Page 1
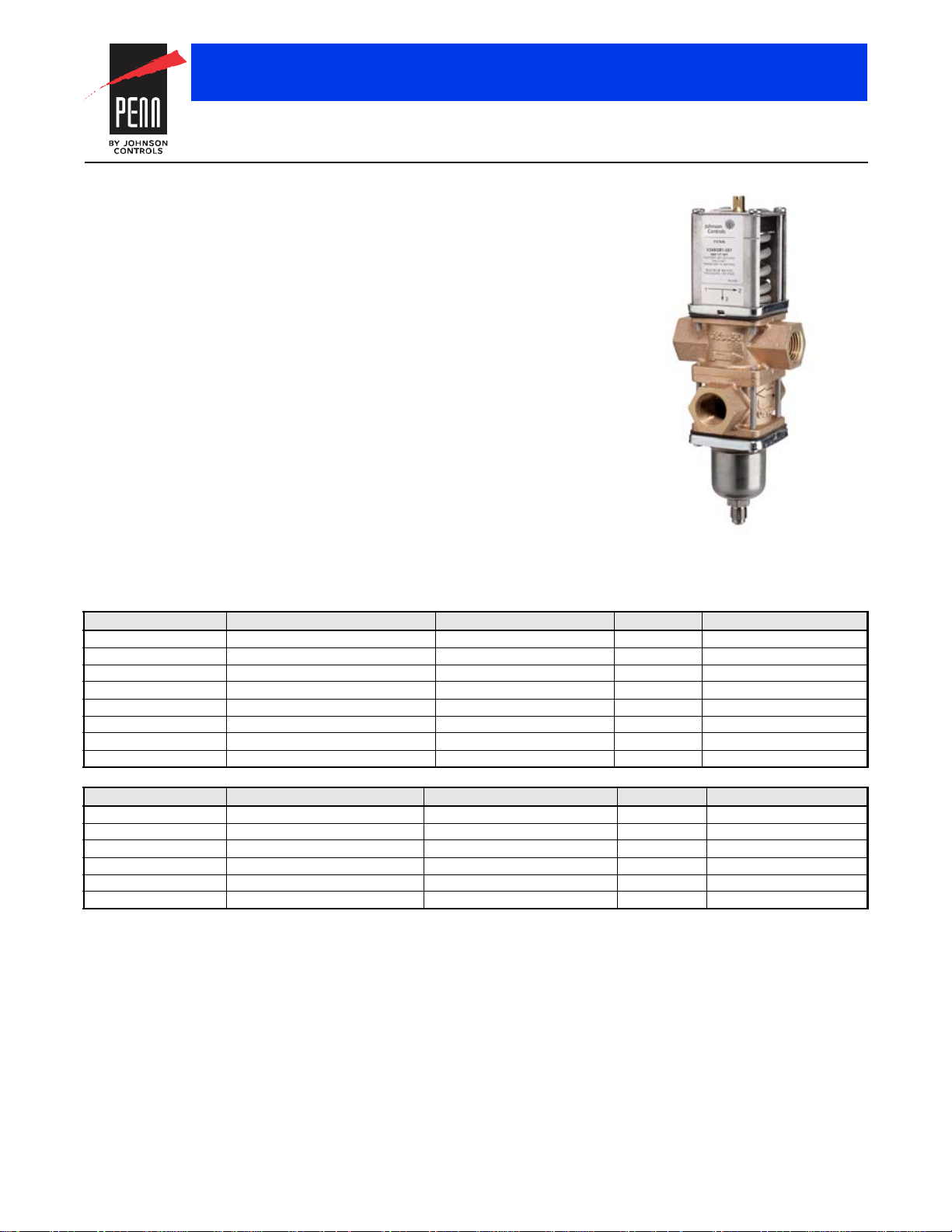
V248 Screw Connection Valve
V248 Series Three-Way Pressure-Actuated Water-Regulating Valves
for High-Pressure Refrigerants
Description
The V248 Series Three-Way
Pressure-Actuated Water-Regulating Valves
for High-Pressure Refrigerants regulate water
flow and control refrigerant head pressure in
systems with single or multiple water-cooled
condensers.
V248 valves have an adjustable opening point
in a refrigerant pressure range of 200 to
400 psi (13.8 to 27.6 bar). V248 valves are
available in 1/2 in. through 1-1/2 in. size for
use with standard, non-corrosive,
high-pressure refrigerants.
Maritime models, which have nickel copper
(Monel®) internal parts, are available for
applications where the media may be
corrosive to the internal parts.
