Page 1

10098
Rev. C
TM-4100GE Progressive Scan Shutter Cameras
Operation Manual
Imaging Products
Page 2

Page 3

Notice Page
A
S
S
O
C
I
A
T
I
O
N
Notice
The material contained in this manual consists of information that is proprietary to JAI PULNiX, Inc., and may only be used
by the purchasers of the product. JAI PULNiX, Inc. makes no warranty for the use of its product and assumes no responsibility
for any errors which may appear or for damages resulting from the use of the information contained herein. JAI PULNiX, Inc.
reserves the right to make changes without notice.
Microsoft, Windows XP, Windows 2000, Windows 98, Windows NT, and Windows Explorer are either registered trademarks
or trademarks of Microsoft Corporation in the United States and/or other countries.
Warranty
For information about the warranty, please contact your factory representative.
Certifications
CE Compliance
The TM-4100GE camera has been certified to conform to the requirements of Council Directive 89/336/EC for electromagnetic compatibility and to comply with the following European Standards:
Immunity: EN 55024: 1998 + A1: 2001 + A2: 2003
Emissions: EN 55022: 1998 + A1: 2000 + A2: 2003
All JAI PULNiX products bearing the CE mark have been declared to be in conformance with the applicable EEC Council
Directives. However, certain factory-installed options or customer-requested modifications may compromise electromagnetic
compatibility and affect CE compliance. Please note that the use of interconnect cables that are not properly grounded and
shielded may affect CE compliance.
i
Contact JAI PULNiX Applications Engineering Department for further information regarding CE compliance.
FCC
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class A digital device, pursuant to Part 15 of the
FCC Rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection against harmful interference when the equipment is
operated in a commercial environment. This equipment generates, uses and can radiate radio frequency energy and, if not
installed and used in accordance with the instruction manual, may cause harmful interference to radio communications. Operation of this equipment in a residential area may cause harmful interference, in which case the user will be required to correct
the interference at his own expense.
WARNING
Changes or modifications to this unit not expressly approved by the party responsible for
FCC compliance could void the user’s authority to operate the equipment.
TM-4100GE Series Operation Manual
JAI PULNiX, Inc.
625 River Oaks Parkway
San Jose, CA 95134
Tel:(408) 383-0300
Tel:(800) 445-5444
Fax:(408) 383-0301
E-mail: imaging@jaipulnix.com
www.jaipulnix.com
D
E
T
A
I
M
M
A
O
G
T
I
N
U
A
MEMBE
G
R
FILE #
A3942
R
E
U
G
L
®
I
S
T
D
E
E
R
JAI PULNiX, INC.
I
F
ISO-9001
M
R
TM-4100GE Progressive Scan Cameras
Page 4

Page 5

Table of Contents
1 Software Introduction. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1
1.1 Scope of the Document . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
1.2 Related Documents. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
1.3 Gigabit Ethernet Camera Interface. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
1.4 Software Installation. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
1.4.1 Before Installing the GigE Series Camera-SDK Software . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
1.4.2 Installing the Software . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
1.4.3 Installing the Software . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
1.4.4 Uninstalling the Software . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
1.4.5 Quick-Start . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
2 Connectors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .7
2.1 Power and Signals Connector. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
2.2 Ethernet. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
3 Configuring the TM-4100GE Camera . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .9
3.1 Setup . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
3.2 Configuring the Imager . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
3.2.1 GUI Features. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
3.3 Configuring the Internal Frame Grabber . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
3.4 Modes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
3.4.1 Check the Current Camera Setting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
3.4.2 Exposure Control . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
3.4.3 Scan Mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
3.4.4 Gain Settings. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
3.4.5 The Gain . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
3.4.6 Look-Up Table . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
3.4.7 Memory Pages . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
3.4.8 Free-Running Mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
3.4.9 Externally Triggered. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
3.4.10 Internally Triggered . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
3.4.11 Save/Restore Settings to Your Hard Disk. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
3.4.12 White Balance Control (Color Versions Only) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
3.4.13 Main Menu: “Option” . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
3.4.14 Version . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
3.4.15 Exit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
iii
4 Signal Handling . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .20
4.1 Camera Inputs. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
4.2 Camera Outputs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
4.3 GPIO Control Block . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
4.4 GPIO Label Table. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
4.5 Pulse Generators. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
5 GigE Series Camera Serial Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .26
6 Hardware Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .31
Page 6

6.1 Product Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
6.2 Features. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
7 Installation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .34
7.1 Getting Started . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
7.1.1 Unpacking Instructions. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
7.1.2 Components . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
7.1.3 Accessories and Options. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
7.2 Camera Setup . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
7.2.1 Heat Dissipation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
7.2.2 Connector Pin Configurations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
7.2.3 Power Supplies and Power Cable Setup. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
7.2.4 Attaching the Camera Lens. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
7.2.5 Adjustable Back-Focus. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
8 Operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .40
8.1 Progressive Scanning . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
8.2 Bayer Color Filter (Color Versions) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
8.2.1 Color Filter Array . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
8.2.2 Bayer Color Filter Array (CFA) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
8.2.3 Starting Pixel Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
8.2.4 Sync and Data . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
8.2.5 Camera Functions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
8.2.6 Interpolation Software . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
8.2.7 Color Interpolation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
8.3 Electronic Shutter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
8.4 Integration. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
8.5 External Sync . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
8.6 Asynchronous Reset . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
8.6.1 Async No Shutter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46
8.6.2 Internal Shutter Speed Control . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47
8.6.3 External VINIT With Pulse Width (No-Delay Shutter) and ROI
(Read-out Inhibit) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 48
8.7 Dynamic Range Control . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
8.7.1 Programmable Look-Up Table (LUT) and Knee Control . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 50
8.8 Camera Timing Charts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 51
iv
9 Troubleshooting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .55
9.1 Problems and Solutions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 55
9.1.1 Symptom: No Video . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 55
9.1.2 Symptom: Dark Video . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 55
9.1.3 Symptom: Non-Synchronized Video . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 55
9.2 Information and Support Resources . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 56
10 Appendix . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .57
10.1 Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 57
10.1.1 TM-4100GE Physical Dimensions. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 58
10.1.2 Spectral Response. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 59
Page 7

List of Tables
TABLE 1. Hirose Connector, Pin Assignment . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
TABLE 2. GPIO Look-Up Table Input Labels . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
TABLE 3. GPIO Look-Up Table Output Labels. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
TABLE 4. TM-4100GE Command List . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
TABLE 5. 18 Bytes Status Report. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
Table 6. 12-Pin Connector . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
TABLE 7. Scan Mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
TABLE 8. Electronic Shutter Speeds . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
TABLE 9. Video Output . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 53
TABLE 10. External HD Locking and External VD Reset. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 54
TABLE 11. Async Reset . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 54
TABLE 12. TM-4100GE Camera Specifications Table . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 57
v
Page 8

vi
Page 9

List of Figures
Figure 1. Scanning for Drivers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
Figure 2. Intel Pro Install Choices. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
FIGURE 3. Change and Remove Buttons. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
FIGURE 4. Network Device Finder Window . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
FIGURE 5. Select Camera Window . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
FIGURE 6. TM-4100GE Back Panel Connectors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
FIGURE 7. HR10A-10R-12P . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
FIGURE 8. Ethernet GigE Socket. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
FIGURE 9. Camera Interface Application Dialog Box . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
FIGURE 10. Advanced Configuration Window . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
FIGURE 11. Integrated GigE Camera Software. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
FIGURE 12. Advanced Configuration - Port Communication . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
FIGURE 13. Exposure Control . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
FIGURE 14. Mode Control Pull-down . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
FIGURE 15. Shutter Speed . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
FIGURE 16. Scan Mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
FIGURE 17. Offset Level . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
FIGURE 18. Look-Up Table. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
FIGURE 19. Memory Pages . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
FIGURE 20. White Balance Control Settings. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
FIGURE 21. GE Camera GPIO Control Block. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
FIGURE 22. GPIO Look-Up Table. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
FIGURE 23. The GPIO Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
FIGURE 24. Pulse Generator Page. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
Figure 24. 12-Pin Connector Pinouts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
Figure 25. GigE Ethernet Connector . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
FIGURE 26. 12P-02S Interface Cable (optional) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
FIGURE 27. Back-Focus Set-Screw Locations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
FIGURE 28. Full Progressive Scan Mode (A) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
FIGURE 29. Bayer Color Filter Response . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
FIGURE 30. Example of Color CCD CFA Pattern. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
FIGURE 31. Example of TMC-4100GE (Same as TM-4100GE) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
FIGURE 32. No-Delay Shutter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 48
FIGURE 33. Read-Out Inhibit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
FIGURE 34. Physical Dimensions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 58
FIGURE 35. Spectral Response . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 59
vii
Page 10

viii
Page 11

September 20, 2006
TM-4100GE Software
Operation Manual
1 Software Introduction
1.1 Scope of the Document
This manual describes how to access and use features specific to JAI PULNiX's Gigabit Ethernet
camera, the TM-4100GE. The camera’s different operation modes are described in the hardware section
of this manual, which begins on page 31.
The TM-4100GE series consists of the TM-4100GE (monochrome) and the TMC-4100GE (color).
Unless otherwise noted, all information contained in this manual is relevant to both models.
1.2 Related Documents
The appendix contains descriptions of the TM-4100GE camera’s internal frame grabber and how to
connect the camera. The appendix complements, and should be used in conjunction with the three
following documents:
• Cam2Net User’s Manual
• Cam2Net IP Device Drivers
• Cam2Net C++ SDK Reference Manual
These documents are part of the GigE software package and are added to your system when the
software is installed.
1.3 Gigabit Ethernet Camera Interface
The GigE interface provides an easily connectable, high-bandwidth imaging solution, where video data
is sent as IP packets over an industry-standard GigE network.
TM-4100GE Software
Page 12

