Page 1

Wireless-G USB 2.0 Adapter
User Manual (GWU523)
®
Page 2

©2005 IOGEAR. All Rights Reserved. PKG-M0146
IOGEAR, the IOGEAR logo, MiniView, VSE are trademarks or registered trademarks of IOGEAR, Inc. Microsoft and Windows are
registered trademarks of Microsoft Corporation. IOGEAR makes no warranty of any kind with regards to the information presented
in this document. All information furnished here is for informational purposes only and is subject to change without notice.
IOGEAR, Inc. assumes no responsibility for any inaccuracies or errors that may appear in this document.
Page 3

Welcome
Thank you for choosing IOGEAR® to serve your wireless needs. In no time you will be sharing files
or surfing the Internet wirelessly. We hope you will have as much fun using your IOGEAR
®
Wireless-G USB 2.0 Adapter, as we had designing it.
Rest assured, your IOGEAR® Wireless-G USB 2.0 Adapter is built rock-solid to ensure maximum
up-time for you to stay up-and-running. If for any reason you have a problem, we stand behind our
products with an industry-leading 3 year factory warranty, so you can have peace-of mind with
your current and future IOGEAR® purchases.
We want you to be happy with your purchase, so we have made every effort to ensure product
quality, reliability, and ease-of-use.
Page 4
Table of contents
Package Contents
Product Overview
Features
○○○○○○○○○○○○○○
System Requirements
Introduction
Installation
○○○○○○○○○○
○○○○○○○○○○
○○○○○○○○○
○○○○○○○○○○○○○○
○○○○○○○○○○○○○○
General Connection Setting
WEP Encryption Setting
WPA Encryption Setting
○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○
Profile
Advanced Setting
System Information
Wireless LAN Basics
IP Address
Specification
○○○○○○○○○○○○
○○○○○○○○○○○○
○○○○○○○○
○○○○○○○○
○○○○○○○○○○
○○○ ○○○○○
○○○○○○○○○
○○○○○○
02
Troubleshooting
03
Gloassay
04
Technical Support
05
Radio & TV Interference Statement
06
Limited Warranty
○○○ ○○○○○○○○○○
○○○○○○○○○○○○○
○○○○○○○○○
○○○ ○○○○○○○
07
15
17
19
21
22
23
24
26
28
○○
30
32
38
39
40
Page 5

Package Contents
This package contains...
1 x 802.11g USB 2.0 Adapter
1 x Quick Start Guide
1 x Installation & Manual CD-ROM
1 x Warranty/Registration Card
Check to make sure that all the components are present and that nothing was damaged in
shipping. If you encounter a problem, contact your dealer.
Read this manual thoroughly and follow the installation and operation procedures carefully to
prevent any damage to the unit, and/or any of the devices that connect to it.
2
Page 6

Overview
Being five times faster than the speed of 802.11b network standard devices, the innovative
802.11g standard lets the wireless network become incredibly easier and faster (up to 54Mbps)
than ever.
Your Wireless-G USB 2.0 Adapter surely will bring you into such a high-speed network sphere.
This document describes how to install your Wireless-G USB 2.0 Adapter, which aims to let your
computer communicate with 802.11 networks quickly and seamlessly. Wireless LAN is local area
networking without wires, which uses radio frequencies to transmit and receive data between PCs
or other network devices.
Additionally, wireless LAN is able to configure either independent networks, which are also known
as ad-hoc networks, or infrastructure networks. The former is suitable for small or temporary peerto peer configurations, and the later offers fully distributed data connectivity to the Internet.
3
Page 7

• Support Microsoft Windows 98SE, Me, 2000 and XP.
• Operating distance of up to 300 meters in free space.
• 54 Mbps Data Rate.
• Support USB 1.1 and 2.0 (preferred) interface.
• Security with 64-bit or 128-bit WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy).
• DSSS (Direct Sequence Spread Spectrum).
• Easy operation and setting up.
4
Features
Page 8
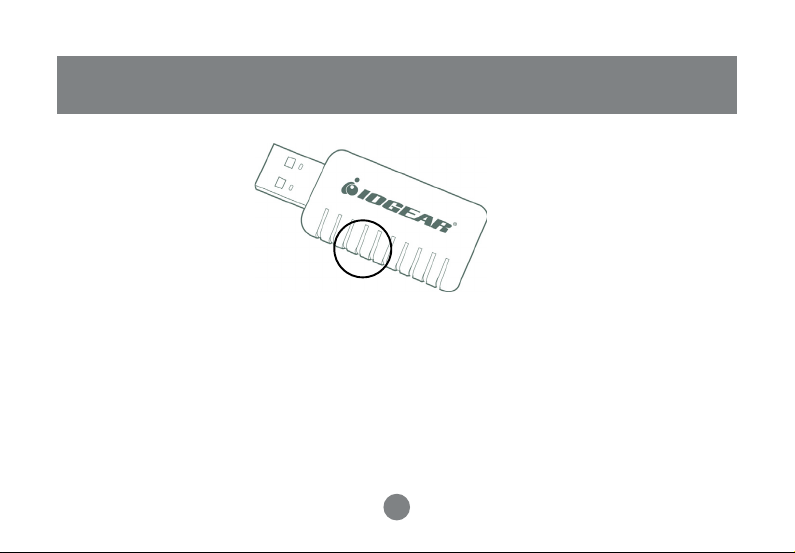
Pictorial Introduction
LED
LED
• LED turns on when POWER is applied to the IOGEAR Wireless-G USB 2.0 Adapter.
• LED is blinking when PC is sending data through IOGEAR Wireless-G USB 2.0 Adapter.
5
Page 9

