Page 1

V146 Series Valve
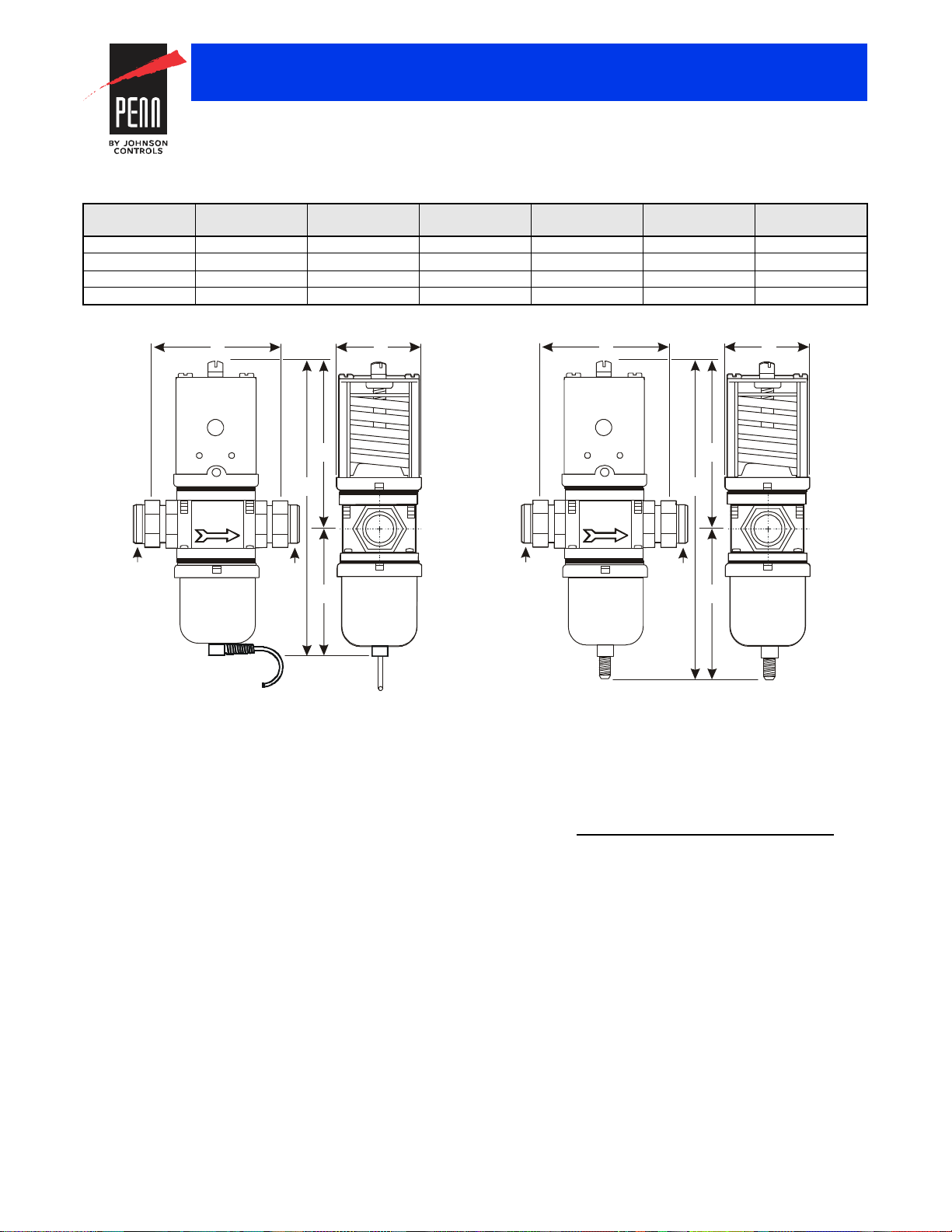
3/4 in. V146EK Valves
Port 1
Port 2
as specified
A
FIG:V146_ rnddim
High Refrigerant Pressure 3/4 in. V146GK1 Valves
E
D
C
A
Port 1
Port 2
FIG:V146GK_dim
V146 Series Two-Way Pressure-Actuated Water-Regulating Valves
Description
The V146 Series Two-Way PressureActuated Water-Regulating Valves regulate
water flow to control refrigerant head pressure
in systems with water-cooled condensers. The
V146 valves are ideal for applications with
system water pressures of up to 350 psig
(24.1 bar), such as high-rise buildings.