Page 2
Software Introduction
Point-to-point (unswitched) transmission is up to 100 meters. With Gigabit Ethernet switches, the
transmission distance is virtually unlimited.
Note: Refer to the section on time-outs and packets in the Cam2Net User’s Manual for more
information on packet sizes for point-to-point and networked applications.
Communication with a GigE camera is completely transparent to the user, so if you are used to working
with Camera Link® or the JAI Cam2Net adapter, you will find it very easy to migrate.
The TM-4100GE camera has internal frame memory, which sends only the actual image data using the
Gigabit Ethernet interface.
At the PC, the Cam2Net Software Development Kit (SDK) provides a communications interface that
maps the RS-232 command channel through the IP link. All commands sent to and received from the
camera are transparently routed to/from the host PC via the GigE link.
Refer to the Cam2Net User’s Manual for details about network requirements, compatibility, and so on.
1.4 Software Installation
The following instructions explain how to install the JAI PULNiX GigE camera-control software on a
PC.
1.4.1 Before Installing the GigE Series Camera-SDK Software
Before installing the JAI PULNiX GigE camera-SDK software, please note the following requirements.
• Your computer must have a Pentium processor running at least 1.4GHZ, and its operating system
must be either Microsoft Windows XP Pro or Windows 2000.
• Installation of the software requires approximately 75 MB of free space in your PC hard disk.
1.4.2 Installing the Software
To install the JAI PULNiX GigE camera-SDK software, read and follow the directions included in the
document download card. If your computer does not have Internet access, call JAI PULNiX at 1 800
445 5444 to request that the software be sent to you on a CD-ROM.
Install the software using the following steps:
1.4.3 Installing the Software
To install the JAI PULNiX GigE camera-control software, read and follow the directions included in the
document download card. If your computer does not have Internet access, call JAI PULNiX at 1 800
445 5444 to request that the software be sent to you on a CD-ROM.
Install the software using the following steps:
1. Open the folder “JAI” and run the IPEngineSDK.exe file to install the Camera Interface
Application.
TM-4100GE Software
Page 13
Page 3
Software Introduction
2. Open the folder “GigE_Software” and run the setup.bat file. This installs the GigE camera
software as part of the Camera Interface Application. It copies the file cycampulnix.dll to the folder
C:\Program Files\JAI\Cam2Net\Binaries.
3. The program initiates a driver scan. Allow the network card driver installation at this time. (If you
cancel the installation for some reason this dialog box can be accessed at a later time; go to “Start”
--> “Programs” --> “JAI AS” --> “Launch Driver Installation Tool” to launch the driver
install).
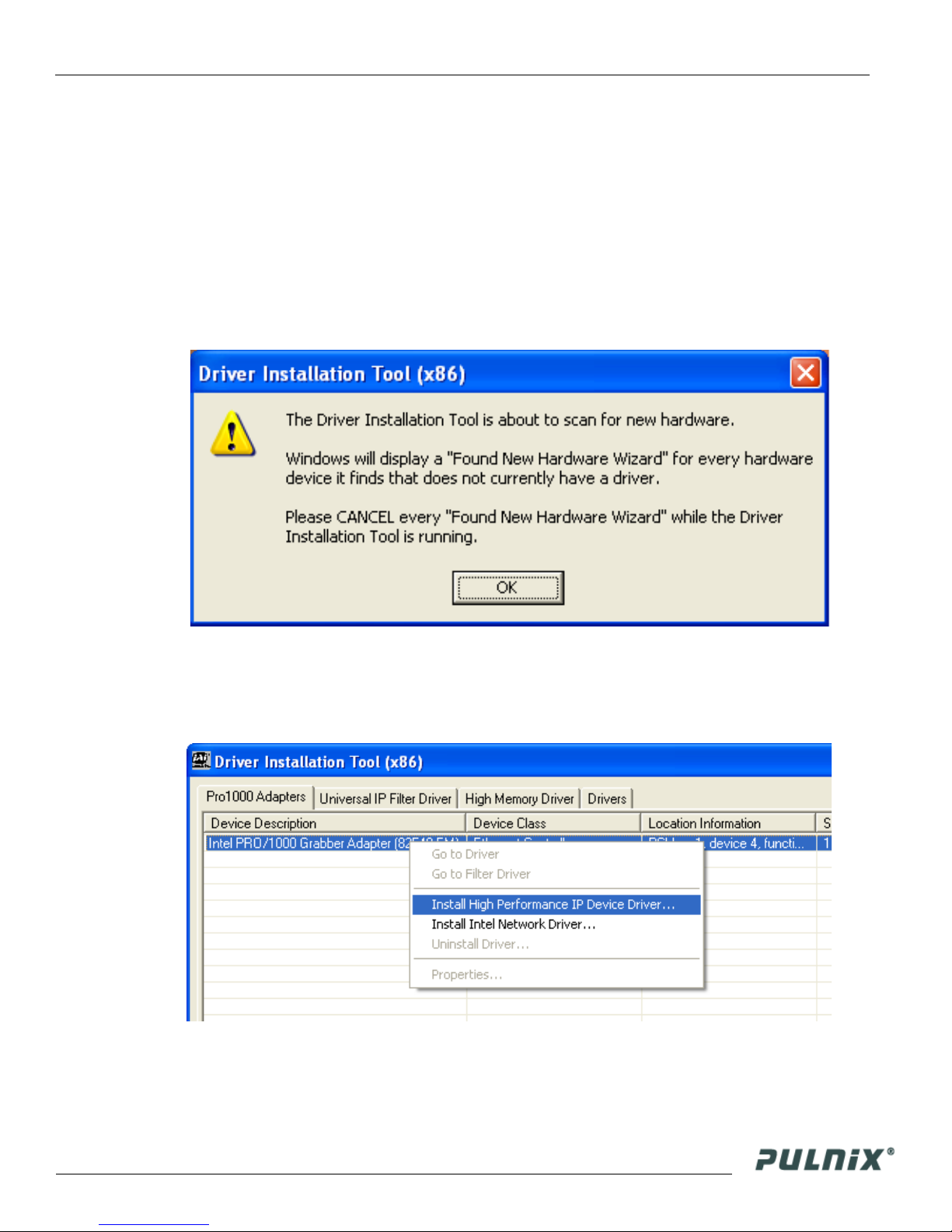
4. A driver installation tool dialog box displays. Read the message about canceling found new devices
and then click “OK”.
Figure 1. Scanning for Drivers
The Driver Installation Tool dialog box appears with a listing of all NIC cards on the system.
5.
6. Right click on the net driver desired for the camera. If the driver is an Intel Pro a high performance
option is available for install.
Figure 2. Intel Pro Install Choices
Right click on the net driver desired for the camera.
7.
8. Select the desired driver install “Install High Performance IP Device Driver” or “Install Intel
Network Driver”. The network installation options vary, based on the NIC card installed on the
TM-4100GE Software
Page 14

Page 4
Software Introduction
9. For information on other network card installs click “Start”-->”JAI A.S”-->”Cam2Net”-->”Docu-
10. Go to “Start” --> “Programs” --> “JAI AS” --> “Cam2Net” --> “Launch Coyote application”
11.
1.4.4 Uninstalling the Software
To uninstall the JAI PULNiX GigE camera-control software from the control panel, use the following
steps:
1. Open “Add or Remove Programs” in the control panel.
2. Select “JAI Cam2Net” from the lists of the installed software.
3. Click the “Change or Remove” button as shown in Figure 1.
FIGURE 3. Change and Remove Buttons
system. A dialog box asks for verification of the selected install. Click “Yes”. Follow the instructions on any additional dialog boxes.
mentation”-->”Cam2Net IP Device Drivers”. An Acrobat file has instruction to help guide you
through the proper install.
to launch the camera control tool.
1.4.5 Quick-Start
Use the following quick-start process when the Camera Interface Application is installed on your PC.
1. Connect the camera. The Hirose pin layout is shown in Table 1 on page 7. Both the Hirose and the
network cable (RJ-45) are illustrated in Figure 6.
2. Run the Camera Interface Application.
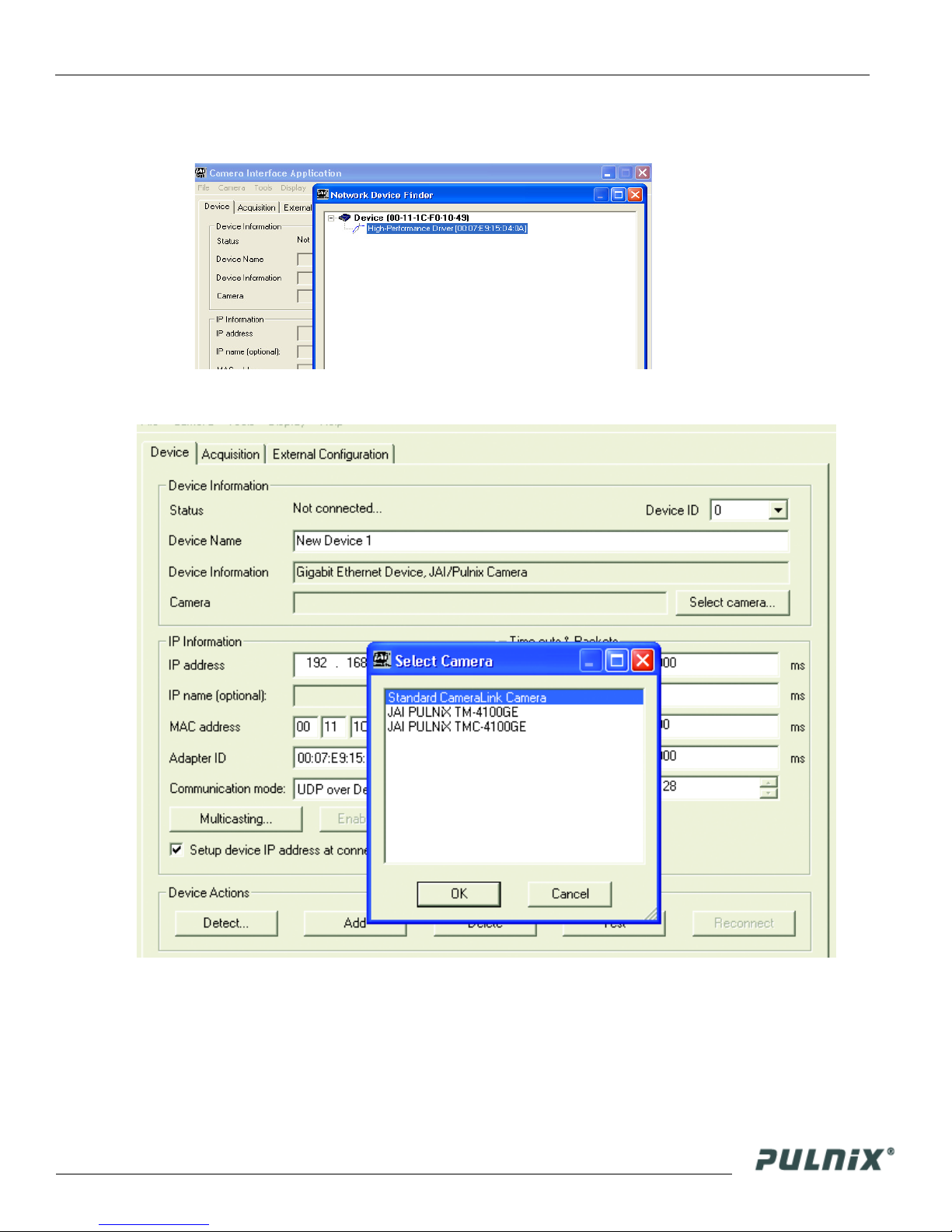
3. Click “Detect.” Assign a suitable IP address to the camera. The window shown in Figure 2 appears.
TM-4100GE Software
Page 15
Software Introduction
FIGURE 4. Network Device Finder Window
Select the appropriate camera from the list, similar to the window shown in Figure 3 and click OK.
4.
FIGURE 5. Select Camera Window
Page 5
5.
Go to the “Acquisition” tab and click Start. An image stream should appear.
6. Click on Configure and open the “GigE Camera Software” dialog box. This is your integrated
control software.
Note: the color version (TMC-4100GE) requires color interpolation to be performed in the frame
grabber or by using the host computer’s CPU. In default mode, the camera supports 2 x 2 color
interpolation. For better color performance, the user can select 3 x 3 interpolation in the Camera
TM-4100GE Software
Page 16

