Page 1

Kocab 18G/Kocab 18P
USER'S MANUAL
M/B For Socket-A Athlon/Duron Processor
NO. G03-NF18G5A
Release date: July 2003
Trademark:
* Specifications and Information contained in this documentation are furnished for information use only, and are
subject to change at any time without notice, and should not be construed as a commitment by manufacturer.
Page 2

i
USER’S NOTICE ..........................................................................................................1
MANUAL REVISION INFORMATION..........................................................................1
COOLING SOLUTIONS ..............................................................................................1
CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION OF Kocab 18G/Kocab 18P MOTHERBOARD
1-1 FEATURE OF MOTHERBOARD.......................................................................... 2
1-2 SPECIFICATION ..................................................................................................... 3
1-3 PERFORMANCE LIST ...........................................................................................4
1-4 LAYOUT DIAGRAM & JUMPER SETTING ......................................................5
CHAPTER 2 HARDWARE INSTALLATION
2-1 HARDWARE INSTALLATION STEPS ................................................................8
2-2 CHECKING MOTHERBOARD'S JUMPER SETTING...................................... 8
2-3 INSTALL CPU ..........................................................................................................9
2-3-1 GLOSSARY ...................................................................................................9
2-3-2 ABOUT AMD ATHLON & DURON 462-PIN CPU.................................. 10
2-4 INSTALL MEMORY ............................................................................................... 11
2-5 EXPANSION CARD .................................................................................................11
2-5-1 PROCEDURE FOR EXPANSION CARD INSTALLATION ..................12
2-5-2 ASSIGNING IRQ FOR EXPANSION CARD ............................................12
2-5-3 INTERRUPT REQUEST TABLE FOR THIS MOTHERBOARD.......... 12
2-5-4 AGP SLOT .....................................................................................................13
2-6 CONNECTORS, HEADERS.................................................................................... 13
2-6-1 CONNECTORS .............................................................................................13
2-6-2 HEADERS ......................................................................................................16
2-7 STARTING UP YOUR COMPUTER..................................................................... 20
CHAPTER 3 INTRODUCING BIOS
3-1 ENTERING SETUP.................................................................................................. 21
3-2 GETTING HELP....................................................................................................... 21
3-3 THE MAIN MENU ...................................................................................................22
3-4 STANDARD CMOS FEATURES............................................................................ 23
3-5 ADVANCED BIOS FEATURES .............................................................................24
3-6 ADVANCED CHIPSET FEATURES ..................................................................... 26
3-7 INTEGRATED PERIPHERALS............................................................................. 27
3-7-1 ONCHIP IDE FUNCTION........................................................................... 28
3-7-2 ONCHIP DEVICE FUNCTION ..................................................................29
3-7-3 ONCHIP SUPER IO FUNCTION ...............................................................29
3-8 POWER MANAGEMENT SETUP .........................................................................30
3-9 PNP/PCI CONFIGURATION SETUP ................................................................... 31
3-9-1 IRQ RESOURCES .......................................................................................32
3-10 PC HEALTH STATUS............................................................................................33
3-11 MISCELLANEOUS CONTROL............................................................................34
3-12 LOAD STANDARD/OPTIMIZED DEFAULTS ..................................................35
3-13 SET SUPERVISOR/USER PASSWORD ..............................................................35
CHAPTER 4 DRIVER & FREE PROGRAM INSTALLATION
MAGIC INSTALL SUPPORTS WINDOWS 9X/NT/2K/XP .........................................36
4-1 NFORCE INSTALL NVIDIA NFORCE PACK DRIVER ..............................37
4-2 VGA INSTALL NVIDIA VGA DRIVER................................................... 38
4-3 SOUND INSTALL ALC AUDIO CODEC DRIVER ....................................38
4-4 USB 2.0 INSTALL NVIDIA USB 2.0 DEVICE DRIVER ...........................39
4-5 SATA INSTALL PROMISE ATA IDE CONTROLLER DRIVER.......... 40
4-6 PC-CILLIN
INSTALL PC-CILLIN2002 ANTI-VIRUS PROGRAM
.........................41
4-7 PC-HEALTH
WINBOND HARDWARE DOCTOR MONITORING SOFTWARE
....42
4-8 MBIOS INSTALL BIOS LIVE UPDATE UTILITY.....................................43
4-9 HOW TO UPDATE BIOS ........................................................................................ 45
TABLE OF CONTENT
Page 3

1
USER’S NOTICE
COPYRIGHT OF THIS MANUAL BELONGS TO THE MANUFACTURER. NO PART OF THIS MANUAL,
INCLUDING THE PRODUCTS AND SOFTWARE DESCRIBED IN IT MAY BE REPRODUCED,
TRANSMITTED OR TRANSLATED INTO ANY LANGUAGE IN ANY FORM OR BY ANY MEANS WITHOUT
WRITTEN PERMISSION OF THE MANUFACTURER.
THIS MANUAL CONTAINS ALL INFORMATION REQUIRED TO USE Kocab 18G/Kocab 18P MOTHER-
BOARD AND WE DO ASSURE THIS MANUAL MEETS USER’S REQUIREMENT BUT WILL CHANGE, CORRECT
ANY TIME WITHOUT NOTICE. MANUFACTURER PROVIDES THIS MANUAL “AS IS” WITHOUT
WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, AND WILL NOT BE LIABLE FOR ANY INDIRECT, SPECIAL, INCIDENTIAL OR
CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES (INCLUDING DAMANGES FOR LOSS OF PROFIT, LOSS OF BUSINESS, LOSS OF
USE OF DATA, INTERRUPTION OF BUSINESS AND THE LIKE).
PRODUCTS AND CORPORATE NAMES APPEARING IN THIS MANUAL MAY OR MAY NOT BE
REGISTERED TRADEMARKS OR COPYRIGHTS OF THEIR RESPECTIVE COMPANIES, AND THEY ARE
USED ONLY FOR IDENTIFICATION OR EXPLANATION AND TO THE OWNER’S BENEFIT, WITHOUT
INTENT TO INFRINGE.
Manual Revision Information
Reversion Revision History Date
5.0 Fifth Edition July 2003
Item Checklist
5
Kocab 18G/Kocab 18P Motherboard
5
Cable for IDE/Floppy
5
CD for motherboard utilities
□
Cable for USB Port 3/4 (Option)
5
Cable for 1394 Ports (One port)
5
Cable for Serial ATA IDE Port
5
SPDIF-IN/SPDIF-OUT Adaptor
5
VGA Port 2 Bracket (Only for Kocab 18G)
5
Kocab 18G/Kocab 18P User’s Manual
AMD Athlon™ / Duron™ Processor Family
Cooling Solutions
As processor technology pushes to faster speeds and higher performance, thermal management becomes
increasingly crucial when building computer systems. Maintaining the proper thermal environment is key to
reliable, long-term system operation. The overall goal in providing the proper thermal environment is keeping the
processor below its specified maximum case temperature. Heatsinks induce improved processor heat dissipation
through increased surface area and concentrated airflow from attached fans. In addition, interface materials allow
effective transfers of heat from the processor to the heatsink. For optimum heat transfer, AMD recommends the
use of thermal grease and mounting clips to attach the heatsink to the processor.
When selecting a thermal solution for your system, please refer to the website below for collection of heatsinks
evaluated and recommended by AMD for use with AMD processors. Note, those heatsinks are recommended for
maintaining the specified Maximum T case requirement. In addition, this collection is not intended to be a
comprehensive listing of all heatsinks that support AMD processors.
For vendor list of heatsink and fan, please visit:
http://www1.amd.com/products/duron/thermals
http://www1.amd.com/products/athlon/thermals
Page 4

2
Chapter 1
Introduction of Kocab 18G/Kocab 18P Motherboard
1-1 Feature of motherboard
The Kocab 18G/Kocab 18P motherboard is design for use AMD Athlon/Duron/Athlon XP
200MHz/266MHz/333MHz (Double Data Rate) Front Side Bus Frequency CPU, which utilize the
Socket-A design.
Kocab 18G motherboard use the newest nVIDIA nForce2 IGP north bridge chipset, integrated
GeForce4 MX series Graphics Processing Unit and TV encoder. Support DDR 266/333 with
internal graphic core, Kocab 18G/ Kocab 18P whose 133MHz/266MHz/333MHz (Double Data
Rate) Front Side Bus frequency delivers a clear upgrade path to the future generation of
266MHz/333MHz processors and memory interface DDR266/DDR333/DDR400(only for Kocab
18P) DDR SDRAM. The motherboard provided three 184-pin DDR DIMMs support PC3200(for
Kocab 18P only) /PC2700/PC2100/PC1600 DDR SDRAMs maximum size up to 3GB. Supports
both 64-bit and 128-bit (Dual Channel) DDR SDRAM. For those wanting even greater graphic
performance, an AGP 4X/8X slot is included on the board. Compliant with AGP 3.0 8x interface
at 533MHz.
The Kocab 18G/Kocab 18P motherboard use nVIDIA nForce2 MCP2-T south bridge offers ULTRA
ATA 66/100/
133
to provide speedier HDD throughout that boosts overall system performance.
These motherboards also have an Audio Processing Unit Support 6-channel speaker for full
surround sound effects. The motherboard provided SPDIF-In/ SPDIF-Out optical function
through Audio-bracket (optional) can connect to SPDIF (Sony & Philips Digital Interface)
Speaker for audio transmission with better quality. Or use SPDIF-In received digital signal from
other SPDIF device.
The motherboard including PCI LAN Controller chip support 10/100 Mb/sec Base transfer rate
for network. The Kocab 18G/Kocab 18P including the 1394 PCI controller provided 100M/
200M/400Mb bandwidth support two 1394 device port, which compliant with IEEE 1394A-2000
standard. With USB control as well as capability of expanding to 6 USB function ports support
USB2.0/USB1.1 Devices, the Kocab 18G/Kocab 18P meet future USB demand.
The motherboard integrated Promise PDC20375 Serial-ATA IDE controller provided two SerialATA port and one Parallel ATA port (Master mode only), support serial ATA HDD meet future
IDE demand increase the data transfer rate.
A special design in hardware for protecting Athlon XP CPU from burned, the system will auto
shutdown power supply when CPU is overheat, or the CPU FAN is stop. The motherboard has
built-in hardware monitor function. This will monitor and protect your computer.
In Kocab 18G/Kocab 18P we design in CPU Vcore Voltage, DDR memory 2.5V Voltage, AGP
1.5V Voltage those can minor adjustable in BIOS setup. This design can let users approach
over clock demand and also can make system more stable
. The Kocab 18G/ Kocab 18P
motherboard provides special function in BIOS Setup to setting CPU Host clock let users to
approach over clocking, and special design in hardware to protect BIOS from virus crash BIOS
data.
Kocab 18G/Kocab 18P provides high performance & meets future specification demand. It is
really wise choice for your computer.
1-2 Specification
Page 5
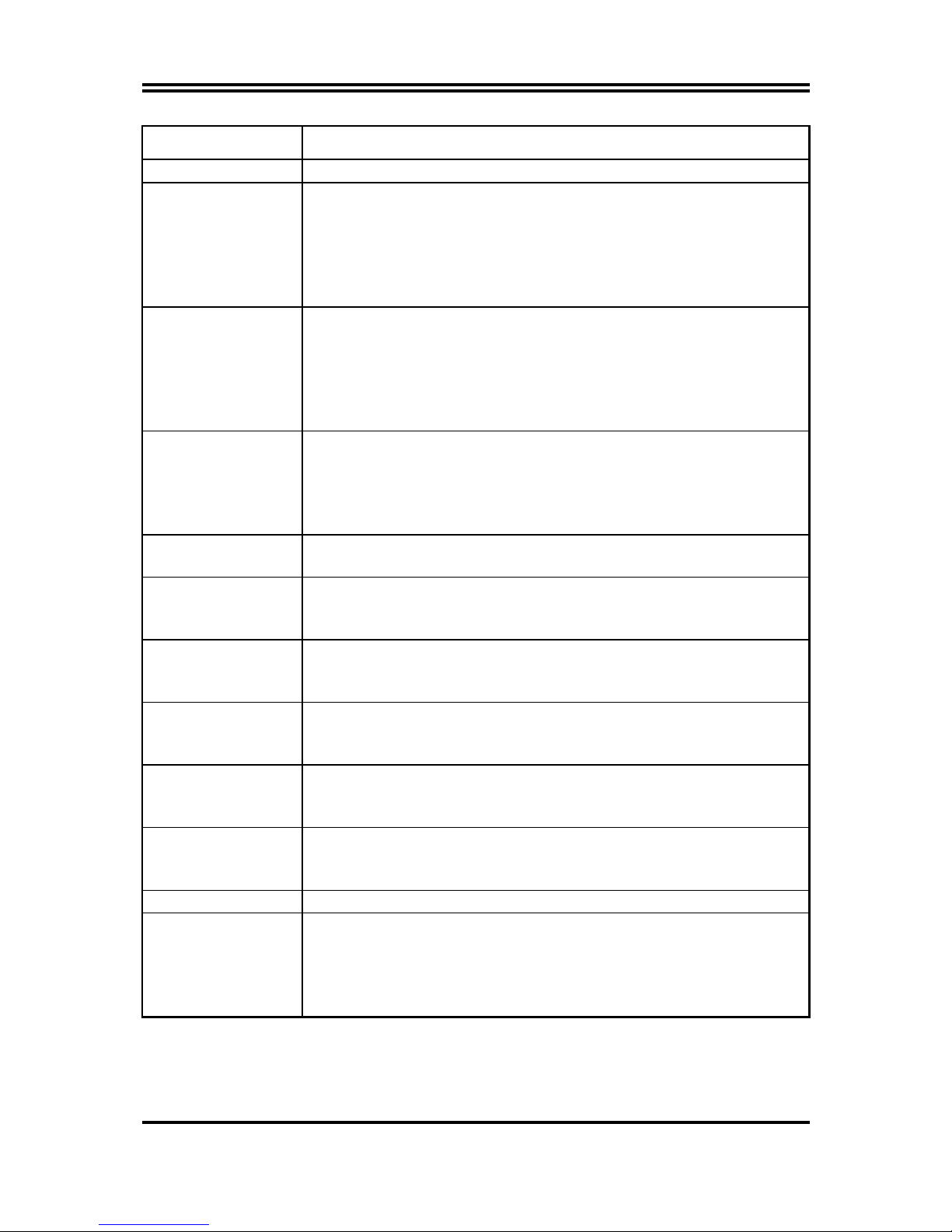
3
Spec Description
Design
∗
ATX form factor 4 layers PCB size: 30.5x24.5cm
Chipset ∗
nVIDIA nForce2 Integrated Graphics Processor (IGP) north
bridge for Kocab 18G
∗
nVIDIA nForce2 System Platform Processor (SSP) north
bridge for Kocab 18P
∗
nVIDIA nForce2 Media and Communications Processor–Turbo
(MCP2-T) south bridge
CPU Socket ∗
Support AMD Athlon 1.1GHz∼1.4GHz processor
∗
Support AMD Duron 900MHz∼1.3GHz processor
∗
Support AMD Athlon XP1500+~XP3000+ processor
∗
Support 200MHz/266MHz/333MHz (Double Data Rate) Front
Side Bus frequency processors
∗
Reserves support for future AMD Athlon XP processors
Memory Socket
(Dual Channel)
∗
184-pin DDR module socket x3
∗
Support DDR266/DDR333/DDR400(for Kocab 18P) DDR
SDRAM
∗
Support both 64-bit and 128-bit (Dual Channel) DDR SDRAM
∗
Expandable to 3.0GB
Expansion Slot &
Headers
∗
AGP slot x1 support AGP 3.0 & 4X/8X mode
∗
32-bit PCI slot x6
Integrate IDE ∗
Two PCI IDE controllers support PCI Bus Mastering, ATA
PIO/DMA and the ULTRA DMA 33/66/100/133 functions that
deliver the data transfer rate up to 133 MB/s
TV-Out/Secondary
CRT
(for Kocab 18G)
∗
Integrated TV-out encoder or Secondary through external bracket
∗
Provided S-Video and RCA composite connector
Serial-ATA IDE
∗
Promise PDC20375 Serial-ATA Controller provide two Serial
ATA ports support 150Mb/s data transfer rate and one Parallel
ATA133 port support 133Mb/s data transfer rate
1394 Port
∗
nVIDIA MCP2-T IEEE 1394 controller provided two 1394 device
ports support 100/200/400Mb bandwidth
∗
Compliant with IEEE 1394A-2000 standard
6 channel Audio ∗
Realtek ALC 650 6-channel AC97’ Codec integrated
∗ SPDIF-In/ SPDIF-Out Optical support
∗
Audio driver and utility included
BIOS
∗
Award 2MBit Flash ROM
Multi I/O ∗
PS/2 keyboard and PS/2 mouse connectors
∗
Floppy disk drive connector x1
∗
Parallel port x1, Serial port x2
∗
USB2.0 connector x2, headers x2 (connecting cable option)
∗
Audio connector (Line-in, Line-out, MIC & Game Port)
1-3 Performance List
Page 6

