Page 1

Distributed by:
www.Jameco.com ✦ 1-800-831-4242
The content and copyrights of the attached
material are the property of its owner.
Page 2

Jameco Part Number 231183
®
SUPERPRO
Universal Programmers
For Windows 95/98/NT/2000
series
User’s Guide
XELTEK
Page 3

COPYRIGHTS
User's Guide Copyrights 1997-2000 XELTEK
This software product is copyrighted. All rights are reserved. The distribution and
sales of the products are intended for use by the original purchaser under the terms
of the License Agreement.
This User's Guide is copyrighted. All rights are reserved. This document may not,
in whole or part, be copied, photocopied, reproduced, translated or reduced to any
electronic medium of machine-readable form without prior consent in writing from.
XELTEK.
SUPERPRO is the registered trademark of XELTEK.
Software Copyrights 1997-2000 XELTEK
Page 4

Contents
1. General Description
1.1 Introduction
1.1.1 What is Superpro?
1.1.2 Manual Organization
1.1.3 Manual Convention
1.1.4 System Requirement
1.3.2 Package
1.2 System Setup
1.2.2 Hardware Installation
1.2.3 Running the Program
1.2.5 Device Insertion
1.3 Programming Operation
1.2.1 Software Installation
1.2.4 Communication Error message
1.3.2 Quick Guide to Programming
1.3.3 Error Messages
2. Description of Menus
2.1 File: <Alt-F>
2.1.1 Load
2.1.2 Save
2.2 Buffer: <Alt-B>
2.2.1 Edit
2.2.2 Encryption Table
2.2.3 Vector Table
2.3 Device: <Alt-D>
2.3.1 Run
2.3.2 EditAuto
Page 5

2.3.3 Select
2.3.4 Word Format
2.4 Test: <Alt-T>
2.4.1 New Pattern
2.4.2 Edit Pattern
2.4.3 Delete Pattern
2.4.4 TTL&CMOS test
2.4.5 Auto find device
2.4.6 Vector test
2.5 Option: <Alt-O>
2.5.1 Setting
2.5.2 Auto Increment
2.5.3 Load configure file
2.5.4 Save configure file
3. Appendices
3.1 Customer Support
3.2 Error Messages
1.General Description
Page 6

1.1 INTRODUCTION
1.1.1 What is Superpro?
The SUPERPRO is a family of affordable, reliable, and fast universal IC device
programmers. They are designed to communicate through a parallel (printer) or USB
port(model dependent) and to operate with Intel 80486- and Pentium-based IBMcompatible desktop computers and notebook computers. Menu-driven software interface
makes them easy to operate.
Programming hardware include the following items.
1. A sleek, low-profile, programming module including a 40 or 48 pin ZIF (Zero
Insertion Force) socket (model dependent).
2. An AC adapter or dual range switching power supply( model dependant).
3. A parallel connecting cable.
4. Optional socket adapters to accommodate PLCC, TSOP, SOIC, SOP, QFP,
TSSOP and BGA packages are available.
Software include the following features:
1. Supports Windows95/98, Windows/NT and Windows2000 (model dependent)
2. Programming support for a large number of devices (1,500 ~ 6,000) including
PROMs, EPROMs, PLDs and Microcontrollers from 60+ manufacturers
3. IC test capability for TTL and CMOS Logic ICs (model dependent).
4. Support for Binary, Intel (linear & segmented) HEX, Motorola S, Tektronix
(linear & segmented), Jedec, pof and prg formats
5. Device insertion test (model dependent) to detect improperly inserted device.
6. Integrated full screen editors with fill, copy, move, locate, swap etc. commands
7. Auto-generation of electronic serial numbers (model dependant)
1.1.2 Manual organization
The Guide consists of three main parts:
Part 1: The chapters provide an introduction to the SUPERPRO. Some of the items
covered are System requirements, Set-up of the hardware and software.
Part 2: The part includes explanation for each software command and functions.
Appendices: Appendices contain information on Customer support and Error messages.
1.1.3 Manual convention
The following conventions are used in this manual:
The names of all keyboard keys are enclosed in angle brackets, < >. For example, the
Enter (or Return) key is shown as <Enter>; the Page Up key is shown as <PgUp>.
The cursor keys are shown as follows:
Left arrow key = <Left arrow>
Right arrow key = <Right arrow>
Page 7