V146EK and V146AL valves have an
adjustable opening point in a refrigerant
pressure range of 70 to 260 psi (4.8 to
17.9 bar). V146EK and V146AL valves are
available in a 3/4 in. and 1 in. size. Use these
valves with standard, non-corrosive
refrigerants.
V146GK1 and V146GL1 valves have an
adjustable opening point in a refrigerant
pressure range of 200 to 400 psi (13.8 to
27.6 bar). The V146GK1 and V146GL1 valves
are available in 3/4 in. and 1 in. size for use
with standard, non-corrosive, high-pressure
refrigerants.
Refer to the V146 Series 2-Way
Pressure-Actuated Water-Regulating Valves
Product Bulletin (LIT-121709) for important
product application information.
Valves and Valve Accessories
Features
• no close-fitting or sliding parts in water
passages
• high-pressure design
• pressure-balanced design
• corrosion-resistant material for internal
parts
• accessible range spring
• take-apart construction
Applications
Each application is unique and requires
specific engineering data to properly size and
design a system to fulfill the appropriate
requirements. Typically, a valve is replaced
with another valve of the same size in a
properly sized and engineered system.
Code No. LIT-1900163
B
D
C
Pressure connection and capillary
The performance specifications are nomina l and con form to accep table ind ustry stand ards. For applicati ons at con ditions be yond these specification s, consult th
Johnson Controls, Inc. shall not be liable for damages resulting from misapplication or misuse of its products. © 2015 Johnson Controls, Inc.
E
B
R-161
Page 2
1 in. V146AL Valves
E
D
C
A
Port 1
Port 2
Pressur e connection and capi ll a r y
as specified.
FIG:V146AL_dim
High Refrigerant Pressure 1 in. V146GL1 Valves
E
D
C
A
Port 1
Port 2
FIG:V146GL_dim
Flow =
(Temp. - Temp. )
Outlet Inlet
Flow Required
Valves and Valve Accessories
V146 Series Two-Way Pressure-Actuated Water-Regulating Valves
(Continued)
Valve Dimensions, Inches (Millimeters)
Product Code
Number
V146EK-1C 3/4 in. 3-3/8 (86) 2-3/16 (55) 7-3/16 (183) 4-3/16 (106) 3 (76)
V146GK1-001C 3/4 in. 3-3/8 (86) 2-3/16 (55) 8 (204) 4-3/16 (106) 3-13/16 (98)
V146AL-1C 1 in. 4-3/4 (121) 2-13/16 (72) 10 (254) 5-15/16 (151) 4-1/16 (103)
V146GL1-001C 1 in. 4-3/4 (121) 2-13/16 (72) 10-1/2 (267) 5-15/16 (151) 4-9/16 (116)
Nominal Valve
Size
A B C D E
Selection
To make a rough field estimate of the size of valve for an application,
find the valve size by locating a point on a flow chart that satisfies these
requirements:
• water flow required by the condenser (Flow)
• refrigerant head pressure rise (P
• available water pressure (P
Follow these steps, and use the information obtained to locate a point
on one of the flowcharts that satisfies all three steps.
1. Take the water flow required by the condenser (Flow) from
information provided by the manufacturer of the condensing unit. If
the manufacturer’s information is unavailable, use the following
information to make a rough approximation of maximum water flow
in gallons per minute (gpm) (cubic meters per hour [m
• System Capacity (Tons of Refrigeration)
• Outlet Water Temperature (Temp.
• Inlet Water Temperature (Temp.
The performance specifications are no minal and co nform t o acceptab le ind ustry standar ds. For appl ications at condition s beyond these specifica tions, consult th
Johnson Controls, Inc. shall not be liable for damages resulting from misapplication or misuse of its products. © 2015 Johnson Controls, Inc.
