JRC NJM3777E3 Datasheet
DUAL STEPPER MOTOR DRIVER
■ GENERAL DESCRIPTION ■ PACKAGE OUTLINE
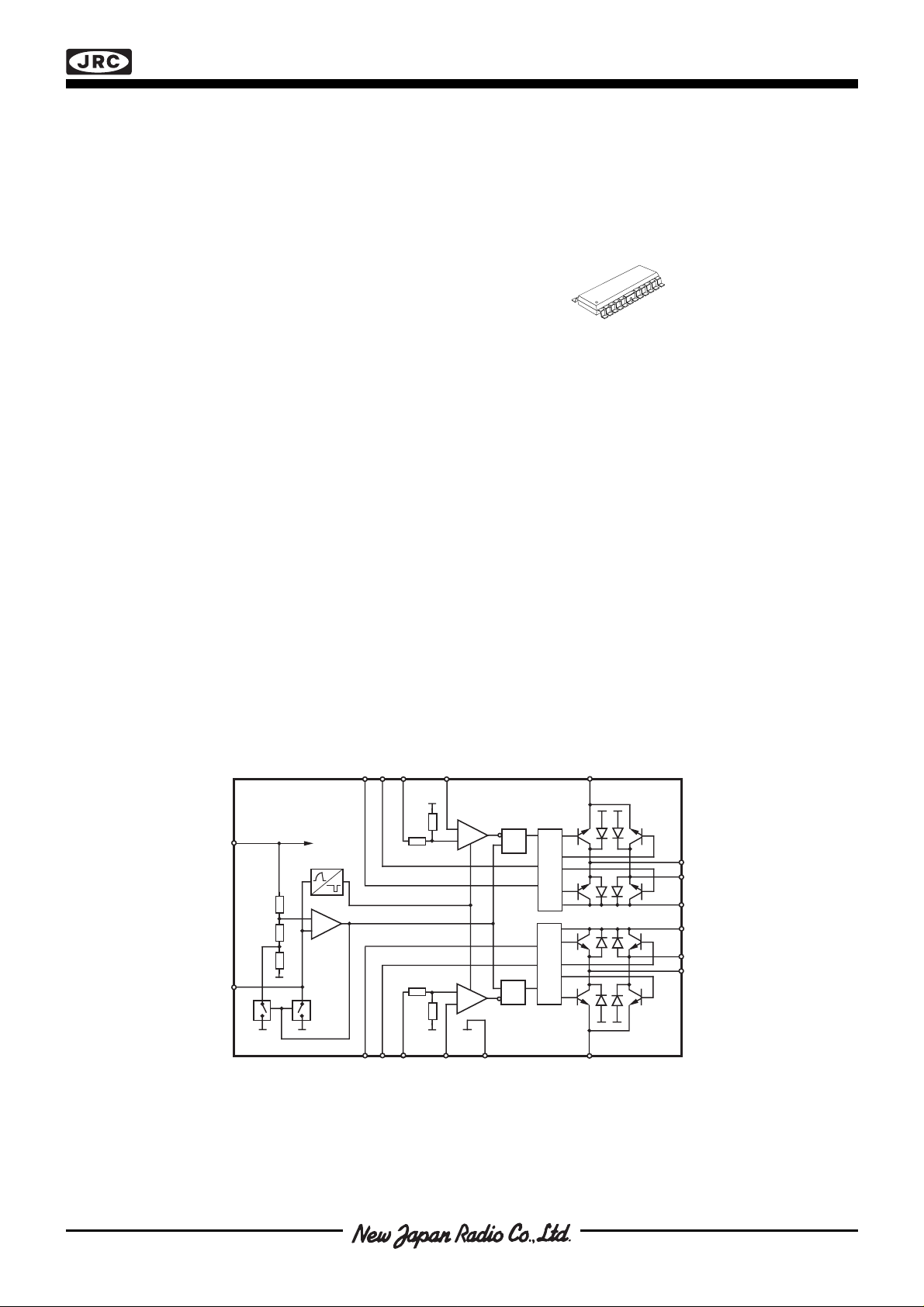
The NJM3777 is a switch-mode (chopper), constant-current
driver with two channels: one for each winding of a two-phase
stepper motor. The NJM3777 is equipped with a Disable input
to simplify half-stepping operation. The NJM3777 contains a
clock oscillator, which is common for both driver channels, a
set of comparators and flip-flops implementing the switching
control, and two output H-bridges, including recirculation
diodes. Voltage supply requirements are + 5 V for logic and +
10 to + 45 V for the motor. Maximum output current is 900mA
per channel.
