Page 1

User Manual
Spark Series
SP-5000M-PMCL
SP-5000C-PMCL
5M CMOS Digital Progressive Scan
Monochrome and Color Camera
Document Version: Ver.1.1
SP-5000-PMCL_Ver.1.1_Oct2013
1046E-1305
Page 2

SP-5000M-PMCL / SP-5000C-PMCL
Notice
The material contained in this manual consists of information that is proprietary to JAI Ltd., Japan and
may only be used by the purchasers of the product. JAI Ltd., Japan makes no warranty for the use of its
product and assumes no responsibility for any errors which may appear or for damages resulting from the
use of the information contained herein. JAI Ltd., Japan reserves the right to make changes without
notice.
Company and product names mentioned in this manual are trademarks or registered trademarks of their
respective owners.
Warranty
For information about the warranty, please contact your factory representative.
Certifications
CE compliance
As defined by the Directive 2004/108/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council, EMC
(Electromagnetic compatibility), JAI Ltd., Japan declares that SP-5000M-PMCL and SP-5000C-PMCL
comply with the following provisions applying to its standards.
EN 61000-6-3 (Generic emission standard part 1)
EN 61000-6-2 (Generic immunity standard part 1)
FCC
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class B digital device, pursuant
to Part 15 of the FCC Rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection against harmful
interference in a residential installation. This equipment generates, uses and can radiate radio
frequency energy and, if not installed and used in accordance with the instructions, may cause harmful
interference to radio communications. However, there is no guarantee that interference will not occu r
in a particular installation. If this equipment does cause harmful interference to radio or television
reception, which can be determined by turning the equipment off and on, the user is encouraged to try
to correct the interference by one or more of the following measures:
- Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna.
- Increase the separation between the equipment and receiver.
- Connect the equipment into an outlet on a circuit different from that to which the receiver is
connected.
- Consult the dealer or an experienced radio/TV technician for help.
Warning
Changes or modifications to this unit not expressly approved by the party
responsible for FCC compliance could void the user’s authority to operate the
equipment.
- 2 -
Page 3
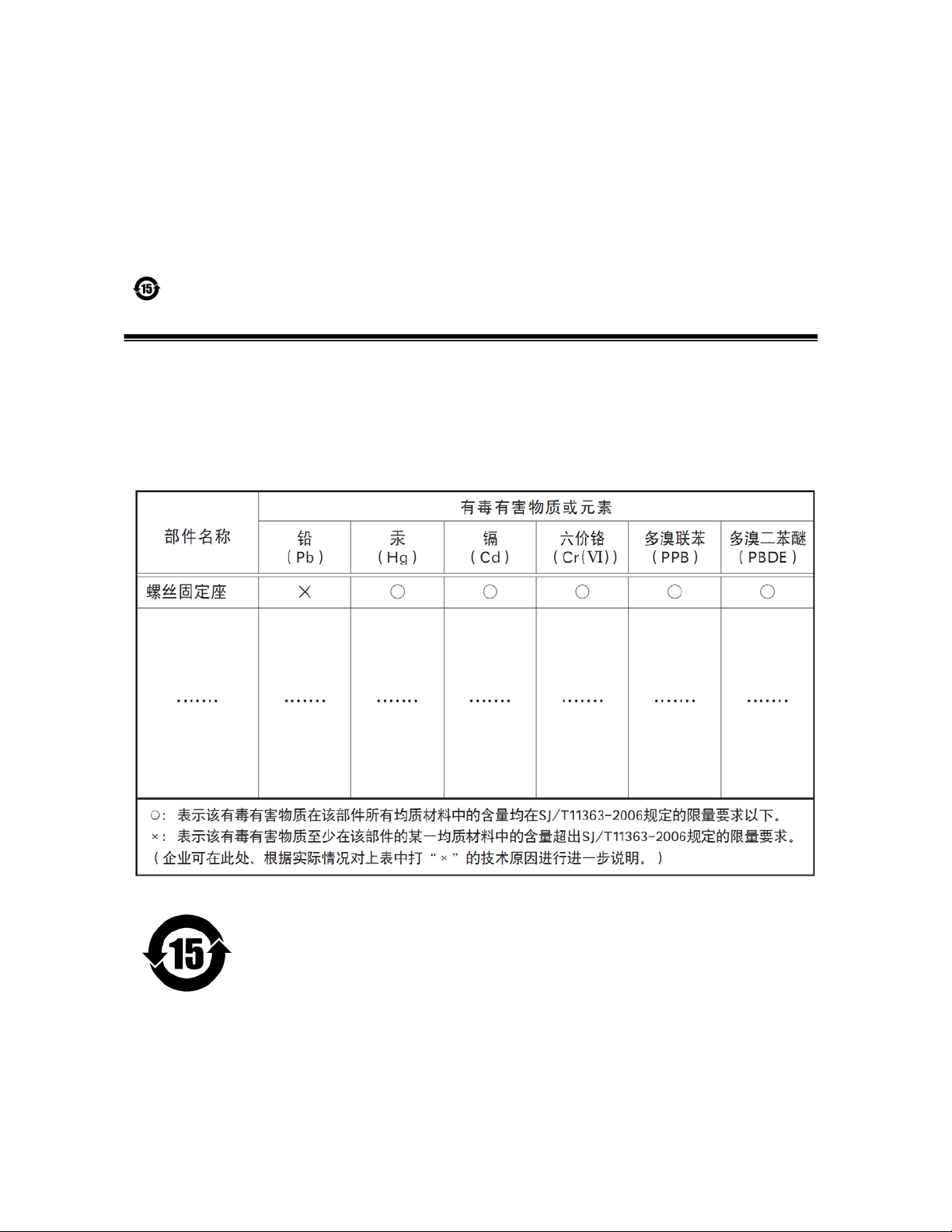
SP-5000M-PMCL
Supplement
The following statement is related to the regulation on “ Measures for the Administration
of the control of Pollution by Electronic Information Products “ , known as “ China RoHS “.
The table shows contained Hazardous Substances in this camera.
mark shows that the environment-friendly use period of contained Hazardous
Substances is 15 years.
嶷勣廣吭並㍻
嗤蕎嗤墾麗嵎賜圷殆兆各式根楚燕
功象嶄鯖繁酎慌才忽佚連恢匍何〆窮徨佚連恢瞳麟半陣崙砿尖一隈〇云恢瞳ゞ 嗤蕎嗤
墾麗嵎賜圷殆兆各式根楚燕 〃泌和
桟隠聞喘豚㍉
窮徨佚連恢瞳嶄根嗤議嗤蕎嗤墾麗嵎賜圷殆壓屎械聞喘議訳周和音氏窟伏翌
亶賜融延、窮徨佚連恢瞳喘薩聞喘乎窮徨佚連恢瞳音氏斤桟廠夛撹冢嶷麟半
賜斤児繁附、夏恢夛撹冢嶷鱒墾議豚㍉。
方忖仝15々葎豚㍉15定。
Page 4
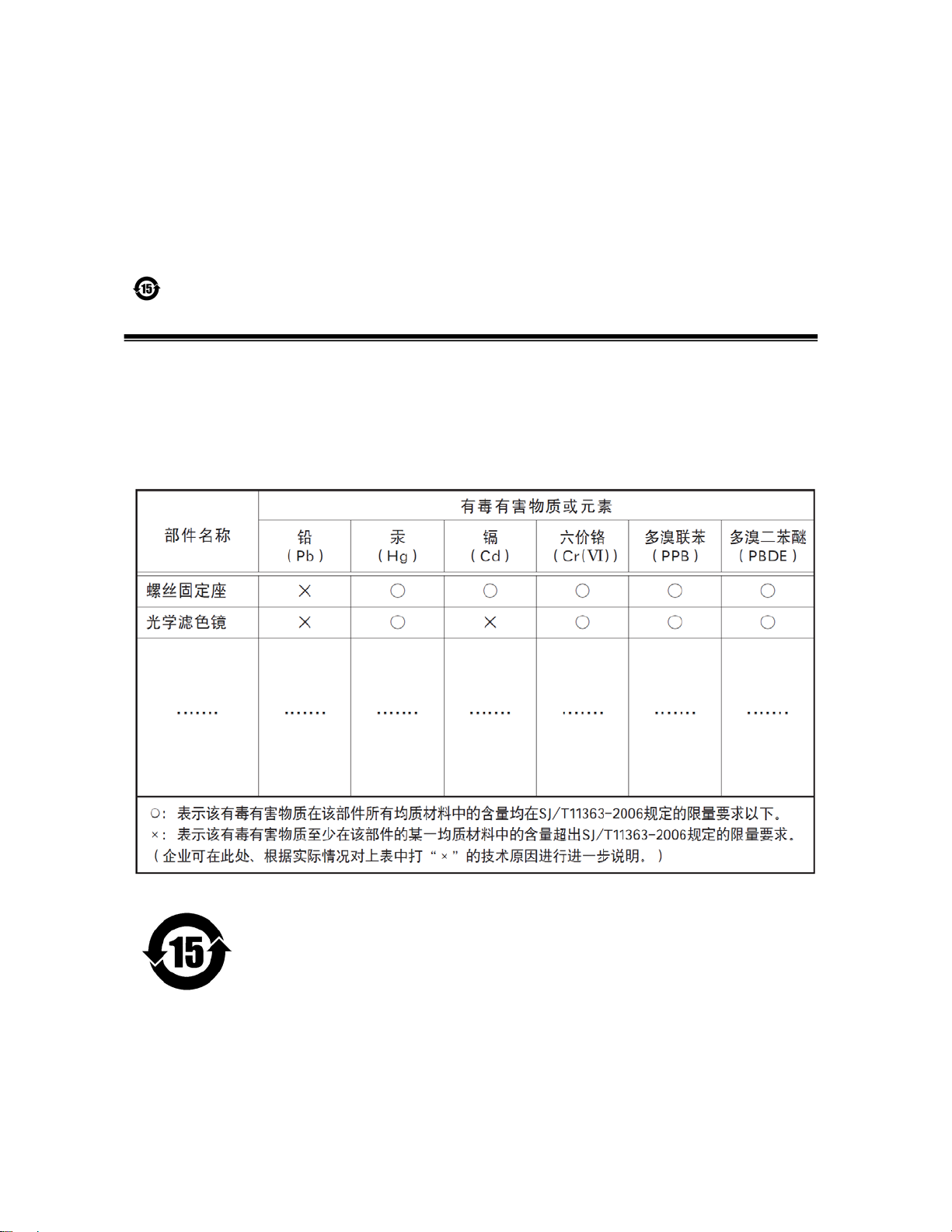
SP-5000C-PMCL
Supplement
The following statement is related to the regulation on “ Measures for the Administration
of the control of Pollution by Electronic Information Products “ , known as “ China RoHS “.
The table shows contained Hazardous Substances in this camera.
mark shows that the environment-friendly use period of contained Hazardous
Substances is 15 years.
嶷勣廣吭並㍻
嗤蕎嗤墾麗嵎賜圷殆兆各式根楚燕
功象嶄鯖繁酎慌才忽佚連恢匍何〆窮徨佚連恢瞳麟半陣崙砿尖一隈〇云恢瞳ゞ 嗤蕎嗤
墾麗嵎賜圷殆兆各式根楚燕 〃泌和
桟隠聞喘豚㍉
窮徨佚連恢瞳嶄根嗤議嗤蕎嗤墾麗嵎賜圷殆壓屎械聞喘議訳周和音氏窟伏翌
亶賜融延、窮徨佚連恢瞳喘薩聞喘乎窮徨佚連恢瞳音氏斤桟廠夛撹冢嶷麟半
賜斤児繁附、夏恢夛撹冢嶷鱒墾議豚㍉。
方忖仝15々葎豚㍉15定。
Page 5

SP-5000M-PMCL / SP-5000C-PMCL
- Contents -
Before using this camera ....................................................................- 6 -
1. General ...................................................................................- 7 -
2. Camera composition ...................................................................- 7 -
3. Key features ..............................................................................- 8 -
4. Parts locations and their functions ...................................................- 9 -
4.1 Parts locations and their functions ....................................................................... - 9 -
4.2 Rear Panel .................................................................................................. - 10 -
5. Input and output ......................................................................... - 11 -
5.1 Connector and its pin configuration ................................................................... - 11 -
5.1.1 12-Pin connector ..................................................................................... - 11 -
5.1.1.1 Figure ............................................................................................. - 11 -
5.1.1.2 Pin configuration ............................................................................... - 11 -
5.1.2 Camera Link Connector ............................................................................. - 11 -
5.1.2.1 Figure ............................................................................................. - 11 -
5.1.2.2 Pin assignment .................................................................................. - 12 -
5.1.3 AUX Standard Hirose 10-Pin connector ..................................................... - 12 -
5.1.3.1 Figure and pin configuration ................................................................. - 12 -
5.1.4 AUX Type 2 HIROSE 10-Pin connector (factory option) ....................................... - 13 -
5.1.5 AUX Type 3 HIROSE 10-Pin connector (factory option) ..................................... - 13 -
5.2 Camera Link interface ................................................................................... - 14 -
5.2.1 Camera Link Interface .............................................................................. - 14 -
5.2.2 Camera Link pixel clock frequency ............................................................... - 15 -
5.3 Digital IN/OUT interface ................................................................................. - 16 -
5.3.1 Line Selector ......................................................................................... - 16 -
5.3.2 Line Source ........................................................................................... - 16 -
5.3.3 Line Mode ............................................................................................. - 16 -
5.3.4 Line Inverter .......................................................................................... - 16 -
5.3.5 Line Status ............................................................................................ - 16 -
5.3.6 Line Format ........................................................................................... - 17 -
5.3.7 GPIO .................................................................................................... - 17 -
5.3.7.1 Basic block diagram ............................................................................ - 17 -
5.3.7.2 Input and output matrix table ............................................................... - 18 -
5.4 Pulse Generator ........................................................................................... - 18 -
5.4.1 Clock Pre-scaler ...................................................................................... - 19 -
5.4.2 Pulse Generator Selector ........................................................................... - 19 -
5.4.3 Pulse Generator Length ............................................................................ - 20 -
5.4.4 Pulse Generator Start Point ....................................................................... - 20 -
5.4.5 Pulse Generator End Point ......................................................................... - 20 -
5.4.6 Pulse Generator Repeat Count .................................................................... - 20 -
5.4.7 Pulse Generator Clear Activation ................................................................. - 20 -
5.4.8 Pulse Generator Clear Sync Mode ................................................................ - 20 -
5.4.9 Pulse Generator Clear Source ..................................................................... - 22 -
5.4.10 Pulse Generator Inverter ......................................................................... - 23 -
5.4.11 Pulse Generator Setting table ................................................................... - 23 -
6. Sensor layout, output format and timing ........................................ - 24 -
6.1 Sensor layout .............................................................................................. - 24 -
6.1.1 Monochrome sensor ................................................................................. - 24 -
6.1.2 Bayer sensor .......................................................................................... - 24 -
6.2 Camera output format (Tap Geometry) .............................................................. - 25 -
6.2.1 1X2–1Y ................................................................................................. - 25 -
6.2.2 1X4–1Y ................................................................................................. - 26 -
6.2.3 1X8–1Y ................................................................................................. - 26 -
- 3 -
Page 6

SP-5000M-PMCL / SP-5000C-PMCL
6.3 Output timing and output image ....................................................................... - 27 -
6.3.1 Horizontal timing .................................................................................... - 27 -
6.3.2 Vertical timing ....................................................................................... - 35 -
Table 28. Continuous Trigger / Vertical timing 1X4–1Y (2/3) ................................... - 40 -
Camera Settings .................................................................................................. - 40 -
Table 29. Continuous Trigger / Vertical timing 1X2–1Y (3/3) .................................... - 41 -
Camera Settings .................................................................................................. - 41 -
6.3.3 ROI (Region Of Interest) setting .................................................................. - 41 -
6.4 Digital output bit allocation ............................................................................ - 42 -
7. Operating modes ...................................................................... - 43 -
7.1. Acquisition control (change the frame rate) ........................................................ - 43 -
7.1.1 Acquisition control .................................................................................. - 43 -
7.2. Exposure setting ......................................................................................... - 47 -
7.2.1 Mode ................................................................................................... - 47 -
7.2.2 ExposureTime ........................................................................................ - 47 -
7.2.3 ExposureAuto ......................................................................................... - 48 -
7.3. Trigger control ........................................................................................... - 48 -
7.3.1 Trigger Selector ...................................................................................... - 48 -
7.3.2 Trigger Mode ......................................................................................... - 48 -
7.3.3 TriggerSource ........................................................................................ - 48 -
7.3.4 TriggerActivation .................................................................................... - 49 -
7.3.5 Triggeroverlap ....................................................................................... - 49 -
7.4. Normal continuous operation (Timed Exposure Mode/Trigger Mode OFF)..................... - 49 -
7.5. Timed mode (EPS operation) .......................................................................... - 49 -
7.5.1 If Overlap setting is OFF ............................................................................ - 50 -
7.5.2 If Overlap setting is Readout ...................................................................... - 50 -
7.6 Trigger width mode (PWC) .............................................................................. - 51 -
7.6.1 If Overlap setting is OFF ............................................................................ - 51 -
7.6.2 If Overlap setting is Readout ...................................................................... - 52 -
7.7. RCT mode ................................................................................................. - 53 -
7.8 PIV (Particle Image Velocimetry) ...................................................................... - 54 -
7.9 Sequence Mode ............................................................................................ - 55 -
7.9.1 Video send mode .................................................................................... - 55 -
7.9.2 Sequence mode ...................................................................................... - 55 -
7.9.3 Sequence mode timing ............................................................................. - 55 -
7.9.4 Sequence ROI setting parameters ................................................................ - 56 -
7.10 Multi ROI function ....................................................................................... - 58 -
7.10.1 Multi ROI setting parameters .................................................................... - 58 -
7.11. Operation and function matrix ....................................................................... - 61 -
Exposure ...................................................................................................... - 61 -
8. Other functions ....................................................................... - 62 -
8.1 Black level control ........................................................................................ - 62 -
8.1.1 Black Level Selector ................................................................................ - 62 -
8.1.2 Black Level ............................................................................................ - 62 -
8.2 Gain control ................................................................................................ - 62 -
8.2.1 Gain Selector ......................................................................................... - 63 -
8.2.2 Gain .................................................................................................... - 63 -
8.2.3 Gain Raw .............................................................................................. - 63 -
8.2.4 Gain Auto ............................................................................................. - 63 -
8.3. LUT ......................................................................................................... - 64 -
8.3.1 LUT Enable ............................................................................................ - 64 -
8.3.2 LUT Index ............................................................................................. - 64 -
8.3.3 LUT Value ............................................................................................. - 64 -
8.4 Gamma...................................................................................................... - 65 -
8.5 Shading Correction ....................................................................................... - 65 -
8.6 Blemish compensation ................................................................................... - 66 -
- 4 -
Page 7

SP-5000M-PMCL / SP-5000C-PMCL
8.7 ALC .......................................................................................................... - 67 -
8.8 HDR (High Dynamic Range) (SP-5000M-PMCL only).................................................. - 67 -
8.9. Lens ........................................................................................................ - 68 -
8.9.1 About P-Iris ........................................................................................ - 69 -
8.9.2 Setting for P-iris lens being used ................................................................. - 69 -
8.9.2.1 P-Iris lens select ................................................................................ - 69 -
8.9.2.2 Step max. ........................................................................................ - 69 -
8.9.2.3 Position ........................................................................................... - 69 -
8.9.2.4 Current F value ................................................................................. - 69 -
8.9.2.5 P-Iris Auto min. / P-Iris Auto max. .......................................................... - 69 -
8.9.3 Motorized lens ........................................................................................ - 69 -
8.9.3.1 Iris ................................................................................................. - 69 -
8.9.3.2 Zoom .............................................................................................. - 70 -
8.9.3.3 Focus+ ............................................................................................ - 70 -
9. Camera control ......................................................................... - 71 -
10. External appearance and dimensions ......................................... - 72 -
11. Specifications ........................................................................ - 73 -
11.1. Camera spectral response ............................................................................ - 73 -
11.2. Specification table ..................................................................................... - 74 -
Appendix 1 Short ASCII Command Communication Protocol ................ - 77 -
1 Communication setting ................................................................ - 77 -
2 Protocol(Short ASCII Command) ............................................... - 77 -
2.1 Transmit the setting command to camera ........................................................... - 77 -
2.2 Transmit the request command to camera .......................................................... - 77 -
2.3 Switching baud rate between PC and camera ....................................................... - 77 -
2.4 Command list (Short ASCII command) ................................................................. - 78 -
2.4.1 GenCP Bootstrap Register .......................................................................... - 78 -
2.4.2 Technology Specific Bootstra Register ........................................................... - 78 -
2.4.3 Device Control ....................................................................................... - 79 -
2.4.4 Image Format Control .............................................................................. - 79 -
2.4.5 Acquisition Control .................................................................................. - 80 -
2.4.6 Digital I/O Control ................................................................................... - 81 -
2.4.7 Analogue Control .................................................................................... - 82 -
2.4.8 LUT Control ........................................................................................... - 82 -
2.4.9 Transport Layer Control ............................................................................ - 83 -
2.4.10 User Set Control .................................................................................... - 83 -
2.4.11 JAI-Custom .......................................................................................... - 83 -
Appendix 2 ................................................................................. - 101 -
1. Precautions .................................................................................................. - 101 -
2. Typical Sensor Characteristics............................................................................ - 101 -
3. Caution when mounting a lens on the camera ........................................................ - 101 -
4. Caution when mounting the camera .................................................................... - 101 -
5. Exportation .................................................................................................. - 102 -
6. References ................................................................................................... - 102 -
Manual change history ................................................................... - 103 -
User's Record .............................................................................. - 104 -
- 5 -
Page 8

SP-5000M-PMCL / SP-5000C-PMCL
Before using this camera
EMVA 1288
With regard to signal to noise ratio in this manual, specifications measured by EMVA 1288 are used
together with specifications by a traditional measurement method.
EMVA 1288 is a more complete measurement that considers multiple noise sources, including random
noise, pattern noise, and shading. Additionally, EMVA 1288 incorporates temporal variances in pixel
output by capturing 100 frames of data and computing the RMS variations over the captured frames.
Because of the comprehensive nature of the noise analysis and the additional consideration for RMS
variances over time, EMVA 1288 SNR measurements are inherently lower than the traditional SNR
measurements given by manufacturers. However, the comprehensive nature combined with rigid test
parameters, means that all manufacturers’ are measuring their products equally and EMVA 1288 tested
parameters can be compared among different manufacturers’ products.
In order to learn more about EMVA 1288, please visit http://www.emva.org
Frame grabber board
The SP-5000M-PMCL and SP-5000C-PMCL comply with “Power over Camera Link” which enables power to
be supplied to the camera through the Camera Link cable(s). Because the power requirements of the
camera exceed the amount of power which can be provided over a single PoCL connection, power must
be supplied via both Camera Link cables in order to utilize the PoCL capabilities. If you plan to use this
function, please be sure that the frame grabber board you are using also complies with this specification.
Alternatively, the camera can be powered via a separate power supply connected to the 12-pin Hirose
connector.
The SP-5000M-PMCL and SP-5000C-PMCL employ output formats which comply with the GenICam
standard. They are 1X10–1Y (10-Tap output), 1X8-1Y (8-Tap output), 1X4–1Y (4-Tap output) and 1X2–1Y
(2-Tap output). 1X10–1Y is available for 8-bit output, 1X8–1Y is available for 8-bit and 10-bit output,
and 1X4-1Y and 1X2–1Y are available for 8-bit, 10-bit and 12-bit output. Please check if the frame
grabber used in the system complies with the mentioned formats.
Ⓡ
Camera control tool
The SP-5000M-PMCL and SP-5000C-PMCL are designed to use the JAI SDK and Control Tool software to
control camera functions. All controllable functions are stored in the camera’s XML file. The JAI SDK can
be downloaded from www.jai.com .
A camera control tool for using the Short ASCII command protocol is not available on the JAI website.
Please contact your local JAI representative if this is required.
- 6 -
Page 9

SP-5000M-PMCL / SP-5000C-PMCL
Tripod base
MP-42
Power supply unit
PD-12 series
1. General
The SP-5000M-PMCL and SP-5000C-PMCL are among the first new “Spark Series” cameras to be
introduced. They provide both high resolution and a high frame rate with excellent image quality for
machine vision applications. The SP-5000M-PMCL is a monochrome progressive scan COMS camera and
the SP-5000C-PMCL is the equivalent Bayer mosaic progressive scan CMOS camera. Both are equipped
with CMOS sensors offering a 1-inch image format, a resolution of 5 million pixels, and a 5:4 aspect ratio.
They provide a maximum of 134 frames per second for continuous scanning with 2560 x 2048 full pixel
resolution in 1x10–1Y output format.
8-bit, 10-bit or 12-bit output can be selected for both monochrome and raw Bayer formats. The new
cameras feature a Mini Camera Link interface supporting a “Power over Camera Link” capability. A full
pixel readout or partial scan readout mode can be selected depending on applications. The readout
format is available for 10-tap, 8-tap, 4-tap or 2-tap output.
The SP-5000M-PMCL and SP-5000C-PMCL have various comprehensive functions needed for automated
optical inspection applications, such as solid state device inspection or material surface inspection. They
incorporate video processing functions such as a look-up table, flat field shading compensation and
blemish compensation in addition to fundamental functions such as trigger, exposure setting and video
level control.
The latest version of this manual can be downloaded from: www.jai.com
The latest version of the JAI SDK for the SP-5000M-PMCL and SP-5000C-PMCL can be downloaded from:
www.jai.com
For camera revision history, please contact your local JAI distributor.
2. Camera composition
The standard camera composition is as follows.
Camera body 1
Sensor protection cap 1
Dear Customer (sheet) 1
The following optional accessories are available.
- 7 -
Page 10

SP-5000M-PMCL / SP-5000C-PMCL
3. Key features
New Spark Series 1-inch CMOS 5-megapixel progressive scan camera
Utilizes Mini Camera Link interface in Medium or Full configurations
Aspect ratio 5:4, 2560 (H) x 2048 (V) - 5 million effective pixels
5 μm square pixels
S/N 55dB for monochrome and 53dB for color (traditional measurement method)
8-bit, 10-bit or 12-bit output for monochrome and Bayer
134 frames/second with full resolution in continuous operation for 10-tap output,
120 frames/second for 8-tap output
Supports ROI (Region Of Interest) modes for faster frame rate
0dB to +24dB gain control for both SP-5000M-PMCL and SP-5000C-PMCL
10 μs (1/100,000) to 8 seconds exposure control in 1 μs step
Auto exposure control
Timed and trigger width exposure control
RCT and PIV trigger modes for specific applications
ALC control with combined function of AGC, Auto Shutter and Auto Iris
Various pre-processing circuits are provided
Programmable LUT
Gamma correction from 0.45 to 1.0
Shading correction
Bayer white balance with manual or one-push auto (SP-5000C-PMCL only)
Blemish compensation
HDR (High Dynamic Range) function (SP-5000M-PMCL only)
Auto iris lens video output with H-sync
New Hirose 10P connector for motorized lenses and P-iris lens control as standard and video/DC
iris or TTL IN and OUT and LVDS IN interfaces as options
C-mount for lens mount
Accepts power over Mini Camera Link or via 12-pin connector
Setup by Windows XP/Vista/7/8 via serial communication
- 8 -
Page 11
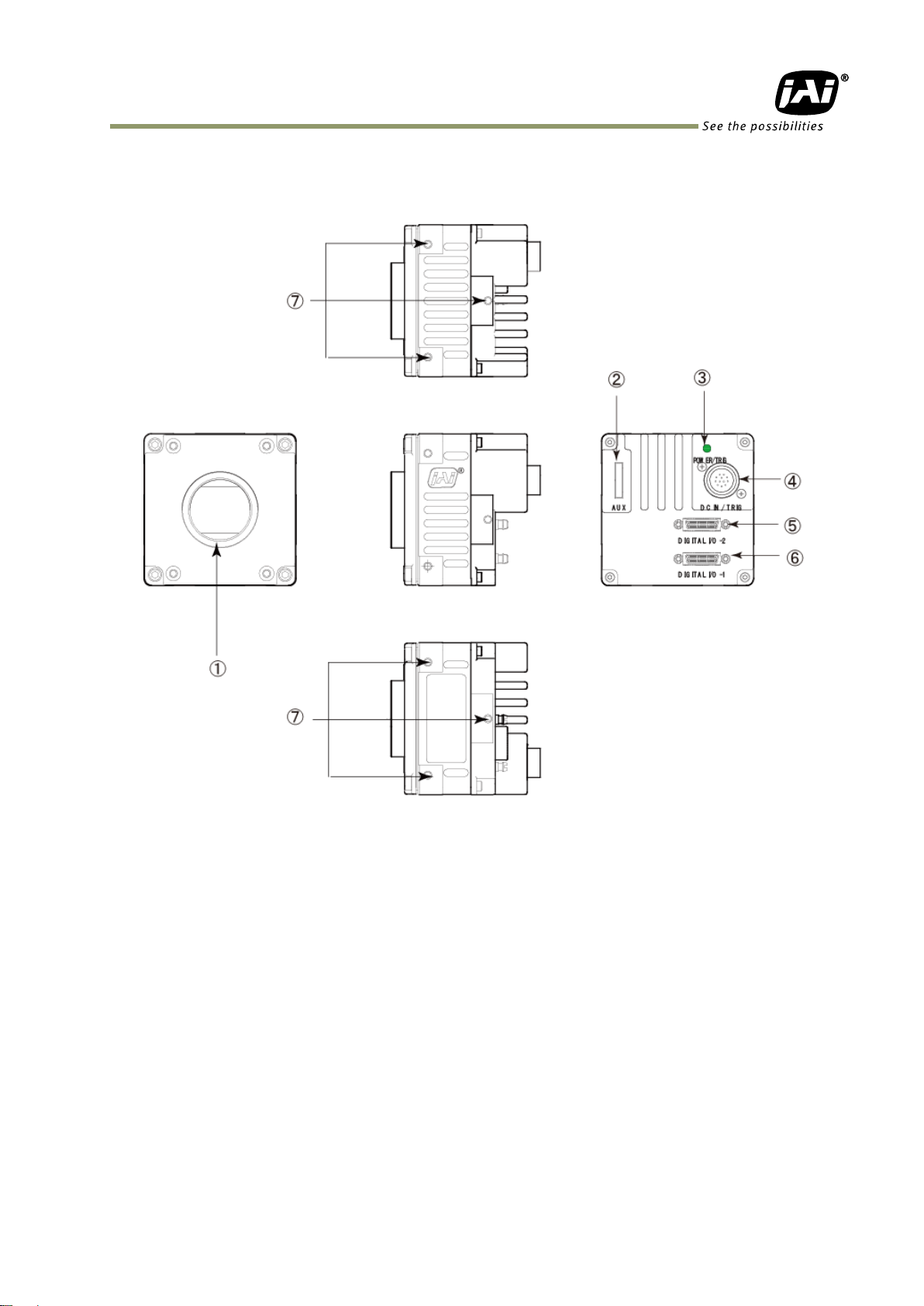
SP-5000M-PMCL / SP-5000C-PMCL
4. Parts locations and their functions
4.1 Parts locations and their functions
Lens mount C-mount (Note *1)
10-pin connector AUX interface connector
LED Indication for power and trigger input
12-pin connector DC+12V and trigger input
Camera Link Connector 2 Digital video output (Medium and Full configuration) (Note *2)
Camera Link Connector 1 Digital video output (Base, Medium and Full config.) (Note *2)
Mounting holes M3 depth 5mm for fixing the camera to the tripod base or
direct installation (Note *3)
*1) Note: Rear protrusion on C-mount lens must be less than 10.0 mm.
*2) Note: When a Camera Link cable is connected to the camera, please do not excessively tighten
screws by using a driver. The Camera Link receptacle on the camera might be damaged.
For security, the strength to tighten screws is less than 0.147 Newton meter (Nm).
Tightening by hand is sufficient in order to achieve this.
*3) Note: The part number for the tripod adapter plate (with 1/4"-20 thread) is MP-42 (option).
Fig. 1 Locations
- 9 -
Page 12

