ISSI IS82C600-9BI, IS82C600-9B, IS82C600-8BI, IS82C600-8B, IS82C600-10BI Datasheet
...
IS82C600
Integrated Silicon Solution, Inc. — 1-800-379-4774
1
PRELIMINARY TB001-0B
01/20/99
ISSI
®
This document contains PRELIMINARY DATA. ISSI reserves the right to make changes to its products at any time without notice in order to improve design and supply the best possible product.
We assume no responsibility for any errors which may appear in this publication. © Copyright 1999, Integrated Silicon Solution, Inc.
TRAILBLAZER
High-Speed SRAM with
Address Decoding and Ready Logic
FEATURES
• Zero wait-state performance on the Primary
Bus
— Point-to-point interface between the SRAM
and the high-speed processor
• Seamless interface to Texas Instruments’
TMS320LC54x high-speed processor
• Integrates the single-ported SRAM with a dualported interface
and handshake
— 9 ns access time to the SRAM
— Can also be used as a standalone, high-
speed SRAM
• Integrates the port-to-port bridge function
— Broadcasts all processor cycles from
Primary Bus to the Secondary Bus
— Programmability to only broadcast
non-SRAM cycles to the Secondary Bus
— Supports older, slower peripheral devices on
the Secondary Bus
— Allows the processor transparent access to
the devices on the Secondary Bus through
XCVR
pin
— Supports a Boot ROM on the Secondary Bus
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The IS82C600 TrailBlazer simplifies high-speed system
design and layout, providing an SRAM with zero wait-state
performance up to 90 MHz, address coding, and “Ready”
logic. In many cases, TrailBlazer allows existing system
designs to be easily upgraded, enabling the re-use of
already available ASICs and glue logic.
A key benefit of the TrailBlazer device is its ability to relieve
high-performance processors from a necessity to drive
heavily loaded multidrop buses by providing a point-to-
• Features Address Decoding and Ready Logic
— A total of six Chip Selects
— Supports “Ready” logic signal generation for
memory and I/O
— Eliminates PALs for address decoding and
ready logic
— No “glue logic” interface for local peripherals
on the Secondary Bus processor
• Allows dynamic re-allocation of memory spaces
for transparent block moves
— Programmable memory decoding allows
memory blocks to be accessed as either
Program Space (PS) or Data Space (DS)
— Programmable registers to map the internal
