Page 1

This Manual is Bookmarked
This Manual is Bookmarked
Operating Instructions and Parts Manual
10" Table Saw
Stock Numbers: 708315BTA, -BTB, -BTC, -LSA, -LSB
708315BTA Table Saw shown
WMH TOOL GROUP
2420 Vantage Drive
Elgin, Illinois 60123 Part No. M-708315
Ph.: 800-274-6848 Revision D 08/05
www.wmhtoolgroup.com Copyright © WMH Tool Group
ESPAGÑOL – PÁGINA 41
Page 2
This manual has been prepared for the owner and operators of a 708315 Table Saw. Its purpose, aside
from machine operation, is to promote safety through the use of accepted correct operating and
maintenance procedures. Completely read the safety and maintenance instructions before operating or
servicing the machine. To obtain maximum life and efficiency from your JET Table Saw, and to aid in
using the machine safely, read this manual thoroughly and follow instructions carefully.
Warranty
WMH Tool Group warrants every product it sells. If one of our tools needs service or repair, one of our
Authorized Repair Stations located throughout the United States can give you quick service.
In most cases, any one of these WMH Tool Group Repair Stations can authorize warranty repair, assist
you in obtaining parts, or perform routine maintenance and major repair on your JET, Wilton, or
Powermatic tools.
For the name of an Authorized Repair Station in your area, please call 1-800-274-6848, or visit
www.wmhtoolgroup.com
More Information
WMH Tool Group is consistently adding new products to the line. For complete, up-to-date product
information, check with your local WMH Tool Group distributor, or visit www.wmhtoolgroup.com
WMH Tool Group Warranty
WMH Tool Group (including JET, Wilton and Powermatic brands) makes every effort to assure that its
products meet high quality and durability standards and warrants to the original retail consumer/purchaser
of our products that each product be free from defects in materials and workmanship as follow: 1 YEAR
LIMITED WARRANTY ON ALL PRODUCTS UNLESS SPECIFIED OTHERWISE. This Warranty does
not apply to defects due directly or indirectly to misuse, abuse, negligence or accidents, normal wear-andtear, repair or alterations outside our facilities, or to a lack of maintenance.
WMH TOOL GROUP LIMITS ALL IMPLIED WARRANTIES TO THE PERIOD SPECIFIED ABOVE,
FROM THE DATE THE PRODUCT WAS PURCHASED AT RETAIL. EXCEPT AS STATED HEREIN,
ANY IMPLIED WARRANTIES OR MERCHANTIBILITY AND FITNESS ARE EXCLUDED. SOME
STATES DO NOT ALLOW LIMITATIONS ON HOW LONG THE IMPLIED WARRANTY LASTS, SO THE
ABOVE LIMITATION MAY NOT APPLY TO YOU. WMH TOOL GROUP SHALL IN NO EVENT BE
LIABLE FOR DEATH, INJURIES TO PERSONS OR PROPERTY, OR FOR INCIDENTAL,
CONTINGENT, SPECIAL, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES ARISING FROM THE USE OF OUR
PRODUCTS. SOME STATES DO NOT ALLOW THE EXCLUSION OR LIMITATION OF INCIDENTAL
OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES, SO THE ABOVE LIMITATION OR EXCLUSION MAY NOT APPLY
TO YOU.
To take advantage of this warranty, the product or part must be returned for examination, postage
prepaid, to an Authorized Repair Station designated by our office. Proof of purchase date and an
explanation of the complaint must accompany the merchandise. If our inspection discloses a defect, we
will either repair or replace the product, or refund the purchase price if we cannot readily and quickly
provide a repair or replacement, if you are willing to accept a refund. We will return repaired product or
replacement at WMH Tool Group’s expense, but if it is determined there is no defect, or that the defect
resulted from causes not within the scope of WMH Tool Group’s warranty, then the user must bear the
cost of storing and returning the product. This warranty gives you specific legal rights; you may also have
other rights, which vary from state to state.
WMH Tool Group sells through distributors only. WMH Tool Group reserves the right to effect at any
time, without prior notice, those alterations to parts, fittings, and accessory equipment, which they may
deem necessary for any reason whatsoever.
2
Page 3

Table of Contents
Warranty........................................................................................................................................................ 2
Warnings .......................................................................................................................................................4
Kickback Prevention...................................................................................................................................... 6
Protection Tips from Kickback.......................................................................................................................6
Specifications ................................................................................................................................................7
Definitions and Terminology..........................................................................................................................7
Shipping Contents.........................................................................................................................................8
Contents of the Shipping Cartons .............................................................................................................8
Tool Required (Not Included) ....................................................................................................................8
Assembly..................................................................................................................................................... 10
Where to Begin........................................................................................................................................10
Leg Assembly.......................................................................................................................................... 10
Mounting the Shelf...................................................................................................................................11
Rubber Feet.............................................................................................................................................11
Installing the Blade Guard and Splitter.................................................................................................... 12
Aligning the Blade Guard and Splitter .....................................................................................................12
Saw Blade ...............................................................................................................................................13
Attaching the Rip Fence ..........................................................................................................................13
Calibrating the Rip Fence Scale..............................................................................................................13
Stamped Steel Extension Wing...............................................................................................................14
Sliding Extension Wing............................................................................................................................ 15
Left Scale Extension................................................................................................................................16
Right Scale Extension .............................................................................................................................16
Optional Left Table Support ....................................................................................................................17
Handwheel Handle ..................................................................................................................................17
Adjustments ................................................................................................................................................18
90 Degree Positive Stop.......................................................................................................................... 18
Scale Calibration .....................................................................................................................................18
Adjusting Blade Parallel to Miter Gauge Slots ........................................................................................19
Replacing the Blade ................................................................................................................................19
Replacing/Adjusting the Drive Belt .......................................................................................................... 20
Miter Gauge Operation............................................................................................................................21
Electrical Connections................................................................................................................................. 21
Operating Controls...................................................................................................................................... 21
Dust Shroud............................................................................................................................................. 11
45 Degree Positive Stop.......................................................................................................................... 18
Operations................................................................................................................................................... 22
Table Saws ..........................................................................................................................................22
Kickbacks.............................................................................................................................................22
Rip Sawing...........................................................................................................................................23
Crosscutting .........................................................................................................................................24
Bevel and Miter Operations ................................................................................................................. 25
Dust Collection.....................................................................................................................................25
Safety Devices ............................................................................................................................................26
Feather Board..........................................................................................................................................26
Push Stick ............................................................................................................................................26
Filler Piece ........................................................................................................................................... 26
Maintenance................................................................................................................................................ 26
Cleaning ..................................................................................................................................................26
Lubrication................................................................................................................................................... 27
Miscellaneous .............................................................................................................................................27
Troubleshooting ..........................................................................................................................................27
Parts............................................................................................................................................................ 27
Ordering Replacement Parts...................................................................................................................27
3
Page 4

Warnings
1. Read and understand the entire owner's manual before attempting assembly or operation.
2. Read and understand the warnings posted on the machine and in this manual. Failure to comply with
all of these warnings may cause serious injury.
3. Replace the warning labels if they become obscured or removed.
4. This Table Saw is designed and intended for use by properly trained and experienced personnel only.
If you are not familiar with the proper and safe operation of a Table Saw, do not use until proper
training and knowledge have been obtained.
5. Do not use this Table Saw for other than its intended use. If used for other purposes, WMH Tool
Group disclaims any real or implied warranty and holds itself harmless from any injury that may result
from that use.
6. Always wear approved safety glasses/face shields while using this Table Saw. Everyday eyeglasses
only have impact resistant lenses; they are not safety glasses.
7. Before operating this Table Saw, remove tie, rings, watches and other jewelry, and roll sleeves up
past the elbows. Remove all loose clothing and confine long hair. Non-slip footwear or anti-skid floor
strips are recommended. Do not wear gloves.
8. Always use the blade guard on all ''through-sawing'' operations. A through-sawing operation is one in
which the blade cuts completely through the workpiece.
9. Kickback occurs when the workpiece is thrown towards the operator at a high rate of speed. If you do
not have a clear understanding of kickback and how it occurs, DO NOT operate this table saw!
10. Wear ear protectors (plugs or muffs) during extended periods of operation.
11. Some dust created by power sanding, sawing, grinding, drilling and other construction activities
contain chemicals known to cause cancer, birth defects or other reproductive harm. Some examples
of these chemicals are:
• Lead from lead based paint.
• Crystalline silica from bricks, cement and other masonry products.
• Arsenic and chromium from chemically treated lumber.
12. Your risk of exposure varies, depending on how often you do this type of work. To reduce your
exposure to these chemicals, work in a well-ventilated area and work with approved safety
equipment, such as face or dust masks that are specifically designed to filter out microscopic
particles.
13. Do not operate this machine while tired or under the influence of drugs, alcohol or any medication.
14. Make certain the switch is in the OFF position before connecting the machine to the power supply.
15. Make certain the machine is properly grounded.
16. Make all machine adjustments or maintenance with the machine unplugged from the power source.
17. Remove adjusting keys and wrenches. Form a habit of checking to see that keys and adjusting
wrenches are removed from the machine before turning it on.
18. Keep safety guards in place at all times when the machine is in use. If removed for maintenance
purposes, use extreme caution and replace the guards immediately.
19. Make sure the Table Saw is firmly secured to the floor or bench before use.
20. Check damaged parts. Before further use of the machine, a guard or other part that is damaged
should be carefully checked to determine that it will operate properly and perform its intended
function. Check for alignment of moving parts, binding of moving parts, breakage of parts, mounting
and any other conditions that may affect its operation. A guard or other part that is damaged should
be properly repaired or replaced.
4
Page 5

21. Provide for adequate space surrounding work area and non-glare, overhead lighting.
22. Keep the floor around the machine clean and free of scrap material, oil and grease.
23. Keep visitors a safe distance from the work area. Keep children away.
24. Make your workshop child proof with padlocks, master switches or by removing starter keys.
25. Give your work undivided attention. Looking around, carrying on a conversation and “horse-play” are
careless acts that can result in serious injury.
26. Maintain a balanced stance at all times so that you do not fall into the blade or other moving parts. Do
not overreach or use excessive force to perform any machine operation.
27. Use the right tool at the correct speed and feed rate. Do not force a tool or attachment to do a job for
which it was not designed. The right tool will do the job better and safer.
28. Use recommended accessories; improper accessories may be hazardous.
29. Maintain tools with care. Keep saw blades sharp and clean for the best and safest performance.
Follow instructions for lubricating and changing accessories.
30. Turn off the machine before cleaning. Use a brush or compressed air to remove chips or debris — do
not use your hands.
31. Do not stand on the machine. Serious injury could occur if the machine tips over.
32. Never leave the machine running unattended. Turn the power off and do not leave the machine until it
comes to a complete stop.
33. Remove loose items and unnecessary work pieces from the area before starting the machine.
Familiarize yourself with the following safety notices used in this manual:
This means that if precautions are not heeded, it may result in minor injury and/or
possible machine damage.
This means that if precautions are not heeded, it may result in serious injury or possibly
even death.
5
Page 6

The most common accidents among table saw users, according to statistics, can
be linked to kickback, the high-speed expulsion of material from the table that can strike the
operator. Kickback can also result in operator’s hands being pulled into the blade.
Kickback Prevention
Tips to avoid the most common causes of
kickback:
• Make sure the blade splitter is always
aligned with the blade. A workpiece can bind
or stop the flow of the cut if the blade splitter
is misaligned and result in kickback.
• Use the blade splitter during every cut. The
blade splitter maintains the kerf in the
workpiece, which will reduce the chance of
kickback.
• Never attempt freehand cuts. The workpiece
must be fed perfectly parallel with the blade,
otherwise kickback will likely occur. Always
use the rip fence or crosscut fence to
support the workpiece.
• Make sure that the rip fence is parallel with
the blade. If not, the chances of kickback are
very high. Take the time to check and adjust
the rip fence.
• Feed cuts through to completion. Anytime
you stop feeding a workpiece that is in the
middle of a cut, the chance of binding,
resulting in kickback, is greatly increased.
Protection Tips from
Kickback
Kickback can happen even if precautions are
taken to prevent it. Listed below are some tips to
always follow to protect you if kickback DOES
occur:
• Stand to the side of the blade when cutting.
An ejected workpiece usually travels directly
in front of the blade.
• Wear safety glasses or a face shield. Your
eyes and face are the most vulnerable part
of your body.
• Never place your hand behind the blade. If
kickback occurs, your hand will be pulled
into the blade.
• Use a push stick to keep your hands farther
away from the moving blade. If a kickback
occurs, the push stick will most likely take
the damage that your hand would have
received.
Read and understand the entire contents of this manual before attempting
assembly or operation! Failure to comply may cause serious injury!
The specifications in this manual are given as general information and are not binding. WMH Tool Group
reserves the right to effect, at any time and without prior notice, changes or alterations to parts, fittings,
and accessory equipment deemed necessary for any reason whatsoever.
6
Page 7

Specifications
Stock Numbers.................................................................................... 708315BTA, -BTB, -BTC, -LSA, -LSB
Saw Blade Diameter ..................................................................................................................................10”
Arbor Diameter..........................................................................................................................................5/8”
Blade Tilt .....................................................................................................................................left, 90 – 45º
Maximum Cutting Depth at 90º ....................................................................................................................3”
Maximum Cutting Depth at 45° ..............................................................................................................2-1/2”
Dado Capacity...........................................................................................................................................1/2"
Table Height (with Stand)...........................................................................................................................35”
Main Table Size ..........................................................................................................................28”W x 18”D
Extension Size (Aluminum).....................................................................................................5 1/2”W x 18”D
Extension Size (Sheet Metal)........................................................................................................8”W x 18”D
Blade Speed (no load) ...................................................................................................................5000 RPM
Motor ....................................................................................................................................... 120VAC, 60Hz
Gross Weight (BTA)............................................................................................................................. 57 lbs.
Net Weight (BTA) ................................................................................................................................. 50 lbs.
Definitions and Terminology
Arbor: Metal shaft that connects the drive
mechanism to the blade.
Bevel Edge Cut: Tilt of the saw arbor and blade
between 0° and 45° to perform an angled cutting
operation.
Blade Guard: Mechanism mounted over the
saw blade to prevent accidental contact with the
cutting edge.
Crosscut: Sawing operation in which the miter
gauge is used to cut across the grain of the
workpiece.
Dado Blade: Blade(s) used for cutting grooves
and rabbets.
Dado Cut: Flat bottomed groove in the face of
the workpiece made with a dado blade.
Featherboard: Device used to keep a board
against the rip fence or table that allows the
operator to keep hands away from the saw
blade.
Kerf: The resulting cut or gap made by a saw
blade.
Kickback: An event in which the workpiece is
lifted up and thrown back toward an operator,
caused when a work piece binds on the saw
blade or between the saw blade and rip fence
(or other fixed object). To minimize or prevent
injury from kickbacks, see the Operating
Instructions section.
Miter Gauge: A component that controls the
workpiece movement while performing a
crosscut of various angles.
Non-Through Cut: A sawing operation that
requires the removal of the blade guard splitter,
resulting in a cut that does not protrude through
the top of the workpiece (includes Dado and
rabbet cuts).
The blade guard and splitter must be re-installed
after performing a non-through cut to avoid
accidental contact with the saw blade during
operation.
Parallel: Position of the rip fence equal in
distance at every point to the side face of the
saw blade.
Perpendicular: 90° (right angle) intersection or
position of the vertical and horizontal planes
such as the position of the saw blade (vertical)
to the table surface (horizontal).
Push Board/Push Stick: An instrument used to
safely push the workpiece through the cutting
operation.
Rabbet: A cutting operation that creates an
L-shaped channel along the edge of the board.
Rip Cut: A cut made along the grain of the
workpiece.
Splitter: Metal plate to which the blade guard is
attached that maintains the kerf opening in the
workpiece when performing a cutting operation.
Standard Kerf: 1/8" gap made with a standard
blade.
Straightedge: A tool used to check that a
surface is flat or parallel.
Through Sawing: A sawing operation in which
the workpiece thickness is completely sawn
through. Proper blade height usually allows a
1/8" of the top of the blade to extend above the
wood stock.
7
Page 8
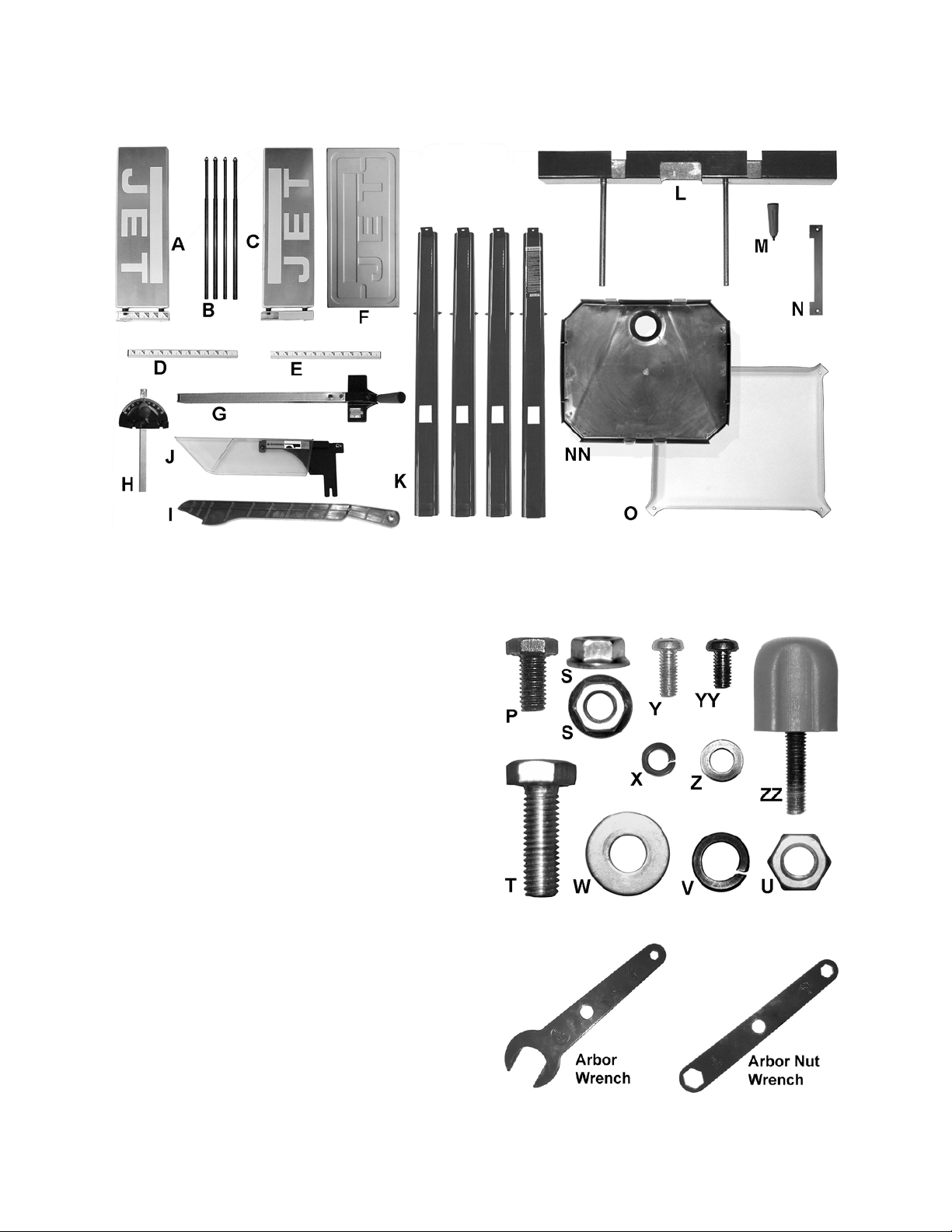
Shipping Contents
Contents of the Table Saw Carton
Contents of the Shipping Cartons
The contents that are contained in the shipping
carton are determined by the model of your
purchase which is determined by the three letter
suffix following the stock number, which is
708315.
Remove all contents from the shipping carton.
Keep the saw table upside down. Do not discard
the carton or packing material until the saw is
assembled and is running satisfactorily.
Important: Packing material is placed inside the
saw to provide support for the motor during
shipping and must be removed.
Compare the contents of the shipping carton
against the Contents Table (following page) for
your particular model. The Index No. in the table
corresponds to the items shown above and this
is your key for identifying each part.
Tool Required (Not Included)
5mm hex wrench (1 ea)
Cross-point Screwdriver (1 ea)
Hardware (actual size)
6mm hex wrench (1 ea)
14mm wrenches (2 ea)
10 mm wrenches (2 ea) or
10mm wrench and socket (1 ea)
Blade Removal Tools
8
Page 9
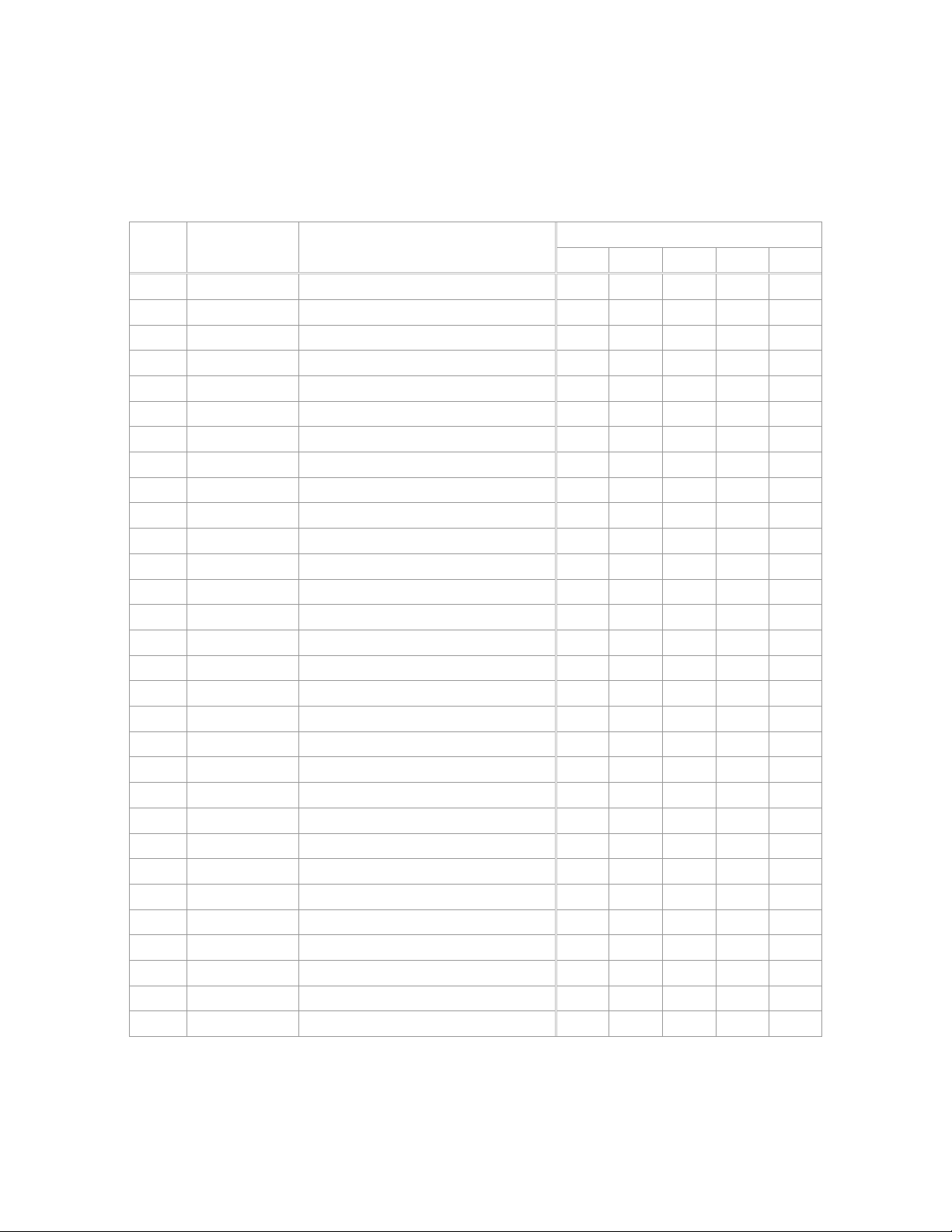
Shipping Contents
Index
No.
NN 708315-159 Dust Shroud 1
YY TS-2284082 M4x8 Pan Head Screw 1 1 2
Part No. Description
-- Table Saw 1 1 1 1 1
A 708315-LEA Left Extension Wing Assy 1
B 708315-105 Extension Rod 2 2 4
C 708315-REA Right Extension Wing Assy 1 1 1
D Left Scale Extension 1
E Right Scale Extension 1 1 1
F 708315-113 Stamped Steel Extension Wing 1
G 708315-RFA Rip Fence 1 1 1 1 1
H 708315-MGA Miter Gauge 1 1 1 1 1
I 708818 Push Stick 1 1 1 1 1
J 708315-BGA Blade Guard Assembly 1 1 1 1 1
K 708315-111 Leg 4 4
L 708315-RSA Rear Support Assembly 1 1 1 1
M 708315-150 Handle 1 1 1 1 1
N 708315-121A Dado Insert 1 1 1 1 1
O 708315-112 Shelf 1 1
P TS-1482021 M6x12 Hex Cap Screw 12 12
S 708315-158 M6 Hex Flange Nut 16 16
T TS-1490041 M8x25 Hex Cap Screw 2
U TS-1540061 M8 Hex Nut 2
V TS-2361081 M8 Lock Washer 2
W TS-1550061 M8 Flat Washer 2
X TS-1551021 M4 Lock Washer 2 2 4
Y TS-1532032 M4x10 Pan Head Screw 2 2 4
Z TS-1550021 M4 Flat Washer 2 2 4
ZZ 708315-134 Lock Knob 6 4 6 6 6
708315-140 Arbor Wrench 1 1 1 1 1
708315-139 Arbor Nut Wrench 1 1 1 1 1
Contents Table
Quantity
BTA BTB BTC LSA LSB
end one column
9
Page 10