SP-5000M-PMCL / SP-5000C-PMCL
4.2 Rear Panel
The rear panel mounted LED provides the following information:
Amber: Power connected – initiating
This light goes OFF after initiating.
Steady green: Camera is operating in Continuous mode
Flashing green: The camera is receiving external triggering
Note: The interval of flashing does not correspond with external
trigger duration.
Fig. 2 Rear panel
- 10 -
Page 13
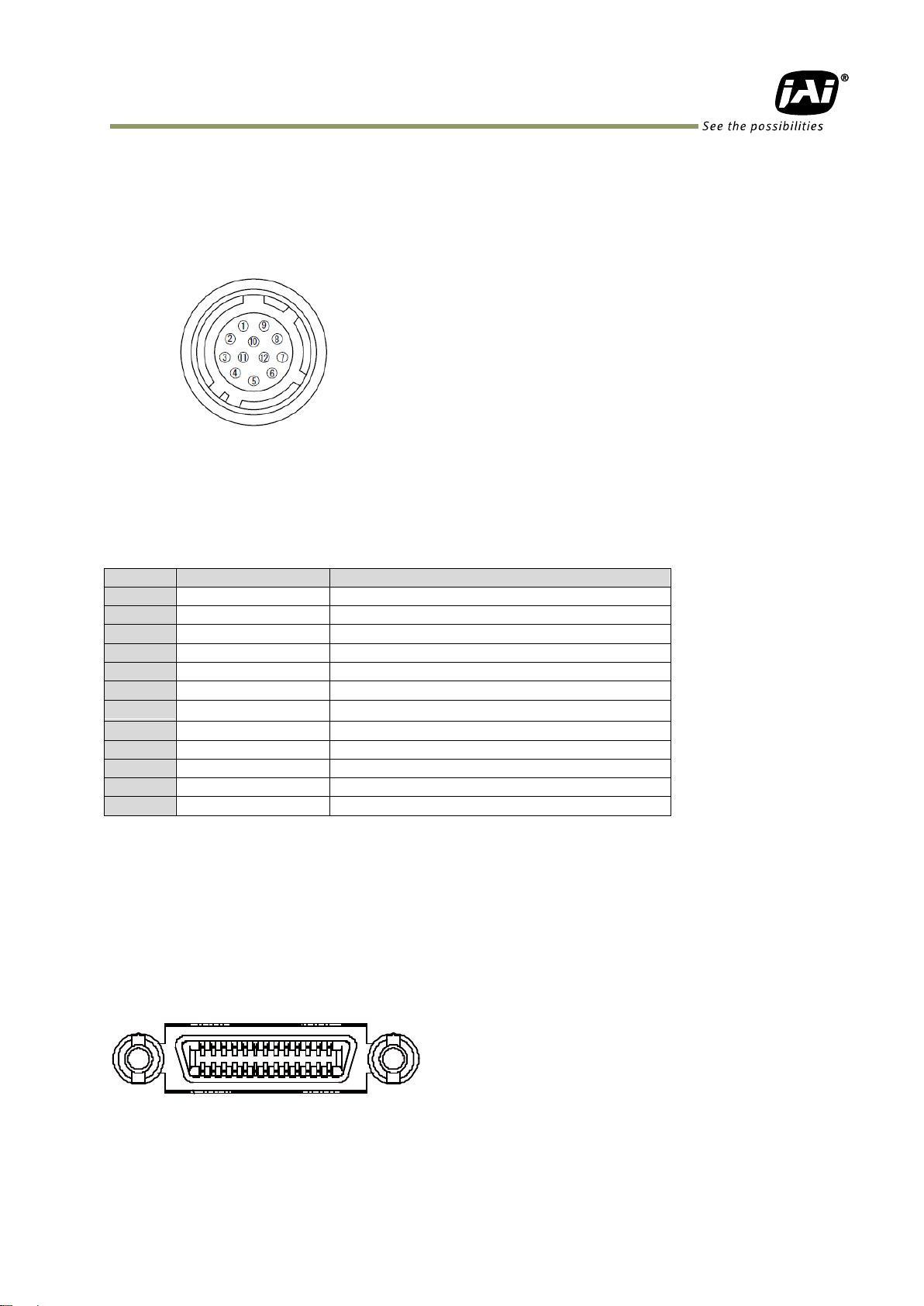
SP-5000M-PMCL / SP-5000C-PMCL
1
14
13
26
Pin no.
Signal
Remarks 1 GND
2
DC input
+12V ~ +24V (note 3)
3
GND
4
Video Iris
Video signal output for lens auto iris
5
NC
6
NC
7
NC
8
NC
9
TTL out 1
Line1 (note 1)
10
TTL In 1
Line4 (note 2)
11
DC input
+12V ~ +24V (note 3)
12
GND
Fig.3 Hirose 12-pin connector
5. Input and output
5.1 Connector and its pin configuration
5.1.1 12-Pin connector
5.1.1.1 Figure
Type: HR-10A-10R-12PB(72) Hirose male or equivalent
5.1.1.2 Pin configuration
Table 1 12-pin configuration
Note 1) Factory default setting is Exposure Active and negative
Exposure Active inside the camera is positive but for the output, it is inverted to negative.
Note 2) Factory default setting is trigger input.
Note 3) See page 6 for notes about power options for these cameras
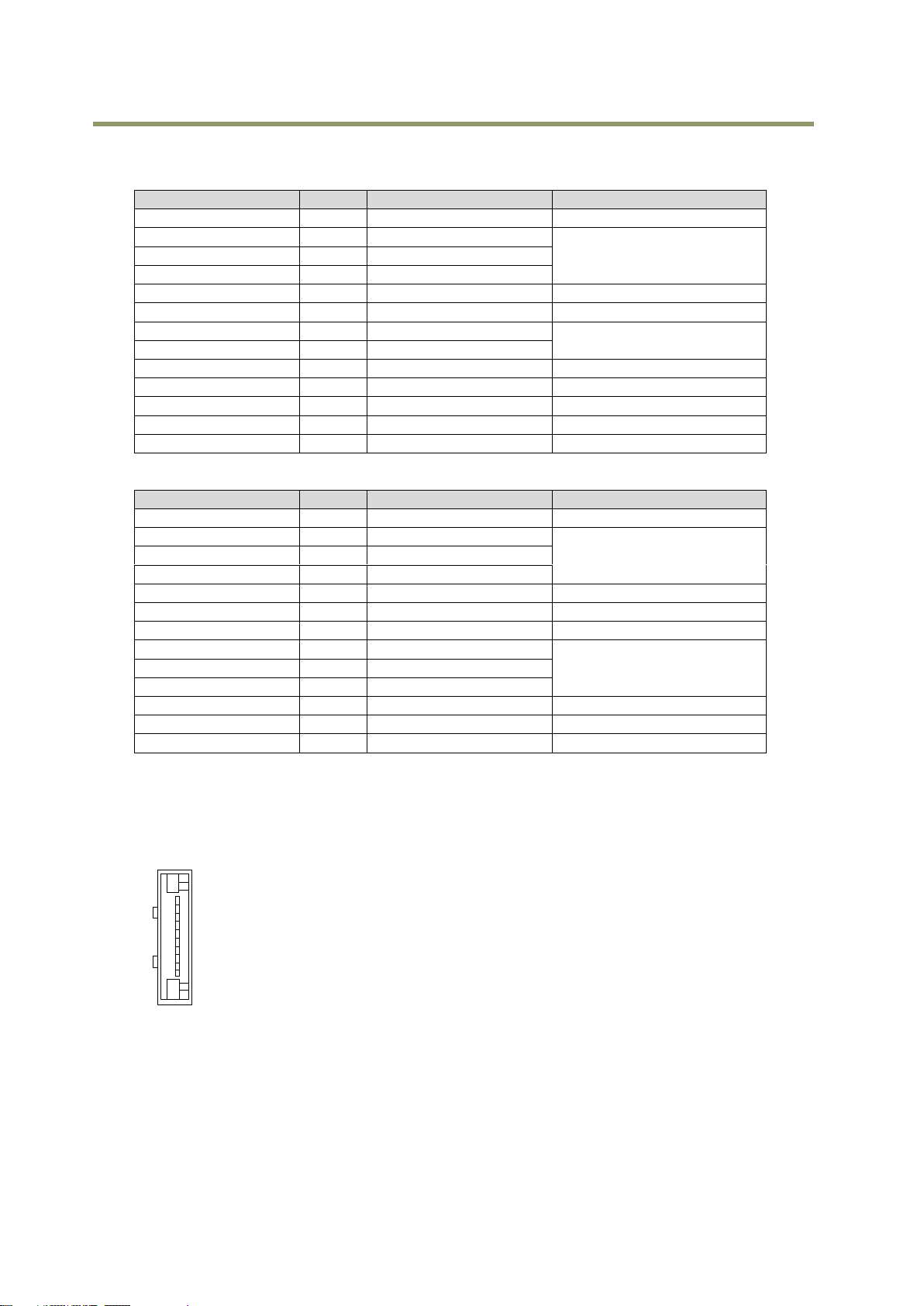
5.1.2 Camera Link Connector
5.1.2.1 Figure
Type: 26-pin Mini Camera Link connector (Honda HDR-EC26FYTG2-SL+) See page 6 for notes about Power
over Camera Link (PoCL) options for this camera.
Fig.4 Camera Link connector
- 11 -
Page 14
SP-5000M-PMCL / SP-5000C-PMCL
Pin No
In/Out
Name
Note
1,26 Power
Power
2(-),15(+)
O
X_OUT0
Data output
3(-),16(+)
O
X_OUT1
4(-),17(+)
O
X_OUT2
5(-),18(+)
O
X_Clk
Clock for CL
6(-),19(+)
O
X_OUT3
Data output
7(+),20(-)
I
SerTC (RxD)
LVDS serial control
8(-),21(+)
O
SerTFG (TxD)
9(-),22(+)
I
CC1 (Trigger)
Trigger input
10(+),23(-)
CC1 (Reserved)
11,24 N.C
12,25 N.C
13,14
Shield
Power Return
Pin No
In/Out
Name
Note
1,26 Power
Power
2(-),15(+)
O
Y_OUT0
Data output
3(-),16(+)
O
Y_OUT1
4(-),17(+)
O
Y_OUT2
5(-),18(+)
O
Y_Clk
Clock for CL
6(-),19(+)
O
Y_OUT3
Data output
7(+),20(-)
I
N.C
8(-),21(+)
O
Z_OUT0
Data output
9(-),22(+)
I
Z_OUT1
10(+),23(-)
Z_OUT2
11,24
Z_Clk
Clock for CL
12,25
Z_OUT3
Data output
13,14
Shield
Power Return
1
8
5.1.2.2 Pin assignment
Table-2 Camera link pin configuration – connector 1
Camera Link connector 2
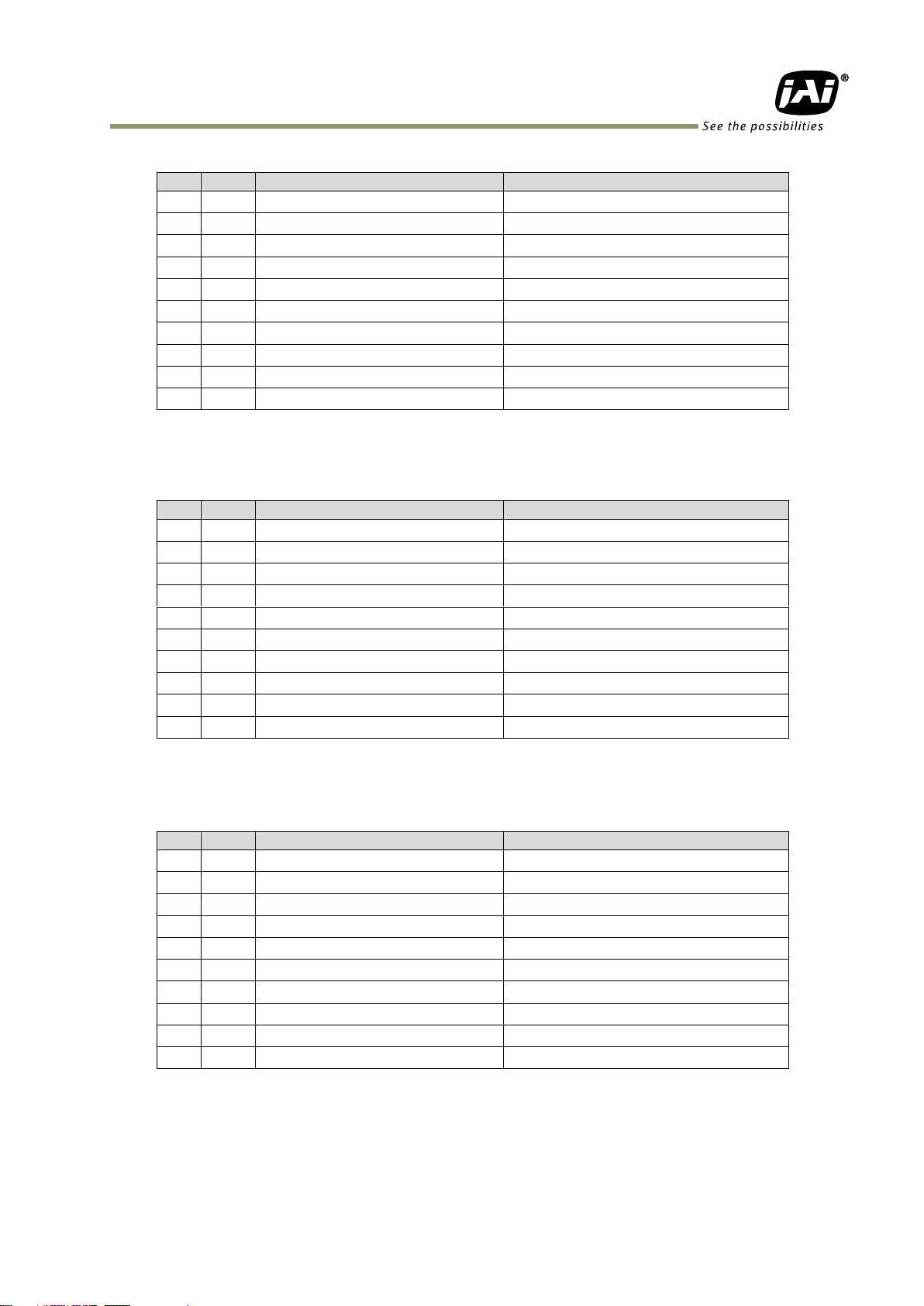
5.1.3 AUX Standard Hirose 10-Pin connector
5.1.3.1 Figure and pin configuration
Type : HIROSE 10-Pin Connector 3260-10S3(55)
Fig.5 Hirose 10-pin connector
- 12 -
Page 15
SP-5000M-PMCL / SP-5000C-PMCL
No
I/O
Name
Note
1
O
DRIVE IRIS+
Motorized Lens
2
O
DRIVE FOCUS+
Motorized Lens
3
O
DRIVE ZOOM+
Motorized Lens
4
O
COMMON
Motorized Lens
5
GND
6 O
P-IRIS OUT1A
P-Iris Lens
7
O
P-IRIS OUT1B
P-Iris Lens
8
O
P-IRIS OUT2A
P-Iris Lens
9
O
P-IRIS OUT2B
P-Iris Lens
10
O
GND
No
I/O
Name
Note
1
O
Video Signal
Video Iris Lens
2
O
Power DC+12V
Video Iris Lens
3
NC
4
NC
5
GND
6
O
DC IRIS DAMP-
DC Iris
7
O
DC IRIS DAMP+
DC Iris
8
O
DC IRIS DRIVE+
DC Iris
9
O
DC IRIS DRIVE-
DC Iris
10
GND
No
I/O
Name
Note
1
O
TTL OUT2
Line8 2 O
TTL OUT3
Line9
3
I
TTL_IN2
Line10
4
NC
5
GND
6 I
LVDS_IN1+
Line11
7
I
LVDS_IN1-
8
NC
9
GND
10
GND
Table -3 AUX Standard Hirose 10-pin connector pin assignment
5.1.4 AUX Type 2 HIROSE 10-Pin connector (factory option)
Type: HIROSE 10-Pin Connector 3260-10S3(55)
Table-4 10-pin pin configuration (option)
5.1.5 AUX Type 3 HIROSE 10-Pin connector (factory option)
HIROSE 10-Pin Connector 3260-10S3(55)
Table – 5 10-pin pin configuration (option)
- 13 -
Page 16