4
The following performance data list is the testing result of some popular benchmark testing
programs. These data are just referred by users, and there is no responsibility for different
testing data values gotten by users (the different Hardware & Software configuration will
result in different benchmark testing results.)
Performance Test Report (for Kocab 18P)
CPU:
AMD Athlon XP 3000+ (FSB 166MHz)
DRAM:
512MB DDR400 X1 (Winbond DDR W942508BH-5)
256MB DDR400 X1 (Winbond DDR W942508BH-5)
VGA Expansion Card:
ATI 9700 PRO (1024x768x32bit color)
Hard Disk Driver:
IBM IC35L040AVVN07-0 (ATA-100 7200RPM)
BIOS:
Award Optimal default
OS:
Win XP Professional
166/166 166/200 166/200
Dual Channel
3D Mark 2001SE 12477 12291 12357
3D Mark 2003 4562 4541 4554
3D Winbench 2000 (32/32bit) 393 394 394
PC Mark 2002
CPU/Memory/HDD 6311 / 5162 / 965 6373 / 5120 / 969 6339 / 5197 / 978
Content Creation Winstone 2002 44.6 43.2 44.7
Content Creation Winstone 2003
Business Winstone 2002 36.6 34.6 36.3
Winbench 99 V1.2 :
Business Disk Winmark99 10300 10300 10100
Hi-end Disk Winmark99 33800 33200 33800
Business Graphic Winmark 752 751 744
Hi-end Graphic Winmark 1830 1820 1840
SYS Mark 2001/2002 : SISMark 2001/2002 Rating ( Internet Content Creation / Office Productivity )
SISMark 2001 245 (246 / 245) 243 (244 / 243) 246 (247 / 245)
SISMark 2002
SISOFT Sandra 2003 :
Dhrystone ALU MIPS 7800 7797 7810
Whetstone FPU MFLOPS 3137 3132 3165
RAM Int Buffered iSSE2 MB/S 2251 2148 2273
RAM Float Buffered iSSE2 MB/S 2100 2045 2093
Integer SSE2 IT/S 11543 11534 11531
Floating-Point SSE2 IT/S 12296 12282 12085
QUAKE3 DEMO1 FPS 239.4 228.3 232.3
DEMO2 FPS 233.7 228.5 232.7
Return to Castle Wolfenstein FPS 124.7 121.7 123.8
WCPUID System / CPU Clock 167.05 / 2171.60 167.05 / 2171.60 167.05 / 2171.60
Performance Test Report (for Kocab 18G)
CPU: AMD Athlon XP 3000+ (FSB 166MHZ)
Page 7
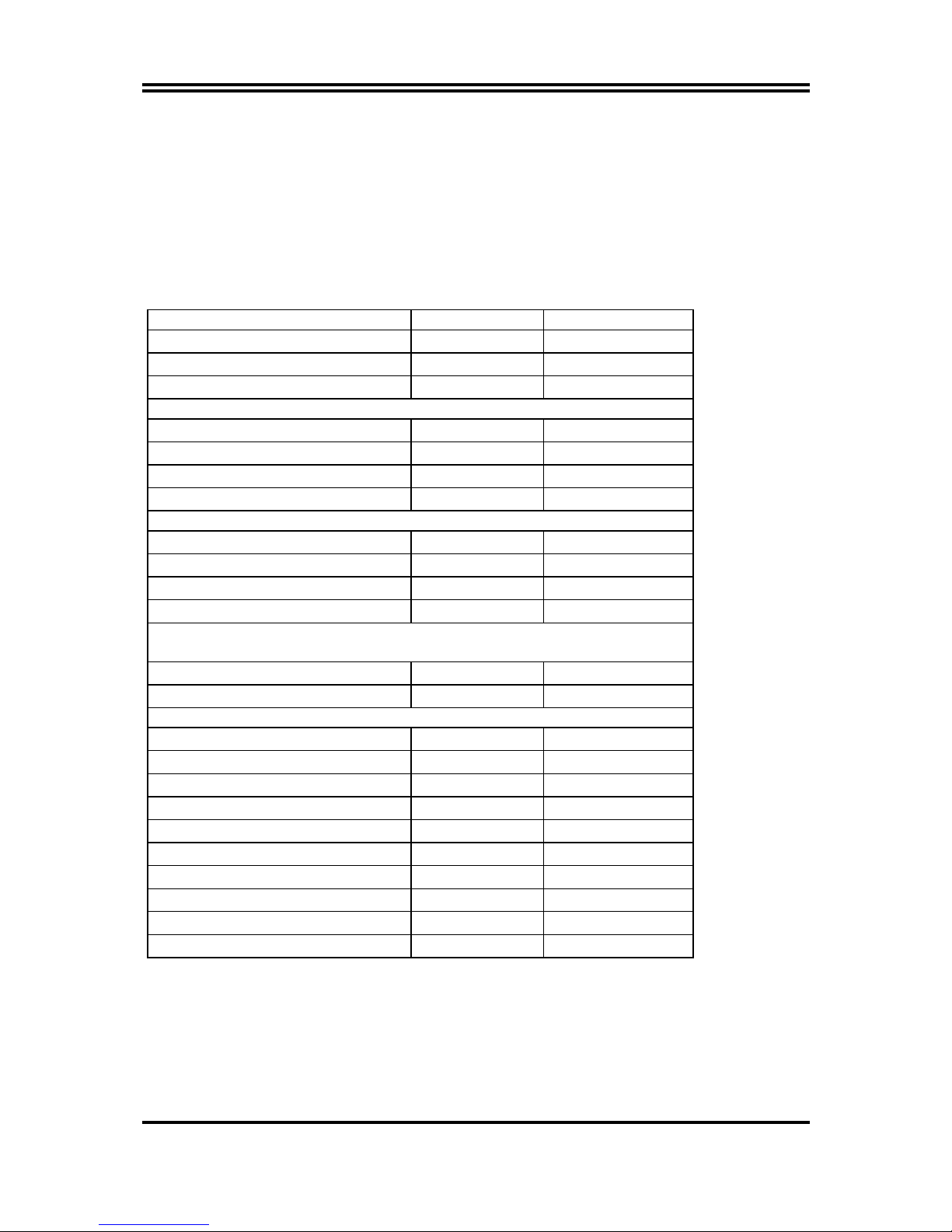
5
DRAM:
512MB DDR400 X1 (Winbond DDR W942508BH-5)
256MB DDR400 X1 (Winbond DDR W942508BH-5)
VGA Expansion Card:
ATI 9700 PRO (1024x768x32bit color)
Hard Disk Driver:
IBM IC35L040AVVN07-0 (ATA-100 7200RPM)
BIOS:
Award Optimal default
OS:
Win XP Professional
166/166 166/166 Dual Channel
3D Mark 2001SE
2934 4390
3D Mark 2003
157 218
3D Winbench 2000 (32/32bit)
80.6 123
PC Mark 2002
CPU/Memory/HDD
6269 / 4276 / 868 6299 / 4663 / 885
Content Creation Winstone 2002
41.7 43.9
Content Creation Winstone 2003
37.1 37.8
Business Winstone 2002
34.2 34.8
Winbench 99 V1.2 :
Business Disk Winmark99
9440 9510
Hi-end Disk Winmark99
31400 32000
Business Graphic Winmark
625 827
Hi-end Graphic Winmark
1790 1880
SYS Mark 2001/2002 : SISMark 2001/2002 Rating ( Internet Content Creation / Office
Productivity )
SISMark 2001
240 (239 / 241) 246 (246 / 247)
SISMark 2002
241 (303 / 191) 248 (321 / 191)
SISOFT Sandra 2003 :
Dhrystone ALU MIPS
7829 7892
Whetstone FPU MFLOPS
3130 3130
RAM Int Buffered iSSE2 MB/S
2251 2181
RAM Float Buffered iSSE2 MB/S
1943 2112
Integer SSE2 IT/S
11539 11536
Floating-Point SSE2 IT/S
12186 12202
QUAKE3 DEMO1 FPS
130.0 188.9
DEMO2 FPS
130.7 189.9
Return to Castle Wolfenstein FPS
82.3 115.7
WCPUID System / CPU Clock
167.04 / 2471.57 167.05 / 2171.59
1-4 Layout Diagram & Jumper Setting
Page 8
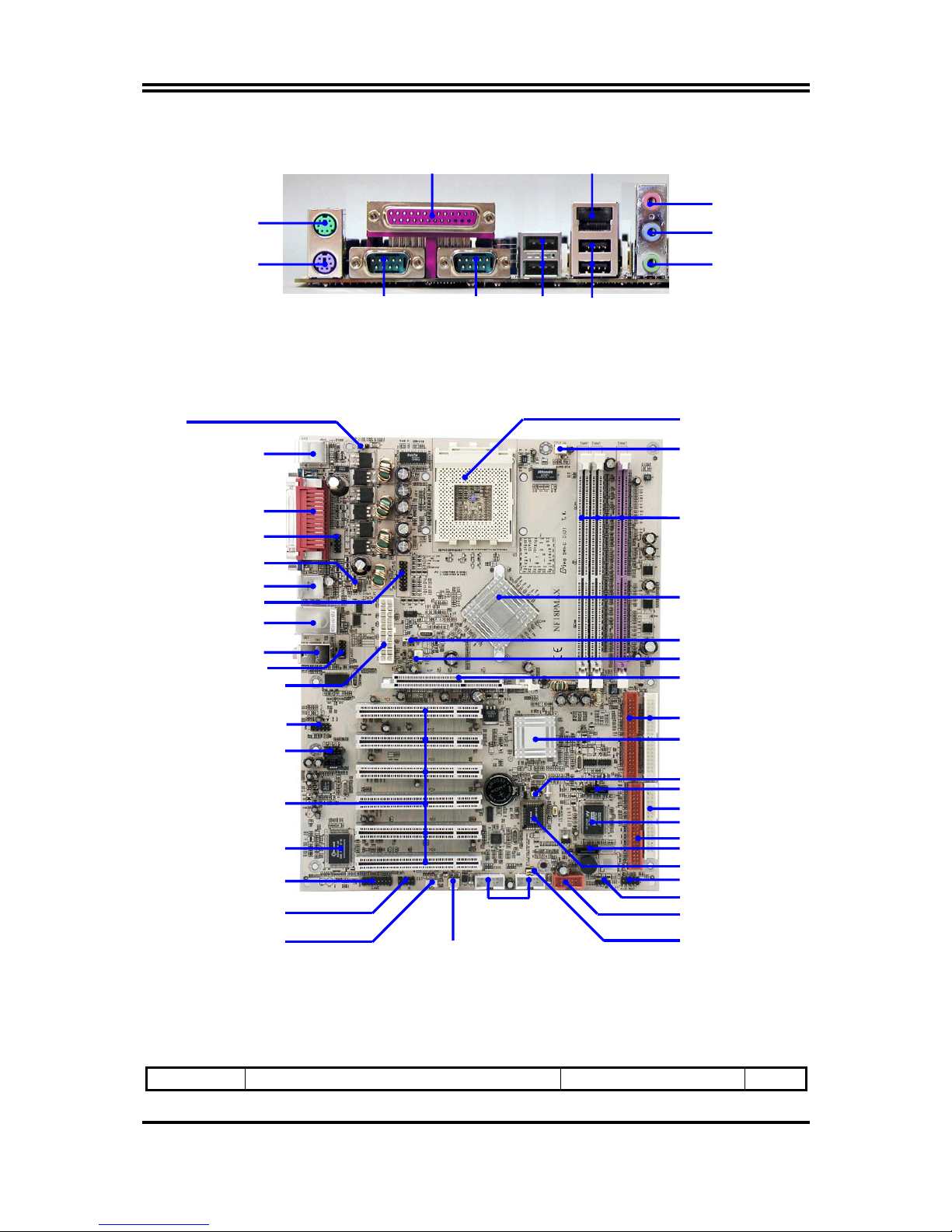
6
Jumpers
Jumper Name Description Page
LINE-OUT
LINE-IN
COM1
VGA/COM2A
(Option)
USB1
MIC
PS/2 Mouse
PS/2 Keyboard
PRINT LAN
Front Panel Audio
PC99 Back Panel
CD Audio
K/B Power ON Jumper (JP1)
USB Port/
LAN Connector
PS2 KB/Mouse Port
USB Port (USB2)
AGP 4X/8X Slot
Floppy Connector
nVIDIA nForce2
IGP/SSP Chip
Front Panel Connector
ATA 133 IDE Conn.
Clear CMOS (JP8)
ATX Power Conn.
CPU FAN
2MBit Flash ROM BIOS
CPU Socket
DDR DIMM X3
SFAN2
nVIDIA nForce2 MCP2-T
Chip
Speak Connector
Serial ATA Controlle
r
ATA 133 IDE Conn.
Winbond 83627HF Chip
GAME Port Connector
PCI Slot
Wake On LAN
SFAN1
(JP5)
CPU F.S.B. Frequency Selector
Serial-ATA Connector (SATA1)
Serial-ATA Connector (SATA2)
USB Wake-Up Jumper (JP10)
USB Port
USB Wake-Up Jumper
(JP2)
Audio Connector (CN1)
1394 Port
(1394A, 1394B)
SPDIF Connector
IR Connector
USB
VGA (for Kocab 18G)
COM2A (for Kocab 18P)
COM2 Connector
(for Kocab 18G)
VGA2 Connector (VGA2)
Page 9
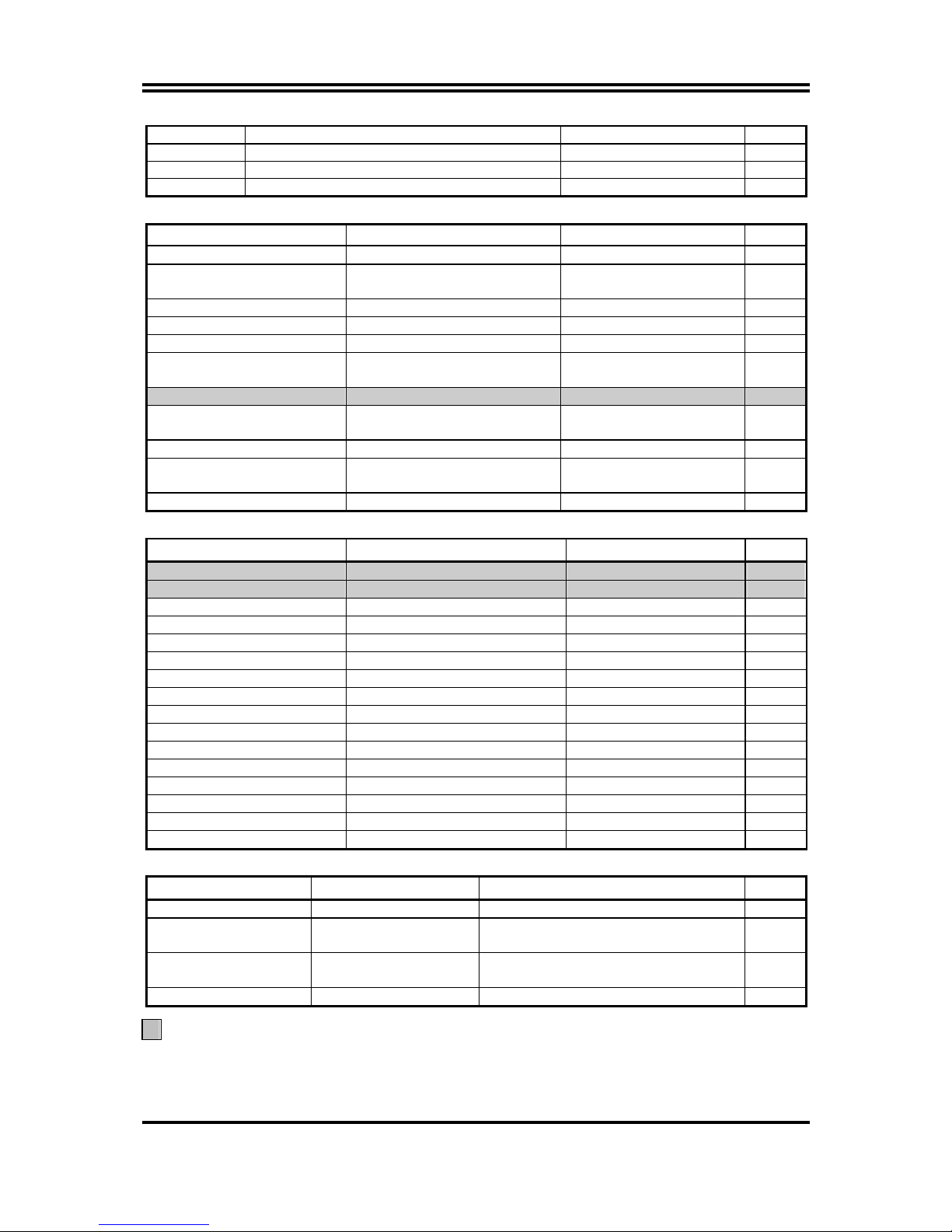
7
JP1 Keyboard Power On Enabled/Disabled 3-pin Block P.8
JP2, JP10 USB Wake-Up Enabled/Disabled 3-pin Block P.8
JP5 CPU Front Side Bus Frequency 4-pin Block P.8
JP8 CMOS RAM Clear jumper 3-pin Block P.9
Connectors
Connector Name Description Page
PWR ATX Power Connector 20-pin Block P.13
KYB PS/2 Mouse & PS/2 Keyboard
Connector
6-pin Female P.13
USB1 USB Port Connector 2 x 4-pin Connector
UL1 USB/LAN Port Connector 2 x 4-pin/RJ45 Connector P.13
LPT Parallel Port Connector 25-pin Female P.13
CN1
(Line-OUT/Line-IN/MIC)
Audio Connector 3 phone jack Connector P.14
VGA VGA Port Connector D-Sub 15-pin Connector P.14
COM1
/COM2A for Kocab 18P
Serial Port COM1/2
Connector
9-pin Connector P.14
FDD Floppy Driver Connector 34-pin Block P.14
IDE1/IDE2
/IDE3
Primary/Secondary
/Third IDE Connector
40-pin Block P.15
SATAT1/2 Serial ATA IDE Connector 7-pin Block P.15
Headers
Header Name Description Page
COM2 Serial Port COM2 Header 9-pin Block P.16
VGA2 VGA Port2 Header 15-pin Block P.16
AUDIO Line-Out, MIC Header 9-pin Block P.16
GAME Game Port Header 15-pin Block P.17
USB2 USB Port Headers 9-pin Block P.17
1394A/1394B 1394 Port Headers 9-pin Block P.17
HD LED IDE activity LED 2-pin Block P.17
RESET Reset switch lead 2-pin Block P.17
SPEAK Speaker connector 4-pin Block P.17
PWR LED Power LED 2-pin Block P.17
PWR BTN Power switch 2-pin Block P.18
WOL Wake On-LAN Headers 3-pin Block P.18
SFAN1, SFAN2, CPUFAN FAN Headers 3-pin Block P.18
IR IR infrared module Headers 5-pin Block P.19
CDIN CD Audio-In Headers 4-pin Block P.19
SPDIF SPDIF In/Out Headers 9-pin Block P.19
Expansion Sockets
Socket/Slot Name Description Page
ZIF Socket 462 CPU Socket 462-pin PPGA CPU Socket P.10
DDR1, DDR2, DDR3 DDR SDRAM
Module Socket
184-pin DDR SDRAM Module
Expansion Socket
P.11
PCI1, PCI2, PCI3,
PCI4, PCI5, PCI6
PCI Slot 32-bit PCI Local Bus Expansion slots P.12
AGP AGP 4X/8X Mode Slot AGP Expansion Slot P.13
Only for Kocab 18G
Chapter 2
Page 10
8
Hardware installation
2-1 Hardware installation Steps
Before using your computer, you had better complete the following steps:
1. Check motherboard setting
2. Install CPU
3. Install Memory
4. Install Expansion cards
5. Connect Ribbon cables, Panel wires, and power supply
6. Setup BIOS
7. Install software driver & utility
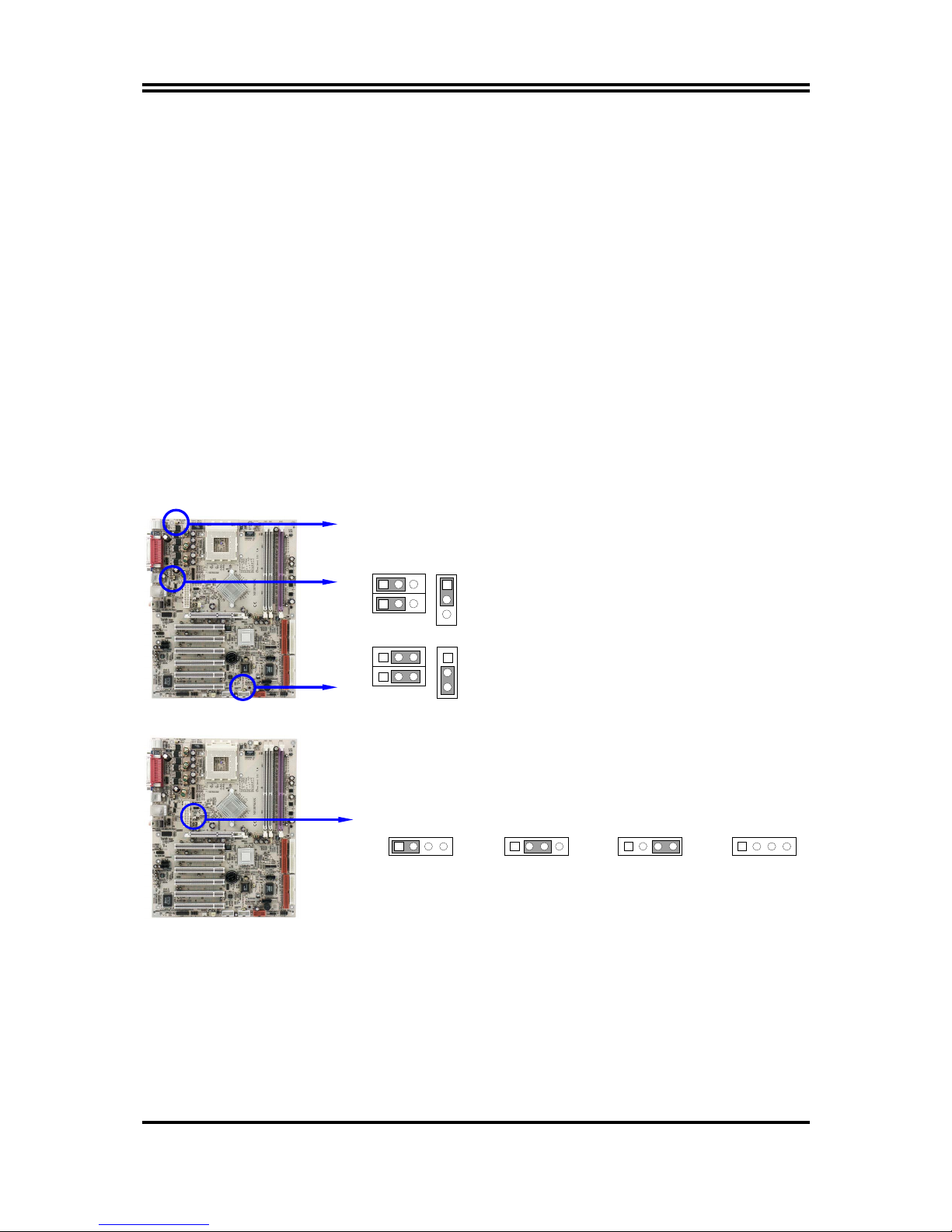
2-2 Checking Motherboard’s Jumper Setting
(1) Keyboard Power On function Enabled/Disabled: JP1
USB Wake-Up function Enabled/Disabled :JP2, JP10
When setting Enabled you can using keyboard by key in password or use USB device to
power on system.
JP2, JP10 2-3 closed USB Wake-Up Enabled
JP1 2-3 closed K/B Power ON Enabled
JP2, JP10 1-2 closed USB Wake-Up Disabled (Default)
JP1 1-2 closed K/B Power ON Disabled (Default) JP1
JP10
1 3
JP1
JP10
1 3
JP2
1
3
JP2
1
3
(2) CPU Front Side Bus Frequency Setting (4-pin) : JP5
CPU Front Side Bus Frequency Setting
1-2 : 133/166MHz
(AUTO)
JP5
1
4
2-3 : 166MHz
JP5
1
4
3-4 : 100MHz
JP5
1
4
OFF : 133MHz
JP5
1
4
Note: CPU Front Side Bus Frequency also can change setting in BIOS SETUP, please
refer page 34 Miscellaneous Control in Host Clock at Next.
Note: When overclocking cause system can not boot up, users have to keeping press the
“INS” key and push the power on button to switch on the system until the screen
have display to recovery the standard Default. Otherwise the CMOS will keep the
faulty data and M/B will not function.
(3) CMOS RAM Clear (3-pin) : JP8
Page 11