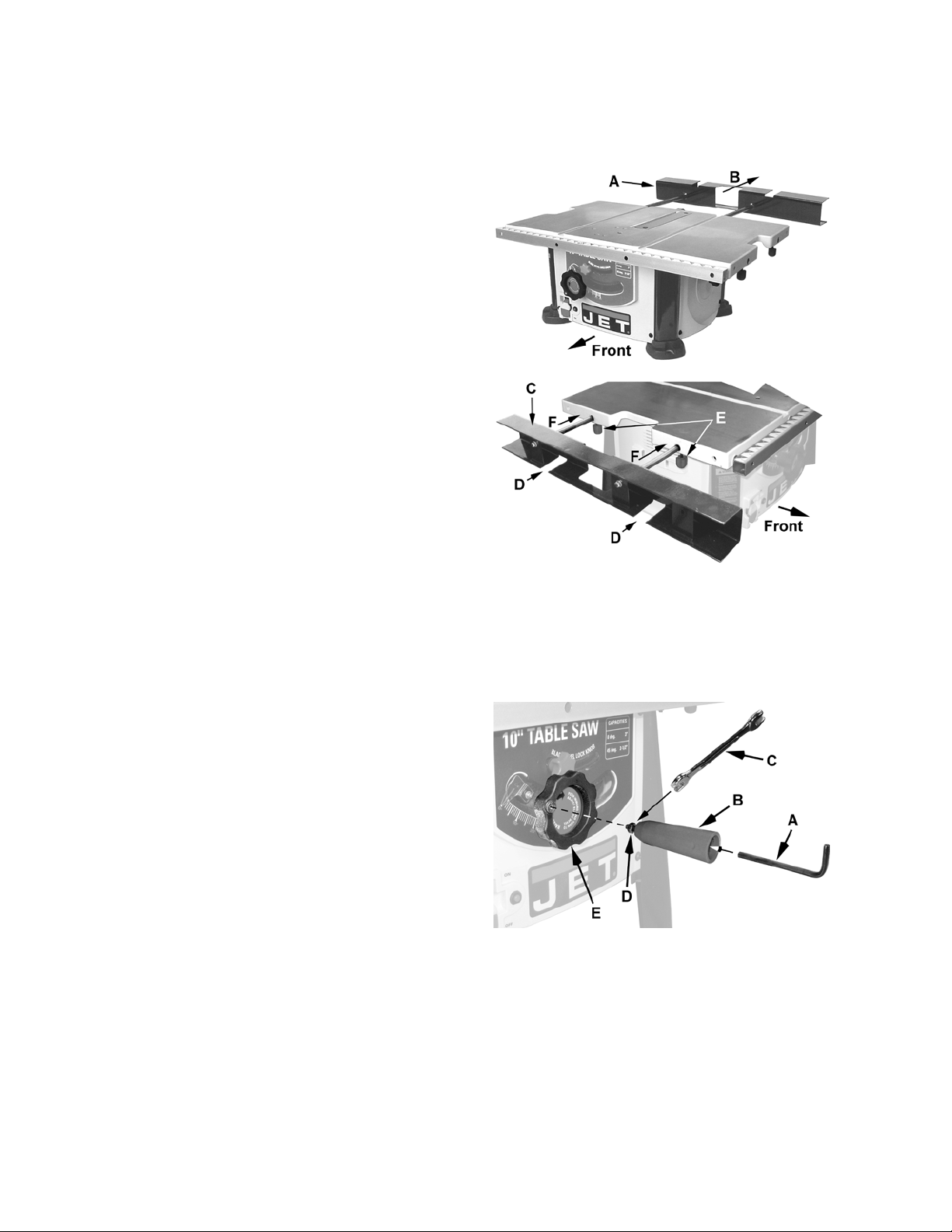
Assembly
Do not plug the table saw into
the power source until all assembly has been
completed! Failure to comply may cause
serious injury!
Where to Begin
Each assembly section will start by listing the
applicable model(s) for that assembly procedure.
The starting point for your particular model,
however, is as follows:
Models LSA, LSB: start with Leg Assembly below.
Models BTA, BTB, BTC: start with Installing the
Blade Guard and Splitter on page 12.
Leg Assembly
Models LSA, LSB
Figure 1
Follow these Leg Assembly instructions if you plan
to use your saw as a floor model. If this saw is to
be used for bench top applications, skip this section
and proceed to the Extension Table section.
Tools required – 10mm socket and wrench
Referring to Figures 1 and 2:
Required hardware (for each leg): two M6x12 hex
cap screws (C) and three M6 flange hex nuts (F).
1. With the saw upside down on the floor, remove
the four rubber feet (A) from each corner of the
base.
2. Take one leg (B) and position it so the outside
tab (G), containing the mounting hole, is
towards the bottom.
3. Mount one leg to a corner of the saw base so
the hole in the outside tab (G) lines up with the
screw (H) and the two holes on the leg's inside
tab (J) rests on top of the base tabs (K) with
the mounting holes lined up.
Note: The leg with the WARNING label must be
mounted on the corner of the saw base that also
has the WARNING label.
4. Insert two hex cap screws (C) through the
mounting holes of the leg tab (J) and base tab
(K). Secure with flange hex nuts (F
tighten only.
). Hand-
1
Figure 2
5. Secure the leg's outside tab (G) to the screw
(H) on the base with a flange hex nut (F
Hand-tighten only.
Mount two more legs in the same manner
described in steps 1–5. Don't mount the last leg
until the shelf is installed as described in the next
section.
).
2
10
Page 11
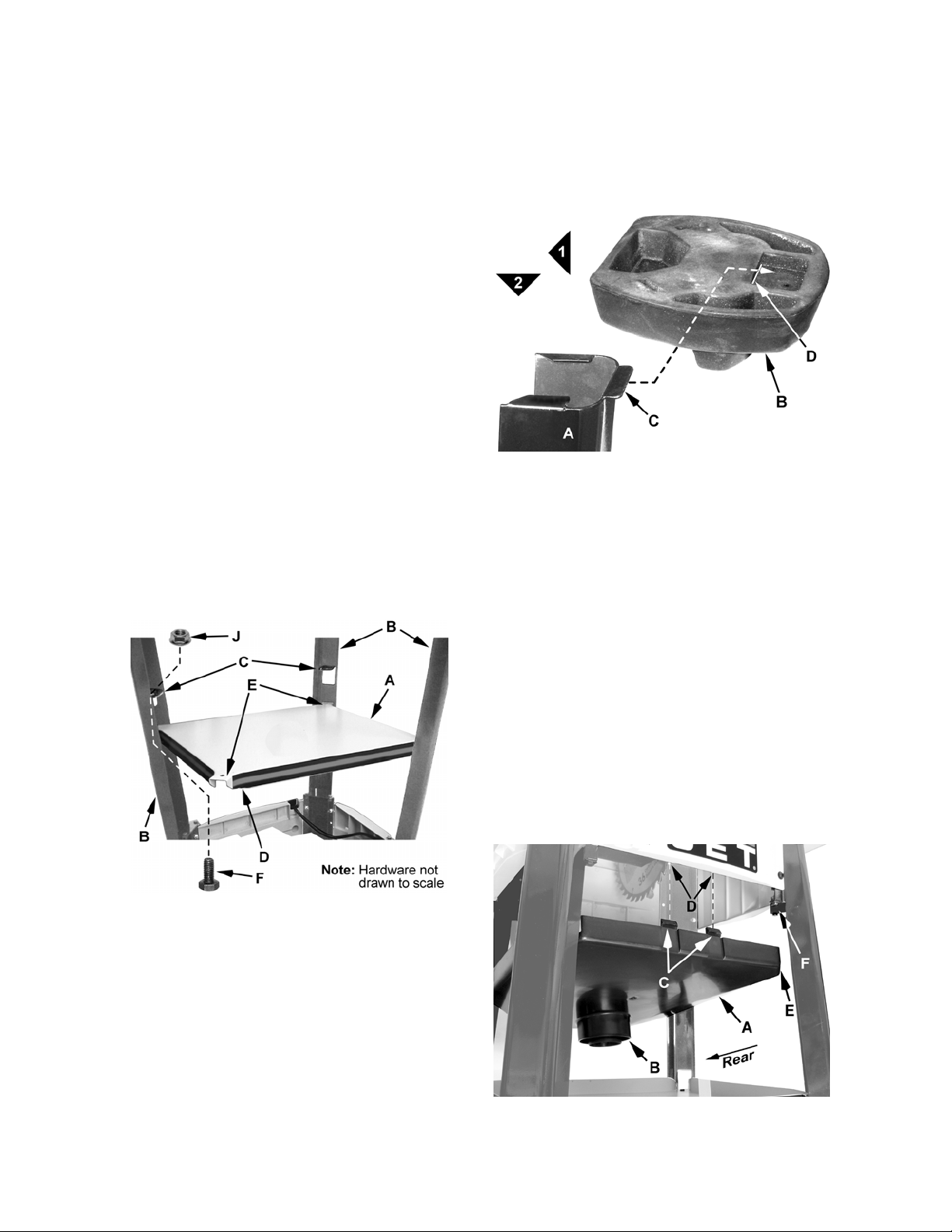
Mounting the Shelf
Models LSA, LSB
Note: The shelf is easier to install when three legs
have been assembled. The fourth leg should be
assembled after this section is completed.
Required hardware (for assembling all four legs):
four M6 flange hex nuts (J).
Referring to Figure 3:
1. While the saw is still upside down, position the
shelf (A) between the three legs (B) and below
the legs' mounting tabs (D). The sides of the
shelf (D) should point down.
2. Bring the shelf up, positioning the tabs of shelf
(E) against the bottom of the mounting tabs on
the legs (C), and line up the mounting holes.
2. Press the foot down (2) until the foot "snaps"
into position on the leg.
3. Repeat for remaining three legs.
At this time, turn the saw right side up. Place on a
level surface and tighten all screws for the leg and
shelf assembly.
3. From underneath the shelf, insert a hex cap
screw (F) up through the mounting holes of the
shelf and leg tabs. Secure the threaded portion
of the screw protruding through the top side of
the leg mounting tab with a flange hex nut (J),
hand-tightening only at this time.
After the shelf is secured to all three legs,
assemble the final leg (described in previous
section) and then finish by securing the remaining
shelf tab to the leg as well.
Figure 4
Dust Shroud
Model LSB only
Note: Install the dust shroud only if a separate dust
collection or vacuum system will be used.
Referring to Figure 5:
1. Place the dust shroud (A) inside the legs with
the port (B) towards the rear of the saw and
positioned down as shown.
2. Bring the front end of the shroud up so the two
front tabs (C) catch the lip (D) of the base,
securing it in position. The opening at the
corners of the shroud (E) should wrap around
the leg tabs (F).
3. Press the back of the shroud up until the rear
tabs snap into place against lip at the back of
the base.
Figure 3
Rubber Feet
Models LSA, LSB
Referring to Figure 4:
While the saw is still upside down,
1. Place rubber foot (B) on the leg (A), sliding
forward (1) while at the same time allowing the
rear tab (C) of the leg to slide through the
opening (D) in the heel of the rubber foot.
11
Figure 5
Page 12
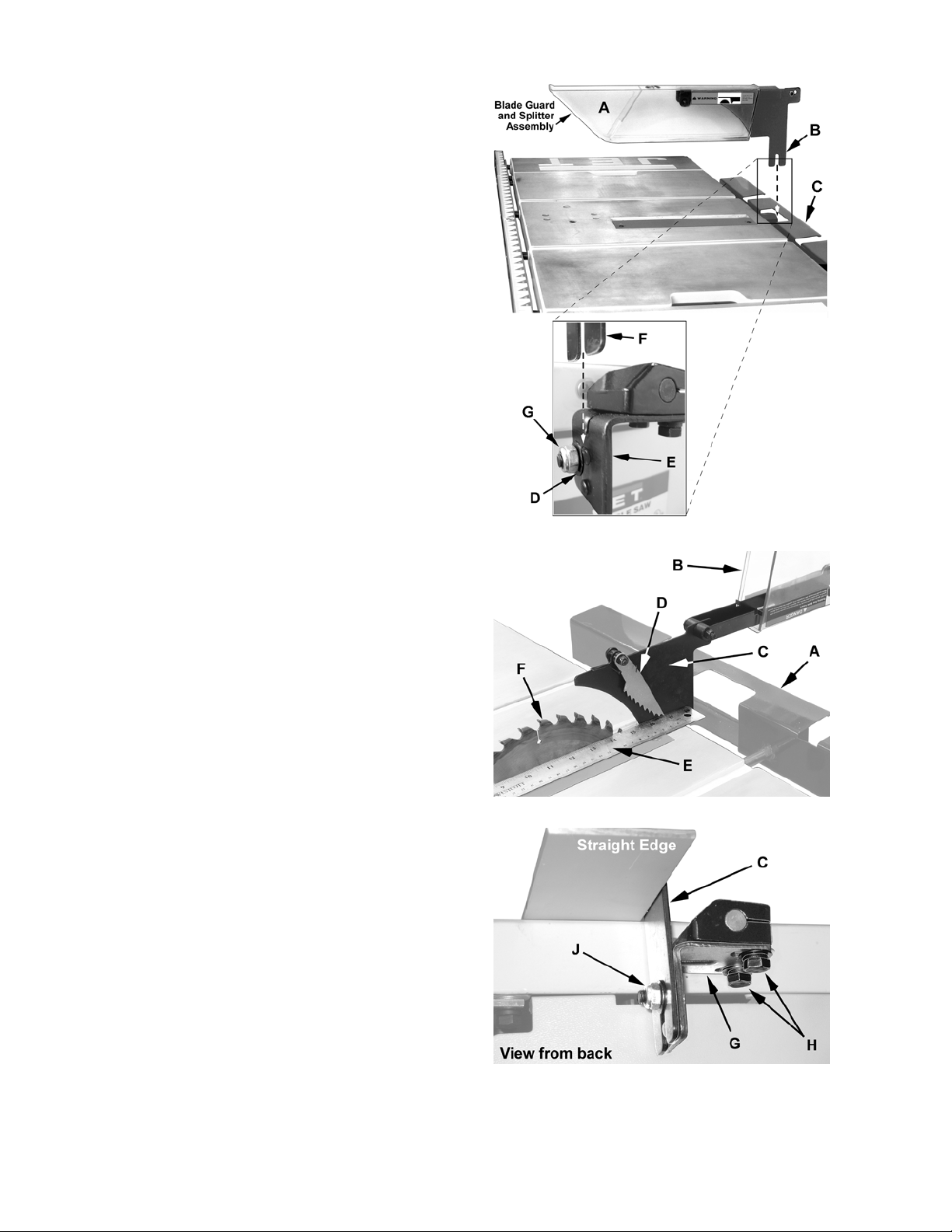
Installing the Blade Guard and Splitter
All models
Referring to Figure 6:
If your table saw came with a back support (C), the
blade guard/splitter installation and alignment will
be facilitated by loosening and sliding the back
support away from the table.
1. Loosen the hex nut (G) on the splitter support
bracket (E) to provide sufficient clearance for
the blade guard and splitter assembly (next
step).
2. Take the blade guard and splitter assembly
and slide the tab of the splitter (B and F) on the
screw of the splitter support bracket (E)
between the flat washer (D) and bracket (E).
3. Tighten the hex nut (G) enough to hold the
blade guard and splitter assembly in place.
Adjustment will be required and is described in the
Adjustment section (see Aligning the Blade Guard
and Splitter).
Figure 6
Aligning the Blade Guard and Splitter
All models
Referring to Figures 7 and 8:
1. Raise the blade guard (B) away from the table.
2. Set a straight edge (E), against the saw blade
(F) on the right side as shown. The anti-kick
pawl (D) needs to be lifted momentarily until
the straight edge is placed in position.
Note: The straight edge needs to rest against
the body of the saw blade and not the saw
teeth.
3. With a 10mm wrench, loosen two hex cap
screws (H) securing the splitter bracket (G) and
adjust the splitter (C) sideways until alignment
with the saw blade (F) is achieved.
4. Tighten the hex cap screws (H).
Make sure the splitter (C) is level with the table and
approximately 1/8" above the table. A 1/8" space
allows the blade guard assembly to tilt to a 45º
angle without contacting the table.
If the splitter level needs adjustment:
Figure 7
5. With two 10mm wrenches, loosen the nut and
screw (J) assembly, adjust the splitter (C) to
1/8" above the table. Tighten the hardware.
Use a square to verify that the splitter is
perpendicular to the table surface and adjust if
required.
12
Figure 8
Page 13
Saw Blade
All Models
The 708315 Table Saw comes with the saw blade
already included and installed from the factory. To
replace a blade, see Replacing the Blade in the
Adjustments section.
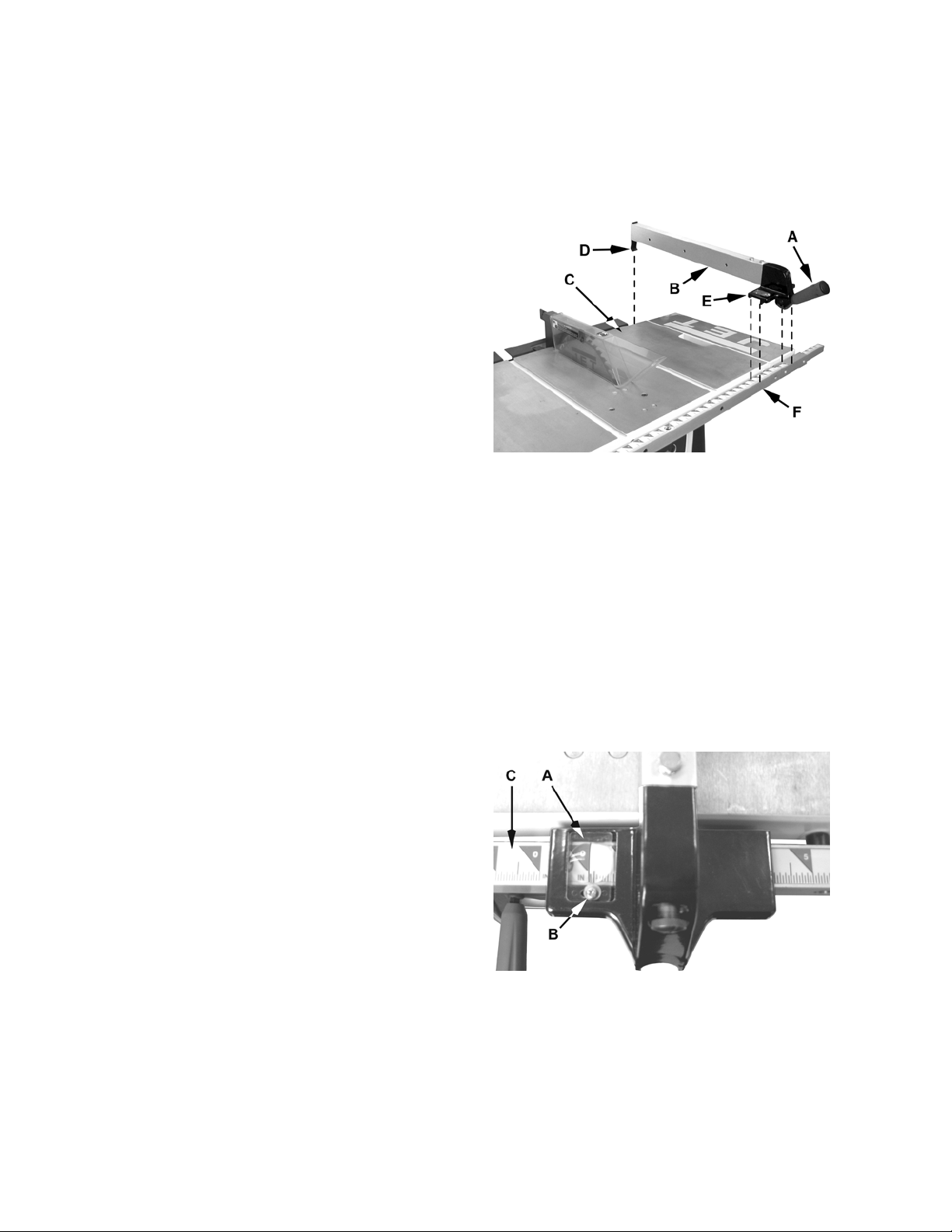
Attaching the Rip Fence
All Models
Referring to Figure 9:
1. Raise the rip fence handle (A) as shown.
2. Position the rip fence (B) over the table (C) as
shown, holding up the front end while engaging
the holding clamp (D) to the rear, then lowering
the front end (E) onto the rail (F).
3. Lower the handle (A) to clamp the fence to the
table
Calibrating the Rip Fence Scale
All Models
1. Attach the rip fence to the table (as described
in the previous section) to the right of the saw
blade, but do not lower the handle to clamp the
fence to the table.
2. Slide the fence against the saw blade.
You will need to raise the blade guard and the
anti-kick pawl to provide clearance for the
fence.
Figure 9
3. With the fence snug against the saw blade,
clamp the fence in position by lowering the
handle.
Referring to Figure 10:
The hairline on the indicator (A) should line up with
0" on the rail (C). If they do not line up:
4. Slightly loosen the screw (B).
5. Slide the indicator until the hairline lines up with
0" on the rail.
6. Tighten the screw.
13
Figure 10
Page 14
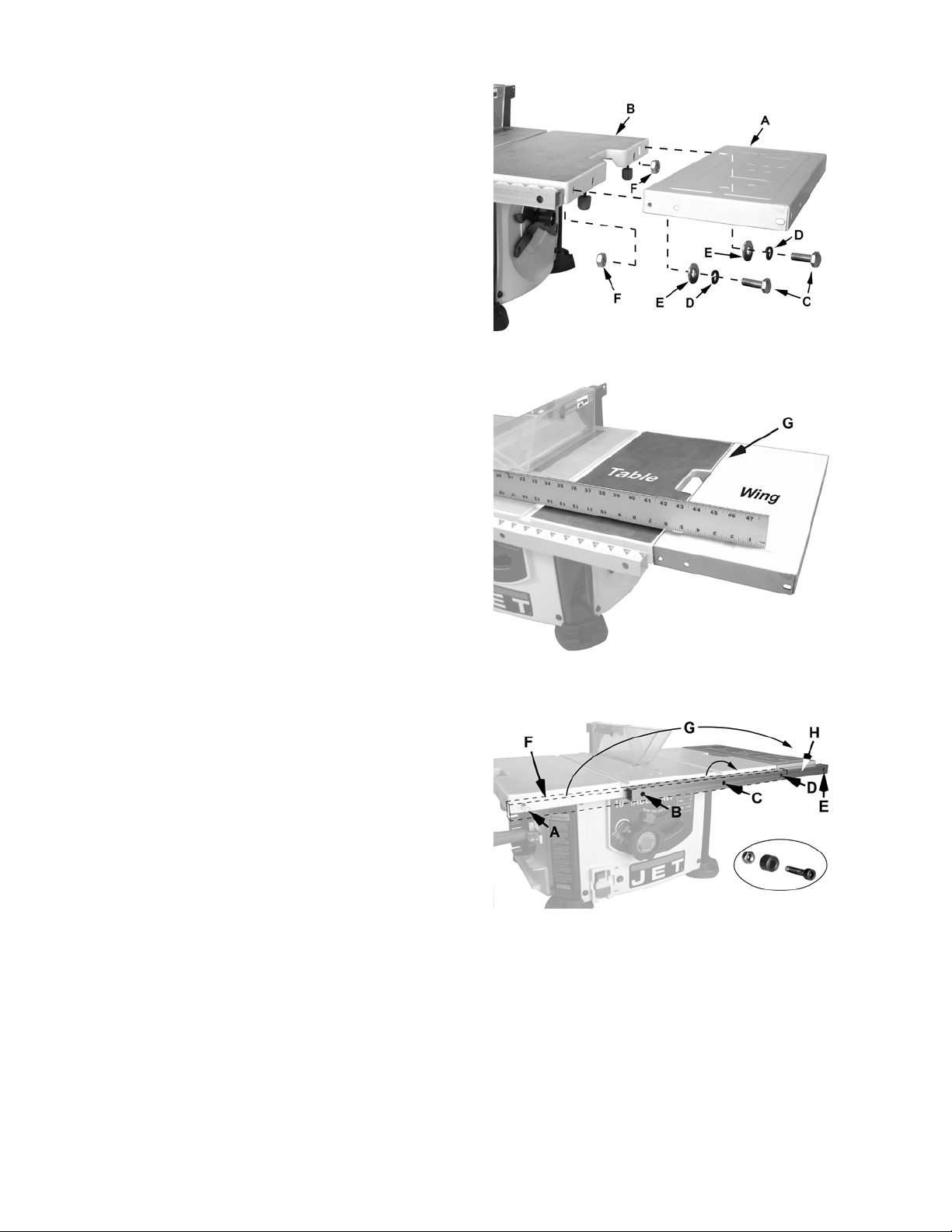
Stamped Steel Extension Wing
Model BTB – the extension wing should look like
(A) in Figure 11
The stamped steel extension wing can be mounted
on the right or left side of the saw table. The
following steps illustrate the right side.
Installation
Referring to Figures 11 and 12:
1. Place the stamped steel extension wing (A)
against the right side of the saw table (B) so
that the mounting holes line up.
2. Place two each M8 lock washers (D) and flat
washers (E) on M8 hex cap screws (C).
3. Insert the screws through the mounting holes
of the extension wing (A) and table (B).
4. Secure with two M8 hex nuts (F) but leave the
assembly loose enough so that the wing can
be moved by hand for adjustment.
Adjustment
5. Place a straight edge across the table and
extension wing near the front as shown in
Figure 12.
Figure 11
6. Raise or lower the extension wing until the
straight edge lies flat across the table and
wing.
7. Move the straight edge so it lies across the
table and wing towards the back (A).
8. Repeat Step 6.
9. When the extension wing is in line with the
table at the front and rear, tighten the screws
(C) and hex nuts (F) with two 14mm wrenches.
Repositioning the Front Rail
Refer to Figure 13.
After the stamped steel extension wing is installed,
the front rail needs to be repositioned to
accommodate the fence when it is positioned over
the extension wing. This is done as follows:
Item F, Fig. 13 shows the initial position of the front
rail.
1. Using a 5mm hex wrench and a 10mm open
end wrench, completely remove the screw,
spacer and lock nut (shown in the inset) that
secure the rail from the two left and far right
mounting holes (A), (B), and (D).
Note: Do not remove mounting hardware from
the third mounting hole (C).
Figure 12
Figure 13
2. Rotate the front rail clockwise (G) until the left
end becomes the right end in front of the
extension wing.
3. Reassemble the three screws, spacers and
lock nuts securing the front rail.
The screws are inserted through the front of
the rail, the spacers are positioned between the
rail and table (or extension), and the lock
washers are fastened to the screw from behind
the lip of the table (or extension).
14
Page 15
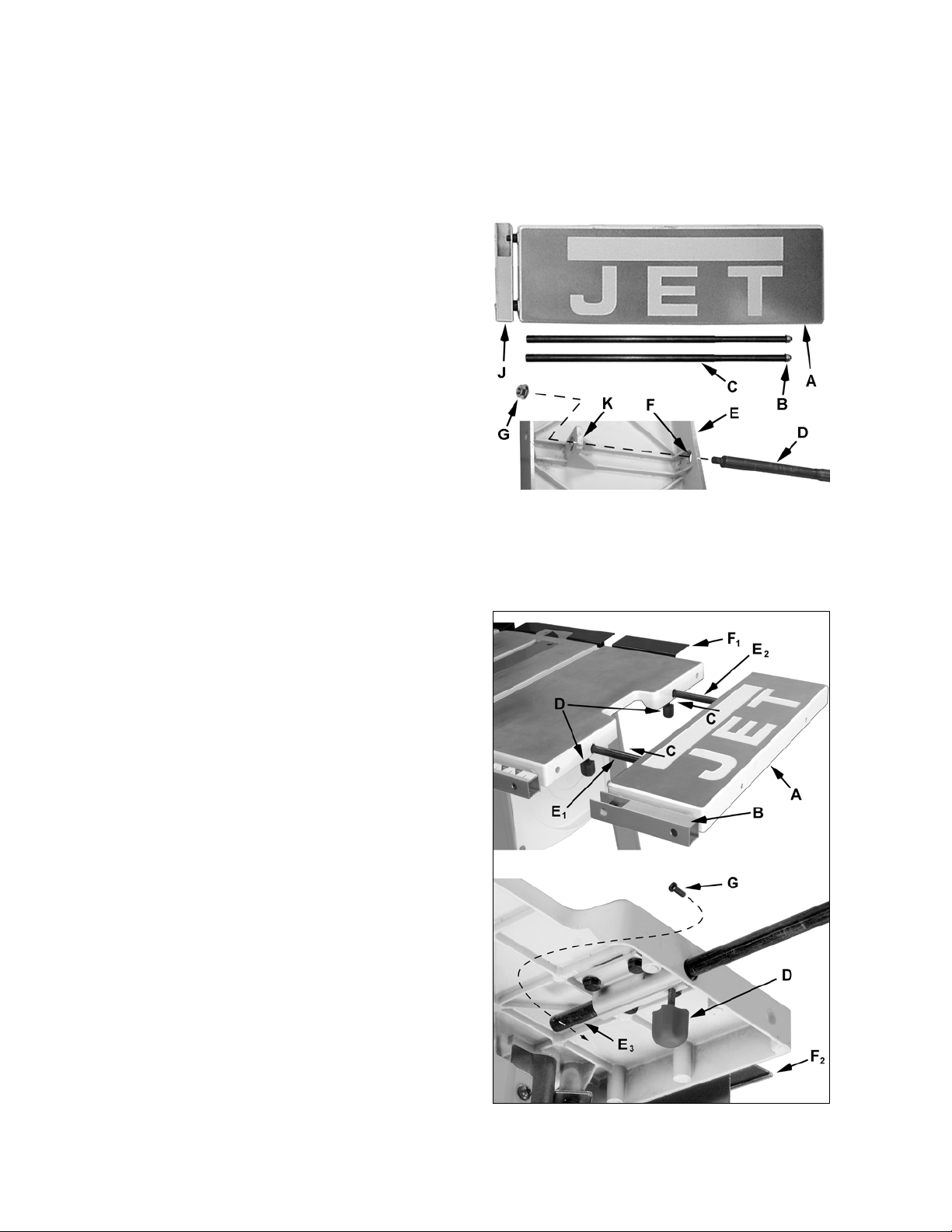
Sliding Extension Wing
Right Wing used on Models BTC, LSA and LSB
Left Wing used on Model LSB
Assembly (if required)
Refer to Figure 14.
For saws using the sliding extension wings, two
extension rods (C) need to be assembled before
mounting to the table. Assembly for the right
extension wing (A), identified by no rule on the rail
(J), is described below. Assembly for the left wing
is the same.
1. Using two 10mm wrenches, remove the lock
nut (B) from the extension rods (C and D).
2. Turn the extension wing (A) over so the JET
logo lays face down and the mounting holes
and tabs (F,K) are visible.
3. Insert the rods (D) through the mounting holes
on the extension wing (F) and tab (K)
The threaded end of the rod (D) should
protrude through the hole in the tab (K).
4. Place hex nuts (G) on the threaded ends of the
extension rods (D), leaving loose enough to
rotate the rods by hand.
5. Rotate the extension rods so that the threaded
holes, located near the ends away from the
extension table, are in line with the top of the
extension table.
Figure 14
6. Secure the extension rods with two 10mm
wrenches, placing one wrench on the hex nut
and the other on the flat indents of the rod.
7. Repeat the above steps for the left extension
wing for models that include it.
Mounting the Right Extension Wing Assembly
Models BTC, LSA and LSB – the right extension
wing looks like A in Figure 15
Referring to Figure 15:
1. Select the right extension table (A), which is
identified by no scale on the guide rail (B).
2. Mount the extension table by sliding the
extension rods into the mounting holes (C) on
the right side of the saw table. The lock
knobs (D) may need to be loosened.
3. From the bottom of the table, thread an M4x8
pan head screw (G) into the hole near the end
of the rear extension rod (E
closest to the rear extension (F
). This is the rod
3
and F2).
1
4. Tighten the lock knobs (D).
Figure 15
15
Page 16
Mounting the Left Extension Wing Assembly
Model LSB only
The left extension table, identified by the scale
(B, Fig. 16) on the rail, is used only with model LSB
The assembly and mounting procedure is the same
manner as for the right extension wing (above).
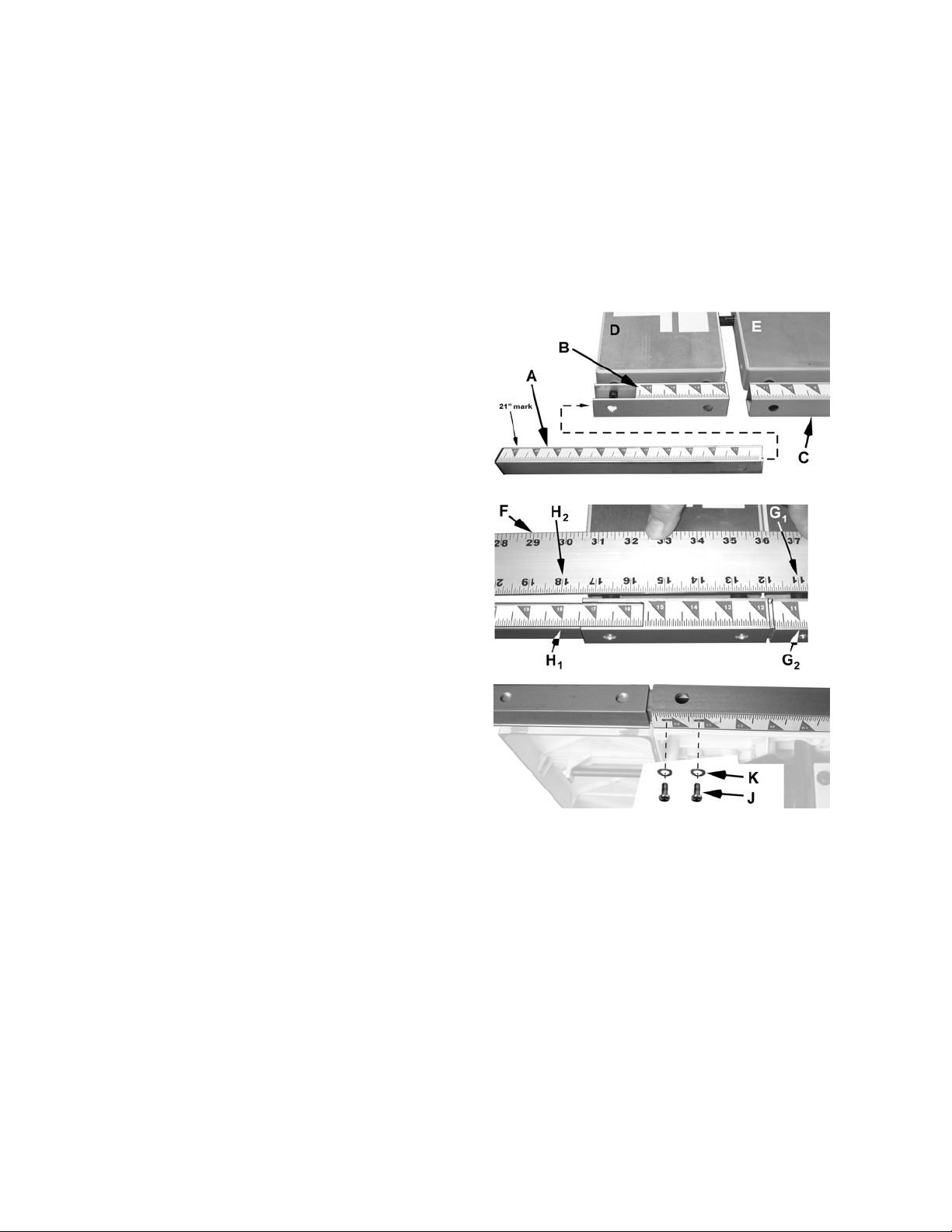
Left Scale Extension
Model LSB only
Referring to Figures 16:
1. If necessary, loosen the extension table lock
knobs and slide the extension table (D) flush
against the saw table (E).
2. Take the left rail extension (A) identified by
scale range 11"–21" and insert into the left
extension table guide rail (B), sliding it all the
way through and into the table guide rail (C).
3. View from underneath and adjust until the two
holes in the rail extension (A) and table rail (C)
are aligned.
4. Insert two each M4x10 pan head screws (J),
M4 lock washers (K) and M4 flat washers (L) to
hold the extension rail in place, but leave loose
enough to permit adjustment (following steps).
5. Place a scale or yardstick (F) across the
extension table and saw table.
6. Align the 11" mark on the ruler (G
mark on the guide rail (G
) and hold ruler firmly
2
) with the 11"
1
in place while performing the next step.
7. Adjust the rail extension (A) until the 18" mark
(H
) is aligned with the 18" mark on the
1
ruler (H
). Release the ruler while making sure
2
the rail extension does not move.
The left rail extension is now properly
calibrated. While holding it in place:
8. Tighten the two screws (K).
Right Scale Extension
Models BTC, LSA and LSB
The assembly steps are the same as for the Left
Scale Extension. For the alignment, use 14" and
21" as the calibration marks.
Figure 16
16
Page 17
Optional Left Table Support
Models BTB, BTC and LSA
Referring to Figure 17:
Table saw models BTB, BTC and LSA do not come
with a left extension table. However the rear
support assembly (A) can be removed and used as
a left table support if needed. To do this:
1. Loosen two lock knobs underneath the back of
the table that secure the rear support
assembly (A).
2. Remove the rear support assembly by sliding it
back (B).
3. Turn the assembly over so that the flat side of
the rail is on top (C) and the two notches (D)
are on the bottom.
4. Loosen the two lock knobs (E) located on the
left side of the table.
5. Install the rear support assembly by inserting
inserting the extension rods into the two
mounting holes on the left side of the table (F).
Remember that the notches (D) are on the
bottom.
7. Tighten the lock knobs.
Handwheel Handle
All Models
Referring to Figure 18:
Figure 17
1. Insert a 5mm hex wrench (A) in the end of the
handle (B) into the socket head cap screw.
2. Thread into the handwheel (E) until almost
tight.
While still maintaining a hold on the hex
wrench (A):
3. Tighten the hex nut (C) with a 10mm wrench
(D) against the handwheel (E) so that the
handle (B) is secure, but its rotation is still
allowed during operation.
17
Figure 18
Page 18
Adjustments
When working around the saw
blade, always disconnect the saw from the
power source! Failure to comply may cause
serious injury!
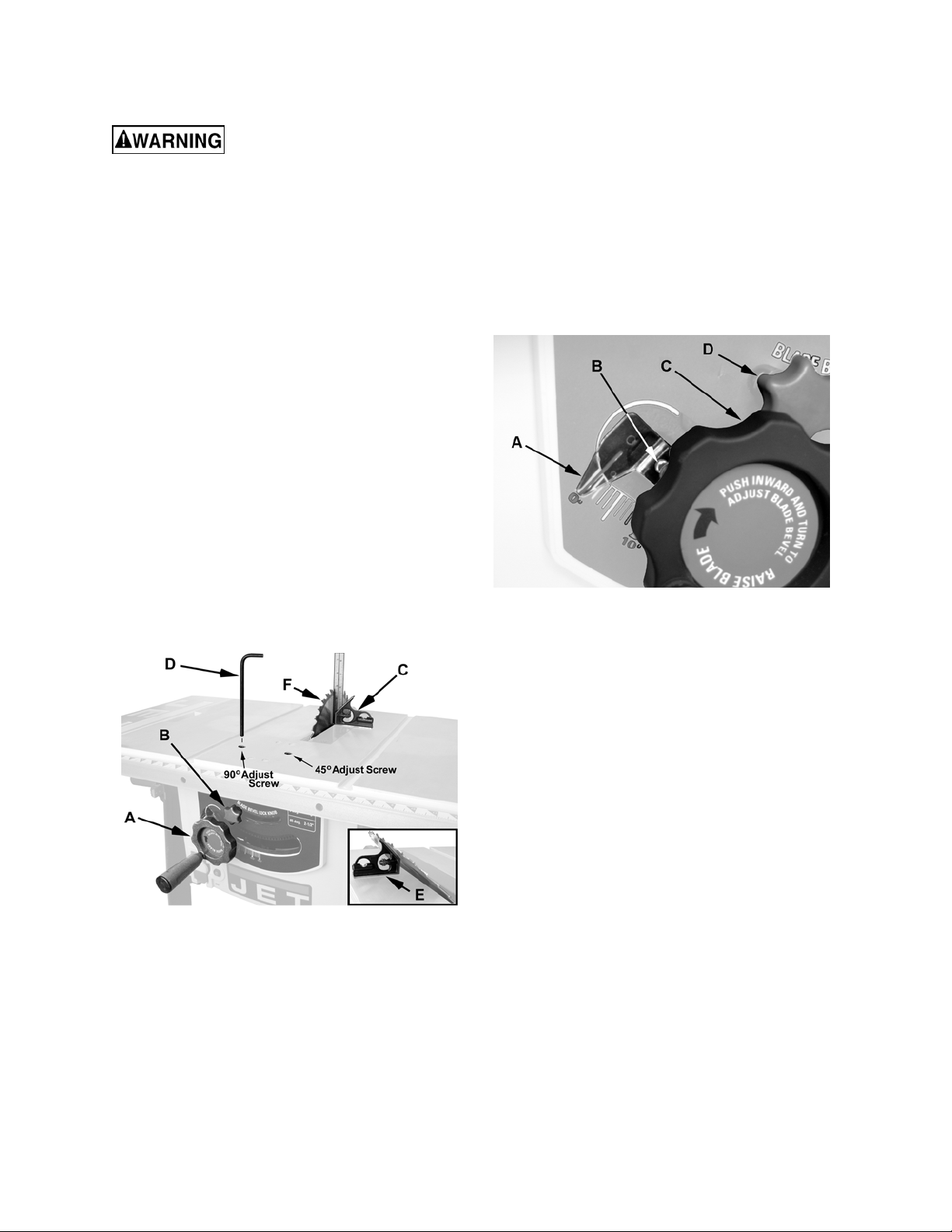
90 Degree Positive Stop
Referring to Figure 19:
1. Turn the handwheel (A) clockwise and raise
the blade to its maximum height.
2. Loosen the blade tilt lock knob (B) by turning
counterclockwise.
3. Push the handwheel (A) in to engage the blade
tilt mechanism; then turn clockwise all the way,
bringing the blade to the 90º position to the
table.
4. Continue holding the handwheel with the blade
in this position. Place a combination square (C)
on the table and against the blade as shown.
If the blade is not 90º to the table:
2. Push the handwheel (C) in to engage the blade
tilt mechanism; then turn clockwise all the way,
bringing the blade to the 90º position to the
table. Hold the handwheel and:
3. Lock the blade tilt lock knob (D).
If the scale does not read exactly 0º:
4. Loosen the screw (B) with an off-set cross-
point screwdriver.
5. Manually adjust the scale (A) until it points
to 0º:
6. Tighten the screw (B).
5. While maintaining the hold on the handwheel,
use a 6mm hex wrench to turn the 90 Adjust
Screw (Figure 19) until the blade is 90º to the
table.
6. Tighten the blade tilt lock knob (B).
Figure 19
Scale Calibration
The scale next to the handwheel needs to be
calibrated after the saw blade has been calibrated
at the 90º positive stop (see previous section) and
the scale does not indicate 0º.
To calibrate the scale (refer to Figure 20):
1. Loosen the blade tilt lock knob (D) by turning
counterclockwise.
Figure 20
45 Degree Positive Stop
Referring to Figure 19:
1. Turn the handwheel (A) clockwise and raise
the blade to its maximum height.
2. Loosen the blade tilt lock knob (B) by turning
counterclockwise.
3. Push the handwheel (A) in to engage the blade
tilt mechanism and turn counterclockwise all
the way, bringing the blade to the 45º position
to the table.
4. Continue holding the handwheel with the blade
in this position. Place a combination square (E)
on the table and against the blade as shown.
If the blade is not 45º to the table:
5. While maintaining the hold on the handwheel,
use a 6mm hex wrench to turn the 45 Adjust
Screw (Figure 19) until the blade is 45º to the
table.
6. Tighten the blade tilt lock knob (B).
18
Page 19
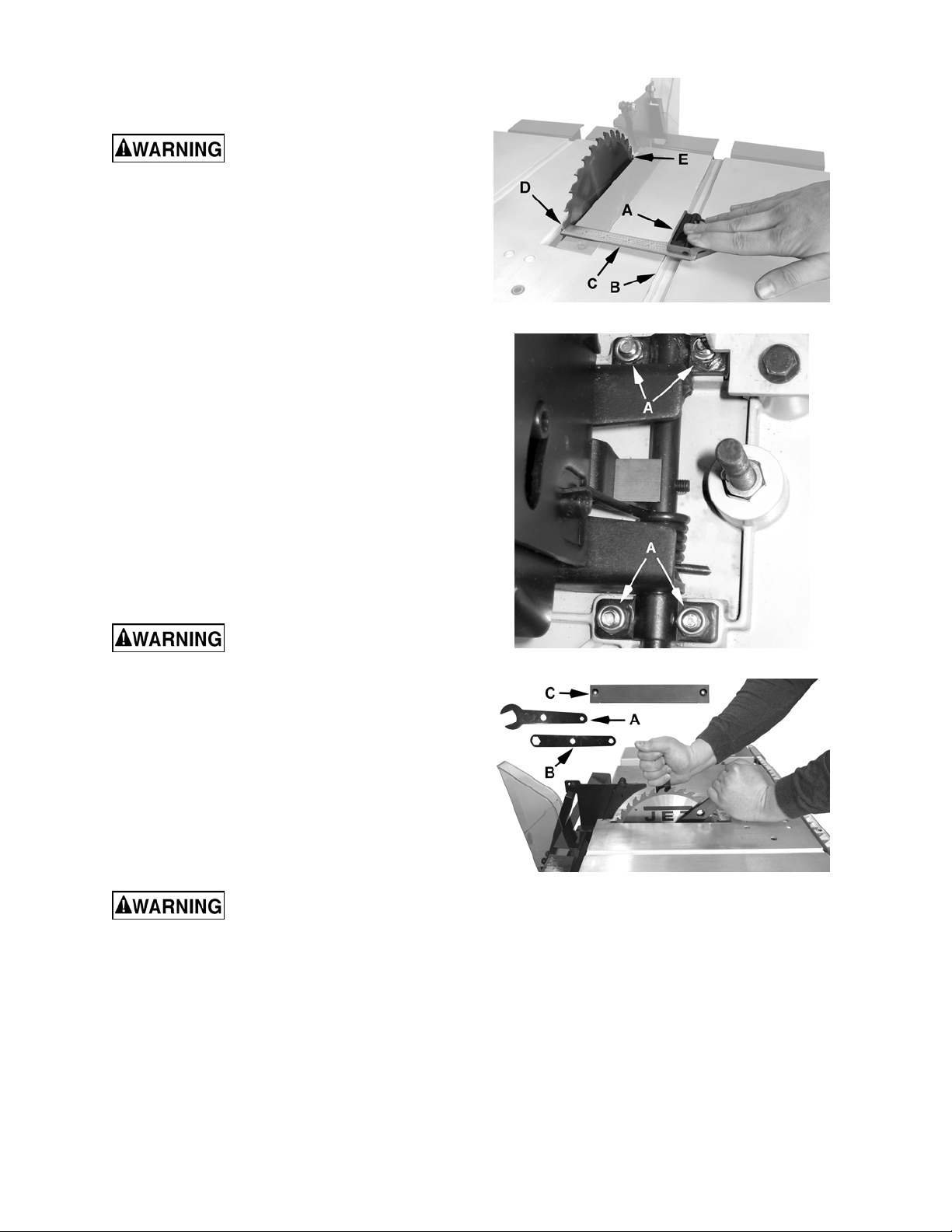
Adjusting Blade Parallel to Miter Gauge
Slots
When working around the saw
blade, always disconnect the saw from the
power source! Failure to comply may cause
serious injury!
The saw blade was adjusted at the factory to be
parallel to the miter gauge slots and should not
need adjustment. However, if upon inspection it is
determined that adjustment is required, follow the
steps below.
1. Using the handwheel (A, Fig. 19), raise the saw
blade as high as it will go.
Referring to Figure 21:
2. Place the base of a combination square (A)
pressed against the edge of the miter slot (B).
Extend the sliding rule (C) so it just touches the
tooth at the near end of the blade (D), then
tighten the locking screw on the combination
square to secure the sliding rule.
3. Move the square to the far end of the blade (E).
Figure 21
If a gap appears or if the base of the
combination square will not rest against the
edge of the miter slot, adjustment is required
as follows:
Saw blades are sharp. Be
extremely careful when working around them!
Failure to comply may cause serious injury!
Referring to Figure 22:
4. From underneath the table saw, loosen 3 (of 4)
screws (A) that secure the motor to the base.
5. Carefully move the saw blade until the blade is
parallel to the miter gauge slot. Check by
repeating steps 2 and 3. When adjustment is
complete, securely tighten the screws (A).
Replacing the Blade
When installing or changing the
saw blade, always disconnect the saw from the
power source! Failure to comply may cause
serious injury!
1. Using the handwheels, raise the blade arbor
fully and lock the saw at zero degrees (see
steps 1–3 in the 90 Degree Positive Stop
section); then tighten the blade tilt lock knob
(B, Fig. 19).
2. Remove the two insert screws and lift the table
insert (C, Fig. 23) out of the pocket of the
table.
Figure 22
Figure 23
3. Place the open end arbor wrench (A, Fig. 23)
on the flat sides of the inside blade flange to
keep the saw arbor from rotating. Rotate the
arbor nut counterclockwise with the closed
arbor nut wrench (B, Fig. 23) and remove the
arbor nut and outer flange.
4. Replace the old blade with a new one, making
certain that the teeth are pointing down at the
front of the table (refer to D, Fig. 21).
5. Assemble the outer flange, arbor nut and
securely tighten the arbor nut clockwise while
holding the arbor steady with the open end
arbor wrench.
19
Page 20
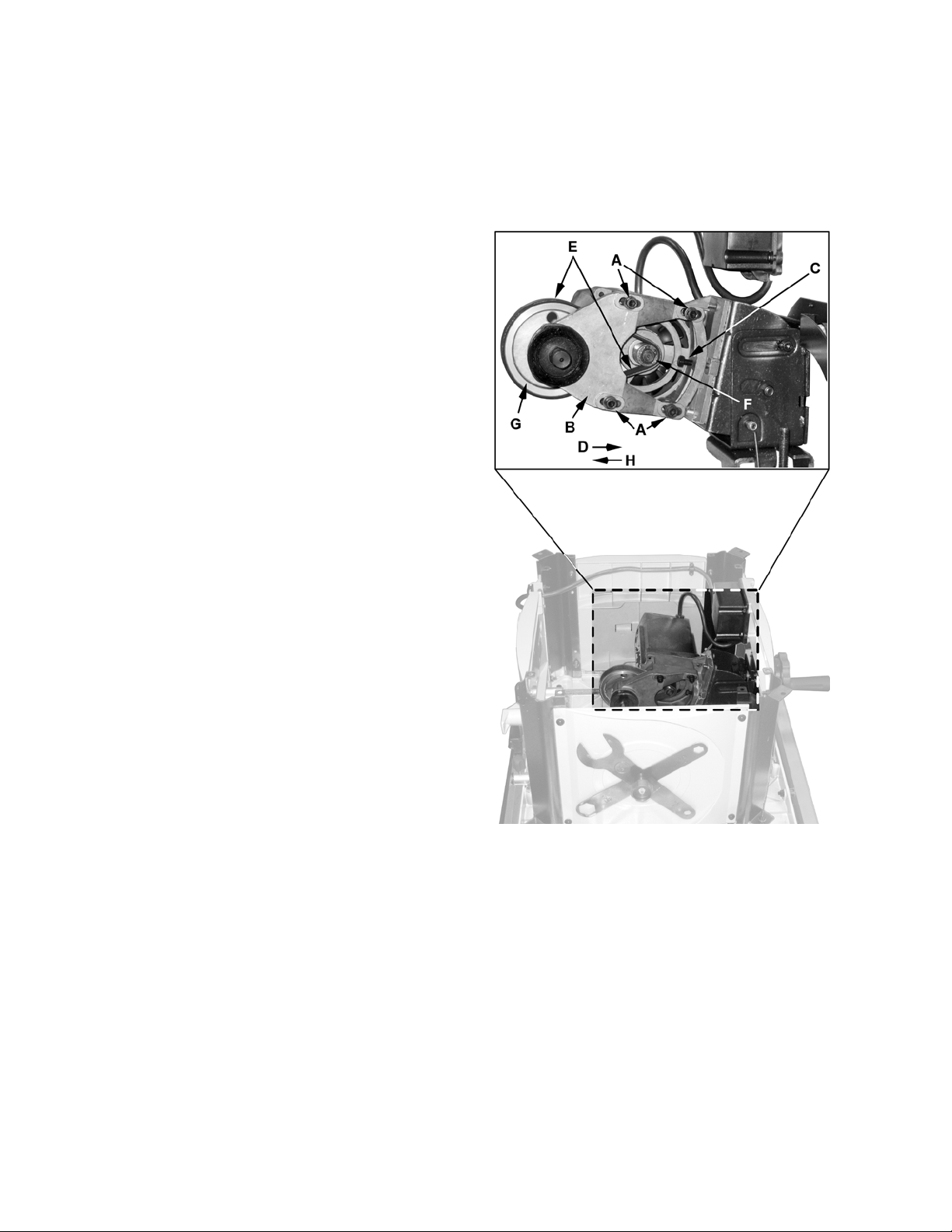
Replacing/Adjusting the Drive Belt
For Replacement and Adjustment
1. Remove the saw blade (see Replacing the
Blade on page 19).
2. Using the front handwheel, lower the blade
arbor to its lowest position (rotate handwheel
counterclockwise).
3. Remove the blade guard and splitter (see
Installing the Blade Guard and Splitter section
on page12), then turn the saw upside down.
4. Remove the dust shroud if applicable.
Referring to Figure 24:
5. With a 5mm hex wrench, loosen four socket
head cap screws (A) that secure the arbor
support (B) to the motor casing.
If adjusting belt tension only (no belt replacement),
skip steps 6 – 10 and proceed to step 11.
6. With a 10mm wrench, loosen the tension adjust
screw (C) by turning counterclockwise.
7. Push the arbor support (B) forward (D) to
relieve tension on the belt (E).
8. Remove belt (E) from the motor and arbor
pulleys (F, G).
9. Replace the old belt with a new belt making
sure that it sits properly on both pulleys.
10. Pull the arbor support (B) back (H), placing
tension on the belt, and hand-tighten the four
mounting screws (A).
Adjustment
11. With a 10mm wrench, turn the tension adjust
screw (C) to place proper tension on the belt.
Adjustment is sufficient when moderate finger
pressure on the belt between the pulleys
results in approximately 1/4" deflection.
12. Tighten the four mounting screws (A) with a
5mm hex wrench.
After the Adjustment
13. Replace the dust shroud (page 11) if
applicable.
14. Turn the table saw right-side up.
15. Replace and adjust the blade guard and splitter
(refer to the Installing the Blade Guard and
Splitter and Adjusting the Blade Guard and
Splitter sections on page 12).
16. Replace the saw blade (Replacing the Blade
on page 19).
Figure 24
20
Page 21
Miter Gauge Operation
Operate the miter gauge by loosening the lock
knob (A, Fig. 25) and turning the miter body
(B, Fig. 25) to the desired angle.
Note: Always make test cuts. Do not rely solely on
miter gauge indicator marks.
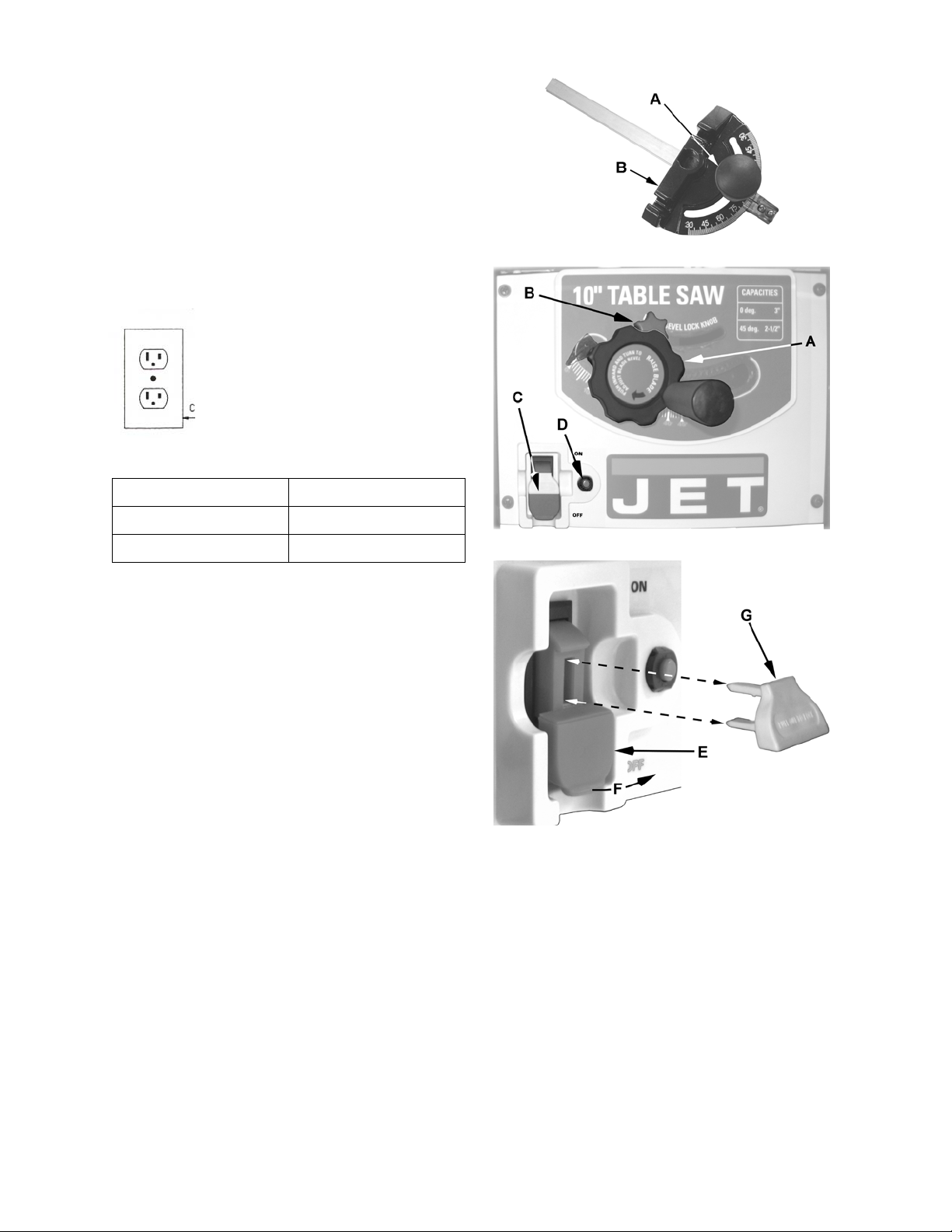
Electrical Connections
This saw has a motor that operates on 120VAC
and is equipped with a power cord that plugs into a
standard grounded 3-prong 120VAC
outlet as shown.
Before hooking up to the power
source, be sure the switch is in the
off position.
If an extension cord is used, select
one with a rating appropriate for the
job from the chart below.
0012 Gauge Cord 000 – 25 feet
Figure 25
0010 Gauge Cord 000 – 50 feet
008 Gauge Cord 000 – 100 feet
Extension Cord Chart
Operating Controls
On/Off Switch – The on/off switch is located on the
front panel of the saw base (C, Fig. 26). To turn the
saw on move the switch to the up position
(F, Fig. 27). To turn the switch off move the switch
to the down position.
Locking Key – When the saw is not in use, the
switch should be locked in the off position. To lock
the switch in the off position, pull out the safety key
(G, Fig. 27). The saw will not start with the key
removed. However, if the key is removed while the
switch is in the on position, it can be turned off
once. The saw will not restart until the key has
been reinserted into the switch.
Overload Protection – This saw is equipped with
a resetable overload relay button (D, Fig. 26). If the
motor shuts off or fails to start due to overloading or
low voltage, turn the switch (C, Fig. 26) to the off
position and let the motor cool down for at least five
minutes. After the motor has cooled down, push the
reset button (D, Fig. 26) to reset the overload
device. The saw should now start when the switch
is returned to the on position.
Blade Height/Tilt Handwheel – The handwheel
located on the front of the saw (A, Fig. 26) sets the
blade height and tilt.
To raise or lower the blade, simply turn the hand-
Figure 26
Figure 27
wheel (A, Fig. 26) clockwise or counterclockwise.
To tilt the blade:
1. Press the handwheel in.
2. Loosen the blade tilt lock knob (B, Fig. 26) by
turning counterclockwise.
3. Still pressing the handwheel in, turn clockwise
or counterclockwise to set the blade between
0º (blade 90º perpendicular to table) and 45º
(left tilt).
When the desired blade angle is set,
4. Continue holding the handwheel (A, Fig. 26) in
until the lock knob (B, Fig. 26) is tightened.
21
Page 22
Operations
Before turning the saw on,
make sure that the table is free of tools,
hardware and debris. These items can
become projectiles and cause serious injury.
Table Saws
Familiarize yourself with the location and
operation of all controls and adjustments and the
use of accessories such as the miter gauge and
rip fence.
Kickbacks
Serious injury can result from kickbacks which
occur when a work piece binds on the saw blade
or binds between the saw blade and rip fence or
other fixed object. This binding can cause the
work piece to lift up and be thrown toward the
operator.
Listed below are conditions, which can cause
kickbacks:
Confining the cutoff piece when crosscutting
or ripping.
Releasing the work piece before completing
the operation or not pushing the work piece
all the way past the saw blade.
Not using the splitter when ripping or not
maintaining alignment of the splitter with the
saw blade.
Using a dull saw blade.
Not maintaining alignment of the rip fence so
that it tends to angle toward rather than
away from the saw blade front to back.
Applying feed force when ripping to the
cutoff (free) section of the work piece
instead of the section between the saw
blade and fence.
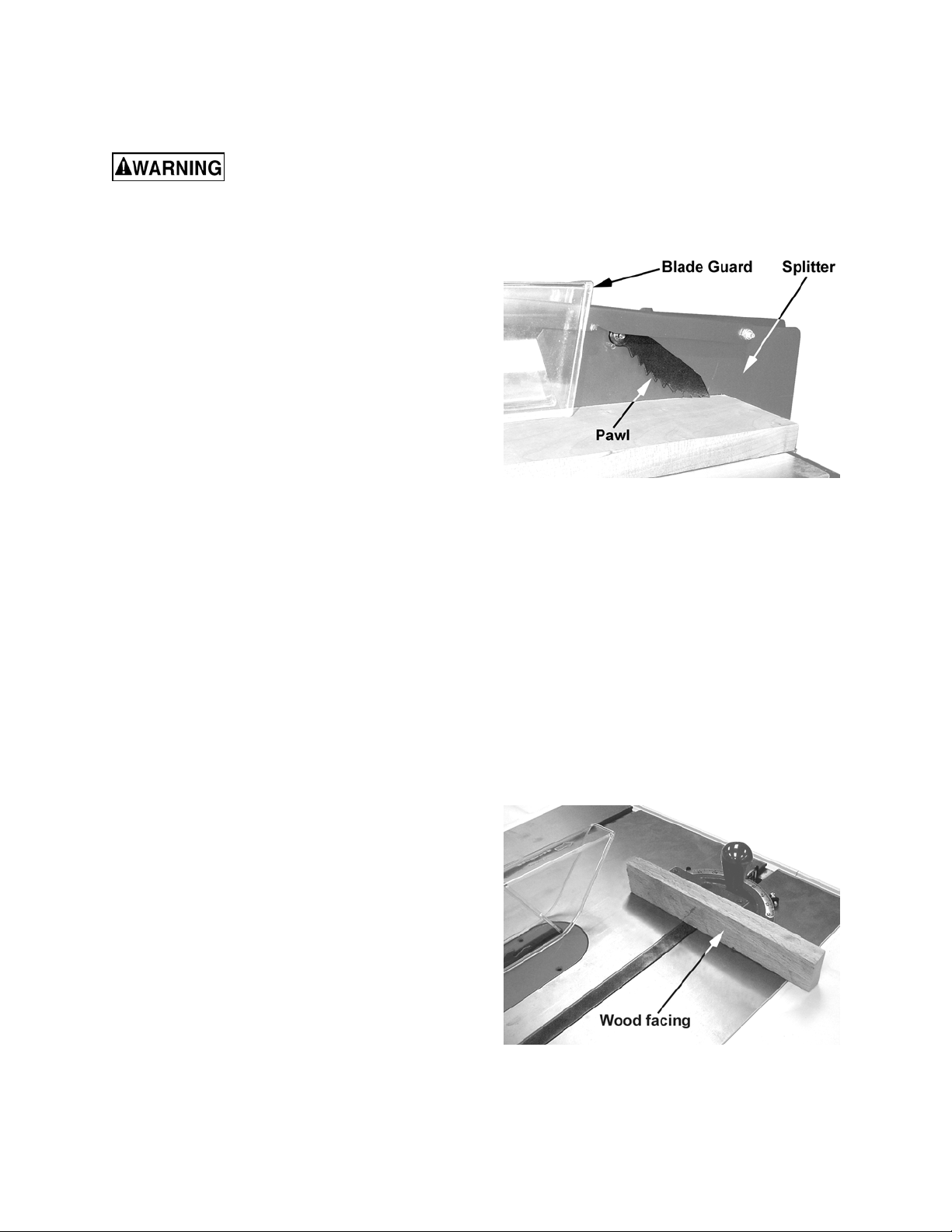
As the machine receives use, the operation
of the anti-kickback pawls should be
checked periodically (Figure 26). If the pawls
do not stop the reverse motion of a
workpiece, resharpen all the points.
Where possible, keep your face and body
out of line with potential kickbacks including
when starting or stopping the machine.
Figure 28
Dull, badly set, improper, or improperly filed
cutting tools and cutting tools with gum or resin
adhering to them can cause accidents. Never
use a cracked saw blade. The use of a sharp,
well maintained, and correct cutting tool for the
operation will help to avoid injuries.
Support the work properly and hold it firmly
against the gauge or fence. Use a push stick or
push block when ripping short, narrow (6" width
or less), or thin work. Use a push block or miter
gauge hold-down when dadoing or molding.
For increased safety in crosscutting, use an
auxiliary wood facing (Figure 29) attached to the
miter gauge using the holes provided in the
gauge.
Ripping wood that is twisted (not flat), or
does not have a straight edge, or a twisted
grain.
To minimize or prevent injury from kickbacks:
Avoid conditions listed above.
Wear a safety face shield, goggles, or
glasses.
Do not use the miter gauge and rip fence in
the same operation unless provision is made
by use of a facing board (auxiliary block) on
the fence so as to allow the cutoff section of
the workpiece to come free before the next
cut is started (see Figure 35).
Figure 29
Never use the fence as a length stop when
crosscutting. Do not hold or touch the free end
or cutoff section of a workpiece. On through-
22
Page 23
sawing operations, the cutoff section must NOT
be confined.
Always keep your hands out of the line of the
saw blade and never reach back of the cutting
blade with either hand to hold the workpiece.
Bevel ripping cuts should always be made with
the fence on the right side of the saw blade so
that the blade tilts away from the fence and
minimizes the possibility of the work binding and
the resulting kickback.
Rip Sawing
Ripping is where the work piece is fed with the
grain into the saw blade using the fence as a
guide and a positioning device to ensure the
desired width of cut (Figure 30).
Figure 31
The rip fence (A, Fig. 31) should be set for the
width of the cut (C, Fig. 31) by using the scale
on the front rail, or by measuring the distance
between the blade (B) and fence (A). Stand out
of line with the saw blade and workpiece to
avoid sawdust and splinters coming off the blade
or a kickback, if one should occur.
If the work piece does not have a straight edge,
nail an auxiliary straight edged board on it to
provide one against the fence. To cut properly,
the board must make good contact with the
table. If it is warped, turn the hollow side down.
Figure 30
Before starting a ripping cut,
be sure the fence is clamped securely and
aligned properly.
Never rip freehand or use the miter gauge in
combination with the fence.
Never rip workpieces shorter than the saw
blade diameter.
Never reach behind the blade with either
hand to hold down or remove the cutoff
piece with the saw blade rotating.
Always use the blade guard, splitter and antikickback pawls. Make sure the splitter is
properly aligned. When wood is cut along the
grain, the kerf tends to close and bind on the
blade and kickbacks can occur.
Note: A caution decal is installed on the guard
and splitter assembly warning of the hazard of
misalignment.
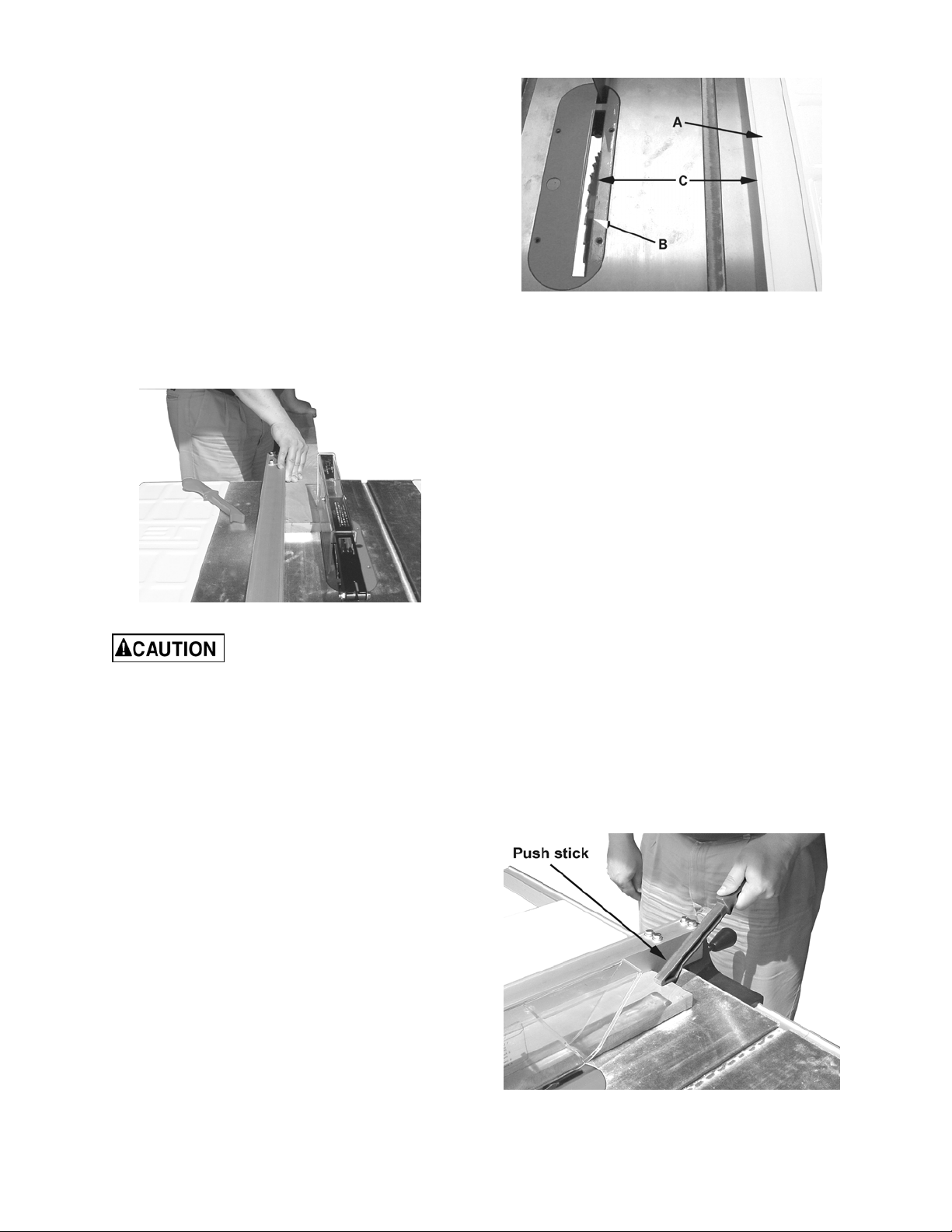
In ripping, use one hand to hold the board down
against the fence or fixture, and the other to
push it into the blade between the blade and the
fence. If the workpiece is narrower than 6" use a
push stick or push block to push it through
between the fence and saw blade (Figure 32).
Never push in a location such that the pushing
hand is in line with the blade. Move the hand
serving as a hold-down a safe distance from the
blade as the cut nears completion. For very
narrow ripping where a push stick cannot be
used, use a push block or auxiliary fence.
Always push the workpiece completely past the
blade at the end of a cut to minimize the
possibility of a kickback.
23
Figure 32
Page 24
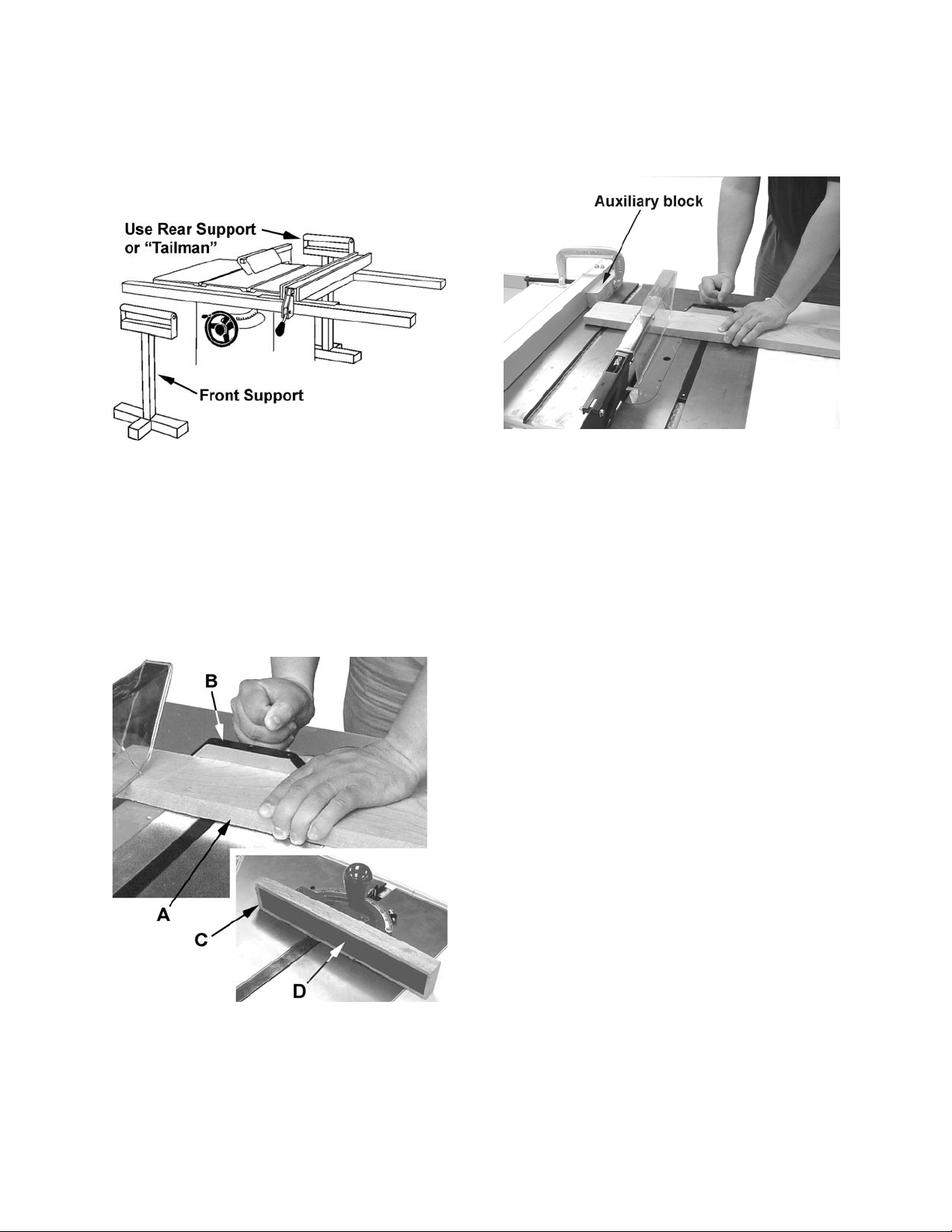
When ripping long boards, use a support at the
front of the table, such as a roller stand, and a
support or "tailman" at the rear as shown in
Figure 33.
Have the blade extend about 1/8" above the top
of the workpiece. Exposing the blade above this
point can be hazardous.
Crosscutting should never be done freehand nor
should the fence be used as an end stop unless
an auxiliary block is clamped to the front of the
blade area such that the cutoff piece comes free
of the block before cutting starts (Figure 35).
Figure 33
Crosscutting
Crosscutting is where the workpiece (A, Fig. 34)
is fed cross grain into the saw blade using the
miter gauge (B, Fig. 34) to support and position
the workpiece.
To improve the effectiveness of the miter gauge
in crosscutting, mount an auxiliary wooden
extension face (C, Fig, 34) with a glued-on strip
of sandpaper (D, Fig. 34) to the miter gauge.
Length stops should not be used on the free end
of the workpiece in the cutoff area.
Do not crosscut workpieces shorter than 6".
Before starting a cut, be sure the miter gauge is
securely clamped at the desired angle. Hold the
workpiece firmly against the table and back
against the miter gauge. Always use the saw
guard and splitter and make sure the splitter is
properly aligned.
For 90 degree crosscutting, most operators
prefer to use the left-hand miter gauge slot.
When using it in this position, hold the workpiece
against the gauge with the left hand and use the
right hand to advance the workpiece. When
using the right hand slot for miter and compound
crosscutting so that the blade tilts away from the
gauge, the hand positions are reversed.
When using the miter gauge, the workpiece
must be held firmly and advanced smoothly at a
slow rate. If the workpiece is not held firmly, it
can vibrate causing it to bind on the blade and
dull the saw teeth.
Figure 35
Provide auxiliary support for any workpiece
extending beyond the table top with a tendency
to sag and lift up off the table.
Have the blade extend about 1/8" above the top
Figure 34
of the workpiece. Exposing the blade above this
point can be hazardous.
24
Page 25
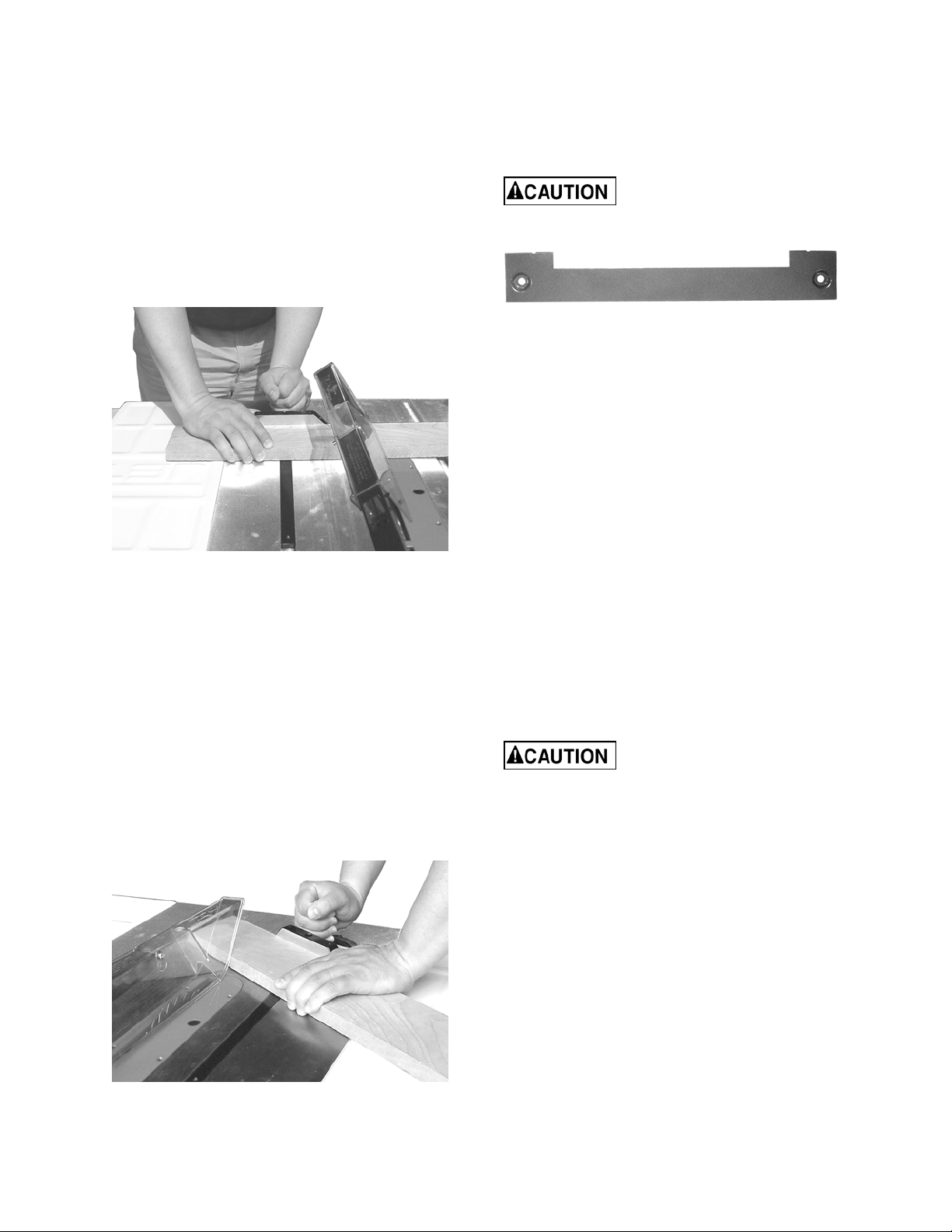
Bevel and Miter Operations
Bevel Cut – A bevel cut is a special type of
operation where the saw blade is tilted at an
angle less than 90 degrees to the table top
(Figure 36). Operations are performed in the
same manner as ripping or crosscutting except
the fence or miter gauge should be used on the
right-hand side of the saw blade to provide
added safety in avoiding a binding action
between the saw blade and the table top. When
beveling with the miter gauge, the workpiece
must be held firmly to prevent creeping.
Figure 36
Crosscut – Crosscuts made at an angle to the edge of the workpiece are called miters (Figure 37). Set the miter gauge at the required angle, lock the miter gauge, and make the cut the same as a normal crosscut except the workpiece must be held extra firmly to prevent creeping.
Note: When making compound miters (with
blade tilted) use the miter gauge in the right
hand slot to provide more hand clearance and
safety.
Have the blade extend only 1/8" above the top of
the workpiece. Exposing the blade above this
point can be hazardous.
Dado Cutting – Dadoing is cutting a wide groove into a workpiece or cutting a rabbet along the edge of a workpiece. A dado insert, shown in Figure 38, is necessary for this type of operation.
Do not use the standard table
insert for dadoing operations.
Figure 38
The process of cutting 1/8" to 1/2" grooves in
workpieces is accomplished by the use of a
stacked dado blade set or an adjustable type
blade mounted on the saw arbor. By using
various combinations of the stacked dado
blades, or properly setting the dial on an
adjustable blade, an accurate width dado can be
made. This is very useful for shelving, making
joints, tenoning, etc. The guard, splitter, and
anti-kickback pawls supplied with the saw
should be used for all cutting operations where
they can be used. When performing operations
where the guard can not be used, as in some
dadoing operations, alternative safety
precautions should be taken. These include
push sticks, feather boards, filler pieces, fixtures,
jigs and any other appropriate device that can
be utilized to keep operator's hands away from
the blade. Upon completion of the operation
requiring removal of the guard, the entire guard
assembly must be placed back on the machine
in its proper working order.
Never use a dado head in a
tilted position. Never operate the saw without
the blade guard, splitter and anti-kickback
pawls for operations where they can be
used.
Dust Collection
If your saw is equipped with a dust shroud, a
dust collection or vacuum system (not included)
should be used during operation. The port on
the dust shroud can accommodate 2.5-inch or
4-inch hoses (Figure 39).
The dust shroud should be checked and cleaned
often to remove dust and chips in order to
prevent blockage from buildup.
Figure 37
25
Page 26

