IRPT2056A
PD 6.099
PRELIMINARY
Power Module for 3 hp Motor Drives
· 3 hp (2.2 kW) power output
Industrial rating at 150% overload for 1 minute
· 180-240V AC input, 50/60 Hz
· 3-phase rectifier bridge
· 3-phase, short circuit rated, ultrafast IGBT inverter
· HEXFRED ultrafast soft recovery-freewheeling diodes
· Brake IGBT and diode
· Low inductance (current sense) shunts in positive
and negative DC rail
· NTC temperature sensor
· Pin-to-baseplate isolation 2500V rms
· Easy-to-mount two-screw package
· Case temperature range -25°C to 125°C operational
IRPT2056A
™
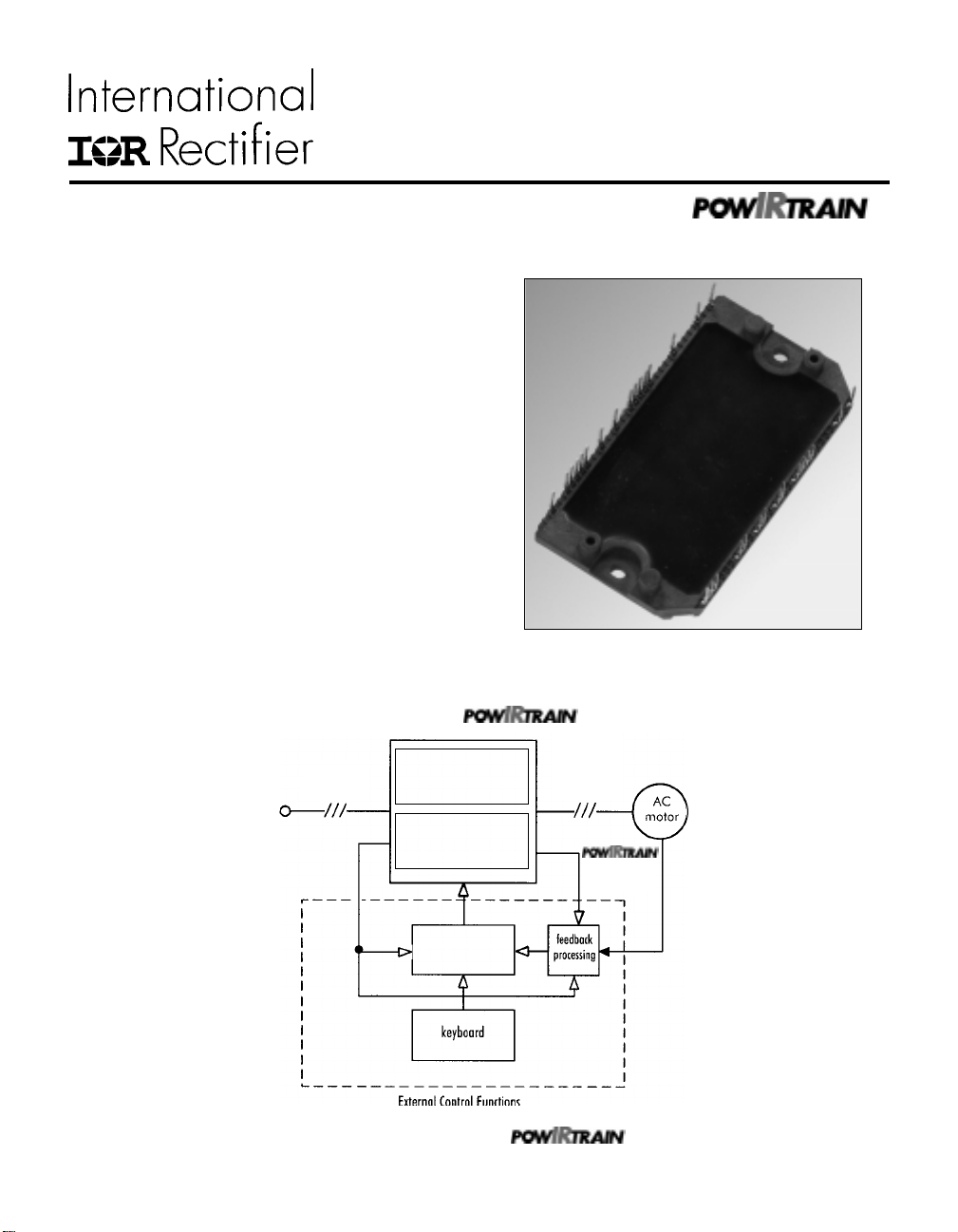
Figure 1. IRPT2056A Power Module
IRPT2056C
PWM
180-240V
3-phase input
Figure 2. The power module and within a
IRPT 2056A
Power
Module
IRPT 2056D
Driver-
Plus
Board
PWM
generator
motor control system
variable
frequency
output
feedback
(non-isolated)
page 1
IRPT2056A
System Description
Power Module
The IRPT2056A Power Module, shown in figure 1, is a chip
and wire epoxy encapsulated module. It houses input rectifiers,
output inverter, current sense shunts and NTC thermistor. The 3phase input bridge rectifiers are rated at 800V. The brake circuit
uses 600V IGBT and freewheeling diode. The inverter section
employs 600V, short circuit rated, ultrafast IGBT's and ultrafast
freewheeling diodes. Current sensing is achieved through 25
mΩ low inductance shunts provided in the positive and negative
DC bus rail. The NTC thermistors provide temperature sensing
capability. The lead spacing on the power module meets UL840
pollution level 3 requirements.