AVAIL
RISE
)
Inlet
)
Outlet
)
B
B
Calculate the flow using the following formula:
Tons of Refrigeration x 30
FIG:flw_eqn
Note: If the outlet temperature is unknown, assume it to be 10F
(5.6C) above the inlet temperature.
2. Determine refrigerant head pressure rise above the valve opening
point (P
a. The Valve Closing Pressure (P
3
/hr]):
)
pressure at the highest ambient temperature the refrigeration
equipment experiences in the Off cycle. Use a
Pressure-Temperature Chart for the refrigerant selected to find
this pressure.
b. To approximate the Valve Opening Pressure (P
about 7 psi (0.5 bar) for EK and AL models or 10 psi (0.7 bar) for
GL1 or GK1 models to the Valve Closing Pressure.
R-162
) using the following steps:
RISE
) is equal to the refrigerant
CLOSE
OPEN
), add
Page 3

Valve Opening Pressure, EK and AL Models (Top) or GK1 and
GL1 Models (Bottom)
FIG:V14
OPEN CLOSE
OPEN CLOSE
Figure 1: Refrigerant Head Pressure Rise
FIG
P = P - P
Available Water Pressure
Cooling Tower
P
1
P
2
P
Loss 2
2-Way
Valve
P
COND
P
P
1P2
=
-
P
P
P
=
+
+ ...
FIG:2 wy_prss _d
3/4 in. V146EK Valve
55
60
40
45 5035302510 15
20
0
5
10
15
20
25
30
35
40
45
(gpm)
20
30
FIG:V146EK_chrt
1 in. V146AL Valve
10 15 20 25
30
35
40 45 50 55
0
5
10
15
20
25
30
35
40
45
50
55
60
65
70
75
(gpm)
10
40
20
30
50
60
FIG:V146AL_chrt
Pressure Drop Through Valve (psi)
Valves and Valve Accessories
V146 Series Two-Way Pressure-Actuated Water-Regulating Valves
(Continued)
P = P +7 psi (0.5 bar)
P = P +10 psi (0.7 bar)
c. From the Pressure-Temperature Chart for the refrigerant
selected, read the Refrigerant Condensing Pressure (P
(operating head pressure) corresponding to the selected
condensing temperature.
d. Subtract the Valve Opening Pressure from the Refrigerant
Condensing Pressure. This gives the head pressure rise.
RISE COND OPEN
3. Determine the available water pressure to the valve (P
the following steps. This is the actual water pressure available to
force water through the valve.
a. Determine the minimum inlet pressure (P
pressure from city water mains, pumps, or other sources.
b. Pressure drop through condenser (P
water pressure between the condenser inlet and the condenser
COND
outlet. Obtain this information from the condenser manufacturer.
c. Estimate or calculate the pressure drop through all associated
piping (P
d. Subtract the P
LOSS
).
COND
and P
from PIN. The result is P
LOSS
:eqn_hd_prssr_rs
AVAIL
). This is the water
IN
) is the difference in
x_eqn_opn _prssr
COND
) using
AVAIL
The maximum recommended differential water pressure across a
valve is 60 psi (4.1 bar).
Flow
60
50
40
)
10
Pressure Drop Thr ough Valve ( psi )
Refrigerant Head Pressure Rise (psi)
Flow
.
Pump
Condenser
Loss 1
4. Select the proper valve size from the flowcharts by locating a point
on a chart that satisfies the flow, the head pressure rise above
opening point, and the pressure drop across the valve.
Use these equations to convert between U.S. and S.I. units.
•1 dm
• 1 bar = 100 kPa = 0.1 MPa 1.02 kg/cm
The performance specifications are no minal and co nform t o acceptab le ind ustry standar ds. For appl ications at condition s beyond these specifica tions, consult th
Johnson Controls, Inc. shall not be liable for damages resulting from misapplication or misuse of its products. © 2015 Johnson Controls, Inc.
P= P- (P+ P)
AVAIL IN COND LOSS
3
/s = 3.6 m3/h = 15.9 U.S. gal. /min. = 13.2 U.K. gal. /min.
