Page 1

1050E-1404
Spark Series
SP-5000M-GE2
SP-5000C-GE2
5M Digital Progressive Scan
Monochrome and Color Camera
Document Version: Ver.1.3
SP-5000-GE2_Ver.1.3_Oct2014
User Manual
Page 2

SP-5000M-GE2 / SP-5000C-GE2
- 2 -
Notice
The material contained in this manual consists of information that is proprietary to JAI Ltd., Japan
and may only be used by the purchasers of the product. JAI Ltd., Japan makes no warranty for the
use of its product and assumes no responsibility for any errors which may appear or for damages
resulting from the use of the information contained herein. JAI Ltd., Japan reserves the right to
make changes without notice.
Company and product names mentioned in this manual are trademarks or registered trademarks of
their respective owners.
Warranty
For information about the warranty, please contact your factory representative.
Certifications
CE compliance
As defined by the Directive 2004/108/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council, EMC
(Electromagnetic compatibility), JAI Ltd., Japan declares that SP-5000M-GE2 and SP-5000C-GE2
comply with the following provisions applying to its standards.
EN 61000-6-3 (Generic emission standard part 1)
EN 61000-6-2 (Generic immunity standard part 1)
FCC
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class B digital device,
pursuant to Part 15 of the FCC Rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection
against harmful interference in a residential installation. This equipment generates, uses and can
radiate radio frequency energy and, if not installed and used in accordance with the instructions,
may cause harmful interference to radio communications. However, there is no guarantee that
interference will not occur in a particular installation. If this equipment does cause harmful
interference to radio or television reception, which can be determined by turning the equipment
off and on, the user is encouraged to try to correct the interference by one or more of the following
measures:
- Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna.
- Increase the separation between the equipment and receiver.
- Connect the equipment into an outlet on a circuit different from that to which the receiver is
connected.
- Consult the dealer or an experienced radio/TV technician for help.
Warning
Changes or modifications to this unit not expressly approved by the party
responsible for FCC compliance could void the user’s authority to operate the
equipment.
Page 3
SP-5000M-GE2
Supplement
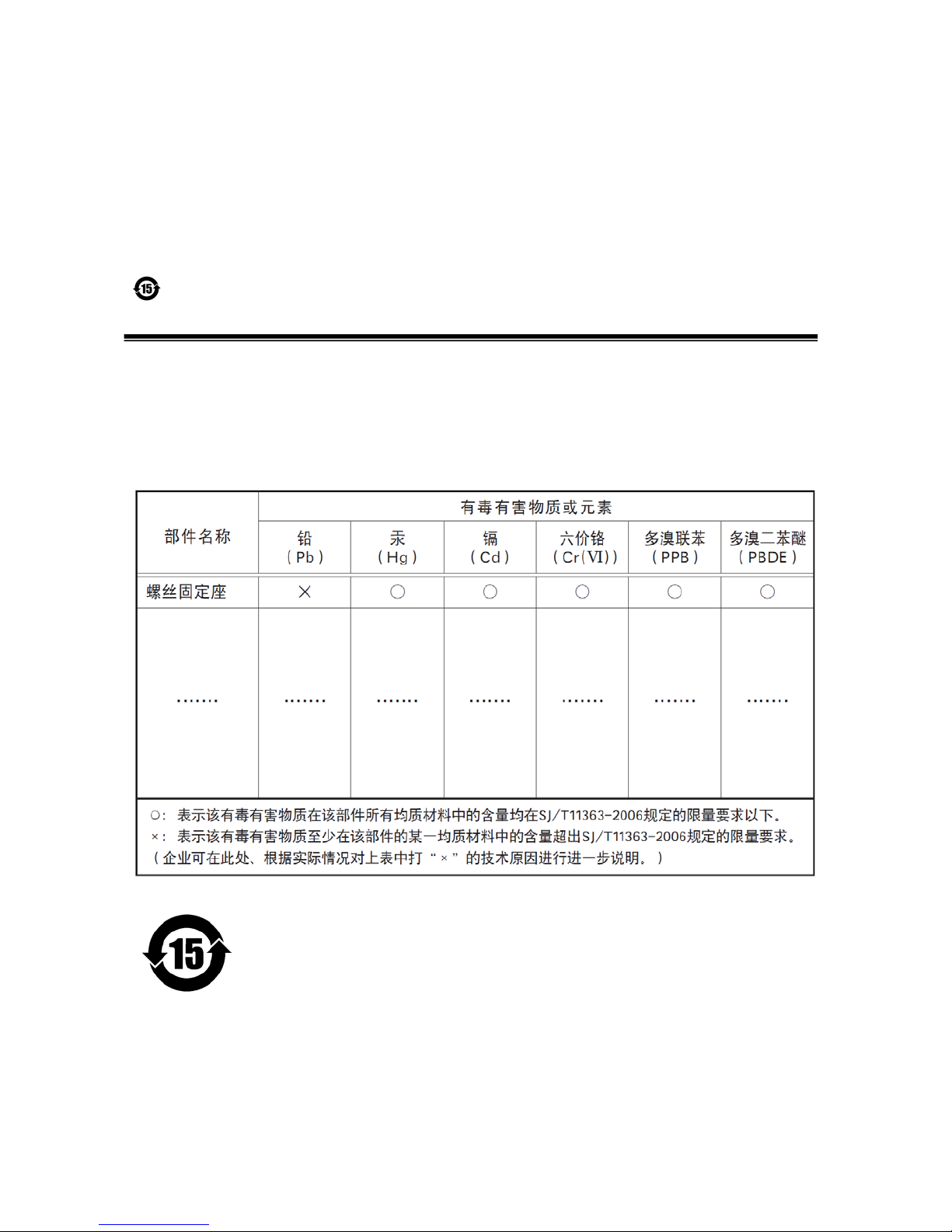
The following statement is related to the regulation on “ Measures for the Administration
of the control of Pollution by Electronic Information Products “ , known as “ China RoHS “.
The table shows contained Hazardous Substances in this camera.
mark shows that the environment-friendly use period of contained Hazardous
Substances is 15 years.
嶷勣廣吭並㍻
嗤蕎嗤墾麗嵎賜圷殆兆各式根楚燕
功象嶄鯖繁酎慌才忽佚連恢匍何〆窮徨佚連恢瞳麟半陣崙砿尖一隈〇云恢瞳ゞ 嗤蕎嗤
墾麗嵎賜圷殆兆各式根楚燕 〃泌和
桟隠聞喘豚㍉
窮徨佚連恢瞳嶄根嗤議嗤蕎嗤墾麗嵎賜圷殆壓屎械聞喘議訳周和音氏窟伏翌
亶賜融延、窮徨佚連恢瞳喘薩聞喘乎窮徨佚連恢瞳音氏斤桟廠夛撹冢嶷麟半
賜斤児繁附、夏恢夛撹冢嶷鱒墾議豚㍉。
方忖仝15々葎豚㍉15定。
Page 4
SP-5000C-GE2
Supplement
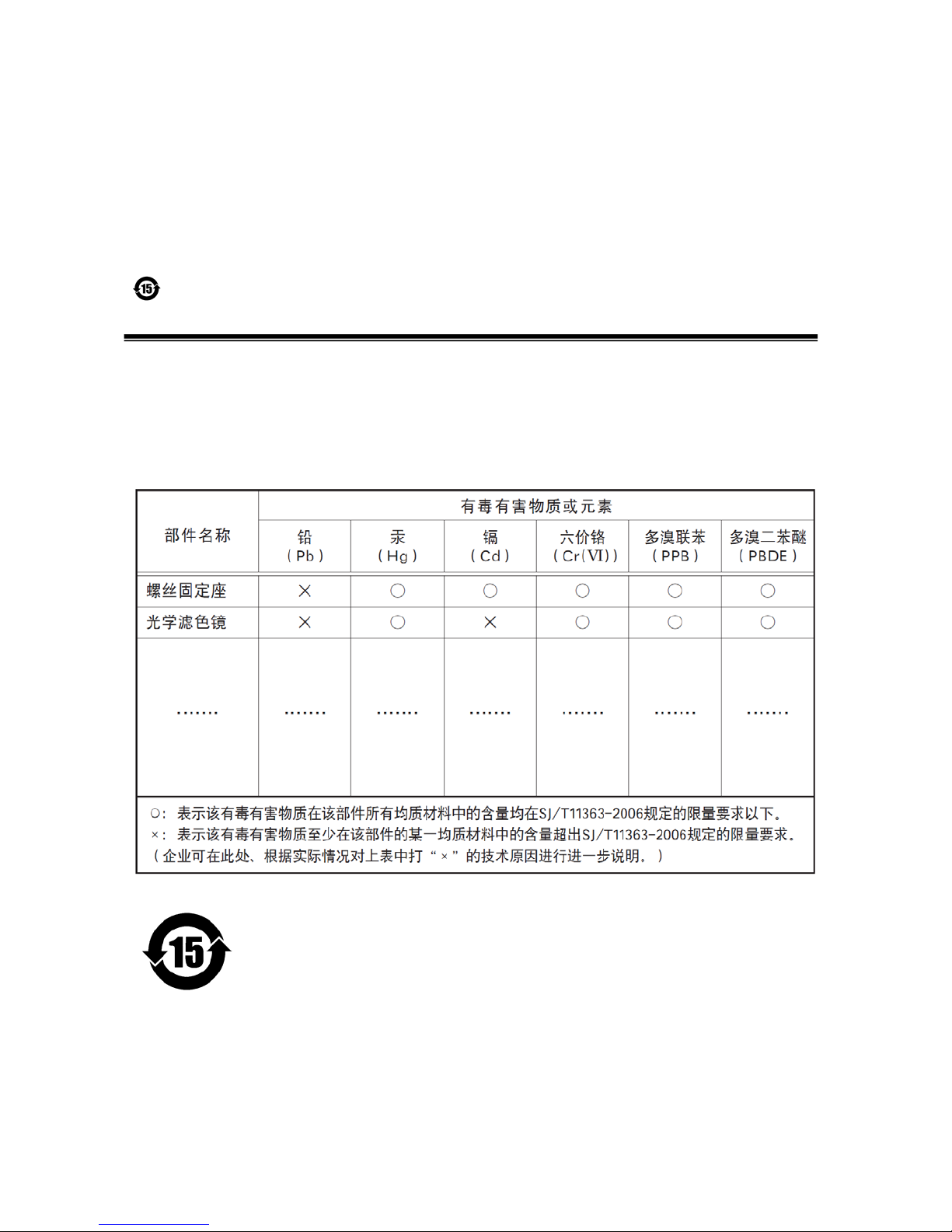
The following statement is related to the regulation on “ Measures for the Administration
of the control of Pollution by Electronic Information Products “ , known as “ China RoHS “.
The table shows contained Hazardous Substances in this camera.
mark shows that the environment-friendly use period of contained Hazardous
Substances is 15 years.
嶷勣廣吭並㍻
嗤蕎嗤墾麗嵎賜圷殆兆各式根楚燕
功象嶄鯖繁酎慌才忽佚連恢匍何〆窮徨佚連恢瞳麟半陣崙砿尖一隈〇云恢瞳ゞ 嗤蕎嗤
墾麗嵎賜圷殆兆各式根楚燕 〃泌和
桟隠聞喘豚㍉
窮徨佚連恢瞳嶄根嗤議嗤蕎嗤墾麗嵎賜圷殆壓屎械聞喘議訳周和音氏窟伏翌
亶賜融延、窮徨佚連恢瞳喘薩聞喘乎窮徨佚連恢瞳音氏斤桟廠夛撹冢嶷麟半
賜斤児繁附、夏恢夛撹冢嶷鱒墾議豚㍉。
方忖仝15々葎豚㍉15定。
Page 5

SP-5000M-GE2 / SP-5000C-GE2
- 3 -
- Contents -
Introduction ..................................................................................... - 7 -
Before using GigE Vision® camera .......................................................... - 7 -
1 JAI GigE Vision® camera operation manuals ........................................................ - 7 -
2 Software installation ................................................................................... - 7 -
3 About GigE Vision Ver2.0 .............................................................................. - 7 -
4 Recommended PC to be used ......................................................................... - 8 -
5 About the network card to be used ................................................................. - 8 -
6 Cables to be used ....................................................................................... - 8 -
7 EMVA 1288 ................................................................................................ - 8 -
Camera Operation Manual ................................................................... - 9 -
1. General ..................................................................................... - 9 -
2. Camera composition .................................................................... - 9 -
3. Main features .......................................................................... - 10 -
4. Locations and functions ............................................................. - 11 -
4.1 Locations and functions ............................................................................- 11 -
4.2 Rear panel ............................................................................................- 12 -
5. Input and output .......................................................................... - 13 -
5.1 GigE interface .......................................................................................- 13 -
5.1.1 GigEVision 2.0 interface extension .........................................................- 13 -
5.1.1.1 Link Aggregation ..........................................................................- 13 -
5.1.1.2 PTP (IEEE 1588-2008: Precision Time Protocol) ....................................- 15 -
5.1.1.3 Manifest ....................................................................................- 15 -
5.1.1.4 Notes for connecting 100BASE-TX......................................................- 16 -
5.1.1.5 Example of setting method of Link Aggregation .....................................- 16 -
5.2 Connectors and pin assignment ...................................................................- 30 -
5.2.1 Output connector for Gigabit Ethernet ....................................................- 30 -
5.2.2 12-Pin connector ..............................................................................- 30 -
5.2.3 AUX Standard Hirose 10-Pin connector ................................................- 31 -
5.2.3.1 Figure and pin configuration ............................................................- 31 -
5.2.4 AUX Type 2 HIROSE 10-Pin connector (factory option) ..................................- 31 -
5.2.5 AUX Type 3 HIROSE 10-Pin connector (factory option) ................................- 32 -
5.3 Digital IN/OUT interface ...........................................................................- 32 -
5.3.1 Line Selector ....................................................................................- 32 -
5.3.2 Line Source......................................................................................- 32 -
5.3.3 Line Mode .......................................................................................- 34 -
5.3.4 Line Inverter ....................................................................................- 34 -
5.3.5 Line Status ......................................................................................- 34 -
5.3.6 Line Format .....................................................................................- 34 -
5.3.7 GPIO ..............................................................................................- 34 -
5.3.7.1 Basic block diagram ......................................................................- 34 -
5.3.7.2 IN and OUT matrix table.................................................................- 36 -
5.4 Optical Interface .....................................................................................- 37 -
5.4.1 Recommended External Input circuit diagram for customer ...........................- 37 -
5.4.2 Recommended External Output circuit diagram for customer .........................- 37 -
5.4.3 Characteristics of optical interface .......................................................- 38 -
5.5 Pulse Generator .....................................................................................- 38 -
5.5.1 Clock Pre-scaler ................................................................................- 39 -
5.5.2 Pulse Generator Selector .....................................................................- 39 -
5.5.3 Pulse Generator Length .......................................................................- 39 -
5.5.4 Pulse Generator Start Point ..................................................................- 40 -
Page 6

SP-5000M-GE2 / SP-5000C-GE2
- 4 -
5.5.5 Pulse Generator End Point ................................................................... - 40 -
5.5.6 Pulse Generator Repeat Count .............................................................. - 40 -
5.5.7 Pulse Generator Clear Activation ........................................................... - 40 -
5.5.8 Pulse Generator Clear Sync Mode ........................................................... - 40 -
5.5.9 Pulse Generator Clear Source ............................................................... - 41 -
5.5.10 Pulse Generator Inverter.................................................................... - 42 -
5.5.11 Pulse Generator Setting Parameters ...................................................... - 42 -
6. Sensor layout, output format and timing ......................................... - 43 -
6.1 Sensor layout ........................................................................................ - 43 -
6.1.1 Monochrome sensor ........................................................................... - 43 -
6.1.2 Bayer color sensor............................................................................ - 43 -
6.2. Camera output format ............................................................................ - 44 -
6.2.1 1X-1Y ............................................................................................. - 44 -
6.2 GigE Vision Pixel Format ........................................................................... - 44 -
6.2.1 Pixel Format .................................................................................... - 44 -
6.2.2 SP-5000M-GE2 Pixel Type ..................................................................... - 45 -
6.2.2.1 GVSP_PIX_MONO8 8-bit output ....................................................... - 45 -
6.2.2.2 GVSP_PIX_MONO10 16-bit output .................................................... - 45 -
6.2.2.3 GVSP_PIX_MONO10PACKED 12-bit output .......................................... - 45 -
6.2.3 SP-5000C-GE2 Pixel Type ..................................................................... - 45 -
6.2.3.1 GVSP_PIX_BAYGR8 8-bit output ...................................................... - 45 -
6.2.3.2 GVSP_PIX_BAYGR10 16-bit output ................................................... - 45 -
6.2.3.3 GVSP_PIX_BAYGR10PACKED 12-bit output .......................................... - 46 -
6.2.3.4 GVSP_PIX_RGB8_PACKED (24-bit) ......................................................... - 46 -
6.2.3.5 GVSP_PIX_YUV411_Packed 12-bit output ........................................... - 46 -
6.2.3.6 GVSP_PIX_YUV422_Packed 16-bit output ........................................... - 46 -
6.2.3.7 GVSP_PIX_YUV444_Packed 24-bit output ......................................... - 46 -
6.2.4 PixelSize ......................................................................................... - 47 -
6.3 Output timing ....................................................................................... - 47 -
6.3.1 Horizontal timing .............................................................................. - 47 -
6.3.1.1 Output format: 1X–1Y, Vertical Binning OFF ......................................... - 47 -
6.3.1.2 Output format: 1X–1Y, Vertical Binning ON .......................................... - 47 -
6.3.2 Vertical timing ................................................................................. - 48 -
6.3.2.1 Output format: 1X–1Y, Vertical Binning OFF ......................................... - 48 -
6.3.2.2 Output format: 1X–1Y, Vertical Binning ON .......................................... - 48 -
6.3.3 ROI (Region Of Interest) setting ............................................................. - 49 -
6.4 Digital output Bit allocation .................................................................... - 49 -
7. Operating modes ...................................................................... - 50 -
7.1. Acquisition control (change the frame rate) .................................................. - 50 -
7.1.1 Acquisition Mode ............................................................................... - 50 -
7.1.1.1 Single Frame operation .................................................................. - 50 -
7.1.1.2 Multi Frame operation ................................................................... - 54 -
7.1.1.3 Continuous ................................................................................. - 58 -
7.1.2 Acquisition frame rate ........................................................................ - 62 -
7.1.3 Calculation of frame rate .................................................................... - 62 -
7.1.3.1 Calculation of sensor output maximum frame rate ................................... - 62 -
7.1.3.2 Calculation of frame rate of network bandwidth ...................................... - 63 -
7.2. Exposure settings .................................................................................. - 64 -
7.2.1 Exposure Mode ................................................................................. - 64 -
7.2.2 Exposure Time .................................................................................. - 65 -
7.2.3 Exposure Auto .................................................................................. - 65 -
7.3. Trigger Control ..................................................................................... - 66 -
7.3.1 Trigger Selector ................................................................................ - 66 -
Page 7

SP-5000M-GE2 / SP-5000C-GE2
- 5 -
7.3.2 Trigger Mode ....................................................................................- 66 -
7.3.3 Trigger Source ..................................................................................- 66 -
7.3.4 Trigger activation ..............................................................................- 67 -
7.3.5 Trigger Overlap .................................................................................- 67 -
7.4. Normal continuous operation (Timed Exposure Mode/Trigger Mode OFF) ................- 68 -
7.5. Timed mode .........................................................................................- 68 -
7.5.1 If the overlap setting is “OFF” ..............................................................- 68 -
7.5.2 If the overlap setting is “Readout” .........................................................- 69 -
7.6. Trigger width mode ................................................................................- 69 -
7.6.1 If the overlap setting is “OFF” ..............................................................- 69 -
7.6.2 If the overlap setting is “Readout” .........................................................- 70 -
7.7. RCT mode ............................................................................................- 71 -
7.8. PIV (Particle Image Velocimetry) ................................................................- 72 -
7.9. Sequence ROI Trigger ..............................................................................- 73 -
7.9.1 Video send mode ...............................................................................- 73 -
7.9.2 Trigger Sequence mode basic timing .......................................................- 74 -
7.9.3 Sequence ROI setting parameters ...........................................................- 74 -
7.9.3.1 Sequence index table (Default) ........................................................- 74 -
7.9.3.2 Descriptions of index table parameters ..............................................- 74 -
7.10 Multi ROI function .................................................................................- 76 -
7.10.1 Multi ROI setting parameters ...............................................................- 77 -
7.11. Operation and function matrix .................................................................- 78 -
8. Other functions ........................................................................ - 79 -
8.1 Black level control ..................................................................................- 79 -
8.1.1 Black Level Selector ...........................................................................- 79 -
8.1.2 Black Level ......................................................................................- 79 -
8.2 Gain control ..........................................................................................- 79 -
8.2.1 Gain Selector ...................................................................................- 80 -
8.2.2 Gain ..............................................................................................- 80 -
8.2.4 Gain Auto ........................................................................................- 80 -
8.2.5 Balance White Auto ............................................................................- 81 -
8.3. LUT ...................................................................................................- 81 -
8.3.1 LUT Enable ......................................................................................- 81 -
8.3.2 LUT Index ........................................................................................- 82 -
8.3.3 LUT value ........................................................................................- 82 -
8.4. Gamma ...............................................................................................- 82 -
8.4.1 Linear and Dark Compression ................................................................- 82 -
8.5. Shading Correction .................................................................................- 83 -
8.6. Blemish compensation ............................................................................- 84 -
8.7. Bayer color interpolation (Only for SP-5000C-GE2) ..........................................- 84 -
8.8 Lens control ..........................................................................................- 85 -
8.8.1 About P-Iris .....................................................................................- 85 -
8.8.2 Setting for P-iris lens being used ............................................................- 86 -
8.8.2.1 P-Iris lens select ..........................................................................- 86 -
8.8.2.2 Step max. ..................................................................................- 86 -
8.8.2.3 Position .....................................................................................- 86 -
8.8.2.4 Current F value ...........................................................................- 86 -
8.8.2.5 P-Iris Auto min. / P-Iris Auto max. .....................................................- 86 -
8.8.3 Motorized lenses ...............................................................................- 86 -
8.8.3.1 Iris ...........................................................................................- 86 -
8.8.3.2 Zoom ........................................................................................- 87 -
8.8.3.3 Focus+ ......................................................................................- 87 -
8.9 ALC ....................................................................................................- 87 -
Page 8

