STEPPER MOTOR CONTROLLER / DRIVER
■ GENERAL DESCRIPTION ■ PACKAGE OUTLINE
NJM3517 is a stepper motor controller/driver, which requires
minimum of external components and drive currents up to 500mA.
The NJM3517 is suited for applications requiring least-possible RFI.
Operating in a bi-level drive mode can increase motor performance;
high voltage pulse is applied to the motor winding at the beginning
of a step, in order to give a rapid rise of current.
■ FEATURES
• Internal complete driver and phase logic
• Continuous-output current 2 x 350mA
• Half- and full-step mode generation
• LS-TTL-compatible inputs
• Bi-level drive mode for high step rates
NJM3517D2
NJM3517E2
NJM3517
• Voltage-doubling drive possibilities
• Half-step position-indication output
• Minimal RFI
• Packages DIP16 / EMP16
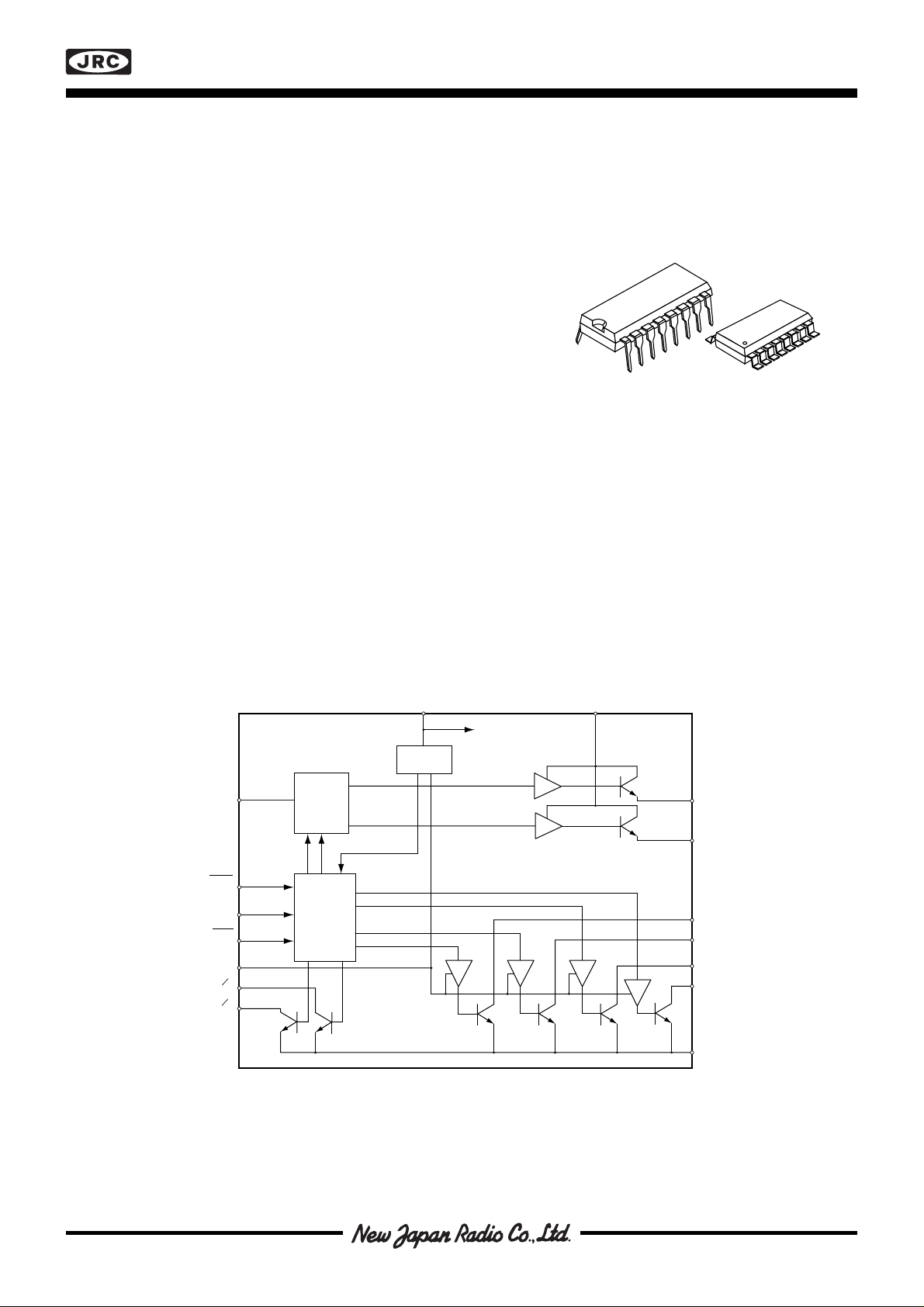
■ BLOCK DIAGRAM
NJM3517
RC
STEP
DIR
HSM
INH
O
OB
A
Mono
F - F
Phase
Logic
V
CC
POR
P
A
P
B
V
SS
L
A
L
B
P
B2
P
B1
P
A2
P
A1
Figure 1. Block diagram
GND
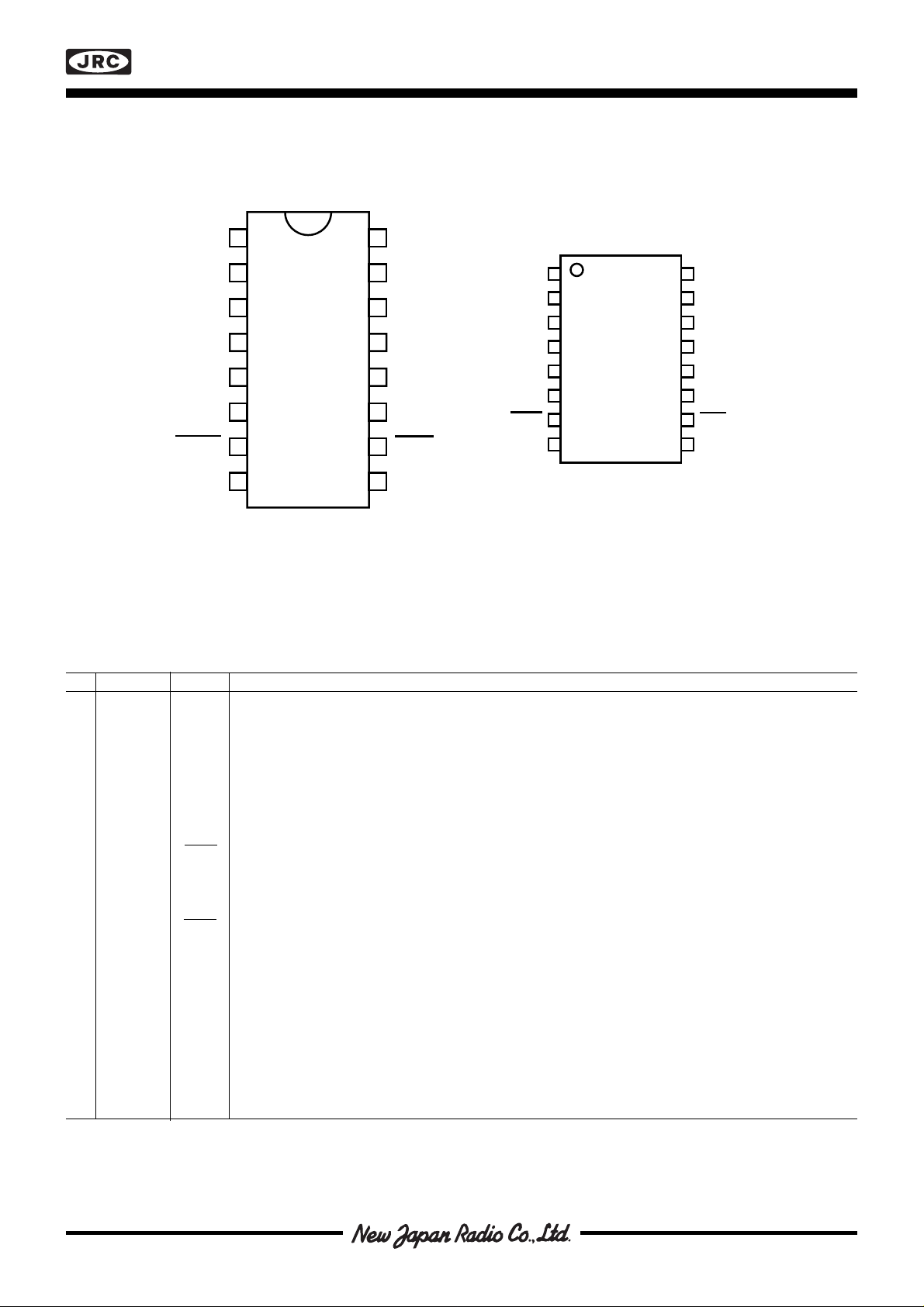
■ PIN CONFIGURATIONS
NJM3517
P
1
B2
P
2
B1
GND
STEP
P
A1
P
A2
DIR
Ø
3
4
5
NJM
3517D2
6
7
8
B
Fugure 2.Pin configurations
■ PIN DESCRIPTION
DIP EMP-pack. Symbol Description
16
15
14
13
12
11
10
9
V
CC
V
SS
L
B
L
A
R
C
INH
HSM
Ø
A
P
P
GND
P