- Windows 98SE, ME, 2000 or XP
- available USB 1.1. or 2.0 port.
System Requirements
6
Page 10
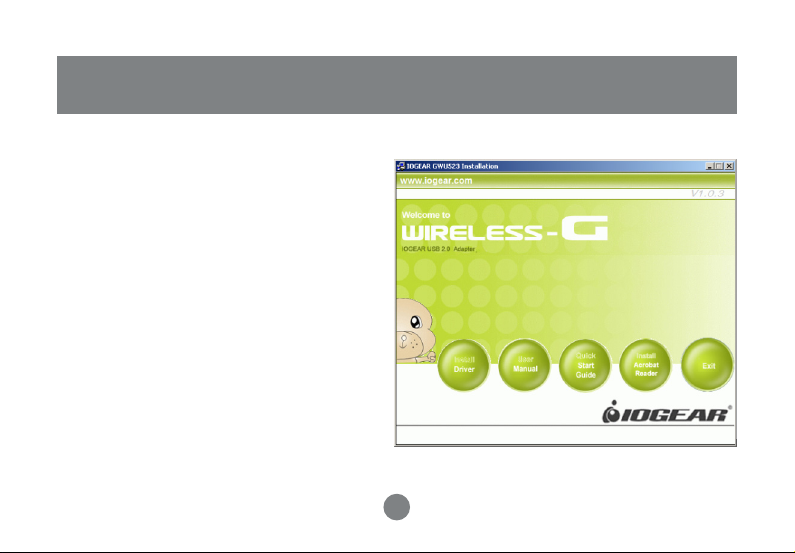
Installation
CONNECTING YOUR WLAN USB ADAPTER TO PC
• Install driver.
• Connect your Wireless-G USB 2.0 Adapter.
Note: Once you insert the installation and
driver CD, it will automatically activate the
Autorun installation program. If your autorun
is disable please run the iogear.exe file on
the CD.
Step 1 :
Insert the Manual and installation CD into
your CD-ROM. You will be prompted with
the following window. Chose install driver to