SP-5000M-GE2 / SP-5000C-GE2
- 6 -
8.10 HDR (High Dynamic Range) (SP-5000M-GE2 only) ............................................ - 88 -
9. Camera setting ......................................................................... - 89 -
9.1 Camera Control Tool ................................................................................ - 89 -
9.2 Camera Default Setting ............................................................................ - 89 -
10. External appearance and dimensions .......................................... - 90 -
11. Specifications ......................................................................... - 91 -
11.1 Spectral response ................................................................................. - 91 -
11.2 Specifications table ............................................................................... - 92 -
Appendix ....................................................................................... - 95 -
1. Precautions ............................................................................................. - 95 -
2. Typical Sensor Characteristics ....................................................................... - 95 -
3. Caution when mounting a lens on the camera ................................................... - 95 -
4. Caution when mounting the camera ............................................................... - 96 -
5. Exportation ............................................................................................. - 96 -
6. References .............................................................................................. - 96 -
Manual change history ...................................................................... - 97 -
User's Record ................................................................................. - 98 -
Page 9
SP-5000M-GE2 / SP-5000C-GE2
- 7 -
Introduction
Before using GigE Vision® camera
All software products described in this manual pertain to the proper use of JAI GigE Vision® cameras.
Product names mentioned in this manual are used only for the explanation of operation. Registered
trademarks or trademarks belong to their manufacturers.
To use the JAI SDK, it is necessary to accept the “Software license agreement” first.
This manual describes necessary equipment and the details of camera functions.
1 JAI GigE Vision® camera operation manuals
To understand and operate this JAI GigE Vision camera properly, JAI provides the following manuals.
User’s manual (this booklet) Describes functions and operation of the hardware
JAI SDK & Control Tool User Guide Describes functions and operation of the Control Tool
JAI SDK Getting Started Guide Describes the network interface
User’s manual is available at www.jai.com
2 Software installation
The JAI GigE Vision SDK & Control Tool can be downloaded from the JAI web site at www.jai.com.
The JAI SDK is available for Windows XP, Vista, and Windows 7, 32-bit and 64-bit.
For the details of software installation, please refer to the “Getting Started Guide” supplied on the
JAI SDK download page.
Important: Please note that if you use LAG function, refer to the chapter 5.1.1.5 first.
It explains the order to install NIC driver and SDK.
3 About GigE Vision Ver2.0
SP-5000-GE2 complies with the latest GigE Vision version 2.0. GigE Vision is the new standard
interface using Gigabit Ethernet for machine vision applications and it was mainly set up by AIA
(Automated Imaging Association) members. GigE Vision is capable of transmitting large amounts of
uncompressed image data through an inexpensive general purpose LAN cable for a long distance.
GigE Vision also supports the GenICamTM standard which is mainly set up by the EMVA (European
Machine Vision Association). The purpose of the GenICam standard is to provide a common program
interface for various machine vision cameras. By using GenICam, cameras from different
manufactures can seamlessly connect in one platform.
As a new extension of standards, GigE Vision Ver.2.0 employs Link Aggregation which combines two
independent ports and identifies these as one port, making much higher transfer rates possible; PTP
(IEEE 1588) which provides more precise time management; and Manifest which enables either GigE
Vision Ver.1.X or Ver.2.0 on demand. SP-5000-GE2 complies with those extensions. For the details,
please refer to Chapter 5.1.
For details about the GigE Vision standard, please visit the AIA web site,
www.machinevisiononline.org and for GenICam, the EMVA web site, www.genicam.org.
Page 10
SP-5000M-GE2 / SP-5000C-GE2
- 8 -
4 Recommended PC to be used
The PC used should have the following performance or better
1) Recommended CPU : Core i3 or better,
2) Recommended memory: DDR3, 4GB fully equipped (Windows 7 32-bit)
DDR3, 8GB fully equipped (Windows 7 64-bit)
3) Graphics card : Should apply with PCI Express Generation 3.0 or better
4) NIC : Use Intel NIC
PCI-Express Bus to install Intel NIC should be better than Generation 2.0.
Generation 1.0 cannot be used.
5) Other: If the picture is always displayed on the monitor, it is not recommended to use
the CPU in the PC.
5 About the network card to be used
SP-5000-GE2 complies with Link Aggregation which handles two ports as one port. To make the best
use of this function, the network card used should comply with 1000BASE-T as well as Link
Aggregation. It also complies with Jumbo Frame. If Jumbo Frame is set to a large value, the PC
processing load can be reduced. The packet overhead is also reduced and as the result, the
bandwidth of the communication line has more room.
Table1. NIC
NIC
manufacturer
Model
PCI-Express Bus
Data
Intel
PRO/1000PT, dual port
Server Adapter
( x4 )
Intel
Gigabit ET2, Quad port
Server Adapter
( x4 )
10 Gbps uni-directional
20 Gbps bi-directional
Intel
i340-T4, Quad port
Server Adapter
( x4 )
Note: Intel Pro/1000PT Quad does not comply with Link Aggregation.
6 Cables to be used
GigEVision configures the system by using 1000BASE-T.
In the market, CAT5e (125MHz), CAT6 (250MHz) and CAT7 (600MHz) cables are available for
1000BASE-T. There are crossover cables and straight through cables available. Currently, as most
equipment complies with Auto MDI/MDI-X, please use straight through cables. (Among crossover
cables, a half crossover type exists, which the Ethernet will recognize as 100BASE-T).
7 EMVA 1288
With regard to signal to noise ratio in this manual, specifications measured by EMVA 1288 are used
together with specifications by a traditional measurement method.
EMVA 1288 is a more complete measurement that considers multiple noise sources, including
random noise, pattern noise, and shading. Additionally, EMVA 1288 incorporates temporal variances
in pixel output by capturing 100 frames of data and computing the RMS variations over the captured
frames. Because of the comprehensive nature of the noise analysis and the additional consideration
for RMS variances over time, EMVA 1288 SNR measurements are inherently lower than the traditional
SNR measurements given by manufacturers. However, the comprehensive nature combined with
rigid test parameters, means that all manufacturers are measuring their products equally and EMVA
1288 tested parameters can be compared among different manufacturers’ products.
In order to learn more about EMVA 1288, please visit http://www.emva.org
Page 11

SP-5000M-GE2 / SP-5000C-GE2
- 9 -
Camera Operation Manual
1. General
The SP-5000M-GE2 and SP-5000C-GE2 are among the first new Spark Series cameras to be
introduced. They are high performance cameras with high resolution and a fast frame rate suitable
for high speed machine vision applications. The SP-5000M-GE2 is a monochrome progressive scan
CMOS camera and the SP-5000C-GE2 is the equivalent Bayer mosaic progressive scan CMOS camera.
Both are equipped with a CMOS sensor offering a 1-inch optical format, a resolution of 5.24 million
pixels, and a 5:4 aspect ratio. They provide up to 44 frames per second for continuous scanning
with 2560 x 2048 full pixel resolution for both monochrome and raw Bayer output.
8-bit or 10-bit output can be selected for both monochrome and raw Bayer formats. The
SP-5000C-GE2 is also capable of performing in-camera color interpolation at reduced frame rates.
The new cameras feature a GigE Vision Ver. 2.0 interface which has a new Link Aggregation (LAG)
extension. LAG handles two ports as one port and this function enables higher data transfer rates
in an Ethernet environment.
The SP-5000M-GE2 and SP-5000C-GE2 have various comprehensive functions needed for automated
optical inspection applications, such as solid state device inspection or material surface inspection.
They incorporate video processing functions such as a look-up table, shading compensation and
blemish compensation in addition to fundamental functions such as trigger, exposure setting and
video level control.
As a common Spark Series feature, a new connector for lens control is employed. SP-5000M-GE2 and
SP-5000C-GE2 support P-iris and motor-driven lenses as standard lens control capabilities. Factory
options are available to configure this connector to support DC iris systems, as well as provide a
video iris output signal, or to provide additional TTL IN and OUT lines.
The latest version of this manual can be downloaded from: www.jai.com
The latest version of the Camera Control Tool for the SP-5000M-GE2 and SP-5000C-GE2 can be
downloaded from: www.jai.com
For camera revision history, please contact your local JAI distributor.
2. Camera composition
The standard camera composition is as follows.
Camera body 1
Sensor protection cap 1
Dear Customer (sheet) 1
The following optional accessories are available.
Tripod base
MP-42
Power supply unit
PD-12 series
Page 12

SP-5000M-GE2 / SP-5000C-GE2
- 10 -
3. Main features
New Spark Series, 1” progressive scan camera
Intelligent body design for easy and flexible installation
Utilizes new GigE Vision ver.2.0
Aspect ratio 5:4, 2560(H) x 2048(V) - 5.2 million effective pixels
5 μm square pixels
S/N 55 dB for monochrome and 53 dB for color
8-bit or 10-bit output for monochrome and Bayer
In-camera color interpolation choices include 3 x 8-bit RGB, YUV411, YUV422, or YUV444
44 frames/second with full resolution in continuous operation (2 ports, 8-bit)
Various readout modes, including horizontal and vertical binning (SP-5000M-GE2 only) and
ROI (Region Of Interest) for faster frame rates
0 dB to +24 dB gain control for both SP-5000M-GE2 and SP-5000C-GE2
10 μs (1/100,000) to 8 seconds exposure control in 1 μs step
Auto exposure control
Timed and trigger width exposure control
RCT and PIV trigger modes for specific applications
ALC control with combined function of AGC, auto exposure and auto iris
HDR (High Dynamic Range) function is available (SP-5000M-GE2 only)
Various pre-processing circuits are provided
Programmable LUT
Gamma correction from 0.45 to 1.0
Shading correction
Bayer white balance with manual or one-push auto (SP-5000C-GE2 only)
Blemish compensation
New Hirose 10P connector for lens interface including P-Iris lens control
C-mount for lens mount
Setup by Windows XP/Vista/7/8 via serial communication
Page 13
SP-5000M-GE2 / SP-5000C-GE2
- 11 -
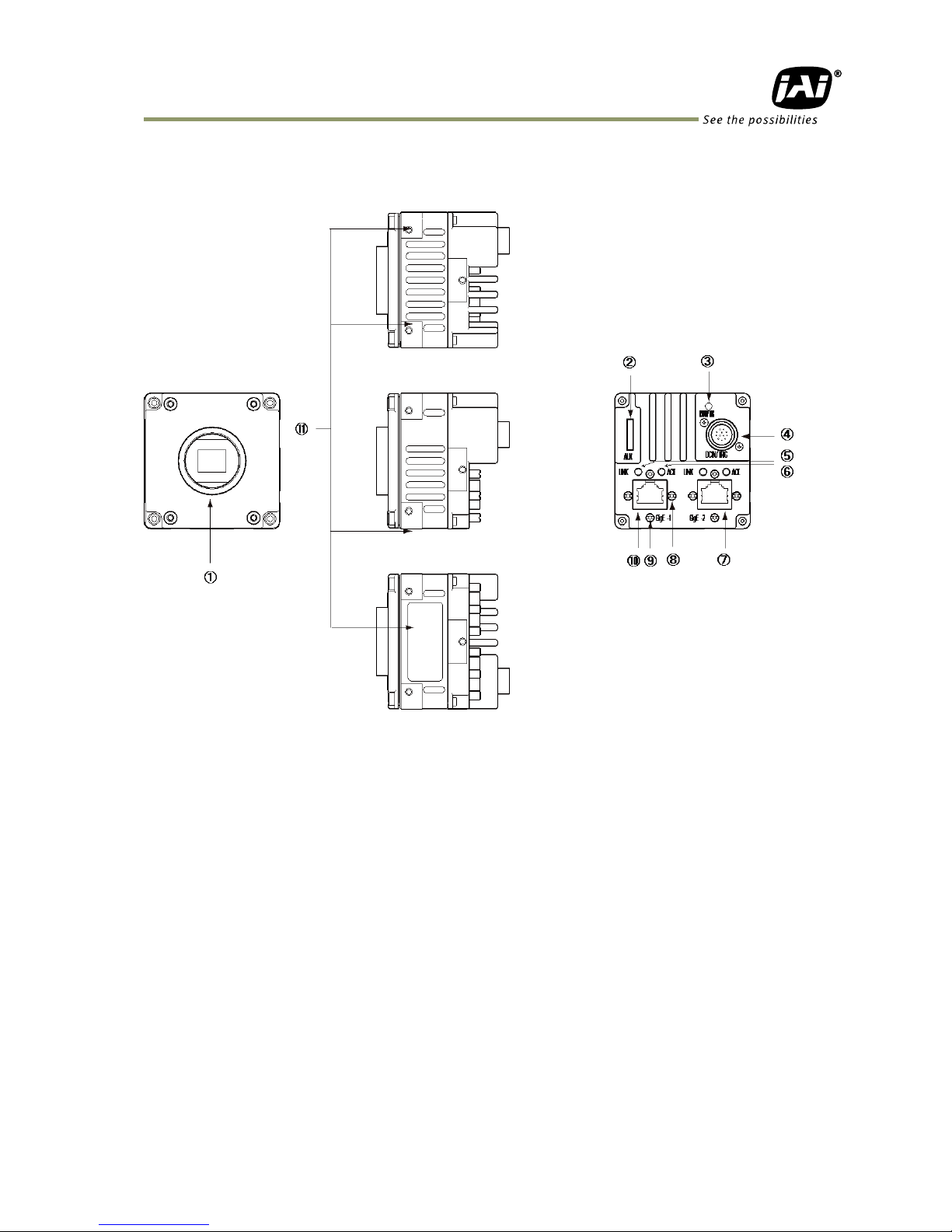
4. Locations and functions
4.1 Locations and functions
Lens mount C-mount (Note *1)
10-pin connector AUX Connector for lens control (Standard)
LED Indicator for power and trigger input
12-pin connector DC and trigger input
LED (LINK) GigE network indication (LINK for GigE 1)
LED (ACT) GigE network indication (ACT for GigE 1)
RJ45 connector GigE connector 2 (With lock mechanism)
Hole for RJ-45 fixing screw Hole for RJ-45 fixing screw (Horizontally) (Note*2)
Hole for RJ-45 fixing screw Hole for RJ-45 fixing screw (Vertically) (Note*2)
RJ45 connector GigE connector 1 (With lock mechanism)
⑪ Mounting holes Holes for mounting tripod base or direct installation.
Depth 5 mm (Note*3)
Note1: Rear protrusion on C-mount lens must be less than 10.0 mm.
Note2: When an RJ-45 cable with thumbscrews is connected to the camera, please do not
Excessively tighten screws by using a screw driver. The RJ-45 receptacle on the camera
might be damaged. For security, the strength to tighten screws is less than 0.147 Newton
meter (Nm). Tightening by hand is sufficient in order to achieve this.
Note3: The part number for the tripod adapter plate (with 1/4"-20 thread) is MP-42 (option).
Fig. 1 Locations
Page 14

