IXYS VUO190-18NO7, VUO190-16NO7, VUO190-14NO7, VUO190-12NO7, VUO190-08NO7 Datasheet
M6x10
7
3
30
27
6.5
6.5
C~
D~ E~
A+
B-
54
15
12
25
66
26
26
72
80
94
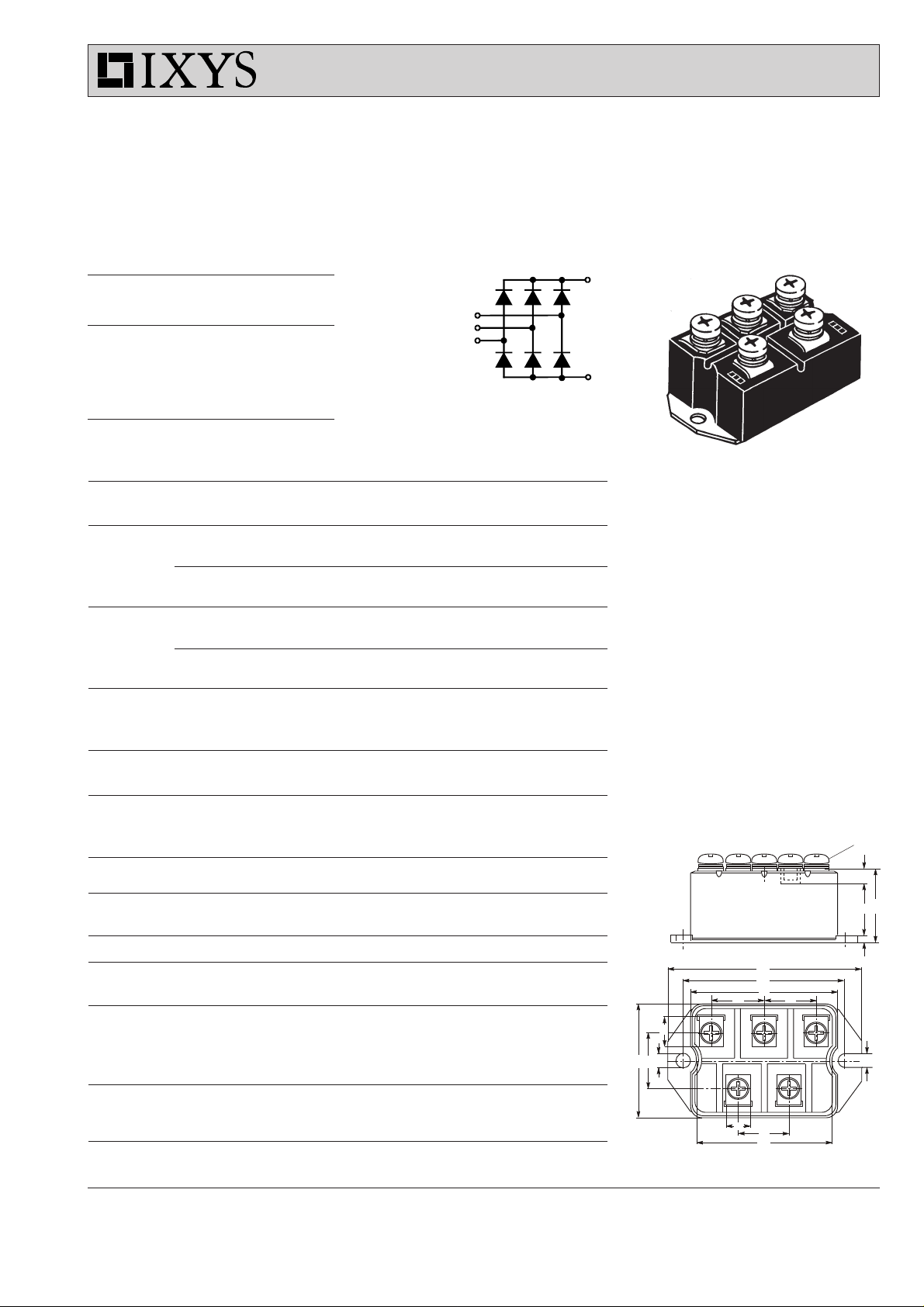
VUO 190
Three Phase
Rectifier Bridge
V
RSM
VV
800 800 VUO 190-08NO7
1200 1200 VUO 190-12NO7
1400 1400 VUO 190-14NO7
1600 1600 VUO 190-16NO7
1800 1800 VUO 190-18NO7*
* delivery time on request
Symbol Test Conditions Maximum Ratings
I
dAV
I
dAV
I
FSM
2
t TVJ = 45°C t = 10 ms (50 Hz), sine 39 200 A2s
I
T
VJ
T
VJM
T
stg
V
ISOL
M
d
Weight typ. 270 g
V
RRM
Type
~
~
~
TC = 100°C, module 248 A
TA = 35°C (R
= 0.2 K/W), module 165 A
thCA
TVJ = 45°C; t = 10 ms (50 Hz), sine 2800 A
VR = 0 t = 8.3 ms (60 Hz), sine 3300 A
TVJ = T
VJM
VR = 0 t = 8.3 ms (60 Hz), sine 2750 A
t = 10 ms (50 Hz), sine 2500 A
VR = 0 t = 8.3 ms (60 Hz), sine 45 000 A2s
TVJ = T
VJM
VR = 0 t = 8.3 ms (60 Hz), sine 31 300 A2s
t = 10 ms (50 Hz), sine 31 200 A2s
-40...+150 °C
150 °C
-40...+125 °C
50/60 Hz, RMS t = 1 min 2500 V~
≤ 1 mA t = 1 s 3000 V~
I
ISOL
Mounting torque (M6) 5 ± 15 % Nm
Terminal connection torque (M6) 5 ± 15 % Nm