proceed with the installation
7
Page 11
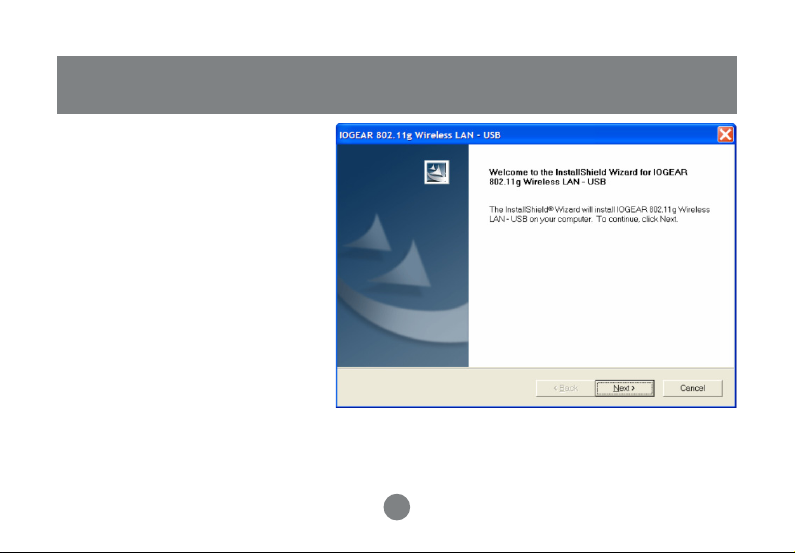
STEP 2
Click Next to continue.
Installation
8
Page 12
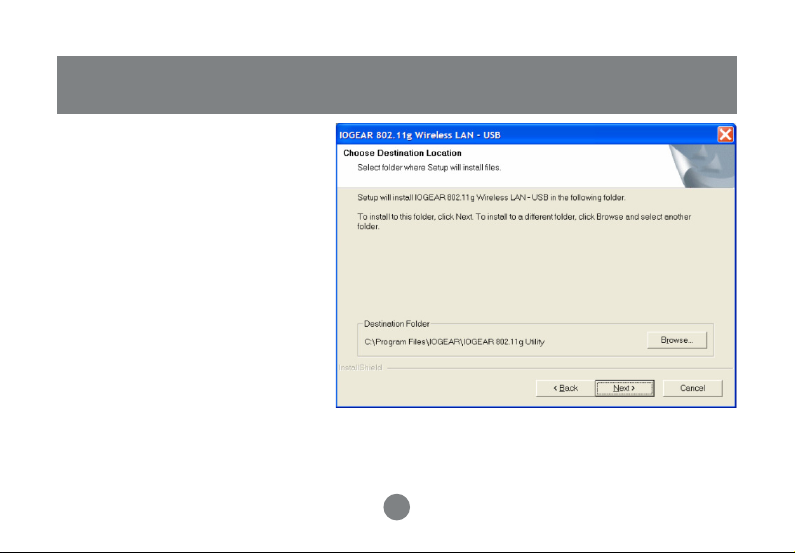
Installation
Step 3 :
Click Next to install at the designated
folder. Or, click “Browse”
to select different folder.
9
Page 13
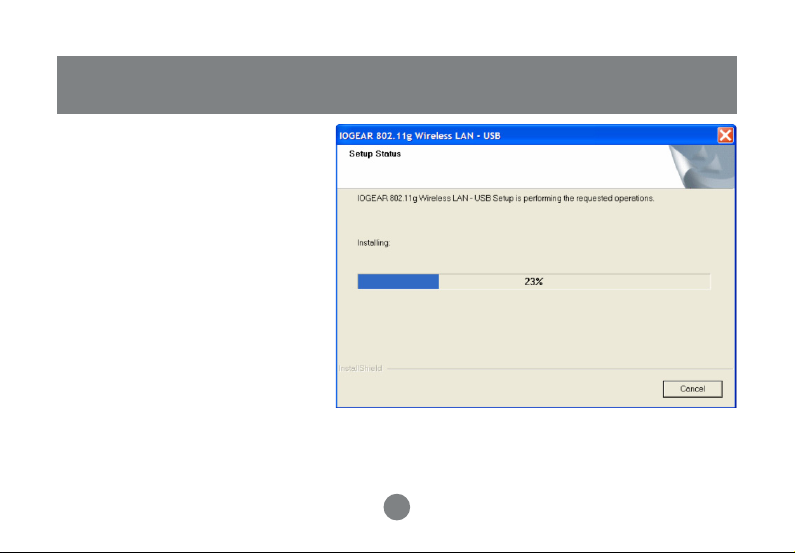
Step 4 :
Start copying files until it finish
the installation.
Installation
10
Page 14
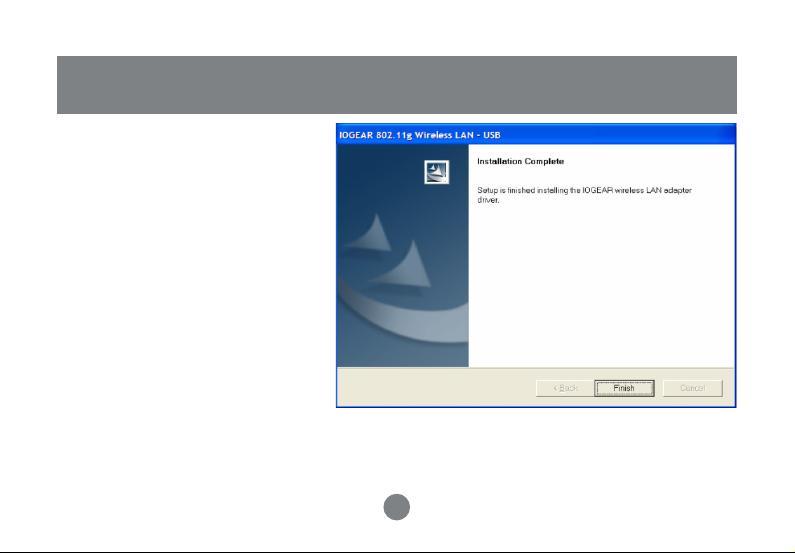
Installation
Step 5 :
Click Finish to complete installation.
11
Page 15