Up arrow key = <Up arrow>
Down arrow key = <Down arrow>
Unless stated otherwise, keystrokes are not case-sensitive. e.g.: Both 'A' and 'a' are
acceptable.
1.3.2 System Requirements
The minimum requirement is as follows:
1. A 486 or Pentium PC, desktop or laptop.
2. One parallel port, such as LPT1 (278H), LPT2 (378H), or LPT3 (3BCH).
3. MS Windows9x, NT or 2000 operating system (model dependant)
4. Diskette drive (3.5" 1.44 Mbytes) or CD-ROM for installation
5. Hard disk storage of at least 10 Mbytes of spare capacity.
6. Color graphic adaptor and monitor.
1.1.5 Programmer Package
Standard package contains the following:
6. A programmer module
7. A parallel connecting cable
8. A dual range switching power supply (model dependant)
9. An installation software diskette (3 1/2") or a CD-ROM
1.2 System Setup
1.2.1 Software Setup
Insert the setup disc or CD-ROM into a drive and run SETUP.EXE. At the beginning of
setup, default folder will be created or you may create/select the folder of your choice.
Setup program creates three sub-folders, BIN, LIB and ALGO. The main program and
configuration files are stored in the Bin folder, the device library files are stored in the
LIB folder, and the programming algorithm files are stored in the ALGO folder. There are
many hundred device programming algorithm files stored in the ALGO folder and less
than 100 files stored in the LIB folder. BIN folder contains the main program. When the
program is run, system operating configuration file is created and stored in the BIN
folder.
When the program is set up but doesn’t run properly, please check the folders and see if
the files are expanded and stored properly.
1.2.2 Hardware Setup
Connect the programmer module to the computer's printer (parallel) port with the cable
provided. Then, connect the power supply adapter and turn on the programmer power
Page 8
switch and observe the power LED coming on bright. Please be sure not to insert any chip
onto the programmer socket at this time.
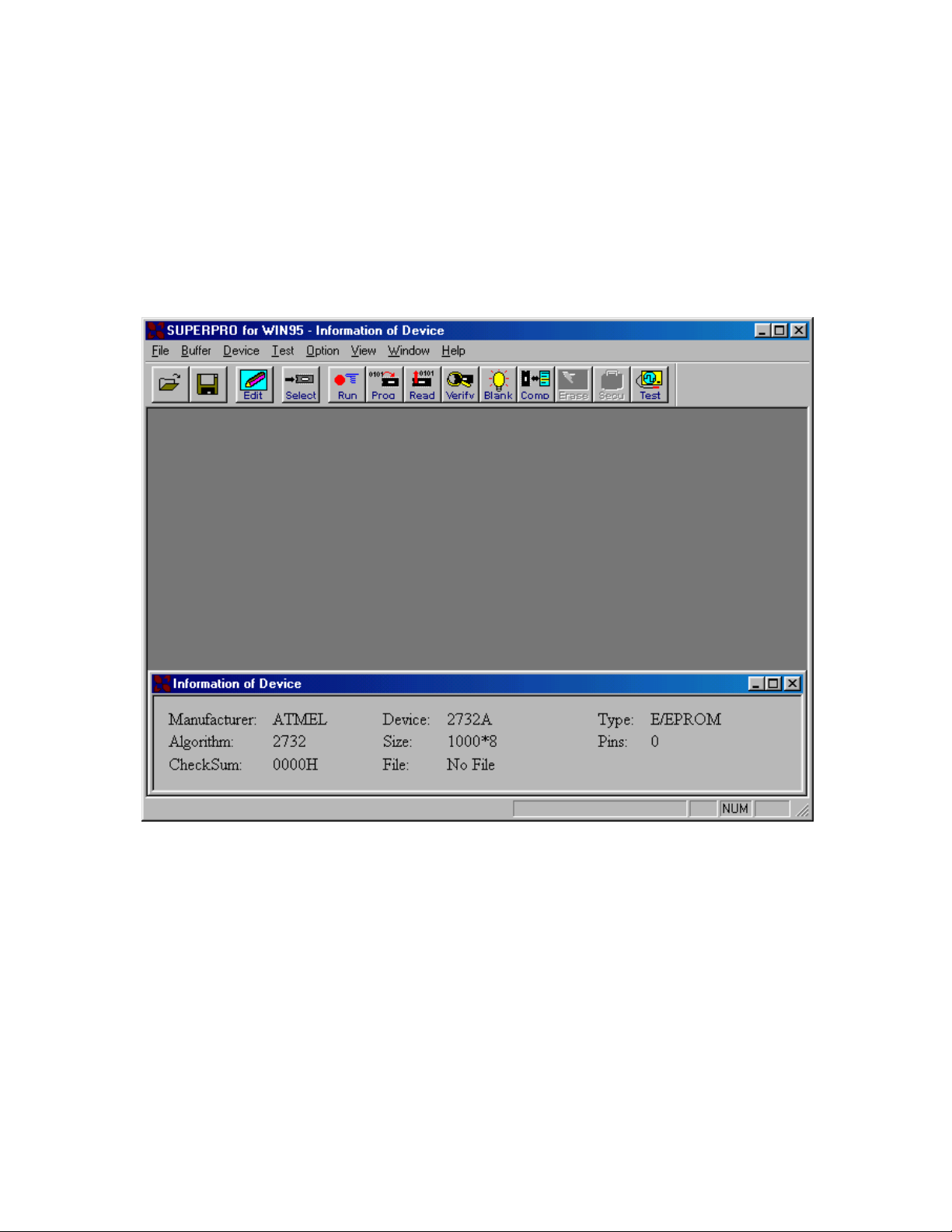
1.2.3 Running the Program
Please run the main program for the programmer. If everything is set up correctly, then
the main screen should come up without any error message. At this point, you may select
a device and proceed with programming operation.
Figure1. Main Screen
1.2.4 Communication Error Message
Communication error may occur if the PC failed to communicate with the programmer.
Please check the setup again and see to it that there is no device inserted in the
programmer socket.
Sometimes, the error message occurs when the programmer hardware is defective. If the
problem persists please contact factory for support.
Page 9