Figure 39
Safety Devices
Feather Board
The feather board (Figure 40) should be made
of straight grain hardwood approximately 1" thick
and 4" to 8" wide depending on the size of the
machine. The length is developed in accordance
with intended use. Feather boards can be
fastened to the table or rip fence by use of
C-clamps. If this method of fastening is used,
provide slots in the feather board for adjustment.
(The illustration shows a method of attaching
and use of the feather board as a vertical comb.
The horizontal application is essentially the
same except that the attachment is to the table
top.)
Push Stick
A push stick is provided with this saw and
should be used as an added level of safety for
the operator.
Filler Piece
A filler piece (Figure 41) is necessary for narrow
ripping and permits the blade guard to remain on
the machine. It also provides space for the safe
use of a push stick.
Figure 40
Figure 41 – Filler Piece
Maintenance
Always disconnect power to
the machine before performing maintenance.
Failure to do this may result in serious
personal injury.
Cleaning
Clean the 708315 Table Saw according to the
schedule below to ensure maximum
performance.
Note: The following maintenance schedule
assumes the saw is being used every day.
Daily:
Clean pitch and resin from the saw blade.
Weekly:
Clean motor housing with compressed air.
Wipe down the table surface, grooves and
fence rails with a dry silicon lubricant.
26
Page 27