SP-5000M-GE2 / SP-5000C-GE2
- 12 -
4.2 Rear panel
The rear panel mounted LEDs provide the following information:
POWER/TRIG
Amber: Power connected – initiating
This light goes OFF after initiating.
Steady green: Camera is operating in Continuous mode
Flashing green: The camera is receiving external triggering
Note: The interval of flashing does not correspond with external
trigger duration.
Fig. 2 Rear panel
GigE 1
LINK
Steady green: Connecting in 1000BASE-T
Flashing green: Connecting in 100BASE-T
ACT
Flashing amber: GigE Network indication
LINK2
LINK
Steady green: Connecting in 1000BASE-T
Flashing green: Connecting in 100BASE-T
ACT
Flashing amber: GigE Network indication
Page 15
SP-5000M-GE2 / SP-5000C-GE2
- 13 -
5. Input and output
5.1 GigE interface
5.1.1 GigEVision 2.0 interface extension
SP-5000-GE2 complies with GigE Vision 2.0. Its extension functions are described below.
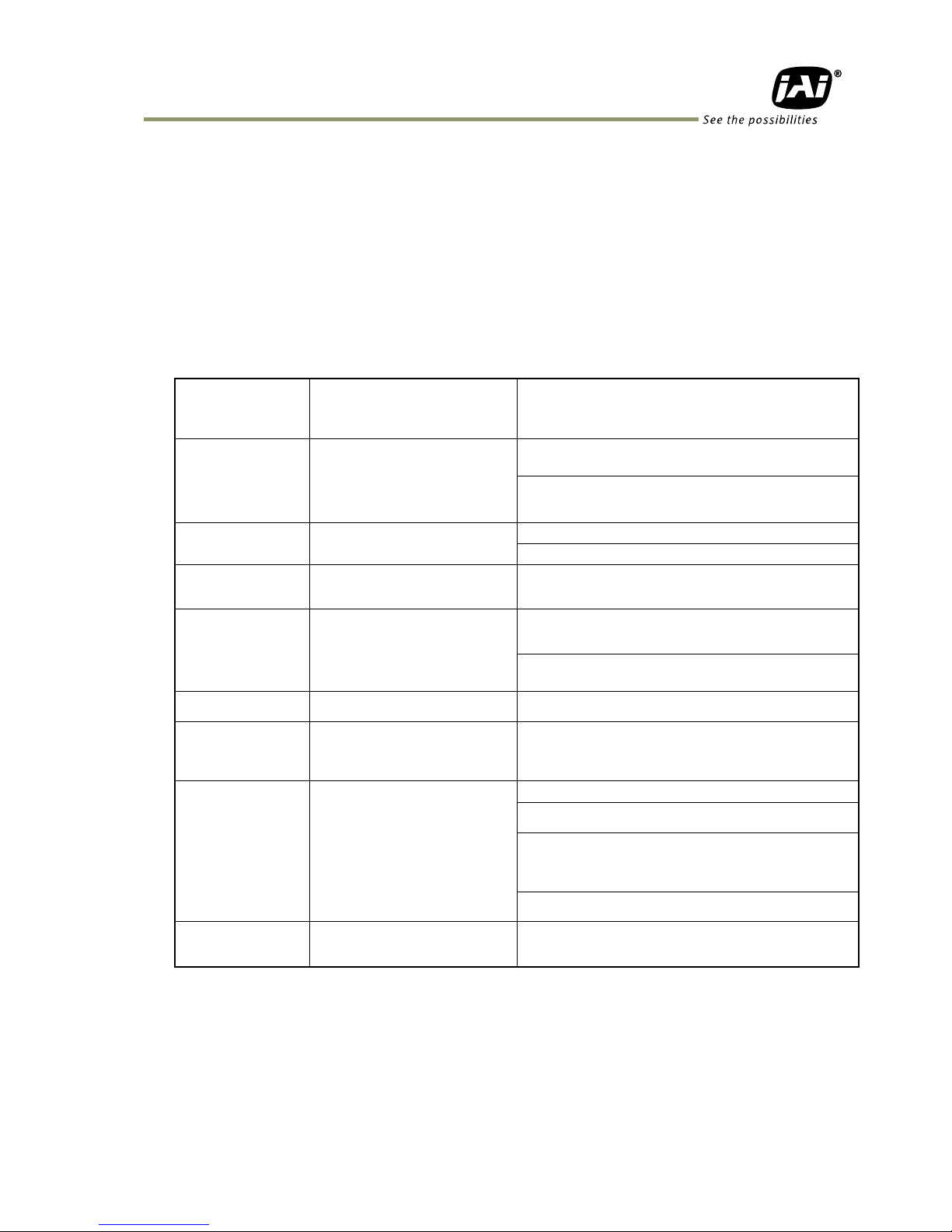
5.1.1.1 Link Aggregation
By handling two ports as one port, the maximum transfer rate can be achieved at 2Gbps.
This function is based on IEEE 802.3ad, IEEE 802.1AX Link Aggregation and GigE Vision 2.0.
Table 2. Link Aggregation Specifications
Link Aggregation
system
sLAG(Static Link
Aggregation Group) and
dLAG(Dynamic Link
Aggregation Group)
When dLAG is selected, LACP selects
automatically.
When sLAG is selected, if HW conditions are not
satisfied, SL(Single Link) is activated.
Load distribution
system
Round-robin processing
GVSP Ether Frame is output from Port 1 or Port
2 alternatively.
When the first packet (Leader packet : Leader
frame) of the video frame is output, the
output port is reset to 1.
Physical Network
Number
2 Ports
Port 1 and Port 2 are enabled.
Multi Link (ML) is not supported.
MAC Address
Number
1
As only SL, sLAG and dLAG are supported, MAC
Address is one. Port 1 and Port 2 use the same
MAC Address.(Note 1)
IP Address
Number
1
As only SL, sLAG and dLAG are supported, IP
Address is one. Port 1 and Port 2 use the same
IP Address.(Note 1)
IP Address is set up at the port which is linked
up initially.
GVCP Port
Automatic selecting
The transmission is executed through the port
which receives GVCP command.
Stream Channel
Number
1 Channel
When SL is used, one stream is output from
either Port1 or Port2 which is linked up.
When sLAG or dLAG is used, one stream is
output in load-balanced from Port 1 and Port2.
SL/sLAG
Selecting
Method
Selected by the status of
Port Link UP
If only 1 port is linked up, it is SL.
If sLAG is enabled, and if Port 1 and Port 2 are
linked up, the status is changed to sLAG.
If dLAG is enabled, and if Port 1 and Port 2 are
linked up, the status is set to dLAG by LACP.
If only one port is linked up, the status is
reverted to SL.
On sLAG or dLAG status, if one port is linked
down, the status is reverted to SL.
Event Message
GEV_EVENT_LINK_SPEED_C
HANGE
If a change of SL to or from LAG occurs,
GEV_EVENT_SPEED_CHANGE Event Message can
be issued.
Note 1: In Link Aggregation operation, two ports use the same MAC Address and IP Address.
Accordingly, if these two ports are connected to only one non-compliant IEEE 802.3ad
or IEEE 802.1AX switch, the function is not properly executed. If non-compliant
IEEE 802.3 and/or IEEE 802.1AX switch is used, 2 sets should be used and connected
to each port.
Page 16
SP-5000M-GE2 / SP-5000C-GE2
- 14 -
Camera
Port
#1
Port
#A
Port
#B
Port
#0
PC
(1)
SL(Single Link) Connection
Camera
Port
#0
Port
#1
Port
#A
Port
#B
PC
Camera
Port
#1
Port
#A
Port
#B
PC
Camera
Port
#1
Port
#A
Port
#B
Port
#0
PC
Port
#0
SL(Single Link)
•@Connection
Camera
Port
#0
Port
#1
Port
#A
Port
#B
PC
SL(Single Link) Connection
Camera
Port
#0
Port
#1
Port
#A
Port
#B
PC
SL(Single Link)
•@Connection
sLAG(Static Link Aggregation Group) or
dLAG(Dynamic Link Aggregation Group)
Connection
sLAG(Static Link Aggregation Group) or
dLAG(Dynamic Link Aggregation Group)
Connection
(2)
(3)
(4)
(5)
(6)
1Gbps (1000Mbps)
1Gbps (1000Mbps)
1Gbps (1000Mbps)
1Gbps (1000Mbps)
2Gbps (2000Mbps)
2Gbps (2000Mbps)
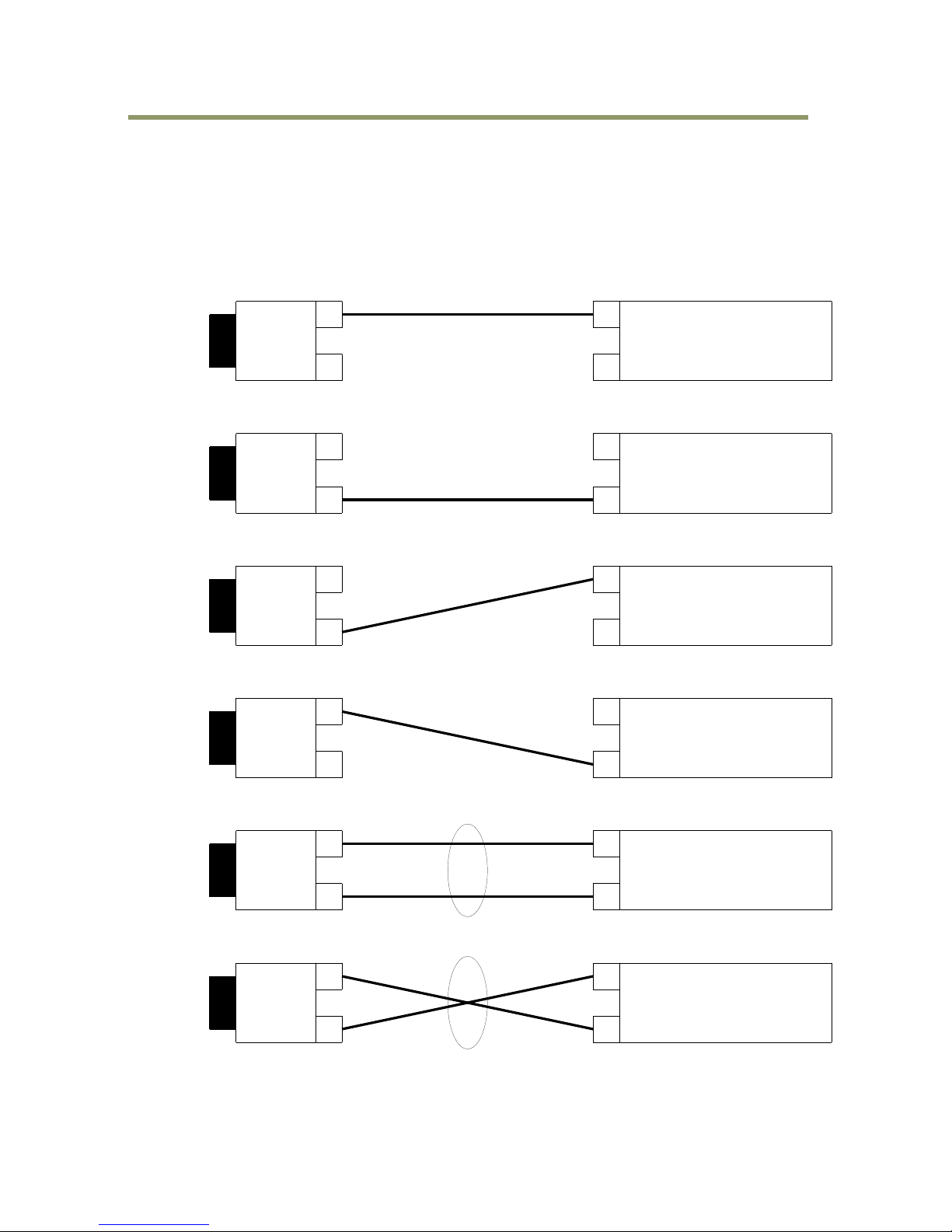
Connecting configuration
1. If only 1 port is linked up, the connecting configuration is SL (Single Link).
2. If Port 1 and Port 2 are linked up, and if dLAG is enabled, the operation is determined by LACP
or if sLAG is enabled, the operation is sLAG connecting configuration.
3. If the connecting status is changed, the operation is automatically changed to appropriate
connecting configuration.
Page 17
SP-5000M-GE2 / SP-5000C-GE2
- 15 -
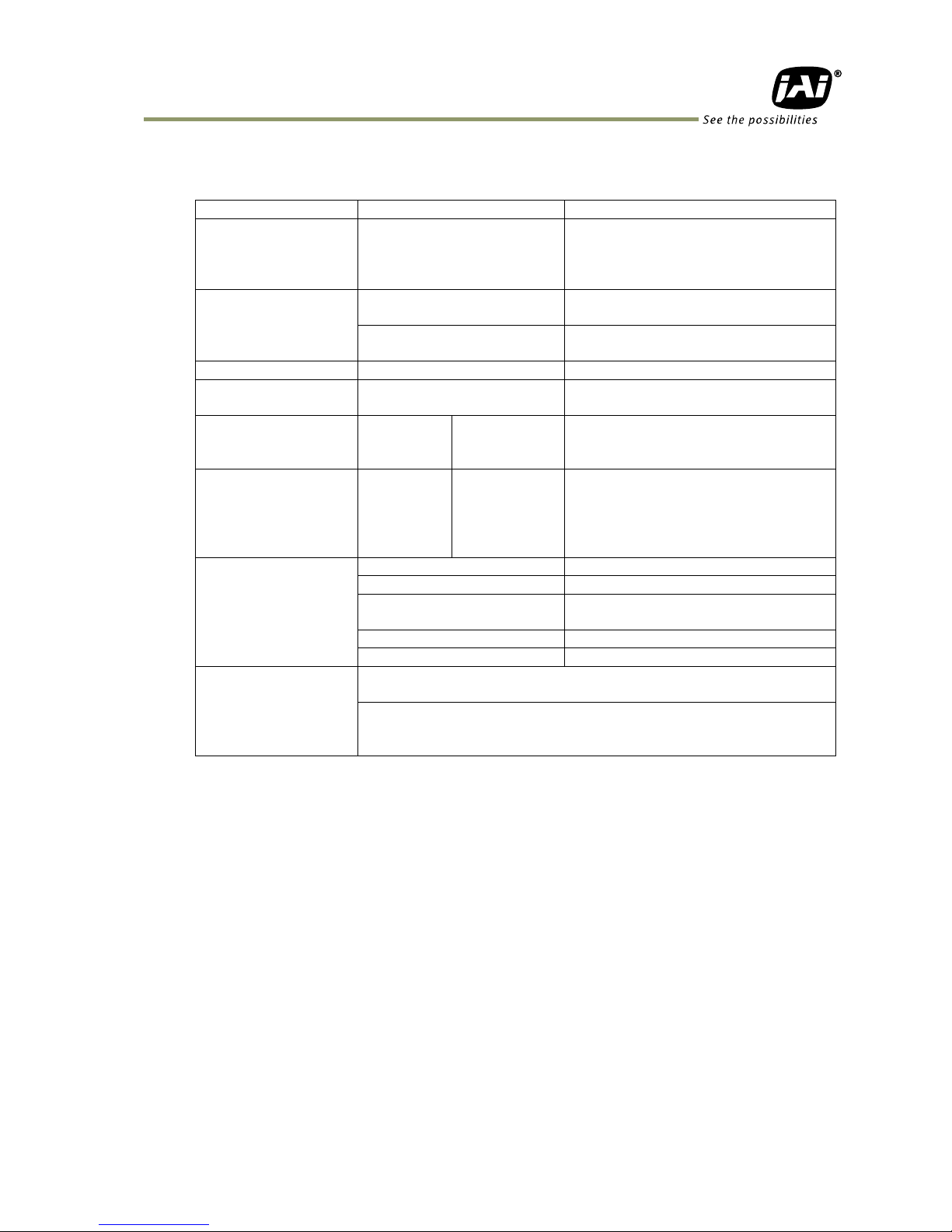
5.1.1.2 PTP (IEEE 1588-2008: Precision Time Protocol)
Table 3. Specifications
Equipped functions
Only slave
Master function is not equipped
Used Transport
Multicast UDP datagram
But, Delay_Req and
Delay_Resp are Unicast UDP
datagram
In IEEE 1588, various transports
including Ether Frame are defined. In
GigE Vision 2.0, it is defined to use
UDP datagram.
Destination Port
number
Event message: 319
Sync, Delay_Req, Pdelay_Req,
Pdelay_Resp
General mesage: 320
Announce, Follow_Up, Delay_Resp,
Pdelay_Resp, Management, Signaling
Multicast address
224.0.1.129
Synchronized item
Time only
Frequency synchronization is not
equipped
PTP Time Data
(Comply with IEEE
1588)
bit length
80 bit
Time with 1 ns unit increment
starting at 00:00:00 on 1/1/1970
Camera Time Stamp
bit length
64 bit
(Note2)
At PTP synchronization, LSB 64 bit of
PTP time data
At PTP non-synchronization, 1 ns unit
increment at starting on any time
(Note 1)
Applicable PTP
Message
Announce message
Receiving only
Sync message
Receiving only
Follow_Up message
Receiving only (used if the master is
2 step clock)
Delay_Req message
Sending only
Delay_Resp message
Receiving only
GigE Vision proper
regulation
Timestamp Tick Frequency register value is fixed at 1,000,000,000
(1 GHz). (Note 3)
While PTP synchronizing operation, Timestamp Reset function is
disabled and if the reset is required, GEV_STATUS_WRITE_PROTECT
status code is returned.
Note1: If there is IEEE 1588 master clock in the network, the camera time stamp is
synchronized at the master clock.
If there is no IEEE 1588 master clock in the network, the camera time stamp
operates by the free running of the internal clock at starting on the power being ON.
Note2: In GenICam standard, 64-bit integer is handled as signed value, thus only 63 bits are
available through GenICam interface.
Note3: As 1 GHz clock is not actually operated, the time stamp is incremented by 8
(1 GHz/125 MHz) on every 1 clock of actual frequency.
5.1.1.3 Manifest
SP-5000-GE2 is equipped with Manifest. Both GenICam Version 1.x and Version 2.0 are applied by
selecting the entry.
Page 18
SP-5000M-GE2 / SP-5000C-GE2
- 16 -
5.1.1.4 Notes for connecting 100BASE-TX
In order to use 100 Mbps network, 100BASE-TX and Full Duplex are available. Half Duplex
cannot be used.
In the case of connecting on 100BASE-TX, the maximum packet size should be 1500 bytes.
In the case of connecting on 100BASE-TX, the specifications such as frame rate, trigger
interval and so on described in this manual cannot be satisfied.
5.1.1.5 Example of setting method of Link Aggregation
1. Intel NIC driver installation
In Windows 7 or Windows 8.1 OS, when a NIC is installed and the PC is started, the default driver
supported by the Microsoft OS may be automatically installed. The Microsoft driver does not have
the “Teaming” function needed for the GigE Vision Link Aggregate Method (LAG). Therefore, in
order to make the “Teaming” function available, it is necessary to install the Intel NIC driver. Please
note that if Intel ceases support for this driver, “Teaming” may not be available on the latest OS.
The following describes the procedure to install the Intel NIC driver.
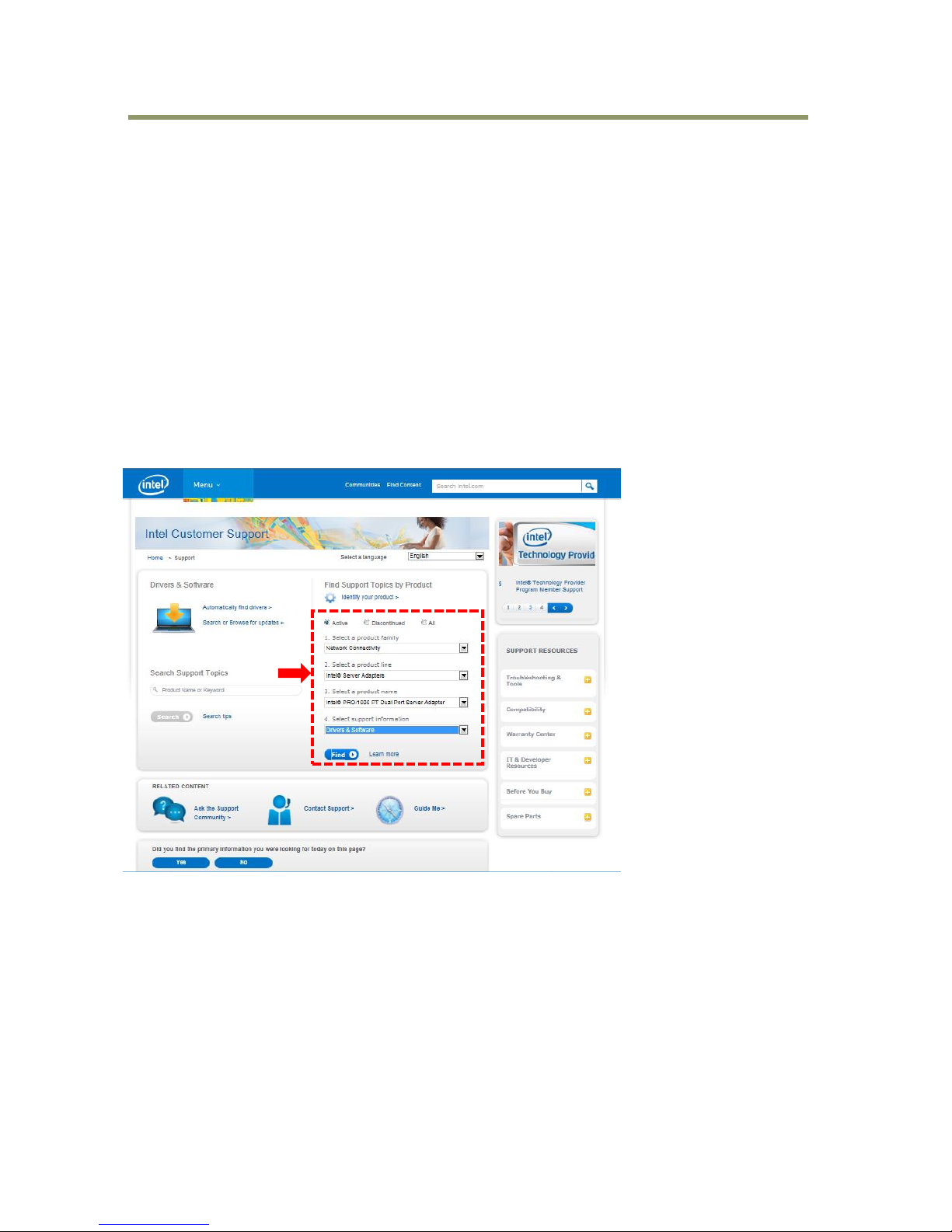
Navigate to the Intel web site and open the Drivers & Software page. Select the appropriate items
from the drop-down selection lists.
In this example, select Network Connectivity, Intel Server Adapters, Intel PRO1000 PT Dual Port
Server Adapter and Drivers & Software. Then click the “Find” button.
Page 19
SP-5000M-GE2 / SP-5000C-GE2
- 17 -
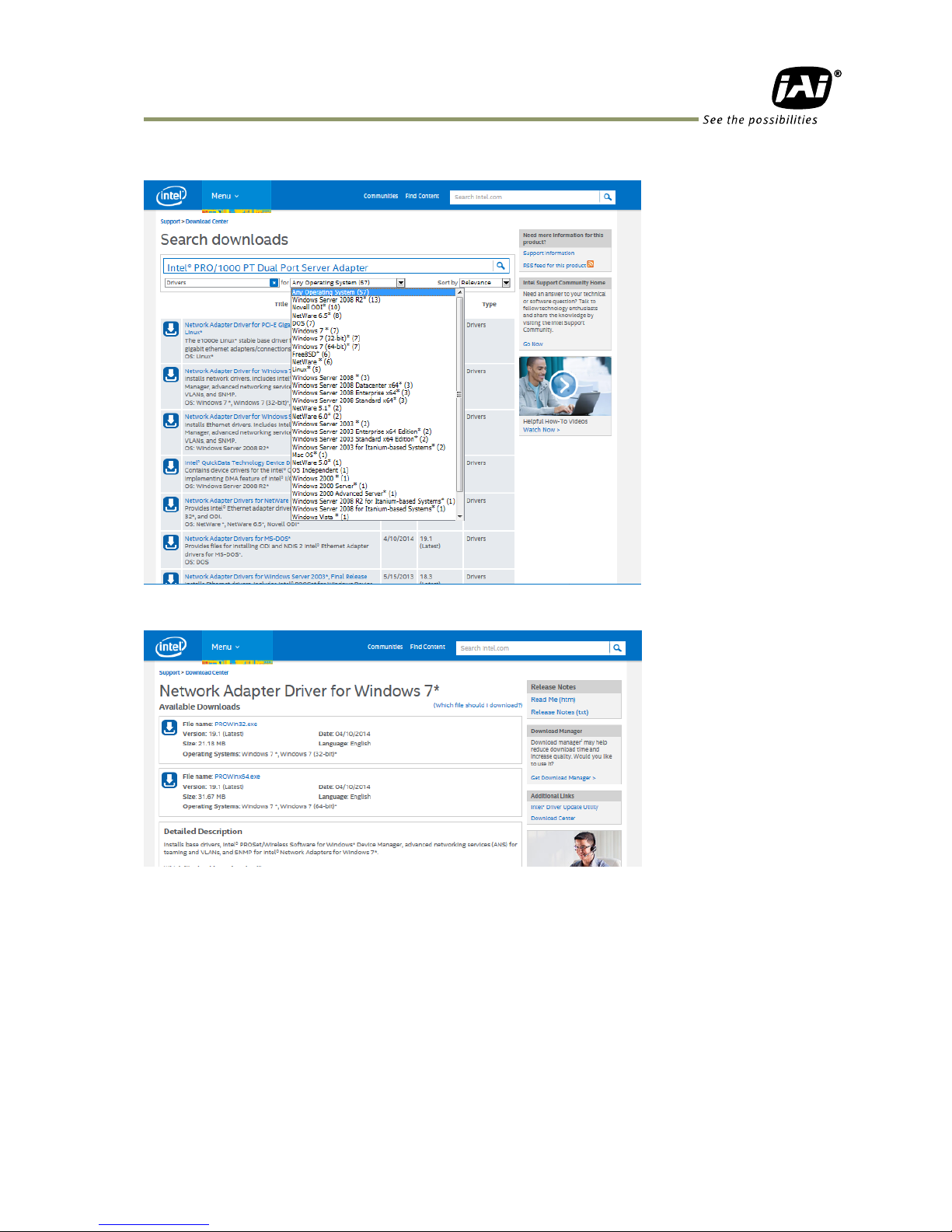
On the Search Downloads page, select your operating system -- in this case Windows 7.
Select either 32-bit or 64-bit version.
After downloading the driver, double-click PROWin32.exe or PROWin64.exe to install the
driver.
Page 20
SP-5000M-GE2 / SP-5000C-GE2
- 18 -
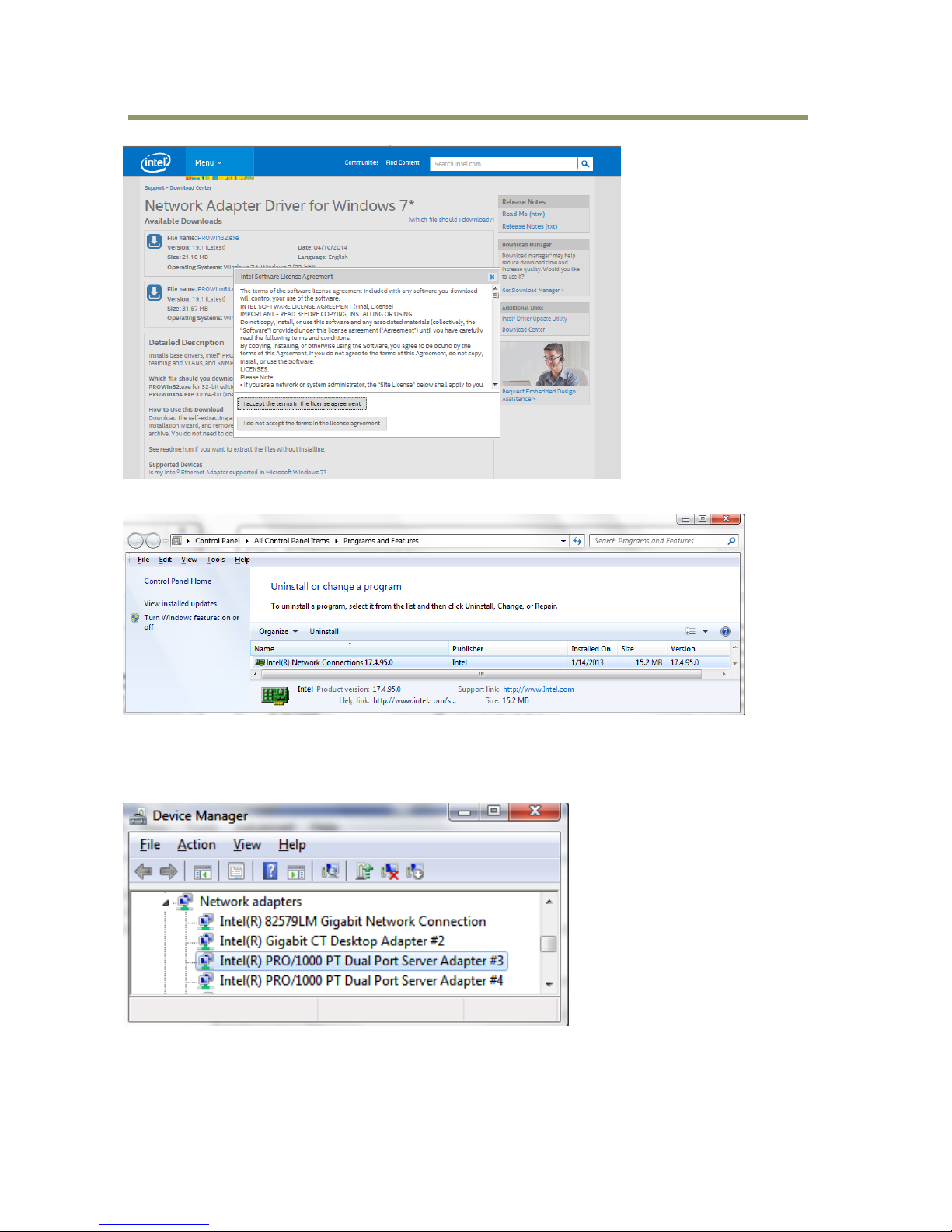
After installing the driver, it is possible to confirm version information about the driver in the listing
on the “Programs and Features” page.
2. Setting of NIC properties
2.1 Settings of each port.
Open the “Device Manager” and find the network adapter, Intel PRO 1000 PT Dual Port Server
Adapter. Click the right mouse button and open “Properties”.
The following settings must be applied to each port. This is especially true for Jumbo Packet and
Interrupt Moderation. If the settings for these items remain as default, it will affect when images are
captured.
Page 21
SP-5000M-GE2 / SP-5000C-GE2
- 19 -
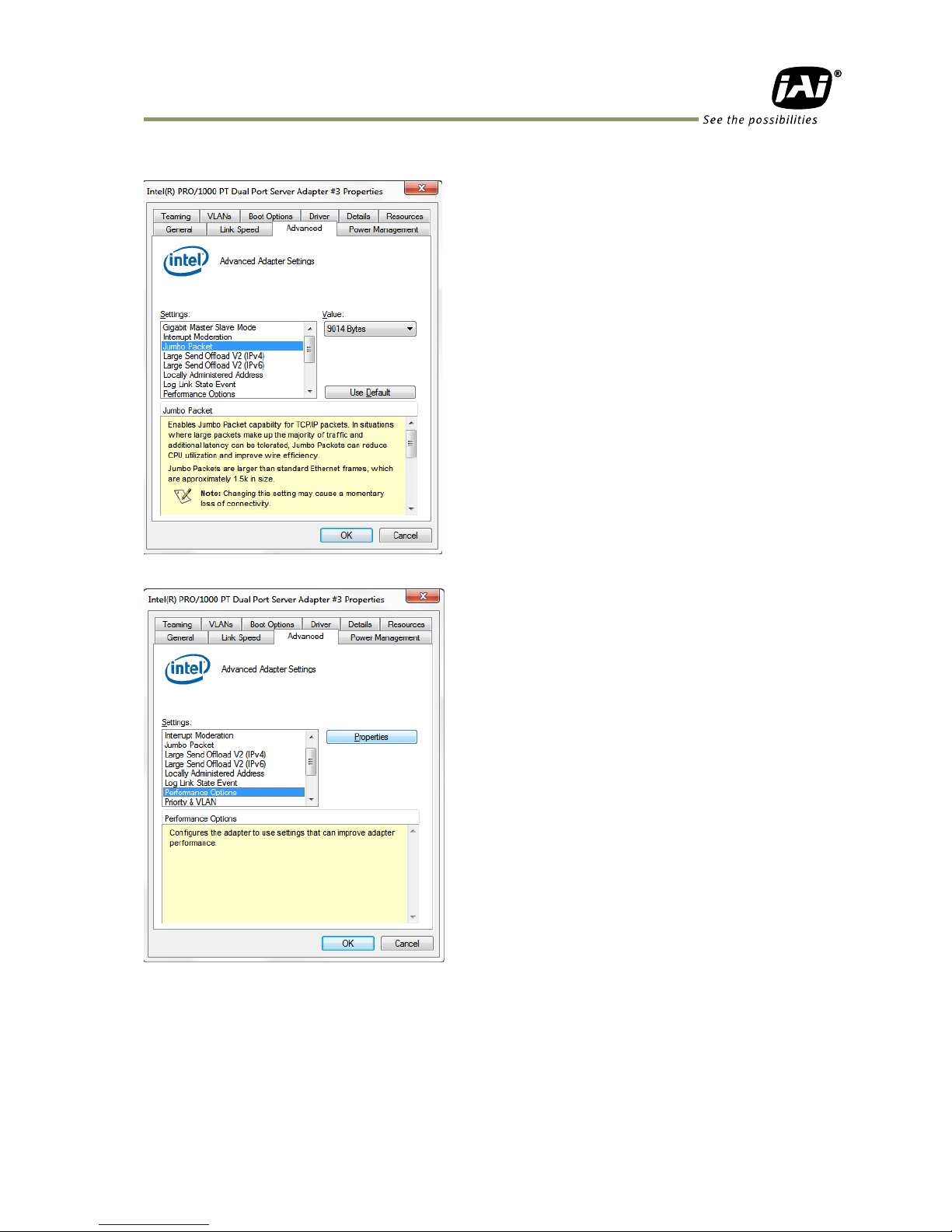
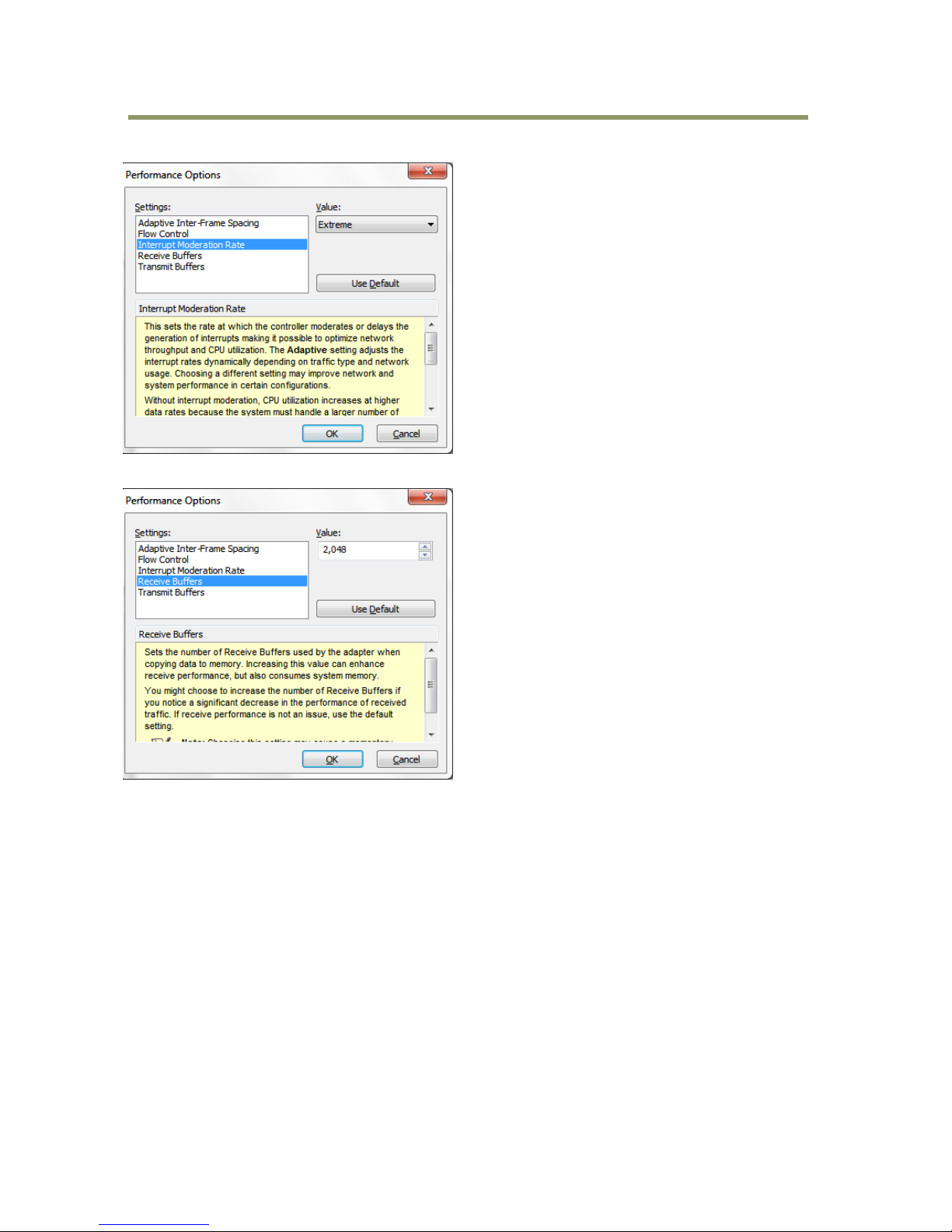
Set Jumbo Frame (Jumbo Packet) to 9014 Bytes.
Select “Performance Options” and click the “Properties” button.
Page 22
SP-5000M-GE2 / SP-5000C-GE2
- 20 -
In setting(s) box, set “Interrupt Moderation Rate” to “Extreme.”
Set “Receive Buffers” at 2048.
2.2 Settings of “Teaming”
Open “Teaming” tab. Check “Team this adapter with other adapters” and click “New Team”
button.
Page 23

