Data Sheet No. PD60161-R
(S) & (PbF)
Features
Floating channel designed for bootstrap operation
•
Fully operational to +600V
IR2108(4)
HALF-BRIDGE DRIVER
Packages
Tolerant to negative transient voltage
dV/dt immune
Gate drive supply range from 10 to 20V
•
Undervoltage lockout for both channels
•
3.3V, 5V and 15V input logic compatible
•
Cross-conduction prevention logic
•
Matched propagation delay for both channels
•
High side output in phase with HIN input
•
Low side output out of phase with
•
Logic and power ground +/- 5V offset.
•
Internal 540ns dead-time, and
•
LIN
input
programmable up to 5us with one
external R
Lower di/dt gate driver for better
•
resistor (IR21084)
DT
noise immunity
Available in Lead-Free
•
Description
The IR2108(4)(S) are high voltage, high speed
power MOSFET and IGBT drivers with dependent high and low side referenced output
channels. Proprietary HVIC and latch immune
8-Lead SOIC
IR2108S
8-Lead PDIP
IR2108
2106/2301//2108//2109/2302/2304 Feature Comparison
Part
2106/2301
21064
2108 Internal 540ns COM
21084
2109/2302 Internal 540ns COM
21094
2304
Input
logic
HIN/LIN no none
HIN/LIN yes
IN/SD yes
HIN/LIN
Cross-
conduction
prevention
logic
yes
14-Lead SOIC
IR21084S
14-Lead PDIP
IR21084
Dead-Time Ground Pins
Programmable 0.54~5 µs
Programmable 0.54~5 µs
Internal 100ns
COM
VSS/COM
VSS/COM
VSS/COM
COM
CMOS technologies enable ruggedized monolithic construction. The logic input is compatible with standard CMOS
or LSTTL output, down to 3.3V logic. The output drivers feature a high pulse current buffer stage designed for
minimum driver cross-conduction. The floating channel can be used to drive an N-channel power MOSFET or
IGBT in the high side configuration which operates up to 600 volts.
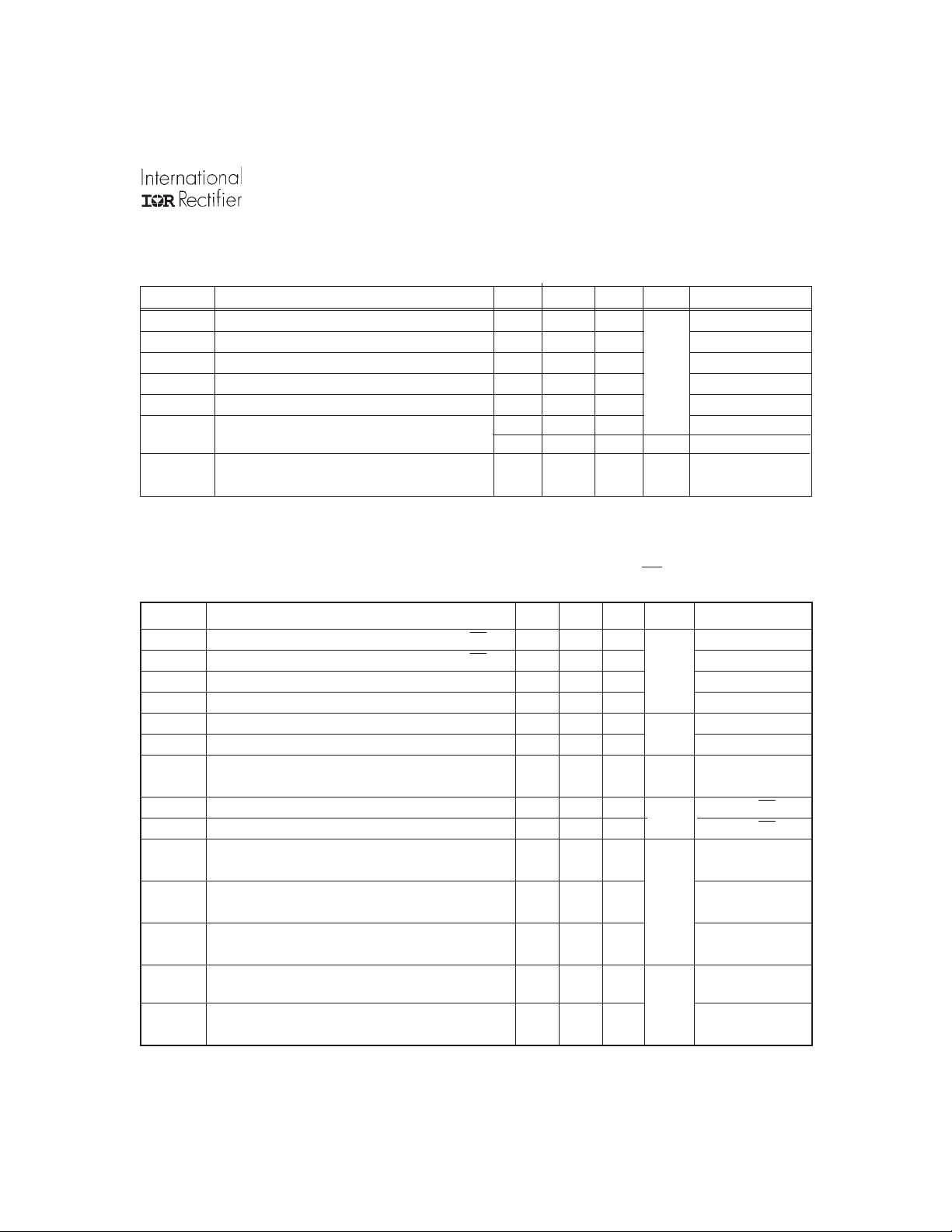
Typical Connection
up to 600V
V
CC
V
V
CC
HIN
LIN