9
A battery must be used to retain the motherboard configuration in CMOS RAM short
1-2 pins of JP8 to store the CMOS data.
To clear the CMOS, follow the procedure below:
1. Turn off the system and unplug the AC power
2. Remove ATX power cable from ATX power connector
3. Locate JP8 and short pins 2-3 for a few seconds
4. Return JP8 to its normal setting by shorting pins 1-2
5. Connect ATX power cable back to ATX power connector
Note: When should clear CMOS
1. Troubleshooting
2. Forget password
3. After over clocking system boot fail
CMOS RAM Clear Setting
2-3 closed Clear CMOS
JP8
13
JP8
13
1-2 closed Normal
2-3 Install CPU
2-3-1 Glossary
Chipset (or core logic) - two or more integrated circuits which control the interfaces between the
system processor, RAM, I/O devises, and adapter cards.
Processor slot/socket - the slot or socket used to mount the system processor on the motherboard.
Slot (AGP, PCI, ISA, RAM) - the slots used to mount adapter cards and system RAM.
AGP - Accelerated Graphics Port - a high speed interface for video cards; runs at 1X (66MHz), 2X
(133MHz), or 4X (266MHz).
PCI - Peripheral Component Interconnect - a high speed interface for video cards, sound cards,
network interface cards, and modems; runs at 33MHz.
ISA - Industry Standard Architecture - a relatively low speed interface primarily used for sound cards
and modems; runs at approx. 8MHz.
Serial Port - a low speed interface typically used for mouse and external modems.
Parallel Port - a low speed interface typically used for printers.
PS/2 - a low speed interface used for mouse and keyboards.
USB - Universal Serial Bus - a medium speed interface typically used for mouse, keyboards, scanners,
and some digital cameras.
Sound (interface) - the interface between the sound card or integrated sound connectors and speakers,
MIC, game controllers, and MIDI sound devices.
LAN (interface) - Local Area Network - the interface to your local area network.
BIOS (Basic Input/Output System) - the program logic used to boot up a computer and establish the
relationship between the various components.
Driver - software, which defines the characteristics of a device for use by another device or other
software.
Page 12
10
Processor - the "central processing unit" (CPU); the principal integrated circuit used for doing the
"computing" in "personal computer"
Front Side Bus Frequency -
the working frequency of the motherboard, which is generated by the
clock generator for CPU, DRAM and PCI BUS.
CPU L2 Cache -
the flash memory inside the CPU, normally Athlon CPU has 256K or above, while
Duron will have 64K.
2-3-2 About AMD Athlon & Duron 462-pin CPU
This motherboard supports Socket-A (Socket-462) AMD Athlon/Duron processors.
This motherboard Provides a ZIF Socket-A. The CPU that comes with the motherboard
should have a cooling FAN attached to prevent overheating. If this is not the case, then
purchase a correct cooling FAN before you turn on your system.
WARNING!
Be sure that there is sufficient air circulation across the processor’s heatsink and
CPU cooling FAN is working correctly, otherwise it may cause the processor and
motherboard overheat and damage, you may install an auxiliary cooling FAN, if
necessary.
WARNING!
Due to this motherboard provides new function of protecting CPU;you must
connect the CPU FAN connector on CPUFAN location in order to obtain this
feature. Without connection on CPUFAN (or you have connect CPU FAN on
SFAN1), the system will shut down immediately to protect both your CPU and
motherboard.
Over heat Protect:
Only for Athlon XP serial CPU, when the CPU overheat, system will auto shut
down power supply. You can hear a continue beep sound, the power button will
be locked up. Users must turn off and turn on the AC power to reset the system
otherwise the power button will no function, the other way is keeping press the
push button few seconds till the beep sound stop, then release the power button
and press the power button again to turn on the power supply.
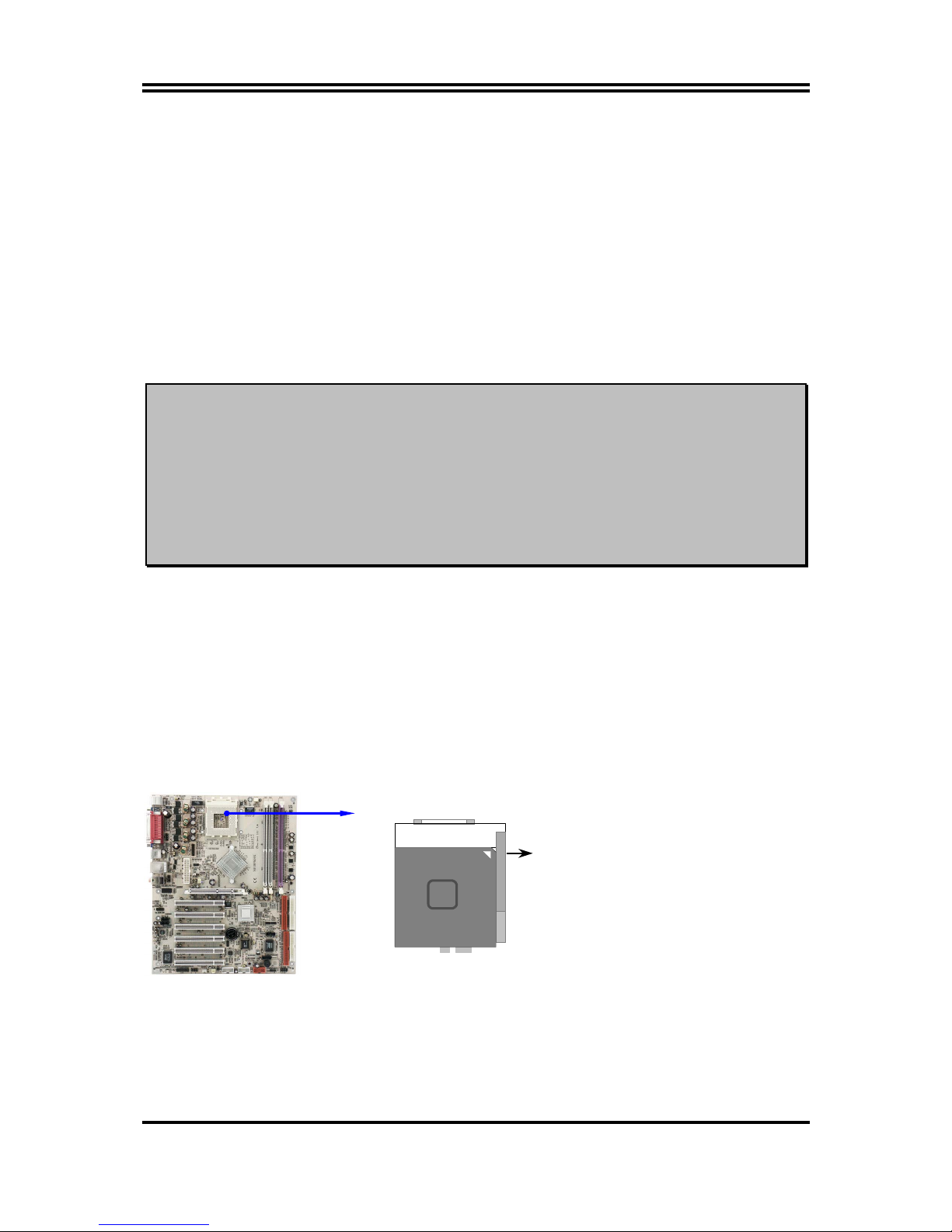
To install a CPU, first turn off your system and remove its cover. Locate the ZIF socket and open it
by first pulling the level sideways away from the socket then upward to a 90-degree angle. Insert the
CPU with the correct orientation as shown below. The notched corner should point toward the end of
the level. Because the CPU has a corner pin for two of the four corners, the CPU will only fit in the
orientation as shown.
CPU ZIF Socket-A
Colden Arrow
Socket 462
When you put the CPU into the ZIF socket. No force require to insert of the CPU, then press
the level to Locate position slightly without any extra force.
2-4 Install Memory
This motherboard provides three 184-pin DUAL INLINE MEMORY MODULES (DIMM)
sites for memory expansion available from minimum memory size of 64MB to maximum
Page 13
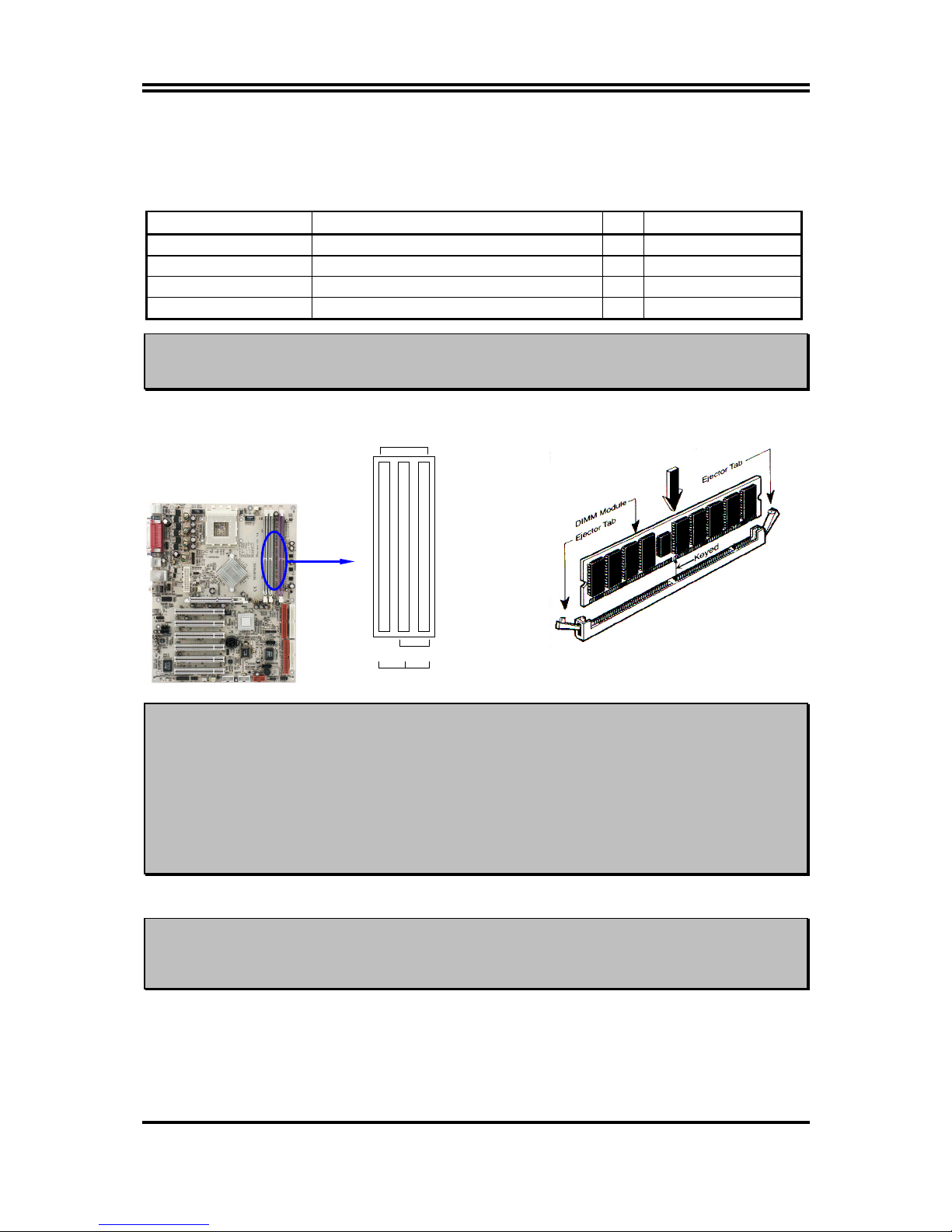
11
memory size of 3.0GB DDR SDRAM.
For Support 128-bit data transfer function (Dual
Channel) must plug both DDR1 & DDR3, DDR2 & DDR3, or DDR1 & DDR2 & DDR3,
other combination only support 64-bit data transfer.
Valid Memory Configurations
Bank 184-Pin DIMM PCS Total Memory
Bank 0, 1 (DDR1) DDR 266/333/400 DDR SDRAM X1
64MB∼1.0GB
Bank 2, 3 (DDR2) DDR 266/333/400 DDR SDRAM X1
64MB∼1.0GB
Bank 4, 5 (DDR3) DDR 266/333/400 DDR SDRAM X1
64MB∼1.0GB
Total System Memory (Max. 3.0GB) 3
64MB∼3.0GB
NOTE!
Make sure the total installed memory does not exceeds 3.0GB, otherwise the
system may hang during startup.
Generally, installing DDR SDRAM modules to your motherboard is very easy, you can refer
to figure 2-4 to see what a 184-Pin
DDR 266/333/400
DDR SDRAM module looks like.
DDR2 (BANK2 + BANK3)
DDR1 (BANK0 + BANK1)
DDR3 (BANK4 + BANK5)
Dual Channel (DDR2 & DDR3)
Dual Channel (DDR1 & DDR3)
Dual Channel (DDR & DDR2 & DDR3)
NOTE!
When you install DIMM module fully into the DIMM socket the eject tab
should be locked into the DIMM module very firmly and fit into its
indention on both sides.
WARNING!
For the DDR SDRAM CLOCK is set at 166MHz, use only DDR333 compliant DDR
Modules. When this motherboard operate at 133Mhz, most system will not even
boot if non-compliant modules are used because of the strict timing issues, if your
DDR Modules are not DDR266-compliant, set the DDR SDRAM clock to 100MHz
to ensure system stability.
2-5 Expansion Cards
WARNING!
Turn off your power when adding or removing expansion cards or other system
components. Failure to do so may cause severe damage to both your motherboard
and expansion cards.
2-5-1 Procedure For Expansion Card Installation
1. Read the documentation for your expansion card and make any necessary hardware or
software setting for your expansion card such as jumpers.
2. Remove your computer’s cover and the bracket plate on the slot you intend to use.
Figure 2-4
Page 14
12
3. Align the card’s connectors and press firmly.
4. Secure the card on the slot with the screen you remove above.
5. Replace the computer system’s cover.
6. Set up the BIOS if necessary.
7. Install the necessary software driver for your expansion card.
2-5-2 Assigning IRQs For Expansion Card
Some expansion cards need an IRQ to operate. Generally, an IRQ must exclusively assign to
one use. In a standard design, there are 16 IRQs available but most of them are already in use.
Standard Interrupt Assignments
IRQ Priority Standard function
0 N/A System Timer
1 N/A Keyboard Controller
2 N/A Programmable Interrupt
3 * 8 Communications Port (COM2)
4 * 9 Communications Port (COM1)
5 * 6 Sound Card (sometimes LPT2)
6 * 11 Floppy Disk Controller
7 * 7 Printer Port (LPT1)
8 N/A System CMOS/Real Time Clock
9 * 10 ACPI Mode when enabled
10 * 3 IRQ Holder for PCI Steering
11 * 2 IRQ Holder for PCI Steering
12 * 4 PS/2 Compatible Mouse Port
13 N/A Numeric Data Processor
14 * 5 Primary IDE Channel
15 * 1 Secondary IDE Channel
* These IRQs are usually available for ISA or PCI devices.
2-5-3 Interrupt Request Table For This Motherboard
Interrupt request are shared as shown the table below:
INT A INT B INT C INT D
PCI slot 1 Shared
PCI slot 2
Shared
PCI slot 3
Shared
PCI slot 4
Shared
PCI slot 5 Shared
PCI slot 6
AGP slot Shared
AC97/MC97
Shared
Onboard USB
Shared
Onboard USB 1
Shared
Onboard USB 2
Shared
IMPORTANT! If using PCI cards on shared slots, make sure that the drivers support “Shared
IRQ” or that the cards don’t need IRQ assignments. Conflicts will arise between
the two PCI groups that will make the system unstable or cards inoperable.
2-5-4 AGP Slot
Page 15
13
This motherboard provides an AGP Slot, support the 4X/8X AGP VGA card.
AGP SLOT
2-6 Connectors, Headers
2-6-1 Connectors
(1) Power Connector (20-pin block) : ATXPOW
ATX Power Supply connector. This is a new defined 20-pins connector that usually comes
with ATX case. The ATX Power Supply allows to use soft power on momentary switch that
connect from the front panel switch to 2-pins Power On jumper pole on the motherboard.
When the power switch on the back of the ATX power supply turned on, the full power will not
come into the system board until the front panel switch is momentarily pressed. Press this
switch again will turn off the power to the system board.
PIN ROW2 ROW1
1 3.3V 3.3V
2 -12V 3.3V
3 GND GND
4 Soft Power On 5V
5 GND GND
6 GND 5V
7 GND GND
8 -5V Power OK
9 +5V +5V (for Soft Logic)
10 +5V +12V
Pin 1
(2) PS/2 Mouse & PS/2 Keyboard Connector: KYB
The connectors for PS/2 keyboard and PS/2 Mouse.
(3) USB Port connector: USB/USB1
The connectors are 4-pin connector that connect USB devices to the system board.
(4) LAN Port connector: LAN
The connector is standard RJ45 connector for network connection
(5) Parallel Port Connector (25-pin female): LPT
Parallel Port connector is a 25-pin D-Subminiature Receptacle connector. The On-board
Parallel Port can be disabled through the BIOS SETUP. Please refer to Chapter 3
“INTEGRATED PERIPHERALS SETUP” section for more detail information.
(6) Audio Connector : LINE-OUT/LINE-IN/MIC
This Connector are 3 phone Jack for LINE-OUT, LINE-IN, MIC
LINE_O :
Audio output to speaker
LINE_I :
Audio input to sound chip
MIC :
Microphone Connector
(7) VGA Connector (15-pin D-Sub) Connector: VGA (for Kocab 18G only)
Page 16