SRAM memory and external secondary port
devices into Data Space (DS), Program
Space (PS) and I/O Space (IS)
• Can also be used as a standalone, high-speed
SRAM
• Allows the shadowing of the ROM on the
Secondary Bus into the on-board SRAM
IS82C600
point, low-load interconnect to the high-speed memory
and buffering of the slower speed devices. This could allow
the processors to operate at a maximum frequency with
zero wait-states. Also, it eases PCB timing and layoutrelated considerations, often allowing a reduction in the
number of PC board layers and the lowering of noise.
Programmable decodes and "Ready" generation logic
built into the TrailBlazer eliminates the need for expensive
PALs, other glue logic, and additional board space.
PRELIMINARY
JANUARY 1999
ISSI
®
2
Integrated Silicon Solution, Inc. — 1-800-379-4774
PRELIMINARY TB001-0B
01/20/99
IS82C600
ISSI
®
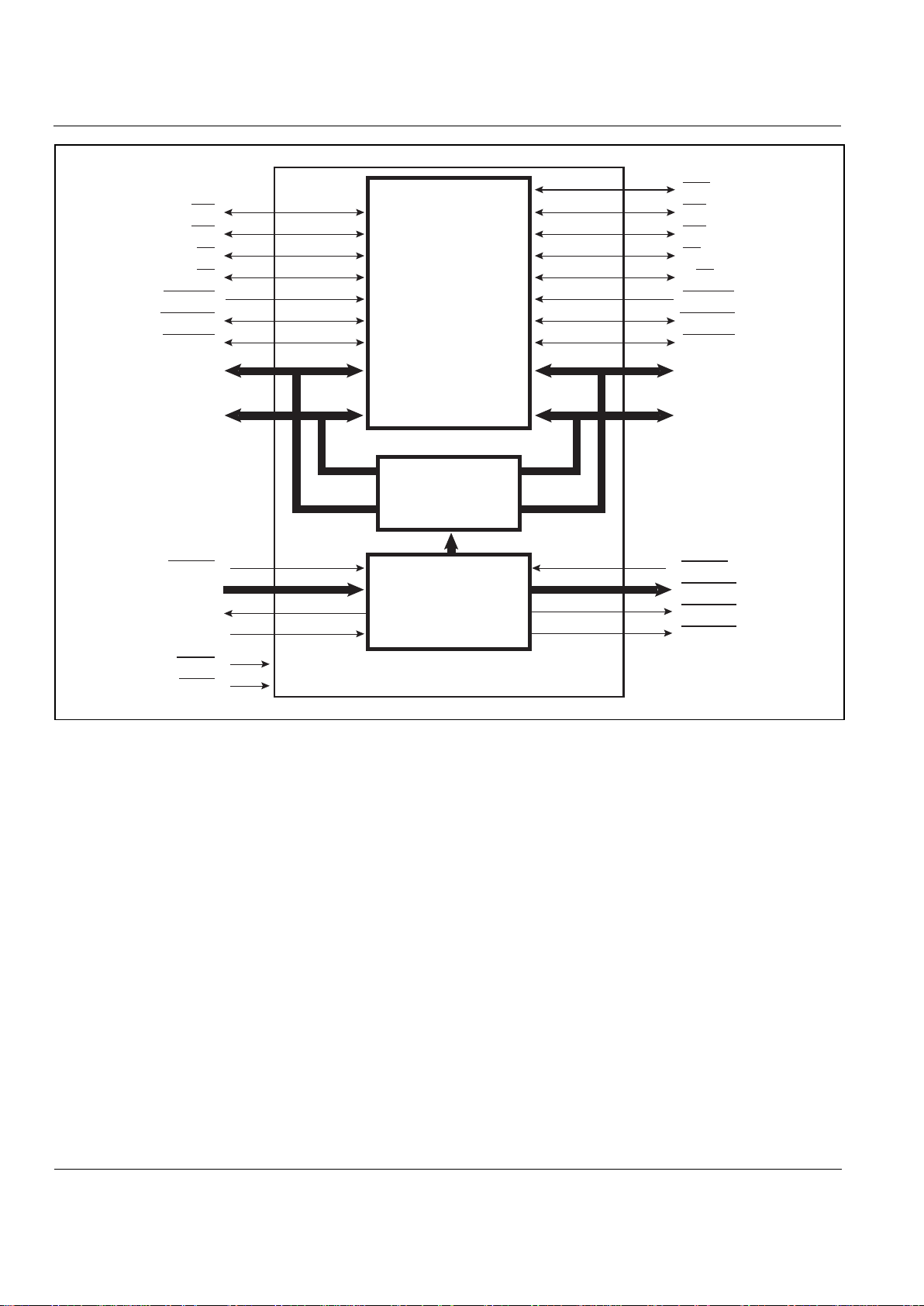
Figure 1. TrailBlazer Functional Block Diagram
PRODUCT OVERVIEW
The IS82C600 TrailBlazer integrates a high-speed 64K x
16 SRAM with a processor port-to-processor port bridge
function. This simplifies any high-speed designs by
providing a fast access time for the processor on the
Primary Port and enabling for a low-cost implementation of
a high-frequency system.
TrailBlazer combines a high-performance memory array,
programmable decodes, and "Ready" logic to achieve
maximum performance and flexibility, while keeping costs
at a minimum. In order to simplify system development,
TrailBlazer duplicates the Primary Bus signals on its
Secondary Bus to permit the use of existing system
components and ASICs together with a new generation of
high-performance processors.
On its Primary Bus, the TrailBlazer provides a high-speed
SRAM interface and then broadcasts the Primary Bus
cycles to its Secondary Bus, allowing the processor on its
Primary Bus to access peripherals on its Secondary Bus.
In many cases, since the peripherals are accessed by the
same signals, existing ASICs can be re-used.
TrailBlazer provides an optimized, seamless interface to
TI TMS320LC54x high-speed processor without the need
for any glue logic interfaces for local peripherals on the
Secondary Bus. TrailBlazer can also be used as shared
Local or Global Memory for a dual processor-based system
where the Chip Select logic on each bus allows for the
same data to be accessed at different locations in memory,
if so desired.