SP-5000M-GE2 / SP-5000C-GE2
- 21 -
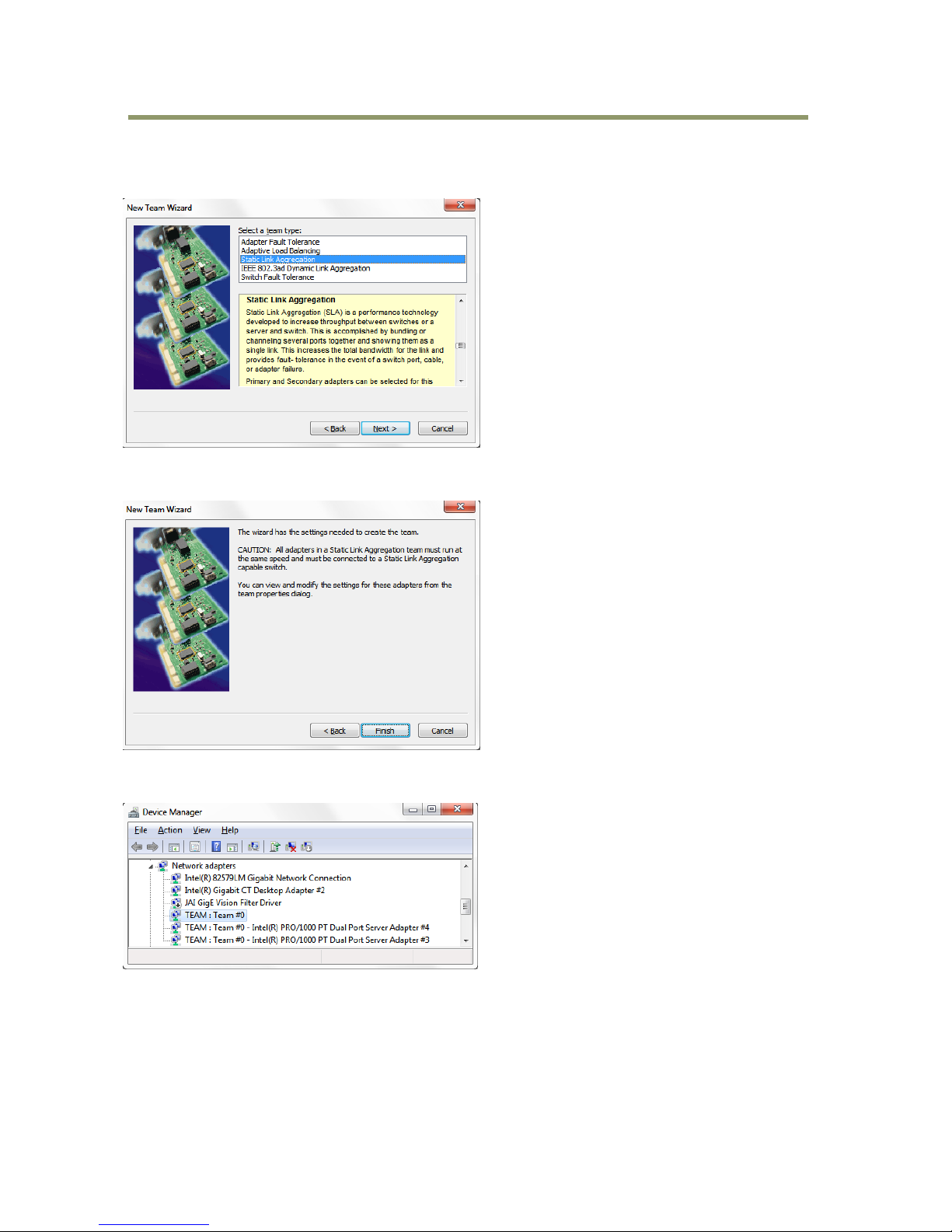
Input “Team” name, if necessary, otherwise leave it as is. Then click “Next”.
The “Select adapters to include in this team” dialog will open.
The adapter with its properties dialog currently open will already be checked. Check the other
adapter, in this case, Intel PRO 1000 PT Dual Port Server Adapter #4. Then click “Next”.
Page 24
SP-5000M-GE2 / SP-5000C-GE2
- 22 -
“Team Type Selection” will open. In the SP-5000-GE2, only “Static Link Aggregation” and “IEEE
802.3ad Dynamic Link Aggregation” are available. In this example, “Static Link Aggregation” is
selected. Then click “Next”.
The confirmation message for creating new team will be displayed. In this example, it is Static Link
Aggregation. Click “Finish”.
When “Teaming” is completed, “Team: Team Number 0” is added to the network adapter in Device
Manager.
Page 25
SP-5000M-GE2 / SP-5000C-GE2
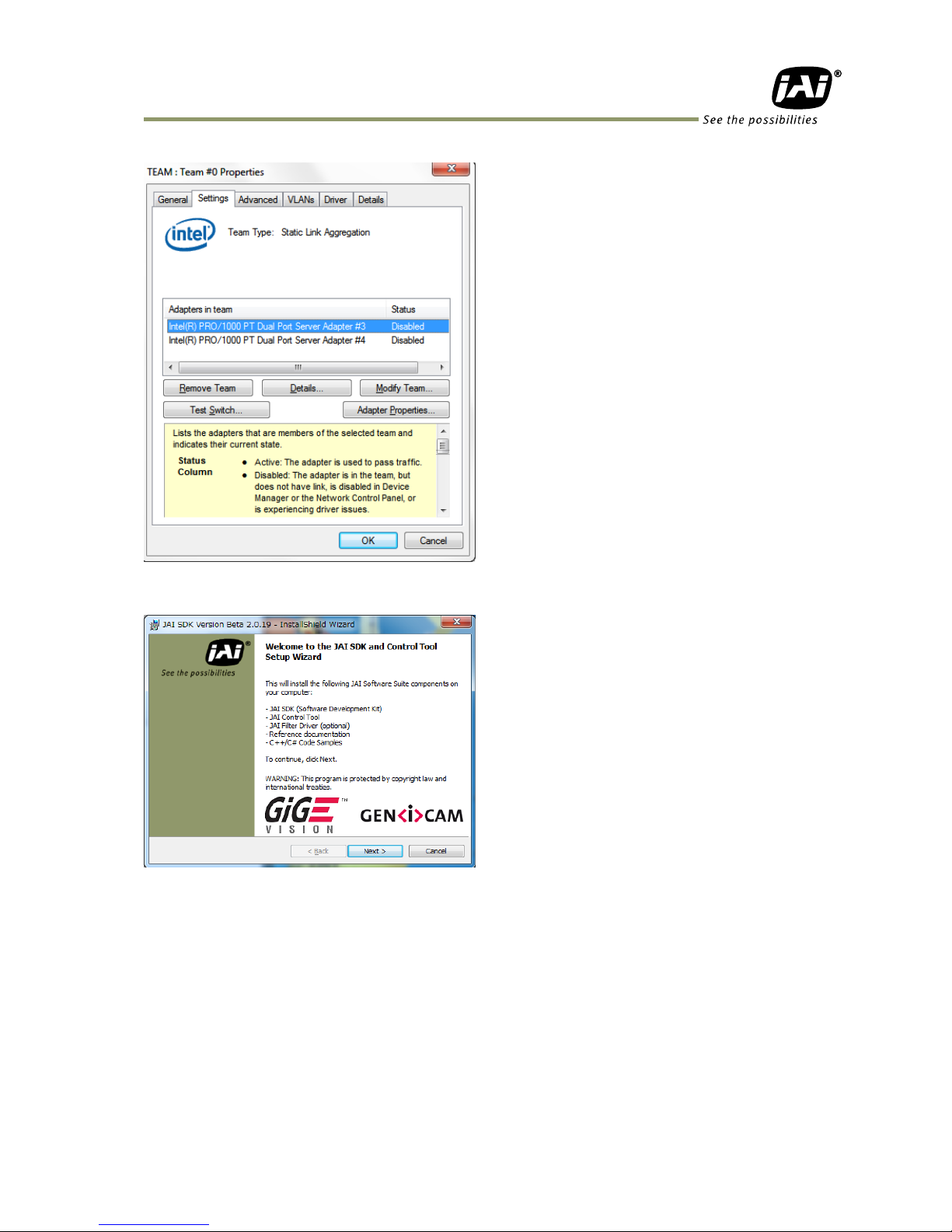
- 23 -
The following are the “Team 0” properties.
3. JAI SDK Install
After “Teaming” of NIC is completed, the JAI SDK must be installed.
Page 26
SP-5000M-GE2 / SP-5000C-GE2
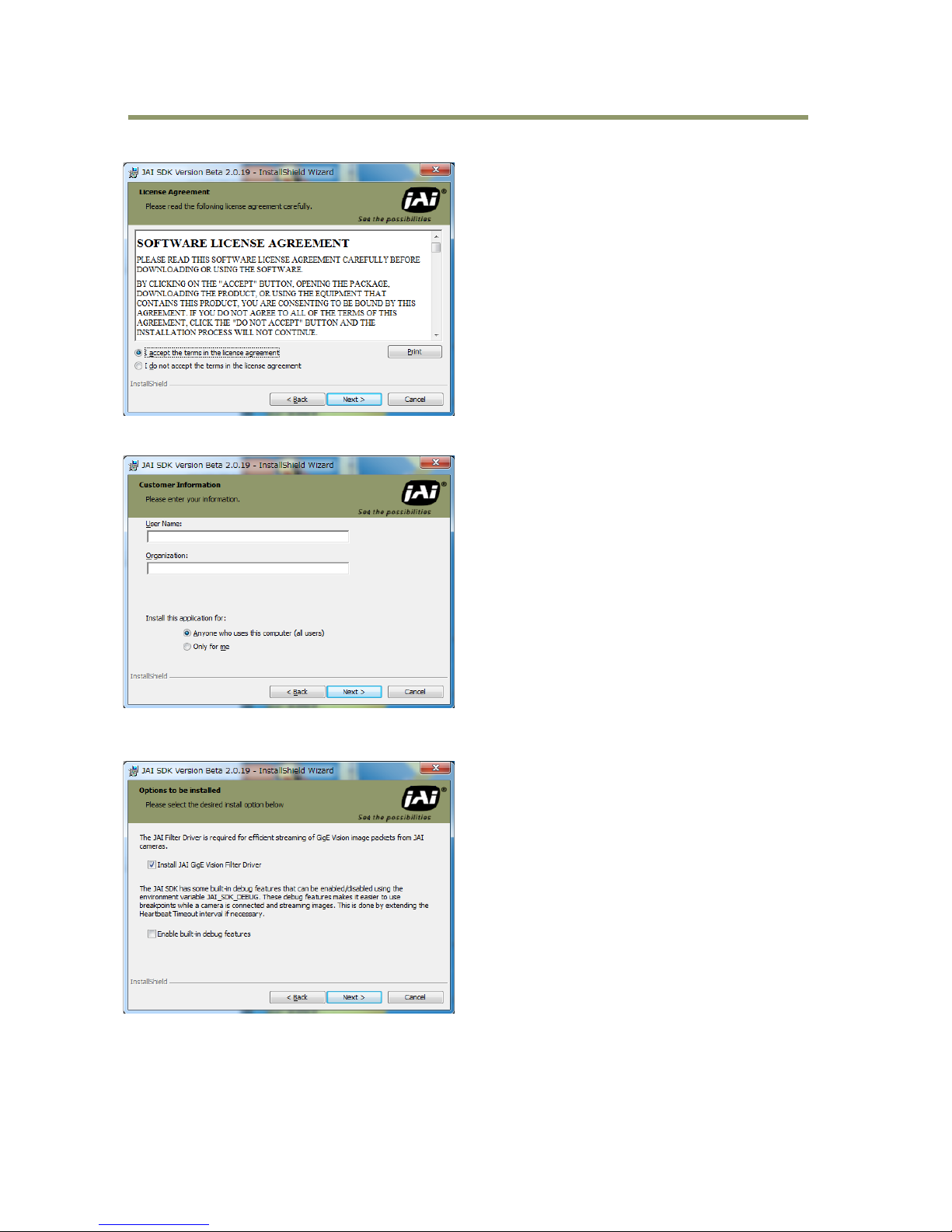
- 24 -
Accept license and click “Next”
」
Fill in the fields if needed. Then click “Next”.
This screen confirms whether or not the JAI GigE Vision Filter Driver is to be installed. When GigE
Vision cameras are used, this must be checked.
Page 27
SP-5000M-GE2 / SP-5000C-GE2
- 25 -
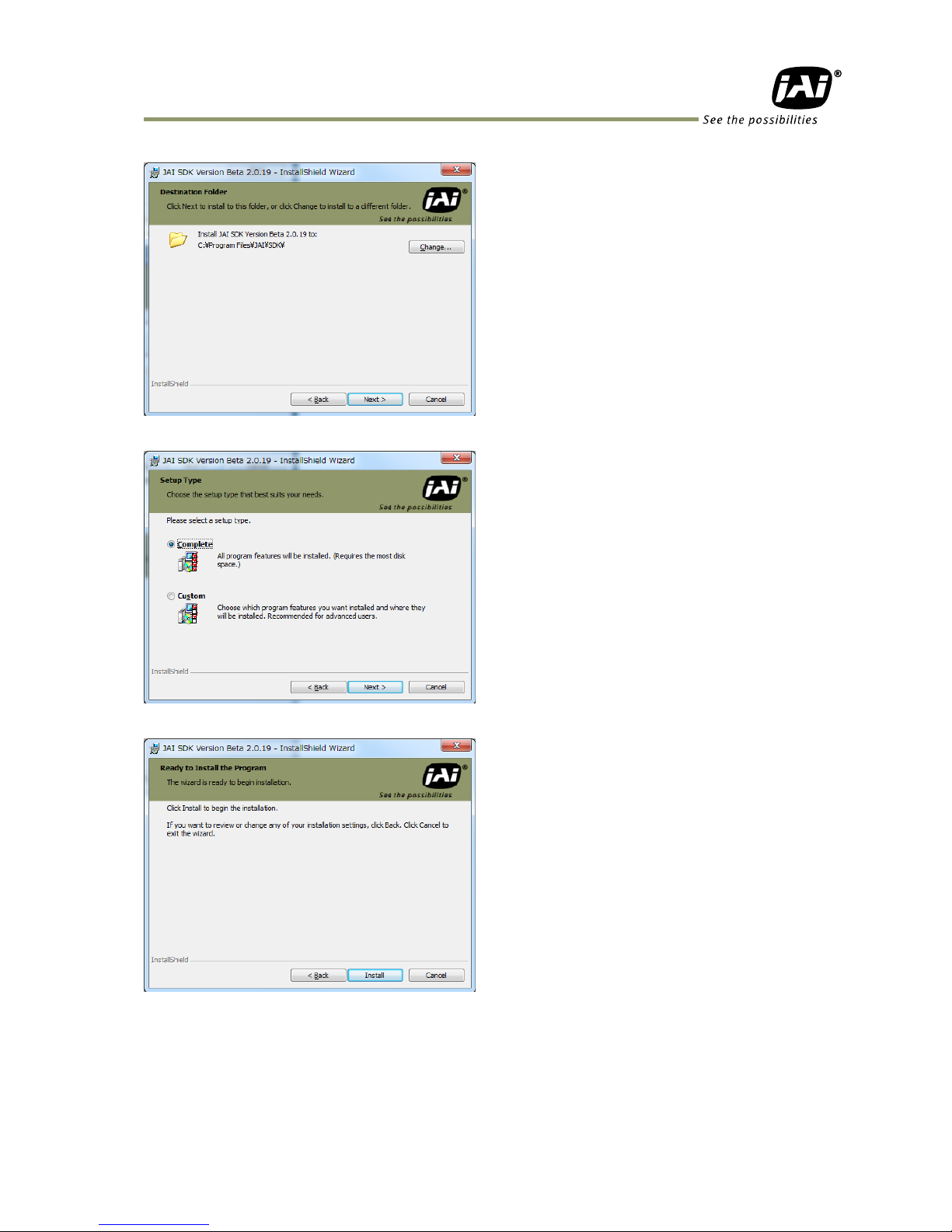
Set the folder to install. If the default setting is OK, just click “Next”.
Select a setup type. If “Complete” is OK, then click “Next”.
Click the “Install” button to start installation.
Page 28
SP-5000M-GE2 / SP-5000C-GE2
- 26 -
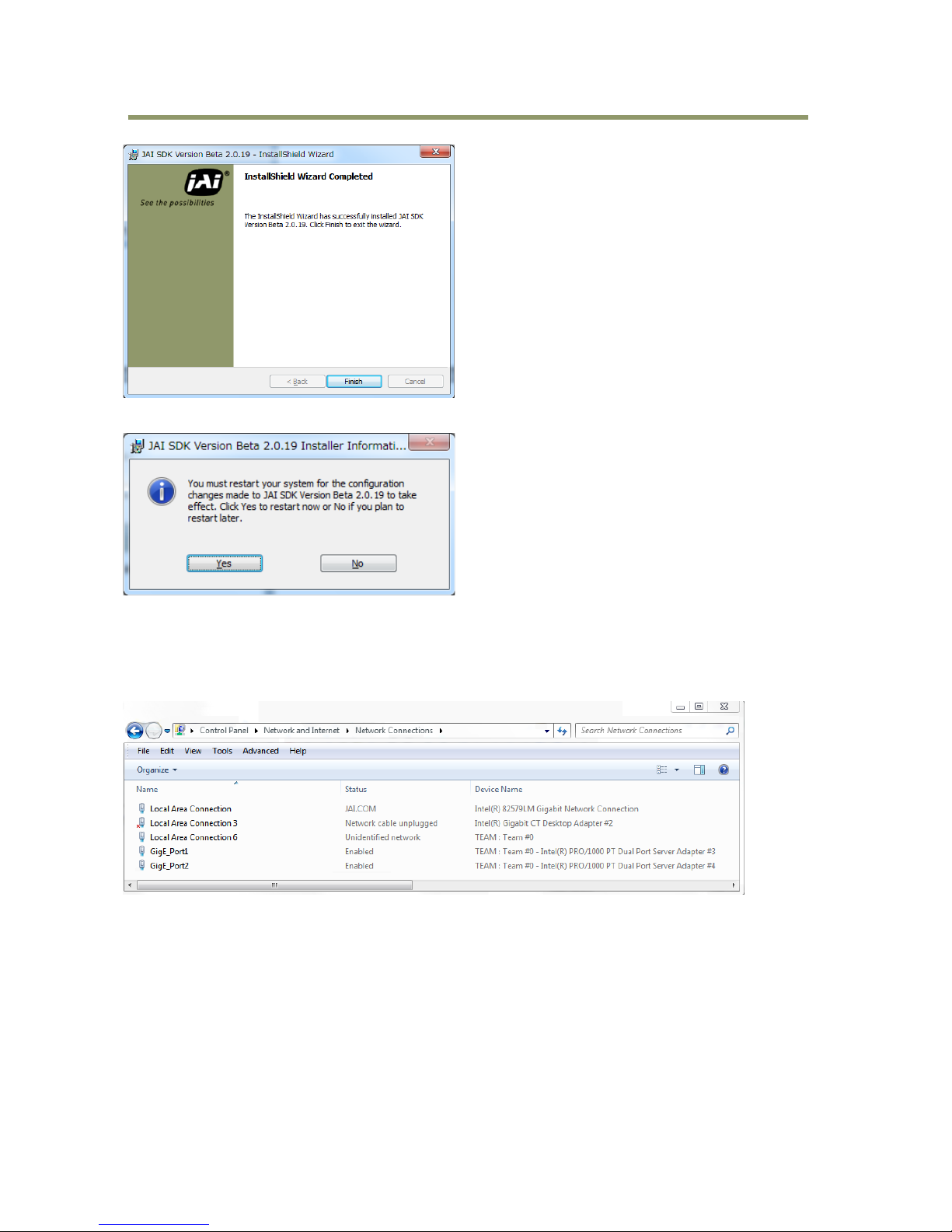
Click “Yes” to restart the PC.
After restarting, check to see that the filter driver is in the local area network.
In the following example, two port names of the Intel PRO 1000 PT Dual Port Server Adapter are
re-named. (GigE_Port and Number)
If the team name used the default setting, the ports are automatically named by local area network
and number.
Page 29
SP-5000M-GE2 / SP-5000C-GE2
- 27 -
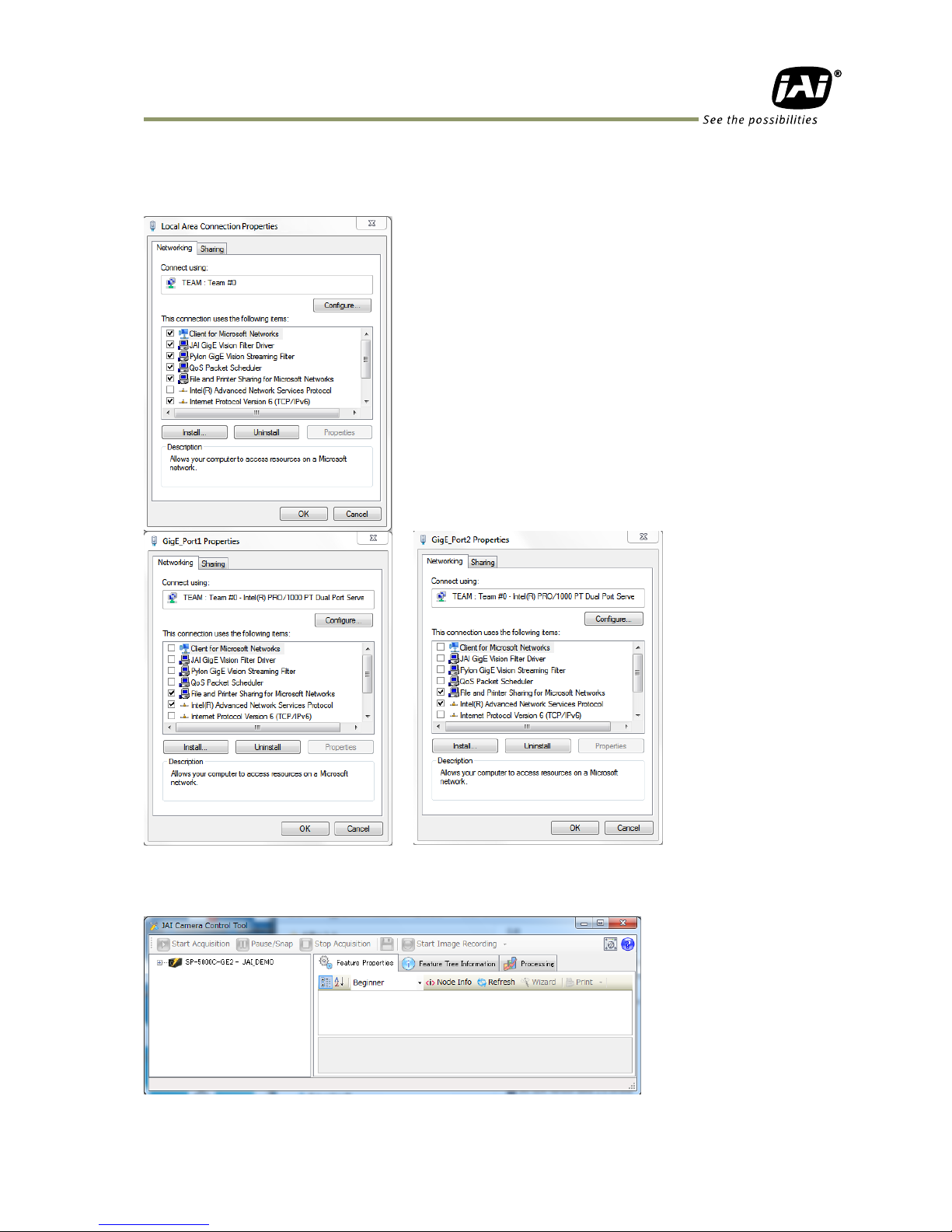
In the Properties window of the Local Area Network which is to be Teamed, the JAI GigE Vision Filter
Driver is initially checked. After “Teaming,” JAI GigE Vision Filter Drivers are not checked in the
Properties of Port 1 and Port 2 of the Intel PRO 1000 PT Dual Port Server Adapter Local Area
Network.
4. Settings of JAI Camera Control Tool
Start JAI Camera Control Tool in Windows Start Menu.
In the default settings, the camera control tool will search automatically for connected cameras.
Page 30
SP-5000M-GE2 / SP-5000C-GE2
- 28 -
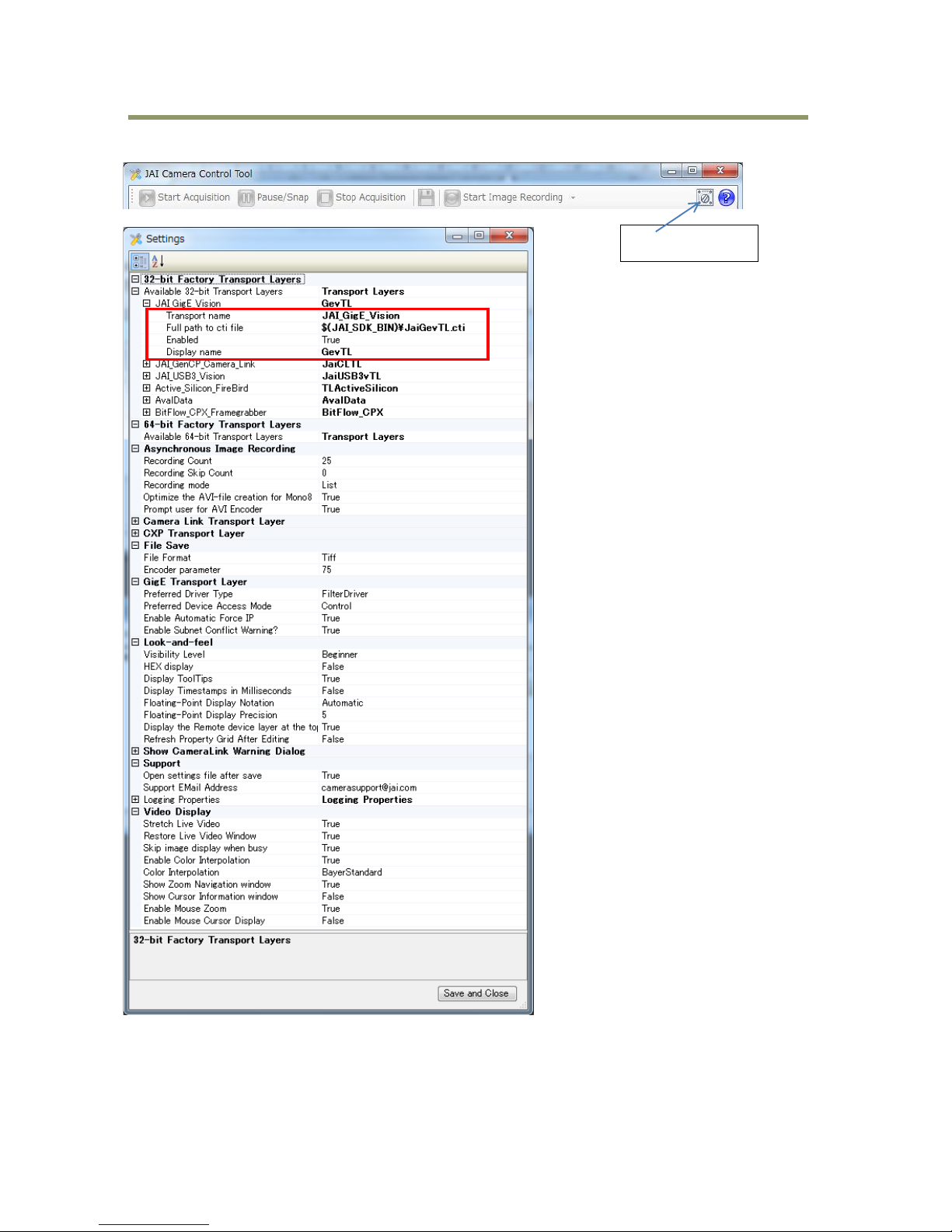
In JAI SDK 2.0.x, the Settings window is updated with the applicable camera interface settings.
Settings button
Page 31

