Page 1

RM/TM-1405GE
RMC/TMC-1405GE
Digital Monochrome/Color
Progressive Scan, Interline-Transfer GE Camera
Document Version: F
Document P/N: 10167
Page 2

Page 3

RM/TM-14
05GE Series
Disclaimer
The material contained in this manual consists of information that is proprietary to JAI Inc., and may only be
used by the purchasers of the product. JAI, Inc. makes no warranty for the use of its product and assumes no
responsibility for any errors which may appear or for damages resulting from the use of the information
contained herein. JAI, Inc. reserves the right to make changes without notice.
Microsoft, Windows 95, 98, NT, 2000, XP, and Windows Explorer are either registered trademarks or trademarks
of Microsoft Corporation in the United States and/or other countries.
Warranty
Please contact your factory representative for details about the warranty.
Certifications
CE Compliance
The RM/TM-1405GE series of cameras has been certified to conform to the requirements of Council Directive
89/336/EC for electromagnetic compatibility and to comply with the following European Standards:
EMC EN55022: 1998 + A1: 2000 CLASS A
EN55024: 1998 + A1: 2001
All JAI Inc. products bearing the CE mark have been declared to be in conformance with the applicable EEC
Council Directives. However, certain factory-installed options or customer-requested modifications may
compromise electromagnetic compatibility and affect CE compliance. Please note that the use of interconnect
cables that are not properly grounded and shielded may affect CE compliance.
Contact the JAI Inc. Applications Engineering Department for further information regarding CE compliance.
FCC
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class A digital device, pursuant to
Part 15 of the FCC Rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection against harmful
interference when the equipment is operated in a commercial environment. This equipment generates, uses
and can radiate radio frequency energy and, if not installed and used in accordance with the instruction
manual, may cause harmful interference to radio communications. Operation of this equipment in a residential
area may cause harmful interference, in which case the user will be required to correct the interference at his
own expense.
Disclaimer iii
Page 4

RM/TM-1405GE Series
WARNING
Changes or modifications to this unit not expressly approved by the party responsible for FCC compliance could
void the user’s authority to operate the equipment.
RM/TM-1405GE Series Operation Manual
JAI Inc.
625 River Oaks Parkway
San Jose, CA 95134
Tel:(408) 383-0300
Tel:(800) 445-5444
Fax:(408) 383-0301
www.jai.com
September 18, 2009
iv Disclaimer
Page 5

RM/TM-14
05GE Series
Table of Contents
Disclaimer Notice ................................................................................................... iii
Table of Contents ................................................................................................... v
List of Figures ....................................................................................................... vii
List of Tables ......................................................................................................... ix
Hardware Introduction ................................................................................ 9
1
1.1 Product Description ................................................................................... 9
1.2 Features ................................................................................................. 9
2 Installation ............................................................................................. 11
2.1 Getting Started ........................................................................................ 11
2.1.1 Unpacking Instructions ............................................................................... 11
2.1.2 Components ............................................................................................ 11
2.1.3 Accessories and Options ............................................................................. 11
2.2 Camera Setup .......................................................................................... 11
2.2.1 Heat Dissipation ....................................................................................... 11
2.2.2 Connector Pin Configurations ....................................................................... 12
2.2.3 Power Supplies and Power Cable Setup ........................................................... 12
2.2.4 Attaching the Camera Lens .......................................................................... 14
2.2.5 Adjustable Back-Focus ............................................................................... 14
3 Operation .............................................................................................. 16
3.1 Progressive Scanning ................................................................................. 16
3.2 Bayer Color Filter (Color Versions) ................................................................. 16
3.2.1 Color Filter Array ..................................................................................... 16
3.2.2 Bayer Color Filter Array (CFA) ...................................................................... 16
3.2.3 Starting Pixel Configuration ......................................................................... 17
3.2.4 Sync and Data ......................................................................................... 17
3.2.5 Camera Functions ..................................................................................... 18
3.2.6 Interpolation Software ............................................................................... 18
3.2.7 Color Interpolation ................................................................................... 19
3.3 Electronic Shutter .................................................................................... 19
3.4 External Sync .......................................................................................... 19
3.5 Asynchronous Reset................................................................................... 19
3.5.1 Async No Shutter ...................................................................................... 19
3.5.2 Async Programmable Shutter Speed Control ..................................................... 20
3.5.3 External VINIT With Pulse Width (No-Delay Shutter) ............................................ 21
3.6 Programmable Look-Up Table (LUT) and Knee Control ......................................... 21
3.7 Camera Timing Charts ................................................................................ 22
3.8 Video Output .......................................................................................... 23
3.9 External HD Locking and External VD Reset ...................................................... 24
3.10 Asynchronous Reset................................................................................... 25
4 Functions & Operations .............................................................................. 26
4.1 GigE Vision Standard Interface ..................................................................... 26
4.2 GigE Vision-Aware Software ......................................................................... 26
4.3 Recommended Network Configurations ........................................................... 26
4.3.1 Verified Network Interface Cards (NICs) .......................................................... 26
4.3.2 Video data rate (network bandwidth) ............................................................. 27
4.3.3 Disable Firewalls ...................................................................................... 27
4.3.4 Enabling Jumbo Frame ............................................................................... 28
4.3.5 Setting Receive Descriptors ......................................................................... 30
Table of Contents v
Page 6

RM/TM-1405GE Series
4.3.6 Interrupt Moderation rate ........................................................................... 30
4.3.7 Calculating and setting Inter-Packet Delay ....................................................... 30
4.3.8 Confirm the Filter Driver is used ................................................................... 31
5 Configuring the Camera .............................................................................. 33
5.1 Acquisition and Trigger Controls ................................................................... 33
5.2 AnalogControls ........................................................................................ 34
5.3 Image Size Controls ................................................................................... 35
5.4 LUT (Look Up Table) ................................................................................. 37
5.5 UserSets ................................................................................................ 38
5.6 DeviceInformation .................................................................................... 39
5.7 GigEVisionTransportLayer ........................................................................... 39
5.7.1 Persistent IP ........................................................................................... 39
5.7.2 Stream Channel Packet Size ........................................................................ 40
5.8 IPEngine ................................................................................................ 40
5.8.1 SignalRoutingBlock ................................................................................... 42
5.8.2 ControlBits ............................................................................................. 44
5.8.3 PLC LookupTable ...................................................................................... 45
5.8.4 PLCSpecialConfigurations ............................................................................ 46
5.8.5 Counters ................................................................................................ 48
5.8.6 Pulse Generators controls ........................................................................... 49
5.8.7 PLC Grabber Features ................................................................................ 50
5.8.8 IPEngine Examples: ................................................................................... 50
5.9 Register Map ........................................................................................... 51
6 Troubleshooting ....................................................................................... 56
6.1 Problems and Solutions .............................................................................. 56
6.1.1 Symptom: No Video................................................................................... 56
6.1.2 Symptom: Dark Video ................................................................................ 56
6.1.3 Symptom: Non-Synchronized Video ................................................................ 56
6.2 Information and Support Resources ................................................................ 56
7 Appendix ............................................................................................... 58
7.1 Specifications .......................................................................................... 58
7.1.1 TM-1405GE Physical Dimensions .................................................................... 59
7.1.2 Spectral Response .................................................................................... 60
vi Table of Contents
Page 7

RM/TM-14
05GE Series
List of Figures
Figure 1.
Figure 2. GigE Ethernet Connector ............................................................................ 12
Figure 3. 12P-02S Interface Cable (optional) ................................................................ 13
Figure 4. Back-Focus Set-Screw Locations .................................................................... 15
Figure 5. Example of Color CCD CFA Pattern ................................................................ 17
Figure 6. Example of TMC-1405GE in Default Mode ......................................................... 18
Figure 7. Async No Shutter ...................................................................................... 20
Figure 8. Async ProgrammableShutter Speed Control ...................................................... 20
Figure 9. No-Delay Shutter ...................................................................................... 21
Figure 10. Acquisition And Trigger Controls Category ....................................................... 33
Figure 11. AnalogControls Category ............................................................................. 35
Figure 12. Image Output Example. .............................................................................. 36
Figure 13. LookUp Table .......................................................................................... 37
Figure 14. UserSets Category .................................................................................... 38
Figure 15. DeviceInformation Category ........................................................................ 39
Figure 16. GigEVisionTransportLayer Persistent IP ........................................................... 40
Figure 17. PLC LUT Diagram ...................................................................................... 41
Figure 18. PLC ...................................................................................................... 42
Figure 19. SignalRoutingBlock .................................................................................... 42
Figure 20. ControlBits ............................................................................................. 45
Figure 21. PLC Q Output .......................................................................................... 45
Figure 22. PLC Special Configurations .......................................................................... 47
Figure 23. CountersAndTimersControls ......................................................................... 47
Figure 24. Physical Dimensions .................................................................................. 59
Figure 25. Monochrome Spectral Response .................................................................... 60
Figure 26. Color Spectral Response ............................................................................. 60
12-Pin Connector Pinouts ............................................................................ 12
List of Figures vii
Page 8

RM/TM-1405GE Series
List of Tables
Table 1 Table 1 12-Pin Connector ............................................................................ 12
Table 2 Video Output (Horizontal Timing) .................................................................. 23
Table 3 Video Output (Vertical Timing) ..................................................................... 24
Table 4 External HD Locking and External VD Reset (Horizontal Timing) ............................. 24
Table 5 External HD Locking and External VD Reset (Vertical Timing) ................................ 24
Table 6 Asynchronous Reset .................................................................................. 25
Table 7 Asynchronous Direct Shutter and Pulse-Width Control ......................................... 25
Table 8 TM-1405GE Camera Specifications Table ......................................................... 58
viii List of Tables
Page 9

RM/TM-14
05GE Series
1 Hardware Introduction
1.1 Product Description
The JAI TM-1405GE is a high-speed progressive scan CCD camera. The interline-type CCD permits full
vertical and horizontal resolution of very high speed shutter images and applications. The electronic
shutter, which has speeds to 1/21,000 second, can be reset asynchronously by external pulse control.
The frame rate for a full image is 30 fps, with partial scan modes of up to 1 line. A 2:1 ratio imager
format with uniform square pixels provides superior image definition in any orientation.
The TM-1405GE has a full dynamic range control function, which can be set at externally selectable
look-up table (LUT) knee slopes to convert 10-bit input to 8-bit output, thereby optimizing the CCD’s
full dynamic range in the normal output signal range. 10-bit linear output is also selectable.
Applications for the TM-1405GE include machine vision, medical imaging, intelligent transportation
systems, high-definition graphics, on-line inspection, gauging, character reading, archiving, and high
security surveillance.
The TM-1405GE series consists of the RM/TM-1405GE (monochrome) and the RMC/TMC-1405GE
(color). Unless otherwise noted, all information contained in this manual is relevant to both models.
TM-1405GE Hardware
Operation Manual
1.2 Features
The TM-1405GE has the following features:
• Miniature size and light weight
The printed circuit boards in the TM-1405GE have been arranged to create modular electronics,
giving the camera flexibility. In addition, the use of miniature solid-state components results in
a compact, lightweight camera that is 50.8mm x 50.8mm x 83.5mm in dimensions, and weighs
only 140 grams.
• Imager
The TM-1405GE uses a progressive scan interline transfer CCD that has the following features:
− Resolution of 1392 x 1040 active pixels for excellent image quality.
− 4.65 x 4.65 µm square pixels for precise dimensional measurement.
− High-speed electronic shutter capability for high dynamic resolution of moving objects
that eliminates the need for a mechanical shutter.
− Progressive scan CCD eliminates interlace deterioration of image and increases ease of
computer interface.
− High sensitivity and low noise at fast scanning. The CCD has an excellent S/N ratio at the
default setting greater than 51dB.
• Electronic shutter
The TM-1405GE has a substrate drain-type shutter mechanism which provides superb pictures at
various speeds without smearing.
Hardware Introduction 9
Page 10