■ FEATURES
• Dual chopper driver
• 900 mA continuous output current per channel
NJM3777E3
NJM3777
• Digital filter on chip eliminates external filtering components
• Package EMP24(Batwing)
■ BLOCK DIAGRAM
C
V
Dis
1
1
R1
–
+
+
–
V
RC
CC
NJM3777
Phase
1
V
CC
+
–
R
S
SRQ
E
1
Q
M
A1
Logic
Logic
M
B1
V
MM1
V
MM2
M
B2
M
A2
Figure 1. Block diagram
Phase
Dis
V
2
2
R2
GNDC
2
E
2
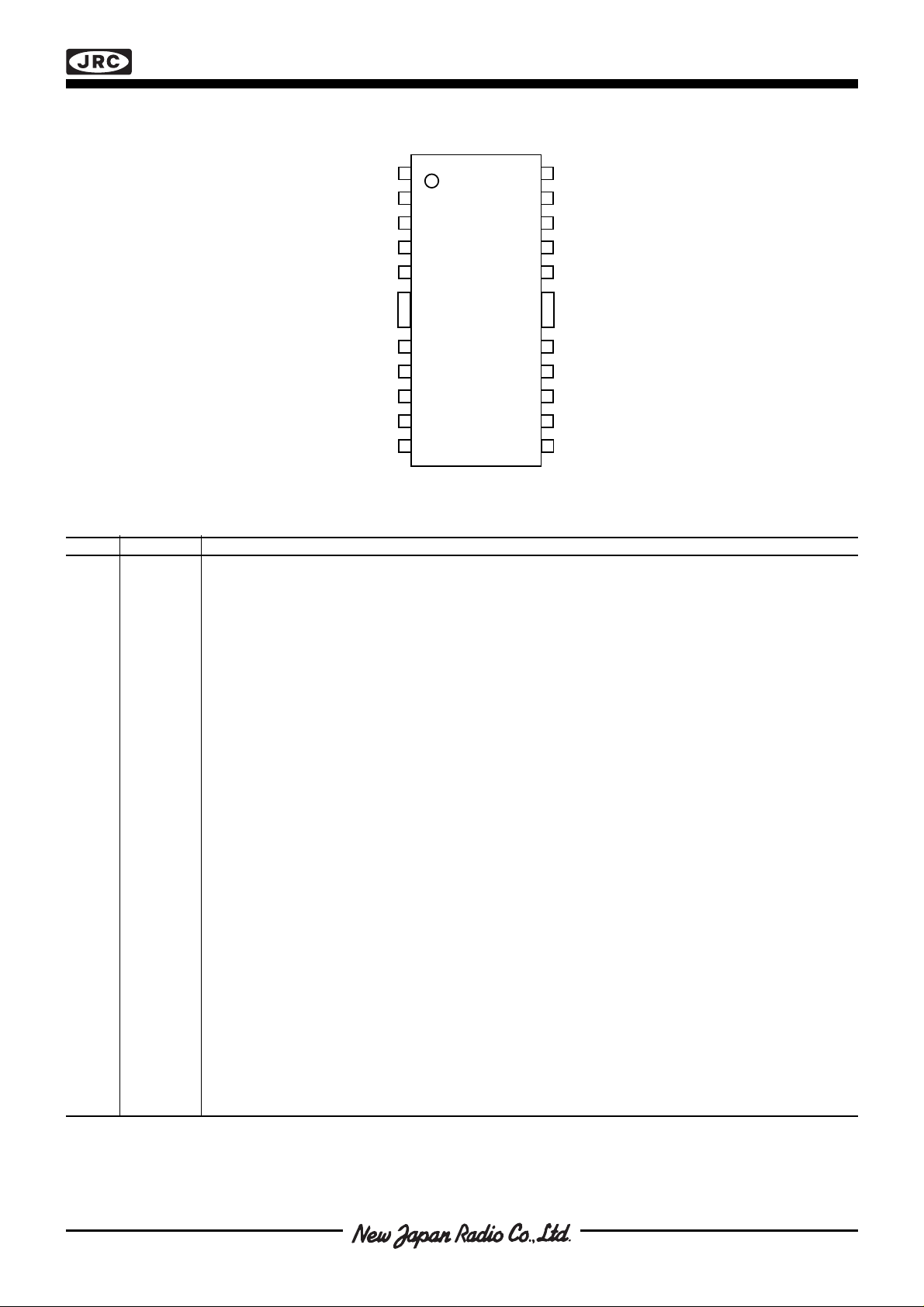
■ PIN CONFIGURATION
Figure 2. Pin configuration
■ PIN DESCRIPTION
NC
MB
MA
VMM
GND
GND
VR
Phase
Dis
RC
NJM3777
1
2
1
E
3
1
4
1
5
1
6
7
8
1
9
C
1
10
1
11
1
NJM
3777E3
24
23
22
21
20
19
18
17
16
15
14
1312
NC
MB
2
E
2
MA
2
VMM
GND
GND
VR
2
C
2
Phase
Dis
2
V
cc
2
2
EMP Symbol Description
1 NC Not connected
2M
3E
4M
5V
B1
1
A1
MM1
Motor output B, channel 1. Motor current flows from MA1 to MB1 when Phase1 is HIGH.