(Refer to Lead Assignments for correct pin
configuration). This/These diagram(s) show
electrical connections only. Please refer to our
Application Notes and DesignTips for proper
circuit board layout.
HIN
LIN
www.irf.com 1
B
HO
V
S
LOCOM
IR2108
V
HIN
LIN
V
TO
LOAD
up to 600V
HO
V
V
CC
CC
SS
HIN
LIN
DT
V
R
DT
B
V
S
COM
SS
LO
IR21084
TO
LOAD

IR2108(4)
(S) & (PbF)
Absolute Maximum Ratings
Absolute maximum ratings indicate sustained limits beyond which damage to the device may occur. All voltage parameters are absolute voltages referenced to COM. The thermal resistance and power dissipation ratings are measured
under board mounted and still air conditions.
Symbol Definition Min. Max. Units
V
B
V
S
V
HO
V
CC
V
LO
DT Programmable dead-time pin voltage (IR21084 only) VSS - 0.3 V
V
IN
V
SS
dVS/dt Allowable offset supply voltage transient — 50 V/ns
P
D
Rth
JA
T
J
T
S
T
L
High side floating absolute voltage -0.3 625
High side floating supply offset voltage VB - 25 VB + 0.3
High side floating output voltage VS - 0.3 V
B
+ 0.3
Low side and logic fixed supply voltage -0.3 25
Low side output voltage -0.3 VCC + 0.3
+ 0.3
CC
Logic input voltage (HIN & LIN)V
Logic ground (IR21084 only) V
- 0.3 V
SS
- 25 V
CC
CC
CC
+ 0.3
+ 0.3
V
Package power dissipation @ TA ≤ +25°C (8 lead PDIP) — 1.0
(8 lead SOIC) — 0.625
(14 lead PDIP) — 1.6
W
(14 lead SOIC) — 1.0
Thermal resistance, junction to ambient (8 lead PDIP) — 125
(8 lead SOIC) — 200
(14 lead PDIP) — 75
°C/W
(14 lead SOIC) — 120
Junction temperature — 150
Storage temperature -50 150
°C
Lead temperature (soldering, 10 seconds) — 300
Recommended Operating Conditions
The Input/Output logic timing diagram is shown in figure 1. For proper operation the device should be used within the
recommended conditions. The VS and VSS offset rating are tested with all supplies biased at 15V differential.
