
ADVANCED INSIGHT SCRIPTS (AI-SCRIPTS)
2.5 RELEASE NOTES
6 October 2010
Revision 1
These release notes accompany Release 2.5R1 of the Advanced Insight Scripts (AI-Scripts).
AI-Scripts are Junos event scripts used to enable Juniper Networks J Serie s, M Serie s, MX
Series, T Series, EX Series, and SRX Series devices to:
React to specific incident events that occur and provide relevant information for analysis
Periodically collect data on events that can be used to predict and prevent risks in the future
Package all incident and intelligence event data into a structured format, such as a Juniper
Message Bundle (JMB), and send it to an archive location to be collected and displayed by
the Advanced Insight Manager (AIM) application
Contents
You can also find these release notes, the Advanced Insight Scripts (AI-Scripts) Release Notes,
and the AIS User Guide on the Juniper Networks Technical Publications Web page, at
http://www.juniper.net/techpubs/software/management/ais/
Summary of Release 2.5 Features..................................................................................................3
AI-Scripts 2.5R1 ........................................................................................................................3
AI-Scripts Operation.........................................................................................................................3
AI-Script Modes................................................................................................................................3
Events Detected by AI-Scripts.........................................................................................................5
Current Software Release..............................................................................................................30
Outstanding Issues ........................................................................................................................30
Issues Fixed Since Last Release...................................................................................................31
Junos PRs That Affect AI-Scripts...................................................................................................31
Installing AI-Scripts ........................................................................................................................32
AI-Scripts System Requirements ............................................................................................32
AI-Scripts/AIM Compatibility....................................................................................................32
AI-Scripts Installation Methods................................................................................................32
Downloading AI-Scripts Install Packages................................................................................32
AI-Scripts Install Package Versioning .....................................................................................33
.
AI-Scripts Install Locations on Devices...................................................................................33
Automatically Installing AI-Scripts Overview...........................................................................33
Copyright© 2010, Juniper Networks, Inc. 1

Advanced Insight Scripts (AI-Scripts) 2.5 Release Notes
©
Automatically Installing AI-Scripts ...........................................................................................34
Manually Configuring and Installing AI-Scripts on Devices.....................................................34
AI-Scripts Commands....................................................................................................................38
Installing an AI-Scripts Package....................................................................................................38
Upgrading an AI-Scripts Package...........................................................................................38
Deleting an AI-Scripts Package...............................................................................................38
Rolling Back an AI-Scripts Package........................................................................................38
Not Saving Copies of AI-Scripts Package Files During Installation ........................................38
Removing AI-Scripts Packages After Installation....................................................................38
JUNOS Documentation and Release Notes..................................................................................39
Requesting Technical Support.......................................................................................................39
Self-Help Online Tools and Resources...................................................................................39
Opening a Case with JTAC.....................................................................................................40
Revision History.............................................................................................................................40
2 Copyright
2010, Juniper Networks, Inc.
3
Summary of Release 2.5 Features
This section describes key features of the current AI-Scripts release.
AI-Scripts 2.5R1
Features
Empty FPC heap / jtree attachments suppressed in AI-Scripts. (PR 540766)
Remove trend-data section from AI-Scripts problem event-scripts. (PR 556345)
Apply AI-Scripts JMB file permissions workaround for Junos PR/513414. (PR 556607)
Event-Scripts
Added AI-Script event for mrvl_brg_port_stg_cist_init. (PR 545325)
Added AI-Script event for cm_read_i2c errno:5. (PR 545466)
Added AI-Script event for /kernel: ifd_request: RTM_ID <48> should only do pointchanges.
(PR 545468)
Added AI script for event %KERN-3: jsr_prl_recv_ack_msg(). (PR 556009)
Resolved Issues
Summary of Release 2.5 Features
Trim the link for the KB note for the event pfestat_req_receive. (PR 545464)
AI-Scripts workaround for JUNOS PR/520377, which generates duplicate cha ssis-module
subtags in Routing Engine section on M320 and some EX Series platforms. (PR 548758)
Modify the problem description field in problem-event-mrvl_brg_port_cist_init.slax to include
the related KB link. (PR 549035)
Trim the KB link for AI-Scripts problem-event-GenCfgBloberror.slax. (PR 551498)
AI-Scripts problem events for protocol-neighbor-related issues in BGP, OSPF, RSVP, and
ISIS have been removed. (PR 555122)
Modify attachments in AI-Scripts event-script problem-event-ichipregerr.slax. (PR 555489)
AI-Scripts Operation
AI-Scripts do the following tasks:
React to specific incident events that occur on devices and provide relevant information about
the problems for analysis
Periodically collect data on events that can be used to predict and prevent risks in the future
Package all incident and intelligence event data into a structured format, such as a Juniper
Message Bundle (JMB), and send it to a remote archive location so that it can be collected
and displayed by Advanced Insight Manager (AIM)
AI-Script Modes
AI-Scripts operate in two distinct modes:
Reactive (incident-driven)—A trigger event occurs and is detected on a device. An AI-Script
is executed. An AI-Script builds a Juniper Message Bundle (JMB) with event and router data,
and sends it to a designated AIM archive location.
Copyright© 2010, Juniper Networks, Inc.