DECODER
SRAM
64K x 16
BUS
REPEATER
PSp
DSp
ISp
R/Wp
HOLDAp
IOSTRBp
MSTRBp
Dp[15:0]
Ap[15:0]
Ds[15:0]
As[15:0]
CSINTp
Ap[21:16]
RDY
CLK
PRGM
XCVR
CSINTs
CSMEMs[5:0]
WEMEMs
OEMEMs
PSs
DSs
ISs
R/Ws
HOLDAs
IOSTRBs
MSTRBs
PSp
DSp
ISp
R/Wp
HOLDAp
IOSTRBp
MSTRBp
WEs
PSs
DSs
ISs
R/Ws
HOLDAs
IOSTRBs
MSTRBs
IS82C600
Integrated Silicon Solution, Inc. — 1-800-379-4774
3
PRELIMINARY TB001-0B
01/20/99
ISSI
®
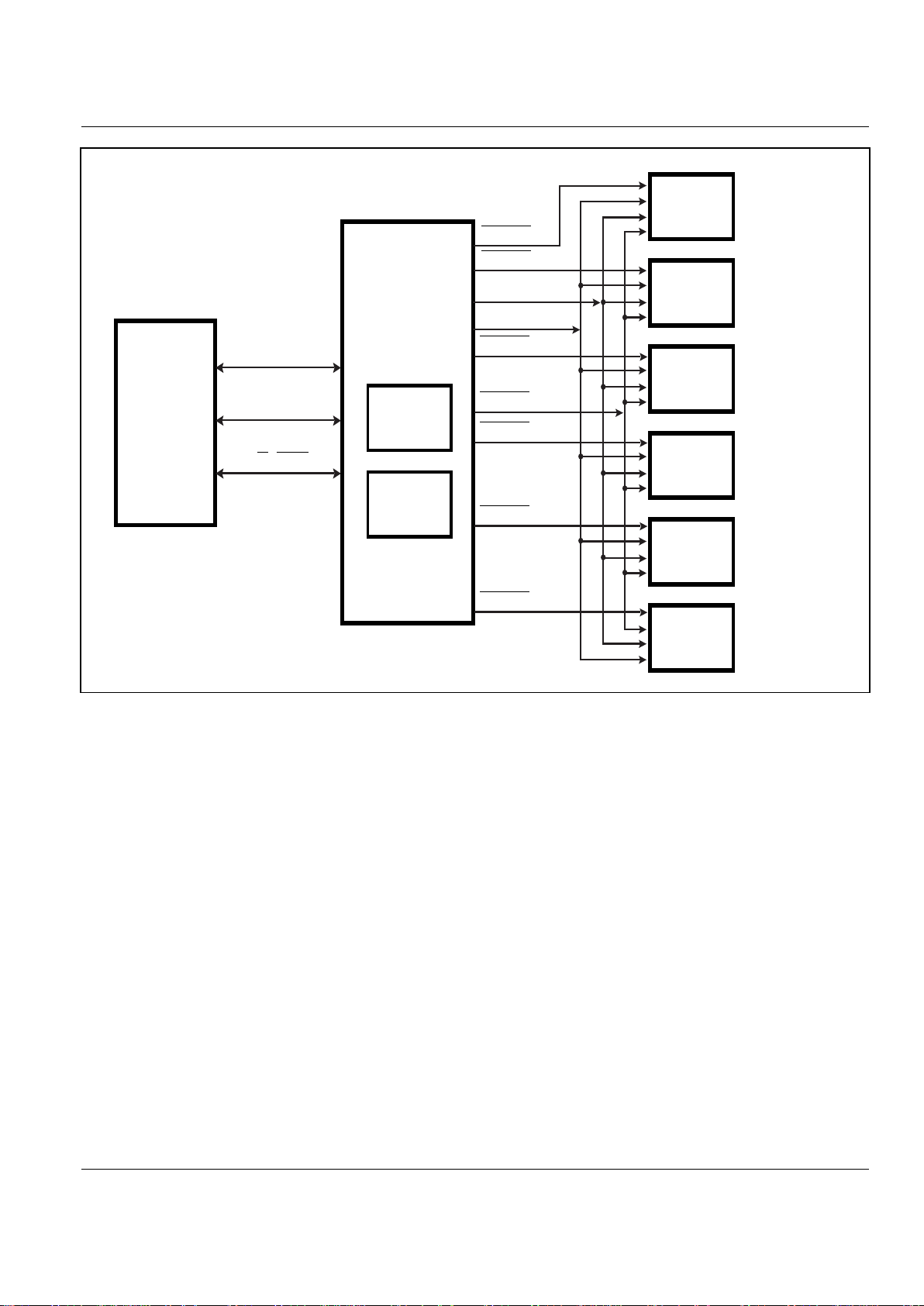
Figure 2. TrailBlazer System Block Diagram with High-Speed DSP on the Primary Bus and
the Slower Existing DSP System Components on the Secondary Bus
DSP
CSMEMs[0]
TRAILBLAZER
IS82C600
LOCAL
DEVICE 1
LOCAL
DEVICE 2
32K x 16
32K x 16
(REGISTER 0) (DEFAULT)
(REGISTER 5)
(REGISTER 4)
(REGISTER 3)
(REGISTER 2)
(REGISTER 1)
LOCAL
DEVICE 3
LOCAL
DEVICE 4
LOCAL
DEVICE 5
LOCAL
DEVICE 6
CSMEMs[1]
As[15:0]
Ap[21:0]
Dp[15:0]
R/W, STRB
Ds[15:0]
CSMEMs[2]
CSMEMs[3]
CSMEMs[4]
CSMEMs[5]
WEMEMs
4
Integrated Silicon Solution, Inc. — 1-800-379-4774
PRELIMINARY TB001-0B
01/20/99
IS82C600
ISSI
®
PIN INFORMATION
Complete pin information on the device is organized as
follows:
• Overview
• Conventions
• Pin Diagram
• Pin Assignment Table—Arranged by Pin Number
• Pin Assignment Table—Arranged by Ball Location
• Detailed Pin Descriptions
Overview
The R/W signal determines the direction of the bus
transaction.
