
FOLD 6
WAVEFOLDER
MULTI-TOPOLOGY
INTRODUCTION
Often considered to be the opposite of filters within a modular system, wavefolders are designed to fold a signal over itself multiple times. This generates additional harmonics, resulting in rich timbres.
While there is a bewildering array of filter types
within the synthesiser world, most wavefolders
fall within only a few categories. Diode
wavefolders in particular come in just two
variants: series and parallel circuit topologies.
Choosing a specific folder also means being
limited to specific sounds and capabilities.
For the first time, Fold 6 puts forward a 6-stage
hybrid series/parallel topology, yielding a greater
sonic palette than ever in just 4 HP. Having both
main (series) and alternate (parallel) outputs
means a single module now gives access to just
about all wavefolding tones imaginable.
CONTENTS
In the Fold 6 box, you’ll find:
Product card, stating serial number and
production batch.
16-to-10-pin Eurorack power cable.
Mounting hardware: two black M3 x 6 mm
hex screws, two black nylon washers and a
hex key.
The Fold 6 module itself, in a protective
cotton bag.
If any of these items are missing, please contact
your dealer or support@joranalogue.com.
To take things even further, an integrated
symmetrical soft clipper limits the output signals
to approximately 10 V
within typical Eurorack levels and making it
easier to create overdriven sounds at high fold
ratios. This clipping stage can be driven
continuously using the shape parameter,
smoothly transforming the folded waveforms
into pulse waves for even more harmonic
content.
Two signal inputs are included, to mix audio
signals or add in a DC voltage for asymmetric
folding. The symmetry can also be manually
controlled using the dedicated knob. Of course,
both fold and shape parameters feature voltage
control, to enable continuous timbral
modulation.
Moving beyond simple signal processing, Fold 6
also lends itself perfectly for feedback patching,
CV folding or frequency multiplication; its
modest size belies the sonic capabilities within.
, keeping the amplitude
pp
1
FOLD 6
WAVEFOLDER
CONTROLS & CONNECTIONS
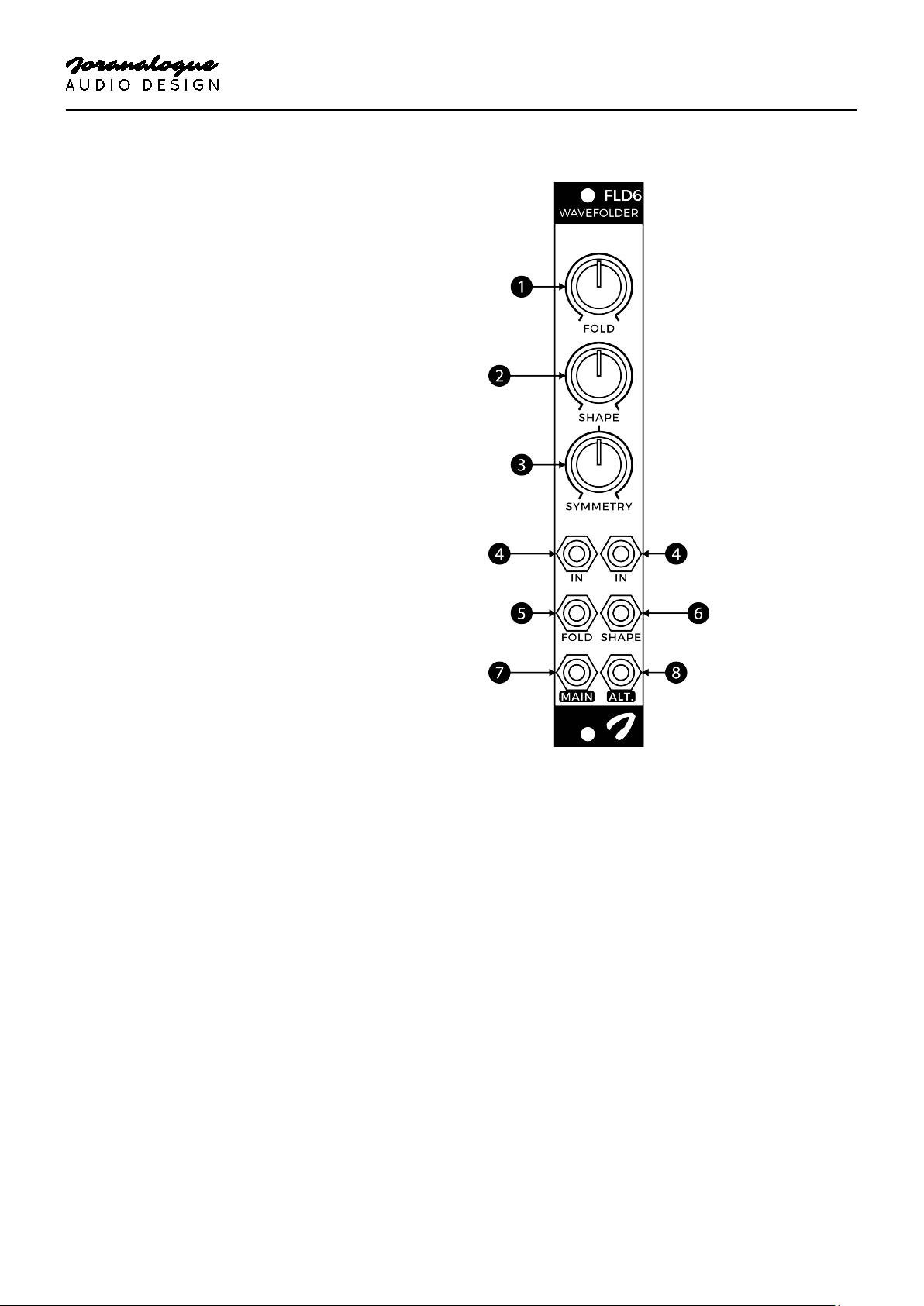
1 FOLD KNOB
The 6-stage wavefolder is preceded by a linear
voltage controlled amplifier (VCA), controlled by
the fold parameter. As the signal amplitude
going into the wavefolder increases, more fold
stages are engaged, resulting in more folds and
thus more harmonics being generated. At the
minimum setting, the input is fully attenuated.
2 SHAPE KNOB
The wavefolding section feeds into an overdrive
circuit. At the minimum setting of the shape
parameter, it is essentially disabled and classic
wavefolder tones are the result. As the circuit is
driven harder, folded continuous waveforms
such as sine and triangle waves are gradually
shaped into pulses, creating a harsher sound.
MULTI-TOPOLOGY
3 SYMMETRY KNOB
The symmetry knob adds a manually variable DC
offset to the signal inputs, ranging from −5 V to
+5 V. This can be used to achieve asymmetric
wavefolding, with either the positive or negative
part of the waveform being folded more than the
other, by turning it away from the centre
position. This knob can also be used re-centre the
wavefolder if there already is a DC offset present
in the input signal(s).
4 SIGNAL INPUTS
Connect the signal(s) to be folded here. These
identical inputs are mixed together, which can
simplify certain patches as it often removes the
need for a separate mixer module. As the entire
signal path is DC-coupled, control voltages (CVs)
as well as audio signals can be processed. These
two signal types can even be combined, for
variable symmetry audio wavefolding.
2

