Page 1

Wireless-G USB2.0 Flex Adapter
User Manual (GWU513)
®
®
Page 2

Page 3

Welcome
Thank you for choosing IOGEAR® to serve your wireless needs. Soon, you will be sharing files or surfing the
Internet wirelessly. We hope you will have as much fun using your IOGEAR® Wireless-G USB 2.0 Flex
Adapter, as we had designing it.
Rest assured, your IOGEAR® Wireless-G USB 2.0 Flex Adapter is b uilt rock-solid to ensure maximum up-time
for you to stay up-and-running. If f or an y reason you ha v e a problem, w e stand behind our products with an
industry-leading 3 year factory warranty , so you can ha v e peace-of-mind with your current and future IOGEAR
purchases.
We want you to be happ y with y our purchase , so we ha v e made e v ery effort to ensure product quality,
reliability , and ease-of-use.
©2003 IOGEAR. All Rights Reserved. PKG-M0095
IOGEAR®, the IOGEAR® logo is the trademark or registered trademark of IOGEAR®, Inc. Microsoft® and Windows® are
registered trademarks of Microsoft® Corporation. IBM is a registered trademark of International Business Machines, Inc.
Macintosh, G3/G4 and iMac are registered trademarks of Apple Computer, Inc. IOGEAR® makes no warranty of any kind with
regards to the information presented in this document. All information furnished here is for informational purposes only and is
subject to change without notice. IOGEAR®, Inc. assumes no responsibility for any inaccuracies or errors that may appear in
this document.
®
Page 4

Table of Contents
Package Contents
Introduction
Features
○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○
Requirements
Pictorial Introduction
Installation
- Installtion Procedures
- Installation Notes – Windows XP
- V erifying a Successful Installtion
Configuration for Windows XP
○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○
○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○
○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○
○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○
○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○
○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○
○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○
○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○
○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○
- To Connect an Av ailable Network via Wireless Zero configuration
- To Configure the Wireless Networks Properties
- To Access to Certain Wireless Network Type
Wireless-G Configuration T ool Basics
- T ray Icon
- Right-Click Menu of the Tray Icon
○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○
○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○
○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○
○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○
○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○
○○○○○○○○○○○○
05
06
07
08
09
10
10
13
15
17
17
18
22
23
23
24
Page 5

- Wireless Radio On
- Wireless Radio Off
- Remove Status Icon
- Wireless Network Status
- Advanced Configuration
- WEP Encryption
- IBSS Channel
- Country/Domain
- Version Information
○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○
○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○
○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○
○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○
○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○
○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○
○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○
○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○
○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○
Configuration Program Controls
- The Status Tab
- The Configuration Tab
- The Encryption Tab
- The Site Survey Tab
- The IBSS Tab
- The Domain Tab
○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○
○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○
○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○
○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○
○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○
○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○
○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○
24
24
24
25
25
25
25
25
25
26
26
30
33
35
36
37
Page 6

- The About Tab
The Advanced Properties Control
- Configuration Profile
- Fragmentation Threshold
- Niro Mode
- Power Sa v e Mode
- RTS Threshold
- The LongShort Retry Limit
Appendix and T roubleshooting
Specification
Glossary
Technical Support
○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○
○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○
○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○
○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○
○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○
○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○
○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○
○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○
○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○
○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○
○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○
○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○
Radio and TV Interf erence Statement
Limited Warranty
○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○
○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○
39
40
42
42
42
43
43
44
45
48
51
55
56
57
Page 7
The package you have received should contain the following items:
• IOGEAR® Wireless-G USB 2.0 Flex Adapter
• Installation/Manual CD
• Quick Start Guide
• Warranty/Registration Card
5
Package Contents
Page 8

Introduction
Being five times faster than the speed of 802.11b network standard devices, the innovative
802.11g standard lets the wireless network become incredibly easier and faster (up to
54Mbps) than ever. Your Wireless-G USB 2.0 Flex Adaptor surely will bring you into such a
high-speed network sphere. This document describes how to install your Wireless-G USB 2.0
Flex Adaptor, which aims to let your computer communicate with 802.11 networks quickly and
seamlessly. Wireless LAN is local area networking without wires, which uses radio frequencies
to transmit and receive data between PCs or other network devices. Additionally, wireless LAN
is able to configure either independent networks, which is also known as peer-to-peer or adhoc network, or infrastructure networks. The former is suitable for small or temporary peer-topeer configurations, and the later is offering fully distributed data connectivity via micro cells
and roaming.
To obtain most benefits your Wireless-G USB 2.0 Flex Adaptor provides, please read this manual carefully before using it.
6
Page 9
Features
Features
• Establish a wireless connection without the hassles and cost of cabling
• Operate Ad-Hoc or Infrastructure mode
• Utilize up to 128-bit WEP encryption
• Enjoy high-speed data transfer rate up to 54 Mbps
• Employ automatic data rate switching which offers maximum reliability,
throughput and connectivity
• Possess the network’s range up to 100 meters indoor and 400 meters outdoor
• Monitor and configure the network via the supplied friendly-interfaced application –
Wireless-G Configuration Tool
7
Page 10