1.2.5 Device Insertion
For chips in DIP package
Follow the reference diagram next to the socket. Chips are always inserted at the bottom
line of the ZIF socket with the pin 1 facing toward upper left corner. For some low-end
models, some devices may need to be inserted in a non-standard way. Instruction for
insertion of such devices will appear on the screen when the selection of the device is
made.
For chips in None-DIP packages
Socket adapters are available for PLCC, QFP, TSOP, PSOP, SSOP, SOIC, SDIP, BGA
etc. packages. All adapters with 48 pins or less are constructed with top and bottom pins
connected 1 to 1.
1) Adapters with 48 pins or less on SuperproIII
Socket adapters are inserted in the same way as DIP packaged devices, which is at the
bottom of the 48 pin DIP ZIF socket. Chip insertion instruction onto the adapter is
displayed when the device is selected on the screen. Be sure to insert chips in correct
orientation.
2) Chips with more than 48 pins on SuperproIII
Optional 100 pin expansion adapter, PEP100, is necessary to program larger devices.
Please remove the standard DIP48 ZIF socket adapter and install the PEP100 adapter in
place and then mount the socket adapter on top.
1.3 Programming Operation
1.3.1 Quick Guide to Programming
Select the device: From the main screen, click on Select, and the Select window will
popup. First select the Category of device (E/EPROM, BPROM, SRAM, PLD or MCU)
followed by Manufacturer and Device name from the screen. Click OK button or doubleclick the device to confirm selection. Chips may also be selected by typing in the device
part number in the Search box.
To load the data to be programmed with, you may load it from disk or copy master data
by reading in the master chip.
Loading a file: You may load a file into the buffer by clicking File menu in the main
screen and Load File screen will pop up. In the Look In dialog box, select the folder and
file name you wish to load. File Type screen will pop up with various data types to
select from. At this point, the selected data will be loaded automatically into the buffer.
Please go to the Buffer and check if the data is loaded properly.
Note, Most HEX or S record files contain non-zero file start address. In this case, the start
address should be entered in the File address box.
Reading data from master chip: Insert the master chip in the socket and make the
Page 10

