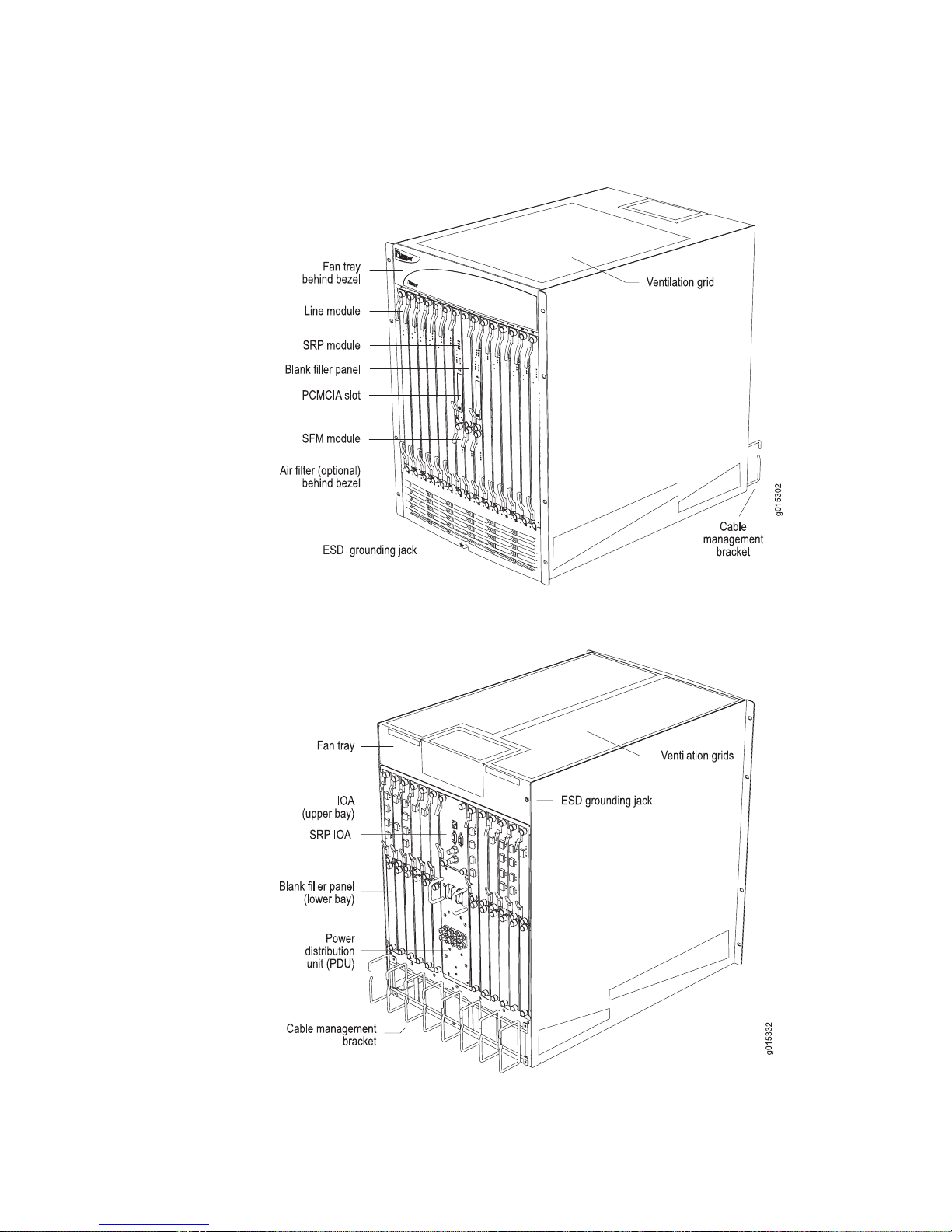
Figure 1: E320 Router, Front View
Chapter 1: E120 and E320 Overview
Figure 2: E320 Router, Rear View
Chassis Overview ■ 5
Page 22
E120 and E320 11.1.x Hardware Guide
E120 Model
A fully configured E120 router consists of 2 switch route processors (SRPs), 3 switch
fabric modules (SFMs), 6 line modules, and up to 2 I/O adapters (IOAs) per line
module. See Figure 3 on page 6 and Figure 4 on page 7.
An IOA shelf (bracket) can be installed on a slot-by-slot basis to create a left and right
IOA bay, enabling you to use up to two IOAs in the same slot. This architecture
enables you to combine different IOA types in the same slot and to support
oversubscribed configurations. Air is pulled in from the right of the router by the fan
tray and is exhausted out the left side.
NOTE: The routers illustrated in this book might look different than your router due
to configuration variations.
Figure 3: E120 Router, Front View
6 ■ Chassis Overview
Page 23
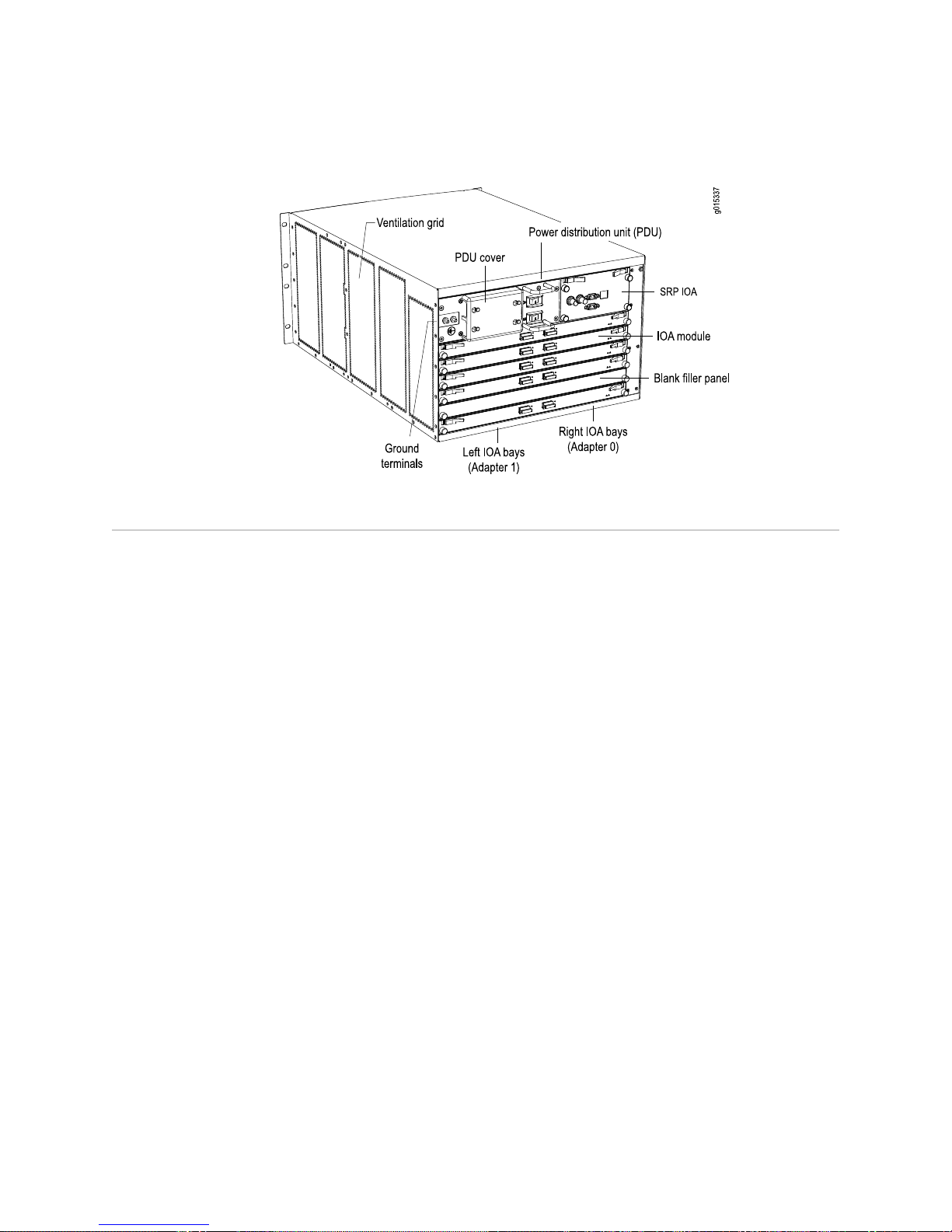
Figure 4: E120 Router, Rear View
Chapter 1: E120 and E320 Overview
E120 and E320 Modules
The routers support SRP modules, SFM modules, line modules, and IOAs. You can
use a line module for access or uplink. Access line modules receive traffic from
low-speed circuits, and the system routes the traffic onto higher-speed uplink line
modules and then to the core of the network. Line modules act as frame forwarding
engines for the physical interfaces (the IOAs) via a passive midplane.
Most line modules, IOAs, SFMs, and SRP modules can be installed in either router.
There are a few exceptions, however:
■ Similar-capacity modules must be used in the same router. For example, you
cannot install an SRP-100 in a router that contains an SFM-320. You can only
use a SRP–100 module with a SFM-100 module.
■ Higher-capacity SRP modules can be used in lower-capacity routers, but
lower-capacity SRP modules cannot be used in high-capacity routers. For example,
an SRP-320 can be used in an E120 router, but an SRP-120 cannot be used in
an E320 router.
■ The SRP-100 module and the SFM-100 module are not supported in the E120
router.
See the E120 and E320 Module Guide for module and chassis compatibility.
The front panel of each module contains a collection of status LEDs (light-emitting
diodes). For information about how to interpret the LEDs, see “Troubleshooting” on
page 79. For complete module specifications, see the E120 and E320 Module Guide.
SRP Module
Switch route processor (SRP) modules perform system management, routing table
calculations and maintenance, forwarding table computations, statistics processing,
configuration storage, and other control plane functions. The SRP module identifies
E120 and E320 Modules ■ 7
Page 24
E120 and E320 11.1.x Hardware Guide
which line modules are physically present in the chassis and monitors and controls
vital functions on the line modules.
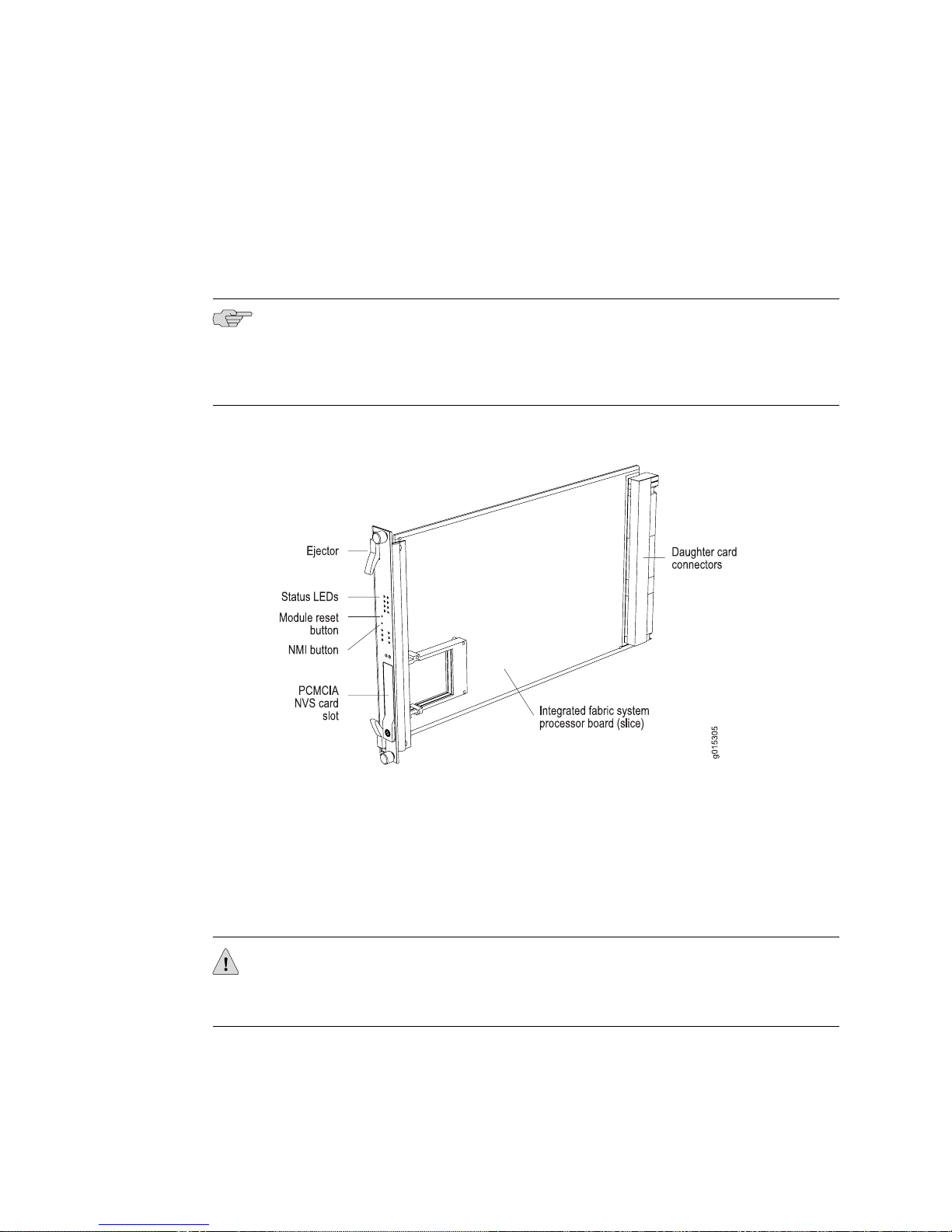
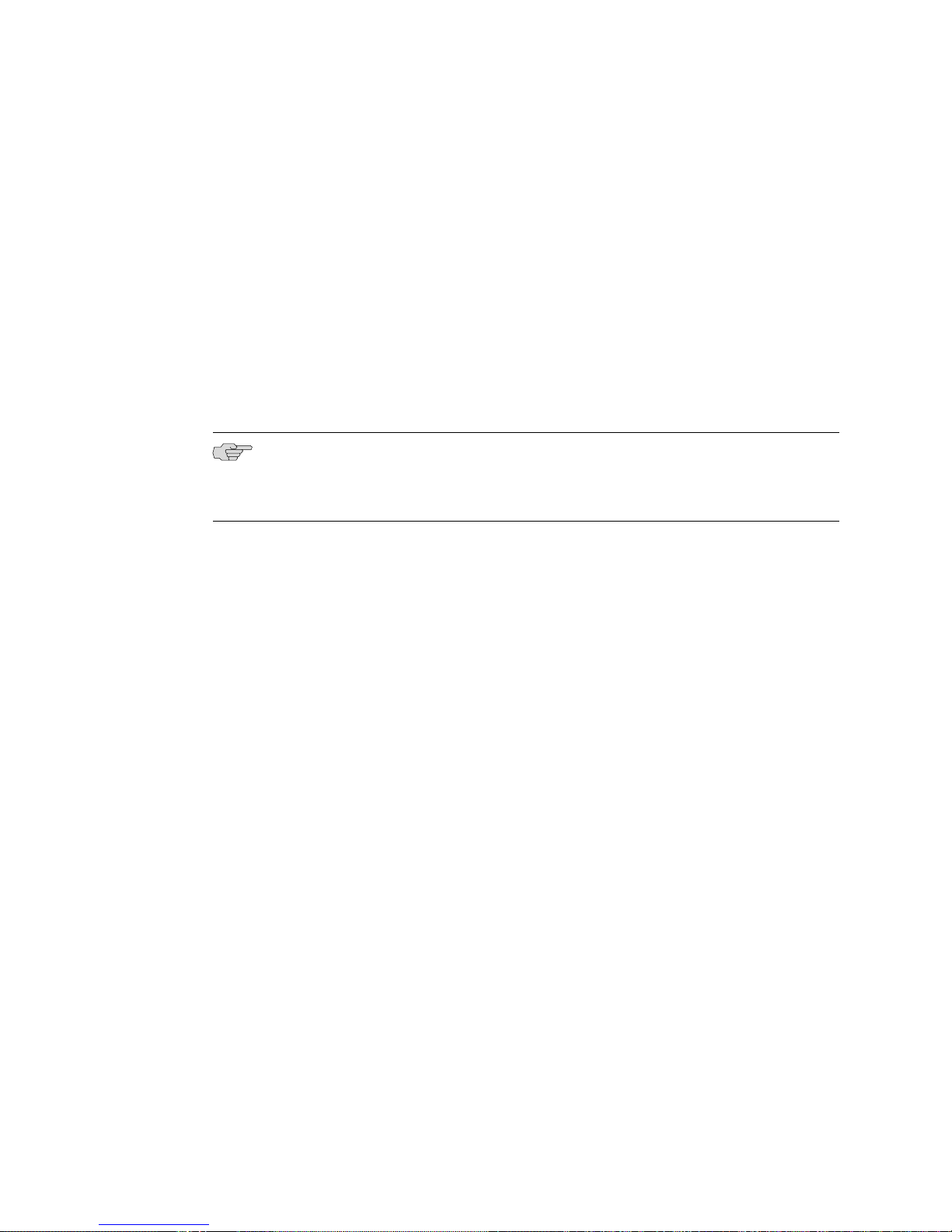
Each SRP module (Figure 5 on page 8) is a PowerPC-based system with its own
memory, nonvolatile storage (NVS), and power converter. The SRP module works
with the SFM modules and contains a switch fabric slice common to both modules.
See “Fabric Slices” on page 10 for more information.
NOTE: Because of different physical dimensions and switch fabric capabilities, SRP
modules are not interchangeable between all routers. For example, the SRP–100
used in the E320 router cannot be used in other E Series routers, and vice versa. See
the E120 and E320 Module Guide for SRP module compatibility.
Figure 5: Representative SRP Module
Module Details
An SRP module must be present for the router to boot. The routers support up to
two redundant SRP modules operating in an active/standby configuration. The
redundant SRP module takes control when a failover occurs. See “Redundancy
Features” on page 14 and the E120 and E320 Module Guide for more SRP module
information.
CAUTION: Do not remove the SRP module while the system is running, unless you
have properly issued the halt command. See JUNOSe System Basics Configuration
Guide, Chapter 6, Managing Modules for information about the halt commands.
8 ■ E120 and E320 Modules
Page 25
Chapter 1: E120 and E320 Overview
NOTE: You cannot use SRP modules of different capacities in the same configuration.
For example, you cannot install a SRP-100 module and a SRP-320 module in the
same router.
For details about installing SRP modules, see “Installing Modules” on page 27.
Nonvolatile Storage
Depending on the model, each SRP module has either two Type II PCMCIA nonvolatile
storage (NVS) cards or two ATA flash cards (0, 1). (See Figure 5 on page 8.) One
card is loaded with the system's software and configuration files while the other card
holds core dumps. The NVS cards in the active SRP module are designated disk0 and
disk1. The NVS cards in the redundant SRP module are designated standby-disk0
and standby-disk1. The PCMCIA card is factory installed.
SFM Module
CAUTION: Before you insert or remove flash cards from a running router, we strongly
recommend that you halt the SRP module or shut down the router. Failure to do this
can result in file corruption in one or both cards. See “Replacing an NVS Card” on
page 72 for more information.
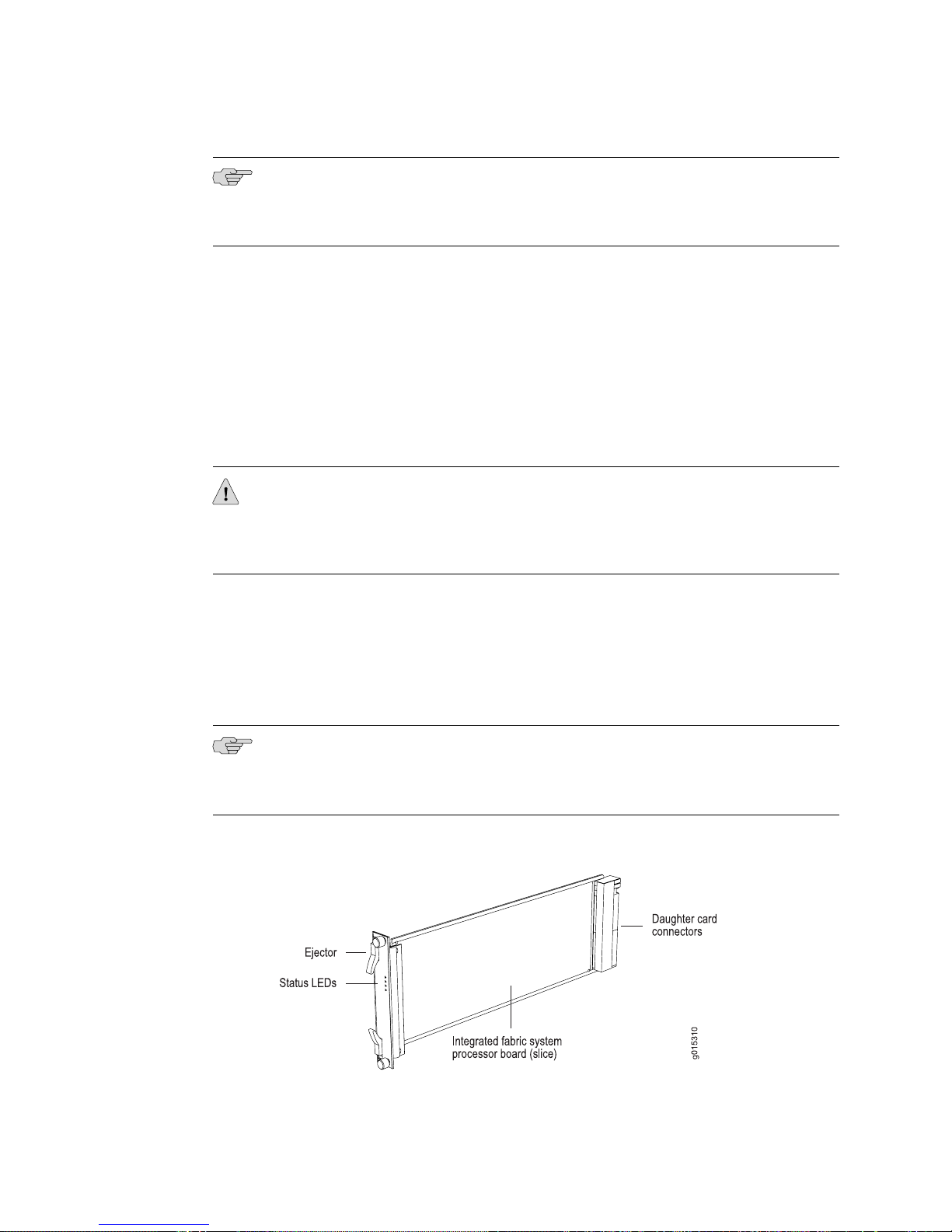
The switch fabric modules (SFMs) work with the SRP module to create a shared
memory fabric for the router. Each SFM module (Figure 6 on page 9) has its own
memory and power converter. Like the SRP module, the SFM module contains a
fabric system processor board (slice). See “Fabric Slices” on page 10.
NOTE: You must use a SRP module that corresponds with the fabric type (SFM
module) that is installed. For example, you can only use a SRP–100 module with a
SFM-100 module. You cannot use a SRP–100 module with a SFM-320 module.
Figure 6: SFM Module
E120 and E320 Modules ■ 9
Page 26
E120 and E320 11.1.x Hardware Guide
Fabric Slices
The router's switch fabric is distributed across two SRP modules and three SFM
modules. Each module has a fabric slice on it. For the router to operate, at least four
of the five slices must be operational.
When all five modules are installed, the fabric slice of the standby SRP acts as a
redundant module. For example, the router can operate with:
■ Two SRP modules (the second of which is redundant) and three SFM modules
■ One SRP module (non-redundant) and three SFM modules
■ Two SRP modules and two SFM modules
NOTE: You cannot use SFM modules of different capacities in the same configuration.
For example, you cannot install a SFM-100 module and a SFM-320 module in the
same router.
SRP IOA
The SRP I/O adapter (IOA) is a single input/output adapter that interfaces with the
SRP modules through the system's midplane. See Figure 2 on page 5 and Figure 4
on page 7 for its location.
Module Details
The SRP IOA provides standard management interfaces, including:
■ 10/100Base-T—The port enables access to the router for Ethernet management
functions through Telnet, Secure Shell Server (SSH), command-line interface
(CLI), or Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP), for example.
■ RS-232—One port (console) provides a serial connection for monitoring the
system's hardware configuration through a PC (running terminal emulation
software) or ASCII terminal and enables direct CLI access. The second port
(auxiliary) provides access to debug ports on specific processors (SRP module,
line module). Juniper Networks customer support engineers use the auxiliary
port. We recommend that users do not use the auxiliary port.
■ External timing inputs—The BNC connectors provide a method of ensuring that
the clock timing used by the router remains synchronized with the network's
system clock.
You can hot-swap SRP IOAs. Hot-swapping enables you to add or remove SRP IOAs
without powering down the system. When you complete hot-swapping an SRP IOA,
its MAC address in the subnet is automatically refreshed without rebooting the SRP
or the chassis. Also, you can re-insert an SRP IOA that you had taken out previously
to the same network without refreshing the MAC address of the SRP IOA.
10 ■ E120 and E320 Modules
Page 27