Symbol Definition Min. Max. Units
VB High side floating supply absolute voltage VS + 10 VS + 20
V
S
V
HO
V
CC
V
LO
V
IN
DT Programmable dead-time pin voltage (IR21084 only) V
V
SS
T
A
Note 1: Logic operational for VS of -5 to +600V. Logic state held for VS of -5V to -VBS. (Please refer to the Design Tip
DT97-3 for more details).
2 www.irf.com
High side floating supply offset voltage Note 1 600
High side floating output voltage V
S
V
Low side and logic fixed supply voltage 10 20
Low side output voltage 0 V
Logic input voltage IR2108 COM V
IR21084 VSS V
SS
CC
CC
CC
V
CC
Logic ground (IR21084 only) -5 5
Ambient temperature -40 125
B
V
°C
IR2108(4)
(S) & (PbF)
Dynamic Electrical Characteristics
V
(VCC, VBS) = 15V, VSS = COM, CL = 1000 pF, TA = 25°C, DT = VSS unless otherwise specified.
BIAS
Symbol Definition Min. Typ. Max. Units Test Conditions
t
on
t
off
MT Delay matching | ton - t
t
t
DT Deadtime: LO turn-off to HO turn-on(DT
MDT Deadtime matching = | DT
Turn-on propagation delay — 220 300 VS = 0V
Turn-off propagation delay — 200 280 VS = 0V or 600V
off
|
Turn-on rise time — 150 220 VS = 0V
r
Turn-off fall time — 50 80 VS = 0V
f
LO-HO) &
HO turn-off to LO turn-on (DT
LO-HO
- DT
HO-LO)
HO-LO
—0 30
nsec
400 540 680 RDT= 0
4 5 6 usec RDT = 200k (IR21084)
— 0 60 RDT=0
|
— 0 600 RDT = 200k (IR21084)
nsec
Static Electrical Characteristics
V
(VCC, VBS) = 15V, VSS = COM, DT= VSS and TA = 25°C unless otherwise specified. The VIL, VIH and I
BIAS
parameters are referenced to VSS/COM and are applicable to the respective input leads: HIN and LIN. The VO, IO and Ron
parameters are referenced to COM and are applicable to the respective output leads: HO and LO.
Symbol Definition Min. Typ. Max. Units Test Conditions
V
IH
V
V
OH
V
OL
I
LK
I
QBS
I
QCC
I
IN+
I
IN-
V