Requirements
System Requirement:
• Pentium® class PC with 200MHz or faster CPU
• Microsoft Windows 98/ME/2000/XP
• Available USB 2.0 port
• CD-ROM drive
8
Page 11
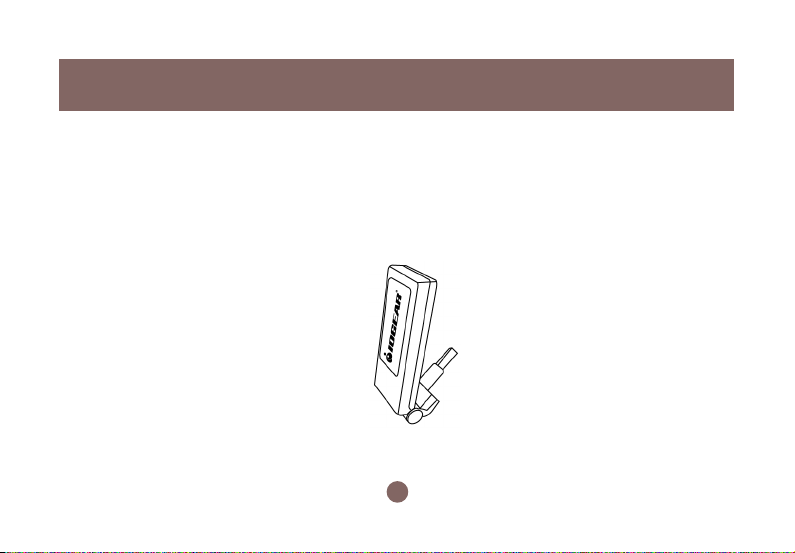
Pictorial Introduction
Your Wireless-G USB 2.0 Flex Adaptor should be located in the USB port of your computer,
and it looks like the following picture:
Concerning to the issue of orientation-controlling, Wireless-G USB 2.0 Flex Adaptor allows you
to twist and rotate the USB connector to meet your needs.
9
Page 12
Installation
Installation Procedures
It’s free and easy for you to install your
Wireless-G USB 2.0 Flex Adaptor and the
attached software – Wireless-G Configura-
tion T ool. Simply with a few clicks of the
mouse, you will succeed the completion of
installation.
To have the Wireless-G USB 2.0 Flex Adaptor
operated appropriately, please read and go
along with the instructions below carefully.
Here we take Windows XP as an example.
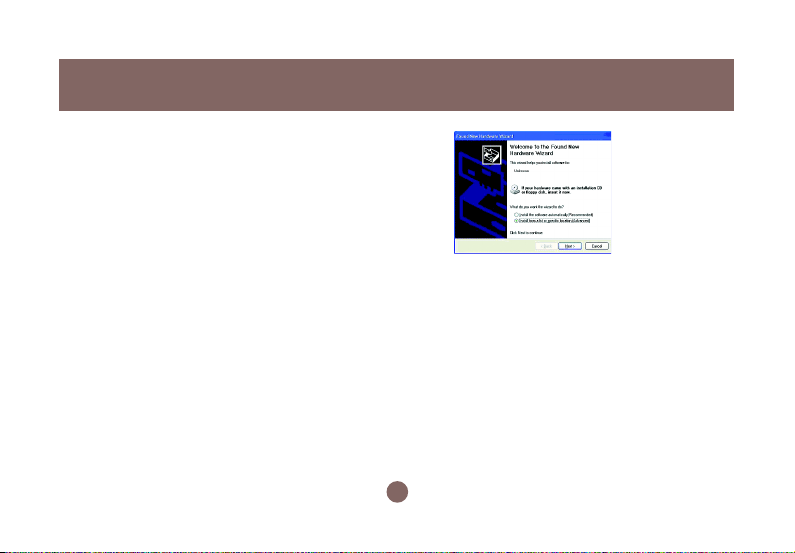
a) Plug your Wireless-G USB 2.0 Flex Adaptor
into a USB 2.0 port on your PC.
b) Your system will detect the device, and the
Found New Hardware Wizard dialog box
will appear. Choose Cancel to proceed.
c) Insert the supplied Setup CD into your
CD-ROM drive, and the Setup Wizard will
run automatically. If it does not, please
manually execute Index.htm.
d) From the prompted startup window,
choose Install Driver to begin the
installation.
10f)11
Page 13
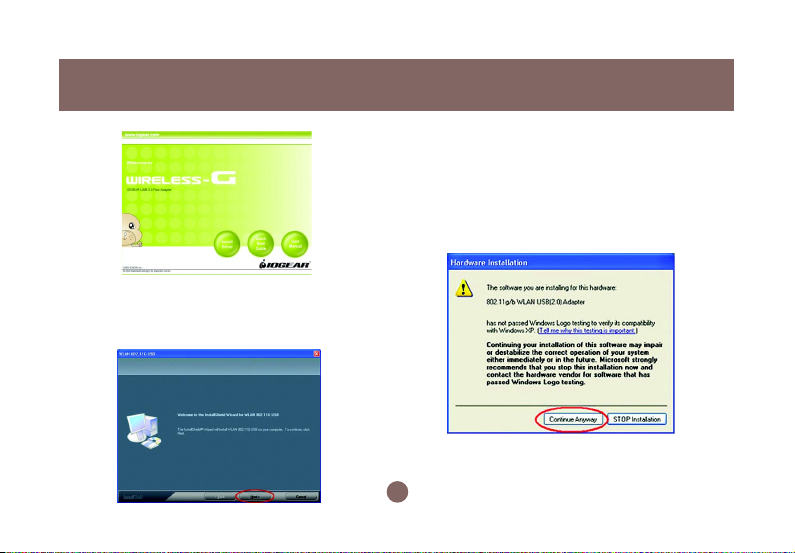
e) Click Next in the WLAN 802.11G USB
window to proceed. The system will start
to copy the drivers found.
Installation
Windows will notify you that the driver has not
passed the Windows Logo testing. Because the
Wireless-G USB Adapter has been tested to
work with Windows XP, please choose Continue
Anyway in the Hardware Installation dialog box.
Page 14