SP-5000M-PMCL / SP-5000C-PMCL
Base Medium Full 80bit Full
2Tap / 12bit 4Tap / 12bit 8 Tap / 8b it 8 Tap / 10b it 10 Tap / 8 bit
1X2 - 1Y 1X4 - 1Y 1x8 - 1Y 1X 8 - 1Y 1X10 - 1Y
Port A0 TxIN 0 Tap1 D0 Tap 1 D0 Tap 1 D0 Tap 1 D2 Tap 1 D0
Port A1 TxIN 1 Tap1 D1 Tap 1 D1 Tap 1 D1 Tap 1 D3 Tap 1 D1
Port A2 TxIN 2 Tap1 D2 Tap 1 D2 Tap 1 D2 Tap 1 D4 Tap 1 D2
Port A3 TxIN 3 Tap1 D3 Tap 1 D3 Tap 1 D3 Tap 1 D5 Tap 1 D3
Port A4 TxIN 4 Tap1 D4 Tap 1 D4 Tap 1 D4 Tap 1 D6 Tap 1 D4
Port A5 TxIN 6 Tap1 D5 Tap 1 D5 Tap 1 D5 Tap 1 D7 Tap 1 D6
Port A6 TxIN 27 Tap1 D6 Tap 1 D6 Tap 1 D6 Tap 1 D8 T ap 4 D1
Port A7 TxIN 5 Tap1 D7 Tap 1 D7 Tap 1 D7 Tap 1 D9 Tap 1 D5
Port B0 TxIN 7 Tap1 D8 Tap 1 D8 Tap 2 D0 Tap 2 D2 T ap 1 D7
Port B1 TxIN 8 Tap1 D9 Tap 1 D9 Tap 2 D1 Tap 2 D3 T ap 2 D0
Port B2 TxIN 9 Tap1 D10 Tap 1 D10 T ap 2 D2 Tap 2 D4 Tap 2 D1
Port B3 TxIN 12 Tap1 D11 Tap 1 D11 Tap 2 D3 T ap 2 D5 Tap 2 D4
Port B4 TxIN 13 Tap2 D8 T ap 2 D8 Tap 2 D4 Tap 2 D6 Tap 2 D5
Port B5 TxIN 14 Tap2 D9 T ap 2 D9 Tap 2 D5 Tap 2 D7 Tap 2 D6
Port B6 TxIN 10 Tap2 D10 Tap 2 D10 Tap 2 D6 T ap 2 D8 Tap 2 D2
Port B7 TxIN 11 Tap2 D11 Tap 2 D11 Tap 2 D7 T ap 2 D9 Tap 2 D3
Port C0 TxIN 15 Tap2 D0 Tap 2 D0 Tap 3 D0 Tap 3 D2 T ap 2 D7
Port C1 TxIN 18 Tap2 D1 Tap 2 D1 Tap 3 D1 Tap 3 D3 T ap 3 D2
Port C2 TxIN 19 Tap2 D2 Tap 2 D2 Tap 3 D2 Tap 3 D4 T ap 3 D3
Port C3 TxIN 20 Tap2 D3 Tap 2 D3 Tap 3 D3 Tap 3 D5 T ap 3 D4
Port C4 TxIN 21 Tap2 D4 Tap 2 D4 Tap 3 D4 Tap 3 D6 T ap 3 D5
Port C5 TxIN 22 Tap2 D5 Tap 2 D5 Tap 3 D5 Tap 3 D7 T ap 3 D6
Port C6 TxIN 16 Tap2 D6 Tap 2 D6 Tap 3 D6 Tap 3 D8 T ap 3 D0
Port C7 TxIN 17 Tap2 D7 Tap 2 D7 Tap 3 D7 Tap 3 D9 T ap 3 D1
- TxIN 24 LVAL LVAL LVAL LVAL L VAL
- TxIN 25 FVAL FVAL FVAL FVAL FVAL
(Port I0) TxIN 26 DVAL DVAL DVAL T ap 1 D0 Tap 4 D0
(Port I1) TxIN 23 Exposure Active Exposure Active Ex posure Active Tap 1 D1 Tap 3 D7
SP-5000M/C-PMCL
Camera Link Configuration
Camera Link port/bit
GenICam Tap Geometry
D
i
g
i
t
a
l
I
/
O
-
1
Port
Base Medium Full 80bit Full
2Tap / 12bit 4Tap / 12bit 8 Tap / 8b it 8 Tap / 10b it 10 Tap / 8 bit
1X2 - 1Y 1X4 - 1Y 1x8 - 1Y 1X 8 - 1Y 1X10 - 1Y
Port D0 TxIN 0 — Tap 4 D0 Tap 4 D0 T ap 4 D2 Tap 4 D2
Port D1 TxIN 1 — Tap 4 D1 Tap 4 D1 T ap 4 D3 Tap 4 D3
Port D2 TxIN 2 — Tap 4 D2 Tap 4 D2 T ap 4 D4 Tap 4 D4
Port D3 TxIN 3 — Tap 4 D3 Tap 4 D3 T ap 4 D5 Tap 4 D5
Port D4 TxIN 4 — Tap 4 D4 Tap 4 D4 T ap 4 D6 Tap 4 D6
Port D5 TxIN 6 — Tap 4 D5 Tap 4 D5 T ap 4 D7 Tap 5 D0
Port D6 TxI N 27 — Tap 4 D6 Tap 4 D6 T ap 4 D8 LVAL
Port D7 TxIN 5 — Tap 4 D7 Tap 4 D7 T ap 4 D9 Tap 4 D7
Port E0 TxIN 7 — Tap 3 D0 Tap 5 D0 Tap 5 D2 Tap 5 D1
Port E1 TxIN 8 — Tap 3 D1 Tap 5 D1 Tap 5 D3 Tap 5 D2
Port E2 TxIN 9 — Tap 3 D2 Tap 5 D2 Tap 5 D4 Tap 5 D3
Port E3 TxI N 12 — Tap 3 D3 Tap 5 D3 Tap 5 D5 Tap 5 D6
Port E4 TxI N 13 — Tap 3 D4 Tap 5 D4 Tap 5 D6 Tap 5 D7
Port E5 TxI N 14 — Tap 3 D5 Tap 5 D5 Tap 5 D7 Tap6 D0
Port E6 TxI N 10 — Tap 3 D6 Tap 5 D6 Tap 5 D8 Tap 5 D4
Port E7 TxI N 11 — Tap 3 D7 Tap 5 D7 Tap 5 D9 Tap 5 D5
Port F0 TxIN 15 — Tap 3 D8 Tap6 D0 Tap 6 D2 Tap6 D1
Port F1 TxIN 18 — Tap 3 D9 Tap6 D1 Tap 6 D3 Tap6 D4
Port F2 TxIN 19 — Tap 3 D10 Tap6 D2 Tap 6 D4 Tap6 D5
Port F3 TxIN 20 — Tap 3 D11 Tap6 D3 Tap 6 D5 Tap6 D6
Port F4 TxIN 21 — Tap 4 D8 Tap6 D4 Tap 6 D6 Tap6 D7
Port F5 TxIN 22 — Tap 4 D9 Tap6 D5 Tap 6 D7 Tap7 D0
Port F6 TxIN 16 — Tap 4 D10 Tap6 D6 Tap 6 D8 Tap6 D2
Port F7 TxIN 17 — Tap 4 D11 Tap6 D7 Tap 6 D9 Tap6 D3
- TxIN 24 — LVAL LVAL LVAL Tap7 D2
(Port I2) TxIN 25 — FVAL FVAL Tap 2 D0 Tap7 D3
(Port I3) TxIN 26 — DVAL DVAL Tap 2 D1 Tap7 D4
(Port I4) TxIN 23 — Exposure Active Exposure Active Tap 3 D0 T ap7 D1
SP-5000M/C-PMCL
D
i
g
i
t
a
l
I
/
O
-
2
(
1
/
2
)
Port
Camera Link Configuration
Camera Link port/bit
GenICam Tap Geometry
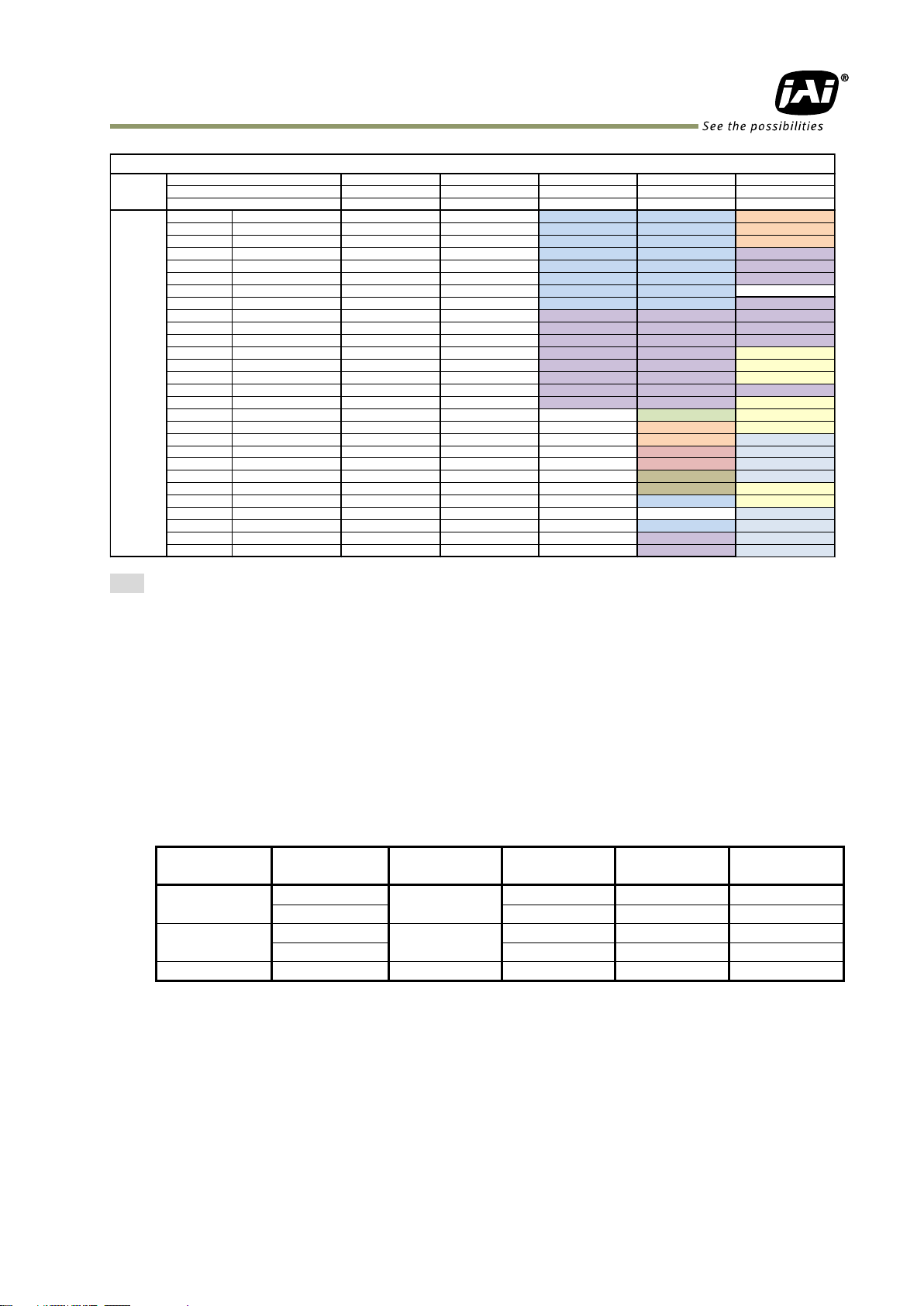
5.2 Camera Link interface
5.2.1 Camera Link Interface
Table-6 Camera Link interface
- 14 -
Page 17
SP-5000M-PMCL / SP-5000C-PMCL
Base Medium Full 80bit Full
2Tap / 12bit 4Tap / 12bit 8 Tap / 8b it 8 Tap / 10b it 10 Tap / 8 bit
1X2 - 1Y 1X4 - 1Y 1x8 - 1Y 1X 8 - 1Y 1X10 - 1Y
Port G0 TxIN 0 — ― Tap 7 D0 Tap 7 D2 Tap7 D5
Port G1 TxIN 1 — ― Tap 7 D1 Tap 7 D3 Tap7 D6
Port G2 TxIN 2 — ― Tap 7 D2 Tap 7 D4 Tap7 D7
Port G3 TxIN 3 — ― Tap 7 D3 Tap 7 D5 Tap8 D0
Port G4 TxIN 4 — ― Tap 7 D4 Tap 7 D6 Tap8 D1
Port G5 TxIN 6 — ― Tap 7 D5 Tap 7 D7 Tap8 D3
Port G6 TxIN 27 — ― Tap 7 D6 Tap 7 D8 LVAL
Port G7 TxIN 5 — ― Tap 7 D7 Tap 7 D9 Tap8 D2
Port H0 TxIN 7 — ― Tap 8 D0 Tap 8 D2 Tap8 D4
Port H1 TxIN 8 — ― Tap 8 D1 Tap 8 D3 Tap8 D5
Port H2 TxIN 9 — ― Tap 8 D2 Tap 8 D4 Tap8 D6
Port H3 TxIN 12 — ― Tap 8 D3 Tap 8 D5 Tap 9 D1
Port H4 TxIN 13 — ― Tap 8 D4 Tap 8 D6 Tap 9 D2
Port H5 TxIN 14 — ― Tap 8 D5 Tap 8 D7 Tap 9 D3
Port H6 TxIN 10 — ― Tap 8 D6 Tap 8 D8 Tap8 D7
Port H7 TxIN 11 — ― Tap 8 D7 Tap 8 D9 Tap 9 D0
(Port I5) TxIN 15 — ― Tap 3 D1 Tap 9 D4
(Port I6) TxIN 18 — ― Tap 4 D0 Tap 9 D7
(Port I7) TxIN 19 — ― Tap 4 D1 Tap10 D0
(Port K0) TxIN 20 — ― Tap 5 D0 Tap10 D1
(Port K1) TxIN 21 — ― Tap 5 D1 Tap10 D2
(Port K2) TxIN 22 — ― Tap 6 D0 Tap10 D3
(Port K3) TxIN 16 — ― Tap 6 D1 Tap 9 D5
(Port K4) TxIN 17 — ― Tap 7 D0 Tap 9 D6
- TxIN 24 — ― LVAL LVAL Tap10 D5
(Port K5) TxIN 25 — ― FVAL Tap 7 D1 Tap10 D6
(Port K6) TxIN 26 — ― DVAL Tap 8 D0 T ap10 D7
(Port K7) TxIN 23 — ― Exposure Active Tap 8 D1 Tap10 D4
SP-5000M/C-PMCL
D
i
g
i
t
a
l
I
/
O
-
2
(
2
/
2
)
Port
Camera Link Configuration
Camera Link port/bit
GenICam Tap Geometry
Camera Link
Pixel Clock
Maximum
length
1X2–1Y
1X4–1Y
1X8-1Y
1X10–1Y
61.7 MHz
10 m
23 fps
— — —
7 m
46 fps
93 fps
115 fps
75.4 MHz
7 m
28 fps
56 fps
112 fps
—
5 m
134 fps
82.3 MHz
5 m
30 fps
61 fps
120 fps
134 fps
Note
1. In this table, not all tap geometry items are described. For instance, 1X4–1Y shows only 12-bit.
In case of 10-bit, upper 2 bits (D10 and D11) are not used and in case of 8-bit, upper 4 bits
(D8 through D11) are not used.
2. Please check whether the frame grabber complies with those formats if you use 80-bit (8-tap/10-bit)
camera configuration.
3. If you use 80-bit (8-tap/10-bit) camera configuration, DVAL and Exposure Active (JAI custom) are
not output through the Camera Link interface. FVAL is only output via Digital I/O-1 connector.
5.2.2 Camera Link pixel clock frequency
In the SP-5000M-PMCL and SP-5000C-PMCL, the Camera Link pixel clock can be selected from
82.3 MHz, 75.4 MHz and 61.7 MHz. If the 61.7 MHz clock is used, the transfer length through
the camera link cable will be extended to 10m. On the other hand, the frame rate will be
reduced. The default setting is 82.3 MHz.
Note: The maximum lengths shown in the above table are guidelines. Operating at these lengths
may generate bit noise, depending on the cable used.
- 15 -
Page 18
SP-5000M-PMCL / SP-5000C-PMCL
Line Selector item
Description
Line 1 TTL 1 Out
TTL 1 output from Hirose 12P #9 pin
Line 8 TTL 2 OUT
TTL 2 output from AUX Hirose 10P #1 pin
Line 10 TTL 3 OUT
TTL 3 output from AUX Hirose 10P #2 pin
NAND 0 IN 1
No. 1 input to the first NAND gate
NAND 0 IN 2
No. 2 input to the first NAND gate
NAND 1 IN 1
No. 1 input to the second NAND gate
NAND 1 IN 2
No. 2 input to the second NAND gate
Line Source item
Description
Low
Connect Low Level signal to line item selected in Line Selector, Default setting
High
Connect High Level signal to line item selected in Line Selector
Frame Trigger Wait
Connect Frame Trigger Wait signal to line item selected in Line Selector
Frame Active
Connect Frame Active signal to line item selected in Line Selector
Exposure Active
Connect Exposure Active signal to line item selected in Line Selector
FVAL
Connect FVAL signal to line item selected in Line Selector
LVAL
Connect LVAL signal to line item selected in Line Selector
PulseGenerator0 Out
Connect Pulse Generator 0 signal to line item selected in Line Selector
PulseGenerator1 Out
Connect Pulse Generator 1 signal to line item selected in Line Selector
PulseGenerator2 Out
Connect Pulse Generator 2 signal to line item selected in Line Selector
PulseGenerator3 Out
Connect Pulse Generator 3 signal to line item selected in Line Selector
TTL 1 In
Connect TTL 1 IN signal to line item selected in Line Selector
CL CC1 In
Connect CL CC1 IN signal to line item selected in Line Selector
NAND 0 Out
Connect NAND 0 signal to line item selected in Line Selector
NAND 1 Out
Connect NAND 1 signal to line item selected in Line Selector
Line 10 TTL 2 In
Connect TTL 2 IN signal to Line 10 (Option)
Line 11 LVDS 1 In
Connect LVDS 1 IN signal to Line 11 (Option)
Note]
As for LVAL, some line items cannot be connected. Refer to “5.3.7.2 GPIO matrix table”
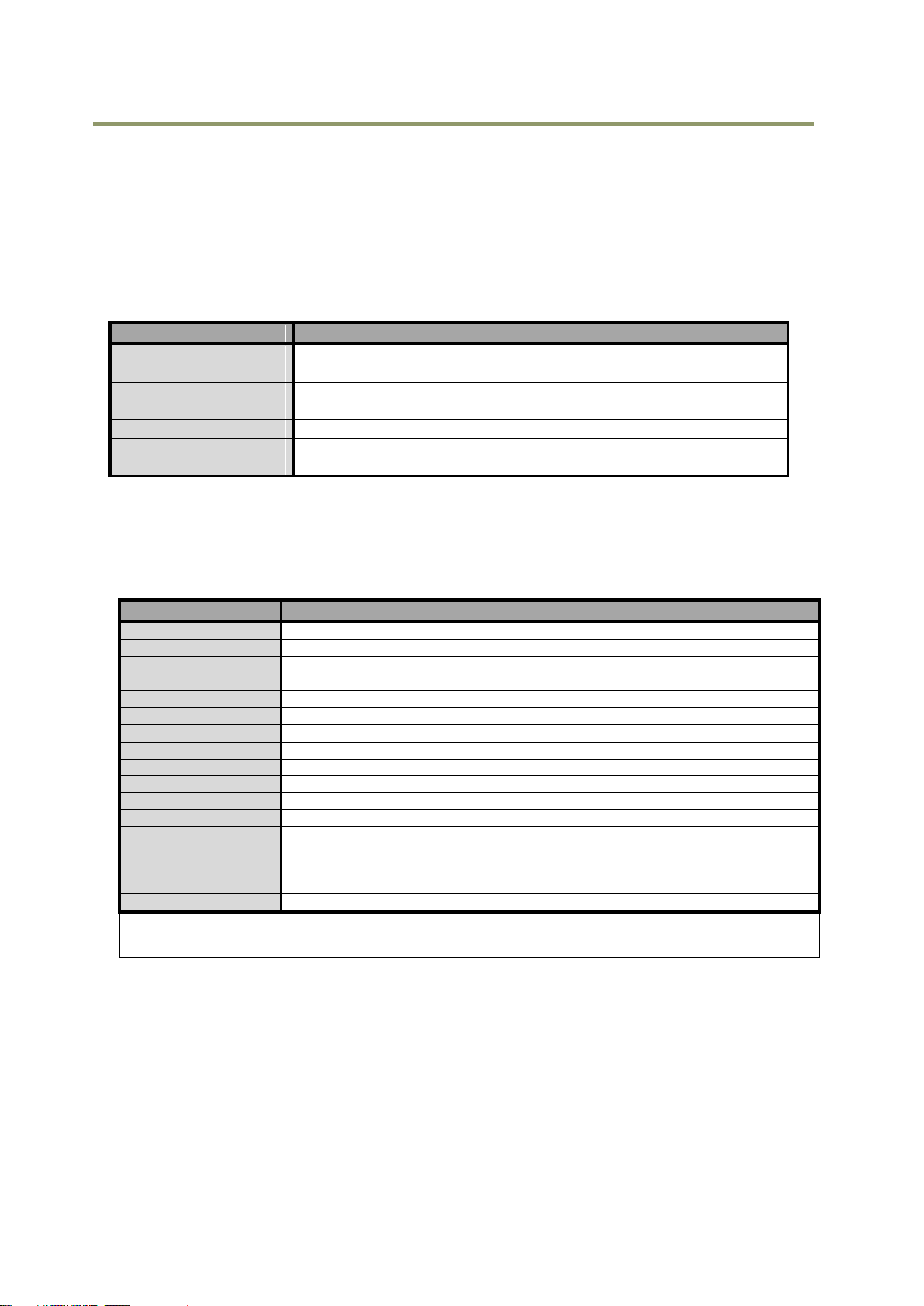
5.3 Digital IN/OUT interface
In the SP-5000M-PMCL and SP-5000C-PMCL, the software control tool can assign the necessary
signals used in the system to digital inputs and outputs (see Section 5.3.7.1 for block diagram).
5.3.1 Line Selector
In the Line Selector, the following input and output signals can be assigned.
Table-7 Line selector
5.3.2 Line Source
Line source signal can be selected from the following table to connect it to the line item which
is selected in the line selector.
Table-8 Line Source
5.3.3 Line Mode
Indicates the status of the item selected in Line Selector. (INPUT or OUTPUT)
5.3.4 Line Inverter
Inverts the signal polarity for the item selected in Line Selector.
(False=Positive, True=Negative)
5.3.5 Line Status
Indicates the status of the selected signal (input or output) (True=High,
False=Low)
- 16 -
Page 19
SP-5000M-PMCL / SP-5000C-PMCL
Soft Trigger
LVAL IN
FVAL IN
Exposure Active
Frame Trigger Wait
Frame Active
GPIO 4 (TTL IN 1)
GPIO 7 (CL CC1)
GPIO 10 (TTL IN2)
GPIO 11 (LVDS IN)
Pixel Clock
Cross Pont
Switch
12 bit Counter
INV
INV
INV N
NAND
INV
Non INV
Pulse Generator
20 bit counter x 4
CLR
Sel Bit (5,0) Sel Bit (7)
Sel Bit (7)
Pulse Generator 0
Pulse Generator 1
Pulse Generator 2
Pulse Generator 3
Trigger 2 (Frame Start)
GPIO 1 (TTL OUT 1)
GPIO 8 (TL OUT 2)
GPIO 9 (TTL OUT 3)
Sel Bit (7)
Clock IN
Clear IN
Gate 1
Gate 2
5.3.6 Line Format
Indicates the interface information of the input and output lines.
Not connected, TTL, LVDS or Opto-coupled
Note: In the SP-5000-PMCL, Opto-coupled interface is not available.
5.3.7 GPIO
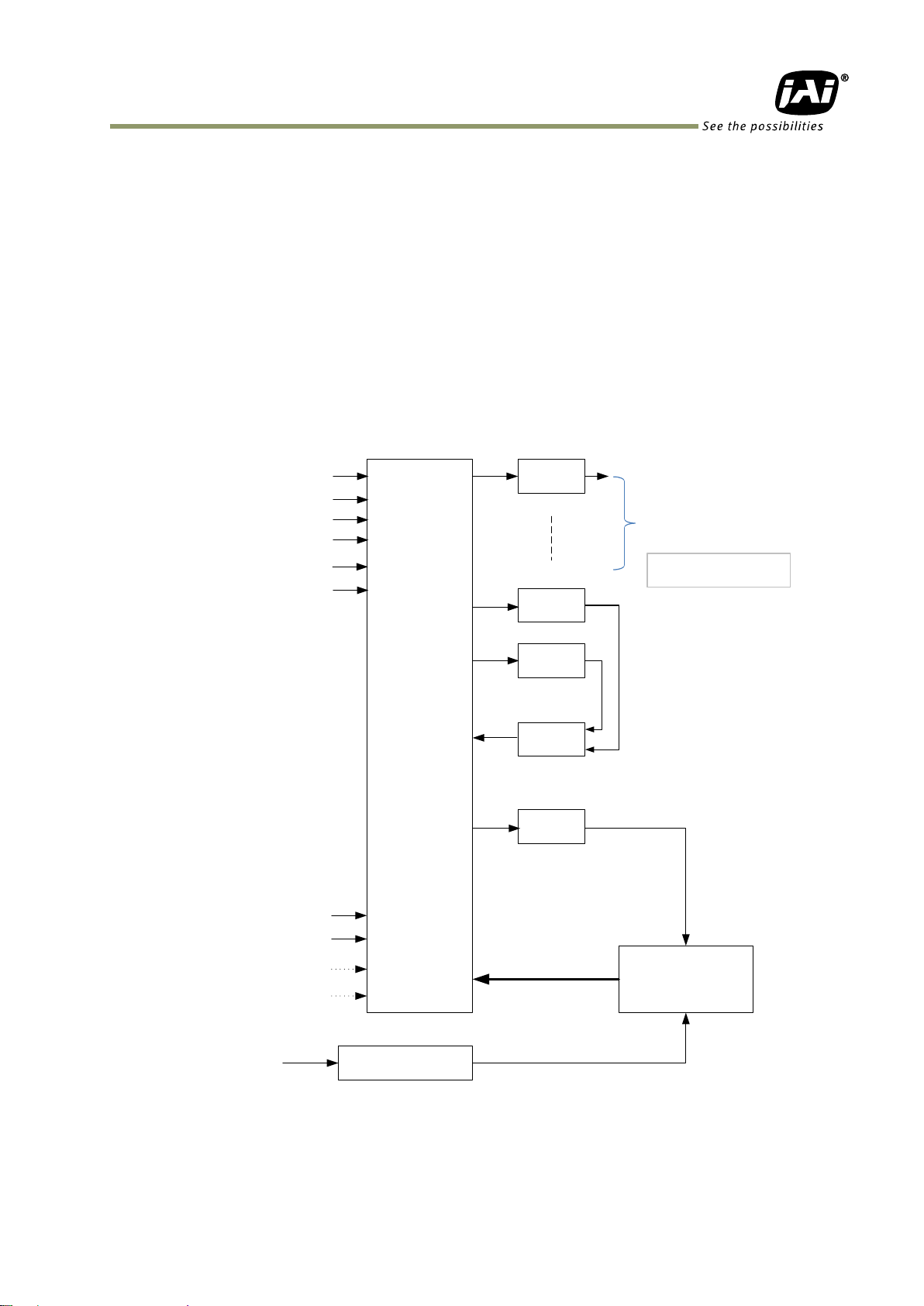
GPIO is a general interface for input and output and controls the I/O for trigger signals and
other valid signals and pulse generators. By using this interface you can control an external light
source, make a delay function for an external trigger signal, or make a precise exposure setting
together with a PWC trigger.
5.3.7.1 Basic block diagram
The basic block diagram is as follows.
In the SP-5000-PMCL, the pixel clock is 48 MHz.
Note: Items written in blue letters are available if the AUX Type 3 option is selected.
Fig.6 GPIO interface
- 17 -
Page 20
SP-5000M-PMCL / SP-5000C-PMCL
Selector (Cross
point switch output)
Source signal
(Cross point switch input)
Low
High
Soft Trigger
Exposure Active
Frame Trigger Wait
Frame Active
FVAL
LVAL
Pulse Generator 0
Pulse Generator 1
Pulse Generator 2
Pulse Generator 3
Line 4 - TTL In1
Line 7 - CL CC1 in
NAND 0 Out
NAND 1 Out 1
Line 10 - TTL 2 In
Line 11 - LVDS 1 In
Trigger Source
Line Selector
Pulse Generator
Selector
Trigger Source
(Frame Start )
Line 1 - 12P TTL Out
Line 8 - TTL 2 Out
Trigger Selector
Pulse Generator
Clear Source
Line Source
Line 9 - TTL 3 Out
NAND 1 In 1
NAND 1 In 2
NAND 2 In 1
NAND 2 In 2
Pulse Generator 0
Pulse Generator 1
Pulse Generator 2
Pulse Generator 3
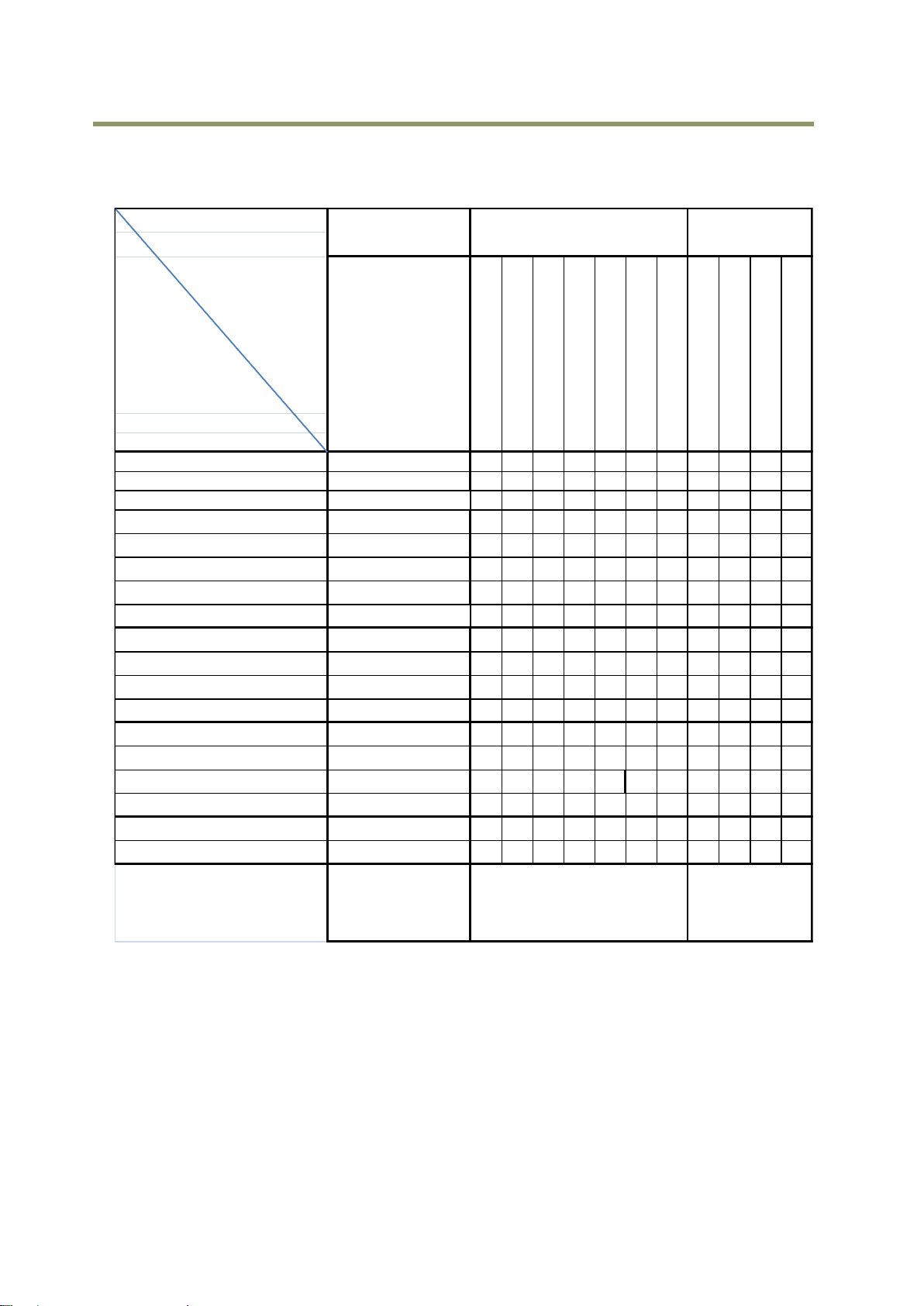
5.3.7.2 Input and output matrix table
The relation between input and output is as follows.
Table-9 GPIO matrix table
Note: In the above table, TTL 2 IN, LVDS IN, TTL 2 Out and TTL 3 Out are available only if AUX Type
3 option is used.
5.4 Pulse Generator
The SP-5000-PMCL has a frequency divider using the sensor clock as the basic clock and four pulse
generators. In each Pulse Generator, various Clear settings are connected to GPIO.
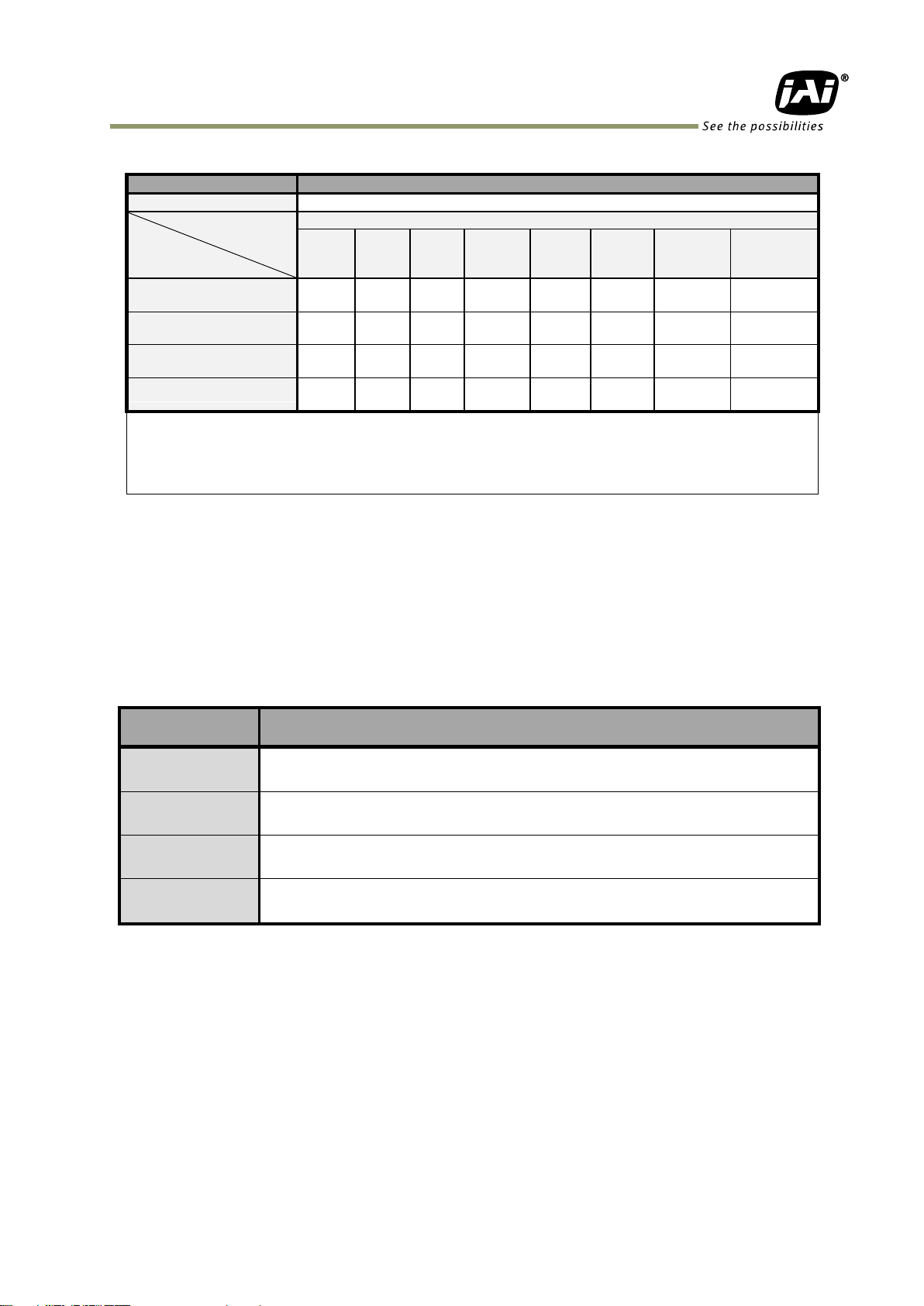
The following shows Pulse Generator default settings.
- 18 -
Page 21
SP-5000M-PMCL / SP-5000C-PMCL
Display Name
Value
Clock Pre-scaler
1
Pulse Generator
Selector
Pulse Generator
Length
Start
Point
End
Point
Repeat
Count
Clear
Source
Clear
Inverter
Clear
Activation
Clear
Sync
Mode
-
Pulse Generator 0
1 0 1 0 Off
True
Off
Async
Mode
-
Pulse Generator 1
1 0 1 0 Off
True
Off
Async
Mode
-
Pulse Generator 2
1 0 1 0 Off
True
Off
Async
Mode
-
Pulse Generator 3
1 0 1 0 Off
True
Off
Async
Mode
Note:]
When Pulse Generator Repeat Count is set to “0”, the camera is operating in free-running mode.
However, based on the above default settings, Length=1, Start Point=0 and End Point=1, Pulse
Generator stops at High output. Therefore, if Start Point=0 and End Point=1 are configured, Length should
be “2” as the minimum active width.
Trigger Selector
item
Description
Pulse Generator
0
If Pulse Generator 0 is selected, Length, Start Point, End Point, Repeat Count, Clear Source, Clear
Inverter, Clear Activation and Clear Sync Mode of Pulse Generator 0 are displayed under the
selector.
Pulse Generator
1
If Pulse Generator 1 is selected, Length, Start Point, End Point, Repeat Count, Clear Source, Clear
Inverter, Clear Activation and Clear Sync Mode of Pulse Generator 1 are displayed under the
selector.
Pulse Generator
2
If Pulse Generator 2 is selected, Length, Start Point, End Point, Repeat Count, Clear Source, Clear
Inverter, Clear Activation and Clear Sync Mode of Pulse Generator 2 are displayed under the
selector.
Pulse Generator
3
If Pulse Generator 3 is selected, Length, Start Point, End Point, Repeat Count, Clear Source, Clear
Inverter, Clear Activation and Clear Sync Mode of Pulse Generator 3 are displayed under the
selector.
Table - 10 Pulse Generator default settings
5.4.1 Clock Pre-scaler
Clock pre-scaler (Divide Value) can set the dividing value of the frequency divider (12-bit
length) and the sensor clock is used for this. Four built-in pulse generators work by the
same clock. In the SP-5000-PMCL, the sensor clock is 48 MHz.
5.4.2 Pulse Generator Selector
This is where you select one of the 4 pulse generators in order to set or modify its
parameters.
Table - 11 Pulse Generator setting
- 19 -
Page 22
SP-5000M-PMCL / SP-5000C-PMCL
Pulse generator
length
Pulse generator Start point
Pulse generator End point
Pulse generator repeat count = N
(Pulse generator length x N)
Pulse generator
Clear source IN
(Clear activation
= Rising edge
Clear SYNC mode
= Async)
Pulse generator
Output
Pulse generator
length
Pulse generator
length
000
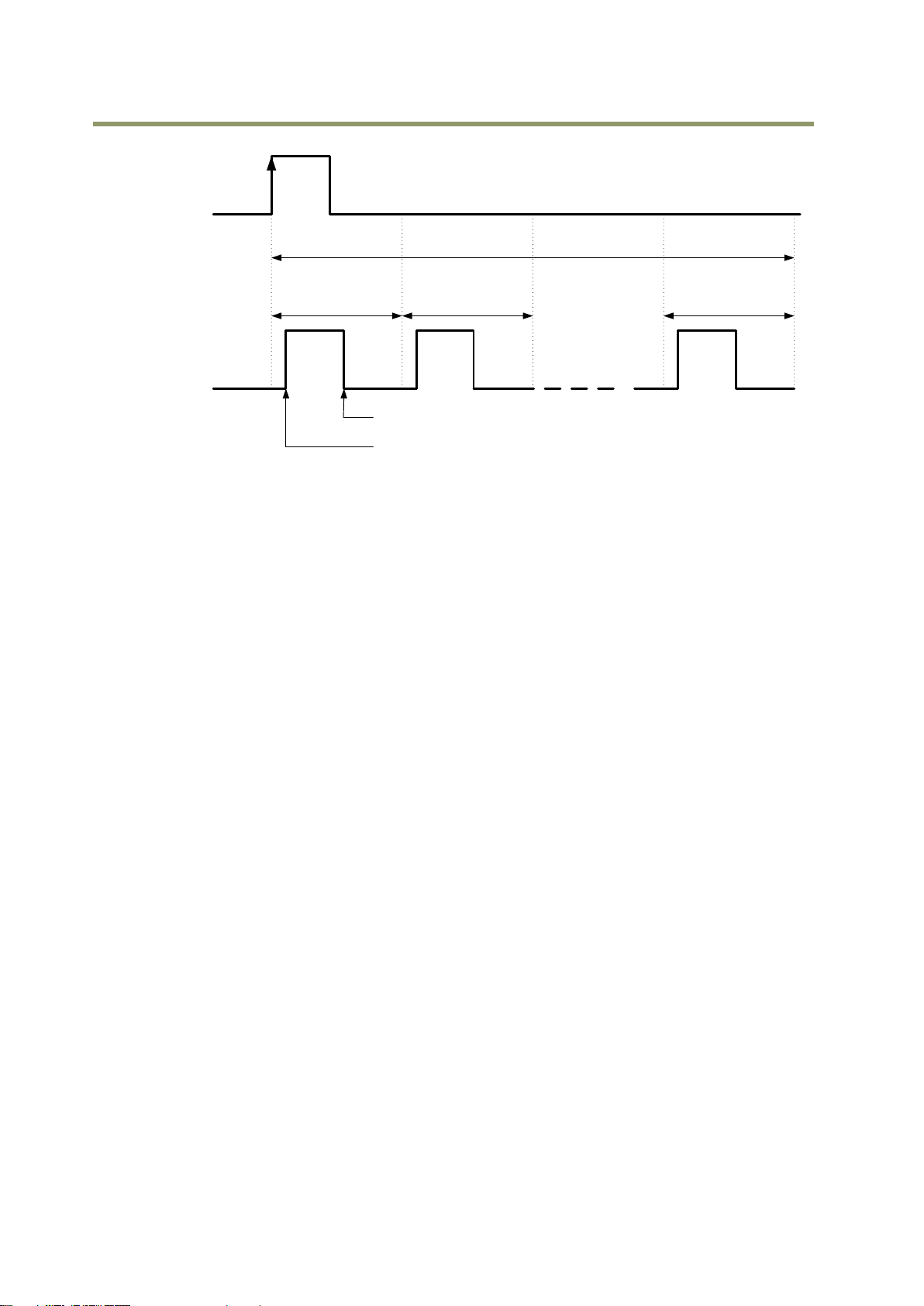
Fig.7 Pulse Generator pulse construction
5.4.3 Pulse Generator Length
Set the counter up value for the selected pulse generator. If Repeat Count value is “0” and
if Pulse Generator Clear signal is not input, the pulse generator generates the pulse
repeatedly until reaching this counter up value.
5.4.4 Pulse Generator Start Point
Set the active output start count value for the selected pulse generator.
However, please note that a maximum 1 clock jitter for the clock which is divided in the clock
pre-scaler can occur.
5.4.5 Pulse Generator End Point
Set the active output ending count value for the selected pulse generator.
5.4.6 Pulse Generator Repeat Count
Set the repeating number of the pulse for the selected pulse generator. After Trigger Clear
signal is input, the pulse generator starts the count set in Repeat Count. Accordingly, an
active pulse which has a start point and end point can be output repeatedly.
However, if Repeat Count is set to“0”, it works as free-running counter.
5.4.7 Pulse Generator Clear Activation
Set the clear conditions of clear count pulse for the selected pulse generator.
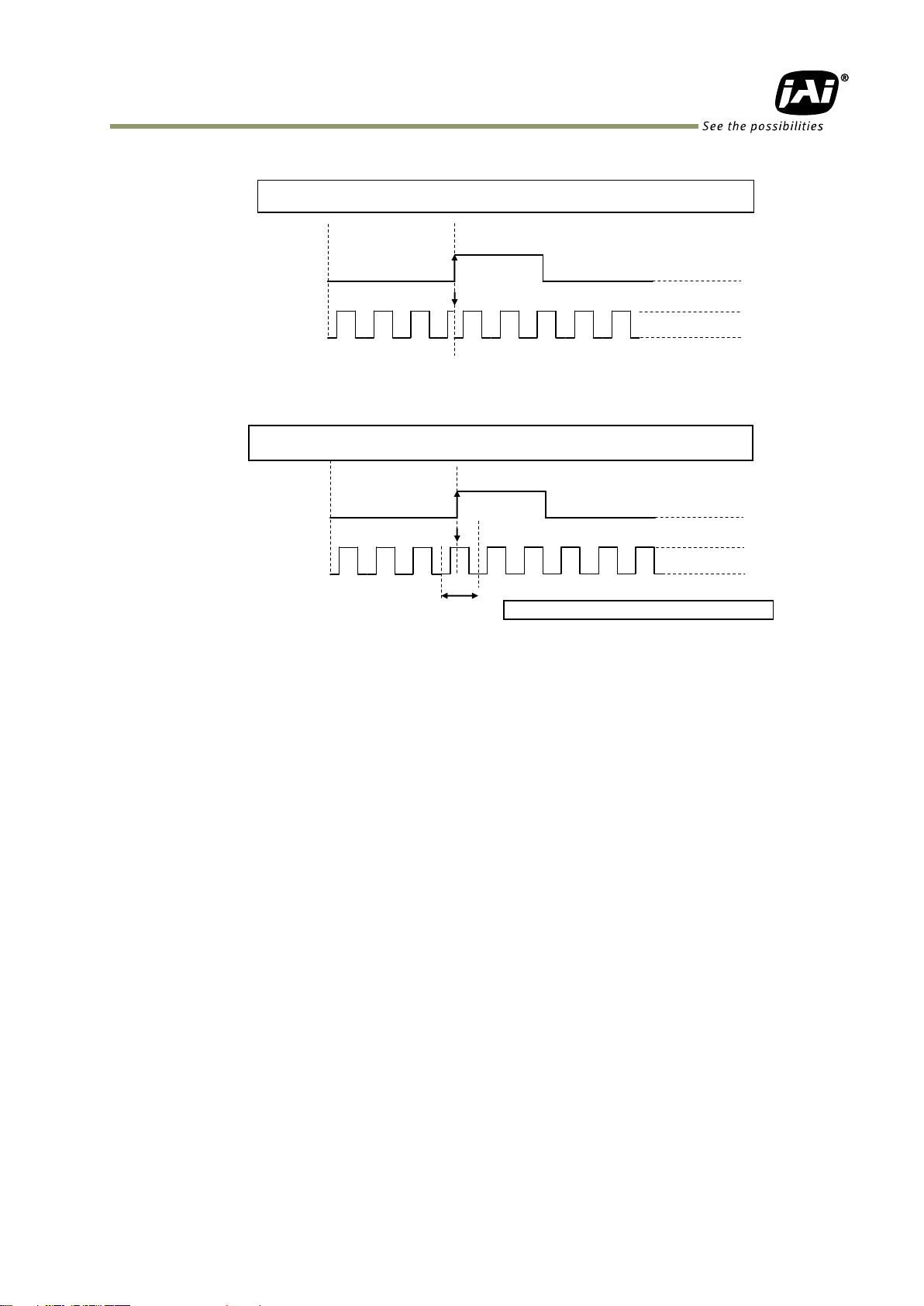
5.4.8 Pulse Generator Clear Sync Mode
Set the count clear method for the selected pulse generator.
In case of Async Mode, if the clear signal is input during the length setting value, the counter
will stop counting according to the clear signal input.
In case of Sync Mode, if the clear signal is input during the length setting value, the counter
will continue to count until the end of the length setting value and then clear the count.
Both modes clear the repeat count when the counter is cleared.
- 20 -
Page 23
SP-5000M-PMCL / SP-5000C-PMCL
0
Clear
↓
Pulse
Generator
Output
Pulse
Generator
Clear Source In
(Example 1) Clear Activation = Rising Edge, Clear Sync Mode = Async Mode,
Clear Inverter = False
(Example 2) Clear Activation = Rising Edge, Clear Sync Mode = Sync Mode,
Clear Inverter = False
Pulse
Generator
Output
Pulse
Generator
Clear Source In
0
Pulse
Generator
Length
0
Clear
↓
Note: Repeat Count is also reset.
Fig.8 Counter clear in Async mode
Fig.9 Counter clear in Sync mode
- 21 -
Page 24
SP-5000M-PMCL / SP-5000C-PMCL
Pulse Generator
Clear Source
item
Description
Low
Connect Low level signal to Clear Source for the selected pulse generator.
Default setting
High
Connect High level signal to Clear Source for the selected pulse
generator.
Frame Trigger Wait
Connect Frame Trigger Wait signal to Clear Source for the selected pulse
generator.
Frame Active
Connect Frame Active signal to Clear Source for the selected pulse
generator.
Exposure Active
Connect Exposure Active signal to Clear Source for the selected pulse
generator.
FVAL
Connect FVAL signal to Clear Source for the selected pulse generator.
LVAL
Connect LVAL signal to Clear Source for the selected pulse generator.
PulseGenerator0
Out
Connect Pulse Generator 0 output to Clear Source for the selected pulse
generator.
PulseGenerator1
Out
Connect Pulse Generator 1 output to Clear Source for the selected pulse
generator.
PulseGenerator2
Out
Connect Pulse Generator 2 output to Clear Source for the selected pulse
generator.
PulseGenerator3
Out
Connect Pulse Generator 3 output to Clear Source for the selected pulse
generator.
TTL 1 In
Connect TTL 1 IN signal to Clear Source for the selected pulse generator.
CL CC1 In
Connect CL CC1 IN signal to Clear Source for the selected pulse
generator.
Nand0 Out
Connect NAND 0 output signal to Clear Source for the selected pulse
generator.
Nand1 Out
Connect NAND 1 output signal to Clear Source for the selected pulse
generator.
Line 10 TTL 2 In
Connect TTL 2 IN signal to Line 10.
Line 11 LVDS 1 In
Connect LVDS 1 IN signal to Line 11.
Note:
The pulse generator output cannot be used as the clear input to the same pulse generator.
Refer to “5.3.7.2.GPIO matrix table”.
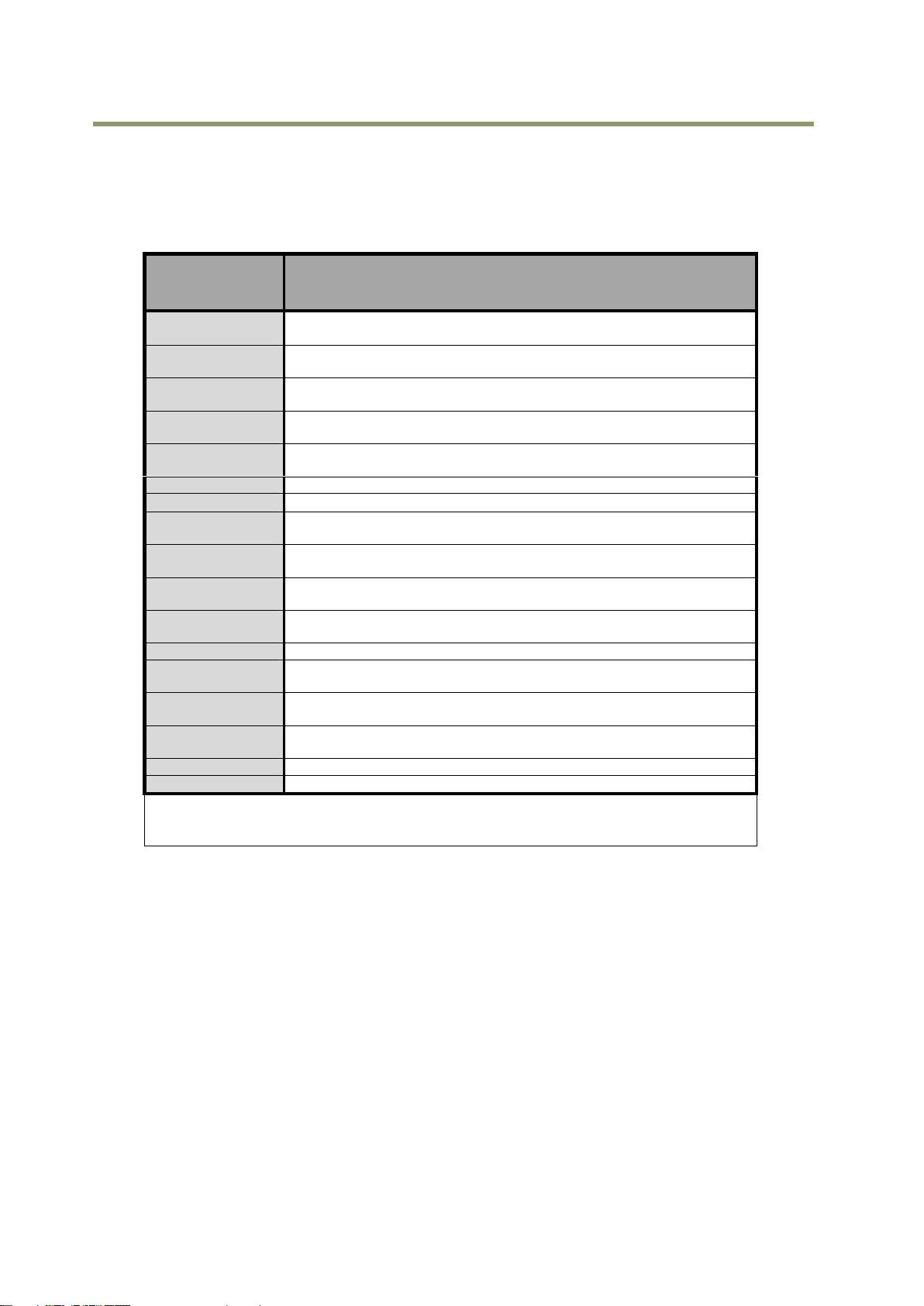
5.4.9 Pulse Generator Clear Source
The following clear sources can be selected as the pulse generator clear signal.
Table - 12 Pulse generator clear source
- 22 -
Page 25