SP-5000M-GE2 / SP-5000C-GE2
- 29 -
In JAI SDK 2.0.x, “Buffer Count” and “Enable Packet Resend” are found under the GenICam (GenTL)
settings as a Device Layer property, while they are found in the Settings dialog in the JAI SDK 1.4.1
camera control tool. These settings can be set every time the camera is connected.
To access the settings in SDK 2.0.x, open the selector of the connected camera, and find the Device
Layer in the properties tree. Expand the Device Layer node to reveal the GenTL Transport layer
under Interface Layer. Buffer Count and Enable Packet Resend are available in the Image Acquisition
section of the settings display.
Page 32

SP-5000M-GE2 / SP-5000C-GE2
- 30 -
5.2 Connectors and pin assignment
5.2.1 Output connector for Gigabit Ethernet
Type: RJ-45
Fig.3 RJ-45 connector
The digital output signals follow the Gigabit Ethernet interface using an RJ-45 conforming connector.
The following table shows pin configuration.
Table 4. RJ-45 pin configuration
5.2.2 12-Pin connector
Type: HR-10A-10R-12PB(72) Hirose male or equivalent.
Table 5. Hirose 12P pin assignment
Pin No.
Input /Output
Description
1
In/Out
MX1+ (DA+)
2
In/Out
MX1- (DA-)
3
In/Out
MX2+ (DB+)
4
In/Out
MX3+ (DC+)
5
In/Out
MX3- (DC-)
6
In/Out
MX2- (DB-)
7
In/Out
MX4+ (DD+)
8
In/Out
MX4- (DD-)
Pin no.
I/O
Signal
Remarks
1
GND
2
I
DC in
+12V ~ +24V
3
I
Opto in2-
Line6
4 I Opto in2+
5
I
Opto in1-
Line5
6 I Opto in1+
7
O
Opto out1-
Line2
8 O Opto out1+
9 O Opto out2-
Line3
10 O Opto out2+
11
I
DC in
+12V ~ +24V
12
GND
Fig.4 12-pin connector
123
45678
Page 33

SP-5000M-GE2 / SP-5000C-GE2
- 31 -
5.2.3 AUX Standard Hirose 10-Pin connector
5.2.3.1 Figure and pin configuration
Type : HIROSE 10-Pin Connector 3260-10S3(55)
Fig.5 Hirose 10-pin connector
Table 6. Hirose 10P pin assignment (Standard)
No
I/O
Name
Note
1 O DRIVE IRIS+
Motorized Lens
2 O DRIVE FOCUS+
Motorized Lens
3 O DRIVE ZOOM+
Motorized Lens
4 O COMMON
Motorized Lens
5 GND
6 O
P-IRIS OUT A+
P-Iris Lens
7 O P-IRIS OUT A-
P-Iris Lens
8 O P-IRIS OUT B+
P-Iris Lens
9 O P-IRIS OUT B-
P-Iris Lens
10 O GND
5.2.4 AUX Type 2 HIROSE 10-Pin connector (factory option)
Type: HIROSE 10-Pin Connector 3260-10S3(55)
Table 7. Hirose 10P pin assignment (Option 1)
No
I/O
Name
Note
1 O Video Signal
Video Iris Lens
2 O Power DC+12V
Video Iris Lens
3 NC
4 NC
5 GND
6 O
DC IRIS DAMP-
DC Iris
7 O DC IRIS DAMP+
DC Iris
8 O DC IRIS DRIVE+
DC Iris
9 O DC IRIS DRIVE-
DC Iris
10 GND
1
8
Page 34

SP-5000M-GE2 / SP-5000C-GE2
- 32 -
5.2.5 AUX Type 3 HIROSE 10-Pin connector (factory option)
Type: HIROSE 10-Pin Connector 3260-10S3(55)
Table 8. HIROSE 10P pin assignment
No
I/O
Name
Note 1 O
TTL OUT2
Line8 2 O
TTL OUT3
Line9 3 I
TTL_IN2
Line10
4 NC 5 GND
6 I
LVDS_IN1+
Line11
7 I LVDS_IN1-
8
NC 9 GND
10 GND
5.3 Digital IN/OUT interface
In the SP-5000M-GE2 and SP-5000C-GE2, the digital IN/OUT capability in the software control tool
can assign the necessary signals needed for the system.
5.3.1 Line Selector
In the Line Selector, the following input and output signals can be assigned.
Table 9. Line selector
Note1: Select and connect the line source signal against the item selected in the line selector.
Note2: Line 8 and 9 are available if AUX Type 3 (Optional configuration) is selected.
5.3.2 Line Source
Line source signal can be selected from the following table to connect it to the line item
which is selected in the line selector.
Line Selector item
Description
Line 2 Opt 1 Out
Opt 1 output from # and #8 pins of DC In/Trigger 12-Pin on the rear
Line 3 Opt 2 Out
Opt Out 2 output from #9 & 10 pins of DC In/Trigger 12-Pin on the rear
Line 8 TTL 2 Out
TTL 2 output from #1pin “AUX” HIROSE 10-Pin on the rear (Factory option)
Line 9 TTL 3 Out
TTL 3 output from #2pin “AUX” HIROSE 10-Pin on the rear (Factory option)
NAND 0 In 1
First input at NAND first gate in GPIO
NAND 0 In 2
Second input at NAND first gate in GPIO
NAND 1 In 1
First input at NAND second gate in GPIO
NAND 1 in 2
Second input at NAND second gate in GPIO
Page 35

SP-5000M-GE2 / SP-5000C-GE2
- 33 -
Table 10. Line Source
Line Source item
Description
Low
Connect Low Level signal to line item selected in Line Selector, Default setting
High
Connect High Level signal to line item selected in Line Selector
Frame Trigger Wait
Connect Frame Trigger Wait signal to line item selected in Line Selector
Frame Active
Connect Frame Active signal to line item selected in Line Selector
Acquisition Trigger Wait
Connect Acquisition Trigger Wait signal to line item selected in Line Selector
Acquisition Active
Connect Acquisition Active signal to line item selected in Line Selector
Exposure Active
Connect Exposure Active signal to line item selected in Line Selector
FVAL
Connect FVAL signal to line item selected in Line Selector
LVAL
Connect LVAL signal to line item selected in Line Selector
PulseGenerator0 Out
Connect Pulse Generator 0 signal to line item selected in Line Selector
PulseGenerator1 Out
Connect Pulse Generator 1 signal to line item selected in Line Selector
PulseGenerator2 Out
Connect Pulse Generator 2 signal to line item selected in Line Selector
PulseGenerator3 Out
Connect Pulse Generator 3 signal to line item selected in Line Selector
User output 0
Connect User Output 0 signal to line item selected in Line Selector
User output 1
Connect User Output 1 signal to line item selected in Line Selector
User output 2
Connect User Output 2 signal to line item selected in Line Selector
User output 3
Connect User Output 3 signal to line item selected in Line Selector
Line 5 Opt 1 In
Connect Opt 1 In signal to line 5 in Line Selector
Line 6 Opt 2 In
Connect Opt 2 In signal to line 6 in Line Selector
NAND 0 Out
Connect NAND 0 signal to line item selected in Line Selector
NAND 1 Out
Connect NAND 1 signal to line item selected in Line Selector
Line 10 TTL 2 In
Connect TTL 2 In signal to Line 10
Line 11 LVDS 1 In
Connect LVDS 1 In signal to Line 11
Note1: As for LVAL, some line items cannot be connected. Refer to “5.3.7.2 GPIO matrix table”
Note2: Line 10 and 11 are available if AYX Type 3 (Optional configuration) is selected.
Page 36

SP-5000M-GE2 / SP-5000C-GE2
- 34 -
5.3.3 Line Mode
Indicates the status of the interface, input or output.
5.3.4 Line Inverter
Sets the polarity of the selected input or output.
5.3.5 Line Status
Indicates the status of the selected signal, input or output (True=High or False=Low)
5.3.6 Line Format
Controls the format of the line item selected in Line Selector.
(No Connect, TTL, LVDS, Opt Coupled)
5.3.7 GPIO
This is a general interface for input and output and controls input and output for trigger signals or
valid signals and pulse generator. By using this interface, you can control an external light source,
make a delayed function to input a trigger signal or make a precise exposure control with PWC
trigger.
5.3.7.1 Basic block diagram
Note: Items written in blue are available only if Type 3 is selected for AUX connector.
Page 37

SP-5000M-GE2 / SP-5000C-GE2
- 35 -
Soft Trigger
LVAL IN
FVAL IN
Exposure Active
Acquisition Trigger Wait
Acquisition Active
Frame Trigger Wait
Frame Active
User output 0
User output 1
User output 2
User output 3
Action 1
Action 2
GPIO 5 (OPT IN 1)
GPIO 6 (OPT IN2)
GPIO 10 (TTL IN2)
GPIO 11 (LVDS IN)
Pixel Clock
Cross Point
Switch
12 bit Counter
INV
INV
INV N
NAND
INV
Non INV
Pulse Generator
20 bit counter x 4
CLR
Trigger 0 (Acquisition Start)
Sel Bit (5,0) Sel Bit (7)
Sel Bit (7)
Pulse Generator 0
Pulse Generator 1
Pulse Generator 2
Pulse Generator 3
Trigger 1 (Acquisition Stop)
Trigger 3 (Transfer Start)
Trigger 2 (Frame Start)
GPIO 2 (OPT OUT 1)
OPT 3 (OPT OUT 2)
GPIO 8 (TL OUT 2)
GPIO 9 (TTL OUT 3)
Sel Bit (7)
Fig. 6 GPIO
Page 38

SP-5000M-GE2 / SP-5000C-GE2
- 36 -
5.3.7.2 IN and OUT matrix table
The following table shows the input and output matrix table.
Table 11. GPIO IN and OUT matrix table
Selector (Cross
point switch output)
Source signal
(Cross point switch input)
LOW
HIGH
Line 5 - 12P OPT 1 In
Line 6 - 12P OPT 2 In
NAND 1 Out 1
NAND 2 Out 1
Pulse Generator 0
Pulse Generator 1
Pulse Generator 2
Pulse Generator 3
User Output 0
User Output 1
User Output 2
User Output 3
Software Trigger
Action 1
Action 2
FVAL
LVAL
Exposure Active
Acquisition Trigger Wait
Acquisition Active
Frame Trigger Wait
Frame Active
Line 10 - TTL 2 In
Line 11 - LVDS 1 In
Extension GPIO
Connection
NAND 2 In 2
Pulse Generator 0
Pulse Generator 1
Pulse Generator 2
Pulse Generator 3
Pulse Generator
Clear Source
Line Source
Line 9 - TTL 3 Out
NAND 1 In 1
NAND 1 In 2
NAND 2 In 1
Trigger
Selector
Line Selector
Pulse Generator
Selector
Acquisition Start
Acquisition Stop
Frame Start
Line 2 - 12P OPT Out 1
Line 8 - TTL 2 Out
Line 3 - 12P Opt Out 2
Note: As for Line 8, Line 9, Line 10 and Line 11 are available if AUX Type 3 is used for AUX connector
configuration.
Page 39

SP-5000M-GE2 / SP-5000C-GE2
- 37 -
5.4 Optical Interface
SP-5000-GE2 is equipped with opto-isolated inputs and outputs, providing galvanic separation
between the camera’s inputs/outputs and peripheral equipment.
In addition to galvanic separation, the opto-isolated inputs and outputs can cope with a wide range
of voltages; the voltage range for inputs is +3.3V to +24V DC whereas outputs will handle +5V to
+24V DC.
The following drawing is the concept of photo coupler
Fig.7 Photo coupler
5.4.1 Recommended External Input circuit diagram for customer
Fig.8 Example of external input circuit
5.4.2 Recommended External Output circuit diagram for customer
+3.3V
Fig.9 Example of external output circuit
Page 40

SP-5000M-GE2 / SP-5000C-GE2
- 38 -
5.4.3 Characteristics of optical interface
The relationship of the input signal to the output signal through the optical interface is as follows.
270Ω
User Power(VCC)
3.3V
5V
12V
24V
Time Delay Rise TDR (us)
0.54
0.54
0.62
0.68
Rise Time RT (us)
1.2
1.2 2 3
Time Delay Fall TDF (us)
1.5
1.5
2.4
2.1
Fall Time FT (us)
3.6
3.4
4.5
6.8
Fig.10 Optical interface characteristics
5.5 Pulse Generator
The SP-5000-GE2 has a frequency divider using the pixel clock as the basic clock and four pulse
generators. In each Pulse Generator, various Clear settings are connected to GPIO.
The following shows Pulse Generator default settings.
Table12. Pulse Generator default settings
Display Name
Value
Clock Pre-scaler
1
Pulse Generator
Selector
Pulse Generator
Length
Start
Point
End
Point
Repeat
Count
Clear
Source
Clear
Inverter
Clear
Activation
Clear
Sync
Mode
-
Pulse Generator 0
1 0 1 0 Off
True
Off
Async Mode
-
Pulse Generator 1
1 0 1 0 Off
True
Off
Async Mode
-
Pulse Generator 2
1 0 1 0 Off
True
Off
Async Mode
-
Pulse Generator 3
1 0 1 0 Off
True
Off
Async Mode
Note: When Pulse Generator Repeat Count is set to “0”, the camera is operating in Free Running mode.
However, based on the above default setting, Length=1, Start Point=0 and End Point=1, Pulse Generator stops at
High output. Therefore, if Start Point=0 and End Point=1 are configured, Length should be “2” as the minimum
active width.
SP-5000-GE2
270Ω
User
Power
Output line
Voltage
Page 41

SP-5000M-GE2 / SP-5000C-GE2
- 39 -
5.5.1 Clock Pre-scaler
Clock pre-scaler (Divide Value) can set the dividing value of the frequency divider (12-bit
length) and the pixel clock is used for this. Four built-in pulse generators work by the same
clock. In the SP-5000-GE2, the pixel clock is set at 48 MHz.
5.5.2 Pulse Generator Selector
This is where you select one of the 4 pulse generators in order to set or modify its
parameters.
Table13. Pulse Generator setting
Pulse generator
length
Pulse generator Start point
Pulse generator End point
Pulse generator repeat count = N
(Pulse generator length x N)
Pulse generator
Clear source IN
(Clear activation
= Rising edge
Clear SYNC mode
= Async)
Pulse generator
Output
Pulse generator
length
Pulse generator
length
000
Fig.11 Pulse Generator Pulse construction
5.5.3 Pulse Generator Length
Set the counter up value (number of clocks, refer to Table 14) for the selected pulse generator.
If Repeat Count value is “0”, and if Pulse Generator Clear signal is not input, the pulse
generator generates the pulse repeatedly until reaching this counter up value.
Trigger Selector
item
Description
Pulse Generator 0
If Pulse Generator 0 is selected, Length Start Point, End Point, Repeat Count, Clear Source, Clear
Inverter Clear Activation and Clear Sync Mode of pulse generator 0 are displayed under the
selector.
Pulse Generator 1
If Pulse Generator 1 is selected, Length Start Point, End Point, Repeat Count, Clear Source, Clear
Inverter Clear Activation and Clear Sync Mode of pulse generator 1 are displayed under the
selector.
Pulse Generator 2
If Pulse Generator 2 is selected, Length Start Point, End Point, Repeat Count, Clear Source, Clear
Inverter Clear Activation and Clear Sync Mode of pulse generator 2 are displayed under the
selector.
Pulse Generator 3
If Pulse Generator 3 is selected, Length Start Point, End Point, Repeat Count, Clear Source, Clear
Inverter Clear Activation and Clear Sync Mode of pulse generator 3 are displayed under the
selector.
Page 42

SP-5000M-GE2 / SP-5000C-GE2
- 40 -
5.5.4 Pulse Generator Start Point
Set the active output start count value for the selected pulse generator.
However, please note that a maximum 1 clock jitter for the clock which is divided in the clock
pre-scaler can occur.
5.5.5 Pulse Generator End Point
Set the active output ending count value for the selected pulse generator.
5.5.6 Pulse Generator Repeat Count
Set the repeating number of the pulse for the selected pulse generator. After Trigger Clear
signal is input, the pulse generator starts the count set in Repeat Count. Accordingly, an active
pulse which has a start point and end point can be output repeatedly.
However, if Repeat Count is set to “0”, it works as a Free-Running counter.
5.5.7 Pulse Generator Clear Activation
Set the clear conditions of clear count pulse for the selected pulse generator.
5.5.8 Pulse Generator Clear Sync Mode
Set the count clear method for the selected pulse generator. In the case of Async Mode, if the
clear signal is input during the length setting value, the counter will stop counting according to
the clear signal input. In the case of Sync Mode, if the clear signal is input during the length
setting value, the counter will continue to count until the end of the length setting value and
then clear the count. Both modes clear the repeat count when the counter is cleared.
Fig.12 Counter clear in Async mode
Fig.13 Counter clear in Sync mode
0
Clear
↓
Pulse
Generator
Output
Pulse
Generator
Clear Source In
(Example 1) Clear Activation = Rising Edge, Clear Sync Mode = Async Mode,
Clear Inverter = False
(Example 2) Clear Activation = Rising Edge, Clear Sync Mode = Sync Mode,
Clear Inverter = False
Pulse
Generator
Output
Pulse
Generator
Clear Source In
0
Pulse
Generator
Length
0
Clear
↓
Note: Repeat Count is also reset.
Page 43

SP-5000M-GE2 / SP-5000C-GE2
- 41 -
5.5.9 Pulse Generator Clear Source
The following clear source can be selected as the pulse generator clear signal.
Table14. Pulse generator clear source
Pulse Generator
Clear Source
item
Description
Low
Connect Low level signal to Clear Source for the selected pulse generator.
Default setting
High
Connect High level signal to Clear Source for the selected pulse
generator.
Frame Trigger Wait
Connect Frame Trigger Wait signal to Clear Source for the selected pulse
generator.
Frame Active
Connect Frame Active signal to Clear Source for the selected pulse
generator.
Exposure Active
Connect Exposure Active signal to Clear Source for the selected pulse
generator.
Acquisition Trigger
wait
Connect Acquisition Trigger Wait signal to Clear Source for the selected
pulse generator.
Acquisition Active
Connect Acquisition Active signal to Clear Source for the selected pulse
generator.
FVAL
Connect FVAL signal to Clear Source for the selected pulse generator.
LVAL
Connect LVAL signal to Clear Source for the selected pulse generator.
PulseGenerator0
Out
Connect Pulse Generator 0 output to Clear Source for the selected pulse
generator.
PulseGenerator1
Out
Connect Pulse Generator 1 output to Clear Source for the selected pulse
generator.
PulseGenerator2
Out
Connect Pulse Generator 2 output to Clear Source for the selected pulse
generator.
PulseGenerator3
Out
Connect Pulse Generator 3 output to Clear Source for the selected pulse
generator.
Action 1
Connect Action 1 input to Clear Source for the selected pulse generator.
Action 2
Connect Action 2 input to Clear Source for the selected pulse generator.
User output0 Out
Connect User output 0 to Clear Source for the selected pulse generator.
User output1 Out
Connect User output 1 to Clear Source for the selected pulse generator.
User output2 Out
Connect User output 2 to Clear Source for the selected pulse generator.
User output3 Out
Connect User output 3 to Clear Source for the selected pulse generator.
Line 5 Opt 1 In
Connect Opt 1 In signal to Clear Source for the selected pulse generator.
Line 6 OPT2 in
Connect Opt 1 In signal to Clear Source for the selected pulse generator.
Nand 0 Out
Connect NAND 0 output signal to Clear Source for the selected pulse
generator.
Nand 1 Out
Connect NAND 1 output signal to Clear Source for the selected pulse
generator.
Line 10 TTL 2 In
Connect TTL 2 In signal to LINE 10.
Line 11 LVDS 1 In
Connect LVDS 1 In signal to Line 11
Note:
The pulse generator output cannot be used as the clear input to the same pulse generator. Refer
to “5.3.7.2. Table 10 ”.
Page 44

SP-5000M-GE2 / SP-5000C-GE2
- 42 -
5.5.10 Pulse Generator Inverter
Clear Source Signal can have polarity inverted.
5.5.11 Pulse Generator Setting Parameters
Table15. Pulse Generator setting parameters
Display Name
Value
Clock Pre-scaler
1 to 4096
Pulse Generator Clock (MHz)
[Pixel Clock:48 MHz]÷[Clock Pre-scaler]
Pulse Generator Selector
- Pulse Generator 0
- Pulse Generator 1
- Pulse Generator 2
- Pulse Generator 3
- Pulse Generator Length
1 to 1048575
- Pulse Generator Length (ms)
([Clock Source]÷[Clock Pre-scaler])-1 x [Pulse Generator Length]
- Pulse Generator Frequency (Hz)
[Pulse Generator Length (ms)]-1
- Pulse Generator Start Point
0 to 1048574
- Pulse Generator Start Point (ms)
([Clock Source]÷[Clock Pre-scaler])-1 x [Pulse Generator Start Point]
- Pulse Generator End Point
1 to 1048575
- Pulse Generator End Point (ms)
([Clock Source]÷[Clock Pre-scaler])-1 x [Pulse Generator End Point]
- Pulse Generator pulse-width (ms)
[ Pulse Generator End Point (ms)]-[ Pulse Generator Start Point (ms)]
- Pulse Generator Repeat Count
0 to 255
- Pulse Generator Clear Activation
Clear Mode for the Pulse Generators
- Off
- High Level
- Low level
- Rising Edge
- Falling Edge
- Pulse Generator Clear Sync Mode
- Async mode
- Sync mode
- Pulse Generator Clear Source-
UserOutput3
- Low
- High
- Frame Trigger Wait
- Frame Active
- Exposure Active
- Fval
- Lval
- PulseGenerator0
- PulseGenerator1
- PulseGenerator2
- PulseGenerator3
- UserOutput 0
- UserOutput 1
- UserOutput 2
- UserOutput 3
- TTL_In1
- Action 1
- Action 2
- Nand0 Out
- Nand1 Out
- Line 10 - TTL 2 In
- Line 11 - LVDS 1 In
- Pulse Generator Inverter(Polarity)
Pulse Generator Clear Inverter
- False
- True
Note:
1. If Pulse Generator Repeat Count is set to “0”, the pulse generator works in Free Running mode.
Page 45

SP-5000M-GE2 / SP-5000C-GE2
- 43 -
6. Sensor layout, output format and timing
6.1 Sensor layout
CMOS sensors used in the SP-5000M-GE2 and SP-5000C-GE2 have the following tap and pixel layout.
6.1.1 Monochrome sensor
2560 Pixels
2048 Pixels
F
Fig.14 Monochrome sensor layout
6.1.2 Bayer color sensor
2560 Pixels
2048 Pixels
F
Adress(0,0)
Fig.15 Bayer color sensor layout
Page 46

