Page 1

Version: 26/9/2016
PoKeys57CNC
User’s manual
Page 2

PoKeys user manual
2
www.poscope.com
Please read the following notes
1. All information included in this document is current as of the date this document is issued. Such information, however, is subject to
change without any prior notice.
2. PoLabs does not assume any liability for infringement of patents, copyrights, or other intellectual property rights of third parties by or
arising from the use of PoLabs products or technical information described in this document. No license, express, implied or otherwise,
is granted hereby under any patents, copyrights or other intellectual property rights of PoLabs or others. PoLabs claims the copyright
of, and retains the rights to, all material (software, documents, etc.) contained in this release. You may copy and distribute the entire
release in its original state, but must not copy individual items within the release other than for backup purposes.
3. Descriptions of circuits, software and other related information in this document are provided only to illustrate the operation of the
products and application examples. You are fully responsible for the incorporation of these circuits, software, and information in the
design of your equipment. PoLabs assumes no responsibility for any losses incurred by you or third parties arising from the use of
these circuits, software, or information.
4. PoLabs has used reasonable care in preparing the information included in this document, but PoLabs does not warrant that such
information is error free. PoLabs assumes no liability whatsoever for any damages incurred by you resulting from errors in or
omissions from the information included herein.
5. PoLabs devices may be used in equipment that does not impose a threat to human life in case of the malfunctioning, such as:
computer interfaces, office equipment, communications equipment, test and measurement equipment, audio and visual equipment,
home electronic appliances, machine tools, personal electronic equipment, and industrial robots.
6. Measures such as fail-safe function and redundant design should be taken to ensure reliability and safety when PoLabs devices are
used for or in connection with equipment that requires higher reliability, for example: traffic control systems, anti-disaster systems,
anticrime systems, safety equipment, medical equipment not specifically designed for life support, and other similar applications.
7. PoLabs devices shall not be used for or in connection with equipment that requires an extremely high level of reliability and safety, as
for example: aircraft systems, aerospace equipment, nuclear reactor control systems, medical equipment or systems for life support
(e.g. artificial life support devices or systems), and any other applications or purposes that pose a direct threat to human life.
8. You should use the PoLabs products described in this document within the range specified by PoLabs, especially with respect to the
maximum rating, operating supply voltage range and other product characteristics. PoLabs shall have no liability for malfunctions or
damages arising out of the use of PoLabs products beyond such specified ranges.
9. Although PoLabs endeavors to improve the quality and reliability of its products, semiconductor products have specific characteristics
such as the occurrence of failure at a certain rate and malfunctions under certain use conditions. Further, PoLabs products are not
subject to radiation resistance design. Please be sure to implement safety measures to guard them against the possibility of physical
injury, and injury or damage caused by fire in the event of the failure of a PoLabs product, such as safety design for hardware and
software including but not limited to redundancy, fire control and malfunction prevention, appropriate treatment for aging
degradation or any other appropriate measures.
10. Usage: the software in this release is for use only with PoLabs products or with data collected using PoLabs products.
11. Fitness for purpose: no two applications are the same, so PoLabs cannot guarantee that its equipment or software is suitable for a
given application. It is therefore the user's responsibility to ensure that the product is suitable for the user's application.
12. Viruses: this software was continuously monitored for viruses during production, however the user is responsible for virus checking the
software once it is installed.
13. Upgrades: we provide upgrades, free of charge, from our web site at www.poscope.com. We reserve the right to charge for updates or
replacements sent out on physical media.
14. Please contact a PoLabs support for details as to environmental matters such as the environmental compatibility of each PoLabs
product. Please use PoLabs products in compliance with all applicable laws and regulations that regulate the inclusion or use of
controlled substances, including without limitation, the EU RoHS Directive. PoLabs assumes no liability for damages or losses occurring
as a result of your noncompliance with applicable laws and regulations.
15. Please contact a PoLabs support at support@poscope.com if you have any questions regarding the information contained in this
document or PoLabs products, or if you have any other inquiries.
16. The licensee agrees to allow access to this software only to persons who have been informed of and agree to abide by these
conditions.
17. Trademarks: Windows is a registered trademark of Microsoft Corporation. PoKeys, PoKeys55, PoKeys56U, PoKeys56E, PoKeys57U,
PoKeys57E, PoKeys57CNC, PoKeys57CNCdb25, PoScope, PoLabs and others are internationally registered trademarks.
Page 3

PoKeys user manual
3
www.poscope.com
Contents
1. Introduction ..................................................................................................................................... 7
2. Features ........................................................................................................................................... 8
3. Device hardware description........................................................................................................... 9
3.1. PoKeys57CNC connector pinout ............................................................................................ 11
Pin types ........................................................................................................................................ 11
Power supply ................................................................................................................................. 11
SSR (Solid State Relay) connector .................................................................................................. 12
Relays connector ........................................................................................................................... 12
Galvanically isolated I/Os .............................................................................................................. 12
LCD connector ............................................................................................................................... 12
Pendant connector ........................................................................................................................ 13
Encoders connector ....................................................................................................................... 15
ADC connector ............................................................................................................................... 15
Motor connectors 1-8 ................................................................................................................... 16
Axis switches connector ................................................................................................................ 16
Additional limit switches ............................................................................................................... 16
DB-25 (LPT-port) IO connector ...................................................................................................... 17
3.2. Pin types and specifications .................................................................................................. 18
Type DI5P: Digital input with filtering ........................................................................................... 18
Type DO5: 5 V digital output ......................................................................................................... 18
Type DO5_D: 5 V digital output without resistor .......................................................................... 18
Type DIO33: 3,3 V digital input or output ..................................................................................... 19
Type OCOC: opto-coupled open-collector output ........................................................................ 19
Type OCSSR: open-collector output for SSR (Solid State Relay) .................................................... 20
Type REL: relay output .................................................................................................................. 20
Type AN33: 3.3 V analog input ...................................................................................................... 20
Type AN33F: 3.3 V analog input with low-pass filter .................................................................... 21
3.3. Status LEDs ............................................................................................................................ 21
4. Requirements ................................................................................................................................ 22
5. Technical specifications ................................................................................................................. 23
5.1. PoKeys57CNC dimensions ..................................................................................................... 23
5.2. Environment specifications ................................................................................................... 23
6. Installation ..................................................................................................................................... 24
Page 4

PoKeys user manual
4
www.poscope.com
6.1. Using USB .............................................................................................................................. 24
6.2. Using Ethernet - direct connection between PoKeys57CNC and computer ......................... 24
6.3. Using Ethernet - PoKeys57CNC connected to a network with DHCP server ......................... 25
6.1. Using USB and Ethernet ........................................................................................................ 25
6.2. Motor drivers and peripherals installation ........................................................................... 25
7. PoKeys configuration options ........................................................................................................ 26
7.1. Digital inputs and outputs ..................................................................................................... 26
PoKeys configuration software usage ........................................................................................... 26
7.2. Digital counters ..................................................................................................................... 28
PoKeys configuration software usage ........................................................................................... 28
7.3. Encoders ................................................................................................................................ 29
PoKeys configuration software usage ........................................................................................... 30
7.4. Pulse engine .......................................................................................................................... 32
Pulse engine status/control dialog parts ....................................................................................... 33
Axis configuration panel ................................................................................................................ 34
Homing algorithm configuration ................................................................................................... 35
Common homing algorithm configurations .................................................................................. 36
Limit and home switch filters ........................................................................................................ 37
PoStep drivers configuration ......................................................................................................... 37
Connecting PoStep drivers to PoKeys57CNC ................................................................................. 38
7.5. Matrix keyboard .................................................................................................................... 40
PoKeys configuration software usage ........................................................................................... 40
7.6. Analog inputs ......................................................................................................................... 42
PoKeys configuration software usage ........................................................................................... 42
7.7. Joystick mapping ................................................................................................................... 43
PoKeys configuration software usage ........................................................................................... 43
7.8. PWM outputs ........................................................................................................................ 44
PoKeys configuration software usage ........................................................................................... 45
7.9. LCD ......................................................................................................................................... 46
PoKeys configuration software usage ........................................................................................... 46
7.10. PoExtBus ............................................................................................................................ 49
PoKeys configuration software usage ........................................................................................... 49
PoExtBus connector type .............................................................................................................. 49
7.11. PoNET ................................................................................................................................ 50
Page 5

PoKeys user manual
5
www.poscope.com
Adding new devices ....................................................................................................................... 51
PoNET kb48CNC keyboard............................................................................................................. 52
7.12. Failsafe settings ................................................................................................................. 53
7.13. Peripheral communication protocols ................................................................................ 54
I2C protocol .................................................................................................................................... 54
1-wire............................................................................................................................................. 55
7.14. EasySensors ....................................................................................................................... 56
EasySensors configuration dialog .................................................................................................. 56
Scan for I2C sensors ....................................................................................................................... 56
Scan for 1-wire sensors ................................................................................................................. 57
Add DHTxx 1-Wire sensor .............................................................................................................. 57
Add analog sensor ......................................................................................................................... 57
List of supported sensors .............................................................................................................. 59
7.15. USB interface configuration .............................................................................................. 60
Start options .................................................................................................................................. 60
Communication interval ................................................................................................................ 60
Enabling/disabling the interfaces .................................................................................................. 61
7.16. Network device functionality ............................................................................................ 62
Device discovery ............................................................................................................................ 62
Default network settings ............................................................................................................... 63
Connecting to device in other network ......................................................................................... 63
Security .......................................................................................................................................... 64
Web interface (dashboard) ........................................................................................................... 65
Modbus .......................................................................................................................................... 68
Reporting data to network server with PoKeys57CNC device ...................................................... 71
7.17. Changing User ID number ................................................................................................. 77
7.18. Saving current configuration to file ................................................................................... 77
7.19. PoIL core functionality ....................................................................................................... 77
8. Device recovery mode ................................................................................................................... 78
9. Frequently asked questions .......................................................................................................... 79
10. Errata information ..................................................................................................................... 80
PoKeys device resets when external power supply is applied or removed .................................. 80
External pull-up resistor needed on the probing input ................................................................. 80
11. Grant of license ......................................................................................................................... 81
Page 6

PoKeys user manual
6
www.poscope.com
Page 7

PoKeys user manual
7
www.poscope.com
1. Introduction
PoKeys products line consists of simple, easy-to-use USB and network devices with the extended list
of features making them powerful input/output devices. PoKeys57CNC features both USB and
Ethernet connectivity, giving user an option to select the preferred connection for the application.
The device is highly adjustable and as such requires no complex knowledge on device programming.
PoKeys57CNC is a blend between general purpose PoKeys device and motor controller. The device is
targeted primarily for controlling up to 8 STEP/DIR signal driven motors (stepper motors, servo
drives, etc.) in various applications with the addition of powerful PoKeys device features. Device
contains dedicated connectors for connections with motor drivers, pendants, (HD44780-compatible)
LCD module, etc. In addition, 5 analog inputs with 12-bit resolution are available. The device also
features four galvanically-isolated open-collector outputs and 0 to 10 V analog output.
The device runs the PoIL core and is fully compatible with PoBlocks graphical programming software,
bringing Programmable Logic Controller to a motor controller board. PoBlocks can be used to simply
automate different peripherals and interchange data with other software applications that are using
PoKeys57CNC device.
PoKeys USB products integrate support for virtual USB keyboard and USB joystick, which can be used
to emulate a standard USB keyboard and joystick. Digital input pins can be mapped to virtual
keyboard and joystick keys, while analog inputs can be mapped to virtual joystick axes. Configuration
is simple by using our intuitive graphical PoKeys configuration application, where each function can
also be tested.
A dedicated PoExtBus/PoNET connector can be used to extend the number of digital outputs for
additional 80 outputs in the form of either relay outputs or open-collector outputs. It can also be
used to connect various additional peripherals (e.g. PoKeysKBD48CNC pendant) and I2C sensors.
Third-party application developers that are adding the support for PoKeys devices, are encouraged to
use the supplied communication DLL that can be simply used in the different .NET framework based
applications and various other programming languages that provide support for ActiveX interface.
There is even an open-source cross-platform C library available at https://bitbucket.org/mbosnak/pokeyslib.
To aid developers that are communicating with PoKeys devices on the low-level, the extensive
documentation on device communication protocol can be downloaded free of charge from the
product webpage.
Page 8

PoKeys user manual
8
www.poscope.com
2. Features
- Compatible with USB 1.1/2.0 HID standard,
- standard English USB keyboard simulation (with triggering support for up/down keys),
- standard USB joystick simulation (6 axes, 32 buttons with triggering support),
- Ethernet 10/100 with DHCP client or fixed IP support,
- TCP or UDP connection with the device,
- Modbus TCP support (access to digital IO, analog inputs, encoder values, digital counters
values, PWM outputs, LCD display, PoExtBus devices, matrix keyboard status),
- web interface with newly designed dashboard and I/O status display with multiple user
accounts,
- 28 digital inputs or outputs (software configurable) with pull-up resistors and available as
virtual USB keyboard keys. There are additional 4 dedicated digital outputs,
- 5 analog inputs (12-bit) with digital low-pass filtering (4 analog inputs also include analog
low-pass filter with 1.9 kHz cut-off frequency),
- multiple encoder pair inputs with three additional dedicated high-speed encoder and one
ultra high-speed encoder inputs,
- digital counters on specific digital input pins,
- high performance 8-axis 125 kHz pulse engine with dedicated motor connectors,
- up to 16x8 matrix keyboard with triggered keys/alternate function support,
- up to 4 high-speed fully configurable PWM outputs (25MHz PWM timer) - two of them with
open-collector transistor outputs,
- dedicated connector for HD44780-based character LCD (up to 4x20 characters),
- dedicated connector for PoPendant1,
- PoExtBus support for adding up to 10 external shift registers (e.g. PoExtBusOC16,
PoExtBusRE, etc.),
- PoNET devices support (48-key CNC keyboard),
- fail-safe support in case of communication interruption,
- support for up to 100 sensors, that can be connected to I
purpose analog inputs,
- intuitive and user-friendly software,
- third-party support via communication DLL library and extensive protocol specification
document that allows porting to other systems.
2
C bus, 1-wire bus or on the general
Page 9