SP-5000M-PMCL / SP-5000C-PMCL
Display Name
Value
Clock Pre-scaler
1 to 4096
Pulse Generator Clock (MHZ)
[Pixel Clock:48MHz]÷[Clock Pre-scaler]
Pulse Generator Selector
- Pulse Generator 0
- Pulse Generator 1
- Pulse Generator 2
- Pulse Generator 3
- Pulse Generator Length
1 to 1048575
- Pulse Generator Length (ms)
([Clock Source]÷[Clock Pre-scaler])-1 x [Pulse Generator Length]
- Pulse Generator Frequency (Hz)
[ Pulse Generator Length (ms)]-1
- Pulse Generator Start Point
0 to 1048574
- Pulse Generator Start Point (ms)
([Clock Source]÷[Clock Pre-scaler])-1 x [Pulse Generator Start Point]
- Pulse Generator End Point
1 to 1048575
- Pulse Generator End Point (ms)
([Clock Source]÷[Clock Pre-scaler])-1 x [Pulse Generator End Point]
- Pulse Generator pulse-width (ms)
[ Pulse Generator End Point (ms)]-[ Pulse Generator Start Point (ms)]
- Pulse Generator Repeat Count
0 to 255
- Pulse Generator Clear Activation
Clear Mode for the Pulse Generators
- Off
- High Level
- Low level
- Rising Edge
- Falling Edge
- Pulse Generator Clear Sync Mode
- Async mode
- Sync mode
- Pulse Generator Clear Source
- Low
- High
- Frame Trigger Wait
- Frame Active
- Exposure Active
- Fval
- Lval
- PulseGenerator0
- PulseGenerator1
- PulseGenerator2
- PulseGenerator3
- TTL_In1
- CL_CC1_In
- Nand0 Out
- Nand1 Out
- Line 10 - TTL 2 In
- Line 11 - LVDS 1 In
- Pulse Generator Inverter(Polarity)
Pulse Generator Clear Inverter
- False
- True
Note:
1. If Pulse Generator Repeat Count is set to “0”, the pulse generator works in free-running mode.
2. The output of the same pulse generator cannot be connected to Clear input.
5.4.10 Pulse Generator Inverter
Clear Source Signal can be have polarity inverted.
5.4.11 Pulse Generator Setting table
Table - 13 Pulse Generator setting parameters
- 23 -
Page 26
SP-5000M-PMCL / SP-5000C-PMCL
2560 Pixels
2048 Pixels
F
Pixel (0,0)
2560 Pixels
2048 Pixels
F
Pixel (0,0)
6. Sensor layout, output format and timing
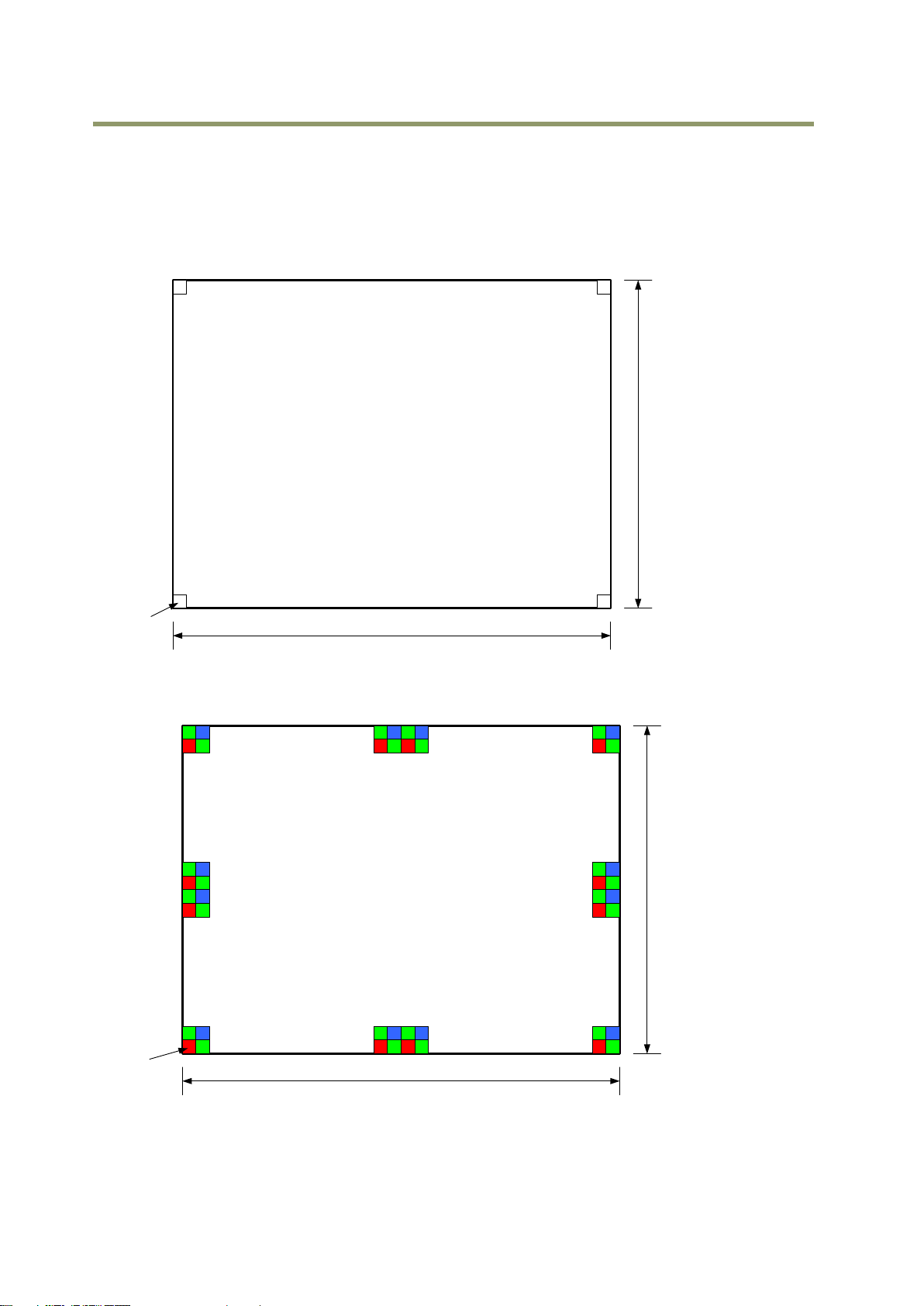
6.1 Sensor layout
The CMOS sensors used in the SP-5000M-PMCL and SP-5000C-PMCL have the following pixel layout.
6.1.1 Monochrome sensor
Fig. 10 Monochrome sensor layout
6.1.2 Bayer sensor
Fig. 11 Color sensor layout
- 24 -
Page 27
SP-5000M-PMCL / SP-5000C-PMCL
Camera output format
Bit assignment
Refer to drawing
1X2–1Y
8-bit, 10-bit, 12-bit
6.2.1
1X4–1Y
8-bit, 10-bit, 12-bit
6.2.2
1X8–1Y
8-bit, 10-bit
6.2.3
1X10–1Y
8-bit
6.2.4
Width = 2560 Pixel 1280 Pixel x 2 Taps
Height = 2048 Pixel
X5120
Y1
X5120
Y3840
X4
Y1
X4
Y2048
X3
Y1
X3
Y2048
X2
Y1
X2
Y2048
X5
Y1
X5
Y2048
X6
Y1
X6
Y2048
X7
Y1
X7
Y2048
X8
Y1
X8
Y2048
X2053
Y1
X2553
Y2048
X2054
Y1
X2554
Y2048
X2055
Y1
X2555
Y2048
X2056
Y1
X2556
Y2048
X2057
Y1
X2557
Y2048
X2058
Y1
X2558
Y2048
X2059
Y1
X2559
Y2048
X2056
Y1
X2056
Y2
X2560
Y2047
X2560
Y2048
X1
Y1
X1
Y2
X1
Y2047
X1
Y2048
Tap 1
Tap 2
Pixel(0,0)
Step Y = 1
Step X = 2
6.2 Camera output format (Tap Geometry)
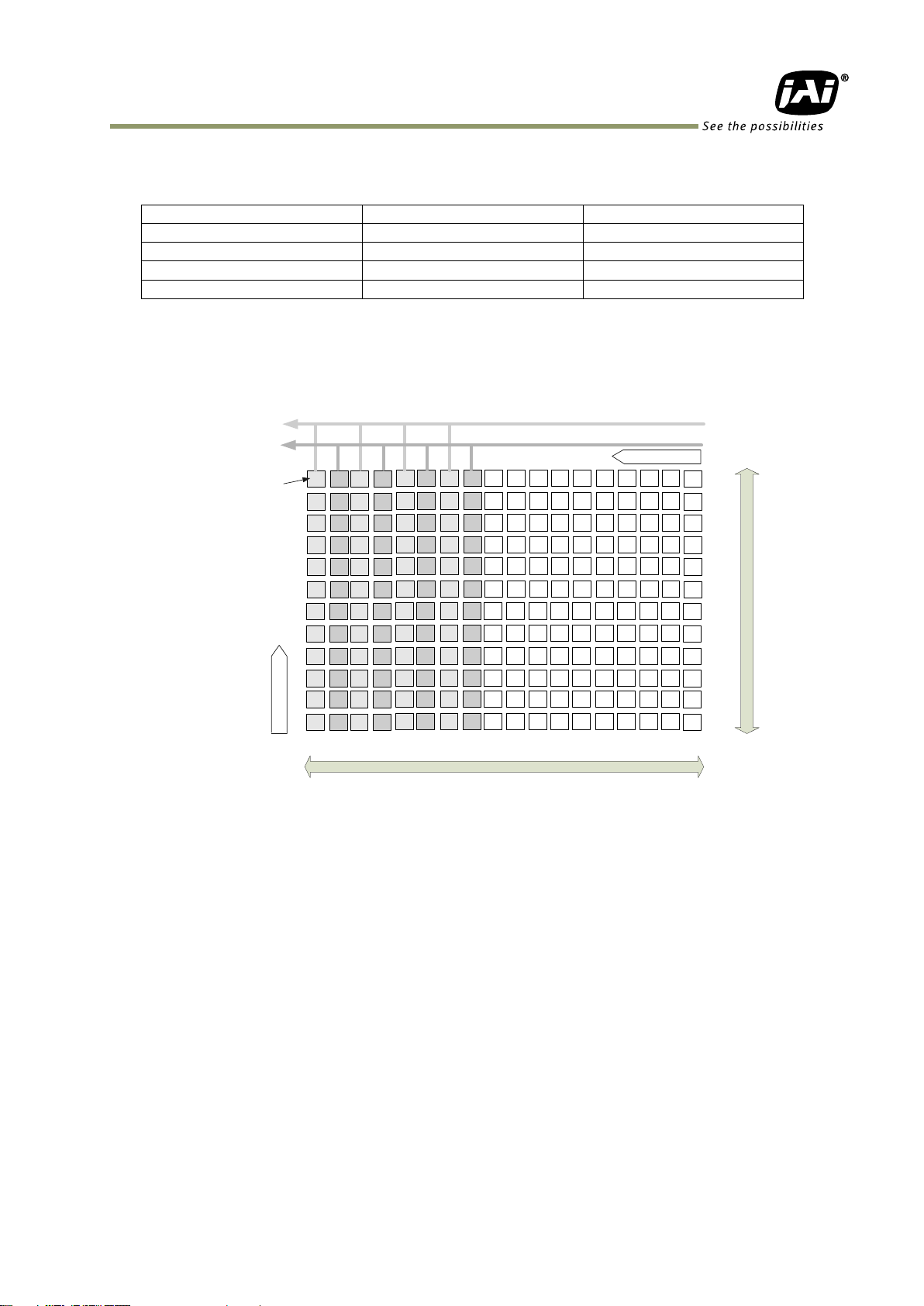
Table - 14 Output format
Note: The camera output description is based on GenICam SFNC Ver.1.5.1.
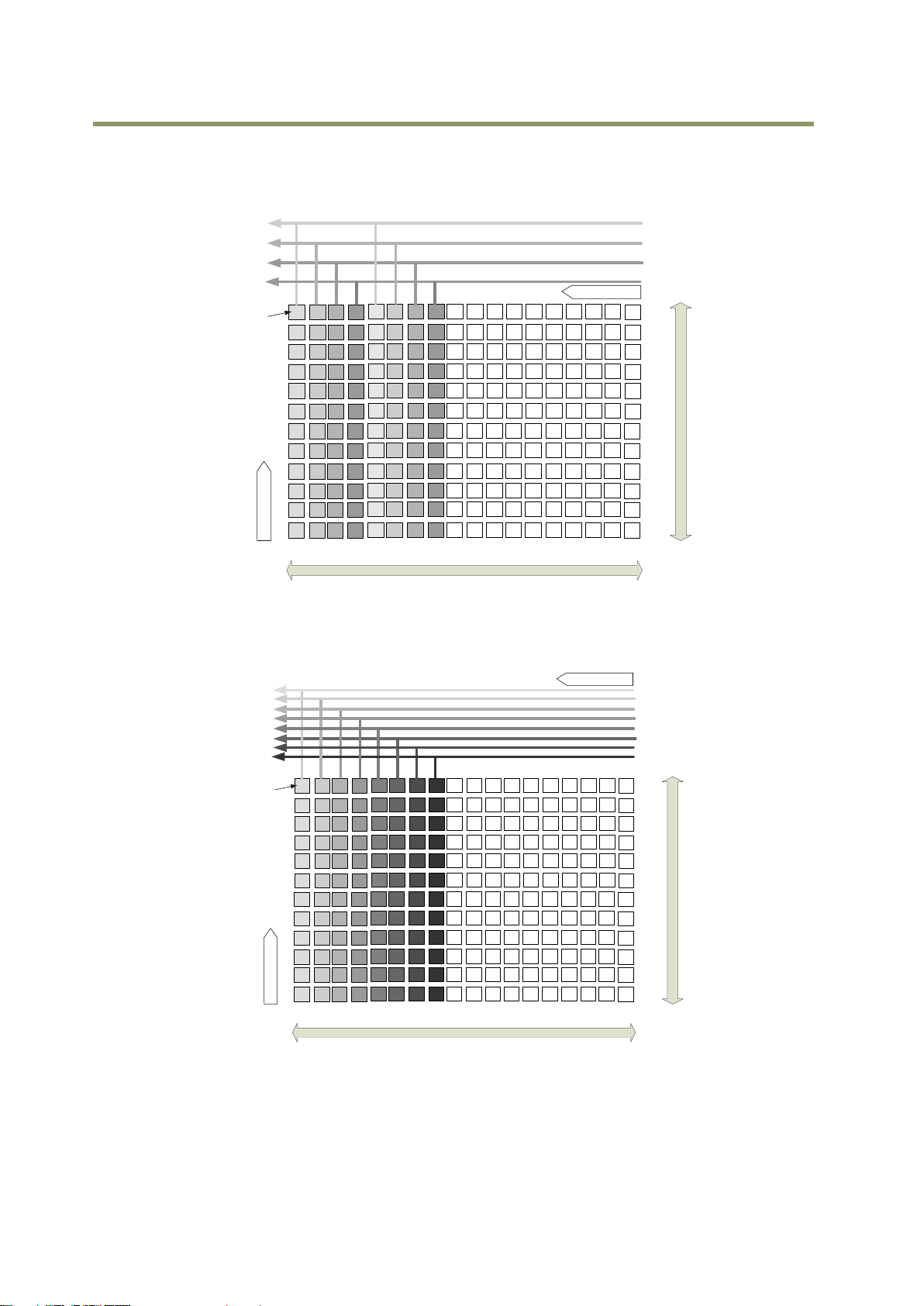
6.2.1 1X2–1Y
1X2–1Y is a 2-tap readout system specified in GenICam Tap Geometry and it outputs as the
following.
Fig.12 1X2–1Y output format
- 25 -
Page 28
SP-5000M-PMCL / SP-5000C-PMCL
Width = 2560 Pixel 1280 Pixel x 2 Taps
Height = 2048 Pixel
X5120
Y1
X5120
Y3840
X4
Y1
X4
Y2048
X3
Y1
X3
Y2048
X2
Y1
X2
Y2048
X5
Y1
X5
Y2048
X6
Y1
X6
Y2048
X7
Y1
X7
Y2048
X8
Y1
X8
Y2048
X2053
Y1
X2553
Y2048
X2054
Y1
X2554
Y2048
X2055
Y1
X2555
Y2048
X2056
Y1
X2556
Y2048
X2057
Y1
X2557
Y2048
X2058
Y1
X2558
Y2048
X2059
Y1
X2559
Y2048
X2056
Y1
X2056
Y2
X2560
Y2047
X2560
Y2048
X1
Y1
X1
Y2
X1
Y2047
X1
Y2048
Tap 1
Tap 2
Pixel(0,0)
Step Y = 1
Step X = 4
Tap 2
Tap 2
Width = 2560 Pixel 1280 Pixel x 2 Taps
Height = 2048 Pixel
X5120
Y1
X5120
Y3840
X4
Y1
X4
Y2048
X3
Y1
X3
Y2048
X2
Y1
X2
Y2048
X5
Y1
X5
Y2048
X6
Y1
X6
Y2048
X7
Y1
X7
Y2048
X8
Y1
X8
Y2048
X2053
Y1
X2553
Y2048
X2054
Y1
X2554
Y2048
X2055
Y1
X2555
Y2048
X2056
Y1
X2556
Y2048
X2057
Y1
X2557
Y2048
X2058
Y1
X2558
Y2048
X2059
Y1
X2559
Y2048
X2056
Y1
X2056
Y2
X2560
Y2047
X2560
Y2048
X1
Y1
X1
Y2
X1
Y2047
X1
Y2048
Tap 1
Tap 4
Pixel(0,0)
Step Y = 1
Step X = 8
Tap 6
Tap 8
Tap 2
Tap 5
Tap 3
Tap 7
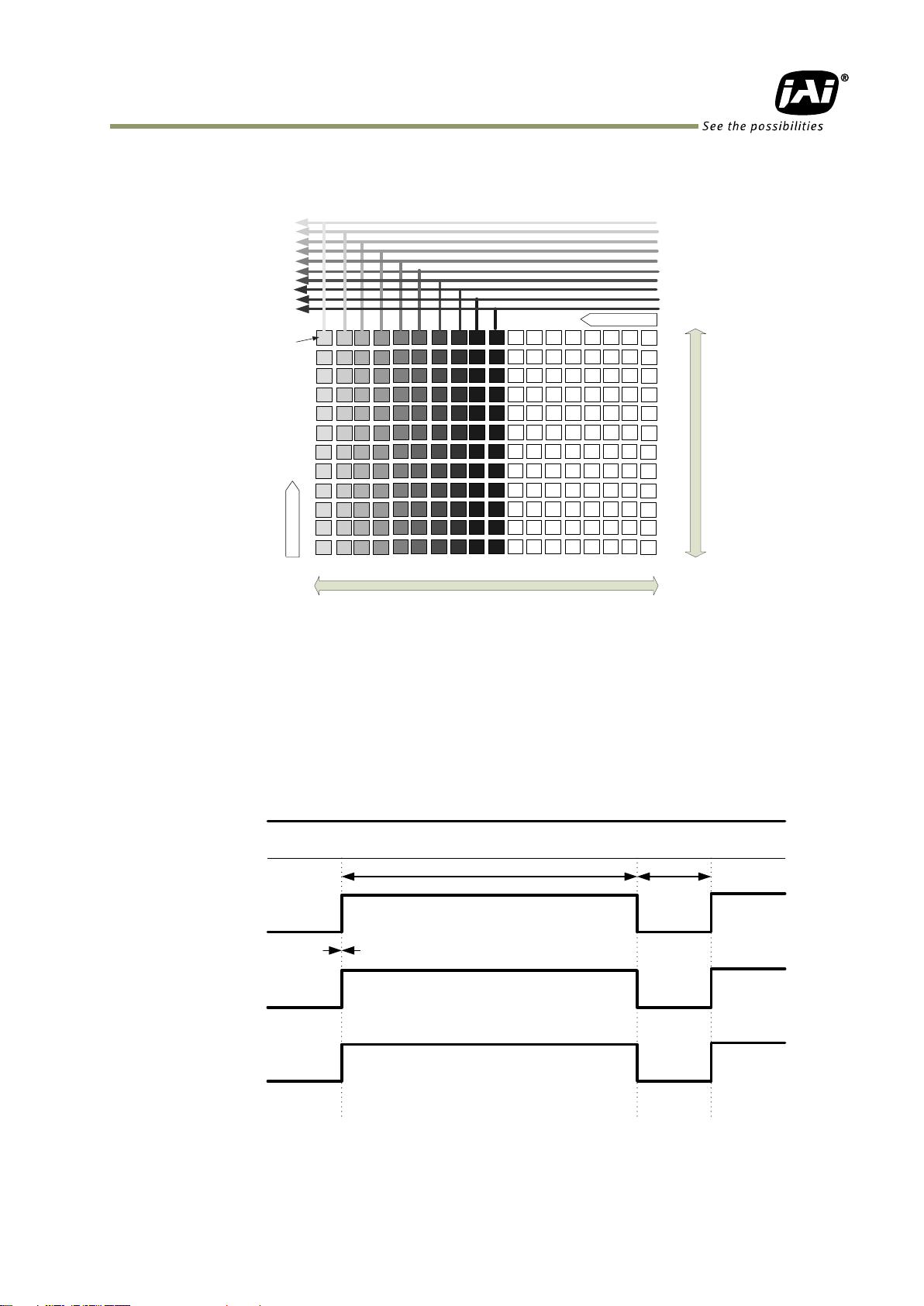
6.2.2 1X4–1Y
1X4–1Y is a 4-tap readout system specified in GenICam Tap Geometry and it outputs as the
following.
Fig. 13 1X4–1Y output format
6.2.3 1X8–1Y
1X8–1Y is an 8-tap readout system and outputs as follows.
Fig. 14. 1X8–1Y output format
- 26 -
Page 29
SP-5000M-PMCL / SP-5000C-PMCL
Width = 2560 Pixel 256 Pixel x 10 Taps
Height = 2048 Pixel
X5120
Y1
X5120
Y3840
X4
Y1
X4
Y2048
X3
Y1
X3
Y2048
X2
Y1
X2
Y2048
X5
Y1
X5
Y2048
X6
Y1
X6
Y2048
X7
Y1
X7
Y2048
X8
Y1
X8
Y2048
X2053
Y1
X2553
Y2048
X2054
Y1
X2554
Y2048
X2055
Y1
X2555
Y2048
X2056
Y1
X2556
Y2048
X2057
Y1
X2557
Y2048
X2058
Y1
X2558
Y2048
X2059
Y1
X2559
Y2048
X2056
Y1
X2056
Y2
X2560
Y2047
X2560
Y2048
X1
Y1
X1
Y2
X1
Y2047
X1
Y2048
Tap 1
Tap 4
Pixel(0,0)
Step Y = 1
Step X = 10
Tap 6
Tap 8
Tap 2
Tap 5
Tap 3
Tap 7
Tap 9
Tap 10
FVAL Active
(a) LVAL Active (b)
(c) H-Offset
FVAL
LVAL
DVAL
DATA
DVAL Active
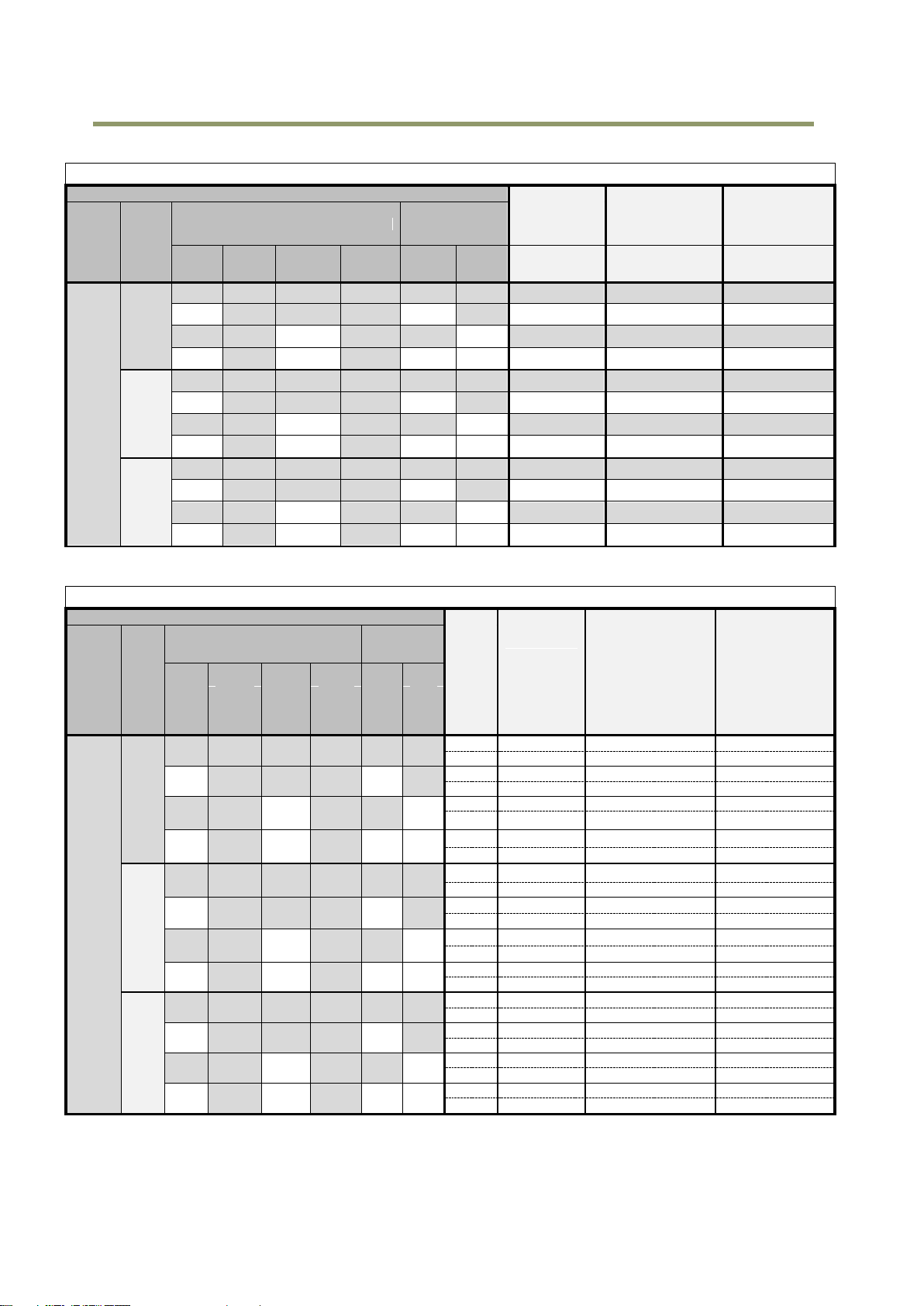
6.2.4 1X10–1Y
1X10-1Y is a 10-tap readout system and outputs as follows.
Fig.15 1X10–1Y Output format
6.3 Output timing and output image
6.3.1 Horizontal timing
The horizontal frequency is changed by setting the Tap Geometry.
In the SP-5000M-PMCL and SP-5000C-PMCL, H-binning is available but the horizontal frequency
is not changed. Therefore, the frame rate is not increased in H-Binning mode.
Fig. 16 Horizontal timing per 1 tap in Camera Link output
- 27 -
Page 30
SP-5000M-PMCL / SP-5000C-PMCL
Table 15. Continuous Trigger / Horizontal timing 1X10–1Y (1/2)
Camera Settings
(a)
(b)
(c)
Tap
Geometry
Camera
Link
Pixel
Clock
AOI
Binning 1: OFF
2* ON
LVAL
Active
LVAL
Non-Active
H-Offset
Width
Offset
X
Height
Offset
Y
Horizont
al
Vertical
[Unit:
Clock]
[Unit:
Clock]
[Unit:
Clock]
1X10
-1Y
82.3
MHz
2560 0 2048 0 1 1 256
27 to 30
0
1280 0 2048
0
2
1
128
155 to 158
0
2560 0 1024
0
1
2
256
27 to 30
0
1280 0 1024
0
2
2
128
155 to 158
0
75.4
MHz
2560 0 2048
0
1
1
256
4 to 6
0
1280 0 2048
0
2
1
128
132 to 134
0
2560 0 1024
0
1
2
256
4 to 6
0
1280 0 1024
0
2
2
128
132 to 134
0
61.7
MHz
2560 0 2048
0
1
1
256
4 to 6
0
1280 0 2048
0
2
1
128
132 to 134
0
2560 0 1024
0
1
2
258
4 to 6
0
1280 0 1024
0
2
2
128
132 to 134
0
Table 16. Continuous Trigger / Horizontal timing 1X10–1Y (2/2)
Camera Settings
Tap
Geometry
Camera
Link
Pixel Clock
AOI
Binning
1: OFF
2: ON
1Line
Total
Clock
Horizontal
Frequency
Horizontal
Period
Width
Offset
X
Height
Offset
Y
Hori
zont
al
Verti
cal
[Unit: Clock]
[Unit: kHz]
[Unit: us]
1X10
-1Y
82.3
MHz
2560 0 2048 0 1
1
a
283 to 286
290.763 to 287.713
3.439 to 3.476
b
284.56
289.169
3.458
1280 0 2048 0 2
1
a
283 to 286
290.763 to 287.713
3.439 to 3.476
b
284.56
289.169
3.458
2560 0 1024 0 1
2
a
283 to 286
290.763 to 287.713
3.439 to 3.476
b
284.56
289.169
3.458
1280 0 1024 0 2
2
a
283 to 286
290.763 to 287.713
3.439 to 3.476
b
284.56
289.169
3.458
75.4
MHz
2560 0 2048 0 1
1
a
260 to 262
290.112 to 287.897
3.447 to 3.473
b
260.86
289.155
3.458
1280 0 2048 0 2
1
a
260 to 262
290.112 to 287.897
3.447 to 3.473
b
260.86
289.155
3.458
2560 0 1024 0 1
2
a
260 to 262
290.112 to 287.897
3.447 to 3.473
b
260.86
289.155
3.458
1280 0 1024 0 2
2
a
260 to 262
290.112 to 287.897
3.447 to 3.473
b
260.86
289.155
3.458
61.7
MHz
2560 0 2048 0 1
1
a
260 to 262
237.362 to 235.550
4.213 to 4.245
b
261.00
236.452
4.229
1280 0 2048 0 2
1
a
260 to 262
237.362 to 235.550
4.213 to 4.245
b
261.00
236.452
4.229
2560 0 1024 0 1
2
a
260 to 262
237.362 to 235.550
4.213 to 4.245
b
261.00
236.452
4.229
1280 0 1024 0 2
2
a
260 to 262
237.362 to 235.550
4.213 to 4.245
b
261.00
236.452
4.229
Note: a: Actual operating value b: Calculation value
- 28 -
Page 31

SP-5000M-PMCL / SP-5000C-PMCL
Table 17. Continuous Trigger / Horizontal timing 1X8-1Y (1/2)
Camera Settings
(a)
(b)
(c)
Tap
Geometry
Camera
Link
Pixel Clock
AOI
Binning
LVAL
Active
LVAL
Non-Active
H-Offset
Width
Offset
X
Height
Offset
Y
Horizont
al
Vertical
[Unit:
Clock]
[Unit:
Clock]
[Unit:
Clock]
1X8
-1Y
82.3
MHz
2560 0 2048
0
1
(Off) 1 (Off)
320
4 to 7
0
1280 0 2048
0
2
(On) 1 (Off)
160
164 to 167
0
2560 0 1024
0
1
(Off) 2 (On)
320
4 to7
0
1280 0 1024
0
2
(On) 2 (On)
160
164 to167
0
75.4
MHz
2560 0 2048
0
1
(Off) 1 (Off)
320
4 to 7
0
1280 0 2048
0
2
(On) 1 (Off)
160
164 to 167
0
2560 0 1024
0
1
(Off) 2 (On)
320
4 to 7
0
1280 0 1024
0
2
(On) 2 (On)
160
164 to 167
0
61.7
MHz
2560 0 2048
0
1
(Off) 1 (Off)
320
3 to 5
0
1280 0 2048
0
2
(On) 1 (Off)
164
164
0
2560 0 1024
0
1
(Off) 2 (On)
320
3 to 5
0
1280 0 1024
0
2
(On) 2 (On)
160
164
0
- 29 -
Page 32

SP-5000M-PMCL / SP-5000C-PMCL
Table 18. Continuous Trigger / Horizontal timing 1X8–1Y (2/2)
Camera Settings
Tap
Geometry
Camera
Link
Pixel Clock
AOI
Binning
1Line
Total
Clock
Horizontal
Frequency
Horizontal
Period
Width
Offset
X
Height
Offset
Y
Horiz
ontal
Verti
cal
[Unit: Clock]
[Unit: kHz]
[Unit: us]
1X8
-1Y
82.3
MHz
2560
0
a
b
0
1
(Off) 1 (Off)
a
324 to 327
253.969 to
3.937 to 3.974
b
325.71
252.639
3.958
1280
0
a
b
0
2
(On) 1 (Off)
a
324 to 327
253.969 to
3.937 to 3.974
b
325.71
252.639
3.958
2560
0
a
b
0
1
(Off) 2 (On)
a
324 to 327
253.969 to
3.937 to 3.974
b
325.71
252.639
3.958
1280
0
a
b
0
2
(On) 2 (On)
a
324 to 327
253.969 to
3.937 to 3.974
b
325.71
252.639
3.958
75.4
MHz
2560
0
a
b
0
1
(Off) 1 (Off)
a
324 to 327
232.806 to 230.670
4.295 to 4.335
b
325.29
231.882
4.313
1280
0
a
b
0
2
(On) 1 (Off)
a
324 to 327
232.806 to 230.670
4.295 to 4.335
b
325.29
231.882
4.313
2560
0
a
b
0
1
(Off) 2 (On)
a
324 to 327
232.806 to 230.670
4.295 to 4.335
b
325.29
231.882
4.313
1280
0
a
b
0
2
(On) 2 (On)
a
324 to 327
232.806 to 230.670
4.295 to 4.335
b
325.29
231.882
4.313
61.7
MHz
2560
0
a
b
0
1
(Off) 1 (Off)
a
323 to 325
191.065 to 189.889
5.234 to 5.266
b
324.00
190.475
5.250
1280
0
a
b
0
2
(On) 1 (Off)
a
328
188.152
5.315
b
324.00
190.475
5.250
2560
0
a
b
0
1
(Off) 2 (On)
a
323 to 325
191.065 to 189.889
5.234 to 5.266
b
324.00
190.475
5.250
1280 0 a
0
2
(On) 2 (On)
a
328
188.152
5.315
b
324.00
190.475
5.250
Note: a: Actual operating value b: Calculation value
- 30 -
Page 33

SP-5000M-PMCL / SP-5000C-PMCL
Table 19. Continuous Trigger / Horizontal timing 1X4–1Y (1/2)
Camera Settings
(a)
(b)
(c)
Tap
Geometry
Camera Link
Pixel Clock
AOI
Binning
LVAL
Active
LVAL
Non-Active
H-Offset
Width
Offset
X
Height
Offset
Y
Horizont
al
Vertical
[Unit:
Clock]
[Unit:
Clock]
[Unit:
Clock]
1X4
-1Y
82.3
MHz
2560 0 2048
0
1
(Off) 1 (Off)
640
3 to 6
0
1280 0 2048
0
2
(On) 1 (Off)
320
323 to 326
0
2560 0 1024
0
1
(Off) 2 (On)
640
3 to 6
0
1280 0 1024
0
2
(On) 2 (On)
320
323 to 326
0
75.4
MHz
2560 0 2048
0
1
(Off) 1 (Off)
640
3 to 6
0
1280 0 2048
0
2
(On) 1 (Off)
320
323 to 326
0
2560 0 1024
0
1
(Off) 2 (On)
640
3 to 6
0
1280 0 1024
0
2
(On) 2 (On)
320
323 to 326
0
61.7
MHz
2560 0 2048
0
1
(Off) 1 (Off)
640
4 to 7
0
1280 0 2048
0
2
(On) 1 (Off)
320
324 to 327
0
2560 0 1024
0
1
(Off) 2 (On)
640
4 to 7
0
1280 0 1024
0
2
(On) 2 (On)
320
324 to 327
0
- 31 -
Page 34

SP-5000M-PMCL / SP-5000C-PMCL
Table 20. Continuous Trigger / Horizontal timing 1X4–1Y (2/2)
Camera Settings
Tap
Geometry
Camera
Link
Pixel Clock
AOI
Binning
1Line
Total
Clock
Horizontal
Frequency
Horizontal
Period
Width
Offset
X
Height
Offset
Y
Horiz
ontal
Verti
cal
[Unit: Clock]
[Unit: kHz]
[Unit: us]
1X4
-1Y
82.3
MHz
2560 0 2048
0
1
(Off) 1 (Off)
a
643 to 646
127.972 to 127.378
7.814 to 7.851
b
644.57
127.632
7.835
1280 0 2048
0
2
(On) 1 (Off)
a
643 to 646
127.972 to 127.378
7.814 to 7.851
b
644.57
127.632
7.835
2560 0 1024
0
1
(Off) 2 (On)
a
643 to 646
127.972 to 127.378
7.814 to 7.851
b
644.57
127.632
7.835
1280 0 1024
0
2
(On) 2 (On)
a
643 to 646
127.972 to 127.378
7.814 to 7.851
b
644.57
127.632
7.835
75.4
MHz
2560 0 2048
0
1
(Off) 1 (Off)
a
643 to 646
117.308 to 116.861
8.525 to 8.557
b
644.29
117.073
8.542
1280 0 2048
0
2
(On) 1 (Off)
a
643 to 646
117.308 to 116.861
8.525 to 8.557
b
644.29
117.073
8.542
2560 0 1024
0
1
(Off) 2 (On)
a
643 to 646
117.308 to 116.861
8.525 to 8.557
b
644.29
117.073
8.542
1280 0 1024
0
2
(On) 2 (On)
a
643 to 646
117.308 to 116.861
8.525 to 8.557
b
644.29
117.073
8.542
61.7
MHz
2560 0 2048
0
1
(Off) 1 (Off)
a
644 to 647
95.829 to 95.385
10.435 to 10.484
b
645.43
95.617
10.458
1280 0 2048
0
2
(On) 1 (Off)
a
644 to 647
95.829 to 95.385
10.435 to 10.484
b
645.43
95.617
10.458
2560 0 1024
0
1
(Off) 2 (On)
a
644 to 647
95.829 to 95.385
10.435 to 10.484
b
645.43
95.617
10.458
1280 0 1024
0
2
(On) 2 (On)
a
644 to 647
95.829 to 95.385
10.435 to 10.484
b
645.43
95.617
10.458
Note: a: Actual operating value b: Calculation value
- 32 -
Page 35

SP-5000M-PMCL / SP-5000C-PMCL
Table 21. Continuous Trigger / Horizontal timing 1X2–1Y (1/2)
Camera Settings
(a)
(b)
(c)
Tap
Geometry
Camera
Link
Pixel Clock
AOI
Binning
LVAL
Active
LVAL
Non-Active
H-Offset
Width
Offset
X
Height
Offset
Y
Horizont
al
Vertical
[Unit:
Clock]
[Unit:
Clock]
[Unit:
Clock]
1X2
-1Y
82.3
MHz
2560 0 2048
0
1
(Off) 1 (Off)
1280
4 to 7
0
1280 0 2048
0
2
(On) 1 (Off)
640
644 to 647
0
2560 0 1024
0
1
(Off) 2 (On)
1280
4 to 7
0
1280 0 1024
0
2
(On) 2 (On)
640
644 to 647
0
75.4
MHz
2560 0 2048
0
1
(Off) 1 (Off)
1280
4 to 7
0
1280 0 2048
0
2
(On) 1 (Off)
640
644 to 647
0
2560 0 1024
0
1
(Off) 2 (On)
1280
4 to 7
0
1280 0 1024
0
2
(On) 2 (On)
640
644 to 647
0
61.7
MHz
2560 0 2048
0
1
(Off) 1 (Off)
1280
3 to 6
0
1280 0 2048
0
2
(On) 1 (Off)
640
643 to 646
0
2560 0 1024
0
1
(Off) 2 (On)
1280
3 to 6
0
1280 0 1024
0
2
(On) 2 (On)
640
643 to 646
0
- 33 -
Page 36

SP-5000M-PMCL / SP-5000C-PMCL
Table 22. Continuous Trigger / Horizontal timing 1X2–1Y (2/2)
Camera Settings
Tap
Geometry
Camera
Link
Pixel Clock
AOI
Binning
1Line
Total
Clock
Horizontal
Frequency
Horizontal
Period
Width
Offset
X
Height
Offset
Y
Horiz
ontal
Verti
cal
[Unit: Clock]
[Unit: kHz]
[Unit: us]
1X2
-1Y
82.3
MHz
2560 0 2048
0
1
(Off) 1 (Off)
a
1284 to 1287
64.086 to 63.936
15.604 to 15.641
b
1285.72
64.000
15.625
1280 0 2048
0
2
(On) 1 (Off)
a
1284 to 1287
64.086 to 63.936
15.604 to 15.641
b
1285.72
64.000
15.625
2560 0 1024
0
1
(Off) 2 (On)
a
1284 to 1287
64.086 to 63.936
15.604 to 15.641
b
1285.72
64.000
15.625
1280 0 1024
0
2
(On) 2 (On)
a
1284 to 1287
64.086 to 63.936
15.604 to 15.641
b
1285.72
64.000
15.625
75.4
MHz
2560 0 2048
0
1
(Off) 1 (Off)
a
1284 to 1287
58.745 to 58.608
17.023 to 17.062
b
1285.44
58.680
17.042
1280 0 2048
0
2
(On) 1 (Off)
a
1284 to 1287
58.745 to 58.608
17.023 to 17.062
b
1285.44
58.680
17.042
2560 0 1024
0
1
(Off) 2 (On)
a
1284 to 1287
58.745 to 58.608
17.023 to 17.062
b
1285.44
58.680
17.042
1280 0 1024
0
2
(On) 2 (On)
a
1284 to 1287
58.745 to 58.608
17.023 to 17.062
b
1285.44
58.680
17.042
61.7
MHz
2560 0 2048
0
1
(Off) 1 (Off)
a
1283 to 1286
48.101 to 47.989
20.789 to 20.838
b
1284.42
48.048
20.812
1280 0 2048
0
2
(On) 1 (Off)
a
1283 to 1286
48.101 to 47.989
20.789 to 20.838
b
1284.42
48.048
20.812
2560 0 1024
0
1
(Off) 2 (On)
a
1283 to 1286
48.101 to 47.989
20.789 to 20.838
b
1284.42
48.048
20.812
1280 0 1024
0
2
(On) 2 (On)
a
1283 to 1286
48.101 to 47.989
20.789 to 20.838
b
1284.42
48.048
20.812
Note: a: Actual operating value b: Calculation value
- 34 -
Page 37