14
VGA is the 15-pin D-Subminiature female connector for display monitor.
(8) Serial Port COM1, COM2 : COM1, COM2A (COM2A only for Kocab 18P)
COM1, COM2 are the 9-pin D-Subminiature mail connector. The On-board serial port can be
disabled through BIOS SETUP. Please refer to Chapter 3 “INTEGRATED PERIPHERALS SETUP”
section for more detail information.
(9) Floppy drive Connector (34-pin block): FDD
This connector supports the provided floppy drive ribbon cable. After connecting the
single plug end to motherboard, connect the two plugs at other end to the floppy drives.
Pin 1
Floppy Drive Connector
(10) Primary IDE Connector (40-pin block): IDE1
This connector supports the provided IDE hard disk ribbon cable. After connecting the single
plug end to motherboard, connect the two plugs at other end to your hard disk(s). If you install
two hard disks, you must configure the second drive to Slave mode by setting its jumpers
accordingly. Please refer to the documentation of your hard disk for the jumper settings.
(11) Secondary IDE Connector (40-pin block): IDE2
This connector connects to the next set of Master and Slave hard disks. Follow the same
procedure described for the primary IDE connector. You may also configure two hard disks to
be both Masters using one ribbon cable on the primary IDE connector and another ribbon cable
on the secondary IDE connector.
Pin 1
IDE2
Pin 1
IDE1
USB1
LINE-OUT
LINE-IN
MIC
PS/2 Mouse PRINT LAN
COM1
VGA/COM2A
(Option)
PS/2 Keyboard USB
Page 17