PoKeys user manual
9
www.poscope.com
3. Device hardware description
Page 10

PoKeys user manual
10
www.poscope.com
Page 11

PoKeys user manual
11
www.poscope.com
Type code
Description
DI5P
5 V digital input with input filtering
DI33P
3,3 V digital input with input filtering
DO5
5 V digital output
DO5_D
5 V digital output without series resistor
DIO33
3,3 V digital input or output without filtering
OCOC
Opto-coupled open-collector output
OCSSR
Open-collector outputs for SSR
REL
Relay output
AN33
3,3 V analog input without filtering
AN33F
3,3 V analog input with 1,9 kHz low-pass
filtering
Pin
Type
Function
1
Supply input
Positive power supply 6-26V (marked with +)
2
Supply input
Negative power supply (ground)
3.1. PoKeys57CNC connector pinout
Pin types
See chapter 3.2 Pin types for details on the listed pin types.
Power supply
PoKeys57CNC requires external 6-26V power supply to be connected to the board in order for the
device to operate correctly (device may not operate according to the specifications if the external
power supply is not present). The device uses switching power converter to scale down the input
power supply to 5V. The power supply should be capable of providing at least 2.5W.
The PoKeys57CNC v1.2 features a jumper to select the power supply source. Move the jumper to
the ‘USB’ position during testing the board without the external power supply connected. Otherwise,
put the jumper to the ‘EXT’ position.
Page 12

PoKeys user manual
12
www.poscope.com
Pin
Type
Function
1
OCSSR
SSR2 output
2
+5V
+5V output (power supply to SSR relay)
3
OCSSR
SSR1 output
Pin
Type
Function
1
REL
Relay 2 NO
2
REL
Relay 2 common
3
REL
Relay 1 NO
4
REL
Relay 1 common
Pin
Type
Label
Function
1
GNDi
GNDi
Isolated ground connection (for use only with signals on this connector)
2
DI5P
SpEr
Spindle error input
3 - 10V
0-10V analog output
4
GNDi
GNDi
Isolated ground connection
5
OCOC
OC4+
Open collector output 4
6
OCOC
OC4-
7
OCOC
OC3+
Open collector output 3
8
OCOC
OC3-
9
OCOC
OC2+
Open collector output 2
10
OCOC
OC2-
11
OCOC
OC1+
Open collector output 1
12
OCOC
OC1-
Pin
Type
Label
Function
1
GND
GND
Ground
2
+5V
+5V
+5V power supply for LCD
3
DIO33
RST
LCD contrast voltage, also used as PoKeys pin 18 with PWM and reset pin
(see Device recovery mode for more details)
4
DIO33
RS
LCD RS signal, also used as PoKeys pin 291
5
DIO33
R/W
LCD R/W signal, also used as PoKeys pin 28
6
DIO33
E
LCD Enable signal, also used as PoKeys pin 301
1
SSR (Solid State Relay) connector
The solid state relays should be connected between +5V output and corresponding SSR output pin.
Note: all +5V output pins on the board share the same power supply and the current is distributed to
all loads.
Relays connector
Galvanically isolated I/Os
This connector contains special I/O signals that are galvanically isolated from the rest of the board.
Signals on pins 2 and 3 should only be referenced to GNDi points (available on pins 1 and 4).
LCD connector
Digital counter functionality can be enabled for this pin
Page 13

PoKeys user manual
13
www.poscope.com
7 - -
not connected
8 - -
not connected
9 - -
not connected
10 - -
not connected
11
DIO33
D4
LCD D4 signal, also used as PoKeys pin 26
12
DIO33
D5
LCD D5 signal, also used as PoKeys pin 25
13
DIO33
D6
LCD D6 signal, also used as PoKeys pin 24
14
DIO33
D7
LCD D7 signal, also used as PoKeys pin 23
15
+5V
LED+
+5 V power supply for LCD backlight with 4,7 Ω resistor in series
16
OC
LED-
Open-collector output (max. 100 mA), also used as PoKeys pin 22 with
PWM
Pin
Type
Label
Function
1
+5V
+5V
+5 V power supply to pendant (used for encoder/MPG power)
2
GND
GND
Ground
3
GND
GND
Ground
4
DI33P
E-stop
E-stop signal input, also used as PoKeys pin 52 (connect E-stop switch
between pins 4 and 6) - see notes below
5
DIO33
FastEncA
Encoder channel A, also used as PoKeys pin 12
6
GND-E
E-Stop
E-stop switch GND - see notes below
7
DIO33
FastEncB
Encoder channel B, also used as PoKeys pin 22
8
GND
GND
Ground
9
+5V
LED+
+5 V power supply for pendant LED
10
DI33P
Ax-B
Axis B selection signal, also used as PoKeys pin 32
11
OC
LED-
Open-collector output (max. 100 mA), also used as PoKeys pin 21 with
PWM
12
DI33P
Ax-C
Axis C selection signal, also used as PoKeys pin 42
13
DI33P
Ax-X
Axis X selection signal, also used as PoKeys pin 92
14 - -
not connected
15
DI33P
Ax-Y
Axis Y selection signal, also used as PoKeys pin 102
16 - -
not connected
17
DI33P
Ax-Z
Axis Z selection signal, also used as PoKeys pin 112
18
GND
GND
Ground
19
DI33P
Ax-A
Axis A selection signal, also used as PoKeys pin 52
20
GND
GND
Ground
21
DI33P
Step x1
Step x1 selection signal, also used as PoKeys pin 62
22
GND
GND
Ground
23
DI33P
Step x10
Step x10 selection signal, also used as PoKeys pin 152
24
GND
GND
Ground
25
DI33P
Step x100
Step x100 selection signal, also used as PoKeys pin 162
26
GND
GND
Ground
2
Pendant connector
Note: E-stop switch can be connected either to dedicated E-stop connector (red 4-pin connector) or
to pendant connector (a combination of both is also allowed since both are wired in series).
Digital counter functionality can be enabled for this pin
Page 14

PoKeys user manual
14
www.poscope.com
a) E-stop switch is connected to dedicated 4-pin E-stop connector between pins 2 and 3.
Jumper 'NeST' must be removed and inserted into the pendant connector between pins 4
and 6
b) E-stop switch is connected to pendant connector (between pins 4 and 6). Jumper 'NeST' must
be present
c) Two E-stop switches are connected - one to dedicated 4-pin E-stop connector (betwen pins 2
and 3) and one to pendant connector (between pins 4 and 6).
Page 15

PoKeys user manual
15
www.poscope.com
Pin
Type
Label
Function
1
+5V
+5V
Axis enable signal (inverted)
2
GND
GND
Ground
3
DIO33
uFEA
Ultra-fast encoder A-channel signal input, also used as PoKeys pin 8
4
GND
GND
Ground
5
DIO33
uFEB
Ultra-fast encoder B-channel signal input, also used as PoKeys pin 12
6
GND
GND
Ground
7
DIO33
uFEI
Ultra-fast encoder index signal input, also used as PoKeys pin 13
8
GND
GND
Ground
9
DIO33
PK20
PoKeys pin 20 with PWM3
10
GND
GND
Ground
Pin
Type
Label
Function
1
GND
GND
Ground
2
GND
GND
Ground
3
AN33F
PK41
PoKeys pin 41
4
AN33F
PK42
PoKeys pin 42
5
+3,3V
+3,3V
6 +3,3V
+3,3V
7 AN33F
PK43
PoKeys pin 43
8
AN33F
PK44
PoKeys pin 44
9
AN33/DIO33
PK45
PoKeys pin 45
10
GND
GND
Ground
3
Encoders connector
ADC connector
Digital counter functionality can be enabled for this pin
Page 16

PoKeys user manual
16
www.poscope.com
Pin
Type
Label
Function
1
DO5
/AXEn
Axis enable signal (inverted)
2
GND
GND
Ground
3
DO5
DIR
Direction signal
4
GND
GND
Ground
5
DO5
STEP
Step signal
6
GND
GND
Ground
7
DI5P
/ERRORin
Error input signal (from stepper driver to PoKeys)
8
GND
GND
Ground
9
+5V
5V
+5V output to stepper driver
10
GND
GND
Ground
Pin
Type
Label
Function
1
GND
GND
Ground
2
GND
GND
Ground
3
DI5P
AX8-
Axis 8 limit- switch
4
DI5P
AX8 H
Axis 8 home switch
5
DI5P
AX7-
Axis 7 limit- switch
6
DI5P
AX7 H
Axis 7 home switch
7
DI5P
AX6-
Axis 6 (C) limit- switch
8
DI5P
AX6 H
Axis 6 (C) home switch
9
DI5P
AX5-
Axis 5 (B) limit- switch
10
DI5P
AX5 H
Axis 5 (B) home switch
11
DI5P
AX4-
Axis 4 (A) limit- switch
12
DI5P
AX4 H
Axis 4 (A) home switch
13
DI5P
AX3-
Axis 3 (Z) limit- switch
14
DI5P
AX3 H
Axis 3 (Z) home switch
15
DI5P
AX2-
Axis 2 (Y) limit- switch
16
DI5P
AX2 H
Axis 2 (Y) home switch
17
DI5P
AX1-
Axis 1 (X) limit- switch
18
DI5P
AX1 H
Axis 1 (X) home switch
19
GND
GND
Ground
20
GND
GND
Ground
Pin
Type
Label
Function
1
GND
GND
Ground
2
DI5P
AX1+
Axis 1 (X) limit+ switch
3
DI5P
AX2+-
Axis 2 (Y) limit+ switch
4
DI5P
AX3+
Axis 3 (Z) limit+ switch
5
DI5P
AX4+
Axis 4 (A) limit+ switch
6
DI5P
AX5+
Axis 5 (B) limit+ switch
7
DI5P
AX6+
Axis 6 (C) limit+ switch
8
DI5P
AX7+
Axis 7 limit+ switch
Motor connectors 1-8
Axis switches connector
Additional limit switches
Page 17