Chapter 1: E120 and E320 Overview
NOTE: Hot-swapping an SRP IOA is unsupported during a unified in-service software
upgrade (ISSU).
If you have configured RADIUS server on an SRP IOA that you want to replace, you
can perform either of the following actions to prevent loss of accounting or logout
information:
■ Disable accounting and, when there is no subscriber login or logout activity,
hot-swap SRP IOA.
■ Increase the timeout value of the RADIUS server configured depending on the
time used for IOA replacement. The maximum timeout value is 1000 seconds.
After you complete hot-swapping the SRP IOA, you can use the show version all
command to display the state of the SRP IOA.
The SRP IOA hot-swapping is supported on the following routers:
Line Modules
■ E320 router with SRP-100 or SRP-320
■ E120 router
NOTE: You must complete the hot-swapping of the SRP IOA within 1800 seconds.
For details about installing the SRP IOA, see “Installing Modules” on page 27.
Line modules (LMs) act as frame forwarding engines for the physical interfaces (the
IOAs) and process data from different types of network connections. For information
about available line modules, and which SRP modules support specific line modules,
see the E120 and E320 Module Guide.
Figure 7 on page 12 shows a representative line module. For details about installing
line modules, see “Installing Modules” on page 27.
E120 and E320 Modules ■ 11
Page 28
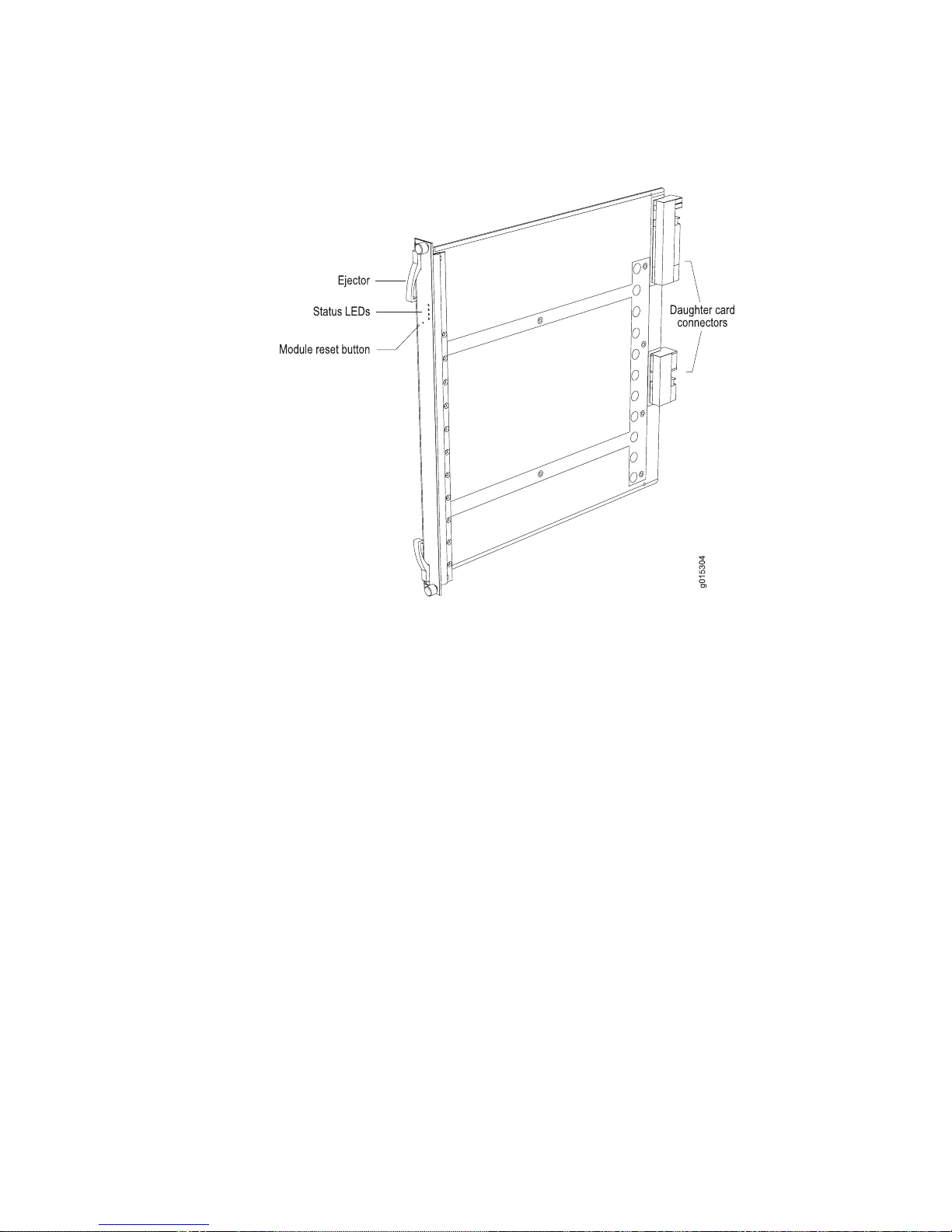
E120 and E320 11.1.x Hardware Guide
Figure 7: Representative Line Module
I/O Adapters
Packet Classification
The line module supports packet classification on ingress. A classification engine on
the line module matches specific fields (such as source and destination IP address,
source and destination port, and protocol), the ingress IP interface, layer 2 fields, or
some combination of these against user-configured filters at wire speed.
Most input/output adapters (IOA) provide the physical interconnection to the network
via small form-factor pluggable transceivers (SFPs). You insert each IOA into the
passive midplane in the rear of the chassis, directly behind a line module. See Figure
2 on page 5 for IOA location in the router and Figure 8 on page 13 for a
representative IOA model. See “Installing and Removing SFPs” on page 44 and the
E120 and E320 Module Guide for information on SFPs.
For a list of hot-swappable IOAs, see Table 4 on page 32.
12 ■ E120 and E320 Modules
Page 29
Figure 8: Representative IOA
Chapter 1: E120 and E320 Overview
An IOA bracket can be installed to create upper and lower IOA bays (E320 router)
or left and right IOA bays (E120 router), enabling you to use two IOAs in the same
slot. This architecture enables you to combine different IOA types in the same slot
and to support oversubscribed configurations.
Restrictions exist concerning which IOAs can be combined in the same slot and
which bay (upper or lower, left or right) they may be installed in. See “IOA Slot
Combinations” on page 32 and the E120 and E320 Module Guide for information. For
details about installing IOAs, see “Installing Modules” on page 27.
Network Management Tools
You can use different management tools to configure the system to meet the specific
networking requirements.
CLI Management
The command-line interface (CLI) provides fully developed and automated
configuration and status functionality through a local RS-232 port, Telnet, or SSH
over any reachable network. For a full discussion of the CLI, see JUNOSe System Basics
Configuration Guide, Chapter 2, Command-Line Interface.
SNMP MIB Management
The system offers a complete SNMP interface for configuration, status, and alarm
reporting. The system supports both Standard and Enterprise MIBs (Management
Information Bases). The Juniper Networks E Series Enterprise MIB is ASN.1 notated
for easy importing into third-party SNMP management applications. For more
information, see JUNOSe System Basics Configuration Guide, Chapter 4, Configuring
SNMP.
Network Management Tools ■ 13
Page 30
E120 and E320 11.1.x Hardware Guide
Redundancy Features
This section describes system redundancy features.
SRP Modules
The router uses a 1:1 redundancy scheme for the SRP module. When two SRP
modules are installed in the router, one acts as the primary (active) and the second
as a redundant (standby) module. Both SRP modules share a single SRP IOA located
in the rear of the chassis. After you install two SRP modules, the modules negotiate
for the primary role. A number of factors determine which module becomes the
primary; however, preference is given to the module in the lower-numbered slot.
The SRP modules record their latest roles and retain them the next time you power
up the system.
If the standby SRP module detects that the primary SRP module is not active (and
high-availability mode is not enabled), it reboots the system and takes control. If
high-availability mode has been enabled, automatic switchover occurs with near
hitless failover. For information about configuring and managing SRP module
redundancy, see JUNOSe System Basics Configuration Guide, Chapter 6, Managing
Modules.
Power
Fans
NVS Cards
Each SRP module has two NVS cards (0, 1). The NVS cards in the active SRP module
are designated disk0 and disk1. The NVS cards in the redundant SRP module are
designated standby-disk0 and standby-disk1. After you install new NVS cards or SRP
modules, you must issue the synchronize command to match the file system of the
NVS card on the redundant SRP module with the file system of the NVS card on the
active SRP module. See “Replacing an NVS Card” on page 72 for more information.
The routers provide a power architecture that distributes redundant –48 VDC feeds
through the router to each line module, IOA, SRP module, SFM module, and fan
module where DC-to-DC converters provide local conversion to the required secondary
voltages.
The E320 router employs a bottom-to-top cooling system to keep the temperature
of the modules and components within normal operating limits. Eight cooling fans
are located in a tray at the top of the router. (See Figure 1 on page 5 and Figure 2
on page 5.) Air is pulled in from the front of the router at the bottom and is
exhausted out the top.
The E120 router employs a right-to-left cooling system. Nine cooling fans are located
in a tray at the left of the router. (See Figure 3 on page 6.) Air is pulled in from the
right of the router and is exhausted out the left.
14 ■ Redundancy Features
Page 31