Installation
Step 6 :
After finished install driver and utility on your system,
Windows XP/2000
Plug the USB adapter into the USB port of your PC. It will automatically detect the USB Adapter.
Windows ME/98SE
You will be asked to restart your PC. After rebooting, plug the USB adapter into the USB port of
your PC. It will automatically detect the USB Adapter.
Wireless USB Adapter uses its own management
software. All functions controlled by users are provided by
this application. When you insert the Wireless USB
Adapter into the USB port of PC, a new icon should appear in the Windows System Tray
automatically.
If the icon does not show in the System
Tray, launch the program from star tprograms-and click-on - ZDWlan:
12
Page 16

Installation
If the icon in the System Tray is in red,
it means that Wireless USB Adapter
configuration is invalid or incomplete.
Double click on that icon and the
configuration window will pop up as
shown below. It shows the SSID of
available network. Once a network is
chosen, the signal strength and link
quality are displayed.
13
Page 17

Installation
The Link Quality and Signal Strength bar chart is only active when the node is in Infrastructure
Mode. The bar graph displays the quality and strength of the link between the node and its Access
Point. Link Quality is a measurement of receiving and transmitting performances over the radio.
Tx/Rx Frame displays the instantaneous wireless Transmit and Receive throughput in bytes per
second. These values are updated every two seconds.
The Configuration Tool contains several fields where operating parameters of the driver can be
viewed or changed. Changes to any of the parameters in this panel can be applied to the driver
without a need to restart the computer.
Current Network Information displays the current network configuration. If you want to change
network configuration, click “More Setting”.
14
Page 18
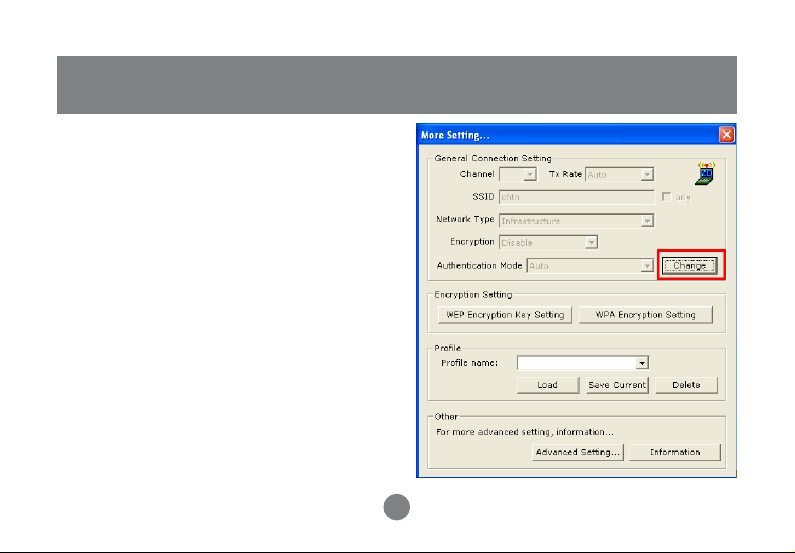
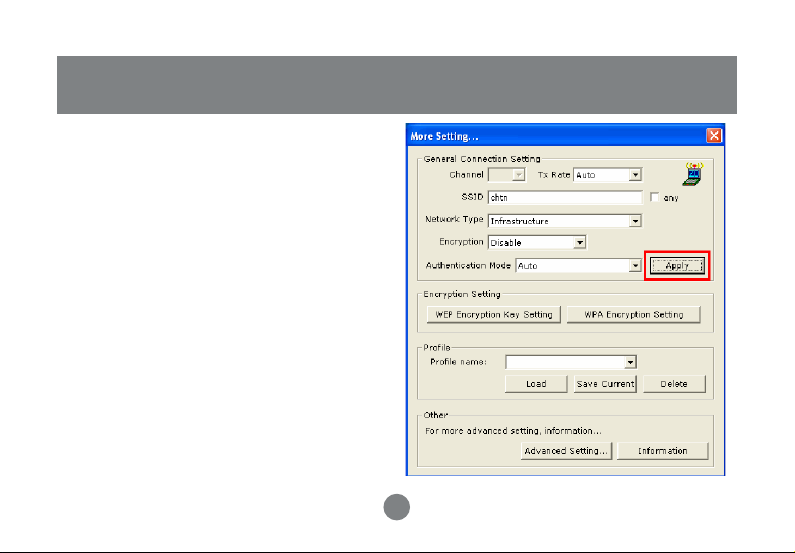
General Connection Setting
In this panel, you can modify the general network
connection setting, enable/disable the WEP, load /
modify profile and other setting. Through this
control panel, you will be able to access the
corporate wireless LAN or hot spots such as
hotel, airport, and conference hall.
Click “Change” to start input of
settings. The settings include :
• SSID.
• Network Type.
• Transmit Rate.
• Encryption.
• Authentication Mode
15
Page 19