Refer to the V248 Series 3-Way
Pressure-Actuated Water-Regulating Valves
for High-Pressure Refrigerants Product
Bulletin (LIT-12011515) for important product
application information.
Valves and Valve Accessories
Features
• no close fitting or sliding parts in water
passages
• accessible range spring
• take-apart construction
• pressure-balanced design
• corrosion-resistant material for internal
parts
Repair Information
If the V248 Series Three-Way
Pressure-Actuated Water-Regulating Valves
for High-Pressure Refrigerants fails to operate
within its specifications, refer to the V248
Series 3-Way Pressure-Actuated
Water-Regulating Valves for High-Pressure
Refrigerants Product Bulletin (LIT-12011515)
for a list of repair parts available.
Code No. LIT-1900576
Selection Charts
North American Standard Production Models - Range 200 to 400 psi
Product Code Number Construction Valve Size and Connection Element Style Shipping Weight, lb (kg)
V248GB1-001C Direct Acting, Commercial 1/2 in. NPT Screw Style 5 5.0 (2.3)
V248GC1-001C Direct Acting, Commercial 3/4 in. NPT Screw Style 5 6.5 (3.0)
V248GD1-001C Direct Acting, Commercial 1 in. NPT Screw Style 5 12.0 (5.4)
V248GE1-001C Direct Acting, Commercial 1-1/4 in. NPT Screw Style 5 16.0 (7.2)
V248GF1-001C Direct Acting, Commercial 1-1/2 in. NPT Screw S tyle 5 25.0 (11.3)
V248GK1-001C Direct Acting, Commercial 3/4 in. Union Sweat Style 5 7.0 (3.2)
V248GL1-001C Direct Acting, Commercial 1 in. Union Sweat Style 5 12.0 (5.4)
V248GM1-001C Direct Acting, Commercial 1-1/4 in. Union Sweat Style 5 13.7 (6.2)
European Standard Production Models - Range 13.8 to 27.8 bar
Product Code Number Construction Valve Size and Connection Element Style Shipping Weight, lb (kg)
V248GB1B001C Direct Acting, Commercial 1/2 in. BSPT Screw, ISO 7 Style 5 5.0 (2.3)
V248GC1B001C Direct Acting, Commercial 3/4 in. BSPT Screw, ISO 7 Style 5 6.5 (3.0)
V248GD1B001C Direct Acting, Commercial 1 in. BSPT Screw, ISO 7 Style 5 12.1 (5.5)
V248GE1B001C Direct Acting, Commercial 1-1/4 in. BSPT Screw, ISO7 Style 5 16.0 (7.2)
V248GF1B001C Direct Acting, Commercial 1-1/2 in. BSPT Screw, ISO 7 Style 5 25.0 (11.3)
V248HC1B001C Direct Acting, Mari tim e 3/4 in. BSPP Screw, ISO 228 Style 5 6.5 (3.0)
The performance specifications are nomina l and con form to accep table ind ustry stand ards. For applicati ons at con ditions be yond these specification s, consult th
Johnson Controls, Inc. shall not be liable for damages resulting from misapplication or misuse of its products. © 2015 Johnson Controls, Inc.
R-181
Page 2
Refrigerant Head Pressure Rise
FIG
P = P - P
Available Water Pressure
Cooling Tower
P
1
P
2
P
Loss 2
3-Way
Valve
P
IN
COND
P
P
1P2
=
-
P
P
P
=
+
+ ...
Balancing Valve
FIG:3wy_ prss_dr
Flow Required
Flow =
(Temp. - Temp. )
Outlet Inlet
FIG:flw_e qn
Valve Opening Pressure
FIG:eqn_
OPEN CLOSE
Valves and Valve Accessories
V248 Series Three-Way Pressure-Actuated Water-Regulating Valves for
High-Pressure Refrigerants (Continued)
Applications
Each application is unique and requires specific engineering data to
properly size and design a system to fulfill the appropriate
requirements. Typically, a valve is replaced with another valve of the
same size in a properly sized and engineered system. In North
America, contact Johnson Controls/PENN® Refrigeration Application
Engineering at 1-800-275-5676 to obtain specific engineering data. In
other areas, contact the local Johnson Controls® sales office to obtain
specific engineering data.
To make a rough field estimate of the size of valve for an application,
find the valve size needed by locating a point on a flow chart that
satisfies these requirements:
• water flow required by the condenser (Flow)
• refrigerant head pressure rise (P
• available water pressure (P
AVAIL
RISE
)
)
Follow these steps, and use the information obtained to locate a point
on one of the flowcharts that satisfies all three steps.