Lubrication
Miscellaneous
Lubricate the areas indicated below every 12
months.
Lubricate blade angling trunnions with 6 or 7
drops of light machine oil.
Lubricate the blade height trunnion with 6 or
7 drops of light machine oil.
Check all adjustments after lubricating.
Troubleshooting
Symptom Possible Cause Correction
Low voltage. Check power line for proper voltage. Motor will not start
Open circuit in motor or loose
connection.
Motor will not start: fuses
or circuit breakers blow.
Motor stalls resulting in
blown fuses or tripped
circuit.
Machine slows when
operating.
Loud, repetitious noise
coming from machine.
Blade is not square with
the miter slot or fence is
not square to the blade.
Blade does not reach 90
degrees.
Short circuit in line cord or plug. Inspect cord or plug for damaged insulation
Short circuit in motor or loose
connections.
Incorrect fuses of circuit breakers in
power line.
Motor overloaded. Reduce load on motor. Motor overheats.
Air circulation through the motor
restricted.
Short circuit in motor or loose
connections.
Low voltage. Correct the low voltage conditions.
Incorrect fuses of circuit breakers in
power line.
Motor overloaded. Reduce load on motor.
Applying too much pressure to
workpiece.
Pulley setscrews or keys are missing or
loose.
V-belt is defective. Replace V-belt.
Blade is warped. Replace saw blade.
Table top is not parallel to the blade. Adjust table parallel to the blade.
Fence is not parallel to the blade. Adjust fence parallel to the blade.
90 degree stop bolt is out of adjustment. Adjust the 90 degree stop bolt.
Table out of alignment. Align the table.
Blade position is incorrect. Adjust the blade position.
Always be aware of the condition of your
machine. Routinely check the condition of the
following items and repair or replace as
necessary:
Mounting bolts
Power switch
Saw blade
Blade guard
Inspect all lead connections on motor for loose
or open connections.
and shorted wires.
Inspect all connections on motor for loose or
shorted terminals or worn insulation.
Install correct fuses or circuit breakers.
Clean out motor to provide normal air
circulation.
Inspect connections on motor for loose or
shorted terminals or worn insulation.
Install correct fuses or circuit breakers.
Feed workpiece slower.
Inspect keys and setscrews. Replace or tighten
if necessary.
Parts
Ordering Replacement Parts
To order parts or reach our service department, call 1-800-274-6848 between 7:30 a.m. and 5:30 p.m.
(CST), Monday through Friday. Having the Model Number and Serial Number of your machine available
when you call will allow us to serve you quickly and accurately.
27
Page 28