selection of the device to read from. Click on Run from the main screen, which will pop
up the Function screen. Click on the Read function, which copies the data from the
master chip into the buffer. At this point you may go to the buffer and examine the data
to see if it is loaded correctly. The data may be saved to a disk for later use.
Program device: Insert blank chip into the socket and enter on Program function.
Device should begin programming at this time followed by verification. Unless the device
is new out of box it may be advisable to check for blank before programming.
9.3.2 Error Messages
For any programming error, please refer to the Error Messages section in the Appendix.
2. Description of Menus
2.1 File: <Alt-F>
The menu deals with data file management and system interface.
2.1.1 Load <Ctrl-O>
Files are loaded into one of two buffer types, HEX/ASCII buffer for EPROMs and
Microcontrollers (MCU) and Logic buffer for PLD/PALs, which requires .JED type file.
For EPROMs and MCUs, data types supported are Binary (also .POF), Intel HEX (also
extended HEX), Motorola S record, and Tektronix HEX types. Select the appropriate type
for the data file.
To select a data file to be loaded, the path and the file name should be entered into the
name field. If the full path or the exact name of the file is unknown, then a partial path
may be entered using wild cards, e.g. ‘*.*’ or ‘*.BIN’.
Some files have non-zero file start or file offset address. This should be entered in the
file start address for proper data loading. Incorrect file offset address will cause FFs to
be stored in the beginning part of the buffer. Incorrect large offset address may cause data
overflow in the buffer and system failure.
For PLD/PAL devices the Load JED File dialogue box will pop up to enter the file
name.
Page 11

Figure 8 Data type
2.1.2 Save
This selection will save the current data in the buffer to disk.
For E(E)PROM, BPROM or MCU device types, Save File window will pop up. Select
the folder and filename to be saved under. Next, File Type dialog box will pop up for
selecting file type to be saved under.
For PLD devices, the Save JED File dialogue box will pop-up to enter the file name.
2.1.3 Exit
This command closes the programmer software and returns you to the control of the
operating system.
2.2 Buffer: <Alt-B>
The menu manages data in the buffer.
2.2.1 Edit
The selection brings up Fuse Buffer Edit window if the device type is a PLD, or Data
Buffer Edit window for memory/MCU devices. The HEX/ASCII data buffer is 8 bit
wide. Tab key may be used to switch between HEX and ASCII data for edit. You may
edit the buffer data on the screen with the following keys:
<PageUp> :Page up
<PageDown> :Page down
<Ctrl-PageUp> :Move cursor to the beginning of the buffer
<Ctrl-PageDown> :Move cursor to the end of the buffer
<Home> :Move cursor to the beginning of the line
<End> :Move cursor to the end of the line
Page 12

Figure 9. Edit Buffer
Locate
The function is convenient for locating a set of data for editing. In the Locate Buffer
dialog box, key in the address you wish to see displayed and press OK. The cursor will
blink at the address specified in the space marked New Address.
Fill
The function will bring up the Fill Buffer dialogue box. It consists of the Start Address,
End Address, Fill Data input lines, OK and Cancel buttons. Input desired data to be
filled into the Fill Data input line, and specify the range by indicating the beginning and
ending addresses. For the Fuse Buffer Edit window, the data will be either 1 or 0. For
the Data Buffer Edit window, it will be a two character HEX code.
Copy
The function displays Copy Buffer dialogue box. It consists of Start Address, End
Address, New Address input lines, OK and Cancel buttons. Data between start address
and end address will be copied to the buffer beginning with new address.
Swap
Page 13

Swap MSB and LSB byte order for the specified word width in the address range.
Figure 13. Swap Buffer
Radix
Toggles between HEX and DEC (Decimal) memory address display.
Search
Searches for a combination of HEX/ASCII codes (search string).
Next
Performs the next search for the search string in Search.
2.2.2 Encryption Table
The Load Encryption Table, with its two sub-menus, manages an encryption array. The
two sub-menus will appear only if the chip selected is equipped with an encryption array.
Load:
Brings up the Load Encryption Table dialogue box. Enter the name of the file to be
loaded in the input line provided.
Edit:
Opens the Encryption Buffer Edit window for viewing and editing.
2.2.3 Vector Table
Page 14