Installation
g)
On the Reboot screen, you may choose
either Yes, I want to restart my computer
now or No, I will restart my computer
later. Then click Finish to complete the
installation.
Now you shall find the Wireless-G Configu-
ration Tool tray icon, ,appeared in the
system tray. The installation is entirely
finished at the moment.
Double-click the icon to launch the application and open the Wireless Settings dialog
box, in which you may freely arrange your
network connection afterwards.
For more details about Wireless-G Configuration Tool, please refer to WLAN-G Configu-
ration T ool Basics in this manual.
12
Page 15
Installation Notes - Windows XP
If your system is running Windows XP, you
shall find that four tabs are contained in the
Wireless Settings dialog box after you’ve
followed the instructions above and successfully installed the drivers. However, normally,
the dialog box should be consisted of seven
tabs. This is because Windows XP has its
built-in configuration tools – Windows XP
Zero Configuration to assist you in networking activities. It is recommended to utilize the
attached Wireless-G Configuration Tool to
enjoy more benefits it will bring.
Thus, to employ your Wireless-G Configura-
tion Tool under Windows XP, please proceed
to the next step to change the default settings
of Windows Zero Configuration to Wireless-
G Configuration Tool.
Installation
13
Page 16
Installation
a)
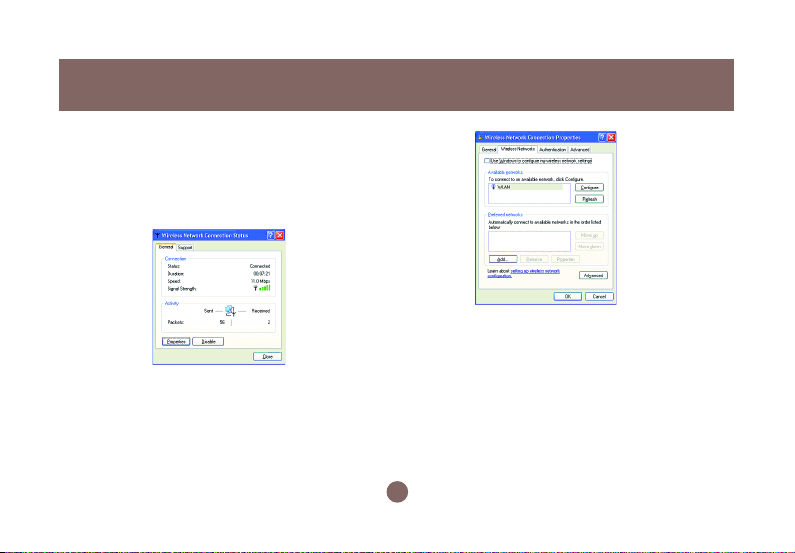
Right-click the Network Connections
icon at the task bar to open the Wireless
Network Connection Status dialog box,
and then select Properties.
b)
Choose the Wireless Networks tab in the
Wireless Network Connection Properties
dialog box, and remove the check from the
Use Windows to configure my wireless
network settings checkbox.
c)
Click OK. Now, you have successfully
removed the Windows Zero Configuration.
To monitor and configure the network via
Wireless-G Configuration Tool, double-click
its tray icon, and you shall find seven tabs
contained in the popped up Wireless Settings
dialog box this time. For more information on
Wireless-G Configuration Tool, please refer to
14
Page 17
Installation
the chapter: Wireless-G Configuration Tool
Basics below.
Note: If you wish to use Windows XP’s built-in configuration
tools – Windows XP Zero Configuration, please refer to the
next chapter: Configuration for Windows XP to configure the
WLAN USB Stick.
Verifying a Successful Installation
To confirm that the Wireless-G USB 2.0 Flex
Adaptor is properly installed, please follow
the procedures below.
1.
Right-click the My Computer desktop icon
and choose Properties from the opened
menu.
In the System Properties dialog box, click
2.
the Hardware Device tab, and then
choose the Device Manager button.
3.
In the opened window, expand Network
adapters to find – 802.11g/b WLAN
USB92.0) Adapter. Right-click over the
item and choose Properties.
4.
From the opened dialog box, on the
General tab, find the descriptions under
15
Page 18
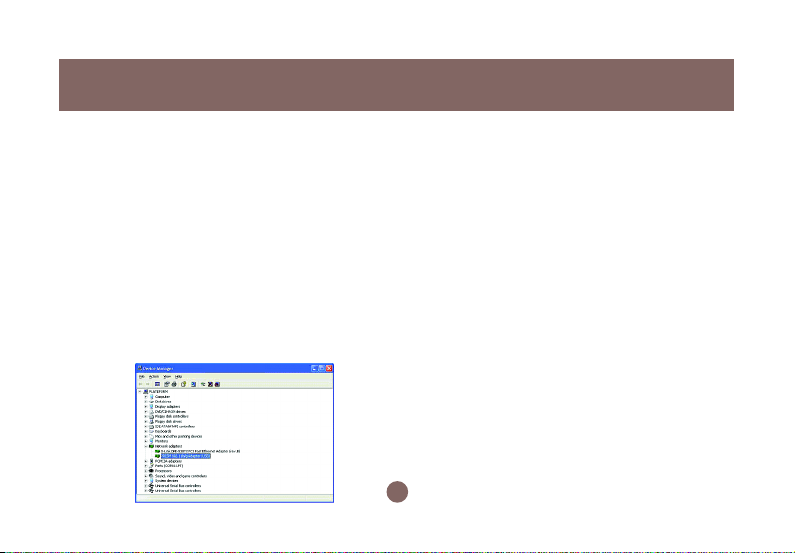
Installation
the Device Status pane to learn if the USB
Adapter is working properly. However, if
there’s an error message shown, please
choose Uninstall from the opened menu
while right-clicking the USB Adapter item, to
which a red or yellow icon is attached
beside, in the Device Manager dialog box.
Then restart your system and go through the
installation procedures again.
The following picture indicates a successful
installation of the Wireless-G USB 2.0 Flex
Adaptor.
16
Page 19