CCUV+VCC
V
BSUV+
V
CCUV-
V
BSUV-
V
CCUVH
V
BSUVH
I
O+
I
O-
Logic “1” input voltage for HIN & logic “0” for LIN 2.9 — — VCC = 10V to 20V
Logic “0” input voltage for HIN & logic “1” for LIN — — 0.8 VCC = 10V to 20V
IL
High level output voltage, V
Low level output voltage, V
Offset supply leakage current — — 50 VB = VS = 600V
Quiescent VBS supply current 20 75 130 V
Quiescent VCC supply current 0.4 1.0 1.6 mA VIN = 0V or 5V
Logic “1” input bias current — 5 20 HIN = 5V, LIN = 0V
Logic “0” input bias current — — 2 HIN = 0V, LIN = 5V
and VBS supply undervoltage positive going 8.0 8.9 9.8
threshold
VCC and V
threshold
Hysteresis 0.3 0.7 —
Output high short circuit pulsed current 120 200 — VO = 0V,
Output low short circuit pulsed current 250 350 — VO = 15V,
supply undervoltage negative going 7.4 8.2 9.0
BS
BIAS
O
- V
O
— 0.8 1.4 IO = 20 mA
— 0.3 0.6 IO = 20 mA
V
µA
µA
V
mA
IN
= 0V or 5V