PoKeys user manual
17
www.poscope.com
9
DI5P
AX8+
Axis 8 limit+ switch
10
GND
GND
Ground
11
GND
GND
Ground
12
DI5P
Probe
Probe input
On PoKeys57CNC v1.0, v1.1 and v1.2 external pull-up resistor must
be used
Pin
Type
Label
Function
1
DO5
/AXEn1
Axis 1 (X) enable signal (inverted)
2
DO5
STEP1
Step signal for axis 1 (X)
3
DO5
DIR1
Direction signal for axis 1 (X)
4
DO5
STEP2
Step signal for axis 2 (Y)
5
DO5
DIR2
Direction signal for axis 2 (Y)
6
DO5
STEP3
Step signal for axis 3 (Z)
7
DO5
DIR3
Direction signal for axis 3 (Z)
8
DO5
STEP4
Step signal for axis 4 (A)
9
DO5
DIR4
Direction signal for axis 4 (A)
10
DI5P
AX3+
Axis 3 (Z) limit+ switch
11
DI5P
AX5+
Axis 5 (B) limit+ switch
12
DI5P
AX2+
Axis 2 (Y) limit+ switch
13
DI5P
AX1+
Axis 1 (X) limit+ switch
14
DO5_D
PK20
PoKeys pin 20 (output only)
15
DI5P
AX4+
Axis 4 (A) limit+ switch
16
DO5_D
PK45
PoKeys pin 45 (output only)
17
DO5
/AXEn2
Axis 2 (Y) enable signal (inverted)
18
GND
GND
Ground
19
GND
GND
Ground
20
GND
GND
Ground
21
GND
GND
Ground
22
GND
GND
Ground
23
GND
GND
Ground
24
GND
GND
Ground
25
GND
GND
Ground
26
GND
GND
Ground
DB-25 (LPT-port) IO connector
Warning: on PoKeys57CNC v1.1 the pinout is not compatible with the LPT-based stepper drivers since
the physical pin numbering sequence in PoKeys57CNC v1.1 differs from that of a real DB-25
connector. Check the pinout diagrams above.
The connector on the PoKeys57CNC v1.2 is compatible with the LPT-based stepper drivers.
Page 18
PoKeys user manual
18
www.poscope.com
Symbol
Parameter
Min
Max
Unit
V
DI5P,MAX
maximum voltage applied to DI5P pin
-
5,5 V V
DI5P,LOW
applied voltage for LOW state
-
0,2 V V
DI5P,HIGH
applied voltage for HIGH state
1,6 - V
Symbol
Parameter
Min
Max
Unit
I
DO5,MAX
maximum current supplied by DO5 pin
- 8 mA
V
DO5,LOW
voltage of LOW state (no current)
-
0,1
V
V
DO5,HIGH
voltage of HIGH state (no current)
4,9 - V
R
DO5,HIGH
internal resistance of the digital output
100
TBD
Ohm
Symbol
Parameter
Min
Max
Unit
I
DO5_D,MAX
maximum current supplied by DO5 pin
-
50
mA
V
DO5_D,LOW
voltage of LOW state (no current)
-
0,1 V V
DO5_D,HIGH
voltage of HIGH state (no current)
4,9 - V
3.2. Pin types and specifications
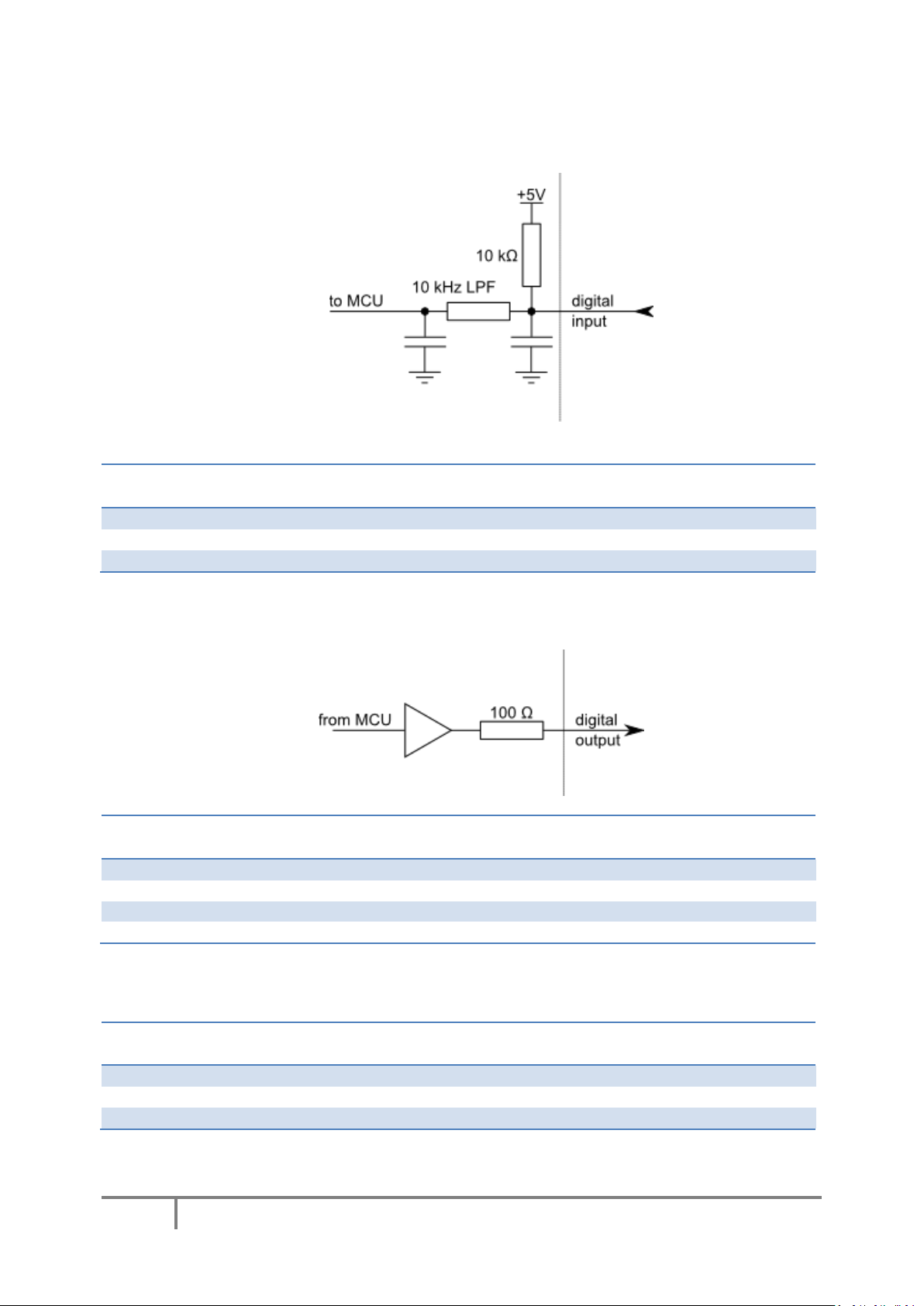
Type DI5P: Digital input with filtering
Type DO5: 5 V digital output
Type DO5_D: 5 V digital output without resistor
Page 19
PoKeys user manual
19
www.poscope.com
Symbol
Parameter
Min
Max
Unit
I
pu
pull-up current
0 (V
I
>= 3.3V)
-100
µA
Pin used as digital output
I
DO33,MAX
maximum current supplied by DO33 pin
- 4 mA
V
DO33,LOW
voltage of LOW state (no current)
0 - V
V
DO33,HIGH
voltage of HIGH state (no current)
-
3,3 V Pin used as digital input
V
DI5,MAX
maximum voltage applied to DI5 pin
-
5,0 V V
DI5,LOW
applied voltage for LOW state
-
0,8
V
V
DI5,HIGH
applied voltage for HIGH state
2,0 - V
Symbol
Parameter
Min
Max
Unit
I
OCOC,MAX
maximum output current
-
50
mA
V
OCOC,DIFF
maximum voltage applied between OC+ and OC-
-
50 V V
OCOC,ISO
isolation voltage (AC for 1min, R.H. 40-60%)
-
3000
V
RMS
Type DIO33: 3,3 V digital input or output
Digital pin directly connected to MCU.
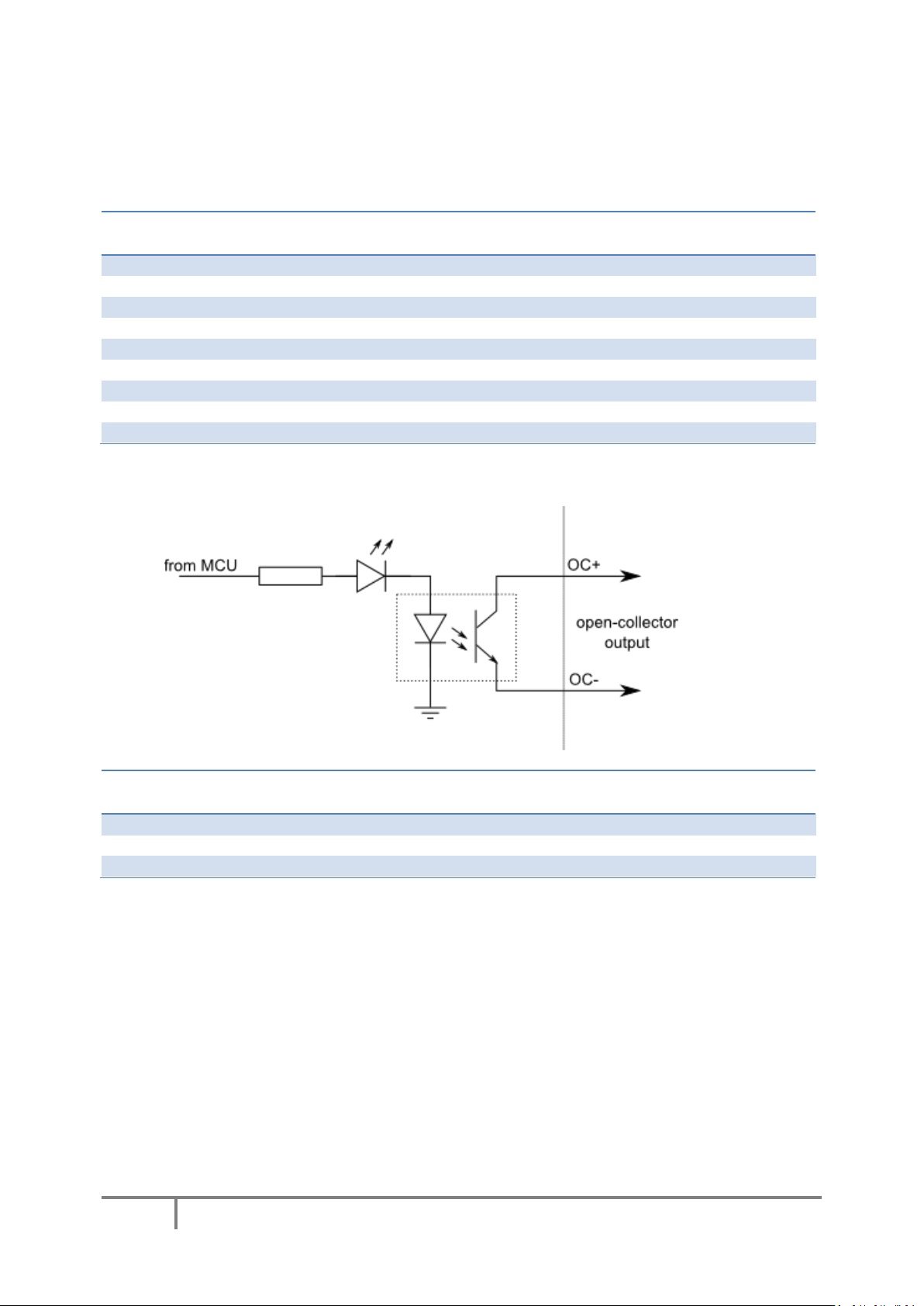
Type OCOC: opto-coupled open-collector output
Page 20

PoKeys user manual
20
www.poscope.com
Symbol
Parameter
Min
Max
Unit
I
OCSSR,MAX
maximum current sunk by OCSSR pin
-
500
mA
U
OCSSR,MAX
maximum voltage applied to OCSSR pin
- 5 V
Symbol
Parameter
Min
Max
Unit
I
REL,28VDC
maximum current switching at 28 VDC
-
10 A I
REL,125VAC
maximum current switching at 125 VAC
-
10 A I
REL,240VAC
maximum current switching at 240 VAC
- 7 A
Symbol
Parameter
Min
Max
Unit
V
IA
analog input voltage on ADC related pins
-0.5
3.3
V
Type OCSSR: open-collector output for SSR (Solid State Relay)
Type REL: relay output
Type AN33: 3.3 V analog input
Page 21

PoKeys user manual
21
www.poscope.com
Symbol
Parameter
Min
Max
Unit
V
IA
analog input voltage on ADC related pins
-0.5
3.3 V f
LP
cut-off frequency of the analog low-pass filter
1.6
2.2
kHz
Type AN33F: 3.3 V analog input with low-pass filter
3.3. Status LEDs
o TBD
Page 22

PoKeys user manual
22
www.poscope.com
4. Requirements
- 6-26 V power supply with 2.5 W or more,
- one available USB 1.1 or USB 2.0 port,
- Ethernet connection between host computer and PoKeys57CNC device,
- USB HID device driver enabled operating system (Windows 98 SE/ME/2000/XP/Vista, Linux,
Mac OS),
- included software requires Windows XP/Vista/7/8/8.1 with .NET framework 3.5 installed.
Page 23
PoKeys user manual
23
www.poscope.com
Parameter
Min
Typ
Max
Unit
Power supply range
6 - 26
V
Operating temperature
0 - 60
°C
Storage temperature
-40 - 85
°C
Humidity
5 - 95 (non-condensing)
% RH
5. Technical specifications
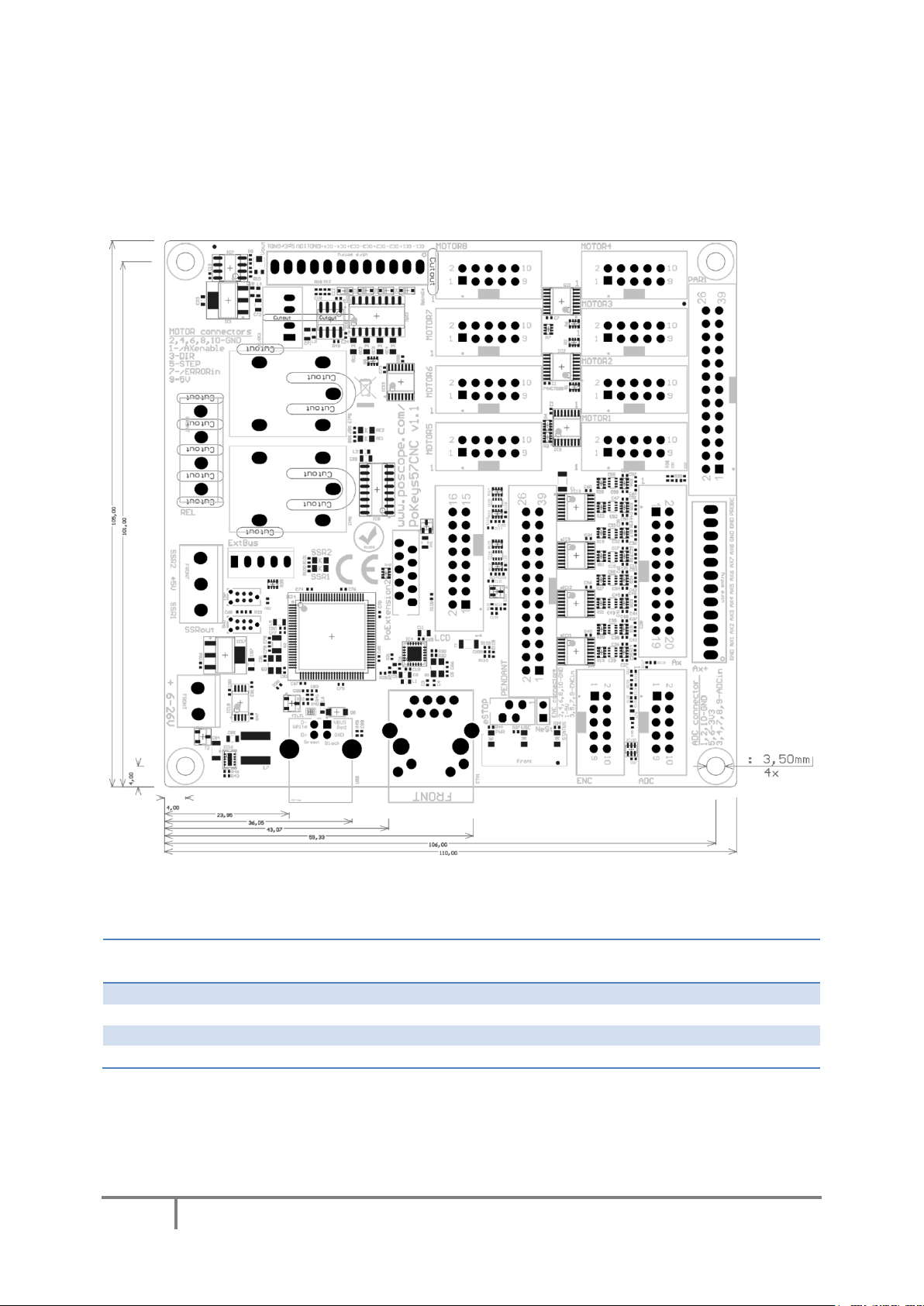
5.1. PoKeys57CNC dimensions
Measurements are in mm.
5.2. Environment specifications
Page 24

PoKeys user manual
24
www.poscope.com
Step 1: Locate a free USB 2.0 port on your
computer (1) and PoKeys57CNC board (2) and
connect them with a standard USB cable.
Step 2: Connect the PoKeys57CNC board to an
appropriate power supply (3).
Step 3: Install PoKeys software
Step 4: Open PoKeys application, connect to
your PoKeys57CNC device and enable Fast USB
interface (go to Settings > Enable Fast USB
interface).
Step 5: Remove the USB cable from
PoKeys57CNC device and insert it again. The
computer will find a new device and search for
drivers. See FAQ section of the manual if driver
installation fails.
Step 1: Locate ethernet ports on your computer
(1) and PoKeys57CNC board (2) and connect
them with RJ-45 cable (standard network cable).
Step 2: Connect the PoKeys57CNC board to an
appropriate power supply (3).
Step 3: Configure your computer's network card
with a static IP address in the 192.168.x.x range
Step 4: Install PoKeys software
Step 5: Start PoKeys software, select the
PoKeys57CNC device in the list and click on
'Configure' button. Select the unique IP address
for the PoKeys57CNC device in the same range as
the computer's network card
6. Installation
6.1. Using USB
PoKeys57CNC is a USB 1.1/2.0 compliant device.
6.2. Using Ethernet - direct connection between PoKeys57CNC and computer
Network firewalls must allow all traffic on TCP/UDP port 20055 between PoKeys57CNC device and
PoKeys-related software running on a computer.
Page 25