Chapter 1: E120 and E320 Overview
The system monitors the temperature of each module. If the temperature of a module
exceeds the maximum limit, the system immediately goes into thermal protection
mode and the LMs and SFM modules are powered off. The system controllers remain
active and respond on all management interfaces. All other modules remain in a
power-off condition. The failure of any two components (fan or converter), or the
absence of the fan tray, causes the chassis to enter thermal protection mode to
prevent hardware damage. For information about troubleshooting high operating
temperatures, see “Troubleshooting” on page 79.
The E320 fan tray has two primary converters that power four fans each. If a primary
converter fails, a third redundant converter takes over. The E120 fan tray has dual
converters that load share for redundancy. If one converter fails, the other redundant
converter takes over. The system software reports an alarm if any of the fans or
converters fail.
Redundancy Features ■ 15
Page 32

E120 and E320 11.1.x Hardware Guide
16 ■ Redundancy Features
Page 33

Part 2
Initial Installation
■ Unpacking and Inspecting the Router on page 19
■ Installing the Router on page 23
■ Installing Modules on page 27
■ Cabling the Router on page 47
■ Powering Up the Router on page 57
■ Accessing E Series Routers on page 61
Initial Installation ■ 17
Page 34

E120 and E320 11.1.x Hardware Guide
18 ■ Initial Installation
Page 35

Chapter 2
Unpacking and Inspecting the Router
This chapter reviews shipping contents and unpacking procedures for the router. It
contains the following sections:
■ Before You Begin on page 19
■ Unpacking the Router on page 19
■ Inspecting Router Components and Accessories on page 20
■ If You Detect or Suspect Damage on page 21
■ Contacting Juniper Networks on page 21
■ The Next Step on page 21
Before You Begin
Before you begin unpacking the router, be sure you have the following tools:
■ A No. 2 Phillips screwdriver
■ A utility knife
■ A mechanical lift, or at least two people to assist in lifting
Unpacking the Router
The router is delivered boxed, bolted, and strapped to a skid. For your convenience,
we recommend that you unpack the router in the location where you want to install
it.
WARNING: Three people are required to install the router in a rack: two to lift the
system into position and one to screw it to the rack.
Before You Begin ■ 19
Page 36

E120 and E320 11.1.x Hardware Guide
To unpack the router:
1. Cut the two straps that secure the carton to the skid, open the carton from the
top, and remove the box of accessories that sits on top of the router.
2. Unlock the four plastic clips that hold the box to the skid by squeezing them in
their center and pulling out, and then lift the carton off the router.
3. Remove the three screws that attach each of the two L-brackets to the router.
4. To avoid scratching the router when removing it from the skid, detach one of
the L-brackets from the skid by removing the three screws. See Figure 9 on
page 20.
Figure 9: Removing an L-bracket
Inspecting Router Components and Accessories
After you remove the equipment from the shipping containers:
■ Confirm the contents of each container.
■ Inspect all external surfaces and external connectors for visible signs of damage.
■ Inspect all accessories shipped with each unit.
■ Document any damage noted during your inspection.
■ Confirm that the router has the correct number and type of modules for your
ordered configuration.
20 ■ Inspecting Router Components and Accessories
Page 37

If You Detect or Suspect Damage
If you detect or suspect damage to any equipment:
■ Contact the shipper responsible for delivery, and formally report the damage.
■ Contact your Juniper Networks sales representative or reseller.
Contacting Juniper Networks
Please contact Juniper Networks at 1-888-314-JTAC (from the United States, Canada,
or Mexico) or 1-408-745-9500 (from elsewhere), or contact your sales representative
if you have any questions or concerns. See “Contacting Customer Support and
Returning Hardware” on page 113 for complete contact information.
The Next Step
Chapter 2: Unpacking and Inspecting the Router
■ To familiarize yourself with the electrical, environmental, and other guidelines
and requirements for installing the router, see “Installation Guidelines and
Requirements” on page 97.
■ If you are familiar with these guidelines and requirements, see “Installing the
Router” on page 23.
If You Detect or Suspect Damage ■ 21
Page 38

E120 and E320 11.1.x Hardware Guide
22 ■ The Next Step
Page 39

Chapter 3
Installing the Router
This chapter describes how to install the router. It contains the following sections:
■ Before You Begin on page 23
■ Freestanding Installation on page 23
■ Rack-Mounted Installation on page 25
■ The Next Step on page 26
Before You Begin
Before installing the router, be sure you:
■ Have a plan for installing the router that takes into consideration future expansion
of your system.
■ Have the tools and accessories needed to complete the installation.
■ Read and understand the clearance requirements for the front and back of the
chassis for cable routing and other unit access. See “Environmental
Requirements” on page 97 for more information.
■ Read and understand the clearance requirements for the top and bottom of the
chassis to ensure adequate ventilation.
■ Prepare the equipment racks by measuring and marking space for each router
and plenum you plan to install.
Freestanding Installation
When installing the system on a table top or in any other freestanding mode, be sure
to leave enough space around the system for adequate ventilation. Position the router
with easy access to the connections that it needs for power, local communications,
and remote communications.
See “Installation Guidelines and Requirements” on page 97, and “System
Specifications” on page 91, for more information.
WARNING: Two people are required to lift the router.
Before You Begin ■ 23
Page 40

E120 and E320 11.1.x Hardware Guide
CAUTION: To prevent electrostatic damage to the system and its components, make
sure persons handling the router wear an antistatic device.
Connectors are located on the IOAs, SRP IOA, and the power distribution unit (PDU).
These modules are installed from the rear of the router (Figure 10 on page 24 and
Figure 11 on page 25). See “Cabling the Router” on page 47 for cabling installation
procedures.
Figure 10: E320 Router, Rear View
24 ■ Freestanding Installation
Page 41