Common emitter, channel 1. This pin connects to a sensing resistor RS to ground.
Motor output A, channel 1. Motor current flows from MA1 to MB1 when Phase1 is HIGH.
Motor supply voltage, channel 1, +10 to +40 V. V
MM1
and V
should be connected together.
MM2
6, 7, GND Ground and negative supply. Note: these pins are used thermally for heat-sinking.
18, 19 Make sure that all ground pins are soldered onto a suitably large copper ground plane for efficient heat -
sinking.
8V
9C
R1
1
Reference voltage, channel 1. Controls the comparator threshold voltage and hence the output current.
Comparator input channel 1. This input senses the instantaneous voltage across the sensing resistor,
filtered by the internal digital filter or an optional external RC network.
10 Phase
11 Dis
Controls the direction of motor current at outputs MA1 and MB1. Motor current flows from MA1 to MB1 when
1
Phase
is HIGH.
1
Disable input for channel 1. When HIGH, all four output transistors are turned off, which results in a
1
rapidly decreasing output current to zero.
12 RC Clock oscillator RC pin. Connect a 12 kohm resistor to V
and a 4 700 pF capacitor to ground to obtain
CC
the nominal switching frequency of 23.0 kHz and a digital filter blanking time of 1.0 µs.
13 V
14 Dis
CC
Logic voltage supply, nominally +5 V.
Disable input for channel 2. When HIGH, all four output transistors are turned off, which results in a
2
rapidly decreasing output current to zero.
15 Phase
16 C
2
Controls the direction of motor current at outputs MA2 and MB2. Motor current flows from MA2 to MB2 when
2
Phase
is HIGH.
2
Comparator input channel 2. This input senses the instantaneous voltage across the sensing resistor,
filtered by the internal digital filter or an optional external RC network.
17 V
20 V
21 M
22 E
23 M
R2
MM2
A2
2
B2
Reference voltage, channel 2. Controls the comparator threshold voltage and hence the output current.
Motor supply voltage, channel 2, +10 to +40 V. V
MM1
and V
should be connected together.
MM2
Motor output A, channel 2. Motor current flows from MA2 to MB2 when Phase2 is HIGH.
Common emitter, channel 2. This pin connects to a sensing resistor RS to ground.
Motor output B, channel 2. Motor current flows from MA2 to MB2 when Phase2 is HIGH.