PoKeys user manual
25
www.poscope.com
Step 1: Locate ethernet ports on your router (1)
and PoKeys57CNC board (2) and connect them
with RJ-45 cable (standard network cable).
Step 2: Connect the PoKeys57CNC board to an
appropriate power supply (3).
Step 3: Install PoKeys software
6.3. Using Ethernet - PoKeys57CNC connected to a network with DHCP server
Network firewalls must allow all traffic on TCP/UDP port 20055 between PoKeys57CNC device and
PoKeys-related software running on a computer.
6.1. Using USB and Ethernet
PoKeys57CNC device can also be connected to computer by using both the USB and Ethernet
connection. In this case, applications will detect two instances of PoKeys57CNC devices and USB
connection will be selected by default by third-party applications.
Follow the above instructions on connecting the PoKeys57CNC device over Ethernet and USB.
6.2. Motor drivers and peripherals installation
Connect motor drivers to dedicated 10-pin axis motor connectors, marked as MOTOR1, MOTOR2 …
MOTOR8.
Connect pendant to the dedicated pendant connector.
Page 26

PoKeys user manual
26
www.poscope.com
4
7. PoKeys configuration options
7.1. Digital inputs and outputs
Unlike generic PoKeys devices, PoKeys57CNC doesn’t have generic pin headers with fully
customizable pin functions. Certain pins of the dedicated connectors on PoKeys57CNC can be reused
for other purposes if not used by the specific peripheral device. See the connector pinout diagram to
discover which pins can be reused as digital inputs or digital outputs. Pin numbers were assigned
according to the available functions of each pin in order to keep the device back-compatible with 3rd
party software.
Although primarily targetted for CNC applications, PoKeys57CNC shares the same virtual USB
keyboard and joystick capability of PoKeys USB series of devices. Digital pins can be mapped to
virtual keyboard keys or virtual joystick buttons. On activation, PoKeys device sends a USB message
with the key code and modifier associated with this pin. Moreover, PoKeys57CNC device can also
simulate a series of key presses, what is called a macro sequence. Up to 64 different macro
sequences can be setup with the combined total length of 3584 characters with each macro
sequence shorter than 128 keys. All macros can be labelled with a 7-character name.
An extension to the USB keyboard mapping described above, PoKeys supports also triggered
mapping of inputs to USB keyboard keys. In triggered mapping mode, only pin state transitions (lowto-high or high-to-low trigger a USB key press) with different key combinations for each transition.
Type-matic like repeat and delay is an additional extension to the triggered key mapping. Instead of
relying on the user’s system to trigger key repeat events, PoKeys can be configured to simulate
repeated key presses at the predefined rate (period between two key presses is adjustable in 5 ms
cycles – 0.78 to 200 repeats possible4) after a predefined delay (adjustable in steps of 5 ms – 0 to
1275 ms possible).
PoKeys configuration software usage
There is graphical representation for configuration of each PoKeys device’s pin on left and right side
of main window. To change pin function, click on pin name and change its function in central ‘Pin
settings’ frame.
Figure 1: PoKeys configuration window
The maximum repeat rate depends on the user's system
Page 27

PoKeys user manual
27
www.poscope.com
There are 6 main pin functions possible: inactive, digital input, triggered digital input, digital output,
analog input, depending on the capabilities of each pin.
Inactive
Any pin (except those fixly mapped to an activated peripheral) can be set as inactive. Inactive pin is
put in high-Z state with internal pull-up resistors enabled.
Digital input
Any free pin can be configured as digital input by selecting ‘Digital input’ option box. If the pin
polarity is wished to be inverted, check the 'Invert pin' box.
There are several additional possibilities for digital input pin functions.
Direct key mapping – only if connected over USB
Digital input set up for direct key mapping acts like a keyboard key. When there is a high state on pin
(on low state when using inverted option), PoKeys device sends a key associated with this pin. Select
a keyboard key from drop-down box and check appropriate key modifiers (Shift, Ctrl, …).
Triggered digital input
Triggered digital input function is activated by selecting ‘Triggered input’ option box. This pin mode
enables user to select a key that is pressed only when a transition in a signal occurs. Different keys
can be selected for ‘LOW-to-HIGH’ or ‘Key up’ event and for ‘HIGH-to-LOW’ or ‘Key down’ event.
Selecting the keys is similar to Direct key mapping described above.
Digital output
Most of the available pins (check the pin capabilities in device pinout section of this manual) can be
configured as digital output by selecting ‘Digital output’ option box. If the polarity of the pin is wished
to be inverted, check the 'Invert pin' box. On startup, all pins (although optionally configured as
digital output) are by default initialized in high-Z state (behaving like inputs). To use the outputs,
SetPinData should be called before attempting to set the output state. However, there is an option to
disable this behaviour - use the ‘Settings > Initialize outputs on startup’ option to either enable or
disable output activation on PoKeys startup.
View status of digital inputs and outputs
Go to ‘Peripherals > Digital inputs and outputs…’ to display the status dialog as shown below.
Figure 2: Input and output status dialog
Page 28

PoKeys user manual
28
www.poscope.com
There are 55 pins represented as colored squares in the dialog, organized in the rows of 8 pins. Each
square contains a pin index number in the lower left corner, while the lower right corner is used to
indicate a digital output (small black triangle is displayed on pins, configured as digital outputs). The
color of the square resembles the current state of the pin – green for the activated (HIGH state) and
white for the unactivated (LOW state).
To change the digital output state, first enable ‘Enable output control’ option, then either left or right
click with mouse on the square representing the digital output to activate or deactivate this output.
7.2. Digital counters
Selected pins of the PoKeys device can be setup to count the number of signal transitions on those
pins. Pin digital counter can be setup to be incremented/decremented on rising, falling or rising and
falling edges of the input signal. If needed, additional pin can be selected to toggle between
incrementing and decrementing mode.
Digital counters are implemented using interrupts and can therefore detect short signal pulses (even
shorter than 1 microsecond). If switches are used in the combination with digital counters, external
debouncing circuit must be installed to keep the digital counters from counting additional pulses due
to switch contact bouncing on making or braking the contact.
Check PoKeys device pinout section to discover which pins are compatible with digital counter
option.
PoKeys configuration software usage
To setup digital counter inputs, first set the selected pin as ‘Digital input’ and if digital counter is
available on the selected pin, the ‘Enable counter’ option will be enabled. Check this option and
check ‘rising’ and/or ‘falling’ edge counting option.
To enable selection between incrementing or decrementing counter modes, a direction pin can be
selected in the ‘Direction pin’ drop-down menu. If no pin is selected, the counter mode defaults to
incrementing mode.
Digital counters values status page (menu ‘Peripherals > Digital counters values…’) can be used to
check the proper working of the configured digital counters
Page 29

PoKeys user manual
29
www.poscope.com
7.3. Encoders
PoKeys devices can handle decoding of up to 26 pairs of quadrature encoder signals. A and B signals
of 25 'normal' encoders can be connected to any digital input and are intended for hand-driven
rotational encoder switches with the quadrature signal frequencies up to 1 kHz.
Three fast encoders input pairs are available only on selected input pins (pins 1-2 as encoder 1, pins
5-6 as encoder 2, pins 15-16 as encoder 3) and can handle quadrature signal frequencies to about
100 kHz. When activated, fast encoders logically replace the 'normal' encoders 1, 2 and 3.
Although fast encoders can track encoders at high speed, using this feature can have an impact on
device performance. It is not advised to use these to track axis position using a high-resolution
encoder in connection with Pulse engine feature.
Ultra-fast encoder support is available on pins 8, 12 with the optional index signal input on pin 13.
This feature uses hardware specialized hardware decoder and can handle even higher frequencies
(up to 5 MHz with digital filtering disabled), but only x2 and x4 step multiplication factors are
available.
Samilarly as simple digital inputs, encoders can be assigned to direct key mapping or keyboard macro
(only when USB connection is used). This is possible for both directions (CW and CCW) separately the keyboard mapping of pin A is activated on positive change of the encoder value, while the
keyboard mapping of pin B is activated on negative change of the encoder value.
Except for ultra-fast encoders, the encoder value can be multiplied by 1x (one ‘tick’), 2x or 4x. The 4x
mode increments encoder value on every signal edge and increases the resolution of the encoder for
a factor of 4.
Figure 3: Encoder settings in PoKeys application
Page 30

PoKeys user manual
30
www.poscope.com
PoKeys configuration software usage
To enable encoder input on the selected pin, define the pin as digital input, switch to
‘Encoders/Counters’ tab, select encoder index with numerical up-down selector and select
appropriate encoder channel. The last step is to check the box ‘Encoder’.
To assign a key combination associated with the encoder, use the same procedure as described in
the ‘Digital inputs and outputs’ section.
Enabling fast encoders
To enable fast encoders, go to menu 'Peripherals > Fast encoders settings’, then check ‘Enable fast
encoders’ option. There are additional options for inverting the encoders’ directions, disabling 4x
step multiplication and enabling the index signal on pins 9, 11 and 27. If index signal input is enabled,
encoder value is automatically reset on low to high index signal transition.
Fast encoders inputs are fixed to pins 1-2 for fast encoder 1, pins 5-6 for fast encoder 2 and pins 1516 for fast encoder 3.
Enabling ultra-fast encoders
To enable ultra-fast encoders, go to menu 'Peripherals > Fast encoders settings’, then check ‘Enable
ultra-fast encoders’ option. There are additional options to enable 4x step multiplication and
inverting the encoder direction. Digital filter sampling delay slider enables setting the digital filter
delay parameter - leftmost position equates to no digital filtering, rightmost position equates to
digital filtering with filter delay constant set to 1000 (sampling frequency reduced to less than 25
kHz).
Displaying encoder raw values
To open encoder raw values dialog, go to Peripherals menu and select ‘Encoder RAW values’. The
following dialog below appears. It simply shows the list of all encoders and their current values. In
additional column, current encoder speed is displayed.
Status of the fast encoders is displayed in green, while the status of an ordinary encoder is displayed
in light grey. Inactive encoders are displayed as dark grey boxes.
At the bottom of the window, there is a command button that can be used to reset the encoders’
values.
Page 31

PoKeys user manual
31
www.poscope.com
Figure 4: Encoders' RAW values
Page 32

PoKeys user manual
32
www.poscope.com
7.4. Pulse engine
PoKeys57CNC is a hybrid device between a USB PoKeys, Ethernet PoKeys nad PoKeysCNCaddon. As
such, it contains an external pulse generator on-board, which is capable of driving of up to 8 axes
controlled by STEP/DIR signals with maximum pulse frequency of 125 kHz.
The pulse engine is fully configurable in terms of:
- Axis switches configuration: each switch (Limit-, Limit+ and Home/Ref) can be independently
enabled, inverted and positioned either on dedicated pins (pin value of 0) or standard PoKeys
pins that are listed in the device pinout
- Axis motion control configuration: each axis can be configured to optionally use an internal
motion controller in either position or speed mode
- Homing/referencing procedure: motion of the reference position search can be inverted if
home/ref switch is positioned in the positive end of the axis travel. The speed of the homing
procedure can be configured in percents of the maximum axis speed.
- Internal motion controller parameters: such as maximum speed, acceleration and
deceleration can be individually configured for each axis.
- Integrated MPG jog mode: where PoKeys can handle the MPG jogging directly - encoder
index and step multiplier can be individually configured
- Other axis settings: axis enable signals, direction inversion, soft limits, etc.
See the description of the Pulse engine status/control dialog on the next page.
Figure 5: Pulse engine status/control dialog
Page 33

PoKeys user manual
33
www.poscope.com
Pulse engine status/control dialog parts
1. Main Pulse engine settings:
a. Enable pulse engine: main switch to enable or disable Pulse engine functionality
b. Lock: when Lock is enabled, the main Pulse engine settings and Pulse generator
settings are disabled
c. Enable safety charge pump output: configure the pin for the charge pump output
d. Invert emergency input polarity: PoKeys expects NC (normally closed switch to be
used as emergency switch) and HIGH signal state on emergency input indicates an
emergency. If NO switch is used, the polarity of the signal must be inverted by
selecting this option
e. Enable backlash compensation: check this option to enable the backlash
compensation in PoKeys device.
2. Pulse generator options: PoKeys57CNC contains an external pulse generator on-board, thus
external pulse generator option with ‘Extended IO’ must be selected. Up to 8 axes can be
enabled
3. Axis configuration - see next page
4. Pulse engine state display and control: this panel displays current PoKeys Pulse engine state
and allows the user to change between the states
a. STOP: stopped mode - the Pulse engine is deactivated momentarily and produces no
pulses. Transition to STOP mode is instantaneous - if there is any motion being
executed, the pulse generation will cease immediately after switching to STOP mode.
b. ERR: error mode - if PoKeys detects any event that results in error (emergency stop,
limit stop, etc.), this mode will automatically be activated. As STOP mode, the
transition is instantaneous
c. Homing: in this mode, PoKeys is executing the homing procedure. The selected axes
are referenced in regards to the position of Home/Ref switch. PoKeys executes
homing procedure in two steps - in first step, course position of the switch is located
using faster motion in the negative direction of the axes (unless Homing direction is
inverted in the settings). When the switch is located, the fine position of the
reference position is located using slower motion in the positive direction of the axis
(again, if not inverted in the settings) until the Home/Ref switch is released.
d. Running: normal operating mode
e. Jogging: jogging mode - in this mode, PoKeys Pulse engine can use the values from
the encoders to directly jog the configured axes
f. Emergency: this field indicates whether device entered Emergency state
g. Limit override: switch that allows the user to activate the limit override
5. Enable axis power and enable charge pump: these options select, when the axis enable and
chargepump output signals are activated (besides normal operating modes)
6. Save configuration button: after the settings are changes, this button must be clicked to
send the settings to device and save them to the on-board non-volatile memory. Since this
operation may produce interruptions in the motion, it is suggested to stop any motion
before commencing configuration save.
7. Pulse engine testing panel:
8. Additional configuration options - here, additional configuration dialogs can be opened
9. Auxilary outputs: these can be used to test the on-board auxilary outputs
Page 34