1. Take the water flow required by the condenser (Flow) from
information provided by the manufacturer of the condensing unit. If
the manufacturer’s information is unavailable, use the following
information to make a rough approximation of water flow in gallons
per minute (gpm) [cubic meters per hour (m
3
/hr)]:
• System Capacity (Tons of Refrigeration)
Inlet
Outlet
)
)
• Outlet Water Temperature (Temp.
• Inlet Water Temperature (Temp.
Calculate the flow using the following formula:
Tons of Refrigeration x 30
RISE COND OPEN
3. Determine the available water pressure to the valve (P
the following steps. This the actual water pressure available to force
:eqn_h d_prssr_r s
AVAIL
water through the valve.
a. Determine the minimum inlet pressure (P
pressure from city water mains, pumps, or other sources.
b. Pressure drop through condenser (P
water pressure between the condenser inlet and the condenser
). This is the water
IN
) is the difference in
COND
outlet. Obtain this information from the condenser manufacturer.
c. Estimate or calculate the pressure drop through all associated
piping (P
d. Subtract the P
LOSS
).
COND
and P
from PIN. The result is P
LOSS
p
Pump
Condenser
P
Loss 1
Bypas s Line
) using
AVAIL
.
Note: If the outlet temperature is unknown, assume it to be 10F
(6C) above the inlet temperature.
2. Determine refrigerant head pressure rise above the valve opening
point (P
) using the following steps:
RISE
a. The Valve Closing Pressure (P
refrigerant pressure at the highest ambient temperature the
refrigeration equipment experiences in the Off cycle. Use a
Pressure-Temperature Chart for the refrigerant selected to find
this pressure.
b. To approximate the Valve Opening Pressure (P
about 10 psig (0.7 bar) to the Valve Closing Pressure.
P = P +10 psi (0.7 bar)
c. From the Pressure-Temperature Chart for the refrigerant
selected, read the Refrigerant Condensing Pressure (P
(operating head pressure) corresponding to the selected
condensing temperature.
d. Subtract the Valve Opening Pressure from the Refrigerant
Condensing Pressure. This gives the head pressure rise.
The performance specifications are no minal and co nform t o acceptab le ind ustry standar ds. For appl ications at condition s beyond these specifica tions, consult th
Johnson Controls, Inc. shall not be liable for damages resulting from misapplication or misuse of its products. © 2015 Johnson Controls, Inc.
Loss 1
Loss 2
) is equal to the
CLOSE
LOSS
P= P- (P+ P)
AVAIL IN COND LOSS
4. Select the proper valve size from the flowcharts by locating a point
on a chart that satisfies the flow, the head pressure rise above
opening point, and the pressure drop across the valve.
OPEN
), add
Metric Conversions
Use these equations to convert between U.S. and S.I. units.
3
•1 dm
• 1 bar = 100 kPa = 0.1 MPa 1.02 kg/cm
opn_prss r
)
COND
/s = 3.6 m3/h = 15.9 U.S. gal. /min. = 13.2 U.K. gal. /min.
2
= 0.987 atm 14.5 psig
R-182
Page 3
1/2 in. Direct Acting Valve Flowchart
0.7 1.4 2.1 2.8 3.5 4.1 4.8 5.5 6.2 6.9
0.0
0.7
1.4
2.0
2.7
3.4
4.1
0
3
6
9
12
15
18
10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 110
Refrigerant Head Pressure Above Opening P
Rise
(bar)
Flow
(m³/hr)
Flow
(gpm)
Refrigerant Head Pressure Above Opening P
Rise
( psig )
FIG:V248_0.5 in. graph
10 (0.7)
5 (0.3)
2 (0.1)
Pressur e Dr o p
Through Valv e,
psig(bar)
14.5 (1.0)
20 (1.4)
3/4 in. Direct Acting Valve Flowchart
0.7 1.4 2.1
2.8
3.5
4.1
4.8
5.5
6.2
6.9
0.0
1.1
2.3
3.4
4.5
5.7
0
5
10
15
20
25
10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90
100
110
Refrigerant Head Pressure Above Opening P
Rise
(bar)
Flow
(M³/hr)
Flow
(gpm)
Refrigerant Head Pressure Above Opening P
Rise
( psig )
10 (0.7)
5 (0.3)
2 (0.1)
Pressure Drop
Through Valv e,
psig (bar)
14.5 (1.0)
20 (1.4)
FIG:V248_0.75 in. graph
Valves and Valve Accessories
V248 Series Three-Way Pressure-Actuated Water-Regulating Valves for
High-Pressure Refrigerants (Continued)
V248 Flowcharts
The maximum recommended differential water pressure across a valve is 20 psig (1.4 bar).