Configuration for Win XP
Configuration for Windows XP
As you have already known, Windows XP
has its built-in configuration tools – Windows
XP Zero Configuration, to assist you in
some basic configurations of wireless
network connection. The service star ts right
after the completion of the installation of
Wireless-G USB 2.0 Flex Adaptor, and you
will find the icon automatically appears in
your system tray like the following picture
shows.
Please refer to the desired topics below to
look for more details about utilizing your
Wireless-G USB 2.0 Flex Adaptor via
Wireless Zero Configuration.
To Connect an Available Network via
Wireless Zero Configuration
1.
Double-click the Wireless Network
Connection icon.
2.
In the opened Connect to Wireless
Network dialog box, the currently available
networks are listed in the Available
networks field. From the list, choose an
item that you intend to associate with.
3.
If the chosen entry requires a WEP
encryption key and also automatically
provides it, leave the Network Key field
blank and then choose the Connect button
to build the connection. Otherwise, you will
need to manually enter the identical key in
the Network Key field before clicking
Connect.
17
Page 20

Configuration for Win XP
4. If the connection is established,
there will be a pop-up message
shown beside the Wireless
Network Connection icon on the
system tray. You could obtain the
information on the status of
connection from the message.
To Configure the Wireless Networks
Properties
If you cannot establish a connection with the
chosen entry or you wish to configure further
wireless network connection settings, choose
the Advanced button in the Connect to
Wireless Network dialogue box.
After clicking Advanced, you will enter into the
Wireless Networks tab of the Wireless
Network Connection Properties dialog box,
18
Page 21

Configuration for Win XP
in which three other tabs are found, including
General, Authentication, and Advanced. The
Wireless Networks tab includes almost the
main settings for the networking connection.
Thus, please check the descriptions below to
learn more about the tab.
Note: For more detailed information about each tab, please
refer to the Windows XP Online-Help.
The Wireless Networks tab is chiefly
consisted of two sections: Available
networks and Preferred networks.
Under the Available networks area, all the
•
available access points or Wireless LAN
PC Card equipped computers are
displayed. You may wish to click Refresh to
update the list. If you choose any listed
item in the field and then click Configure,
the Wireless Network Properties dialog
box will appear. Check the descriptions
below the figure to obtain more information
about the dialog box.
•
In the Preferred networks area, you could
add any displayed networks to the list by
clicking over the intended item from
Available networks and then selecting
19
Page 22

Configuration for Win XP
the Add button. After clicking Add, the
Wireless Network Properties dialog box will
appear as Figure 3.2-3 displays. Note that to
delete any item under the Preferred
networks area, simply click on it and then
select the Remove button. Additionally, you
may adjust the items in the list by clicking the
desired item and then choosing the Move up
or Move down button. It is, however,
important to realize that Windows XP will
always choose the first one in the list to
establish the networking connection.
Note: Once you choose an item from the Preferred
networks list and then click Properties, the Wireless
Network Properties dialog box will also be provoked.
•
In the opened Wireless Network
Properties dialog box, edit texts in the
Network Name (SSID) field to identify the
chosen network entry in the wireless LAN.
20
Page 23

•
If there’s a need, go to the Wireless
network key (WEP) area to set the keys
as the associated access point or
Wireless LAN PC Card equipped
computer requests. To set WEP, select
Data encryption (WEP enabled) and
Network Authentication. Then enter the
encryption key for the network you intend
to connect in the Network key filed. Prior
to typing texts as the network key, you
may wish to define the Key format and
Key length. Click OK when you are
finished, and you will return to the
Wireless Network Connection Properties dialog box.
Configuration for Win XP
Note: For more details of this tab, you may click the link: setting
up wireless network configuration at the bottom of the
Wireless networks tab to launch the Windows XP Online-Help.
21
Page 24

Configuration for Win XP
To Access to Certain Wireless Network Type
The default network type of Windows XP
Zero Configuration is any available access
points (Access Point mode) or WLAN Card
equipped computers (Ad-Hoc mode) within
the range at the given time. However, you
may wish to connect to a certain network
type sometimes. To change the default
settings, click the Advanced button in the
Wireless Network Connection Properties
dialog box.
The Advanced dialog box provides three
options, Any available network, Access
point networks only, and Computer-tocomputer networks only. Choose one of them
according to your need and click Close to
finish. Then you will find under the Available
networks area in the Wireless Network
Connection Properties dialog box, only the
specified networks are displayed.
Note: If you wish to use the attached application – Wireless-G
Configuration Tool of the Wireless-G USB 2.0 Flex Adaptor
instead of Windows XP’s Wireless Zero Configuration, please
refer to Installation Notes –Windows XP in this manual to
change the settings. (Page 13)
22
Page 25

Wireless-G Configuration Tool Basics
After successfully installing the driver for
your Wireless-G USB 2.0 Flex Adaptor on
your computer, you may now access
Wireless-G Configuration Tool for better
control your wireless network.
In this chapter, four topics are covered: Tray
Icon, Right-Click Menu of the Tray Icon,
Program Controls, and The Advanced
Properties Tab.
Tray Icon
As long as you finish installing Wireless-G
Configuration T ool on your computer system,
you will see its icon, ,shown at the right
bottom corner of your screen. When you move
the mouse cursor over it, the information on the
current link quality will appear in the tips.
Furthermore, the color of the icon varies with
the current state of your network connection.
Check the list below to learn the definition of
each color.
23
Page 26