PoKeys user manual
34
www.poscope.com
a. Relays 0 and 1 control the SSR outputs
b. Relays 2 and 3 control the on-board relays
c. OC-outputs control the galvanically isolated open-collector outputs
Axis configuration panel
This panel contains settings for each axis.
Figure 6: Axis configuration panel
1. Limit switch configuration: individual limit switch (on axis positive and negative ends) can be
individually enabled and inverted (in NO switches are used). Since PoKeys57CNC uses
external pulse generator with extended IO, 0 should be selected as pin number.
2. Home/Ref switch configuration: this switch can be configured as a separate switch or shared
with either Limit+ or Limit- switches. See below for Homing algorithm description.
3. Axis enabled output: pin 0 should be selected in dedicated signal pin on motor connector is
to be used. The state of the signal can be inverted if motor drivers require it.
4. MPG jog setup: select encoder and multiplier factor to setup direct MPG jogging that is active
in Jogging operating mode
5. Copy to all axes: all settings are copied to all other axes by clicking on this button
6. Motion configuration: axis direction can be inverted here. Optionally, internal motion
controller can be activated, allowing PoKeys device to produce the motion signals based on
position or speed reference setup. The ‘Mask enable’ option is for testing purposes and
enables third-party software to enable individual axes independently.
7. Homing configuration: use these settings to invert homing direction and set the speed of the
motion during homing procedure
8. Motion parameters: use these fields in case that Internal motion controller is enabled to
setup the maximum speed, acceleration and deceleration values. When the value is entered
Page 35

PoKeys user manual
35
www.poscope.com
into the fields, confirm the value by pressing ‘Enter’ (‘Return’) key - the field will change
color from red to white.
9. Soft limits configuration: optionally, soft limits can be configured for each axis. When internal
motion controller detects the current position has gone out of these limits, the motion is
softly stopped and only motion in the out-of-limit direction is allowed.
10. Backlash compensation: PoKeys devices support backlash compensation feature. Enter the
size of the backlash (in pulses) and the maximum acceleration used for compensation.
Homing algorithm configuration
PoKeys devices support customization of the homing algorithm. The algorithm is based on executing
selected actions on different events:
- On Home event (home switch contact is detected) - this event happens when the machine
touches and activates the home switch (configured in the options above)
- Out Home event (home switch contact is released) - this event happens when the machine
backs off the switch or gets past the home switch.
On these two events, the combination of the following actions can be configured (selection boxes
from left to right):
- Stop and reset the position - this action marks last position as home position and commands
the motion to stop. It also finishes the homing procedure for the axis
- Arm the encoder index for stop - this action arms the encoder index input for the selected
axis. On the next encoder index signal, the position of the axis is marked as home, axis is
commanded to stop and the homing procedure for the axis is finished. Fast encoders index
inputs 1, 2, 3 (pins 9, 10 and 11 on PoKeys57CNC and 9, 11 and 27 for other PoKeys devices)
are used for axes 1, 2, 3, while ultra fast encoder index input is used for axis 4.
- Reverse direction - reverse the homing direction
- Slow down - slow down the homing speed to the reduced speed, as configured
Figure 7: Homing algorithm selection boxes - default configuration (reverse and reduce speed on home and stop on home
release)
Figure 8: Built-in help
Page 36

PoKeys user manual
36
www.poscope.com
Common homing algorithm configurations
Although the homing algorithm is configurable, there are some standard configurations that fit most
CNC machine configurations:
1. Standard homing configuration
2. Homing without reverse
3. Homing with encoder index - standard
4. Homing with encoder index - without reverse
Page 37

PoKeys user manual
37
www.poscope.com
Limit and home switch filters
The limit and home switch inputs support digital filtering. The filter value defines the minimum time
for the limit or home switch signal activation (1 unit equals to 100 µs = 0.0001 s) - possible values are
between 0 (no filtering) to 254 (25.4 ms).
PoStep drivers configuration
If PoStep60-256 drivers are connected with PoKeys57CNC device using PoExtension2 bus,
configuration (step mode, temperature limit, motor current settings) of the drivers can be done via
PoKeys57CNC device. Status of the drivers (temperature, voltage, input states, faults) can also be
displayed.
In order to establish connection between PoStep drivers and PoKeys57CNC, configure unique I2C
addresses to each PoStep device using PoStep configuration tool (Figure 12). PoKeys device functions
as a proxy between the PC application and PoStep drivers.
Open PoStep driver configuration dialog using the 'Configure PoStep drivers' button on the Pulse
engine dialog. Select one of the axes and select the I2C address for the driver (the address must be
set to the value equal to what was set in the PoStep configuration tool in previous step).
Figure 9: PoStep driver configuration dialog
The configuration dialog contains the list of PoStep drivers on the top and selected driver
configuration and status at the bottom. In top right, there are buttons to retrieve settings from the
PoStep device and to refresh the settings.
Once the device is configured, the driver mode, step mode, temperature limit and current settings
are made available to the user. PoKeys device automatically configures the PoStep driver according
to the selected values. Numeric selection settings require the user to press the 'Set' button.
Although, the settings are sent to PoStep drivers, they are only valid until the PoStep device is reset to save the settings as default startup settings, click on 'Save to EEPROM'.
Page 38

PoKeys user manual
38
www.poscope.com
Automatic refresh of PoStep status can be enabled by configuring the auto-refresh options. Select
the values to refresh and click on 'Configure'. PoKeys will periodically scan through PoStep devices
and retrieve their statuses.
Connecting PoStep drivers to PoKeys57CNC
Connect PoStep drivers (PoStep60-256) in parallel with PoKeys57CNC device using PoExtension2 bus.
All connectors on the PoExtension2 bus must be crimped in parallel to each other (take care of the
connector polarity) - see pictures below.
Figure 10: Two PoStep60-256 stepper motor drivers connected to PoKeys57CNC device
Figure 11: PoExtension2 cable for connecting PoStep drivers with PoKeys57CNC device
Page 39

PoKeys user manual
39
www.poscope.com
Figure 12: I2C address configuration in PoStep configuration tool
Page 40

PoKeys user manual
40
www.poscope.com
Figure 13: Standard 4x3 matrix keyboard
Figure 14: 4x4 matrix keyboard internal structure
7.5. Matrix keyboard
Matrix keyboard is a set of buttons, connected into a mesh. All buttons in a row share one contact,
same goes for each of the buttons in the column. If a button is pressed, a key press is detected with a
periodic scanning of each of the rows and columns. PoKeys devices use digital outputs for setting the
voltage levels on rows and read column voltage levels using digital inputs that already have internal
pull-up resistors, so no external circuitry is needed.
PoKeys devices support matrix keyboards of up to 16x8 in size, simpler 3x3, 4x3, 4x4 and others are
of course fully supported.
Similarly to simple digital inputs, keys of the matrix keyboard connected to the PoKeys device can be
configured as USB keyboard keys. Direct mapping, mapping to macro sequence and triggered
mapping are all supported. Additional alternate function can be used to assign two different
keyboard keys to each of the matrix keyboard buttons. If additional (and freely selectable from the
list of digital inputs) Fn+ input pin is inactive, the default function key is used. If the Fn+ key input pin
is activated, an alternate function key is used instead of the default.
On all devices, the status of key presses of the matrix keyboard can be read using the PoKeys library
commands without the need to setup the mapping described above.
PoKeys configuration software usage
Before any matrix keyboard configuration can be done, go to ‘Peripherals > Matrix keyboard…’, check
the ‘Enable matrix keyboard’ option and select the number of rows and columns. Close the dialog
and continue by selecting column and row pins.
Page 41

PoKeys user manual
41
www.poscope.com
Figure 15: Assigning row and column pins
Matrix keyboard column selection
Each free digital input pin can be assigned as matrix keyboard column input. Make sure the selected
pin is configured as digital input, then check the ‘Matrix keyboard’ option for the pin and select the
appropriate column letter from the list.
Matrix keyboard row selection
Each free digital output pin can be assigned as matrix keyboard row output. Make sure the selected
pin is configured as digital output, then check the ‘Matrix keyboard’ option for the pin and select the
appropriate row number from the list.
Keyboard mapping configuration
Open the ‘Peripherals > Matrix keyboard…’ menu for configuration of the keyboard mapping. Matrix
keyboard is schematically drawn in the dialog below. On the right, key mapping settings can be
selected. To setup mapping, click on one of the keys in the matrix keyboard drawing and select
appropriate key mapping options on the right.
To test the matrix keyboard, first make sure that the settings have been saved to device (close the
Matrix keyboard dialog and click on ‘Send to device’ button). The matrix keyboard dialog can then be
used to test the matrix keyboard – just press any key on your matrix keyboard and the appropriate
button in the matrix keyboard drawing will be highlighted.
To setup different key presses for ‘key press’ and ‘key release’ events, check ‘Triggered mapping’
option and select different settings for ‘Down key’ (‘key press’ event) and ‘Up key’ (‘key release’
event).
Page 42

PoKeys user manual
42
www.poscope.com
Figure 16: Matrix keyboard configuration for a 4x3 matrix keyboard
7.6. Analog inputs
Analog input function is only available on pins 41 to 45. These analog inputs can also be freely
mapped to any of the 6 joystick axis; X, Y, Z, rotation X, rotation Y and throttle.
Analog inputs have a resolution of 12 bits and are sampled at a fixed rate of 10 kHz, then fed through
adjustable digital low-pass filter with the following equation
where y(k) is the output analog value, u(k) is a new A/D sample and filter is a user-adjustable
constant. For proper operation of the digital filter, an analog low-pass filter with a cut-off frequency
of 5 kHz must be used on each analog input. The following equation gives the relation between value
of filter and filter’s cut-off frequency:
Sample u(k) is produced according to the following equation
where U(k) (in Volts) is a voltage present on the selected analog input pin.
PoKeys configuration software usage
To open analog inputs dialog, go to Peripherals menu and select ‘Analog inputs and outputs’. Dialog
below appears. To enable display of analog input channel, check the appropriate check box. It is
enabled only when the input is set up as analog input.
The progress bar displays the current voltage at the pin with the maximum at 3.3V. Below the input
selection boxes user can set low-pass filtering for analog inputs. When analog input signal appears to
Page 43

PoKeys user manual
43
www.poscope.com
be flickering or jumping due to analog signal noise, move the value for the filter to the right towards
label ‘slow signals’ and then press Set button.
Figure 17: Analog inputs and outputs dialog
7.7. Joystick mapping
Each axis of the PoKeys virtual joystick can be assigned an analog input source. In addition, analog to
digital mapping option can be enabled, which allows user to connect an analog joystick to a PoKeys
devices and simulate key presses for each direction of the joystick. User can freely select dead band
and saturation ranges.
Besides mapping the analog inputs to virtual joystick axes, digital inputs (or encoder switching
events) can be mapped to any of the 32 virtual joystick buttons (either directly or ‘triggered’) or 4way POV hat selector. The triggered mapping to joystick buttons enables used to select different pins
that triggers selected joystick button on off-to-on transition (Down Event) and on on-to-off transition
(Up Event).
PoKeys configuration software usage
Joystick axis and buttons mapping can be setup via Joystick mapping dialog. Go to ‘Peripherals’ and
select ‘Joystick settings…’. The dialog on Figure 18 appears.
Each axis can be assigned an analog input. In addition, analog to digital mapping option can be
enabled. This allows user to connect an analog joystick to a PoKeys devices and simulate key presses
for each direction of the joystick. To do so, first check ‘Map to key’ option. Then set the dead band
(when input value will be between lower and upper dead band margins, no keys will be activated)
using sliders. In the lower part of the window, select the mapping options.
Page 44

PoKeys user manual
44
www.poscope.com
For simple direct mapping (pin input status is directly reflected in joystick button status) use the
‘Direct mapping’ option and select pin number to be associated with selected joystick button. If more
advanced behavior is needed (joystick button is pressed for a short time only on transitions of pin
status), user should select ‘Triggered mapping’ option to select one pin that triggers selected joystick
button on off-to-on transition (Down Event) and one pin that triggers this joystick button on on-tooff transition (Up Event).
If joystick button mapping is to be used in connection with encoder inputs, use ‘Triggered mapping’
option (encoder’s values cannot be directly translated into direct mapping) and select a pin with the
appropriate encoder channel. For example: pins 5 and 6 are set up as digital inputs with encoder
(channel A on pin 5 and channel B on pin 6). When pin 5 is selected as Down event pin for joystick
Button 2 and pin 6 is selected as Down event pin for joystick Button 3, rotating the encoder in
positive direction will trigger joystick Button 2 on each detent. Similarly, rotating the encoder in
negative direction, joystick Button 3 will be triggered on each detent. Up Event pin option cannot be
used in connection with encoders.
Figure 18: Joystick mapping settings
7.8. PWM outputs
PoKeys57CNC device supports PWM output function on 4 pins (pins 18, 20, 21 and 22). Different duty
cycles can be assigned to each PWM output however, all outputs share the same PWM period. PWM
outputs can be easily amplified using an external transistor and used for control of loads with
Page 45

PoKeys user manual
45
www.poscope.com
increased current demand - pins with such function embedded are marked as OC (open-collector) in
the pinout diagram. PoKeys PWM outputs can also be used to drive various R/C servo motors that
accept PWM signal with 50 Hz frequency (20 ms PWM period) and duty cycles between 5 and 10 % (1
to 2 ms).
PoKeys devices have an in-built PWM module that operates at a fixed clock frequency (25 MHz). Both
the PWM period and the PWM duty cycles must be expressed as number of module clock cycles (i.e.
20 ms PWM period equates to 0.020 x 25 000 000 = 500 000).
Figure 19: PWM output
PoKeys configuration software usage
PoKeys device’s PWM (pulse width modulation) module can be setup via Peripherals > PWM
outputs….
Figure 20: PWM outputs settings
In this window, user can enter PWM period and set PWM duties for each channel. Channels can be
independently enabled or disabled. After a change is made, user must click 'Set values' button or
check 'Send to device on change' checkbox. Left position of a slider means 0% and right position
100% respectively.
Page 46