Page 6
Software Introduction
Interface Application. Go to the “Acquisition” tab and click Configure. In the Advanced Configuration
Window, select the “Pixel Type” tab. Make sure the camera is set to the proper color space and pixel
depth, then click the check-box labeled “Use 3 x 3 Bayer Interpolation” in the “Conversion Options”
panel. More information on color interpolation and the color filter array (CFA) can be found in Section
8.2 beginning on page 38 of this manual.
TM-4100GE Software
Page 17

2 Connectors
The camera has two sockets, as shown in Figure 6 below:
• 12-pin Hirose for power, trigger, RS-232 communication and TTL I/O.
• RJ-45 for Gigabit Ethernet.
FIGURE 6. TM-4100GE Back Panel Connectors
Page 7
Connectors
GigE
These connectors are described in Section 2.1 and Section 2.2 below.
2.1 Power and Signals Connector
The GE camera receives power and signal through a 12-pin Hirose connector. Table 1 lists the pin
layout and describes the function of each pin. The table lists the GPIO assignments for the relevant pins.
A magnified illustration of each pin’s assignment follows in Figure 7 on page 8.
TABLE 1. Hirose Connector, Pin Assignment
Pin # Definition Description GPIO Assignment
1 GND Power ground
2 +12V Power supply in
3 AGND Analog ground (video)
4 Reserved Reserved
5 GND Ground (TTL) - Digital
6
7
8
9
10 RESV Reserved
11
12 RESV Reserved
TTL IN
(EXT_TRIG)
TTL IN
(EXT_VD)
TTL OUT
(STROBE)
TTL IN
(EXT_HD)
TTL IN
(INTG_CON)
INTG IN (CC2 equivalent) I0
POWER
HD in (CC4 equivalent) I1 (can bypass GPIO LUT)
Strobe output Q0
VD in (CC3 equivalent) I2 (can bypass GPIO LUT)
Reserved I3
TM-4100GE Software
Page 18

Page 8
Connectors
FIGURE 7. HR10A-10R-12P
1
2
11
3
10
9
8
12 7
2.2 Ethernet
The GigE socket, marked on the camera’s back panel as “GigE,” is a standard RJ-45 Ethernet socket.
Use at least cat5e UTP cables (Cat6 cables are preferred). If you wish to connect the camera directly to
a PC, you must use a cross-over cable. Refer to the Cam2Net User's Manual for details.
FIGURE 8. Ethernet GigE Socket
4
6
5
1
GigE
1. JAI PULNiX recommends the use of shielded cables to reduce emissions and for CE/FCC
compliance. Double-shielded cables will further reduce emissions.
TM-4100GE Software
Page 19

3 Configuring the TM-4100GE Camera
The configuration of your GigE camera consists of two parts:
• The imager configuration (CCD and control circuits)
• The internal frame grabber configuration
The imager can be configured for partial scan, binning, and so on, just like a Camera Link camera. The
internal frame grabber is automatically configured for the pixel type, windowing, image size, I/O and so
on, by the GigE camera software.
3.1 Setup
If you have a peer-to-peer connection between the TM-4100GE camera and your PC without network
switches, your packet size can be the default value (8128 bytes) as shown in Figure 7. However, if you
are connecting the TM-4100GE to your PC through a network switch, then you need to know the
maximum packet size that your network switch supports. Typically, if your switch supports jumbo
packets, then you should keep the packet size to 8128 bytes. If your switch does not support jumbo
packets, then you may need to change the packet size to 1440 bytes.
Page 9
Configuring the TM-4100GE Camera
FIGURE 9. Camera Interface Application Dialog Box
Note: If you connect the
camera through a network
switch, you may need to
modify the packet size.
TM-4100GE Software
Page 20

Page 10
Configuring the TM-4100GE Camera
To use the integrated GigE camera software, use the following steps:
1. Start the Camera Interface Application. The dialog box shown in Figure 9 appears.
2. Click the Detect button to detect the device and driver in the “Device Actions” panel.
3. Click Select Camera and select TM-4100GE or TMC-4100GE (color) from the camera list.
4. Select the “Acquisition” tab and click Configure. The camera configuration dialog box displays.
5. Select the “GigE Camera Software” tab. This is the Integrated GigE Camera Software shown in
Figure 11 on the next page.
The TM-4100GE camera can operate in either 8-bit or 10-bit digital output mode. The 8-bit/10-bit
selection is possible through the GigE integrated software. To select the mode, open the Configure page
and select the Pixel Type tab. Under the Pixel Type, select either Grayscale 8, or Grayscale 10. Note
that when Grayscale 10, 2 taps is selected, the LUT (Look-Up Table) is not available in this mode.
FIGURE 10. Advanced Configuration Window
TM-4100GE Software
Page 21

3.2 Configuring the Imager
To configure the TM-4100GE’s imager, use the integrated GigE camera software that is part of the
Cam2Net Camera Interface Application. You can also use the dual-tap AccuPiXEL GigE control tool,
but that will not update any internal grabber settings. “Hardware Introduction” on page 27 of this
manual contains a description of the different image settings of the camera.
FIGURE 11. Integrated GigE Camera Software
Page 11
Configuring the TM-4100GE Camera
TM-4100GE Software
Page 22

Page 12
Configuring the TM-4100GE Camera
3.2.1 GUI Features
You can control the following camera functions using the integrated camera software.
• Shutter Speed and Mode
• Scan Mode
• Gain Control
• Offset Level
• Memory Pages
• LUT (Look-Up Table) Control
3.3 Configuring the Internal Frame Grabber
The integrated camera software updates the internal frame grabber settings automatically. In addition,
because the internal frame grabber configuration is independent of the imager configuration, you can set
up (that is, “window”) the internal frame grabber separately, for example, the Image Settings tab in the
integrated camera software. This has the added benefit of reducing unnecessary traffic on the GigE
network, hence freeing bandwidth for other cameras.
3.4 Modes
This section includes examples of various types of setup actions available through the camera
configuration dialog box.
3.4.1 Check the Current Camera Setting
You can manually send camera commands from the “Serial Free From” tab of the Configuration
window shown in Figure 12. Use the serial port and click the “CR” check box. Enter :RPST and click
Send to get the current camera setting. For detailed information about the current camera setting, refer
to Table 4 on page 26.
TM-4100GE Software
Page 23

Configuring the TM-4100GE Camera
FIGURE 12. Advanced Configuration - Port Communication
Page 13
3.4.2 Exposure Control
In Exposure Control, under the GigE Camera software tab, shown in Figure 13, you can specify the
shutter mode and set the shutter speed and direct shutter values.
FIGURE 13. Exposure Control
TM-4100GE Software
Page 24

Page 14
Configuring the TM-4100GE Camera
Shutter Mode
Use the pull-down menu shown in Figure 14. to select from Manual or Async mode.
FIGURE 14. Mode Control Pull-down
Shutter Speed
The shutter speed setting, shown in Figure 15, allows you to select the specific shutter speed for manual
shutter and Async shutter. Manual shutter speed 0 is No Shutter mode; Async shutter speed 0 is Async No Shutter mode; Async shutter speed 9 is Async - No Delay shutter mode (pulse width control). Direct
Shutter allows you to select shutter speed for direct shutter count by the video line. Please note that
manual shutter 1 and 2 are not available in scan mode B and D.
FIGURE 15. Shutter Speed
3.4.3 Scan Mode
The TM-4100GE camera has full and partial scan modes as shown in Figure 16. The partial scan area
allows you to select the different scan lines. When the scan area starts from an odd line, for a color
camera, an offset of 1 is added in the vertical direction. The TM-4100GE camera has no binning modes.
FIGURE 16. Scan Mode
TM-4100GE Software
Page 25

Page 15
Configuring the TM-4100GE Camera
3.4.4 Gain Settings
3.4.4 (a) Gain
The Gain Settings control box, shown in Figure , allows you to change the Gain value from 2.97dB to
21.96 dB. To change the value, move the slider or enter the value directly into the text box.
3.4.4 (b) Gain Channel Balance Control
Click the “Channel Balance” button to enable gain channel balancing. Once gain channel balancing has
finished, the software disables this feature automatically. Please note that when channel balancing,
channel B aligns to channel A. Good channel balance is obtained by exposing the camera to a uniform
light source under 80% saturation. If the camera is in Async trigger mode and the trigger frequency is
low (or slow), it may take longer to collect enough frames to balance the channel. Another condition in
which Channel Balance may not work properly is when you use the high-speed shutter under lowfrequency light, such as fluorescent light. In both cases, the channel balance will time-out in 10 seconds
if the balance is not reached.
3.4.5 The Gain
Offset Level
The Channel A offset level is master, the channel B is slave. The offset level box, shown in Figure 17,
allows you to change Channel A offset voltage. To change the value, move the slider or enter the value
directly into the box. The camera itself automatically adjusts Channel B offset voltage, every other
frame. Please note that offset level control is not available in scan modes C and D.
FIGURE 17. Offset Level
TM-4100GE Software
Page 26

Page 16
Configuring the TM-4100GE Camera
3.4.6 Look-Up Table
The look-up table (LUT) control, shown in Figure 18, allows you to change two knee point values.
FIGURE 18. Look-Up Table
Enter X1, Y1, X2, Y2 values directly to adjust the knee curve. In the integrated camera software, the
look-up table can also be controlled interactively. The Table Selection pull-down menu allows you to
select the Linear or Gamma 45 option. This control also allows you to check the positive or negative
box to choose an image option.
3.4.7 Memory Pages
All the camera parameters such as shutter mode, shutter speed, gain, offset level, scan mode, and LUT
can be saved into seven available memory pages on the EEPROM in the camera. The pages are
numbered 0-6. The Load Page button loads the corresponding camera settings from the EEPROM while
the write page button writes the current camera settings to the corresponding memory page in the
EEPROM.
Page 1, shown in Figure 19, is the power-up default page. Page 0 is the factory default. To save your
current camera settings for power up default, write the settings to memory page 1.
FIGURE 19. Memory Pages
To reset memory page 1 to the factory default settings, load memory page 0 and save those settings to
memory page 1. Page 0 is password-protected and you cannot write to it. If you find that you do need to
write to page 0, contact JAI PULNiX for password access.
TM-4100GE Software
Page 27