Advanced Insight Scripts (AI-Scripts) 2.5 Release Notes
©
Each AI-Script corresponds to a specific device event. The list of device problem events that
can be detected and reported will evolve over time. See Table 1 on page 3.
Proactive (intelligence-driven)—AI-Scripts monitor device system resources for fluctuations
that could signal a future problem. AI-Scripts collect intelligence data for analysis. A tailored
AI-Script builds a JMB with intelligence data and sends it to a designated remote AIM archive
location.
4 Copyright
2010, Juniper Networks, Inc.
Events Detected by AI-Scripts
5
Events Detected by AI-Scripts
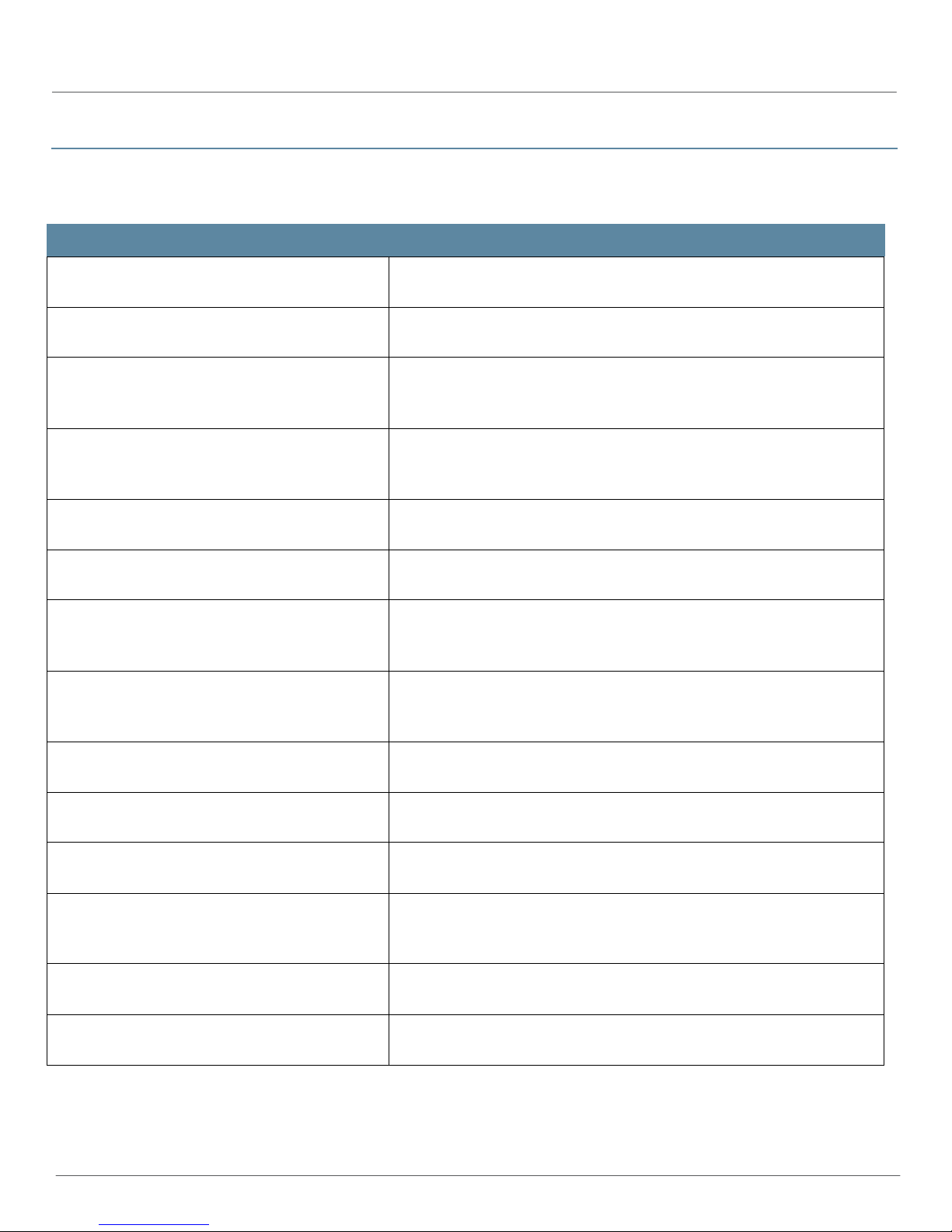
Table 1 on page 3 lists the events detected by Release 2.5 of the AI-Scripts.
Table 1: Events Detected by AI-Scripts
EVENT ID
ACCT_MALLOC_FAILURE The accounting statistics process could not allocate memory from the
ACCT_XFER_POPEN_FAIL A failed call to the popen() function when the accounting statistics process
ASP_IDS_INV_CLEAR_QUERY The intrusion detection services (IDS) receives a request to clear
ASP_IDS_INV_CLEAR_QUERY_VER The intrusion detection services (IDS) receives a request to clear
ASP_L2TP_NO_MEM The Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol (L2TP) could not allocate the memory it
DESCRIPTION
heap.
invokes the indicated command to transfer the indicated file.
information from the IDS tables. The request includes the indicated type of
query, which the IDS cannot interpret.
information from the IDS tables. The request version number did not match
the version number of requests that the IDS can service.
needed to create a flow for the indicated tunnel and session.
ASP_L2TP_OBJ_CAC_FAIL The Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol (L2TP) could not allocate memory from an
object cache for the flow defined by the indicated unit, tunnel, and session.
ASP_PGCP_IPC_PIPE_WRITE_FAILED The Packet Gateway Control Protocol (PGCP) client on the Services Port
Interface Card failed to write an interprocess communication (IPC)
message to the end of its pipe.
ASP_PGCP_IPC_PIPE_WRITE_FAILED The Packet Gateway Control Protocol (PGCP) client on the Services Port
Interface Card failed to write the contents of its interprocess
communication (IPC) pipe to the socket layer.
AUDITD_RADIUS_OPEN_FAILED The audit process (auditd) could not create a RADIUS object handle used
for various RADIUS operations.
AUDITD_RADIUS_OPEN_FAILED The audit process (auditd) could not create a RADIUS object handle used
for various RADIUS operations.
AUDITD_RADIUS_REQ_CREATE_FAILED The audit process (auditd) could not create a RADIUS accounting request
for the indicated reason.
AUDITD_SOCKET_FAILURE The audit process (auditd) listens on a Transmission Control Protocol
(TCP) socket for system accounting events reported by other processes on
the device. The indicated socket operation failed with the indicated error.
AUTHD_AUTH_CREATE_FAILED The generic authentication service process (authd) could not allocate an
authentication object for the indicated reason.
AUTHD_SERVER_INIT_BIND_FAIL The generic authentication service process (authd) could not bind the
Copyright© 2010, Juniper Networks, Inc.
server to the address specified.
Advanced Insight Scripts (AI-Scripts) 2.5 Release Notes
©
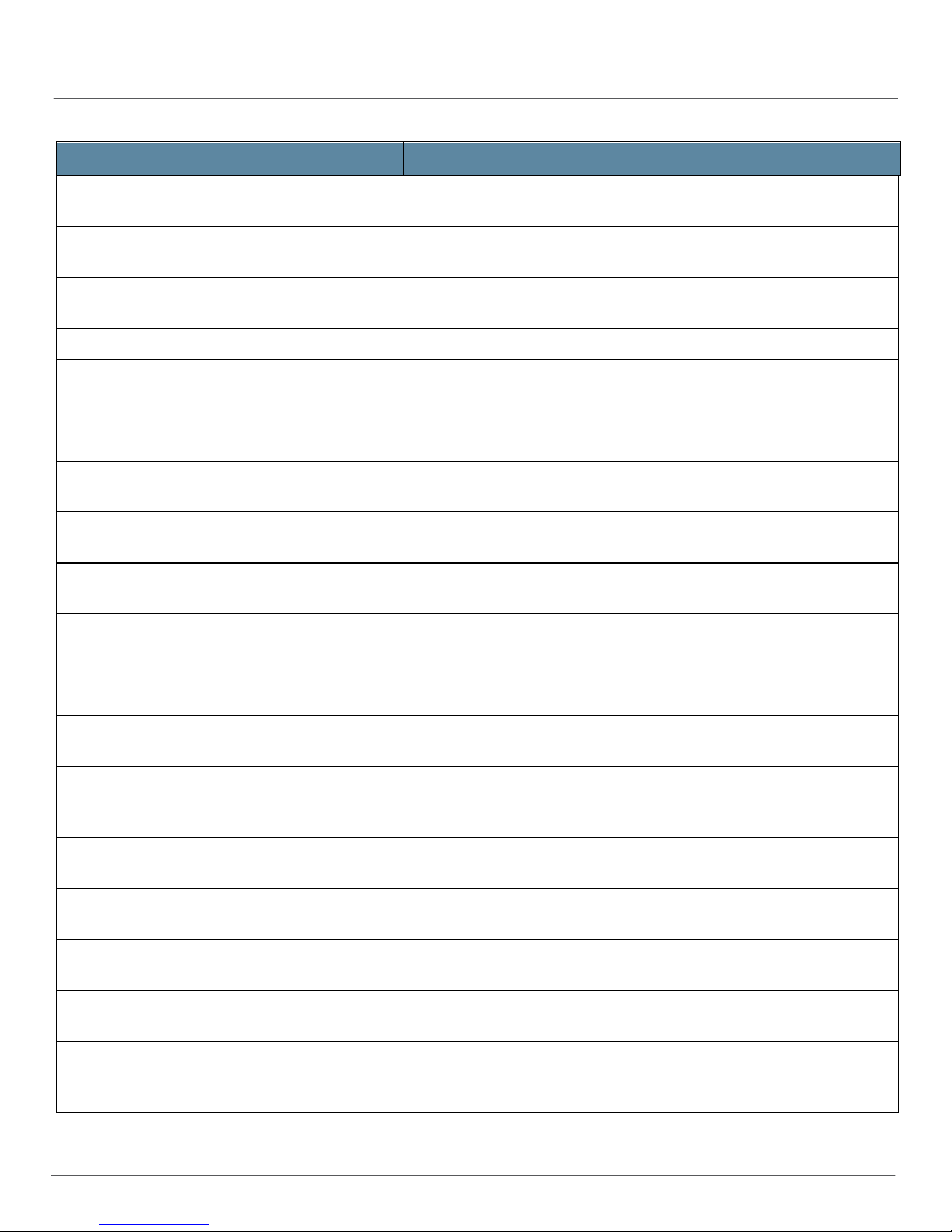
Table 1: Events Detected by AI-Scripts (continued)
EVENT ID
AUTHD_SERVER_INIT_LISTEN_FAIL The generic authentication service process (authd) could not initialize
AUTHD_SETSOCKOPT_FAILED The generic authentication service process (authd) could not set socket
AUTHD_SOCKET_FAILED The generic authentication service process (authd) could not open a
AUTOCONFD_AUTH_NO_MEM The memory allocation (malloc) for username authentication failed.
AUTOD_RECV_FAILURE The autoinstallation process (autod) received the indicated error when it
AUTOD_SEND_FAILURE The autoinstallation process (autod) receives the indicated error when it
AUTOD_SOCKET_CREATE_FAILURE The autoinstallation process (autod) receives the indicated error when it
AV_PATTERN_KL_CHECK_FAILED The device is unable to use the Kaspersky pattern file. The error message
DESCRIPTION
listening on the server for the indicated socket.
options during the indicated operation.
socket during the indicated operation.
tried to receive data on a socket.
sends data on a socket.
creates a socket.
provides information to give to Juniper Networks technical support.
AV_PATTERN_TOO_BIG The pattern file size specified in the server ini t ialization file (server.ini)
exceeds the maximum prescribed limit.
AV_PATTERN_WRITE_FS_FAILED The device is unable to save the contents of an antivirus pattern file to the
file system.
BFDD_READ_ERROR The bidirectional forwarding detection pr ocess (bfdd) could not read a
message available on the indicated type of pipe.
BFDD_WRITE_ERROR The bidirectional forwarding detection process (bfdd) could not write a
message to the indicated type of pipe.
BOOTPD_HWDB_ERROR The boot parameter process (tnp.bootpd) could not complete an operation
in the hardware database maintained by the chassis process (chassisd),
for the indicated reason.
CFMD_RTSOCK_OPEN_FAILURE The connectivity fault management process (cfmd) could not successfully
open a routing socket to the kernel, for the indicated reason.
CHASSISD_BUS_DEVICE_OPEN_FAILURE The chassis process (chassisd) could not open the indicated bus device,
for the indicated reason.
CHASSISD_CFEB_POWER_FAILURE The chassis process (chassisd) could not turn on or turn off the power to
the indicated Compact Forwarding Engine Board (CFEB).
CHASSISD_CLOCK_FAILURE The chassis process (chassisd) determined that the indicated clock source
failed in the indicated way.
CHASSISD_CMB_READBACK_ERROR The chassis process (chassisd) could not read back information from the
6 Copyright
Chassis Management Bus (CMB) about the indicated component (fieldreplaceable unit, or FRU).
2010, Juniper Networks, Inc.
Events Detected by AI-Scripts
7
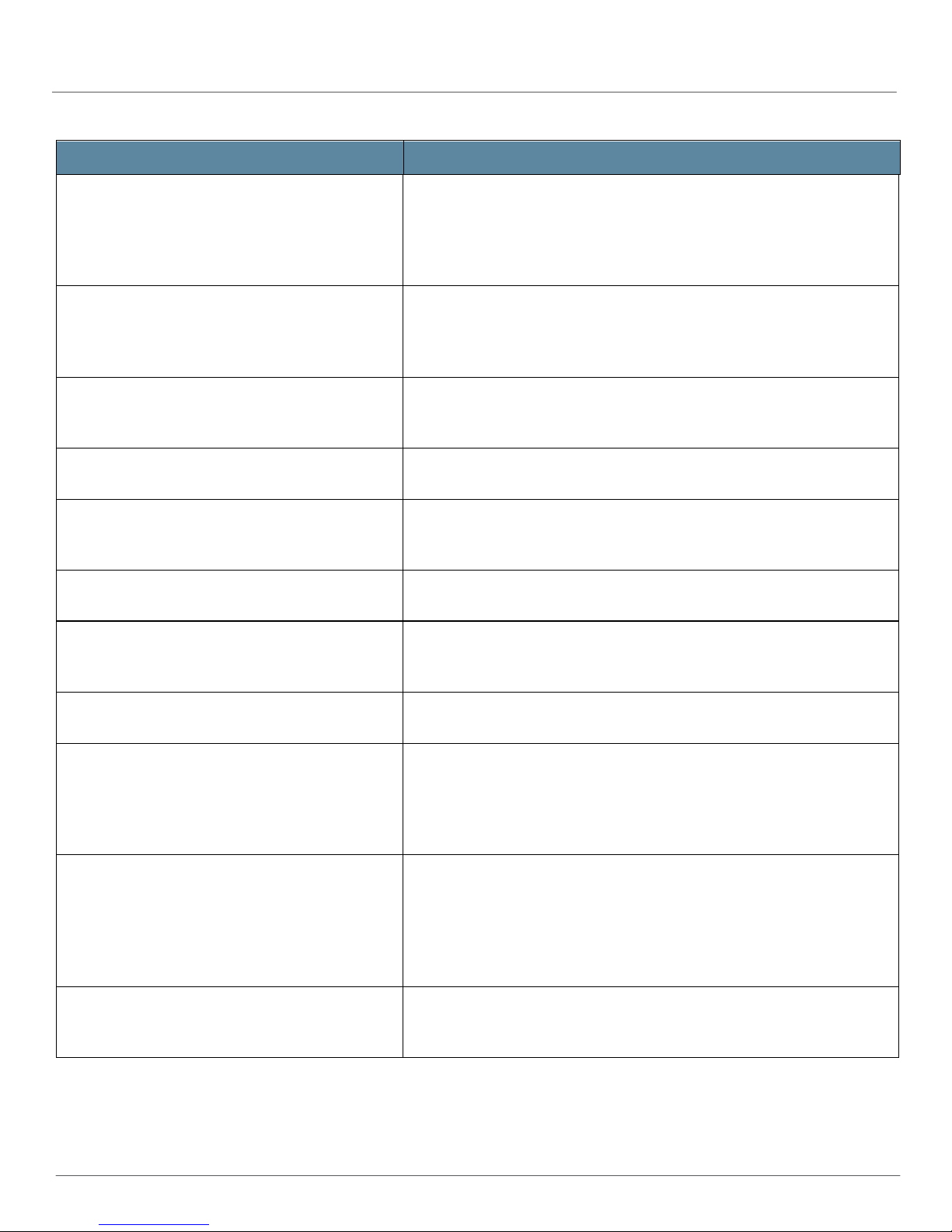
Table 1: Events Detected by AI-Scripts (continued)
EVENT ID
CHASSISD_COMMAND_ACK_ERROR The chassis process requested that the indicated component (field-
CHASSISD_COMMAND_ACK_SFM_ERROR The chassis process (chassisd) requires an acknowledgment from each
CHASSISD_FAN_FAILURE The indicated fan or impeller failed. The chassis process (chassisd) raised
CHASSISD_FASIC_FTOKEN_ERROR The chassis process (chassisd) detected an underflow or overflow error on
CHASSISD_FASIC_FTOKEN_INIT_ERROR The chassis process (chassisd) encountered an error while initializing
DESCRIPTION
replaceable unit, or FRU) confirm that it was online. The indicated error
occurred when the FRU sent its response. In the normal case, the chassis
process performed any additional action necessary to guarantee that the
FRU came online.
Switching and Forwarding Module (SFM) before it registers a Flexible PIC
Controller (FPC) as online. The acknowledgment message from the
indicated SFM failed for the indicated FPC.
an alarm and increased the speed of the remaining fans (and impellers, if
applicable) to full speed.
the indicated F chip on the indicated Control Board (CB).
memory at the indicated address for the indicated F chip on the indicated
Control Board (CB).
CHASSISD_FASIC_HSL_CONFIG_ERROR The chassis process (chassisd) could not configure high-speed links (HSL)
for the indicated F chip on the indicated Control Board (CB).
CHASSISD_FASIC_HSL_LINK_ERROR The chassis process (chassisd) detected an error for the indicated high-
speed link (HSL) for the indicated F chip on the indicated Control Board
(CB).
CHASSISD_FASIC_INIT_ERROR The chassis process (chassisd) detected that F chips were not yet
initialized on the Control Board (CB).
CHASSISD_FASIC_INPUT_DROP The Packet Forwarding Engine divides packets into smaller units called
cells for more efficient processing. As the indicated F chip on the indicated
Control Board (CB) processed data that was received from the indicated
Packet Forwarding Engine on the indicated Flexible PIC Concentrator
(FPC), it dropped the indicated number of cells per second.
CHASSISD_FASIC_OUTPUT_DROP The Packet Forwarding Engine divides packets into smaller units called
cells for more efficient processing. As the indicated F chip on the indicated
Control Board (CB) processed data before sending it to the indicated
Packet Forwarding Engine on the indicated Flexible Port Concentrator
(FPC) for outgoing transmission, it dropped the indicated number of cells
per second.
CHASSISD_FASIC_PIO_READ_ERROR The indicated routine failed with a read error at the indicated address and
register for the indicated F chip and link on the indicated Control Board
(CB).
Copyright© 2010, Juniper Networks, Inc.
Advanced Insight Scripts (AI-Scripts) 2.5 Release Notes
©
Table 1: Events Detected by AI-Scripts (continued)
EVENT ID
CHASSISD_FASIC_PIO_WRITE_ERROR The indicated routine failed with a write error at the indicated address and
CHASSISD_FASIC_PLL_ERROR The chassis process (chassisd) could not lock a phased-lock loop (PLL) for
CHASSISD_FASIC_RESET_ERROR The chassis process (chassisd) could not reset the indicated F chip on the
CHASSISD_FASIC_SRAM_ERROR The chassis process (chassisd) detected that SRAM failed to initialize for
CHASSISD_FCHIP_CONFIG_MD_ERROR The chassis process (chassisd) detected an invalid number of Md chips for
CHASSISD_FCHIP_HSR_ERROR The chassis process (chassisd) detected an error in the high-speed
DESCRIPTION
register for the indicated F chip and link on the indicated Control Board
(CB).
the indicated F chip on the indicated Control Board (CB).
indicated Control Board (CB).
the indicated F chip on the indicated Control Board (CB).
the indicated F chip, Packet Forwarding Engine, and Flexible PIC
Concentrator (FPC).
receiver (HSR) subsystem for the F chip with the indicated characteristics.
CHASSISD_FCHIP_HST_ERROR The chassis process (chassisd) detected an error in the high-speed
transmitter (HST) subsystem for the F chip with the indicated
characteristics.
CHASSISD_FCHIP_LINK_ERROR The chassis process (chassisd) detected an error for the indicated high-
speed receiver (HSR) or high-speed transmitter (HST) link for an F chip on
the indicated Switch Interface Board (SIB).
CHASSISD_FCHIP_MONITOR_ERROR The chassis process (chassisd) detected an invalid F-chip module while
enabling or disabling the monitoring of F-chip functional blocks.
CHASSISD_FCHIP_PIO_READ_ERROR The indicated routine failed with a read error at the indicated address and
register for the indicated F chip and link.
CHASSISD_FCHIP_PIO_WRITE_ERROR The indicated routine failed with a write error at the indicated address and
register for the indicated F chip and link.
CHASSISD_FHSR_READ_REG_ERROR The high-speed receiver (HSR) read routine failed at the indicated address
on an F-chip register.
CHASSISD_FHSR_WRITE_REG_ERROR The high-speed receiver (HSR) write routine could not record the indicated
value at the indicated address on an F-chip register.
CHASSISD_FHST_READ_REG_ERROR The high-speed transmitter (HST) read routine failed at the indicated
address on an F-chip register.
CHASSISD_FHST_WRITE_REG_ERROR The high-speed transmitter (HST) write routine could not record the
indicated value at the indicated address on an F-chip register.
CHASSISD_FILE_OPEN The chassis process (chassisd) could not open the indicated file for the
8 Copyright
indicated reason.
2010, Juniper Networks, Inc.