When settings are input, click “Apply” to
confirm changes of them.
General Connection Setting
16
Page 20
WEP Encryption Key Setting
WEP Encryption Key Setting
You may want an additional measure of
security on your wireless network, which can
be achieved by using WEP (Wired Equivalent
Privacy) encryption. WEP encrypts each
frame transmitted from the radio using one of
the Keys entered in this panel.
When an encrypted frame is received it will
only be accepted if it decrypts correctly. This
will only happen if the receiver has the same
WEP Key used by the transmitter.
17
Page 21
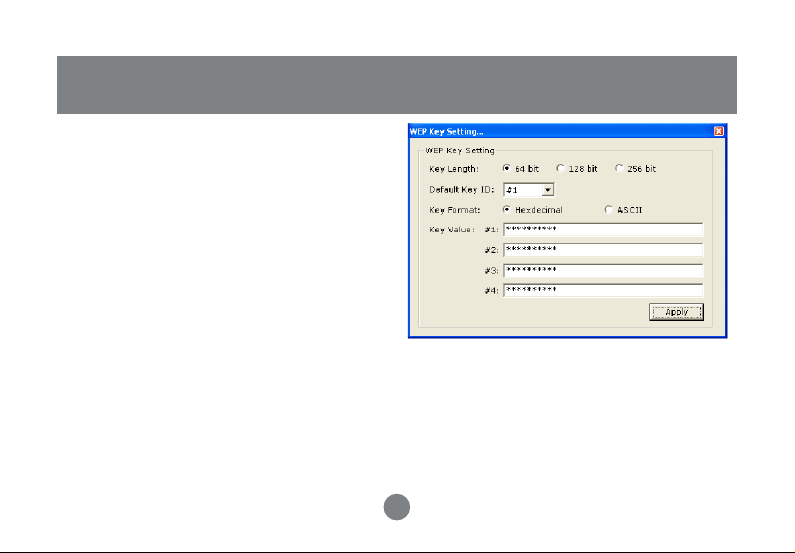
WEP Encryption Key Setting
The default state in Encryption Setting is WEP
disabled. Check “Enable WEP” to enable the
encryption.
For more WEP key setting, Click “WEP
Encryption Key Setting”.
Three authentication modes are available: Open
System, Shared Key and Auto. The Open
System uses a default key to authenticate the
station and Access Point. Once both parties are
authenticated, the station is allowed to send and
receive data from the network. However, the data is not encrypted.
In Shared Key system, the station and Access Point authenticate each other. The data frame is
also encrypted by the WEP key.
In Auto Mode, the Access Point takes control of network security setting and station will follow the
setting required from AP.
18
Page 22

WPA Encrytion Setting
Click the “x” at the upper right hand corner to
return to Configuration Tool.
WPA Encrytion Setting
WPA (Wi-Fi Protected Access) is a security
technology for wireless networks. WPA
improves on the authentication and encryption
features of WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy).
To improve data encryption, WPA utilizes its
Temporal Key Integrity Protocol (TKIP). TKIP
provides important data encryption
enhancements including a per-packet key
mixing function, a message integrity check
(MIC, named Michael), an extended
initialization vector (IV) with sequencing rules,
and a re-keying mechanism.
19
Page 23

WPA Pre-Shared Key (WPA-PSK) is a
simplified but still powerful form of WPA most
suitable for home Wi-Fi networking. To use
WPA-PSK, a person sets a static key or
“passphrase” as with WEP. But, using TKIP,
WPA-PSK automatically changes the keys at a
preset time interval, making it much more
difficult for hackers to find and exploit them.
The pre-shared key is consisting of alphanumeric characters including punctuation and
spaces between 8 and 63 characters
long.Wireless clients are only required to enter
the pre-shared key.If the preshared keys
match, secure wireless communications can
begin to take place.
For more WPA setting, Click “WPA Encryption
Setting”
WPA Encrytion Setting
20
Page 24
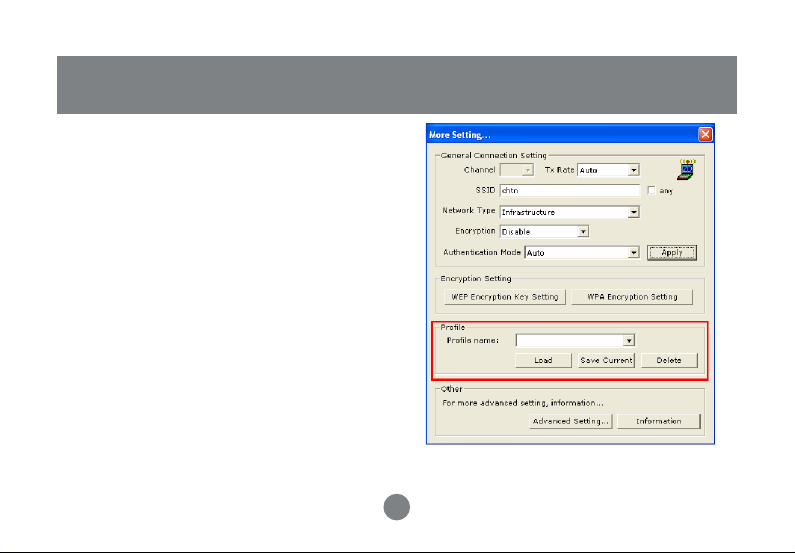
Profile
Each profile represents specific settings of the
USB adapter. You can set the settings for each
profile. Next time when you want to change the
USB adapter settings, you can just select the
profile you want to use.
21
Page 25