This opens the Vector Buffer Edit window. If a test vector table is included in the
JEDEC file, the software will load the test vector table to the buffer automatically when
the JEDEC file is loaded. Refer to the following when editing the test vector.
Z: High impedance state
X: Don't care state
N: Vcc and ground (output pins are not tested)
H: Output logic High (Voh)
L: Output logic low (Vol)
C: Clock pin
1: Input logic High (Vih)
0: Input logic Low (Vil)
2.3 Device: <Alt-D>
This menu is used to select programming Functions, IC manufacturer, Device Category,
Part Number of the Device and to specify the Word Format. Enter on Select to make
device selection. When you are ready to operate on a device (e.g. program or read), click
on Run, which displays Function dialog box for programming operation.
2.3.1 Run
The selection is used to perform actual operation on a device, e.g. Program, Read, Blank
Check, Erase, etc. It brings up the Function dialogue box and displays information on the
selected device, which are Function Select list viewer, Message (and the blue
information display windows on the bottom), Chip Start, Chip End, Buff Start, Buff
End input lines, OK and Cancel buttons.
The Function Select list in the Function dialogue box may differ from chip to chip
and it reflects the functions available for the chip from the manufacturer.
Page 15

Figure 15. Run
Program
The function writes the data from the buffer into the chip. The Verify function is
performed automatically after programming. If an error occurs, the error message will be
displayed along with the addresses and data of the chip and buffer where the error
occurred. Any other result will be displayed in the message section. The current address
is incremented in the Current Address display window while the chip is being
programmed or verified.
Read
The function reads the content of the chip into the buffer. After reading is complete,
checksum of the data will be displayed at the lower-left corner of the screen. If the chip
selected is either a PLD or GAL, blow count will be shown instead of the checksum.
When a GAL is programmed, the sub-device should be specified correctly.
For PROM or MCU devices, the data between the chip start address and end address will
be read into the buffer.
If the chip is protected or secured, data read will be incorrect or shown as blank.
Page 16

Verify
The function compares the content of the buffer to that of the chip. If there is any
discrepancy, verify failure message and the address where it started failing will be
displayed in the Message window. For PROM or MCU devices, verification of range
between start and end addresses (specified by you) is available.
Blank Check
The function checks if the device is in blank state. For a ROM or MCU, checking of a
range between a start and end address (specified by you) is possible.
Data Compare
The function compares Buffer and Chip contents and for any discrepancy it finds data
table is generated and store in the BIN directory in the name of the device.cmp. For
example, if the device is AMD 27256, the file name will be 27256.CMP.
Auto
The function executes series of operations in sequence, which should help with repeat
operation. Blank check, Program, and Verify could be included in the function. List of
the functions may be put together using the Edit Auto menu.
For GAL devices it executes the Erase function at the beginning and sets the security bits
at the end.
Security
The function applies to PLDs and MCUs equipped with security function. If the security
is set, the data programmed into a chip will not be read correctly.
Note: Lock and Protect are also names used for the same purpose.
Encryption
The function applies only to some MCU chips with the feature. This will program the
content of the encryption table onto the encryption array of the chip. The content of the
encryption table can be loaded, edited and saved. Once encryption is completed, the data
in the main buffer will be the Exclusive-NORed data with the encryption table.
Message
Result of the operation and any error message is displayed in the message area.
Environment
It displays the selected manufacturer (MFR), device name (Device), checksum
(Checksum) for HEX files, and blow count (Blow Count) for JED file, etc.
Chip Start
Input an address of the chip where you would like a selected function of downloading or
uploading to start. This is normally set to zero.
Page 17

Chip End
Input an address for the chip where you would like a selected function of downloading or
uploading to end. This is normally set to the end address of the chip.
Buff Start
This sets the address in the buffer where file loading begins. By changing the address, a
file can be loaded at any desired location.
Buff End
This sets address in the buffer where file loading ends. By changing the address, a file
can end loading at any desired location.
Note: Chip Start, Chip End, Buff Start, and Buff End, are used in multiple file
loading and offset programming. Multiple loading allows the buffer to be filled with
different files at different location. Offset programming allow the chip start address toi
be other than at zero.
2.3.2 EditAuto
Functions included in the Auto menu may be edited using the EditAuto menu. In the
Edit-Auto dialog box double click on the functions listed in the left column to be
included in the Auto sequence. New Auto sequence is created and saved as a file.
Figure 16. Edit Auto
2.3.3 Select( Device)
This selection brings up the Select Device dialogue box, which includes Manufacturer
List viewer, Device List viewer, Type radio button, OK and Cancel buttons and Search
Page 18