24 NC Not connected
NJM3777
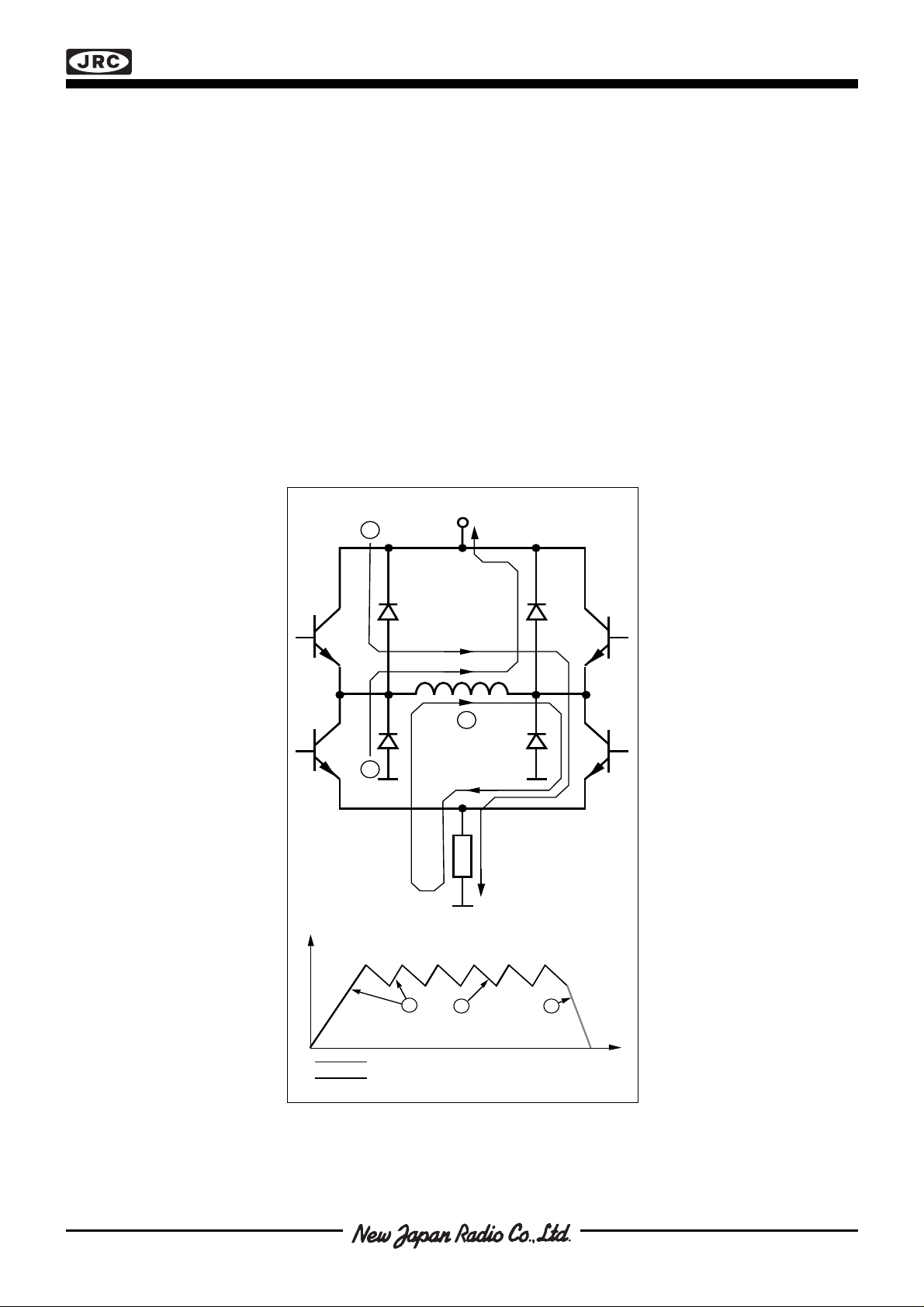
■ FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION
Each channel of the NJM3777 consists of the following sections: an output H-bridge with four transistors and four
recirculation diodes, capable of driving up to 800 mA continuous current to the motor winding, a logic section that
controls the output transistors, an S-R flip-flop, and a comparator. The clock-oscillator is common to both channels.
Constant current control is achieved by switching the output current to the windings. This is done by sensing the
peak current through the winding via a current-sensing resistor RS, effectively connected in series with the motor
winding. As the current increases, a voltage develops across the sensing resistor, which is fed back to the comparator. At the predetermined level, defined by the voltage at the reference input VR, the comparator resets the flipflop, which turns off the upper output transistor. The turn-off of one channel is independent of the other channel.
The current decreases until the clock oscillator triggers the flip-flops of both channels simultaneously, which turns
on the output transistors again, and the cycle is repeated.
To prevent erroneous switching due to switching transients at turn-on, the NJM3777 includes a digital filter. The
clock oscillator provides a blanking pulse which is used for digital filtering of the voltage transient across the
current sensing resistor during turn-on.
The current paths during turn-on, turn-off and phase shift are shown in figure 3.
V
MM
1
2
3
R
S
Motor Current
1 2
Fast Current Decay
Slow Current Decay
3
Figure 3. Output stage with current paths
during turn-on, turn-off and phase shift.
Time
 Loading...
Loading...