Advanced Setting
Advanced Setting Click “Advanced Setting” to select power
consumption setting that has 3 different modes.
In this panel, you can select different user
interface and country roaming.
It also allows you to set the threshold of
fragmentation and RTS/CTS.
22
Page 26

System Information
System Information Click “Information” and the pop-up window
will show the Driver Version,
Utility Version, MAC address of this USB
adapter and so on.
23
Page 27

Wirelss LAN Basics
WIRELESS LAN BASICS
Wireless LAN network defined by IEEE
802.11b/g standard committee could be
configured as :
1. Ad Hoc wireless LAN, or
2. Infrastructure wireless LAN.
Ad Hoc network is a group of PCs installed
with wireless LAN cards, this group of PCs is
called a BSS (Basic Service Set). PCs in this
group can use their wireless LAN cards to
communicate with each other, but can not
connect to the Internet.
The most obvious difference between
Infrastructure wireless network and Ad Hoc
wireless network is that the PCs in
Infrastructure wireless network can access
the resource in the Internet through Access
Point.
Depending on your requirement, you can
easily set up your PC’s network to be a “Ad
Hoc” or “Infrastructure” wireless network.
Generally speaking, if in your network, there is
an Access Point in it, we recommend you to
set your network as an “Infrastructure”, so it
can connect to the Internet.
24
Page 28

Wirelss LAN Basics
Internet
AD-HOC
Computer to computer
No Access points required
INFRASTRUCTURE
Access to Internet
Access points required
25
Page 29

IP Address
IP ADDRESS
To use the Wireless-G USB 2.0 Adapter with a
computing device, your computer must be
equipped with an USB 1.1 or 2.0 available
ports. All drivers and supporting software for
the Wireless-G USB 2.0 Adapter must be
installed and configured first. Ask your system
administrator for the following information,
which you may need to provide during driver
installation :
• Your Wireless Client Name.
• Your Wireless SSID.
• Your computer’s unique client name and
workgroup name.
• For your network account, your user name
and password.
• Your IP address, gateway address, and
subnet mask if you’re not using a DHCP
server.
Any computer on a network is identified by a
unique network address. There are two
methods to assign a network address to a
computer on a TCP/IP network :
• Static IP addressing.
• Dynamic IP addressing (DHCP).
26
Page 30

IP Address
In network with static IP addressing, the network
administrator manually assigns an IP address to
each computer. Once a static IP address is
assigned, a computer uses the same IP address
every time it reboots and logs on to the network.
You may manually change the IP address in the
Network Properties dialog box. Network using
static IP address is easy to set up and do not
require additional network management
software.
In network with dynamic IP addressing, a DHCP
server in the network dynamically assigns IP
addresses to all clients every time they log on to
the network. Network using dynamic IP address
requires setting up and running a DHCP Server.
27
Page 31

Specification
Product Name
Standard
Frequency Band
Modulation Method
Data Rate
Operating Mode
Transmitter Output Power
Receive Sensitivity
Operating Range
Antenna
Security
Wireless-G USB 2.0 Adapter
IEEE 802.11b/g
2.400 GHz
802.11b: QPSK/BPSK/CCK
802.11g: OFDM
54/48/36/24/18/12/11/9/6/5.5/2/1Mbps
A d hoc
Infrastructure (Access Points needed)
<15 dBm
Operating at 11Mbps @ -80dBm
Operating at 54 Mbps @ -70dBm
30 to 200 m, depending on surrounding environment
Chip antenna
64-bit, 128-bit or 256-bit WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy);
WPA (Wi-Fi Protected Access)
~ 2.4835 GHz unlicensed ISM band
28
Page 32
Specification
Product Name
I/O Interface
LED
Operating System Supported
Management
Regulation
Dimensions
Weight
Operating Temperature
Storage Temperature
Humidity
Wireless-G USB 2.0 Adapter
USB 2.0/1.1
Link/Active
Windows 98SE/ME/2000/XP
Windows-based configuration utility and status monitoring
FCC for North America
CE/ETSI for European
77.5mm(L) x 27mm(W) x 10.5mm(H)
13g
0 ~ 50ºC
-20 ~ 70ºC
5 ~ 90% (non-condensing)
29
Page 33