15
•
Two hard disks can be connected to each connector. The first HDD is referred to as the
“Master” and the second HDD is referred to as the “Slave”.
•
For performance issues, we strongly suggest you don’t install a CD-ROM or DVD-ROM drive
on the same IDE channel as a hard disk. Otherwise, the system performance on this channel may
drop.
(12) Third IDE Connector (40-pin block): IDE3 (Master Mode only)
This connector supports the provided IDE hard disk ribbon cable. After connecting the single
plug end to motherboard, connect the two plugs at other end to your hard disk(s). Because this
connector only support Master Mode, you must configure the drive to Master mode by setting
its jumpers accordingly. Please refer to the documentation of your hard disk for the jumper
settings.
Pin 1
IDE3
(13) Serial ATA IDE Connector (7-pin block): SATA1/ SATA2
This connector support the provided Serial ATA IDE cable for connect the Serial ATA hard
disk.
Serial-ATA Port Connector
Pin 1
SATA2
SATA1
2-6-2 Headers
(1) Serial Port2 COM2 Header (9-pin) : COM2 (only for Kocab 18G)
Page 18

16
COM 2
Pin 1
N
ote: Orient the read marking on the
COM2 ribbon cable to pin 1
Serial Port2 COM2 Header
(2) VGA Port2 Header (15-pin) : VGA2 (only for Kocab 18G)
This header is for secondary CRT Display and TV-out the user only can get one display either
the CRT2 or the TV-out at the same time.
Note: Because VGA port 2 bracket works with the onboard graphic core. When plug in
external VGA card in AGP slot , the VGA port2 bracket will not function.
Pin 1
VGA Port2 Header
(3) Line-Out, MIC Header (9-pin): AUDIO
This header connect to Front Panel Line-out, MIC connector with cable.
Line-Out, MIC Headers
AUDI O
Pin 1
AUD_MIC
AUD
_
FPOUT_L
AUD_MIC_BI AS
AUD_FPOUT_R
HP_ON
AUD_GND
AUD
_
RET_L
AUD
_
RET_R
AUD
_
VCC
2
910
(4) GAME Port Header (15-pin) : GAME
This 15-pin header can through a cable with a 15-pin D-Subminiature Receptacle Connector for
joystick/MIDI Device.
VGA2
SVIDEO
RCA
VGA Port2 Bracket
Page 19

17
Pin 1
GAME Port Header
(5) USB Port Header (9-pin) : USB2
The header are used for connecting the additional USB port plug. By attaching an option USB
cable, your can be provided with two additional USB plugs affixed to the back panel.
USB Port Headers
Pin 1
USB2
VCC
-
DATA
GND
+ DAT A
VCC
OC
-
DATA
GND
+ DAT A
(6) 1394 Port Headers (9-pin): 1394A, 1394B
1394 Port Headers
1394A
Pin 1
TPA-
GND
VCC
TPB-
TPA+
GND
GND
VCC
TPB+
1394B
Pin 1
TPA-
GND
VCC
TPB-
TPA+
GND
GND
VCC
TPB+
(7) IDE Activity LED: HD LED
This connector connects to the hard disk activity indicator light on the case.
(8) Reset switch lead: RESET
This 2-pin connector connects to the case-mounted reset switch for rebooting your computer
without having to turn off your power switch. This is a preferred method of rebooting in order
to prolong the lift of the system’s power supply. See the figure below.
(9) Speaker connector: SPEAK
This 4-pin connector connects to the case-mounted speaker. See the figure below.
(10) Power LED: PWR LED
The Power LED is light on while the system power is on. Connect the Power LED from the
system case to this pin.
(11) Power switch: PWR BTN
This 2-pin connector connects to the case-mounted power switch to power ON/OFF the system.
Page 20

18
System Case Connections
HDLED
RESET
VCC5
GND
VCC5
PWR LED
PWRBTN
PWRBTN
PWRLED
HDDLED
RST S W
NC
GND
FPSPEAK
SPK
R
GND
NC
VCC5
Pin 1
Pin 1
(12) Wake On-LAN Headers (3-pin) : WOL
This connector connects to a LAN card with a WAKE ON-LAN output. This connector
power up the system when a wake up signal is received through the LAN card.
NOTE:
This feature requires that Wake On LAN or Ring In Wake up is enabled.
Wake-On-LAN Headers
WOL
13
5VSB
GND
WOL
(13) FAN Speed Headers (3-pin) : SFAN1, SFAN2, CPUFAN
These connectors support cooling fans of 350mA (4.2 Watts) or less, depending on the
fan manufacturer, the wire and plug may be different. The red wire should be positive,
while the black should be ground. Connect the fan’s plug to the board taking into
consideration the polarity of connector.
CPUFAN
13
SFAN2
13
SFAN1
1
3
(14) IR infrared module Headers (5-pin) : IR
Page 21