RM/TM-1405GE Series
• Asynchronous reset
The TM-1405GE captures asynchronous reset images and provides single-shot video output with
single FDV. This makes it simpler for an ordinary frame grabber to capture the asynchronous
reset images. The TM-1405GE’s asynchronous reset is flexible and accepts external horizontal
drive (HD) for phase locking. When the VINIT (5V) pulse is applied to pin 6 on the Hirose, or the
PLC 12-pin connector, it resets the camera's scanning and purging of the CCD.
The TM-1405GE has three modes to control the asynchronous reset and shutter speed:
− Async, no shutter. The video signal and FDV are reset by external VINIT.
− Async Programmable shutter. The shutter speed depends on the number of horizontal
lines controlled by the user.
− External VINIT with pulse width. The duration between pulse edges controls the shutter
speed externally.
• Output
The TM-1405GE has a 10-bit/8-bit Gigabit Ethernet output. The analog output is 714 mV p-p
composite video (75 ohms) on all models.
• Warranty
Contact your factory representative for details about the warranty.
10 Hardware Introduction
Page 11

05GE Series
2 Installation
The following instructions will help you to set up your camera quickly and easily. JAI suggests that
you read through these instructions first, before you unpack and set up your camera system.
2.1 Getting Started
2.1.1 Unpacking Instructions
JAI recommends that you save the original packing cartons for the cameras and accessories in case
you need to return or exchange an item.
We also recommend that you bench-test any equipment being sent to another location for field
installation to assure that everything is fully operational as a system.
2.1.2 Components
When you receive your TM-1405GE camera from JAI, the contents of the shipping box should include
the camera and a document download card. If either of these items are missing, contact your JAI
representative immediately. The document download card includes instructions and web locations
for downloading the datasheet, manual, and camera-control software. If you do not have Internet
access, contact JAI to receive this material on a CD-ROM.
RM/TM-14
2.1.3 Accessories and Options
The following additional accessories and options may be required for your application:
• PD-12U series power supply
• 12P-02S power cable
• Cat5e or cat6 shielded Ethernet cable (not supplied by JAI)
• Tripod Mounting Kit: TP-20
(for dimensions go to:
www.jai.com/EN/CameraSolutions/Products/Accessories/Pages/Home.aspx
Check with your JAI representative before you install your camera to determine what you might
need.
)
2.2 Camera Setup
2.2.1 Heat Dissipation
The TM-1405GE is a compact camera. Since all the electronics have been packed in a compact
package, the outer case of the camera can become hot because of heat dissipation. For optimal
performance, JAI recommends using a cooling fan to set up a positive air flow around the camera
and following the precautions below.
• Mount the camera on a large heat sink (camera bracket) made out of a heat-conductive
material like aluminum.
• Make sure the flow of heat from the camera case to the bracket is not blocked by a non-
conductive material like plastic.
• Make sure the camera has enough open space around it to facilitate the free flow of air.
Installation 11
Page 12

RM/TM-1405GE Series
7
8
9
10
11
2.2.2 Connector Pin Configurations
The TM-1405GE has a 12-pin Hirose connector for power input and signal integration as shown in
Figure 1.
Figure 1. 12-Pin Connector Pinouts
Pin #1 is Ground and pin #2 is +12V DC. Table1 shows the pin-out table.
Table 1 Table 1 12-Pin Connector
Pin Description
1 GND
2 +12V DC
3 GND (analog)
4 Video out
5 GND (digital)
6
VINIT in
(External_Trigger)
Pin
12 Reserved
Description
VD in
Strobe
HD in
Reserved
Reserved
Figure 2. GigE Ethernet Connector
Use at least cat5e UTP cables (cat6 cables are preferred). JAI recommends the use of shielded cables
to reduce emissions and for CE/FCC compliance. Double-shielded cables further reduce emissions.
2.2.3 Power Supplies and Power Cable Setup
2.2.3.1 Power Supplies
The TM-1405GE camera requires 12V DC power obtained through the 12-pin connector located on the
rear panel of the camera. JAI, Inc. power supplies feature a 122-240V AC / 12V DC 1.2A universal
voltage supply. JAI recommends the following power supplies:
PD-12UU PD-12UU no 12-pin connector
PD-12UUP PD-12UU with 12-pin connector
PD-12UE PD-12UU no 12-pin connector
PD-12EUP PD-12UU with 12-pin connector
If you are providing power through the 12-pin connector, the PD-12P, PD-12UEP and PD-12UUP power
supplies are available with the 12-pin mating connector already attached to the leads from the
power supply. You can connect the PD-12UU and PD-12UE power supplies to the JAI power cable
using a terminal strip or directly.
US Plug
US Plug
European Plug
European Plug
12 Installation
Page 13
RM/TM-14
05GE Series
When wiring the PD-12UU and PD-12UE power supplies directly, note the following:
• Twist the lead ends together and tin-solder for strength and electrical continuity.
• Use shrink tubing or a similar insulator to prevent exposed leads from touching and shorting.
• The +12V lead is marked with a red stripe or white lettering; be sure not to reverse the leads.
• Make sure all connections are properly insulated to prevent shorting.
2.2.3.2 JAI Power Cables
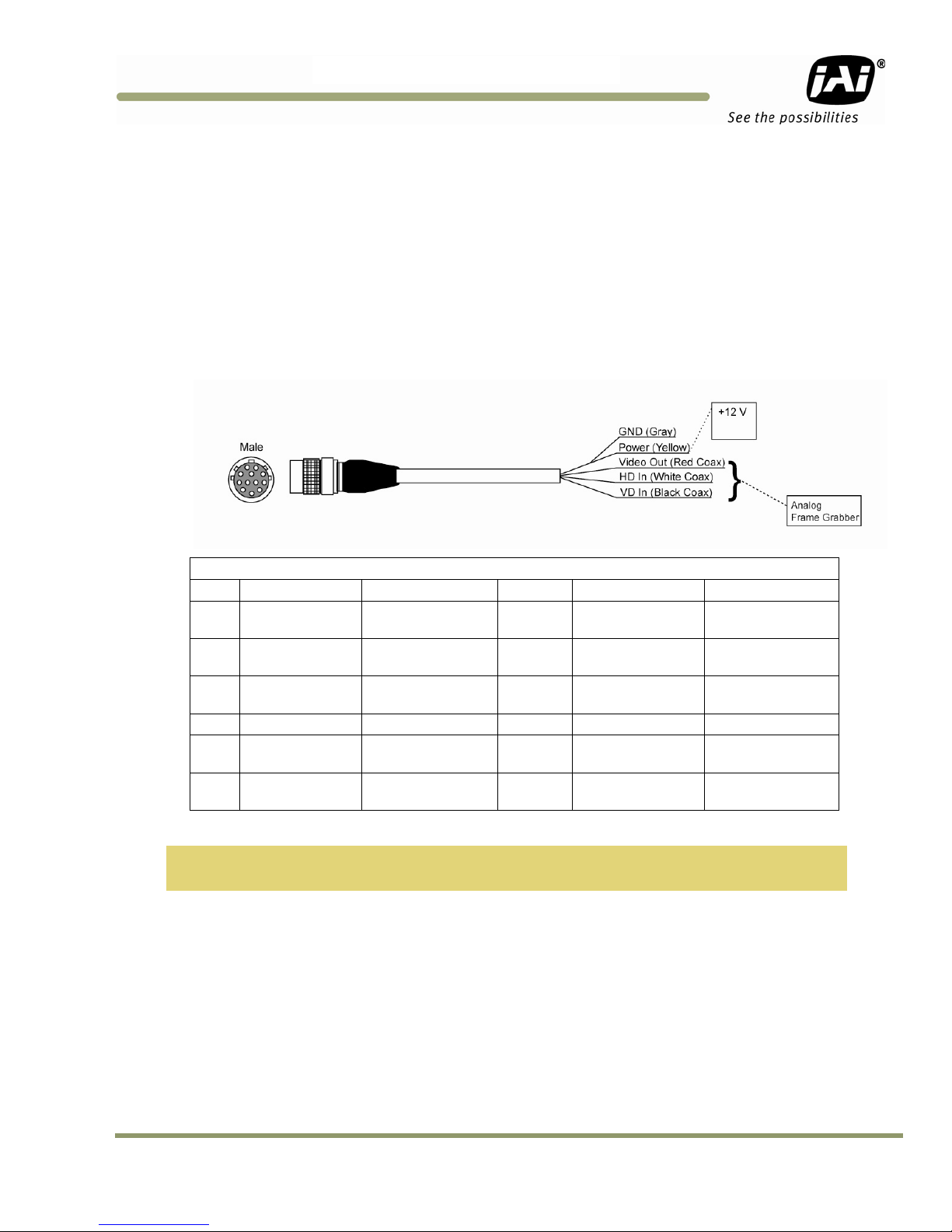
If you are using JAI power cables, such as the 12P-02S, refer to the Figure 3 which shows the cable
pin-out diagram and pinouts. The color-coded leads use Gray for Ground and Yellow for +12V.
Figure 3. 12P-02S Interface Cable (optional)
12P-02S Interface Cable
Pin# Lead Color Function
1 Gray
2 Yellow +12V DC (Power In) 8 White coax shield
3 Red coax shield
4 Red coax
5
6 Orange coax
Note: Make sure that the unused leads are not touching and that there is no possibility that exposed
2.2.3.3 Building Your Own Power Cable
Refer to the 12-pin connector pin-out in Figure 1. Connect the Ground lead to pin #1, and the +12V
DC lead to pin #2 of the 12-pin connector. Power must be DC-regulated, and of sufficient current to
properly power the camera.
2.2.3.4 Attaching the Power Cable to the Connector
The 12-pin connector is keyed and will only fit in one orientation. To properly attach the power
cable to the camera connector, use the following steps:
1. Rotate the connector while applying slight pressure until the keyways line up.
2. Press the connector into place until firmly seated.
3. Plug the power cord into the 100V AC socket. This powers up the camera.
Orange coax
shield
wires could cause the leads to short.
GND (Power
Ground)
GND (Analog
Ground)
VIDEO (Analog Out)
GND (Digital
Ground)
TTL IN
(External_Trigger)
Pin#
7 Black coax
9 White coax
10
11 Blue RESV
12 Black coax shield RESV
Lead Color Function
TTL IN
(External_VD)
TTL OUT
(STROBE)
TTL IN
(External_HD)
Brown
RESV
Installation 13
Page 14