Wireless-G Configuration Tool Basics
Right Click Menu of the Tray Icon
Right-clicking the Wireless-G Configuration
Tool icon in the system tray will open a menu
as the following picture:
Wireless Radio On
Choose the Wireless Radio On command to
receive the radio frequency signal.
Wireless Radio Off
Choosing the Wireless Radio Off command
will stop receiving the radio frequency signal.
Remove Status Icon
If you do not wish to have the Wireless-G
Configuration T ool icon displayed in the
system tray, choose this command to open the
Remove Wireless Status Icon dialog box, and
then choose Yes to have the icon disappeared.
The icon will reappear next time when you
restart the computer. If you intend to remove it
permanently, put a check in the checkbox next
to the Remove Status Icon Permanently
option. To launch the utility hereafter, click Start
on the taskbar, choose Program from the
menu, and then point to Wireless-G Configura-
tion T ool of the submenu of WirelessLAN 11G
USB T ools. Clicking No will undo the removal.
24
Page 27

Wireless Network Status
Choose this command to launch the Status
tab of the Wireless Settings dialog box.
Advanced Configuration
Choose this command to launch the Configuration tab of the Wireless Settings dialog box.
WEP Encryption
Choose this command to launch the Encryption tab of the Wireless Settings dialog box.
This tab offers you a number of options to
maintain the secure management in a wireless
LAN environment.
Wireless-G Configuration Tool Basics
IBSS Channel
Choosing this command will launch the IBSS
tab of the Wireless Settings dialog box.
Country/Domain
Choosing this command will launch the
Domain tab of the Wireless Settings dialog
box.
Version Information
Choosing this command will launch the About
tab of the Wireless Settings dialog box. The
About tab reveals general information on your
Wireless-G USB 2.0 Flex Adaptor, including
the release version of driver and the Wireless-
G Configuration Tool and the USB network
adapter’s MAC Address.
25
Page 28

Configuration Program Controls
When you double-click the Wireless-G
Configuration T ool tray icon, the Wireless
Settings dialog box will be prompted as the
picture shows below. You may also launch this
dialog box via clicking Start on the taskbar,
choosing Program from the menu, and then
pointing to Wireless-G Configuration Tool
from the submenu of WLAN-G TOOLS.
The application is a window-based program,
which is consisted of seven tabs, including
Status, Configuration, Encryption, Site
Survey, IBSS, Domain, and About. The
following figure displays the Wireless
Settings dialog box.Check the desired items
below to obtain more details about these tabs.
The Status Tab
In the Wireless Settings dialog box, click the
Status tab to bring up the following display.
Here presents the status of your current
connection. To close the window, click OK.
26
Page 29

Configuration Program Controls
Note: The texts before “Wireless Settings” in the caption bar
of the dialog box are the profile name of the current
connection. Thus, the caption contexts vary according to the
connectivity at the given time. From the left picture, the
associated profile is named
about profiles, please refer to the “The Configuration Tab”
section in the manual.
“Default”.
For more information
From the window, the general information on
the status of currently connected entry is
presented. You may want to click the
Rescan button to reinitiate the scanning
process and update the status. Later the
result of scanning will be renewed and
displayed in the window. If you wish to stop
the networking connection, click the Disable
Radio button to stop scanning. Meanwhile,
the State tab will indicate that the radio has
been stopped and the remaining areas
under this tab display either a zero or Not
Applicable. However, if you are already in the
disabled radio mode, you will find the Enable
Radio button here instead. Click Enable
Radio to regain the link then.
State:
Here displays the MAC Address of the current
associated entry, which could be a connected
access point in the Infrastructure mode or
computers joining in the Peer-to-Peer network.
27
Page 30

Configuration Program Controls
28
Page 31

Configuration Program Controls
Current Tx Rate:
This feature indicates the transmission rate
of the current connection.
Current Channel:
Here reveals the current channel operated in
the wireless network. Note that the channel
number differs as the radio scans any
available channels in the Infrastructure
mode.
Throughout (bytes/sec):
This feature indicates the rates of transmitting (Tx) and receiving (Rx) data of your
Wireless-G USB 2.0 Flex Adaptor within a
short period of time; thus, the values vary on
a time basis.
Link Quality:
Link Quality is based on the percentage of
successfully transmitted or received signal of
the associated access point beacon within a
limited period. The higher the percentage, the
better the link quality. The bar graph beside
also provides a visual interpretation of the
current link quality.
Signal Strength:
You may learn the received signal strength of
the baseband processor of the beacon signal
from the Signal Strength bar beside, and it’s
also presented in terms of percentage. As the
signal gets stronger, the signal percentage rate
gets higher.
Note: Signal Strength and Link Quality features only apply to
the Infrastructure mode. Not applicable to Ad-Hoc mode.
29
Page 32

Configuration Program Controls
The Configuration Tab
Click this tab to edit different profiles for
different network configurations. When finish
changing the settings, please click Apply to
perform the new configuration at last.
Note: Choosing the Advanced Configuration command from
the right-click menu of Wireless-G Configuration Tool tray
icon will launch this tab too.
Profile Name:
A profile is a named set of operating
parameters for your Wireless-G USB 2.0 Flex
Adaptor. By clicking the down arrow at the
right of this item to display any available
profiles for your Wireless-G USB 2.0 Flex
Adaptor. You may set values for the chosen
pre-defined profile. When you finish setting
up the new changes, choose Apply to save
the profile.
Note: You will have at least one profile named Default. When
selecting any link from the list under the Site Survey tab,
you have already automatically established a new profile for
it under the Configuration tab.
30
Page 33