LOSS
2
= 0.987 atm 14.5 psi
Loss 2
P
Loss 1
IN
rp
60
Refrigerant Head Pressure Rise (psi)
R-163
Page 4

High Refrigerant Pressure 3/4 in. V146GK1 Valves
45
40
35
30
25
20
15
10
5
0
Flow
(GPM)
Flow
3
10090
8070605040
302010
Refrigerant Head Pressure Rise (psig)
Refrigerant Head Pressure Rise (bar)
Pressure Drop
Through Valve,
psi (bar)
FIG:V146GK1_chrt
5 (0.3)
2 (0.1)
High Refrigerant Pressure 1 in. V146GL1 Valves
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
Flow
GPM
1.3 2.3 3.3 4.3
5.3 6.3 7.3
3
8.2
6.2
4.2
2.2
0.2
)
Refrigerant Head Pressure Rise (psig)
10 20 30
40 50
60
70
80
90
3
FIG:V146GL_chrt
Valves and Valve Accessories
V146 Series Two-Way Pressure-Actuated Water-Regulating Valves
(Continued)
1.70.7
4.73.72.7
5.7
6.7
(m /hr)
60 (4.1)
10
50 (3.4)
40 (2.8)
8
30 (2.1)
25 (1.7)
20 (1.4)
10 (0.7)
6
4
2
0
The performance specifications are no minal and co nform t o acceptab le ind ustry standar ds. For appl ications at condition s beyond these specifica tions, consult th
Johnson Controls, Inc. shall not be liable for damages resulting from misapplication or misuse of its products. © 2015 Johnson Controls, Inc.
Refrigerant Head Pressure Rise (bar
Pressure Drop Thr ough Valve psig (m/ hr )
R-164
60 (4.1)
50 (3.4)
40 (2.8)
30 (2.1)
25 (1.7)
20 (1.4)
10 (1.0)
5 (0.3)
2 (0.1)
Flow
m/hr
16.2
14.2
12.2
10.2
Page 5

Pressure Connection Styles
Style 5
Style 46
1/4-in. SAE E x ternal Flare Connector
Copper Capillary with
1/4-in. SAE Internal Flare Connector
(Inc l udes Valve Stem Depr e ssor)
Valves and Valve Accessories
V146 Series Two-Way Pressure-Actuated Water-Regulating Valves
(Continued)
Selection Chart
Product Code Number Nominal Valve Size Inlet and Outlet Ports Pressure Connection
Style
V146EK-1C 3/4 in. Union (Sweat) 46 4.3 (2.0)
V146GK1-001C 3/4 in. Union (Sweat) 5 4.3 (2.0)
V146AL-1C 1 in. Union (Sweat) 46 9.3 (4.0)
V146GL1-001C 1 in. Union (Sweat) 5 9.3 (4.0)
Shipping Weight, lb (kg)
Repair Information
If the V146 Series Two-Way Pressure-Actuated Water-Regulating Valve fails to operate within its specifications, refer to the V146 Series
Two-Way Pressure-Actuated Water-Regulating Valves Product Bulletin (LIT-1201709) for a list of repair parts available.
Technical Specifications
V146 Series 2-Way Pressure-Actuated Water-Regulating Valves
Maximum Refrigerant Pressure V146EK: 370 psi (25.5 bar)
Maximum Working Pressure V146GK1, V146GL1: 630 psi (43.4 bar)
Opening Point Adjustment Range V146EK, V146AL: 70 to 260 psi (4.8 to 17.9 bar)
Factory-Set Opening Point V146EK, V146AL: 165 psi (11.4 bar)
Media 350 psi (24.1 bar) maximum,
V146AL: 320 psi (22.1 bar)
V146GK1, V146GL1: 200 to 400 psi (13.8 to 27.6 bar)
V146GK1, V146GL1: 275 psi (19.0 bar)
-4F to 170F (-20C to 77C) glycol/water or liquids with low freezing points that are compatible with valve materials
The performance specifications are no minal and co nform t o acceptab le ind ustry standar ds. For appl ications at condition s beyond these specifica tions, consult th
Johnson Controls, Inc. shall not be liable for damages resulting from misapplication or misuse of its products. © 2015 Johnson Controls, Inc.
R-165
 Loading...
Loading...