Page 1
ETHERNET
PN: 100
-
05072
ITherm™/POSjet™/BANKjet™
USERS GUIDE
Rev C
Apr-2004
Page 2

General Information ITherm™ POSjet™ BANKjet™ Programmer’s Guide
Ethernet Adapter
Change Log
Rev A Initial Release
Rev B Rewritten in many places for clarity.
Rev C Minor Edits for clarity.
Page ii Rev C Apr-04
Page 3

Programmer’s Guide ITherm™ POSjet™ BANKjet™ General Information
Ethernet Adapter
Disclaimer
NOTICE TO ALL PERSONS RECEIVING THIS DOCUMENT:
The information in this document is subject to change without notice. No part of this document
may be reproduced, stored or transmitted in any form or by any means, electronic or mechanical,
for any purpose, without the express written permission of TransAct Technologies, Inc.
("TransAct"). This document is the property of and contains information that is both
confidential and proprietary to TransAct. Recipient shall not disclose any portion of this
document to any third party.
TRANSACT DOES NOT ASSUME ANY LIABILITY FOR DAMAGES INCURRED,
DIRECTLY OR INDIRECTLY, FROM ANY ERRORS, OMISSIONS OR DISCREPANCIES
IN THE INFORMATION CONTAINED IN THIS DOCUMENT.
Some of the product names mentioned herein are used for identification purposes only and may
be trademarks and/or registered trademarks of their respective companies.
TRANSACT , PowerPocket, Magnetec, Insta-Load, POSjet, Ithaca, 50Plus, PcOS, BANKjet and
"Made to Order. Built to Last" are registered trademarks and Flex-Zone, IthaColor and iTherm
are trademarks of TRANSACT Technologies, Inc.
© 2004 TransAct Technologies, Inc. All rights reserved.
Federal Communications Commission Radio Frequency Interference
Statement
TransAct Printers and Wired Ethernet Adapters comply with the limits for a Class A computing
device in accordance with the specifications in Part 15 of FCC rules. These regulations are
designed to minimize radio frequency interference during installation; however, there is no
guarantee that radio or television interference will not occur during any particular installation.
Interference can be determined by turning the equipment off and on while the radio or television
is on. If the printer causes interference to radio or television reception, try to correct the
interference by one or more of the following measures:
1. Reorient the radio or television receiving antenna
2. Relocate the printer with respect to the receiver
3. Plug the printer and receiver into different circuits
If necessary, the user should consult their dealer or an experienced radio/television technician for
additional suggestions. The user may find the following booklet prepared by the Federal
Communications Commission helpful: How to Identify and Resolve Radio/TV Interference
Problems. This booklet is available from the US Government Printing Office, Washington, DC
20402. Ask for stock number 004-000-00345-4.
Apr-04 Rev C Page iii
Page 4

General Information ITherm™ POSjet™ BANKjet™ Programmer’s Guide
Ethernet Adapter
Canadian Department of Communications Radio Interference Statement
TransAct Printers do not exceed Class A limits for radio noise emissions from digital apparatus
set out in the Radio Interference Regulations of the Canadian Department of Communications.
Regulatory Compliance
FCC Class A
ULc
CE Mark
UL 1950
TUV
Page iv Rev C Apr-04
Page 5

Programmer’s Guide ITherm™ POSjet™ BANKjet™ General Information
Ethernet Adapter
Table of Contents
Disclaimer iii
Federal Communications Commission Radio Frequency Interference Statement iii
Canadian Department of Communications Radio Interference Statement iv
Regulatory Compliance iv
Table of Contents 5
Table of Figures 7
GENERAL DESCRIPTION 8
Standard Features 8
Print Server Features Standard Ethernet Connection 8
Supported Protocols 8
User Interface/Configuration 8
Other 9
Advanced Features 9
Host Name 9
Support Utilities 9
System Requirements 9
Electromagnetic Compatibility Requirements 9
Environmental 9
Electrical Characteristics 10
Cash Drawer Drivers 10
Where Can You Find More Information? 10
Our Internet Support and Sales Services 10
TransAct Product Support 10
Internet Support 10
Contacting TransAct’s Ithaca Facility 11
Technical Support 11
Sales 11
Installation 12
POSjet and BANKjet adapter Installation 12
iTherm Installation 16
Ethernet Connection 18
Apr-04 Rev C Page 5
Page 6

Network Basics ITherm™ POSjet™ BANKjet™ Programmer's Guide
Ethernet Adapter
CONFIGURATION 19
TransAct Locator Program 19
Installation. 19
Using Locator 19
Using a Web Browser 22
Printer Identification Page 23
Printer Address Page 23
Printer Protocols Page 24
Printer Security Page 25
Adapter Firmware Update Page 26
The Reset Button 27
Installing Windows
TM
Printer Drivers 27
Printer Driver Installation Instructions for XP 27
To Install the Virtual COM drivers 28
NETWORK BASICS 30
Other 802.x standards 30
10BaseT 31
TCP/IP Basics, the TCP/IP protocol 31
TCP/IP Introduction 31
IP Addresses 31
Subnet Masks 31
Gateway addresses 31
Protocols in the TCP/IP suite 32
Automatic IP address allocation 32
Manual IP address allocation 32
TransAct Ethernet Adapter 33
DEFINITIONS 34
Page 6 Rev C Apr-04
Page 7