The power circuit and layout within the module are carefully
designed to minimize inductance in the power path, to reduce
noise during inverter operation and to improve the inverter
efficiency. The Driver-Plus Board required to run the inverter
can be soldered to the power module pins, thus minimizing
assembly and alignment. The power module is designed to be
mounted to a heat sink with two screw mount positions, in order
to insure good thermal contact between the module substrate and
the heat sink.
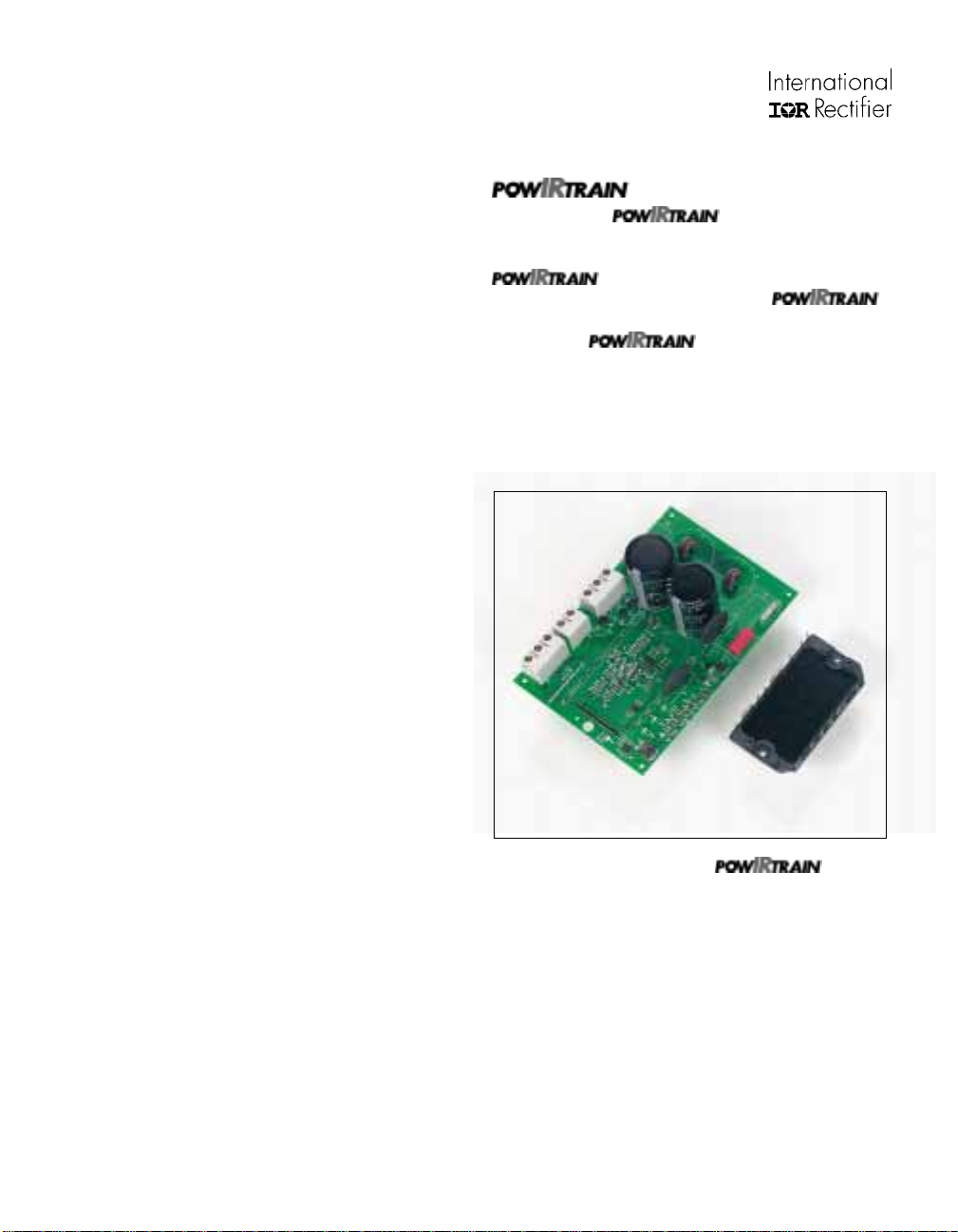
and Design Kit
The IRPT2056C (Figure 3) provides the
complete power conversion function for a 3 hp (2.2 kW) variable
voltage, variable frequency AC motor controller. The
combines the Power Module (IRPT2056A)
with a Driver-Plus Board (IRPT2056D). The
Design Kit, IRPT2056E includes the following:
• Complete integrated power stage