RM/TM-1405GE Series
Note: If using a power supply other than the standard PD-12U Series from JAI, certain
characteristics are required of the power supply and the wiri ng in order to properly power the
camera. The camera requires 12V immediately upon start-up; no slow ramps. Once power is
applied, the power supply must be able to support a 2A to 2.5A in-rush current for
approximately 200µs to prevent the voltage at the camera from dropping below the 10.8V
minimum required. Dropping below this will result in the camera’s internal power supply
lowering its impedance in an attempt to draw more current. Since no more current will be
available, the voltage at the camera will drop instead. This will result in a steady state hangup which will damage the camera’s power supply and cause the camera to cease operating or
to operate in an unstable manner.
2.2.4 Attaching the Camera Lens
The TM-1405GE camera accepts 1/2” or larger format size C-mount lenses. To attach the C-mount
1
lens1
to the camera, carefully engage the threads and rotate the lens clockwise until it firmly seats
on the mounting ring. Do not force the lens if it does not seat properly.
Note: Some lenses with extremely long flangebacks may exceed the mounting depth of the camera.
2.2.5 Adjustable Back-Focus
Before cameras are shipped, back focus is carefully set using a collimator, oscilloscope and other
specialized equipment. While the factory-set focus serves well in most cases, an adjustable back
focus makes it possible to improve image sharpness when using lower-cost zoom lenses, custom
optics, or in unusual parameters.
There should be an obvious need to refocus the lens before attempting to change the back focus.
This is a very exacting task. Some cameras have been returned to the factory to reset the back focus
after failed attempts to change the focus by customers. It might be wise to label cameras whose
back focus was adjusted
1. The camera must be connected to a monitor before attempting to adjust the back focus.
2. To back focus the camera, first attach a C-mount lens in the mount. Be certain that the lens is
properly seated.
3. Next set the lens focus to infinity (if the lens is a manual iris, set the iris to a high f number
while still retaining a well illuminated image).
4. Loosen the three miniature hex set-screws (use a 0.9 mm hex wrench) that lock the focus ring
in place (two screws for a CS-mount). Slowly turn the lens and focus ring assembly back and
forth until you obtain the best image of the desired object. This sets the back focus. Once the
best image is obtained, tighten the focus ring set-screws until they are snug. Do not overtighten the screws.
Note: Mini-bayonet cameras adapted to C-mount do not have the back focus feature.
1
C-mount to F-mount and C-mount to K-mount adapters are available for larger format lenses (35 mm). Check
with local photography dealers for these lens adapters.
14 Installation
Page 15

RM/TM-14
05GE Series
Figure 4. Back-Focus Set-Screw Locations
Installation 15
Page 16

3 Operation
3.1 Progressive Scanning
The TM-1405GE uses a state-of-the-art progressive scanning interline transfer CCD which scans all
lines sequentially from top to bottom at one frame rate. Like a non-interlace computer screen, it
generates a stable, crisp image without alternating lines and provides full vertical TV resolution of
1040 lines.
The interline transfer architecture is also important to generate simultaneous shuttering. This is
different from full frame transfer architecture, which requires a mechanical shutter or strobe light in
order to freeze the object motion.
The TM-1405GE outputs the progressive scanned image with an electronic shutter in two different
formats.
• Progressive scanning digital - The CCD signal goes through A/D converters 10-bit in, 10-bit/8-bit
out. The digital output is available using the Gigabit Ethernet connector.
• Analog output - The analog output is the same as 75 ohms, 714mV format available from BNC
and 12-pin connector. Analog video does not conform to the RS-170 standard and is not RS-170
compatible.
RM/TM-1405GE Series
3.2 Bayer Color Filter (Color Versions)
JAI AccuPiXEL series color cameras are high-resolution, high-speed progressive scan CCD cameras.
The interline transfer, progressive scan CCD permits full vertical and horizontal resolution of images
acquired at very high shutter speeds. The electronic shutter, which has speeds to 1/21,000 sec., can
be reset asynchronously by external pulse control. Uniform square pixels provide superior image
definition in any orientation. On-chip micro lenses mean increased sensitivity.
3.2.1 Color Filter Array
JAI AccuPiXEL cameras use Bayer CFA (color filter array) as their standard primary color filter. This
filter provides the most popular color interpolation supported by numerous software suppliers.
The digital format allows the camera to output accurate pixel data, including the color information.
When the data is stored in the frame buffer of a frame grabber or computer, the color information is
easily manipulated to restore the original color images. Because the color filter array contains only a
single R, G or B color in each pixel, the restored image has to fill in colors in the missing pixel
locations. The software uses neighboring pixel information to “guess” the missing colors to make
smooth, clear images. This is called “color interpolation.” Today’s high-speed computers allow such
color interpolation to be done almost in real time. Because these cameras do not contain internal
color processing circuitry, they are smaller and less expensive than full-function color cameras.
3.2.2 Bayer Color Filter Array (CFA)
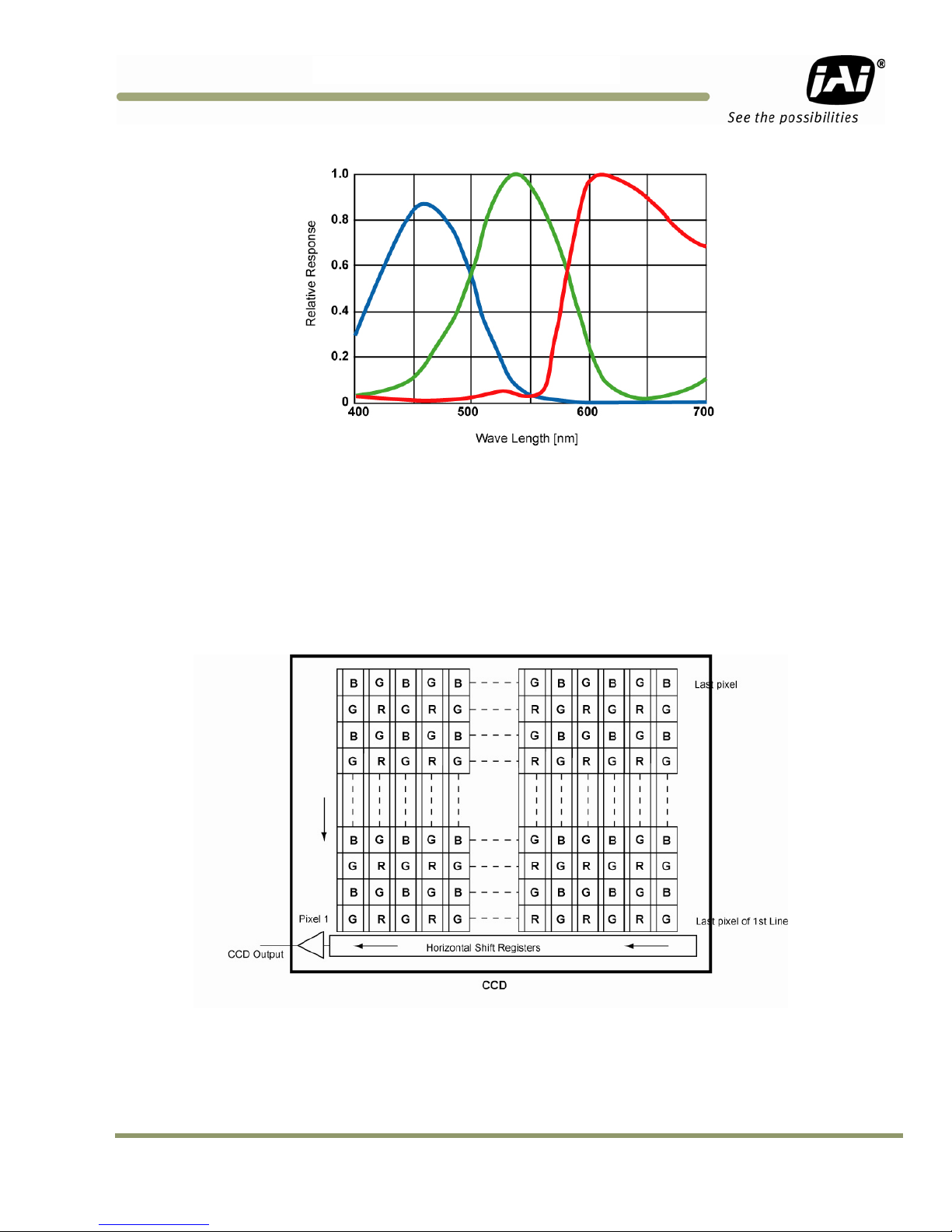
The Bayer CFA is an R, G, B primary color filter array. This is the most widely accepted CFA for the
single-chip CCD progressive scan format. This type of array layout has a specific order for each
color’s pixels. Since the human eye’s resolution and color recognition are highest at green, the CFA
contains two greens per each red and blue.
It is critical for the frame grabber and color interpolation to know where the individual color pixels
exist relative to sync (LDV and FDV) timing.
This requirement makes digital output the preferred choice, because the timing relationships are
very accurate.
16 Operation
Page 17
RM/TM-14
05GE Series
3.2.3 Starting Pixel Configuration
All manufacturers produce identical Bayer CFAs, but there are slight differences between the CCDs
produced by different manufacturers. The first line is generally R and G. The camera timing can be
adjusted to start with either G or R by skipping the very first pixels at each line. The majority of
color interpolation software can select between a variety of pixel relations, such as R/G start or G/R
start, as well as G/B start and B/G start. Once the correct scanning is configured, the rest of the
interpolation will be exactly the same. Please contact JAI for further information regarding CCD
manufacturers.
Figure 5. Example of Color CCD CFA Pattern
3.2.4 Sync and Data
The individual color data is exactly the same as the pixel data. This means that the timing
relationships of the color cameras are also the same as of the B/W cameras.
For a detailed timing chart, please refer to each B/W camera’s data sheet and manual.
Operation 17
Page 18
RM/TM-1405GE Series
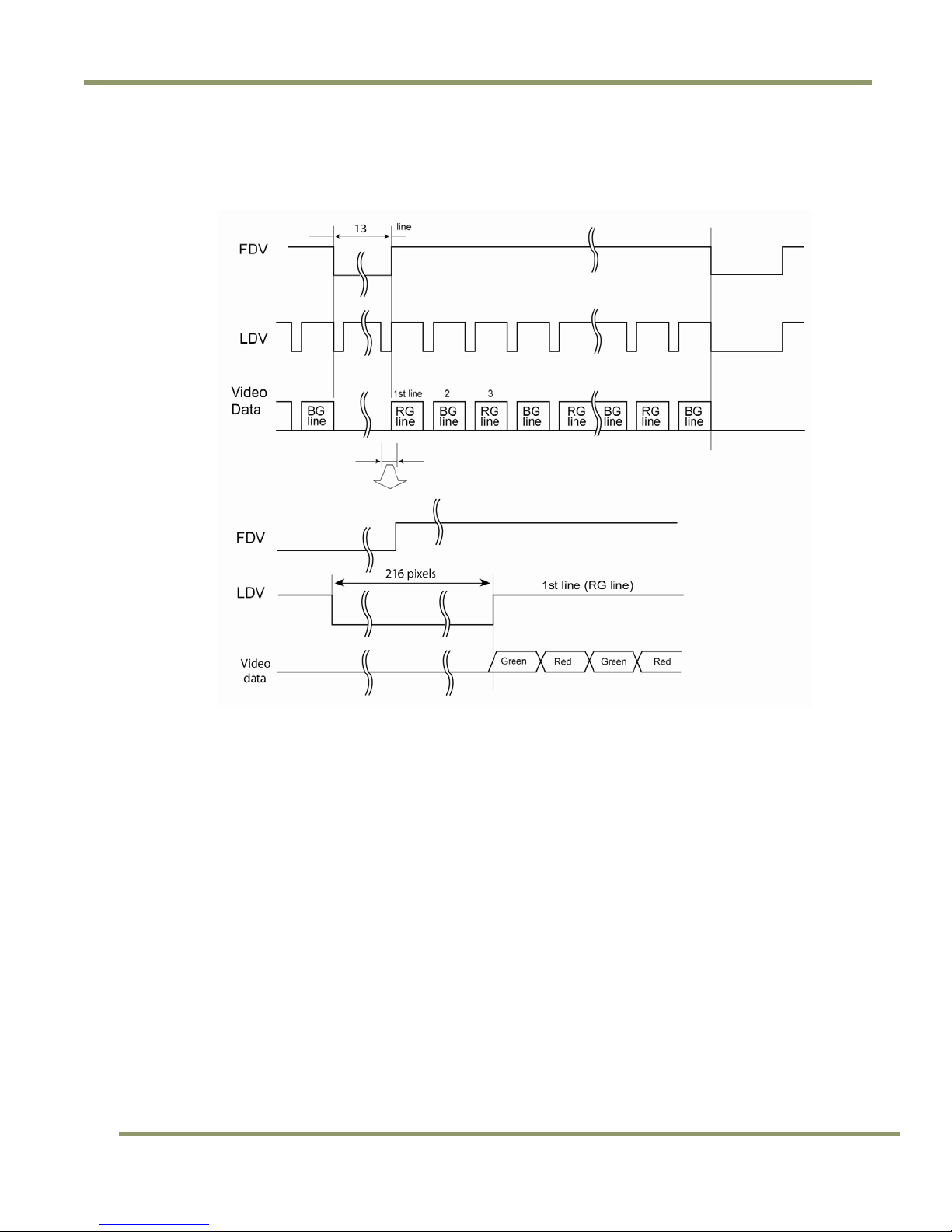
The following diagram is an example of the TMC-1405GE default mode. FDV and LDV are used
internally for the GigE interface.
Figure 6. Example of TMC-1405GE in Default Mode
3.2.5 Camera Functions
AccuPiXEL color cameras perform all functions the same way as monochrome cameras. However,
because of color characteristics, the LUT (Look-up Table) is different. The LUT is a powerful tool to
adjust the dynamic range as well as the color dynamic range. Since human color perception is nonlinear, LUT selection can help optimize color contrast by selecting the LUT value. Gamma 0.45 is
logarithmic and is close to human perception.
When LUT is selected, black-level adjustment must be more accurate than for B/W cameras.
For a detailed timing chart, please refer to the standard AccuPiXEL camera data sheet, or contact
JAI.
3.2.6 Interpolation Software
The color interpolation can be performed in the frame grabber or by using the host computer’s CPU.
Most major frame grabbers with processing capability provide tools for color interpolation. Software
vision packages also provide color interpolation capability, but speed and performance may be
determined by the PC’s resources and by the complexity of the interpolation routine.
18 Operation
Page 19