Programmer’s Guide ITherm™ POSjet™ BANKjet™ General Information
Ethernet Adapter
Table of Figures
Figure 1 POSjet and BANKjet Ethernet adapter .......................................................................... 12
Figure 2 iTherm Ethernet Adapter ................................................................................................ 16
Figure 3 Locator Scan................................................................................................................... 19
Figure 4 Locator Device Selection................................................................................................ 20
Figure 5 Locator Configuration.................................................................................................... 21
Figure 6 Adapter firmware upgrade.............................................................................................. 21
Figure 7 Printer Identification....................................................................................................... 22
Figure 8 Printer Address ............................................................................................................... 23
Figure 9 Printer Protocols ............................................................................................................. 24
Figure 10 Printer Security............................................................................................................. 25
Figure 11 Adapter Firmware Update ............................................................................................ 26
Apr-04 Rev C Page 7
Page 8

General Information ITherm™ POSjet™ BANKjet™ Programmer's Guide
Ethernet Adapter
General Description
There are two basic Wired Ethernet Adapters covered by this users guide. One is for the
iTherm 280 Thermal printer and the other is for the POSjet and BANKjet product families. Both
adapters are powered by the printer and provide the same basic functionality.
These Wired Ethernet Adapters provide fast and easiest way to network, share and printers to
your system. Ethernet provides a consistent common connection between printers and
computers using standard protocols supported by Windows® 95, 98, Me, NT, 2000, XP, as well
as many other platforms. Ethernet, being the most common networking medium, and thus
allows printers to be easily added, moved and removed with inexpensive common cabling and
off the self components.
This users manual is intended to show you how to install, connect and configure your Wired
Ethernet Adapters with the iTherm, POSjet and BANKjet printers. Installation is easy and
similar to serial port, parallel port and USB adapters. However, with Ethernet, connecting an
additional printer is a easy as plugging it in to the Ethernet hub, no special ports required.
Setup is easy too. A web style interface and a special locator program are provided to make
configuration simple from any PC with a web browser.
Standard Features
Print Server Feat ures Standard Ethernet Connection
• 10 Mbps Speed
• 10 Base T RJ45 network connection
• Network Traffic LED indicator
• Configured through networked PC Web Browser
• Works with Virtually All Major Operating Systems
• Integrated into the Printer
• Large RAM Buffer for fast continuous printing
• 512K Flash Memory for Future Upgrades
Supported Protocols
• Line Printer Daemon Protocol (LPR)
• Port 9100 (RAW)
• The TFTP Protocol (Revision 2)
• Telnet COM Port
• Hypertext Transfer Protocol (for configuration)
User Interface/Configuration
HTTP/Web Interface
• Login Page
Page 8 Rev C Apr-04
Page 9

Programmer’s Guide ITherm™ POSjet™ BANKjet™ General Information
Ethernet Adapter
• Configuration Page
o IP Address / Subnet Mask
o Auto-IP, DHCP, Static IP…
o Printer Textual Name (User Defined)
o Printer Location String (User Defined)
o Protocols Enabled/Disabled, Port
o LPR, Port 9100, Telnet
• Adapter Firmware Update
Other
• Push Button for Initial IP Address reset and adapter reset.
• Self-Diagnostics
• Firmware Upgrade via TFTP and HTTP
Advanced Features
Host Name
The Host Name, provided on the Printer Identification Page, is provided to the DHCP server
when DHCP is enabled. With this a decent DHCP-server, that is connected with the Domain
Name Server (DNS), as can be configured in Linux, allows programs access it using the
device name for it's IP address.
Support Utilities
• Locator
• Windows COM Port Virtualization
System Requirements
Printing – Any operating system that supports printing via RAW, LPR or Telnet connections
over TCP/IP. This includes, but is not limited to, Windows®, DOS, Linux, Unix and MAC OS.
Virtual COM Port – Windows® 2000, Windows® XP
Locator – Windows® 2000, Windows® XP
Electromagnetic Compatibility Requirements
The Wired Ethernet adapter shall meet all compatibility requirements specified for the PJ1000,
PJ1500, BANKjet and the iTherm.
Environmental
The Wired Ethernet adapter will match the environmental specifications for the PJ1000, PJ1500
and the iTherm
Apr-04 Rev C Page 9
Page 10