Edit box. When the highlighted cursor is placed over a name of the manufacturer, names
of the devices for the manufacturer selected will be displayed instantly in the Device
column.
Type radio button allows you to select one of the different device types, such as,
E/EPROM, PLD, MCU,etc. Select the device type first before selecting Manufacturer of
a device.
Search Edit box allows you to search device quickly.
Figure 17. Select Device
2.3.4 Word Format
Page 19

The Word Format window allows you to specify the data format loaded into the buffer.
The default setting is Byte format. Word or Double Word format may be selected. For
programming into byte- wide chip further selection to byte level is needed.
Byte
8-bit data format is selected.
Even Word
In the 16 bit word format, selection of Even Word will program only the even data bytes
For example, if the data is;
buffer address 00 01 02 03 04 05 06
buffer data 01 23 45 67 89 AB CD
Result after programming will be;
device address 00 01 02 03 …
device data 01 45 89 CD …
Odd Word
In the 16 bit word format, selection of Odd Word will program only the odd data bytes
For example, if the data is;
buffer address 00 01 02 03 04 05 06
buffer data 01 23 45 67 89 AB CD
Result after programming will be;
device address 00 01 02 03 …
device data 23 67 AB …
In the Double Word format, there are four bytes to be selected from
For example,
buffer address 00 01 02 03 04 05 06 07 08 09 0A 0B
buffer data 01 23 45 67 89 AB CD EF FE DC BA 98
Double Word 0 selection will process the data at addresses 00, 04, 08,.. for reading,
verifying, and programming, which are 01 89 FE.
Double Word 1selection will process the data at locations 01, 05, 09,..which are 23,
AB, DC.
Double Word 2 selection will process the data at locations 02, 06, 0A,.. which are 45,
CD, BA,..
Double Word 3 selection will process the data at addresses 03, 07, 0B, which are 67 EF
98.
Page 20

Figure 18. Word Format
2.4. Test: <Alt-T>
The SUPERPROs can test logic ICs and RAM devices, as well as perform vector testing
on PLDs. The user-friendly software provides an easy interface for loading files, editing
test patterns, and downloading and uploading data between the buffer and the device.
The SUPERPROs provide a 74/54 and 4000/45000 TTL/CMOS logic device test library,
and memory test algorithms. Following sections describe the functions available for
testing logic ICs and RAMs.Tests are performed by applying the input(s) specified in the
test pattern (see below) and checking for the specified output(s). Up to 291 I/O
combinations can be specified in a test pattern, allowing quite complex devices to be
tested.
2.4.1 New Pattern
To test a new device that is not included in TTL.LIB, a new test pattern may be created.
To access this function, click on the Test menu from the main screen, and then click on
New Pattern. This selection brings up the Append dialogue box, which consists of IC
Type input line, Pin Number input line, and the OK and Cancel buttons. You can input
the new IC name and number of pins in the input lines. If the name and the number of
pins is not in the current library, pressing OK will open the XXXX edit window (XXXX
is the new device name that was entered). Refer to the following when editing a pattern.
The following symbols are used throughout the sub-menus of Test:
V: Vcc pin
G: GND (Ground) pin
X: Unused or power pin; output values will not be tested
H: Output Logic High (Voh)
Page 21

L: Output Logic Low (Vol)
C: Clock pin
1: Input Logic High (Vih)
0: Input Logic Low (Vil)
2.4.2 Edit Pattern
This selection is used for editing a test pattern in the library. When you are in the Test
menu, click on Edit Pattern. This brings up the Select Chip to Edit dialogue box. It
consists of Select Type input line, a Device List viewer, and the OK and Cancel buttons.
You can enter the device name into the input line, or select from the list viewer. Upon
acceptation of the device name, the software opens the edit window with the name of the
device at the top. You may now use the above information to edit your pattern.
Figure20 .Edit Pattern
2.4.3 Delete Pattern
This selection deletes a test pattern in the library. Click on the Delete Pattern sub-menu
in the Test menu. This will bring up the Select Chip to Delete dialogue box. Highlight
the test pattern you wish to delete and click on the OK button. The test pattern will be
Page 22