IN
RDT=0
PW ≤ 10 µs
PW ≤ 10 µs
www.irf.com 3
IR2108(4)
(S) & (PbF)
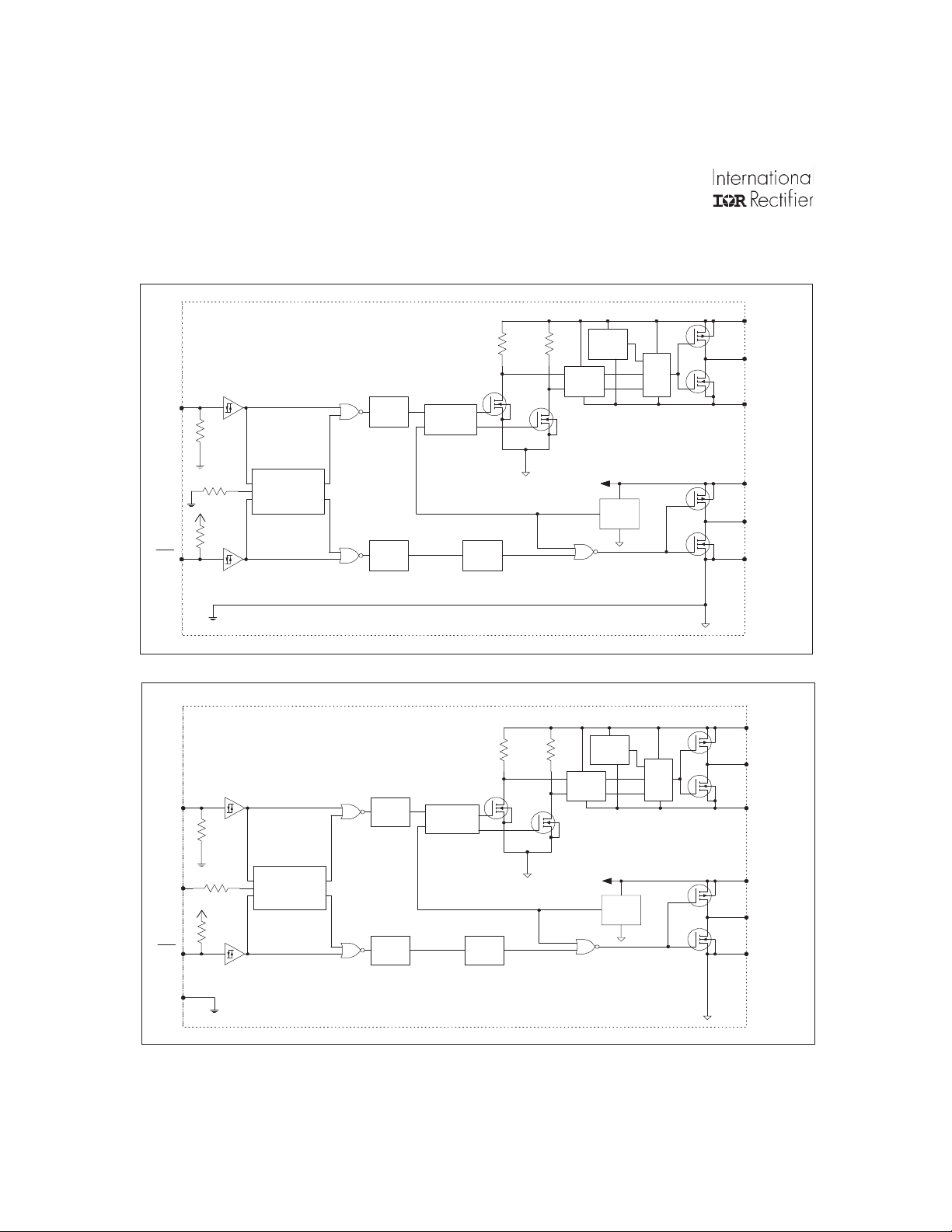
Functional Block Diagram
2108
HIN
VSS/COM
LEVEL
SHIFT
PULSE
GENERATOR
HV
LEVEL
SHIFTER
PULSE
FILTER
UV
DETECT
VB
R
Q
R
S
HO
VS
LIN
HIN
DT
LIN
DT
+5V
+5V
VSS
DEADTIME &
SHOOT-THROUGH
PREVENTION
21084
DEADTIME &
SHOOT-THROUGH
PREVENTION
VSS/COM
LEVEL
SHIFT
VSS/COM
LEVEL
SHIFT
VSS/COM
LEVEL
SHIFT
PULSE
GENERATOR
DELAY
DELAY
HV
LEVEL
SHIFTER
PULSE
FILTER
DETECT
UV
DETECT
DETECT
VCC
UV
LO
COM
VB
R
Q
R
S
HO
VS
VCC
UV
LO
COM
VSS
4 www.irf.com
IR2108(4)
(S) & (PbF)
Lead Definitions
Symbol Description
HIN Logic input for high side gate driver output (HO), in phase (referenced to COM for IR2108 and
VSS for IR21084)
LIN
DT Programmable dead-time lead, referenced to VSS. (IR21084 only)
VSS Logic Ground (21084 only)
V
B
HO High side gate driver output
V
S
V
CC
LO Low side gate driver output