PoKeys user manual
46
www.poscope.com
7.9. LCD
PoKeys devices support connecting one alphanumeric LCD module up to a size of 4x20 (4 rows, 20
columns). The selection of the module is limited by support for HD44780 or compatible chipset.
Usually these displays come in various sizes - 1/2/4 line with 8/16/20 characters and colors (black
letters on green background, white letters on blue background ...).
PoKeys57CNC device has a dedicated connector for such LCD displays - see the pinout section of the
manual for connector pinout description.
Figure 21: Typical 2x16 character LCD
LCD display can be used to display various data. A third-party application or a script can execute all
supported operations, including LCD initializing, clearing, moving cursor, setting display shifting
mode, custom character defining and displaying text.
PoKeys57CNC devices by default function in buffered LCD mode. In this mode, any LCD-related
command that is sent to PoKeys device is first buffered and when possible, PoKeys device executes
the LCD refresh on its own. In this mode, some LCD operations are not operational – cursor
movement is controlled by the PoKeys device and cursor move or display commands may not work
as expected. If this low-level control is desirable, buffered mode must be deactivated first. In other
cases, it is advisable to use buffered mode in order to allow better load balancing in PoKeys devices
and in the end obtain greater communication speed.
Before LCD initialization, the LCD module size (number of rows and columns) must be specified and
appropriate pin assignment (primary or secondary, see the table above) must be selected. Secondary
pins must be selected in case of matrix LED display 2 in use.
PoKeys configuration software usage
Functions of this interface can be tested through PoKeys settings application. Just open Peripherals >
Test LCD… and dialog below will appear.
Page 47

PoKeys user manual
47
www.poscope.com
Figure 22: Character LCD testing dialog
LCD settings
In this part, user can set number of rows and columns in the LCD used. Support for LCD can be
enabled or disabled also.
LCD operations
Before user can start using the LCD, LCD module must be initialized. This is done via 'Initialize LCD'
button. Button 'Clear LCD' clears LCD display and moves cursor to home position. LCD module is
initialized automatically by PoKeys device on device startup if ‘Enable LCD support’ option is enabled.
User can also set entry mode settings of LCD module. Cursor can be set-up to move either right
(normally) or left after each character displayed. If 'Display' shift is enabled, whole display shifts with
every new character displayed.
Settings are processed after user clicks button 'Set Entry mode' and work only in ‘unbuffered’ mode
described above.
Display on/off settings
User can set on/off switches for whole display, cursor and cursor blinking.
Settings are processed after user clicks button 'Set LCD on/off' work only in ‘unbuffered’ mode
described above.
Custom characters
Simple interface enables to draw up to 8 custom characters. These characters can then be used on
display. Selecting 'Live edit' mode will transfer the character each time a change is made to any of
the pixels. Character can be previewed via button 'Print', which puts current custom character on the
LCD display. The ‘Copy code’ button can be used to export the character data in a form of C-style
array, as shown in the table below.
Page 48

PoKeys user manual
48
www.poscope.com
LCD custom character editor
Produced code
unsigned char uCustomChar[8] = {
0x10,
0x1C,
0x04,
0x04,
0x04,
0x04,
0x07,
0x01,
};
Move cursor
This section enabled user to move cursor to any position on the screen works only in ‘unbuffered’
mode described above.
Print text
Sends entered text to display module. If advanced characters are needed, enter character code in
lower text box and press 'Print character'.
Page 49

PoKeys user manual
49
www.poscope.com
7.10. PoExtBus
PoExtBus bus support enables user to add additional ten 8-bit shift registers to add up to 80
additional digital outputs to PoKeys device.
Figure 23: PoExtBus outputs chaining
PoKeys configuration software usage
To set-up and test PoExtBus, open 'Peripherals' > PoExtBus...'. The dialog below (Figure 24) appears.
By using mouse left and right clicks, user can turn on or off each of the outputs.
Figure 24: PoExtBus setup dialog
PoExtBus connector type
- Female wire-side connector: Molex 22-01-2055
- Cable contacts: 08-50-0032 (5 pcs needed)
- Prepared cables: 88941-0700 (5 pcs needed)
Page 50

PoKeys user manual
50
www.poscope.com
PoKeys
PoNET
PoNET
PoNET
PoExtBus
PoExtBus
PoKeys
PoNET
device
PoNET
device
PoNET
device
PoExtBus
PoExtBus
7.11. PoNET
PoKeys57CNC device supports PoNET devices (such as kb48CNC CNC keyboard).
Multiple PoNET and PoExtBus devices can be linked together. While the PoNET devices and PoExtBus
devices share the same PoExtBus/PoNET connector, user should pay attention in connecting devices
of both types together (see the schematics below).
All PoNET devices must be connected in parallel to each other and directly to the PoExtBus/PoNET
connector, while the PoExtBus devices should be connected in series after the PoNET devices, as
described below
- PoNET devices must be connected in parallel to each other
- PoExtBus devices must be connected in series
- There should be no PoExtBus device between PoKeys device and PoNET devices
device
device
device
device
device
device
device
device
device
Page 51

PoKeys user manual
51
www.poscope.com
Adding new devices
After connecting new PoNET device, go to ‘Peripherals > PoNET...’. The following dialog will appear
Figure 25: PoNET settings dialog with an unconfigured device
In order to register new device, double click on the 'Unconfigured device' icon. In the next 10
seconds press any key on the device that is about to be added. If the process is successful, status LED
on the device will stop blinking and will be constantly lit. The device will also be listed as in the dialog
below:
Figure 26: PoNET settings dialog with a successfully configured device
Page 52

PoKeys user manual
52
www.poscope.com
PoNET kb48CNC keyboard
The device can be virually mapped to PoKeys matrix keyboard. Third party software can set the
status of LEDs under the keys, read the light sensor that measure the amount of light in the
environment and set the intensity of the LEDs.
To map the PoNET keyboard to PoKeys matrix keyboard, initialize the PoNET bus as described above
in 'Adding new devices', select the keyboard in the device list and check the checkbox 'Enable
mapping to matrix keyboard'.
Page 53

PoKeys user manual
53
www.poscope.com
Peripheral
Failsafe setting
Digital outputs
Active Off / Active On
PoExtBus outputs
Active Off / Active On
PWM outputs
Fixed duty cycle in %
Pulse engine
No setting – Pulse engine enters emergency
mode on failsafe activation
7.12. Failsafe settings
PoKeys devices support the configuration of the failsafe state for the digital outputs, PWM outputs,
PoExtBus devices and PoKeys Pulse engine.
When the communication with the device is interrupted for longer than a period defined in the
failsafe configuration, peripherals listed above enter the failsafe mode, which can be setup in
‘Failsafe settings’ dialog (Peripherals > Failsafe settings…)
Figure 27: Failsafe settings dialog
Page 54

PoKeys user manual
54
www.poscope.com
Pin 1
Power supply 5V
Pin 2
Ground
Pin 3
Serial data
Pin 4
Pin 5
Serial clock
7.13. Peripheral communication protocols
I2C protocol
The I2C bus was designed by Philips in the early '80s to allow easy communication between
components which reside on the same circuit board. Philips Semiconductors migrated to NXP in
2006. The name I2C translates into "Inter IC". Sometimes the bus is called IIC or I²C bus.
PoKeys devices support communication with I2C slave devices, connected to the PoExtBus/PoNET
connector. As I2C, PoNET and PoExtBus use the same connector, PoExtBus, PoNET and I2C functions
are automatically switched by the PoKeys device.
Marking the pin closer to the edge of the PoKeys57CNC board as pin 1, the I2C devices should be
connected as follows:
Protocol can be tested via PoKeys configuration software. Click on Peripherals > I2C bus test... The
following dialog appears.
Figure 28: I2C protocol test dialog
Page 55

PoKeys user manual
55
www.poscope.com
1-wire
1-Wire is a device communications bus system designed by Dallas Semiconductor Corp. that provides
low-speed data, signaling, and power over a single signal wire. 1-Wire is similar in concept to I²C, but
with lower data rates and longer range. It is typically used to communicate with small inexpensive
devices such as digital thermometers and weather instruments.
PoKeys devices support communication with 1-Wire slave devices (without parasitic power supply),
connected to the pin 55 with external pull-up resistor (of approximately 5 kΩ).
Protocol can be tested via PoKeys configuration software. Click on Peripherals > 1-Wire bus test...
The following dialog appears.
Figure 29: 1-Wire protocol test dialog
Page 56

PoKeys user manual
56
www.poscope.com
7.14. EasySensors
PoKeys57 series devices implement a feature called EasySensors. It is an improvement of the original
support for various sensors in PoKeys56 series devices. EasySensors feature allows the user to setup
up to 100 sensors on various communication buses (including I2C, 1-wire, DHTxx 1-wire and analog
inputs). The feature is accessible in Peripherals > EasySensors menu.
EasySensors configuration dialog
The main EasySensors configuration dialog contains a list of all configured sensors with
corresponding sensor information. Here, the sensory type, reading and refresh rate can be changed.
Figure 30: EasySensors configuration dialog
The changed sensor entries are marked with red color - in order for the changes to take effect, click
on ‘Send to device’ button, which transfers the EasySensors configuration to device (note that this
action does not save the settings to device’s non-volatile memory and ‘Send to device’ on main
PoKeys configuration window must be clicked to do that).
There are 4 types of sensors supported and each type of sensor can be added by clicking a
corresponding button at the bottom of the dialog.
Scan for I2C sensors
This command opens the ‘Add I2C sensor’ dialog, which is automatically populated with detected I2C
devices and sensor type suggestions. Sensor type, reading and refresh rate can be changed using the
selections on the right part of the diagram. In order to add the configuration of I2C sensor, check the
corresponding item in the detected I2C devices list and click on ‘Finish.
Figure 31: Scanning for I2C sensors
Page 57
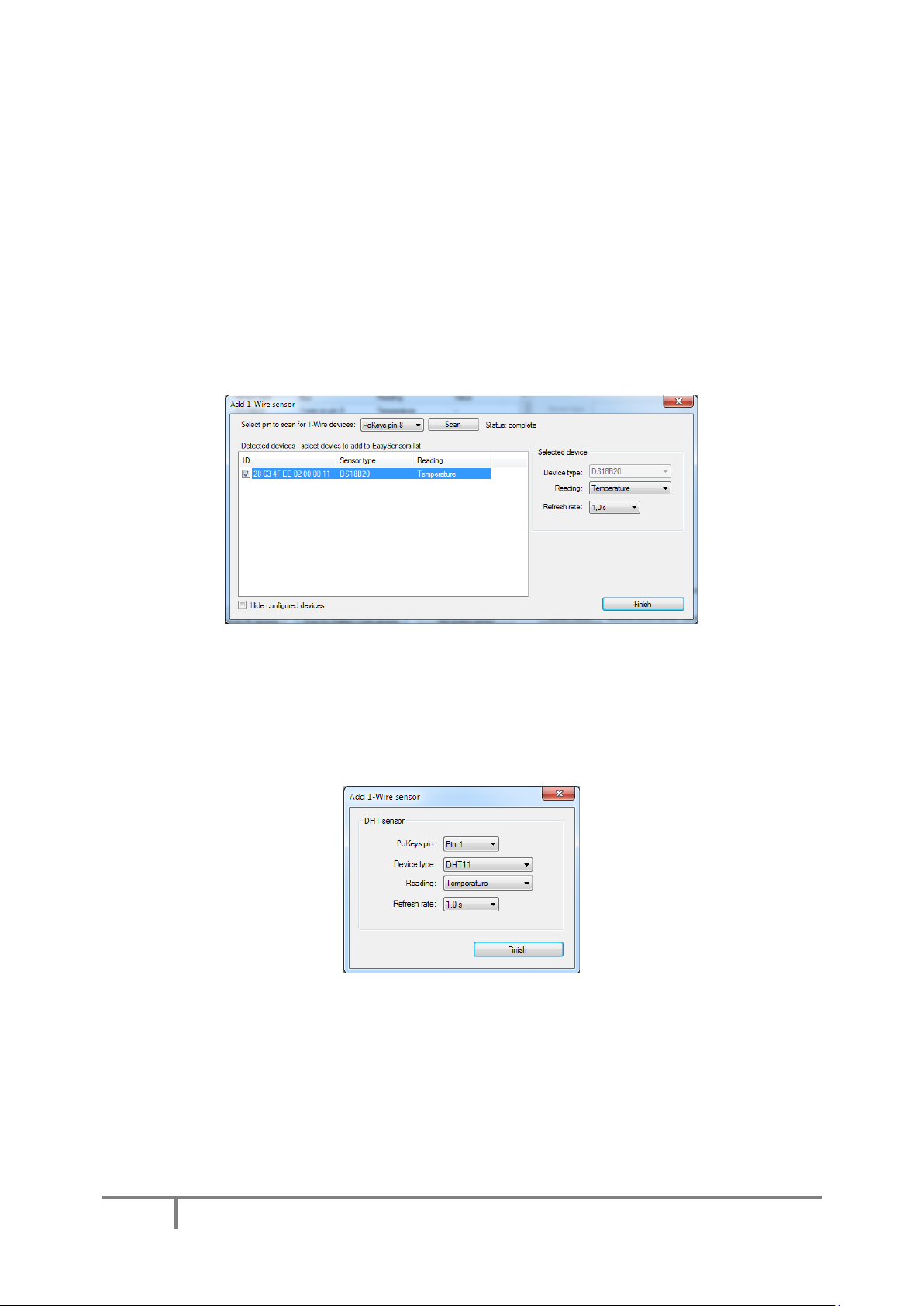
PoKeys user manual
57
www.poscope.com
Scan for 1-wire sensors
The command opens the ‘Add 1-Wire sensor’ dialog that allows the user to select PoKeys pin, where
the 1-Wire bus is connected to. By clicking ‘Scan’, PoKeys device scans the 1-Wire bus for devices.
The EasySensors 1-wire bus implementation can detect multiple 1-Wire devices on the bus at once
and thus simplifying the configuration process.
The list of available devices is then shown in the ‘Detected devices’ list (if ‘Hide configured devices’
option is selected, already configured 1-Wire devices are not displayed in the list). On the right side,
reading type and refresh rate of the selected sensor can be configured.
To add the sensor to the EasySensors list, check the checkbox of the sensor in the list and click
‘Finish’.
Figure 32: Scanning for I2C sensors
Add DHTxx 1-Wire sensor
Three types of DHTxx 1-Wire sensors are supported by PoKeys device (sensors differ in temperature
and humidity resolution and accuracy). Any of the available PoKeys pins can be selected as DHTxx 1Wire bus, but only one sensor can be connected per pin.
Figure 33: Adding the DHTxx 1-Wire sensor
Add analog sensor
EasySensors feature supports reading of simple analog sensors connected to PoKeys analog inputs. A
linear transformation is applied to analog input reading to produce the sensor value. There are two
possible ways to set up the sensor
Page 58