Events Detected by AI-Scripts
9
Table 1: Events Detected by AI-Scripts (continued)
EVENT ID
CHASSISD_FM_ERROR During execution of the indicated fabric management routine, the indicated
CHASSISD_FM_ERROR_SIB_L_FB_HSR In a routing matrix, packets traverse both electrical and optical media as
CHASSISD_FM_ERROR_SIB_L_FB_SMF In a routing matrix, packets traverse both electrical and optical media as
DESCRIPTION
error occurred between the indicated Switch Interface Board (SIB) and the
indicated Packet Forwarding Engine on the indicated Fle xible PIC
Concentrator (FPC).
they travel between the Switch Interface Boards (SIBs) in the T640 router
(called SIB-Ls) and the SIBs in the TX Matrix platform (called SIB-Ss). The
chassis process (chassisd) on the routing node that houses the indicated
SIB-L detected an error in the electrical path between the indicated ports
on the SIB-L and the corresponding SIB-S.
they travel between the Switch Interface Boards (SIBs) in the TX Matrix
(the switch-card chassis, or SCC) and the SIBs in the T640 routers (called
SIB-Ls). The chassis process (chassisd) on the T640 router that houses
the indicated SIB-L detected the indicated error as packets that were
traveling in the indicated direction were translated between electrical and
optical media.
CHASSISD_FM_ERROR_SIB_S_FB_HSR In a routing matrix, packets traverse both electrical and optical media as
they travel between the Switch Interface Boards (SIBs) in the TX Matrix
platform (called SIB-Ss) and the SIBs in the T640 routers (called SIB-Ls).
The chassis process (chassisd) on the TX Matrix detected an error in the
electrical path between the indicated port on the indicated SIB-S and the
indicated port on a SIB-L installed in the indicated T640 router (line-card
chassis, or LCC).
CHASSISD_FM_ERROR_SIB_S_FB_SMF In a routing matrix, packets traverse both electrical and optical media as
they travel between the Switch Interface Boards (SIBs) in the TX Matrix
(called SIB-Ss) and the SIBs in the T640 routers (line-card chassis, or
LCCs). The chassis process (chassisd) on the TX Matrix platform detected
the indicated error as packets that were traveling to or from the indicated
LCC were translated between electrical and optical media.
CHASSISD_FM_SIB_ERROR The chassis process (chassisd) detected the indicated type of error on the
indicated Switch Interface Board (SIB) and performed the indicated action.
CHASSISD_FPC_PIC_DETECT_TIMEOUT The chassis process (chassisd) expects to receive notification within a
timeout period that each Flexible PIC Concentrator (FPC) has attached the
PIC that it houses. It did not receive notification from the indicated FPC.
CHASSISD_FRU_INVALID_SLOT The chassis process (chassisd) detected that the indicated hardware
component (field-replaceable unit, or FRU) was inserted in a slot that is not
valid for that component type.
CHASSISD_GBUS_NOT_READY The GBUS was not ready when the chassis process (chass isd) first tried to
Copyright© 2010, Juniper Networks, Inc.
power it on, and the power-up operation timed out.
Advanced Insight Scripts (AI-Scripts) 2.5 Release Notes
©
Table 1: Events Detected by AI-Scripts (continued)
EVENT ID
CHASSISD_GBUS_READBACK_ERROR There was an error when the chassis process (chassisd) tried to read back
CHASSISD_HSR_FIFO_ERROR A first-in, first-out (FIFO) read error occurred during execution of the
CHASSISD_I2C_BAD_IDEEPROM_FORMAT The chassis process (chassisd) determined that the ID EEPROM format
CHASSISD_I2C_READ_ERROR The chassis process (chassisd) cannot read I2C data from the indicated
CHASSISD_I2CS_READBACK_ERROR The chassis process (chassisd) cannot read back information from the I2C
CHASSISD_IFDEV_DETACH_FPC The chassis process (chassisd) detached the interface devices for all PICs
DESCRIPTION
information from the GBUS on the indicated component (field-replaceable
unit, or FRU).
indicated routine on the indicated high-speed receiver (HSR).
specified for the indicated type of hardware component (field-replaceable
unit, or FRU) is not valid for it.
device.
slave (I2CS) about the indicated component (field-replaceable unit, or
FRU).
on the indicated Flexible PIC Concentrator (FPC).
CHASSISD_IFDEV_DETACH_PIC The chassis process (chassisd) detached the interface devices for the
indicated PIC.
CHASSISD_IPC_CONNECTION_DROPPED The chassis process (chassisd) dropped the interprocess communication
(IPC) connection to the indicated component (field-replaceable unit, or
FRU).
CHASSISD_IPC_DAEMON_WRITE_ERROR The chassis process (chassisd) could not write to a socket because of the
indicated error. The socket is for a connection to another process that runs
on the Routing Engine and helps manage the chassis.
CHASSISD_IPC_MSG_DROPPED T he chassis process (c hassisd) dropped an interprocess communication
(IPC) message because the message queue had already reached
maximum capacity.
CHASSISD_IPC_MSG_UNHANDLED The chassis process (chassisd) received an interprocess communication
(IPC) message about the indicated FRU. The message had the indicated
characteristics. chassisd could not handle the message.
CHASSISD_IPC_WRITE_ERR_NULL_ARGS The chassis process (chassisd) could not send a message to the indicated
component (field-replaceable unit, or FRU) because one or more required
parameters had a null value.
CHASSISD_MAC_ADDRESS_ERR The chassis process (chassisd) could not obtain a media access control
(MAC) address for the indicated interface because of an internal error.
CHASSISD_MAC_ADDRESS_FABRIC_ERR The chassis process (chassisd) could not obtain a media access control
10 Copyright
(MAC) address for the indicated fabric interface because of an internal
error.
2010, Juniper Networks, Inc.
Events Detected by AI-Scripts
Table 1: Events Detected by AI-Scripts (continued)
EVENT ID
CHASSISD_MALLOC_FAILURE The chassis process (chassisd) could not allocate memory. chassisd tried
CHASSISD_MBE_DETECTED A multibit ECC parity error was detected in the Routing Engine DRAM.
CHASSISD_OVER_TEMP_CONDITION The temperature of one or more components (field-replaceable units, or
CHASSISD_OVER_TEMP_SHUTDOWN_TIME The chassis process (chassisd) shut down the device because the
CHASSISD_PEM_OVERLOAD The indicated power entry module (PEM) reported an output voltage
DESCRIPTION
to continue functioning, but the lack of memory usually causes the process
to fail. An administrator needs to restart it.
FRUs) exceeded the indicated temperature, which is the upper of two
thresholds. The fans (and impellers, if applicable) were in the indicated
state. If the temperature does not go below the threshold within four
minutes after the chassis process (chassisd) detects this condition,
chassisd shuts down the device. When this message was logged, the
indicated number of seconds remained before shutdown.
temperature of one or more components exceeded the indicated threshold
temperature for the indicated amount of time. Continued operation at the
excessive temperature could damage the device.
overload condition.
CHASSISD_PEM_VOLTAGE The indicated power entry module (PEM) reported a problem with its
output voltage.
CHASSISD_PIC_HWERROR The indicated PIC experienced a hardware error. The chassis process
(chassisd) did not bring the PIC online.
CHASSISD_POWER_CONDITION The temperature of the indicated Routing Engine exceeded the indicated
temperature, which is the upper of two thresholds.
CHASSISD_PSU_ERROR The chassis process (chassisd) detected the indicated error condition for
the indicated power supply unit (PSU).
CHASSISD_PSU_FAN_FAIL The PSU fan-fail bit is set in the status for the indicated power supply unit
(PSU).
CHASSISD_PSU_INPUT_BAD The chassis process (chassisd) detected the input voltage/warning fault
condition for the indicated power supply unit (PSU).
CHASSISD_PSU_OVERLOAD The indicated power supply unit (PSU) reported an output voltage overload
condition.
CHASSISD_PSU_TEMPERATURE The chassis process (chassisd) detected that the temperature check bit
was set in the status bit mask for the indicated power supply unit (PSU).
CHASSISD_PSU_VOLTAGE The indicated power supply unit (PSU) reported a problem with its output
voltage.
CHASSISD_RE_OVER_TEMP_CONDITION The temperature of the indicated Routing Engine exceeded the indicated
Copyright© 2010, Juniper Networks, Inc. 11
temperature, which is the upper of two thresholds.
Advanced Insight Scripts (AI-Scripts) 2.5 Release Notes
©
Table 1: Events Detected by AI-Scripts (continued)
EVENT ID
CHASSISD_RE_OVER_TEMP_SHUTDOWN The chassis process (chassisd) performed the indicated action because
CHASSISD_RE_OVER_TEMP_WARNING The temperature of the indicated Routing Engine exceeded the indicated
CHASSISD_SBE_DETECTED Too many single-bit correctable ECC parity errors were detected in
CHASSISD_SIB_INVALID_SLOT The chassis process (chassisd) detected the presence of a Switch
CHASSISD_SMB_INVALID_PS The chassis process (chassisd) could not set the status (enabled or
DESCRIPTION
the temperature of the indicated Routing Engine exceeded the maximum
threshold for more than four minutes. Continued operation at the excessive
temperature could damage device components.
temperature, which is the upper of two thresholds. If the temperature does
not go below the threshold within four minutes after the chassis process
(chassisd) detects this condition, chassisd shuts down the indicated
component. When this message was logged, the indicated number of
seconds remained before shutdown.
Routing Engine DRAM.
Interface Board (SIB) in an invalid slot. The SIB remains offline.
disabled) for a power supply because it received the indicated power
supply status code, which is invalid.
CHASSISD_SMB_IOCTL_FAILURE The indicated ioctl() operation failed at the indicated address on the s ystem
management bus (SMB).
CHASSISD_SMB_READ_FAILURE A read() operation failed at the indicated address on the system
management bus (SMB).
CHASSISD_TEMP_SENSOR_FAILURE The temperature sensor for the indicated component (field-replaceable
unit, or FRU) either did not respond to a request from the chassis process
(chassisd) for a temperature reading or sent a value that is outside the
normal operating range.
CHASSISD_TIMER_VAL_ERR The chassis process (chassisd) started a timer to track the timeout period
for an event. The timer returned a null identifier, so chassisd could not
clear the timer.
CHASSISD_UNEXPECTED_EXIT The chassis process (chassisd) exited unexpectedly and reported the
indicated error.
CHASSISD_VOLTAGE_READ_FAILED The chassis process (chassisd) could not read the voltage data from the
indicated component (field-replaceable unit, or FRU).
CHASSISD_VOLTAGE_SENSOR_INIT The chassis process (chassisd) could not initialize the voltage sensor for
the indicated component (field-replaceable unit, for FRU).
CONNECTION_CHASSISD_FAIL The alarm process (alarm d) was unable to connect to the chassis process
(chassisd).
CONNECTION_CRAFTD_FAIL The alarm process (alarmd) was unable to connect to the craft process
12 Copyright
(craftd).
2010, Juniper Networks, Inc.
Events Detected by AI-Scripts
3
Table 1: Events Detected by AI-Scripts (continued)
EVENT ID
CONNECTION_RTLOGD_FAIL The alarm proc ess (alarmd) was unable to connect to the Juniper
CONNECTION_SEND_ERROR The alarm process (alarmd) received an error while it was trying to send a
COSD_GENCFG_WRITE_FAILED The class-of-service (CoS) process (cosd) uses GENCFG to read and
COSD_MALLOC_FAILED The class-of-service (CoS) process (cosd) could not dynamically allocate
COSD_RTSOCK_LIB_ERR The class-of-service (CoS) process (cosd) uses rtsock library for reading
COSD_RTSOCK_WRITE_FAILED The class-of-service (CoS) process (cosd) uses rtsock to read/write data
COSD_UNEXPECTED_EXIT The class-of-service (CoS) process (cosd) waits for the event notifications
DESCRIPTION
Networks J Series Services Router (JSR) log process (rtlogd).
message.
write data from the kernel. If the write fails, the kernel returns an error.
memory, for the indicated reason.
and writing data from and to kernel. The specified error occurred while
using rtsock library to read/write data.
from kernel. If the write fails kernel returns an error.
and processes the events that it is registered for. There was an error
during event-handling initialization.
COSD_UNKNOWN_TRANSLATION_TABLE The class-of-service (CoS) process (cosd) did not recognize the indicated
translation table type from the rtsock library.
Daemon Crash A Junos daemon crash occurred with a core dump.
DCD_CONFIG_WRITE_FAILED The interface process (dcd) encountered an error while trying to send an
interface configuration to the kernel over the routing socket.
DCD_GET_ERROR The interface process (dcd) encountered an error while trying to load the
kernel interface configuration over the routing socket.
DCD_PARSE_STATE_EMERGENCY The interface process (dcd) encountered an unhandled internal state
during interface parsing.
DCD_RTSOCK_READ_SYNC_NOBUF The interface process (dcd) communicates with the kernel by writing
messages to and reading messages from routing sockets. The DCD could
not allocate memory to use to read messages from the kernel.
DCD_RTSOCK_SEND_NOBUF If the Routing Engine is busy or operating under a heavy load, messages
between the interface process (dcd) and the kernel may be dropped. To
detect whether messages have been dropped, dcd and the kernel place
sequence numbers in messages. dcd detected that a message was
dropped. In an attempt to recover the message, dcd retries the operation.
DCD_TRASHED_RED_ZONE When DCD is allocating heap memory, it uses a private memory allocato r
that writes a special pattern at the end of each allocated segment of heap
memory. Later, when de-allocating this memory, DCD checks for the
pattern. Not finding the previously written pattern means the memory was
overwritten, which indicates an error in DCD.
Copyright© 2010, Juniper Networks, Inc. 1