Figure 11: E120 Router, Rear View
Chapter 3: Installing the Router
Rack-Mounted Installation
We recommend that you use a standard EIA distribution rack. See “Equipment Rack
Requirements” on page 99 for rack information.
Installation Guidelines
Before installing the systems in a rack, consider the following guidelines:
■ You can install up to three E320 Broadband Services Routers or six E120
Broadband Services Routers in a single 7-ft. (2.1-m) rack. Installing multiple
systems in a single rack enables you to maximize your available space.
CAUTION: To maintain airflow requirements, a plenum must be installed above the
E320 router before any piece of equipment (other than an E320 router) is installed
above the router. This plenum is available from Juniper Networks. Plenums are not
required when E320 routers are installed above one another because the router has
a built-in plenum at the bottom. See “Installation Guidelines and Requirements” on
page 97 and Figure 34 on page 101.
■ Install heavier systems, such as an E320 router, on the bottom of the rack. Mount
lighter systems higher in the rack.
NOTE: An optional mounting kit is available for mid-chassis mounting. Contact your
Juniper Networks sales representative for more information.
Rack-Mounted Installation ■ 25
Page 42

E120 and E320 11.1.x Hardware Guide
Preparing the Equipment Racks
Following your installation plan, use a tape measure and marking pen to measure
and mark space on each equipment rack for each router component. For horizontal
spacing follow Network Equipment Building System (NEBS) requirements. To maintain
airflow requirements, a plenum must be installed above the E320 router before any
piece of equipment (other than an E320 router) is installed above the router. If you
choose not to install a plenum, be sure to include 2 U of space between the E320
router and the other component for proper exhaust. A plenum, however, is highly
recommended.
Installing the Router
To complete the installation of the router in a rack, you need:
■ A No. 2 Phillips screwdriver
■ Eight 10-32 x 3/8 Phillips screws (provided with the router) for each router to be
installed
The Next Step
WARNING: Do not use the cable management bracket as a handle to lift the E320
router.
To install the router in the rack:
1. With one person standing on the left side of the router and another standing on
the right side, lift the router into the rack.
2. Position the router in its designated location in the equipment rack. Make sure
the holes of the mounting brackets align evenly with the holes of the equipment
rack on both sides.
3. Starting at the bottom of the router, have the third person secure the router in
the equipment rack by using the 10-32 x 3/8 Phillips screws.
4. Connect the necessary cables. (See “Cabling the Router” on page 47 for
instructions on installing the cables.)
After you finish installing the router:
■ If you need to install any modules, see “Installing Modules” on page 27.
■ If the router was delivered with the modules already installed, see “Cabling the
Router” on page 47, for instructions on connecting cables.
26 ■ The Next Step
Page 43

Chapter 4
Installing Modules
This chapter describes how to install and remove modules. For information about
managing installed modules, see JUNOSe System Basics Configuration Guide, Chapter 6,
Managing Modules.
This chapter contains the following sections:
■ Overview on page 27
■ Safety Guidelines on page 38
■ Installing an SRP Module or SFM Module on page 38
■ Installing an IOA Shelf on page 40
■ Installing a Line Module or an IOA on page 41
■ Removing Modules and IOAs on page 42
■ Installing and Removing SFPs on page 44
■ The Next Step on page 46
Overview
Slots for line modules, switch route processor (SRP) modules, and switch fabric
module (SFM) modules are located in the front of the router, while slots for
input/output adapters (IOAs) and SRP IOAs are located in the rear.
■ In the E320 Broadband Services Router, modules mount vertically in a 15–slot
chassis, numbered left to right (0–16). See Figure 12 on page 28 and Figure 13
on page 29 for front and rear views of the router.
Overview ■ 27
Page 44

E120 and E320 11.1.x Hardware Guide
Figure 12: E320 Router, Front View
28 ■ Overview
Page 45

Figure 13: E320 Router, Rear View
Chapter 4: Installing Modules
■ In the E120 Broadband Services Router, modules mount horizontally in a 9–slot
chassis, numbered bottom to top (0–10). See Figure 14 on page 29 and Figure
15 on page 30 for front and rear views of the router.
Figure 14: E120 Router, Front View
Overview ■ 29
Page 46

IOA
Ground terminals
SRP module
Power distribution unit (PDU)
Blank filler panel
g015339
Left IOA bays
(Adapter 1)
Right IOA bays
(Adapter 0)
ESD grounding jack
E120 and E320 11.1.x Hardware Guide
Figure 15: E120 Router, Rear View
Slot Numbering
For details about available line modules, IOAs, and compatibility between line modules
and SRP modules, see the E120 and E320 Module Guide.
Slot numbering for the routers is similar.
■ In the E320 router, modules mount vertically in a 15–slot chassis, numbered left
to right (0–16). See Figure 16 on page 31 and Table 3 on page 31 for slot
locations. Because two half-height IOAs can be installed in a slot, the upper bay
is designated Adapter 0 and the lower bay is designated Adapter 1. The router
does not have slot groups.
30 ■ Overview
Page 47

Figure 16: E320 Slot Numbering
Chapter 4: Installing Modules
■ In the E120 router, modules mount horizontally in a 9–slot chassis, numbered
bottom to top (0–10). See Figure 17 on page 31 and Table 3 on page 31 for slot
locations. Because two half-height IOAs can be installed in a slot, the right bay
is designated Adapter 0 and the left bay is designated Adapter 1. The router does
not have slot groups.
Figure 17: E120 Slot Numbering
Table 3: Module Slot Locations
SlotChassis LocationComponent
FrontLM (line module)
E320 router—0–5, 11–16
■
E120 router—0–5
■
6, 7FrontSRP module
FrontBlank filler panel
Non-numbered empty slot
between 6 and 7
Overview ■ 31
Page 48

E120 and E320 11.1.x Hardware Guide
Table 3: Module Slot Locations (continued)
SlotChassis LocationComponent
8, 9, 10FrontSFM module
IOA Slot Combinations
Depending on the software release and IOA type, you must install IOAs in certain
slots and bays combined with other IOAs in the same slot:
■ You must insert some IOAs only in the upper bay or right bay (Adapter 0) of
■ If you insert an unrecognized IOA, such as an IOA that is not supported by a
RearIOA
E320 router—0–5, 11–16
■
Upper bay: Adapter
■
0
Lower bay: Adapter
■
1
E120 router—0–5
Right bay: Adapter
■
0
Left bay: Adapter 1
■
each IOA module slot. If you insert one of these IOAs into a lower bay or left
bay (Adapter 1) slot, the line module diagnostics fail, an error message states
that the bottom slot is not supported for the currently installed software release,
and the slot is disabled.
particular software release, the line module diagnostics fail, an error is generated,
and the slot is disabled.
■ If you remove an IOA and replace it with a different IOA in the same slot, an
error message states the mismatch and the slot is disabled.
■ Full-height IOAs take up the entire slot (both Adapter 0 and Adapter 1).
For information about working with modules and IOAs, see JUNOSe System Basics
Configuration Guide, Chapter 6, Managing Modules. See Table 4 on page 32 for currently
available IOAs and the bays in which you may insert them.
Table 4: IOA Locations and Combinations
Upper/Right Bay
(Adapter 0)IOA
Lower/Left Bay
(Adapter 1)
Both Bays
Concurrently
Combined with
Other IOAs in
Same Slot
Hot-Swapping
Support
YesNoNoYesYesES2-S1 GE-4
32 ■ Overview
Page 49

Table 4: IOA Locations and Combinations (continued)
Upper/Right Bay
(Adapter 0)IOA
Lower/Left Bay
(Adapter 1)
Both Bays
Concurrently
Chapter 4: Installing Modules
Combined with
Other IOAs in
Same Slot
Hot-Swapping
Support
ES2-S3 GE-20
ES2-S1 10GE
ES2-S2 10GE PR
ATM
ATM
(Full-height IOA)
(Full-height IOA)
(Full-height IOA)
YesYesYesES2-S1 GE-8
YesYes (GE-8 when
paired with ES2
4G LM or ES2
10G LM; GE-8,
OC3/STM1, and
OC12/STM4 IOAs
when paired with
ES2 4G LM)
NoNot applicableNot applicableNot applicableYes
NoNot applicableNot applicableNot applicableYes
NoNot applicableNot applicableNot applicableYes
YesYesYesES2-S1 OC3-8 STM1
YesYes (GE-8,
OC3/STM1, and
OC12/STM4 IOAs
only)
YesYesYesES2-S1 OC12-2 STM4
YesYes (GE-8,
OC3/STM1, and
OC12/STM4 IOAs
only)
POS
POS
ES2-S1 SERVICE
ES2-S1 REDUND
(Full-height IOA)
(Full-height IOA;
slots 0 and 11
only)
YesYesYesES2-S1 OC12-2 STM4
YesYes (GE-8,
OC3/STM1, and
OC12/STM4 IOAs
only)
YesNoNoYesYesES2-S1 OC48 STM16
NoNot applicableNot applicableNot applicableYes
NoNot applicableNot applicableNot applicableYes
Overview ■ 33
Page 50

E120 and E320 11.1.x Hardware Guide
Module Combinations
Line modules can only be paired with specific IOA, SFM, and SRP modules. See Table
5 on page 34 for valid combinations.
Table 5: Module Combinations
SRP Modules
This module is only
supported in the E320
router.
ES2 10G ADV LMES2 10G LMES2 10G UPLINK LMES2 4G LMModules
–√√√SRP-100
√√√√SRP-120
This module is only
supported in the E120
router.
SFM Modules
This module is only
supported in the E320
router.
This module is only
supported in the E120
router.
IOA Modules
√√√√SRP-320
√√√√SFM-100
–√√√SFM-120
–√√√SFM-320
–––√ES2-S1 GE-4
√√–√ES2-S1 GE-8
√√––ES2-S3 GE-20
34 ■ Overview
–––√ES2-S1 10GE
√√√–ES2-S2 10GE PR
–––√ES2-S1 OC3-8 STM1 ATM
–––√ES2-S1 OC12-2 STM4 ATM
Page 51

Table 5: Module Combinations (continued)
IOAs Requiring SFPs
Small form-factor pluggable transceivers (SFPs) are used on most IOAs. A range of
SFPs that support different optical modes (multimode and single mode) and cabling
distances are available. You can replace SFPs without disabling the interface or
removing the module from the system. See “Installing and Removing SFPs” on
page 44 for more information and the E120 and E320 Module Guide for IOAs that use
SFPs.
Chapter 4: Installing Modules
ES2 10G ADV LMES2 10G LMES2 10G UPLINK LMES2 4G LMModules
–––√ES2-S1 OC12-2 STM4 POS
–––√ES2-S1 OC48 STM16 POS
√√√√ES2-S1 REDUND
–––√ES2-S1 SERVICE
NOTE: Because SFPs are the same shape and size, you are able to insert an SFP that
is not compatible with the IOA. Be sure the SFP you are installing is appropriate for
the interface you are plugging it into. If you insert the wrong SFP, software diagnostics
detect the error.
Proper Handling of ES2 4G LMs
Use extra caution when handling an ES2 4G LM so that you do not damage module
components or dislodge the heat sinks.
NOTE: When lifting, carrying, or holding the module, do not grasp it near the six
heat sinks along the top and bottom edge of the module. Instead, hold the module
along the faceplate and the edges, keeping your fingers and thumbs away from all
components.
Do not use either row of heat sinks as a handle when carrying the module. You might
dislodge or damage them.
Overview ■ 35
Page 52

E120 and E320 11.1.x Hardware Guide
Figure 18: LM4 Heat Sink Locations
ES2 10G Uplink Line Modules
In a 100 Gbps fabric configuration, you must install the ES2 10G Uplink line module
in slot 2 or slot 4 only.
■ If you install the line module in a slot other than slot 2 or slot 4, it will be disabled.
■ If you install the module next to a configured line module that is already installed
in slot 3 or slot 5, the ES2 10G Uplink line module will be disabled.
Conversely, if you install a line module in slot 3 or slot 5 next to a previously installed
ES2 10G Uplink module, the non-ES2 10G Uplink module will be disabled. For
example, if you install an ES2 10G Uplink line module in both slot 2 and slot 4 in an
E320 router, you can install the ES2 4G line module in the following locations: 0-1
and 6-11.
Managing Modules Using the Software
For information about software procedures associated with replacing and managing
modules and IOAs, see JUNOSe System Basics Configuration Guide, Chapter 6, Managing
Modules.
Order of Installation
Before you attempt to install or replace a line module (inserted in the front of the
chassis), make sure a compatible IOA (inserted in the rear of the chassis) is already
36 ■ Overview
Page 53

in place. The slot diagnostics run when a line module is installed in a chassis slot. If
a compatible IOA module is not present, the diagnostics fail, and you need to remove
and reinsert the line module.
Hot-Swapping Modules
The router supports hot-swapping of line modules and IOAs. Hot-swapping enables
you to add or remove a line module without powering down the system. IOAs that
support hot-swapping enable you to add or remove an IOA without rebooting the
line module. See Table 4 on page 32 for a list of hot-swappable IOAs.
Protecting Modules and Slots
The E320 router has two ESD (electrostatic discharge) grounding jacks. The front
jack is located below the air filter bezel in the center of the router. The rear jack is
located in the upper-right corner of the chassis. The E120 router has one ESD
grounding jack located in the upper-right corner of the chassis in the rear. To prevent
damage from electrostatic discharge, wear an antistatic wrist strap and connect it to
one of the jacks when handling components.
Chapter 4: Installing Modules
To protect the modules, IOAs, and slots when installing components, observe the
following guidelines:
CAUTION: When handling components, use an antistatic wrist strap connected to
one of the router's ESD grounding jacks. This action helps to protect the module
from damage by electrostatic discharge.
CAUTION: Always handle a module by its edges. Do not touch the components, pins,
leads, or solder connections.
CAUTION: If you meet strong resistance when attempting to seat a module using
the ejectors, remove it from the chassis and confirm that the slot is designed to hold
the module. Also, be sure that you have aligned the top and bottom edges in the
correct matching card guides.
CAUTION: Be sure to cover every empty slot with a blank filler panel to protect the
system from dust or other foreign substances and to ensure proper system cooling.
CAUTION: Do not discard the antistatic bag. When a module is not in use, store it
in an antistatic bag.
Overview ■ 37
Page 54