deleted and you will return to the main menu. Make sure you have made the correct
selection. The only way to retrieve a deleted test pattern is to recreate the pattern (using
'New Pattern').
2.4.4 TTL&CMOS test
This selection tests TTL and CMOS devices. Click on the sub-menu TTL & CMOS
Test in the Test menu. This will open the Select Chip to Test dialogue box. Highlight
the device that you wish to test, and then click on the OK button. The result of the test
will be displayed in the window Test TTL, which will appear after clicking the OK
button in the Select Chip to Test dialogue box. If the device passes the test, a 'passed'
test message will be displayed. If the test fails, information about where it failed is
displayed. If you want to repeat the test, click on the Repeat button. Otherwise click on
the Cancel button.
2.4.5 Auto Find Device
This selection finds the name of an unknown device. Click on the sub-menu Auto Find
Device. This will initiate a search for the device type in the socket. The device name
found will be listed in the list viewer, List of Detected Chips, if the device can be listed.
If the device cannot be found, it will display an error message, No chip found. Only the
devices which are registered in the programmer may be found.
2.4.6 Vector Test
To perform vector test of a PAL/PLD device inserted into the programmer, click on the
Vector Test sub-menu in the Test menu. This will initiate the test procedure and open
up the Test Vector window. Here, the result of the testing will be displayed. Test vector
for the programmed device in the socket must be loaded into the buffer prior to the test.
2.5 Options: <Alt-O >
The menu deals with optional settings such as parallel port address and path for the
software.
.
2.5.1 Setting
This menu deals with optional settings, such as communication, and specifying paths for
the software. This selection brings up the Setting dialogue box, which consists of the
Directory, CPU Speed, and other options depending on the programmer. Grayed area is
not selectable for the model.
Directory: You may change where the files and libraries are located. User will have a
chance to set this at time of the installation.
CPU Speed: On some early PCs, the parallel port is unable to keep up with the data rate
normally used to communicate with the programmer hardware. In this case you should
set the speed to Low in CPU Speed.
Page 23

Option: Check Insertion Test if you want the programmer to do an insertion test before
any operation on the device. Check Beeper if you want the programmer to beep after any
operation. .
Initialize Programmer: Clicking on communication will search the programmer through
all possible parallel port. If it finds the programmer, the communication will be
successful. If not, Error message will appear.
Data Buffer Clear: If checked, buffer will be cleared each time IC is changed or when
loading new data from disk. Normally, this should be checked. For multiple file load, it
should be unchecked.
2.5.2 Auto Increment (model dependant)
The function allows serial number or signature to be embedded into EPROM or MCU
devices automatically.
The selection brings up the Auto Increment set dialogue box. You can set Auto start and
Auto end addresses in the buffer, you can also set increment value with any number less
than 10. The increment format allows increment as Binary, ASCII HEX and ASCII
Decimal. If you want to change the current increment data, open the data edit window and
enter data.
For example, suppose you want to program 64 ea chips with IDs of from XT00 to X63 at
end of EPROM locations of 87C51. 4 bytes of decimal format is selected.
a) Click Option > Auto Increment
b) Set Start to FFC and End to FFF
c) Set IncValue to 1
d) Set Format to ASCII Decimal
e) Check out Enable Auto Increment
f) Go into Buffer Edit screen at ASCII zone. Change buffer as follows:
FFC : X FFD: T FFE: 0 FFF: 0
Page 24

e) Start programming.
Figure 21 .Auto Increment
2.5.3 Load config file
Operational Configuration is created automatically during operation and saved as a file in
the BIN directory. When the program is started the file is loaded automatically to restore
the previous operational status, which includes device related information, parallel port
and other setup information. The file may be edited and saved for later use.
2.5.4 Save config file
The selection brings up the Save Config File dialogue box. Edited config file may be
saved .
3.Appendices
3.1 Customer Support
Calling For Customer Support
Page 25