Advanced Insight Scripts (AI-Scripts) 2.5 Release Notes
©
Table 1: Events Detected by AI-Scripts (continued)
EVENT ID
DFCD_GENCFG_MALLOC_FAILED The dynamic flow capture process (dfcd) could not allocate memory for the
DFCD_GENCFG_WRITE_FAILED The dynamic flow capture process (dfcd) could not send the GENCFG
DFCD_LINH_MALLOC_FAILED The dynamic flow capture process (dfcd) could not allocate memory for the
DFWD_CONFIG_WRITE_FAILED The firewall process (dfwd) encountered an error while trying to send an
DFWD_MALLOC_FAILED The firewall process (dfwd) must dynamically malloc memory for its needs.
DFWD_PARSE_STATE_EMERGENCY The firewall process (dfwd) encountered an unhandled internal state while
DFWD_TRASHED_RED_ZONE When the firewall process (dfwd) is allocating heap memory, it uses a
DESCRIPTION
GENCFG message.
message for the indicated reason.
LINH message.
interface configuration to the kernel over the routing socket.
This allocation request failed. The specific data structure that was being
allocated is listed in the message.
parsing an interface.
private memory allocator that writes a special pattern at the end of each
allocated segment of heap memory. Later, when de-allocating this memory,
dfwd checks for the pattern. Not finding the previously written pattern
means the memory was overwritten, which indicates an error in dfwd.
DH_SVC_RTSOCK_OPEN_FAILURE The Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) services process (dhcp-
service) could not successfully open a routing socket to the kernel. The
error string accompanying this log entry indicates the specific error.
DH_SVC_RTSOCK_REGISTER_FAILURE The Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) services process (dhcp-
service) could not successfully register a callback function with a routing
socket. The error string accompanying this log entry indicates the specific
error.
DH_SVC_SETSOCKOPT_FAILURE The Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) services process (dhcp-
service) could not set the indicated socket option.
DH_SVC_SOCKET_FAILURE The Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) services process (dhcp-
service) could not create a socket.
ESPTASK_PARSE_CMD_ARG This process terminated because of an internal error.
ESPTASK_PARSE_CMD_EXTRA This process terminated because of an invalid option.
ESWD_PPM_READ_ERROR The ethernet bridging process (eswd) could not read a message available
on the read pipe from the periodic packet management process (ppmd).
ESWD_PPM_WRITE_ERROR The ethernet bridging process (eswd) could not write a message on the pipe
to the periodic packet management process (ppmd).
ESWD_STP_BASE_MAC_ERROR This condition occurs when STP cannot derive the base MAC address of
the system.
EVENTD_EVENT_SEND_FAILED Junos processes can request that the event process ing process (eventd)
notify them when a specific event occurs. eventd could not send an event
notification for the indicated reason.
14 Copyright
2010, Juniper Networks, Inc.

Events Detected by AI-Scripts
5
Table 1: Events Detected by AI-Scripts (continued)
EVENT ID
EVENTD_FORK_ERR The event processing process (eventd) could not create a child process for
EVENTD_PIPE_ERR The event processing process (eventd) could not create a pipe for
EVENTD_VERSION_MISMATCH The event processing process (eventd) received an event with the indicated
FPCLOGIN_IP_ADDRESS_GET_FAILURE The fpclogin module attempted to get the IP address of the physical
FSAD_ERROR The file system access process (fsad) internal error message.
FUD_MEMORY_ALLOCATION_FAILURE The UDP forwarding process (fud) could not allocate the indicated amount
FUD_RTSOCK_WRITE_FAILURE The UDP forwarding process (fud) could not write to its routing socket for
DESCRIPTION
executing policies.
interprocess communication.
version indicator, which does not match the indicated version expected by
eventd.
interface module. The attempt failed.
of memory from the heap.
the indicated reason.
FUD_SENDMSG_FAILURE The UDP forwarding process (fud) could not send data to the indicated
destination port and address using the indicated interface and routing
instance, which it needs to do during normal operation.
FUD_SENDMSG_NOINT_FAILURE The UDP forwarding process (fud) could not send data to the indicated
destination port and address using the indicated routing instance, which it
needs to do during normal operation.
FUD_SETSOCKOPT_FAILURE The UDP forwarding process (fud) could not set the indicated socket option.
FUD_SOCKET_FAILURE The UDP forwarding process (fud) could not create a socket.
GGSN_ALARM_TRAP_SEND An alarm trap to be relayed by the services PICs process (serviced) failed to
initialize.
GGSN_TRAP_SEND The system sent a GGSN trap of an unrecognized type.
GRAPH_NO_MEMORY The graphing process could not allocate memory while trying to create a
graph.
HNCACHED_PATRICIA_ERROR A call to a Patricia tree library function returns an error.
ICCPD_ASSERT_SOFT The source code for the interchassis communication process (iccpd)
includes internal self-consistency checks. As iccpd with the indicated
process ID (PID) executed the binary compiled from the indicated source
file, a check failed at the indicated line number in the file. iccpd created a
diagnostic core file for analysis by technical support personnel and
continued to run.
ICCPD_OPEN_ERROR The interchassis communication process (iccpd) could not initialize.
IDP_DAEMON_INIT_FAILED An attempt to start the IDP policy daemon failed because an error was
Copyright© 2010, Juniper Networks, Inc. 1
encountered during initialization.

Advanced Insight Scripts (AI-Scripts) 2.5 Release Notes
©
Table 1: Events Detected by AI-Scripts (continued)
EVENT ID
IDP_INTERNAL_ERROR The IDP daemon encountered an internal error.
IKED_CFG_PATRICIA_ERROR A call to a Patricia tree library function returned an error.
JCS_BBD_LOAD_FAILURE The JCS process (jcsd) could not load blade bay data for the specified
JCS_BBD_LOCAL_MISMATCH The blade bay data retrieved for the specified blade does not match the
JCS_BBD_NOT_FOUND The blade bay data was not found for the specified blade.
JCS_BBD_NOT_VALID The blade b ay data for the specified blade is invalid.
JCS_BBD_PARSE_ERROR The blade bay data for the specified blade did not parse correctly.
JCS_BBD_PEER_MISMATCH The blade bay data retrieved for the specified peer blade does not match
DESCRIPTION
blade.
data loaded during the reboot process. This error usually indicates that
blade bay data in the JCS Management Module was changed since the last
reboot.
the data retrieved for the local blade. This error indicates that blade bay
data in the JCS Management Module was not configured properly.
JCS_KERNEL_RSD_LINK_DOWN The JCS process (jcsd) has disabled kernel RSD communication for the
specified reason.
JCS_MM_COMMUNICATION_ERROR The JCS process (jcsd) could not send an SNMP request to the
Management Module because of the indicated error.
JCS_READ_BANDWIDTH_ERROR The indicated error occurred when attempting to read the current switch
bandwidth.
JCS_READ_BBD_ERROR The indicated error occurred when attempting to read the current blade bay
data via a sysctl call.
JCS_SWITCH_COMMUNICATION_ERROR The JCS process (jcsd) could not send an SNMP request to the indicated
Switch Module because of the indicated error.
JSRPD_DAEMONIZE_FAILED The Juniper Se rvices Redundancy Protocol process (jsrpd) could not create
a version of itself to run in the background as a daemon.
JSRPD_EVLIB_EXIT_FAILURE The Juniper Services Redundancy Protocol process (jsrpd) returned from
an event loop, which it should never do.
JSRPD_SOCKET_LISTEN_FAILURE The Juniper Services Redundancy Protocol process (jsrpd) could not
successfully listen on a socket.
JSRPD_SOCKET_RECV_HB_FAILURE The Juniper Services Redundancy Protocol process (jsrpd) was not
successfully received on a socket.
KERNEL:.*jsr_prl_recv_ack_msg.* received PRL
ACK message
KERNEL:GENCFG: op 2 (Gencfg Blob) failed.* Kernel error message generated because it does not have a handler for a
16 Copyright
Non-stop routing replication message acknowledgment received by backup
Routing Engine.
certain GENCFG blob message.
2010, Juniper Networks, Inc.

Events Detected by AI-Scripts
7
Table 1: Events Detected by AI-Scripts (continued)
EVENT ID
KERNEL:ifd_request: RTM_ID.* Some Junos daemons were not originally included in a list of processes that
KERNEL:ifd_request: RTM_ID.* Some Junos daemons were not originally included in a list of processes that
KERNEL:parity error detected, fll reinit: mpfe.* The message indicates that the Packet Forwarding Engine was reset when
KERNEL:pfestat_req_receive: request.* Kernel message regarding PFE statistics counter request.
DESCRIPTION
can modify an inteface definition. These messages are only informational
and can be ignored.
can modify an inteface definition. These messages are informational only
and can be ignored.
detecting a parity error in the ASIC.
KERNEL:Process .* has exceeded 85% of
RLIMIT_DATA
This message indicates that the virtual memory size of a process’s data-
segment area (RLIMIT_DATA) has exceeded its current soft limit.
KERNEL:rdp retransmit error The kernel is indicating that no system buffer space is available.
KERNEL:RT_PFE: NH IPC failed, err 6 (No
Memory)
The kernel is reporting that the Packet Forwarding Engine cannot install or
change routing table entries because it is running out of memory.
KMD_SNMP_PIC_NO_RESPONSE The indicated PIC did not respond to a request from the key management
process (kmd) for Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) statistics
about IP Security (IPSec) security associations.
L2ALD_IPC_PIPE_WRITE_ERROR The Layer 2 address learning process (l2ald) could not write to an
interprocess communication (IPC) pipe for the indicated reason.
L2ALD_PIP_IFD_READ_RETRY The Layer 2 address learning process (l2ald) could not read the provide-in-
provider interface (pip0) interface from the kernel.
L2CPD_ABORT The Layer 2 Control Protocol process (l2cpd) terminated because of an
internal error.
L2CPD_ASSERT The source code for the Layer 2 Control Protocol process (l2cpd) includes
internal self-consistency tests. l2cpd with the indicated executable name
and process ID (PID) terminated because the indicated test failed at the
indicated line number in the indicated source file. The process created a
diagnostic core file for analysis by technical support personnel.
L2CPD_ASSERT_SOFT The source code for the Layer 2 Control Protocol process (l2cpd) includes
L2CPD_PPM_WRITE_ERROR The Layer 2 Control Protocol process (l2cpd) could not write a message o n
Copyright© 2010, Juniper Networks, Inc. 1
internal self-consistency tests. l2cpd with the indicated executable name
and process ID (PID) terminated because the indicated type of check failed
at the indicated line number in the indicated source file. The process
continued to run, but created a diagnostic core file for analysis by technical
support personnel.
the pipe to the periodic packet management process (ppmd).