E120 and E320 11.1.x Hardware Guide
Required Tools and Safety Items
You need the following tools to install a line module:
■ A No. 2 Phillips screwdriver
■ A flathead screwdriver
■ An ESD wrist strap or other grounding device
Safety Guidelines
Before and during the installation process, observe the following precautions:
WARNING: Do not work on the system or connect or disconnect cables during
lightning activity.
WARNING: Be sure circuit breakers for the power source are in the OFF position
before attaching power cables.
WARNING: Remove jewelry (including rings, necklaces, and watches) before working
on equipment that is connected to power lines. Metal objects heat up when connected
to power and ground and can cause serious burns or become welded to the terminals.
WARNING: Do not insert any metal object, such as a screwdriver, into an open slot
or the midplane. Doing so can cause electric shock and serious burns.
WARNING: Never attempt to repair parts of modules yourself. Only trained customer
service personnel are authorized to service parts. Call Juniper Networks Customer
Service to make arrangements to return defective modules for repair.
Installing an SRP Module or SFM Module
You must install SRP modules in slot 6 or slot 7, and SFM modules in slots 8, 9, or
10. Four of the five fabric slots (SRP and SFM modules) must have a module installed
for the router to function. A minimum system configuration requires all three SFMs
and at least one SRP module to be installed. See “Fabric Slices” on page 10 for more
information.
To install an SRP module or SFM module:
38 ■ Safety Guidelines
Page 55

Chapter 4: Installing Modules
1. Ground yourself by using an antistatic wrist strap or other device and connect
it to one of the ESD grounding jacks on the chassis.
2. Choose the slot in which you want to install the module.
■ SRP module – slot 6 or 7
■ SFM module – slot 8, 9, or 10
See Figure 12 on page 28 and Figure 14 on page 29 for module locations.
NOTE: Four of the five fabric slots (SRP and SFM modules) must have a module
installed for the router to function. A minimum system configuration requires all
three SFMs and at least one SRP module to be installed.
3. With a No. 2 Phillips screwdriver, loosen the captive screws that secure the blank
filler panel covering the empty chassis slot, if present, and remove the filler
panel.
4. Remove the module from its antistatic bag, being careful not to touch module
components, pins, leads, or solder connections.
5. Verify that the ejectors are in the open position, as shown in Figure 19 on
page 39.
Figure 19: Closing Ejectors from the Open Position
Installing an SRP Module or SFM Module ■ 39
Page 56

E120 and E320 11.1.x Hardware Guide
6. Slide the module into the chassis by placing it between the guides of the selected
slot and pushing the module until it stops.
The module stops sliding when the ejectors make contact with the front of the
chassis.
CAUTION: If you meet strong resistance when attempting to seat the module using
the ejectors, remove it from the chassis and confirm that the slot is designed to hold
the module. Also, be sure that you have aligned the top and bottom edges in the
correct matching tracks.
7. Insert the module into the backplane by simultaneously depressing both ejectors
(as shown in Figure 19 on page 39), exerting forward pressure on the module.
8. Tighten the module's captive screws using the No. 2 Phillips screwdriver.
NOTE: Tighten the captive screws completely before installing an adjacent module
so that proper EMI gasket compression occurs. Failure to do this can make it difficult
to install adjacent modules.
CAUTION: Do not overtighten the screws.
Installing an IOA Shelf
Use an IOA shelf (also called an IOA bracket) when installing half-height IOAs in the
router. IOA shelves screw into the midplane between the upper/right bay (Adapter
0) and lower/left bay (Adapter 1). For example, in an E320 router, IOAs in the upper
bay rest on the shelf, while IOAs in the lower bay use the guides on the bottom of
the shelf to remain vertical. See Figure 20 on page 40.
Figure 20: IOA Shelf
40 ■ Installing an IOA Shelf
Page 57

Chapter 4: Installing Modules
CAUTION: We recommend that you power down the router before removing or
installing an IOA shelf between two slots that have modules installed in them already.
Otherwise, you might short-circuit the installed modules if you accidentally touch
the shelf to a module. An IOA shelf installation guide is available to ensure safe
installation. Contact your account representative for more information.
To install an IOA shelf:
1. Ground yourself by using an antistatic wrist strap or other device and connect
it to one of the ESD grounding jacks.
2. Remove the blank IOA filler panel from the slot.
3. Align the shelf's guide pins with the corresponding holes in the midplane and
insert the threaded shaft into the hole in the midplane between the upper/right
bay and lower/left bay. Be sure the threaded shaft is visible from the right side.
(See Figure 20 on page 40.)
4. Using a flathead screwdriver, tighten the screw snugly to secure the shelf.
Installing a Line Module or an IOA
This section describes the procedures for installing line modules and IOAs.
NOTE: Install the IOA module before you install the corresponding line module;
otherwise, the diagnostics fail and the line module's status is listed as inactive when
you issue the show version command. If this occurs, remove and reinsert the line
module.
The router supports hot-swapping of line modules and IOAs. Hot-swapping enables
you to add or remove a line module without powering down the system. IOAs that
support hot-swapping enable you to add or remove an IOA without rebooting the
line module. See Table 4 on page 32 for a list of hot-swappable IOAs.
To install a line module or IOA:
1. Ground yourself by using an antistatic wrist strap or other device and connect
it to one of the ESD grounding jacks.
2. Choose the slot where you want to insert the line module or IOA.
NOTE: Line modules are in the front of the system and IOAs are in the back of the
system. See Table 4 on page 32 for IOA slot locations and combinations.
3. With a No. 2 Phillips screwdriver, loosen the screws that secure the blank filler
panel covering the empty chassis slot, if present, and remove the filler panel.
4. Remove the line module or IOA from its antistatic bag, being careful not to touch
module components, pins, leads, or solder connections.
Installing a Line Module or an IOA ■ 41
Page 58

E120 and E320 11.1.x Hardware Guide
5. Verify that the ejectors are in the open position, as shown in Figure 19 on
page 39.
6. Guide the line module or IOA into the chassis by placing it between the guides
of the selected slot and pushing the module until it stops.
The module or IOA stops sliding when the ejectors make contact with the chassis.
CAUTION: If you meet strong resistance when attempting to seat the line module or
IOA using the ejectors, remove it from the chassis and confirm that the slot is designed
to hold the component. Also, be sure that you have aligned the top and bottom edges
in the correct matching tracks.
7. Insert the line module or IOA into the midplane by simultaneously depressing
both ejectors (as shown in Figure 19 on page 39) and exerting forward pressure
on the module.
8. Tighten the module's captive screws using a No. 2 Phillips screwdriver.
NOTE: Tighten the captive screws completely before installing an adjacent module
so that proper EMI gasket compression occurs. Failure to do this can make it difficult
to install adjacent modules.
CAUTION: Do not overtighten the screws.
Removing Modules and IOAs
This section describes the procedures for removing modules and IOAs. For a list of
hot-swappable IOAs, see Table 4 on page 32.
NOTE: We recommend that you issue the slot disable command from the CLI before
removing a line module or IOA.
CAUTION: If you do not use the halt command before removing or powering down
an SRP module, the system's NVS card can become corrupted.
To remove a module or an IOA:
42 ■ Removing Modules and IOAs
Page 59

Chapter 4: Installing Modules
1. For SRP modules and SRP IOAs, issue the appropriate halt command (halt, halt
primary-srp, or halt standby-srp).
See JUNOSe System Basics Configuration Guide, Chapter 6, Managing Modules for
information about the halt commands.
2. Ground yourself by using an antistatic wrist strap or other device and connect
it to an ESD grounding jack.
3. Use a No. 2 Phillips screwdriver to loosen the captive screws located at the top
and bottom of the module panel.
4. If the module has ejector handles, pull them to the open position, as shown in
Figure 21 on page 43.
Figure 21: Opening Ejectors from the Closed Position
5. Carefully slide the module out of the chassis.
6. Place the module in its antistatic bag, being careful not to touch module
components, pins, leads or solder connections.
7. Cover the empty chassis slot with a blank filler panel, and tighten the filler panel's
captive screws using a No. 2 Phillips screwdriver. Turn both screws several times
before tightening them completely.
CAUTION: Do not overtighten the screws.
Removing Modules and IOAs ■ 43
Page 60

E120 and E320 11.1.x Hardware Guide
If you remove an IOA and not the corresponding line module, the line module reboots.
Its status becomes inactive when you issue the show version command.
If you remove a line module and do not delete the corresponding configuration, the
status of the line module is listed as not present when you issue the show version
command.
Installing and Removing SFPs
This section describes how to replace small form-factor pluggable transceivers (SFPs)
on IOAs that support these devices. A range of SFPs that support different optical
modes (multimode, single mode, and so forth) and cabling distances is available.
You can replace the SFPs without disabling the interfaces or removing the module
from the system.
Installing SFPs
To install SFPs:
1. Ground yourself by using an antistatic wrist strap or other device and connect
it to an ESD grounding jack.
2. Identify the following items on the SFP (Figure 22 on page 44):
■ The connection circuitry on the base
■ The cable connectors on the front (which are protected by a dust cover)
Figure 22: Representative SFP
CAUTION: Be sure to position the SFP correctly before you install it.
3. Hold the SFP so that:
■ The connection circuitry is adjacent to the LK and ACT markings on the
■ The cable connectors will be visible when you install the SFP.
For the correct orientation, see Figure 23 on page 45.
44 ■ Installing and Removing SFPs
IOA's faceplate.
Page 61

Figure 23: Installing an SFP on an IOA
Chapter 4: Installing Modules
Removing SFPs
4. Slide the SFP as far as you can into the IOA until the SFP clicks into place.
If the SFP does not slide smoothly into the IOA, make sure that the orientation
of the SFP is correct.
5. Gently pull the SFP to confirm that it is inserted correctly.
If the SFP comes out of the slot when you pull it, repeat Step 4.
6. Remove the dust cover that protects the cable connectors.
7. Connect the new cables to the SFP.
To remove an SFP:
1. Obtain an antistatic container for the SFP you plan to remove. (See “Storing
Modules and Components” on page 69.)
2. Ground yourself by using an antistatic wrist strap or other device and connect
it to an ESD grounding jack.
3. Disconnect the cable from the SFP on the IOA.
4. Identify the release mechanism for the SFP.
Different SFPs use different release mechanisms. See Figure 24 on page 46 for
possible release mechanisms, which include:
■ A button that you press inward
■ A ring that you press inward
Installing and Removing SFPs ■ 45
Page 62

E120 and E320 11.1.x Hardware Guide
■ A bar that you pull sideways, then outward
■ A tab that you pull sideways, then outward
Figure 24: Possible Release Mechanisms on the SFP
5. Release the SFP and pull it out of the slot.
The Next Step
6. Place the SFP in an antistatic bag.
When you have replaced the SFPs and connected the cables, issue the appropriate
show interface command for each interface to verify that the interface is operational
(up).
After you install the modules, you can connect cables to the system. See “Cabling
the Router” on page 47.
46 ■ The Next Step
Page 63

Chapter 5
Cabling the Router
This chapter describes how to cable the router. Before you cable the router, ensure
that you have completed all installation instructions identified in previous chapters.
This chapter contains the following sections:
■ Cabling Overview on page 47
■ Required Tools, Wires, and Cables on page 48
■ Cabling the SRP IOA on page 49
■ Cabling IOAs on page 51
■ Cabling the Router for Power on page 52
■ The Next Step on page 56
Cabling Overview
Cabling the router requires the following main tasks:
1. Familiarize yourself with the module ports, and ensure that you have the cables
and wires needed to complete each cabling procedure. (See Figure 25 on
page 48.)
2. Read and understand all safety warnings. (See “Installation Guidelines and
Requirements” on page 97.)
3. (Optional) Connect timing ports.
4. Connect the SRP IOA to the network and to a management console.
5. Connect grounding wires to the router chassis.
6. Connect the power cables from the power source to the power distribution unit
(PDU).
7. Connect the IOAs to their appropriate network interface.
Cabling Overview ■ 47
Page 64

E120 and E320 11.1.x Hardware Guide
Figure 25: E320 Router Rear Ports and Connectors
Required Tools, Wires, and Cables
Cabling your system takes only a few minutes. You need the following items and
those listed in Table 6 on page 49 for proper installation:
■ 1/8-inch flathead screwdriver
■ 3/8-inch wrench or 3/8-inch nut-driver
■ No. 2 Phillips screwdriver
■ Ground wires—We recommend a minimum of 6-AWG ground wire.
■ Two #10 kep nuts (supplied) to connect the ground (earth) wire to the ground
terminal.
■ PDU wiring—We recommend a minimum of 4-AWG wire for the router with a
dual stud terminal lug with 5/8-inch spacing.
48 ■ Required Tools, Wires, and Cables
Page 65