6.3.2 Vertical timing
FVAL
LVAL
DVAL
DATA
Exposure
Active
(Camera Link
“Spare” bit)
Exposure time (Min)
FVAL Active (A)
(B)
(C) V-Offset 0 Line
DVAL Active (A)
(F) Exposure End to FVAL Active Start
(E) Exposure time (Max)
(D)
Tap Geometry
Camera Link
Clock
Exposure Active – At FVAL Active Overlap,
FVAL Active extended time
[Unit: us]
[Unit: Line]
1X10-1Y
82.3 MHz
55.60
16
75.4 MHz
55.40
16
61.7 MHz
67.70
16
1X8-1Y
82.3 MHz
63.40
16
75.4 MHz
69.10
16
61.7 MHz
84.10
16
1X4-1Y
82.3 MHz
125.40
16
75.4 MHz
136.60
16
61.7 MHz
167.40
16
1X2-1Y
82.3 MHz
250.00
16
75.4 MHz
273.00
16
61.7 MHz
333.50
16
Figure 17 shows the vertical timing of Camera Link output during continuous trigger operation.
However, with 1X8-1Y 10-bit and 1X10–1Y 8-bit geometries, which are 80-bit configurations,
DVAL and Exposure Active, which are normally output to Camera Link spare bits, are not output
through the Camera Link interface as data bits are applied to those bits.
In the SP-5000M-PMCL, H-Binning and V-Binning functions are available but H-Binning function
does not make the frame rate faster.
SP-5000M-PMCL / SP-5000C-PMCL
In the SP-5000-PMCL, if the trigger overlap is set to “Readout”, the image readout is
stopped at the start point of the exposure and delayed in order to avoid interference
from the exposure. Therefore, the FVAL Active period is extended by the period for
which the readout has been stopped.
Table 23. FVAL Active extended time if FVAL Active is overlapped
Fig. 17 Vertical timing
- 35 -
Page 38

SP-5000M-PMCL / SP-5000C-PMCL
Table 24. Continuous Trigger / Vertical timing 1X10-1Y, 1X8–1Y (1/3)
Camera Settings
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
Tap
Geometry
Camera
Link
Pixel Clock
Frame
Period
(Typ.)
ROI
Binning
FVAL &
DVAL
Active
FVAL
Non
-Active
V -Offset
Exposure
Time
(Min)
Width
Offset
X
Height
Offset
Y
Horizontal
Vertical
[Unit: Line]
[Unit: Line]
[Unit: Line]
[Unit: us]
1X10
-1Y
82.3
MHz
7463
2560 0 2048
0
1
(Off) 1 (Off)
2048
110.1 or 111.1
0
10
1280 0 2048
0
2
(On) 1 (Off)
1028
110.5 or 111.5
3732
2560 0 1024
0
1
(Off) 2 (On)
2048
56.1 or 57.1
1280 0 1024
0
2
(On) 2 (On)
1028
56.5 or 57.5
75.4
MHz
8141
2560 0 2048
0
1
(Off) 1 (Off)
2048
306.0 or 307.0
0
10
1280 0 2048
0
2
(On) 1 (Off)
1028
306.5 or 307.5
4071
2560 0 1024
0
1
(Off) 2 (On)
2048
154.0 or 155.0
1280 0 1024
0
2
(On) 2 (On)
1028
154.5 or 155.5
61.7
MHz
9951
2560 0 2048
0
1
(Off) 1 (Off)
2048
305.0 or 306.0
0
10
1280 0 2048
0
2
(On) 1 (Off)
1028
305.5 or 306.5
4976
2560 0 1024
0
1
(Off) 2 (On)
2048
153.0 or 154.0
1280 0 1024
0
2
(On) 2 (On)
1028
153.5 or 154.5
1X8
-1Y
82.3
MHz
8333
2560 0 2048
0
1
(Off) 1 (Off)
2048
57.0 or 58.0
0
10
1280 0 2048
0
2
(On) 1 (Off)
1028
57.5 or 58.5
4167
2560 0 1024
0
1
(Off) 2 (On)
2048
29.0 or 30.0
1280 0 1024
0
2
(On) 2 (On)
1028
29.5 or 30.5
75.4
MHz
9091
2560 0 2048
0
1
(Off) 1 (Off)
2048
60.0 or 61.0
0
10
1280 0 2048
0
2
(On) 1 (Off)
1028
60.5 or 61.5
4546
2560 0 1024
0
1
(Off) 2 (On)
2048
30.0 or 31.0
1280 0 1024
0
2
(On) 2 (On)
1028
30.5 or 31.5
61.7
MHz
11111
2560 0 2048
0
1
(Off) 1 (Off)
2048
68.0 or 69.0
0
10
1280 0 2048
0
2
(On) 1 (Off)
1028
68.5 or 69.5
5556
2560 0 1024
0
1
(Off) 2 (On)
2048
34.0 or 35.0
1280 0 1024
0
2
(On) 2 (On)
1028
34.5 or 35.5
[Note] The above FVAL Active period is the value, when the exposure time is set at “10”.
As mentioned before, if the next frame readout is overlapped on the previous frame readout,
FVAL Active period is reduced by 16 lines.
- 36 -
Page 39

SP-5000M-PMCL / SP-5000C-PMCL
Table 25. Continuous Trigger / Vertical timing 1X10-1Y (2/3)
Camera Settings (E)
(F)
Tap
Geometry
Camera
Link
Pixel Clock
Frame
Period
(Typ.)
ROI
Binning
Frame
Rate
Exposure
Time
(Max.)
Exposure
End
to
FVAL
Active
Start
Width
Offset
X
Height
Offset
Y
Horizontal
Vertical
[Unit: Hz]
[Unit: us]
[Unit: Line]
[Unit: us]
1X10
-1Y
82.3
MHz
7463
2560
0
2048
0
1
(Off) 1 (Off)
133.93
[Frame Period] - 100=
7463 - 100=7363
9.1
to
31.5
to
1280
0
2048
0
2
(On) 1 (Off)
8.1
to
9.1
28.1
to
31.6
3732
2560
0
1024
0
1
(Off) 2 (On)
267.71
3732 - 100=3632
9.1
to
10.1
31.5
to
34.9
1280
0
1024
0
2
(On) 2 (On)
8.1
to
9.1
28.2
to
31.6
75.4
MHz
8141
2560
0
2048
0
1
(Off) 1 (Off)
122.78
8141 - 100=8041
9.1
to
31.5
to
1280
0
2048
0
2
(On) 1 (Off)
8.1
to
9.1
28.2
to
31.6
4071
2560
0
1024
0
1
(Off) 2 (On)
245.44
4071 - 100=3971
9.1
to
10.1
31.5
to
34.9
1280
0
1024
0
2
(On) 2 (On)
8.2
to
9.1
28.2
to
31.6
61.7
MHz
9951
2560
0
2048
0
1
(Off) 1 (Off)
100.46
9951 - 100=9851
7.8
to
33.1
to
1280
0
2048
0
2
(On) 1 (Off)
7.0
to
8.0
29.8
to
34.0
4976
2560
0
1024
0
1
(Off) 2 (On)
200.82
4976 - 100=4876
7.8
to
8.8
33.1
to
37.2
1280
0
1024
0
2
(On) 2 (On)
7.0
to
8.0
29.8
to
33.9
- 37 -
Page 40

SP-5000M-PMCL / SP-5000C-PMCL
Table 26. Continuous Trigger / Vertical timing 1X8–1Y (3/3)
Camera Settings (E)
(F)
Tap
Geometry
Camera
Link
Pixel Clock
Frame
Period
(Typ.)
ROI
Binning
Frame
Rate
Exposure
Time
(Max.)
Exposure
End
to
FVAL
Active
Start
Width
Offset
X
Height
Offset
Y
Horizontal
Vertical
[Unit: Hz]
[Unit: us]
[Unit: Line]
[Unit: us]
1X8
-1Y
82.3
MHz
8333
2560
0
2048
0
1
(Off) 1 (Off)
119.96
8333 - 100 = 8233
8.3
to
9.2
32.9
to
36.4
1280
0
2048
0
2
(On) 1 (Off)
7.4
to
8.4
29.3
to
33.1
2560
0
1024
0
1
(Off) 2 (On)
239.79
4167 - 100 = 4067
8.2
to
9.3
32.5
to
36.7
1280
0
1024
0
2
(On) 2 (On)
7.4
to
8.4
29.2
to
33.1
75.4
MHz
9091
2560
0
2048
0
1
(Off) 1 (Off)
109.95
9091 - 100 = 8991
7.7
to
8.7
33.2
to
37.5
1280
0
2048
0
2
(On) 1 (Off)
6.9
to
7.9
29.9
to
34.2
2560
0
1024
0
1
(Off) 2 (On)
219.81
4546 - 100=4446
7.7
to
8.7
33.2
to
37.5
1280
0
1024
0
2
(On) 2 (On)
6.9
to
7.9
29.9
to
34.2
61.7
MHz
11111
2560
0
2048
0
1
(Off) 1 (Off)
89.97
11111 - 100=11011
7.6
to
8.6
40.0
to
45.2
1280
0
2048
0
2
(On) 1 (Off)
7.0
to
8.0
36.7
to
41.9
2560
0
1024
0
1
(Off) 2 (On)
179.86
5556 - 100=5456
7.6
to
8.6
40.0
to
45.17
1280
0
1024
0
2
(On) 2 (On)
7.6
to
8.7
40.0
to
45.2
- 38 -
Page 41

SP-5000M-PMCL / SP-5000C-PMCL
Table 27. Continuous Trigger / Vertical timing 1X4–1Y, 1X2–1Y (1/3)
Camera Settings
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
Tap
Geometry
Camera
Link
Pixel Clock
Frame
Period
(Typ.)
ROI
Binning
FVAL &
DVAL
Active
FVAL
Non
-Active
V -Offset
Exposure
Time
(Min)
Width
Offset
X
Height
Offset
Y
Horizontal
Vertical
[Unit: Line]
[Unit: Line]
[Unit: Line]
[Unit: us]
1X4
-1Y
82.3
MHz
16393
2560
0
2048
0
1
(Off) 1 (Off)
2048
45.0 or 46.0
0
10
1280
0
2048
0
2
(On) 1 (Off)
1028
45.5 or 46.5
8197
2560
0
1024
0
1
(Off) 2 (On)
2048
22.0 or 23.0
1280
0
1024
0
2
(On) 2 (On)
1028
22.5 or 23.5
75.4
MHz
17883
2560
0
2048
0
1
(Off) 1 (Off)
2048
45.0 or 46.0
0
10
1280
0
2048
0
2
(On) 1 (Off)
1028
45.5 or 46.5
8942
2560
0
1024
0
1
(Off) 2 (On)
2048
23.0 or 24.0
1280
0
1024
0
2
(On) 2 (On)
1028
23.5 or 24.5
61.7
MHz
21858
2560
0
2048
0
1
(Off) 1 (Off)
2048
42.0 or 43.0
0
10
1280
0
2048
0
2
(On) 1 (Off)
1028
42.5 or 43.5
10929
2560
0
1024
0
1
(Off) 2 (On)
2048
21.0 or 22.0
1280
0
1024
0
2
(On) 2 (On)
1028
21.5 or 22.5
1X2
-1Y
82.3
MHz
33333
2560
0
2048
0
1
(Off) 1 (Off)
2048
85.0 or 86.0
0
10
1280
0
2048
0
2
(On) 1 (Off)
1028
85.5 or 86.5
16667
2560
0
1024
0
1
(Off) 2 (On)
2048
42.0 or 43.0
1280
0
1024
0
2
(On) 2 (On)
1028
42.5 or 43.5
75.4
MHz
36363
2560
0
2048
0
1
(Off) 1 (Off)
2048
85.0 or 86.0
0
10
1280
0
2048
0
2
(On) 1 (Off)
1028
85.5 or 86.5
18182
2560
0
1024
0
1
(Off) 2 (On)
2048
43.0 or 44.0
1280
0
1024
0
2
(On) 2 (On)
1028
43.5 or 44.5
61.7
MHz
44444
2560
0
2048
0
1
(Off) 1 (Off)
2048
87.0 or 88.0
0
10
1280
0
2048
0
2
(On) 1 (Off)
1028
87.5 or 88.5
22222
2560
0
1024
0
1
(Off) 2 (On)
2048
43.0 or 44.0
1280
0
1024
0
2
(On) 2 (On)
1028
43.5 or 44.5
[Note] The above FVAL Active period is the value, when the exposure time is set at “10”.
As mentioned before, if the next frame readout is overlapped on the previous frame readout, FVAL
Active period is reduced by 16 lines. In 1X4–1Y and 1X2–1Y tap geometries, FVAL active starting point
becomes earlier depending on the exposure time value. Therefore, FVAL Active period is shortened
further.
- 39 -
Page 42

SP-5000M-PMCL / SP-5000C-PMCL
Table 28. Continuous Trigger / Vertical timing 1X4–1Y (2/3)
Camera Settings
(E)
(F)
Tap
Geometry
Camera
Link
Pixel Clock
Frame
Period
(Typ.)
ROI
Binning
Frame
Rate
Exposure
Time
(Max.)
Exposure Active End
to
FVAL Active Start
Width
Offset X
Height
Offset Y
Horizontal
Vertical
[Unit:
Hz]
[Unit: us]
[Unit: Line]
[Unit: us]
Max
Min
Max
Min
1X4
-1Y
82.3
MHz
16393
2560
0
2048
0
1
(Off) 1 (Off)
60.97
16393 - 100
=16293
11.0
to
12.0
5.1
to
6.1
86.5
to
94.2
40.3
to
48.1
1280
0
2048
0
2
(On) 1 (Off)
10.6
to
11.6
4.7
to
5.7
83.1
to
90.9
37.0
to
44.7
8197
2560
0
1024
0
1
(Off) 2 (On)
121.95
8197 - 100
=8097
11.0
to
12.0
5.1
to
6.1
86.5
to
94.2
40.3
to
48.1
1280
0
1024
0
2
(On) 2 (On)
10.6
to
11.6
4.7
to
5.7
83.1
to
90.9
36.9
to
44.7
75.4
MHz
17883
2560
0
2048
0
1
(Off) 1 (Off)
55.90
17883 - 100
=17783
11.6
to
12.6
4.9
to
5.9
99.3
to
107.6
41.8
to
50.1
1280
0
2048
0
2
(On) 1 (Off)
11.2
to
12.2
4.5
to
5.5
95.9
to
104.3
38.4
to
46.9
8942
2560
0
1024
0
1
(Off) 2 (On)
111.78
8942 - 100
=8842
11.6
to
12.6
4.9
to
5.9
99.2
to
107.7
41.7
to
50.2
1280
0
1024
0
2
(On) 2 (On)
11.2
to
12.2
4.5
to
5.5
95.9
to
104.4
38.4
to
46.9
61.7
MHz
21858
2560
0
2048
0
1
(Off) 1 (Off)
45.73
21858 - 100
=21758
12.8
to
13.8
4.4
to
5.4
133.7
to
144.1
45.6
to
56.0
1280
0
2048
0
2
(On) 1 (Off)
12.5
to
13.5
4.0
to
5.0
130.4
to
140.8
42.3
to
52.7
10929
2560
0
1024
0
1
(Off) 2 (On)
91.45
10929 - 100
=10829
12.8
to
13.8
4.4
to
5.4
133.8
to
144.1
45.6
to
56.0
1280
0
1024
0
2
(On) 2 (On)
12.5
to
13.5
4.0
to
5.0
130.4
to
140.8
42.3
to
52.7
[Note] In 1X4-1Y Tap Geometry, “Exposure Active End to FVAL Active Start” period varies depending on the
exposure time setting. When the exposure time is set at “10”, it is the maximum period and if the exposure time is
incremented by 1 us, it is decreased.
- 40 -
Page 43

SP-5000M-PMCL / SP-5000C-PMCL
Table 29. Continuous Trigger / Vertical timing 1X2–1Y (3/3)
Camera Settings
(E)
(F)
Tap
Geometry
Camera
Link
Pixel Clock
Frame
Period
(Typ.)
ROI
Binning
Frame
Rate
Exposure
Time
(Max.)
Exposure Active End
to
FVAL Active Start
Width
Offset X
Height
Offset Y
Horizontal
Vertical
[Unit: Hz]
[Unit: us]
[Unit: Line]
[Unit: us]
Max
Min
Max
Min
1X2
-1Y
82.3
MHz
33333
2560
0
2048
0
1
(Off) 1 (Off)
29.99
33333 - 100
=33233
14.5
to
15.5
3.6
to
4.6
226.9
to
242.2
56.0
to
71.4
1280
0
2048
0
2
(On) 1 (Off)
14.3
to
15.3
3.4
to
4.4
223.5
to
238.9
52.6
to
68.0
16667
2560
0
1024
0
1
(Off) 2 (On)
59.98
16667 - 100
=16567
14.5
to
15.5
3.6
to
4.6
226.7
to
242.3
55.9
to
71.4
1280
0
1024
0
2
(On) 2 (On)
14.3
to
15.3
3.4
to
4.4
223.4
to
238.9
52.7
to
68.1
75.4
MHz
36363
2560
0
2048
0
1
(Off) 1 (Off)
27.49
36363 - 100
=36263
14.8
to
15.8
3.4
to
4.4
252.3
to
269.2
58.8
to
75.7
1280
0
2048
0
2
(On) 1 (Off)
14.6
to
15.6
3.3
to
4.3
248.9
to
265.9
55.5
to
72.4
18182
2560
0
1024
0
1
(Off) 2 (On)
54.96
18182 - 100
=18082
14.8
to
15.8
3.4
to
4.4
252.3
to
269.2
58.8
to
75.7
1280
0
1024
0
2
(On) 2 (On)
14.6
to
15.6
3.3
to
4.2
249.0
to
265.9
55.5
to
72.4
61.7
MHz
44444
2560
0
2048
0
1
(Off) 1 (Off)
22.49
44444 - 100
=44344
15.4
to
16.4
3.2
to
4.2
320.2
to
340.9
66.3
to
87.1
1280
0
2048
0
2
(On) 1 (Off)
15.2
to
16.2
3.0
to
4.0
316.9
to
337.5
63.1
to
83.7
22222
2560
0
1024
0
1
(Off) 2 (On)
44.98
22222 - 100
=22122
15.4
to
16.4
3.2
to
4.2
320.1
to
340.9
66.3
to
87.1
1280
0
1024
0
2
(On) 2 (On)
15.2
to
16.2
3.0
to
4.0
316.8
to
337.6
63.1
to
83.7
[Note] In 1X2-1Y Tap Geometry, “Exposure Active End to FVAL Active Start” period varies depending on the
exposure time setting. When the exposure time is set at “10”, it is the maximum period and if the exposure time
is incremented by 1 us, it is decreased.
6.3.3 ROI (Region Of Interest) setting
In the SP-5000-PMCL, a subset of the image can be output by setting Width, Height, Offset-X,
and Offset-Y. If the height is decreased, the number of lines read out is decreased and as the
result, the frame rate is increased. However, in the horizontal direction, the horizontal
frequency is not changed if the width is decreased. In the SP-5000M-PMCL, the minimum width
is “16” and minimum height is “1”. In the SP-5000C-PMCL, the minimum width is “16” and
minimum height is “2”.
- 41 -
Page 44

SP-5000M-PMCL / SP-5000C-PMCL
OffsetX
Width
OffsetY
Height
Width
2560 Width Max
2048 Height Max
Readout area
CCD out
Digital Out
8-bit
10-bit
12-bit
Black
0%
8LSB
32LSB
128LSB
Monochrome
100%
222LSB
890LSB
3560LSB
Color
Monochrome
115%
255LSB
1023LSB
4095LSB
Color
Digital Out [LSB]
32
70025
Anal og Ou t [m V]
890
1023
Blac k Leve l
0
Whit e Cli p Le vel
800
100% Level
Setting example (1)
Binning Horizontal = 1
Binning Vertical = 1
Setting example (2)
Binning Horizontal = 2
Binning Vertical = 2
OffsetX
OffsetY
Height
Width
1280 Width Max
1024 Height Max
Readout area
Fig. 18 Setting example ( No binning) Fig.19 Setting example (Binning)
6.4 Digital output bit allocation
Table -30 Output level
Fig. 20 Bit allocation (10-bit)
- 42 -
Page 45

SP-5000M-PMCL / SP-5000C-PMCL
Shortest
to
Longest
Time required to expose and
read out all pixels in the area
set by ROI command
to
0.125 Hz = 8 seconds
7. Operating modes
7.1. Acquisition control (change the frame rate)
7.1.1 Acquisition control
With Trigger OFF (free-running mode he frame rate) less than Height Max.rmal ROI setting.. As
described before, in Multi ROI operation, h is the same for all 8 e default frame rate. However,
it is possible to specify a free-running frame rate (i.e., no trigger needed) that is slower than
the default rate. This can be useful when a longer exposure time is needed for a specific ROI.
Modification of the frame rate is done by entering a value in the AcquisitionFrameRate control
corresponding to the number of microseconds to be allocated to each frame period. Allowed
values range from 167 µs to 8,000,000 (8 seconds) depending on the ROI and the tap geometry
specified. However if the value entered is less than the time required for the default frame rate,
the setting is ignored and the default frame rate is used. For example, in 1X10–1Y camera
output format with an 82.3 MHz Camera Link pixel clock, the minimum frame period for the
smallest possible ROI (1 line) requires 167 microseconds, so any entry less than 167 will always
be ignored in this configuration.
The setting range in Acquisition Frame Rate is:
How to set:
ROI should be set first.
The available number shown in Acquisition Frame Rate will correspond to the standard frame
period for the specified ROI.
The value can be increased up to 8,000,000 (8 seconds).
If ROI is changed from a smaller size to a larger size, the default frame rate of the ROI is
automatically recalculated inside the camera and changed to the slower frame rate of the
larger ROI.
ROI setting:
Height: 1 line to 2048 lines for SP-5000M-PMCL
2 lines to 2048 lines for SP-5000C-PMCL
As for the details of ROI settings, refer to section 6.3.3.
7.1.2 Frame Rate Calculation
The frame rate can be calculated by using the following tables.
- 43 -
Page 46

SP-5000M-PMCL / SP-5000C-PMCL
Table 31. Frame rate calculation (Continuous Trigger, HDR Mode =“Off”)
Tap
Geometry
Camera
Link
Clock
V
-Binning
Continuous Trigger / HDR Mode =“Off”
ART Command Minimum value setting calculation
[Unit: us]
1X10-Y
82.3
MHz
Off
= ROUND((([Height]x284.56)+13495)÷(82.286MHz)x10^6)
On
= ROUND((([Height]x284.56)+(13495÷ 2))÷(82.286MHz)x10^6)
75.4
MHz
Off
= ROUND((([Height]x260.86)+13495)÷(75.429MHz)x10^6)
On
= ROUND((([Height]x260.86)+(13495÷2))÷(75.429MHz)x10^6)
61.7
MHz
Off
= ROUND((([Height]x261.00)+13495)÷(61.714MHz)x10^6)
On
= ROUND((([Height]x261.00)+(13495÷2))÷(61.714MHz)x10^6)
1X8-Y
82.3
MHz
Off
= ROUND((([Height]x325.71)+13495)÷(82.286MHz)x10^6)
On
= ROUND((([Height]x325.71)+(13495÷2))÷(82.286MHz)x10^6)
75.4
MHz
Off
= ROUND((([Height]x325.29)+13495) / (75.429MHz)x10^6)
On
= ROUND((([Height]x325.29)+(13495 / 2)) / (75.429MHz)x10^6)
61.7
MHz
Off
= ROUND((([Height]x324.00)+13495)÷(61.714MHz)x10^6)
On
= ROUND((([Height]x324.00)+(13495÷2))÷(61.714MHz)x10^6)
1X4-Y
82.3
MHz
Off
= ROUND((([Height]x644.57)+23369) ÷(82.286MHz)x10^6)
On
= ROUND((([Height]x644.57)+(23369 ÷2))÷(82.286MHz)x10^6)
75.4
MHz
Off
= ROUND((([Height]x644.29)+23369)÷(75.429MHz)x10^6)
On
= ROUND((([Height]x644.29)+(23369÷2))÷(75.429MHz)x10^6)
61.7
MHz
Off
= ROUND((([Height]x645.43)+23369)÷(61.714MHz)x10^6)
On
= ROUND((([Height]x645.43)+(23369÷2))÷(61.714MHz)x10^6)
1X2-Y
82.3
MHz
Off
= ROUND((([Height]x1285.72)+64677) / (82.286MHz)x10^6)
On
= ROUND((([Height]x1285.72)+(64677 / 2)) / (82.286MHz)x10^6)
75.4
MHz
Off
= ROUND((([Height]x1285.44)+64677)÷(75.429MHz)x10^6)
On
= ROUND((([Height]x1285.44)+(64677÷2))÷(75.429MHz)x10^6)
61.7
MHz
Off
= ROUND((([Height]x1284.42)+64677)÷(61.714MHz)x10^6)
On
= ROUND((([Height]x1284.42)+(64677÷2)) ÷(61.714MHz)x10^6)
Table 32. Frame rate calculation (Continuous Trigger, HDR Mode =“ON”)
Tap
Geometry
Camera
Link
Clock
Continuous Trigger / HDR Mode =“On”
ART Command Minimum value setting calculation
[Unit: us]
1X10-1Y
82.3
MHz
=ROUND(((([Height])×284.56) + 4855 − 284.56 + ([Width]÷10) )
÷ 82.286MHz x 10^6) + [Exposure Time]
75.4
MHz
=ROUND(((([Height])×260.86) + 4855 − 260.86 + ([Width]÷10) )
÷ 75.429MHz x 10^6) + [Exposure Time]
61.7
MHz
=ROUND(((([Height])×261.00) + 4855 − 261.00 + ([Width]÷10) )
÷ 61.714MHz x 10^6) + [Exposure Time]
1X8-1Y
82.3
MHz
=ROUND(((([Height])×325.71) + 5513 − 325.71 + ([Width]÷8) )
÷ 82.286MHz x 10^6) + [Exposure Time]
75.4
MHz
=ROUND(((([Height])×325.29) + 5513 − 325.29 + ([Width]÷8) )
÷ 75.429MHz x 10^6) + [Exposure Time]
61.7
MHz
=ROUND(((([Height])×324.00) + 5513 − 324.00 + ([Width]÷8) )
÷ 61.714MHz x 10^6) + [Exposure Time]
1X4-1Y
82.3
MHz
=ROUND(((([Height])×644.57) + 10944− 644.57 + ([Width]÷4) )
÷ 82.286MHz x 10^6) + [Exposure Time]
75.4
MHz
=ROUND(((([Height])×644.29) + 10944 − 644.29 + ([Width]÷4) )
÷ 75.429MHz x 10^6) + [Exposure Time]
61.7
MHz
=ROUND(((([Height])×645.43) + 10944 − 645.43 + ([Width]÷4) )
÷ 61.714MHz x 10^6) + [Exposure Time]
1X2-Y
82.3
MHz
=ROUND(((([Height])×1285.72) + 21888− 1285.72 + ([Width]÷2) )
÷ 82.286MHz x 10^6) + [Exposure Time]
75.4
MHz
=ROUND(((([Height])×1285.44) + 21888 − 1285.44 + ([Width]÷2) )
÷ 75.429MHz x 10^6) + [Exposure Time]
61.7
MHz
=ROUND(((([Height])×1284.42) + 21888 − 1284.42 + ([Width]÷2) )
÷ 61.714MHz x 10^6) + [Exposure Time]
[Note] The same formula is applied if Binning function is enabled.
- 44 -
Page 47

SP-5000M-PMCL / SP-5000C-PMCL
Table 33. Frame rate setting range(Typical) (Continuous Trigger) (1/2)
Camera Settings
ART Command value : limited reference
Tap
Geometry
Camera
Link
Pixel Clock
Binning
Vertical
Height
HDR
Mode
Min.
Max.
Setting value
Actual period
Setting value
Actual time
/period
1X10
-1Y
82.3
MHz
1
(Off)
2048
Off
7246
(138.007fps)
137.9 fps
8 000 000
8 sec /
0.125 Hz
2
(On)
1024
Off
3623
(276.014fps)
275.7 fps
75.4
MHz
1
(Off)
2048
Off
7262
(137.703fps)
137.6 fps
2
(On)
1024
Off
3631
(275.406fps)
275.1 fps
61.7
MHz
1
(Off)
2048
Off
8880
(112.613fps)
112.5 fps
2
(On)
1024
Off
4440
(225.225fps)
225.2 fps
82.3
MHz
1
(Off)
2048
On
7151
(139.841fps)
139.7 fps
2
(On)
1024
On
3610
(277.008fps)
276.7 fps
75.4
MHz
1
(Off)
2048
On
7157
(139.723fps)
139.6 fps
2
(On)
1024
On
3616
(276.549fps)
276.3 fps
61.7
MHz
1
(Off)
2048
On
8750
(114.286fps)
114.2 fps
2
(On)
1024
On
4419
(226.296fps)
226.1 fps
1X8
-1Y
82.3
MHz
1
(Off)
2048
Off
8271
(120.904fps)
120.8 fps
2
(On)
1024
Off
4135
(241.838fps)
241.8 fps
75.4
MHz
1
(Off)
2048
Off
9011
(110.975fps)
110.9 fps
2
(On)
1024
Off
4505
(221.976fps)
221.9 fps
61.7
MHz
1
(Off)
2048
Off
10971
(91.149fps)
91.1 fps
2
(On)
1024
Off
5485
(182.315fps)
182.3 fps
82.3
MHz
1
(Off)
2048
On
8183
(122.205fps)
122.1 fps
2
(On)
1024
On
4130
(242.131fps)
241.9 fps
75.4
MHz
1
(Off)
2048
On
8915
(101.885fps)
112.1 fps
2
(On)
1024
On
4499
(222.272fps)
222.1 fps
61.7
MHz
1
(Off)
2048
On
10851
(92.157fps)
92.1 fps
2
(On)
1024
On
5475
(182.648fps)
182.5 fps
[Note]
(1) The SP-5000-PMCL has maximum 1 line jitter even in continuous trigger operation. Therefore,
the actual frame rate might be slower than the setting value.
(2) If HDR Mode is set to “On”, the exposure of the next frame cannot be done while the previous
frame is read out. Due to this, the frame rate is slower than with HDR Mode “Off”.
(3) If HDR Mode is set to “On”, the fastest frame rate can be achieved when the exposure time is set
to “10”. As mentioned before, the image readout and exposure cannot be overlapped when HDR
mode is ON, thus the fastest frame rate is influenced by the exposure time.
- 45 -
Page 48

SP-5000M-PMCL / SP-5000C-PMCL
Table 34. Frame rate setting range(Typical) (Continuous Trigger) (2/2)
Camera Settings
ART Command: Limited Reference
Tap
Geometry
Camera
Link
Pixel
Clock
Binning
Vertical
Height
HDR
Mode
Min.
Max.
Setting Value
Actual Period
Setting
Value
Actual time
/period
1X4
-1Y
82.3
MHz
1
(Off)
2048
Off
16327
(61.248fps)
61.2 fps
8 000 000
8 sec /
0.125 Hz
2
(On)
1024
Off
8163
(122.504fps)
122.5 fps
75.4
MHz
1
(Off)
2048
Off
17803
(56.170fps)
56.1 fps
2
(On)
1024
Off
8905
(112.296fps)
112.2 fps
61.7
MHz
1
(Off)
2048
Off
21797
(45.878fps)
45.8 fps
2
(On)
1024
Off
10889
(91.836fps)
91.7 fps
82.3
MHz
1
(Off)
2048
On
16186
(61.782fps)
61.7 fps
2
(On)
1024
On
8164
(122.489fps)
122.4 fps
75.4
MHz
1
(Off)
2048
On
17648
(56.664fps)
56.6
2
(On)
1024
On
8902
(112.334fps)
112.2 fps
61.7
MHz
1
(Off)
2048
On
21606
(112.334fps)
46.2 fps
2
(On)
1024
On
10897
(91.768fps)
91.7 fps
1X2
-1Y
82.3
MHz
1
(Off)
2048
Off
32786
(30.501fps)
30.5 fps
2
(On)
1024
Off
16393
(61.002fps)
61.0 fps
75.4
MHz
1
(Off)
2048
Off
35759
(27.965fps)
27.9 fps
2
(On)
1024
Off
17879
(55.932fps)
55.9 fps
61.7
MHz
1
(Off)
2048
Off
43672
(22.898fps)
22.8 fps
2
(On)
1024
Off
21836
(45.796fps))
45.7 fps
82.3
MHz
1
(Off)
2048
On
32276
(30.983fps)
30.9 fps
2
(On)
1024
On
16276
(61.440fps)
61.4 fps
75.4
MHz
1
(Off)
2048
On
35202
(28.407fps)
28.4 fps
2
(On)
1024
On
17751
(56.335fps)
56.3 fps
61.7
MHz
1
(Off)
2048
On
43022
(23.244fps)
23.2 fps
2
(On)
1024
On
21693
(46.098fps)
46.0 fps
- 46 -
Page 49

SP-5000M-PMCL / SP-5000C-PMCL
Exposure Mode
Trigger Control
Trigger mode OFF
Trigger mode ON
Frame Start
Behavior
OFF
OFF or ON
Free-running
No exposure control
-
Timed (EPS)
Timed(RCT)
Timed (PIV)
OFF
Free-running
Exposure control
available
ON - Operate in EPS, RCT
or PIV
Trigger width
OFF
Free-running
No exposure control
-
ON - Exposure control by
trigger width
7.2. Exposure setting
7.2.1 Mode
Exposure Mode sets which exposure mode is to be used.
If the trigger is used, Frame Start must also be used.
When Exposure Mode is set to Timed or Trigger Width, the combination of Exposure Mode
and Frame Start can set various operations.
The following table shows the operation depending on the combination.
Table -35 Exposure mode and trigger control matrix table
Trigger Control select
Frame Start trigger: Sets whether the start of the frame is controlled externally or not.
Trigger mode ON: If Acquisition Active is active and Exposure Mode chooses Timed or
Trigger Width, the exposure will be started by using the signal set
in Frame Trigger as the trigger.
Trigger mode OFF: If Acquisition Active is active, the camera operates in free-running mode.
Exposure mode can be selected from the followings.
OFF: No shutter control
Timed: The exposure will be done in the preset period. The setting can be done in
μsec units.
Frame Start OFF: Free-running mode and exposure control is available.
Frame Start ON: EPS operation mode
In this status, if RCT or PIV is selected as the Trigger option,
the camera will operate in each mode respectively.
Trigger Width: The exposure will be controlled by the width of the trigger pulse.
Frame Start OFF: Free-running mode and control the exposure
Frame Start ON: PWC operation mode
7.2.2 ExposureTime
This command is effective only when Exposure Mode is set to Timed. It is for setting exposure
time. The setting step for exposure time is 1 μsec per step.
Minimum: 10 μsec
Maximum: 8 seconds
- 47 -
Page 50

SP-5000M-PMCL / SP-5000C-PMCL
Trigger Selector
Item
Description
Frame Start
Frame Start Trigger
Note: In the continuous trigger mode (Frame Start Trigger Mode: OFF), the maximum setting
value of the exposure time is limited by the frame rate setting. In the SP-5000-PMCL,
the maximum value of exposure time is “Frame Rate – 100”. If the exposure mode is
OFF, the maximum value of exposure time is set in the camera. If the frame period is
changed, then the maximum value of exposure time is renewed.
7.2.3 ExposureAuto
This is a function to control the exposure automatically. It is effective only for Timed.
ALC Reference controls the target brightness level.
There are three modes: OFF, Once and Continuous.
OFF: No exposure control
Once: Exposure adjusts when the function is set, then remains at that setting
Continuous: Exposure continues to be adjusted automatically
In this mode, the following settings are available.
ALC Speed: Rate of adjustment speed can be set (common with Gain Auto)
Exposure Auto Max: The maximum value for the exposure time to be controlled can
be set
Exposure Auto Min: The minimum value for the exposure time to be controlled can
be set
ALC Reference: The reference level of the exposure control can be set (common
with Gain Auto)
ALC Channel Area: The measurement area of the exposure control can be set
(common with Gain Auto)
7.3. Trigger control
7.3.1 Trigger Selector
Selects the trigger operation. In the SP-5000-PMCL, only Frame Start is available.
Table - 36 Trigger selector
7.3.2 Trigger Mode
Select either free-running operation or external trigger operation.
OFF: Free-running operation
ON: External trigger operation
7.3.3 TriggerSource
Select the trigger source to be used for trigger operation (Frame Start for the
SP-5000-PMCL) from the following:
OFF
Line 4 ( TTL IN1)
Line 7 (Camera Link CC1 IN)
Soft trigger
Pulse generator 0
Pulse generator 1
Pulse generator 2
Pulse generator 3
- 48 -
Page 51