Troubleshooting
Symptom :
The LED is off.
Remedy :
Make sure the PC Card is inserted properly. Otherwise contact your vendor.
Symptom :
The LED is always on not blinking.
Remedy :
Make sure that you have installed the driver from attached CD. Otherwise contact your vendor.
Symptom :
The LED is blinking but the PC Card icon does not appear in your icon tray.
Remedy :
Make sure that you have installed the Utility from the attached CD.
30
Page 34

Troubleshooting
Symptom :
The PC Card is linking, but can’t share files with others.
Remedy :
Make sure the file and printer sharing function is enabled. You can enable the function by
checking the icon of My Computer -> Control Panel -> Network -> file and printer sharing -> I
want to be able to give others to access to my files.
Symptom :
Slow or poor performance.
Remedy :
Try to select another channel for the communicating group or move your
device closer to the Access Point.
31
Page 35

Glossary
GLOSSARY
IEEE 802.11 Standard
The IEEE 802.11 Wireless LAN standards subcommittee, which is formulating a standard for the industry.
Access Point
An internetworking device that seamlessly connects wired and wireless networks together.
Ad Hoc
An Ad Hoc wireless LAN is a group of computers, each with a WLAN adapter, connected as an independent
wireless LAN. Ad Hoc wireless LAN is applicable at a departmental scale for a branch or SOHO operation.
BSSID
A specific Ad Hoc LAN is called a Basic Service Set (BSS). Computers in a BSS must be configured with the
same BSSID.
DHCP
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol - a method in which IP addresses areassigned by server dynamically to
clients on the network. DHCP is used for Dynamic IP Addressing and requires a dedicated DHCP server on the
network.
32
Page 36

Glossary
Direct Sequence Spread Spectrum
This is the method the wireless cards use to transmit data over the frequency spectrum. The other method is
frequency hopping. Direct sequence spreads the data over one frequency range (channel) while frequency hopping
jumps from one narrow frequency band to another many times per second.
ESSID
An Infrastructure configuration could also support roaming capability for mobile workers. More than one BSS can
be configured as an Extended Service Set (ESS). Users within an ESS could roam freely between BSSs while
served as a continuous connection to the network wireless stations and Access Points within an ESS must be
configured with the same ESSID and the same radio channel.
Ethernet
Ethernet is a 10/100Mbps network that runs over dedicated home/office wiring. Users must be wired to the
network at all times to gain access.
Gateway
A gateway is a hardware and software device that connects two dissimilar systems, such as a LAN and a mainframe.
In Internet terminology, a gateway is another name for a router. Generally a gateway is used as a funnel for all
traffic to the Internet.
33
Page 37

Glossary
IEEE
Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers Infrastructure An integrated wireless and wired LAN is called an
Infrastructure configuration. Infrastructure is applicable to enterprise scale for wireless access to central database,
or wireless application for mobile workers.
ISM Band
The FCC and their counterparts outside of the U.S. have set aside bandwidth for unlicensed use in the so-called
ISM (Industrial, Scientific and Medical) band. Spectrum in the vicinity of 2.4 GHz, in particular, is being made
available worldwide. This presents a tr uly revolutionary opportunity to place convenient high-speed wireless
capabilities in the hands of users around the globe.
Local Area Network (LAN)
A LAN is a group of computers, each equipped with the appropriate network adapter card connected by cable/air,
that share applications, data, and peripherals. All connections are made via cable or wireless media, but a LAN
does not use telephone services. It typically spans a single building or campus.
Network
A network is a system of computers that is connected. Data, files, and messages can be transmitted over this
network. Networks may be local or wide area networks.
34
Page 38

Glossary
Protocol
A protocol is a standardized set of rules that specify how a conversation is to take place, including the format,
timing, sequencing and/ or error checking.
Roaming
In an infrastructure network, this is when a wireless PC moves out of range of the previously connected access
point and connects to a newly connected access point. Throughout the network environment where access point
is deployed, PCs can always be connected regardless of where they are located or roam.
SSID
A Network ID unique to a network. Only clients and Access Points that share the same SSID are able to communicate
with each other. This string is case-sensitive.
Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP)
Simple Network Management Protocol is the network management protocol of TCP/IP. In SNMP, agents-which
can be hardware as well as software- monitor the activity in the various devices on the network and report to the
network console workstation. Control information about each device is maintained in a structure known as a
management information block.
Static IP Addressing
A method of assigning IP addresses to clients on the network. In networks with Static IP address, the network
administrator manually assigns an IP address to each computer. Once a Static IP address is assigned, a computer
uses the same IP address every time it reboots and logs on to the network, unless it is manually changed.
35
Page 39