General Information ITherm™ POSjet™ BANKjet™ Programmer's Guide
Ethernet Adapter
Electrical Characteristics
The TransAct Ethernet adapter conforms to the IEEE 802.3, 10BaseT Ethernet interface
standards
10BaseT Ethernet specifications
• Maximum segment length: 100m (330 ft.)
• Topology: Star
• Cable type: UTP (CAT 3 or above)
• Connector type: RJ-45
• Transmission speed: 10 Mbps
Cash Drawer Drivers
The POSjet and BANKjet adapters provide the cash drawer interface for the printer. This
adapter is fixed to the Ithaca configuration and cable adapter must be used for STAR and Epson
cash drawers. The iTherm 280 provides a cash drawer interface that is not part of the interface
adapter. Refer to the iTherm Programmers guide for configuration information.
Where Can You Find More Information?
Our Internet Support and Sales Services
Web address : www.TransAct-tech.com
TransAct Technologies Incorporated maintains an Internet web site with content devoted to
supporting our products. Within the Support Services section you can find documentation for
TransAct Printers, including a current copies of the Programmer’s Guides.
TransAct Product Support
After entering TransAct’s web site, you will be brought to the “Welcome to TransAct” page. On
this page you will find the Ithaca® Brand listed at the top right.
Click the Ithaca® logo; locate the category “Support Services” on the next page.
Click on the “iTherm™ 280” sub-section on the lower half of the Ithaca® page.
Windows 95/98/Me Print Driver with Documentation Part No. 100-9167
Windows NT 4.0 2K and XP Print Driver with Documentation Part No. 100-9170
OPOS Drivers with Documentation Part No. 100-9732
Internet Support
TransAct Technologies Incorporated maintains an Internet web site. The address is
http://www.TransAct-tech.com The technical support page contains support information for our
printers. The iTherm™ 280 Printer support pages offer the latest information. The pages
Page 10 Rev C Apr-04
Page 11

Programmer’s Guide ITherm™ POSjet™ BANKjet™ General Information
Ethernet Adapter
include the current version of this manual; program examples; test procedures; programming
instructions; and supported print drivers.
Contacting TransAct’s Ithaca Facility
Contact TransAct’s Ithaca facility for information about the iTherm™ 280 Printer and how it
works with your system. For information on International distribution, visit our web site at
www.TransAct-tech.com. Contact the TransAct’s Sales and Technical Support Departments at
the following address and telephone or fax numbers.
Technical Support
Receive technical support, order documentation, request additional information, or send in a
printer for service.
Sales
Order supplies, receive more product information, or order product brochures.
TransAct Technologies Incorporated
Ithaca Facility
20 Bomax Drive
Ithaca, NY 14850 USA
Telephone (877) 7ithaca or (607) 257-8901
Main fax (607) 257-8922
Sales fax (607) 257-3868
Technical Support fax (607) 257-3911
Web site: http://www.TransAct-tech.com
Apr-04 Rev C Page 11
Page 12