Chapter 5: Cabling the Router
Consider the distance from the connection point and the configuration of the system
when determining the size of wire used.
See “System Specifications” on page 91 for more information on router specifications.
Table 6: Required Cables
Port and Cable UsedConnection
Cabling the SRP IOA
Before powering up the router, you must set up a management console. The console
enables you to communicate with your system during the power-up process and to
manage your system using the command-line interface (CLI).
When connecting a console directly to the SRP IOA, use a cable appropriate for your
terminal connector. The cable must have a female DB-9 connector to attach to the
RS-232 port on the SRP IOA. See Figure 26 on page 50.
The console port is considered a data terminal equipment interface (DTE). Direct
connection to a terminal or PC (which also have DTE interfaces) requires a crossover
cable.
The router has network timing ports and management ports located on the SRP IOA.
See Figure 26 on page 50 and Table 7 on page 49 for details on each component.
Management connection between SRP IOA
and the LAN
Management connection between SRP IOA
and a management console
Direct connections to IOAs
One 10/100Base-T Ethernet management port with
an RJ-45 connector
One RS-232 port with a DB-9 connector for VT100
management access
See the E120 and E320 Module Guide for specific IOA
connector information
Table 7: SRP IOA Ports
Network timing
ports
Management ports
DescriptionPort
Two dual-purpose BNC connectors for BITS timing clock sources (E1
■
or T1)
User-configurable through the CLI
■
Primary (A) and secondary (B)
■
75-ohm E1 2.048-Mbps/T1 1.544–Mbps inputs terminating with a
■
120/75 ohm or 100/75 ohm balun
One 10/100Base-T Ethernet management port with an RJ-45
■
connector
Two RS-232 ports with a DB-9 connector for direct CLI (Console) and
■
debug (Auxiliary) access.
The Auxiliary port is used to debug ports on a specific processor (SRP
module, LM).
Cabling the SRP IOA ■ 49
Page 66

E120 and E320 11.1.x Hardware Guide
Network Timing Ports
The SRP IOA has two input ports for external network clock sources (75-ohm E1
2.048-Mbps/T1 1.544–Mbps inputs with BNC connectors). These ports provide a way
to ensure that the router system clock remains synchronized with the network's
system clock. The primary clock is labeled A; the secondary, redundant clock, is
labeled B. See Figure 26 on page 50.
NOTE: We recommend you use shielded cables to connect the external clock sources
to the clock source input ports. Shielded cables are not required for the operation of
the system and do not need to be grounded at both ends.
Figure 26: SRP IOA
To connect the clock source input ports:
1. Attach the BNC connector to Clock A's network timing port.
2. Attach the opposite end of the network timing cable to your network's clock
source A.
3. Repeat steps 1 and 2 for the Clock B connections.
50 ■ Cabling the SRP IOA
Page 67

Management Ports
Chapter 5: Cabling the Router
The Management section of the SRP IOA has three ports (Figure 26 on page 50) for
management access:
■ One 10/100Base-T Ethernet port—Accepts an RJ-45 (male) connector, providing
an out-of-band connection for LAN access through a Telnet session or SNMP.
■ Two RS-232 management ports—Accept a DB-9 (female) connector. One port
provides direct CLI access from a console terminal; the other Auxiliary port
provides debug access from a console terminal.
The management port is considered a data terminal equipment interface (DTE).
Direct connection to a terminal or PC (which also have DTE interfaces) requires a
crossover cable.
See “Accessing E Series Routers” on page 61 for more information about management
access.
Connecting to the Network
To connect the router to the network:
1. Insert an Ethernet cable (RJ-45) connector into the 10/100Base-T (RJ-45) port on
the SRP IOA until it clicks into place.
2. Connect the other end of the cable to the appropriate Ethernet network for an
out-of-band connection.
Connecting to a Console Terminal
When you connect a console directly to the SRP IOA, use a cable appropriate for
your terminal connector. The cable must have a female DB-9 connector to attach to
the RS-232 port on the SRP IOA.
To connect the console to the SRP IOA:
1. Insert the female DB-9 connector into the RS-232 port, and tighten the screws.
CAUTION: Do not overtighten the screws.
2. Connect the other end of the cable to your terminal's serial port (VT100/ANSI).
Cabling IOAs
This section describes the common connector types used with IOAs.
Cabling IOAs ■ 51
Page 68

E120 and E320 11.1.x Hardware Guide
LC Duplex Connectors
In accordance with EN60825-1, Safety of Laser Products - Part 1: Equipment Class,
Requirements, and User's Guide (2001), multimode IOAs with LC connectors are
defined as follows:
CLASS 1 LED PRODUCT.
In accordance with EN60825-1, Safety of Laser Products - Part 1: Equipment Class,
Requirements, and User's Guide (2001), single-mode IOAs with LC connectors are
defined as follows:
CLASS 1 LASER PRODUCT.
WARNING: Do not look directly into LC-style fiber connectors. The fiber-optic laser
used in single-mode fiber (SMF) meets the regulatory requirements for casual exposure
to the eye; however, looking directly into a laser can cause eye damage.
WARNING: EN60825-1, Class 1 laser fiber connectors are for connection only to
Class 1 laser devices.
SFPs
See “IOAs Requiring SFPs” on page 35 and the E120 and E320 Module Guide for
information on small form-factor pluggable transceivers (SFPs) used on IOAs.
Cabling the Router for Power
After you have correctly cabled the SRP IOA, you must attach grounding and electrical
wires before you attempt system power-up. See Figure 27 on page 54.
Three main tasks are involved:
1. Switch all router power switches to OFF.
CAUTION: Switches may have inadvertently flipped to ON during shipping and
installation.
2. Connect the grounding wires to the chassis.
WARNING: Always connect the grounding wires first (before connecting the power
cables) and disconnect them last when installing or servicing the router.
52 ■ Cabling the Router for Power
Page 69

3. Connect the power cables to the PDUs.
See “System Specifications” on page 91 for the power requirements for the router.
Table 8 on page 53 identifies the cabling requirements.
Table 8: E320 Router PDU Cables and Wires Needed
Figure 27 on page 54 shows the main components of a PDU.
Chapter 5: Cabling the Router
ToFromCable/Wire
Termination groundPDU ground terminalOne 6-AWG ground wire
Appropriate leads on power source No.1PDU Power A –48 VDC and RTN leadsTwo 4-AWG wire leads
Appropriate leads on power source No.2PDU Power B –48 VDC and RTN leadsTwo 4-AWG wire leads
Cabling the Router for Power ■ 53
Page 70

E120 and E320 11.1.x Hardware Guide
Figure 27: PDU
Task 1: Turn Off All Router Power
Before starting to cable the router, push all router power switches to OFF to turn off
the router.
Task 2: Connect the Grounding Cables
The router has two grounding studs located in the rear of the chassis, near the power
inputs. Each stud provides grounding for a single power unit.
To ground each power unit:
1. Locate the grounding studs on the router (Figure 27 on page 54).
2. Remove the nuts and locking washers from the grounding studs.
54 ■ Cabling the Router for Power
Page 71

Chapter 5: Cabling the Router
NOTE: We recommend a minimum of 6-AWG ground wire with a ring-style terminal.
3. Place the grounding cable lead on one of the grounding studs and tighten the
nuts to secure the connection.
4. Connect the other end of the ground cable to the appropriate ground termination
lead.
5. Repeat Steps 3–4 for the remaining grounding stud.
NOTE: When grounding the router, leave a service loop in the grounding cable to
ensure that the grounding cable is the last cable to disconnect from the shelf if strain
is placed on the electrical cables.
Task 3: Connect the Power Cables
To connect power cables to the router, follow these steps. See Figure 27 on page 54
as needed.
NOTE: Juniper Networks has qualified an AC power supply unit for use with the
router. Contact your account representative for more information.
WARNING: Before you begin this procedure, be sure the power source is turned off,
the router is turned off, and proper grounding wires are attached.
1. Be sure you have completed “Task 1: Turn Off All Router Power” on page 54
and “Task 2: Connect the Grounding Cables” on page 54.
2. If applicable, loosen the screws from the clear power input module cover and
remove it.
WARNING: The wiring color code of the power cables depends on the color coding
of the DC power source installed at your site. Color code standards for DC wiring do
not exist. To ensure that the correct polarity is connected to the router power units,
confirm the connection of the power cables to the + (positive) and – (negative) leads
at the power source.
NOTE: Loosen the top and bottom thumbscrews (using a No. 2 Phillips screwdriver,
if necessary)
Cabling the Router for Power ■ 55
Page 72

E120 and E320 11.1.x Hardware Guide
3. Remove the nuts and locking washers from the posts for the power input (A or
B) using a small insulated adjustable wrench.
4. Place one negative (neutral) cable lead on the post labeled –48 VDC.
5. Replace the locking washers and nuts, and tighten the nuts to secure the
connection.
6. Place the other cable lead on the post labeled RTN.
7. Replace the locking washer and nut, and firmly tighten the nut to secure the
connection.
8. Attach the opposite end of Power A's wire leads to the appropriate leads on your
power source.
NOTE: To provide redundancy, do not use the same power source for Power A and
Power B leads.
The Next Step
9. Place the clear plastic guard over the terminal posts, and secure it in place by
tightening the four screws.
10. Repeat Steps 1–9 for each power input module in your configuration.
See “Powering Up the Router” on page 57.
56 ■ The Next Step
Page 73

Chapter 6
Powering Up the Router
This chapter describes how to power up the router and determine whether it has
booted properly. It contains the following sections:
■ Before You Power Up the System on page 57
■ Powering Up on page 57
■ Status LEDs on page 58
■ Powering Down on page 59
■ The Next Step on page 59
Before You Power Up the System
Before powering up the system, make sure you complete the following tasks. See
the appropriate chapters in this guide for information about these tasks.
WARNING: Be sure the power source is turned off and the system is turned off before
you perform the installation tasks.
Powering Up
■ Installing an SRP Module or SFM Module on page 38
■ Installing a Line Module or an IOA on page 41
■ Cabling the SRP IOA on page 49
■ Cabling IOAs on page 51
■ Cabling the Router for Power on page 52
NOTE: In this procedure we assume that the system is already connected to a power
source. See “Cabling the Router” on page 47.
NOTE: Juniper Networks has qualified an AC power supply unit for use with the
router. Contact your account representative for more information.
Before You Power Up the System ■ 57
Page 74

E120 and E320 11.1.x Hardware Guide
For specifications on the electrical requirements for the system, see “System
Specifications” on page 91. For details on the power consumed by the different
modules, see the E120 and E320 Module Guide.
CAUTION: Evaluate the overall loading of the branch circuit before you install any
equipment into a rack.
To power up the system:
1. Verify that the power source is operational and turned on.
2. Inspect all grounding and power connections to the router chassis.
3. Confirm that all connections are secure.
4. Switch the power switches to ON.
5. Monitor the LEDs on the SRP modules and SFM modules to verify that the system
is booting properly. See Table 11 on page 84 for LED status explanations.
6. Enter the enable command to access Privileged Exec mode:
Initialization Sequence
Each line module is initialized independently. As a result, the CLI on the SRP module
can become available before the line modules have completed initialization.
Commands relating to a line module might fail if the module has not completed
initialization. You can use the show version command to display line module status,
but do not enter commands for a line module until its state is online.
Status LEDs
Upon initial power-up, the components of the router run boot code, go through a
series of self diagnostic tests, and synchronize with each other.
When the prompt appears on the system console, the system is in User Exec
mode and is ready to be configured:
host1>
host1>enable
host1#
In Privileged Exec mode you can begin to configure the system. See JUNOSe
System Basics Configuration Guide, Chapter 2, Command-Line Interface for more
information.
When the tests are complete, use the LEDs on each module to determine the status
of the router. Observe the module LEDs on the front and rear components.
See “Troubleshooting” on page 79 for information on the system's LEDs.
58 ■ Status LEDs
Page 75

Powering Down
Chapter 6: Powering Up the Router
NOTE: In the fan tray for the E320 Broadband Services Router, four of the eight fans
turn on immediately upon initial power-up and the other four fans turn on after a
delay of 10 seconds.
If you need to power down or remove the SRP module, first enter the halt command
to temporarily suspend the system's operation. See JUNOSe System Basics
Configuration Guide, Chapter 5, Managing the System for more information.
CAUTION: If you do not use the halt command before removing or powering down
an SRP module, the system's NVS card might become corrupted.
If you shut down the system improperly, it runs an investigation of the file allocation
table (FAT) the next time it reboots.
The Next Step
If you have problems powering up the system, see “Troubleshooting” on page 79
for help.
If the system boots properly, see “Accessing E Series Routers” on page 61.
Powering Down ■ 59
Page 76