Page 17
Configuring the TM-4100GE Camera
Note: Configurations such as grabber settings, pulse generator, GPIO, and image setting must be saved
into the XML file. Refer to Section 3.4.1, “Check the Current Camera Setting,” on page 12 for more
information.
3.4.8 Free-Running Mode
The camera must be in “Manual Shutter” or “Direct Shutter” mode. In the example below, there is no
partial scan.
1. Connect to the camera.
2. Under the “Device Features” tab, set the GPIO look-up table to Q5=1.
3. Under the “GigE Software” tab, change the manual shutter or direct shutter values.
4. Click Start.
You should now see a free-running video stream.
3.4.9 Externally Triggered
The external trigger is sent through pin 6 of the 12-pin Hirose connector. To use the software to enable
the external trigger, use the following steps:
1. Change the GigE camera software shutter mode to Async. Shutter.
2. Set the GPIO look-up table to Q4 = I0 and Q5 = 1.
3.4.10 Internally Triggered
The camera-control software includes pulse generators that you can use to trigger the camera internally.
To do this, use the following steps:
1. Select “Pulse Generator 0” under the “Device Features” tab. Set the pulse width and delay and
check the “Periodic” option if needed.
2. Set the GPIO look-up table to Q5=1 and Q4=I7.
3. Set the shutter mode in the GigE camera software page to async shutter. For more information,
refer to Section 3.4.2, “Exposure Control,” on page 13.
3.4.11 Save/Restore Settings to Your Hard Disk
To save your current settings into the XML file, go to the main menu, select “File” and click on Save
As. The XML file saves all your configurations such as grabber settings, pulse generator, GPIO and
language settings.
The XML file will not, however, save camera parameters such as shutter mode, shutter speed, gain
settings, offset level, scan mode, and LUT. For more information about saving these camera
parameters, please refer to Section 3.4.7, “Memory Pages,” on page 16.
TM-4100GE Software
Page 28

Page 18
Configuring the TM-4100GE Camera
3.4.12 White Balance Control (Color Versions Only)
To determine white balance, use the following steps:
1. Select scan mode A and no binning in the GigE Camera Software tabbed dialog. shown in
Figure 11 on page 11.
2. Start the live video by clicking Start in the Acquisition tab of the Camera Interface Application dia-
log box.
3. Select “Color Adjustment” under tools in the main menu. Show the camera a piece of white paper
to make sure that the image is not saturated.
4. Click Analyze to automatically calculate the white balance.
5. Once white balance has been calculated, click Apply Results to apply white balance. You can also
assign custom gain and offset values to the R, G, and B channels. If you choose to assign custom
values, click Apply Results.
FIGURE 20. White Balance Control Settings.
Custom white
balance.
Gain/Offset
Automatic white
balance control.
3.4.13 Main Menu: “Option”
3.4.13 (a) Test Pattern
The Grabber Settings tabbed dialog box has a check box to enable the test pattern that is internally
generated by the integrated camera software.
3.4.14 Version
View the version number of the Cam2Net camera interface application by clicking on Help--> About.
The version number of the integrated GigE camera software is seen in a text box control called
“Version” in the GigE Camera tabbed dialog box.
TM-4100GE Software
Page 29

Configuring the TM-4100GE Camera
3.4.15 Exit
From the main menu, select “File,” and click “Exit” to exit the software.
Page 19
TM-4100GE Software
Page 30

Page 20
Signal Handling
4 Signal Handling
This section briefly describes the signal handling of the GE cameras in the following sections:
• “Camera Inputs” on page 19
• “GPIO Control Block” on page 20
• “GPIO Look-Up Table” on page 22
• “GPIO Label Tables” on page 22
• “Pulse Generators” on page 24
Refer to the Cam2Net User’s Manual for additional details.
4.1 Camera Inputs
For information on the polarity and type of the signals required to support specific camera functions,
refer to “Asynchronous Reset” on page 39.
The TM4100GE has four externally controllable standard signals:
• Trigger (VINIT or EXT_TRIG) (CC1 equivalent)
• Integration Control (INTEG/ROI) (CC2 equivalent)
• VD in (EXT_VD) (CC3 equivalent)
• HD in (EXT_HD) (CC4 equivalent)
The labels for these signals in the GPIO Control Block programming language are:
• I0, for VINIT (must be configured as EXT_TRIG)
• I1, for VD in (must be configured as EXT_VD)
• I2, for HD in (must be configured as EXT_HD)
• I4, for Integration control (must be configured as INT)
For normal exposure operation, the INTEG signal must be high. In the GPIO lookup table language:
Q5=1. When it is low, the CCD readout is inhibited. To use the Integration Control, set Q5=I3 in the
GPIO lookup table.
4.2 Camera Outputs
When the Asynchronous Trigger is used, the strobe output indicates the exposure period.
• I-4 for strobe output (must be configured as CAM_STROBE)
TM-4100GE Software
Page 31

4.3 GPIO Control Block
Figure 21 below shows the GPIO Control Block signals for the GE Cameras.
FIGURE 21. GE Camera GPIO Control Block
Page 21
Signal Handling
EXT_VD
EXT_HD
TTLIN(EXT_TRIG)
FDV
TTLIN(EXT_VD)
LDV
CTRL2
TTLIN(EXT_HD)
CTRL1
TTLN(INT)
CAM_STROBE
CTRL0
pulse_out0
pulse_out1
pulse_out2
pulse_out3
I0
I1
I2
I3
LUT
I4
8-to-16
I5
I6
I7
Pulse_Gen0
Pulse_Gen1
Pulse_Gen2
Pulse_Gen3
Q0
Q1
Q2
Q3
Q4
Q5
Q6
Q7
Q8
Q9
Q10
Q11
Q12
Q13
Q14
Q15
TTLOUT(STROBE)
EVINIT
INTG_CON
TRIG
RESV
pulse_trig0
pulse_trig1
pulse_trig2
pulse_trig3
Inputs I0 through I7 can be either external or internal inputs to the look-up table. The outputs are used
by the imager part of the GE camera.
The HD and VD signals can be passed through, bypassing the GPIO lookup table. Figure 23 on page 22
shows a screen dump of the GPIO function select page, where HD/VD bypass selection can be made.
The default value 0 (zero) is through the lookup table. Value 1 (one) is bypassing the lookup table.
The SDK and the Cam2Net Camera Interface Application both supply methods to select GPIO bypass
of the external VD and HD (I1 and I2).
It is also possible to select which signal source to lead to the GPIO inputs. This is done in the GPIO
look-up table page as shown in Figure 22.
TM-4100GE Software
Page 32

Page 22
Signal Handling
FIGURE 22. GPIO Look-Up Table
Q0 = I4
FIGURE 23. The GPIO Configuration
TM-4100GE Software
Page 33

4.4 GPIO Label Table
Table 2 shows which GPIO inputs carry the different signals. The top line for each label contains the
default signal.
TABLE 2. GPIO Look-Up Table Input Labels
Page 23
Signal Handling
Input
Label
I0
I1
I2
I3
I4
I5
I6
I7
Signal Description
TTL_IN(EXT_TRIG) TTL-input 0. Used for external trigger.
FDV Internal signal. Frame Data Valid.
TTL_IN(EXT_VD) TTL-input 1. Used for external vertical drive.
LDV Internal signal. Line Data Valid.
CTRL2 Internal control signal.
TTL_IN(EXT_HD) TTL-input 2. Used for external horizontal drive.
CTRL1 Internal control signal.
TTL_IN(INT) TTL-input 3. Used for external integration control.
CAM_STROBE Internal signal. Strobe Input.
PULSE_GEN3 Pulse Generator 3 signals go here.
CTRL0 Internal control signal.
PULSE_GEN2 Pulse Generator 2 signals go here.
PULSE_GEN1 Pulse Generator 1 signals go here.
N/A
PULSE_GEN0 Pulse Generator 0 signals go here.
N/A
TM-4100GE Software
Page 34

Page 24
Signal Handling
Table 3 shows which output labels carry the output signals.
TABLE 3. GPIO Look-Up Table Output Labels
Output label Signal Description
Q0 TTL-OUT(STROBE) Strobe output
Q1 N/A
Q2 N/A
Q3 N/A
Q4 EVINIT Trigger
Q5 INTG_CON Integration control
Q6 EXT_VD Vertical Drive
Q7 EXT_HD Horizontal Drive
Q8 pulse_trig1 Pulse Generator 1 gets its trigger here
Q9 pulse_trig0 Pulse Generator 0 gets its trigger here
Q10 pulse_trig3 Pulse Generator 3 gets its trigger here
Q11 pulse_trig2 Pulse Generator 2 gets its trigger here
Q12 N/A
Q13 N/A
Q14 TRIG Trigger for camera’s internal frame grabber
Q15 RESV Reserved
TM-4100GE Software
Page 35

4.5 Pulse Generators
The TM-4100GE camera has four independently programmable pulse generators. These generators can
run as either periodic or triggered. To run the pulse generators as triggered, they can be triggered on
either levels or signal edges. These generators can be tied to the camera inputs (camera-control lines).
For example, you can set pulse generator 0 in the Device Features tabbed dialog box to the following
values:
Delay = 600
Width = 14,000
Granularity = 1
Now check the Periodic option and change the camera settings to Async 9. This triggers the camera,
based on the pulse width set in the Pulse Generator page.
Be careful with the pulse generator’s GPIO input and output polarity. If the delay and pulse-width
duration are switched around, the output polarity must be negated in the GPIO lookup table.
Page 25
Signal Handling
The pulse generators are configured in the “Pulse Generator” section of the “Device Features” tab of the
Advanced Configuration window as shown in Figure 24.
FIGURE 24. Pulse Generator Page
TM-4100GE Software
Page 36