• Specification and operating instructions
• Bill of materials
• Electrical schematic
• Mechanical layout of the Driver-Plus Board
• Software transferrable file for easy design integration
• Application information and layout considerations
page 2
Figure 3. IRPT2056C
IRPT2056A
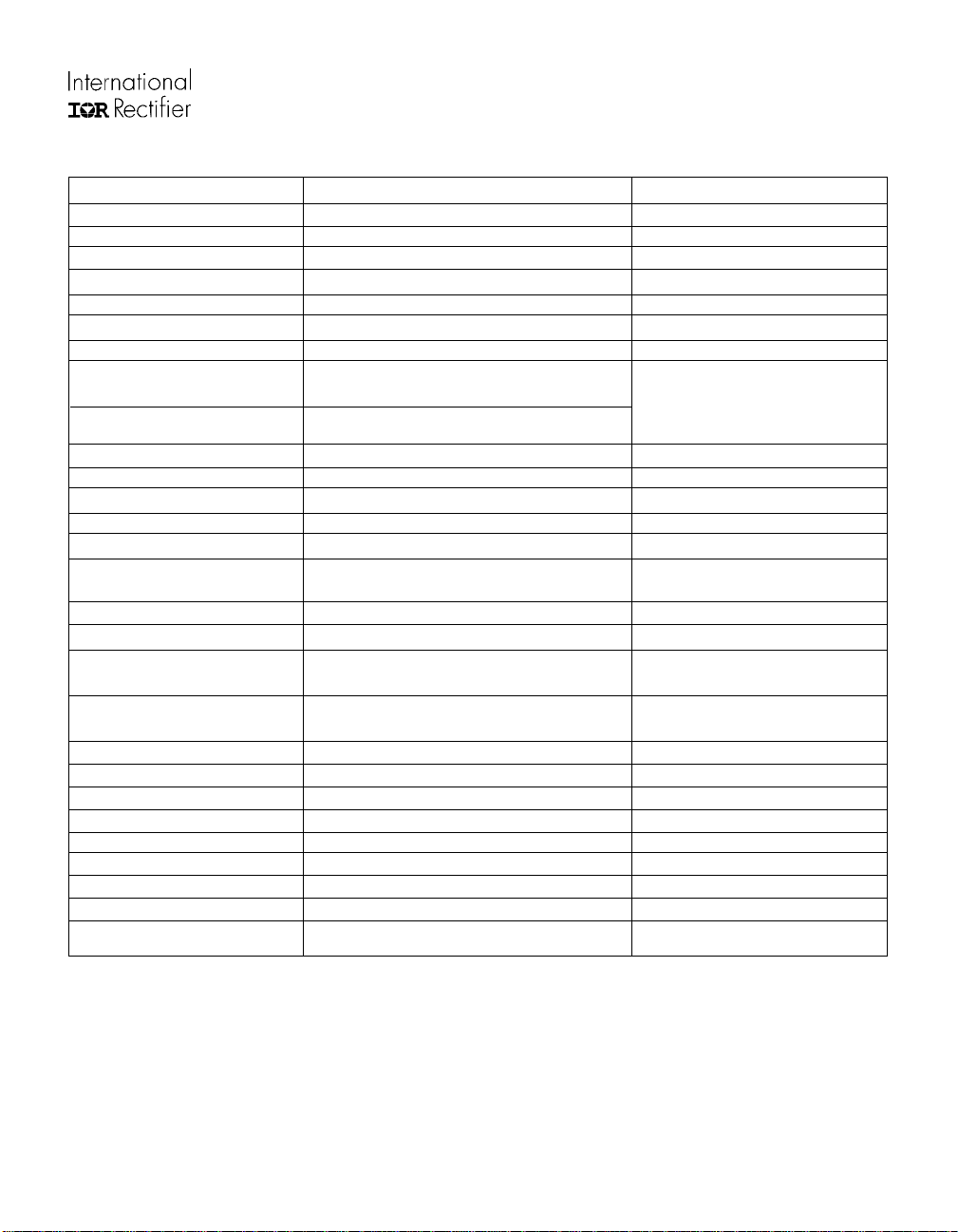
Specifications
PARAMETERS VALUES CONDITIONS
Input Power
Voltage 220V AC, -15%, +10%, 3-phase
Frequency 50/60 Hz
Current 15.4A rms @ nominal output TA = 40°C, R
I
FSM
400A 10ms half-cycle, non-repetitive surge
Output Power
Voltage 0-230V rms defined by external PWM control
Nominal motor hp (kW) 3 hp (2.2 kW) nominal full load power Vin = 230V AC, f
Nominal motor current 11A nominal full load power T
150% overload for 1 minute fo = 60 Hz,
= 40°C, R
16.5A 150% overload for 1 minute
A
DC Link
DC link voltage 400V maximum
Brake
Current 20A
Sensor