Some processors, including TI TMS320LC54X, have three
major memory spaces. Program Space (PS); Data Space
(DS); and I/O Space (IS). The Memory Space signals (DS,
PS
, and IS) select the memory address space being
accessed (Data, Program, or I/O). No more than one of the
Memory Space signals can be asserted at the same time.
Data or Program spaces (or any part of these spaces) can
be mapped into either internal SRAM of the TrailBlazer or
any external devices. I/O space can only be mapped to
external devices. The TrailBlazer’s internal SRAM has two
32KB regions that are restricted to either DS or PS space.
Register 0 controls the decoding for the internal SRAM.
Registers 1 through 5 control the address decoding for the
external devices on the Secondary Bus. For processors
that have A15 as the MSB, the three memory
spaces are restricted to 64KB each. However, the registers
do allow for programmable address ranges in 8KB blocks.
For processors with A[21:16] as the MSB, there is a 4MB
maximum address space that can be partitioned by
programming Registers 1 to 5.
Chip Selects (
CSMEM
x) are used to select external devices
on the Secondary Bus. These signals are generated by
combinations of the Memory Space signals and Addresses
Ap[13:21].
Strobes (
MSTRB
and
IOSTRB
) validate Memory Space
selections. PS and DS have to be validated by the assertion
of
MSTRB
and IS has to be validated by the assertion of
IOSTRB
.
The following provides detailed technical information
related to the pins on the device. For ease of reference, the
pin information is presented in a table format arranged both
by pin numbers and by pin names. A pin diagram has also
been included to be used as a visual point of reference.
Conventions
Table 1 details conventions that are used to present
information on the pins.
Table 1. Pin Conventions
Convention Meaning
NC This pin is reserved for ISSI, Inc. and must
be left as a 'No Connect'
I Input-only
O Output-only
I/O Input or Output (Bi-directional)
Power Power pin
Ground Ground pin
SIGNAL
Active (or asserted) state occurs when pin
is at a low voltage
/ Multiplexed or Dual functionality
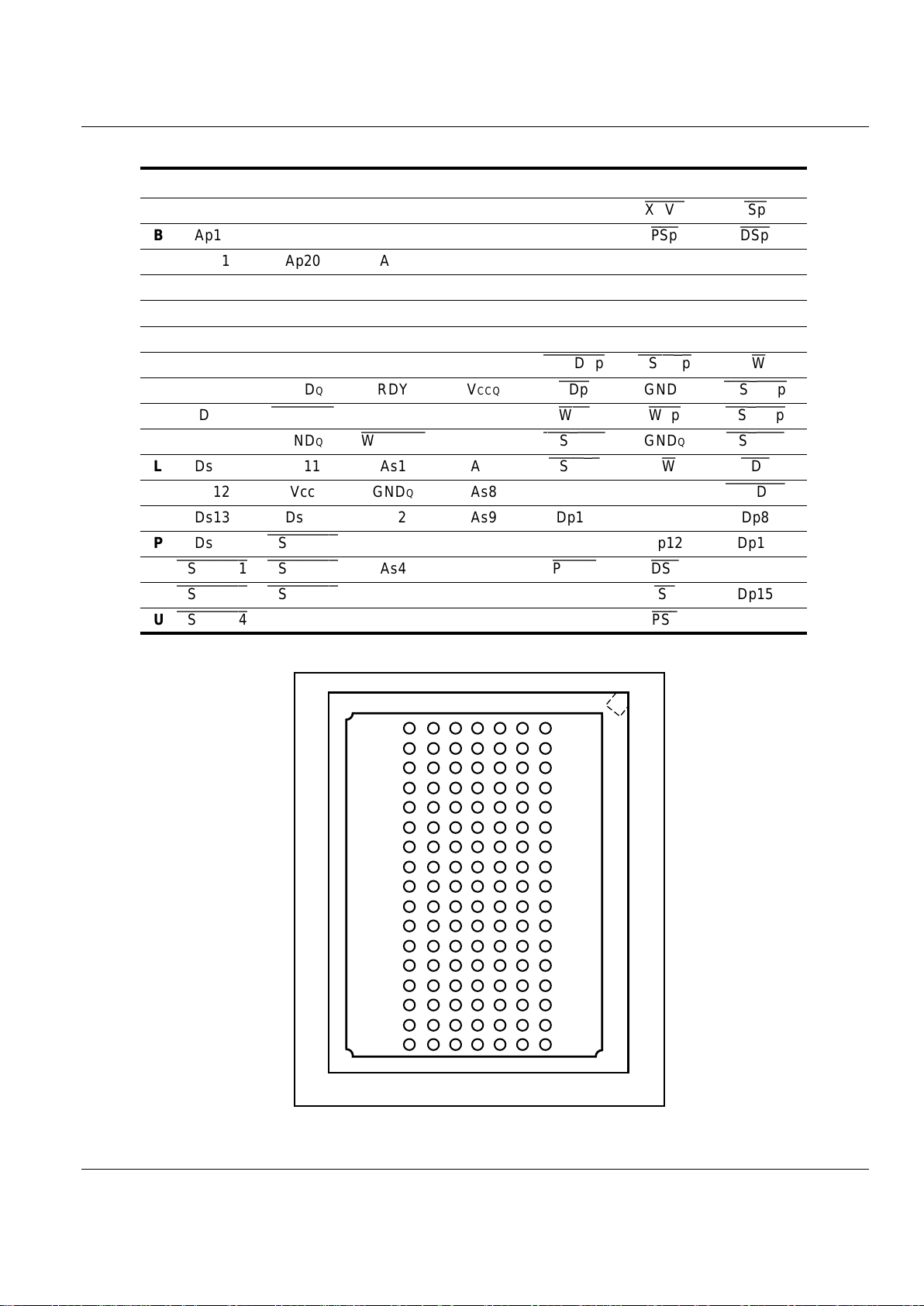
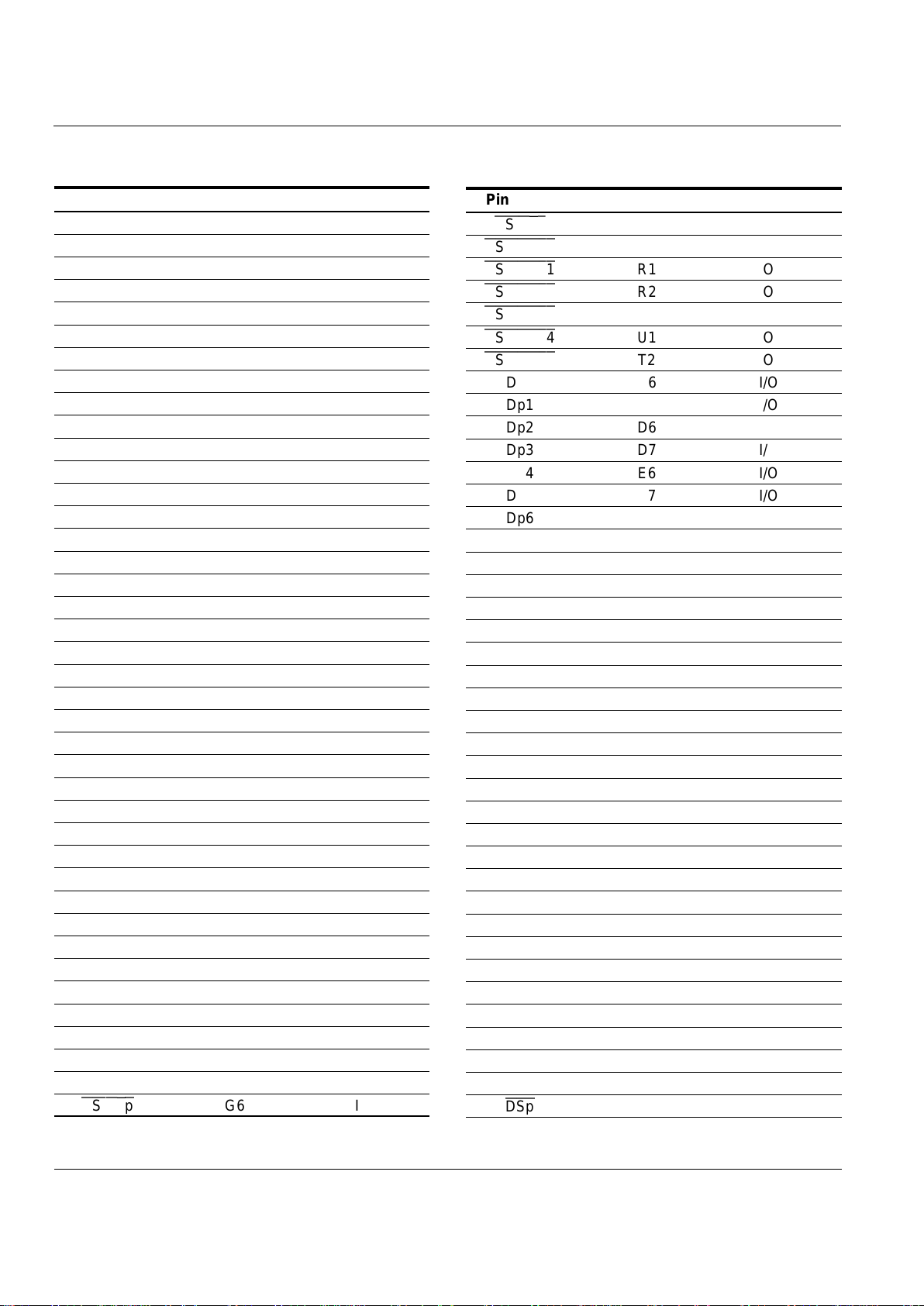
Pin Diagram
Refer to Figure 3 and Table 2 for the pin diagram for the
TrailBlazer device. It depicts the pin names and the