Installation ITherm™ POSjet™ BANKjet™ Programmer's Guide
Ethernet Adapter
Installation
If the Wired Ethernet Adapter came installed in the printer, skip directly to Printer Connection.
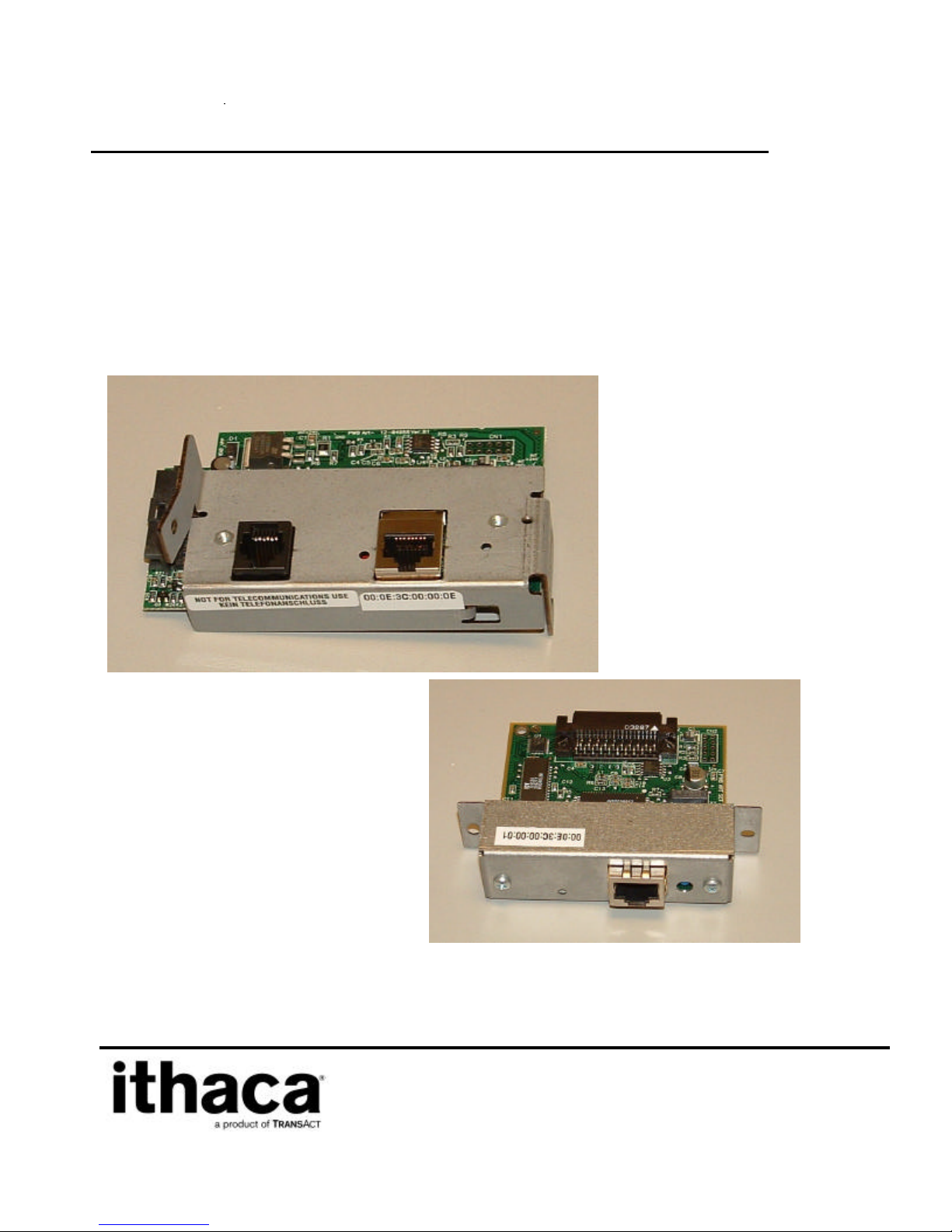
POSjet and BANKjet adapter Installation
The POSjet and BANKjet adapters require that the power supply be removed before the adapter
can be removed. Follow the following sequence to replace the current adapter with the Wired
Ethernet adapter.
Figure 1 POSjet and BANKjet Ethernet adapter
1. Disconnect all cables from the printer.
Page 12 Rev C Apr-04
Page 13

Programmer’s Guide ITherm™ POSjet™ BANKjet™ Installation
Ethernet Adapter
2. Remove the power supply-retaining clip.
3. Remove the power Supply
4. Unscrew the adapter interface from the printer side frame.
5. Slid the adapter sideways and then up and out of the printer.
Apr-04 Rev C Page 13
Page 14

Installation ITherm™ POSjet™ BANKjet™ Programmer's Guide
Ethernet Adapter
6. Install the Ethernet Adapter by carefully placing the adapter into slot and then sliding
is sideways until it is fully seated. (Do not force it.)
7. Reinstall the retaining screw
Page 14 Rev C Apr-04
Page 15

Programmer’s Guide ITherm™ POSjet™ BANKjet™ Installation
Ethernet Adapter
8. Connect and install the power supply.
9. Snap the retaining clip back over the power supply.
10. If the Cash Drawer label does not indicate that the printer is equipped with an Ithaca
Compatible interface, remove the label and install an Ithaca Compatible label as shown
above.
11. Reconnect the power, and install the Ethernet cable.
Apr-04 Rev C Page 15
Page 16

Installation ITherm™ POSjet™ BANKjet™ Programmer's Guide
Ethernet Adapter
iTherm Installation
Figure 2 iTherm Ethernet Adapter
1. Disconnect all wires and cables from the iTherm.
Page 16 Rev C Apr-04
Page 17

Programmer’s Guide ITherm™ POSjet™ BANKjet™ Installation
Ethernet Adapter
2. Remove the two retaining screws and remove the current adapter.
3. Take care that the cash drawer connector does not get out of position. If required,
reposition it as shown in the above picture.
4. Carefully insert the new adapter and make sure it is seated correctly. Do not force it.
5. Reinstall the retaining screws.
Apr-04 Rev C Page 17
Page 18

Installation ITherm™ POSjet™ BANKjet™ Programmer's Guide
Ethernet Adapter
6. Reconnect the power and the cash drawer connections if required
Ethernet Connection
Connecting the printer to the network is simple.
• Using a standard CAT5 Ethernet cable, connect one end to the RJ45 connector on the
Wired Ethernet Adapter. Connect the other end to an open Ethernet port in your Ethernet
hub, switch or router.
• Connect power to the printer and turn it on.
The printer should then print its IP address, which will be used to configure the Wired Ethernet
Adapters.
Note: If the printer does not print the IP address within two minutes, press the recessed button on
the Wired Ethernet Adapter for five (5) seconds and then release. This will reset the
Wired Ethernet Adapter, not the printer, back to its factory defaults. The IP address
should then be printed.
Page 18 Rev C Apr-04
Page 19