Motor/Trunnion – Parts List
Index No. Part No. Description Size Qty
1 ...............708315-1..................Motor ................................................................... .................................... 1
2 ...............708315-2..................Brush Assembly................................................... .................................... 2
3 ...............708315-3..................Motor Sheave....................................................... .................................... 1
4 ...............708315-4..................Retaining Ring ..................................................... ....................................1
5 ...............708315-5..................Key....................................................................... 3x6.5x16 .................... 1
6 ...............TS-1490011 .............Hex Cap Screw .................................................... M8x12 .........................1
7 ...............TS-1550061 .............Flat Washer..........................................................M8 ............................... 1
8 ...............708315-8..................Arbor Sheave ....................................................... .................................... 1
9 ...............708315-9..................Belt....................................................................... .................................... 1
10 .............TS-2286252 .............Pan Head Screw .................................................. M6x25 ......................... 1
11 .............TS-1540041 .............Hex Nut ................................................................M6............................... 7
12 .............BB-6002Z.................Bearing................................................................. 6002Z ......................... 1
13 .............708315-13 ................Arbor Support....................................................... .................................... 1
14 .............708315-14 ................Arbor Shaft ........................................................... .................................... 1
15 .............TS-1503111 .............Socket Head Cap Screw...................................... M6x50 ......................... 2
16 .............BB-6003Z.................Bearing................................................................. 6003Z ......................... 1
17 .............TS-1532042 .............Pan Head Screw .................................................. M4x12 ......................... 3
18 .............708315-18 ................Cover Plate .......................................................... .................................... 1
19 .............708315-19 ................Arbor Flange ........................................................ .................................... 1
20 .............708315-20 ................Saw Blade ............................................................10”x36T....................... 1
21 .............708315-21 ................Arbor Collar .......................................................... .................................... 1
22 .............708315-22 ................Arbor Nut.............................................................. .................................... 1
23 .............TS-1503081 .............Socket Head Cap Screw...................................... M6x35 ......................... 2
24 .............TS-1551041 .............Lock Washer ........................................................M6............................... 4
25 .............TS-1550041 .............Flat Washer.......................................................... M6............................... 4
26 .............TS-1482051 .............Hex Cap Screw .................................................... M6x25 ........................ 1
27 .............TS-2236801 .............Socket Head Cap Screw...................................... M6x80 ......................... 1
28 .............708315-28 ................Motor Bracket....................................................... .................................... 1
29 .............708315-29 ................Spacer.................................................................. .................................... 1
30 .............708315-30 ................Spacer.................................................................. .................................... 1
31 .............708315-31 ................Shaft Support ....................................................... .................................... 1
32 .............708315-32 ................Nut........................................................................M10 ............................ 4
33 .............TS-1550071 .............Flat Washer.......................................................... M10............................. 1
34 .............708315-34 ................Special Washer .................................................... .................................... 1
35 .............708315-35 ................Spacer.................................................................. .................................... 2
36 .............TS-1503061 .............Socket Head Cap Screw...................................... M6x25 ......................... 2
37 .............708315-37 ................Bracket ................................................................. .................................... 1
38 .............TS-2284082 .............Pan Head Screw .................................................. M4x8 ........................... 2
39 .............TS-1550021 .............Flat Washer.......................................................... M4............................... 2
40 .............TS-1551021 .............Lock Washer ........................................................M4............................... 2
41 .............708315-41 ................Roll Pin................................................................. M3x18 ......................... 1
42 .............708315-42 ................Raising Shaft........................................................ .................................... 1
43 .............708315-43 ................Pointer.................................................................. .................................... 1
44 .............708315-44 ................Bracket ................................................................. .................................... 1
45 .............708315-45 ................Roll Pin................................................................. M8x90 ......................... 1
46 .............708315-46 ................Trunnion Bracket.................................................. .................................... 1
47 .............TS-1503051 .............Socket Head Cap Screw...................................... M6x20 ......................... 3
48 .............708315-48 ................Pin ........................................................................ M3x10 ......................... 1
49 .............708315-49 ................Bracket ................................................................. .................................... 1
50 .............TS-2285302 .............Pan Head Screw .................................................. M5x30 ......................... 1
51 .............708315-51 ................Rod Support ......................................................... .................................... 1
52 .............708315-52................Hold Down Strap.................................................. .................................... 4
28
Page 29

Motor/Trunnion – Parts List
Index No. Part No. Description Size Qty
53 .............708315-53 ................Angle Rod ............................................................ .................................... 1
54 .............TS-2286251 .............Flat Head Screw .................................................. M6x25 ......................... 2
55 .............708315-55 ................Rod Support Plate................................................ .................................... 1
56 .............708315-56 ................Spring................................................................... .................................... 1
57 .............708315-57 ................Carriage Bolt ....................................................... M6x32 ......................... 1
58 .............708315-58 ................Spacer.................................................................. .................................... 1
59 .............TS-1541021 .............Nylon Insert Lock Nut...........................................M6 ............................. 39
29
Page 30

Motor/Trunnion -- Assembly
30
Page 31

Blade Guard Assembly
Index No. Part No. Description Size Qty
.................708315-BGA ............Blade Guard Assembly (Complete)1.................... ......................................
25 .............TS-1550041 .............Flat Washer.......................................................... M6............................... 4
59 .............TS-1541021 .............Nylon Insert Lock Nut...........................................M6 ............................... 3
60 .............TS-1482041 .............Hex Cap Screw .................................................... M6x20 ......................... 4
61 .............708315-61 ................Splitter Bracket..................................................... .................................... 1
62 .............708315-62 ................Support................................................................. ....................................1
63 .............708315-63 ................Carriage Bolt ........................................................ M6x12 ......................... 1
64 .............708315-64 ................Splitter .................................................................. .................................... 1
65 .............708315-65 ................Anti-Kickback Pawl .............................................. .................................... 2
66 .............708315-66 ................Spacer.................................................................. .................................... 2
67 .............708315-67 ................Guard Support ..................................................... .................................... 1
68 .............708315-68 ................Guard ................................................................... ....................................1
69 .............708315-69 ................Rivet ..................................................................... .................................... 2
70 .............708315-70 ................Retaining Washer ................................................ .................................... 2
71 .............708315-71 ................Pin ........................................................................ M3x22 ......................... 1
72 .............708315-72 ................Spring................................................................... .................................... 1
1
A complete Blade Guard Assembly, if purchased, includes all parts except Items 60 – 63.
31
Page 32

Miter Gauge Assembly
Index No. Part No. Description Size Qty
.................708315-MGA............Miter Gauge Assembly (Complete)...................... ......................................
38 .............TS-2284082 .............Pan Head Screw .................................................. M4x8 ........................... 2
73 .............708315-73 ................Bar........................................................................ .................................... 1
74 .............708315-74 ................Pointer.................................................................. .................................... 1
75 .............708315-75 ................Handle.................................................................. .................................... 1
76 .............708315-76 ................Handle Cap .......................................................... .................................... 1
77 .............708315-77 ................Miter Gauge Body ................................................ .................................... 1
78 .............708315-78 ................Pin ........................................................................ M6x15 ......................... 1
32
Page 33

Rear Support Assembly
Index No. Part No. Description Size Qty
.................708315-RSA ............Rear Support Assembly (Complete) .................... ......................................
59 .............708315-158 ..............Flanged Hex Nut .................................................. M6............................... 2
79 .............708315-79 ................Rod....................................................................... .................................... 2
80 .............708315-80 ................Rear Support........................................................ .................................... 1
33
Page 34

Rip Fence Assembly
Index No. Part No. Description Size Qty
.................708315-RFA.............Rip Fence Assembly (Complete) ......................... ......................................
25 .............TS-1550041 .............Flat Washer.......................................................... M6............................... 2
38 .............TS-2284082 .............Pan Head Screw .................................................. M4x8 ........................... 1
76 .............708315-76 ................Handle Cap .......................................................... .................................... 1
82 .............708315-82 ................Rear Clamp .......................................................... .................................... 1
83 .............708315-83 ................Spring................................................................... .................................... 1
84 .............708315-84 ................Rod....................................................................... .................................... 1
85 .............708315-85 ................Fence Body .......................................................... .................................... 1
86 .............TS-1482011 .............Hex Cap Screw .................................................... M6x10 ......................... 2
87 .............708315-87 ................External Tooth Lock Washer................................ M6 ............................... 2
88 .............708315-88 ................Front Block ........................................................... .................................... 1
89 .............708315-89 ................Spring................................................................... .................................... 1
90 .............708315-90 ................Adjustment Screw ................................................ .................................... 1
91 .............708315-91 ................Cam Lock ............................................................. .................................... 1
92 .............708315-92 ................Handle.................................................................. .................................... 1
93 .............708315-93 ................Pin ........................................................................ .................................... 1
94 .............708315-94 ................Front Clamp ......................................................... .................................... 1
95 .............708315-95 ................Pin ........................................................................ .................................... 1
96 .............708315-96 ................Leaf Spring........................................................... .................................... 1
97 .............TS-1532032 .............Pan Head Screw .................................................. M4x10 ......................... 1
98 .............708315-98 ................Cursor .................................................................. .................................... 1
99 .............708315-99 ................Support................................................................. ....................................2
34
Page 35

Right Extension Assembly
Index No. Part No. Description Size Qty
.................708315-REA ............Right Extension Assembly (Complete) ................ ......................................
39 .............TS-1550021 .............Flat Washer.......................................................... M4............................... 2
40 .............TS-1551021 .............Lock Washer ........................................................M4............................... 2
59 .............708315-158 ..............Flanged Hex Nut .................................................. M6............................... 4
97 .............TS-1532032 .............Pan Head Screw .................................................. M4x10 ......................... 2
100 ...........708315-100..............Rail End Cap ........................................................ .................................... 1
101 ...........TS-1503071 .............Socket Head Cap Screw...................................... M6x30 ......................... 2
102 ...........708315-102..............Front Rail.............................................................. .................................... 1
103 ...........708315-103..............Spacer.................................................................. .................................... 2
104 ...........708315-104..............Extension Table ................................................... ....................................1
105 ...........708315-105..............Extension Rod...................................................... .................................... 2
106 ...........708315-106..............Guide Rail ............................................................ .................................... 1
107 ...........708315-107..............Scale .................................................................... .................................... 1
35
Page 36

Left Extension Assembly
Index No. Part No. Description Size Qty
.................708315-LEA .............Left Extension Assembly (Complete)................... ......................................
39 .............TS-1550021 .............Flat Washer.......................................................... M4............................... 2
40 .............TS-1551021 .............Lock Washer ........................................................M4............................... 2
59 .............708315-158 ..............Flanged Hex Nut .................................................. M6............................... 4
97 .............TS-1532032 .............Pan Head Screw .................................................. M4x10 ......................... 2
100 ...........708315-100..............Rail End Cap ........................................................ .................................... 1
101 ...........TS-1503071 .............Socket Head Cap Screw...................................... M6x30 ......................... 2
102 ...........708315-102..............Front Rail.............................................................. .................................... 1
103 ...........708315-103..............Spacer.................................................................. .................................... 2
104 ...........708315-104..............Extension Table ................................................... ....................................1
105 ...........708315-105..............Extension Rod...................................................... .................................... 2
106 ...........708315-106..............Guide Rail ............................................................ .................................... 1
108 ...........708315-108..............Scale .................................................................... .................................... 1
109 ...........708315-109..............Scale .................................................................... .................................... 1
36
Page 37

Main Saw – Parts
Index No. Part No. Description Size Qty
11 .............TS-1540041 .............Hex Nut ................................................................M6............................... 1
24 .............TS-1551041 .............Lock Washer ........................................................M6............................... 4
25 .............TS-1550041 .............Flat Washer.......................................................... M6............................. 34
59 .............TS-1541021 .............Nylon Insert Lock Nut...........................................M6 ............................. 16
60 .............TS-1482041 .............Hex Cap Screw .................................................... M6x20 ......................... 8
101 ...........TS-1503071 .............Socket Head Cap Screw...................................... M6x30 ......................... 4
103 ...........708315-103..............Spacer.................................................................. .................................... 4
110 ...........TS-1482021 .............Hex Cap Screw .................................................... M6x12 ....................... 16
117 ...........TS-1540061 .............Hex Nut ................................................................M8............................... 2
118 ...........708315-118..............Extension Bracket ................................................ .................................... 6
119 ...........708315-119..............Main Table ........................................................... .................................... 1
120 ...........TS-1533032 .............Pan Head Screw .................................................. M5x10 ......................... 2
121 ...........708315-121..............Table Insert .......................................................... .................................... 1
122 ...........708315-122..............Special Table Screw ............................................ ....................................4
123 ...........TS-1504041 .............Socket Head Cap Screw...................................... M8x20 ......................... 1
124 ...........TS-1504121 .............Socket Head Cap Screw...................................... M8x60 ......................... 1
125 ...........708315-125..............Front Rail.............................................................. .................................... 1
126 ...........708315-126..............Rail Cap ............................................................... .................................... 2
127 ...........708315-127..............Brass Screw (Grounding)..................................... M5x8 ........................... 1
128 ...........708315-128..............External Tooth Lock Washer................................ M5............................... 1
129 ...........708315-129..............Leg ....................................................................... .................................... 4
130 ...........708315-130..............Rear Panel ........................................................... .................................... 1
131 ...........708315-131..............Self-Tapping Screw.............................................. M4x14......................... 7
132 ...........708315-132..............Strain Relief.......................................................... .................................... 1
133 ...........708315-133..............Lock Knob ............................................................ .................................... 6
134 ...........708315-134..............Right Side Panel .................................................. ....................................1
135 ...........708315-135..............Lock Knob ............................................................ .................................... 1
136 ...........708315-136..............Threaded Stud ..................................................... ....................................4
137 ...........708315-137..............Grommet .............................................................. .................................... 1
138 ...........708315-138..............Left Side Panel..................................................... .................................... 1
139 ...........708315-139..............Arbor Nut Wrench ................................................ .................................... 1
140 ...........708315-140..............Open End Wrench ............................................... .................................... 1
141 ...........708818 .....................Push Stick ............................................................ .................................... 1
142 ...........TS-2286202 .............Pan Head Screw .................................................. M6x20 ....................... 16
143 ...........708315-143..............Front Panel........................................................... .................................... 1
144 ...........708315-144..............Front Plate............................................................ .................................... 1
145 ...........708315-145..............Bevel Rack ........................................................... .................................... 1
146 ...........TS-2284081 .............Flat Head Screw .................................................. M4x8 ........................... 9
147 ...........708315-147..............Lock Knob ............................................................ .................................... 1
148 ...........708315-148..............Spring................................................................... .................................... 1
149 ...........708315-149..............Hand Wheel ......................................................... ....................................1
150 ...........708315-150..............Handle.................................................................. .................................... 1
151 ...........708315-151..............Circuit Breaker (Overload) Switch ....................... .................................... 1
152 ...........708315-152..............Wire...................................................................... .................................... 1
153 ...........708315-153..............On/Off Switch ....................................................... .................................... 1
154 ...........708315-154..............Rubber Gasket..................................................... .................................... 1
155 ...........708315-155..............Switch Box ........................................................... .................................... 1
156 ...........708315-156..............Power Cord .......................................................... .................................... 1
157 ...........708315-157..............Rubber Foot ......................................................... .................................... 4
37
Page 38
Main Saw – Assembly
38
Page 39

Stand Assembly
Index No. Part No. Description Size Qty
.................708315-SA ...............Stand Assembly (Complete) ................................ ......................................
11 .............708315-158 ..............Flanged Hex Nut .................................................. M6............................. 12
110 ...........TS-1482021 .............Hex Cap Screw .................................................... M6x12 ....................... 12
111 ...........708315-111..............Leg ....................................................................... .................................... 4
112 ...........708315-112..............Shelf ..................................................................... .................................... 1
Steel Wing Assembly
Index No. Part No. Description Size Qty
.................708315-SSEWA.......Stamped Steel Extension Wing Assembly (Complete)...............................
113 ...........708315-113..............Stamped Steel Extension Wing ........................... ....................................1
114 ...........TS-1490041 .............Hex Cap Screw .................................................... M8x25 ......................... 2
115 ...........TS-2361081 .............Lock Washer ........................................................M8............................... 2
116 ...........TS-1550061 .............Flat Washer.......................................................... M8............................... 2
117 ...........TS-1540061 .............Hex Nut ................................................................M8............................... 2
Accessories
Index No. Part No. Description Size Qty
159 ...........708315-159..............Dust Shroud)
39
Page 40

WMH Tool Group
2420 Vantage Drive
Elgin, Illinois 60123
Phone: 800-274-6848
www.wmhtoolgroup.com
40
Page 41

This Manual is Bookmarked
This Manual is Bookmarked
Instrucciones de operación y Manual de repuestos
Sierra de mesa de 10 pulgadas
Número de inventario: 708315BTA, -BTB, -BTC, -LSA, -LSB
708315BTA Sierra de mesa
WMH TOOL GROUP
2420 Vantage Drive
Elgin, Illinois 60123 Número de parte M-708315
Ph.: 800-274-6848 Revisión D 08/05
www.wmhtoolgroup.com Copyright © WMH Tool Group
41
ENGLISH – PAGE 1
Page 42

Este manual ha sido preparado para los propietarios y operadores de la Sierra de mesa 708315. Su
propósito, además de conocer la operación de la máquina, es promover la seguridad mediante el uso de
procedimientos de operación y mantenimiento que sean correctos. Lea todas las instrucciones de
seguridad y mantenimiento antes de operar o efectuar el servicio de mantenimiento de esta máquina.
Lea este manual detenidamente y siga todas las instrucciones con cuidado para lograr el máximo de
rendimiento y eficacia de la Sierra de mesa JET.
Garantía
WMH Tool Group garantiza todos sus productos. En caso de que necesite mantenimiento o reparaciones
para alguna de nuestras herramientas, alguno de nuestros talleres autorizados para efectuar
reparaciones en Estados Unidos puede ofrecerle un servicio rápido.
En la mayoría de los casos, alguno de los talleres de reparaciones de WMH Tool Group puede autorizar
la reparación bajo garantía, ayudarle a obtener partes o hacer el mantenimiento de rutina y reparaciones
mayores de las herramientas JET, Wilton o Powermatic.
Para obtener el nombre de un Taller de Reparaciones Autorizado (Authorized Repair Station) en su zona,
sírvase llamar al 1-800-274-6848 o visítenos en www.wmhtoolgroup.com.
Más información
WMH Tool Group incorpora constantemente nuevos productos a su línea. Consulte a uno de los
distribuidores locales de WMH Tool Group o visítenos en www.wmhtoolgroup.com para obtener
información actualizada sobre nuestros productos.
Garantía de WMH Tool Group
WMH Tool Group (incluso las marcas JET, Wilton y Powermatic) se esmeran todo lo posible para
garantizar que sus productos cumplan con el más alto grado de calidad y durabilidad, y garantiza al
consumidor/comprador original que cada uno de sus productos está libre de todo defecto de material y
mano de obra de la siguiente manera: GARANTÍA LIMITADA DE 1 AÑO PARA TODOS LOS
PRODUCTOS SALVO QUE SE ESPECIFIQUE LO CONTRARIO. Esta Garantía no corresponde a
aquellos defectos que sean consecuencia directa o indirecta del mal uso, abuso, negligencia o de
accidentes, desgaste normal, reparaciones o alteraciones fuera de nuestras instalaciones o a la falta de
mantenimiento.
WHM TOOL GROUP LIMITA TODAS LAS GARANTÍAS IMPLÍCITAS AL PERÍODO ESPECIFICADO
ANTERIORMENTE, A PARTIR DE LA FECHA DE COMPRA DEL PRODUCTO EN UNA TIENDA
MINORISTA. SALVO QUE SE INDIQUE LO CONTRARIO, TODA GARANTÍA IMPLÍCITA O DE
COMERCIALIZACIÓN Y DE APTITUD QUEDAN EXCLUIDAS. ALGUNOS ESTADOS PROHÍBEN LA
LIMITACIÓN DE LA VIGENCIA DE LAS GARANTÍAS IMPLÍCITAS, POR LO TANTO, ES POSIBLE QUE
LA PRESENTE LIMITACIÓN NO CORRESPONDA A SU CASO. WHM TOOL GROUP NO SERÁ
RESPONSABLE EN CASO ALGUNO POR MUERTE, LESIONES PERSONALES O DAÑOS
MATERIALES, NI POR DAÑOS FORTUITOS, CONTINGENTES, ESPECIALES O DERIVADOS QUE
PUEDAN SURGIR POR EL USO DE NUESTROS PRODUCTOS. ALGUNOS ESTADOS PROHÍBEN LA
EXCLUSIÓN O LIMITACIÓN DE DAÑOS FORTUITOS O DERIVADOS, POR LO TANTO, ES POSIBLE
QUE LA LIMITACIÓN O EXCLUSIÓN ANTERIOR NO CORRESPONDA A SU CASO.
Para utilizar esta garantía, deberá enviar el producto o parte para su inspección, con franqueo
prepagado, a un Taller de reparaciones autorizado que le indiquen nuestras oficinas. La mercadería
deberá estar acompañada por el comprobante de la fecha de compra y una explicación del problema. Si
nuestra inspección detecta algún defecto, se reparará o repondrá el producto, o bien, en el caso de que
no podamos efectuar su reparación o reposición, se le reembolsará el precio de compra del producto, si
usted está dispuesto a aceptarlo. La devolución del producto reparado o nuevo se hará a cuenta de
WMH Tool Group, pero si se determina que no existe defecto alguno, o bien que el defecto se debe a
causas fuera del alcance de la garantía de WMH Tool Group, entonces el usuario deberá correr con los
gastos de almacenaje y devolución del producto. Esta garantía le otorga derechos legales específicos;
es posible que tenga otros derechos que varían de un estado a otro.
WMH Tool Group vende sus productos únicamente a través de sus distribuidores. WMH Tool Group se
reserva el derecho a cambiar o modificar las partes, acoples y accesorios que estime necesarios, por
cualquier motivo y en cualquier momento, sin previo aviso.
42
Page 43

Índice
Garantía ......................................................................................................................................................42
Advertencia! ................................................................................................................................................44
Prevención de contragolpes........................................................................................................................46
Consejos prácticos para protegerse contra los contragolpes..................................................................... 46
Especificaciones .........................................................................................................................................47
Definiciones y terminología......................................................................................................................... 47
Contenido....................................................................................................................................................48
Contenido de las cajas ............................................................................................................................48
Herramientas necesarias (no incluidas) ..................................................................................................48
Armado........................................................................................................................................................ 50
Para empezar .......................................................................................................................................... 50
Montaje del estante .................................................................................................................................51
Pies de caucho ........................................................................................................................................ 51
Cubierta contra el polvo...........................................................................................................................52
Instalación del resguardo de la hoja y placa abridora.............................................................................53
Alineación del resguardo de la hoja y placa abridora .............................................................................53
Hoja de la sierra ......................................................................................................................................54
Ajuste de la guía para cortar al hilo.........................................................................................................54
Calibrado de la escala de la guía para cortar al hilo ............................................................................... 54
Prolongación de la mesa en acero estampado.......................................................................................55
Prolongación deslizable de la mesa........................................................................................................56
Prolongación de la escala izquierda........................................................................................................ 57
Prolongación de la escala derecha .........................................................................................................57
Soporte izquierdo para la mesa, opcional...............................................................................................58
Rueda de mano....................................................................................................................................... 58
Parada positiva de 90 grados.................................................................................................................. 59
Calibrado de la escala.............................................................................................................................59
Ajuste de la hoja paralela a las ranuras del calibre de ingletes ..............................................................60
Cambio de la Hoja................................................................................................................................... 61
Reemplazo/Ajuste de la Correa de Accionamiento................................................................................. 61
Conexiones Eléctricas................................................................................................................................. 63
Controles de Operación ..............................................................................................................................63
Parada positiva de 45 grados.................................................................................................................. 59
Operación del calibre de ingletes ............................................................................................................ 62
Operaciones................................................................................................................................................64
Sierras de mesa...................................................................................................................................64
Contragolpes........................................................................................................................................64
Cortes al hilo ........................................................................................................................................65
Cortes transversales ............................................................................................................................ 66
Operaciones de bisel e inglete ............................................................................................................67
Recolección del polvo.......................................................................................................................... 68
Dispositivos de seguridad ...........................................................................................................................68
Tabla escalonada ....................................................................................................................................68
Pieza de madera de empuje ...................................................................................................................68
Pieza de relleno.......................................................................................................................................69
Mantenimiento.............................................................................................................................................69
Limpieza ..................................................................................................................................................69
Lubricación .............................................................................................................................................. 69
Varios.......................................................................................................................................................69
Identificación y solución de problemas .......................................................................................................70
Partes..........................................................................................................................................................71
Las especificaciones que aparecen en este manual se ofrecen como información general y no son
vinculantes. WMH Tool Group se reserva el derecho a cambiar o modificar las partes, acoples y
accesorios que estime necesarios, por cualquier motivo y en cualquier momento, sin previo aviso.
43
Page 44