P
DIR
STEP
Ø
1
B2
2
B1
3
NJM
4
A1
3517E2
5
A2
6
7
8
B
V
16
CC
15
V
SS
14
L
B
13
L
A
12
R
C
11
INH
10
HSM
9
Ø
A
11 PB2Phase output 2, phase B. Open collector output capable of sinking max 500 mA.
22 P
3 3 GND Ground and negative supply for both V
44 P
55 P
Phase output 1, phase B. Open collector output capable of sinking max 500 mA.
B1
and VSS.
CC
Phase output 1, phase A.
A1
Phase output 2, phase A.
A2
6 6 DIR Direction input. Determines in which rotational direction steps will be taken.
7 7 STEP Stepping pulse. One step is generated for each negative edge of the step signal.
8 8 ØB Zero current half step position indication output for phase B.
9 9 ØA Zero current half step position indication output for phase A.
10 10 HSM Half-step mode. Determines whether the motor will be operated in half or full-step
mot. When pulled low, one step pulse will correspond to a half step of the motor.
11 11 INH A high level on the inhibit input turns all phase output off.
12 12 RC Bi-level pulse timing pin. Pulse time is approximately t
= 0.55 • RT • C
on
T
13 13 LA Second level (bi-level) output, phase A.
14 14 LB Second level (bi-level) output, Phase B.
15 15 V
16 16 V
Second level supply voltage, +10 to +40 V.
SS
Logic supply voltage, nominally +5 V.
CC
NJM3517
■ FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION
The circuit, NJM3517, is a high performance motor driver, intended to drive a stepper motor in a unipolar, bi-level
way. Bi-level means that during the first time after a phase shift, the voltage across the motor is increased to a
second voltage supply, VSS, in order to obtain a more-rapid rise of current, see figure 25.
The current starts to rise toward a value which is many times greater than the rated winding current. This com-
pensates for the loss in drive current and loss of torque due to the back emf of the motor.
After a short time, tOn, set by the monostable, the bi-level output is switched off and the winding current flows from
the VMM supply, which is chosen for rated winding current. How long this time must be to give any increase in
performance is determined by VSS voltage and motor data, the L/R time-constant.
In a low-voltage system, where high motor performance is needed, it is also possible to double the motor voltage
by adding a few external components, see figure 4.
The time the circuit applies the higher voltage to the motor is controlled by a monostable flip-flop and determined
by the timing components RT and CT.
The circuit can also drive a motor in traditional unipolar way.