Programmer’s Guide ITherm™ POSjet™ BANKjet™ Configuration
Ethernet Adapter
Configuration
The Wired Ethernet Adapter is ready to be configured once the printer prints the IP address. The
TransAct Locator program or your internet web browser may be used to configure the Ethernet
Adapter.
TransAct Locator Program
TransAct provides a WindowsTM program to allow TransAct Ethernet devices to be located and
configured on a local subnet.
The Locator program allows the system administrator to find all TransAct Wired Ethernet
Adapters on the local network regardless of the IP addresses assigned to each adapter. The
Locator program is a Microsoft Windows program it will run on Windows 98II, XP and 2000.
Installation.
The program is available on the TransAct Web site www.transact-tech.com and is downloaded
as a compressed install. The locator program consists of two files. Locator.exe and
UbicomUCP.dll. These files must exist in a single directory and be run from that directory. Run
the install file, from any convent directory and Locator.exe and the required dll will be placed in
that directory.
Using Locator
Figure 3 Locator Scan
Apr-04 Rev C Page 19
Page 20

Configuration ITherm™ POSjet™ BANKjet™ Programmer's Guide
Ethernet Adapter
Locator will scan the local subnet and locate any TransAct printers connected to the network.
When all printers are found, you may select a printer by clicking on any printer in the list.
Figure 4 Locator Device Selection
Once selected the Adapter can be configured, upgraded, or you can activate your web browser to
configure the printer.
To configure the printer directly form the Locator program, click the Configure button. NOTE:
the locator program bypasses the printer security features. This program should only be made
available during setup and installation.
Page 20 Rev C Apr-04
Page 21

Programmer’s Guide ITherm™ POSjet™ BANKjet™ Configuration
Ethernet Adapter
Figure 5 Locator Configuration
To update the firmware in the adapter, select Update.
Figure 6 Adapter firmware upgrade
Browse your system for the upgrade 100-05059-xxx.bin file and select Upgrade.
Apr-04 Rev C Page 21
Page 22

Configuration ITherm™ POSjet™ BANKjet™ Programmer's Guide
Ethernet Adapter
Using a Web Browser
Using a web browser enter the IP address of the printer in the browser’s Address box. The
Printers IP address will be printed at power up b the printer.
Figure 7 Printer Identification
The following web pages are available to configure the Wired Ethernet Adapter:
Identification This page maintains names associate with the printer and
helpful for network management.
Address This page defines the printer’s address on the network.
Protocols This page defines which standard protocols the adapter will
use to communication with the network computers.
Security This pages provides a means to protect the Wired Ethernet
Adapter’s configuration from inadvertent change.
Firmware Provides the means to update the firmware in the Wired
Ethernet Adapter as it is made available from TransAct.
Page 22 Rev C Apr-04
Page 23

Programmer’s Guide ITherm™ POSjet™ BANKjet™ Configuration
Ethernet Adapter
Printer Identification Page
The Printer Identification page provides means to give the printer a name meaningful to it’s
application and position in the network. The Name and Location information will be retained by
the Wired Ethernet Adapter solely for to support the system manager in identifying and locating
resources. The Host Name is provided to the DHCP server, if AutoIP or DHCP is enabled on the
Printer Address Page, to provide automatic name identification of the printer on some networks.
See Advanced Features for more information.
When you are satisfied with the values entered, press the Apply button to save the values.
Printer Address Page
The Printer Address page provides for the proper addressing of the printer on the network. By
default the Wired Ethernet Adapter automatically obtains an address from a DHCP server or
makes up a random address consistent with the current network. It then prints this address on the
printer so that the printer may be accessed. However, because the address assigned to the printer
may change every time that the printer is rebooted, it is usually best to assign a fixed IP address
to the printer, known as a Static IP address. The Static IP address must be selected consistent
Apr-04 Rev C Page 23
Figure 8 Printer Address
Page 24

Configuration ITherm™ POSjet™ BANKjet™ Programmer's Guide
Ethernet Adapter
with the rest of the network. It must be unique and within the same subnet as the remainder of
the network.
When you are satisfied with the values entered, press the Apply button to save the values.
Printer Protocols Page
The Printer Protocol page enables or disables the protocols the Wired Ethernet Adapter will
accept. Three protocols are supported, Line Printer Protocol (LPR), Port 9100 (RAW) and
Telnet. In most cases, leaving all protocols enabled is best.
When you are satisfied with the values entered, press the Apply button to save the values.
Page 24 Rev C Apr-04
Figure 9 Printer Protocols
Page 25