SP-5000M-PMCL / SP-5000C-PMCL
Trigger Mode
Readout Mode
Time (Min. trigger
period )
Timed Exposure Mode
Trigger Mode OFF
(Note1)
Full
30.9 ms
AOI Center 2/3
21.5 ms
AOI Center 1/2
15.5 ms
AOI Center 1/4
7.7 ms
AOI Center 1/8
3.9 ms
V Binning ON (Full) (Note2)
15.5 ms
Trigger Activation Setting
Exposure Mode
Rising Edge
Falling Edge
Level High
Level Low
Timed
○ ○ ×
×
Trigger width
× × ○
○
Timed PIV
○ ○ ×
×
Timed RCT
○ ○ ×
×
7.3.4 TriggerActivation
This command can select how to activate the trigger.
Rising edge: At the rising edge of the pulse, the trigger is activated.
Falling edge: At the falling edge of the pulse, the trigger is activated.
Level High: During the high level of trigger, the accumulation is activated
Level Low: During the low level of trigger, the accumulation is activated
If Exposure Mode is set to Trigger Width, Level High or Level Low must be used.
Table - 37 Trigger Activation
7.3.5 Triggeroverlap
This function defines whether or not a trigger pulse can be accepted while data is being read
out.
OFF: The trigger pulse is not accepted during CMOS readout.
Read Out: The trigger pulse can be accepted during CMOS readout.
7.4. Normal continuous operation (Timed Exposure Mode/Trigger Mode OFF)
This is used for applications which do not require triggering. In this mode, the video signal for
the auto-iris lens is available.
For the video timing, refer to chapter 6.3.
Table – 38 Minimum interval (1X8–1Y)
Note 1: Readout setting in Trigger Overlap is not available
Note 2: SP-5000M-PMCL only
7.5. Timed mode (EPS operation)
This mode captures image(s) with a preset exposure time by using the external trigger. An
additional setting determines if the trigger pulse can be accepted during the exposure period.
Primary settings to use this mode
Acquisition Mode = Single frame, Multi-frame or Continuous
Trigger Mode = ON
Exposure Mode = Timed
- 49 -
Page 52

SP-5000M-PMCL / SP-5000C-PMCL
Trigger Mode
Readout Mode
Time (Min. Trigger
Period)
Timed Exposure Mode
Trigger Mode ON
Full
30.9 ms + 8.01 µs
AOI Center 2/3
21.5 ms + 8.01 µs
AOI Center 1/2
15.5 ms + 8.01 µs
AOI Center 1/4
7.7 ms + 8.01 µs
AOI Center 1/8
3.9 ms + 8.01 µs
V Binning ON (Full) (Note 1)
15.5 ms + 8.01 µs
Trigger
CMOS
Exposure
FVAL
Exposure
Active
Exposure Period
t4
t1
t2 t3
t1
t2
t3
t4
2L(Min.)
218 clocks
10.13 µs
8L to 9L
Trigger
CMOS
Exposure
FVAL
Exposure
Active
Exposure Period
t4
t1
t2 t3
t1
t2
t3
t4
2L (Min.)
1L
10.13 µs
8L to 9L
Table - 39 Trigger minimum interval (Trigger Overlap = Readout) (1X8–1Y)
Note1: SP-5000M-PMCL only
Note2: If Trigger Overlap is OFF, the accumulation time is added to the above table.
7.5.1 If Overlap setting is OFF
7.5.2 If Overlap setting is Readout
Fig. 22 Overlap Readout
Fig. 21 Overlap OFF
- 50 -
Page 53

SP-5000M-PMCL / SP-5000C-PMCL
Trigger Mode
Readout Mode
Time (Min.
Trigger Period)
Trigger Width Exposure Mode
Full
30.9 ms + 8.01 µs
AOI Center 2/3
21.5 ms + 8.01 µs
AOI Center 1/2
15.5 ms + 8.01 µs
AOI Center 1/4
7.7 ms + 8.01 µs
AOI Center 1/8
3.9 ms + 8.01 µs
V Binning ON (Full) (Note1)
15.5 ms + 8.01 µs
Trigger
CMOS
Exposure
FVAL
Exposure
Active
Exposure Period
t3
t1
t2
t1
t2
t3
2L (Min.)
208 clocks
7L to 8L
7.6 Trigger width mode (PWC)
In this mode, the exposure time is equal to the trigger pulse width. Accordingly, longer
exposure times are supported. Additional settings determine if the trigger pulse can be
accepted during the exposure period.
Primary settings to use this mode
Trigger Mode = ON
Exposure Mode = Trigger Width
Table - 40 Minimum trigger interval (Trigger Overlap = Readout) (1X8–1Y)
Note1: SP-5000M-PMCL only
Note2: If Trigger Overlap is OFF, the accumulation time is added to the above table.
7.6.1 If Overlap setting is OFF
Fig. 23 Overlap = OFF
- 51 -
Page 54

SP-5000M-PMCL / SP-5000C-PMCL
Trigger
CMOS
Exposure
FVAL
Exposure
Active
Exposure Period
t3
t1
t2
t4
t1
t2
t3
t4
2L (Min.)
208 clocks
7L to 8L
1L
7.6.2 If Overlap setting is Readout
Fig. 24 Overlap: Readout
- 52 -
Page 55

7.7. RCT mode
Trigger Mode
Readout Mode
Time (Min. Trigger Period)
Reset Continuous
Trigger Mode
(Note2)
Full
30.9 ms + Exposure time + 1.562 ms
AOI Center 2/3
21.5 ms + Exposure time + 1.562 ms
AOI Center 1/2
15.5 ms + Exposure time + 1.562 ms
AOI Center 1/4
7.7 ms + Exposure time + 1.562 ms
AOI Center 1/8
3.9 ms + Exposure time + 1.562 ms
V Binning ON (Full)
(Note1)
15.5 ms + Exposure time + 1.562 ms
t1
t2
Trigger
CMOS
Exposure
Exposure
Active
FVAL
DVAL
t1
t2
28L
9L ~10L
Until the trigger is input, the camera operates continuously and the video signal for the
auto-iris lens is output. At this moment, the video signal, FVAL and LVAL are output but DVAL is
not output. When the trigger is input, the fast dump is activated to read out
the electronic charge very quickly, after which the accumulation and the readout are
performed. When the accumulated signal against the trigger is read out, FVAL, LVAL and DVAL
are output too.
Primary settings to use this mode
Trigger Mode = ON
Exposure Mode = Timed
Trigger Option = RCT
Table – 41 Minimum trigger interval (1X8–1Y)
SP-5000M-PMCL / SP-5000C-PMCL
Note1: SP-5000M-PMCL only
Note2: Trigger Overlap “Readout” is not available for this trigger mode.
Fig.25 RCT mode timing
- 53 -
Page 56

SP-5000M-PMCL / SP-5000C-PMCL
Trigger Mode
Readout Mode
Time (Min. Trigger Period)
PIV mode
(Note1)
Full
30.9 ms x 2 + Exposure time + 8.01 µs
AOI Center 2/3
21.5 ms x 2 + Exposure time + 8.01 µs
AOI Center 1/2
15.5 ms x 2 + Exposure time + 8.01 µs
AOI Center 1/4
7.7 ms x 2 + Exposure time + 8.01 µs
AOI Center 1/8
3.9 ms x 2 + Exposure time + 8.01 µs
V Binning ON (Full)
(Note2)
15.5 ms x 2 + Exposure time + 8.01 µs
td te1
te2
itf tframe1
tframe2T
Trigegr
Exposure
Exposure
Active
FVAL
DVAL
Time name
Description
Time
td
Exposure beginning delay
5270 clocks
te1
First exposure time period
10µs to 8s
te2
Second exposure time
8.1 ms
itf
Interframing time
10435 clocks
T
FVAL no active
42 LVAL
tframet1
First frame readout
1 frame
tframe2
Second frame readout
1 frame
7.8 PIV (Particle Image Velocimetry)
The Particle Image Velocimetry mode can be used in applications where 2 images need to be
taken with a very short time interval. It can only be used with strobe flash as illumination. The
first accumulation time is 10 sec to 2 sec. Then, the second exposure will be taken. The first
strobe is activated during the first exposure duration and the second strobe is pulsed while the
first frame is being read out. In this way, two strobe flashes generate two video outputs.
Basic settings to use this mode
Trigger Mode = ON
Exposure Mode = Timed
Trigger Option = PIV
Table – 42 Minimum trigger interval (1x8–1Y)
Note 1. Overlap mode=Readout is not available
Note 2. SP-5000M-PMCL only
Fig. 26 PIV mode
- 54 -
Page 57

7.9 Sequence Mode
Video Send Mode
How to select Index
Trigger Sequence
The index can be selected by the
frame start trigger signal. (Setting
index is determined by the next index
setting)
Command Sequence
Select the index directly by setting
the index number by Command
Sequence Index command.
Trigger Mode
Readout Mode
Time (Min. Trigger Period)
PIV mode
Full
30.9ms + Exposure time + 8.01µs
ROI Center 2/3
21.5ms + Exposure time + 8.01µs
ROI Center 1/2
15.5ms + Exposure time + 8.01µs
ROI Center 1/4
7.7ms + Exposure time + 8.01µs
ROI Center 1/8
3.9ms + Exposure time + 8.01µs
V Binning ON (Full)
(Note 1)
15.5ms + Exposure time + 8.01µs
Index 0 Index 1 Index 2 Index 3 Index 4
Frame Start
Trigger In
Sequence
behavior
Frame count
=1
Next Index =
Index 1
Frame count
=1
Next Index =
Index 2
Frame count
=1
Next Index =
Index 3
Frame count
=1
Next Index =
Index 4
Frame count
=1
Next Index =
Index 5
This is a function to capture images in sequence based on preset ROI, Exposure Time, Gain and
other parameters in the sequence index table. In order activate this function:
7.9.1 Video send mode
Sequence Mode has two operating modes and it is set in the video send mode.
7.9.2 Sequence mode
Basic setting to use this function
Trigger Mode: ON
Exposure mode : Timed
Trigger option : Sequence
Table – 43 Minimum trigger interval (1x8–1Y)
SP-5000M-PMCL / SP-5000C-PMCL
Note 1: SP-5000M-PMCL only
Note 2: The minimum trigger interval assumes that the exposure time is the same for each index in the
sequence. If the exposure time is different, the difference in period should be added to the
interval calculation.
Note 3: If it is necessary to use different exposure times, it is recommended to arrange the exposure
times from the shortest to the longest.
Note 4: In sequence mode, the exposure should be adjusted so that the operation is not in LVAL sync
accumulation.
7.9.3 Sequence mode timing
The following drawing shows the sequence mode timing concept.
Fig. 27 Behavior of Sequence trigger
In this mode, it is not possible to overlap the next exposure while the previous trigger operation
(Index table) is in progress.
Sequence Index Table should proceed through Index 0 and after Index 0 is activated, the next
index can be processed.
- 55 -
Page 58

SP-5000M-PMCL / SP-5000C-PMCL
Table 44. Sequence mode: Sequence Index default value
Sequence
ROI Index
Sequence ROI
Width
Height
Offset
Gain Selector
Exposure
Time
Black
Level
Binning
LUT
Enable
Frame
Count
Next
Index
X
Y
Gain
(ALL)
Red
Blue
Horizontal
Vertical
- Index 0
2560
2048
0 0 100 0 0
180000
0
1 (Off)
1 (Off)
Off
1
Index
0
- Index 1
2560
2048
0 0 100 0 0
180000
0
1 (Off)
1 (Off)
Off
1
Index
0
- Index 2
2560
2048
0 0 100 0 0
180000
0
1 (Off)
1 (Off)
Off
1
Index
0
- Index 3
2560
2048
0 0 100 0 0
180000
0
1 (Off)
1 (Off)
Off
1
Index
0
- Index 4
2560
2048
0 0 100 0 0
180000
0
1 (Off)
1 (Off)
Off
1
Index
0
- Index 5
2560
2048
0 0 100 0 0
180000
0
1 (Off)
1 (Off)
Off
1
Index
0
- Index 6
2560
2048
0 0 100 0 0
180000
0
1 (Off)
1 (Off)
Off
1
Index
0
- Index 7
2560
2048
0 0 100 0 0
180000
0
1 (Off)
1 (Off)
Off
1
Index
0
- Index 8
2560
2048
0 0 100 0 0
180000
0
1 (Off)
1 (Off)
Off
1
Index
0
- Index 9
2560
2048
0 0 100 0 0
180000
0
1 (Off)
1 (Off)
Off
1
Index
0
7.9.4 Sequence ROI setting parameters
Setting parameters for Sequence ROI are as follows.
(1) Sequence ROI Index Selector
In Sequence ROI Index Selector, Index 0 to 9 can be selected.
Sequence ROI – Width, Height, Offset X, Offset Y, Gain Selector - Gain/Red/Blue, Exposure
Time, Black Level, Binning Horizontal, Binning Vertical, LUT Enable, Frame Count, Next Index
for the selected index are displayed.
(2) Sequence ROI Width
Set the width of sequence ROI. The setting range is 8 to 2560 pixels.
Rules for setting area and step number are the same as the normal ROI mode set by [Video
Send Mode] =“Normal”.
(3) Sequence ROI Height
Set the height of sequence ROI. The setting range is 1 to 2048 lines.
Rules for setting area and step number are the same as the normal ROI mode set by [Video
Send Mode] =“Normal”.
(4) Sequence ROI Offset X
Set Offset X of sequence ROI.
Sequence ROI Binning Horizontal =1 (Off) :
Setting range is 0 to (2560 - [Sequence ROI Width])
Sequence ROI Binning Horizontal =2 (On) :
Setting range is 0 to (1280 - [Sequence ROI Width])
The limitations of step number and other factors are the same as the normal ROI mode set by
[Video Send Mode] =“Normal”.
- 56 -
Page 59

SP-5000M-PMCL / SP-5000C-PMCL
(5) Sequence ROI Offset Y
Set Offset Y of sequence ROI.
Sequence ROI Binning Vertical =1 (Off) :
Setting range is 0 to (2048 - [Sequence ROI Height])
Sequence ROI Binning Vertical =2 (On) :
Setting range is 0 to (1024 - [Sequence ROI Height])
The limitations of step number and other factors are the same as the normal ROI mode set by
[Video Send Mode] =“Normal”.
(6) Sequence ROI Gain Selector
In Sequence ROI Gain Selector, the gain settings for each index are available.
SP-5000C-PMCL: Gain(ALL), Red and Blue can be set.
SP-5000M-PMCL: Only Gain is displayed and can be set.
(7) Sequence ROI Black Level
Black Level setting is available for each index.
(8) Sequence ROI Exposure Time
Exposure Time setting is available for each index.
(9) Sequence ROI Binning Horizontal
ON or OFF of Horizontal Binning for each index can be set.
(10) Sequence ROI Binning Vertical
ON or OFF of Vertical Binning for each index can be set.
(11) Sequence ROI LUT Enable
Enable or disable of LUT function for each index 0 to 9 can be set.
(12) Sequence ROI Frame Count
This can set how many times the selected index is repeated. This is applied to each index.
Triggers are input according to numbers set in Frame Count and index is repeated and moves
to the next index. Therefore, the same number of triggers as Frame Count must be input.
(13) Sequence ROI Next Index
The number of the index that will follow the current index can be set.
If [Video Send Mode] is set to “Trigger Sequence” and the trigger pulse is input in EPS
trigger, the sequence is executed from index 0.
(14) Sequence ROI Reset Command
This command resets the current index pointer and reverts to index 0 in the table. Frame
Count is also re-initialized.
- 57 -
Page 60

SP-5000M-PMCL / SP-5000C-PMCL
Multi ROI Index Max
1
Multi ROI Width
2560
Multi ROI
Index Selector
Multi ROI
Height
Offset
X
Y
- Index 1 1 0
0
- Index 2 1 0
0
- Index 3 1 0
0
- Index 4 1 0
0
- Index 5 1 0
0
- Index 6 1 0
0
- Index 7 1 0
0
- Index 8 1 0
0
Video Send Mode
Frame Start
Trigger In
“Normal”
“Trigger Sequence”
Sequence Index
Can be changed
Sequence Index
Cannot be changed
Sequence
Index
Execute from
Index 0
Sequence Index
Can be changed
“Normal”
Sequence
Index
Pointer
&
Repetition
Count
Clear
Sequence
Index Execute
From Index 0
“Trigger Sequence”
Sequence Index
Cannot be changed
Frame Active
Out
Sequence Index
Performing
Sequence Index
Stop
Sequence Index
Performing
Sequence Index
Stop
Sequence Reset
Command
“Execute”
Sequen
ce
Index
Execute
from
Index 0
7.10 Multi ROI function
Fig. 28 Sequence trigger timing
This function divides one frame image into a maximum of 8 images vertically and reads out all
areas in one frame. In this function, width is the same for all 8 images.
Multi ROI setting
Video Sending Mode: Set to Multi ROI
Table 45 Multi ROI Index table default values
7.10.1 Multi ROI setting parameters
(1) Multi ROI Index Max:Setting value = 1 ~ 8
Maximum 8 ROI settings are possible in a frame. Set Index 1 through 8 in Multi ROI Index
table as an application requires.
- 58 -
Page 61

SP-5000M-PMCL / SP-5000C-PMCL
(2) Multi ROI Width
The setting range and Step number are the same as the normal ROI setting in which
[Width] plus [Offset X] should be equal to [Width Max]. In Multi ROI operation, the
maximum offset value in index 1 to index 8 is the object in this calculation.
(3) Multi ROI Index Selector:
Index 1 to 8 can be selected. [Height], [Offset X], and [Offset Y] of the selected Multi ROI
Index are displayed and can be set.
(4) Multi ROI Offset X:
Offset X can be set for each ROI area of Multi ROI Index 1 to 8.
The restriction for setting Step and other factors are the same as the normal ROI setting.
As described before, in Multi ROI operation, Multi ROI Width is a common width setting for
Multi ROI Index 1 to 8.
(5) Multi ROI Height:
Height can be set for each ROI area of Multi ROI Index 1 to 8.
The restriction for setting Step and other factors are the same as the normal ROI setting.
(6) Multi ROI Offset Y:
Offset Y can be set for each ROI area of Multi ROI Index 1 to 8.
The restriction for setting Step and other factors is the same as the normal ROI setting.
The sum of Multi ROI Height values of index 1 to 8 should be less than Height Max.
- 59 -
Page 62

SP-5000M-PMCL / SP-5000C-PMCL
V-Binning Off
Height Max
= 2048
ROI setting explanation if Multi ROI Index Max is set to 4
Index 1
Offset X
Index 1 Height
Index 2
Offset X
Index 2 Height
Index 3 Height
Index 4 Height
Index 3
Offset X
Index 4
Offset X
Index 4
Offset Y
Index 2
Offset Y
Index 1
Offset X
Index 3
Offset X
H-Binning Off
Width Max = 2560
Video output of Multi ROI
[Width]=
[Multi ROI Width]
[Height]=
[Index 1 Multi ROI Height]+
[Index 2 Multi ROI Height]+
[Index 3 Multi ROI Height]+
[Index 4 Multi ROI Height]
- 60 -
Page 63

SP-5000M-PMCL / SP-5000C-PMCL
Exposure
operation
Trigger
Mode
Trigger
Option
Binning
Vertical
(Note1)
Binning
Horizontal
(Note1)
Exposure
Time
AOI
Auto
White
Balance
(Note2)
Auto Iris
Output
Auto
Gain
Auto
Exposure
Overlap
OFF
OFF
OFF
1
1
× ○ ○ ○ ○ × ×
2
2
× ○ ○ ○ ○ × ×
Timed
OFF
OFF
1
1
○ ○ × ○ ○ ○ ×
2
2
○ ○ × ○ ○ ○ ×
Timed
ON
OFF
1
1
○ ○ × × × × ○
2
2
○ ○ × × × × ○
Trigger
Width
ON
OFF
1
1
× ○ × × × × ○
2
2
× ○ × × × × ○
RCT
ON
RCT
1
1
○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ×
2
2
× × ○ × × × ×
PIV
ON
PIV
1
1
× ○ × × × × ×
2
2
× × × × × × ×
Sequence
Trigger
ON
Sequence
Trigger
1
1
○ ○ × × × × ×
2
2
○ ○ × × × × ×
Fig. 29 Multi ROI settings and output image
7.11. Operation and function matrix
Table - 46 Operation and function matrix
(Note1) SP-5000M-PMCL only
(Note2) SP-5000C-PMCL only
- 61 -
Page 64

SP-5000M-PMCL / SP-5000C-PMCL
8. Other functions
8.1 Black level control
This function adjusts the setup level.
Variable range: -256 to 255 LSB (at 10-bit output)
8.1.1 Black Level Selector
The following items can be adjusted.
Monochrome: Black Level All
Color: Black Level All/ Black Level Red/ Black Level Blue
8.1.2 Black Level
The black level can be adjusted in the following range.
Monochrome: Black Level All : -256 ~+255
Color: Black Level All : -256 ~+255
Black Level Red/Blue: -512 ~+511
8.2 Gain control
In the SP-5000-PMCL, the gain control uses Analog Base Gain and Digital Gain.
Analog Base Gain can be set at 0dB, +6dB or +12dB. The digital gain is used for the master gain
setting.
For setting the gain,
1. Set analog gain (Select from 0dB, +6dB and +12dB)
2. Set digital gain
The master gain (DigitalAll) for both monochrome and color can be set x1(0dB) to
x16(+24dB) against the analog base gain. The resolution for gain setting is
0.01%/step which is 0.05dB to 0.08dB, depending on the setting value.
In the SP-5000C-PMCL, blue and red gain can be set from x0.45 to x5.62 against the
master gain setting and its resolution is x0.01/step.
Note: If the gain up function is used, it is recommended to use the analog base gain as the
master gain setting. For instance, if +12dB gain up is required, the analog base gain is set
at +12dB and no digital gain is added. This is because the signal-to-noise is better on
analog gain performance. However, the AGC function works only in digital gain.
Additionally, the analog base gain is effective in order to minimize the drop of the
histogram at higher gain settings. Please note that the analog base gain has less accuracy
due to its variability.
- 62 -
Page 65

x50.56
x16
x7.15
x3.16
x1
x0.45
1600
100
Gain
Amplitude
Gain
Setting
Value
Gain Control Range for
Monochrome
24dB
0dB
X89.12
X16
X7.15
X5.62
X1
X0.45
1600
0
Gain
Magnification
Gain Setting Value
(Magnification)
37846 (X5.62)
0 (X1)
-4523 (X0.45)
Gain
Setting
Value
Master
R&B
Master Red
Blue
Gain Control Range for Bayer Color
39dB
-7dB
0dB
24dB
15dB
0dB
-7dB
15dB
0dB
-7dB
15dB
37846 (X5.62)
0 (X1)
-4523 (X0.45)
SP-5000M-PMCL / SP-5000C-PMCL
Fig.30 Gain control
8.2.1 Gain Selector
The following parameters can be set.
Monochrome: Digital All
Color: Digital All/Digital Red/ Digital Blue
8.2.2 Gain
The range for adjustment is as follows.
Monochrome: Digital All: 1 ~ 16 (x1 (0dB) ~x16 (+24dB))
Color: Digital All: 1 ~ 16 (x1 (0dB) ~ x16 (+24dB))
Digital Red: -0.4476 ~ 5.6235 (-7dB ~+15dB)
Digital Blue: 0.4476 ~ 5.6235 (-7dB ~+15dB)
8.2.3 Gain Raw
The range for adjustment is as follows.
Mono: Gain Raw Digital All:100 ~ 1600 (0dB~24dB)
Color: Gain Raw Digital All:100 ~ 1600(0dB~24dB)
Gain Raw Digital Red / Gain Raw Digital Blue :-4533~37876
8.2.4 Gain Auto
This provides automatic control of the gain level.
This is controlled by the command JAI ALC Reference.
There are three modes.
OFF: Adjust manually.
Once: Operate only one time when this command is set
Continuous: Operate the auto gain continuously
The following detailed settings are also available.
ALC Speed: The rate of adjustment of GainAuto can be set (common with
Exposure Auto)
Gain Auto Max: The maximum value of GainAuto control range can be set
- 63 -
Page 66

If there is no data, use
adjacent data on both sides
Average data is used for
Low
Right
Low
Mid-right
Low
Mid-left
Low
Left
Mid-Low
Mid-left
Mid-High
Mid-left
High
Mid-left
Mid-Low
Left
Mid-High
Left
High
Left
High
Mid-right
Mid-High
Mid-right
Mid-Low
Mid-right
High
Right
Mid-High
Right
Mid-
Low
Right
SP-5000M-PMCL / SP-5000C-PMCL
Gain Auto Min: The minimum value of GainAuto control range can be set
ALC Reference: The reference level of Gain Auto control can be set (common with
Exposure Auto)
ALC channel area: The measurement area of GainAuto control can be set, either
entire area or individual section (Common with Exposure Auto)
Fig.31 ALC channel area
8.3. LUT
This function can be used to convert the input to the desired output characteristics.
The Look-Up Table (LUT) has 256 points for setup. The output level can be created by multiplying
the gain data by the input level.
8.3.1 LUT Enable
ON or OFF LUT function.
8.3.2 LUT Index
The number of LUT data elements is 256. The lowest level is Index 0 and the highest level is
Index 255.
8.3.3 LUT Value
There are 256 LUT data elements to which a value can be assigned. The minimum LUT is value is
0 and the maximum LUT value is 255.
The data between LUT data elements is calculated from adjacent data elements.
In the color camera, LUT characteristics for R, G and B are the same.
Output Data = Video IN x LUT data
- 64 -
Page 67

SP-5000M-PMCL / SP-5000C-PMCL
Adjustable range
Less 30%
Fig.32 LUT data processing method
8.4 Gamma
This command is used set gamma between gamma 0.45 and gamma 1.0 (OFF).
8 steps are provided. The gamma value is an approximate value.
Fig.33 Gamma correction
8.5 Shading Correction
This function compensates for shading (non-uniformity) caused by the lens or the light source
used. This compensation can be performed even if shading issues are not symmetrical in
horizontal and/or vertical directions.
There are two methods of correction.
Flat shading correction:
The method to compensate the shading is to measure the highest luminance level in the image
and use that data as the reference. Luminance levels of other areas are then adjusted so that
the level of the entire area is equal. The block grid for compensation is 20 (H) x 16(V) and each
block contains 128 x 128 pixels. The complementary process is applied to produce the
compensation data with less error.
Fig.34 Concept drawing of flat shading correction
Color shading correction (For SP-5000C-PMCL only):
In this case, R channel and B channel are adjusted to match with G channel characteristics. The
block grid for compensation is 20 (H) x 16(V) and each block contains 128 x 128 pixels. The
complementary process is applied to produce the compensation data with less error.
- 65 -
Page 68

SP-5000M-PMCL / SP-5000C-PMCL
B/W
Color
Blemish Compensation Principle
Defective Pixel
Avaraging
Defective pixels Defective pixels
Avaraging
8.6 Blemish compensation
Before adjustment After adjustment
Fig. 35 Concept drawing of color shading correction
Note: Under the following conditions, the shading correction circuit may not work properly.
If there is some area in the image with a video level less than 70%
If part of the image or the entire image is saturated
If the highest video level in the image is less than 300LSB (at 10-bit output)
The SP-5000-PMCL has a blemish compensation circuit. This function compensates blemishes on
the CMOS sensor (typically pixels with extremely high response or extremely low response). This
applies to both monochrome and color versions. Pixels that fulfill the blemish criteria can be
compensated by averaging the data from pixels in both adjacent columns and, in the case of the
SP-5000C-PMCL, the defective pixels can be compensated by averaging the data from the same
Bayer color pixels in adjacent columns. The number of pixels that can be compensated is up to
512 pixels.
Fig. 36 Blemish compensation
If several consecutive pixels are defective in the horizontal direction, 3 pixels for monochrome
and 2 same color pixels for color can be compensated.
Fig 37. Compensation of consecutive defective pixels
- 66 -
Page 69

8.7 ALC
Gain is fixed at Min.
Dark Light changes Bright
Auto Shutter
Max
Auto shutter operation
Max ~ Min (User set)
Auto Shutter
fixed at Min
Iris diaphragm fixed (Open)
Auto iris
operation
AGC works:
Auto shutter works:
Auto iris works:
AGC operation
Max ~ Min (User set)
AGC
Max
Iris stops just
before close
Operation if light changes
from dark to bright
Operation if light changes
from bright to dark
In the SP-5000-PMCL, auto gain, auto shutter and auto iris functions can be combined to provide
a wide ranging automatic exposure control from dark to bright or vice versa. The functions are
applied in the sequence shown below and if one function is disabled, the linkage between the
other two is maintained.
In order to make the ALC function effective, set the Auto Iris Lens Control Signal Output to “ON”.
The auto iris function works together with AGC and Exposure Auto.
If the lighting condition is changed from bright to dark AIC ― ASC ― AGC
If the lighting condition is changed from dark to bright AGC ― ASC ― AIC
SP-5000M-PMCL / SP-5000C-PMCL
Fig.44 ALC function concept
ALC Reference will determine the target video level for AGC, Auto Shutter and/or Auto iris. For
instance, if ALC Reference is set to 100% video level, AGC, Auto Shutter and/or Auto iris will
function to maintain 100% video level.
8.8 HDR (High Dynamic Range) (SP-5000M-PMCL only)
HDR sensing mode can be set when HDR Mode is set to ON while Exposure Mode is Timed.
The parameters to configure dynamic range are HDR_SLOPE Level 1, Level 2, Level 3 and Level 4.
The user can select any one of those parameters as required for their application.
In this mode, the timed exposure is used as the reference and the value selected in
HDR_SLOPE will compensate to get an appropriate dynamic range by changing the exposure
time.
Notes:
1. If the exposure mode is OFF and the HDR mode is set to ON, the exposure mode is
2. If horizontal binning and/or vertical binning are set to ON, the HDR mode cannot be set.
3. In this mode, exposure overlapped behavior is not available and the frame rate is slower than
automatically changed to Timed.
In this case, the HDR mode must be set first before H-Binning and/or V-Binning are set.
- 67 -
Page 70

SP-5000M-PMCL / SP-5000C-PMCL
Knee Slope
Dynamic Range [%]
1
(200)
2
(400)
3
(800)
4
(1600)
Lens Select
Description (Control with
camera)
Note
P-Iris Lens
1) Iris position can be remotely
controlled manually
2) Auto iris control is also
available
If P-iris lens is used, the
specific model name should be
selected in lens select.
Motor controlled lens
1) Iris position can be remotely
controlled manually
2) Auto iris control is also
available
Video iris lens
Only auto iris control is
available
Option
DC iris lens
Only auto iris control is
available
Option
the normal operation.
4. The exposure time value is fixed at the value when HDR Mode is activated. When the
exposure time is changed, HDR Mode should be off. Once the exposure time is changed, the
HDR Mode can be set to ON again.
5. In this mode, Exposure Auto function is disabled.
8.9. Lens
The SP-5000M-PMCL and SP-5000C-PMCL can be used with 4 different types of lenses. The lens
used must be selected in Lens Select.
Table -47 Lens selector
Fig. 39 HDR characteristics
- 68 -
Page 71

SP-5000M-PMCL / SP-5000C-PMCL
P-Iris lens select
Description
Control step number
Open F value
TBD
8.9.1 About P-Iris
New Spark Series SP-5000M-PMCL and SP-5000C-PMCL come equipped with P-Iris control as part
of the standard lens control function. The P-Iris system is a newly developed lens control
method designed to control the iris more precisely. Especially for video cameras in surveillance
applications utilizing megapixel CCD or CMOS imagers, it becomes a very important factor to
control an iris in order to achieve the maximum camera performance. In surveillance
applications, depending on shooting conditions, resolution and depth of field are important
factors. The iris is deeply related with these factors. If the iris diaphragm is smaller, but not too
small, resolution gets better and the depth of field is also deeper. The P-Iris system controls the
iris diaphragm precisely and maintains the best image with the highest resolution and depth of
field. P-Iris can also combine with gain and electronic shutter to keep the appropriate iris
position under changing lighting conditions (ALC function).
8.9.2 Setting for P-iris lens being used
P-iris lens uses an absolute setting value control system and therefore, if the following
parameters are input, precise iris position control is possible.
8.9.2.1 P-Iris lens select
Select the lens used from the P-iris select list. At this moment, there are no 1-inch P-Iris
lenses available in the list.
8.9.2.2 Step max.
The iris control step depends on the lens. This setting uses the value stored in the camera.
8.9.2.3 Position
The iris position can be set between 0 to Step max. 0 means to open the iris and step max is
to close the iris.
In the following conditions, the camera initializes P-iris control and acquires iris position.
1) When the camera is powered
2) When a lens is selected in the P-Iris select list
3) If the lens selection is changed in the P-iris lens select list
8.9.2.4 Current F value
The current F value is indicated by using iris position information based on commands sent from
the camera to the P-iris lens during auto-iris operation.
The relationship between iris position and F value depends on the lens used.
8.9.2.5 P-Iris Auto min. / P-Iris Auto max.
This function can set the control range when the iris is operated automatically. Auto max. sets
the limit when the iris opens and Auto min. sets the limit when the iris closes. Auto max. can be
set to fully open but Auto min. is stopped at F5.6 as lens performance typically begins to
degrade if the iris closes past this point.
8.9.3 Motorized lens
The SP-5000M-PMCL and SP-5000C-PMCL can use a motorized lens for zoom, focus and iris.
The following functions are available to control the lens via the 10-pin AUX connector.
8.9.3.1 Iris
Open: While this command is being sent, the iris continues to open.
Close: While this command is being sent, the iris continues to close.
Stop: When this command is supplied, the iris operation stops.
- 69 -
Page 72

SP-5000M-PMCL / SP-5000C-PMCL
8.9.3.2 Zoom
Wide: While this command is being sent, the zoom continues to move towards wide angle.
Tele: While this command is being sent, the zoom continues to move towards telephoto.
Stop: When this command is supplied, the zoom operation stops.
8.9.3.3 Focus+
Near: While this command is being sent, the focus continues to move towards close range.
Far: While this command is being sent, the focus continues to move towards infinity.
Stop: When this command is supplied, the focus operation stops.
- 70 -
Page 73

SP-5000M-PMCL / SP-5000C-PMCL
9. Camera control
In the SP-5000-PMCL, control of all camera functions is done by the JAI SDK and Control Tool
software. All controllable camera functions are stored in an XML file inside of the camera. The
JAI SDK and Control Tool software can be downloaded from www.jai.com.
If you need to use the Short ASCII communication protocol and associated control tool, please
contact your local JAI representative.
Specific notes regarding Control Tool use:
1. For SP-5000-PMCL, the JAI SDK and Control Tool 2.0 can be used to control the camera,
provided the PC on which the JAI software is installed is connected to the camera via a
GenCP-compliant Camera Link frame grabber. Many frame grabber vendors also provide their
own GenICam control tool software, as do a number of third-party software companies. Software
conflicts can occur between these GenICam tools and the JAI SDK and Control Tool causing one or
both tools to function improperly. Therefore, if you intend to use the JAI SDK and Control Tool
you should A) not install any other GenICam software on your host PC, or B) install the JAI SDK
and Control Tool last, after installing any other software. This will, in most cases, ensure that
the JAI SDK and Control Tool functions properly. If not, please contact the frame grabber
manufacturer or JAI to determine other ways to eliminate any software conflict.
2. The frame grabber used must be compliant with Camera Link Specification v1.1 or greater
in order to communicate with the JAI SDK and Control Tool. If it is not, the JAI SDK and Control
Tool cannot be used, and the Short ASCII communication protocol and associated control tool
should be used instead.
- 71 -
Page 74

SP-5000M-PMCL / SP-5000C-PMCL
46
46
38
62
52
62
24. 5
24. 5
24. 5( 9. 8)
( 9. 8)
4
46
φ 31
13
C Mount
( 9. 8)
370. 3
DI GITAL I/O -1
DI GITAL I/O -2
D C IN/ TRI G
3- M3 Dept h5
3- M3 Dept h5
3- M3 Depth5
500. 35. 2
4- M3 Dept h3
AU X
POWER/TRIG
10. External appearance and dimensions
Dimensions tolerance: ±0.3mm Unit: mm
Fig. 40 Appearance and Dimensions
- 72 -
Page 75

SP-5000M-PMCL / SP-5000C-PMCL
80.00
70.00
60.00
50.00
40.00
30.00
20.00
10.00
0.00
400 500 600 700 800 900 1000
FFxQE[%]
wavelength (nm)
11. Specifications
11.1. Camera spectral response
Fig.41 SP-5000M-PMCL Spectral response
Fig.42 SP-5000C-PMCL Spectral response
- 73 -
Page 76