Advanced Insight Scripts (AI-Scripts) 2.5 Release Notes
©
Table 1: Events Detected by AI-Scripts (continued)
EVENT ID
L2CPD_SCHED_SLIP The Layer 2 Control Protocol process (l2cpd) delayed an event, such as
L2CPD_SYSTEM_CALL_FAILED A system call made by the Layer 2 Control Protocol process (l2cpd) failed.
L2TPD_EVLIB_CREATE_FAILED The Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol process (l2tpd) could not create a context
L2TPD_EVLIB_CREATE_FAILED The Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol process (l2tpd) could not create a conte xt
L2TPD_SERVER_START_FAILED The Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol (L2TP) server did not start.
LIBESPTASK_SNMP_CONN_PROG The indicated error occurred while the process using libesptask was
LIBESPTASK_SNMP_SOCKOPT_RECVBUF The process using libesptask could not set the size of the kernel receive
DESCRIPTION
issuing an adjacency establishment message that was supposed to occur at
a particular time. The event did not occur at the right time.
for handling asynchronous events.
for handling asynchronous events.
connecting to the SNMP master agent.
buffer, which allows it to accept the largest possible packet from the Simple
Network Management Protocol (SNMP) master agent.
LIBESPTASK_SNMP_SOCKOPT_SENDBUF The process using libesptask could not set the size of the kernel send
buffer, which allows it to send the largest possible packet to the Simple
Network Management Protocol (SNMP) master agent.
LIBJNX_DEFAULT_IP_ADDR_NOT_SET A Junos process could not retrieve the system default IP address from the
kernel because the address is not defined there.
LIBJNX_EVLIB_FAILURE A Junos process called the indicated function in the event library. The
function failed for the indicated reason.
LIBJNX_EXEC_SIGNALED A Junos process created a child process to execute the indicated command.
The child process received the indicated signal and exited.
LIBJNX_REPLICATE_RCP_ERROR The rcp command failed during replication.
LIBJNX_SNMP_ENGINE_FILE_FAILURE A Junos process could not perform the indicated operation on the indicated
SNMP engine data file.
LIBJNX_SNMP_ENGINE_SCAN_FAILURE A Junos process could not perform the scan operation on the indicated
SNMP engine data file.
LIBJNX_SOCKET_FAILURE Various system processes use Transmission Control Protocol (TCP), User
Datagram Protocol (UDP), and Reliable Data Protocol (RDP) sockets. The
indicated socket operation failed for the indicated reason.
LIBJSNMP_NS_LOG_EMERG SNMP errors with LOG_EMERG as severity.
LIBMSPRPC_CLIENT_INIT_FAILED A Junos process (mspinfo) could not establish initialization of the RPC
LIBMSPRPC_CLIENT_KCOM_FAILED A Junos process (mspinfo) could not establish initialization of the KCOM
18 Copyright
client.
subsystem.
2010, Juniper Networks, Inc.

Events Detected by AI-Scripts
9
Table 1: Events Detected by AI-Scripts (continued)
EVENT ID
LIBMSPRPC_CLIENT_KCOM_NO_IF A Junos process (mspinfo) could not find any configured and active
LIBMSPRPC_CLIENT_NO_CONNECTION Remote execution of the command given from the Routing Engine to the
LIBMSPRPC_CLIENT_NO_REPLY Remote execution of the command given from the Routing Engine to the
LIBMSPRPC_CLIENT_PIC_DOWN Remote execution of the command given from the Routing Engine to the
LIBMSPRPC_CLIENT_WRONG_OUTPUT Remote execution of the command given from the Routing Engine to the
LIBSERVICED_CLIENT_CONNECTION An attempt to establish a client connection failed.
LIBSERVICED_SOCKET_BIND An attempt to bind a server socket for receiving client requests failed.
LIBSERVICED_SOCKET_PRIVATIZE An attempt to attach a socket to the management routing instance for
DESCRIPTION
extension-provider interfaces.
PIC failed. The Routing Engine cannot connect to the PIC.
PIC failed. There was no reply from the PIC.
PIC failed. The PIC is down.
PIC failed. The PIC returned unexpected output.
communication between the Routing Engine and GGSN-C PICs failed.
LICENSE_EXPIRED A time-based license for a feature has expired. The feature will remain
inactive until a new license is installed.
LICENSE_GRACE_PERIOD_APPROACHING The grace period for a licensable feature is about to expire. Unless a new
license is installed, the feature will become inactive after the grace period
expires.
LICENSE_GRACE_PERIOD_EXCEEDED The grace period for a scale license is about to expire. Unless the scale
license is upgraded, the license will scale back to the licensed limit after the
grace period expires.
LICENSE_GRACE_PERIOD_EXPIRED The grace period for a licensable feature has expired. Strict license
enforcement will remain active until a new license is installed.
LICENSE_NEARING_EXPIRY A time-based license for a feature is about to expire. Unless a new license
is installed, the feature will become inactive after the license expires.
LLDPD_SYSTEM A system call made by the Link Layer Discovery Protocol process (LLDPD)
failed.
LPDFD_DYN_PDB_OPEN_FAILED The local policy decision function process (lpdfd) failed to open the profile
database.
LPDFD_DYN_REGISTER_FAILED The local policy decision function process (lpdfd) failed to register with the
dynamic configuration subsystem.
LPDFD_DYN_SDB_OPEN_FAILED The local policy decision function process (lpdfd) failed to open the session
database.
LPDFD_PCONN_SERVER The local policy decision function process (lpdfd) pconn server failed to
Copyright© 2010, Juniper Networks, Inc. 1
initialize.
Advanced Insight Scripts (AI-Scripts) 2.5 Release Notes
©
Table 1: Events Detected by AI-Scripts (continued)
EVENT ID
LPDFD_RTSOCK_OPEN_FAILURE The local policy decision function (LPDF) services process could not
MIB2D_REALPATH_FAILURE When MIB2D is copying the /var/db/dcd.snmp_ix file, it could not resolve
MIB2D_RTSLIB_READ_FAILURE A call to the indicated function in the routing socket library failed during the
MIB2D_SNMP_INDEX_ASSIGN MIB2D cannot assign an SNMP index for each interface.
MIB2D_SNMP_INDEX_DUPLICATE The first interface name was assigned the same SNMP index as the second
MIB2D_SNMP_INDEX_UPDATE_STAT MIB2D cannot get the status of the SNMP index file.
MIB2D_SNMP_INDEX_WRITE MIB2D cannot write to a file containing all the indices.
NSD_MEMORY_ALLOC_FAILED The network security process (nsd) could not allocate the indicated number
DESCRIPTION
successfully open a routing socket to the kernel. The error string
accompanying this log entry indicates the specific error.
its real path.
indicated operation on the indicated object.
interface name.
of bytes of memory.
NSD_SEC_NODE_COMP_SYNC_FAILED One or more subcomponents of the network security process (nsd) failed to
synchronize their state when the nsd restarted on secondary mode.
NSTRACED_MEMORY_ALLOC_FAILED The USP trace process (nstraced) could not allocate the indicated number
of bytes of memory.
NSTRACED_SSAMLIB_CALL_FAILED The indicated error occurred when the usp trace daemon process (nstraced)
called a function in the ssamlib library or tried to process a callback from the
library.
PFE Crash Any Packet Forwarding Engine board crash that occurs in conjunction with a
system exception message.
PFE: ASIC Initialization Error Any Packet Forwarding Engine ASIC initialization error that occurs in
conjunction with a system exception message, such as: router-name fpc5
CMG: Fatal ASIC initialization error, Offlining FPC
PFE: CMRFEB: Fatal HSL2 errors for FPC A s witching bo ard (for example, FEB) is reporting a bad fabric connection to
an FPC.
PFE: DFW: jtree cutover failed The firewall filter configuration cannot be applied due to insufficient amount
of contiguous memory on the SRAM.
PFE: Failed to find MC RT_NH entry:.* Informational message logged when multicast next-hop traffic ages from the
switch routing tables.
PFE: HSL2–HSL2 detected fatal error The FPC detected a fatal HSL2 error.
PFE: I-CHIP New illegal link errors in WO DESRD Potential ICHIP stream problem possibly due to IFL flooding. Potential
20 Copyright
match with PR/289104—may need software upgrade.
2010, Juniper Networks, Inc.

Table 1: Events Detected by AI-Scripts (continued)
EVENT ID
DESCRIPTION
Events Detected by AI-Scripts
PFE: I-CHIP New packet errors in WO HDRF,
iwo_hdrf_poll_stats
Potential ICHIP stream problem possibly due to IFL flooding. Potential
match with PR/289104—may need software upgrade.
PFE: imq_stream_disable_stream The I-chip wedge issue described in PR 277853, which can lead to packet
corruption or packet loss. The Event trigger contains the string:
imq_stream_disable_stream.
PFE: LCHIPnew errors in LSIF The FPC is reporting LCHIP interface errors.
PFE: mrvl_dfw_log_effuse_status:Firewall rows The TCAM error messages listed indicate a permanent non-fixable error
with TCAM, if they persist after rebooting the EX Switch or Virtual Chassis
(VC). These errors are TCAM hardware issues on this FPC and are not
harmless. ACLs will be unreliable on this FPC.
PFE: Multi-bit ECC error The Packet Forward Engine detected a multi-bit error correcting code (ECC)
error in one of the forwarding engine boards.
PFE: Multiple Correctable ECC The Packet Forward Engine board is reporting multiple correctable ECC
memory errors.
PFE: Multiple UnCorrectable ECC The Packet Forward Engine board is reporting multiple uncorrectable ECC
memory errors.
PFE: Packet drop in Ichip The Ichip packet writer drop counter is incrementing, possibly indicating
packet drops which may, but not necessarily, be due to a faulty switching
board.
PFE: RCHIP: SRAM parity error SRAM parity error detected on FPC RCHIP.
PFE: Route TCAM rows could not be redirected on
device
The TCAM error messages listed indicate a permanent non-fixable error
with TCAM, if they persist after rebooting the EX Switch or Virtual Chassis
(VC). These errors are TCAM hardware issues on this FPC and are not
harmless. ACLs will be unreliable on this FPC.
PFE: RT: Failed prefix change These messages indicate that the Routing Engine is trying to delete routes
from the Packet Forwarding Engine, but it can't because the routes aren't
there. This usually means the Packet Forwarding Engine has run out of
memory. For example, if you bring up many BGP peers, the number of
routes the Routing Engine can hold may surpass the number the Packet
Forwarding Engine can hold. In this case, the Packet Forwarding Engine
runs out of memory and can't add the routes. Later, when the Routing
Engine tries to remove the routes, the prefix it’s looking for is unknown.
PFE: SDRAM ECC Error Any Packet Forwarding Engine SDRAM ECC error that occurs in
conjunction with a system exception message, for example: router-name
fpc0 ADPC: detected 1 DDR SDRAM Single-bit ECC errors in the last 30
seconds.
PFE: SHEAF: possible leak Possible FPC SHEAF memory leak.
Copyright© 2010, Juniper Networks, Inc. 21

Advanced Insight Scripts (AI-Scripts) 2.5 Release Notes
©
Table 1: Events Detected by AI-Scripts (continued)
EVENT ID
PFE: SRAM Parity Error Any Packet Forwarding Engine SDRAM ECC error that occurs in
PFE: SRCHIP-SRAM parity error The FPC SRCHIP has detected an SRAM parity error.
PFE:%PFE- PIO Read error. The PIO read error could indicate a hardware issue with the PIC.
PFE:.*CCHIP: .*abnormal discard seen.* Packet Forwarding Engine board is reporting CCHIP abnormal discard
PFE:.*clock error.* Clock error reported on PFE board.
PFE:.*mrvl_brg_port_stg_cist_init.* Initialization Warning message pertaining to MSTP/STP/RSTP configured
DESCRIPTION
conjunction with a system exception message, for example: router-name
ssb CCHIP: %PFE-3: SRAM parity error 0x80000 bank 0x1.
errors.
ports for any spanning tree groups shared common IST(CIST).
PFE:.*RSMON: Resource Category:jtree
RSMON is reporting critical jtree memory resource shortage.
Instance.*less than LWM limit.*
PFE:.SFP receive power low warning SFP receive power low warning.
PPMD_ASSERT_SOFT The source code for the periodic package management process (ppmd)
includes internal self-consistency checks. As ppmd with the indicated
process ID (PID) executed the binary compiled from the indicated source
file, a check failed at the indicated line number in the file. ppmd created a
diagnostic core file for analysis by technical support personnel and
continued to run.
PPMD_READ_ERROR The source code for the periodic package management process (ppmd)
includes internal self-consistency checks. As ppmd with the indicated
process ID (PID) executed the binary compiled from the indicated source
file, a check failed at the indicated line number in the file. ppmd created a
diagnostic core file for analysis by technical support personnel and
continued to run.
problem-event-ichipfcheck The FPC is reporting a bad fabric connection to one or more destinations.
Another FPC is likely to be causing the packet corruption.
problem-event-jbuserror An error occurred on the FPC control bus used for packet memory
allocation.
problem-event-l2cacheerror The Packet Forwarding Engine component is reporting that Layer 2 Cache
Single-bit ECC errors were detected in the last 30 seconds. If the problem
persists, this situation is likely to result in a component crash or failure.
problem-event-lchipcrc T he outbound FPC is reporting a corrupt packet received on the Nchip-to-
problem-event-nfabcrcerror The fabric connection to the ingress FPC is reporting a bad connection.
RDD_EVLIB_CREATE_FAILURE The redundant interfaces process (rdd) could not create a context used for
22 Copyright
Lchip interface. Another FPC is likely to be causing the packet corruption.
handling all asynchronous events (such as timers and message av ailability).
2010, Juniper Networks, Inc.