PoKeys user manual
58
www.poscope.com
a) Using gain and offset: specify the gain and offset characteristics of the sensor. The gain
specifies the number of sensor units per 1 V of analog voltage, while the offset specifies the
sensor value of analog voltage input of zero.
Figure 34: Analog sensor setup with gain / offset option
b) Using two point mapping: in this mode, two sensor values with corresponding analog voltage
must be entered into the fields provided. Gain and offset of the sensor are automatically
calculated.
Figure 35: Analog sensor setup with mapping
Analog sensors use the following formula to convert the analog input voltage into sensor reading
where is a measurement of the analog-to-digital converter (a value between 0 and 4095),
is gain (32-bit integer number) and
is result offset (32-bit integer number). The value of
is a integer number that gets divised by 100 for the display (the temperature of 15.58 °C is
represented by . A gain of 330 therefore gives the true voltage on the analog input pin. The
analog sensor dialog shows the gain and offset settings in the bottom left corner of the dialog and
should not be confused with Gain and Offset setup parameters.
Page 59

PoKeys user manual
59
www.poscope.com
List of supported sensors
- LM75 (Maxim, TI, NXP) temperature sensor for the temperature range -55 °C to +125 °C with
the resolution of 0.5 °C. The sensor has configurable address and up to 8 sensors can be
connected.
- SHT21 (Sensirion) temperature and humidity sensor for the temperature range -40 °C to
+125 °C with the resolution of 0.01 °C and air relative humidity in range 0 to 100 %.
- Si7020 (SiLabs) air temperature and relative humidity sensor
- Si1141 (SiLabs) IR and visible light intensity and reflection
- MCP3425 (Microchip) A/D converter with selectable gain
- MCP9600 (Microchip) thermocouple to temperature converter
- iAQ-Core C (AMS) indoor air quality module, measures VOC (volatile organic compound) and
CO2 levels
- MMA7660 (NXP) 3-axis accelerometer
- LIS2DH12 (ST) 3-axis accelerometer
- BH1750 (Rohm) light sensor
- BME280 (Bosch) air temperature, relative humidity and absolute pressure
- ADS1115 (TI) 16-bit 4-channel A/D converter with selectable gain (up to 16x)
- DS18B20 (Maxim) temperature sensor for the temperature range of -55 °C to +125 °C with
the resolution of 0.0625 °C. As each sensor has its own unique sequence ID, up to 10 sensors
can be connected to PoKeys.
- DS18S20 (Maxim) temperature sensor
- DS2413 (Maxim) GPIO inputs
- DHT11, DHT21 and DHT22 (AM2302) temperature and humidity sensors
Figure 36: Thermal image of a temperature sensor being connected directly to a circuit board. The thermal conductivity
of the sensor's leads causes the sensor to register higher temperature than the ambient real temperature. Use properly
longer connections between sensor and sensor host board for the accurate readings
Page 60

PoKeys user manual
60
www.poscope.com
7.15. USB interface configuration
The operation of the USB PoKeys devices can be adjusted in the Device > USB interface', as shown on
the figure below.
Figure 37: Accessing USB interface options
By adjusting these options, the user is given the possibility to configure how device reacts on the
system start, change the communication interval and configure which interfaces are visible to the
system. In some situations, omitting the unused interfaces can result in achieving better
performance of the device due to lower load to the system drivers.
Start options
USB PoKeys devices can be configured to either report the support for boot operation or not. Some
PC BIOS versions have problems configuring non-simple (plain keyboard and mouse) devices and may
halt the boot sequence if such device is present. By omitting the PC boot support, this is usually
overcome.
If this however does not fix the problems during the boot sequence, delayed start option give the
possibility to delay the PoKeys device registration on USB for the predetermined delay, which will
result in BIOS not detecting the device and continuing the boot sequence. Adjust the value according
to your system in this case.
Communication interval
By default, PoKeys USB devices use 1 millisecond communication interval for the communication
interface. If for any reason slower communication is required, it can be adjusted using the
Communication interval settings dialog. Communication intervals between 1 millisecond and 20
milliseconds can be configured.
Page 61

PoKeys user manual
61
www.poscope.com
Enabling/disabling the interfaces
Each USB PoKeys device uses 4 USB interfaces (i.e. USB devices) and thus appears as 'USB Composite
Device' in the Device manager. If not needed, some (or all) interfaces can be disabled.
Note: if all communication interfaces are disabled, configuration of the device will no longer be
possible. In that case, follow the instructions in the section 'Restoring factory defaults' to restore the
device's functionality.
Page 62
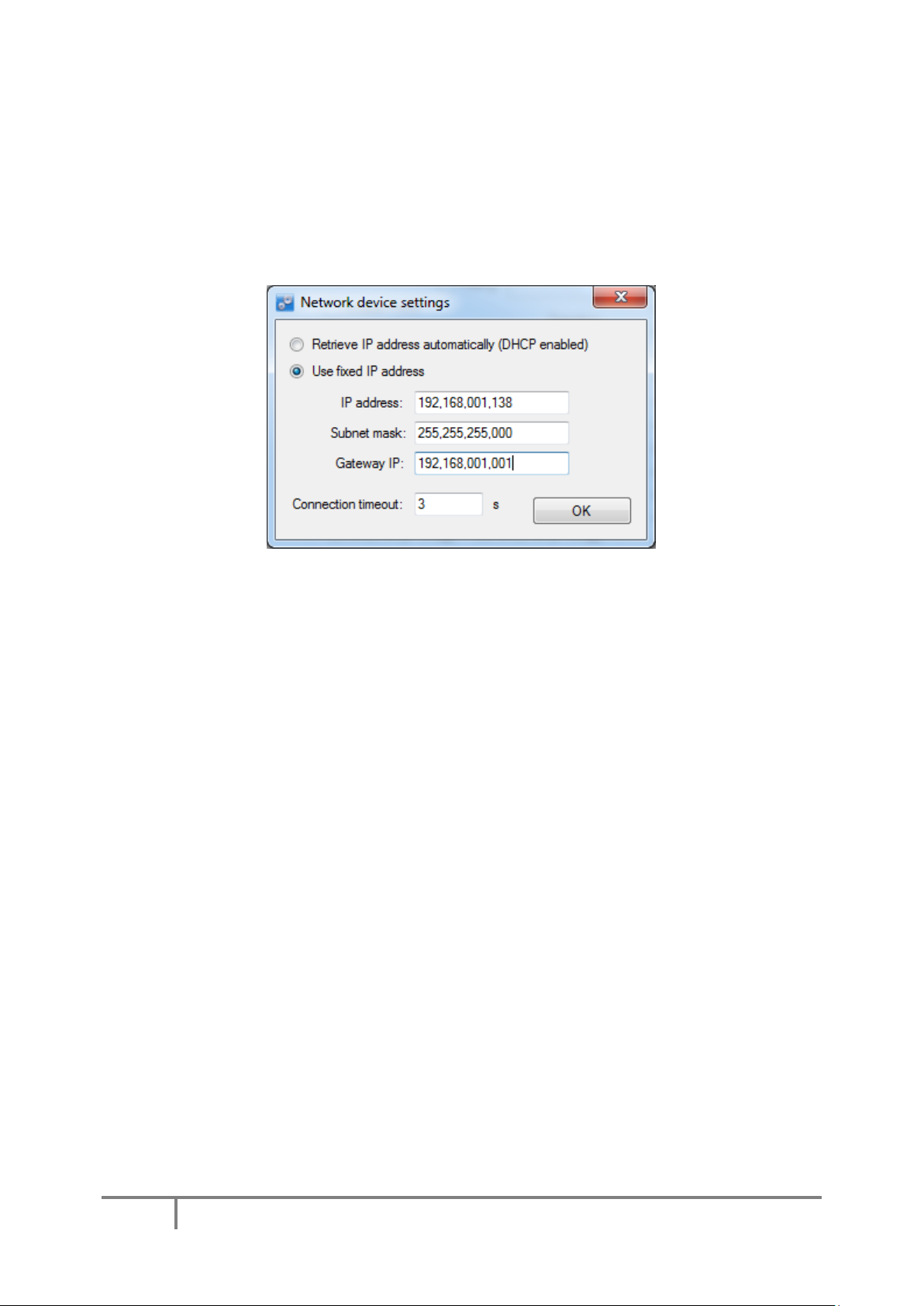
PoKeys user manual
62
www.poscope.com
7.16. Network device functionality
PoKeys57CNC device can be connected to Ethernet 10/100 network with standard RJ-45 cable.
By default, the device is set to use the DHCP functionality of the network router. User can later turn
on or off the DHCP support. If DHCP is not required or available, fixed IP address must be defined for
the device. To set the network settings of the device, go to Device menu and click Network device
settings...
Figure 38: Device network settings
The device communicates using TCP and UDP port of 20055. Please ensure the firewall settings
allow communication with this port. Also, please make sure that your network card (which you
have connected the PoKeys device to) has an IP address assigned with the subnet mask
255.255.255.0 (check it in IPv4 settings in your system).
By default, PoKeys device is configured to close the connection with the host after 3 seconds of
inactivity. This connection timeout value can be set in the dialog, shown in Figure 38.
Device discovery
Unless PoKeys device is configured with a fixed IP address or static DHCP lease option is enabled on
the router, user has no direct display of what IP the PoKeys device is configured or assigned with.
Therefore, PoKeys device feature an automatic discovery mechanism that uses discovery packets
sent from software looking for PoKeys device and discovery response packets that PoKeys device
constructs as an answer to a discovery. The discovery response packet contains vital PoKeys device
information that can be used to identify and find the PoKeys device in the network.
In case the DHCP server is not available in the network or if discovery packet was received from
different subnet than the one used by PoKeys device, the device will change to a temporary IP
address from the same subnet (defaulting to 255.255.255.0 subnet mask) that the request was sent
from. This temporary address can be recognized by ending in .250 and should only be used to find a
misconfigured device and setup it with proper network configuration. The discovery process can be
disabled under Device > Network device settings by clicking ‘Advanced’ button.
More information on this mechanism can be found in the Protocol specification document.
Page 63

PoKeys user manual
63
www.poscope.com
DHCP:
enabled
Port:
20055
Security:
Full access
Default network settings
Connecting to device in other network
When the device is not detected automatically (either there is a firewall blocking the UDP broadcast
messages or the device is not in the same network as a computer), custom IP address of the device
can be entered by clicking on the 'Network settings... ' button on the ‘Connect to device’ dialog. The
following dialog appears.
Figure 39: Additional network settings
IP address of the device can be entered in the text box on the right and added to the list by clicking
the button 'Add'. The list of additional devices is saved on application exit.
Page 64

PoKeys user manual
64
www.poscope.com
Security
Due to exposed nature of a network device, an authentication mechanism was implemented in
network PoKeys that allows three levels of access rights:
- Full access (default): the device is fully accessible from the network
- Read-only access: unauthorized users are allowed only to fetch a limited set of data from the
device, while an authenticated users can acccess all functions of the device
- Full lock: unauthorised users can not neither read or write to the device. A user password is
required to unlock access.
The security is set up in PoKeys configuration software – on the Device menu, click Set device
security... The password can contain any character and can be up to 32 characters long.
Figure 40: Device security settings window
Page 65

PoKeys user manual
65
www.poscope.com
General settings
Dashboard
items list
Dashboard item
configuration
Web users
configuration
and selection
Web interface (dashboard)
Network PoKeys devices can be monitored through the simple web interface (that is already enabled
by default).
Figure 41: PoKeys device web interface
The interface can be disabled or configured in dialog accessible via menu Device->Web interface
configuration. The following dialog appears
The dialog presents the following three options in the upper left corner:
Figure 42: Web interface settings – Dashboard configuration
- Disable web interface: check this field to disable web interface.
- Allow anonymous access to dashboard and I/O status: if this field is checked, users can
access web interface directly without entering user name and password.
Page 66

PoKeys user manual
66
www.poscope.com
- Allow toggling outputs via web interface: if this field is checked, users can toggle the pins that
are setup as outputs. If this field is unchecked, users are only presented with the status of
each pin.
Dashboard items configuration
Up to 100 dashboard items can be configured. In order to add a new item, click on ‘Add new’ and
enter the item information in the fields below (‘Selected item’ settings).
Figure 43: Dashboard item configuration
The following settings are available for each item:
- Item caption: a string of up to 13 characters describing the item (note: some web services
have limitations on what characters can be used - the software will provide you with a
warning if incorrect characters are used)
- Data source: select the data source from available sources (digital inputs or outputs,
PoExtBus outputs, Sensors, digital counters, PoIL shared slot data) with respective index of
the item from the second list
- Display type: there are different display type options available based on the data source
type. The digital signals can be represented by ON/OFF value with optional On/Off or
On/Off/Toggle buttons. The (analog) value signals can be represented by numeric value
display with optional bar graph. The numeric value can be mad editable - double-click on the
displayed value shows an editor box, that allows the user to enter a new value, which is sent
back to device (for use with PoIL shared data values).
- Data unit: the PoKeys device comes preconfigured with a variety of data units. If the desired
unit is missing from the list, up to 20 custom units can be configured.
- Min/max value: use the minimum and maximum value boxes to set the values for the bar
graph boundaries.
- Access rights: select users from the list that should have access to the selected item.
Custom unit editing
PoKeys device contains 20 custom units that allow the user to setup additional units if needed. Since
the units are displayed on a dashboard in a web browser, HTML code for the unit can be entered,
allowing different text formatting.
Page 67

PoKeys user manual
67
www.poscope.com
Figure 44: Custom unit editor
Managing the web user accounts
The dashboard configuration dialog contains a list of available users. To edit the user, double-click on
the entry in the list - a ‘User account’ dialog will pop up, allowing the changes to user name and
password.
By default, PoKeys contains a user named ‘Admin’ with password set to ‘root0’. Both the username
and password of this user can also be changed.
Usernames and passwords can be configured for up to 4 users with the length of each limited to 8
(ASCII) characters.
Figure 45: Editing user account
Accessing the dashboard items data
The information on dashboard items data and their values can be accessed by fetching the following
files from the device:
- devStat.xml: contains values of all digital inputs and outputs, encoder values, analog inputs,
sensors, PoIL shared data values and digital counters
Page 68