Page 26
GigE Series Camera Serial Commands
5 GigE Series Camera Serial Commands
You can control the GigE series cameras by serial command either using RS-232 or Camera Link. The
Start character is always “:” and the End character is always <CR> (return). For example, to set
Asynchronous Pulse Width Mode, send the command :ASH=9<CR> to the camera. Table 4 lists serial
commands that can be used to control the camera.
TABLE 4. TM-4100GE Command List
Command Parameters
:MGA= DDD <cr> :o<cr> Set CDS gain for ch A (DDD = 042 ~ 1E8)
:MGB= DDD <cr> :o<cr> Set CDS gain for ch B (DDD = 042 ~ 1E8)
:MGA? <cr> :oGA[DDD]<cr> Enquire CDS gain for ch A
:MGB? <cr> :oGB[DDD]<cr> Enquire CDS gain for ch B
:EABL <cr> :o<cr> Enable auto gain balance
:DABL <cr> :o<cr> Disable auto gain balance
:ABL? <cr> :oAB[N]<cr>
:VRA= DDD <cr> :o<cr>
:VRB= DDD <cr> :o<cr>
:VRA? <cr> :oVA[DDD]<cr> Enquire reference voltage for ch A
:VRB? <cr> :oVB[DDD]<cr> Enquire reference voltage for ch B
End of
Command
ADC Reference Voltage Control
Ack Response Description
Gain Control
Check if auto gain balance is enable (N = 1
Enable, N = 0 : Disable)
Set reference voltage for ch A (XXX = 000
~ 1FF)
Set reference voltage for ch B (XXX = 000
~ 1FF)
:MSH= S <cr> :o<cr> Set Manual shutter (S = 0 ~ 9)
:DSH= DDD <cr> :o<cr>
:ASH= S <cr> :o<cr> Set Async shutter (S = 0 ~ 9)
:ADS= DDD <cr> :o<cr> Set Async Direct Shutter (DDD=000-81F)
:SHR? <cr> :o[shtr]<cr> Enquire current shutter mode and number
TM-4100GE Software
Shutter Control
Set Direct shutter (DDD = 000 ~ XXX
*
)
Page 37

Page 27
GigE Series Camera Serial Commands
TABLE 4.
Command Parameters
TM-4100GE Command List (Continued)
End of
Command
Ack Response Description
Lookup Table
:GM45 <cr> :o<cr> Set gamma (.45) table
:LINR <cr> :o<cr> Set linear table
:KNEE= X1Y1X2Y2 <cr> :o<cr> Set knees (X1, Y1, X2, Y2 = 00 ~ FF)
Set positive knee or negative knee (N = 0 :
:SLUT N <cr> :o<cr>
positive,
M = 1 : negative)
:LUT? <cr> :o[lut]<cr> Enquire current LUT setting
Memory Pages
Write Page N (N = 0 ~ 6; Page 0 is factory
:WRPG N <cr> :o<cr>
setting and not allowed to change by customer)
:LDPG N <cr> :o[settings]<cr> Load Page N (N = 0 ~ 6)
:RDPG N <cr> :o[settings]<cr> Read (Report) Page N (N = 0 ~ 6)
Scan Mode
:SMD M <cr> :o<cr> Set Mode (M = A, B, C, D)
:SMD? <cr> :oMD[mode]<cr> Enquire current scan mode
Miscellaneous
:RPST <cr> :o[settings]<cr> Report Current Overall Settings
Enable/Disable Test Pattern (N = 1 :
:TPTN N <cr> :o<cr>
Enable,
N = 0 : Disable)
:CAM? <cr> [CamMode] Enquire Camera Model
:VER? <cr> [version] Enquire current version of firmware
*. Maximum size is equal to the maximum line number of each scan mode.
Note: If a command is not accepted for any reason, the camera will return a Nack response “:e”<cr>
Report Command: RPST<cr>
TS Return : O RR + “24 bytes” + <cr>
TM-4100GE Software
Page 38

Page 28
GigE Series Camera Serial Commands
TABLE 5. 18 Bytes Status Report
Byte 1, 2 MGA Channel A Gain Control (H’042 - H’1E8)
Byte 3, 4 VRA Channel A Offset Voltage (H’000 - H’1FF)
Byte 5, 6 MGB Channel B Gain Control (H’042 - H’1E8)
Byte 7, 8 VRB Channel B Offset Voltage (H’000 - H’1FF)
Byte 9 Function Flag 0
Bit 7 output pixel order 1
Bit 6 output pixel order 0
Bit 5
Bit 4
Bit 3
Bit 2
Bit 1
Bit 0
Byte 10 Function Flag 1
Bit 7 ShutterMode2 “000”=Manual Shutter
Bit 6 ShutterMode1
Bit 5 ShutterMode0
Bit 4 Output Data Depth 0=8 bit 0=8bit; 1=10bit
Bit 3 ShutterSpeed3
Bit 2 ShutterSpeed2
Bit 1 ShutterSpeed1
Bit 0 ShutterSpeed0
Byte 11 Function Flag 2
Bit 7 LUTSIGN 0=Positive LUT; 1=Negative LUT
Bit 6
Bit 5
Bit 4
Bit 3
Bit 2 LUTTABLE2 “000”=Linear LUT
Bit 1 LUTTABLE1
Bit 0 LUTTABLE0
“00”=<-- “10”=<-“01”=<--
“00” = Scan area A
“01”=Scan area B
“10”=Scan area C
“11”=Scan area D
“001”=Async Shutter
“011”=Direct Shutter
“0000” - “1001” Shutter Speed 0 - 9
“001”=Gamma.45 LUT
“010”=Two Knee Table
TM-4100GE Software
Page 39

TABLE 5. 18 Bytes Status Report (Continued)
Byte 12 Function Flag 3
Bit 7 TESTPATTERN 0=Disable TP; 1=Enable TP
Bit 6 PASSWORD 0=Disable PW; 1=Enable PW
Bit 5
Bit 4
Bit 3
Bit 2
Bit 1
Bit 0 AUTOBALANCING 0=Disable AB; 1=Enable AB
Byte 13 X1
Byte 14 Y1
Byte 15 X2
Byte 16 Y2
Byte 17 Reserved
Byte 18 Reserved
Byte 19 Reserved
Byte 20 Reserved
Byte 21, 22 Direct Shutter H’000 - H’81F
Byte 23, 24 Reserved Total line number H’040 - H’1F3
Page 29
GigE Series Camera Serial Commands
(X1, Y1) Coordinate for Knee 1
(X1, Y1 = H’00 - H’FF)
(X2, Y2) Coordinate for Knee 1
(X2, Y2 = H’00 - H’FF)
TM-4100GE Software
Page 40

Page 30
GigE Series Camera Serial Commands
TM-4100GE Software
Page 41

September 20, 2006
TM-4100GE Hardware
Operation Manual
6 Hardware Introduction
6.1 Product Description
The JAI PULNiX TM-4100GE series1 is a Gigabit Ethernet output, high-resolution progressive scan
CCD camera. The interline-type CCD permits full vertical and horizontal resolution of very high speed
shutter images and applications. The electronic shutter, which has speeds to 1/16,000 sec., can be reset
asynchronously by external pulse control. The frame rate for a full image is 15 fps. A square imager
format with uniform square pixels provides superior image definition in any orientation. On-chip micro
lenses provide increased sensitivity.
The TM-4100GE
look-up table (LUT) knee slopes to convert 10-bit input to 8-bit output, thereby optimizing the CCD’s
full dynamic range in the normal output signal range. As a Gigabit Ethernet output camera, the TM4100GE has semi-auto-gain balancing functions.
Applications for the TM-4100GE include machine vision, medical imaging, intelligent transportation
systems, high-definition graphics, on-line inspection, gauging, character reading, archiving, and highsecurity surveillance.
2
has a full dynamic range control function, which can be set at externally selectable
1. Unless otherwise stated, all information in this manual applies to both cameras in the TM-4100GE
series, the TM-4100GE and the TMC-4100GE.
2. The TM-4100GE is available with either 8-bit processing or 10-bit processing. You must specify
your choice of configurations when you purchase the camera.
TM-4100GE Hardware
Page 42

Page 32
Hardware Introduction
6.2 Features
• Miniature size and light weight
The printed circuit boards in the TM-4100GE have been arranged to create modular electronics,
giving the camera flexibility. In addition, the use of miniature solid-state components results in a
compact, lightweight camera that is 50.8mm x 50.8mm x 81.5mm in dimensions, and weighs only
155 grams.
• Imager
The TM-4100GE uses a dual-tap progressive scan interline transfer CCD that has the following
features:
• Electronic shutter
- Resolution of 2k x 2k active pixels for excellent image quality.
- 7.4 x 7.4 µm square pixels for precise dimensional measurement.
- High-speed electronic shutter capability for high dynamic resolution of moving objects that
eliminates the need for a mechanical shutter.
- Progressive scan CCD eliminates interlace deterioration of image and increases ease of
computer interface.
- High sensitivity and low noise at fast scanning. The CCD has an excellent S/N ratio at the
default setting that is greater than 48dB.
- The CCD has a built-in microlens for increased quantum efficiency.
The TM-4100GE has a substrate drain-type shutter mechanism which provides superb pictures at
various speeds without smearing. For more information, please see Section 8.3, “Electronic
Shutter,” on page 44.
• Asynchronous reset
The TM-4100GE captures async reset images and provides single-shot video output with single
FDV. This makes it simpler for an ordinary frame grabber to capture the asynchronous reset
images. The TM-4100GE’s asynchronous reset is flexible and accepts external horizontal drive
(HD) for phase locking. When the VINIT (5V) pulse is applied to CC1, it resets the camera's
scanning and purging of the CCD.
The TM-4100GE has three modes to control the asynchronous reset and shutter speed:
- Async, no shutter. The video signal and FDV are reset by external VINIT.
- Internal shutter speed control. The speed control varies from 1/60 to 1/16,000 sec. The
video signal and FDV starts with internal V reset timing related to shutter speed.
- External VINIT with pulse width. The duration between pulse edges controls the shutter
speed externally.
TM-4100GE Hardware
Page 43

Hardware Introduction
• Output
The TM-4100GE has a dual-tap 10-bit/8-bit Gigabit Ethernet output.
• Dual-channel auto black level balancing and semi-auto gain balancing
The TM-4100GE, as a dual-tap output camera, has auto black level balancing and semi-auto gain
balancing functions.
• Integration
The TM-4100GE is capable of capturing high-resolution integration images. Its CCD imager can
be exposed for longer than the normal scan timing of 1/15 sec. This integration feature provides
extra sensitivity for applications in dark environments. The progressive scan imager permits a full
frame of resolution in non-interlace format. Integration is achieved by applying INTEG signal to
CC2 control of Gigabit Ethernet or by feeding VINIT pulse width control up to 1 sec of the pulse
width in async pulse width control mode for the frames to be integrated.
• Warranty
Please contact your factory representative for details about the warranty.
Page 33
TM-4100GE Hardware
Page 44