Programmer’s Guide ITherm™ POSjet™ BANKjet™ Configuration
Ethernet Adapter
Printer Security Page
Figure 10 Printer Security
The Printer Security page allows the configuration of the Wired Ethernet Adapter to be protected
from accidental change by a password. By default, a user name and password are not necessary
to modify the Wired Ethernet Adapter configuration. However, it is recommended that upon
completion of the configuration that a username and password be assigned to the adapter to
minimize the possibility of an unauthorized person changing the configuration.
When the username and password have been enabled, users will be prompted to supply the
username and password before allowing access to the configuration pages.
The Enable Authentication box must be checked in order for the username and password to take
effect.
When you are satisfied with the values entered, press the Apply button to save the values. These
values will take effect immediately and if authentication has been enabled, further access to the
configuration web pages will require correct entry of the username and password.
NOTE: This security will be bypassed by the locator program.
Apr-04 Rev C Page 25
Page 26

Configuration ITherm™ POSjet™ BANKjet™ Programmer's Guide
Ethernet Adapter
Adapter Firmware Update Page
The Adapter Firmware Upgrade Page provides a means to upgrade the Wired Ethernet Adapter’s
firmware in the field. For details about upgrading the Wired Ethernet Adapter’s firmware, see
the documentation accompanying upgrades provided by TransAct.
Note: The current adapter firmware and Revision is shown at the bottom of the display. Do not
update the firmware unless you are having some problem and are asked to upgrade the adapter
by TransAct Customer service.
Page 26 Rev C Apr-04
Figure 11 Adapter Firmware Update
Page 27

Programmer’s Guide ITherm™ POSjet™ BANKjet™ Configuration
Ethernet Adapter
The Reset Button
The reset button provides three functions.
1. Resetting the print server.
2. Printing the print server configuration.
3. Resetting the print server configuration to the default.
Briefly pressing and releasing the reset button for less than 1 second will reset the print server.
This will clear all pending print in the buffers and restart the adapter.
Briefly pressing the reset button for about 1 second, releasing it for about 1 second and then
pressing and holding it will reset the adapter and force it to print it’s configuration.
Pressing and holding the reset button for about 5 seconds, will reset the adapters configuration to
factory defaults.
Installing Windows
TM
Printer Drivers
Printer Driver Installation Instructions for XP
NOTE: (Note Windows 2000 is similar but not identical)
1. Insert the “Windows XP, 2000 printer driver” floppy disk into your diskette drive.
2. Click on “Start” menu -> “Settings” -> “Printers”.
3. Double Click on “Add Printer” Icon.
4. Select Next then select “Local printer attached to this computer” then Click Next
5. Select Create a new port and then select Standard TCP/IP Port in the window and click
Next
6. Select next
7. Enter the IP address of the printer, and optional a printer name then click Next
8. Select Next to the defaults.
9. Select Finish.
You now have to install the TransAct Driver
10. If you have the driver already loaded on the system select it any you are done. If not
select have disk.
11. Select A:\ or where ever the driver is located.
12. Follow the instructions and you are done.
It may be necessary to change the IP address being used by the adapter.
1. Select Start->Settings->Printers
2. Open the Printer
3. Select Printer->Properties
Apr-04 Rev C Page 27
Page 28

Configuration ITherm™ POSjet™ BANKjet™ Programmer's Guide
Ethernet Adapter
4. Sel ect the Ports tab
5. Press the Configure
6. Edit the port address as required.
7. Select either RAW or LPR.
8. If LPR is selected, Byte Counting is not recommended.
9. In general LPR should be avoided as it is not compatible with some of the enhanced
driver features.
10. If RAW is selected, use port 9100.
To Install the Virtual COM drivers
1. Run VSerialInstall.exe.
2. Answer the questions. You must accept the license agreement to use this program.
3. Click through the two driver signing messages
4. The following configuration screen will be presented:
5. Enter the correct IP address of the Wired Ethernet Adapter.
6. None of the Serial port options need be changed. They are not used.
7. It is recommended to reboot your system at this time.
Changing the configuration.
Page 28 Rev C Apr-04
Page 29

Programmer’s Guide ITherm™ POSjet™ BANKjet™ Configuration
Ethernet Adapter
A quick configuration is provided by clicking Start -> Programs -> TransAct -> Configure
Remote Serial Port
This will display the current configuration and allow it to be altered. If you want to change
the COM port being used, you must use the configuration screen on the control panel.
Under the system hardware settings, select “Ports (COM & LPT)”
Select the TransAct Remote Serial port.
Under the “Port Setting” tab, select Advanced button, you may select any unused COM port.
NOTE: If you change the communications port, you will have to re-boot your computer for it
to be fully effective. Some devices and drivers only enumerate the communications ports at
boot up.
Apr-04 Rev C Page 29
Page 30