Events Detected by AI-Scripts
3
Table 1: Events Detected by AI-Scripts (continued)
EVENT ID
RMON_EVENT_cfeb_high_buffer_utilization Remote monitoring event reporting high buffer utilization on CFEB.
RMON_EVENT_cfeb_high_heap_utilization Remote monitoring event reporting high heap utilization on CFEB.
RMON_EVENT_feb_high_buffer_utilization Remote monitoring event reporting high buffer utilization on FEB.
RMON_EVENT_feb_high_heap_utilization Remote monitoring event reporting high heap utilization on FEB.
RMON_EVENT_fpc_high_buffer_utilization Remote monitoring event reporting high buffer utilization on FPC.
RMON_EVENT_fpc_high_cpu_utilization High CPU utilization on FPC.
RMON_EVENT_fpc_high_heap_utilization Remote monitoring event reporting high heap utilization on FPC.
RMON_EVENT_fwdd_high_buffer_utilization Remote monitoring event reporting high buffer utilization on FWDD.
RMON_EVENT_fwdd_high_heap_utilization Remote monitoring event reporting high heap utilization on FWDD.
RMON_EVENT_pfe_aged_notification Remote monitoring event reporting Packet Forwarding Engine notification:
RMON_EVENT_pfe_corrupt_notification Remote monitoring event reporting Packet Forwarding Engine notification:
DESCRIPTION
aged packets.
corrupt packets.
RMON_EVENT_pfe_dmafail_notification Remote monitoring event reporting Packet Forwarding Engine notification:
DMAfail packets.
RMON_EVENT_pfe_getfail_notification Remote monitoring event reporting Packet Forwarding Engine notification:
Getfail packets.
RMON_EVENT_pfe_giant_notification Remote monitoring event reporting Packet Forwarding Engine notification:
Giant packets.
RMON_EVENT_pfe_illegal_notification Remote monitoring event reporting Packet Forwarding Engine notification:
Illegal packets.
RMON_EVENT_re_high_dram_utilization Remote monitoring event reporting high DRAM CPU utilization on the
Routing Engine.
RMON_EVENT_sfm_high_buffer_utilization Remote monitoring event reporting high buffer utilization on SFM.
RMON_EVENT_sfm_high_heap_utilization Remote monitoring event reporting high heap utilization on SFM.
RMON_EVENT_spmb_high_buffer_utilization Remote monitoring event reporting high buffer utilization on SPMB.
RMON_EVENT_spmb_high_heap_utilization Remote monitoring event reporting high heap utilization on SPMB.
RMON_EVENT_ssb_high_buffer_utilization Remote monitoring event reporting high buffer utilization on SSB.
RMON_EVENT_ssb_high_heap_utilization Remote monitoring event reporting high heap utilization on SSB.
RPD_ABORT The routing protocol process (rpd) terminated because of an internal error.
RPD_ACTIVE_TERMINATE After receiving multiple termination requests, the routing protocol process
Copyright© 2010, Juniper Networks, Inc. 2
(rpd) exited without performing the indicated cleanup tasks.

Advanced Insight Scripts (AI-Scripts) 2.5 Release Notes
©
Table 1: Events Detected by AI-Scripts (continued)
EVENT ID
RPD_ASSERT The source code for the routing protocol process (rpd) includes internal self -
RPD_ASSERT_SOFT The source code for the routing protocol process (rpd) includes internal sel f -
RPD_BGP_NEIGHBOR_STATE_CHANGED During the BGP negotiation with the local router, the state of the indicated
RPD_DYN_CFG_BAD_REQ_OPCODE The routing protocol process (rpd) received a dynamic configuration request
DESCRIPTION
consistency checks. A check failed at the indicated line number in the
indicated source file, causing the instance of rpd that was using the
indicated binary and had the indicated process ID (PID) to terminate. The
process created a diagnostic core dump for analysis by technical support
personnel.
consistency checks. A check failed at the indicated line number in the
indicated source file, but the instance of rpd that was using the indicated
binary and had the indicated process ID (PID) continued running. The
process created a diagnostic core dump for analysis by technical support
personnel.
BGP neighbor (peer) changed as indicated. The ESTABLISHED state is the
final state in the neighbor negotiation.
with an unexpected operation code.
RPD_DYN_CFG_BUSY_SIGNAL_FAILED The routing protocol process (rpd) failed to notify dynamic configuration
clients about its availability to process dynamic configuration requests.
RPD_DYN_CFG_GET_PROF_NAME_FAILED The routing protocol process (rpd) tried to get the profile name from the
session snapshot and failed.
RPD_DYN_CFG_GET_PROFILE_FAILED The routing protocol process (rpd) tried to load a profil e from the database
and failed.
RPD_DYN_CFG_GET_SES_STATE_FAILED The routing protocol process (rpd) failed to get the session state from the
session snapshot.
RPD_DYN_CFG_GET_SNAPSHOT_FAILED The routing protocol process (rpd) tried to load client session data from the
database and failed.
RPD_DYN_CFG_PDB_CLOSE_FAILED The routing protocol process (rpd) tried to close the profile database and
failed.
RPD_DYN_CFG_PDB_OPEN_FAILED The routing protocol proc ess (rpd) tried to open the profile database and
failed.
RPD_DYN_CFG_PROCESSING_FAILED The routing protocol process (rpd) tried to process dynamic configuration
and failed.
RPD_DYN_CFG_REGISTER_FAILED The routing protocol process (rpd) tried to register with the dynamic
configuration subsystem and failed.
RPD_DYN_CFG_REQUEST_ACK_FAILED The routing protocol process (rpd) tried to ACK a dynamic config uration
24 Copyright
request and failed.
2010, Juniper Networks, Inc.

Events Detected by AI-Scripts
5
Table 1: Events Detected by AI-Scripts (continued)
EVENT ID
RPD_DYN_CFG_SCHEMA_OPEN_FAILED The routing protocol process (rpd) tried to open the configuration schema
RPD_DYN_CFG_SDB_CLOSE_FAILED The routing protocol process (rpd) tried to close the session database and
RPD_DYN_CFG_SDB_OPEN_FAILED The routing protocol process (rpd) tried to open the session database and
RPD_DYN_CFG_SES_RECOVERY_FAILED The routing protocol process (rpd) tried to recover a session and failed.
RPD_ISIS_ADJDOWN An IS-IS adjacency with the indicated neighboring router was terminated.
RPD_ISIS_LSPCKSUM The indicated IS-IS informational link-state PDU (LSP) failed an internal
RPD_ISIS_OVERLOAD The IS-IS link-state database is full and no additional memory can be
DESCRIPTION
and failed.
failed.
failed.
The local router will no longer exchange routing information with, or direct
traffic to, the neighboring router.
checksum validity test, indicating that it was corrupted.
allocated for it.
RPD_KRT_KERNEL_BAD_ROUTE As it restarted, the routing protocol process (rpd) could not process a route
obtained from the kernel because the route contained references to objects
that are no longer valid.
RPD_KRT_Q_RETRIES The routing protocol process (rpd) attempted to update the kernel for the
indicated times and failed. It will continue retrying.
RPD_LMP_UNEXPECTED_OPCODE The routing protocol process (rpd) received the indicated type of message,
which had the indicated invalid operation code.
RPD_OS_MEMHIGH The routing protocol process (rpd) is using the indicated amount and
percentage of Routing Engine memory, which is considered excessive.
RPD_OSPF_NBRDOWN An OSPF adjacency with the indicated neighbori ng router was terminated.
The local router will no longer exchange routing information with, or direct
traffic to, the neighboring router.
RPD_RSVP_NBRDOWN The RSVP neighbor to the indicated address was terminated.
RPD_RT_ERROR A route in the r outing table was found to be in an unrecoverable error state.
RPD_TASK_FORK The routing protocol process failed to create the indicated child process.
RT_SCREEN_TCP A TCP attack category.
RT_SCREEN_UDP A UDP attack category.
RTLOGD_DAEMONIZE_FAILED The JSR log daemon could not create a version of itself to run in the
background as a daemon.
RTLOGD_EVLIB_FAILURE The JSR log daemon called the indicated event library function. The
Copyright© 2010, Juniper Networks, Inc. 2
function failed with the indicated error.

Advanced Insight Scripts (AI-Scripts) 2.5 Release Notes
©
Table 1: Events Detected by AI-Scripts (continued)
EVENT ID
RTLOGD_GET_TNP_ADDRESS_FAILED JSR log daemon failed to determine local TNP address used to receive JSR
RTLOGD_LOG_BIND_ERROR The JSR log daemon received the JSR log from a JSR log forwarder. The
RTLOGD_LOG_READ_ENABLE_ERROR The JSR log daemon received the JSR log from a JSR log forwarder. The
RTLOGD_LOG_READ_ERROR The JSR log daemon relayed the JSR logs from the dataplane to the system
RTPERF_CPU_THRESHOLD_EXCEEDED The Packet Forwarding Engine CPU threshold has been exceeded.
SAVAL_RTSOCK_FAILURE The MAC SA Validate system process (jsavald) experienced the indicated
SDXD_DAEMONIZE_FAIL The Service Depl oyment System process (sdxd) could not create a version
DESCRIPTION
log.
JSR log daemon failed to connect to the forwarder.
JSR log daemon failed to enable the reading of the JSR log from the
forwarder.
event daemon for logging. The JSR log daemon failed to read JSR logs for
the indicated reason.
error with a routing socket.
of itself to run in the background as a daemon.
SERVICED_CLIENT_DISCONNECTED The remote client closed the connection or stopped responding.
SERVICED_CLIENT_ERROR An I/O error caused the termination of a connection with an interface client.
SERVICED_COMMAND_FAILED An error caused a command being executed on an interface client to be
cancelled.
SERVICED_CONNECTION_ERROR The remote client closed the connection when data was expected.
SERVICED_EVENT_FAILED The services PICs process (serviced) could not continue processing a task
because a call to a function in the event library failed.
SERVICED_INIT_FAILED One of the steps in the initialization sequence for the services PICs process
(serviced) failed.
SERVICED_INTERNAL_INCONSISTENCY An internal consistency check failed due to a mismatch between expected
and received values for the specified object.
SERVICED_MALLOC_FAILURE The services PICs process (serviced) could not allocate the number of bytes
needed to hold the indicated object.
SERVICED_NETWORK_FAILURE An attempt to use the indicated network library call failed with an error.
SERVICED_PID_FILE_LOCK As a part of normal startup, the services PICs process (serviced) locks a file
and writes its process ID (PID) into it. It could not lock the file.
SERVICED_PID_FILE_UPDATE As a part of normal startup, the services PICs process (serviced) locks a file
and writes its process ID (PID) into it. It could not write to the file.
SERVICED_RTSOCK_SEQUENCE The services PICs process (serviced) encountered a sequence error while
26 Copyright
receiving messages from the routing socket library.
2010, Juniper Networks, Inc.

Events Detected by AI-Scripts
7
Table 1: Events Detected by AI-Scripts (continued)
EVENT ID
SERVICED_SIGNAL_HANDLER As a part of normal functioning, the services PICs process (serviced)
SERVICED_SOCKET_CREATE An attempt by the services PICs process (serviced) to create a new socket
SERVICED_SOCKET_IO A call to a socket library function indicated that an error occurred while
SERVICED_SOCKET_OPTION An attempt to set an option on a socket failed.
SERVICED_STDLIB_FAILURE The value returned by a call to a library function indicated that an error
SNMP_PATRICIA_ERROR A call to a Patricia tree library function returns an error.
SNMP_RTSLIB_FAILURE A call to the indicated function in the routing socket library failed with the
SNMPD_FILE_FAILURE The Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) agent process (snmpd)
DESCRIPTION
attempted to initialize a signal-handling function. Part of the initialization
failed with an error.
for communication with an interface client failed with an error.
attempting to perform I/O.
occurred.
indicated error
could not access the indicated file.
SNMPD_RMONFILE_FAILURE The indicated operation failed on the indicated remote monitoring (RMON)
data file.
SNMPD_SEND_FAILURE The Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) agent process (snmpd)
could not send either a protocol data unit (PDU) to the User Datagram
Protocol (UDP) or a message to a subagent.
SNMPD_SOCKET_FATAL_FAILURE The Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) agent process (snmpd)
uses sockets for communication with subagents. The process exited after a
socket operation, such as creation or removal, failed.
SNMPD_SUBAGENT_NO_RESOURCES The Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) agent process (snmpd)
uses certain resources for communication with subagents. However, the
resources were not available for communication with the indicated
subagent.
SPD_DAEMONIZE_FAILED The adaptive services process (spd) could not create a version of itself to
run in the background as a daemon.
SPD_EVLIB_CREATE_FAILURE The adaptive services process (spd) could not create a context used for
handling all asynchronous events (such as timers and message av ailability).
SPD_GEN_NUM_FAIL The adaptive services process (spd) attempted to initialize the generation-
number for the service sets. However, the memory allocation failed.
SYSTEM: Alarm set: Temp Too Warm The system is indicating that the sensor on an EX FPC is exceeding the
temperature threshold.
SYSTEM: Keepalive timeout of *. Assuming RE
mastership.
Copyright© 2010, Juniper Networks, Inc. 2
The backup Routing Engine assumed mastership due to an Routing Engine
keepalive timeout.