SP-5000M-GE2 / SP-5000C-GE2
- 44 -
6.2. Camera output format
The following table shows the relationship between camera output and sensor readout system.
Camera output format
Sensor readout system
Reference figure
1X–1Y
1-tap readout
6.2.1
Note: The description of camera output format is based on GenICam SFNC Ver.1.5.1.
6.2.1 1X-1Y
1X–1Y is defined in GenICam SFNC Ver.1.5.1 for 1-tap readout and the readout system is the
following.
Width = 2560 Pixel
Height = 2048 Pixel
X5120
Y1
X5120
Y3840
X4
Y1
X4
Y2048
X3
Y1
X3
Y2048
X2
Y1
X2
Y2048
X5
Y1
X5
Y2048
X6
Y1
X6
Y2048
X7
Y1
X7
Y2048
X8
Y1
X8
Y2048
X2053
Y1
X2553
Y2048
X2054
Y1
X2554
Y2048
X2055
Y1
X2555
Y2048
X2056
Y1
X2556
Y2048
X2057
Y1
X2557
Y2048
X2058
Y1
X2558
Y2048
X2059
Y1
X2559
Y2048
X2056
Y1
X2056
Y2
X2560
Y2047
X2560
Y2048
X1
Y1
X1
Y2
X1
Y2047
X1
Y2048
Tap 1
Pixel(0,0)
Step Y = 1
Step X = 1
Fig.16 1X – 1Y readout
6.2 GigE Vision Pixel Format
6.2.1 Pixel Format
Model
Supported Pixel Formats
SP-5000M-GE2
Mono8, Mono10, Mono10_Packed
SP-5000C-GE2
BayGR8, BayGR10, BayGR10_PackedRGB8_PACKED, YUV411_PACKED,
YUV422_PACKED, YUV444_PACKED
Page 47

SP-5000M-GE2 / SP-5000C-GE2
- 45 -
6.2.2 SP-5000M-GE2 Pixel Type
6.2.2.1 GVSP_PIX_MONO8 8-bit output
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7
Y0 Y1 Y2
6.2.2.2 GVSP_PIX_MONO10 16-bit output
X0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 X X X X X X 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7
Y0 Y0 Y1
98 X X X X X X
Y1
6.2.2.3 GVSP_PIX_MONO10PACKED 12-bit output
2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 0 1 X X 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9X X 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 0 1 X X 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9X X
Y0 Y1 Y2 Y3
6.2.3 SP-5000C-GE2 Pixel Type
6.2.3.1 GVSP_PIX_BAYGR8 8-bit output
odd Line
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7
R1 G2G0
Even Line
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7
B0 G1 B2
6.2.3.2 GVSP_PIX_BAYGR10 16-bit output
Odd Line
X0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 X X X X X X 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7
G0 G0 R1
98 X X X X X X
R1
Even Line
X0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 X X X X X X 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7
B0 B0 G1
98 X X X X X X
G1
Page 48

SP-5000M-GE2 / SP-5000C-GE2
- 46 -
6.2.3.3 GVSP_PIX_BAYGR10PACKED 12-bit output
Odd Line
2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 0 1 X X 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9X X
G0 R1
Even Line
2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 0 1 X X 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9X X
B0 G1
6.2.3.4 GVSP_PIX_RGB8_PACKED (24-bit)
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7
R0 G0 B0
6.2.3.5 GVSP_PIX_YUV411_Packed 12-bit output
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 70 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 70 1 2 3 4 5 6 S 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 S
U11 Y11 Y12 V11 Y13 Y14
4 pixels/6 Bytes
6.2.3.6 GVSP_PIX_YUV422_Packed 16-bit output
U0 Y11 V11 Y12
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 S 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 S0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7
2 pixels/4 bytes
U11
6.2.3.7 GVSP_PIX_YUV444_Packed 24-bit output
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7
U11 Y11 V11
1 pixel/3 Bytes
Page 49

SP-5000M-GE2 / SP-5000C-GE2
- 47 -
6.2.4 PixelSize
Table16. Pixel size
Bit per Pixel
Pixel Format
SP-5000M-GE2
SP-5000C-GE2
Bpp8
Mono8
BayerGR8
Bpp12
Mono10Packed
BayerGR10Packed
YUV411Packed
Bpp16
Mono10
BayerGR10
YUV422Packed
Bpp24
RGB8Packed
YUV444Packed
6.3 Output timing
6.3.1 Horizontal timing
6.3.1.1 Output format: 1X–1Y, Vertical Binning OFF
1 clock = 20.833 ns
1
5
160
1
165
LVAL
DVAL
Video
Exposure Active
Fig.17 Horizontal Timing (Vertical timing OFF)
6.3.1.2 Output format: 1X–1Y, Vertical Binning ON
1
5
160
1
165
LVAL
DVAL
Video
Exposure Active
Fig. 18 Horizontal timing (Vertical binning ON)
Page 50

SP-5000M-GE2 / SP-5000C-GE2
- 48 -
6.3.2 Vertical timing
6.3.2.1 Output format: 1X–1Y, Vertical Binning OFF
1L = 165 clocks
FVAL
DVAL
CCD
Exposure
Video
Exposure
Active
Frame
Active
2048L
47 ~48L(Min)
9 ~10L
Fig.19 Vertical Timing (Vertical binning OFF)
6.3.2.2 Output format: 1X–1Y, Vertical Binning ON
FVAL
DVAL
CCD
Exposure
Video
Exposure
Active
Frame
Active
1024L
47 ~48L(Min)
9 ~10L
Fig.20 Vertical timing (Vertical binning ON)
Page 51

SP-5000M-GE2 / SP-5000C-GE2
- 49 -
6.3.3 ROI (Region Of Interest) setting
In the SP-5000-GE2, a subset of the image can be output by setting Width, Height, Offset-X, and Offset-Y.
If the height is decreased, the number of lines read out is decreased and as the result, the frame rate is
increased. However, in the horizontal direction, the horizontal frequency is not changed if the width is
decreased. In the SP-5000-GE2, the minimum width is “8” and minimum height is “8”.
OffsetX
Width
OffsetY
Height
Width
2560 Width Max
2048 Height Max
Readout area
Fig.21 Setting example ( No binning) Fig.22 Setting example (Binning)
6.4 Digital output Bit allocation
Table17. Digital output
CCD out
Digital Out
8-bit
10-bit
12-bit
Black
0%
8LSB
32LSB
128LSB
Monochrome
100%
222LSB
890LSB
3560LSB
Color
Monochrome
115%
255LSB
1023LSB
4095LSB
Color
Digital Out [LSB]
32
70025
Analog Out [ mV]
890
1023
Black Lev el
0
White Cli p L eve l
800
100% Leve l
Fig.23 Bit allocation (10-bit)
Setting example (1)
Binning Horizontal = 1
Setting example (2)
Binning Horizontal = 2
Binning Vertical = 2
OffsetX
OffsetY
Height
Width
1280 Width Max
1024 Height Max
Readout area
Page 52

SP-5000M-GE2 / SP-5000C-GE2
- 50 -
7. Operating modes
7.1. Acquisition control (change the frame rate)
7.1.1 Acquisition Mode
In the SP-5000-GE2, the following three acquisition modes are available.
Single frame : One frame can be output by AcqusitionStart command
Multi frames : The number of frames which is specified in Acquistion Frame Count, are
output by AcquisitionStart command
Continuous : Images are continuously output by AcquisitionStart command until
AcqusitionStop command is input.
7.1.1.1 Single Frame operation
In single frame mode, executing the AcquisitionStart command causes one frame to be captured.
After one frame is captured, this operation is automatically stopped.
In order to restart the capture, it is necessary to input the AcquisitionStart command again. BlockID
is not reset until AcquisitionStop is input and is incremented when the AcquisitionStart command is
called.
In the case of PIV operation, 2 frames are captured.
◆ Normal single frame operation
1) AcquisitionStart command is input
2) AcquisitionActive becomes “TRUE” (accepts capture)
3) 1 frame is output
4) AcquisitionActive becomes “FALSE” (stop capturing)
◆ Forcing acquisition to stop
While AcquisitionActive is “TRUE”, if AcquisitionStop or AcquisitionAbort is
initiated, AcquisitionActive becomes “FALSE” (stop capturing).
However, if AcqusitionStop command is initiated during image output period,
AcqusitionActive becomes “FALSE” (stop capturing) after image output is completed.
Associated commands:Acqusition Start, Acqusition Stop
Page 53

SP-5000M-GE2 / SP-5000C-GE2
- 51 -
Setting condition 1
Acquisition Mode: Single
Trigger Selector: Acquisition Start
Trigger Mode: OFF
Note: On the above timing chart, signals indicated by ( ) describe operation inside the camera.
Fig.24 Single Frame operation timing(1)
FVAL(Sensor Read out)
Acquisition Trigger Wait
Frame Trigger Wait
Acquisition Active
Exposure Active
Frame Active
(Sensor Exposure)
(Stream Active)
Acquisition Status
Output Signals
Acquisition Trigger Wait =
L
Frame Trigger Wait = L
Acquisition Active
Frame Active
Exposure Active
FALSE
TRUE
FALSE
FALSE
TRUE
FALSE
FALSE
TRUE
FALSE
FALSE
FALSE
Acquisition Start
command
Page 54

SP-5000M-GE2 / SP-5000C-GE2
- 52 -
Setting condition 2
Acquisition Mode: Single
Trigger Selector: Acquisition Start
Trigger Mode: ON
Fig.25 Single Frame operation timing (2)
FVAL(Sensor Read out)
Acquisition Trigger Wait
Frame Trigger Wait
Acquisition Active
Exposure Active
Frame Active
(Sensor Exposure)
(Stream Active)
Acquisition Status
Output Signals
Frame Trigger Wait = L
Acquisition Active
Frame Active
Exposure Active
FALSE
TRUE
FALSE
FALSE
TRUE
FALSE
FALSE
TRUE
FALSE
FALSE
FALSE
Acquisition Start
command
Trigger
Acquisition Trigger Wait
TRUE
FALSE
Page 55

SP-5000M-GE2 / SP-5000C-GE2
- 53 -
Setting condition 3
Acquisition Mode: Single
Trigger Selector: Frame Start
Trigger Mode: ON
Fig.26 Single Frame operation timing (3)
FVAL(Sensor Read out)
Acquisition Trigger Wait
Frame Trigger Wait
Acquisition Active
Exposure Active
Frame Active
Sensor Exposure
Stream Active
Acquisition Status
Output Signals
Acquisition Trigger Wait
= L
Acquisition Active
Frame Active
Exposure Active
FALSE
TRUE
FALSE
FALSE
TRUE
FALSE
FALSE
TRUE
FALSE
FALSE
FALSE
Acquisition Start
command
Trigger
Frame Trigger Wait
TRUE
FALSE
Page 56

SP-5000M-GE2 / SP-5000C-GE2
- 54 -
7.1.1.2 Multi Frame operation
In this mode, the AcquisitionStart command captures the number of frames which are specified by
AcquisitionFrameCount.
◆ Normal multi-frame operation
1) AcquisitionStart command is input
2) AcquisitionTriggerWait becomes effective
3) AcquisitionActive becomes “TRUE”(accepts capture)
4) Output N frames as specified by AcquisitionFrameCount
5) AcquisitionActive becomes “FALSE”. Then the output stops. (See the following
diagram)
◆ Forcing acquisition to stop
While AcquisitionActive is “TRUE”, if AcquisitionStop or AcquisitionAbort is
initiated, AcquisitionActive becomes “FALSE” (stop capturing).
Once the operation is set to “FALSE”, the internal FrameCount is reset.
However, if AcqusitionStop command is initiated during image output period,
AcqusitionActive becomes “FALSE” (stop capturing) after image output is completed.
Once, AcqusitionActive becomes “FALSE”, the internal count is reset.
Acqusition Frame Count (16-bit): Can be set in the range of 1 to 65535
In PIV mode, Acquisition Frame Count (16-bit) can be set in the range of 2 to 65535.
The setting for PIV mode is 2 steps.
Associated commands: Acqusition Start, Acqusition Frame Count, Acquisition Stop
Page 57

SP-5000M-GE2 / SP-5000C-GE2
- 55 -
Setting condition 1
Acquisition Mode: Multi
Trigger Selector: Acquisition Start
Acquisition Frame Count : 2
Trigger Mode: OFF
Fig.27 Multi Frame operation timing (1)
FVAL(Sensor Read out)
Acquisition Trigger Wait
Frame Trigger Wait
Acquisition Active
Exposure Active
Frame Active
(Sensor Exposure)
(Stream Active)
Acquisition Status
Output Signals
Acquisition Trigger Wait =
Frame Trigger Wait = L
Acquisition Active
Frame Active
Exposure Active
FALSE
TRUE
FALSE
FALSE
TRUE
FALSE
TRUE
FALSE
FALSE
FALSE
Acquisition Start
command
FALSE
TRUE
FALSE
Page 58

SP-5000M-GE2 / SP-5000C-GE2
- 56 -
Setting operation 2
Acquisition Mode: Multi
Trigger Selector: Acquisition Start
Acquisition Frame Count: 2
Trigger Mode: ON
Fig.28 Multi Frame operation timing (2)
FVAL(Sensor Read out)
Acquisition Trigger Wait
Frame Trigger Wait
Acquisition Active
Exposure Active
Frame Active
(Sensor Exposure)
(Stream Active)
Acquisition Status
Output Signals
Frame Trigger Wait = L
Acquisition Active
Frame Active
Exposure Active
FALSE
TRUE
FALSE
FALSE
FALSE
TRUE
FALSE
FALSE
FALSE
Acquisition Start
command
Trigger
Acquisition Trigger
Wait
TRUE
FALSE
TRUE
FALSE
TRUE
FALSE
Page 59

SP-5000M-GE2 / SP-5000C-GE2
- 57 -
Setting operation 3
Acquisition Mode: Multi
Trigger Selector: Frame Start
Acquisition Frame Count: 2
Trigger Mode: ON
Fig.29 Multi Frame operation timing (3)
FVAL(Sensor Read out)
Acquisition Trigger Wait
Frame Trigger Wait
Acquisition Active
Exposure Active
Frame Active
(Sensor Exposure)
(Stream Active)
Acquisition Status
Output Signals
Acuisition Trigger Wait
= L
Acquisition Active
Frame Active
Exposure Active
FALSE
TRUE
FALSE
FALSE
FALSE
TRUE
FALSE
FALSE
FALSE
Acquisition Start
command
Trigger
Frame Trigger Wait
TRUE
FALSE
TRUE
FALSE
TRUE
FALSE
Page 60

SP-5000M-GE2 / SP-5000C-GE2
- 58 -
7.1.1.3 Continuous
In this mode, when the AcquisitionStart command is set, the image is continuously output at the
current frame rate. This is the default setting for the SP-5000M-GE2 and SP-5000C-GE2.
1) AcquisitionStart command is input
2) AcquisitionTriggerWait becomes effective
3) AcquisitionActive becomes “TRUE”
4) Images begin outputting continuously
5) AcquisitionStop command is sent
6) AcquisitionActive becomes “FALSE”. At this moment, the output stops.
However, if AcqusitionStop command is initiated during image output period,
AcqusitionActive becomes “FALSE” (stop capturing) after image output is completed.
Associated commands: Acqusition Start, Acqusition Stop
Page 61

SP-5000M-GE2 / SP-5000C-GE2
- 59 -
Setting operation 1
Acquisition Mode: Continuous
Trigger Selector: Acquisition Start
Trigger Mode: OFF
Fig.30 Continuous operation timing (1)
FVAL(Sensor Read out)
Acquisition Trigger Wait
Frame Trigger Wait
Acquisition Active
Exposure Active
Frame Active
(Sensor Exposure)
(Stream Active)
Acquisition Status
Output Signals
Acquisition Trigger Wait
= L
Frame Trigger Wait
= L
Acquisition Active
Frame Active
Exposure Active
FALSE
TRUE
FALSE
FALSE
TRUE
FALSE
TRUE
FALSE
FALSE
FALSE
Acquisition Start
command
FALSE
TRUE
FALSE
Acquisition Stop
command
TRUE
FALSE
Page 62

SP-5000M-GE2 / SP-5000C-GE2
- 60 -
Setting condition 2
Acquisition Mode: Continuous
Trigger Selector: Acquisition Start
Trigger Mode: ON
Fig.31 Continuous operation timing (2)
FVAL(Sensor Read out)
Acquisition Trigger Wait
Frame Trigger Wait
Acquisition Active
Exposure Active
Frame Active
(Sensor Exposure)
(Stream Active)
Acquisition Status
Output Signals
Frame Trigger Wait
= L
Acquisition Active
Frame Active
Exposure Active
FALSE
TRUE
FALSE
FALSE
FALSE
TRUE
FALSE
FALSE
FALSE
Acquisition Start
command
Trigger
Acquisition Trigger
Wait
TRUE
FALSE
TRUE
FALSE
TRUE
FALSE
Acquisition Stop
command
Page 63

SP-5000M-GE2 / SP-5000C-GE2
- 61 -
Setting condition 3
Acquisition Mode: Continuous
Trigger Selector: Frame Start
Trigger Mode: ON
Fig.32 Continuous operation timing (3)
FVAL(Sensor Read out)
Acquisition Trigger Wait
Frame Trigger Wait
Acquisition Active
Exposure Active
Frame Active
(Sensor Exposure)
(Stream Active)
Acquisition Status
Output Signals
Acuisition Trigger Wait
= L
Acquisition Active
Frame Active
Exposure Active
FALSE
TRUE
FALSE
FALSE
FALSE
TRUE
FALSE
FALSE
FALSE
Acquisition Start
command
Trigger
Frame Trigger Wait
TRUE
FALSE
TRUE
FALSE
TRUE
FALSE
Acquisition Stop
command
TRUE
FALSE
FALSE
TRUE
Page 64

SP-5000M-GE2 / SP-5000C-GE2
- 62 -
7.1.2 Acquisition frame rate
With Trigger OFF (free running mode – see section 7.2.1), the default frame rate of the camera is
based on the specified ROI. The smaller the ROI, the faster the default frame rate. However, it is
possible to specify a free-running frame rate (i.e., no trigger needed) that is slower than the
default rate. This can be useful when a longer exposure time is needed for a specific ROI.
Modification of the frame rate is done by entering a value in the AcquisitionFrameRate control
corresponding to the frame frequency. Allowed values range from 6999 Hz to 0.125 Hz (µs) for
SP-5000-GE2, however if the value entered is less than the time required for the default frame rate,
the setting is ignored and the default frame rate is used. For example, the minimum frame period
for the smallest possible ROI (8 lines) requires 6999 Hz (fps)(8-bit, LAG), so any entry more than
6999 Hz (fps) will always be ignored.
The setting range in Acquisition Frame Rate is:
Shortest
to
Longest
Inverse number of time
required to drive all pixels in
the area set by ROI
command or
inverse number of time
required to transmit one
frame data
to
0.125 Hz (fps) = 8 seconds
For the above setting, Acquisition Frame Rate is used and its unit is Hz (fps).
Acquisition Frame Rate: 6999 Hz (fps) to 0.125 Hz (fps)
7.1.3 Calculation of frame rate
The actual frame rate is the smaller one between the sensor output frame rate and frame rate of
network bandwidth. If frame rate of network bandwidth is smaller than sensor output frame rate,
sensor output frame rate is automatically adjusted to match frame rate of network bandwidth.
The calculation formula for each frame rate is the following.
7.1.3.1 Calculation of sensor output maximum frame rate
Parameters
400 Mono8, Bayer8
770 Mono10, Mono10Packed,Bayer10, Bayer10Packed, YUV411Packed, YUV422Packed
1500 RGB8, YUV444Packed
32 Mono10Packed, Bayer10Packed, YUV411Packed
0 Other formats
1 OFF
2 ON
Clock of line
Additional clock
Horizontal binning
Page 65

SP-5000M-GE2 / SP-5000C-GE2
- 63 -
Clock number of 1 line
ValidClocksOfLine = (ClocksOfLine - AddtionalClocks) x (Width + 127) / 128 x 128 / 2560 +
1 + AddtionalClocks
If the result is less than 165, ValidClocksOfLine = 165;
Clock number of 1 frame
ClocksOfFrame = (ValidClocksOfLine + (BinningHorizontal - 1) x 4 ) x (Height + 7) + 858
The maximum frame that sensor can operate
SensorFrameRate (Hz) = 48000000 / ClocksOfFrame
7.1.3.2 Calculation of frame rate of network bandwidth
Parameters
1000000000 Single link
2000000000 LAG(sLAG, dLAG)
8 Mono8, Bayer8
12 Mono10Packed, Bayer10Packed, YUV411Packed
16 Mono10, Bayer10, YUV422Packed
24 RGB8, YUV444Packed
Network bit rate
Bit per pixel
Packet_Size:
Value set in Packet Size register (GevSCPSPacketSize)
Byte number of 1 frame image
ImageSize = Width * Height x BitsPerPixel / 8
Image byte number of last packet
SizeOfLastPacket = The reminder of the calculation [ImageSize mod (PacketSize - 36)]
Ethernet Frame Size of 1 frame image
If SizeOfLastPacket is 0,
FrameSize = [ImageSize / (PacketSize - 36)] x (PacketSize + 28) + 146
If SizeOfLastPacket is not 0,
FrameSize = [ImageSize / (PacketSize - 36)] x (PacketSize + 28) + 210 +
SizeOfLastPacket
The maximum frame rate which can be transferred through network
NetworkFrameRate (Hz) = Network_Bit_Rate x 0.11625 / FrameSize
Note: 0.11625 is coefficient which limits the bandwidth at 93%.
Page 66

SP-5000M-GE2 / SP-5000C-GE2
- 64 -
7.2. Exposure settings
This section describes how to set the exposure settings.
7.2.1 Exposure Mode
The exposure mode can be selected from the following three ways.
Table18. Exposure mode
Exposure Mode setting
Exposure operation
OFF
No exposure control (free-running operation)
Timed
Exposure operation at the value set in Exposure Time. Setting value is usec unit.
・If Trigger Mode setting is OFF, the camera is in free-running operation.
・If Trigger Mode setting is ON, the exposure operation depends on the setting of
Trigger Option.
Trigger Width
The exposure is controlled by the pulse width of the external trigger.
・Trigger Mode is forced to ON.
For trigger operation, Exposure Mode must be set to something other than OFF and Trigger Mode of
Frame Start must be ON.
If Exposure Mode is set at Timed, the exposure operation can be selected as follows by setting
Trigger Option
Table19. Trigger option
Trigger Option setting
Exposure operation
OFF
Timed (EPS) mode
RCT
RCT mode
PIV
PIV (Particle Image Velocimetry) mode
The effect of the combination of Exposure Mode, Trigger Option and Trigger Mode is as follows.
Table20. The combination of Exposure Mode, Trigger Option and Trigger Mode
Exposure Mode
Trigger Option
Trigger Mode
(Frame Start)
Operation
OFF
N/A
N/A
Self-running operation
Exposure control by Exposure Time
is not possible
Timed
OFF
OFF
Self-running operation
Exposure control by Exposure Time
is not possible
ON
Timed (EPS) Operation
Exposure can be controlled by
Exposure Time
RCT
Forced to ON
RCT Operation
Exposure can be controlled by
Exposure Time
PIV
Forced to ON
PIV Operation
Exposure can be controlled by
Exposure Time
Trigger Width
N/A
Forced to ON
Exposure is controlled by the pulse
width of the external trigger
Page 67

SP-5000M-GE2 / SP-5000C-GE2
- 65 -
7.2.2 Exposure Time
This command is effective only when Exposure Mode is set to Timed. It is for setting exposure time.
The setting step for exposure time is 1 μsec per step.
Minimum: 10 μsec
Maximum: 8 seconds (Note – noise may make image unusuable after 2 seconds)
7.2.3 Exposure Auto
This is a function to control the exposure automatically. It is effective only for Timed.
JAI ALC Reference controls the brightness.
There are three modes, OFF, Once and Continuous.
OFF: No exposure control
Once: Exposure adjusts when the function is set, then remains at that setting
Continuous: Exposure continues to be adjusted automatically
In this mode, the following settings are available.
ALC Speed: Rate of adjustment can be set
ASC Max: The maximum value for the exposure time to be controlled can
be set
ASC Min: The minimum value for the exposure time to be controlled can
be set
ALC Reference: The reference level of the exposure control can be set
ALC Area Type: The area for exposure control can be set (common with Gain
Auto)
ALC Customer Area Selector: Select the exposure area from 16 choices (4x4)
ALC Area Enable: This can Enable or Disable the area selected by ALC
Custom Area Selector
Fig.33 ALC Area Type
Fig.32 ALC Custom Area selector
Row0
Row1
Row2
Row3
Column 0 Column 1 Column 2 Column 3
Half Width Half Height
Half Width and Half Height
All
Page 68