Network Basics ITherm™ POSjet™ BANKjet™ Programmer's Guide
Ethernet Adapter
Network Basics
The IEEE (Institute of Electrical and Electronic Engineers) project 802 decided to use Ethernet
version 2 as the basis for its new CSMA/CD network standard. By enhancing the DEC, Intel and
Xerox Ethernet 2 design, they produced the IEEE 802.3 specification, which is now the standard
format for Ethernet based systems.
The name 10Base indicates a signaling speed of 10 million bits per second with a base band
signaling scheme.
• 10BaseT 10Mbs Ethernet running over twisted pair cable 100 meter Max..
• 100BaseT 100Mbs Ethernet running over twisted pair cable 100 meter Max.
Other 802.x standards
The IEEE committee are also responsible for other 802 networking specifications:
• 802.1, this group produced an overview of the work of the project and defined the LAN
reference model.
• 802.2, this describes the logical link control services used in all IEEE specified LANs.
• 802.3, describes Ethernet based networks.
• 802.3z, describes the Gigabit Ethernet format.
• 802.4, describes networks using a token-passing bus.
• 802.5, describes networks using a token-passing ring.
• 802.6, specifications for a metropolitan area network.
• 802.7, this group advised other working groups on issues relating to broadband
transm ission.
• 802.8, this group are the technical advisory group for FDDI and fibre optic.
• 802.9, this group explores integrated data and voice networks.
• 802.11, group for wireless Ethernet
Page 30 Rev C Apr-04
Page 31

Programmer’s Guide ITherm™ POSjet™ BANKjet™ Network Basics
Ethernet Adapter
10BaseT
10baseT is also sometimes known as twisted pair. A distance of up to 30 meters between the
connected devices is the recommended limit. The TransAct Ethernet adapter is a 10BaseT
device.
TCP/IP Basics, the TCP/IP protocol
TCP/IP Introduction
TCP/IP or Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol is the network protocol used for the
internet and many local area networks.
Each device is given it’s own Internet Protocol address typically referred to as the IP Address. IP
Addresses are assigned either automatically or manually. This IP address is unique to the device
and cannot be used by any other device else inside the local network.
A typical IP address might look something like this: 192.168.1.80
IP Addresses
IP address consist of 4, 8 bit digits. Being an 8 bit value they may have values from 0 to 255.
For convenience the addresses are written as 4 numbers separated by periods. For example
“192.168.1.80”. A local network or Subnet will typically have the first 3 numbers the same.
For example two devices on a local network might have 192.168.1.80 and 192.168.1.81
respectively. The first number in the group IE the 192 can have additional meaning, however,
local networks are typically assigned value of 192.
Subnet Masks
Typically a subnet mask will look like this: 255.255.255.0. Each bit is a subnet mask is used to
determine if the IP address is in the subnet. If a bit is set in the subnet mask the IP. This
effectively defines how many devices can be in the subnet. In this case 255 because the last 8 bit
value is not masked and all possible values will be recognized as being part of the subnet.
Gateway addresses
One feature TCP/IP is that it is routable. That means that you can use a router or gateway to
expand a local network into multiple networks.
The router allows the two networks to talk to each other. If a user wants to pass information from
network A to network B, the router will pass the information back and forth.
The Gateway address is the IP address of the router that is interconnecting the local subnet to the
remainder of the network.
Apr-04 Rev C Page 31
Page 32

Network Basics ITherm™ POSjet™ BANKjet™ Programmer's Guide
Ethernet Adapter
Protocols in the TCP/IP suite
Inside the TCP/IP protocol are additional standards that allow different types of devices to
interact. For example for file transfers, FTP or File Transfer Protocol is used. It has an
additional identification called the Port.
The following table identifies various protocols within the TCP/IP suite and the ports that they
use.
Protocol Port Description
DHCP 67 Used for automatic TCP/IP allocation
HTTP 80 Used on Internet WWW servers
TELNET 23 Used for terminal type access
FTP 21 Used to send or retrieve data
LPR
Raw 9100 Used to send and receive data directly to a TCP/IP port
515 Used to send data to printers
Automatic IP address allocation
It is possible to have the local network setup and have one device on the network assign an IP
address automatically. The TransAct print server supports DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration
Protocol) for automatic IP address assignment. This requires that there be a DHCP server in the
local network to perform the assignment. This assignment process may have some
disadvantages in a POS network. It is difficult to assure that a given device is always assigned
the same address. For this reason, static IP addresses are generally manually assigned to devices.
Manual IP address al location
Rather than allow DHCP to assign an IP address it is possible to assign an address manually. If
the IP address is assigned manually, it must follow the requirements of the rest of the network to
operate correctly.
The TransAct Ethernet adapter is easily configured to use manual address assignments. In the
POS environment, it is important to make sure that print data be sent to the correct printer. By
using manual IP address assignments, you can assure that the print data will always be sent to the
correct printer.
Page 32 Rev C Apr-04
Page 33