corresponding ball location. Pins marked as 'NC' are not
available and are defined as 'No Connect' pins. For more
detailed information on the pins refer to Table 5.
IS82C600
Integrated Silicon Solution, Inc. — 1-800-379-4774
5
PRELIMINARY TB001-0B
01/20/99
ISSI
®
Figure 3. TrailBlazer Pin Diagram
7654
BOTTOM VIEW
321
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
H
J
K
L
M
N
P
R
T
U
Table 2. Pin Configuration: 119-pin PBGA
1234567
AAp18 Ap16 Ap4 Ap5 Ap11
XCVR ISp
B Ap19 Ap17 Ap3 Ap6 Ap12
PSp DSp
C Ap21 Ap20 Ap2 Ap7 Ap13 Dp0 Dp1
D Ds1 Ds0 Ap1 Ap8 Ap14 Dp2 Dp3
E Ds3 Ds2 Ap0 Ap9 Ap15 Dp4 Dp5
F Ds4 GND GNDQ Ap10 GNDQ VCC Dp6
G Ds7 Ds6 Ds5 Dp7
HOLDAp CSINTp
R/Wp
H CLK GNDQ RDY VCCQ
RDp
GNDQ
IOSTRBp
J Ds8
OEMEMs
VCCQ VCCQ
WEs WEp MSTRBp
K Ds9 GNDQ
WEMEMs
VCCQ
IOSTRBs
GNDQ
MSTRBs
L Ds10 Ds11 As1 As7
CSINTs
R/Ws
RDs
M Ds12 Vcc GNDQ As8 GNDQ GND
HOLDAs
N Ds13 Ds14 As2 As9 Dp10 Dp9 Dp8
P Ds15
CSMEMs0
As3 As10 Dp13 Dp12 Dp11
R
CSMEMs1 CSMEMs2
As4 As11
PRGM DSs
Dp14
T
CSMEMs3 CSMEMs5
As5 As12 As15
ISs
Dp15
U
CSMEMs4
As0 As6 As13 As14
PSs
NC
6
Integrated Silicon Solution, Inc. — 1-800-379-4774
PRELIMINARY TB001-0B
01/20/99
IS82C600
ISSI
®
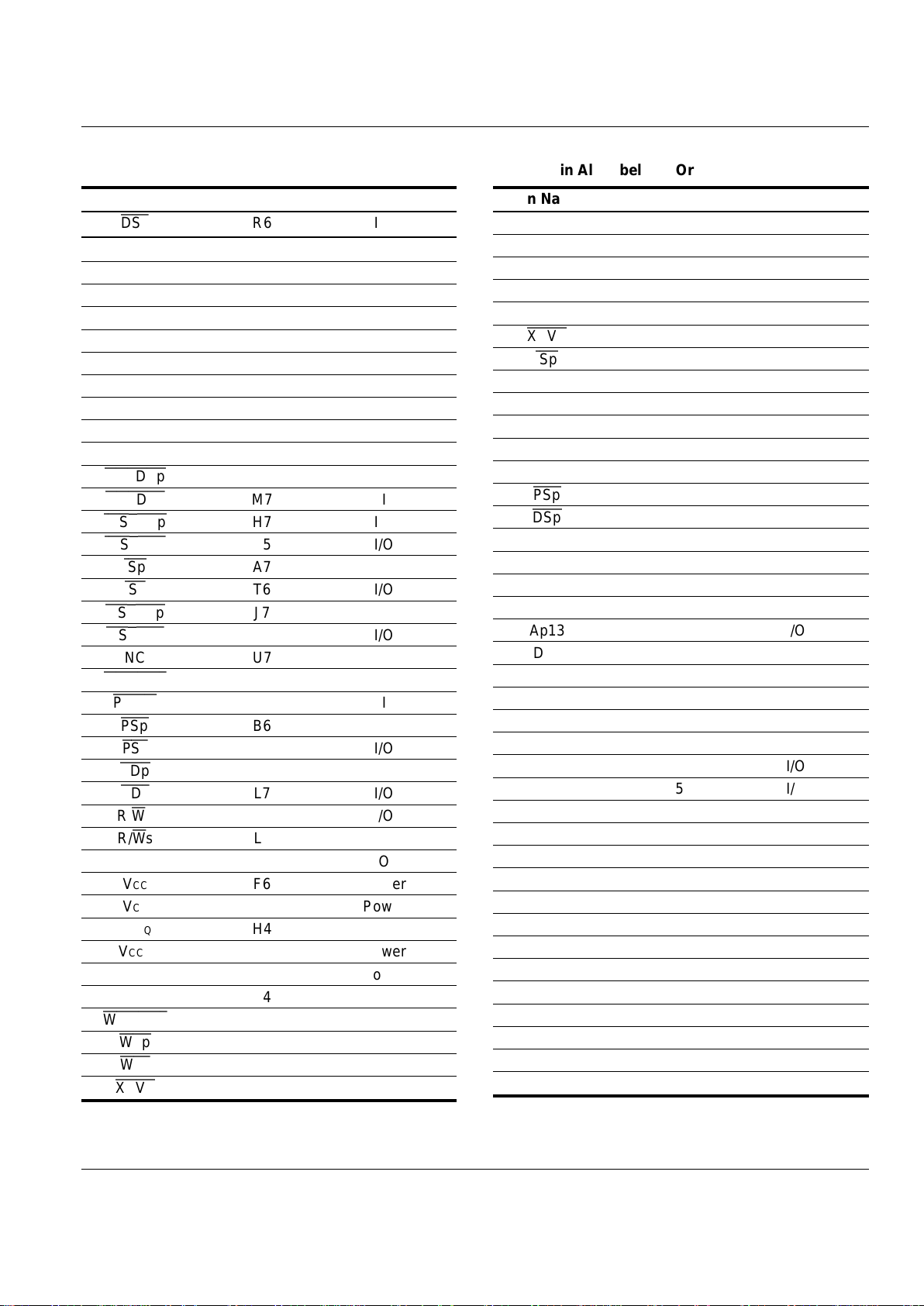