Advanced Insight Scripts (AI-Scripts) 2.5 Release Notes
©
Table 1: Events Detected by AI-Scripts (continued)
EVENT ID
SYSTEM: writing kernel A kernel crash event. A writing kernel message is captured after the router
SYSTEM:.*cm_read_i2c errno is 5.* The chassis manager event message results from an error in calculating the
SYSTEM:.*cm_read_i2c errno is 5.* The chassis manager event message results from an error in calculating the
SYSTEM:.*snp_igmp_io_flood: relay failed.* This message indicates that the device is flooding IGMP unknown packet
TASK_OS_MEMHIGH The process is using the indicated amount and percentage of Routing
TASK_SYSTEM A system call made by this process failed.
UI_DBASE_REBUILD_FAILED The management process (mgd) could not rebuild the configuration
UI_DBASE_REBUILD_SCHEMA_FAILED The management process (mgd) cou ld not rebuild the schema for the
DESCRIPTION
reboots.
DC power budget for POE interfaces.
DC power budget for POE interfaces.
back on the same port that it was received on.
Engine memory, which is considered excessive.
database file.
configuration database.
UI_DBASE_REOPEN_FAILED After rebuilding the schema file for the configuration database, the
management process (mgd) closes the file and reopens it in read-only mode
to prevent corruption. It could not reopen the file.
UI_SCHEMA_SEQUENCE_ERROR The Junos use r interface schema file records all CLI commands and
configuration statements available in the Junos operating system. The
management process (mgd) rebuilds the schema as necessary to be
compatible with the Junos software installed on the device. A sequence
number in the schema acts as a checksum that represents its content and
format. A Junos process attempted to access the schema but determined
that the schema's sequence number means that it is incompatible with the
process.
UTMD_MALLOC_FAILURE The example process (utmd) could not allocate memory for a resource,
possibly due to a lack of memory.
UTMD_SSAMLIB_FAILURE The example process (utmd) encountered an error while calling a function
or from a callback of the ssamlib library.
VCCPD_PROTOCOL_LSPCKSUM The indicated vccpd link-state PDU (LSP) failed an internal checksum
validity test, implying that it was corrupted.
VCCPD_PROTOCOL_OVERLOAD The vccpd link-state database is full and no additi onal memory can be
allocated for it.
VRRPD_MISSING_VIP The indicated interface received a Virtual Routing Redundancy protocol
(VRRP) packet for the indicated VRRP group in which the indicated Virtual
IP address was missing.
28 Copyright
2010, Juniper Networks, Inc.

Events Detected by AI-Scripts
9
Table 1: Events Detected by AI-Scripts (continued)
EVENT ID
WEB_ALLOCATE The Web management process (httpd) could not allocate the indicated
WEB_MEMORY_ALLOC The Web management process (httpd) could not allocate the indicated
WEB_MGD_LISTEN_ERROR The Web management process (httpd) could not open the mgd listening
WEB_SOCKET The Web management process (httpd) could not create a socket, for the
WEBFILTER_CACHE_NOT_ENABLED The category cache Web filter failed to enable.
WEBFILTER_REQUEST_NOT_CHECKED The Web filtering failed to check a Web request.
DESCRIPTION
amount of memory, for the indicated reason.
number of bytes of memory, for the indicated reason.
socket.
indicated reason.
Copyright© 2010, Juniper Networks, Inc. 2

Advanced Insight Scripts (AI-Scripts) 2.5 Release Notes
Current Software Release
The current AI-Scripts release is Release 2.5R1.
Outstanding Issues
The following issues exist in the current AI-Scripts release:
J Series Services Routers or SRX Series Service Gateways running Junos software with
Enhanced Services in cluster node configurations must have AI-Scripts installed on each
node separately. There is no method for installing the AI-Scripts on both nodes
simultaneously with a single install command. (PR 409931/410417)
Use Junos Scope 9.0R2 or later in conjunction with AI-Scripts 1.1R2 or later to automatically
install AI-Scripts to multiple devices at once.
To upgrade from AI-Scripts 1.0R2 to 1.1R2, follow these steps:
1. Delete the existing scripts by using the request system scripts delete CLI command.
2. At the [edit groups juniper-ais event-options destinations] hierarchy level, change
and commit the event-options destinations name as follows:
user@host# edit groups juniper-ais event-options destinations
user@host# rename juniper-junoscope to juniper-aim
Sometimes a device running AI-Scripts may not appear in the AIM Console. To view the
device in AIM, do the following:
1. From the device to the archive location, make an sFTP or scp connection.
2. For a secure connection, ensure that the host authenticity to the AIM server is
established. For example,
root@staging-sw1% scp test25 jadmin@66.129.225.17:/opt/jmb-archives1/ The
authenticity of host '66.129.225.17 (66.129.225.17)' can't be established. RSA key
fingerprint is 40:16:92:af:d5:7e:54:4f:ad:f7:c8:9a:9a:90:1f:95. Are you sure you want
to continue connecting (yes/no)? yes Warning: Permanently added ‘66.129.225.17'
(RSA) to the list of known hosts. jadmin@66.129.225.17's password:
Intelligence JMBs (iJMBs) may not appear in an AIM archive location, and, therefore, may not
appear in AIM Intelligence Manager. To resolve this issue, follow these steps:
1. Log in to the device as root user.
2. Connect to the AIM server using an SSH connection.
3. Accept the security authentication.
4. Change the archive directory (for example, /var/aim/jmb-archives4/) permissions from
the default of 755 to 733 to allow JMB files to be written using the following command:
chmod 733 jmb-archives4
To confirm directory permissions, use the following command:
ls –l
drwx-wx-wx 2 root root 4096 Sep 16 12:01 jmb-archives4
Copyright© 2010, Juniper Networks, Inc. 30

Issues Fixed Since Last Release
Issues Fixed Since Last Release
The following issues have been fixed in this AI-Scripts release:
Trim the link for the KB note for the event pfestat_req_receive. (PR 545464)
AI-Scripts workaround for JUNOS PR/520377, which generates duplicate cha ssis-module
subtags in Routing Engine section on M320 and some EX Series platforms. (PR 548758)
Modify the problem description field in problem-event-mrvl_brg_port_cist_init.slax to include
the related KB link. (PR 549035)
Trim the KB link for AI-Scripts problem-event-GenCfgBloberror.slax. (PR 551498)
AI-Scripts problem events for protocol-neighbor-related issues in BGP, OSPF, RSVP, and
ISIS have been removed. (PR 555122)
Modify attachments in AI-Scripts event-script problem-event-ichipregerr.slax. (PR 555489)
Junos PRs That Affect AI-Scripts
The following Junos PRs impact certain devices running AI-Scripts (See Table 2 on page 3).
Table 2: Junos PRs Affecting Devices Running AI-Scripts
PR/SUMMARY FIX VERSIONS IMPACT ON DEVICES RUNNING AI-SCRIPTS
Encoder error resulting in invalid JMBs
seen when performing API requests.
(PR 441511)
The AI-Scripts activation sequence
repeats every hour on EX platforms. (PR
440360)
Correct the transient-commit behavior.
(PR 386499)
AI-Scripts increase the commit time to
approximately 10 times, even with and
empty commit. (PR 294131)
• Junos OS Release 9.3R4
• Junos OS Release 9.4R3
• Junos OS Release 9.5R2
• Junos OS Release 9.6R1
• Junos OS Release 10.0R1
• Junos OS Release 9.6R1
• Junos OS Release 9.5R3
• Junos OS Release 10.0R1
• Junos OS Release 9.5S1
• Junos OS Release 9.5R1
• Junos OS Release 9.6R1
• Junos OS Release 9.3R1
• Junos OS Release 9.0R4
• Junos OS Release 9.4R1
• Junos OS Release 9.2R3
• Junos OS Release 9.1R4
• Junos OS Release 9.5R1
All Junos platforms running Junos releases 9.3R1 –
R3. 9.4R1 – R2, or 9.5R1 can experience invalid or
incomplete JMBs generated when problem events are
detected.
Low-end devices without a hard drive may have
frequent log file rollovers, which signals eventd
internal times to reset, generating an iJMB.
Every commit signals eventd internal times to reset,
generating an iJMB, as well as extending the normal
commit time by approximately 20%.
Every commit time may be extended up to 10 times
the normal commit time.
The logger command causing an eventd
crash. (PR 428256)
Copyright© 2010, Juniper Networks, Inc. 31
• Junos OS Release 9.5R2
• Junos OS Release 9.4R3
• Junos OS Release 9.6R1
Any event script that captures an event with two or
more attributes may cause eventd to crash.

Advanced Insight Scripts (AI-Scripts) 2.5 Release Notes
©
Installing AI-Scripts
NOTE: See the “AIS Quick Setup Checklist” in the AIS User Guide for the
sequence of installing all of the AIS components.
AI-Scripts System Requirements on page 3
AI-Scripts/AIM Compatibility on page 3
AI-Scripts Installation Methods on page 3
Downloading AI-Scripts Install Packages on page 3
AI-Scripts Install Package Versioning on page 3
AI-Scripts Install Locations on Devices on page 3
Automatically Installing AI-Scripts Overview on page 3
Automatically Installing AI-Scripts on page 3
Manually Configuring and Installing AI-Scripts on Devices on page 3
AI-Scripts System Requirements
Ensure that all devices on which you install AI-Scripts are running Junos OS Release 9.0 or later.
AI-Scripts/AIM Compatibility
Use Advanced Insight Manager (AIM) release 1.3R1 or later in conjunction with AI-Scripts
releases 1.3R1 or later. For further details regarding compatibility among versions, refe r to the
compatibility matrix at https://www.juniper.net/support/csc/swdist-encr/swdist-ais/
AI-Scripts Installation Methods
There are two ways to install AI-Scripts:
Automatically, using the Junos Scope Script Management feature to automatically install AI-
Scripts to multiple devices at once. For more information about automatically installing AIScripts, see “Automatically Installing AI-Scripts” on page 3.
Manually, by installing AI-Scripts on one device at time. For more information about manually
installing AI-Scripts to devices, see “Manually Configuring and Installing AI-Scripts on
Devices” on page 3.
Downloading AI-Scripts Install Packages
AI-Scripts are released in AI-Scripts install packages. AI-Scripts install packages are available for
download from the AIS download site. Download also the AI-Scripts Release Notes.
To download an AI-Scripts install package, follow these steps:
1. Using a Web browser, go to the following location:
https://www.juniper.net/support/csc/swdist-encr/swdist-ais/
2. Log in to the Juniper Networks authentication system using the username and password
supplied by Juniper Networks.
.
To download the software, you must have a service contract and an access account. If you
do not have an access account, complete the registration form at the Juniper Networks Web
site, https://www.juniper.net/registration/Register.jsp.
32 Copyright
2010, Juniper Networks, Inc.