RM/TM-14
05GE Series
3.2.7 Color Interpolation
The Bayer pattern color filter array (CFA) consists of R, G, and B primary colors. Each pixel
represents one of three colors. In order to display or print color images, the signal has to be
converted to RGB output, which has three independent channels (outputs) and sync signals.
Color interpolation software or firmware performs the color preprocessing by
filling the missing color pixels with neighboring pixels. It then separates the
stream of data, (8-bit or 10-bit) into 3 (RGB) data (8-bit x 3) and adds the color
matrix to adjust and balance each of the R, G, and B channels (white balance or
color balance).
The image quality depends on the camera’s own pixel data (including pixel data
independency from neighboring pixels, noise and color filter), and interpolation
of the software algorithm such as 3 x 3 interpolation, 2 x 2 interpolation, color
matrix, white balance capability, etc.
All AccuPiXEL color cameras are carefully designed for maximum color performance. JAI strongly
suggests that you use digital output for the best performance.
Some software is used on board (FPGA or DSP) to perform the interpolation. Other software simply
uses the host computer’s memory and CPU. The processing speed may vary depending on the
architecture and speed of the computer.
3.3 Electronic Shutter
The TM-1405GE has a substrate drain-type shutter mechanism which provides a superb picture at
various speeds without smearing. A built-in flexible shutter speed control selects the electronic
shutter rate from 1/30 to 1/21,000.
With VINIT high (CC1), the CCD keeps discharging. With an active low pulse to VINIT, the camera
resets and purges the charge momentarily. Then it starts integrating for the period of shutter control
set by either an external pulse width or internal shutter control. Progressive scanning permits a full
1040 lines of vertical resolution, as compared to a conventional CCD camera which captures only half
the vertical lines per shutter.
3.4 External Sync
The TM-1405GE accepts an external synchronization of standard HD and VD on CC3 and CC4 of the
Gigabit Ethernet connector for general locking to an external source. The tolerance is ±2% horizontal
frequency.
3.5 Asynchronous Reset
The TM-1405GE camera includes the following modes to control the asynchronous reset and shutter
speed:
• Async No Shutter (recommended for strobe applications)
• Async Programmable shutter
• External VINIT with Pulse Width (No-Delay Shutter)
3.5.1 Async No Shutter
Async No Shutter allows for standard strobe and back-to-back strobing applications (strobing both
before the transfer gate and right after).
Operation 19
Page 20

RM/TM-1405GE Series
Figure 7. Async No Shutter
3.5.2 Async Programmable Shutter Speed Control
In Asynchronous Programmable Shutter mode, the video signal starts with internal VINIT. When the
external VINIT pulse is applied, internal VINIT is latched to HD and the internal VINIT is delayed to
set up the shutter speed period. Video output timing starts right after the internal VINIT and single
shots, FDV is output at the internal VINIT timing. Shutter speed is determined by a direct shutter
value entered from 1 to 1040 via the camera’s control software. The shutter value equals 1.5H
(horizontal line time) or 47.6 μsec for each increment.
Figure 8. Async Programmable Shutter Speed Control
20 Operation
Page 21

RM/TM-14
05GE Series
3.5.3 External VINIT With Pulse Width (No-Delay Shutter)
For multiple-camera applications such as 2D or 3D measurement and multi-angle inspection,
simultaneous image capturing at an exact shutter timing for all cameras is a critical requirement.
The TM-1405’s asynchronous pulse-width control mode provides no-delay shutter as standard.
Regardless of the internal pulse timing, the camera discharges at the VINIT leading edge and
transfers charges at the trailing edge of the pulse. Even though each camera runs with slightly
different H and data clock timing, the image capturing is exactly simultaneous.
Figure 9. No-Delay Shutter
3.6 Programmable Look-Up Table (LUT) and Knee Control
The TM-1405GE has a built-in LUT (look-up table) for dynamic range control.
At a specific gain setting, the offset (minimum level.... dark point) and A/D reference top voltage
(maximum level... saturation point) are set to 10-bit A/D input so that the full dynamic range of the
CCD is utilized at 10-bit references as the input and the LUT output is converted into 8-bit to adjust
the gamma correction. Notice that the LUT (look-up table) is not available in the 10-bit grayscale
mode.
The look-up table has two knee points (variable gamma selection) that allow the 10-bit input to be
segmented into three regions. The look-up table selection can be made by knee curve direct input.
Operation 21
Page 22

3.7 Camera Timing Charts
RM/TM-1405GE Series
22 Operation
Page 23

RM/TM-14
05GE Series
0
0
3.8 Video Output
Table 2 Video Output (Horizontal Timing)
Horizontal Timing
Number of pixels
A 1608
B 216
C 1392
D 0
E 0
F 48
G 61
H 107
30fps (μs)
32.16
4.32
27.84
0.96
1.22
2.14
Operation 23
Page 24

RM/TM-1405GE Series
y
K
y
0
0
3
R
<1
9
y
0
Table 3 Video Output (Vertical Timing)
Vertical Timing
Full Scan Area User Scan Area (SP:x, TL:y)
Number of lines 30fps (μs)
J 1053 33864.48
13 418.08
L 1040 33446.40
M 0 0
N 0 0
P 3 96.48
Q 3 96.48
7 225.12
Where
Number of lines
(nfp+11)+nrp+
(nfp+11)+nrp
nrp+6
nfp+5
30fps (μs)
((nfp+11)+nrp+y)*32.12
((nfp+11)+nrp)*32.16
y*32.16
0
0
(nrp+6)*32.12
96.48
(nfp+5)*32.16
3.9 External HD Locking and External VD Reset
Table 4 External HD Locking and External VD Reset (Horizontal Timing)
Horizontal Timing
Number of pixels
eA <1
eB 160
eC 1448
eD 15
Table 5 External HD Locking and External VD Reset (Vertical Timing)
Vertical Timing
Full Scan Area
Number of lines 30fps (μs) Number of lines
eE <1 <32.16
eF 9 289.44
eG 1404 45152.64
eH 0 0
(nfp+2)+nrp+
30fps (μs)
<0.02
3.20
28.96
0.30
User Scan Area (SP:x, TL:y)
30fps (μs)
<32.16
289.44
((nfp+2)+nrp+y)*32.16
0
24 Operation
Page 25

RM/TM-14
05GE Series
K
K
(K
3.10 Asynchronous Reset
Table 6 Asynchronous Reset
aA <1L
aB 9L + 960P
aC 160P
aD 9L
Table 7
Asynchronous Direct Shutter and Pulse-Width Control
(L: lines)
(P: pixels)
30 fps
(μs)
<32.16
308.64
3.20
289.44
aE <1L <32.16
aF 53P 0.972
aG (n+1)L+960P (n+1)*32.16+1.92
aH
Asynchronous Direct Shutter
(ADS=n)
(L: lines)
(P: pixels)
-1 (K-1)*32.16
30 fps (μs) (L: lines) 30 fps (μs)
Pulse-Width Control
(Pulse Width=z)
<10P
36P
z+960P
-1 to K
<0.2
0.72
z+1.92
-1 to K)*32.16
Operation 25
Page 26