19
This connector supports the optional wireless transmitting and receiving infrared
module. You must configure the setting through the BIOS setup to use the IR function.
IR infrared module Headers
IR
Pin 1
GND
IRRX
NC
VCC
IRTX
2
5
6
(15) CD Audio-In Headers (4-pin) : CDIN
CDIN is the connector for CD-Audio Input signal. Please connect it to CD-ROM CD-Audio
output connector.
CD Audio-In Headers
4 1
CDI N
(16) SPDIF-Bracket Connector : SPDIF
The connector allows you to connect a SPDIF-Bracket for Sony & Philips Digital Interface
(SPDIF). The SPDIF-Bracket offers 2 SPDIF jacks for digital audio transmission and receiver
(for optional optical fiber) and 2 analog Line-Out jacks for 4-channel audio output.
To attach the fiber-optic cable to optical SPDIF jack, you have to remove the plug from the
jack first.
SPDIF-Bracket Connector
Pin 1
SPDIF
NC
SPDIF
-
OUT
GENT ER
GND
12V
GND
SURROUND
-
L
SPDIF-I N
SURROUND-R
210
9
BASS
2-7 Starting Up Your Computer
Connect to SPDIF
Page 22

20
1. After all connection are made, close your computer case cover.
2. Be sure all the switch are off, and check that the power supply input voltage is set to
proper position, usually in-put voltage is 220V∼240V or 110V∼120V depending on your
country’s voltage used.
3. Connect the power supply cord into the power supply located on the back of your system
case according to your system user’s manual.
4. Turn on your peripheral as following order:
a. Your monitor.
b. Other external peripheral (Printer, Scanner, External Modem etc…)
c. Your system power. For ATX power supplies, you need to turn on the power supply
and press the ATX power switch on the front side of the case.
5. The power LED on the front panel of the system case will light. The LED on the monitor
may light up or switch between orange and green after the system is on. If it complies
with green standards or if it is has a power standby feature. The system will then run
power-on test. While the test are running, the BIOS will alarm beeps or additional
message will appear on the screen.
If you do not see any thing within 30 seconds from the time you turn on the power. The
system may have failed on power-on test. Recheck your jumper settings and connections
or call your retailer for assistance.
Beep Meaning
One short beep when displaying logo No error during POST
Long beeps in an endless loop No DRAM install or detected
One long beep followed by three short
beeps
Video card not found or video card memory
bad
High frequency beeps when system is
working
CPU overheated
System running at a lower frequency
6. During power-on, press <Delete> key to enter BIOS setup. Follow the instructions in
BIOS SETUP.
7.
Power off your computer:
You must first exit or shut down your operating system
before switch off the power switch. For ATX power supply, you can press ATX power
switching after exiting or shutting down your operating system. If you use Windows 9X,
click
“Start”
button, click
“Shut down”
and then click
“Shut down the computer?”
The power supply should turn off after windows shut down.
Page 23

21
Chapter 3
Introducing BIOS
The BIOS is a program located on a Flash Memory on the motherboard. This program is a
bridge between motherboard and operating system. When you start the computer, the BIOS
program gain control. The BIOS first operates an auto-diagnostic test called POST (power on
self test) for all the necessary hardware, it detects the entire hardware device and configures
the parameters of the hardware synchronization. Only when these tasks are completed done it
gives up control of the computer to operating system (OS). Since the BIOS is the only
channel for hardware and software to communicate, it is the key factor for system stability,
and in ensuring that your system performance as its best.
In the BIOS Setup main menu of Figure 3-1, you can see several options. We will explain
these options step by step in the following pages of this chapter, but let us first see a short
description of the function keys you may use here:
•
Press <Esc> to quit the BIOS Setup.
•
Press
↑↓←→
(up, down, left, right) to choose, in the main menu, the option you want
to confirm or to modify.
•
Press <F10> when you have completed the setup of BIOS parameters to save these
parameters and to exit the BIOS Setup menu.
•
Press Page Up/Page Down or +/– keys when you want to modify the BIOS parameters
for the active option.
3-1 Entering Setup
Power on the computer and by pressing <Del> immediately allows you to enter Setup.
If the message disappears before your respond and you still wish to enter Setup, restart the
system to try again by turning it OFF then ON or pressing the “RESET” button on the system
case. You may also restart by simultaneously pressing <Ctrl>, <Alt> and <Delete> keys. If
you do not press the keys at the correct time and the system does not boot, an error message
will be displayed and you will again be asked to
Press <F1> to continue, <Ctrl-Alt-Esc> or <Del> to enter Setup
3-2 Getting Help
Main Menu
The on-line description of the highlighted setup function is displayed at the bottom of the
screen.
Status Page Setup Menu/Option Page Setup Menu
Press F1 to pop up a small help window that describes the appropriate keys to use and the
possible selections for the highlighted item. To exit the Help Window, press <Esc>.
Page 24

22
3-3 The Main Menu
Once you enter Award BIOS CMOS Setup Utility, the Main Menu (Figure 3-1) will appear
on the screen. The Main Menu allows you to select from fourteen setup functions and two
exit choices. Use arrow keys to select among the items and press <Enter> to accept or enter
the sub-menu.
CMOS Setup Utility – Copyright(C) 1984-2003 Award Software
Standard CMOS Features
Advanced BIOS Features
Advanced Chipset Features
Integrated Peripherals
Power Management Setup
PnP/PCI Configurations
PC Health Status
Miscellaneous Control
Load optimized Defaults
Load Standard Defaults
Set Supervisor Password
Set User Password
Save & Exit Setup
Exit Without Saving
Esc : Quit
↑↓→←
: Select Item
F10 : Save & Exit Setup
Time, Date, Hard Disk Type...
Figure 3-1
Standard CMOS Features
Use this Menu for basic system configurations.
Advanced BIOS Features
Use this menu to set the Advanced Features available on your system.
Advanced Chipset Features
Use this menu to change the values in the chipset registers and optimize your system’s
performance.
Integrated Peripherals
Use this menu to specify your settings for integrated peripherals.
Power Management Setup
Use this menu to specify your settings for power management.
PnP/PCI configurations
This entry appears if your system supports PnP/PCI.
PC Health Status
This entry shows your PC health status.
Miscellaneous Control
Use this menu to specify your settings for Miscellaneous control.
Page 25

23
Load Optimized Defaults
Use this menu to load the BIOS default values that are factory settings for optimal
performances system operations.
Load Standard Defaults
Use this menu to load the BIOS default values for the minimal/stable performance system
operation.
Set Supervisor/User Password
Use this menu to set User and Supervisor Passwords.
Save & Exit Setup
Save CMOS value changes to CMOS and exit setup.
Exit Without Saving
Abandon all CMOS value changes and exit setup.
3-4 Standard CMOS Features
The items in Standard CMOS Setup Menu are divided into several categories. Each category
includes no, one or more than one setup items. Use the arrow keys to highlight the item and
then use the <PgUp> or <PgDn> keys to select the value you want in each item.
CMOS Setup Utility – Copyright(C) 1984-2003 Award Software
Standard CMOS Features
Item Help
Date (mm:dd:yy) Fri, Mar, 21 2003
Time (hh:mm:ss) 16 : 45 : 35
> IDE Primary Master Press Enter None
> IDE Primary Slave Press Enter None
> IDE Secondary Master Press Enter None
> IDE Secondary Slave Press Enter None
Drive A 1.44M, 3.5 in.
Drive B None
Video EGA/VGA
Halt On All,But Keyboard
Base Memory 640K
Extended Memory 56320K
Total Memory 57344K
Menu Level >
Change the day, month,
year and century
↑↓→←
Move Enter:Select +/-/PU/PD:Value F10:Save ESC:Exit F1:General Help
F5:Previous Values F6:Optimized Defaults F7:Standard Defaults
Date
The date format is <day><month><date><year>.
Day
Day of the week, from Sun to Sat, determined by BIOS. Read-only.
Month
The month from Jan. through Dec.
Date
The date from 1 to 31 can be keyed by numeric function keys.
Year
The year depends on the year of the BIOS.
Time
Page 26

24
The time format is <hour><minute><second>.
Primary Master/Primary Slave
Secondary Master/Secondary Slave
Press PgUp/<+> or PgDn/<–> to select Manual, None, Auto type. Note that the specifications
of your drive must match with the drive table. The hard disk will not work properly if you
enter improper information for this category. If your hard disk drive type is not matched or
listed, you can use Manual to define your own drive type manually.
If you select Manual, related information is asked to be entered to the following items. Enter
the information directly from the keyboard. This information should be provided in the
documentation from your hard disk vendor or the system manufacturer.
If the controller of HDD interface is SCSI, the selection shall be “None”.
If the controller of HDD interface is CD-ROM, the selection shall be “None”
Access Mode
The settings are Auto Normal, Large, and LBA.
Cylinder
number of cylinders
Head
number of heads
Precomp
write precomp
Landing Zone
landing zone
Sector
number of sectors
3-5 Advanced BIOS Features
CMOS Setup Utility – Copyright(C) 1984-2003 Award Software
Advanced BIOS Features
Item Help
Anti-Virus Protection Disabled
CPU L1 Cache Enabled
CPU L2 Cache Enabled
Quick Power On Self Test Enabled
SATA & SCSI Boot Order ATA, SCSI
HDD Boot Sprite Disabled
First Boot Device Floppy
Second Boot Device HDD-0
Third Boot Device CDROM
Boot other Device Enabled
Swap Floppy Drive Disabled
Boot Up Floppy Seek Enabled
Boot Up NumLock Status On
Gate A20 Option Normal
Typematic Rate Setting Disabled
Typematic Rate (Chars/Sec) 6
Typematic Delay (Msec) 250
Security Option Setup
OS Select For DRAM > 64MB Non-OS2
HDD S.M.A.R.T. Capability Disabled
Video BIOS Shadow Enabled
Menu Level >
↑↓→←
Move Enter:Select +/-/PU/PD:Value F10:Save ESC:Exit F1:General Help
F5:Previous Values F6:Optimized Defaults F7:Standard Defaults
Anti-Virus Protection
Page 27

25
Allows you to choose the VIRUS Warning feature for IDE Hard Disk boot sector protection.
If this function is enabled and someone attempt to write data into this area, BIOS will show a
warning message on screen and alarm beep.
Disabled
(default) No warning message to appear when anything attempts to access the
boot sector or hard disk partition table.
Enabled
Activates automatically when the system boots up causing a warning
message to appear when anything attempts to access the boot sector of
hard disk partition table.
CPU L1 Cache
The default value is Enabled.
Enabled
(default) Enable cache
Disabled
Disable cache
Note: The internal cache is built in the processor.
CPU L2 Cache
Choose Enabled or Disabled. This option enables the Level 2 cache memory.
Quick Power On Self-Test
This category speeds up Power On Self Test (POST) after you power on the computer. If this
is set to Enabled. BIOS will shorten or skip some check items during POST.
Enabled
(default) Enable quick POST
Disabled
Normal POST
First/Second/Third/Fourth Boot Device
The BIOS attempts to load the operating system from the devices in the sequence selected in
these items. The settings are Floppy, LS/ZIP, HDD-0/HDD-1/HDD-3, SCSI, CDROM, LAD
and Disabled.
Swap Floppy Drive
Switches the floppy disk drives between being designated as A and B. Default is Disabled.
Boot Up Floppy Seek
During POST, BIOS will determine if the floppy disk drive installed is 40 or 80 tracks. 360K
type is 40 tracks while 760K, 1.2M and 1.44M are all 80 tracks.
Boot Up NumLock Status
The default value is On.
On
(default)
Keypad is numeric keys.
Off
Keypad is arrow keys.
Gate A20 Option
Normal
The A20 signal is controlled by keyboard controller or chipset hardware.
Fast
(default) The A20 signal is controlled by port 92 or chipset specific method.
Typematic Rate Setting
Keystrokes repeat at a rate determined by the keyboard controller. When enabled, the
typematic rate and typematic delay can be selected. The settings are: Enabled/Disabled.
Typematic Rate (Chars/Sec)
Page 28

26
Sets the number of times a second to repeat a keystroke when you hold the key down. The
settings are: 6, 8, 10, 12, 15, 20, 24, and 30.
Typematic Delay (Msec)
Sets the delay time after the key is held down before is begins to repeat the keystroke. The
settings are 250, 500, 750, and 1000.
Security Option
This category allows you to limit access to the system and Setup, or just to Setup.
System
The system will not boot and access to Setup will be denied if the
correct password is not entered at the prompt.
Setup
(default) The system will boot, but access to Setup will be denied if the correct
password is not entered prompt.
OS Select For DRAM > 64MB
Allows OS2 to be used with >64MB or DRAM. Settings are Non-OS/2 (default) and OS2.
Set to OS/2 if using more than 64MB and running OS/2.
3-6 Advanced Chipset Features
The Advanced Chipset Features Setup option is used to change the values of the chipset
registers. These registers control most of the system options in the computer.
CMOS Setup Utility – Copyright(C) 1984-2003 Award Software
Advanced Chipset Features
Item Help
System Performance Standard
X CPU Interface Optimal
X T(RAS) 6
X T(RCD) 3
X T(RP) 3
X CAS Latency 2.5
Frame Buffer Size 32M
AGP Aperture Size 64M
AGP 8X Support Enabled
AGP Fast Write Capability Enabled
System BIOS Cacheable Disabled
Video RAM Cacheable Disabled
Menu Level >
↑↓→←
Move Enter:Select +/-/PU/PD:Value F10:Save ESC:Exit F1:General Help
F5:Previous Values F6:Optimized Defaults F7:Standard Defaults
CAS Latency
Page 29