SP-5000M-GE2 / SP-5000C-GE2
- 66 -
7.3. Trigger Control
The following 6 types of Trigger Control are available by the combination of Trigger Selector, Trigger
Mode, Exposure Mode and Trigger Option.
Table21. Trigger control
7.3.1 Trigger Selector
Selects the trigger operation. In the SP-5000-GE2, the following trigger operation can be
selected as the trigger.
Table22. Trigger selector
7.3.2 Trigger Mode
Select either free-running operation or external trigger operation.
OFF: Free-running operation
ON: External trigger operation
7.3.3 Trigger Source
The following signals can be used as the trigger source signal.
Camera Settings
JAI Custom
Trigger Mode
Name
Description
Trigger
Selector
Trigger
Option
Trigger
Mode
Exposure
Mode
Frame
Start
Off
Off
Off
Continuous
Trigger
Free running operation with the
maximum exposure time per the frame
rate
Off
Timed
Off
Continuous
Trigger
Free running operation with a user-set
exposure time.
On
Timed
Off
EPS Trigger
Externally triggered operation with a
user-set exposure time
On
Timed
RCT
RCT Trigger
Externally triggered operation for RCT
On
Timed
PIV
PIV Trigger
Externally triggered operation for PIV
On
Trigger
Width
Off
PWC Trigger
Externally triggered operation with a
pulse width exposure time
Trigger Selector Item
Description
Frame Start
Frame Start Trigger operation
Acquisition Start
Acquisition Start Trigger operation
Acquisition End
Acquisition End Trigger operation
Page 69

SP-5000M-GE2 / SP-5000C-GE2
- 67 -
Table23. Trigger source
7.3.4 Trigger activation
This command can select how to activate the trigger.
Rising Edge: At the rising edge of the pulse, the trigger is activated.
Falling Edge: At the falling edge of the pulse, the trigger is activated.
Note: When Trigger Width mode is used, the trigger is initiated at the rising edge or falling
edge and the exposure time is the duration at the falling edge or rising edge of the
trigger input pulse.
7.3.5 Trigger Overlap
This function defines whether or not a trigger pulse can be accepted while data is being read out.
OFF: The trigger pulse is not accepted during the sensor readout.
Read Out: The trigger pulse can be accepted during the sensor readout.
Trigger Source
item
Description
Low
Connect LOW level signal to the selected trigger operation
Default setting
High
Connect HIGH level signal to the selected trigger operation
Soft Trigger
Connect Soft Trigger signal to the selected trigger operation
Trigger can be input manually by the execution of the software trigger
Trigger software is available on each trigger source.
PulseGenerator0
Out
Connect Pulse generator 0 signal to the selected trigger operation
PulseGenerator1
Out
Connect Pulse generator 1 signal to the selected trigger operation
PulseGenerator2
Out
Connect Pulse generator 2 signal to the selected trigger operation
PulseGenerator3
Out
Connect Pulse generator 3 signal to the selected trigger operation
Line 5 - OPT IN 1
Connect TTL 1 IN signal to the selected trigger operation
Line 6 - OPT IN 2
Connect OPTO IN 1 signal to the selected trigger operation
NAND 0 Out
Connect NAND 0 OUT signal to the selected trigger operation
NAND 1 Out
Connect NAND 1 OUT signal to the selected trigger operation
User Output 0
Connect User Output 0 signal to the selected trigger operation.
0 or 1 status can be sent by User 0 command from PC (Host side).
User Output 1
Connect User Output 1 signal to the selected trigger operation.
0 or 1 status can be sent by User 0 command from PC (Host side).
User Output 2
Connect User Output 2 signal to the selected trigger operation.
0 or 1 status can be sent by User 0 command from PC (Host side).
User Output 3
Connect User Output 3 signal to the selected trigger operation.
0 or 1 status can be sent by User 0 command from PC (Host side).
Action1
Connect Action 1 signal to the selected trigger operation.
Action2
Connect Action 2 signal to the selected trigger operation.
Line 10 - TLL IN 2
Connect TTL 2 IN signal to Line 10
Line 11 - LVDS IN
Connect LVDS 1 IN signal to Line 11
Page 70

SP-5000M-GE2 / SP-5000C-GE2
- 68 -
7.4. Normal continuous operation (Timed Exposure Mode/Trigger Mode OFF)
This is used for applications which do not require triggering. In this mode, the video signal for the
auto-iris lens is available if AUX connector is configured with option Type 2.
For the video timing, refer to chapter 6.3.
Primary settings to use this mode
Trigger Mode: Off
7.5. Timed mode
This mode allows a single image frame to be captured with a preset exposure time by using the
external trigger. Additional settings determine if the trigger pulse can be accepted during the
exposure period.
Primary settings to use this mode
Exposure Mode: Timed
Trigger Mode: ON
Trigger Option: OFF
7.5.1 If the overlap setting is “OFF”
Trigger
CCD
Exposure
XEEN
FVAL
Exposure
Active
Exposure Period
t5
t1
t2
t3
t4
t1
t2
t3
t4
t5
2L (Min)
30 µs
10.13 µs
2.51 µs
8L to 9L (18.142 µs)
Fig.34 Overlap OFF
Page 71

SP-5000M-GE2 / SP-5000C-GE2
- 69 -
7.5.2 If the overlap setting is “Readout”
Trigger
CCD
Exposure
XEEN
FVAL
Exposure
Active
Exposure Period
t5
t1
t2
t3
t4
Fig.35 Readout
7.6. Trigger width mode
In this mode, the exposure time is equal to the trigger pulse width. Accordingly, longer
exposure times are supported. Additional settings determine if the trigger pulse can be accepted
during the exposure period.
The frame rate of full pixels readout is 44 fps.
Primary settings to use this mode
Exposure Mode: Trigger Width
Trigger Mode: ON
Trigger Option: OFF
7.6.1 If the overlap setting is “OFF”
Trigger
CCD
Exposure
XEEN
FVAL
Exposure
Active
Exposure Period
t6
t1
t2
t3
t4
t5
Fig.36 Overlap = OFF
t1
t2
t3
t4
t5
2L
30 µs
10.13 µs
2.51 µs
8L to 9L (18.142 µs)
t1
t2
t3
t4
t5
t6
2L (Min)
30 µs
10.158 µs
2.75 µs
226 ns
7L to 8L
Page 72

SP-5000M-GE2 / SP-5000C-GE2
- 70 -
7.6.2 If the overlap setting is “Readout”
Trigger
CCD
Exposure
XEEN
FVAL
Exposure
Active
Exposure Period
t6
t1
t2
t3
t4
t5
Fig.37 Readout
Note: Timing at the end of the trigger if the trigger overlap is set to READOUT
As for the timing for the end of the exposure by the external trigger pulse, its input-prohibited
end time from the previous frame varies based on the pixel format used.
Input-prohibited end time of the trigger
End of the exposure
t
If the trigger overlap is set to READOUT, the period from FVAL end to Input-prohibited end time of
the trigger varies depending on the pixel format used.
Fig. 38 Trigger end time
t1
t2
t3
t4
t5
t6
2L(min)
30 µs
10.158 µs
2.75 µs
226 ns
7L to 8L
t
8-bit
5.5 ms
10-bit Unpacked
12.34 ms
10-bit Packed
0.952 ms
Page 73

SP-5000M-GE2 / SP-5000C-GE2
- 71 -
7.7. RCT mode
Until the trigger is input, the camera operates continuously and the video signal for the auto-iris
lens is output, provided the AUX connector has been ordered with a Type 2 configuration option.
At this moment, the video signal, FVAL and LVAL are output but DVAL is not output. When the trigger
is input, the fast dump is activated to read out the electronic charge very quickly, after which the
accumulation and the readout are performed. When the accumulated signal against the trigger is
read out, FVAL, LVAL and DVAL are output too.
Primary settings to use this mode
Exposure Mode: Timed
Trigger Mode: ON
Trigger Option: RCT
In this mode, the setting of Trigger Overlap is invalid.
t1
t2
Trigger
CCD
Exposure
Exposure
Active
XEEN
FVAL
DVAL
Fig.39 RCT mode timing
t1
t2
100µs
8L ~9L
Page 74

SP-5000M-GE2 / SP-5000C-GE2
- 72 -
7.8. PIV (Particle Image Velocimetry)
The Particle Image Velocimetry mode can be used in applications where 2 images need to be
taken with a very short time interval. It can only be used with strobe flash as illumination.
The first accumulation time is 10 sec to 2 sec. Then, the second exposure will be taken.
The accumulation is LVAL asynchronous. The first strobe is activated during the first exposure
duration and the second strobe is pulsed while the first frame is being read out. In this way, two
strobe flashes generate two video outputs.
Primary Settings
Exposure Mode: Timed
Trigger Mode: ON
Trigger Option: PIV
In this mode, the setting of Trigger Overlap is invalid.
td te1
te2
itf tframe1
tframe2T
Trigegr
Exposure
Exposure
Active
FVAL
DVAL
Fig.40 PIV mode
time name
description
time
td
Exposure beginning delay
755clk
te1
First exposure time period
10μs ~ 2s
te2
Second exposure time
2515 frames
itf
Inter framing time
3514clk
T
FVAL non active
10LVAL
tframe1
First Frame read out
1 frame
tframe2
Second Frame read out
1 frame
Page 75

SP-5000M-GE2 / SP-5000C-GE2
- 73 -
7.9. Sequence ROI Trigger
This mode allows the user to define a preset sequence of up to 10 images, each with its own ROI,
exposure time and gain values.
Primary settings to use this mode
Exposure Mode: Timed
Trigger Mode: ON
Video Send Mode: Trigger Sequence or Command Sequence
7.9.1 Video send mode
The sequential trigger mode is selected via the Video Send Mode command and has the
following options.
Table 24. Video send mode
Mode selected
Index selection method
Trigger Sequence
Select the index by using the Frame Start trigger signal. (The
setting index can be determined by the Next Index setting.)
Command Sequence
Select the index number to assign directly by using the
Command Sequence Index command.
Fig. 41 Behavior if Video Send Mode is set to Trigger Sequence
Video Send Mode
Frame Start
Trigger In
“Normal”
“Trigger Sequence”
Sequence Index
Can be changed
Sequence Index
Cannot be changed
Sequence
Index
Execute from
Index 0
Sequence Index
Can be changed
“Normal”
Sequence
Index
Pointer
&
Repetition
Count
Clear
Sequence
Index Execute
From Index 0
“Trigger Sequence”
Sequence Index
Cannot be changed
Frame Active
Out
Sequence Index
Performing
Sequence Index
Stop
Sequence Index
Performing
Sequence Index
Stop
Sequence Reset
Command
“Execute”
Sequen
ce
Index
Execute
from
Index 0
Page 76

SP-5000M-GE2 / SP-5000C-GE2
- 74 -
7.9.2 Trigger Sequence mode basic timing
In this mode, as each trigger input is received, the image data associated with the next
index within the preset sequence is output.
Index 0 Index 1 Index 2 Index 3 Index 4
Frame Start
Trigger In
Sequence
behavior
Frame count
=1
Next Index =
Index 1
Frame count
=1
Next Index =
Index 2
Frame count
=1
Next Index =
Index 3
Frame count
=1
Next Index =
Index 4
Frame count
=1
Next Index =
Index 5
Fig. 42 Behavior of Sequence trigger
7.9.3 Sequence ROI setting parameters
7.9.3.1 Sequence index table (Default)
The following table shows the default settings.
Table25. Sequence Index table (Default)
7.9.3.2 Descriptions of index table parameters
(1) Sequence ROI Index Selector
In Sequence ROI Index Selector, Index 0 to 9 can be selected.
Sequence ROI – Width, Height, Offset X, Offset Y, Gain Selector - Gain/Red/Blue,
Exposure Time, Black Level, Binning Horizontal, Binning Vertical, LUT Enable, Frame
Count, Next Index for the selected index are displayed.
(2) Sequence ROI Width
Set the width of sequence ROI. The setting range is 8 to 2560 pixels.
Rules for setting area and step number are the same as the normal ROI mode set by
[Video Send Mode] =“Normal”.
(3) Sequence ROI Height
Set the height of sequence ROI. The setting range is 8 to 2048 lines.
Rules for setting area and step number are the same as the normal ROI mode set by
[Video Send Mode] =“Normal”.
(4) Sequence ROI Offset X
Sequence
ROI Index
Sequence ROI
Width
Height
Offset
Gain Selector
Exposure
Time
Black
Level
Binning
LUT
Enable
Frame
Count
Next
Index
X
Y
Gain
(ALL)
Red
Blue
Horizontal
Vertical
- Index 0
2560
2048 0 0
100 0 0
180000 0 1 (Off)
1 (Off)
Off 1 Index 0
- Index 1
2560
2048 0 0
100 0 0
180000 0 1 (Off)
1 (Off)
Off 1 Index 0
- Index 2
2560
2048 0 0
100 0 0
180000 0 1 (Off)
1 (Off)
Off 1 Index 0
- Index 3
2560
2048 0 0
100 0 0
180000 0 1 (Off)
1 (Off)
Off 1 Index 0
- Index 4
2560
2048 0 0
100 0 0
180000 0 1 (Off)
1 (Off)
Off 1 Index 0
- Index 5
2560
2048 0 0
100 0 0
180000 0 1 (Off)
1 (Off)
Off 1 Index 0
- Index 6
2560
2048 0 0
100 0 0
180000 0 1 (Off)
1 (Off)
Off 1 Index 0
- Index 7
2560
2048 0 0
100 0 0
180000 0 1 (Off)
1 (Off)
Off 1 Index 0
- Index 8
2560
2048 0 0
100 0 0
180000 0 1 (Off)
1 (Off)
Off 1 Index 0
- Index 9
2560
2048 0 0
100 0 0
180000 0 1 (Off)
1 (Off)
Off 1 Index 0
Page 77

SP-5000M-GE2 / SP-5000C-GE2
- 75 -
Set Offset X of sequence ROI.
Sequence ROI Binning Horizontal = 1 (Off):
Setting range is 0 to (2544 - [Sequence ROI Width]) for Monochrome
Setting range is 0 to (2552 - [Sequence ROI Width]) for Color
Sequence ROI Binning Horizontal = 2 (On):
Setting range is 0 to (1272 - [Sequence ROI Width])
The limitations of step number and other factors are the same as the normal ROI mode
set by [Video Send Mode] =“Normal”.
(5) Sequence ROI Offset Y
Set Offset Y of sequence ROI.
Sequence ROI Binning Vertical = 1 (Off):
Setting range is 0 to (2046 - [Sequence ROI Height]) for both Monochrome and
Color
Sequence ROI Binning Vertical = 2 (On):
Setting range is 0 to (1023 - [Sequence ROI Height])
The limitations of step number and other factors are the same as the normal ROI mode
set by [Video Send Mode] =“Normal”.
(6) Sequence ROI Gain Selector
In Sequence ROI Gain Selector, the gain settings for each index are available.
SP-5000C-GE2: Gain (ALL), Red and Blue can be set.
SP-5000M-GE2: Only Gain is displayed and can be set.
(7) Sequence ROI Black Level
Black Level setting is available for each index.
(8) Sequence ROI Exposure Time
Exposure Time setting is available for each index.
(9) Sequence ROI Binning Horizontal
ON or OFF of Horizontal Binning for each index can be set.
(10) Sequence ROI Binning Vertical
ON or OFF of Vertical Binning for each index can be set.
(11) Sequence ROI LUT Enable
Enable or disable of LUT function for each index 0 to 9 can be set.
(12) Sequence ROI Frame Count
This can set how many times the selected index is repeated. This is applied to each
index. Triggers are input according to numbers set in Frame Count and index is
repeated and moves to the next index. Therefore, the same number of triggers as
Frame Count must be input.
(13) Sequence ROI Next Index
The number of the index that will follow the current index can be set.
If [Video Send Mode] is set to “Trigger Sequence” and the trigger pulse is input in EPS
trigger, the sequence is executed from index 0.
Page 78

SP-5000M-GE2 / SP-5000C-GE2
- 76 -
(14) Sequence ROI Reset Command
This command resets the current index pointer and reverts to index 0 in the table.
Frame Count is also re-initialized.
7.10 Multi ROI function
This function divides one frame image into a maximum of 5 images vertically and reads out all areas in
one frame. In this function, the width and the height can be set individually as required. Each ROI can
also be overlapped. Refer to Fig. 43. The multi ROI function is enabled if [Video Sending Mode] is set to
“Multi ROI”.
Table26. Multi ROI Index table default values
Multi ROI Index Max
Width Offset X Height Offset Y
- Index 0 8 0 8 0
- Index 1 8 0 8 0
- Index 2 8 0 8 0
- Index 3 8 0 8 0
- Index 4 8 0 8 0
1
Multi ROI
Width
Height
M ulti ROI
Index Selector
Fig.43 Multi ROI setting example
ROI 2
ROI 3
ROI 1
Width max. 2560
Offset X 1 0 ~ 2544(2552)
Width 8 ~ 2560 (2560)
Offset Y1 0 ~ 2046 (2046)
Note: Figures inside ( ) is for SP-5000C-Ge2
Height 8 ~ 2048 (2048)
Height max. 2048
Page 79

SP-5000M-GE2 / SP-5000C-GE2
- 77 -
7.10.1 Multi ROI setting parameters
(1) Multi ROI Index Max:Setting value = 0 ~ 4
Maximum 5 ROI settings are possible in a frame. Set Index 0 through 4 in Multi ROI Index
table as an application requires.
(2) Multi ROI Width
Multi ROI Width can be set individually for Multi ROI Index 0 to 4. The setting range and
Step number are the same as the normal ROI setting in which
“Video Send Mode” is set to ”Normal”. The restriction for setting Step and other factors are
the same as the normal ROI setting.
(3) Multi ROI Index Selector:
Index 0 to 4 can be selected. [Height], [Offset X], and [Offset Y] of the selected Multi ROI
Index are displayed and can be set.
(4) Multi ROI Offset X:
Offset X can be set for each ROI area of Multi ROI Index 0 to 4.
The restriction for setting Step and other factors are the same as the normal ROI setting.
The sum of Offset X and ROI Width must not be greater than Width Max.
(5) Multi ROI Height:
Height can be set for each ROI area of Multi ROI Index 0 to 4.
The restriction for setting Step and other factors are the same as the normal ROI setting.
(6) Multi ROI Offset Y:
Offset Y can be set for each ROI area of Multi ROI Index 0 to 4.
The restriction for setting Step and other factors is the same as the normal ROI setting.
The sum of Offset Y and ROI Height must not be greater than Height Max.
Page 80

SP-5000M-GE2 / SP-5000C-GE2
- 78 -
7.11. Operation and function matrix
Table27. Operation and function matrix
Exposure
Operation
Trigger
mode
Trigger
Option
V-Binning
Note1
H-Binning
Note1
Exposu
re Time
ROI
AWB
Note2
Auto Iris
Output
Auto
Gain
Auto
Exposur
e
Trigger
Over
lap
Video Send
Mode
HDR
Note1
Multi
ROI
Sequ
ence
ROI
OFF
OFF
OFF
1 1 × ○ ○ ○ ○ × × ○ ×
×
2 2 × ○ ○ ○ ○ × × ○ ×
×
Timed
OFF
OFF
1 1 ○
○ × ○ ○ ○ × ○ × ○
2 2 ○
○ × ○ ○ ○ × ○ × ○
Timed
(EPS)
ON
OFF
1 1 ○
○
×
○
(Note3)
○ × ○ ○ ○
○
(Note4)
2 2 ○
○
×
○
(Note3)
○ × ○ ○ ○
○
(Note4)
Trigger
Width
ON
OFF
1 1 ×
○
×
○
(Note3)
○ × ○ ○ × × 2 2 ×
○
×
○
(Note3)
○ × ○ ○ ×
×
Timed
(RCT)
ON
RCT
1 1 ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ × ○ ×
×
2 2 × × ○ × × × × × ×
×
Timed
(PIV)
ON
PIV
1 1 ×
○ × × × × × ○ × × 2 2
×
× × × × × × × × ×
Note 1. Only SP-5000M-GE2
Note 2: Only SP-5000C-GE2
Note 3: If the trigger interval is long period, the iris may occur the hunting.
Note 4: Trigger Overlap is OFF
Page 81

SP-5000M-GE2 / SP-5000C-GE2
- 79 -
8. Other functions
8.1 Black level control
This function adjusts the setup level.
The adjusting level is -64 to +63LSB at 10-bit output.
8.1.1 Black Level Selector
The following factors can be set.
SP-5000M-GE2: DigitalAll
SP-5000C-GE2: DigitalAll/DigitalRed/ DigitalBlue
8.1.2 Black Level
The black level can be set in the following range.
SP-5000M-GE2: DigitalAll:-512~ +511
SP-5000C-GE2: DigitalAll:-512~ +511
DigitalRed/DigitalBlue:-512~ +511
8.2 Gain control
In the SP-5000-GE2, the gain control uses Analog Base Gain and Digital Gain.
Analog Base Gain can be set at 0dB, +6dB or +12dB for for both SP-5000M-GE2 and SP-5000C-GE2. In the
SP-5000C-GE2, R, G and B channel can be adjusted individually or simultaneously.
The digital gain is used for the master gain setting.
For setting the gain,
1. Set analog gain (Select from 0dB, +6dB and +12dB)
2. Set digital gain
The master gain (DigitalAll) for both monochrome and color can be set x1 (0dB)
to x16 (+24dB) against the analog base gain. The resolution for gain setting is
x0.01/step which is 0.05dB to 0.08dB, depending on the setting value.
3. In the SP-5000C-GE2, blue and red gain can be set from x0.45 to x5.62 against
the master gain setting and its resolution is x0.01/step.
4. In the SP-5000C-GE2, analog gain can be applied to R, G and B channel
respectively in order to cover wider range of color temperature.
Note1: If the gain up function is used, it is recommended to use the analog base gain as the
master gain setting. For instance, if +12dB gain up is required, the analog base gain
is set at +12dB and no digital gain is added. This is because the signal-to-noise is
better on analog gain performance. However, the AGC function works only in
digital gain.
Additionally, the analog base gain is effective in order to minimize the drop of the
histogram at higher gain settings. Please note that the analog base gain has less
accuracy due to its variability.
Note2: If Analog Base Gain is set at 0dB and Digital Gain is used at high gain setting, the
video level may be unstable and fluctuating approx. 5%. In this case, it is suggested
to set the analog base gain at +6dB or +12dB.
Page 82

SP-5000M-GE2 / SP-5000C-GE2
- 80 -
x16
x1
16
1
Gain
Amplitude
Gain
Setting
Value
Gain Control Range for
Monochrome
24dB
0dB
The master gain control uses Digital Gain Control. All digital gain can be set by x0.01/step. If the
digital gain is set too high, a break in the Histogram may occur.
The above drawing shows the relation among gain setting value (command), gain amplitude,
and dB indication. For example, the gain amplitude “x 5.643” equals 15dB.
Fig.44 Gain control
8.2.1 Gain Selector
The following parameters can be set.
SP-5000M-GE2: DigitalAll
SP-5000C-GE2: DigitalAll/Digital Red All/Digital Blue All
8.2.2 Gain
This is the reference value upon which gain adjustments are based. The operational adjustment is
done in Gain Raw.
SP-5000M-GE2: DigitalAll:1~16 (0dB to +24dB)
SP-5000C-GE2: DigitalAll:1~16 (0dB to +24dB)
Digital Red All:0.4466~5.643
Digital Blue All:0.4466~5.643
8.2.4 Gain Auto
This function automatically controls the gain level.
This is controlled by the command JAI ALC Reference.
There are three modes.
OFF: Adjust manually.
Once: Operate only one time when this command is set
Continuous: Operate the auto gain continuously
The following detailed settings are also available.
ALC Speed: The rate of adjustment of GainAuto can be set (Common with
ExposureAuto).
X90.288
X16
X7.15
X5.643
X1
X0.45
16
1
Gain
Gain
Setting
Value
5.643
0
0.4466
Gain
Setting
Value
Master
R&B
Master Red
Blue
Gain Control Range for Bayer Color
39dB
-7dB
0dB
24dB
15dB
0dB
-7dB
15dB
0dB
-7dB
15dB
0
0.4466
17dB
5.643
Page 83

SP-5000M-GE2 / SP-5000C-GE2
- 81 -
Gain Auto Max: The maximum value of GainAuto control range can be set
Gain Auto Min: The minimum value of GainAuto control range can be set
ALC Reference: The reference level of Gain Auto control can be set (Common
with ExposureAuto)
ALC Area Type: The area for exposure control can be set(common with
Exposure Auto)
ALC Customer Area Selector: Select the exposure area from 16 choices (4x4)
ALC Area Enable: This can Enable or Disable the area selected by ALC
Fig.45 ALC Area Type
Fig.46 ALC Custom Area selector
8.2.5 Balance White Auto
This is a function to achieve auto white balance by using R and B gain.
There are three operations.
OFF: Manual operation
Once: Only when this operation is set, the auto white balance is executed.
Continuous: The auto white balance is continuously executed.
AWB Area Type: The control area of BALANCE WHITE AUTO can be set.
AWB Customer Area Selector: One of 16 (4x4) AWB setting areas can be selected.
AWB Area Enable : Set Enable or Disable for the area selected by ALC Custom Area Selector
Note: The figures for AWB Area Type and AWB Custom Area Selector are the same as ALC.
8.3. LUT
This function can be used to convert the input to the desired output characteristics.
The Look-Up Table (LUT) has 256 points for setup. The output level can be created by multiplying
the gain data by the input level.
8.3.1 LUT Enable
Can be selected from OFF, Gamma or LUT table.
Row0
Row1
Row2
Row3
Column 0 Column 1 Column 2 Column 3
Half Width Half Height
Half Width and Half Height
All
Page 84