Advertencia!
1. Lea y entienda bien todo el manual del propietario antes de comenzar con el armado o de operar la
sierra.
2. Lea cuidadosamente las advertencias adheridas a la máquina y que figuran en este manual. El
incumplimiento de estas advertencias puede causar lesiones graves.
3. Reemplace las etiquetas de advertencia si se oscurecen o si se desprenden.
4. Esta sierra de mesa está diseñada para ser usada por personal capacitado y con experiencia. No
use este equipo si no está familiarizado con la operación correcta y segura de una sierra de mesa o
hasta haber recibido la capacitación y los conocimientos necesarios.
5. No use la sierra de mesa para ningún otro fin que no sea el previsto. En caso de usar con otros fines,
WMH Tool Group no asume responsabilidad alguno por toda garantía real o implícita y se mantiene
indemne de cualquier lesión que pueda producirse por dicho uso.
6. Use siempre gafas de seguridad o careta de protección aprobadas cuando use la sierra de mesa.
Las gafas comunes sólo tienen lentes resistentes a los impactos; no son gafas de seguridad.
7. Antes de operar la sierra de mesa, quítese la corbata, los anillos, relojes y cualquier otro tipo de
alhaja. Arremánguese la camisa hasta arriba de los codos. Quítese toda ropa suelta y sujete el
cabello largo. Se recomienda el uso de calzado con suela antideslizante y tiras de material
antideslizante para el piso. No use guantes.
8. Siempre use el resguardo de la hoja en todas las operaciones de “aserrado total”. Una operación de
aserrado total consiste en pasar la hoja completamente a través de la pieza de trabajo para cortarla.
9. Los contragolpes se producen cuando la pieza de trabajo retrocede hacia el operador a alta
velocidad. ¡Si no comprende claramente lo que significa un contragolpe y cómo se produce, NO
opere la sierra de mesa!
10. Protéjase los oídos con tapones o tapaorejas si los períodos de operación son prolongados.
11. Algunos trabajos de construcción realizados con herramientas eléctricas, por ejemplo: lijar, aserrar,
afilar, esmerilar y taladrar, entre otros, producen polvo que contiene sustancias químicas. Se ha
demostrado que estas sustancias químicas causan cáncer, defectos de nacimiento y otros
problemas congénitos. A continuación incluimos algunos ejemplos de estas sustancias:
• Plomo, de las pinturas con base de plomo.
• Sílice cristalina, de ladrillos, cemento y otros productos de albañilería.
• Arsénico y cromo de maderas tratadas con productos químicos.
12. Su riesgo a la exposición varía según la frecuencia con que realice este tipo de trabajo. Para reducir
su exposición a estos productos químicos, trabaje en un área bien ventilada y use un equipo de
seguridad aprobado, como máscaras protectoras contra el polvo especialmente diseñadas para filtrar
partículas microscópicas
13. No opere esta máquina cuando esté cansado o bajo la influencia de drogas, alcohol o cualquier
medicamento.
14. Asegúrese de que el interruptor esté apagado (posición OFF) antes de conectar la máquina a la
fuente de alimentación.
15. Asegúrese de que la máquina esté correctamente conectada a tierra.
16. Haga todos los ajustes o mantenimiento con la máquina desenchufada de la fuente de alimentación.
17. Retire todos las llaves y herramientas de ajuste. Acostúmbrese a comprobar que todas las llaves o
herramientas de ajuste se hayan retirado de la máquina antes de encenderla.
18. Mantenga los resguardos de seguridad en su lugar cuando use la máquina. Si los retira para las
tareas de mantenimiento, tome las debidas precauciones y reponga los resguardos inmediatamente.
44
Page 45

Advertencia!
19. Asegúrese de que la sierra de mesa está bien afianzada al piso o al banco antes de usarla.
20. Inspeccione las partes dañadas. Antes de continuar con el uso de la máquina, se deberá
inspeccionar el resguardo o cualquier otra parte dañada para determinar que funcionará
correctamente y realizará las funciones en la forma prevista. Verifique el alineamiento de las partes
movibles, el atascamiento de partes movibles, rotura de piezas, montaje o cualquier otra condición
que pueda afectar la operación. Los resguardos o cualquier otra pieza dañada se deben reparar o
cambiar.
21. Proporcione un espacio adecuado alrededor del área de trabajo con iluminación alta que sea
antirreflejo.
22. Mantenga limpio el piso alrededor de la máquina, sin desechos de material, aceite o grasa.
23. Mantenga a los visitantes alejados del área de trabajo. Mantenga a los niños alejados.
24. Prepare el taller para que quede a prueba de niños: use candados, interruptores maestros o quite las
llaves de los dispositivos de arranque.
25. Concéntrese en su trabajo. No se distraiga. Al distraerse y alejar la vista, conversar o "payasear”,
cometerá un acto de descuido que puede causar lesiones graves.
26. Mantenga el equilibrio en todo momento para no caer sobre la hoja u otras partes movibles. No se
estire demasiado ni use demasiada fuerza para realizar cualquier operación con la máquina.
27. Utilice la herramienta adecuada con la velocidad correcta y con una velocidad de alimentación
apropiada. No fuerce la herramienta ni el accesorio utilizándolos en trabajos para los cuales no
fueron diseñados. La herramienta adecuada funcionará mejor y será más segura.
28. Utilice los accesorios recomendados; los accesorios incorrectos pueden ser peligrosos.
29. Mantenga las herramientas con cuidado. Mantenga las hojas de la sierra afiladas y limpias para
lograr un mejor funcionamiento sin correr peligros. Siga las instrucciones de lubricación y cambio de
accesorios.
30. Apague la máquina antes de limpiarla. Use un cepillo o aire comprimido para quitar las virutas o
desechos: no use las manos.
31. Nunca se pare sobre la máquina. Si la máquina se vuelca puede causar lesiones graves.
32. Nunca deje de vigilar una máquina que esté funcionando. Apáguela y no deje de vigilar la máquina
hasta que se detenga por completo.
33. Retire del área todos los artículos sueltos y piezas de trabajo innecesarios antes de arrancar la
máquina.
Familiarícese con los siguientes avisos de seguridad utilizados en este manual:
Este aviso significa que el hecho de no prestar atención a estas precauciones
puede causar lesiones leves y posiblemente daño a la máquina.
Este aviso significa que el hecho de no prestar atención a estas precauciones
puede causar lesiones graves, hasta la muerte.
45
Page 46

Según las estadísticas, los accidentes más comunes entre los operadores de
sierras de mesa están relacionados con el contragolpe: la expulsión a alta velocidad del material
de la mesa que puede golpear al operador. Un contragolpe también puede empujar las manos del
operador hacia la hoja.
Prevención de contragolpes
Consejos útiles para evitar las causas más
comunes del contragolpe:
• Asegúrese de que la placa abridora esté
siempre alineada con la hoja. Si la placa
abridora no está alineada, la pieza de
trabajo se puede atascar o parar el flujo del
corte y causar un contragolpe.
• Use la placa abridora en todos los cortes. La
placa abridora mantiene la entalla de la
pieza de trabajo, lo que reducirá la
posibilidad de un contragolpe.
• Nunca trate de cortar a pulso. Se debe
alimentar la pieza de trabajo en forma
totalmente paralela a la hoja, de lo contrario
puede causar un contragolpe. Use siempre
la guía para cortar al hilo, o transversalmente a la pieza de trabajo.
• Asegúrese de que la guía para cortar al hilo
esté paralela a la hoja. De no ser así, habrá
muchas posibilidades de que se produzca
un contragolpe. Inspeccione bien todo y
ajuste la guía para cortar al hilo.
• Alimente los cortes hasta terminarlos. Cada
vez que deja de alimentar el material de
trabajo en la mitad de un corte, aumenta la
posibilidad de atascamiento, lo que puede
causar un contragolpe.
Consejos prácticos para
protegerse contra los
contragolpes
Los contragolpes pueden producirse, aun
cuando se tomen precauciones para evitarlos. A
continuación figuran algunos consejos prácticos
que se deben seguir siempre para protegerse
en caso de que OCURRA un contragolpe.
• Párese a un lado de la hoja cuando efectúe
un corte. Una pieza de trabajo expulsada
sale directamente en frente de la hoja.
• Use gafas de seguridad o una careta de
protección. La cara y las manos son las
partes más vulnerables del cuerpo.
• Nunca coloque las manos detrás de la
mesa. En caso de un contragolpe, la mano
del operador entrará en contacto con la
hoja.
• Use una pieza de madera de empuje para
mantener las manos lo más alejadas posible
de la hoja en movimiento. En caso de un
contragolpe, la pieza de madera de empuje
recibirá todo el daño que hubiera recibido su
mano.
Lea y entienda bien todo el material que aparece en este manual antes de
comenzar con el armado y la operación de la sierra. ¡El incumplimiento de esta advertencia puede
causar lesiones graves!
46
Page 47

Especificaciones
Números de inventario........................................................................ 708315BTA, -BTB, -BTC, -LSA, -LSB
Diámetro de la hoja....................................................................................................................................10”
Diámetro de la mandril..............................................................................................................................5/8”
Inclinación de la hoja......................................................................................................... izquierda, 90 – 45º
Profundidad máxima de corte a 90º............................................................................................................. 3”
Profundidad máxima de corte a 45°.......................................................................................................2-1/2”
Capacidad del corte de mortaja ................................................................................................................1/2"
Altura de la mesa (con soporte).................................................................................................................35”
Dimensiones de la mesa principal .....................................................................28” ancho x 18” profundidad
Tamaño de la prolongación (aluminio)...........................................................5 1/2” ancho x 18” profundidad
Tamaño de la prolongación (chapa de metal) .....................................................8” ancho x 18” profundidad
Velocidad de la hoja (sin carga)..................................................................................................... 5000 RPM
Motor ...................................................................................................................................... 120 VCA, 60Hz
Peso bruto (BTA) .............................................................................................................................. 57 libras
Peso neto (BTA)................................................................................................................................ 50 libras
Definiciones y terminología
Mandril: Eje de metal que conecta el mecan-
ismo de arrastre con la hoja.
Corte en bisel: Inclinación del eje de la sierra y
de la hoja de 0° a 45° para realizar un operación
de corte en ángulo.
Protección de la hoja: Mecanismo montado
sobre la hoja de la sierra para evitar el contacto
accidental con el borde de corte.
Corte transversal: Corte donde se usa el
calibre de ingletes para cortar transversalmente
a la veta de la pieza de trabajo.
Hoja para cortar mortajas: Hojas que se
utilizan para cortar mortajas y rebajos.
Corte de mortaja: Ranura de fondo plano en la
cara de una pieza de trabajo realizada con una
hoja para cortar mortajas.
Tabla escalonada: Dispositivo que se utiliza
para mantener una tabla contra la guía para
cortar al hilo o la mesa que permite colocar las
manos alejadas de la hoja.
Entalla: El corte o la separación que hace la
hoja.
Contragolpe: Cuando se levanta la pieza de
trabajo y retrocede hacia el operador, a causa
de un atascamiento en la hoja o entre la hoja y
la guía para cortar al hilo (u otro objeto fijo).
Para evitar las lesiones a causa de contragolpes
o para reducirlas a un mínimo, consulte la
sección Instrucciones de operación.
Calibre de ingletes: Un componente que
controla el movimiento de la pieza de trabajo
cuando se realiza un corte transversal angulado.
Corte parcial: Una operación de aserrado que
requiere quitar el resguardo de la placa abridora
de la hoja para obtener un corte que no
sobresalga de la parte superior de la pieza de
trabajo (incluye cortes con hojas de mortajas y
rebajo).
El resguardo de la hoja y la placa abridora
deben volver a instalarse después de una corte
parcial para evitar el contacto accidental con la
hoja durante la operación de la máquina.
Paralelo: Posición de la guía para cortar al hilo
en forma equidistante de la cara de la hoja en
todos sus puntos.
Perpendicular: La intersección o posición de
los planos horizontal y vertical en un ángulo de
90° (ángulo recto) como la posición de la sierra
(vertical) con respecto a la superficie de la mesa
(horizontal).
Pieza de madera de empuje: Un instrumento
que se utiliza para empujar sin peligro la pieza
de trabajo durante la operación de corte.
Rebajo: Una operación de corte que crea un
canal en forma de L a lo largo del borde la tabla.
Corte al hilo: Un corte que se hace en el
sentido de la veta de la pieza de trabajo.
Placa abridora: Placa de metal acoplada al
resguardo de la hoja que mantiene la entalla
abierta en la pieza de trabajo mientras se realiza
una operación de corte.
Entalla estándar: Separación de 1/8 pulgada
hecha con una hoja estándar.
Escuadra: Una herramienta que se utiliza para
controlar que la superficie esté plana o paralela.
Aserrado total: Una operación de aserrado en
donde se corta todo el espesor de la pieza de
trabajo. Por lo general, la altura correcta de la
hoja permite que la parte superior de la hoja se
extienda por sobre la pieza de madera.
47
Page 48

Contenido
Contenido de las cajas
Contenido de las cajas
El contenido está determinado por el modelo de
su compra e indicado en las tres letras de sufijo
del número de inventario 708315.
Saque todas las piezas de la caja. Mantenga la
mesa de la sierra con las patas hacia arriba. No
deseche el material de embalaje hasta que la
sierra esté totalmente armada y funcionando
satisfactoriamente.
Importante: El material de embalaje colocado
adentro de la sierra proporciona soporte al
motor durante el envío y se debe quitar.
Compare el contenido de la caja contra la Tabla
de contenido (página siguiente) de su modelo
en particular. El N.º índice en la tabla,
corresponde a los artículos que se muestran
arriba y es la clave que se utiliza para identificar
cada parte.
Herramientas necesarias (no
incluidas)
Llave hexagonal de 5 mm (1)
Llave hexagonal de 6mm (1)
Llave hexagonal de 14mm (2)
Llaves de 10 mm (2 ) o Llaves de 10mm y
manguito de 10 mm (1)
Destornillador de punta en cruz (1)
48
Contenido de la bolsa de tornillería
(tamaño real)
Herramientas para quitar la hoja
Page 49

Contenido
Núm. de
Índice
-- Sierra de mesa 1 1 1 1 1
A 708315-LEA
B 708315-105 Varilla de prolongación 2 2 4
C 708315-REA
D
E Prolongación de la escala derecha 1 1 1
F 708315-113
G 708315-RFA Guía para cortar al hilo 1 1 1 1 1
H 708315-MGA Calibre de ingletes MGA 1 1 1 1 1
I 708818 Pieza de madera de empuje 1 1 1 1 1
J 708315-BGA Ensamble del resguardo de la hoja 1 1 1 1 1
K 708315-111 Pata 4 4
L 708315-RSA Ensamble del soporte trasero 1 1 1 1
M 708315-150 Manija 1 1 1 1 1
N 708315-121A
NN 708315-159 Cubierta contra el polvo 1
O 708315-112 Estante 1 1
P TS-1482021
S 708315-158 Tuerca de brida hexagonal M6 16 16
T TS-1490041
U TS-1540061 Tuerca hexagonal M8 2
V TS-2361081 Arandela de bloqueo M8 2
W TS-1550061 Arandela plana M8 2
X TS-1551021 Arandela de bloqueo M4 2 2 4
Y TS-1532032 Tornillo de cabeza plana M4x10 2 2 4
Z TS-1550021 Arandela plana M4 2 2 4
ZZ 708315-134 Perilla de fijación 6 4 6 6 6
708315-140 Llave del mandril 1 1 1 1 1
708315-139 Llave para tuerca del mandril 1 1 1 1 1
Núm. de
parte
Descripción
Ensamble de la prolongación
izquierda de la mesa
Ensamble de la prolongación
derecha de la mesa
Prolongación de la escala
izquierda
Prolongación de la mesa en acero
estampado
Accesorio de inserción de la hoja
para mortajas
Tornillo de cabeza hexagonal
M6x12
Tornillo de cabeza hexagonal
M8x25
Tabla de contenido
Cantidad
BTA BTB BTC LSA LSB
1
1 1 1
1
1
1 1 1 1 1
12 12
2
49
Page 50

Armado
No enchufe la sierra de
mesa a una fuente de alimentación hasta no
haber completado todo el armado. ¡El
incumplimiento de esta advertencia puede
causar lesiones graves!
Para empezar
Cada sección de armado comienza con una lista
de los modelos que corresponden a ese
procedimiento de armado. El punto de inicio para
su modelo en particular, es el siguiente:
Modelos LSA, LSB: empiece con el Armado de las
patas.
Modelos BTA, BTB, BTC: comience con la
Instalación del resguardo de la hoja y placa
abridora que aparece en la página 12.
Armado de las patas
Modelos LSA, LSB
Siga estas instrucciones para el Armado de las
patas si piensa usar la sierra como modelo de piso.
Si piensa usar la sierra para aplicaciones sobre el
banco, pase por alto esta sección y continúe con la
sección Prolongación de la mesa.
Figura 1
Herramientas necesarias: llave y manguito de
10 mm
Consulte las Figuras 1 y 2:
Tornillería necesaria para cada pata: dos tornillos
de cabeza hexagonal M6x12 (C) y tres tuercas de
brida hexagonales M6 (F).
1. Con la sierra en el piso, patas hacia arriba,
retire los cuatro pies de caucho (A) de cada
una de las esquinas de la base.
2. Tome una pata (b) y colóquela de manera que
la pestaña exterior (G), con el agujero de
montaje, quede hacia abajo.
3. Monte una pata en una esquina de la base de
la sierra, de manera que la pestaña exterior
(G) se alinee con el tornillo (H) y los dos
agujeros de la pestaña interior (J) descansen
sobre la las pestañas de la base (K) con los
agujeros de montaje alineados.
Nota: Se debe montar la pata que tiene una
etiqueta que dice WARNING (advertencia) en la
esquina de la base de la sierra que tiene la otra la
etiqueta de Advertencia.
4. Introduzca los dos tornillos de cabeza
hexagonal (C) en los agujeros de montaje de la
pestaña de la pata (J) y pestaña de la base
(K). Asegure con tuercas de brida hexagonales
(F1). Apriete con la mano únicamente.
Figura 2
5. Asegure la pestaña exterior de la pata (G) al
tornillo (H) en la base con una tuerca de brida
hexagonal (F
únicamente.
Monte otras dos patas de la misma manera
descrita en los pasos 1 a 5. No monte la última
pata hasta no haber instalado el estante como se
describe en la próxima sección.
). Apriete con la mano
2
50
Page 51

Montaje del estante
Modelos LSA, LSB
Nota: El estante es más fácil de instalar después
de haber instalado tres patas. La cuarta parte se
deberá colocar después de haber completado esta
sección.
Tornillería necesaria para armar las cuatro patas:
cuatro tornillos de cabeza hexagonal M6x12 (F) y
cuatro tuercas de brida hexagonales M6 (J).
Consulte la Figura 3:
1. Cuando todavía tenga la sierra con las patas
hacia arriba, coloque el estante (A) entre las
tres patas (B) y por debajo de las pestañas de
montaje (D) de las patas. Los costados del
estante (D) deben quedar mirando hacia abajo.
2. Lleve el estante hacia arriba, colocando las
pestañas del estante (E) contra la parte inferior
de las pestañas de montaje de las patas (C) y
procure que los agujeros de montaje queden
alineados.
3. Desde la parte de abajo del estante, introduzca
un tornillo de cabeza hexagonal (F) en los
agujeros de montaje de las pestañas del
estante y de la pata. Asegure la porción
roscada del tornillo que sobresale del lado
superior de la pestaña de montaje de la pata,
con una tuerca de brida hexagonal (J), y
apriete únicamente con la mano.
Después de que el estante esté bien colocado en
las tres patas, arme la última pata (como se
describe en la sección anterior) y termine de
colocar la última pestaña del estante en la pata.
Pies de caucho
Modelos LSA, LSB
Consulte la Figura 4:
Figura 3
Mientras la sierra esté todavía con las patas hacia
arriba:
1. Coloque el pie de caucho (B) en la pata (A),
deslizándolo hacia adelante (1) al mismo
tiempo que permite que la pestaña trasera (C)
de la pata se desliza a través de la abertura
(D) en el talón del pie de caucho.
2. Empuje el pie hacia abajo (2) hasta que encaje
a presión en la pata.
3. Repita estos pasos para el resto de las patas.
Ahora puede dar vuelta la sierra. Coloque en una
superficie nivelada y apriete todos los tornillos del
conjunto de las patas y estante.
51
Figura 4
Page 52

Cubierta contra el polvo
Modelo LSB únicamente
Nota: Instale la cubierta contra el polvo
únicamente si se utiliza un sistema de recolección
o aspiración de polvo por separado.
Consulte la figura 5:
1. Coloque la cubierta contra el polvo (A) dentro
de las patas con el puerto (B) hacia la parte
trasera de la sierra y mirando hacia abajo,
según se ilustra.
2. Lleve la parte delantera de la cubierta hacia
arriba de manera que las pestañas (C) se
enganchen en el reborde (D) de la base, para
fijarlo en su lugar. Las aberturas de las
esquinas de la cubierta (E) debe envolver las
pestañas (F) de las patas.
3. Presione la parte trasera de la cubierta hasta
que las pestañas de atrás encajen contra el
reborde en la parte trasera de la base.
Figure 5
52
Page 53

Instalación del resguardo de la hoja y
placa abridora
Todos modelos
Consulte la Figura 6:
Si la sierra de mesa vino con un soporte trasero
(C), la instalación y alineación del resguardo/placa
abridora de la hoja será más fácil si se afloja y
desliza el soporte trasero hacia afuera.
1. Afloje la tuerca hexagonal (C) del montante del
soporte del abridor (E) para que quede
suficiente luz para el ensamble del resguardo
de la hoja y placa abridora (paso siguiente).
2. Tome el ensamble del resguardo de la hoja y
placa abridora y deslice la pestaña de la placa
abridora (B y F) sobre el tornillo del montante
del soporte de la placa abridora (E) entre la
arandela plana (D) y el montante (E).
3. Apriete la tuerca hexagonal (C) lo suficiente
como para que sostenga el ensamble del
resguardo de la hoja y la placa abridora en su
lugar.
Necesitará algunos ajustes tal como se describe en
la sección Ajuste (consulte Alineación del
resguardo de la hoja y placa abridora).
Figura 6
Alineación del resguardo de la hoja y
placa abridora
Todos modelos
Consulte la Figuras 7 y 8:
1. Suba el resguardo de la hoja (B) de la mesa.
2. Coloque la regla (E) contra el lado derecho de
la hoja (F) como se muestra en la Figura. Para
colocar la regla en su lugar deberá levantar los
trinquetes anticontragolpes (D) temporalmente.
Nota: La regla debe descansar contra el
cuerpo de la hoja y no contra los dientes.
3. Con una llave de 10 mm, afloje los dos tornillos
de cabeza hexagonal (H) asegurando el
soporte de la placa abridora (G) y ajuste la
placa abridora (C) hacia los costados hasta
que quede alineada con la hoja (F).
4. Apriete los tornillos de cabeza hexagonal (H).
Asegúrese de que la placa abridora (C) esté
nivelada con la mesa y a aproximadamente
1/8 pulgada sobre la mesa. Un espacio de
1/8 pulgada permite inclinar el ensamble de
resguardo de la hoja a un ángulo de 45º sin que
entre en contacto con la mesa.
En caso de que la placa abridora necesite ajuste:
5. Use dos llaves de 10 mm para aflojar el
ensamble de la tuerca y tornillo (J), ajuste el
abridor (C) a 1/8 pulgada sobre la mesa.
Figura 7
Figura 8
Apriete la tornillería.
Use una escuadra para verificar que la placa
abridora esté perpendicular a la superficie de la
mesa y ajuste tal como sea necesario.
53
Page 54

Hoja de la sierra
Todos modelos
La sierra de mesa 708315 viene con una hoja
instalada en fábrica. Para reemplazar la hoja,
consulte Reemplazo de la hoja en la sección
Ajustes.
Ajuste de la guía para cortar al hilo
Todos modelos
Consulte la Figura 9:
1. Suba la manija (A) de la guía para cortar al
hilo, tal como se muestra.
2. Coloque la guía para cortar al hilo (B) sobre la
mesa (C) como se muestra, sujetando el
extremo delantero al mismo tiempo que
engancha la abrazadera (D) en la parte de
atrás, y luego baje el extremo delantero (E)
sobre el riel (F).
3. Baje la manija (A) para que la guía quede
sujeta a la mesa.
Calibrado de la escala de la guía para
cortar al hilo
Todos modelos
1. Acople la guía para cortar al hilo a la mesa
(como se describe en la sección anterior) a la
derecha de la hoja, pero no baje la manija para
sujetar la guía a la mesa.
Figura 9
2. Deslice la guía contra la hoja.
Deberá levantar el resguardo de la hoja y el
trinquete anticontragolpes para dejar lugar
para la guía.
3. Con la guía apretada contra la hoja, baje la
manija para sujetar la guía en su lugar.
Consulte la Figura 10:
La línea de referencia del indicador (A) debe
quedar alineada con 0” en el riel (C). Si no quedan
alineadas:
4. Afloje levemente el tornillo (B).
5. Deslice el indicador hasta que la línea de
referencia quede alineada con 0” en el riel (C).
6. Apriete el tornillo.
Figura 10
54
Page 55

Prolongación de la mesa en acero
estampado
Modelo BTB – la prolongación de la mesa debe
asemejarse a (A) en la Figura 11.
La prolongación de la mesa en acero estampado
se puede montar en el lado derecho o izquierdo de
la sierra de mesa. Los pasos a continuación
ilustran el lado derecho.
Instalación
Consulte la Figuras 11 y 12:
1. Coloque la prolongación de la mesa en acero
estampado (A) contra el lado derecho de la
sierra de mesa (B) de manera que los agujeros
queden alineados.
2. Coloque dos arandelas de bloqueo M8 (D) y
arandelas planas (E) en los tornillos de cabeza
hexagonal M8 (C).
3. Introduzca los tornillos en los agujeros de
montaje de la prolongación de la mesa (A) y de
la mesa (B).
4. Asegure con dos tuercas hexagonales M8 (F)
pero deje el ensamble lo suficientemente flojo
para que la prolongación de la mesa se pueda
mover a mano para ajustarla.
Ajustes
5. Coloque una regla sobre la mesa y la
prolongación de la mesa cerca de la parte
delantera como se muestra en la Figura 12.
6. Suba o baje la prolongación hasta que la regla
quede completamente plana sobre la superficie
de la mesa y de la prolongación.
7. Mueva la regla hasta que quede cerca de la
parte trasera (A) de la mesa y la prolongación.
8. Repita el paso 6.
9. Cuando la prolongación de la mesa esté
alineada con la mesa, tanto en el frente como
en la parte trasera, apriete los tornillos (C) y las
tuercas hexagonales (F) con dos llaves de
14 mm.
Reposicionamiento del riel delantero
Después de la instalación de la prolongación de la
mesa en acero estampado, se debe reposicionar el
riel delantero para acomodar la guía sobre la
prolongación de la mesa. Ello se logra de la
siguiente manera:
Figura 13 (F) muestra la posición inicial del riel
delantero.
1. Con una llave hexagonal de 5 mm y una llave
de extremo abierto de 10 mm, retire el tornillo,
el es paciador y la tuerca de bloqueo (ver el
Figura 11
Figura 12
Figura 13
detalle) que aseguran el riel, de los dos
agujeros de montaje izquierdos y del extremo
derecho (A), (B) y (D).
Nota: No retire los tornillos del tercer agujero
de montaje (C).
2. Haga rotar el riel del frente en sentido horario
(G) hasta que el extremo izquierdo se
convierta en el extremo derecho de la
prolongación de la mesa.
3. Coloque nuevamente los tres tornillos,
espaciadores y tuercas de bloqueo para
asegurar el frente del riel.
Los tornillos se introducen desde el frente del riel,
los espaciadores se colocan entre el riel y la mesa
(o la prolongación) y las arandelas de bloqueo se
colocan en el tornillo desde la parte de atrás de la
pestaña de la mesa (o prolongación).
55
Page 56