4 Functions & Operations
4.1 GigE Vision Standard Interface
The TM-1405GE series cameras are designed in accordance with the GigE Vision standard. Digital
images are transmitted over Cat5e or Cat6 Ethernet cables. All camera functions are also controlled
via the GigE Vision interface.
The camera can operate in continuous mode, providing an endless stream of images. For capturing
individual images, related to a specific event, the camera can also be triggered. For precise
triggering, it is recommended to use a hardware trigger applied to the Hirose 12-pin connector. It is
also possible to initiate a software trigger through the GigE Vision interface. However, when using a
software trigger, certain latency inherent to the GigE interface must be anticipated. This latency,
that manifests itself as jitter, greatly depends on the general conditions and traffic on the GigE
connection. The frame rate described in this manual is for the ideal case and may deteriorate
depending on conditions.
When using multiple cameras (going through a switch and/or a single path) or when operating in a
system with limited transmission bandwidth the Delayed Readout Mode and Inter-Packet Delay
functions can be useful.
RM/TM-1405GE Series
4.2 GigE Vision-Aware Software
A GigE Vision camera can be controlled by any software that understands the protocol. At JAI we
provide the JAI GigE Vision SDK and Control Tool to interface with our cameras. The remainder of the
manual will show screenshots of the JAI Control Tool but other 3rd party software will provide
similar functionalities.
4.3 Recommended Network Configurations
Although the TM-1405GE series cameras conform to Gigabit Ethernet (IEEE 802.3) not all
combinations of network interface cards (NICs) and switches/routers are suitable for use with the
GigE Vision compliant camera.
4.3.1 Verified Network Interface Cards (NICs)
At the time of publishing this document these combinations have been verified:
NIC: Intel Pro/1000MT, Pro/1000GT, Pro/1000PT.
CPU: Intel Core 2 Duo 1.84Ghz.
Memory: 2 GB
Video Card: video card on PCI Express bus with at least 256MB of VRAM.
Functions such as screen saver and power save should not be used. Unnecessary applications such as
Word, Excel or others should not be used.
26 Functions & Operations
Page 27

RM/TM-14
05GE Series
4.3.2 Video data rate (network bandwidth)
The video bit rate for TM-1405GE series cameras at the continuous mode and full scan area. is:
Model Pixel Type Frame Rate
Mono8 30 fps 352.2Mbit/s
TM-1405GE
TMC-1405GE
Note: The Mono10, and BayerR G/GB10 settings at full frame rate will exceed GigE bandwidth. It is
recommended to use Mono8 Mono10Packed or BayerRG/GB8 for max frame rate.
For TM-1405GE series cameras, the jumbo frame can be set at a maximum 16260 Bytes (Factory
setting is 1428 Bytes). To set Jumbo Frames, refer to section 4.3.4.
To ensure the integrity of packets transmitted from the camera it is recommended that you follow
these simple guidelines:
− Whenever possible use a peer-to-peer network.
− When connecting several cameras going through a network switch, make sure it is capable
− Configure inter-packet delay to avoid congestion in network switches.
− Disable screen saver and power save functions on computers.
− Use high performance computers with multi-CPU, hyper-thread and 64-bit CPU, etc.
− Only use Gigabit Ethernet equipment and components together with the camera.
− Use at least Cat5e or preferably Cat6 Ethernet cables.
− Whenever possible, limit the camera output to Mono8 or Mono10Packed for Monochrome
Mono10 30fps1 704.3Gbit/s
Mono10Packed 30 fps 541.4Mbit/s
BayerRG/GB8 30fps 352.2Mbit/s
BayerRG/GB10 30fps1 704.3Gbit/s
of handling jumbo packets and that it has sufficient memory capacity.
cameras, and BayerRG/GB8 for color.
Packet data volume
(GevSCPSPacketSize of 4040)
4.3.3 Disable Firewalls
To ensure proper operation of the JAI SDK & Control Tool, all firewalls must be disabled. This also
includes the Windows firewall.
Click [Start], [Control Panel] for accessing the Windows
firewall configuration.
Functions & Operations 27
Page 28

RM/TM-1405GE Series
4.3.4 Enabling Jumbo Frames
(1) Click [Start] and click [Control Panel].
(2) Click [Performance and Maintenance].
(3) Click [System].
(4) Click [Hardware] tab.
(5) Click [Device Manager]
(6) Expand [Network adapters].
(7) Select target NIC, right-click, and click [Properties].
Note: The following procedure uses the Intel(R) PRO/1000 as an example. If a different NIC is used,
the setup tabs will likely be different. In that case, set the item in a manner similar to what is
described here.
28 Functions & Operations
Page 29

RM/TM-14
05GE Series
(8)Click [Advanced] tab.
(9) Select Jumbo Frames in the Property list, and select the desired Value. This setting defines the
maximum GevSCPS Packet Size the camera can use.
(10)Click [OK].
(11)Close [Device Manager].
(12)Close [System Properties] clicking [OK].
Functions & Operations 29
Page 30

RM/TM-1405GE Series
4.3.5 Setting Receive Descriptors
If the Network Connection Properties list contains a property called Receive Descriptors, then change
its property to the maximum value supported by the NIC installed in the computer.
Click “OK“ to save the property.
4.3.6 Interrupt Moderation rate
If the Network Connection Properties list contains a property
called Interrupt Moderation Rate, then it is possible to set the
preferred value. When it is changed from Minimal, M High and
Extreme, number of interruption is decreased to get better
performance. Set it to “Extreme.”
Click “OK“ to save the property.
4.3.7 Calculating and setting Inter-Packet Delay
When connecting several cameras to one network interface card via a switching hub, it is important
to optimize the Inter-Packet Delay of the cameras to avoid congestion in the switch. A sure sign of
congestion is the loss of packets.
30 Functions & Operations
Page 31

RM/TM-14
05GE Series
Since increasing the inter-packet delay also adds overhead to the data transfer it is important to
calculate the optimal setting in order to make best use of the video bandwidth.
JAI Control Tool has a built in wizard for calculating Inter-Packet Delay. When the Inter-Packet Delay
function is activated, a button appears on the right hand side of the bar. Click the button to open
the calculation wizard window.
At first, type in the frame rate of the connected camera.
TM-1405GE series cameras are 30 fps.
Set the bandwidth at 80%.
Click the calculation tab.
New value is calculated.
Click OK. This shown value is automatically transferred
to the Packet Delay column of the Control Tool.
4.3.8 Confirm the Filter Driver is used
The filter driver is installed as an optional function when JAI SDK is installed. If the filter driver is
not installed at that time, it can be installed from All Programs => JAI SDK => GigE Vision Filter
Driver => Install GigE Vision Filter Driver.
Functions & Operations 31
Page 32

RM/TM-1405GE Series
If the Filter Driver is installed properly, the Camera Control Tool indicates “Driver Type Filter Driver”
in the Network Interface.
If it is not shown, confirm the setting in the “Settings” window. Access the “Settings” window by
clicking on the icon to the left of the blue question mark icon. Refer to the “Getting Started Guide”
provided with the JAI GigE Vision SDK and Control Tool for more information about controls in the
“Settings” window.
32 Functions & Operations
Page 33

RM/TM-14
05GE Series
5 Configuring the Camera
The following sections describe the various features of the camera.
5.1 Acquisition and Trigger Controls
These controls affect exposure mode, exposure time, and image acquisition operations.
Figure 10. Acquisition And Trigger Controls Category
AcquisitionMode: controls how the camera behaves during image acquisition.
The possible options are:
• Continuous: Images will be acquired continuously.
• SingleFrame: A single image will be acquired.
• MultiFrame: the camera acquires the number of images as specified by AcquisitionFrameCount
feature (see next page).
• ContinuousRecording: The camera will continuously acquire and store images onto the onboard
memory. Acquisition is stopped when the onboard memory capacity is reached unless
AcquisitionRecordingWrapAround is set to True. Images can be read from the camera using
either ContinuousReadout or SingleFrameReadout.
• ContinuousReadout: recorded images will be read continuously from the camera’s onboard
memory. When no more images are available, timeouts may occur in some software.
Configuring the Camera 33
Page 34

RM/TM-1405GE Series
• SingleFrameRecording: Acquire a single image and store onto the onboard memory. Images can
be read from the camera using SingleFrameReadout.
• SingleFrameReadout: A single image will be read from the onboard memory. If no frames are
available, a timeout may occur in some software. To retrieve the next image simply execute
AcquisitionStart once.
AcquisitionStart: tells the camera to start acquiring images in the mode as specified by
AcquisitionMode.
AcquisitionStop: tells the camera to stop acquiring images.
AcquisitionFrameCount: specifies the number of frames to be acquired in the MultiFrame Acquisition
mode. Valid range is from 1 to 255.
AcquisitionRecordingWrapAround: for use with ContinuousRecording mode. Possible options:
• True: when the recording buffer is full the oldest recorded image will be overwritten by the
newest image.
• False: continuous recording will stop when buffer is full.
BlockBufferCount: shows the number of images recorded. The number of available Block Buffers
depends on image size, GevSCPSPacketSize, and GrbCh0AcqCfgMemoryWaterLevel. It is
recommended to use at least 1440 for GevSCPSPacketSize. See “PLC Grabber Features” in section
5.8.7 for a description of GrbCh0AcqCfgMemoryWaterLevel.
BlockBufferCurrentIndex: for use with ContinuousReadout and SingleFrameReadout modes. Sets the
index of the image that would be delivered next when AcquisitionStart or Start Acquisition is
executed. Index 0 refers to the oldest image. Subsequent AcquisitionStart commands automatically
increment this value. It is a write only register so you will not see the value change.
ExposureMode: specifies mode of operation for the exposure control (or shutter). All Async modes,
and PulseWidthControl require a trigger signal. The possible options are:
• Off: No shutter.
• ContinuousProgrammable: Puts the camera into ContinuousProgrammable mode and enables
the ContinuousProgrammable value feature below.
• AsyncNoShutter: this mode is meant to be used in a dark environment in conjunction with
strobe light. This setting and all settings below require a trigger signal.
• PulseWidthControl
• AsyncProgrammable: Puts the camera into AsyncProgrammable mode and enables the
AsyncProgrammable value feature below.
ContinuousProgrammable: user defined shutter time in unit of scan lines. Available only when
ExposureMode is in ContinuousProgrammable.
AsyncProgrammable: user defined shutter time in unit of scan lines. Available only when
ExposureMode is in AsyncProgrammable. Requires trigger signal.
TriggerPolarity: this feature selects which signal state, high or low, of the trigger signal will initiate
an image capture for triggered ExposureModes.
5.2 AnalogControls
These controls allow you to make adjustment to image intensities (Gain), Black Level, and auto black
level.
34 Configuring the Camera
Page 35

RM/TM-14
05GE Series
Figure 11. AnalogControls Category
GainRaw: controls the Gain value.
VTop: affects digital gain. Decreasing the value results in a brighter image. It is recommended to
use values below 220.
VBottom: adjusts the black level of the image. Increasing the value will increase the black level and
darken the image. Available only when AutoBlackLevel is disabled.
AutoBlackLevel: adds tiny positive or negative voltages to both Vtop and Vbottom to compensate
black level changes due to temperature. The camera will use AutoBlackLevelRaw as the target.
Enabling this will disable VBottom adjustment.
AutoBlackLevelRaw: sets the Auto Black Level target value. Available when AutoBlackLevel is
enabled.
5.3 Image Size Controls
These controls allow you to make adjustment to the image’s size, and scan mode. ImageSizeControl
category
Configuring the Camera 35
Page 36