An inhibit input (INH) is used to switch off the current completely.
■ LOGIC INPUTS
All inputs are LS-TTL compatible. If any of the logic inputs are left open, the circuit will accept it as a HIGH level.
NJM3517 contains all phase logic necessary to control the motor in a proper way.
STEP — Stepping pulse
One step is generated for each negative edge of the STEP signal. In half-step mode, two pulses will be required to
move one full step. Notice the set up time, ts, of DIR and HSM signals. These signals must be latched during the
negative edge of STEP, see timing diagram, figure 6.
V
SS
V
MM
+ 5V
CMOS, TTL-LS
Input / Output-Device
HALF / FULL STEP
NORMAL /INHIBIT
(Optional Sensor)
GND (V
CC
V
MM
+ 5V
CMOS, TTL-LS
Input / Output-Device
GND (V
V
CC
STEP
CW / CCW
GND
)
V
CC
STEP
CW / CCW
HALF / FULL STEP
NORMAL /INHIBIT
(Optional Sensor)
GND
)
CC
D3
+++
C3C4C
V
CC
16
PQR
RC 12
Mono
F - F
C
R
T
T
R9
R8
STEP 7
DIR 6
HSM 10
INH 11
9
O
A
OB 8
RC 12
C
R
T
T
R9
R8
STEP 7
DIR 6
HSM 10
INH 11
9
O
A
OB 8
Phase
Logic
Phase
Logic
Mono
F - F
P
A
P
B
C3C
V
CC
16
PQR
P
A
P
B
5
V
++
R1
4
V
SS
15
NJM3517
SS
15
13 L
A
14 L
B
1 P
B2
2 P
B1
5 P
A2
4 P
A1
3 GND
NJM3517
13 L
A
14 L
B
Equal to
1 P
B2
Phase A
2 P
B1
5 P
A2
4 P
A1
3 GND
Q1
Q3
R2
R4
R5
D2 D1
R11 R10
MOTOR
C1
+
1/2 MOTOR
R12 R13
Q5
D3-D6
D3-D6 are
UF 4001 or
BYV 27
trr < 100 ns
GND (VMM,VSS)
D1
R10
Q6
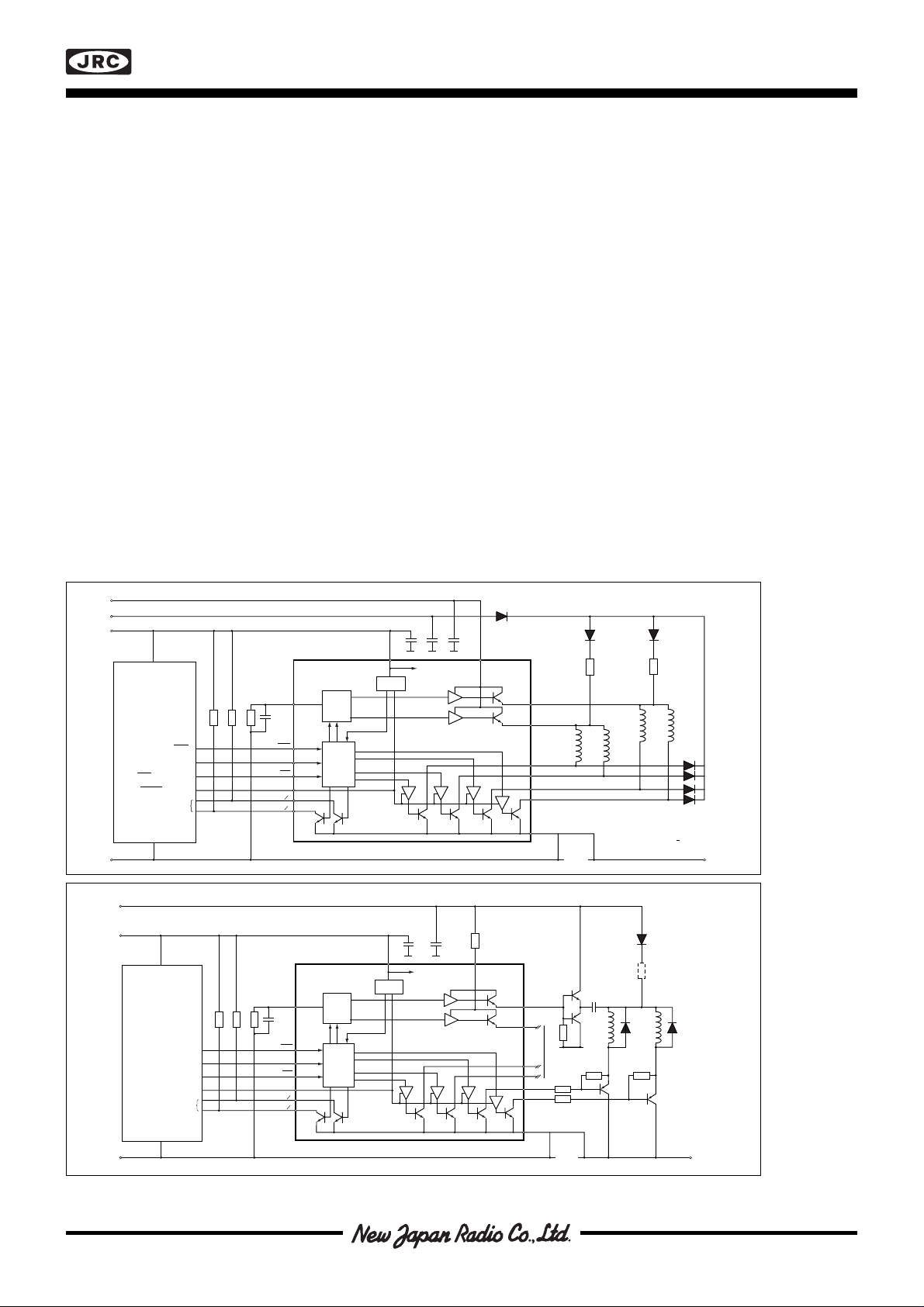
Figure 3.
Typical
application
Figure 4.
Voltage
doubling with
external
GND (V
MM,VSS
)
transistors

NJM3517
DIR — Direction
DIR determines in which direction steps will be taken. Actual direction depends on motor and motor connections.