27
When synchronous DRAM is installed, the number of clock cycles of CAS latency depends
on the DRAM timing. The settings are: 2T and 2.5T.
System BIOS Cacheable
Selecting Enabled allows caching of the system BIOS ROM at F0000h-FFFFFh, resulting in
better system performance. However, if any program writes to this memory area, a system
error may result. The settings are: Enabled and Disabled.
Video RAM Cacheable
Select Enabled allows caching of the video BIOS, resulting in better system performance.
However, if any program writes to this memory area, a system error may result. The settings
are: Enabled and Disabled.
Frame Buffer Size
You can choose the On board VGA memory size share from system memory. The settings are:
8M, 16M, 32M, 64M, Disabled.
3-7 Integrated Peripherals
CMOS Setup Utility – Copyright(C) 1984-2003 Award Software
Integrated Peripherals
Item Help
> Onboard IDE Function Press Enter
> Onboard Device Function Press Enter
> Onboard Super IO Function Press Enter
Init Display First PCI Slot
Power On Function Button Only
X KB Power On Password Enter
X Hot Key Power On Ctrl+F1
Power Loss Function Always off
Menu Level >
↑↓→←
Move Enter:Select +/-/PU/PD:Value F10:Save ESC:Exit F1:General Help
F5:Previous Values F6:Optimized Defaults F7:Standard Defaults
Onboard IDE Function
Please refer to section 3-7-1
Onboard Device Function
Please refer to section 3-7-2
Onboard Super IO Function
Please refer to section 3-7-3
Init Display First
This item allows you to decide to activate whether PCI Slot or AGP VGA first. The settings
are: PCI Slot, AGP Slot.
Power Loss Function
This item allows the system power ON/OFF automatic when power loss and recovery again, you
can choose Auto for recovery pre-state, or always ON/OFF after power recovery.
Page 30

28
3-7-1 Onboard IDE Function
CMOS Setup Utility – Copyright(C) 1984-2003 Award Software
OnChip IDE Function
Item Help
OnChip IDE Channel0 Enabled
OnChip IDE Channel1 Enabled
Primary Master PIO Auto
Primary Slave PIO Auto
Secondary Master PIO Auto
Secondary Slave PIO Auto
Primary Master UDMA Auto
Primary Slave UDMA Auto
Secondary Master UDMA Auto
Secondary Slave UDMA Auto
IDE 32-bit Transfer Mode Enabled
IDE HDD Block Mode Enabled
IDE Prefetch Mode Enabled
Delay For HDD (Secs) 0
Menu Level >>
↑↓→←
Move Enter:Select +/-/PU/PD:Value F10:Save ESC:Exit F1:General Help
F5:Previous Values F6:Optimized Defaults F7:Standard Defaults
OnChip IDE Channal0/Channel1
The integrated peripheral controller contains an IDE interface with support for two IDE
channels. Select Enabled to activate each channel separately. The settings are: Enabled and
Disabled.
Primary/Secondary Master/Slave PIO
The four IDE PIO (Programmed Input/Output) fields let you set a PIO mode (0-4) for each of
the four IDE devices that the onboard IDE interface supports. Modes 0 through 4 provide
successively increased performance. In Auto mode, the system automatically determines the
best mode for each device. The settings are: Auto, Mode 0, Mode 1, Mode 2, Mode 3, Mode
4.
Primary/Secondary Master/Slave UDMA
Ultra DMA/33 implementation is possible only if your IDE hard drive supports it and the
operating environment includes a DMA driver (Windows 95 OSR2 or a third-party IDE bus
master driver). If your hard drive and your system software both support Ultra DMA/33 and
Ultra DMA/66, select Auto to enable BIOS support. The settings are: Auto, Disabled.
IDE HDD Block Mode
Block mode is also called block transfer, multiple commands, or multiple sector read/write. If
your IDE hard drive supports block mode (most new drives do), select Enabled for automatic
detection of the optimal number of block read/writes per sector the drive can support. The
settings are: Enabled, Disabled.
Page 31

29
3-7-2 Onboard Device Function
CMOS Setup Utility – Copyright(C) 1984-2003 Award Software
OnChip Device Function
Item Help
AC97 Sound Device Auto
Game Port Address 201
Midi Port Address Disabled
X Midi Port IRQ 10
1394 ontroller Auto
nVIDIA LAN Function Auto
USB Host Controller Enabled
USB 2.0 Support Enabled
USB Keyboard Legacy Support Disabled
Menu Level >>
↑↓→←
Move Enter:Select +/-/PU/PD:Value F10:Save ESC:Exit F1:General Help
F5:Previous Values F6:Optimized Defaults F7:Standard Defaults
Game Port Address/Midi Port Address
This will determine which Address the Game Port/Midi Port will use.
USB Host Controller
Select Enabled if your system contains a Universal Serial Bus (USB) controller and you have
a USB peripherals. The settings are: Enabled, Disabled.
USB Keyboard Support
Select Enabled if your system contains a Universal Serial Bus (USB) controller and you have
a USB keyboard. The settings are: Enabled, Disabled.
3-7-3 Onboard Super IO Function
CMOS Setup Utility – Copyright(C) 1984-2003 Award Software
Onboard Super IO Function
Item Help
Onboard FDD Controller Enabled
Onboard Serial Port 1 3F8/IRQ4
Onboard Serial Port 2 2F8/IRQ3
UART2 Mode Normal
X RxD, TxD Active Hi, Lo
X IR Transmission Delay Enabled
X IR Duplex Mode Half
X IR Pins IRRX/IRTX
Onboard Parallel Port 378/IRQ7
Parallel Mode SPP
X EPP Mode Select EPP1.9
X ECP Mode Use DMA 3
Menu Level >>
↑↓→←
Move Enter:Select +/-/PU/PD:Value F10:Save ESC:Exit F1:General Help
F5:Previous Values F6:Optimized Defaults F7:Standard Defaults
Page 32

30
Onboard FDD Controller
Select Enabled if your system has a floppy disk controller (FDD) installed on the system board and
you wish to use it. If you install add-on FDC or the system has no floppy drive, select Disabled in this
field. The settings are: Enabled and Disabled.
Onboard Serial Port 1/Port 2
Select an address and corresponding interrupt for the first and the second serial ports. The settings
are: 3F8/IRQ4, 2E8/IRQ3, 3E8/IRQ4, 2F8/IRQ3, Disabled, Auto.
UART2 Mode
This item allows you to determine which InfraRed(IR) function of the onboard I/O chip, this functions
uses.
Onboard Parallel Port
There is a built-in parallel port on the on-board Super I/O chipset that Provides Standard, ECP, and
EPP features. It has the following option:
Disabled
(3BCH/IRQ7)/
Line Printer port 0
(278H/IRQ5)/
Line Printer port 2
(378H/IRQ7)
Line Printer port 1
Parallel Port Mode
SPP : Standard Parallel Port
EPP : Enhanced Parallel Port
ECP : Extended Capability Port
SPP/EPP/ECP/ECP+EPP
To operate the onboard parallel port as Standard Parallel Port only, choose “SPP.” To operate the
onboard parallel port in the EPP modes simultaneously, choose “EPP.” By choosing “ECP”, the
onboard parallel port will operate in ECP mode only. Choosing “ECP+EPP” will allow the
onboard parallel port to support both the ECP and EPP modes simultaneously. The ECP mode
has to use the DMA channel, so choose the onboard parallel port with the ECP feature. After
selecting it, the following message will appear: “ECP Mode Use DMA” at this time, the user can
choose between DMA channels 3 to 1. The onboard parallel port is EPP Spec. compliant, so
after the user chooses the onboard parallel port with the EPP function, the following message will
be displayed on the screen: “EPP Mode Select.” At this time either EPP 1.7 spec. or EPP 1.9
spec. can be chosen.
3-8 Power Management Setup
The Power Management Setup allows you to configure your system to most effectively save
energy saving while operating in a manner consistent with your own style of computer use.
CMOS Setup Utility – Copyright(C) 1984-2003 Award Software
Power Management Setup
Item Help
ACPI Function Enabled
ACPI Suspend Type S1(POS)
Video off Method V/H SYNC+Blank
Power Button Function Instant-Off
Wake-Up on PCI PME Disabled
Wake-Up on Ring/LAN Disabled
USB Resume from S3/S4 Disabled
Wake Up on RTC Alarm Disabled
X Time(dd:hh:mm) of Alarm 0: 0: 0
Menu Level >
↑↓→←
Move Enter:Select +/-/PU/PD:Value F10:Save ESC:Exit F1:General Help
F5:Previous Values F6:Optimized Defaults F7:Standard Defaults
Page 33

31
ACPI Function
This item allows you to Enabled/Disabled the Advanced Configuration and Power Management
(ACPI). The settings are Enabled and Disabled.
Video Off Method
This determines the manner in which the monitor is blanked.
DPMS
(default) Initial display power management signaling.
Blank Screen
This option only writes blanks to the video buffer.
V/H SYNC+Blank
This selection will cause the system to turn off the vertical and
horizontal synchronization ports and write blanks to the video buffer.
Power Button Function
Pressing the power button for more than 4 seconds forces the system to enter the Soft-Off state.
The settings are: Delay 4 Sec, Instant-Off.
Wake Up On Ring/PME/LAN
During Disabled, the system will ignore any incoming call from the modem/LAN. During
Enabled, the system will boot up if there’s an incoming call from the modem.
Wake Up on RTC Alarm
This function is for setting date and time for your computer to boot up. During Disabled, you
cannot use this function. During Enabled, choose the Date and Time Alarm:
Time(dd:hh:mm) of Alarm
You can choose which day of month , what hour, minute the system will boot up.
Note: If you have change the setting, you must let the system boot up until it goes to the
operating system, before this function will work.
3-9 PnP/PCI Configuration Setup
This section describes configuring the PCI bus system. PCI, or Personal Computer
Interconnect, is a system which allows I/O devices to operate at speeds nearing the speed the
CPU itself uses when communicating with its own special components. This section covers
some very technical items and it is strongly recommended that only experienced users should
make any changes to the default settings.
CMOS Setup Utility – Copyright(C) 1984-2003 Award Software
PnP/PCI Configurations
Item Help
Reset Configuration Data Disabled
Resources Controlled By Manual
x IRQ Resources Press Enter
PCI/VGA Palette Snoop Disabled
Assign IRQ For VGA Enabled
Assign IRQ For USB Enabled
Menu Level >
↑↓→←
Move Enter:Select +/-/PU/PD:Value F10:Save ESC:Exit F1:General Help
F5:Previous Values F6:Optimized Defaults F7:Standard Defaults
Page 34

32
Reset Configuration Data
Normally, you leave this field Disabled. Select Enabled to reset Extended System Configuration
Data (ESCD) when you exit Setup if you have installed a new add-on and the system
reconfiguration has caused such a serious conflict that the operating system can not boot. The
settings are: Enabled and Disabled.
Resource Controlled By
The Award Plug and Play BIOS has the capacity to automatically configure all of the boot and
Plug and Play compatible devices. However, this capability means absolutely nothing unless
you are using a Plug and Play operating system such as Windows95/98. If you set this field
to “manual” choose specific resources by going into each of the sub menu that follows this
field (a sub menu is preceded by a “>”).
The settings are: Auto(ESCD), Manual.
IRQ Resources
When resources are controlled manually, assign each system interrupt a type, depending on
the type of device using the interrupt.
Please refer to section 3-9-1
PCI/VGA Palette Snoop
Leave this field at Disabled. The settings are Enabled, Disabled.
3-9-1 IRQ Resources
CMOS Setup Utility – Copyright(C) 1984-2003 Award Software
IRQ Resources
Item Help
IRQ3 assigned to PCI Device
IRQ4 assigned to PCI Device
IRQ5 assigned to PCI Device
IRQ7 assigned to PCI Device
IRQ9 assigned to PCI Device
IRQ10 assigned to PCI Device
IRQ11 assigned to PCI Device
IRQ12 assigned to PCI Device
IRQ14 assigned to PCI Device
IRQ15 assigned to PCI Device
Menu Level >>
↑↓→←
Move Enter:Select +/-/PU/PD:Value F10:Save ESC:Exit F1:General Help
F5:Previous Values F6:Optimized Defaults F7:Standard Defaults
Page 35

33
3-10 PC Health Status
This section shows the Status of you CPU, Fan, Warning for overall system status. This is
only available if there is Hardware Monitor onboard.
CMOS Setup Utility – Copyright(C) 1984-2003 Award Software
PC Health Status
Item Help
Shutdown Temperature Disabled
Show PC Health in Post Enabled
Current System Temperature 25°C
Current CPU Temperature 38°C
Current CPUFAN Speed 5000 rpm
Current SYSFAN1 Speed 5000 rpm
Current SYSFAN2 Speed 5000 rpm
Vcore 1.78V
Vcc3.3 3.31V
+ 5V 4.98V
+12V 12.22V
-12V -12.36V
VBAT(V) 3.21V
5VSB(V)
5.02V
Menu Level >
↑↓→←
Move Enter:Select +/-/PU/PD:Value F10:Save ESC:Exit F1:General Help
F5:Previous Values F6:Optimized Defaults F7:Standard Defaults
Shutdown Temperature
This item can let users setting the Shutdown temperature, when CPU temperature over this
setting the system will auto shutdown to protect CPU.
Show PC Health in Post
During Enabled, it displays information list below. The choice is either Enabled or Disabled
Current CPU Temperature/Current System Temp/Current FAN1, FAN2 Speed/Vcore/
Vdd/3.3V/+5V/+12V/-12V/VBAT(V)/5VSB(V)
This will show the CPU/FAN/System voltage chart and FAN Speed.
Detect CPUFAN in Post
During Enabled, system will warn the user if CPU Fan is not functioning.
Page 36