Glossary
Temporal Key Integrity Protocol (TKIP)
The Temporal Key Integrity Protocol, pronounced tee-kip, is part of the IEEE 802.11i encryption standard for
wireless LANs. TKIP is the next generation of WEP, the Wired Equivalency Protocol, which is used to secure
802.11 wireless LANs. TKIP provides per-packet key mixing, a message integrity check and a re-keying mechanism,
thus fixing the flaws of WEP.
Transmission Control Protocol / Internet Protocol (TCP/IP)
TCP/IP is the protocol suite developed by the Advanced Research Projects Agency (ARPA). It is widely used in
corporate Internet works, because of its superior design for WANs. TCP governs how packet is sequenced for
transmission the network. The term “TCP/IP” is often used generically to refer to the entire suite of related protocols.
Transmit / Receive
The wireless throughput in Bytes per second averaged over two seconds.
Wi-Fi Alliance
The Wi-Fi Alliance is a nonprofit international association formed in 1999 to certify interoperability of wireless
Local Area Network products based on IEEE 802.11 specification. The goal of the Wi-Fi Alliance’s members is to
enhance the user experience through product interoperability. The organization is formerly known as WECA.
36
Page 40

Glossary
Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA)
The Wi-Fi Alliance put together WPA as a data encryption method for 802.11 wireless LANs. WPA is an industrysupported, pre-standard version of 802.11i utilizing the Temporal Key Integrity Protocol (TKIP), which fixes the
problems of WEP, including using dynamic keys.
Wide Area Network (WAN)
A WAN consists of multiple LANs that are tied together via telephone services and / or fiber optic cabling. WANs
may span a city, a state, a country, or even the world.
Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP)
Now widely recognized as flawed, WEP was a data encryption method used to protect the transmission between
802.11 wireless clients and APs. However, it used the same key among all communicating devices. WEP’s problems
are well-known, including an insufficient key length and no automated method for distributing the keys. WEP can
be easily cracked in a couple of hours with off-the-shelf tools.
Wireless LAN (WLAN)
A wireless LAN does not use cable to transmit signals, but rather uses radio or infrared to transmit packets
through the air. Radio Frequency (RF) and infrared are the commonly used types of wireless transmission. Most
wireless LANs use spread spectrum technology. It offers limited bandwidth, usually under 11Mbps, and users
share the bandwidth with other devices in the spectrum; however, users can operate a spread spectrum device
without licensing from the Federal Communications Commission (FCC).
37
Page 41

Technical Support
If you need technical support, please check out our IOGEAR Tech Info Library (T.I.L.) at
www.iogear.com/support for the latest tips, tricks, and troubleshooting. The IOGEAR T.I.L. was
designed to provide you with the latest technical information about our products. Most of the
answers to your questions can be found here, so please try it out before contacting technical
support.
Technical support is available Monday through Friday from 8:00 am to 5:00 pm PST and can be
reached at 866-946-4327.
38
Page 42

Radio & TV Interference Statement
WARNING!!! This equipment generates, uses and can radiate radio frequency energy and, if not
installed and used in accordance with the instruction manual, may cause interference to radio
communications. This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class
B computing device pursuant to Subpart J of Part 15 of FCC Rules, which are designed to provide
reasonable protection against such interference when operated in a commercial environment.
Operation of this equipment in a residential area is likely to cause interference, in which case the
user at his own expense will be required to take whatever measures may be required to correct
the interference.
39
Page 43

Limited Warranty
IN NO EVENT SHALL THE DIRECT VENDOR’S LIABILITY FOR DIRECT, INDIRECT, SPECIAL,
INCIDENTAL OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES RESULTING FROM THE USE OF THE
PRODUCT, DISK, OR ITS DOCUMENTATION EXCEED THE PRICE PAID FOR THE PRODUCT.
The direct vendor makes no warranty or representation, expressed, implied, or statutory with
respect to the contents or use of this documentation, and especially disclaims its quality,
performance, merchantability, or fitness for any particular purpose.
The direct vendor also reserves the right to revise or update the device or documentation without
obligation to notify any individual or entity of such revisions, or updates. For further inquires please
contact your direct vendor.
40
Page 44

®
Contact info.
23 Hubble • Irvine, CA 92618 • (P) 949.453.8782 • (F) 949.453.8785 • www.iogear.com
 Loading...
Loading...