DIR can be changed at any time, but not simultaneously with STEP, see timing diagram, figure 6.
HSM determines whether the motor will be controlled in full-step or half-step mode. When pulled low, a steppulse will correspond to a half step of the motor. HSM can be changed at any time, but not simultaneously with
STEP, see timing diagram, figure 6.
INH — Inhibit
A HIGH level on the INH input,turns off all phase outputs to reduce current consumption.
■ RESET
An internal Power-On Reset circuit connected to Vcc resets the phase logic and inhibits the outputs during power
up, to prevent false stepping.
■ OUTPUT STAGES
The output stage consists of four open-collector transistors. The second high-voltage supply contains Darlington
transistors.
■ PHASE OUTPUT
The phase outputs are connected directly to the motor as shown in figure 3.
■ BI-LEVEL TECHNIQUE
The bi-level pulse generator consists of two monostables with a common RC network.
The internal phase logic generates a trigger pulse every time the phase changes state. The pulse triggers its own
monostable which turns on the output transistors for a precise period of time:
tOn = 0.55 • CT • RT.
See pulse diagrams, figures 7 through 11.
■ BIPOLAR PHASE LOGIC OUTPUT
The ØA and ØB outputs are generated from the phase logic and inform an external device if the A phase or the B
phase current is internally inhibited. These outputs are intended to support if it is legal to correctly go from a halfstep mode to a full-step mode without loosing positional information.
The NJM3517 can act as a controller IC for 2 driver ICs, the NJM3770A. Use PA1 and PB1 for phase control, and
ØA and ØB for I0 and I1 control of current turnoff.
 Loading...
Loading...