PoKeys user manual
68
www.poscope.com
Address (0-based)
Access (R – Read, W – Write)
Description
0-54
R/W
55 pin inputs/outputs
100-126 (100-149 on
PoKeys57 series)
R
Sensor OK statuses
200-263
R/W
PoIL shared data (binary data) overlapped with 32-bit PoIL shared
data at 1000-1127 (16-bit)
1000-1127
R
Matrix keyboard inputs
1400-1527
W
I2C Matrix keyboard LED
1600-1727
R/W
LED matrix
2000-2079
R/W
PoExtBus
2000
Device 10 – Output H
2001
Device 10 – Output G
...
2079
Device 1 – Output A
- devData.xml: information on the PoKeys device (network configuration and some other
device data)
- sensorList.xml*: contains information on dashboard items configuration and value
- sensorList.json*: same as above, but in json format
- setS.html*: is used to change the sensor value
- setDO.html: is used to change digital output value
The setS.html and setDO.html have the following syntax
http://<IP address>/setDO.html?Pin=<Pin ID>&State=<0/1/T>&u=<Username>&p=<Password>
http://<IP address> /setS.html?Sensor=<Item ID>&State=<Value>&u=<Username>&p=<Password>
The <Pin ID> is 1-based PoKeys pin index (same as indicated on the device), while <Item ID> is 0based dashboard item index of the current user.
Modbus
PoKeys57CNC device supports slave (server) operation of Modbus TCP communication protocol.
Modbus TCP compatible devices on the network can read the values from the device and set the
outputs. To elevate the security, user can define which peripherals are accessible via Modbus TCP.
Modbus TCP uses TCP protocol on port 502 (default), which can be changed in Modbus settings
(accessible from the menu Device – Modbus configuration...). The Modbus TCP connection is
disconnected after 3 seconds of inactivity (this default value can be changed in the Modbus settings).
Discrete inputs/outputs
Supported operations:
0x01: Read coils
0x02: Read discrete input
0x05: Write single coil
0x0F: Write multiple coils
Page 69

PoKeys user manual
69
www.poscope.com
Address (0-based)
Access (R – Read, W – Write)
Description
0-1 R Serial number of the device
(PoKeys57 only)
10-16
R
Analog inputs
20-45
RW
Encoder counter values (lower 16bit)
100-154
RW
Digital counter values
200-213
RW
PWM
200,201
PWM period (MSB first)
202,203
PWM duty1 (MSB first) – pin 22
...
212,213
PWM duty6 (MSB first) – pin 17
300-304
RW
PoExtBus
400-453 (400-499 on
PoKeys57 series)
R
Sensors (32-bit values, LSB first)
500-579
RW
LCD buffer
590 W LCD configuration (0=disabled,
1=primary or 2=secondary) - writing
to this register will re-init and clear
the LCD
591 W Number of rows (lower byte) and
number of columns (upper byte) of
the LCD module
592 W Not used
593 W Clear LCD (both bytes = 0xAA)
600 R Tick counter (lower 16-bit)
700-751
R[W]
Digital encoder values (32-bit values,
LSB first) - any write to these
registers causes the reset of the
encoder value to 0
800-909
RW
Digital counter values (32-bit values,
LSB first)
1000-1127
RW
PoIL shared data (32-bit, LSB first)
Address (0-based)
Register description
300
A B C D E F G H A B C D E F G
H
Device 10
Device 9
301
A B C D E F G H A B C D E F G
H
Device 8
Device 7
302
A B C D E F G H A B C D E F G
H
Device 6
Device 5
Registers
Supported operations:
0x03: Read holding register
0x04: Read input register
0x06: Write single register
0x10: Write multiple registers
PoExtBus channel mapping:
Page 70

70
www.poscope.com
303
A B C D E F G H A B C D E F G
H
Device 4
Device 3
304
A B C D E F G H A B C D E F G
H
Device 2
Device 1
15
14
13
12
11
10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Modbus word bit
A B C D E F G H A B C D E F G H PoExtBus device bit
mapping
Device 10
Device 9
where
PoKeys user manual
Figure 46: Modbus configuration
Page 71

PoKeys user manual
71
www.poscope.com
PUT /v2/feeds/62592.csv HTTP/1.1
Host: api.xively.com
X-ApiKey:
CAb3XX634daSAKxZc3M0M3I1NWVZVT0g
User-Agent: PoKeys56E
Content-Type: text/csv
Content-Length: 010
Connection: close
Test1234,-15000.00
The HTTP header without 'Connection' and
'Content-length' tags must be provided by the
user
The 'Connection' and 'Content-length' tags are
automatically inserted by the PoKeys device
Data is inserted at the end of the packet
PUT /v2/feeds/62592.csv HTTP/1.1
Host: api.xively.com
X-ApiKey: CAb3XX634daSAKxZc3M0M3I1NWVZVT0g
User-Agent: PoKeys56E
Content-Type: text/csv
Reporting data to network server with PoKeys57CNC device
PoKeys57CNC devices can automatically report sensor values to various network servers using the
HTTP POST, HTTP PUT or text-only protocols.
To use this reporting feature, user must specify reports type (RAW, UDP, Xively, Standard HTTP
POST/PUT or custom), server IP, server port number and update rate.
Custom report type
The request header is constructed of two parts – HTML header and data header, divided by double
new line character (\n). Example header (Xively.com web service):
The above example is specified as
The extra new line at the end is essential.
Page 72

PoKeys user manual
72
www.poscope.com
POST /myScript.php HTTP/1.1
Host: api.xively.com
User-Agent: MyCustomDeviceAgent
Content-Type: text/csv
Content-Length: 010
Connection: close
MyData: Test1234,-15000.00
The HTTP header without 'Connection' and
'Content-length' tags must be provided by the
user
The 'Connection' and 'Content-length' tags are
automatically inserted by PoKeys device
POST /myScript.php HTTP/1.1
Host: api.xively.com
User-Agent: MyCustomDeviceAgent
Content-Type: text/csv
MyData:
More customized header:
The above example must be specified as
Again, an extra new line character in fifth line is essential.
Total length of final header and data is limited to 350 bytes.
Setup for Xively web service
Xively web service is an on-line database service allowing users to connect sensor-derived data (eg.
energy and environment data from objects) to the Web and to build their own applications based on
that data.
PoKeys57CNC devices feature a direct support for the Xively web service. To configure PoKeys device
for Xively, follow these steps:
1. Sign-up for a free account at http://xively.com/
2. Navigate to Develop and create a new private device
3. Under the created device information, you can find ‘Feed ID’ and ‘API key’ for your newly
created device, as shown in the figure below.
Page 73

PoKeys user manual
73
www.poscope.com
Your Xively API key
Your Xively Feed ID
4. Open Device > Server reports configuration. Check ‘Xively web service’ option.
5. Enter your Xively API key and Feed ID, created in step 3, leave other fields with default values
6. Select the update rate on the right
7. Click Send to device button. If you wish to save the settings to non-volatile memory, click
‘Send to device’ on main PoKeys screen.
8. Go back to Device > Web interface settings to edit the dashboard items. Define entries as
described in the ‘Web interface’ chapter of this manual. To enable uploading of the
Figure 47: Reports server settings for Xively service
Page 74

PoKeys user manual
74
www.poscope.com
dashboard item to the Xively service, select ‘Server reports’ as the user. The ‘Item caption’
field is used to identify the datastream in the selected Xively feed.
Make sure that item caption does not contain any invalid characters for Xively channel name (+, -, _,
letters and numbers are allowed)
Figure 48: Item configuration for the Xively service
9. Save the settings again by clicking 'Send to device' button.
10. Make sure the PoKeys device has properly configured network settings and that it is
connected to the internet
11. After a update interval, check the status of the Xively updates in the Xively 'Develop' page
Page 75

PoKeys user manual
75
www.poscope.com
12. Open your Xively feed by clicking the Feed URL – you should see the recorded data
Figure 49: Xively feed overview page
Setup for standard HTTP POST or PUT data upload
Let's assume that the user wants to send sensor data to his server script that accepts POST method
for data upload. The user's server script is available at the address
www.userdomain.com/PoKeysDataUpload.asp. The user also wants that the data in the POST stream
to have the HTTP type of 'text/plain' and preceded with the string 'MyData: '. The data should be
transferred every 10 minutes. The settings are displayed in Figure 50.
To setup PoKeys to use these settings, the following steps must be taken (enter text without '
quotes):
1. Open Device > Server reports configuration.
2. Select 'Standard HTTP request’ and check HTTP POST option
3. Enter 'www.userdomain.com/PoKeysDataUpload.asp' in the Destination field
4. Enter 'text/plain' in the 'Content-type' field.
5. Enter 'MyData: ' in the 'Data header' field
6. Enter the server's IP address and port number in the fields below.
7. Enter 600 in the update time field
8. Click Close and click Send to device button.
9. Go to Device > Web interface settings and define entries as described in the ‘Web interface’
chapter of this manual. To enable uploading of the dashboard item to the web server, select
‘Server reports’ as the user. The ‘Item caption’ field is used to identify the datastream.
10. Save the settings again by clicking 'Send to device' button.
11. Make sure the PoKeys device has properly configured network settings and that it is
connected to the internet
Page 76

PoKeys user manual
76
www.poscope.com
Figure 50: Example of HTTP POST service setup
Page 77

PoKeys user manual
77
www.poscope.com
7.17. Changing User ID number
Users can freely assign their own User ID number that represents a specific PoKeys device (enables
distinguishing between different PoKeys devices in case there is more than one connected to a single
host PC). To change the User ID number, go to ‘Device’ > ‘Change user ID’ menu. Simply enter any
number between 0 and 255, and click the 'Change user ID' button.
Figure 51: Device user ID dialog
7.18. Saving current configuration to file
To save the current configuration to a file, go to ‘File’ > 'Save' menu and select a new filename. To
reload a saved configuration from a file, go to ‘File’ > ‘Open’ menu and select the appropriate file. To
transfer new settings to the device, click on the ‘Save to device’ button.
7.19. PoIL core functionality
PoKeys57CNC contains PoIL core that is fully compatible with other PoKeys devices. Read the
separate PoIL core documentation for more information.
Due to the omission of the 3V lithium backup battery, PoKeys57CNC does not support value
retention in case of power failure.
Page 78

PoKeys user manual
78
www.poscope.com
8. Device recovery mode
If configuration editor cannot be used to reconfigure the device, use the following steps to start the
device in the recovery mode. Recovery mode can be used to clear the configuration or update the
firmware.
1. Disconnect PoKeys57CNC device from USB and remove power supply
2. Locate LCD connector on the PoKeys57CNC device and short the pins 1 and 3 as shown below
3. Reconnect the PoKeys device to USB (or reconnect power)
4. Green status light should start flashing rapidly and PoKeys device will connect in recovery
mode
5. Open PoKeys configuration application
6. PoKeys configuration application should detect PoKeys57CNC device in recovery mode.
a. To reset the device configuration, use the option ‘Clear settings’. By clicking this
button and confirming your decision on the next dialog, settings will be erased.
b. To recover from bad firmware update, click ‘Recover’.
7. After completing the operation, unplug PoKeys device and remove the short from the LCD
connector
8. If resetting the configuration, ensure the device is properly cleared – replug PoKeys57CNC
device, connect to it and execute Device > Clear settings in device.
Page 79

PoKeys user manual
79
www.poscope.com
9. Frequently asked questions
What software must be installed to operate the device?
On first use or when reconfiguring the device, the supplied software must be installed. If USB
connection is to be used, device driver must be used that should be automatically installed by the
setup package.
Can I use both USB and Ethernet connections?
Yes, both USB and Ethernet connections can be connected at the same time, but USB connection will
have a priority over Ethernet.
Windows can not find drivers for PoKeys57CNC device
The drivers should automatically be installed by PoKeys setup package. If this is not the case and
Windows reports unknown device, install the drivers manually by instructing the Windows device
setup wizard to look for drivers in PoKeys installation folder (C:\Program Files\PoLabs\PoKeys\ by
default).
I misconfigured the device and device no longer responds. What can I do?
If you misconfigured the device in such a way that configuration utility cannot be used to repair the
configuration, see the section ‘Quick resetting the device configuration’ in this manual.
There is spontaneous triggering of some of the pins. What is wrong?
Although the device implements basic noise filtering on the digital inputs, long wires between PoKeys
device and switches can cause spontaneous triggering if those wires are located near high-power
electrical wiring. Use twisted pair wires, shielding and try to route the signal wires away from power
supply wires.
The connection with the PoKeys device cannot be established with 10BASE-T router
Please check that you are using proper cable that is supported by 10BASE-T standard. The following
diagram shows the correct wiring for different connection standards.
(source: http://www.okidensen.co.jp/en/prod/cable/lan/img/cate6_n_fig05.gif)
Page 80

PoKeys user manual
80
www.poscope.com
10. Errata information
This section describes special limitations of the device.
PoKeys device resets when external power supply is applied or removed
If PoKeys device is connected to USB, the device resets when external power supply is either applied
or removed.
External pull-up resistor needed on the probing input
On PoKeys57CNC v1.0, v1.1 and v1.2 hardware, external pull-up resistor is required for correct
operation of the probing input.
Page 81

PoKeys user manual
81
www.poscope.com
11. Grant of license
The material contained in this release is licensed, not sold. PoLabs grants a license to the person who installs this software,
subject to the conditions listed below.
Access
The licensee agrees to allow access to this software only to persons who have been informed of and agree to abide by these
conditions.
Usage
The software in this release is for use only with PoLabs products or with data collected using PoLabs products.
Copyright
PoLabs claims the copyright of, and retains the rights to, all material (software, documents etc) contained in this release.
You may copy and distribute the entire release in its original state, but must not copy individual items within the release
other than for backup purposes.
Liability
PoLabs and its agents shall not be liable for any loss or damage, howsoever caused, related to the use of PoLabs equipment
or software, unless excluded by statute.
Fitness for purpose
No two applications are the same, so PoLabs cannot guarantee that its equipment or software is suitable for a given
application. It is therefore the user's responsibility to ensure that the product is suitable for the user's application.
Mission Critical applications
Because the software runs on a computer that may be running other software products, and may be subject to interference
from these other products, this license specifically excludes usage in 'mission critical' applications, for example life support
systems.
Viruses
This software was continuously monitored for viruses during production, however the user is responsible for virus checking
the software once it is installed.
Support
No software is ever error-free, but if you are unsatisfied with the performance of this software, please contact our technical
support staff, who will try to fix the problem within a reasonable time.
Upgrades
We provide upgrades, free of charge, from our web site at www.poscope.com. We reserve the right to charge for updates
or replacements sent out on physical media.
Trademarks
Windows is a registered trademark of Microsoft Corporation. PoKeys, PoKeys55, PoKeys56U, PoKeys56E, PoScope, PoLabs
and others are internationally registered trademarks.
support: www.poscope.com
 Loading...
Loading...