I
dA V
V
+
= 248 A
= 800-1800 V
RRM
~
~
~
–
+
Features
●
Package with screw terminals
●
Isolation voltage 3000 V~
●
Planar passivated chips
●
Blocking voltage up to 1800 V
●
Low forward voltage drop
●
UL registered E72873
Applications
●
Supplies for DC power equipment
●
Input rectifiers for PWM inverter
●
Battery DC power supplies
●
Field supply for DC motors
Advantages
●
Easy to mount with two screws
●
Space and weight savings
●
Improved temperature and power
cycling
Dimensions in mm (1 mm = 0.0394")
-
Symbol Test Conditions Characteristic Values
I
R
V
F
V
T0
r
T
R
thJC
R
thJH
d
S
d
A
a Max. allowable acceleration 50 m/s
Data according to IEC 60747 and refer to a single diode unless otherwise stated
IXYS reserves the right to change limits, test conditions and dimensions.
© 2000 IXYS All rights reserved
VR = V
VR = V
IF= 300 A; TVJ = 25°C ≤ 1.43 V
For power-loss calculations only 0.8 V
per diode, 120° 0.45 K/W
per module 0.075 K/W
per diode, 120°0.6K/W
per module 0.1 K/W
Creeping distance on surface 10 mm
Creepage distance in air 9.4 mm
;T
RRM
;T
RRM
= 25°C ≤ 0.3 mA