Table 3. Pin Assignment Table—Arranged by Pin
Name in Alphabetical Order
Pin Name Ball Location Pin Type
Ap0 E3 I/O
Ap1 D3 I/O
Ap2 C3 I/O
Ap3 B3 I/O
Ap4 A3 I/O
Ap5 A4 I/O
Ap6 B4 I/O
Ap7 C4 I/O
Ap8 D4 I/O
Ap9 E4 I/O
Ap10 F4 I/O
Ap11 A5 I/O
Ap12 B5 I/O
Ap13 C5 I/O
Ap14 D5 I/O
Ap15 E5 I/O
Ap16 A2 I
Ap17 B2 I
Ap18 A1 I
Ap19 B1 I
Ap20 C2 I
Ap21 C1 I
As0 U2 I/O
As1 L3 I/O
As2 N3 I/O
As3 P3 I/O
As4 R3 I/O
As5 T3 I/O
As6 U3 I/O
As7 L4 I/O
As8 M4 I/O
As9 N4 I/O
As10 P4 I/O
As11 R4 I/O
As12 T4 I/O
As13 U4 I/O
As14 U5 I/O
As15 T5 I/O
CLK H1 I
CSINTp
G6 I
Pin Name Ball Location Pin Type
CSINTs
L5 I
CSMEMs0
P2 O
CSMEMs1
R1 O
CSMEMs2
R2 O
CSMEMs3
T1 O
CSMEMs4
U1 O
CSMEMs5
T2 O
Dp0 C6 I/O
Dp1 C7 I/O
Dp2 D6 I/O
Dp3 D7 I/O
Dp4 E6 I/O
Dp5 E7 I/O
Dp6 F7 I/O
Dp7 G4 I/O
Dp8 N7 I/O
Dp9 N6 I/O
Dp10 N5 I/O
Dp11 P7 I/O
Dp12 P6 I/O
Dp13 P5 I/O
Dp14 R7 I/O
Dp15 T7 I/O
Ds0 D2 I/O
Ds1 D1 I/O
Ds2 E2 I/O
Ds3 E1 I/O
Ds4 F1 I/O
Ds5 G3 I/O
Ds6 G2 I/O
Ds7 G1 I/O
Ds8 J1 I/O
Ds9 K1 I/O
Ds10 L1 I/O
Ds11 L2 I/O
Ds12 M1 I/O
Ds13 N1 I/O
Ds14 N2 I/O
Ds15 P1 I/O
DSp
B7 I/O
IS82C600
Integrated Silicon Solution, Inc. — 1-800-379-4774
7
PRELIMINARY TB001-0B
01/20/99
ISSI
®