Temp. sense resistance 50 kOhms ±5% @ T
3.1kOhms ±10% @ T
Current sense 25mOhms ±5% @ T
Protection
IGBT short circuit time 10 µs DC bus = 400V, VGE = 15V,
line to line short
Recommended short circuit- 70A peak
shutdown current
Gate Drive
Q
G
Recommended gate driver IR2133 (see Figure 10)
120 nC (typical) @ VGE = 15V, refer figure 5b
Module
Isolation voltage 2500V rms pin-to-baseplate, 60 Hz, 1 minute
Operating case temperature -25°C to 125°C 95% RH max. (non-condensing)
Mounting torque 1 Nm M4 screw type
Storage temperature range -40°C to 125°C
Soldering temperature for 10 sec. 260°C maximum at the pins (.06" from case)
thSA
thSA
NTC
NTC
SHUNT
= 25°C
= 100°C
= 25°C
= 0.42°C/W
= 4kHz,
pwm
= 0.42°C/W
page 3
IRPT2056A
0.6
0.5
°C/W)
thSA
0.4
0.3
Power
150%
R
100% Load Continuous
thSA
10-60 Hz
3 hp
(2.2 kW)
300
250
200
150
Power
100%
Thermal Resistance (R
0.2
0.1
R
150% Load (1 min.)