VJ
= T
VJ
VJM
≤ 5mA
2.2 mΩ
2
049
1 - 2
VUO 190
300
A
250
I
F
200
150
100
TVJ=150°C
TVJ= 25°C
50
0
0.0 0.5 1.0 1.5
V
V
F
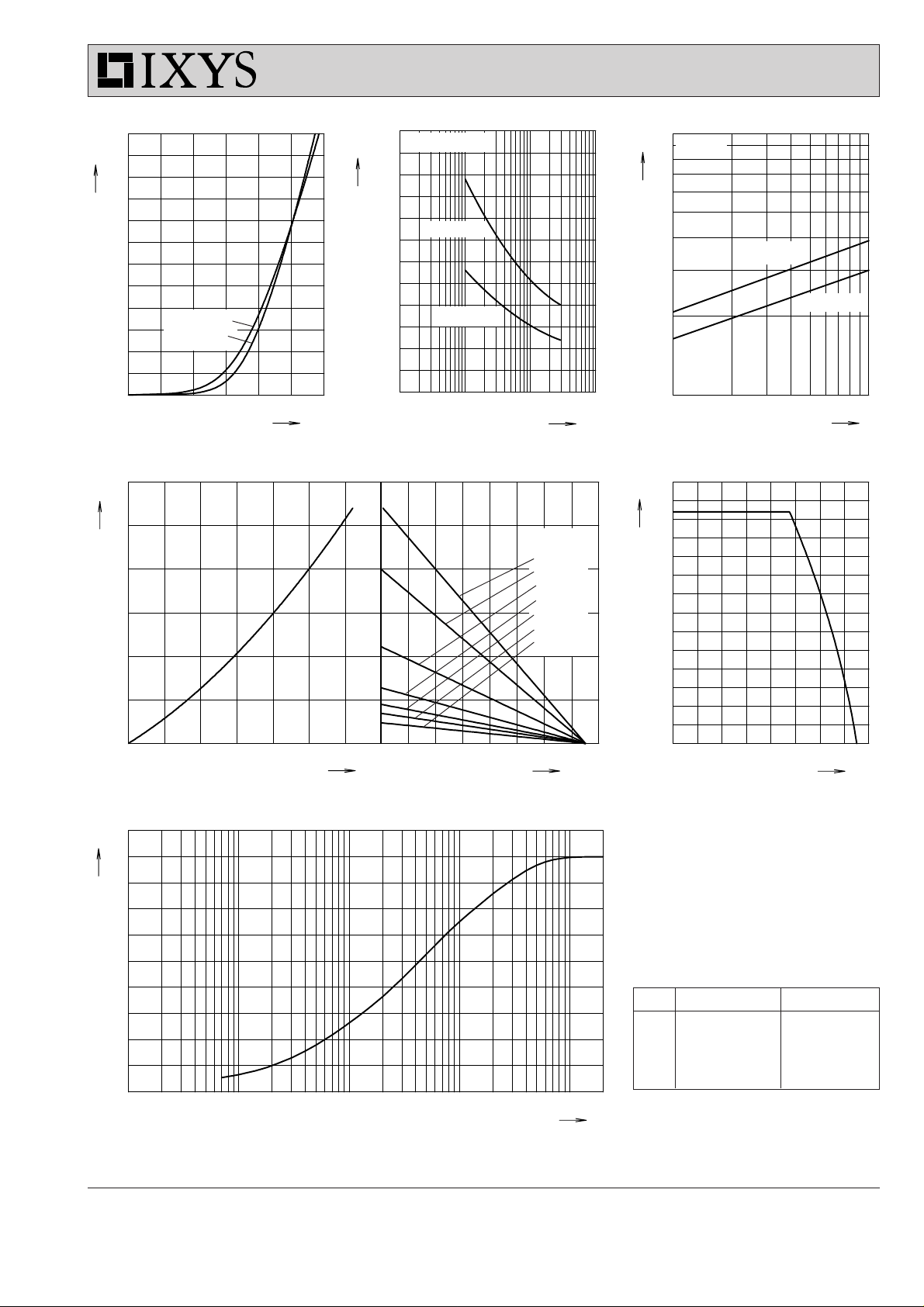
Fig. 4 Forward current versus voltage
drop per diode
600
W
P
tot
400
200
3000
A
50Hz, 80% V
RRM
10
A
5
2
s
VR = 0 V
2500
I
FSM
2000
1500
1000
T
VJ
T
VJ
= 45°C
= 150°C
I2t
T
= 45°C
VJ
500
0
0.001 0.01 0.1 1
s
10
4
23456789110
t
Fig. 5 Surge overload current Fig. 6 I2t versus time per diode
280
A
240
R
thHA
0.1 K/W
0.2 K/W
0.5 K/W
1.0 K/W
1.5 K/W
2.0 K/W
3.0 K/W
:
I
d(AV)M
200
160
120
80
T
VJ
= 150°C
ms
t
40
0
0 40 80 120 160 200 240
I
d(AV)M
0 20406080100120140
A
T
amb
°C °C
0
0 20406080100120140
T
C
Fig. 7 Power dissipation versus direct output current and ambient temperature Fig. 8 Max. forward current versus
case temperature
0.5
K/W
0.4
Z
thJC
0.3
0.2
Constants for Z
iR
calculation:
thJC
(K/W) ti (s)
thi
1 0.013 0.0012
0.1
2 0.072 0.047
3 0.175 0.326
4 0.19 2.03
0.0
0.001 0.01 0.1 1 10
Fig. 9 Transient thermal impedance junction to case
VUO 190
s
t
© 2000 IXYS All rights reserved
2 - 2
 Loading...
Loading...