E120 and E320 11.1.x Hardware Guide
60 ■ The Next Step
Page 77

Chapter 7
Accessing E Series Routers
This chapter discusses how to access the system to manage it. Managing your router
includes both configuring and monitoring it. For basic information on the management
of the system, see JUNOSe System Basics Configuration Guide, Chapter 5, Managing
the System.
This chapter contains the following sections:
■ Setting Up Management Access on page 61
■ Console Port Setup on page 61
■ Telnet Setup on page 64
■ SNMP on page 65
■ The Next Step on page 66
Setting Up Management Access
Before you power up the system, you must set up a management console. (See
“Connecting to a Console Terminal” on page 51.) You use the console to communicate
with the system during the power-up process, set an IP address, and manage the
system using the command-line interface (CLI).
You can monitor and manage the router through either of these methods:
■ Console terminal—Connect a console (PC, Macintosh, or UNIX workstation)
directly to the system's RS-232 serial port.
■ Remote console—Connect 10/100Base-T port on the SRP IOA to an Ethernet
network, and run Telnet from a remote console.
For initial access to the system, you need to physically connect your console directly
to the system's RS-232 port. Through this connection you use the CLI to set an IP
address on the system. After you configure the IP address, you can access the system
remotely (for example, via Telnet).
Console Port Setup
You can connect a console terminal (PC, Macintosh, or UNIX workstation) directly
to the SRP IOA via the RS-232 terminal port. When you connect a console directly
to the system, you can configure the system without an IP address.
Setting Up Management Access ■ 61
Page 78

E120 and E320 11.1.x Hardware Guide
To communicate with the system, you must have a terminal emulation program
running on your PC or Macintosh. You can use any terminal emulation program,
such as HyperTerminal. A UNIX workstation can use the emulator TIP.
Using HyperTerminal
If your console uses a version of Microsoft Windows (such as Windows XP or Windows
NT 4.0) that supports the HyperTerminal application, you can access the system via
HyperTerminal.
1. Click the Start button and select Programs, Accessories, Communications, and
HyperTerminal.
2. In the HyperTerminal window, select HyperTerminal.
3. In the Connection Description dialog box, enter a name for your router (for
example, e320) in the Name field.
4. Select any icon to represent your terminal emulation, and click OK.
5. In the Connect To dialog box, in the Connect using field, select the appropriate
COM port to use (for example, COM1), and click OK.
6. In the COM1 Properties dialog box, select the following settings:
■ Bits per second: 9600
■ Data bits: 8
■ Parity: None
■ Stop bits: 1
■ Flow control: Xon/Xoff
7. Click OK.
Connecting Directly to the Router
When you connect a console directly to the system, use a cable appropriate for your
terminal connector. The cable must have a female DB-9 connector to attach to the
RS-232 port on the system.
The console port is considered a data terminal equipment interface (DTE). Direct
connection to a terminal or PC (which also have DTE interfaces) requires a crossover
cable.
To connect a console directly to the system:
1. Connect the female DB-9 connector to the RS-232 port on the router's SRP IOA.
See Figure 28 on page 63.
62 ■ Console Port Setup
Page 79

Figure 28: Router Management Ports
Chapter 7: Accessing E Series Routers
2. Connect the crossover adapter connector to your PC's serial port.
3. Power up the system.
NOTE: Direct access through the RS-232 serial port enables you to monitor the system
while it boots.
Assigning an IP Address
When your console is ready to communicate with the system, power up the system.
(See “Powering Up the Router” on page 57.) Then set an IP address for the system.
The system powers up in User Exec mode. To assign an IP address:
1. Enter the enable command at the User Exec prompt.
When you power up the system, the CLI appears on your console's screen. The
system is now in User Exec mode, and you can begin configuration. For more
information on using the CLI and configuring the system, see the JUNOSe System
Basics Configuration Guide.
host1>enable
host1#
Console Port Setup ■ 63
Page 80

E120 and E320 11.1.x Hardware Guide
The system is now in Privileged Exec mode.
2. Set an IP address on the Ethernet interface:
■ Specify the identifier of the FastEthernet interface in the format:
■ Use an IP address valid for the system.
3. Continue to configure the system's parameters as needed.
After you have assigned an IP address to the system, you can communicate remotely
by running Telnet over an Ethernet network. See “Telnet Setup” on page 64.
slot/adapter/port.
host1#configure terminal
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.
host1(config)#interface FastEthernet 6/0/0
host1(config-if)#ip address 10.10.7.3 255.255.255.0
Telnet Setup
When you have configured an IP address for the system, you can run Telnet from a
host to access the system through its Ethernet port. To connect the Ethernet port to
the network:
1. Connect an Ethernet cable (RJ-45) to the system's 10/100Base-T (RJ-45) port on
the SRP IOA. See Figure 28 on page 63.
2. Connect the other end of the cable to the appropriate Ethernet network for an
out-of-band connection.
Before you can access the system with Telnet, you must either configure a password
for Telnet access or disable the password requirement from the management console.
In the following example, you disable the password.
1. Enter the enable command.
host1>enable
host1#
The system is now in Privileged Exec mode.
2. Enter the configure command.
host1#configure terminal
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.
host1(config)#
The system is now in Global Configuration mode.
3. Enter the line command.
The system is now in Line Configuration mode.
64 ■ Telnet Setup
host1(config)#line vty 0 4
host1(config-line)#
Page 81

Chapter 7: Accessing E Series Routers
4. Disable the password.
host1(config-line)#no login
NOTE: In this example, you disabled the password requirement, but you can choose
to set a password instead. See JUNOSe System Basics Configuration Guide, Chapter 8,
Passwords and Security for information on setting a password.
5. Run Telnet from a host on the same Ethernet network as the system.
6. Enter the IP address of the system to open the Telnet session.
The User Exec prompt appears when the Telnet session to the system is
established.
host1>
7. Enter the enable command.
SNMP
host1>enable
host1#
The system is now in Privileged Exec mode.
8. Enter the configure command.
host1#configure terminal
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.
host1(config)#
The system is now in Global Configuration mode, from which you can configure
the system. See JUNOSe System Basics Configuration Guide, Chapter 2,
Command-Line Interface.
CAUTION: Do not change the IP address for the Ethernet interface that you are using
to communicate with the system. If you change the address, you will lose the Telnet
session.
The system supports Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP), a standard
management protocol for IP networks. You can configure the system as an SNMP
agent.
As an SNMP agent, the system provides access to management information that it
maintains. See JUNOSe System Basics Configuration Guide, Chapter 4, Configuring
SNMP for information on SNMP. See JUNOSe Command Reference Guide A to M and
JUNOSe Command Reference Guide N to Z for the commands that are available for
configuring the system as an SNMP agent.
SNMP ■ 65
Page 82

E120 and E320 11.1.x Hardware Guide
The Next Step
See “Maintaining the Router” on page 69.
66 ■ The Next Step
Page 83

Part 3
Hardware Maintenance, Replacement, and
Troubleshooting Procedures
■ Maintaining the Router on page 69
■ Troubleshooting on page 79
Hardware Maintenance, Replacement, and Troubleshooting Procedures ■ 67
Page 84

E120 and E320 11.1.x Hardware Guide
68 ■ Hardware Maintenance, Replacement, and Troubleshooting Procedures
Page 85

Chapter 8
Maintaining the Router
This chapter lists the tools, items, and steps needed for installing and uninstalling
router components. Other maintenance procedures must be performed by an
authorized Juniper Networks technician.
This chapter contains the following sections:
■ Required Tools and Items on page 69
■ Storing Modules and Components on page 69
■ Cleaning the System on page 70
■ Upgrading NVS Cards on SRP Modules on page 70
■ Replacing an NVS Card on page 72
■ Replacing Fan Trays on page 73
■ Installing an Air Filter on page 75
■ Replacing a Power Distribution Unit on page 76
Required Tools and Items
You need the following tools and other items to replace router components:
■ Flathead and No. 2 Phillips screwdrivers
■ Insulated adjustable wrench
■ Antistatic wrist strap
■ Antistatic bags (or other protective packaging to hold components)
■ Plastic boots or other protective covers for fiber-optic SC and LC connectors
Storing Modules and Components
Retain the packaging in which a module or component was shipped, and use this
packaging to store the item. Modules are shipped in antistatic bags and protective
packaging. Components, such as transceivers and nonvolatile storage (NVS) cards,
are shipped in antistatic plastic containers within an antistatic padded box.
Required Tools and Items ■ 69
Page 86

E120 and E320 11.1.x Hardware Guide
CAUTION: Failure to store electronic modules and components correctly can lead to
damage of these items.
Follow these guidelines for storing modules and components:
■ Store each module in a separate antistatic bag.
■ Store components in an antistatic plastic container. Some of these containers
can accommodate several components in separate compartments.
■ Do not store multiple modules or components in an antistatic bag or container
where they can touch other items.
■ (Optional) Store the item in its antistatic bag or container within the protective
packaging or padded box that the item was shipped in.
Cleaning the System
Dust is attracted to the where the air intake vents are located. Clean the area with a
dry cloth every few weeks to prevent excessive accumulation of dust. This cleaning
helps to maintain the efficiency of the cooling system and to prevent damage to
electronic components.
WARNING: Do not insert any metal object, such as a screwdriver, or place your hand
into an open slot or the backplane when the router is on. Remove jewelry (including
rings, necklaces, and watches) before working on equipment that is connected to
power lines. These actions prevent electric shock and serious burns.
CAUTION: When cleaning the system, wear an antistatic wrist strap connected to
an ESD grounding jack. This action helps to protect modules from damage by
electrostatic discharge.
Upgrading NVS Cards on SRP Modules
This section describes how to install higher-capacity NVS cards on switch route
processor (SRP) modules. The procedure you use depends on the number of SRP
modules in the system. A new NVS card already contains the software release you
ordered.
NOTE: The new NVS card must contain the same software release that you are
running on the system.
70 ■ Cleaning the System
Page 87

Upgrading a System That Contains One SRP Module
If the system contains only one SRP module, you must power down the system
before you upgrade the NVS card.
CAUTION: If you do not use the halt command before removing or powering down
an SRP module, the system's NVS card can become corrupted.
To upgrade the NVS card on a system that contains one SRP module:
1. Enter the halt command.
See JUNOSe System Basics Configuration Guide, Chapter 6, Managing Modules for
information about the halt command.
Chapter 8: Maintaining the Router
WARNING: Do not insert any metal object, such as a screwdriver, or place your hand
into an open slot or the backplane when the router is on. Remove jewelry (including
rings, necklaces, and watches) before working on equipment that is connected to
power lines. These actions prevent electric shock and serious burns.
CAUTION: When handling modules, use an antistatic wrist strap connected to an
ESD grounding jack. This action helps to protect the module from damage by
electrostatic discharge.
2. Connect the antistatic wrist strap to an ESD grounding jack on the router.
3. Power down the system.
4. Remove the SRP module.
5. Replace the NVS card on the SRP module. (See “Replacing an NVS Card” on
page 72.)
6. Reinsert the SRP module into the chassis.
7. Power up the system. (See “Powering Up the Router” on page 57.)
Upgrading a System That Contains Two SRP Modules
In a system that contains two SRP modules, you can upgrade the NVS cards on the
SRP modules without powering down the system.
WARNING: Do not insert any metal object, such as a screwdriver, or place your hand
into an open slot or the backplane when the router is on. Remove jewelry (including
rings, necklaces, and watches) before working on equipment that is connected to
power lines. These actions prevent electric shock and serious burns.
Upgrading NVS Cards on SRP Modules ■ 71
Page 88

E120 and E320 11.1.x Hardware Guide
CAUTION: When handling modules, use an antistatic wrist strap connected to an
ESD grounding jack. This action helps to protect the module from damage by
electrostatic discharge.
To upgrade the NVS cards on the SRP modules in a system that contains two SRP
modules:
1. Wear an antistatic wrist strap and connect it to one an ESD grounding jack on
the router.
2. Halt the redundant SRP module.
3. Remove the redundant SRP module from the chassis.
4. Replace the NVS card on this SRP module. (See “Replacing an NVS Card” on
page 72.)
host1#halt standby-srp
5. Reinsert the SRP module into the chassis.
6. When this SRP module is available, synchronize the SRP modules.
host1#synchronize
7. When the SRP modules are synchronized, reboot the SRP module that you
upgraded.
host1#reload standby-srp
8. When this SRP module is available, synchronize the SRP modules.
host1#synchronize
9. When the SRP modules are synchronized, force the redundant SRP module to
take over from the primary SRP module.
host1#srp switch
10. Halt the redundant (former primary) SRP module.
host1#halt standby-srp
11. Immediately remove the former primary SRP module.
12. Repeat Steps 4–8 for the former primary SRP module.
Replacing an NVS Card
To replace an NVS card in slot 0 or slot 1 of an SRP module:
CAUTION: Before you insert or remove an NVS card from a running SRP module,
we strongly recommend that you halt the SRP module or shut down the router.
72 ■ Replacing an NVS Card
Page 89

Chapter 8: Maintaining the Router
Failure to do this can result in file corruption in one or both cards. See JUNOSe System
Basics Configuration Guide, Chapter 6, Managing Modules for information about the
halt command.
1. Obtain an antistatic container for the NVS card you plan to remove. (See “Storing
Modules and Components” on page 69.)
2. Be sure you have halted the SRP module using the halt command. See “Upgrading
a System That Contains One SRP Module” on page 71.
3. With a small flathead screwdriver, remove the faceplate from the NVS card slot
on the SRP module.
4. Eject the NVS card. (See Figure 29 on page 73.)
■ Slot 0—Insert a paperclip or similar device in the hole beneath slot 0 to eject
the NVS card.
■ Slot 1—Use a screwdriver or similar device to depress the button beneath
slot 1 and eject the card.
Figure 29: NVS Card Slots and Eject Buttons
5. Remove the NVS card and place it in the antistatic container.
6. Insert the new NVS card into the slot and push it until it clicks into place.
7. Replace the faceplate on the NVS card slot.
Replacing Fan Trays
A tray of cooling fans provides forced air cooling for components in the router. The
fan tray is hot-swappable; you can replace it without powering down the system.
Replacing Fan Trays ■ 73
Page 90