SP-5000M-PMCL / SP-5000C-PMCL
Specifications
SP-5000M-PMCL
SP-5000C-PMCL
Scanning system
Progressive scan
Synchronization
Internal
Interface
CameraLink Specifications (V.2.0 RC2), Conforming with PoCL specifications
Camera Link Pixel Clock: 61.7 MHz, 75.4 MHz, 82.3 MHZ selectable
(Default setting: 82.3 MHz)
Image sensor
1 inch Monochrome CMOS
1 inch Bayer color CMOS
Aspect ratio
5:4
Effective image size
12.8 (h) x 10.24 (v) mm 16.39 mm diagonal
Cell size
5.0 (h) x 5.0 (v) m
Active pixels
2560 (h) x 2048 (v)
Pixel clock
48 MHz
Acquisition
Frame rate
1X2 – 1Y
30 fps (Max.) to 0.125s (Min.) 8-bit
30 fps (Max.) to 0.125s (Min.) 10-bit
30 fps (Max.) to 0.125s (Min.) 12-bit
30 fps (Max.) to 0.125s (Min.) 8-bit
30 fps (Max.) to 0.125s (Min.) 10-bit
30 fps (Max.) to 0.125s (Min.) 12-bit
1X4 – 1Y
61 fps (Max.) to 0.125s (Min.) 8-bit
61 fps (Max.) to 0.125s (Min.) 10-bit
61 fps (Max.) to 0.125s (Min.) 12-bit
61 fps (Max.) to 0.125s (Min.) 8-bit
61 fps (Max.) to 0.125s (Min.) 10-bit
61 fps (Max.) to 0.125s (Min.) 12-bit
1x8 – 1Y
120 fps (Max.) to 0.125s (Min.) 8-bit
120 fps (Max.) to 0.125s (Min.) 10-bit
120 fps (Max.) to 0.125s (Min.) 8-bit
120 fps (Max.) to 0.125s (Min.) 10-bit
1x10 – 1Y
134 fps (Max.) to 0.125s (Min.) 8-bit
134 fps (Max.) to 0.125s (Min.) 8-bit
Binning
H1/V2
268 fps (Max.) ~0.125s (Min.)
1X10-1Y
—
H2/V1
134 fps(Max.) ~0.125s (Min.)
1X10-1Y
—
H2/V2
268 fps (Max.) ~0.125s (Min.)
1X10-1Y
—
EMVA 1288 Parameters
Absolute sensitivity
Maximum SNR
At 10-bit output
23.50 p (λ = 525 nm)
41.48 dB
At 10-bit output
36.08 p (λ = 525 nm)
38.00 dB
SN ratio (Traditional)
55dB (Typical)
(0dB gain, Black))
53dB (Typical)
(0dB gain, Green Pixel Black)
Image
Output
Format
Digital
Full image
2560 (h) x 2048 (v)
2560 (h) x 2048 (v)
ROI
Height
1 ~2048 lines, 1 line / step
2 ~2048 lines, 2 lines / step
OFFSET Y
0 ~2047 lines, 1 line / step
0 ~2046 lines, 2 lines / step
Width
1X2–1Y, 1X4-1Y, 1X8–1Y
16 ~2560 pixels, 16 pixels/step
1X10-1Y
80 ~2560 pixels, 80 pixels/step
1X2–1Y, 1X4-1Y, 1X8–1Y
16 ~2560 pixels, 16 pixels/step
1X10-1Y
80 ~2560 pixels, 80 pixels/step
OFFSET X
1X2–1Y, 1X4-1Y, 1X8–1Y
0 ~2544 pixels, 16 pixels/step
1X10-1Y
0 ~2480 pixels, 80 pixels/step
1X2–1Y, 1X4-1Y, 1X8–1Y
0 ~2544 pixels, 16 pixels/step
1X10-1Y
0 ~2480 pixels, 80 pixels/step
H Binning
H1
2560 pixels
2560 pixels
11.2. Specification table
Table – 48 Specification table
- 74 -
Page 77

SP-5000M-PMCL / SP-5000C-PMCL
H2
1280 pixels
The frame rate is not changed.
—
V Binning
V1
2048 lines
2048 lines
V2
1024 lines
—
Bit assignment
8-bit, 10-bit, 12-bit
8-bit, 10-bit, 12-bit
Acquisition Mode
Continuous
Trigger selector
Frame Start
Trigger mode
Continuous, Timed(EPS), Trigger Width,
Trigger option
Overlap ON/OFF, Long time exposure, PIV, Timed (RCT) with ALC
Timed (RCT) with ALC continuous
Trigger input signal
Line4 (TTL IN), Line7 (Camera link CC1), Pulse Generator 0/1/2/3, Soft Trigger,
NAND0 (out), NAND1 (out) Optional: Line10 (TTL IN2), Line11 (LVDS IN)
Exposure
Mode
Timed
10 μs (Min) ~ 8 sec. (Max), Step: 1μs
Trigger Width
10 μs (Min) ~ ∞ (Max)
Auto exposure
OFF / Once / Continuous
Exposure Auto response speed
1 ~8
Digital I/O
Line Selector (Hirose 12P): GPIO IN / GPIO OUT
Black
level
adjust
Reference
33.5LSB 10-bit (Average of 100*100)
Adj. range
-256 ~+255LSB 10-bit
Resolution
1 STEP = 1LSB
Analog Base Gain
x1(0dB), x2(+6dB), x4(+12dB)
Gain
Adjust
Manual adj. range
0dB ~+24dB, 0.01%/step
0dB ~+24dB、0.01%/step
WB gain
—
R / B : -7dB to +15dB, 0.01dB/ step
WB area
—
4 x 4
WB range
—
3000K ~ 9000K
White balance
—
OFF, Once, continuous
Blemish
comp.
Detection
Detect white blemish above the threshold value
(Black blemish is detected only by factory )
Compensation
Complement by adjacent pixels (Continuous blemishes are not compensated)
Correct Numbers
Up to 512 pixels
ALC (Note 1)
AGC, Auto Shutter, and Auto Iris can be combined and automatically controlled
Gamma (Note1)
0.45 ~ 1.0 (8 steps are available)
LUT(Note1)
OFF: γ=1.0, ON=256 points can be set
Shading compensation(Note1)
Flat field
Block based (20 x 16 blocks))
Flat field, Color shading
Block based (20 x 16 blocks)
HDR Mode
Level 1, 2, 3 and 4 based of the
exposure time setting
—
Power
supply
Power input
DC+12V to +24V ± 10% (at the input terminal)
Current
380mA (12V input, full image)
Power Consumption
4.5W (12V input, full image)
Lens mount
C mount, Rear protrusion of the lens is less than 10 mm.
Flange back
C mount : 17.526 mm, Tolerance 0 to -0.05 mm
Optical filter
Protection glass : Not provided
IR cut filter (Half value is 670 nm)
Operating temperature
/ Humidity
(Performance guaranteed)
-5C to +45C / 20% – 80% (non-condensing)
- 75 -
Page 78

SP-5000M-PMCL / SP-5000C-PMCL
Operating temperature
/ Humidity
-45C to +70C / 20% – 80% (non-condensing)
Storage Temp. / Humidity
-45C to +70C / 20% - 80 % (non-condensing)
Regulation
CE (EN61000-6-2 and EN61000-6-3), FCC part 15 class B, RoHS, WEEE
Housing Dimensions
62 x 62 x 55.5 mm (W x H x D) (excluding protrusion)
Weight
215 g
Note 1) These functions are effective on 12-bit output. If the output is 8-bit or 10-bit, there are some
restrictions about setting range and functionalities.
Note 2) The above specifications are based on 82.3 MHz Camera Link Pixel Clock.
Note 2) Approximately 5 minutes pre-heating is required to achieve these specifications.
Note 3) The above specifications are subject to change without notice.
- 76 -
Page 79

SP-5000M-PMCL / SP-5000C-PMCL
Baud Rate
9600
Data Length
8bit
Start Bit
1bit
Stop Bit
1bit
Parity
Non
Xon/Xoff Control
Non
Appendix 1 Short ASCII Command Communication Protocol
This chapter described the communication control protocol based on the short ASCII command as the
reference
1 Communication setting
2 Protocol(Short ASCII Command)
2.1 Transmit the setting command to camera
NN is any kind of command.
NN=[Param.]<CR><LF>
e.g.
Send to camera: GA=0 <CR><LF>
Camera response: COMPLETE<CR><LF>
When camera receives a valid command, camera will return 'COMPLETE'.
If camera receives an improper command, camera will return one of the following:
e.g.
Send to camera: GAX=0 <CR><LF>
Camera response: 01 Unknown Command!!<CR><LF>
e.g.
Send to camera: GA=1000 <CR><LF>
Camera response: 02 Bad Parameters!!<CR><LF>
2.2 Transmit the request command to camera
The status of camera's settings can be queried by transmitting NN?<CR><LF>, where NN is any valid
command.
The camera will return the current setting data.
e.g.
Send to camera: GA? <CR><LF>
Camera response: GA=0<CR><LF>
2.3 Switching baud rate between PC and camera
Camera always starts up with 9600 bps. This can be switched to higher baud rates after
communication has been established. When switching to other baud rates the procedure is as
follows.
e.g. Change baud rate to 115200 bps
1. Confirm baud rates camera supported
Send to camera: SBDRT? <CR><LF>
Camera response: SBDRT=31(0x1F)<CR><LF>
2. Request new baud rate
Send to camera: CBDRT=16(0x10) <CR><LF>
Camera response: COMPLETE<CR><LF>
(Change baud rate to 115200 bps)
- 77 -
Page 80

SP-5000M-PMCL / SP-5000C-PMCL
Name
Interface
Acce
ss
Short
ASCII
Values
MIN
MAX
DEFAU
LT
Description
DeviceVendorN
ame
I String
R/O
DVN
"JAI Ltd., Japan"
- - -
DVN?<CR><LF>
DeviceModelNa
me
I String
R/O
MD
- - -
MD?<CR><LF>
DeviceVersion
I String
R/O
DV
Indicate device
version
(e.g. “0.1.0.0” )
- - -
DV?<CR><LF>
DeviceID
I String
R/O
ID
Revision+Order-Numb
er
- - -
ID?<CR><LF>
DeviceUserID
I String
R/W
UD
User can save and
load free text.
(12 or less characters)
UD=[Param.]<CR><LF
>
UD?<CR><LF>
Name
Interface
Acce
ss
Short
ASCII
Values
MIN
MAX
DEFAU
LT
Description
SupportedBaudr
ates
I Integer
R/O
SBDR
T
Indicate
Support/Non-support
status for each baud
rate
bit0: 9600bps
bit1: 19200bps
bit2: 38400bps
bit3: 57600bps
bit4: 115200bps
bit5: 230400bps
bit6: 460800bps
bit7: 921600bps
0x01
0xFF
0x1F
SBDRT?<CR><LF>
This camera supports
9600bps, 19200bps,
38400bps, 57600bps,
and 115200bps.
CurrentBaudrat
e
I Integer
R/W
CBDR
T
READ: Indicate
current baud rate
WRITE: Set any bit of
baud rate
bit0: 9600bps
bit1: 19200bps
bit2: 38400bps
bit3: 57600bps
bit4: 115200bps
bit5: 230400bps
bit6: 460800bps
bit7: 921600bps
0x01
0x80
1
(9600b
ps)
CBDRT=[Param.]<CR>
<LF>
CBDRT?<CR><LF>
In case of WRITE
execution (change
baud rate), it needs
to control in the
proper sequence
between Host and
Camera.
(Refer to the section
3.3)
3. Rewrite new baud rate again with new baud rate (Confirmation command)
Send to camera: CBDRT=16(0x10) <CR><LF>
Camera response: COMPLETE<CR><LF>
In case the camera does not receive the confirming command with new baud rate within
250 ms after sending the acknowledgement it falls back to the original baud rate (9600 bps).
2.4 Command list (Short ASCII command)
2.4.1 GenCP Bootstrap Register
2.4.2 Technology Specific Bootstra Register
- 78 -
Page 81

SP-5000M-PMCL / SP-5000C-PMCL
Name
Interface
Acce
ss
Short
ASCII
Values
MIN
MAX
DEFA
ULT
Description
DeviceFirmwar
e
Version
I String
R/O
VN
Firm Ver. No.
- - -
VN?<CR><LF>
DeviceReset
I
Comman
d
W/O
CRS00
1
- - -
CRS00=1<CR><LF>
Name
Interface
Acce
ss
Short
ASCII
Values
MIN
MAX
DEFA
ULT
Description
Height
I Integer
R/W
HTL
Min~(Max - OffsetY)
1(Mon
o)
2(Bay
er)
2048
2048
HTL=[Param.]<CR><LF
>
HTL?<CR><LF>
Width
I Integer
R/W
WTC
Min~(Max - OffsetX)
16
2560
2560
WTC=[Param.]<CR><LF
>
WTC?<CR><LF>
Offset Y
I Integer
R/W
OFL
Min~(Max – Height)
0
2047
(Mono
)
2046
(Baye
r)
0
OFL=[Param.]<CR><LF
>
OFL?<CR><LF>
Offset X
I Integer
R/W
OFC
Min~(Max – Width)
0
2544
0
OFC=[Param.]<CR><LF
>
OFC?<CR><LF>
BinningHorizont
al
I Integer
R/W
HB
1: Normal / 2: Binning
mode
1 2 1
HB=[Param.]<CR><LF>
HB?<CR><LF>
only Mono
BinningVertical
I Integer
R/W
VB
1: Normal / 2: Binning
mode
1 2 1
VB=[Param.]<CR><LF>
VB?<CR><LF>
only Mono
PixelFormat
I
Enumera
tion
R/(
W)
BA
Mono model:
0: Mono8
1: Mono10
2: Mono12
Bayer model:
0: BayerRG8
1: BayerRG10
2: BayerRG12
0 2 0
BA=[Param.]<CR><LF>
BA?<CR><LF>
TestImageSelec
tor
I
Enumera
tion
R/W
TPN
0: Off
1:
GreyHorizontalRamp
2: GreyVerticalRamp
3:GreyHorizontal
RampMoving
4: Horizontal Colorbar*
5: Vertical Colorbar*
6: Moving Colorbar*
(* Bayer model
only)
0 6 0
TPN=[Param.]<CR><LF
>
TPN?<CR><LF>
2.4.3 Device Control
2.4.4 Image Format Control
- 79 -
Page 82

SP-5000M-PMCL / SP-5000C-PMCL
Name
Interface
Acce
ss
Short
ASCII
Values
MIN
MAX
DEFA
ULT
Description
FrameStartTrig
Mode
I
Enumera
tion
R/W
TM
Off/On
0 1 0
TM=[Param.]<CR><LF>
TM?<CR><LF>
TrigSoftware
I
Comman
d
(R)/
W
STRG
0
- - -
STRG=0<CR><LF>
FrameStartTrig
Source
I
Enumera
tion
R/W
TI
0: Low
1: High
2: SoftTrigger
8: PulseGenerator0
9: PulseGenerator1
10: PulseGenerator2
11: PulseGenerator3
12: TTL_In1
13: CL_CC1_In
14: Nand0
15: Nand1
16: TTL_In2(Option)
17: LVDS_In(Option)
0
17
0
TI=[Param.]<CR><LF>
TI?<CR><LF>
FrameStartTrig
Activation
I
Enumera
tion
R/W
TA
0: RisingEdge
1: FallingEdge
2: LevelHigh
3: LevelLow
0 3 0
TA=[Param.]<CR><LF>
TA?<CR><LF>
FrameStartTrig
Over Lap
I
Enumera
tion
R/W
TO
0: Off / 1: ReadOut
0 1 0
TO=[Param.]<CR><LF>
TO?<CR><LF>
ExposureMode
I
Enumera
tion
R/W
EM
0: Off
1: Timed
2: TriggerWidth
0 2 0
EM=[Param.]<CR><LF>
EM?<CR><LF>
ExposureTimeR
aw
I Integer
R/W
PE
Min~Max[us]
10
80000
00
18000
PE=[Param.]<CR><LF>
PE?<CR><LF>
ExposureAuto
I
Enumera
tion
R/W
ASC
0: Off
2: Once
1: Continuous
0 2 2
ASC=[Param.]<CR><LF>
ASC?<CR><LF>
2.4.5 Acquisition Control
- 80 -
Page 83

2.4.6 Digital I/O Control
Name
Interface
Acces
s
Short
ASCII
Values
MIN M
AX
DE
FA
UL
T
Description
LineInverter_Line1
I Boolean
R/W
LI0
False/True
0 1 0
LI0=[Param.]<CR><LF>
LI0?<CR><LF>
LineInverter_Line8
I Boolean
R/W
LI1
False/True
0 1 0
LI1=[Param.]<CR><LF>
LI1?<CR><LF>
LineInverter_Line9
I Boolean
R/W
LI2
False/True
0 1 0
LI2=[Param.]<CR><LF>
LI2?<CR><LF>
LineInverter_Nand0In
1
I Boolean
R/W
ND0IN
V1
False/True
0 1 0
ND0INV1=[Param.]<CR><LF>
ND0INV1?<CR><LF>
LineInverter_Nand0In
2
I Boolean
R/W
ND0IN
V2
False/True
0 1 0
ND0INV2=[Param.]<CR><LF>
ND0INV2?<CR><LF>
LineInverter_Nand1In
1
I Boolean
R/W
ND1IN
V1
False/True
0 1 0
ND1INV1=[Param.]<CR><LF>
ND0INV1?<CR><LF>
LineInverter_Nand1In
2
I Boolean
R/W
ND1IN
V2
False/True
0 1 0
ND1INV2=[Param.]<CR><LF>
ND0INV2?<CR><LF>
LineSource_Line1
I
Enume
ration
R/W
LS0
0: Low
1: High
3: Frame
TriggerWait
4: Frame
Active
5: Exposure
Active
6: Fval
7: Lval
8: Pulse
Generator0
9: Pulse
Generator1
10: Pulse
Generator2
11: Pulse
Generator3
12: TTL_In
13:
CL_CC1_In
14: Nand0
15: Nand1
16: TTL_In2
(Option)
17: LVDS_In
(Option)
0
17
0
LS0=[Param.]<CR><LF>
LS0?<CR><LF>
For 12pin TTL out
LineSource_Line8
I
Enume
ration
R/W
LS1
Same as for
Line1
0
17
0
LS1=[Param.]<CR><LF>
LS1?<CR><LF>
For Option TTL out
LineSource_Line9
I
Enume
ration
R/W
LS2
Same as for
Line1
0
17
0
LS2=[Param.]<CR><LF>
LS2?<CR><LF>
For Option TTL out
LineSource_Nand0In1
I
Enume
ration
R/W
ND0IN1
Same as for
Line1
0
17
0
ND0IN1=[Param.]<CR><LF>
ND0IN1?<CR><LF>
LineSource_Nand0In2
I
Enume
ration
R/W
ND0IN2
Same as for
Line1
0
17
0
ND0IN2=[Param.]<CR><LF>
ND0IN2?<CR><LF>
LineSource_Nand1In1
I
Enume
ration
R/W
ND1IN1
Same as for
Line1
0
17
0
ND1IN1=[Param.]<CR><LF>
ND1IN1?<CR><LF>
SP-5000M-PMCL / SP-5000C-PMCL
- 81 -
Page 84

LineSource_Nand1In2
I
Enume
ration
R/W
ND1IN2
Same as for
Line1
0
17
0
ND1IN2=[Param.]<CR><LF>
ND1IN2?<CR><LF>
Name
Interface
Acc
ess
Short
ASCII
Values
MIN
MAX
DEFAU
LT
Description
GainRawDigital
All
I Integer
R/W
FGA
min~0~max
100
1600
100
FGA=[Param.]<CR><L
F>
FGA?<CR><LF>
GainRawDigital
RedAll
I Integer
R/W
PGR
min~0~max
-4533
28400
0
PGR=[Param.]<CR><L
F>
PGR?<CR><LF>
(Bayer model only)
GainRawDigital
BlueAll
I Integer
R/W
PGB
min~0~max
-4533
28400
0
PGB=[Param.]<CR><L
F>
PGB?<CR><LF>
(Bayer model only)
GainAuto
I
Enumerat
ion
R/W
AGC
0: Off
1: Continuous
2: Once
0 2 0
AGC=[Param.]<CR><L
F>
AGC?<CR><LF>
BlackLevelRaw
All
I Integer
R/W
BL
min~0~max
-256
255
0
BL=[Param.]<CR><LF>
BL?<CR><LF>
BlackLevelRaw
Red
I Integer
R/W
BLR
min~0~max
-512
511
0
BLR1=[Param.]<CR><L
F>
BLR1?<CR><LF>
(Bayer model only)
BlackLevelRaw
Blue
I Integer
R/W
BLB
min~0~max
-512
511
0
BLB1=[Param.]<CR><L
F>
BLB1?<CR><LF>
(Bayer model only)
BalanceWhiteA
uto
I
Enumerat
ion
R/W
AWB
0: Off
1: Once
2: Continuous
0 2 0
AWB=[Param.]<CR><L
F>
AWB?<CR><LF>
(Bayer model only)
Name
Interface
Acce
ss
Short
ASCII
Values
MIN
MAX
DEFAU
LT
Description
LUTValueRed
I Integer
R/W
LUTR
Param 1: LUT index
Param 2:LUTdata
(Min~Max)
(Bayer model only)
0
4095
γ09
相当値
LUT*=[Param1],[Para
m2]<CR><LF>
LUT*?[Param1]<CR><L
F>
LUTValueGreen
(Mono)
I Integer
R/W
LUTG
Param 1: LUT index
Param 2:LUTdata
(Min~Max)
0
4095
LUTValueBlue
I Integer
R/W
LUTB
Param 1: LUT index
Param 2:LUTdata
(Min~Max)
(Bayer model only)
0
4095
2.4.7 Analogue Control
SP-5000M-PMCL / SP-5000C-PMCL
2.4.8 LUT Control
- 82 -
Page 85

SP-5000M-PMCL / SP-5000C-PMCL
Name
Interface
Acce
ss
Short
ASCII
Values
MIN
MAX
DEFAU
LT
Description
DeviceTapGeom
etry
I
Enumera
tion
R/(
W)
TAGM
1: Geometry_1X2_1Y
3: Geometry_1X4_1Y
5: Geometry_1X8_1Y
6: Geometry_1X10_1Y
1 6 5
TAGM=[Param.]<CR><
LF>
TAGM?<CR><LF>
Name
Interface
Access
Short
ASCII
Values
MIN
MAX
DE
FAULT
Description
UserSetLoad
I Command
(R)/W
LD
0:
Default
1:
UserSet1
2:
UserSet2
3:
UserSet3
0 3 0
LD=[Param.]<CR><LF>
LD?<CR><LF>
UserSetSave
I Command
(R)/W
SA
1:
UserSet1
2:
UserSet2
3:
UserSet3
1 3 1
SA=[Param.]<CR><LF>
SA?<CR><LF>
Name
Interface
Acce
ss
Short
ASCII
Values
MIN
MAX
DE
FAUL
T
Description
BlemishWhiteEn
able
I Boolean
R/W
BMW
0: False
1: True
0 1 0
BMW=[Param.]<CR><L
F>
BMW?<CR><LF>
BlemishWhiteD
etect
I
Comman
d
W/O
BMRC
W
0 0 0 0 BMRCW=0<CR><LF>
BlemishWhiteD
etect Threshold
I Integer
R/W
BMTH
W
0 0 100
10
BMTHW=[Param.]<CR>
<LF>
BMTHW?<CR><LF>
BlemishWhiteD
etect PositionX
I Integer
R/W
BMPXW
Param 1: Blemish
index
Param 2: X
position(Min~Max)
0
2559
0
BMPXW=[Param1],[Par
am2]<CR><LF>
BMPXW?
[Param1]<CR><LF>
BlemishWhiteD
etect PositionY
I Integer
R/W
BMPYW
Param 1: Blemish
index
Param 2: Y
position(Min~Max)
0
2047
0
BMPYW=[Param1],[Par
am2]<CR><LF>
BMPYW?
[Param1]<CR><LF>
ShadingCorrecti
on Mode
I
Enumera
tion
R/W
SDCM
0: Flat Shading
1: Color Shading*
(*Bayer model only)
0 1 0
SDCM=[Param.]<CR><L
F>
SDCM?<CR><LF>
ShadingCorrect
I
Comman
d
W/O
RS 0 0 0 BMRCW=0<CR><LF>
RequestShading
DetectResult
I
Enumera
tion
R/O
SDRS
0=Complete.
1=Too Bright.
2=Too dark.
3=Timeout Error.
0 6 0
SDRS?<CR><LF>
2.4.9 Transport Layer Control
2.4.10 User Set Control
2.4.11 JAI-Custom
- 83 -
Page 86

SP-5000M-PMCL / SP-5000C-PMCL
4=Busy.
5=Limit.
6= Trig is not set as
Normal.
ShadingMode
I
Enumera
tion
R/W
SDM
0: OFF
1: User 1
2: User 2
3: User 3
0 3 0
SDM=[Param.]<CR><LF
>
SDM?<CR><LF>
VideoSendMode
I
Enumera
tion
R/W
VSM
0: Normal
1: Trigger Sequence
2: Command
Sequence
3: Multi Roi Mode
0 3 0
VSM=[Param.]<CR><LF
>
VSM?<CR><LF>
SequenceModeI
ndex
I
Enumera
tion
R/W
SQI
0: Index0
1: Index1
2: Index2
3: Index3
4: Index4
5: Index5
6: Index6
7: Index7
8: Index8
9: Index9
0 9 0
SQI=[Param.]<CR><LF
>
SQI?<CR><LF>
SequenceModeF
rame
Count0
I Integer
R/W
SQF1
Min~Max
1
255
1
SQF1=[Param.]<CR><L
F>
SQI1?<CR><LF>
SequenceModeF
rame
Count1
I Integer
R/W
SQF2
Min~Max
1
255
1
SQF2=[Param.]<CR><L
F>
SQI2?<CR><LF>
SequenceNodeF
rame
Count2
I Integer
R/W
SQF3
Min~Max
1
255
1
SQF3=[Param.]<CR><L
F>
SQI3?<CR><LF>
SequenceModeF
rame
Count3
I Integer
R/W
SQF4
Min~Max
1
255
1
SQF4=[Param.]<CR><L
F>
SQI4?<CR><LF>
SequenceModeF
rame
Count4
I Integer
R/W
SQF5
Min~Max
1
255
1
SQF5=[Param.]<CR><L
F>
SQI5?<CR><LF>
SequenceModeF
rame
Count5
I Integer
R/W
SQF6
Min~Max
1
255
1
SQF6=[Param.]<CR><L
F>
SQI6?<CR><LF>
SequenceModeF
rame
Count6
I Integer
R/W
SQF7
Min~Max
1
255
1
SQF7=[Param.]<CR><L
F>
SQI7?<CR><LF>
SequenceModeF
rame
Count7
I Integer
R/W
SQF8
Min~Max
1
255
1
SQF8=[Param.]<CR><L
F>
SQI8?<CR><LF>
SequenceModeF
rame
Count8
I Integer
R/W
SQF9
Min~Max
1
255
1
SQF9=[Param.]<CR><L
F>
SQI9?<CR><LF>
SequenceModeF
rame
Count9
I Integer
R/W
SQF10
Min~Max
1
255
1
SQF10=[Param.]<CR><
LF>
SQI10?<CR><LF>
SequenceModeN
ext
Index0
I
Enumera
tion
R/W
SQNI1
Same as
SequenceRoiIndex
0 9 0
SQNI1=[Param.]<CR><
LF>
SQNI1?<CR><LF>
SequenceModeN
ext
Index1
I
Enumera
tion
R/W
SQNI2
Same as
SequenceRoiIndex
0 9 0
SQNI2=[Param.]<CR><
LF>
SQNI2?<CR><LF>
- 84 -
Page 87

SP-5000M-PMCL / SP-5000C-PMCL
SequenceModeN
ext
Index2
I
Enumera
tion
R/W
SQNI3
Same as
SequenceRoiIndex
0 9 0
SQNI3=[Param.]<CR><
LF>
SQNI3?<CR><LF>
SequenceModeN
ext
Index3
I
Enumera
tion
R/W
SQNI4
Same as
SequenceRoiIndex
0 9 0
SQNI4=[Param.]<CR><
LF>
SQNI4?<CR><LF>
SequenceModeN
ext
Index4
I
Enumera
tion
R/W
SQNI5
Same as
SequenceRoiIndex
0 9 0
SQNI5=[Param.]<CR><
LF>
SQNI5?<CR><LF>
SequenceModeN
ext
Index5
I
Enumera
tion
R/W
SQNI6
Same as
SequenceRoiIndex
0 9 0
SQNI6=[Param.]<CR><
LF>
SQNI6?<CR><LF>
SequenceModeN
ext
Index6
I
Enumera
tion
R/W
SQNI7
Same as
SequenceRoiIndex
0 9 0
SQNI7=[Param.]<CR><
LF>
SQNI7?<CR><LF>
SequenceModeN
ext
Index7
I
Enumera
tion
R/W
SQNI8
Same as
SequenceRoiIndex
0 9 0
SQNI8=[Param.]<CR><
LF>
SQNI8?<CR><LF>
SequenceModeN
ext
Index8
I
Enumera
tion
R/W
SQNI9
Same as
SequenceRoiIndex
0 9 0
SQNI9=[Param.]<CR><
LF>
SQNI9?<CR><LF>
SequenceModeN
ext
Index9
I
Enumera
tion
R/W
SQNI10
Same as
SequenceRoiIndex
0 9 0
SQNI10=[Param.]<CR>
<LF>
SQNI10?<CR><LF>
SequenceMode
Height0
I Integer
R/W
SQH1
Min~Max
1(Mon
o)
2(Bay
er)
2048
2048
SQH1=[Param.]<CR><L
F>
SQH1?<CR><LF>
SequenceMode
Height1
I Integer
R/W
SQH2
Min~Max
1(Mon
o)
2(Bay
er)
2048
2048
SQH2=[Param.]<CR><L
F>
SQH2?<CR><LF>
SequenceMode
Height2
I Integer
R/W
SQH3
Min~Max
1(Mon
o)
2(Bay
er)
2048
2048
SQH3=[Param.]<CR><L
F>
SQH3?<CR><LF>
SequenceMode
Height3
I Integer
R/W
SQH4
Min~Max
1(Mon
o)
2(Bay
er)
2048
2048
SQH4=[Param.]<CR><L
F>
SQH4?<CR><LF>
SequenceMode
Height4
I Integer
R/W
SQH5
Min~Max
1(Mon
o)
2(Bay
er)
2048
2048
SQH5=[Param.]<CR><L
F>
SQH5?<CR><LF>
SequenceMode
Height5
I Integer
R/W
SQH6
Min~Max
1(Mon
o)
2(Bay
er)
2048
2048
SQH6=[Param.]<CR><L
F>
SQH6?<CR><LF>
SequenceMode
Height6
I Integer
R/W
SQH7
Min~Max
1(Mon
o)
2(Bay
er)
2048
2048
SQH7=[Param.]<CR><L
F>
SQH7?<CR><LF>
SequenceMode
Height7
I Integer
R/W
SQH8
Min~Max
1(Mon
o)
2(Bay
er)
2048
2048
SQH8=[Param.]<CR><L
F>
SQH8?<CR><LF>
SequenceMode
Height8
I Integer
R/W
SQH9
Min~Max
1(Mon
o)
2(Bay
er)
2048
2048
SQH9=[Param.]<CR><L
F>
SQH9?<CR><LF>
- 85 -
Page 88

SP-5000M-PMCL / SP-5000C-PMCL
SequenceMode
Height9
I Integer
R/W
SQH10
Min~Max
1(Mon
o)
2(Bay
er)
2048
2048
SQH10=[Param.]<CR><
LF>
SQH10?<CR><LF>
SequenceMode
OffsetY0
I Integer
R/W
SQOY1
Min~Max
0
2047
(Mno)
2046
(Baye
r)
0
SQOY1=[Param.]<CR><
LF>
SQOY1?<CR><LF>
SequenceMode
OffsetY1
I Integer
R/W
SQOY2
Min~Max
0
2047
(Mno)
2046
(Baye
r)
0
SQOY2=[Param.]<CR><
LF>
SQOY2?<CR><LF>
SequenceMode
OffsetY2
I Integer
R/W
SQOY3
Min~Max
0
2047
(Mno)
2046
(Baye
r)
0
SQOY3=[Param.]<CR><
LF>
SQOY3?<CR><LF>
SequenceMode
OffsetY3
I Integer
R/W
SQOY4
Min~Max
0
2047
(Mno)
2046
(Baye
r)
0
SQOY4=[Param.]<CR><
LF>
SQOY4?<CR><LF>
SequenceMode
OffsetY4
I Integer
R/W
SQOY5
Min~Max
0
2047
(Mno)
2046
(Baye
r)
0
SQOY5=[Param.]<CR><
LF>
SQOY5?<CR><LF>
SequenceMode
OffsetY5
I Integer
R/W
SQOY6
Min~Max
0
2047
(Mno)
2046
(Baye
r)
0
SQOY6=[Param.]<CR><
LF>
SQOY6?<CR><LF>
SequenceMode
OffsetY6
I Integer
R/W
SQOY7
Min~Max
0
2047
(Mno)
2046
(Baye
r)
0
SQOY7=[Param.]<CR><
LF>
SQOY7?<CR><LF>
SequenceMode
OffsetY7
I Integer
R/W
SQOY8
Min~Max
0
2047
(Mno)
2046
(Baye
r)
0
SQOY8=[Param.]<CR><
LF>
SQOY8?<CR><LF>
SequenceMode
OffsetY8
I Integer
R/W
SQOY9
Min~Max
0
2047
(Mno)
2046
(Baye
r)
0
SQOY9=[Param.]<CR><
LF>
SQOY9?<CR><LF>
SequenceMode
OffsetY9
I Integer
R/W
SQOY1
0
Min~Max
0
2047
(Mno)
2046
(Baye
r)
0
SQOY10=[Param.]<CR>
<LF>
SQOY10?<CR><LF>
SequenceMode
Gain0
I Integer
R/W
SQGA1
Min~Max
100
1600
0
SQGA1=[Param.]<CR>
<LF>
SQGA1?<CR><LF>
SequenceMode
Gain1
I Integer
R/W
SQGA2
Min~Max
100
1600
0
SQGA2=[Param.]<CR>
<LF>
SQGA2?<CR><LF>
- 86 -
Page 89

SP-5000M-PMCL / SP-5000C-PMCL
SequenceMode
Gain2
I Integer
R/W
SQGA3
Min~Max
100
1600
0
SQGA3=[Param.]<CR>
<LF>
SQGA3?<CR><LF>
SequenceMode
Gain3
I Integer
R/W
SQGA4
Min~Max
100
1600
0
SQGA4=[Param.]<CR>
<LF>
SQGA4?<CR><LF>
SequenceMode
Gain4
I Integer
R/W
SQGA5
Min~Max
100
1600
0
SQGA5=[Param.]<CR>
<LF>
SQGA5?<CR><LF>
SequenceMode
Gain5
I Integer
R/W
SQGA6
Min~Max
100
1600
0
SQGA6=[Param.]<CR>
<LF>
SQGA6?<CR><LF>
SequenceMode
Gain6
I Integer
R/W
SQGA7
Min~Max
100
1600
0
SQGA7=[Param.]<CR>
<LF>
SQGA7?<CR><LF>
SequenceMode
Gain7
I Integer
R/W
SQGA8
Min~Max
100
1600
0
SQGA8=[Param.]<CR>
<LF>
SQGA8?<CR><LF>
SequenceMode
Gain8
I Integer
R/W
SQGA9
Min~Max
100
1600
0
SQGA9=[Param.]<CR>
<LF>
SQGA9?<CR><LF>
SequenceMode
Gain9
I Integer
R/W
SQGA1
0
Min~Max
100
1600
0
SQGA10=[Param.]<CR
><LF>
SQGA10?<CR><LF>
SequenceMode
ExposureTime0
I Integer
R/W
SQPE1
Min~Max
10
8000000
18000
SQPE1=[Param.]<CR><
LF>
SQPE1?<CR><LF>
SequenceMode
ExposureTime1
I Integer
R/W
SQPE2
Min~Max
10
8000000
18000
SQPE2=[Param.]<CR><
LF>
SQPE2?<CR><LF>
SequenceMode
ExposureTime2
I Integer
R/W
SQPE3
Min~Max
10
8000000
18000
SQPE3=[Param.]<CR><
LF>
SQPE3?<CR><LF>
SequenceMode
ExposureTime3
I Integer
R/W
SQPE4
Min~Max
10
8000000
18000
SQPE4=[Param.]<CR><
LF>
SQPE4?<CR><LF>
SequenceMode
ExposureTime4
I Integer
R/W
SQPE5
Min~Max
10
8000000
18000
SQPE5=[Param.]<CR><
LF>
SQPE5?<CR><LF>
SequenceMode
ExposureTime5
I Integer
R/W
SQPE6
Min~Max
10
8000000
18000
SQPE6=[Param.]<CR><
LF>
SQPE6?<CR><LF>
SequenceMode
ExposureTime6
I Integer
R/W
SQPE7
Min~Max
10
8000000
18000
SQPE7=[Param.]<CR><
LF>
SQPE7?<CR><LF>
SequenceMode
ExposureTime7
I Integer
R/W
SQPE8
Min~Max
10
8000000
18000
SQPE8=[Param.]<CR><
LF>
SQPE8?<CR><LF>
SequenceMode
ExposureTime8
I Integer
R/W
SQPE9
Min~Max
10
8000000
18000
SQPE9=[Param.]<CR><
LF>
SQPE9?<CR><LF>
SequenceMode
ExposureTime9
I Integer
R/W
SQPE1
0
Min~Max
10
8000000
18000
SQPE10=[Param.]<CR>
<LF>
SQPE10?<CR><LF>
SequenceMode
Hbinning0
I
Enumera
tion
R/W
SQHB1
1: Hbinning = OFF
2: Hbinning = ON
1 2 1
SQHB1=[Param.]<CR><
LF>
SQHB1?<CR><LF>
(Mono model only)
- 87 -
Page 90