RM/TM-1405GE Series
SensorDigitizationTaps: the TM-1405GE is a single tap camera and uses one channel to read out
images from the image sensor.
WidthMax: shows the current valid maximum value for Width.
HeightMax: shows the current valid maximum value for Height.
Width: sets the width of the output image. When ScanMode is changed it is necessary to set this
value to equal to or less than WidthMax.
Height: sets the height of the output image. When ScanMode is changed it is necessary to set this
value to equal to or less than HeightMax.
OffsetX: specify the offset from the left edge of the image captured by the sensor to be sent out of
the camera. Width must be set lower than WidthMax before this value can be increased.
OffsetY: specify the offset from the top of the image captured by the sensor to be sent out of the
camera. Height must be set lower than HeightMax before this value can be increased.
• Offset Example:
• ScanMode is set to A_1392x1040
• Width to 600 and Height to 100.
• OffsetX can have a range of 0 to 40. OffsetX is then set to 20.
• OffsetY can have a range to 0 to 80. OffsetY is then set to 35.
• The resulting image is of size 600x100 with the upper left pixel offset by 20 pixels horizontally
and 35 vertically
Figure 12. Image Output Example.
PixelFormat: specifies the image type captured from the image sensor. Available options:
Monochrome
• Mono8: 8-bit monochrome image.
• Mono10: 10-bit monochrome image with 1 pixel needing 2 bytes.
• Mono10Packed: 10-bit monochrome image with 2 pixels packed into 3 bytes.
Bayer
row.
:
: BayerGB patterns are used for Programmable User Scan Area with odd numbered starting
• BayerRG8: 8-bit Bayer pattern with Red and Green pixels in first row.
• BayerGB8: 8-bit Bayer pattern with Green and Blue pixels in first row.
• BayerRG10: 10-bit Bayer pattern with Red and Green pixels in first row.
36 Configuring the Camera
Page 37

RM/TM-14
05GE Series
• BayerGB10: 10-bit Bayer pattern with Green and Blue pixels in first row.
ScanMode: controls the image size captured by the image sensor. By changing to a smaller size you
can achieve a faster frame rate. After changing ScanMode it is necessary to adjust the Width and
Height value to a valid value. Available options (expressed in unit of Width x Height pixels):
• A_1392x1040
• UserProgrammable: user programmable scan area via UserScanAreaStart and UserScanAreaLines
features.
UserScanAreaStart: sets the starting line of the User Programmable scan area. First line has a value
of 0 and corresponds to the top of the image sensor. For color cameras (TMC/RMC-1405GE) this
value changes the Bayer pattern of the captured image. Sets PixelFormat to BayGB for odd value,
and BayerRG for even value.
UserScanAreaLines: sets the number for the height of the User Programmable scan area.
TestImageSelector: shows a software generated test pattern. Use this feature for debugging
purposes. Available options are:
• Off: turn off test pattern generator and resume normal operation.
• DeviceSpecific: shows diagonal lines on black background. Generated by the camera’s CPU.
• IPEngineTestPattern: shows horizontal striped gradients running right to left.
5.4 LUT (Look Up Table)
The camera’s Lookup Table is used for dynamic range control when the camera is in 8-bit output
mode.
Figure 13. LookUp Table
LUTMode: controls which LUT table to use. There are 2 predefined tables and 1 user configurable
table. Available options:
• Linear: a linear mapping
• Gamma45: also known as Gamma 0.45.
• Knee: you can specify the curve by controlling two points. The camera will calculate the table
base on the Knee values below.
Configuring the Camera 37
Page 38

5.5 UserSets
RM/TM-1405GE Series
KneeX1: controls the X value of first Knee point.
KneeY1: controls the Y value of first Knee point.
KneeX2: controls the X value of second Knee point. This value must be greater than KneeX1.
KneeY2: controls the Y value of second Knee point.
KneeSet: after you have changed the values of the knee points click KneeSet to apply the setting.
The camera will take a few seconds to calculate the LUT table. It is recommended to stop image
acquisition during this time.
LUTInversion: invert the current LUT table. This creates the negative of image.
These controls are for saving camera settings to the onboard memory and selection of which setting
will be used during bootup.
Figure 14. UserSets Category
UserSetSelector: selects which memory page to load, or save.
Available options:
• Default: contains factory settings.
• UserSet1: contains saved user settings.
• …
• UserSet6: contains saved user settings.
UserSetSave: save the camera settings to the currently selected memory page. If Default is selected
in UserSetSelector then UserSetSave is grayed out (Default factory settings won’t be overwritten).
UserSetLoad: load the camera settings from the selected memory page.
UserSetDefaultSelector: chooses which memory page the camera will use as setting during boot up.
38 Configuring the Camera
Page 39

RM/TM-14
05GE Series
5.6 DeviceInformation
Show camera’s general information such as version, model, and serial number.
Figure 15. DeviceInformation Category
DeviceVendorName: shows JAI, Inc.
DevicModelName: shows the camera model name.
DeviceVersion: shows the current camera version.
DeviceID: the device serial ID. This is set at the factory and only available in Expert and Guru
visibility modes.
DeviceUserID: User’s modifiable ID. You can enter any character string up to a limit of 16 characters.
5.7 GigEVisionTransportLayer
More advanced controls for setting IP Address, GigE Vision Stream Channel settings, etc…
A complete explanation of GigE is out of the scope of this manual therefore the user should seek out
various online guides about: Persistent/Static IP, DHCP, LLA, IP Address, Subnet Mask, and
networking.
5.7.1 Persistent IP
When powered up and connected to the network the camera will use the following sequence to
obtain an IP Address:
1. Persistent IP
2. DHCP: a DHCP server on the network will assign the camera an IP Address.
3. Link-Local Address (LLA): an IP Address in the 169.254.X.X ranged is assigned.
By default only DHCP and LLA are enabled. LLA will always be enabled. To disable DHCP mode set
GevCurrentIPConfigurationDHCP to false.
You can also assign a static IP Address to the camera so the camera will always boot up with this IP
Address. To do so follow these instructions:
4. Set Visibility to at least Expert.
Configuring the Camera 39
Page 40

RM/TM-1405GE Series
5. Set GevCurrentIPConfigurationPersistenIP to True.
6. Set GevPersistentIPAddress to the IP Address of your choosing. (Ex: 169.254.0.11)
7. Set GevPersistentSubnetMask to the subnet mask of your choosing (Ex: 255.255.0.0)
Subnet Mask must match the device to which the camera is communicating.
8. Set GevPersistentDefaultGateway to the IP Address of your gateway. (Ex: 0.0.0.0)
Figure 16. GigEVisionTransportLayer Persistent IP
5.7.2 Stream Channel Packet Size
GevSCPSPacketSize: Images are sent via the StreamChannel in GigE Vision terminology. The camera is
able to adjust the size of the data packets sent on this channel. The minimum value of 1440 is
required to get images without dropped packets. It is recommended that a value of 4040 or higher is
used. If setting to above 1428, the network to which the camera is connected must be able to
support Jumbo Frames. To change the stream channel packet size, follow these instructions:
1. Stop image acquisition.
2. Switch Visibility to at least Expert.
3. Set GevSCPSPacketSize to a desired value.
GevHeartbeatTimeout: specifies the current heartbeat timeout in milliseconds. Available only in
Guru visibility mode. The host software must send at least one command to the camera during this
period otherwise it loses control of the camera. This is usually handled by the control tool.
5.8 IPEngine
The camera is sectioned into two logical modules: a camera head and the IPEngine. The camera head
contains the components to capture images, while the IPEngine takes care of interfacing to the
outside world and transmitting captured images. The IPEngine contains the Programmable Logic
Controller (PLC) and the Grabber.
The Grabber is responsible for image transmission. All input and output signals pass through the
Programmable Logic Controller (PLC). The PLC contains a Signal Routing Block, Control Bits, and
Lookup Table. The PLC also contains 4 Pulse Generators and 1 general purpose counter. By GenICam
naming convention the Pulse Generators are called Timers. The Counter and Timers are controlled
40 Configuring the Camera
Page 41

RM/TM-14
05GE Series
under the CountersAndTimersControls category, and the other parts are controlled under the
IPEngine category.
Figure 17. PLC LUT Diagram
Note: Ext_VD, EXT_HD, EVINIT and INTG_CON all go the camera head. TTL Output (Strobe) goes
outside the camera via Pin 8 of the 12-Pin cable.
Configuring the Camera 41
Page 42

RM/TM-1405GE Series
Figure 18. PLC
5.8.1 SignalRoutingBlock
The Signal Routing Block is a group of switches that lets you route signals to the PLC Lookup Table.
There are a total of 8 input lines, numbered from I0 to I7. Each input line can accept a number of
different signals. The input signals can be from the camera head, externally from the 12-Pin cable,
or the PLC itself.
Figure 19. SignalRoutingBlock
42 Configuring the Camera
Page 43

RM/TM-14
05GE Series
Here are the possible input signals into the PLC:
Signal Source Signal Name / Input Pin
12 Pin External_Trigger_In_Pin6 External trigger signal.
12 Pin External_VD_In_Pin7 External vertical drive signal.
12 Pin External_HD_In_Pin9 External horizontal drive signal.
12 Pin External_INT_In External Integration Control / Read Out Inhibit signal.
Camera Internal_FDV_Out Frame Data Valid output signal generated by camera head.
Camera Internal_LDV_Out Line Data Valid output signal generated by camera head.
Camera Internal_CAM_STROBE_Out Strobe output signal generated by the camera head.
PLC PLC_ctrl0 True / False (High/Low) switch used for software trigger. (1)
PLC PLC_ctrl2 True / False (High/Low) switch used for software trigger. (1)
PLC PLC_ctrl3 True / False (High/Low) switch used for software trigger. (1)
PLC PLC_Q2 PLC output that can be routed back to the PLC.
PLC PLC_Q3 PLC output that can be routed back to the PLC.
PLC PLC_Q6 PLC output. This signal is also connected to the EXT_VD that
PLC PLC_Q7 PLC output. This signal is also connected to the EXT_HD that
Counter Counter1Gt Counter1’s output signaling when the current count value is
Counter Counter1Eq Counter1’s output signaling when the current count value
Pulse Generator Timer1Out Pulse Generator 1 output signal.
Pulse Generator Timer2Out Pulse Generator 2 output signal.
Pulse Generator Timer3Out Pulse Generator 3 output signal.
Pulse Generator Timer4Out Pulse Generator 4 output signal.
Description
goes to the camera head. Please see the
PLCSpecialConfigurations section below.
goes to the camera head. Please see the
PLCSpecialConfigurations section below.
greater than some user defined value. Please see Counter
section below.
equals some user defined value. Please see Counter section
below.
Note: (1) There is no PLC_ctrl1.
Configuring the Camera 43
Page 44

RM/TM-1405GE Series
I1 I2 I3 I4 I5
X X X X
X X X
X
X
X
X X X
X
X X
X X X
X X X
X
X X
X X X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
This table show possible signals each input line can accept (“(D)” specifies factory defaults):
Signal Name / Input Pin I0
External_Trigger_In_Pin6 X(D) X
External_VD_In_Pin7 X
External_HD_In_Pin9 X
External_INT_In
Internal_FDV_Out X
Internal_LDV_Out X
Internal_CAM_STROBE_Out X
PLC_ctrl0 X
PLC_ctrl2 X
PLC_ctrl3
PLC_Q2 X
PLC_Q3
PLC_Q6 X
PLC_Q7 X X X X
Counter1Gt
Counter1Eq
Timer1Out X
Timer2Out X
Timer3Out
Timer4Out
X(D) X
X(D)
X(D)
X(D)
I6 I7
X X
X X
X
X X
X
X X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X(D)
X(D)
X(D) X
X
5.8.2 ControlBits
There are 3 Control Bits: PLC_ctrl0, PLC_ctrl2, and PLC_ctrl3. Note that PLC_ctrl1 is not available.
The control bits can be used as software triggers by toggling between two states: True and False.
True sets the signal High, while False sets the signal to Low.
When a bit is toggled on the host software, a Write Register command is sent to the camera. The
arrival time of the packet depends on current network traffic therefore is varied. These are
recommended for testing purposes. For more precise trigger usage please use an external input
trigger signal thru the 12-Pin connector. For a constant periodic trigger signal please use the Pulse
Generators (Timers).
44 Configuring the Camera
Page 45