E120 and E320 11.1.x Hardware Guide
However, if you do not replace the fan tray within 60 seconds, the system enters
thermal protection mode. For information about thermal protection mode, see
“Monitoring Temperatures of Modules” on page 85. You can monitor fan status by
observing the LEDs on the SRP module or on the fan tray behind the faceplate. For
complete LED information, see “Understanding Status LEDs to Troubleshoot” on
page 80.
NOTE: On the SRP module or fan tray, if the red FAN FAIL LED is illuminated, either
a critical or non-critical failure exists. Fan tray LEDs are located behind the fan tray
bezel.
CAUTION: If the FAN FAIL LED on the SRP module is illuminated and none of the
fans are spinning when you remove the fan tray, quickly power down the system
until a new fan tray is available. Operating a router with inadequate air circulation
can damage the modules.
Removing an E320 Fan Tray
To remove the fan tray:
1. Place a flathead screwdriver in the groove where the top bezel meets the chassis
on the top of the system, and lever the top bezel off the front of the system.
2. With an appropriate screwdriver, loosen the captive screws located at the corners
of the fan tray.
WARNING: Do not place your fingers near the fans when removing the fan tray. The
blades might still be moving.
NOTE: Loosen the top and bottom thumbscrews (using a No. 2 Phillips screwdriver,
if necessary)
3. Pull the fan tray halfway out of the shelf until it stops on the safety catch.
4. Pull both red safety handles upward while gripping the sides of the fan tray and
pull the tray out slightly until the safety catch is released.
5. Place one hand under the fan tray and the other on the front handle and continue
to pull the fan tray out of the chassis.
Use two hands to hold the fan tray after it comes out of the chassis.
Installing an E320 Fan Tray
To install the fan tray:
74 ■ Replacing Fan Trays
Page 91

Chapter 8: Maintaining the Router
CAUTION: Do not use the fan tray handle to carry the fan tray assembly. Use the
handle only to push the tray into the chassis.
1. With two hands hold the tray horizontally or so that the captive screws point
toward you and you can read text on the labels.
2. Place the bottom corners of the tray housing in the fan tray compartment and
push toward the back of the chassis until the tray stops.
An electrical connector on the back of the fan tray pairs with an electrical
connector at the back of the shelf.
3. With an appropriate screwdriver, tighten the captive screws.
Alternate between screws when tightening them to ensure that the electrical
connectors at the back of the tray fit tightly.
CAUTION: Do not overtighten the screws.
4. Fold down the fan tray handle and push the top bezel back on the front of the
Installing an Air Filter
Air filters are hot-swappable; you do not have to power down the system to replace
the filter. The filter is located behind the fan tray bezel located at the bottom of the
front of the system. Remove the bezel to access the air filter. See Figure 30 on
page 76.
system.
Installing an Air Filter ■ 75
Page 92

E120 and E320 11.1.x Hardware Guide
Figure 30: Installing an Air Filter into an E320 Router
To install an air filter:
1. Ground yourself by using an antistatic wrist strap or other device and connect
it to one of the ESD grounding jacks.
2. Remove the front bezel by grabbing the edges and pulling straight out toward
you.
3. Unscrew the two captive screws on the air filter door and swing the door down
to open it.
4. Remove the old air filter (if present).
5. Insert the new filter by sliding it in on the shelf guides. Be sure the mesh side is
facing up.
6. Close the door, tighten the captive screws, and snap the bezel on.
CAUTION: Do not overtighten the screws.
Replacing a Power Distribution Unit
To replace a power distribution unit (PDU):
1. Power down the router. See “Powering Down” on page 59.
2. Remove the clear plastic guard covering the PDU.
76 ■ Replacing a Power Distribution Unit
Page 93

Chapter 8: Maintaining the Router
WARNING: Be sure the power source is turned off and all power switches are in the
OFF position.
3. Disconnect the power cables and grounding cables. See Figure 31 on page 78.
4. With an appropriate screwdriver, loosen the screws located at the corners of the
PDU.
NOTE: Loosen the top and bottom thumbscrews (using a No. 2 Phillips screwdriver,
if necessary)
5. Using two hands, pull the PDU out of the chassis.
6. Install the new PDU and tighten the screws.
CAUTION: Do not overtighten the screws.
7. Reconnect the power cables and grounding cables. See “Cabling the Router for
Power” on page 52
8. Replace the clear plastic guard.
9. Power up the router. See “Powering Up the Router” on page 57.
Replacing a Power Distribution Unit ■ 77
Page 94

E120 and E320 11.1.x Hardware Guide
Figure 31: PDU
78 ■ Replacing a Power Distribution Unit
Page 95

Chapter 9
Troubleshooting
This chapter explains how you can troubleshoot a specific problem, such as abnormal
LED activity or no system power, when you power up the router. It contains the
following sections:
■ Diagnosing Problems on page 79
■ Troubleshooting Power Failures on page 80
■ Understanding Status LEDs to Troubleshoot on page 80
■ Monitoring Temperatures of Modules on page 85
■ Resetting Line Modules and SRP Modules on page 86
■ Double-Bit Errors on SRP Modules on page 86
Diagnosing Problems
When you first encounter a system problem:
1. Make sure power connections are secure attached.
2. Observe the system's LEDs carefully.
3. Make sure cable connections on the system modules are securely attached.
If a problem is beyond the scope of this chapter, see “Contacting Customer Support
and Returning Hardware” on page 113 for further instructions.
NOTE: Running the show version, show hardware, and show environment
commands is often a good first step when trying to troubleshoot a problem.
Initialization Sequence
Each line module is initialized independently. As a result, the command-line interface
(CLI) on the switch route processor (SRP) module might become available before the
line modules have completed initialization. Commands relating to a line module
might fail if the module has not completed initialization. Use the show version
command to display line module status. Do not enter commands for a line module
until its state is online.
Diagnosing Problems ■ 79
Page 96

E120 and E320 11.1.x Hardware Guide
Troubleshooting Power Failures
The system's distributed power system is designed to consume low levels of power
and dissipate low levels of heat. See “System Specifications” on page 91 for
specifications of power consumption and heat dissipation. If you suspect a power
problem, see Table 9 on page 80.
Table 9: Causes of Power Failures
ActionsPossible ProblemsSymptom
System does not
power up.
System shuts
down.
System is not receiving
■
power.
Module's power supply has
■
malfunctioned.
Power source cannot handle
■
system load.
Temperature is too high.
■
Power is lost.
■
The following actions apply to all of the possible problems:
Verify that all power connections are correct.
1.
Verify that the power supply is delivering the correct voltage,
2.
current, and wattage to the system. See “System Specifications”
on page 91.
If the system still does not operate, contact the Juniper Networks
3.
Technical Assistance Center (JTAC).
The following actions apply to all of the possible problems:
Verify that power connections are properly attached.
1.
Verify that system is receiving power.
2.
Look to see whether or not the LEDs are lit.
3.
Run diagnostics on SRP and line modules.
4.
If system does not reset, contact JTAC.
5.
Understanding Status LEDs to Troubleshoot
Module LEDs can show you the immediate status of a module and alert you to a
problem with the module or one of its ports. We recommend you familiarize yourself
with LED activity so that you can easily detect and correct a module-related problem
with minimal or no system downtime.
LED Identification
Most modules have two sets of status LEDs. The top set indicates basic functional
status of the router or module. The bottom set indicates system status for that module,
such as port status (line modules and IOAs) or fan status (SRP modules). See Figure
32 on page 81 and Figure 33 on page 81 for LED locations and labeling. See Table
10 on page 82 for descriptions of LED activity for all modules and IOAs.
80 ■ Troubleshooting Power Failures
Page 97

Figure 32: Typical IOA LEDs
Chapter 9: Troubleshooting
Figure 33: SRP IOA Module LEDs
Understanding Status LEDs to Troubleshoot ■ 81
Page 98

E120 and E320 11.1.x Hardware Guide
NOTE: The primary SRP module illuminates the REDUNDANT LED when the SRP
module is part of a redundancy group and it is up and running (or ready to take over).
The standby SRP module monitors an activity signal from the primary SRP module
to determine its state; it does not shadow the operations of the primary SRP module.
If the standby SRP module detects that the primary SRP module is not active (and
high-availability mode is not enabled), it reboots the system and takes control. If
high-availability mode has been enabled, automatic switchover occurs with near
hitless failover.
Table 10: LED Identification and Activity Descriptions
All modules
ON to OFFOFF to ONLED ColorLED IndicatorLED LabelLED Location
Failure detectedSelf-test passedGreenModule statusOK
Line module
SFM module
SRP module
Failure detectedRedModule statusFAIL
GreenRedundancyREDUN
GreenRedundancyREDUN
GreenRedundancyREDUN
Module is active,
and a standby
module is
available
N+1 redundancy
is enabled; 2 SRPs
and 3 SFMs must
be installed and
working.
When LED is lit,
you can remove
the module
without
interrupting
service.
Module is the
spare system
controller, is up,
and is ready to
take the role of the
online system
controller.
Diagnostic test
running
Module offlineModule onlineGreenModule statusONLINE
Module is active,
and no standby
module is
available
One of the five
fabric slices is
down or not
installed.
N+1 redundancy
is not enabled.
Module is no
longer acting as
the spare system
controller.
82 ■ Understanding Status LEDs to Troubleshoot
GreenPower APA
source A.
Power is off.Power is online on
Page 99

Table 10: LED Identification and Activity Descriptions (continued)
Chapter 9: Troubleshooting
ON to OFFOFF to ONLED ColorLED IndicatorLED LabelLED Location
IOAs
GreenPower BPB
NOTE: You can run the show environment command to see whether a noncritical
fan failure exists.
NOTE: In case of SRP hot-swap, when SRP IOA is removed, LK is turned off. When
an SRP IOA is inserted, LK is green and stable.
GreenEthernet activityAC
NOTE: In case of SRP hot-swap, when SRP IOA is removed, AC is turned off. When
an SRP IOA is inserted, AC is green and blinking.
NOTE: Not all IOAs have the following LEDs.
YellowPort statusALM
source B.
Ethernet link is up.GreenEthernet linkLK
Blinks when
Ethernet traffic is
on link.
The remote end of
the link is
experiencing loss
of signal (FERF).
Power is off.Power is online on
Critical fan failure.Fan is online.GreenFan onlineFO
Fan is online.Critical fan failure.RedFan failureFF
Ethernet link is
down.
No Ethernet traffic
is on link.
No FERF present,
port is working
correctly.
LED Activity
RedPort status
Port statusOK
Port is
experiencing loss
of signal.
Physical link is
connected
properly and is
functioning
properly.
Port is working
correctly; in sync.
Physical link is not
connected
properly and is not
functioning
properly.
When the system boots, it runs a series of tests for each module installed in the
system, and the LEDs display various configurations. See Table 11 on page 84 and
Table 12 on page 84 to understand normal and abnormal LED activity.
NOTE: When you reboot the system after installing a new version of the software,
the line modules appear to boot twice.
Understanding Status LEDs to Troubleshoot ■ 83
Page 100

E120 and E320 11.1.x Hardware Guide
Table 11: Normal Activity of Functional Status LEDs During Booting
Status ProcessONLINEFAILOK
offoffoff
offonoff
If the system detects an error during booting, the FAIL LED lights. Some failure
conditions can cause the module not to boot. In this case, the LEDs might all be off.
The system then resets the module.
If the operational software detects an error, the FAIL LED lights. Some errors can
cause a module reset. Crash information is displayed at the console on the next
reboot.
Table 12: Troubleshooting Abnormal LED Activity on Modules
ActionsPossible ProblemsDiagnostic Signs
POWER A (PA)
■
LED is not lit
POWER B (PB)
■
LED is not lit
System is not receiving power
■
from Power A.
System is not receiving power
■
from Power B.
Make sure Power A and Power B terminal connections are
1.
securely attached.
Verify that power switches are on.
2.
Make sure connections to power sources are securely
3.
attached.
If system still does not operate, contact the Juniper
4.
Networks Technical Assistance Center.
1. Module is in the power-up restart state; the FAIL LED
stays on briefly.
2. Module is initializing, and diagnostic tests are
running; the FAIL LED stays on briefly.
3. Module passed the diagnostics; the system boots.offoffon
4. Module is now up and running.onoffon
FAIL LED lights
The line module and IOA are
■
incompatible.
A hardware failure, such as a
■
failed module.
FAN OK LED
■
does not light
FAN FAIL LED
■
Fan is not working properly
■
or has slowed down.
Fan needs replacement.
■
lights
84 ■ Understanding Status LEDs to Troubleshoot
Make sure that the line modules and IOAs are compatible;
1.
replace if necessary.
If you replaced the IOA only, issue the reload slot
2.
slot_number command.
If you replaced the line module or if there was a hardware
3.
failure, the system is supposed to automatically reset the
module.
If the condition persists, contact the Juniper Networks
4.
Technical Assistance Center.
Contact the Juniper Networks Technical Assistance Center; the
system must be serviced.
NOTE: In the fan tray for the E320 Broadband Services Router,
four of the eight fans turn on immediately upon initial power-up
and the other four fans turn on after a delay of 10 seconds.
 Loading...
Loading...