COM Low side return
Logic input for low side gate driver output (LO), out of phase (referenced to COM for IR2108
and VSS for IR21084)
High side floating supply
High side floating supply return
Low side and logic fixed supply
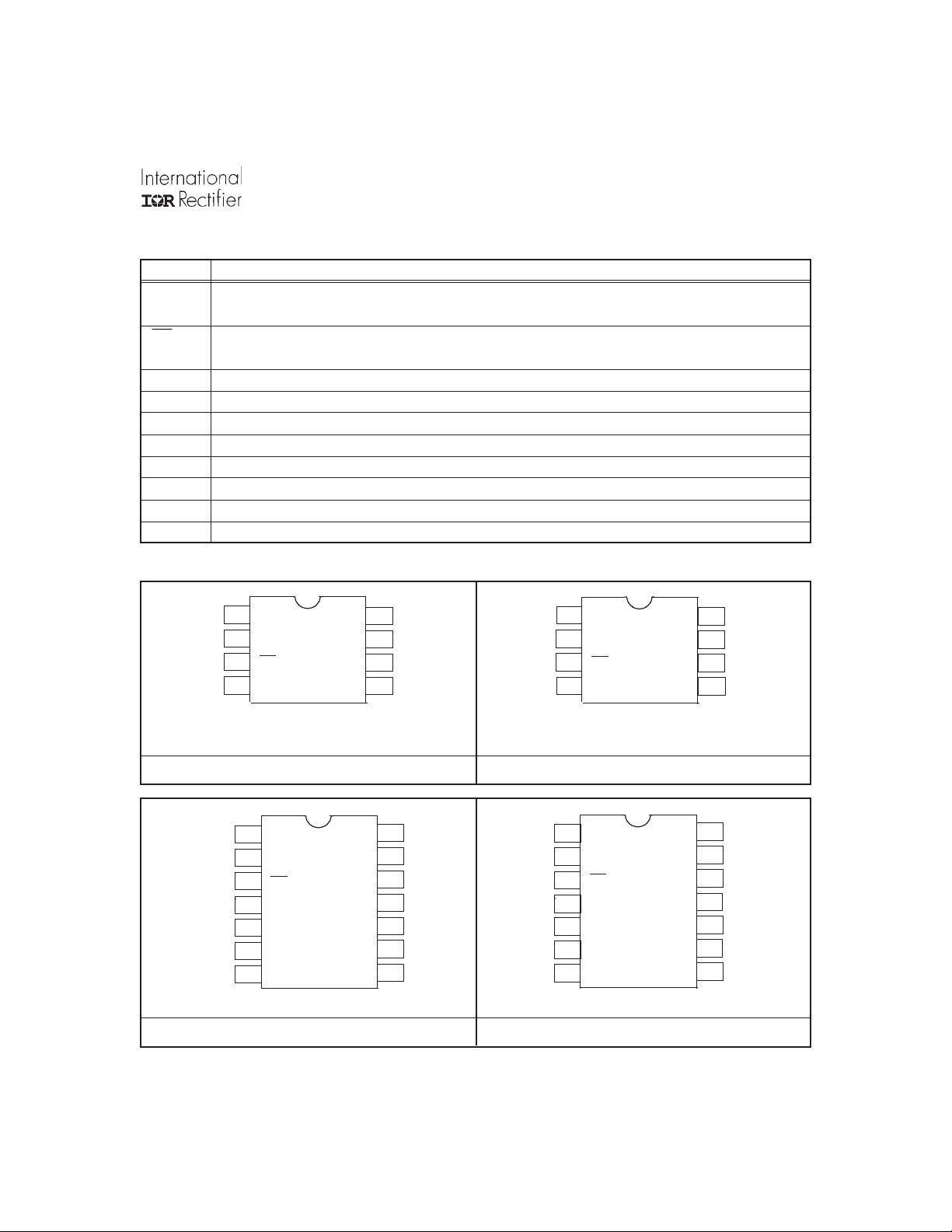
Lead Assignments
V
1
CC
HIN
2
LIN
3
COM
4
V
HO
V
LO
8
B
7
6
S
5
V
1
CC
HIN
2
LIN
3
COM
4
8 Lead PDIP 8 Lead SOIC
IR2108 IR2108S
V
HO
V
14
13
B
12
11
S
10
9
8
V
1
CC
HIN
2
LIN
3
DT
4
VSS
5
COM
6
LO
7
14 Lead PDIP 14 Lead SOIC
V
1
CC
HIN
2
LIN
3
DT
4
VSS
5
COM
6
LO
7
IR21084 IR21084S
V
HO
V
LO
V
HO
V
8
B
7
6
S
5
14
13
B
12
11
S
10
9
8
www.irf.com 5
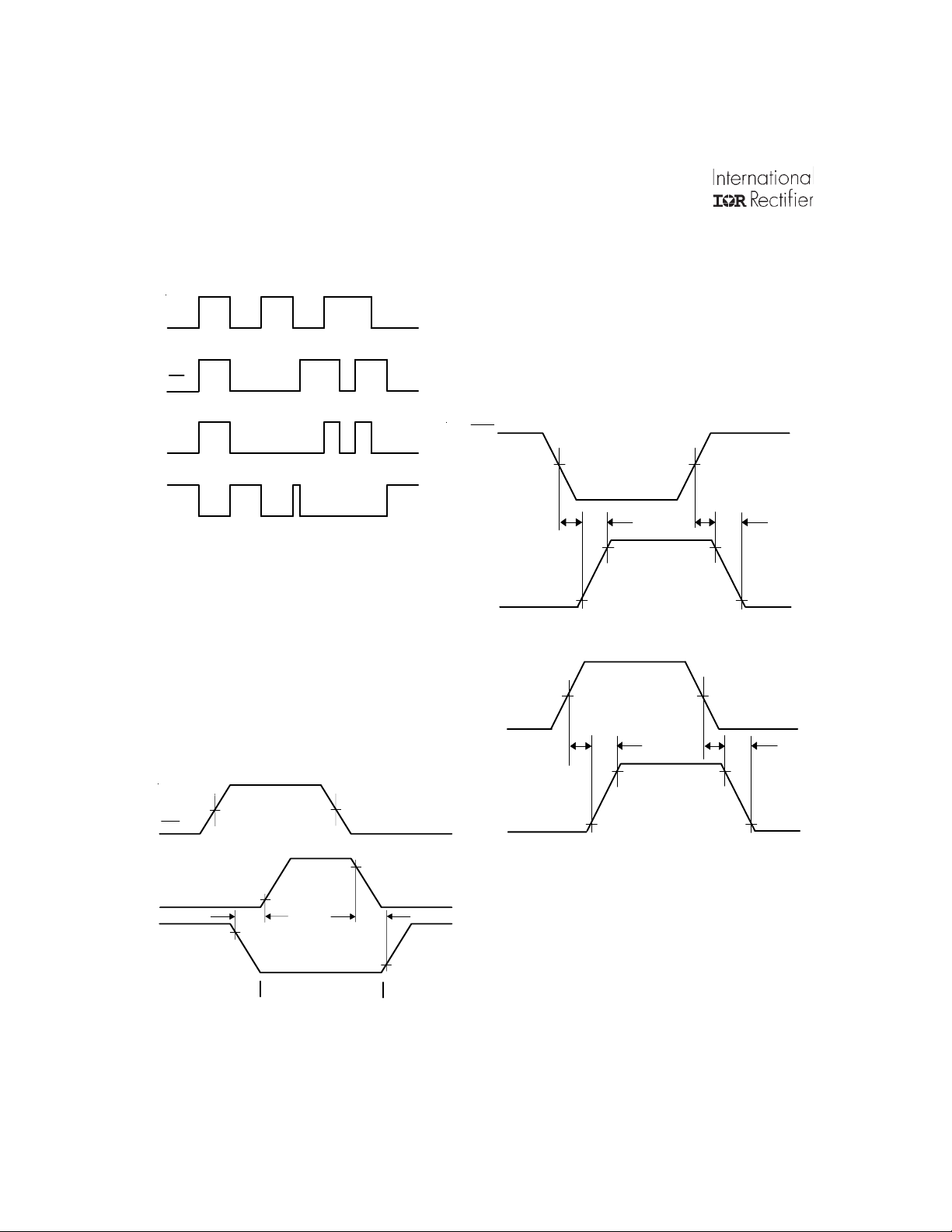
IR2108(4)
HIN
LIN
(S) & (PbF)
HO
LO
Figure 1. Input/Output Timing Diagram
HIN
LIN
50% 50%
90%
LIN
50%
t
off
90% 90%
50%
LO
50%
t
on
t
r
10% 10%
50%
HIN
t
on
t
r
90% 90%
HO
10% 10%
Figure 2. Switching Time Waveform Definitions