Page 34
Installation
7 Installation
The following instructions are provided to help you to set up your camera quickly and easily. We
suggest that you read through these instructions before you unpack and set up your camera system.
7.1 Getting Started
7.1.1 Unpacking Instructions
We recommend that you save the original packing cartons for the cameras and accessories in case you
need to return or exchange an item.
We also recommend that you bench-test any equipment being sent to another location for field
installation to assure that everything is fully operational as a system.
7.1.2 Components
When you receive your TM-4100GE camera from JAI PULNiX, the contents of the shipping box
should include the camera and a document download card. If either of these items are missing, please
contact your JAI PULNiX representative immediately. The document download card includes
instructions and web locations for downloading the datasheet, manual, and camera-control software. If
you do not have Internet access, please contact JAI PULNiX to receive this material on a CD-ROM.
7.1.3 Accessories and Options
Following is a list of additional accessories and options that may be required for your application.
Please check with your JAI PULNiX representative before you install your camera to determine what
you might need.
• PD-12U series power supply
• 12P-02S power cable
• Cat5e or cat6 shielded Ethernet cable (not supplied by JAI PULNiX)
TM-4100GE Hardware
Page 45

7.2 Camera Setup
7.2.1 Heat Dissipation
The TM-4100GE is a compact 2k by 2k camera. Since all the electronics have been packed in a
compact package, the outer case of the camera can become hot due to heat dissipation. For optimal
performance, JAI PULNiX recommends using a cooling fan to set up a positive air flow around the
camera and following the precautions below.
• Mount the camera on a large heat sink (camera bracket) made out of heat-conductive material like
aluminum.
• Make sure the flow of heat from the camera case to the bracket is not blocked by a non-conductive
material like plastic.
• Make sure the camera has enough open space around it to facilitate the free flow of air.
Please contact JAI PULNiX, Inc. at (800) 445-5444 or send an E-mail to imaging@jaipulnix.com if you
have any questions.
Page 35
Installation
7.2.2 Connector Pin Configurations
7.2.2 (a) 12-Pin Connector
The TM-1327GE has a 12-pin Hirose connector for power input and signal integration as shown in
Figure 24.
Figure 24. 12-Pin Connector Pinouts
1
9
2
10
3
11
4
5
Pin #1 is Ground and pin #2 is +12V DC. Table 6 shows the pin-out table.
Table 6. 12-Pin Connector
Pin Description Pin Description
1 GND 7 VD in
2 +12V DC 8 Strobe
3 GND (analog) 9 HD in
4 Reserved 10 Reserved
5 GND (digital) 11 Reserved
6 VINIT in 12 Reserved
12
8
7
6
TM-4100GE Hardware
Page 46

Page 36
Installation
7.2.2 (b) Ethernet Connector
The GigE socket, marked on the camera’s back panel as “GigE,” is a standard
RJ-45 Ethernet socket as shown in Figure 25.
Figure 25. GigE Ethernet Connector
GigE
Use at least cat5e UTP cables (cat6 cables are preferred). Refer to the Cam2Net User’s Manual for
details. JAI PULNIX recommends the use of shielded cables to reduce emissions and for CE/FCC
compliance. Double-shielded cables further reduce emissions.
7.2.3 Power Supplies and Power Cable Setup
7.2.3 (a) Power Supplies
The TM-4100GE camera requires 12V DC power that is obtained through the 12-pin connector located
on the rear panel of the camera. JAI PULNiX recommends the following power supplies:
PD-12UU 100-240V AC/12V DC 1.2A universal voltage power supply,
US Plug
PD-12UUP PD-12UU with12-pin connector US plug
PD-12UE PD-12UU European plug
PD-12UEP PD-12UU with 12-pin connector European plug
For users providing power through the 12-pin connector, the PD-12P, PD-12UEP and PD-12UUP
power supplies are available with the 12-pin mating connector already attached to the leads from the
power supply. The PD-12UU and PD-12UE power supplies can be connected to the JAI PULNiX
power cable either directly or using a terminal strip.
When wiring the PD-12UU and PD-12UE power supplies directly, please note the following:
• The lead ends must be twisted together and tin-soldered for strength and electrical continuity.
• Shrink tubing or a similar insulator should be used to prevent exposed leads from touching and
shorting.
• The +12V lead is marked with a red stripe or white lettering; be sure not to reverse the leads.
• All connections must be properly insulated to prevent shorting.
TM-4100GE Hardware
Page 47

7.2.3 (b) JAI PULNiX Power Cables
If you are using JAI PULNiX power cables such as the 12P-02S, please refer to the 12-pin connector
pin-out diagram below. The cable pin-out diagram is shown in Figure 26. The color-coded leads use
Gray for Ground and Yellow for +12V.
FIGURE 26. 12P-02S Interface Cable (optional)
+12 V
GND (Gray)
Male
Power (Yellow)
Video Out (Red Coax)
HD In (White Coax)
VD In (Black Coax)
Analog Ch. A only
External sync input
}
12P-02S Interface Cable
Pin# Lead Color Function Pin# Lead Color Function
1 Gray GND 7 Black coax TTL IN (EXT_VD)
2 Yellow +12V DC 8 White coax shield TTL OUT (STROBE)
3 Red coax shield AGND 9 White coax TTL IN (EXT_HD)
4 Red coax RESV 10 Brown RESV
5 Orange coax shield GND 11 Blue TTL IN (INTG_CON)
6 Orange coax TTL IN (EXT_TRIG) 12 Black coax shield RESV
Page 37
Installation
Note: Make sure that the unused leads are not touching and that there is no possibility that
exposed wires could cause the leads to short.
7.2.3 (c) Building Your Own Power Cable
Refer to the 12-pin connector pin-out in Figure 24 on page 35. Connect the Ground lead to pin #1, and
the +12V DC lead to pin #2 of the 12-pin connector. Power must be DC-regulated, and of sufficient
current to properly power the camera.
7.2.3 (d) Attaching the Power Cable to the Connector
The 12-pin connector is keyed and will only fit in one orientation. Follow these directions to properly
attach the power cable to the camera connector:
1. Rotate the connector while applying slight pressure until the keyways line up.
2. Press the connector into place until firmly seated.
3. Plug the power cord into the 100V AC socket. This powers-up the camera.
TM-4100GE Hardware
Page 48

Page 38
Installation
7.2.4 Attaching the Camera Lens
The TM-4100GE camera accepts 1.2" or larger format size C-mount lenses. To attach the C-mount
1
to the camera, carefully engage the threads and rotate the lens clockwise until it firmly seats on the
lens
mounting ring. Do not force the lens if it does not seat properly. Please note that some lenses with
extremely long flangebacks may exceed the mounting depth of the camera.
7.2.5 Adjustable Back-Focus
Before cameras are shipped,back focus is carefully set using a collimator, oscilliscope and other
specialized equipment. While the factory-set focus serves well in most cases, an adjustable back focus
makes it possible to improve image sharpness when using lower-cost zoom lenses, custom optics, or in
unusual parameters.
There should be an obvious need to refocus the lens before attempting to change the back focus. This is
a very exacting task. Some cameras have been returned to the factory to reset the back focus after failed
attempts to change the focus by customers. It might be wise to label cameras whose back focus was
adjusted
1. The camera must be connected to a monitor before attempting to adjust the back focus.
2. To back focus the camera, first attach a C-mount lens in the mount. Be certain that the lens is prop-
erly seated.
3. Next set the lens focus to infinity (if the lens is a manual iris, set the iris to a high f number while
still retaining a well illuminated image).
4. Loosen the three miniature hex set-screws (use a 0.9 mm hex wrench) that lock the focus ring in
place (two screws for a CS-mount). Slowly turn the lens and focus ring assembly back and forth
until you obtain the best image of the desired object. This sets the back focus. Once the best image
is obtained, tighten the focus ring set-screws until they are snug. Do not over-tighten the screws.
Note: Mini-bayonet cameras adapted to C-mount do not have the back focus feature.
1. C-mount to F-mount and C-mount to K-mount adapters are available for larger format lenses
(35mm). Check with local photography dealers for these lens adapters.
TM-4100GE Hardware
Page 49

FIGURE 27. Back-Focus Set-Screw Locations
Loosen the three
2mm screws around
the perimeter of the
C-mount lens collar
(two 2mm screws for a
CS-mount) to adjust the
back focus. Unless you
absolutely must, do not
attempt to adjust this
focus.
Page 39
Installation
TM-4100GE Hardware
Page 50

Page 40
Operation
8 Operation
8.1 Progressive Scanning
Standard TV-system scanning is 525 lines interlace scanning as specified in the RS-170 protocol. Every
other horizontal line (odd lines and even lines) is scanned at a 60Hz rate per field, and the scanning is
completed with two fields (one frame) at 30Hz rate. Because of the interlace scanning, the vertical
resolution of CCD cameras is limited at 350 TV lines, regardless of the horizontal resolution. When
electronic shutter is applied, the CCD can hold only one field of charge at each exposure. This means
that the vertical resolution of the electronic shutter camera is only 244 TV lines. The situation is the
same for an HDTV-format camera, since it has interlaced scanning and the vertical resolution of the
shuttered image is 500 lines.
The TM-4100GE uses a state-of-the-art progressive scanning interline transfer CCD which scans all
lines sequentially from top to bottom at one frame rate. Like a non-interlace computer screen, it
generates a stable, crisp image without alternating lines and provides full vertical TV resolution of 2048
lines (a normal computer monitor has a maximum display of 1600 lines).
The interline transfer architecture is also important to generate simultaneous shuttering. This is different
from full frame transfer architecture, which requires a mechanical shutter or strobe light in order to
freeze the object motion.
The TM-4100GE outputs the progressive scanned image with an electronic shutter in two different
formats. See Table 8 on page 45 for more information.
1. Progressive scanning digital output
The CCD signal goes through A/D converters 10-bit in, 10-bit/8-bit out. The digital
output is available using the Gigabit Ethernet connector.
2. Full Progressive Scan
Normal scanning mode for the TM-4100GE is 2k x 2k pixels. The standard speed with
dual-channel output is 15 frame/sec at the pixel clock of 40 MHz. The progressive scan
reads every line from top to bottom and all lines are exposed with a single electronic
shutter.
FIGURE 28. Full Progressive Scan Mode (A)
line 1
line 2
n
n+1
TM-4100GE Hardware
Page 51