Configuration Program Controls
To identify a new profile, enter texts in the Profile
Name field. After defining the configurations
below, click the Apply button to establish a new
profile. To switch between any existing profiles,
click the arrow button at the right of the Profile
Name field to open the pull-down menu and then
select an intended one from it.
Network Name:
Network Name, also known as SSID (Service
Set Identifier), must be unique to distinguish
itself as a particular wireless network, while all
wireless points in this network area share the
same SSID. Type the identical SSID in the
Network Name field to associate with access
points or stations within the specified wireless
LAN. To change the Network Name, highlight
the texts in the box, edit a new SSID, and then
click Apply to save the changes.
Network Type:
Two network types are offered here: Access
Point and Peer-to-Peer. Choose an intended
type from the two options. The Access Point
mode, which is also known as the Infrastructure mode, allows you to communicate with a
wired network via an access point. If you
attempt to operate this mode, you must indicate
the identical Network Name to make a
communication with the intended access point.
On the other hand, the Peer-to-Peer mode
provides you with the so-called Ad-Hoc
communication, which means each wirelessequipped computers within a group is able to
connect with each other as an independent
wireless LAN without the use of an access
point. Each station within this Ad-Hoc network
has to define the same Network Name.
31
Page 34

Configuration Program Controls
Peer-to-Peer Channel:
This command is only available while you are
operating the Peer-to-Peer mode, the socalled Ad-Hoc mode. Specify the operating
radio frequency channel from the pull-down
menu if you are the creator of the wireless
network. If you are the joiner, just configure the
SSID and click Apply. Note that the available
channels differ from country to country, and the
channel number must be the same between
the entries/stations within the range, so that
each can communicate with each other. While
in the Access Point mode, the channel
number would be the same as the associated
access point. Thus, there’s no need to
manually set up the value.
Transmit Rate:
This command allows you to indicate the rate
of transferring the data packet from the
associated access point or any nodes within
the range. There are four options for you:
Auto 1 or 2 Mb, 5.5 Mb, 11 Mb, and Fully
Automatic. Specify the rate from the
provided options according to the speed of
your wireless network, or you may simply
choose Fully Automatic to set the best
available rate according to the received
signal quality and the capabilities of the
associated access point or station.
32
Page 35

The Encryption Tab
Click the Encryption tab to define the
encryption settings for a specific profile. It
offers you various options concerning the
so-called WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy)
to maintain the secure management in a
wireless LAN environment. See the
explanations below for more details, and
before making any activation of the new
settings, click Apply. To leave the window,
click OK. To undo the new settings, select
the Cancel button.
Note: Choosing the WEP Encryption command from the
right-click menu of Wireless-G Configuration Tool tray
icon will launch this tab too.
Configuration Program Controls
Encryption (WEP security):
If you choose Disabled from the pull-down list,
you will have the Wireless-G USB Adapter
communicated with all stations within the
same networking community without any data
encryption. Otherwise, two key lengths are
offered: 64 bit and 128 bit. Specify a preferred
one from the two, so that you may use the
identical WEP key to make a communication
10
with the chosen access point.
33
Page 36

Configuration Program Controls
Create Keys Manually:
Once you set the Encryption type as 64 bit or
128 bit, you may choose to edit WEP keys
manually or create them via the passphrase of
your wireless network. If you choose the
Create Keys Manually option, you may
directly enter up to 4 WEP keys for use in WEP
encryption. To generate the WEP keys, please
define the key entry method as Alphanumeric
or Hexadecimal (for hexadecimal characters,
only digits 0-9 and letters A-F are valid). Then
edit the texts in the blank fields below, from
Key 1 to Key 4, as the encryption codes. Note
that these codes/keys shall be identical
between the wireless nodes within the range
and the access point only. Check the table right
to find valid key length of each encryption type:
Use WEP Key:
Indicate which WEP key you intend to apply
to activate the WEP encryption from the pulldown menu. Make sure that the intended
access point on the wireless network shares
the same keys. By default, Key 1 will be
used.
Create Keys with Passphrase:
Choose this command when the associated
wireless network uses a passphrase to
create WEP keys. Enter the passphrase
34
Page 37

Configuration Program Controls
string in the Passphrase field to generate four
encryption keys in the Key fields above. Note
that only letters A-Z are valid for the
Passphrase feature.
After finish configuring the Encryption
features, remember to click Apply to initiate
the new settings.
Note: When entering the passphrase here, ensure that you
have specified an accurate type of the Encryption (WEP
security) above according to the associated agent’s
configuration. Otherwise, the inaccuracy will cause any failure
of performance.
The Site Survey Tab
From the offered information, you may learn
the general information on the status of
current scan lines, including BSSID, SSID,
signal strength, the channel number, WEP
type, and network type.
In addition, to directly make an association
with any site on the list, double-click the
BSSID field of the intended entry, and you
will be led to the Status tab then.
Please use Rescan to refresh the network
information.
35
Page 38

Configuration Program Controls
The IBSS Tab
If you, as a creator of the wireless network, are
communicating with other stations via the IBSS
(802.11 Ad-hoc) mode to form peer-to-peer
networks, click the IBSS (Independent Basic
Service Set) tab to specify an operating radio
frequency channel from the pull-down list
under the IBSS Channel Selection section.
Note that the available channels differ from
country to country, and the channel number
must be the same between the entries/stations
within the range, so that each can communicate
with each other. Or you may simply click
Defaults to automatically determine the
channel number for you. When done, click
Apply to activate the new configuration.
On the other hand, while in the Access Point
mode, you will find the channel number is the
same as the associated access point. Thus,
there’s no need to manually set the value.
Note: Choosing the IBSS Channel command from the
right-click menu of Wireless-G Configuration Tool tray
icon will launch this tab too.
36
Page 39

The Domain Tab
While in the 2.4GHz range, the network
operation may differ from country to country, or
domain to domain. This is because the 802.11d
protocol was established. To have the
operation normally processed, choose the
Domain tab to change relevant settings. Note
that if you specify Peer-to-Peer as the network
type, you must specify None in the 802.11d
support field.
Note: Choosing the Country/Domain command from the right-
click menu of Wireless-G Configuration Tool tray icon will
launch this tab too.
Configuration Program Controls
802.11d Support:
802.11d Support lets you operate multi-
country roaming. To automatically adjust
regulatory domain while operating network in
different countries, choose either Strict or
Flexible according to your need.
Choosing Strict will allow your Wireless-G
USB Adapter to communicate with the
access points that provide 802.11d support.
On this occasion, the Wireless-G USB
37
Page 40