t
off
t
f
t
f
HO
LO
DT
LO-HO
MDT=
90%
DT
10%
LO-HO
- DT
DT
HO-LO
HO-LO
10%
Figure 3. Deadtime Waveform Definitions
6 www.irf.com
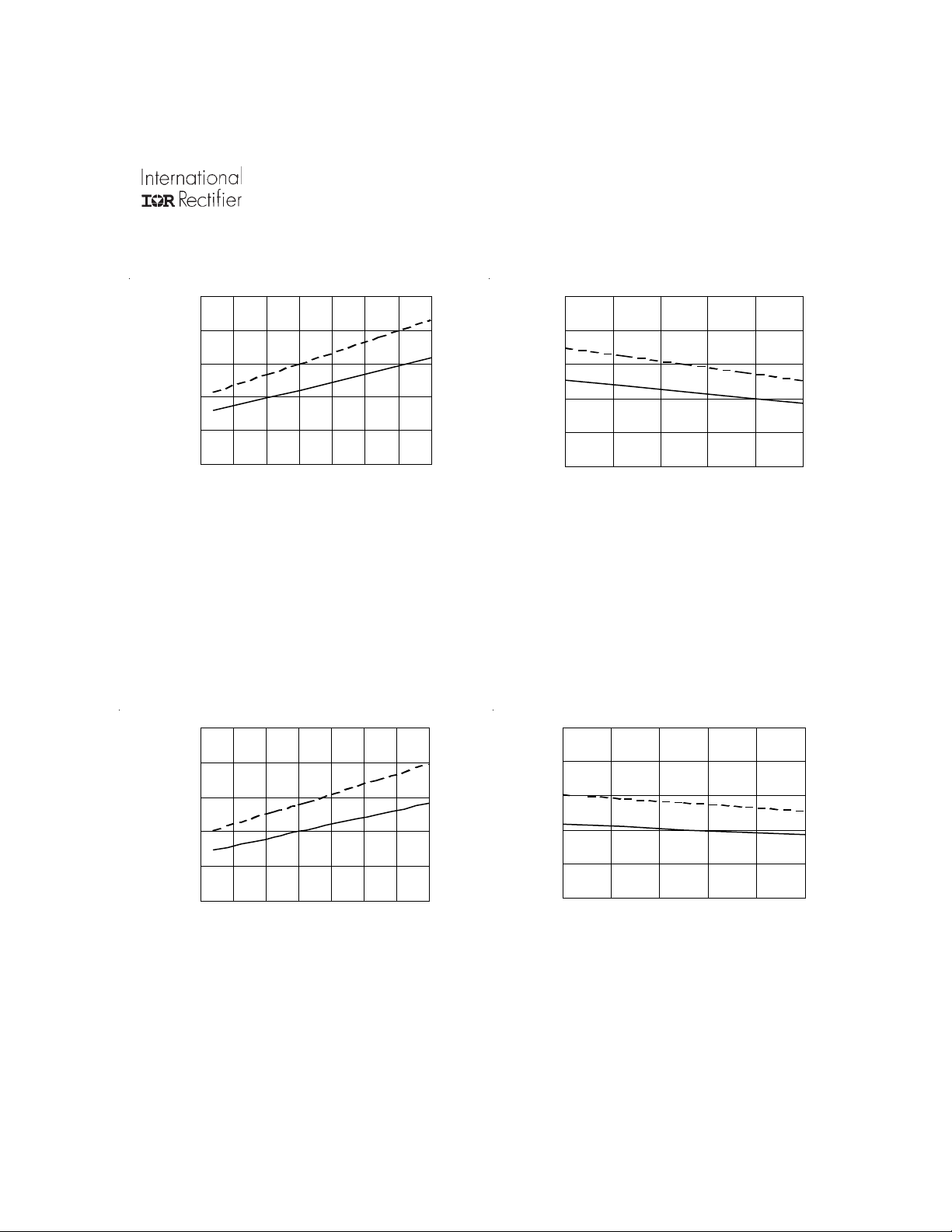
IR2108(4)
)
)
(S) & (PbF)
500
400
300
Max .
200
Typ.
100
0
Turn-on Propagation Delay (ns
-50 -25 0 25 50 75 100 125
Temperature (
o
C)
Figure 4A. Turn-on Propagation De lay
vs. Tempe ratur e
500
500
400
Max.
300
Typ.
200
100
0
Turn-on Propagation Delay (ns
10 12 14 16 18 20
V
Supply Voltage (V)
BIAS
Figure 4B. Turn-on Propagation Delay
vs. Supply Voltage
500
400
300
Max.
200
Typ.
100
Turn-off Propagation Delay (ns)
0
-50 -25 0 25 50 75 100 125
Temperature (
o
C)
Figure 5A. Turn-off Propagation Delay
vs.Temperature
400
Max.
300
Typ.
200
100
0
Turn-off Propagation Delay (ns)
10 12 14 16 18 20
V
Supply V oltage (V )
BIAS
Figure 5B. Turn-off Propagation Delay
vs. Supp ly Voltage
www.irf.com 7
 Loading...
Loading...