SP-5000M-PMCL / SP-5000C-PMCL
SequenceMode
Hbinning1
I
Enumera
tion
R/W
SQHB2
1: Hbinning = OFF
2: Hbinning = ON
1 2 1
SQHB2=[Param.]<CR><
LF>
SQHB2?<CR><LF>
(Mono model only)
SequenceMode
Hbinning2
I
Enumera
tion
R/W
SQHB3
1: Hbinning = OFF
2: Hbinning = ON
1 2 1
SQHB3=[Param.]<CR><
LF>
SQHB3?<CR><LF>
(Mono model only)
SequenceMode
Hbinning3
I
Enumera
tion
R/W
SQHB4
1: Hbinning = OFF
2: Hbinning = ON
1 2 1
SQHB4=[Param.]<CR><
LF>
SQHB4?<CR><LF>
(Mono model only)
SequenceMode
Hbinning4
I
Enumera
tion
R/W
SQHB5
1: Hbinning = OFF
2: Hbinning = ON
1 2 1
SQHB5=[Param.]<CR><
LF>
SQHB5?<CR><LF>
(Mono model only)
SequenceMode
Hbinning5
I
Enumera
tion
R/W
SQHB6
1: Hbinning = OFF
2: Hbinning = ON
1 2 1
SQHB6=[Param.]<CR><
LF>
SQHB6?<CR><LF>
(Mono model only)
SequenceMode
Hbinning6
I
Enumera
tion
R/W
SQHB7
1: Hbinning = OFF
2: Hbinning = ON
1 2 1
SQHB7=[Param.]<CR><
LF>
SQHB7?<CR><LF>
(Mono model only)
SequenceMode
Hbinning7
I
Enumera
tion
R/W
SQHB8
1: Hbinning = OFF
2: Hbinning = ON
1 2 1
SQHB8=[Param.]<CR><
LF>
SQHB8?<CR><LF>
(Mono model only)
SequenceMode
Hbinning8
I
Enumera
tion
R/W
SQHB9
1: Hbinning = OFF
2: Hbinning = ON
1 2 1
SQHB9=[Param.]<CR><
LF>
SQHB9?<CR><LF>
(Mono model only)
SequenceMode
Hbinning9
I
Enumera
tion
R/W
SQHB1
0
1: Hbinning = OFF
2: Hbinning = ON
1 2 1
SQHB10=[Param.]<CR>
<LF>
SQHB10?<CR><LF>
(Mono model only)
SequenceMode
Vbinning0
I
Enumera
tion
R/W
SQVB1
1: Hbinning = OFF
2: Hbinning = ON
1 2 1
SQVB1=[Param.]<CR><
LF>
SQVB1?<CR><LF>
(Mono model only)
SequenceMode
Vbinning1
I
Enumera
tion
R/W
SQVB2
1: Hbinning = OFF
2: Hbinning = ON
1 2 1
SQVB2=[Param.]<CR><
LF>
SQVB2?<CR><LF>
(Mono model only)
SequenceMode
Vbinning2
I
Enumera
tion
R/W
SQVB3
1: Hbinning = OFF
2: Hbinning = ON
1 2 1
SQVB3=[Param.]<CR><
LF>
SQVB3?<CR><LF>
(Mono model only)
SequenceMode
Vbinning3
I
Enumera
tion
R/W
SQVB4
1: Hbinning = OFF
2: Hbinning = ON
1 2 1
SQVB4=[Param.]<CR><
LF>
SQVB4?<CR><LF>
(Mono model only)
SequenceMode
Vbinning4
I
Enumera
tion
R/W
SQVB5
1: Hbinning = OFF
2: Hbinning = ON
1 2 1
SQVB5=[Param.]<CR><
LF>
SQVB5?<CR><LF>
(Mono model only)
SequenceMode
Vbinning5
I
Enumera
tion
R/W
SQVB6
1: Hbinning = OFF
2: Hbinning = ON
1 2 1
SQVB6=[Param.]<CR><
LF>
SQVB6?<CR><LF>
(Mono model only)
- 88 -
Page 91

SP-5000M-PMCL / SP-5000C-PMCL
SequenceMode
Vbinning6
I
Enumera
tion
R/W
SQVB7
1: Hbinning = OFF
2: Hbinning = ON
1 2 1
SQVB7=[Param.]<CR><
LF>
SQVB7?<CR><LF>
(Mono model only)
SequenceMode
Vbinning7
I
Enumera
tion
R/W
SQVB8
1: Hbinning = OFF
2: Hbinning = ON
1 2 1
SQVB8=[Param.]<CR><
LF>
SQVB8?<CR><LF>
(Mono model only)
SequenceMode
Vbinning8
I
Enumera
tion
R/W
SQVB9
1: Hbinning = OFF
2: Hbinning = ON
1 2 1
SQVB9=[Param.]<CR><
LF>
SQVB9?<CR><LF>
(Mono model only)
SequenceMode
Vbinning9
I
Enumera
tion
R/W
SQVB1
0
1: Hbinning = OFF
2: Hbinning = ON
1 2 1
SQVB10=[Param.]<CR>
<LF>
SQVB10?<CR><LF>
(Mono model only)
SequenceMode
LutEnable0
I
Enumera
tion
R/W
SQLUT
1
Off/On
0 1 0
SQLUT1=[Param.]<CR>
<LF>
SQLUT1?<CR><LF>
SequenceMode
LutEnable1
I
Enumera
tion
R/W
SQLUT
2
Off/On
0 1 0
SQLUT2=[Param.]<CR>
<LF>
SQLUT2?<CR><LF>
SequenceMode
LutEnable2
I
Enumera
tion
R/W
SQLUT
3
Off/On
0 1 0
SQLUT3=[Param.]<CR>
<LF>
SQLUT3?<CR><LF>
SequenceMode
LutEnable3
I
Enumera
tion
R/W
SQLUT
4
Off/On
0 1 0
SQLUT4=[Param.]<CR>
<LF>
SQLUT4?<CR><LF>
SequenceMode
LutEnable4
I
Enumera
tion
R/W
SQLUT
5
Off/On
0 1 0
SQLUT5=[Param.]<CR>
<LF>
SQLUT5?<CR><LF>
SequenceMode
LutEnable5
I
Enumera
tion
R/W
SQLUT
6
Off/On
0 1 0
SQLUT6=[Param.]<CR>
<LF>
SQLUT6?<CR><LF>
SequenceMode
LutEnable6
I
Enumera
tion
R/W
SQLUT
7
Off/On
0 1 0
SQLUT7=[Param.]<CR>
<LF>
SQLUT7?<CR><LF>
SequenceMode
LutEnable7
I
Enumera
tion
R/W
SQLUT
8
Off/On
0 1 0
SQLUT8=[Param.]<CR>
<LF>
SQLUT8?<CR><LF>
SequenceMode
LutEnable8
I
Enumera
tion
R/W
SQLUT
9
Off/On
0 1 0
SQLUT9=[Param.]<CR>
<LF>
SQLUT9?<CR><LF>
SequenceMode
LutEnable9
I
Enumera
tion
R/W
SQLUT
10
Off/On
0 1 0
SQLUT10=[Param.]<CR
><LF>
SQLUT10?<CR><LF>
SequenceMode
BlackLevel0
I Integer
R/W
SQBL1
Min~Max
-256
255
0
SQBL1=[Param.]<CR><
LF>
SQBL1?<CR><LF>
SequenceMode
BlackLevel1
I Integer
R/W
SQBL2
Min~Max
-256
255
0
SQBL2=[Param.]<CR><
LF>
SQBL2?<CR><LF>
SequenceMode
BlackLevel2
I Integer
R/W
SQBL3
Min~Max
-256
255
0
SQBL3=[Param.]<CR><
LF>
SQBL3?<CR><LF>
SequenceMode
BlackLevel3
I Integer
R/W
SQBL4
Min~Max
-256
255
0
SQBL4=[Param.]<CR><
LF>
SQBL4?<CR><LF>
SequenceMode
BlackLevel4
I Integer
R/W
SQBL5
Min~Max
-256
255
0
SQBL5=[Param.]<CR><
LF>
SQBL5?<CR><LF>
- 89 -
Page 92

SP-5000M-PMCL / SP-5000C-PMCL
SequenceMode
BlackLevel5
I Integer
R/W
SQBL6
Min~Max
-256
255
0
SQBL6=[Param.]<CR><
LF>
SQBL6?<CR><LF>
SequenceMode
BlackLevel6
I Integer
R/W
SQBL7
Min~Max
-256
255
0
SQBL7=[Param.]<CR><
LF>
SQBL7?<CR><LF>
SequenceMode
BlackLevel7
I Integer
R/W
SQBL8
Min~Max
-256
255
0
SQBL8=[Param.]<CR><
LF>
SQBL8?<CR><LF>
SequenceMode
BlackLevel8
I Integer
R/W
SQBL9
Min~Max
-256
255
0
SQBL9=[Param.]<CR><
LF>
SQBL9?<CR><LF>
SequenceMode
BlackLevel9
I Integer
R/W
SQBL10
Min~Max
-256
255
0
SQBL10=[Param.]<CR>
<LF>
SQBL10?<CR><LF>
SequenceMode
GainRed0
I Integer
R/W
SQPGR
1
Min~Max
-4533
17713
0
SQPGR1=[Param.]<CR
><LF>
SQPGR1?<CR><LF>
(Bayer model only)
SequenceMode
GainRed1
I Integer
R/W
SQPGR
2
Min~Max
-4533
17713
0
SQPGR2=[Param.]<CR
><LF>
SQPGR2?<CR><LF>
(Bayer model only)
SequenceMode
GainRed2
I Integer
R/W
SQPGR
3
Min~Max
-4533
17713
0
SQPGR3=[Param.]<CR
><LF>
SQPGR3?<CR><LF>
(Bayer model only)
SequenceMode
GainRed3
I Integer
R/W
SQPGR
4
Min~Max
-4533
17713
0
SQPGR4=[Param.]<CR
><LF>
SQPGR4?<CR><LF>
(Bayer model only)
SequenceMode
GainRed4
I Integer
R/W
SQPGR
5
Min~Max
-4533
17713
0
SQPGR5=[Param.]<CR
><LF>
SQPGR5?<CR><LF>
(Bayer model only)
SequenceMode
GainRed5
I Integer
R/W
SQPGR
6
Min~Max
-4533
17713
0
SQPGR6=[Param.]<CR
><LF>
SQPGR6?<CR><LF>
(Bayer model only)
SequenceMode
GainRed6
I Integer
R/W
SQPGR
7
Min~Max
-4533
17713
0
SQPGR7=[Param.]<CR
><LF>
SQPGR7?<CR><LF>
(Bayer model only)
SequenceMode
GainRed7
I Integer
R/W
SQPGR
8
Min~Max
-4533
17713
0
SQPGR8=[Param.]<CR
><LF>
SQPGR8?<CR><LF>
(Bayer model only)
SequenceMode
GainRed8
I Integer
R/W
SQPGR
9
Min~Max
-4533
17713
0
SQPGR9=[Param.]<CR
><LF>
SQPGR9?<CR><LF>
(Bayer model only)
SequenceMode
GainRed9
I Integer
R/W
SQPGR
10
Min~Max
-4533
17713
0
SQPGR10=[Param.]<C
R><LF>
SQPGR10?<CR><LF>
(Bayer model only)
SequenceMode
GainBlue0
I Integer
R/W
SQPGB
1
Min~Max
-4533
17713
0
SQPGB1=[Param.]<CR
><LF>
SQPGB1?<CR><LF>
(Bayer model only)
- 90 -
Page 93

SP-5000M-PMCL / SP-5000C-PMCL
SequenceMode
GainBlue1
I Integer
R/W
SQPGB
2
Min~Max
-4533
17713
0
SQPGB2=[Param.]<CR
><LF>
SQPGB2?<CR><LF>
(Bayer model only)
SequenceMode
GainBlue2
I Integer
R/W
SQPGB
3
Min~Max
-4533
17713
0
SQPGB3=[Param.]<CR
><LF>
SQPGB3?<CR><LF>
(Bayer model only)
SequenceMode
GainBlue3
I Integer
R/W
SQPGB
4
Min~Max
-4533
17713
0
SQPGB4=[Param.]<CR
><LF>
SQPGB4?<CR><LF>
(Bayer model only)
SequenceMode
GainBlue4
I Integer
R/W
SQPGB
5
Min~Max
-4533
17713
0
SQPGB5=[Param.]<CR
><LF>
SQPGB5?<CR><LF>
(Bayer model only)
SequenceMode
GainBlue5
I Integer
R/W
SQPGB
6
Min~Max
-4533
17713
0
SQPGB6=[Param.]<CR
><LF>
SQPGB6?<CR><LF>
(Bayer model only)
SequenceMode
GainBlue6
I Integer
R/W
SQPGB
7
Min~Max
-4533
17713
0
SQPGB7=[Param.]<CR
><LF>
SQPGB7?<CR><LF>
(Bayer model only)
SequenceMode
GainBlue7
I Integer
R/W
SQPGB
8
Min~Max
-4533
17713
0
SQPGB8=[Param.]<CR
><LF>
SQPGB8?<CR><LF>
(Bayer model only)
SequenceMode
GainBlue8
I Integer
R/W
SQPGB
9
Min~Max
-4533
17713
0
SQPGB9=[Param.]<CR
><LF>
SQPGB9?<CR><LF>
(Bayer model only)
SequenceMode
GainBlue9
I Integer
R/W
SQPGB
10
Min~Max
-4533
17713
0
SQPGB10=[Param.]<C
R><LF>
SQPGB10?<CR><LF>
(Bayer model only)
CommnadSeque
nce
Index
I
Enumera
tion
R/W
SQI
Same as
SequenceModeIndex
0 9 0
CSQI=[Param.]<CR><L
F>
CSQI?<CR><LF>
CurrentSequenc
e
Index
I
Enumera
tion
R/O
SQIDX
Same as
SequenceModeIndex
0 9 0
SQIDX?<CR><LF>
SequenceReset
I
Enumera
tion
W/O
SQRST
0 0 0
0
SQRST=[Param.]<CR><
LF>
SequenceLutMo
de
I
Enumera
tion
R/W
SQLUT
0: Gamma
1: LUT
0 1 0
SQLUT=[Param.]<CR><
LF>
SQLUT?<CR><LF>
MultiRoiIndexM
ax
I Integer
R/W
MRIM
Min~Max
1 8 1
MRIM=[Param.]<CR><L
F>
MRIM?<CR><LF>
MultiRoiWidth
I Integer
R/W
MRW
Min~Max
8
5120
8
MRW=[Param.]<CR><L
F>
MRW?<CR><LF>
MultiRoiHeight1
I Integer
R/W
MRH1
Min~Max
0
3840
1
MRH1=[Param.]<CR><
LF>
MRH1?<CR><LF>
MultiRoiHeight2
I Integer
R/W
MRH2
Min~Max
0
3840
1
MRH2=[Param.]<CR><
LF>
MRH2?<CR><LF>
- 91 -
Page 94

SP-5000M-PMCL / SP-5000C-PMCL
MultiRoiHeight3
I Integer
R/W
MRH3
Min~Max
0
3840
1
MRH3=[Param.]<CR><
LF>
MRH3?<CR><LF>
MultiRoiHeight4
I Integer
R/W
MRH4
Min~Max
0
3840
1
MRH4=[Param.]<CR><
LF>
MRH4?<CR><LF>
MultiRoiHeight5
I Integer
R/W
MRH5
Min~Max
0
3840
1
MRH5=[Param.]<CR><
LF>
MRH5?<CR><LF>
MultiRoiHeight6
I Integer
R/W
MRH6
Min~Max
0
3840
1
MRH6=[Param.]<CR><
LF>
MRH6?<CR><LF>
MultiRoiHeight7
I Integer
R/W
MRH7
Min~Max
0
3840
1
MRH7=[Param.]<CR><
LF>
MRH7?<CR><LF>
MultiRoiHeight8
I Integer
R/W
MRH8
Min~Max
0
3840
1
MRH8=[Param.]<CR><
LF>
MRH8?<CR><LF>
MultiRoiOffsetX
1
I Integer
R/W
MROX1
Min~Max
0
5118
0
MROX1=[Param.]<CR>
<LF>
MROX1?<CR><LF>
MultiRoiOffsetX
2
I Integer
R/W
MROX2
Min~Max
0
5118
0
MROX2=[Param.]<CR>
<LF>
MROX2?<CR><LF>
MultiRoiOffsetX
3
I Integer
R/W
MROX3
Min~Max
0
5118
0
MROX3=[Param.]<CR>
<LF>
MROX3?<CR><LF>
MultiRoiOffsetX
4
I Integer
R/W
MROX4
Min~Max
0
5118
0
MROX4=[Param.]<CR>
<LF>
MROX4?<CR><LF>
MultiRoiOffsetX
5
I Integer
R/W
MROX5
Min~Max
0
5118
0
MROX5=[Param.]<CR>
<LF>
MROX5?<CR><LF>
MultiRoiOffsetX
6
I Integer
R/W
MROX6
Min~Max
0
5118
0
MROX6=[Param.]<CR>
<LF>
MROX6?<CR><LF>
MultiRoiOffsetX
7
I Integer
R/W
MROX7
Min~Max
0
5118
0
MROX7=[Param.]<CR>
<LF>
MROX7?<CR><LF>
MultiRoiOffsetX
8
I Integer
R/W
MROX8
Min~Max
0
5118
0
MROX8=[Param.]<CR>
<LF>
MROX8?<CR><LF>
MultiRoiOffsetY
1
I Integer
R/W
MROY1
Min~Max
0
3839
0
MROY1=[Param.]<CR>
<LF>
MROY1?<CR><LF>
MultiRoiOffsetY
2
I Integer
R/W
MROY2
Min~Max
0
3839
0
MROY2=[Param.]<CR>
<LF>
MROY2?<CR><LF>
MultiRoiOffsetY
3
I Integer
R/W
MROY3
Min~Max
0
3839
0
MROY3=[Param.]<CR>
<LF>
MROY3?<CR><LF>
MultiRoiOffsetY
4
I Integer
R/W
MROY4
Min~Max
0
3839
0
MROY4=[Param.]<CR>
<LF>
MROY4?<CR><LF>
MultiRoiOffsetY
5
I Integer
R/W
MROY5
Min~Max
0
3839
0
MROY5=[Param.]<CR>
<LF>
MROY5?<CR><LF>
- 92 -
Page 95

SP-5000M-PMCL / SP-5000C-PMCL
MultiRoiOffsetY
6
I Integer
R/W
MROY6
Min~Max
0
3839
0
MROY6=[Param.]<CR>
<LF>
MROY6?<CR><LF>
MultiRoiOffsetY
7
I Integer
R/W
MROY7
Min~Max
0
3839
0
MROY7=[Param.]<CR>
<LF>
MROY7?<CR><LF>
MultiRoiOffsetY
8
I Integer
R/W
MROY8
Min~Max
0
3839
0
MROY8=[Param.]<CR>
<LF>
MROY8?<CR><LF>
LUTMode
I
Enumera
tion
R/W
LUTC
0: Off
1: Gamma
2: LUT
0 2 0
LUTC=[Param.]<CR><L
F>
LUTC?<CR><LF>
AlcSpeed
I Integer
R/W
ALCS
Min~Max
1 8 4
ALCS=[Param.]<CR><L
F>
ALCS?<CR><LF>
for AGC and ASC
ExposureAutoM
ax
I Integer
R/W
ASCEA
Min~Max[us]
101
80000
00
18000
ASCEA=[Param.]<CR><
LF>
ASCEA?<CR><LF>
Maximum value is
varied depending on
frame rate.
ExposureAutoMi
n
I Integer
R/W
ASCEI
Min~Max
100
79999
99
100
ASCEI=[Param.]<CR><
LF>
ASCEI?<CR><LF>
Maximum value is
varied depending on
frame rate.
RequestExposur
eAuto
Result
I
Enumera
tion
R/O
ASRS
0=Complete.
1=Too Bright.
2=Too dark.
3=Timeout Error.
4=Busy.
5=Limit.
6= Trig is not set as
Normal.
0 6 0
ASRS?<CR><LF>
TriggerOption
I
Enumera
tion
R/W
TRGOP
0: Off
1: RCT
2: PIV
3: Smear-less
4: RCT Continuous
0 4 0
TRGOP=[Param.]<CR>
<LF>
TRGOP?<CR><LF>
AlcReference
I Integer
R/W
AGCF
Min~Max[%]
1
100
50
AGCF=[Param.]<CR><L
F>
AGCF?<CR><LF>
GainAutoMax
I Integer
R/W
AGCGA
Min~Max
101
1600
1600
AGCGA=[Param.]<CR>
<LF>
AGCGA?<CR><LF>
GainAutoMin
I Integer
R/W
AGCGI
Min~Max
100
1599
100
AGCGI=[Param.]<CR><
LF>
AGCGI?<CR><LF>
RequestGainAut
o
Result
I
Enumera
tion
R/O
AGRS
0=Complete.
1=Too Bright.
2=Too dark.
3=Timeout Error.
4=Busy.
5=Limit.
6= Trig is not set as
Normal.
0 6 0
AGRS?<CR><LF>
AutoIrisLensCon
trol
SignalOutput
I
Enumera
tion
R/W
AIC
0: Off
1: On
0 1 0
AIC=[Param.]<CR><LF
>
AIC?<CR><LF>
- 93 -
Page 96

SP-5000M-PMCL / SP-5000C-PMCL
LensSelect
I
Enumera
tion
R/W
AIS
0: None
1: P-IRIS Lens
2: MOTOR Iris Lens
3: Video Iris Lens
4: DC Iris Lens
0 4 0
AIS=[Param.]<CR><LF>
AIS?<CR><LF>
VideoIrisStateC
ontrol
I
Enumera
tion
R/W
ISC
0: Video
1: Close
2: Open
0 1 2
ISC=[Param.]<CR><LF>
ISC?<CR><LF>
ALCChannelAre
aAll
I
Enumera
tion
R/W
ALCA
0: Off / 1: On
0 1 0
ALCA=[Param.]<CR><L
F>
ALCA?<CR><LF>
ALCChannelAre
a LowRight
I
Enumera
tion
R/W
ALCLR
0: Off / 1: On
0 1 1
ALC**=[Param.]<CR><L
F>
ALC**?<CR><LF>
ALCChannelAre
a
LowMidRight
I
Enumera
tion
R/W
ALCLM
R
0: Off / 1: On
0 1 1
ALCChannelAre
a
LowMidLeft
I
Enumera
tion
R/W
ALCLM
L
0: Off / 1: On
0 1 1
ALCChannelAre
a
LowLeft
I
Enumera
tion
R/W
ALCLL
0: Off / 1: On
0 1 1
ALCChannelAre
a
MidLowRight
I
Enumera
tion
R/W
ALCML
R
0: Off / 1: On
0 1 1
ALCChannelAre
a
MidLowMidRight
I
Enumera
tion
R/W
ALCML
MR
0: Off / 1: On
0 1 1
ALCChannelAre
a
MidLowMidLeft
I
Enumera
tion
R/W
ALCML
ML
0: Off / 1: On
0 1 1
ALCChannelAre
a
MidLowLeft
I
Enumera
tion
R/W
ALCML
L
0: Off / 1: On
0 1 1
ALCChannelAre
a
MidHighRight
I
Enumera
tion
R/W
ALCMH
R
0: Off / 1: On
0 1 1
ALCChannelAre
a
MidHighMidRigh
t
I
Enumera
tion
R/W
ALCMH
MR
0: Off / 1: On
0 1 1
ALCChannelAre
a
MidHighMidLeft
I
Enumera
tion
R/W
ALCMH
ML
0: Off / 1: On
0 1 1
ALCChannelAre
a
MidHighLeft
I
Enumera
tion
R/W
ALCMH
L
0: Off / 1: On
0 1 1
ALCChannelAre
a
HighRight
I
Enumera
tion
R/W
ALCHR
0: Off / 1: On
0 1 1
ALCChannelAre
a
HighMidRight
I
Enumera
tion
R/W
ALCHM
R
0: Off / 1: On
0 1 1
ALCChannelAre
a
HighMidLeft
I
Enumera
tion
R/W
ALCHM
L
0: Off / 1: On
0 1 1
ALCChannelAre
a
HighLeft
I
Enumera
tion
R/W
ALCHL
0: Off / 1: On
0 1 1
- 94 -
Page 97

SP-5000M-PMCL / SP-5000C-PMCL
AWBChannelAre
aAll
I
Enumera
tion
R/W
AWBA
0: Off / 1: On
0 1 0
AWBA=[Param.]<CR><
LF>
AWBA?<CR><LF>
AWBChannelAre
a
LowRight
I
Enumera
tion
R/W
AWBLR
0: Off / 1: On
0 1 1
AWB**=[Param.]<CR><
LF>
AWB**?<CR><LF>
(Bayer model only)
AWBChannelAre
a
LowMidRight
I
Enumera
tion
R/W
AWBLM
R
0: Off / 1: On
0 1 1
AWBChannelAre
a
LowMidLeft
I
Enumera
tion
R/W
AWBLM
L
0: Off / 1: On
0 1 1
AWBChannelAre
a
LowLeft
I
Enumera
tion
R/W
AWBLL
0: Off / 1: On
0 1 1
AWBChannelAre
a
MidLowRight
I
Enumera
tion
R/W
AWBML
R
0: Off / 1: On
0 1 1
AWBChannelAre
a
MidLowMidRight
I
Enumera
tion
R/W
AWBML
MR
0: Off / 1: On
0 1 1
AWBChannelAre
a
MidLowMidLeft
I
Enumera
tion
R/W
AWBML
ML
0: Off / 1: On
0 1 1
AWBChannelAre
a
MidLowLeft
I
Enumera
tion
R/W
AWBML
L
0: Off / 1: On
0 1 1
AWBChannelAre
a
MidHighRight
I
Enumera
tion
R/W
AWBM
HR
0: Off / 1: On
0 1 1
AWBChannelAre
a
MidHighMidRigh
t
I
Enumera
tion
R/W
AWBM
HMR
0: Off / 1: On
0 1 1
AWBChannelAre
a
MidHighMidLeft
I
Enumera
tion
R/W
AWBM
HML
0: Off / 1: On
0 1 1
AWBChannelAre
a
MidHighLeft
I
Enumera
tion
R/W
AWBM
HL
0: Off / 1: On
0 1 1
AWBChannelAre
a
HighRight
I
Enumera
tion
R/W
AWBHR
0: Off / 1: On
0 1 1
AWBChannelAre
a
HighMidRight
I
Enumera
tion
R/W
AWBH
MR
0: Off / 1: On
0 1 1
AWBChannelAre
a
HighMidLeft
I
Enumera
tion
R/W
AWBH
ML
0: Off / 1: On
0 1 1
AWBChannelAre
a
HighLeft
I
Enumera
tion
R/W
AWBHL
0: Off / 1: On
0 1 1
RequestBalance
White
AutoResult
I
Enumera
tion
R/O
AWRS
0=Complete.
1=Too Bright.
2=Too dark.
3=Timeout Error.
4=Busy.
5=Limit.
6= Trig is not set as
Normal.
0 6 0
AWRS?<CR><LF>
(Bayer model only)
- 95 -
Page 98

SP-5000M-PMCL / SP-5000C-PMCL
CurrentAreaNoR
equest
I Integer
R/O
EA
0: Factory area
1: User 1 area
2: User 2 area
3: User 3 area
0 3 0
EA?<CR><LF>
The camera return the
latest used DATA
AREA.
PirisLensSelect
I
Enumera
tion
R/W
PLS
No lens available
PLS=[Param.]<CR><LF
>
PLS?<CR><LF>
PIrisStepMax
I Integer
R/O
PIS
Indicate P-IRIS
control step
maximum value
0
255
128
PIS?<CR><LF>
Different depending
on PirisLensSelect
value
PIrisPosition
I Integer
R/W
PIP
Min~Max
0
255
128
PIP=[Param.]<CR><LF
>
PIP?<CR><LF>
Maximum value is
PIrisStepMax
PirisAutoMin
I
Enumera
tion
R/W
PLI
0: FULL OPEN
1: F1.4
2: F2
3: F2.8
4: F4
5: F5.6
6: F8
7: F11
8: F16
9: F22
10: F32
11: CLOSE
0
11
1
PLI=[Param.]<CR><LF>
PLI?<CR><LF>
Minimum value and
Maximum value are
different depending
on PirisLensSelect
value
PirisAutoMax
I
Enumera
tion
R/W
PLA
Same as above.
0
11
5
PLI=[Param.]<CR><LF>
PLI?<CR><LF>
Minimum value and
Maximum value are
different depending
on PirisLensSelect
value
PirisCurrentFval
ue
I
Enumera
tion
R/O
PCV
Same as above.
0
11 0 PCV?<CR><LF>
AcquisitionFram
eLine
I Integer
R/W
AR
Min~Max
1
32578
6
774
AR=[Param.]<CR><LF>
AR?<CR><LF>
Maximum value is
calcurated depending
on Height and Offset Y
settings
GammaSelector
I Integer
R/W
GMA
0(γ=1) ~ 8(γ=0.45) ~
15(γ=TBD)
0
15
8
GMA=[Param.]<CR><L
F>
GMA?<CR><LF>
Temperature
I Integer
R/O
TMP0
value
- - -
TMP0?<CR><LF>
(Value÷128) =
Temperature[℃]
GpioPulseGenDi
vide Value
I Integer
R/W
PGDEV
Min~Max
1
4096
1
PGDEV=[Param.]<CR>
<LF>
PGDEV?<CR><LF>
GpioPulseGenLe
ngth0
I Integer
R/W
PGL0
Min~Max
1
10485
75
1
PGL0=[Param.]<CR><L
F>
PGL0?<CR><LF>
- 96 -
Page 99

SP-5000M-PMCL / SP-5000C-PMCL
GpioPulseGenLe
ngth1
I Integer
R/W
PGL1
Min~Max
1
10485
75
1
PGL1=[Param.]<CR><L
F>
PGL1?<CR><LF>
GpioPulseGenLe
ngth2
I Integer
R/W
PGL2
Min~Max
1
10485
75
1
PGL2=[Param.]<CR><L
F>
PGL2?<CR><LF>
GpioPulseGenLe
ngth3
I Integer
R/W
PGL3
Min~Max
1
10485
75
1
PGL3=[Param.]<CR><L
F>
PGL3?<CR><LF>
GpioPulseGenSt
art Point0
I Integer
R/W
PGST0
Min~Max
0
10485
74
0
PGST0=[Param.]<CR><
LF>
PGST0?<CR><LF>
GpioPulseGenSt
art Point1
I Integer
R/W
PGST1
Min~Max
0
10485
74
0
PGST1=[Param.]<CR><
LF>
PGST1?<CR><LF>
GpioPulseGenSt
art
Point2
I Integer
R/W
PGST2
Min~Max
0
10485
74
0
PGST2=[Param.]<CR><
LF>
PGST2?<CR><LF>
GpioPulseGenSt
art Point3
I Integer
R/W
PGST3
Min~Max
0
10485
74
0
PGST3=[Param.]<CR><
LF>
PGST3?<CR><LF>
GpioPulseGenEn
d Point0
I Integer
R/W
PGEN0
Min~Max
1
10485
75
1
PGEN0=[Param.]<CR><
LF>
PGEN0?<CR><LF>
GpioPulseGenEn
d Point1
I Integer
R/W
PGEN1
Min~Max
1
10485
75
1
PGEN1=[Param.]<CR><
LF>
PGEN1?<CR><LF>
GpioPulseGenEn
d Point2
I Integer
R/W
PGEN2
Min~Max
1
10485
75
1
PGEN2=[Param.]<CR><
LF>
PGEN2?<CR><LF>
GpioPulseGenEn
d Point3
I Integer
R/W
PGEN3
Min~Max
1
10485
75
1
PGEN3=[Param.]<CR><
LF>
PGEN3?<CR><LF>
GpioPulseGenR
epeat Count0
I Integer
R/W
PGRPT
0
Min~Max
0
255
0
PGRPT0=[Param.]<CR
><LF>
PGRPT0?<CR><LF>
GpioPulseGenR
epeat Count1
I Integer
R/W
PGRPT
1
Min~Max
0
255
0
PGRPT1=[Param.]<CR
><LF>
PGRPT1?<CR><LF>
GpioPulseGenR
epeat Count2
I Integer
R/W
PGRPT
2
Min~Max
0
255
0
PGRPT2=[Param.]<CR
><LF>
PGRPT2?<CR><LF>
GpioPulseGenR
epeat Count3
I Integer
R/W
PGRPT
3
Min~Max
0
255
0
PGRPT3=[Param.]<CR
><LF>
PGRPT3?<CR><LF>
GpioPulseGenCl
ear Mode0
I
Enumera
tion
R/W
PGCM0
0: Free Run
1: Level High
2: Level Low
3: Rising Edge
4: Falling Edge
0 4 0
PGCM0=[Param.]<CR>
<LF>
PGCM0?<CR><LF>
GpioPulseGenCl
ear Mode1
I
Enumera
tion
R/W
PGCM1
Same as above.
0 4 0
PGCM1=[Param.]<CR>
<LF>
PGCM1?<CR><LF>
GpioPulseGenCl
ear Mode2
I
Enumera
tion
R/W
PGCM2
Same as above.
0 4 0
PGCM2=[Param.]<CR>
<LF>
PGCM2?<CR><LF>
GpioPulseGenCl
ear Mode3
I
Enumera
tion
R/W
PGCM3
Same as above.
0 4 0
PGCM3=[Param.]<CR>
<LF>
PGCM3?<CR><LF>
- 97 -
Page 100

SP-5000M-PMCL / SP-5000C-PMCL
GpioPulseGenSy
nc Mode0
I
Enumera
tion
R/W
PGSM0
0: Async Mode
1: Sync Mode
0 1 0
PGSM0=[Param.]<CR>
<LF>
PGSM0?<CR><LF>
GpioPulseGenSy
nc Mode1
I
Enumera
tion
R/W
PGSM1
Same as above.
0 1 0
PGSM1=[Param.]<CR>
<LF>
PGSM1?<CR><LF>
GpioPulseGenSy
nc Mode2
I
Enumera
tion
R/W
PGSM2
Same as above.
0 1 0
PGSM2=[Param.]<CR>
<LF>
PGSM2?<CR><LF>
GpioPulseGenSy
nc Mode3
I
Enumera
tion
R/W
PGSM3
Same as above.
0 1 0
PGSM3=[Param.]<CR>
<LF>
PGSM3?<CR><LF>
GpioPulseGenIn
put0
I
Enumera
tion
R/W
PGIN0
0:Low
1:High
2:Soft
3:AcquisitionTrigger
Wait
4:FrameTriggerWait
5:FrameActive
6:ExposureActive
7:FVAL
8:LVAL
9:PG0
10:PG1
11:PG2
12:PG3
13: TTL in
14:CL CC1 in
15:nand0
16:nand1
17: OPTTL in2
18: OPLVDS in
0
18
0
PGIN0=[Param.]<CR><
LF>
PGIN0?<CR><LF>
GpioPulseGenIn
put1
I
Enumera
tion
R/W
PGIN1
Same as above.
0
18
0
PGIN1=[Param.]<CR><
LF>
PGIN1?<CR><LF>
GpioPulseGenIn
put2
I
Enumera
tion
R/W
PGIN2
Same as above.
0
18
0
PGIN2=[Param.]<CR><
LF>
PGIN2?<CR><LF>
GpioPulseGenIn
put3
I
Enumera
tion
R/W
PGIN3
Same as above.
0
18
0
PGIN3=[Param.]<CR><
LF>
PGIN3?<CR><LF>
GpioPulseGenIn
vert0
I
Enumera
tion
R/W
PGINV0
0:Non-Inv
1:Inv
0 1 0
PGIN0=[Param.]<CR><
LF>
PGIN0?<CR><LF>
GpioPulseGenIn
vert1
I
Enumera
tion
R/W
PGINV1
Same as above.
0 1 0
PGIN1=[Param.]<CR><
LF>
PGIN1?<CR><LF>
GpioPulseGenIn
vert2
I
Enumera
tion
R/W
PGINV2
Same as above.
0 1 0
PGIN2=[Param.]<CR><
LF>
PGIN2?<CR><LF>
GpioPulseGenIn
vert3
I
Enumera
tion
R/W
PGINV3
Same as above.
0 1 0
PGIN3=[Param.]<CR><
LF>
PGIN3?<CR><LF>
- 98 -
 Loading...
Loading...