RM/TM-14
05GE Series
Figure 20. ControlBits
5.8.3 PLC LookupTable
The PLC Lookup Table lets you connect any input signal I0-I7 to any Lookup Table output signal Q0Q17. You can manipulate your inputs using simple or complex Boolean operations. Each Q output
results from the Boolean operations of 4 input variables and 3 Boolean operators.
Figure 21. PLC Q Output
The Q output allows the following Boolean operations:
• Variable0 Op0 Variable1 Op1 Variable2 Op2 Variable3
• (Variable0 Op0 Variable1) Op1 Variable2 Op2 Variable3
• Variable0 Op0 Variable1 Op1 (Variable2 Op2 Variable3)
Configuring the Camera 45
Page 46

RM/TM-1405GE Series
• (Variable0 Op0 Variable1) Op1 (Variable2 Op2 Variable3)
All Q# controls follow this format:
• PLC_Q#_Variable0: the first input signal.
• PLC_Q#_Operator0: a Boolean operator.
• PLC_Q#_Variable1: the second input signal.
• PLC_Q#_Operator1: a Boolean operator.
• PLC_Q#_Variable2: the third input signal.
• PLC_Q#_Operator2: a Boolean operator.
• PLC_Q#_Variable3: the fourth input signal.
Each Variable has this selection:
• Zero: low signal.
• One: high signal.
• PLC_I0
• …
• PLC_I7
• PLC_I0_Not: a Not operation is applied to the signal.
• …
• PLC_I7_Not: a Not operation is applied to the signal.
Operator0 and Operator2 can have the following Boolean operations:
• And
• Or
• Xor
• AndParenthesis: creates a “(Variable0 & Variable1)”, or “(Variable2 & Variable3)” operation.
• OrParenthesis: creates a “(Variable0 | Variable1)”, or “(Variable2 | Variable3)” operation.
• XorParenthesis: creates a “(Variable0 XOR Variable1)”, or “(Variable2 XOR Variable3)”
operation.
Operator1 can have the following Boolean operations:
• And
• Or
• Xor
5.8.4 PLCSpecialConfigurations
Switch Visibility mode to at least Expert to get access to these controls. There are two controls of
interest in this category: PLC_Q6_Configuration and PLC_Q7_Configuration. These two controls
affect which signal source the EXT_VD and EXT_HD come from.
PLC_Q6_Configuration: affects the EXT_VD signal.
• Set to Zero to get the signal from the PLC_Q6 output.
• Set to One to bypass the PLC LUT and get the signal directly from external 12-Pin cable.
PLC_Q7_Configuration: affects the EXT_HD signal.
• Set to Zero to get the signal from the PLC_Q7 output.
• Set to One to bypass the PLC LUT and get the signal directly from external 12-Pin cable.
Note: If the EXT_VD and EXT_HD are not being used set PLC_Q6_Configuration and
PLC_Q7_Configuration to Zero to prevent spurious signals. Improper setting can r esult in black
lines across captured images.
46 Configuring the Camera
Page 47

RM/TM-14
05GE Series
Figure 22. PLC Special Configurations
Figure 23. CountersAndTimersControls
Configuring the Camera 47
Page 48

RM/TM-1405GE Series
5.8.5 Counters
The General Purpose Counter lets you maintain a count between 0 and 232-1 (long integer). You can
use different inputs to increment, decrement, or clear the counter value.
The General Purpose Counter outputs two separate signals that indicate when the count is equal to
and greater than the compare value that you set: Counter1Gt and Counter1Eq. These signals are
available on the Input lines in the Signal Routing Block.
CounterSelector: selects which counter to configure. There is only 1 counter called Counter1.
CounterDecrementEventSource: selects the events that will decrement the counter. This signal
comes from the Q16 pin of the PLC LUT.
Available options:
• Off: no decrement events
• PLC_Q16_RisingEdge: decrement when the signal goes from Low to High
• PLC_Q16_FallingEdge: decrement when the signal goes from High to Low.
• PLC_Q16_AnyEdge: decrement on any Falling or Rising Edge.
• PLC_Q16_LevelHigh: decrement when the signal is at the High section.
• PLC_Q16_LevelLow: decrement when the signal is at the Low section.
CounterDuration: sets the value that the CounterValue will be compared to. When the CounterValue
and CounterDuration are equal, the Counter1Eq signal will go high and stay high as long as the values
are equal. When the CounterValue is greater than CounterDuration, the Counter1Gt signal will go
high.
CounterEventSource: selects the signal event type that will increment the counter. This signal comes
from the Q17 pin of the PLC LUT.
Available options:
• Off: no increment events
• PLC_Q17_RisingEdge: increment when the signal goes from Low to High
• PLC_Q17_FallingEdge: increment when the signal goes from High to Low.
• PLC_Q17_AnyEdge: increment on any Falling or Rising Edge.
• PLC_Q17_LevelHigh: increment when the signal is at the High section.
• PLC_Q17_LevelLow: increment when the signal is at the Low section.
48 Configuring the Camera
Page 49

RM/TM-14
05GE Series
CounterResetActivation: select the signal event type that will reset the counter. The counter will be
reset to 0.
Available options:
• Off: no decrement events
• RisingEdge: increment when the signal goes from Low to High
• FallingEdge: increment when the signal goes from High to Low.
• AnyEdge: increment on any Falling or Rising Edge.
• LevelHigh: increment when the signal is at the High section.
• LevelLow: increment when the signal is at the Low section.
CounterResetSource: selects the source for the reset signal.
Available options:
• PLC_Q3
• PLC_Q7
• PLC_Q8
• PLC_Q9
• PLC_Q10
• PLC_Q11
• PLC_Q16
• PLC_Q17
CounterTriggerSource: select the source signal to start the counter. Currently it is set to Off,
meaning always on.
CounterValue: the read only value showing the current counter value.
5.8.6 Pulse Generators controls
The Pulse Generator lets you create a pulsed digital signal with a configurable frequency. They can
be configured to emit a continuous (periodic) pulse. One use of this feature is to create a periodic
trigger signal. The low section of the signal is called Delay, and the high is called Duration.
TimerSelector: chooses which Timer to configure.
TimerDelayRaw: configures the raw value of the low section of the output signal. The formula to
calculate actual time is:
Duration of Low (nsec) = (Granularity + 1) * (TimerDelayRaw +1) * 30
TimerDurationRaw: configures the raw value of the high section of the output signal. The formula to
calculate actual time is:
Duration of High (nsec) = (Granularity + 1) * TimerDurationRaw * 30
TimerFrequency: a read-only field that shows the frequency of the pulse in Hz.
Configuring the Camera 49
Page 50

RM/TM-1405GE Series
TimerGranularityFactor: a multiplier value used to scale the Delay and the Duration in increments of
30 nsec.
TimerPeriod: shows the timer’s period in units of nsec.
TimerTriggerActivation: select the signal state of the TriggerSource to start the Timer.
• RisingEdge: starts when the trigger signal goes from Low to High
• LevelHigh: starts when the trigger signal is at the High state.
• FallingEdge: starts when the trigger signal goes from High to Low.
• AnyEdge: starts on any Falling or Rising Edge.
• LevelLow: starts when the trigger signal is at the Low state.
TimerTriggerSource: select the source of trigger to start the Timer.
• PLC_Q: the trigger source comes from the PLC Q output. Each Timer has their source from
different Q output port:
− Timer1 trigger comes from PLC_Q9
− Timer1 trigger comes from PLC_Q8
− Timer1 trigger comes from PLC_Q11
− Timer1 trigger comes from PLC_Q10
• Continuous: the Timer is always running.
5.8.7 PLC Grabber Features
IPEngine -->Grabber --> Channel0 -->AcquisitionConfiguration
GrbCh0AcqCfgMemoryWaterLevel: the camera has 16MB of memory for frame buffer. Water level
setting specifies how much of that memory to use with the AcquistionMode’s recording features.
Once the buffer is full no more images will be stored. Possible settings are:
• Level50: 50%
• Level75: 75%
• Level87Point5: 87.5%
• Level100: 100%
GrbCh0AcqCfgInvertPixelData: invert pixel data turning the image into a negative image.
• True: turn on pixel inversion.
• False: turn off pixel inversion.
IPEngine -->Grabber --> Channel0 --> TriggerConfiguration
GrbCh0TrigCfgFrameToSkip: set the number of images to discard for every one it keeps from the
camera head.
5.8.8 IPEngine Examples:
Example 1: Setting the camera to accept external trigger signal:
Set ExposureMode to one of the Asynchronous modes.
Setup SignalRoutingBlock
a. Goto IPEngine > ProgrammableLogicController > SignalRoutingBlock
b. Set Trigger Input line by setting PLC_I0 to External_Trigger_In_Pin6
c. Set Camera Strobe Output by setting PLC_I4 to “Internal CAM_STROBE_Out”.
Setup the PLC to route the external trigger signal to the camera’s trigger line.
d. Goto IPEngine > ProgrammableLogicController > LookupTable > Q0/Q4/ Q5
i. Set PLC_Q0_Variable0 to PLC_I4 (Strobe output)
ii. Set PLC_Q4_Variable0 to PLC_I0 (Trigger Line)
50 Configuring the Camera
Page 51

RM/TM-14
05GE Series
r
iii. Set PLC_Q5_Variable0 to One. (Integration signal always on.)
Example 2: Setting the camera to accept internal trigger signal generated via Timer 1:
Set ExposureMode to one of Asynchronous modes.
Setup the Timer (Pulse Generator)
a. Set TimerSelector to Timer1.
b. Set TimerTriggerSource to Continuous.
c. Set TimerDurationRaw, TimerDelayRaw, TimerGranularityFactor according to
values below.
i. These are example values only; other combinations can also be used.
ii. TimerFrequency tells you the rate of the trigger, hence frame rate.
<0.5 fps
1 fps
5 fps
TimerDurationRaw 200
TimerDelayRaw 10000
TimerGranularityFactor 7000
Setup SignalRoutingBlock
200
4550
7000
200
750
7000
a. Goto IPEngine > ProgrammableLogicController > SignalRoutingBlock
b. Set PLC_I4 to “Internal CAM_STROBE_Out”.
c. Set PLC_I7 to Timer1Out.
Setup the ProgrammableLogicController (PLC) to route the Timer1 output to the camera’s trigger
line.
a. Goto IPEngine > ProgrammableLogicController > LookupTable
i. Set Q4 > PLC_Q4_Variable0 to PLC_I7 (Trigger Line)
ii. Set Q0 > PLC_Q0_Variable0 to PLC_I4 (Strobe output)
iii. Set Q5 > PLC_Q5_Variable0 to One. (Integration signal always on.)
Example 3: Setting up Integration Signal routing from external source:
Goto IPEngine > ProgrammableLogicController > SignalRoutingBlock
Set PLC_I3 to External_INT_In
Goto IPEngine > ProgrammableLogicController > LookupTable
Set Q5 > PLC_Q5_Variable0 to PLC_I3. (Integration signal always on.)
5.9 Register Map
Category / Feature
AcquisitionAndTriggerControls
AcquisitionMode RW Continuous
Configuring the Camera 51
Read/
Write
Value Range Default Value
Continuous Beginne
SingleFrame
MultiFrame
ContinuousRecording
ContinuousReadout
SingleFrameRecording
SingleFrameReadout
Visibility
Level
Page 52