3
3. Download the AI-Scripts install package. If you will install AI-Scripts manually, move the
package to the /var/sw/pkg directory on the device.
If you do not move the AI-Scripts install package to the device, you have to use ftp or scp in
conjunction with the request system scripts add command. (Optional) If you will use the
Junos Scope software to automatically install an AI-Scripts package to a group of devices at
once, download the AI-Scripts install package on the same server as Advanced Insight
Manager (AIM).
AI-Scripts Install Package Versioning
AI-Scripts install packages are versioned as follows:
jais-m.nZx.x--signed.tgz
or
jais-2.4R1.5-signed.tgz
m and n are two integers that represent the software release number; m denotes the major
release number; n the minor.
Z is a capital letter that indicates the type of software release. In most cases, it is an R, to
indicate that this is released software. If you are involved in testing prereleased software, this
letter might be a B (for beta-level software).
x.x is the software build number and spin number.
Installing AI-Scripts
The AI-Scripts files that are in the install package are compressed into a tgz tarball file.
Each AI-Scripts install package supports up to three previous years of Junos OS releases.
The show version CLI operational command displays the version of the AI-Scripts install
package that is installed on a device.
The JMB contains the output of the show version CLI command to indicate the version of the AI-
Scripts install package installed on a device.
AI-Scripts Install Locations on Devices
AI-Scripts are installed on a device hard disk in the following location:
/var/db/scripts/
AI-Scripts are installed on a device flash drive in the following location:
/config/scripts
NOTE: If you configure the load-scripts-from-flash option, the system reads AI-
Scripts from the /config/scripts/ directory; otherwise, the system reads AIScripts from the /var/db/scripts/ directory. The /var/run/scripts directory will
always point to the right scripts directory.
Automatically Installing AI-Scripts Overview
Automatically installing AI-Scripts install packages to one or more devices involves AIM
interaction with Junos Scope software Script Management.
The automated AI-Scripts installation process requires the following key tasks:
Install and set up Junos Scope 9.0 or later. See the Junos Scope Software User Guide.
Install AIM. See the AIS User Guide.
Set up AIM settings. See the AIS User Guide.
Copyright© 2010, Juniper Networks, Inc. 3

Advanced Insight Scripts (AI-Scripts) 2.5 Release Notes
©
General settings.
Junos Scope settings (Settings > General > JUNOScope Settings).
Set up AI-Scripts bundles (Settings > General > Script Bundles).
Set up organizations.
Set up user groups.
Set up users.
Automatically Installing AI-Scripts
You can optionally use AIM to install AI-Scripts bundles (also known as AI-Scripts install
packages) on devices as long as there is a Junos Scope software installation. AIM communicates
with Junos Scope to install AI-Scripts bundles on devices running Junos OS managed by Junos
Scope.
To configure auto-installation of AI-Scripts bundles to devices, follow these steps:
1. Configure the credentials used to communicate with Junos Scope.
2. Import devices that are managed by Junos Scope.
3. Configure Script Bundles settings.
4. Associate imported devices with a device group.
5. Configure the Script Bundle of the device group and set the No-copy and Unlink installation
attributes.
6. Add archive locations specifying the upload command password attributes. Use the archive
location local directory for JMB files only.
7. Press the Save Changes button. AIM sends a message to Junos Scope to install the selected
script bundle on the associated devices.
If you do not want to use AIM to install AI-Scripts bundles, you can manually configure and
install AI-Script bundles to each device separately. To install AI-Scripts bundles manually,
see “Manually Configuring and Installing AI-Scripts on Devices” on page 3.
Manually Configuring and Installing AI-Scripts on Devices
Within AIM, devices that are configured for AIS manually are automatically added to the device
group that is associated with the AIM archive location to which the JMB was sent. When the AIM
detects a JMB for a device that is not managed by Junos Scope Script Management, it will note it.
NOTE: If you are manually installing to a device that communicates with Junos
Space or Service Now, your login credentials must allow discovery of devices in
Junos Space. This procedure includes the configuration differences required for
configuring the location for JMBs on a Junos Space device.
34 Copyright
2010, Juniper Networks, Inc.

Installing AI-Scripts
5
To manually configure and install AI-Scripts on devices, follow these steps:
1. Download AI-Scripts install packages. See “Downloading AI-Scripts Install Packages” on
page 3.
2. Configure the device configuration as follows to activate AI-Scripts:
a. Enter the device CLI configuration mode. Type the configure command or the edit
command from the CLI operation mode. The CLI prompt changes from user@host> to
user@host# and a banner appears to indicate the hierarchy level.
b. For non–Junos Space devices only: Configure an AIS destination under group juniper-
ais:
user@host#set groups juniper-ais event-options destination juniper-aim {…}
This sets the AIS archive location where JMBs are deposited for a device. The group
name juniper-ais is mandatory. The group destination name juniper-aim is mandatory.
c. For Junos Space devices only: Set the local host address and configure an AIS
destination under group juniper-ais:
user@host#set groups juniper-ais interfaces lo0 unit 0 family inet address
127.0.0.1/32
This sets the local host address 127.0.0.1 to the device loopback address. It is used with
the next command to ensure that JMBs can be sent to and retrieved from the local
device.
user@host#set groups juniper-ais event-options destination juniper-aim
archive-sites "scp://<user>@127.0.0.1://var/tmp" password <password for
user>
Configure this line exactly as shown, substituting <user> and <password for user> with
the Service Now user name and password required for accessing the device. This
configuration ensures the JMBs generated by AI-Scripts are sent to and from the
/var/tmp directory of the device, using the correct permissions for the device. The group
name juniper-ais is mandatory. The group destination name juniper-aim is mandatory.
d. Configure the commit script:
user@host#set groups juniper-ais system scripts commit file jais-activate-
scripts.slax optional
The AI-Scripts installer creates this script to activate AI-Scripts on the device. The
optional setting is required to prevent the configuration from committing if the jaisactivate-scripts.slax file is not present. That file is not present until the scripts bundle is
installed.
e. Configure the allow-transients option to allow transient changes:
user@host#set groups juniper-ais system scripts commit allow-transients
Transient changes are configuration changes made by commit scripts that do not appear
in the configuration (except with a special command).
f. Apply the juniper-ais group:
user@host#set apply-groups juniper-ais
g. (Optional) Configure the load-scripts-from-flash option:
user@host#set groups juniper-ais system scripts load-scripts-from-flash
Copyright© 2010, Juniper Networks, Inc. 3

Advanced Insight Scripts (AI-Scripts) 2.5 Release Notes
©
NOTE: If you configure the load-scripts-from-flash option, the system reads AIScripts from the /config/scripts/ directory; otherwise, the system reads AIScripts from the /var/db/scripts/ directory. The /var/run/scripts directory will
always point to the right scripts directory.
3. Verify that the syntax of a configuration is correct by using the configuration mode commit
check command:
[edit]
user@host# commit check
configuration check succeeds
4. Commit the configuration. To save software configuration changes to the configuration
database and activate the configuration on the router, use the commit configuration mode
command. You can issue the commit command from any hierarchy level.
[edit]
user@host# commit
commit complete
5. View the configuration:
Example Configuration for AIM
groups {
juniper-ais {
system {
scripts {
commit {
allow-transients;
file jais-activate-scripts.slax {
optional;
}
}
load-scripts-from-flash;
}
}
event-options {
destinations {
juniper-aim {
archive-sites {
"ftp://anonymous@10.7.0.124/aimdemo";
}
. . .
Example Configuration for Junos Space
groups {
juniper-ais {
system {
scripts {
commit {
allow-transients;
file jais-activate-scripts.slax {
optional;
}
}
}
}
36 Copyright
2010, Juniper Networks, Inc.

Installing AI-Scripts
7
interfaces {
lo0 {
unit 0 {
family inet {
address 127.0.0.1/32;
}
}
}
}
event-options {
destinations {
juniper-aim {
archive-sites {
"scp://lab@127.0.0.1://var/tmp" password " ... ";
}
}
}
}
}
}
6. If you have not moved the AI-Scripts to the device, do so now. See “Downloading AI-Scripts
Install Packages” on page 3.
7. Install the AI-Scripts package using the following command (see “AI-Scripts Commands” on
page 3):
user@host# request system scripts add <package-name>
8. Verify that the AI-Scripts are activated:
user@host# show groups juniper-ais | display commit-scripts
system {
scripts {
commit {
allow-transients;
file jais-activate-scripts.slax {
optional;
}
}
}
}
event-options {
event-script {
file problem-event-pfecrash.slax;
file problem-event-dcrash.slax;
file intelligence-event-main.slax;
file SPD_EVLIB_CREATE_FAILURE.slax;
file SPD_DAEMONIZE_FAILED.slax;
file RPD_TASK_FORK.slax;
. . .}
destinations {
juniper-aim {
archive-sites {
"ftp://anonymous@10.7.0.124/aidemo";
}
}
}
}
Copyright© 2010, Juniper Networks, Inc. 3

Advanced Insight Scripts (AI-Scripts) 2.5 Release Notes
©
AI-Scripts Commands
Installing an AI-Scripts Package on page
Upgrading an AI-Scripts Package on page 3
Deleting an AI-Scripts Package on page 3
Rolling Back an AI-Scripts Package on page 3
Not Saving Copies of AI-Scripts Package Files During Installation on page 3
Removing AI-Scripts Packages After Installation on page 3
Installing an AI-Scripts Package
To install an AI-Scripts install package on a device, use the following command:
user@host> request system scripts add package-name
Upgrading an AI-Scripts Package
To upgrade an AI-Scripts package, perform steps 1, 7, and 8 of “Manually Configuring and
Installing AI-Scripts on Devices” on page 3.
Deleting an AI-Scripts Package
To delete AI-Scripts from a router, use the following command:
user@host> request system scripts delete
Rolling Back an AI-Scripts Package
After the deletion of an AI-Scripts install package, you can roll back to the last installed package
by using the following command:
user@host> request system scripts rollback
Not Saving Copies of AI-Scripts Package Files During Installation
To prevent the installer from saving copies of AI-Scripts package files in the /var/sw/pkg directory,
use the following command:
user@host> request system scripts add no-copy package-name
NOTE: If you use the no-copy option during the jais installation, the jais package
cannot be rolled back.
You can specify the no-copy option in AIM Device Group settings by selecting the no-copy check
box.
Removing AI-Scripts Packages After Installation
To remove the AI-Script bundle after successful installation, use the following command:
user@host> request system scripts add unlink package-name
You can specify the unlink option in AIM Device Group settings by selecting the unlink check box.
38 Copyright
2010, Juniper Networks, Inc.

9
JUNOS Documentation and Release Notes
For a list of related JUNOS documentation, see http://www.juniper.net/techpubs/software/junos/
If the information in the latest release notes differs from the information in the documentation,
follow the JUNOS Release Notes.
To obtain the most current version of all Juniper Networks
product documentation page on the Juniper Networks website at
http://www.juniper.net/techpubs/.
Juniper Networks supports a technical book program to publish books by Juniper Networks
engineers and subject matter experts with book publishers a round the world. These books go
beyond the technical documentation to explore the nuances of network architecture, deployment,
and administration using the Junos operating system (Junos OS) and Ju niper Networks devices.
In addition, the Juniper Networks Technical Library, published in conjunction with O'Reilly Media,
explores improving network security, reliability, and availability using Junos OS configuration
techniques. All the books are for sale at technical bookstores and book outlets around the world.
The current list can be viewed at http://www.juniper.net/books.
Requesting Technical Support
Technical product support is available through the Juniper Networks Technical Assistance Center
(JTAC). If you are a customer with an active J-Care or JNASC support contract, or are covered
under warranty, and need post-sales technical support, you can access our tools and resources
online or open a case with JTAC.
JUNOS Documentation and Release Notes
®
technical documentation, see the
JTAC policies—For a complete understanding of our JTAC procedures and policies, review
the JTAC User Guide located at http://www.juniper.net/us/en/local/pdf/resourceguides/7100059-en.pdf.
Product warranties—For product warranty information, visit
http://www.juniper.net/support/warranty/.
JTAC hours of operation—The JTAC centers have resources available 24 hours a day, 7
days a week, 365 days a year.
Self-Help Online Tools and Resources
For quick and easy problem resolution, Juniper Networks has designed an online self-se rvice
portal called the Customer Support Center (CSC) that provides you with the following features:
Find CSC offerings: http://www.juniper.net/customers/support/
Search for known bugs: http://www2.juniper.net/kb/
Find product documentation: http://www.juniper.net/techpubs/
Find solutions and answer questions using our Knowledge Base: http://kb.juniper.net/
Download the latest versions of software and review release notes:
http://www.juniper.net/customers/csc/software/
Search technical bulletins for relevant hardware and software notifications:
https://www.juniper.net/alerts/
Join and participate in the Juniper Networks Community Forum:
http://www.juniper.net/company/communities/
Open a case online in the CSC Case Management tool: http://www.juniper.net/cm/
To verify service entitlement by product serial number, use our Serial Number Entitlement (SNE)
Tool: https://tools.juniper.net/SerialNumberEntitlementSearch/
Copyright© 2010, Juniper Networks, Inc. 3

Advanced Insight Scripts (AI-Scripts) 2.5 Release Notes
©
Opening a Case with JTAC
You can open a case with JTAC on the Web or by telephone.
Use the Case Management tool in the CSC at http://www.juniper.net/cm/.
Call 1-888-314-JTAC (1-888-314-5822 toll-free in the USA, Canada, and Mexico).
For international or direct-dial options in countries without toll-free numbers, see
http://www.juniper.net/support/requesting-support.html
Revision History
6 October 2010—Advanced Insight Scripts (AI-Scripts) 2.5R1
40 Copyright
2010, Juniper Networks, Inc.

Revision History
Copyright
©
2010, Juniper Networks, Inc. All rights reserved.
Juniper Networks, Junos, Steel-Belted Radius, NetScreen, and ScreenOS are registered tradema rks of Junipe r Networks,
Inc. in the United States and other countries. The Juniper Networks Logo, the Junos logo, and JunosE are trademarks of
Juniper Networks, Inc. All other trademarks, service marks, registered trademarks, or registered service marks are the
property of their respective owners.
Juniper Networks assumes no responsibility for any inaccuracies in this document. Juniper Networks reserves the right to
change, modify, transfer, or otherwise revise this publication without notice.
Products made or sold by Juniper Networks or components thereof might be covered by one or more of the followin g
patents that are owned by or licensed to Juniper Networks: U.S. Patent Nos. 5,473,599, 5,905,725, 5,909,440, 6,192,051,
6,333,650, 6,359,479, 6,406,312, 6,429,706, 6,459,579, 6,493,347, 6,538,518, 6,538,899, 6,552,918, 6,567,902,
6,578,186, and 6,590,785.
Copyright© 2010, Juniper Networks, Inc. 41
 Loading...
Loading...