XELTEK software has been designed to require a minimum of technical support. The
program comes with a comprehensive User's Guide. If you cannot find the answer in the
manual, you can turn to your dealer, or distributor, or to XELTEK.
XELTEK Technical Support:
Should your local distributor be unable to solve your problem, XELTEK provides
telephone technical assistance during normal business hours (8:00 am to 6:00 p.m. EST).
Have your invoice number ready when calling, as we cannot answer your questions
without it. To help us serve you better, please review the check list on the following page
prior to placing your call. Software updates are available free from the web site.
XELTEK
3444 De La Cruz Blvd, Santa Clara, CA 95054, U.S.A.
Tel: 1- 408-5889940
Fax: 1-408-5889944
E-mail: info@xeltek.com
Web: http://www.xeltek.com
Pre-call Check List
If you're having difficulty understanding the program, have you studied the User's Guide?
The manual explains the program operation in some depth.
If there seems to be a problem with the software, can you reproduce it?
If the program has displayed an error message, please write down the message.
When phoning or faxing or e-mailing for technical assistance, have your invoice number
ready (or quote it in written correspondence).
Be familiar with the hardware configuration that you are using. We may need to know
the brand/model of your computer, the total amount of memory available when starting
up the software, your graphics adapter and version of the Disc Operating System .
If possible, call our Customer Support Department while you are at your computer. Be
prepared to repeat the sequence of steps leading up to the problem.
License Agreement
The purchaser is granted a non-exclusive license to use the program on a single computer,
subject to the terms and restrictions set fourth in this agreement. This license is not a
sale. The copyright of the program and User's Guide remain the property of XELTEK.
You may:
Copy the program for back-up purposes ONLY in support of its use on a single computer.
Transfer the program from computer to computer, provided that it is not operated on
more than one computer at a time.
Transfer the program and license to another party if the other party agrees to accept the
terms and conditions of this agreement. If you transfer the program, you must either
transfer all copies to the same party, or destroy any copies not transferred.
You may not:
Use this product in a computer system or network, which allows the program to be
operated by more than one user at a time.
Page 26

Modify, copy, or transfer the User's Guide, other documentation or any copy.
Reverse engineer, decompile, or disassemble any program module or security device.
This license is effective until terminated. You may terminate it by destroying or returning
the program, manuals, and all copies thereof. This license will terminate if you fail to
comply with any term or condition of this agreement.
Limited Warranty
XELTEK warrants that its products will be free from defects in workmanship and
materials, and shall conform to specifications current at the time of shipment, for a period
of one year from the date of shipment. During the one year period, any defective software
or hardware products will be repaired or replaced, at Seller's option, on a return to factory
basis.
This warranty applies only to products properly installed and operated within specified
environmental conditions.
XELTEK's responsibility under this warranty does not apply to:
(a) Any product which has been repaired, worked upon, or altered by any person not
duly authorized in writing by XELTEK; or
(b) Any product which has been subject to misuse, negligence or accident, or whose
serial number has been altered, defaced, or removed; or
(c) Any fault induced into the program by physical damage to the diskette or to the
corruption of the program by electronic or electrical or magnetic interference.
All efforts have been made to verify the proper operation of the software and the accuracy
of the User's Guide. XELTEK does not warrant that the operation of the program will be
uninterrupted or totally error free.
New features and enhancements to the existing programs may be added, and verified
program faults or necessary amendments will be rectified through the issue of periodic
software revisions. Notice of these may be sent to registered buyers only. Failure to
return the completed Software registration card with correct mailing address will exclude
the purchaser from automatically receiving notification of revisions to the program.
Software updates and revisions may be subject to a fee.
XELTEK does not accept liability for any damages, including loss of profit or savings,
other incidental or consequential damages arising out of the use, misuse, or inability to
use the program.
This warranty to repair or replace products not conforming to specification is specifically
in lieu of all other warranties expressed or implied including, without limitation (to the
extent permitted by law), the warranties of merchantability and fitness for use. No agent
or representative of XELTEK has any authority to bind XELTEK to any affirmation,
representation, or warranty concerning products made by XELTEK; and XELTEK will
have no liability whatsoever for any damage, loss, cost, or expense (whether direct,
special or consequential) suffered or incurred by buyer if products fail to conform with
XELTEK's warranty herein.
3.2 Error Messages
Page 27

3.2.1 Invalid File Type:
An input file with wrong format is selected. Please select right format for the
input file.
3.2.2 Init Programmer Error(Programmer initialization error):
Communication searches no programmer connected. Software only works in
demo mode. Make sure programmer powering on, search programmer with
communication (See Setting sub menu) again.
3.2.3 Algorithm file Not Found:
Every device has an algorithm file. After selecting the device, algorithm file will
be loaded (DLL file). If loading fails, this message will appear.
 Loading...
Loading...