The performance specifications are no minal and co nform t o acceptab le ind ustry standar ds. For appl ications at condition s beyond these specifica tions, consult th
Johnson Controls, Inc. shall not be liable for damages resulting from misapplication or misuse of its products. © 2015 Johnson Controls, Inc.
R-183
Page 4

1 in. Direct Acting Valve Flowchart
0.7 1.4 2.1 2.8
3.5
4.1
4.8
5.5
6.2
6.9
0.0
2.3
4.5
6.8
9.1
11.4
0
10
20
30
40
50
10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 110
Refrigerant Head Pressure Above Opening P
Rise
(bar)
Flow
(m³/hr)
Flow
(gpm)
Refrigerant Head Pressure Above Opening P
Rise
( psig )
10 (0.7)
5 (0.3)
2 (0.1)
14.5 (1.0)
20 (1.4)
Pressure Drop
Through Valv e,
psig(bar)
FIG:V248_1.0 in. graph
1-1/4 in. Direct Acting Valve Flowchart
0.7 1.4 2.1 2.8
3.5
4.1
4.8
5.5
6.2
6.9
0.0
2.3
4.5
6.8
9.1
11.4
13.6
15.9
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 110
Refrigerant Head Pressure Above Opening P
Rise
(bar)
Flow
(m³/hr)
Flow
(gpm)
Refrigerant Head Pressure Above Opening P
Rise
( psig )
10 (0.7)
5 (0.3)
2 (0.1)
14.5 (1.0)
20 (1.4)
Pressure Drop
Through Valv e,
psig(bar)
FIG:V248_1.25 in. graph
1-1/2 in. Direct Acting Valve Flowchart
0.7 1.4 2.1 2.8
3.5
4.1
4.8
5.5
6.2
6.9
0.0
2.3
4.5
6.8
9.1
11.4
13.6
15.9
18.2
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
80
10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 110
Refrigerant Head Pressure Above Opening P
Rise
(bar)
Flow
(m³/hr)
Flow
(gpm)
Refrigerant Head Pressure Above Opening P
Rise
( psig )
10 (0.7)
5 (0.3)
2 (0.1)
14.5 (1.0)
20 (1.4)
Pressure Drop
Through Valv e,
psig(bar)
FIG:V248_1.5 in. graph
Valves and Valve Accessories
V248 Series Three-Way Pressure-Actuated Water-Regulating Valves for
High-Pressure Refrigerants (Continued)
The performance specifications are no minal and co nform t o acceptab le ind ustry standar ds. For appl ications at condition s beyond these specifica tions, consult th
Johnson Controls, Inc. shall not be liable for damages resulting from misapplication or misuse of its products. © 2015 Johnson Controls, Inc.
R-184
Page 5
A
Port 1
Port 3
Port 2
FIG:V248_u nbdy
Port 3
Port 1
Port 2
FIG:V248_t hdd
F
E
PORT 1
PORT 2
PORT 3
FIG:V248_3 way valve
Valves and Valve Accessories
V248 Series Three-Way Pressure-Actuated Water-Regulating Valves for
High-Pressure Refrigerants (Continued)
A
B
D
C
E
Plugged
V248 1/2 in. Through 1-1/4 in. Screw Connection Valves
Dimensions
B
C
D
E
Plugged
F
V248 Union Sweat Connection Valves Dimensions
V248 1-1/2 in. Screw Connection Valves Dimensions
The performance specifications are no minal and co nform t o acceptab le ind ustry standar ds. For appl ications at condition s beyond these specifica tions, consult th
Johnson Controls, Inc. shall not be liable for damages resulting from misapplication or misuse of its products. © 2015 Johnson Controls, Inc.