Programmer’s Guide ITherm™ POSjet™ BANKjet™ Network Basics
Ethernet Adapter
TransAct Ethernet Adapter
The TransAct 10BaseT Ethernet adapter allows the user to communicate to the printer in two
ways. Raw data to Port 9100, LPR or port 515 or through TELNET port 23. The one you use
will largely depend on the application and how the interaction is to occur.
A word of caution on the use of LPR. LPR is a protocol within itself. Typically LPR is used by
a windows printer driver and supports the protocol in a way that is largely hidden from the
application. If you elect to use LPR you should not try to intermix LPR and any other protocol.
The TransAct Windows driver, supports enhanced features such as cash drawer status and
enhanced printer monitoring. These enhanced features use RAW data transfers. For that reason,
the TransAct print server should be used in RAW mode whenever possible.
The adapter supports. DHCP or static IP addressing. To make initial network setup easier, the
adapter will initially be configured to Auto IP. Auto IP attempts to DHCP or a Name server to
obtain an IP address assignment. If that fails, the network is monitored and an address consistent
with the active network is temporarily assigned and allow final configuration. (Note: Auto IP
should not be left active because the printers address may change and could conflict with
inactive devices in your network.) Turn off the Auto IP feature by setting DHCP or Static IP
using the Locator program or from the Address web page.
Apr-04 Rev C Page 33
Page 34

Definitions ITherm™ POSjet™ BANKjet™ Programmer's Guide
Ethernet Adapter
Definitions
Adapter - This is a device that adds network functionality to your Printer.
AutoIP – This is a means to automatically assign a temporary IP address to the printer long
enough to allow a static IP address to be assign.
Browser - A browser is an application program that provides a way to look at and interact with
all the information on the World Wide Web.
CAT5– Is an abbreviation for an Ethernet cable adhering to the Category 5 cable standard.
DNS (Domain Name System) - The capability of having a website, FTP, or e-mail server-with a
dynamic IP address-use a fixed domain name.
Default Gateway - A device that forwards Internet traffic from your local area network.
DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) - A protocol that lets one device on a local
network, known as a DHCP server, assign temporary IP addresses to the other network devices,
typically computers.
Download - To receive a file transmitted over a network.
Driver – A driver is typically a low level program specifically targeted to a specific hardware
adapter or feature.
Dynamic IP Address - A temporary IP address assigned by a DHCP server.
Ethernet - An IEEE standard network protocol that specifies how data is placed on and retrieved
from a common transmission medium.
Firmware – Firmware is name associated with software that is present in a system that is firm or
not subject to change. For example the BIOS in a computer is referred to as firmware.
FTP (File Transfer Protocol) - A standard protocol for sending files between computers over a
TCP/IP network and the Internet.
Gateway - A system that interconnects networks.
HTTP (HyperText Transport Protocol) - The communications protocol used to connect to
servers on the World Wide Web.
Hub – A device used to expand or extend the network
IEEE (The Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers) - An independent institute that
develops networking standards.
IP (Internet Protocol) - A protocol used to send data over a network.
IP Address - The address used to identify a computer or device on a network.
LAN (Local Area Network) - The computers and networking products that make up the network
in your home or office.
Page 34 Rev C Apr-04
Page 35

Programmer’s Guide ITherm™ POSjet™ BANKjet™ Definitions
Ethernet Adapter
Locator - A Windows 2000 and XP utility that displays the IP address for a particular
networking device.
MAC (Media Access Control) Address - The unique address that a manufacturer assigns to each
networking device.
Mbps (Megabits Per Second) - One million bits per second; a unit of measurement for data
transmission.
Network - A series of computers or devices connected for the purpose of data sharing, storage,
and/or transmission between users.
Packet - A unit of data sent over a network.
Ping - (Packet INternet Groper) - An Internet utility used to determine whether a particular IP
address is online.
Port 9100 – Port 9100 is the port ID used to communicate RAW data to and from the printer.
RAW - A term used to refer to data with no standardized embedded protocol.
RJ-45 (Registered Jack-45) - An Ethernet connector that holds up to eight wires.
SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol) - A widely used network monitoring and
control protocol.
Static IP Address - A fixed address assigned to a computer or device that is connected to a
network.
Subnet Mask - An address code that determines the size of the network.
Switch – A device used to expand a network. It is similar to a hub, however it tries to enhance
network performance by directing network traffic in a more efficient manor.
TCP/IP (Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol) - A network protocol for transmitting
data that requires acknowledgement from the recipient of data sent.
Telnet - A user command and TCP/IP protocol used for accessing remote PCs.
TFTP (Trivial File Transfer Protocol) - A version of the TCP/IP FTP protocol that uses UDP
and has no directory or password capability.
Topology - The physical layout of a network.
Upgrade - To replace existing software or firmware with a newer version.
Upload - To transmit a file over a network.
URL (Uniform Resource Locator) - The address of a file located on the Internet.
WAN (Wide Area Network) - The Internet.
Apr-04 Rev C Page 35
 Loading...
Loading...