Table 3. Pin Assignment Table—Arranged by Pin
Name in Alphabetical Order
(continued)
Pin Name Ball Location Pin Type
DSs
R6 I/O
GND F2 Ground
GND M6 Ground
GNDQ F3 Ground
GNDQ F5 Ground
GNDQ H2 Ground
GNDQ H6 Ground
GNDQ K2 Ground
GNDQ K6 Ground
GNDQ M3 Ground
GNDQ M5 Ground
HOLDAp
G5 I
HOLDAs
M7 I
IOSTRBp
H7 I/O
IOSTRBs
K5 I/O
ISp
A7 I/O
ISs
T6 I/O
MSTRBp
J7 I/O
MSTRBs
K7 I/O
NC U7
OEMEMs
J2 O
PRGM
R5 I
PSp
B6 I/O
PSs
U6 I/O
RDp
H5 I/O
RDs
L7 I/O
R/Wp G7 I/O
R/Ws L6 I/O
RDY H3 O
VCC F6 Power
VCC M2 Power
VCCQ H4 Power
VCCQ J3 Power
VCCQ J4 Power
VCCQ K4 Power
WEMEMs
K3 O
WEp
J6 I/O
WEs
J5 I/O
XCVR
A6 I
Table 4. Pin Assignment Table—Arranged by Ball
Location in Alphabeltical Order
Pin Name Ball Location Pin Type
Ap18 A1 I
Ap16 A2 I
Ap4 A3 I/O
Ap5 A4 I/O
Ap11 A5 I/O
XCVR
A6 I
ISp
A7 I/O
Ap19 B1 I
Ap17 B2 I
Ap3 B3 I/O
Ap6 B4 I/O
Ap12 B5 I/O
PSp
B6 I/O
DSp
B7 I/O
Ap21 C1 I
Ap20 C2 I
Ap2 C3 I/O
Ap7 C4 I/O
Ap13 C5 I/O
Dp0 C6 I/O
Dp1 C7 I/O
Ds1 D1 I/O
Ds0 D2 I/O
Ap1 D3 I/O
Ap8 D4 I/O
Ap14 D5 I/O
Dp2 D6 I/O
Dp3 D7 I/O
Ds3 E1 I/O
Ds2 E2 I/O
Ap0 E3 I/O
Ap9 E4 I/O
Ap15 E5 I/O
Dp4 E6 I/O
Dp5 E7 I/O
Ds4 F1 I/O
GND F2 Ground
GNDQ F3 Ground
Ap10 F4 I/O
 Loading...
Loading...