Prolongación deslizable de la mesa
Prolongación derecha de la mesa utilizada con los
Modelos BTC, LSA y LSB. Prolongación izquierda
de la mesa, utilizada con el Modelo LSB
Armado
Consulte la Figura 14.
Para las sierras que utilizan prolongaciones de la
mesa deslizables, las dos varillas de prolongación
(C) se deben armar antes de montarlas. Las
instrucciones para el ensamble para la
prolongación derecha de la mesa (A), identificada
por no tener una regla en el riel (J) se describe a
continuación. El armado para la prolongación
izquierda de la mesa es el mismo.
1. Con dos llaves de 10 mm, retire la tuerca de
bloqueo (B) de las varillas de prolongación (C
y D).
2. Vuelque la prolongación de la mesa (A) de
manera que el logotipo de JET quede boca
abajo y los agujeros de montaje y pestañas
(F, K) estén visibles.
3. Introduzca las varillas (D) en los agujeros de
montaje de la prolongación de la mesa (F) y la
pestaña (K).
Figura 14
El extremo roscado de la varilla (D) debe
sobresalir por el agujero de la pestaña (K).
4. Coloque las tuercas de brida hexagonales (G)
en los extremos roscados de las varillas de
prolongación (D) y no las apriete demasiado
para que pueda girar las varillas a mano.
5. Haga girar las varillas de prolongación para
que los agujeros roscados, ubicados cerca de
los extremos opuestos a la mesa de
prolongación, estén en línea con la superficie
de la mesa de prolongación.
6. Asegure las varillas de extensión con dos
llaves de 10 mm, colocando una de las llaves
en la tuerca hexagonal y la otra en las
muescas planas de la varilla.
7. Repita los pasos anteriores para la
prolongación izquierda de la mesa en los
modelos que la incluyen.
Montaje del ensamble de la prolongación derecha
de la mesa
Modelos BTC, LSA y LSB – la prolongación
derecha de la mesa debe asemejarse A en la
Figura 15.
Consulte la Figura 15:
1. Seleccione la prolongación derecha de la
mesa (A), identificada por no tener una regla
en el riel (B).
Figura 15
2. Monte la prolongación de la mesa deslizando
las varillas de extensión en los agujeros de
montaje (C) en el lado derecho de la mesa de
la sierra. Quizá deba aflojar las perillas de
fijación (D).
3. Desde abajo de la mesa, enrosque un tornillo
de cabeza plana M4x8 (G) en el agujero cerca
del extremo de la varilla de prolongación
trasera (E
prolongación trasera (F
). Esta es la varilla más cercana a la
3
y F2).
1
4. Apriete las perillas de fijación (D).
56
Page 57

Montaje del ensamble de la prolongación
izquierda de la mesa
Modelo LSB únicamente
La prolongación izquierda de la mesa, identificada
por tener una regla en el riel (B, Figura 16), se usa
únicamente con el modelo LSB. El procedimiento
de ensamble y armado es el mismo que el que se
usa para la prolongación derecha de la mesa
(explicado anteriormente).
Prolongación de la escala izquierda
Modelo LSB únicamente
Consulte la Figura 16:
1. De ser necesario, afloje las perillas de fijación
de la extensión de la mesa y deslice la
prolongación de la mesa (D) a ras de la mesa
de la sierra (E).
2. Tome la prolongación del riel izquierdo (A),
identificada por la escala de 11" a 21", e
introduzca en el riel de guía de la prolongación
izquierda de la mesa (B) deslizándolo hasta el
fondo en el riel de guía de la mesa (C).
3. Mire la parte de abajo y córralo hasta que los
agujeros de la prolongación del riel (A) y del
riel de la mesa (C) estén alineados.
4. Introduzca dos tornillos de cabeza plana
M4x10 (J), arandelas de bloqueo M4 (K) y
arandelas planas M4 (L) para sostener la
prolongación del riel en su lugar, pero
dejándolo lo suficientemente flojo como para
permitir ajustarlo (pasos siguientes).
5. Coloque una regla (F) sobre la prolongación de
la mesa y la mesa de la sierra.
6. Alinee la marca de 11”de la regla (G1) con la
marca de 11” del riel de guía (G2) y mantenga
la regla firmemente en su lugar mientras
realiza el próximo paso.
7. Ajuste la prolongación del riel (A) hasta que la
marca de 18” (H1) esté alineada con la marca
de 18” de la regla (H2). Suelte la regla
mientras se asegura de que la prolongación
del riel no se mueva.
La prolongación izquierda del riel está ahora
calibrada correctamente. Mientras la sostiene
bien en su lugar:
8. Apriete los dos tornillos (K).
Prolongación de la escala derecha
Modelos BTC, LSA y LSB
Los pasos para el armado son iguales a los de la
prolongación izquierda de la mesa. Para alinearla,
use las marcas de calibración de 14” y 21”.
57
Figura 16
Page 58

Soporte izquierdo para la mesa,
opcional
Modelos BTB, BTC y LSA
Consulte la Figura 17:
Los modelos de sierra de mesa BTB, BTC y LSA
no vienen con la prolongación izquierda de la
mesa. No obstante, se puede quitar el ensamble
de soporte trasero (A) y, de ser necesario, usarlo
como soporte izquierdo para la mesa. Para ello:
1. Afloje las dos perillas de fijación debajo de la
parte trasera de la mesa que aseguran el
ensamble del soporte trasero (A).
2. Retire el ensamble del soporte trasero
deslizándolo hacia atrás (B).
3. Vuelque el ensamble de manera que el lado
plano del riel quede hacia arriba (C) y que las
dos muescas (D) estén hacia abajo.
4. Afloje las dos perillas de fijación (E) ubicadas
en el lado izquierdo de la mesa.
5. Instale el ensamble del soporte trasero
insertando las varillas de extensión en los dos
agujeros de montaje en el lado izquierdo de la
mesa. Recuerde que las muescas (D) están en
la parte de abajo.
6. Apriete las perillas de fijación.
Rueda de mano
Todos modelos
Figura 17
Consulte la Figura 18:
1. Introduzca una llave hexagonal de 5 mm (A) en
el extremo de la manija (B) en el tornillo de
cabeza hexagonal.
2. Enrosque en la rueda de mano (E) hasta que
esté casi apretado.
Mientras sostiene la llave hexagonal (A):
3. Apriete la tuerca hexagonal (C) con una llave
de 10 mm (D) contra la rueda de mano (E) de
manera tal que la manija (B) esté segura, pero
que todavía permita rotarla mientras la usa.
58
Figura 18
Page 59

Ajustes
¡Cuando trabaje cerca de
la hoja, siempre desconecte la sierra de la
fuente de alimentación! ¡El incumplimiento de
esta advertencia puede causar lesiones graves!
Parada positiva de 90 grados
Consulte la Figura 19:
1. Haga girar la rueda de mano (A) en sentido
horario y suba la hoja hasta su altura máxima.
2. Afloje la perilla de fijación de inclinación de la
hoja (B) haciéndola girar en sentido contrahorario.
3. Empuje la rueda de mano (A) hacia adentro
para que enganche con el mecanismo de
inclinación de la hoja; luego hágala girar en
sentido horario completamente hasta que la
hoja quede en la posición de 90º con respecto
a la mesa.
4. Continúe sosteniendo la rueda de mano con la
hoja en esta posición. Coloque una escuadra
de combinaciones (C) sobre la mesa y contra
la hoja tal como se muestra.
Si la hoja no está a 90º con respecto a la mesa:
5. Mientras continúa sujetando la rueda de mano,
use una llave hexagonal de 6 mm para girar el
tornillo de ajuste de 90º (Figura 18) hasta que
la hoja quede a 90º con respecto a la mesa.
6. Apriete la perilla de fijación de la inclinación de
la hoja (B).
2. Empuje la rueda de mano (C) hacia adentro
para que enganche con el mecanismo de
inclinación de la hoja; luego hágala girar
completamente hasta que la hoja quede en la
posición de 90º con respecto a la mesa.
Sostenga la rueda de mano y:
3. Bloquee la perilla de fijación de la inclinación
de la hoja (D).
Figura 20
Si la escala no indica exactamente 0º:
4. Afloje el tornillo (B) con un destornillador de
punta en cruz con vástago descentrado.
5. Ajuste manualmente la escala (A) hasta que
señale 0º:
6. Apriete el tornillo (B).
Parada positiva de 45 grados
Consulte la Figura 19:
Figura 19
Calibrado de la escala
La escala junto a la rueda de mano debe calibrarse
después de calibrar la hoja en la posición de
parada positiva de 90º (consulte la sección
anterior) y la escala no indica 0º.
Calibrado de la escala: (consulte la Figura 20):
1. Afloje la perilla de fijación de la inclinación de
la hoja (D) haciéndola girar en sentido
contrahorario.
59
1. Haga girar la rueda de mano (A) en sentido
horario y suba la hoja hasta su altura máxima.
2. Afloje la perilla de fijación de la inclinación de
la hoja (B) haciéndola girar en sentido
contrahorario.
3. Empuje la rueda de mano (A) hacia adentro
para que enganche con el mecanismo de
inclinación de la hoja; luego hágala girar en
sentido contrahorario completamente hasta
que la hoja quede en la posición de 45º con
respecto a la mesa.
4. Continúe sosteniendo la rueda de mano con la
hoja en esta posición. Coloque una escuadra
de combinaciones (E) sobre la mesa y contra
la hoja tal como se muestra.
Si la hoja no está a 45º con respecto a la mesa:
5. Mientras continúa sujetando la rueda de mano,
use una llave hexagonal de 6 mm para girar el
tornillo de ajuste de 45º (Figura 19) hasta que
la hoja quede a 45º con respecto a la mesa.
6. Apriete la perilla de fijación de la inclinación de
la hoja (B).
Page 60

Ajuste de la hoja paralela a las ranuras
del calibre de ingletes
¡Cuando trabaje cerca de
la hoja, siempre desconecte la sierra de la
fuente de alimentación! ¡El incumplimiento de
esta advertencia puede causar lesiones graves!
Se ajustó la hoja en fábrica para que quede
paralela a las ranuras del calibre de ingletes y no
debiera necesitar ningún otro ajuste. No obstante,
si después de inspeccionarla se determina que
necesita ajuste, siga los pasos a continuación:
1. Con la rueda de mano (A, Figura 19), suba la
hoja hasta su altura máxima.
Consulte la Figura 21:
2. Coloque la base de la escuadra de
combinaciones (A) contra el borde de la ranura
de inglete (B). Extienda la regla deslizante (C)
de manera que apenas toque los dientes en el
extremo cercano de la hoja (D). Apriete el
tornillo de bloqueo en la escuadra de
combinaciones para que la regla deslizante
quede fija.
3. Mueva la escuadra al extremo más distante de
la hoja (E).
En caso de que aparezca una separación, o si
la base de la escuadra de combinaciones no
descansa sobre el borde de la ranura de
ingletes, deberá ajustarse de la siguiente
manera:
Las hojas de las sierras
son filosas. ¡Tenga muchísimo cuidado cuando
trabaje con ellas! ¡El incumplimiento de esta
advertencia puede causar lesiones graves!
Figura 21
Consulte la Figura 22:
4. Reemplace la hoja usada por una nueva,
asegurándose de que los dientes en la parte
delantera de la mesa estén orientados hacia
abajo (consulte D, Figura 21).
5. Mueva cuidadosamente la hoja hasta que
quede paralela a la ranura del calibre de
ingletes. Verifique repitiendo los pasos 2 y 3.
Cuando haya terminado el ajuste, apriete bien
los tornillos (A).
60
Figura 22
Page 61

Cambio de la Hoja
¡Cuando instale o cambie
la hoja, siempre desconecte la sierra de la
fuente de alimentación! ¡El incumplimiento de
esta advertencia puede causar lesiones graves!
1. Con las ruedas de mano, suba el eje de la hoja
al máximo y fije la sierra a cero grados
(consulte los pasos 1 a 3 en la sección Parada
positiva de 90 grados); luego apriete la perilla
de fijación de la inclinación de la hoja
(B, Figura 19).
2. Retire los dos tornillos de inserción y retire el
accesorio de inserción de la mesa
(C, Figura 23) del bolsillo de la mesa.
3. Coloque la llave de extremo abierto para el
mandril (A, Figura 23) en los extremos planos
del interior de la brida de la hoja para evitar
que gire. Haga girar la tuerca del mandril en
sentido contrahorario con la llave de extremo
cerrado para el mandril (B, Figura 23) y retire
la tuerca y la brida exterior del mandril.
4. Reemplace la hoja usada por una nueva,
asegurándose de que los dientes en la parte
delantera de la mesa estén orientados hacia
abajo (consulte D, Figura 21).
5. Ensamble la brida exterior, la tuerca del
mandril y apriete bien la tuerca del mandril en
sentido horario. al mismo tiempo que sujeta
firmemente el mandril con la llave de extremo
abierto.
Reemplazo/Ajuste de la Correa de Accionamiento
Reemplazo y ajuste
1. Retire la hoja (consulte Cambio de la hoja en la
página 21).
2. Use rueda de mano delantera para bajar el eje
de la hoja a su posición más baja (gire la rueda
de mano en sentido contrahorario).
Figura 23
61
Page 62

3. Retire el resguardo de la hoja y la placa
abridora (consulte la sección Instalación del
resguardo de la hoja y placa abridora que
aparece en la página 12).
4. De ser necesario, retire la cubierta contra el
polvo.
Consulte la figura 24:
5. Use una llave hexagonal de 5mm para aflojar
los cuatro tornillos de cabeza hexagonal (A)
que sujetan el soporte del mandril (B) a la caja
del motor.
Si solo está ajustando la tensión de la correa (sin
reemplazarla), salte los pasos 6 a 10 y continúe
con el 11.
6. Con una llave de 10mm, afloje el tornillo de
ajuste de la tensión (C) haciéndolo girar en
sentido contrahorario.
7. Empuje el soporte del mandril (B) hacia
adelante (D) para aflojar la tensión de la correa
(E).
8. Retire la correa (E) de las poleas del motor y
mandril (F, G).
9. Reemplace la correa usada con una nueva
asegurándose de que esté apoyada
correctamente sobre ambas poleas.
10. Empuje el soporte del mandril (B) hacia atrás
(H) para poner tensión en la correa y apriete a
mano los cuatro tornillos de montaje (A).
Ajustes
11. Con una llave de 10mm, gire el tornillo de
ajuste de la tensión (C) para ajustar la correa a
la tensión correcta.
La tensión es suficiente cuando se obtiene
aproximadamente 1/4" de flexión de la correa
entre las poleas con la presión moderada que
ejerce un dedo.
12. Apriete los cuatro tornillos de montaje (A) con
una llave hexagonal de 5mm.
Después del ajuste
13. Vuelva a colocar la cubierta contra el polvo
(página 12) si corresponde.
14. Coloque la sierra de mesa mirando hacia
arriba.
Figure 24
Operación del calibre de ingletes
Para utilizar el calibre de ingletes, afloje la perilla
de fijación (A, Figura 25) y gire el calibre de
ingletes (B, Figura 25) al ángulo deseado.
Nota: Haga siempre cortes de prueba. No se
confíe únicamente en las marcas del indicador del
calibre de ingletes.
15. Reemplace y ajuste el resguardo de la hoja y
la placa abridora (consulte las secciones
Instalación del resguardo de la hoja y placa
abridora y Ajuste del resguardo de la hoja y
placa abridora que aparecen en la página 12).
16. Reemplace la hoja (consulte Cambio de la hoja
en la página 21).
62
Figura 25
Page 63

Conexiones Eléctricas
Esta sierra tiene un motor que funciona con
120VCA y viene con un cordón eléctrico que se
enchufa en un tomacorriente de
120VCA de tres patillas con
descarga a tierra, como se muestra.
Antes de enchufarlo a la fuente
eléctrica, asegúrese de que el
interruptor esté apagado (posición
Off).
Si se utiliza un cordón eléctrico de prolongación,
seleccione uno con una capacidad apropiada para
el trabajo según la tabla que figura a continuación.
00Cordón calibre 12 000 a 25 pies
00Cordón calibre 10 000 a 50 pies
0 Cordón calibre 8 000 a 100 pies
Tabla de cordones de prolongación
Controles de Operación
Interruptor de conexión/desconexión (On/Off):
El interruptor de conexión/desconexión (On/Off)
está ubicado en el panel delantero de la base de la
sierra (C, Figura 26). Para encender (On) la sierra,
coloque el interruptor en la posición de encendido
(hacia arriba) (F, Figura 27). Para apagar (Off) la
sierra, coloque el interruptor en la posición de
apagado (hacia abajo).
Llave de bloqueo: Cuando la sierra no esté en
funcionamiento, el interruptor debe estar
bloqueado en la posición Off. Para bloquear el
interruptor en la posición Off, saque la llave de
seguridad (G, Figura 27). La sierra no arrancará sin
esta llave. No obstante, si retira la llave cuando el
interruptor está en la posición On, puede apagarla
una vez. La sierra no arrancará nuevamente hasta
colocar la llave en el interruptor.
Protección de sobrecarga: Esta sierra tiene un
botón de relé de sobrecarga reposicionable
(D, Figura 26). Si el motor se apaga o no arranca
nuevamente debido a una sobrecarga o a bajo
voltaje, coloque el interruptor (C, Figura 26) en la
posición Off y deje que el motor se enfríe durante
cinco minutos por lo menos. Después de que el
motor se haya enfriado, apriete el botón de reinicio
(D, Figura 26) para volver a iniciar el dispositivo de
sobrecarga. La sierra debiera arrancar nuevamente
cuando el interruptor se coloca en la posición On.
Figura 26
Figura 27
Rueda de mando para la altura o inclinación de
la hoja: La rueda de mano ubicada en el panel
delantero de la sierra (A, Figura 26) fija la altura e
inclinación de la hoja.
Para subir o bajar la hoja, gire la rueda de mano
(A, Figura 26) en sentido horario o contrahorario.
Para inclinar la hoja:
1. Empuje la rueda de mano hacia adentro.
2. Afloje la perilla de fijación de la inclinación de
la hoja (B, Figura 26) haciéndola girar en
sentido contrahorario.
3. Mientras empuja sobre la rueda de mano, gire
en sentido horario o contrario para fijar la
inclinación de la hoja entre 0º (hoja a 90º
perpendicular con respecto a la mesa) y a 45º
(inclinación izquierda).
Cuando haya fijado el ángulo deseado,
4. Continúe empujando la rueda de mano
(A, Figura 26) hasta que la perilla de fijación
(B, Figura 26) esté apretada.
63
Page 64

Operaciones
Antes de encender la
sierra, asegúrese de que no haya herramientas, tornillería o desechos sobre la
mesa. Estos artículos pueden convertirse en
proyectiles y causar lesiones graves.
Sierras de mesa
Debe familiarizarse con la ubicación y operación
de todos los controles y ajustes de la sierra y
con el uso de los accesorios, como el calibre de
ingletes o la guía para cortar al hilo.
Contragolpes
Los contragolpes pueden causar lesiones
graves. Estos se producen cuando una pieza de
trabajo se atasca en la hoja o entre la hoja y la
guía para cortar al hilo u otro objeto fijo. Este
atascamiento puede hacer que la pieza de
trabajo se levante y se lance hacia el operador.
A continuación se enumeran algunas condiciones que pueden causar contragolpes:
No use el calibre de ingletes y la guía para
cortar al hilo durante la misma operación, a
menos que se use una tabla de refrentado
plano (bloque auxiliar) en la guía para
permitir que la sección cortada de la pieza
de trabajo quede libre antes de que se inicie
el próximo corte (consulte la Figura 35).
A medida que se va usando la máquina, se
debe inspeccionar periódicamente la
operación de los trinquetes anticontragolpes
(Figura 26). Si los trinquetes no detienen el
movimiento de retroceso de una pieza de
trabajo, afile las puntas.
Siempre que sea posible, mantenga la cara
y el cuerpo fuera de la línea de posibles
contragolpes, incluso cuando hace arrancar
la máquina y cuando la apaga.
Restringir la pieza cortada cuando se
realizan cortes al hilo o transversales.
Soltar la pieza de trabajo antes de
completar la operación o no empujar la
pieza de trabajo hasta que termine de pasar
por la hoja.
No usar la placa abridora cuando se hacen
cortes al hilo o no mantener la alineación de
la placa abridora con la hoja.
Usar hojas desafiladas.
No mantener la alineación de la guía para
cortes al hilo de manera que tienda a
inclinarse hacia la hoja en vez de hacerlo
hacia fuera, de adelante para atrás.
Aplicar demasiado fuerza durante el corte
sobre la sección de la pieza de trabajo
cortada (libre) en vez de hacerlo entre la
hoja y la guía.
Cortes de maderas combadas o torcidas (no
planas) o que no tengan un borde derecho o
la veta torcida.
Para evitar las lesiones causadas por
contragolpes, o para reducirlas a un mínimo:
Evite las condiciones mencionadas
anteriormente.
Use gafas o anteojos de seguridad o una
careta de protección.
Figura 28
Las herramientas de corte desafiladas, mal
colocadas, inapropiadas o mal afiladas y las
herramientas de corte con goma o cola de
pagar, o resina adherida pueden causar
accidentes. Nunca use una hoja fracturada. El
uso de una herramienta de corte filosa, bien
mantenida y apropiada ayudará a evitar
lesiones.
Sostenga la pieza de trabajo correctamente y
sujétela bien contra el calibre o la guía. Use una
pieza o bloque de madera de empuje cuando
tenga que cortar piezas cortas, angostas (de
6 pulgadas de anchura o menos) o delgadas.
Use una pieza de empuje o el calibre de ingletes
para sujetar los trabajos de mortaja o molduras
que haga.
Para aumentar la seguridad en los cortes
transversales, use una tabla de refrentado plano
(Figura 29) acoplada a los agujeros del calibre
de ingletes.
64
Page 65

Figura 29
Nunca use la guía como tope de longitud en los
cortes transversales. No sostenga ni toque el
extremo libre o la sección de cortado de una
pieza de trabajo. En las operaciones de
“aserrado total”, la sección de cortado NO debe
estar restringida.
Mantenga siempre las manos alejadas de la
línea de la hoja y nunca las coloque más allá de
la hoja para sujetar la pieza de trabajo.
Se debe hacer siempre los cortes biselados al
hilo con el resguardo colocado a la derecha de
la hoja, de manera tal que la inclinación de la
hoja se aleje del resguardo para reducir al
mínimo la posibilidad de que el trabajo se
atasque y de que se produzca un contragolpe.
Cortes al hilo
Los cortes al hilo son aquellos donde la pieza de
trabajo se alimenta con la veta hacia la hoja
utilizando la guía y un dispositivo de
posicionamiento para asegurar el ancho del
corte deseado (Figura 30).
Nunca haga cortes más cortos que el
diámetro de la hoja.
Nunca coloque las manos más allá de la
hoja para sujetar o quitar la pieza de corte
cuando la hoja esté girando.
Use siempre el resguardo de la hoja, la placa
abridora y los trinquetes anticontragolpes.
Asegúrese de que la máquina esté
correctamente conectada a tierra. Cuando se
corta la madera en el sentido de la veta, la
entalla tiende a cerrarse y a apretar contra la
hoja. Se pueden producir contragolpes.
Nota: Hay una calcomanía en el ensamble del
resguardo y de la placa abridora para advertir
sobre el peligro que representa una alineación
incorrecta.
Figura 31
Se debe colocar la guía para cortar al hilo
(A, Figura 31) para el ancho del corte
(C, Figura 31) usando la escala en el frente del
riel o midiendo la distancia entre la hoja (B) y la
guía (A). Párese fuera de la línea de la hoja y de
la pieza de trabajo para evitar el aserrín y las
astillas que pueden saltar de la hoja o la
posibilidad de contragolpes.
Figura 30
Antes de proceder con
un corte al hilo, asegúrese de que la guía
esté segura y alineada correctamente.
Nunca realice a pulso los cortes al hilo, ni
use un calibre de ingletes en combinación
con la guía.
Si la pieza de trabajo no tiene un borde derecho,
clave una tabla auxiliar con borde derecho para
que haya uno contra la guía. Para cortar
correctamente, la tabla tiene que estar bien en
contacto con la mesa. Si está combada, coloque
el lado hueco hacia abajo.
En los cortes al hilo, use una mano para sujetar
la tabla contra la guía o dispositivo y la otra para
empujarla contra la hoja entre la hoja y la guía.
Si la pieza de trabajo es de menos de
6 pulgadas de ancho, use una pieza o bloque de
madera de empuje para colocarla entre la guía y
la hoja (Figura 32). Nunca empuje en un lugar
de manera que la mano que empuje quede en
línea con la hoja. Mueva la mano que utiliza
para sujetar a una distancia segura de la hoja
cuando esté a punto de completar el corte. Para
65
Page 66

los cortes muy angostos, donde no pueda usar
una pieza de empuje, use un bloque o una guía
auxiliar. Empuje siempre toda la pieza de
trabajo más allá de la hoja para terminar un
corte para reducir al mínimo la posibilidad de un
contragolpe.
Figura 32
Cuando corte tablas largas, use un soporte con
rodillos en la parte delantera de la mesa y un
soporte o "tailman” en la parte trasera como se
ilustra en la Figura 33.
Deje que la hoja se extienda alrededor de 1/8
pulgada por arriba de la pieza de trabajo. Puede
ser peligroso exponer la hoja por arriba de ese
punto.
Figura 33
Cortes transversales
El corte transversal es aquel donde la pieza de
trabajo (A, Figura 34) se alimenta a la hoja en
contra de la veta con el calibre de ingletes (B,
Figura 34) para soportar y posicionar la pieza de
trabajo.
Para mejorar la eficacia del calibre de ingletes
en los cortes transversales, monte una tabla
auxiliar de refrentado plano (C, Figura 34) con
un pedazo de papel de lija (D, Figura 34)
pegado en el calibre de ingletes.
Figura 34
Nunca se debe hacer a pulso los cortes
transversales, ni se debe usar la guía como tope
a menos que el bloque auxiliar esté sujeto
adelante de la zona de la hoja de manera que la
pieza de cortado quede libre del bloque antes
de que se inicie el corte (Figura 35).
Figura 35
No se deberá utilizar topes de longitud en el
extremo libre de la pieza de trabajo en la pieza
cortada.
No haga cortes transversales en piezas de
menos de 6 pulgadas. Antes de comenzar con
el corte, asegúrese de que el calibre de ingletes
esté sujeto firmemente en el ángulo deseado.
Mantenga la pieza de trabajo bien firme contra
la mesa y contra el calibre de ingletes. Use
siempre el resguardo de la sierra y la placa
abridora y asegúrese de que ésta esté alineada
correctamente.
66
Page 67