3. Partial Scan Mode
By selection, the camera has three partial scan modes: centered 1000 lines, centered 500
lines, and 250 lines. Partial scan mode 1000 lines. Partial scan’s frame rate is 28 fps, 500
lines is 50 fps, 250 lines is 80 fps.
TABLE 7. Scan Mode
Page 41
Operation
Scan Area Active Area
A 2048 x 2048 14.79
B 2048 x 1000 27.7
C 2048 x 500 49.63
D 2048 x 250 79.92
Vertical Frequency
8.2 Bayer Color Filter (Color Versions)
JAI PULNiX AccuPiXEL series color cameras are high-resolution, high-speed progressive scan CCD
cameras. The interline transfer, progressive scan CCD permits full vertical and horizontal resolution of
images acquired at very high shutter speeds. The electronic shutter, which has speeds to 1/16,000 sec.,
can be reset asynchronously by external pulse control. Uniform square pixels provide superior image
definition in any orientation. On-chip micro lenses mean increased sensitivity.
8.2.1 Color Filter Array
JAI PULNiX AccuPiXEL cameras use Bayer CFA (color filter array) as their standard primary color
filter. This filter provides the most popular color interpolation supported by numerous software
suppliers.
(Hz)
Horizontal
Frequency (kHz)
30.77 40
Output Data Clock
(MHz)
The digital format allows the camera to output accurate pixel data, including the color information.
When the data is stored in the frame buffer of a frame grabber or computer, the color information is
easily manipulated to restore the original color images. Because the color filter array contains only a
single R, G or B color in each pixel, the restored image has to fill in colors in the missing pixel
locations. The software uses neighboring pixel information to “guess” the missing colors to make
smooth, clear images. This is called “color interpolation.” Today’s high-speed computers allow such
color interpolation to be done almost in real time. Because these cameras do not contain internal colorprocessing circuitry, they are smaller and less expensive than full-function color cameras.
8.2.2 Bayer Color Filter Array (CFA)
The Bayer CFA is an R, G, B primary color filter array. This is the most widely accepted CFA for the
single-chip CCD progressive scan format. This type of array layout has a specific order for each color’s
pixels. Since the human eye’s resolution and color recognition are highest at green, the CFA contains
two greens per each red and blue.
It is critical for the frame grabber and color interpolation to know where the individual color pixels exist
relative to sync (LDV and FDV) timing.
TM-4100GE Hardware
Page 52

Page 42
Operation
This requirement makes digital output the preferred choice, because the timing relationships are very
accurate
FIGURE 29. Bayer Color Filter Response.
8.2.3 Starting Pixel Configuration
All manufacturers produce identical Bayer CFAs, but there are slight differences between the CCDs
produced by different manufacturers. The first line is generally R and G. The camera timing can be
adjusted to start with either G or R by skipping the very first pixels at each lines. The majority of color
interpolation software can select between a variety of pixel relations, such as R/G start or G/R start, as
well as G/B start and B/G start. Once the correct scanning is configured, the rest of the interpolation will
be exactly the same. Please contact JAI PULNiX for further information regarding CCD manufacturers.
FIGURE 30. Example of Color CCD CFA Pattern
GG GG G
CCD Output
BBB BBB
GGG GGG
RR RR R
GG GG G
BBB BBB
GGG GGG
RR RR R
GG GG G
BBB BBB
GGG GGG
RR RR R
GG GG G
BBB BBB
Pixel 1
GGG GGG
RR RR R
Horizontal Shift Registers
Last pixel
Last pixel of 1st Line
TM-4100GE Hardware
CCD
Page 53

8.2.4 Sync and Data
The individual color data is exactly the same as the pixel data. This means that the timing relationships
of the color cameras are also the same as of the B/W cameras.
For a detailed timing chart, please refer to each B/W camera’s data sheet and manual.
The following diagram is an example of the TMC-4100GE default mode. FDV and LDV are used
internally for the GigE interface.
FIGURE 31. Example of TMC-4100GE (Same as TM-4100GE)
32 line
FDV
LDV
Page 43
Operation
Video
Data
BG
line
FDV
LDV
Video
data
8.2.5 Camera Functions
1st line 2 3
RG
line
276pixels
BG
line
RG
line
Green
BG
line
RG
line
1st line (RG line)
RG
BG
line
line
GreenRed Red
BG
line
AccuPiXEL color cameras perform all functions the same way as B/W cameras. However, because of
color characteristics, the LUT (Look-up Table) is different. The LUT is a powerful tool to adjust the
dynamic range as well as color dynamic range. Since human color perception is non-linear, LUT
TM-4100GE Hardware
Page 54

Page 44
Operation
selection can help optimize color contrast by selecting the LUT value. Gamma 0.45 is logarithmic and is
closed to human perception.
When LUT is selected, black-level adjustment must be more accurate than for B/W cameras.
For a detailed timing chart, please refer to the standard AccuPiXEL camera data sheet, or contact JAI
PULNiX.
8.2.6 Interpolation Software
The color interpolation can be performed in the frame grabber or by using the host computer’s CPU.
Most major frame grabbers with processing capability provide tools for color interpolation. Software
vision packages also provide color interpolation capability, but speed and performance may be
determined by the PC’s resources and by the complexity of the interpolation routine.
8.2.7 Color Interpolation
The Bayer pattern color filter array (CFA) consists of R, G, and B primary colors. Each pixel represents
one of three colors. In order to display or print color images, the signal has to be converted to RGB
output, which has three independent channels (outputs) and sync signals.
Color interpolation software or firmware performs the color
preprocessing by filling the missing color pixels with neighboring
pixels. It then separates the stream of data, (8-bit or 10-bit) into 3 (RGB)
data (8-bit x 3) and adds the color matrix to adjust and balance each of
the R,G, and B channels (white balance or color balance).
The image quality depends on the camera’s own pixel data (including
pixel data independency from neighboring pixels, noise and color filter),
and interpolation of the software algorithm such as 3 x 3 interpolation, 2
x 2 interpolation, color matrix, white balance capability, and so on.
All AccuPiXEL color cameras are carefully designed for maximum color performance. JAI PULNiX
strongly suggests that you use digital output for the best performance.
Some software is used on board (FPGA or DSP) to perform the interpolation. Other software simply
uses the host computer’s memory and CPU. The process speed may vary depending on the architecture
and speed of the computer.
8.3 Electronic Shutter
The TM-4100GE has a substrate drain-type shutter mechanism which provides a superb picture at
various speeds without smearing. A built-in fixed shutter speed control selects the electronic shutter
rate.
Green Green
Green
Red
Green
Blue Blue
GreenRed
TM-4100GE Hardware
Page 55

Page 45
Operation
TABLE 8. Electronic Shutter Speeds
Shutter Speed Number Manual Async.
0 1/frame rate Async No Shutter
1 1/60 sec 1/16,000 sec
2 1/125 sec 1/8,000 sec
3 1/250 sec 1/4,000 sec
4 1/500 sec 1/2,000 sec
5 1/1,000 sec 1/1,000 sec
6 1/2,000 sec 1/500 sec
7 1/4,000 sec 1/250 sec
8 1/8,000 sec 1/125 sec
9 1/16,000 sec PWC (pulse width control)
With VINIT high (CC1), the CCD keeps discharging. With an active low pulse to VINIT, the camera
resets and purges the charge momentarily. Then it starts integrating for the period of shutter control set
by either an external pulse width or internal shutter control. Progressive scanning permits a full 2048
lines of vertical resolution, as compared to a conventional CCD camera which captures only half the
vertical lines per shutter.
8.4 Integration
The CCD imager of the TM-4100GE can be exposed for longer than the normal scan timing of 1/200
sec. This integration feature provides extra sensitivity for dark-environment applications. The
progressive scan imager permits a full frame of resolution in non-interlace format. Integration is
achieved by controlling CC2 Camera Control line through the Gigabit Ethernet cable to low (GND) or
providing pulse-width control up to 1 sec. Please refer to Figure 26, “12P-02S Interface Cable
(optional),” on page 37 for pin-out information on the 12-pin connector.
8.5 External Sync
The TM-4100GE accepts an external sync of standard HD and VD on CC3 and CC4 of the Gigabit
Ethernet connector for general locking to an external source.The frequency requirement is shown in
Table 8 on page 45. The tolerance is ±2% horizontal frequency.
8.6 Asynchronous Reset
The TM-4100GE camera includes three modes to control the asynchronous reset and shutter speed:
• Async No Shutter (recommended for strobe applications)
• Internal Shutter Speed Control
• External VINIT with Pulse Width (No-Delay Shutter) and ROI (read-out-inhibit)
TM-4100GE Hardware
Page 56

Page 46
Operation
8.6.1 Async No Shutter
Ext. Vinit
During FDV Blanking
Transfer Gate
Discharge
Strobe
FDV
LDV
Analog Video
During Active Video Period
Vinit trigger starts the first exposure period within one line (1H = 32.5 μsec.) and transfers the frame
after a 9.5H exposure. After the first transfer, a new full frame exposure period (67.6 μsec.) begins.
Async No Shutter allows for strobe and back-to-back strobing (strobing both before the transfer gate
and right after) applications.
TM-4100GE Hardware
Page 57

8.6.2 Internal Shutter Speed Control
EXT. VINIT
HD
INT. VINIT with shutter speed control
Page 47
Operation
Discharge
Transfer Gate
Strobe
FDV
Analog Video Sync
Exposure time set by shutter speed
The video signal starts with internal VINIT. When the external VINIT pulse is applied, internal VINIT
is latched to HD and the internal VINIT is delayed to set up the shutter speed period. The shutter speed
is controlled by communication software from “1” to “8.” Video output timing starts right after the
internal VINIT and single shots, FDV is output at the internal VINIT timing.
TM-4100GE Hardware
Page 58

Page 48
Operation
8.6.3 External VINIT With Pulse Width (No-Delay Shutter) and ROI (Read-out
Inhibit)
For multiple-camera applications such as 2D or 3D measurement and multi-angle inspection,
simultaneous image capturing at an exact shutter timing for all cameras is a critical requirement. The
TM-4100’s asynchronous pulse-width control mode provides no-delay shutter as standard. Regardless
of the internal pulse timing, the camera discharges at the VINIT leading edge and transfers charges at
the trailing edge of the pulse. Even though each camera runs with slightly different H and data clock
timing, the image capturing is exactly simultaneous.
FIGURE 32. No-Delay Shutter
HD
INT. VINIT after trailing edge of EXT. VINIT
Discharge
Transfer Gate
Strobe
FDV
Analog Video Sync
Exposure time set by pulse width
Vsync
The TM-4100GE camera also has read-out-inhibit control (ROI) to control the vertical clock start
(Async Shutter #9). When ROI is low, V-clock is stopped and the transferred charges remain in the
vertical shift registers, which work like CCD memory. When the ROI is high, it clocks out the CCD
data. This helps a single frame grabber process multiple images in pipeline processing (sequential
process).
Note: When the ROI function is not used, make sure that the INTEG/ROI CC2 input is kept logic
high during Async. pulse width control mode.
TM-4100GE Hardware
Page 59