R-185
Page 6

Valves and Valve Accessories
V248 Series Three-Way Pressure-Actuated Water-Regulating Valves for
High-Pressure Refrigerants (Continued)
V248 1/2 in. Through 1-1/4 in. Screw Connection Valves Dimensions
Valve Size Dimensions in Inches (Millimeters)
A B C D E F
1/2 in. 3-1/16 (78) 2 (51) 8-11/16 (220) 3-13/16 (96) 1-1/2 (38) 3-3/8 (86)
3/4 in. 3-3/8 (86) 2-3/16 (55) 9-3/4 (248) 4-3/16 (106) 1-3/4 (44) 3-13/16 (98)
1 in. 4-3/4 (121) 2-13/16 (71) 12-1/2 (318) 5-15/16 (151) 2-1/16 (52) 4-1/2 (114)
1-1/4 in. 4-3/4 (121) 2-13/16 (71) 13-1/4 (336) 6-1/8 (156) 2-3/8 (60) 4-3/4 (121)
V248 Union Sweat Connection Valves Dimensions
Valve Size Dimensions in Inches (Millimeters)
A B C D E F
3/4 in. 3-3/8 (86) 2-3/16 (55) 9-3/4 (248) 4-3/16 (106) 1-3/4 (44) 3-13/16 (98)
1 in. 4-3/4 (121) 2-13/16 (71) 12-1/2 (318) 5-15/16 (151) 2-1/16 (52) 4-1/2 (1 14)
1-1/4 in. 4-3/4 (121) 2-13/16 (71) 13-1/4 (336) 6-1/8 (156) 2-3/8 (60) 4-3/4 (121)
V248 1-1/2 in. Screw Connection Valves Dimensions
Valve Size Dimensions in Inches (Millimeters)
A B C D E F
1-1/2 in. 6 (152) 3-1/2 (89) 15-1/4 (382) 8 (203) 9-5/16 (237) 6-7/8 (175)
The performance specifications are no minal and co nform t o acceptab le ind ustry standar ds. For appl ications at condition s beyond these specifica tions, consult th
Johnson Controls, Inc. shall not be liable for damages resulting from misapplication or misuse of its products. © 2015 Johnson Controls, Inc.
R-186
Page 7

Valves and Valve Accessories
V248 Series Three-Way Pressure-Actuated Water-Regulating Valves for
High-Pressure Refrigerants (Continued)
Materials
North American V248 Materials
Nominal Valve Size: 3/8 in. to 3/4 in.
Material
Body Cast brass Cast iron/rust resisting finish Cast bronze
Seat Aluminum bronze Aluminum bronze Monel
Disc BUNA-N BUNA-N BUNA-N
Disc Cup Brass Brass Monel
Disc Stud Brass Brass Monel
Stem/Extension Sleeve Brass Brass Monel
Diaphragms Nylon reinforced BUNA-N Nylon reinforced BUNA-N Nylon reinforced BUNA-N
(Commercial)
Refrigerant Contact
Pressure
Element
Cup 300 Series stainless steel 300 Series stainless steel 300 Series stainless steel
Bellows 300 Series stainless steel 300 Series stainless steel 300 Series stainless steel
Bellows Ring Steel/nickel plated Steel/nickel plated Steel/nickel plated
European V248 Materials
Nominal Valve Size: 3/8 in. to 3/4 in.
Material
Body Hot forged brass Cast iron/rust resisting finish Cast bronze
Seat Aluminum bronze Aluminum bronze Monel
Disc BUNA-N BUNA-N BUNA-N
Disc Cup Brass Brass Monel
Disc Stud Brass Brass Monel
Stem/Extension Sleeve Brass Brass Monel
Diaphragms Nylon reinforced BUNA-N Nylon reinforced BUNA-N Nylon reinforced BUNA-N
Refrigerant Contact
Pressure Element Cup 300 Series stainless steel 300 Series stainless steel 300 Series stainless steel
Bellows 300 Series stainless steel 300 Series stainless steel 300 Series stainless steel
Bellows Ring Steel/nickel plated Steel/nickel plated Steel/nickel plated
(Commercial)
1 in. to 1-1/2 in.
(Commercial)
1 in. to 1-1/2 in.
(Commercial)
Maritime (All Sizes)
Maritime (All Sizes)
Technical Specifications
V248 Series Pressure-Actuated Water-Regulating Valves for High-Pressure Refrigerants
Maximum Working Pressure 630 psig (43.4 bar)
Factory-Set Opening Point (Port 1 to
Port 2)
Opening Point Adjustment Range
(Port 1 to Port 2)
Throttling Range 120 psi (8.3 bar) for 1/2 in. size
Media 150 psig (10.3 bar) maximum,
275 psig (19.0 bar)
200 to 400 psi (13.8 to 27.6 bar)
100 psi (6.9 bar) for 3/4 in., 1 in., and 1-1/4 in. sizes
140 psi (9.6 bar) for 1-1/2 in. size
-4F to 170F (-20C to 77C) glycol/water or liquids with low freezing points that are compatible with valve materials
The performance specifications are no minal and co nform t o acceptab le ind ustry standar ds. For appl ications at condition s beyond these specifica tions, consult th
Johnson Controls, Inc. shall not be liable for damages resulting from misapplication or misuse of its products. © 2015 Johnson Controls, Inc.
R-187
 Loading...
Loading...