thSA
Down to 3 Hz
0
1 4 8 12 20
R
150% Load
thSA
1 min.)10-60 Hz
16 24
100
50
0
PWM Frequency (kHz) – (Induction Motor Load)
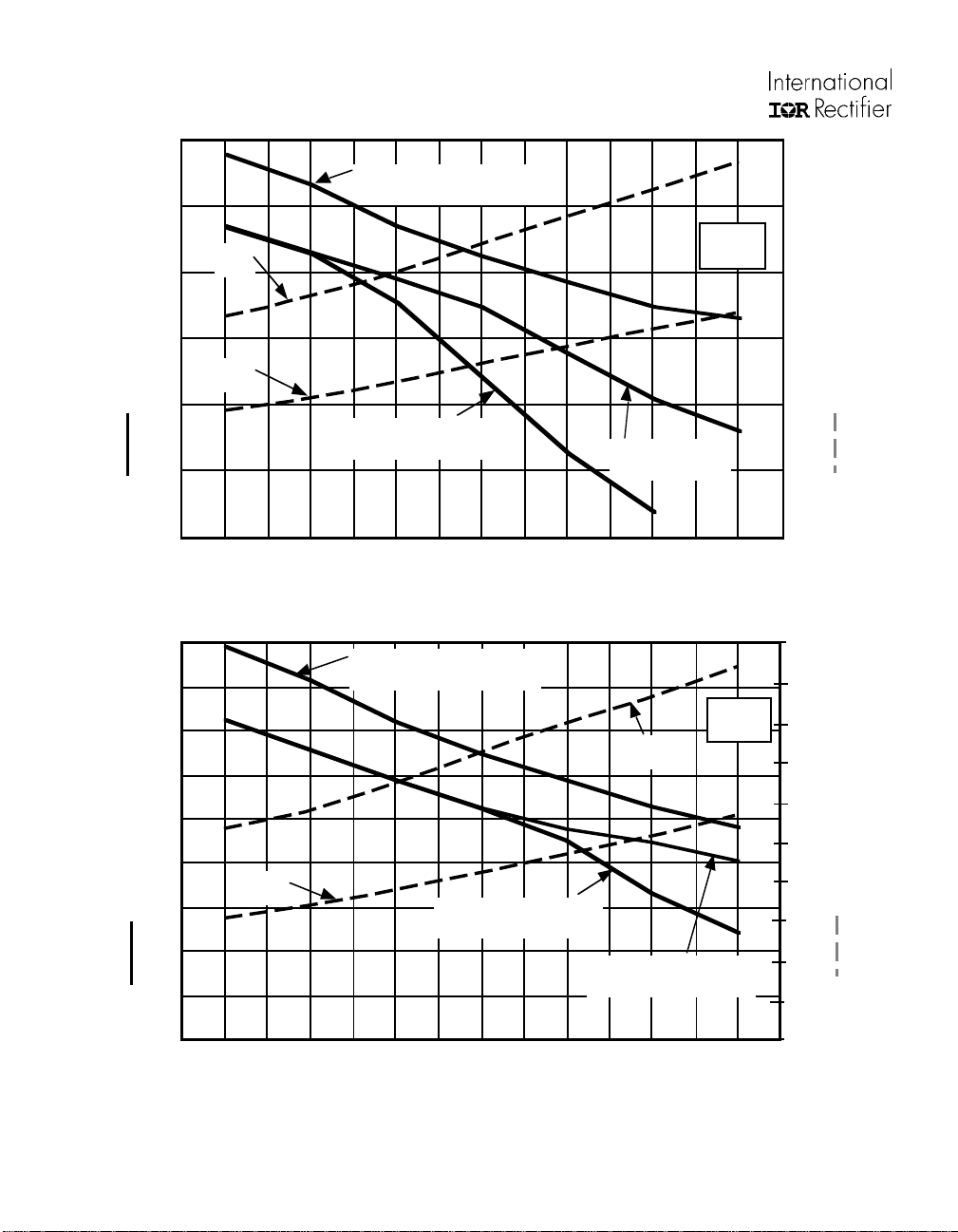
Figure 4a. 3hp/11A output Heat Sink Thermal Resistance and Power Dissipation vs. PWM Frequency
0.9
0.8
0.7
°C/W)
thSA
0.6
R
100% Load Continuous
thSA
10-60 Hz
Power
150%
2 hp
(1.5 kW)
200
180
160
140
120
0.5
100
0.4
0.3
Thermal Resistance (R
0.2
0.1
Power
100%
R
150% Load (1 min.)
thSA
Down to 3 Hz
R
150% Load (1 min.)
thSA
10-60 Hz
80
60
40
20
Total Power Dissipation (Watts)
Total Power Dissipation (Watts)
0
1 4 8 12 16 20 24
PWM Frequency (kHz) – (Induction Motor Load)
Figure 4b. 2hp/8A output Heat Sink Thermal Resistance and Power Dissipation vs. PWM Frequency
NOTE: For Figures 4a and 4b: Operating Conditions: Vin = 230V
during 1 minute overload to 10°C
page 4
, MI =1.15, PF = 0.8, TA = 40°C, Tj < 145°C, Ts < 95°C, Z
rms
0
thSA
limits ∆T
c
 Loading...
Loading...