Para los cortes transversales de 90 grados, la
mayoría de los operadores prefieren usar la
ranura izquierda del calibre de ingletes. Cuando
se use en esta posición, sujete la pieza de
trabajo contra el calibre con la mano izquierda y
use la mano derecha para avanzar la pieza de
trabajo. La posición de las manos cambia
cuando se usa la ranura derecha para los cortes
de inglete y cortes compuestos de manera que
la inclinación de la hoja se aleja del calibre.
Cuando se usa el calibre de ingletes, se debe
sujetar firmemente la pieza de trabajo y hacerla
avanzar despacio. Si no se sujeta bien la pieza
de trabajo, puede vibrar y atascarse en la hoja y
mellar los dientes.
Proporcione sostén auxiliar para cualquier
pieza de trabajo que sobresalga de la superficie
de la mesa con una tendencia a combarse y
levantarse de la mesa.
Deje que la hoja se extienda alrededor de
1/8 pulgada por arriba de la pieza de trabajo.
Puede ser peligroso exponer la hoja por arriba
de ese punto.
Operaciones de bisel e inglete
Corte en inglete – El corte en bisel es un tipo
de operación especial en la que la hoja se
inclina a un ángulo de menos de 90 grados con
respecto a la superficie de la mesa (Figura 36).
Las operaciones se realizan de la misma
manera que los cortes al hilo o transversales,
excepto que la guía o el calibre de ingletes se
debe usar a la derecha de la hoja para obtener
mayor seguridad y evitar un atascamiento entre
la hoja y la superficie de la mesa. Cuando se
hacen cortes de bisel con el calibre de ingletes,
se debe sujetar bien la pieza de trabajo y
hacerla avanzar despacio.
Corte transversal – Los cortes transversales en
ángulo al borde de la pieza de trabajo se llaman
ingletes (Figura 37). Coloque el calibre de
ingletes en el ángulo deseado y fíjelo. Haga el
corte de la misma manera que lo hace para los
cortes transversales normales, salvo que debe
sujetar bien la pieza de trabajo para evitar que
se desplace.
Nota: Cuando corte ingletes compuestos (con la
hoja inclinada) use el calibre de ingletes en la
ranura derecha para tener más espacio para la
mano y mayor seguridad.
Deje que la hoja se extienda únicamente
1/8 pulgada por arriba de la pieza de trabajo.
Puede ser peligroso exponer la hoja por arriba
de ese punto.
Figura 37
Corte de mortaja – El corte de mortaja es una ranura ancha en la pieza de trabajo o un rebajo en el borde de una pieza de trabajo. Para este tipo de operación se necesita el accesorio de inserción de la hoja para mortajas. Consulte la Figura 38.
No use el accesorio de
inserción estándar de la mesa para estas
operaciones de corte de mortaja.
Figura 36
67
Figura 38
Page 68

Para cortar ranuras de 1/8”a 1/2”en las piezas
de trabajo, se usa un juego de hojas
escalonadas para mortajas o un tipo de hoja
ajustable, montada en el mandril de la sierra.
Con el uso de esta combinación de hojas
escalonadas para mortajas, o fijando
correctamente el dial de una hoja ajustable, se
puede conseguir el ancho correcto de una
mortaja. Ello es muy útil para la fabricación de
estantes, juntas, espigas, etc. Se debe utilizar
el resguardo, la placa abridora y los trinquetes
anticontragolpes que vienen con la sierra para
todas las operaciones de corte con las que se
puedan usar. Se deberá tomar otras medidas de
seguridad cuando se realicen operaciones
donde no se pueda utilizar el resguardo, como
en los cortes de mortaja. Estos incluyen las
piezas de empuje, tablas escalonadas, piezas
de relleno, accesorios, guías y otros dispositivos
apropiados que se pueden utilizar para
mantener las manos del operador alejadas de la
hoja. Se deberá volver a colocar el ensamble
del resguardo completo en la máquina una vez
terminada una operación que requiera quitarlo.
Nunca use una cabeza
de corte de mortaja en la posición inclinada.
Nunca opere la sierra sin el resguardo de la
hoja, la placa abridora o los trinquetes
anticontragolpes en operaciones de corte
donde se puedan usar.
Dispositivos de seguridad
Tabla escalonada
La tabla escalonada (Figura 37) debe fabricarse
de madera dura con veta longitudinal de
aproximadamente 1 pulgada de espesor y de 4
a 8 pulgadas de ancho, dependiendo del
tamaño de la máquina. El largo está determinado por el uso que se le quiera dar. Las
tablas escalonadas pueden sujetarse a la mesa
o a la placa abridora con abrazaderas tipo C. Si
se utiliza este método de fijación, coloque
ranuras en la tabla escalonada para ajustar. (La
Figura muestra un método para acoplar y usar
una tabla escalonada como peine vertical. La
aplicación horizontal es casi igual, excepto que
se acopla a la superficie de la mesa.)
Pieza de madera de empuje
Con esta sierra viene una pieza de madera de
empuje y debe usarse como un elemento más
de seguridad para el operador.
Recolección del polvo
Para sierras equipadas con una cubierta contra
el polvo, debe utilizarse un sistema de
recolección o aspiración de polvo (no incluido).
El puerto en la cubierta contra el polvo puede
acomodar una manguera de 2.5 pulgadas o de
4 pulgadas (Figura 39).
La cubierta contra el polvo se debe inspeccionar
y limpiar frecuentemente para evitar el bloqueo
que puede causar la acumulación del polvo y
aserrín.
Figure 39
Figura 37
68
Page 69

Pieza de relleno
Mantenimiento
Es necesario contar con una pieza de relleno
(Figura 38) para los cortes al hilo que sean
angostos, ya que permite no retirar que el
resguardo de la hoja. También proporciona
espacio para el uso sin riesgos de una pieza de
empuje.
Figura 38 – Madera dura
Desconecte siempre la
fuente de alimentación de la máquina antes
de realizar cualquier trabajo de
mantenimiento. No hacerlo podría causar
lesiones personales graves.
Limpieza
Para obtener el máximo rendimiento de la sierra
de mesa 708315, límpiela según lo siguiente.
Nota: El siguiente plan de mantenimiento
presupone que la sierra se utiliza todos los días.
Todos los días:
Limpie la brea y resina de la hoja.
Una vez por semana:
Limpie la caja del motor con aire
comprimido.
Limpie la superficie de la mesa, ranura y
rieles de la guía con un lubricante seco de
siliconas.
Lubricación
Lubrique las áreas indicadas a continuación
cada 12 meses.
Lubrique los muñones de inclinación de la
hoja con 6 ó 7 gotas de aceite liviano para
máquinas.
Lubrique el muñón de altura de la hoja con 6
ó 7 gotas de aceite liviano para máquinas.
Inspeccione todos los ajustes después de
lubricar.
Varios
Siempre tenga en cuenta el estado de la
máquina. Inspeccione periódicamente el estado
de las piezas siguientes y repare o reemplace
según sea necesario:
Pernos de montaje
Interruptor eléctrico
Hoja de la sierra
Resguardo de la hoja
69
Page 70

Identificación y solución de problemas
Síntoma Causa posible Solución
El motor no arranca.
El motor no arranca: se
queman los fusibles o
interruptores de circuito.
Se para el motor y se
queman los fusibles o
salta el interruptor de
circuito.
La máquina baja de
velocidad cuando
funciona.
La máquina emite ruidos
fuertes y repetitivos.
Bajo voltaje. Inspeccione la línea eléctrica para comprobar
si tiene el voltaje correcto.
Circuito abierto o conexión floja en el
motor.
Cortocircuito en el cable de alimentación
o enchufe.
Cortocircuito o conexiones flojas en el
motor.
Los fusibles del interruptor de circuito en
la línea no son los correctos.
Sobrecarga del motor. Reduzca la carga del motor. El motor se sobrecalienta.
Está restringida la circulación de aire en
el motor.
Cortocircuito o conexiones flojas en el
motor.
Bajo voltaje. Corrija las condiciones de bajo voltaje.
Los fusibles del interruptor de circuito en
la línea no son los correctos.
Sobrecarga del motor. Reduzca la carga del motor.
Se aplica demasiada presión a la pieza
de trabajo.
Los tornillos o las llaves de fijación de la
polea no están o están flojos.
La correa en V tiene algún defecto. Reemplace la correa en V.
Inspeccione todas las conexiones principales
del motor para comprobar que no estén flojas
o abiertas.
Inspeccione el cable o el enchufe para ver que
no esté dañada la aislación o haya alambres
en cortocircuito.
Inspeccione todas las conexiones del motor
para determinar que no estén flojas, en
cortocircuito o tengan la aislación gastada.
Instale los fusibles o interruptor de circuito
correctos.
Limpie el motor para proporcionar circulación
de aire normal.
Inspeccione las conexiones del motor para
determinar que no estén flojas, en cortocircuito
o tengan la aislación gastada.
Instale los fusibles o interruptor de circuito
correctos.
Alimente la pieza de trabajo más despacio.
Inspeccione las llaves y los tornillos de fijación.
Reemplace o apriete si es necesario.
La hoja no está en
escuadra con la ranura de
inglete, o la guía no está
en escuadra con la hoja.
La hoja no alcanza los
90 grados.
La hoja está combada. Cambie la hoja.
La superficie de la mesa no está paralela
a la hoja.
La guía no está paralela a la hoja. Ajuste la superficie de la mesa para que esté
El perno de parada de 90 grados está
fuera de ajuste.
La tabla no está alineada. Alinee la mesa.
La posición de la hoja es incorrecta. Ajuste la posición de la hoja.
Ajuste la superficie de la mesa para que esté
paralela a la hoja.
paralela a la hoja.
Ajuste el perno de parada de 90 grados.
70
Page 71

Partes
Pedido de repuestos
Para hacer un pedido de partes o comunicarse con nuestro departamento de servicios, llame al
1-800-274-6848, de lunes a viernes de 7:30 a.m. a 5:30 p.m. Para poder atenderlo más rápidamente y
con mayor precisión, sírvase tener a mano el número de modelo y el número de serie de su máquina.
Motor/Muñón - Lista de partes
Núm. de Núm. de
índice parte
1 ...............708315-1..................Motor ................................................................... .................................... 1
2 ...............708315-2..................Ensamble de los cepillos ..................................... .................................... 2
3 ...............708315-3..................Polea del motor.................................................... .................................... 1
4 ...............708315-4..................Anillo de retención ............................................... ....................................1
5 ...............708315-5..................Llave..................................................................... 3x6.5x16 .................... 1
6 ...............TS-1490011 .............Tornillo de cabeza hexagonal.............................. M8x12 ......................... 1
7 ...............TS-1550061 .............Arandela plana..................................................... M8............................... 1
8 ...............708315-8..................Polea del mandril ................................................. .................................... 1
9 ...............708315-9..................Correa .................................................................. .................................... 1
10 .............TS-2286252 .............Tornillo de cabeza achatada................................ M6x25 ......................... 1
11 .............TS-1540041 .............Tuerca hexagonal ................................................M6 ............................... 7
12 .............BB-6002Z .................Cojinete ................................................................ 6002Z ......................... 1
13 .............708315-13 ................Soporte del mandril .............................................. .................................... 1
14 .............708315-14 ................Eje del mandril ..................................................... .................................... 1
15 .............TS-1503111 .............Tornillo de cabeza hueca..................................... M6x50 ......................... 2
16 .............BB-6003Z .................Cojinete ................................................................ 6003Z ......................... 1
17 .............TS-1532042 .............Tornillo de cabeza achatada................................ M4x12 ......................... 3
18 .............708315-18 ................Cubierta................................................................ .................................... 1
19 .............708315-19 ................Brida del mandril .................................................. .................................... 1
20 .............708315-20 ................Hoja de la sierra ................................................... 10”x36T....................... 1
21 .............708315-21 ................Collar del mandril ................................................. .................................... 1
22 .............708315-22 ................Tuerca del mandril ............................................... ....................................1
23 .............TS-1503081 .............Tornillo de cabeza hueca..................................... M6x35 ......................... 2
24 .............TS-1551041 .............Arandela de bloqueo............................................ M6............................... 4
25 .............TS-1550041 .............Arandela plana .....................................................M6 ............................... 4
26 .............TS-1482051 .............Tornillo de cabeza hexagonal ..............................M6x25 ........................1
27 .............TS-2236801 .............Tornillo de cabeza hueca..................................... M6x80 ......................... 1
28 .............708315-28 ................Soporte del motor ................................................ .................................... 1
29 .............708315-29 ................Espaciador ........................................................... .................................... 1
30 .............708315-30 ................Espaciador ........................................................... .................................... 1
31 .............708315-31 ................Soporte del eje ..................................................... .................................... 1
32 .............708315-32 ................Tuerca .................................................................. M10 ............................ 4
33 .............TS-1550071 .............Arandela plana ..................................................... M10 ............................. 1
34 .............708315-34 ................Arandela especial ................................................ .................................... 1
35 .............708315-35 ................Espaciador ........................................................... .................................... 2
36 .............TS-1503061 .............Tornillo de cabeza hueca..................................... M6x25 ......................... 2
37 .............708315-37 ................Soporte................................................................. .................................... 1
38 .............TS-2284082 .............Tornillo de cabeza achatada................................ M4x8 ...........................2
39 .............TS-1550021 .............Arandela plana .....................................................M4 ............................... 2
40 .............TS-1551021 .............Arandela de bloqueo............................................ M4............................... 2
41 .............708315-41 ................Pasador................................................................ M3x18 ......................... 1
42 .............708315-42 ................Eje de elevación................................................... .................................... 1
43 .............708315-43 ................Señalador............................................................. .................................... 1
44 .............708315-44 ................Soporte................................................................. .................................... 1
Descripción Tamaño Cant.
71
Page 72

Motor/Muñón - Lista de partes
Núm. de Núm. de
índice parte Descripción
45 .............708315-45 ................Pasador................................................................ M8x90 ......................... 1
46 .............708315-46 ................Soporte del muñón............................................... .................................... 1
47 .............TS-1503051 .............Tornillo de cabeza hueca..................................... M6x20 ......................... 3
48 .............708315-48 ................Pasador................................................................ M3x10 ......................... 1
49 .............708315-49 ................Soporte................................................................. .................................... 1
50 .............TS-2285302 .............Tornillo de cabeza achatada................................ M5x30 ......................... 1
51 .............708315-51 ................Soporte de la varilla ............................................. .................................... 1
52 .............708315-52 ................Abrazadera........................................................... .................................... 4
53 .............708315-53 ................Varilla angular ...................................................... .................................... 1
54 .............TS-2286251 .............Tornillo de cabeza hueca..................................... M6x25 ......................... 2
55 .............708315-55 ................Placa de soporte de la varilla............................... .................................... 1
56 .............708315-56 ................Resorte................................................................. .................................... 1
57 .............708315-57 ................Perno de carruaje ................................................ M6x32 ......................... 1
58 .............708315-58 ................Espaciador ........................................................... .................................... 1
59 .............TS-1541021 .............Tuerca de bloqueo del accesorio ........................ ......................................
................. .................................de inserción de nylon........................................... M6 ............................. 39
Tamaño Cant.
72
Page 73

Motor/Muñón - Ensamble
73
Page 74

Ensamble del resguardo de la hoja
Núm. de Núm. de
índice parte Descripción
.................708315-BGA ............Ensamble del resguardo de la hoja (Completo)2. ......................................
25 .............TS-1550041 .............Arandela plana .....................................................M6 ............................... 4
59 .............TS-1541021 .............Tuerca de bloqueo del accesorio
................. .................................de inserción de nylon........................................... M6 ............................... 3
60 .............TS-1482041 .............Tornillo de cabeza hexagonal ..............................M6x20 .........................4
61 .............708315-61 ................Soporte de la placa abridora................................ .................................... 1
62 .............708315-62 ................Soporte................................................................. .................................... 1
63 .............708315-63 ................Perno de carruaje ................................................ M6x12 ......................... 1
64 .............708315-64 ................Placa abridora ...................................................... .................................... 1
65 .............708315-65 ................Trinquete anticontragolpes .................................. .................................... 2
66 .............708315-66 ................Espaciador ........................................................... .................................... 2
67 .............708315-67 ................Soporte del resguardo ......................................... .................................... 1
68 .............708315-68 ................Resguardo............................................................ .................................... 1
69 .............708315-69 ................Remache.............................................................. .................................... 2
70 .............708315-70 ................Arandela de retención.......................................... .................................... 2
71 .............708315-71 ................Pasador................................................................ M3x22 ......................... 1
72 .............708315-72 ................Resorte................................................................. .................................... 1
Tamaño Cant.
1
La compra del Ensamble completo de resguardo de la hoja incluye todas las partes menos los piezas 60 a 63.
74
Page 75

Ensamble del calibre de ingletes
Núm. de Núm. de
índice parte Descripción
.................708315-MGA............Ensamble del calibre de ingletes (Completo) ...... ......................................
38 .............TS-2284082 .............Tornillo de cabeza achatada................................ M4x8 ...........................2
73 .............708315-73 ................Barra .................................................................... .................................... 1
74 .............708315-74 ................Señalador............................................................. .................................... 1
75 .............708315-75 ................Manija................................................................... .................................... 1
76 .............708315-76 ................Tapa de la manija ................................................ .................................... 1
77 .............708315-77 ................Cuerpo del calibre de ingletes ............................. .................................... 1
78 .............708315-78 ................Pasador................................................................ M6x15 ......................... 1
Tamaño Cant.
75
Page 76

Ensamble del soporte trasero
Núm. de Núm. de
índice parte Descripción
.................708315-RSA ............Ensamble del soporte trasero (Completo) ........... ......................................
59 .............708315-158 ..............Tuerca de brida hexagonal ..................................M6............................... 2
79 .............708315-79 ................Varilla ................................................................... ....................................2
80 .............708315-80 ................Soporte trasero .................................................... .................................... 1
Tamaño Cant.
76
Page 77

Ensamble de la guía para cortar al hilo
Núm. de Núm. de
índice parte Descripción
.................708315-RFA.............Ensamble de la guía para cortar al hilo ............... ......................................
................. .................................(Completo) ........................................................... ......................................
25 .............TS-1550041 .............Arandela plana .....................................................M6 ............................... 2
38 .............TS-2284082 .............Tornillo de cabeza achatada................................ M4x8 ...........................1
76 .............708315-76 ................Tapa de la manija ................................................ .................................... 1
82 .............708315-82 ................Abrazadera trasera .............................................. ....................................1
83 .............708315-83 ................Resorte................................................................. .................................... 1
84 .............708315-84 ................Varilla ................................................................... ....................................1
85 .............708315-85 ................Cuerpo de la guía ................................................ .................................... 1
86 .............TS-1482011 .............Tornillo de cabeza hexagonal ..............................M6x10 .........................2
87 .............708315-87 ................Arandela de bloqueo con dientes externos ......... M6 ............................... 2
88 .............708315-88 ................Bloque delantero.................................................. .................................... 1
89 .............708315-89 ................Resorte................................................................. .................................... 1
90 .............708315-90 ................Tornillo de ajuste.................................................. .................................... 1
91 .............708315-91 ................Bloqueo de leva ................................................... ....................................1
92 .............708315-92 ................Manija................................................................... .................................... 1
93 .............708315-93 ................Pasador................................................................ .................................... 1
94 .............708315-94 ................Abrazadera delantera .......................................... .................................... 1
95 .............708315-95 ................Pasador................................................................ .................................... 1
96 .............708315-96 ................Resorte de hoja.................................................... .................................... 1
97 .............TS-1532032 .............Tornillo de cabeza achatada................................ M4x10 ......................... 1
98 .............708315-98 ................Cursor .................................................................. .................................... 1
99 .............708315-99 ................Soporte................................................................. .................................... 2
Tamaño Cant.
77
Page 78

Ensamble de la prolongación derecha de la mesa
Núm. de Núm. de
índice parte Descripción
.................708315-REA ............Ensamble de la prolongación derecha ............... ......................................
................. .................................de la mesa (Completo)......................................... ......................................
39 .............TS-1550021 .............Arandela plana .....................................................M4 ............................... 2
40 .............TS-1551021 .............Arandela de bloqueo............................................ M4............................... 2
59 .............708315-158 ..............Tuerca de brida hexagonal ..................................M6............................... 4
97 .............TS-1532032 .............Tornillo de cabeza achatada................................ M4x10 ......................... 2
100 ...........708315-100..............Tapa del extremo del riel ..................................... .................................... 1
101 ...........TS-1503071 .............Tornillo de cabeza hueca..................................... M6x30 .........................2
102 ...........708315-102..............Riel delantero....................................................... .................................... 1
103 ...........708315-103..............Espaciador ........................................................... .................................... 2
104 ...........708315-104..............Mesa de prolongación.......................................... .................................... 1
105 ...........708315-105..............Varilla de prolongación ........................................ .................................... 2
106 ...........708315-106..............Guía del riel.......................................................... .................................... 1
107 ...........708315-107..............Escala .................................................................. .................................... 1
Tamaño Cant.
78
Page 79

Ensamble de la prolongación izquierda de la mesa
Núm. de Núm. de
índice parte Descripción
.................708315-LEA .............Ensamble de la prolongación izquierda............... ......................................
................. .................................de la mesa (Completo)......................................... ......................................
39 .............TS-1550021 .............Arandela plana .....................................................M4 ............................... 2
40 .............TS-1551021 .............Arandela de bloqueo............................................ M4............................... 2
59 .............708315-158 ..............Tuerca de brida hexagonal ..................................M6............................... 4
97 .............TS-1532032 .............Tornillo de cabeza achatada................................ M4x10 ......................... 2
100 ...........708315-100..............Tapa del extremo del riel ..................................... .................................... 1
101 ...........TS-1503071 .............Tornillo de cabeza hueca..................................... M6x30 .........................2
102 ...........708315-102..............Riel delantero....................................................... .................................... 1
103 ...........708315-103..............Espaciador ........................................................... .................................... 2
104 ...........708315-104..............Mesa de prolongación.......................................... .................................... 1
105 ...........708315-105..............Varilla de prolongación ........................................ .................................... 2
106 ...........708315-106..............Guía del riel.......................................................... .................................... 1
108 ...........708315-108..............Escala .................................................................. .................................... 1
109 ...........708315-109..............Escala .................................................................. .................................... 1
Tamaño Cant.
79
Page 80

Sierra principal - Partes
Núm. de Núm. de
índice parte Descripción
11 .............TS-1540041 .............Tuerca hexagonal ................................................M6 ............................... 1
24 .............TS-1551041 .............Arandela de bloqueo............................................ M6............................... 4
25 .............TS-1550041 .............Arandela plana .....................................................M6 ............................. 34
59 .............TS-1541021 .............Tuerca de bloqueo del accesorio......................... ......................................
................. .................................de inserción de nylon........................................... M6 ............................. 16
60 .............TS-1482041 .............Tornillo de cabeza hexagonal ..............................M6x20 .........................8
101 ...........TS-1503071 .............Tornillo de cabeza hueca..................................... M6x30 .........................4
103 ...........708315-103..............Espaciador ........................................................... .................................... 4
110 ...........TS-1482021 .............Tornillo de cabeza hexagonal ..............................M6x12 .......................16
117 ...........TS-1540061 .............Tuerca hexagonal ................................................M8 ............................... 2
118 ...........708315-118..............Soporte de la prolongación de la mesa ............... ....................................6
119 ...........708315-119..............Mesa principal...................................................... .................................... 1
120 ...........TS-1533032 .............Tornillo de cabeza achatada................................ M5x10 ......................... 2
121 ...........708315-121..............Accesorio de inserción de la mesa ...................... .................................... 1
122 ...........708315-122..............Tornillo especial para la mesa ............................. .................................... 4
123 ...........TS-1504041 .............Tornillo de cabeza hueca..................................... M8x20 .........................1
124 ...........TS-1504121 .............Tornillo de cabeza hueca..................................... M8x60 .........................1
125 ...........708315-125..............Riel delantero....................................................... .................................... 1
126 ...........708315-126..............Tapa del riel ......................................................... ....................................2
127 ...........708315-127..............Tornillo de latón (puesta a tierra)......................... M5x8 ........................... 1
128 ...........708315-128..............Arandela de bloqueo con dientes externos ......... M5 ............................... 1
129 ...........708315-129..............Pata...................................................................... .................................... 4
130 ...........708315-130..............Panel trasero........................................................ .................................... 1
131 ...........708315-131..............Tornillo autorroscante ..........................................M4x14 ......................... 7
132 ...........708315-132..............Aliviador de tensión.............................................. .................................... 1
133 ...........708315-133..............Perilla de fijación.................................................. .................................... 6
134 ...........708315-134..............Panel lateral derecho ........................................... .................................... 1
135 ...........708315-135..............Perilla de fijación.................................................. .................................... 1
136 ...........708315-136..............Perno roscado...................................................... .................................... 4
137 ...........708315-137..............Arandela de refuerzo ........................................... .................................... 1
138 ...........708315-138..............Panel lateral izquierdo ......................................... .................................... 1
139 ...........708315-139..............Llave para tuerca del mandril............................... .................................... 1
140 ...........708315-140..............Llave de extremo abierto ..................................... .................................... 1
141 ...........708818 .....................Pieza de madera de empuje ................................ .................................... 1
142 ...........TS-2286202 .............Tornillo de cabeza achatada................................ M6x20 ....................... 16
143 ...........708315-143..............Panel delantero.................................................... .................................... 1
144 ...........708315-144..............Placa delantera .................................................... .................................... 1
145 ...........708315-145..............Placa dentada para bisel ..................................... ....................................1
146 ...........TS-2284081 .............Tornillo de cabeza hueca..................................... M4x8 ........................... 9
147 ...........708315-147..............Perilla de fijación.................................................. .................................... 1
148 ...........708315-148..............Resorte................................................................. .................................... 1
149 ...........708315-149..............Rueda de mano ................................................... .................................... 1
150 ...........708315-150..............Manija................................................................... .................................... 1
151 ...........708315-151..............Interruptor automático de circuito (sobrecarga)... .................................... 1
152 ...........708315-152..............Alambre................................................................ .................................... 1
153 ...........708315-153..............Interruptor de conexión/desconexión (On/Off)..... .................................... 1
154 ...........708315-154..............Junta de caucho................................................... .................................... 1
155 ...........708315-155..............Caja del interruptor .............................................. .................................... 1
156 ...........708315-156..............Cordón de alimentación ....................................... .................................... 1
157 ...........708315-157..............Pie de caucho ...................................................... ....................................4
Tamaño Cant.
80
Page 81

Sierra principal -– Ensemble
81
Page 82

Ensamble del soporte
Núm. de Núm. de
índice parte Descripción
.................708315-SA ...............Ensamble del soporte (Completo) ....................... ......................................
11 .............708315-158 ..............Tuerca de brida hexagonal ..................................M6............................. 12
110 ...........TS-1482021 .............Tornillo de cabeza hexagonal ..............................M6x12 .......................12
111 ...........708315-111..............Pata...................................................................... .................................... 4
112 ...........708315-112..............Estante ................................................................. .................................... 1
Tamaño Cant.
Ensamble de la prolongación de la mesa en acero
Núm. de Núm. de
índice parte Descripción
.................708315-SSEWA.......Ensamble de la prolongación de la ..................... ......................................
................. .................................mesa en acero (Completo) .................................. ......................................
113 ...........708315-113 ..............Prolongación de la mesa en acero estampado ... .................................... 1
114 ...........TS-1490041 .............Tornillo de cabeza hexagonal ..............................M8x25 .........................2
115 ...........TS-2361081 .............Arandela de bloqueo............................................ M8............................... 2
116 ...........TS-1550061 .............Arandela plana ..................................................... M8 ............................... 2
117 ...........TS-1540061 .............Tuerca hexagonal ................................................M8 ............................... 2
Tamaño Cant.
Accesorios
Núm. de Núm. de
índice parte Descripción Tamaño Cant.
159 ...........708315-159..............Cubierta contra el polvo
82
Page 83

83
Page 84

WMH Tool Group
2420 Vantage Drive
Elgin, Illinois 60123
Phone: 800-274-6848
www.wmhtoolgroup.com
84
 Loading...
Loading...