34
3-11 Miscellaneous Control
This section is for setting CPU Frequency/Voltage Control.
CMOS Setup Utility – Copyright(C) 1984-2003 Award Software
Miscellaneous Control
Item Help
** Current Host Clock is
Host Clock at Next Boot is 100MHz
** Current DRAM Clock is
DRAM Clock at next Boot is 133MHz
CPU Vcore Select Default
CPU Ratio Select Default
Core_VDD Select 1.7V(Default)
VDD_AUXC Select 1.6V(Default)
VAGP Output 1.5V(Default)
VRAM Output 2.6V(Default)
VAUX Output Default
VTT Voltage 1.25V
VAGP LUV Protect Enabled
VRAM LUV Protect Enabled
Dual3.3V LUV Protect Disabled
Flash Parts Write Protect Enabled
Menu Level >
↑↓→←
Move Enter:Select +/-/PU/PD:Value F10:Save ESC:Exit F1:General Help
F5:Previous Values F6:Optimized Defaults F7:Standard Defaults
Host Clock at next Boot is
This item allows you to select CPU frequency step by step increasing
The choice are: 100MHz, 133MHz, 166MHz, 200MHz, 236MHz, 240MHz, 242MHz, 244MHz,
245MHz, 250MHz
DRAM Clock at next Boot is
This field displays the capability of the memory modules that you can use
The choice is either 100MHz, 110MHz, 125MHz, 133MHz, 138MHz, 166MHz, 200MHz, 208MHz,
221MHz, 249MHz
CPU Vcore Select
This item allows you to select Vcore of the CPU. The choice are: +1.100V∼+1.850V.
CPU Ratio Select
This item allows you to select Ratio of the CPU. The choice are:X5~X24
VDD AUXC Select
This item allows you to select Chip Voltage. The choice are 1.6V(Default), 1.7V
VAGP Output
This item allows you to select 1.5V of the AGP 4X VGA card. The choice are: 1.5V, 1.6V,1.7V
VRAM Output
This item allows you to select 2.5V of the DDR Module. The choice are: 2.5V~ 3.0V.
VAUX Output
This item allows you to select AUX voltage. The choice are: Default, 2%, 4%, 8%,12%, 16%.
VTT Voltage
This item allows you to select VTT voltage. The choice are: 1.25V, VDIMM/2.
VAGP/VRAM LUV Protect
This item allows you enabled the protect function on motherboard when over current. The choice are:
Enabled(Default), Disabled
Flash Part Write Protect
This item allows you protect BIOS prevent the data destroy by virus. The choice are: Enabled,
Disabled. Before flash BIOS you have to change the setting to Disabled otherwise it can not flash
BIOS.
Page 37

35
3-12 Load Standard/Optimized Defaults
Load Standard Defaults
When you press <Enter> on this item, you get confirmation dialog box with a message similar
to:
Load Standard Defaults (Y/N)? N
Pressing <Y> loads the BIOS default values for the most stable, minimal-performance system
operations.
Load Optimized Defaults
When you press <Enter> on this item, you get a confirmation dialog box with a message
similar to:
Load Optimized Defaults (Y/N)? N
Pressing <Y> loads the default values that are factory settings for optimal performance system
operations.
3-13 Set Supervisor/User Password
You can set either supervisor or user password, or both of them. The differences are:
Supervisor password: Can enter and change the options of the setup menus.
User password: Can only enter but do not have the right to change the options of the
setup menus. When you select this function, the following message
will appear at the center of the screen to assist you in creating a
password.
ENTER PASSWORD:
Type the password, up to eight characters in length, and press <Enter>. The password typed
now will clear any previously entered password from CMOS memory. You will be asked to
confirm the password. Type the password again and press <Enter>. You may also press
<Esc> to abort the selection and not enter a password.
To disable a password, just press <Enter> when you are prompted to enter the password. A
message will confirm that the password will be disabled. Once the password is disabled, the
system will boot and you can enter Setup freely.
PASSWORD DISABLED.
When a password has been enabled, you will be prompted to enter it every time you try to
enter Setup. This prevents an unauthorized person from changing any part of your system
configuration.
Additionally, when a password is enabled, you can also require the BIOS to request a
password every time your system is rebooted. This would prevent unauthorized use of your
computer.
You determine when the password is required within the BIOS Features Setup Menu and its
Security option. If the Security option is set to “System”, the password will be required both
at boot and at entry to Setup. If set to “Setup”, prompting only occurs when trying to enter
Setup.
Page 38

36
Chapter 4
DRIVER & FREE PROGRAM INSTALLATION
Check your package and there is A MAGIC INSTALL CD included. This CD consists of all
DRIVERS you need and some free application programs and utility programs. In addition, this
CD also include an auto detect software which can tell you which hardware is installed, and
which DRIVERS needed so that your system can function properly. We call this auto detect
software MAGIC INSTALL.
MAGIC INSTALL Supports WINDOWS 98SE/ME/NT4.0/2000/XP
Insert CD into your CD-ROM drive and the MAGIC INSTALL Menu should appear as below.
If the menu does not appear, double-click MY COMPUTER / double-click CD-ROM drive or
click START / click RUN / type X:\SETUP.EXE (assuming X is your CD-ROM drive).
From MAGIC INSTALL MENU you may make 12 selections:
1. nFORCE install NVIDIA nForce chipset system driver
2. VGA install NVIDIA VGA driver (for Kocab 18G)
3. SOUND install ALC Audio Codec driver
4. USB2.0 install USB 2.0 driver
5. SATA install Serial ATA driver
6. DirectX8 install Microsoft DirectX 8.1 driver
7. PC-CILLIN install PC-CILLIN2002 anti-virus program
8. PC-HEALTH install PC-HEALTH monitor Utility
9. MBIOS install BIOS Live Update Utility
10. Audio Hotfix install Audio Patch File (Only for WIN98SE OS)
11. BROWSE CD to browse the contents of the CD
12. EXIT to exit from MAGIC INSTALL menu
4-1 nFORCE install NVIDIA nFORCE Pack driver
Page 39

37
* The path of the file is X:\DRIVER\SETUP.EXE
IDE : VIDIA ATAPI VENDOR SUPPORT DRIVER IS USED TO FIXED COMPATIBILITY
ISSUE FOR IDE DEVICES
AGP : NVIDIA AGP DRIVER IS TO BE INSTALLED, IF YOU ARE USING AN AGP
VGA CARD, NVIDIA GART WILL PROVIDE SERVICE ROUTINES TO YOUR
VGA DRIVER AND INTERFACE DIRECTLY TO HARDWARE, PROVIDING
FAST GRAPHIC ACCESS
MEMCTL : NVIDIA Memory Controller driver
SMBUS : NVIDIA SMBUS Controller driver
ETHERNET : NVIDIA nFORCE MCP networking
1. Click nFORCE when MAGIC INSTALL
MENU appears
2. Click NEXT when NVIDIA Windows98/
ME/2000/XP nForce Drivers Wizard appears
3. Click Finish to restart computer
4-2 VGA install NVIDIA VGA Driver (Only for Kocab 18G)
Page 40

38
1. Click VGA when MAGIC INSTALL MENU
appears
2. Click NEXT When NVIDIA Win95/98/ME/
2000/XP Display Driver
Windows appear
3. If You Want Re-start Computer , Click
FINISH
4-3 Sound Install ALC650 Audio Codec Driver
1. Click SOUND when MAGIC INSTALL
MENU appears
2. Then auto detect operation system language
edition, click OK, start to install DRIVER
Page 41

39
3. Click Finish and Restart Windows
4. Click Start→Program→Avance Sound
Manager→AvRack. Then AVRACK Windows
appears
5. Sound Effect select and KaraOK Mode
Function
6. Manual Sound Effect Setting
Note: The path of the file
For WIN98/NT4.0/WIN2K/XP is X:\CODEC\ALC\SETUP.EXE
4-4 USB2.0 Install NVIDIA USB 2.0 Driver
Windows 98SE/ME/2000 USB 2.O Driver installation
1. Click USB2.0 when MAGIC INSTALL
MENU appears
2. Click CLOSE and Restart Computer
Page 42

40
Windows XP USB 2.O Driver installation
1. Install Windows XP Service Pack 1 or later
2. Select My Computer, Press Right Button, Select Properties,
Go to Hardware \ Device Manager, Remove Other Device \ Universal Serial Bus (USB)
Controller
Restart Your Computer, It Will Find “NVIDIA USB2.0 Enhanced Host Controller”
And “USB2.0 Root Hub Device”
4-5 SATA Install Promise ATA IDE Controller Driver
1. Click SATA in MAGIC INSTALL MENU 2. Install PROMISE SERIAL ATA Controller
Driver
3. Click Yes to Restart your computer after
Driver Install Finish
The path of the file:
For Windows 9X is X:\SATA375\WIN98-ME (including Win95/98/ME)
For Windows NT4.0 is X:\SATA375\NT4
For Windows 2000 is X:\SATA375\WIN2000
For Windows XP is X:\SATA375\WINXP
When you use Serial ATA install Window NT4.0/2000/XP OS,
Please insert Serial ATA DISK from A:\, and Press F6 key install driver firest
Page 43

41
4-6 PC-CILLIN Install PC-CILLIN 2002 Anti-virus program
1. Click PC-CILLIN when MAGIC INSTALL
MENU appear
2. (1) Click "Install PC-CILLIN" when PC-
CILLIN 2002 main menu appears, and Click
NEXT when "Install Shield Wizard For PCCILLIN 2002"
(2) Click Open Manual. you can learn PCCILLIN 2002 how to use
3. This is license agreement, select "I Accept
the terms" and Click NEXT
4. Click NEXT and Enter your Customer
Information, Click NEXT or choose Change
to change the path for the file to be stored
5. Click INSTALL, Start to install the software 6. Setup Complete and click FINISH
Page 44

42
7. After PC-CILLIN 2002 complete, Please
register your information and get LICENSE
KEY from TREND MICRO web site, enter
your license key and click FINISH
8. finish register process, we recommend select
update item to download newest engine code
and virus code
Note : Please install ACROBAT READER, Before you read PC-CILLIN 2002 User
Manual, the path at X:\acrobat\ar500eng.exe
4-7 PC-HEALTH Install Winbond Hardware Doctor Utility
The path of the file is X:\83627HD\SETUP.EXE (support WINDOWS 98SE/ME/2000/XP)
1. Click PC-Health when Magic Install Menu
appears
2. Click Next when Winbond Hardware Doctor
Setup Window appears
3. Click Next to continue installation 4. Select Program Group name or enter a new
group name, click Next, and click Finish after
setup complete
Page 45

43
4-7-1 How To Utilize PC-HEALTH
1. Click Program → Winbond Hardware Doctor
→ Hardware Doctor the Winbond Hardware
Doctor will appears
You can remove the Utility in Control Panel
→ Add/Remove Program icon
2. After executing Winbond Hardware Doctor it
supports system voltage, Fan speed and
CPU/SYSTEM Temperature. Because this is
a On-time Monitoring program therefore the
value will change after it detected, if the value
is over default setting the system will have
warning picture and beeps. This is a System
Voltage status
3. This is a CPU/System Fan Speed and
Temperature status information
4-8 MBIOS Install BIOS Live Update Utility
1. Click Magic BIOS when Magic Install
MENU appears
2. Click Next to install the Magic BIOS in
Destination Folder
Page 46

44
3. After finish Setup you will have a Magic
BIOS icon in your screen
4. Double click the Magic BIOS icon you will
have this picture, choose from internet you can
upgrade BIOS On-line
5. When On-line update BIOS the program will
auto-check your BIOS version
6. Click Next if you need update BIOS, after
upgrade BIOS, the system will clear CMOS
and automatically restart
7. Click Yes if you want to update the BIOS
otherwise choose No to exit
8. When System programming BIOS don’t turn
off power, after finish update BIOS, the
system will clear CMOS and automatically
Restart
9. When choose From Local Driver to update
BIOS, you must have the correct BIOS file
in your Local Driver
10. Choose the correct BIOS file to update BIOS
Page 47

45
4-9 HOW TO UPDATE BIOS
Before update BIOS please choose Disabled in “Flash Part Write Protect” item on
“Miscellaneous Control” in BIOS Setup, please refer page 33
Method 1. Use “Magic BIOS” update BIOS in Windows 98 (refer page 43)
Method 2. In DOS Mode
STEP 1. Prepare a boot disc. (you may make one by click START click RUN type SYS A:
click OK)
STEP 2. Copy utility program to your boot disc. You may copy from DRIVER CD
X:\FLASH\AWDFLASH.EXE or download from our web site.
STEP 3. Copy latest BIOS for Kocab 18G/Kocab 18P from our web site to your boot disc.
STEP 4. Insert your boot disc into A:,
start the computer, type “Awdflash A:\Kocab18GAxxx.BIN /SN/PY/CC/R”
Kocab18Gxxx.BIN is the file name of latest BIOS it can be Kocab18GA3.BIN or
Kocab18GB2.BIN
SN means don’t save existing BIOS data
PY means renew existing BIOS data
CC means clear existing CMOS data
R means restart computer
STEP 5. Push ENTER and the BIOS will be updated, computer will be restarted
automatically.
 Loading...
Loading...