Configuration Program Controls
Adapter scans all communications channels
for an access point which provides information about the channels, frequencies, and
power levels permitted in your location. Once
it finds such an access point, the Wireless-G
USB Adapter conforms its operations to these
standards. The Wireless-G USB Adapter will
not communicate with an access point that
does not provide this information, nor will it
join or create a peer-to-peer network.
On the other hand, if you choose Flexible in
this field, your Wireless-G USB Adapter can
communicate with any access point it finds. In
this case, you must also choose the county in
the Countries/Domains field which corresponds to your location. Your Wireless-G USB
Adapter then searches for an access point
that offers information about the channels,
frequencies, and power levels permitted in
your location. If it finds such an access point,
the Wireless-G USB Adapter conforms its
operations to these standards.
If you choose None, the task will be
terminated.
Countries/Domains:
If you choose Flexible above, go on defining
the regulatory domain from the drop-down
menu of this command according to the
country you are located in. More detailed
information about the defined country/domain
will be listed below afterwards.
When you are done, remember to click Apply
to let the new settings take effect.
38
Page 41

Configuration Program Controls
The About Tab
This tab provides general information on your
Wireless-G USB Adapter, including the
following items.
Note: Choosing the Version Information command from the
right-click menu of Wireless-G Configuration Tool tray icon
will launch this tab too.
Network Driver:
Displays the current version and released
date of the Wireless-G USB 2.0 Flex
Adaptor’s driver.
Configuration Utility:
Displays the current version and released
date of Wireless-G Configuration Tool.
NIC Firmware:
Displays the current NIC card firmware
version and the MAC (Media Access Control)
address of your Wireless-G USB Adapter. It
is consisted of 12-digit hexadecimal numbers
(48 bits in length) to identify your computer’s
physical address on the local area network.
39
Page 42

Advanced Properties Control
The Advanced Properties tab provides
access to operating parameters for the network
adaptor, which are not controlled by the
configuration utility. These properties are
accessed through the Windows hardware
device manager. The following steps describe
how to access these properties under
Windows XP. For Windows 2000, the details
may differ slightly; consult your operating
system documentation or your system
administrator. Also, the properties that appear
in the list displayed by the device manager
may differ depending on the adapter installed
in your computer.
To display these properties, complete the
following steps:
Right-click the My Computer desktop icon
1.
and choose Properties from the opened
menu.
Choose the Hardware tab in the System
2.
Properties dialog box, and click Device
Manager.
3.
In the opened window, expand Network
adapters to find the USB Stick – 802.11g/b
WLAN USB(2.0) Adapter. Right-click over
the item and choose Properties from the
opened menu.
40
Page 43

4.
When you click on the Advanced tab in the
opened dialog box, a display similar to the
following appears.
Advanced Properties Control
You shall see the value for any of these
properties by clicking on an item displayed in
the Property field. If a value has been set for
the property, it appears in the Value field to
the right of the list. You may click to specify
the Value settings from the offered drop-down
list. To change a numeric value, simply move
the mouse pointer to the Value field and click
once with the left mouse button to highlight
and type the value for the property according
to your needs. Choosing Not Present under
the Value field will disable a value.
The following section explains the items in the
Property list displayed by this tab.
41
Page 44

Advanced Properties Control
Configuration Profile
Specify a pre-defined profile with standard
parameters from here. The provided profiles
include:
• B only – for operation in 802.11b
environments only
• B WIFI – for operation in 802.11b
environments conforming to Wi-Fi
standards
• G only – for operation in 802.11g
environments only
• Mixed – for operation in either 802.11b
or 802.11g environments
• Mixed Long – for long-range operation in
either 802.11b or 802.11g environments
• Test – for operation under the widest variety
of 802.11 conditions
Fragmentation Threshold
The fragmentation threshold defines the size
(in bytes) at which a packet is split into
smaller packets for transmission. You can
enter a value from 256 to 2432 in increments
of 128. Normally, you should disable this
property unless directed otherwise by your
Network Administrator.
Nitro Mode
This feature may increase data throughput
over the WLAN and is particularly effective in
mixed 802.11b/g environments. This property
determines whether Nitro mode is enabled in
your wireless USB Stick. A value of 0 (zero)
disables this mode; a value of 1 (one)
enables it.
42
Page 45

Advanced Properties Control
Power Save Mode
This property turns the Station Power Save
feature on or off, or sets it to Auto. When in
Auto mode, the station enters Power Save
based on the battery condition (XP only) on
the host. Power Save Mode decreases the
amount of power consumed by the adapter
by powering off the radio for short periods.
Enabling Power Save Mode trades off
performance for battery life.
• Auto Dynamic – specifies Disable mode
when on AC power and Dynamic mode
when on battery
• Auto Maximum – specifies Disable mode
when on AC power and Maximum mode
when on battery
Note: Auto Dynamic and Auto Maximum require NDIS
5.1 or later, typically available only on Windows XP.
• Disabled – specifies continuous access mode
and is the default
• Dynamic – specifies a fast power saving
mode that provides the best combination of
performance and power usage
• Maximum – specifies the greatest power
saving mode
RTS Threshold
The RTS threshold is the packet size (in bytes)
at which packet transmission is governed by the
RTS/CTS transaction.
You can enter a value from 0 to 2432 in increments of 64 for this property. Normally you should
leave this property disabled unless directed
otherwise by your Network Administrator.
43
Page 46