FOLD 6
WAVEFOLDER
5 FOLD INPUT
The fold CV input provides linear voltage control
over the input VCA. The exact number of fold
stages being engaged depends on the
amplitude of the input signal(s). While the knob
range is restricted to +5 V for optimal control, it is
possible to drive the wavefolder even harder
using external control voltages.
6 SHAPE INPUT
The shape CV input provides voltage control over
the overdrive circuit. With the shape knob at the
minimum setting, the response is no drive at 0 V,
to maximum drive at +5 V. Negative voltages will
result in attenuation, allowing the shape CV to be
used for output amplitude control as well.
MULTI-TOPOLOGY
7 MAIN OUTPUT
This output provides the most classic
wavefolding action, as found in earlier designs
utilising the ‘series’ circuit topology.
Unlike most wavefolding modules, Fold 6’s
overdrive circuit constrains the output
waveforms to within approximately −5 V and
+5 V. This means the waveforms are always kept
to around the nominal Eurorack amplitude level
of 10 V
. It also ensures symmetric clipping once
pp
the final folding stage has been engaged,
creating a purer sound.
Keep in mind that due to Fold 6’s high-gain
circuitry, some noise and DC offset is to be
expected in the output signals, especially at high
fold and/or shape levels.
8 ALTERNATE OUTPUT
The alternate output simultaneously provides
waveforms such as those from ‘parallel’
wavefolders, with fold levels and directions
varying between the different stages, the result
being a more mellow sound for most input
signals.
3

FOLD 6
WAVEFOLDER
MULTI-TOPOLOGY
SPECIFICATIONS
MODULE FORMAT
Doepfer A-100 ‘Eurorack’ compatible module
3 U, 4 HP, 35 mm deep (inc. power cable)
Milled 2 mm aluminium front panel with nonerasable graphics
MAXIMUM CURRENT DRAW
+12 V: 40 mA
−12 V: 40 mA
POWER PROTECTION
Reverse polarity (MOSFET)
I/O IMPEDANCE
All inputs: 100 kΩ
All outputs: 0 Ω (compensated)
OUTER DIMENSIONS (H X W X D)
128.5 x 20 x 52 mm
SUPPORT
As all Joranalogue Audio Design products, Fold 6
is designed, manufactured and tested with the
highest standards, to provide the performance
and reliability music professionals expect.
In case your module isn’t functioning as it should,
make sure to check your Eurorack power supply
and all connections first.
If the problem persists, contact your dealer or
send an email to support@joranalogue.com.
Please mention your serial number, which can be
found on the product card or on the module’s
rear side.
REVISION HISTORY
Revision C: initial release.
MASS
Module: 60 g
Including packaging and accessories: 135 g
4

With compliments to the following fine people,
who helped to make Fold 6 a reality!
Ben ‘DivKid’ Wilson Björn Jauss
Boris Uytterhaegen Gregory Delabelle
Jan D’Hooghe Janus Coorevits
Jérémy Bocquet Jeroen De Pessemier
Lieven Stockx Marcin Staniszewski
Quincas ‘Synth DiY Guy’ Moreira Sebastiaan Tulkens
Simon Nuytten
Fold 6 User Manual
version 2020-12-25
21st Century Analogue Synthesis—Made in Belgium
© 2020
info@joranalogue.com
https://joranalogue.com/
 Loading...
Loading...