RM/TM-1405GE Series
1
r
r
r
f
f
r
r
r
r
r
r
r
r
0
r
r
Q
Q
r
Category / Feature
AcquisitionFrameCount RW 1-255
AcquisitionStart RO Execute Command
Read/
Write
Value Range Default Value
Visibility
Level
Beginne
Beginne
AcquisitionStop RO Execute Command
AcquisitionRecordingWrapAr
ound
BlockBufferCount RO Depends on image size.
BlockBufferCurrentIndex WO 0 to (BlockBufferCount – 1)
ExposureMode RW Of
AsyncProgrammable RW 0 - 2079
ContinousProgrammable RW 0 - 1052
TriggerPolarity RW ActiveLow
AnalogControls
GainRaw RW 71 - 231
VTop RW 0 – 255 (Max 220
RW False
True
ContinuousProgrammable
AsyncNoShutter
PulseWidthControl
AsyncProgrammable
ActiveHigh
recommended)
Beginne
False
Of
Factory Set Beginne
Factory Set Beginne
ActiveLow Beginne
Factory Set Beginne
Factory Set Guru
Expert
Expert
Expert
Beginne
VBottom RW 0 – 255
AutoBlackLevel RW Enable
Disable
AutoBlackLevelRaw RW 0 – 255
CountersAndTimersControls
TimerSelector RW Timer1
Timer2
Timer3
Timer4
TimerDelayRaw RW 1-65535
TimerDurationRaw RW 1-65535
TimerGranularityFactor RW 1-65535
TimerTriggerActivation RW RisingEdge
LevelHigh
FallingEdge
AnyEdge
LevelLow
TimerTriggerSource RW PLC_
Continuous
52 Configuring the Camera
Factory Set Guru
Factory Set Guru
Factory Set Guru
Timer1
1024
4096
RisingEdge Beginne
PLC_
Beginne
Beginne
Beginne
Beginne
Beginne
Page 53

RM/TM-14
05GE Series
r
f
f
r
0
r
f
f
r
f
f
r
r
f
Off
r
r
r
r
r
r
r
Category / Feature
CounterSelector RW Counter1
Read/
Write
Value Range Default Value
Counter1
Visibility
Level
Beginne
CounterDecrementEventSour
ce
CounterDuration RW 0-4294967295
CounterEventSource RW Of
CounterResetActivation RW Of
CounterResetSource RW PLC_Q3
CounterTriggerSource RW Of
RW Of
PLC_Q16_RisingEdge
PLC_Q16_FallingEdge
PLC_Q16_AnyEdge
PLC_Q16_LevelHigh
PLC_Q16_LevelLow
PLC_Q17_RisingEdge
PLC_Q17_FallingEdge
PLC_Q17_AnyEdge
PLC_Q17_LevelHigh
PLC_Q17_LevelLow
RisingEdge
FallingEdge
AnyEdge
LevelHigh
LevelLow
PLC_Q7
PLC_Q8
PLC_Q9
PLC_Q10
PLC_Q11
PLC_Q16
PLC_Q17
Of
Of
Of
PLC_Q3
Beginne
Beginne
Beginne
Beginne
Beginne
Beginne
CounterValue RO 0 - 4294967295
DeviceInformation
DeviceVendorName RO
DeviceModelName RO
DeviceManufacturerInfo RO
DeviceVersion RO
DeviceID RO
DeviceUserID RW User definable string.
Maximum 16 characters.
GigEVisionTransportLayer
GevSCPSPacketSize RW 72 - 16260
GevPersistentIPAddress RW 000.000.000.000 - 255.255.255 000.000.000.000 Expert
GevPersistentSubnetMask RW 000.000.000.000 - 255.255.255 000.000.000.000 Expert
1428
Beginne
Beginne
Beginne
Beginne
Beginne
Expert
Beginne
Expert
Configuring the Camera 53
Page 54

RM/TM-1405GE Series
f
r
r
r
r
r
r
r
r
r
r
r
f
f
r
r
r
r
r
r
r
r
r
Category / Feature
GevPersistentDefaultGateway RW 000.000.000.000 - 255.255.255 000.000.000.000 Expert
Read/
Write
Value Range Default Value
Visibility
Level
GevCurrentIPConfigurationPe
rsistenIP
ImageSizeControl
SensorDigitizationTaps RW One
WidthMax RO 0 – 1392
HeightMax RO 0 - 1040
Width RW 0 to (WidthMax - OffsetX)
Height RW 0 to (HeightMax - OffsetY)
OffsetX RW WidthMax - Width
OffsetY RW HeightMax - Height
PixelFormat RW Monochrome:
ScanMode RW A_1392x1040
UserScanAreaStart RW 0 to (1040 - UserScanAreaLines
RW On
Off
Mono8
Mono10
Mono10Packed
Bayer:
BayerRG8
BayerGB8
BayerRG10
BayerGB10
UserProgrammable
- 1)
Of
One
Monochrome:
Mono8
Bayer:
BayerRG8
A_1392x1040
0
Beginne
Expert
Beginne
Beginne
Beginne
Beginne
Beginne
Beginne
Beginne
Beginne
Beginne
UserScanAreaLines RW 0 to (1040 - UserScanAreaStart) 500
TestImageSelector RW Of
DeviceSpecific
IPEngineTestPattern
LUT
LUTMode RW Linea
Gamma45
Knne
KneeX1 RW 0 - 255
KneeY1 RW 0 - 255
KneeX2 RW 0 - 255
KneeY2 RW 0 - 255
LUTInversion RW Execute Command
54 Configuring the Camera
Of
Linea
255
255
255
255
Beginne
Beginne
Beginne
Beginne
Beginne
Beginne
Beginne
Beginne
Page 55

05GE Series
r
r
R
r
Category / Feature
UserSets
RM/TM-14
Read/
Write
Value Range Default Value
Visibility
Level
UserSetLoadStatus RO InProgress
Failure
Success
UserSetSelector RW Default
UserSet1
…
UserSet6
UserSetLoad RW Execute Command
UserSetSave
UserSetDefaultSelector RW Default
W Execute Command
UserSet1
…
UserSet6
UserSet1
Expert
Beginne
Beginne
Beginne
Expert
Configuring the Camera 55
Page 56

6 Troubleshooting
6.1 Problems and Solutions
Following are troubleshooting tips for common problems. In general, the problems listed in this
section are solved by following these instructions. If there is no solution listed to the problem you
are encountering, contact a JAI Inc. representative.
6.1.1 Symptom: No Video
Remedies: Check that the following are properly connected and operational.
RM/TM-1405GE Series
Power supplies
Power cables
Main power source
Shutter control
Async mode
Lens
Digital output cable
Analog video cable
6.1.2
Symptom: Dark Video
Remedies: Check that the following are properly connected and operational.
Shutter selection
Iris opening on the lens
6.1.3 Symptom: Non-Synchronized Video
Remedies: Check that the following are properly connected and operational.
Proper mode output
Frame grabber software camera selection
6.2 Information and Support Resources
For further information and support:
North American Technical Support
Phone 408-383-0300
E-Mail: camerasupport.americas@jai.com
Phone: +45 4457 8950
E-Mail: camerasupport@jai.com
Phone +81 45 440 0154
E-Mail: camerasupport@jai.com
56 Troubleshooting
European Technical Support
Japan/Asia Technical Support
Page 57

RM/TM-14
05GE Series
y
Mailing Address
Mail: JAI, Inc.
Sales Department
625 River Oaks Parkwa
San Jose, CA 95134
ATTN: Video Applications
Web Site: www.jai.com
Troubleshooting 57
Page 58

7 Appendix
7.1 Specifications
Table 8 TM-1405GE Camera Specifications Table
Feature TM-1405GE
Imager 1/2” progressive scan interline transfer CCD (ICX205AL/AK)
Active Area 6.47mm x 4.84mm
Active Pixels 1392 (H) x 1040 (V)
Cell Size 4.65μm x 4.65μm
Display Mode
(Active Pixels)
Sync
Data Clock Output 50.00 MHz
Resolution Digital: 1392 (H) x 1040 (V)
S/N Ratio 51dB min.
Min. Illumination
Video Output
Gamma Programmable LUT (1.0 std.)
Lens Mount C-mount (use >1/2” format lenses or larger)
Power Requirement 12V DC ±10%, 420mA (typical at 25°C)
Operating Temp. -10°C to 50°C*
Vibration 7 Grms (10 Hz to 2000 Hz) Random
Shock 70G, 11 ms half sine
Size (W x H x L) 50.8mm x 50.8mm x 83.5mm
Weight 212 grams (7.47 oz.) without tripod
Optional Functions OP 3-1, Internal IR filter added;
Optional Accessories
Power Cable
Power Supply
Tripod Mounting Kit
*. Refer to Section 2.2.1 for information on camera heat dissipation. Image quality
degrades with increasing temperature.
RM/TM-1405GE Series
1392 (H) x 1040 (V) @ 30 Hz
Internal/External auto switch
HD/VD, 4.0 Vp-p impedance 4.7 K Ω
VD=30.00 Hz ±5%, non-interlace
HD=31.1 kHz ±5%
Monochrome = 0.8 lux; Color = 6.0 lux
f = 1.4 without IR cut filter (no shutter)
Analog: 714 mV, 75 Ω, (750 mV white clip)
Digital output: Gigabit Ethernet (8- or 10-bit selectable)
OP 3-2, optical filter removal (color only);
OP 7-5, configure to 15 fps;
OP21-1QUV, glassless CCD imager with Quartz window (color)
12P-02S
PD-12U series
TP-20
58 Appendix
Page 59

RM/TM-14
05GE Series
7.1.1 TM-1405GE Physical Dimensions
Figure 24. Physical Dimensions
Caution: When mounting the camera to any fixture, do not use screws that extend more than 5 mm
into the camera housing to avoid possible damage to the internal circuitry. For attaching
the tripod mounting plate, only the supplied screws should be used.
Appendix 59
Page 60

RM/TM-1405GE Series
7.1.2 Spectral Response
Figure 25. Monochrome Spectral Response
Figure 26. Color Spectral Response
60 Appendix
Page 61

Page 62

Europe, Middle East & Africa
Phone +45 4457 8888
Fax +45 4491 3252
Asia Pacific
Phone +81 45 440 0154
Fax +81 45 440 0166
Americas
Phone (Toll-Free) 1 800 445-5444
Phone +1 408 383-0301
www.jai.com
 Loading...
Loading...