SP-5000M-GE2 / SP-5000C-GE2
- 82 -
8.3.2 LUT Index
This represents the “starting” or “input” pixel value to be modified by the Lookup Table. The
SP-5000-GE2 has a 256-point Lookup Table, meaning the index points are treated like an 8-bit
image with 0 representing a full black pixel and 255 representing a full white pixel. The index
points are automatically scaled to fit the internal pixel format of the camera. This is common
for all output configurations.
8.3.3 LUT value
This is the “adjusted” or “output” pixel value for a given LUT index. It has a range of 0 to 4095
(12-bit) and is automatically scaled to the bit depth of the current operating mode (8-bit or 10-bit).
Note: linear interpolation is used if needed to calculate LUT values between index points. In the
color mode, the LUT function works the same regardless of the color of the pixel.
Output Data = Video IN x LUT data
Fig. 47 LUT value
8.4. Gamma
This command is used to set gamma between gamma 0.45 and gamma 1.0 (OFF) in 16 steps.
The gamma value is an approximate value.
Fig. 48 Gamma compensation
8.4.1 Linear and Dark Compression
SP-5000-CXP2 has a dark compression circuit to improve the signal-to-noise ratio in the dark portion
of the image.
If there is no data, use
adjacent data on both sides
Average data is used for
compensation
Page 85

SP-5000M-GE2 / SP-5000C-GE2
- 83 -
Dark Compression 0: Dark Compression
1: Linear (Default)
Dark Compression
Function
Linear(Factory default)
No compression, Gamma=1.0
Dark Compression
Compress the signal level in the dark portion. It can improve the signal to
noise ratio, but on the other hand, the linearity will be deteriorated.
8.5. Shading Correction
This function compensates for shading (non-uniformity) caused by the lens or the light source used.
This compensation can be performed even if shading issues are not symmetrical in horizontal and/or
vertical directions.
There are two methods of correction.
Flat shading correction:
The method to compensate the shading is to measure the highest luminance level in the
image and use that data as the reference. Luminance levels of other areas are then
adjusted so that the level of the entire area is equal. Compensation is performed using a
block grid of 20 blocks (H) x 16 blocks (V). Each block contains 128 x 128 pixels. The
complementary process is applied to produce the compensation data with less error.
Adjustable range
Less 30%
Fig. 49 Flat shading correction concept drawing
Color shading correction (For SP-5000C-GE2 only):
In this case, R channel and B channel are adjusted to match with G channel characteristics.
The block grid for compensation is 20 blocks (H) x 16 blocks (V). Each block contains 128 x
128 pixels and the complementary process is applied to produce the compensation data
with less error.
Before adjustment After adjustment
Fig.50 Color shading correction concept drawing
Page 86

SP-5000M-GE2 / SP-5000C-GE2
- 84 -
Note: Under the following conditions, the shading correction circuit may not work properly.
If there is some area in the image with a video level less than 70%
If part of the image or the entire image is saturated
If the highest video level in the image is less than 300LSB (at 10-bit output)
8.6. Blemish compensation
The SP-5000M-GE2 and SP-5000C-GE2 have a blemish compensation circuit. This function
compensates blemishes on the CMOS sensor (typically pixels with extremely high response or
extremely low response). This applies to both monochrome and color versions. Pixels that fulfill the
blemish criteria can be compensated by adjacent pixels in both columns and, in the case of the
SP-5000C-GE2, the defective pixels can be compensated by the same Bayer color pixels in both
adjacent columns. Please refer to the following drawing. As for white blemishes, the automatic
detection function is available and after its execution, the data is stored in memory. The customer
can use the data by setting the blemish compensation ON. For black blemishes, only compensation
that has been done in the factory is available. The number of pixels that can be compensated is up
to 512 pixels.
B/W
Color
Defective Pixel
Fig.51 Blemish compensation
Note: If defective pixels are found consecutively in the horizontal direction, the blemish
compensation circuit does not work.
8.7. Bayer color interpolation (Only for SP-5000C-GE2)
This function is available only for SP-5000C-GE2. The SP-5000C-GE2 uses a CMOS sensor with an RGB
Bayer pattern. If the in-camera Bayer color interpolation is not used, the following RAW data can be
output.
GrRGr
R
BGbB
Gb
GrRGrRGr
R
B
Gb
Gr
R
BGbBGbB
Gb
B
Gb
Gr
R
B
Gb
Gr
R
B
Gb
Gr
R
B
Gb
Gr
R
Fig.52 Bayer pattern
Page 87

SP-5000M-GE2 / SP-5000C-GE2
- 85 -
The RAW data contains only luminance information for each color and outputs as a monochrome
signal. The Bayer color interpolation function can complement lacking color information on each
pixel and output RGB or YUV color data as the result. Color interpolation compensates for the lack
of color information by using information from adjacent pixels. The following is the concept
drawing for the color interpolation process. It is invoked when one of the interpolated pixel formats
(RGB or YUV) is selected.
Gr
B3
Gb2
B4
B1
Gb1
B2
Gr1RGr2
Gb3B2Gb4
Gb1B1Gb2
R1GrR2
R3
Gr2
R4
R1
Gr1
R2
Gb1BGb2
Fig.53 Color interpolation concept drawing
8.8 Lens control
The SP-5000M-GE2 and SP-5000C-GE2 can be used with 4 different types of auto iris lenses, in
addition to standard lenses with manual iris control. If an auto iris function is to be utilized, the lens
type used must be selected in Lens Select.
Table28. Lens selector
Lens Select
Description (Control with
camera)
Note
P-Iris Lens
1) Iris position can be
remotely controlled manually
2) Auto iris control is also
available
If P-iris lens is used, the
specific model name should
be selected in Lens Select.
Motor controlled lens
1) Iris position can be
remotely controlled manually
2) Auto iris control is also
available
Video iris lens
Only auto iris control is
available
Factory Option
DC iris lens
Only auto iris control is
available
Factory Option
8.8.1 About P-Iris
New Spark Series SP-5000M-GE2 and SP-5000C-GE2 come equipped with P-Iris control as part of the
standard lens control function. The P-Iris system is a newly developed lens control method designed
to control the iris more precisely. Especially for video cameras in surveillance applications utilizing
megapixel CCD or CMOS imagers, it becomes a very important factor to control an iris in order to
achieve the maximum camera performance. In surveillance applications, depending on shooting
conditions, resolution and depth of field are important factors. The iris is deeply related with these
factors. If the iris diaphragm is smaller, but not too small, resolution gets better and the depth of
field is also deeper. The P-Iris system controls the iris diaphragm precisely and maintains the best
image with the highest resolution and depth of field. P-Iris can also combine with gain and
electronic shutter to keep the appropriate iris position under changing lighting conditions (ALC
function).
Page 88

SP-5000M-GE2 / SP-5000C-GE2
- 86 -
8.8.2 Setting for P-iris lens being used
P-iris lenses use an absolute setting value control system and therefore, if the following
parameters are input, precise iris position control is possible.
8.8.2.1 P-Iris lens select
Select the lens used from the P-iris select list. At this moment, there are no 1-inch P-Iris lenses
available in the list. When P-Iris Les Select is opened, the following lenses are indicated but they
are 2/3 inch format. If they are used, the corners of the image may be vignetted.
Table – 29 P-iris lens select
P-Iris lens select
Description
Control step number
Open F value
LM16JC5MM
Kowa 16mm 2/3”
74
F1.4
LM35JC5MM
Kowa 35mm 2/3”
73
F2.0
8.8.2.2 Step max.
Iris control step depends on lens. The setting value uses the value stored in the camera.
8.8.2.3 Position
The iris position can be set between 0 to Step Max. 0 means to open the iris and Step Max
means to close the iris.
In the following conditions, the camera initializes P-iris control and acquires iris position.
1) When the camera is powered
2) When the lens is selected in P-Iris Lens Select
3) If the lens is changed in P-iris Lens Select
8.8.2.4 Current F value
The current F value is indicated by using iris position information. This can be indicated during auto
iris operation. The relation between iris position and F value depends on the lens used.
8.8.2.5 P-Iris Auto min. / P-Iris Auto max.
This function can set the control range when the iris is operated automatically. Auto max. sets the
limit when the iris goes open and Auto min. sets the limit when the iris goes closed. Auto max. can
be set to fully open but Auto min. is stopped at F5.6 as lens performance typically degrades if the
iris is closed beyond this point.
8.8.3 Motorized lenses
The SP-5000C-GE2 and SP-5000C-GE2 can use the 3-axis motorized lens control for zoom, focus and
iris. The following functions are available via the motorized lens commands.
8.8.3.1 Iris
Open: While this command is supplied, the iris will continue to open.
Close: While this command is supplied, the iris will continue to close.
Stop: When this command is supplied, the iris operation stops.
Page 89

SP-5000M-GE2 / SP-5000C-GE2
- 87 -
8.8.3.2 Zoom
Wide: While this command is supplied, the zoom will continue to move towards wide
angle.
Tele: While this command is supplied, the zoom will continue to move towards telephoto.
Stop: When this command is supplied, the zoom operation stops.
8.8.3.3 Focus+
Near: While this command is supplied, the focus will continue to shift closer to the
camera.
Far: While this command is supplied, the focus will continue to move towards infinity.
Stop: When this command is supplied, the focus operation stops.
8.9 ALC
In the SP-5000M-GE2 and SP-5000C-GE2, auto gain, auto shutter and auto iris functions can be
combined to provide a wide ranging automatic exposure control from dark to bright or vice versa.
The functions are applied in the sequence shown below and if one function is disabled, the linkage
between the other two is maintained.
In order to make the ALC function effective, set the Auto Iris Lens Control Signal Output to “ON”.
The auto iris function (AIC) works together with AGC and Exposure Auto (ASC).
If the lighting condition is changed from bright to dark AIC ― ASC ― AGC
If the lighting condition is changed from dark to bright AGC ― ASC ― AIC
Gain is fixed at Min.
Dark Light changes Bright
Auto Shutter
Max
Auto shutter operation
Max ~ Min (User set)
Auto Shutter
fixed at Min
Iris diaphragm fixed (Open)
Auto iris
operation
AGC works:
Auto shutter works:
Auto iris works:
AGC operation
Max ~ Min (User set)
AGC
Max
Iris stops just
before close
Operation if light changes
from dark to bright
Operation if light changes
from bright to dark
Fig.54 ALC function concept
ALC Reference will determine the target video level for AGC, Auto Shutter and/or Auto iris.
For instance, if ALC Reference is set to 100% video level, AGC, Auto Shutter and/or Auto Iris
will function to maintain 100% video level.
Please note that ALC function is available only in continuous mode, as well as RCT
mode.
Page 90

SP-5000M-GE2 / SP-5000C-GE2
- 88 -
8.10 HDR (High Dynamic Range) (SP-5000M-GE2 only)
HDR sensing mode can be set when HDR Mode is set to ON while Exposure Mode is Timed.
The parameters to configure dynamic range are HDR_SLOPE Level 1, Level 2, Level 3 and
Level 4.
The user can select any one of those parameters as required for their application.
In this mode, the timed exposure is used as the reference and the value selected in
HDR_SLOPE will compensate to get an appropriate dynamic range by changing the exposure
time.
Notes:
1. If the exposure mode is OFF and the HDR mode is set to ON, the exposure mode is
automatically changed to Timed.
2. If horizontal binning and/or vertical binning are set to ON, the HDR mode cannot be set.
In this case, the HDR mode must be set first before H-Binning and/or V-Binning are set.
3. In this mode, exposure overlapped behavior is not available and the frame rate is slower than
the normal operation.
4. The exposure time value is fixed at the value when HDR Mode is activated. When the
exposure time is changed, HDR Mode should be off. Once the exposure time is changed, the
HDR Mode can be set to ON again.
5. In this mode, Exposure Auto function is disabled.
Fig.55 HDR characteristics
Knee Slope
Dynamic Range [%]
1
(200)
2
(400)
3
(800)
4
(1600)
Page 91

SP-5000M-GE2 / SP-5000C-GE2
- 89 -
9. Camera setting
9.1 Camera Control Tool
In the SP-5000M-GE2 and SP-5000C-GE2, control of all camera functions is done by the JAI SDK and
Control Tool software. All controllable camera functions are stored in an XML file inside of the
camera. The JAI SDK and Control Tool software can be downloaded from www.jai.com.
9.2 Camera Default Setting
When the camera is connected to PC and JAI SDK 2.0 is started up, XML file which stores default
settings of the camera is downloaded to JAI_SDK camera control tool.
The default settings of SP-5000-GE2 are as follows.
Image Format
Bit allocation
8-bit
Width
2560
Height
2048
Binning Horizontal
1(OFF)
Binning Vertical
1(OFF)
Acquisition Control
Acquisition mode
Continuous
Acquisition Frame Rate
44
Trigger Selector
Frame Acquisition Start
Trigger Mode
OFF
Trigger Activation
Rising Edge
Trigger Source
Low
Trigger Overlap
Readout
Exposure Control
Exposure Mode
OFF
Gain
Analog base gain
0dB
Gain Auto
OFF
Gamma
0.45
Video Send Mode
Normal
Page 92

SP-5000M-GE2 / SP-5000C-GE2
- 90 -
10. External appearance and dimensions
Dimensions tolerance: ± 0.3mm
Unit: mm
Fig.56 Outside dimensions
Page 93

SP-5000M-GE2 / SP-5000C-GE2
- 91 -
11. Specifications
11.1 Spectral response
Fig.57 Spectral response (SP-5000M-GE2)
Fig.58 Spectral response (SP-5000C-GE2) (With IR Cut Filter)
Note: Full sensor response. IR-cut filter not shown.
Page 94

SP-5000M-GE2 / SP-5000C-GE2
- 92 -
11.2 Specifications table
Specifications
SP-5000M-GE2
SP-5000C-GE2
Scanning system
Progressive scan, 1-tap
Synchronization
Internal
Interface
1000Base-T Ethernet (GigE Vision 2.0) x 2Ports (100Base-T can be used)
Complies with Single, sLAG (Static Link Aggregation)
and dLAG (Dynamic Link Aggregation)
Image sensor
1 inch Monochrome CMOS
1 inch Bayer color CMOS
Aspect Ratio
5:4
Image size(Effective Image)
12.8 (h) x 10.24 (v) mm, 16.39 mm diagonal
Pixel size
5 (h) x 5 (v) m
Effective Image output Pixels
2560 (h) x 2048 (v)
2560 (h) x 2048 (v)
Pixel Clock
48 MHz
Maximum
Acquisition
Frame Rate
per
Tap
Geometry
(minimum is
0.125 fps for
all
geometries
and formats)
Single Port
22 fps @ 8-bit
14 fps @ 10-bit Packed
11 fps @ 10-bit
22 fps @ Bayer 8-bit
14 fps @ Bayer 10-bit Packed
11 fps @ Bayer 10-bit
7.3 fps @ RGB 8-bit
14fps@ YUV411 Packed
11 fps @ YUV422 Packed
7.3 fps @ YUV444 Packed
2 Ports LAG
44 fps @ 8-bit
29 fps @ 10-bit Packed
22 fps @ 10-bit
44 fps @ Bayer 8-bit
29 fps @ Bayer 10-bit Packed
22 fps @ Bayer 10-bit
14.6 fps @ RGB 8-bit
29 fps @ YUV411 Packed
22 fps @ YUV422 Packed
14.6 fps @ YUV444 Packed
Binning
H1,V2
44fps @ 8-bit LAG
-
H2,V1
88fps @ 8-bit LAG
-
H2,V2
175fps @ 8-bit LAG
-
EMVA 1288 Parameters
Absolute sensitivity
Maximum SNR
At 10-bit output
23.50 p (λ = 525 nm)
41.48 dB
At 10-bit output
36.08 p (λ = 525 nm)
38.00 dB
SN ratio (traditional method)
Dark Compression:55 dB (Typical)
Linear: 50dB (Typical)
(0dB gain, Black)
Dark Compression: 53 dB (Typical)
Linear: 45dB (Typical)
(0dB gain, Green Black)
42dB (Typical)
(0dB gain, Level:890LSB, 10-bit)
37dB (Typical)
(0dB gain, Green Pixel Level:890LSB, 10-bit)
Image
Output
format
Digital
Full pixels
2560 (h) x 2048 (v)
Bayer 2560 (h) x 2048 (v)
ROI
Width
8 ~2560, 2 pixels/step
8 ~2560, 2 pixels/step
OFFSET X
0 ~2544, 16 pixels/step
0 ~2552, 4 pixels/step
Height
8 ~2048 lines,2 line/step
8 ~2048 lines,2 line/step
OFFSET Y
0 ~2046 lines, 2 line/step
0 ~2046 lines, 2 line/step
Binning
H
1
2560 (H)
2560 (H)
2
1280 (H)
-
V
1
2048 (V)
2048 (V)
2
1024 (V)
-
Bit assignment
Mono8, Mono10, Mono10 Packed
BayerGR, BayerGR10, BayerGR10 Packed,
RGB8 Packed, YUV411 Packed,
YUV422 Packed, YUV444 Packed
Acquisition mode
Continuous / Single Frame / Multi Frame (1 ~255)
Page 95

SP-5000M-GE2 / SP-5000C-GE2
- 93 -
Acquisition Frame Rate
44 fps (Max) ~ 0.125 fps (Min), at 8-bit output
Trigger Selector
Acquisition
Acquisition Start/ Acquisition Stop
Exposure
Frame Start
Transfer
Acquisition Start/ Acquisition Stop / Frame Transfer
Exposure mode
OFF, Continuous, Timed (EPS), Trigger Width
Trigger option
OFF / PIV / RCT (with ALC function)
Trigger Overlap
OFF / Readout (Frame Transfer Start only)
Trigger Input Signal
Software, PG0/1/2/3, UserOutput0/1/2/3, Action1/2, Line5(Optical In1),
Line6(Optical In 2), Line10(Option TTL In 2), Line11(Option LVDS In)
Exposure
Mode
Timed
10 μs (Min.) ~ 8 second (Max. Note1), Variable unit: 1 μs
Trigger Width
10 μs (Min.) ~ ∞ (Max.Note 1))
Auto Exposure
OFF / Once / Continuous
Auto Exposure Response Speed
1 ~ 8
Digital I/O
Line Selector (12P): GPIO IN / GPIO OUT
Black
Level
Adjust.
Ref. level
33.5LSB 10-bit (Average value of 100*100)
Adj. range
-64 ~ +63LSB 10-bit
Resolution
1 STEP = 0.25LSB
Analog Base Gain
0dB, 6dB, 12dB
0dB, 6dB, 12dB (R/G/B individual setting)
Gain
Control
Manual
Adj. range
-0dB ~+24dB (Note2)
1 step=x0.01 (0.005dB to 0.08dB)
Varies by setting value
-0dB ~+24dB (Note2)
1 step=x0.01 (0.005dB to 0.08dB)
Varies by setting value
WB Gain
—
R / B : -7dB to +15dB, 1 step = 0.01dB
WB Area
—
4 x 4
Color Temp.
Range (Preset)
—
4600K, 5600K, 6500K
WB Range
—
3000K ~ 9000K
White Balance — OFF, Once, Continuous
Blemish
Comp.
Detection
Detect white blemish above the threshold value
(Black blemish is detected only by factory )
Compensation
Complement by adjacent pixels (Continuous blemishes are not compensated)
Numbers
512 pixels
ALC
AGC, auto exposure, iris control can be combined and automatically controlled
Gamma
0.45 ~ 1.0 (16 steps are available)
LUT
OFF: γ=1.0, ON=256 points can be set
HDR Correction
4 settings
Level 1, 2, 3 and 4
—
Shading Compensation
Flat Field
Block Comp. (20 x 16 blocks)
Block size: 128 x 128 pixels
Flat Field, Color shading
Block comp. (20 x 16 blocks)
Block size: 128 x 128 pixels
Bayer Color Interpolation
—
3 x 3 matrix, Linear compensation
Power
Input range
DC+12V to +24V ± 10% (At the input terminal)
Current
Single Link
450mA (At 12V input, Full pixels)
450mA (At 12V input, Full pixels)
LAG
520mA (At 12V input, Full pixels)
520mA (At 12V input, Full pixels)
Power
Single Link
5.4W (At 12V input, Full pixels)
5.4W (At 12V input, Full pixels)
Lag
6.25W (At 12V input, Full pixels)
6.25W (At 12V input, Full pixels)
Lens mount
C mount Rear protrusion of the lens is less than 10 mm
Flange back
17.526 mm, Tolerance: 0 to -0.05 mm
Optical filter
Protection glass: Not provided
IR cut filter (Half value is 670 nm)
Page 96

SP-5000M-GE2 / SP-5000C-GE2
- 94 -
Operating temperature/Humidity
Performance guaranteed
-10C to +50C / 20 – 80% (No-condensing)
Operating Temperature / Humidity
-45C to +70C/20% to 80% (No-condensing)
Storage Temp. / Humidity
-45C to +70C/20% to 80 % (no-condensing)
Regulation
CE (EN61000-6-2 and EN61000-6-3), FCC part 15 class B, RoHS, WEEE
Housing Dimensions
62 x 62 x 55.5 mm (W x H x D) (excluding protrusion)
Weight
215g
Note1): Usable performance will be up to 2 seconds.
Note2): A minimum of +12dB of gain can be applied without causing any breaks in the histogram.
Note3): Approximately 5 minutes pre-heating is required to achieve these specifications.
Note4): The above specifications are subject to change without notice.
Page 97

SP-5000M-GE2 / SP-5000C-GE2
- 95 -
Appendix
1. Precautions
Personnel not trained in dealing with similar electronic devices should not service this camera.
The camera contains components sensitive to electrostatic discharge. The handling of these devices
should follow the requirements of electrostatic sensitive components.
Do not attempt to disassemble this camera.
Do not expose this camera to rain or moisture.
Do not face this camera towards the sun, extreme bright light or light reflecting objects.
When this camera is not in use, put the supplied lens cap on the lens mount.
Handle this camera with the maximum care.
Operate this camera only from the type of power source indicated on the camera.
Power off the camera during any modification such as changes of jumper and switch setting.
2. Typical Sensor Characteristics
The following effects may be observed on the video monitor screen. They do not indicate any fault
of the camera, but are associated with typical sensor characteristics.
V. Aliasing
When the CMOS camera captures stripes, straight lines or similar sharp patterns, jagged edges
may appear on the monitor.
Blemishes
All cameras are shipped without visible image sensor blemishes.
Over time some pixel defects can occur. This does not have a practical effect on the operation
of the camera. These will show up as white spots (blemishes).
Exposure to cosmic rays can cause blemishes to appear on the image sensor. Please take care to
avoid exposure to cosmic rays during transportation and storage. It is recommended using sea
shipment instead of air flight in order to limit the influence of cosmic rays on the camera. Pixel
defects/blemishes also may emerge due to prolonged operation at elevated ambient
temperature, due to high gain setting, or during long time exposure. It is therefore
recommended to operate the camera within its specifications.
Patterned Noise
When the sensor captures a dark object at high temperature or is used for long time integration,
fixed pattern noise may appear on the video monitor screen.
3. Caution when mounting a lens on the camera
When mounting a lens on the camera dust particles in the air may settle on the surface of the lens
or the image sensor of the camera. It is therefore important to keep the protective caps on the lens
and on the camera until the lens is mounted. Point the lens mount of the camera downward to
prevent dust particles from landing on the optical surfaces of the camera. This work should be done
in a dust free environment. Do not touch any of the optical surfaces of the camera or the lens.
Page 98

SP-5000M-GE2 / SP-5000C-GE2
- 96 -
4. Caution when mounting the camera
When you mount the camera on your system, please make sure to use screws of the recommended
length described in the following drawing. Longer screws may cause serious damage to the PCB
inside the camera.
If you mount the tripod mounting plate, please use the provided screws.
5. Exportation
When exporting this product, please follow the export regulation of your own country.
6. References
1. This manual can and datasheet for SP-5000M-GE2 / SP-5000C-GE2 can be downloaded from
www.jai.com
2. Camera control software can be downloaded from www.jai.com
Camera chassis
Fixing plate
Mounting the camera to fixing plate
5.0mm ± 0.2mm
Camera chassis
Tripod mount
5.0mm ± 0.2mm
Attaching the tripod mount
4.5mm ± 0.2mm
4.5mm ± 0.2mm
Page 99

SP-5000M-GE2 / SP-5000C-GE2
- 97 -
Manual change history
Date
Revision
Changes
April 2014
Preliminary
New Release
July 2014
1.0
New release
Aug. 2014
1.1
Revise LAG settings information
Sept. 201
1.2
Revise Spectral response
Oct. 2014
1.3
Revised B/W Spectral response with wider wave length, Add the
description of the dark compression
Page 100

SP-5000M-GE2 / SP-5000C-GE2
- 98 -
User's Record
Camera type: SP-5000M-GE2 / SP-5000C-GE2
Revision: ……………..
Serial No. ……………..
Firmware version. ……………..
For camera revision history, please contact your local JAI distributor.
User's Mode Settings.
User's Modifications.
Company and product names mentioned in this manual are trademarks or registered trademarks of their respective owners.
JAI A-S cannot be held responsible for any technical or typographical errors and reserves the right to make changes to products and
documentation without prior notification.
Europe, Middle East & Africa
Asia Pacific
Americas
Phone +45 4457 8888
Fax +45 4491 3252
Phone +81 45 440 0154
Fax +81 45 440 0166
Phone (toll-free) +1 800 445 5444
Phone +1 408 383 0300
Visit our web site at www.jai.com
 Loading...
Loading...