FIGURE 33. Read-Out Inhibit
VINIT (External Pulse Width Control Trigger)
No-Delay Shutter (All cameras)
Discharge
No-delay Exposure
Transfer Gate
ROI Control: Camera #1
Camera #1 Video
FDV/Vsync
ROI Control: Camera #2
Camera #2 Video
Page 49
Operation
ROI pulse width: Min. 1H to 1frame
Max. 1H delay
8.7 Dynamic Range Control
mV
600
400
CCD OUTPUT VOLTAGE
200
0
0
The typical interline transfer CCD has fixed noise levels based on dark current (thermal or KT noise),
pattern noise, and the operating clock speed. In general, the level of the 40 MHz pixel clock CCD at
room temperature is around 20 to 30 electrons. The maximum capacity of CCD charges is limited by
the well capacity at saturation. The range is limited by the structure and the pixel size.
The TM-4100GE uses a CCD with 7.4 µm x 7.4 µm pixel and two-phase vertical shift register structure.
The well capacity is 40,000 electrons. The theoretical dynamic range is 40,000:30 = 1333:1 (60 dB).
Max. Digital dynamic range at 3 dB amp
Digital saturation at 16 dB amp
Analog saturation at 20 dB amp
20
40
80
LUMINANCE
10060120
Blooming adj. = 13. 5 V
Lens: F=5.6
Vsub = 8 V
Vsub = 10 V
Vsub = 12 V
Vsub = 14 V
Vsub = 16 V
Vsub = 18 V
160
140
FL
TM-4100GE Hardware
Page 60

Page 50
Operation
A typical CCD camera does not use the full dynamic range due to the nominal gain and the output
specification such as RS-170. The typical CCD camera’s gain is set at 16 to 22 dB and the RS-170 video
level is 714 mV. Using 20 dB gain for the calculation, CCD output is limited to 714/10 = 71.4 mV.
Machine vision and outdoor applications cannot afford to miss image information behind the saturation,
which is why the dynamic range adaptation is critical.
8.7.1 Programmable Look-Up Table (LUT) and Knee Control
The TM-4100GE has a built-in LUT (look-up table) for dynamic range control. At a specific gain
setting, the offset (minimum level.... dark point) and A/D reference top voltage (maximum level...
saturation point) are set to 10-bit A/D input so that the full dynamic range of the CCD is utilized at
10-bit references as the input and the LUT output is converted into 8-bit to adjust the gamma correction.
Notice that the LUT (look-up table) is not available in the 10-bit grayscale mode.
The look-up table has two knee points (variable gamma selection) that allow the 10-bit input to be
segmented into three regions. The look-up table selection can be made by knee curve direct input.
TM-4100GE Hardware
Page 61

8.8 Camera Timing Charts
1. Video Output
Page 51
Operation
>> Line Video Timing
LDV
Digital Video
>> Field Video Timing
FDV
Digital Video
D
B
N
E
L
2. External HD Locking & External VD Reset
>> External HD Locking
External HD
Internal HD
LDV
eA
eC
eE
A
C
K
M
O
eB
eD
>> External VD Reset
External VD
Internal VD
FDV
eF
eG
eH
eJ
eI
TM-4100GE Hardware
Page 62

Page 52
Operation
3. Async Reset
>> Async No Shutter (async shutter 0)
External Vinit
Discharge
Transfer Gate
Strobe
FDV
>> Async Normal Shutter (async shutter 1-8) & Async No-delay Shutter (async shutter 9)
External Vinit
Discharge
Transfer Gate
Strobe
FDV
ROI/Integration
aA
aE
aB
aF
L
aG
aC
aD
aC
aD
... ...
aH
M
... ...
M
... ...
>> Read-Out Inhibit (ROI, async shutter 9)
External Vinit
Discharge
Transfer Gate
Strobe
FDV
ROI/Integration
TM-4100GE Hardware
aJ
aI
aK
... ...
M
Page 63

4. Video Output Order
LDV
Data Clock
>> A (Default)
Ch. A Video Data
Ch. B Video Data
>> B
Ch. A Video Data
A
B
i -1 Line i
... ...
C
2C
C
... ... C-1
... ...
... ... C-1
1
C+1
1
2
C+2
2
3
C+3
3
C
... ...
... ...
... ...
... ...
C-2
2C-2
C-2
2C-1
C
2C
C
Page 53
Operation
i +1
... ...
... ...
... ...
... ...
Ch. B Video Data
>> C
Ch. A Video Data
Ch. B Video Data
Scan
Area
Data
Clock
C+1
2C-1
TABLE 9. Video Output
ABCDEKLMNO
A
B 1100 100 1000
40MHz
C 620 120 500
25 ns
1300 276 1024 0 0
... ...
... ... 2C-3
... ...
2C
2C-1
1
2
2C-2
3
4
5
6
Horizontal (pixels) Vertical (lines)
2080 32 2048
D 385 135 250
... ...
... ...
... ...
C+3
2C-5
2C-4
C+2
2C-2
00
C+1
2C-1
2C2C
... ...
... ...
... ...
TM-4100GE Hardware
Page 64

Page 54
Operation
TABLE 10. External HD Locking and External VD Reset
Scan
Area
Pixel
Clock
Freq.
(kHz)
Time
(μsec)
A
B 27.7 35.75 1100 1091
Horizontal
40MHz
C 49.63 20.15 620 611
25ns
30.77 32.5 <20ns 1300 100 1200 0
External HD Locking Timing
(pixels)
eA eB eC eD eE
Vertical
Freq.
(Hz)
Time
(msec)
14.79 67.6
Vertical VD Reset Timing
(lines)
eF eG eH eI eJ
2080
<2
2071
9
1
D 79.92 12.51 385 376
TABLE 11. Async Reset
Async Reset Timing
Scan
Area
aA
(lines)
aB
(μsec)
aC aD aE
aF
(μsec)
aG
(lines)
A
B101
C121
>1 &
<2
s1-8: <1
line s9:
<125ns
aH (lines)
s1-8 s9
33
>aH &
<aH +1
aI (lines
>aH + 1
&
<aH +2
aJ
(sec)
(lines)
<1 <2
aK
D136
Note: s1=1
s2=3
s3=7
s4=15
s5=30
s6=61
s7=122
s8=245
s9=PW
TM-4100GE Hardware
Page 65

9 Troubleshooting
9.1 Problems and Solutions
Following are troubleshooting tips for common problems. In general, problems can easily be solved by
following these instructions. If the following remedies fail to offer a solution to your problems, please
contact a JAI PULNiX representative.
9.1.1 Symptom: No Video
Remedies: Check that the following are properly connected and operational.
• Power supplies
• Power cables
• Main power source
• Shutter control
• Async mode
Page 55
Troubleshooting
• Lens
• Digital output cable
• Analog video cable
9.1.2 Symptom: Dark Video
Remedies: Check that the following are properly connected and operational.
• Shutter selection
• Iris opening on the lens
9.1.3 Symptom: Non-Synchronized Video
Remedies: Check that the following are properly connected and operational.
• Proper mode output
• Frame grabber software camera selection
TM-4100GE Hardware
Page 66

Page 56
Troubleshooting
9.2 Information and Support Resources
For further information and support:
Phone: (408) 383-0300
(800) 445-5444
Fax: (408) 383-0301
E-mail: imaging@jaipulnix.com
Mail: JAI PULNiX, Inc.
Sales Department
625 River Oaks Parkway
San Jose, CA 95134
ATTN: Video Applications
Web Site: www.jaipulnix.com
TM-4100GE Hardware
Page 67

10 Appendix
10.1 Specifications
TABLE 12. TM-4100GE Camera Specifications Table
Feature TM-4100GE
Imager 1.2" progressive scan interline transfer CCD
Active Area 15.15mm x 15.15mm
Active Pixels 2048 (H) x 2048 (V)
Cell Size 7.4µm x 7.4µm
2048 (H) x 2048 (V) @ 15 Hz (full image)
Display Mode
(Active Pixels)
Sync
Data Clock Output 40.00 MHz
Resolution
S/N Ratio 48dB min.
Min. Illumination
Video Output
Gamma Programmable LUT (1.0 std.)
Lens Mount C-mount (use >1.2" format lenses or larger)
Power Requirement 12V DC, ±10%, 600mA (typical at 25°C)
Operating Temp.
Vibration 7 Grms (10Hz to 2000Hz) Random, 11 ms half sine
Shock 70G
Size (W x H x L) 51mm x 51mm x 85mm
Weight 197 grams (6.9 oz.) without tripod
Optional Functions
Optional Accessories
Power Cable
Power Supply
Digital output: 8-bit x 2 / 10-bit x 2 Gigabit Ethernet (selectable at
2048 (H) x 1000 (V) @ 28 Hz (partial scan)
2048 (H) x 500 (V) @ 50Hz (partial scan)
2048 (H) x 250 (V) @ 80Hz (partial scan)
Internal/External auto switch
HD/VD, 4.0 Vp-p impedance 4.7 K ohms
VD=14.79±2%, non-interlace
HD=30.78kHz±2%
Digital: 2048 (H) x 2048 (V),
(Analog: over 800 TV lines (H) x 1600 TV lines (V))
Monochrome: 0.12 lux. Color: 0.8 lux.
f = 1.4 (no shutter) @ 15 fps. Sensitivity: 31μV/e-
factory)
-10°C to 50°C
12P-02S
PD-12UUP series (includes power connector)
*
Page 57
Appendix
*. Refer to Section 7.2.1 on page 35 for information on camera heat dissipation. Image quality will degrade
with increasing temperature.
TM-4100GE Hardware
Page 68

Page 58
Appendix
10.1.1 TM-4100GE Physical Dimensions
FIGURE 34. Physical Dimensions
1" -32
50.8 [2.00]
GigE
POWER
50.8 [2.00]
25.4 [1.00]
25.4 [1.00]
6.5 [0.26]
7.0 [0.28]
25.6 [1.01]
21.6 [0.85]
8X M3
18.0 [0.71]
EFFECTIVE
IMAGE AREA
Gigabit Ethernet
18.0 [0.71]
84.6 [3.33]
93.3 [3.67]
22.0 [0.87]
11.0 [0.43]
1/4 - 20
2X M6
TM-4100GE Hardware
Page 69

10.1.2 Spectral Response
FIGURE 35. Spectral Response
0.4
0.35
0.3
0.25
0.2
0.15
Absolute Quantum Efficiency
0.1
0.05
Page 59
Appendix
0
400 450 500 550 600 650 700 750 800 850 900 950 1000
Wavelength (nm)
TM-4100GE Hardware
Page 70

Page 60
Appendix
TM-4100GE Hardware
Page 71

Imaging Products
JAI PULNiX, Inc.
625 River Oaks Parkway
San Jose, CA 95134
Email: imaging@jaipulnix.com
Tel: 408-383-0300
Tel: 800-445-5444
Fax: 408-383-0301
www.jaipulnix.com
10098
Rev. C
 Loading...
Loading...