Advanced Properties Control
The Long/Short Retry Limit
The Long Retry Limit or Short Retry Limit is
the maximum number of retransmission of a
data packet because of the failure of receiving
CTS or ACK.
44
Page 47

Appendix and TroubleShooting
This section provides solutions to problems
that you might encounter during the installation
and operation of your Wireless-G USB 2.0 Flex
Adaptor. Please refer to the desired topics
below and read the description to solve your
problems.
Uninstall Wireless-G Configuration Tool and
the Stick’s Driver
Prior to starting the uninstalling, please make
sure that Wireless-G Configuration Tool is
closed, and then go along with the procedures
below to entirely uninstall Wireless-G
Configuration T ool and the Stick driver.
Right-click the My Computer desktop icon
1.
and choose Properties from the opened
menu.
In the System Properties dialog box, click
2.
the Hardware tab, and then choose the
Device Manager button.
In the opened window, expand Network
3.
adapters to find – 802.11g/b WLAN
USB(2.0) Adapter. Right-click over the
item and choose Uninstall from the
opened menu.
45
Page 48

Appendix and TroubleShooting
In the Confirm Device Removal message
4.
box, click OK to proceed with the removal
of the hardware.
5.
Click Start on the taskbar and choose
Control Panel from the Settings menu.
Select Add or Remove Programs to open
6.
the dialog box showed as below.
Click the Change/Remove button under
7.
WLAN 802.11G USB.
8.
Please follow the on-screen instruction to
complete the removal.
46
Page 49

Appendix and TroubleShooting
The Wireless-G USB 2.0 Flex Adaptor Does
Not Work Properly
If this happens, follow the guidelines below.
Right-click the My Computer desktop icon
1.
and choose Properties to open the System
Properties dialog box.
Click the Hardware tab and then choose the
2.
Device Manager button.
In the opened window, find your Wireless-G
3.
USB Adapter to see if the installation is
successful. If you see a yellow exclamation
mark beside the item, please go along with
the steps below to reinstall the drivers.
4.
Uninstall the software and hardware drivers
from your PC. (Please refer to the previous
topic for details)
Restart your computer and repeat the
5.
installation procedures as indicated in this
chapter in this manual: Installation of the
Wireless-G USB 2.0 Flex Adaptor.
When finished, open the Device Manager
6.
window again to verify if the installation is
approved. The yellow exclamation mark shall
be removed for this time.
47
Page 50

Specification
48
Page 51

Specification
49
Page 52

Specification
50
Page 53

Glossary
802.11b – 802.11b is one of the IEEE standards for wireless LANs and specifies a data
transfer rate of 5.5 and up to 11 megabit per second in the 2.4 gigahertz radio band. 802.11b
is recently given other widespread names as Wi-Fi or Wireless Fidelity.
802.11g – 802.11g is the newest addition of the IEEE standards for wireless LANs and
specifies a data transfer rate up to 54 megabit per second in the 2.4 gigahertz radio band.
802.11g is also part of the family of Wi-Fi.
Ad-hoc Network – Ad-hoc network, also known as peer-to-peer network, means a wireless
network which is composed only of stations. This type of network is created with a group of
wireless-equipped computers. With the wireless devices, each computer, functioning as a
server and a client at the same time, can establish a LAN to directly communicate with other
computers without any access points involved. It is easy to set up a peer-to-peer network;
however, because all stations must be within a specific distance in order to be capable of
communicating with each other, it is also limited. Thus, such a type of network is widely used
at small networking requirements, like between a few computers or devices at departmental
scales.
51
Page 54

Glossary
IEEE – IEEE, the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers, is the world’s largest
technical professional society and is consisted of more than 366,000 members in approximately 150 countries. As a leading authority on areas ranging from for computer engineering,
biomedical technology and telecommunications, IEEE endeavours to set more than 800 active
consensus standards till now and publish 30 percent of the world’s literature in electrical
engineering, computers and control technology.
Infrastructure Network – Infrastructure network allows you to communicate with wired LAN
via an access point. Unlike Ad-hoc network that all wireless-equipped stations within the range
may directly communicate with each other, clients of Infrastructure network can only transmit
and receive data through the use of a central access point. The associated access point also
provides communication with the wired network.
MAC Address – The MAC (Media Access Control) address is the serial number of your
Network Interface card. It has been burnt into the chip and could not be changed. MAC
address is thus unique. While a computer on the network is transferring data, its MAC address
is also conveyed and attached to be part of the header of the data packets.
52
Page 55

Glossary
Roaming – Roaming is an ability to allow users from one cell (or BSS) to another without
losing connection via a wireless device.
SSID – SSID, Ser vice Set Identifier, is a 32-character unique identifier for a workgroup of the
wireless network. An SSID of one WLAN should be different from that of others, so all access
points and other devices intending to communicate with a specific WLAN cannot achieve
successful network connectivity unless presenting the identical SSID. From some perspective,
an SSID performs as a kind of password to supply a measure of security on the WLAN.
However, if an access point is configured to “broadcast” its SSID, this essential security is no
longer remained. An SSID is also known as a Network Name.
USB – USB, standing for Universal Serial Bus, was designed to make a connection between
the computer and its peripherals, such as keyboards, scanners, webcams, printers, etc., via
an easy operation of plug-and-play. USB has proved to be a good solution that allows users to
quickly and easily connect and add peripherals to computers. Through the USB interface,
there’s even no need to turn the computer off while adding new peripherals mentioned above
to a computer. Due to its convenience and simplicity, USB has won worldwide popularity, and
most peripherals for computers these days are designed for the USB standard.
53
Page 56

Glossary
WEP – Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP) is a security mechanism for wireless local area
networks. It is designed for 802.11 standard to offer an equal level of security as that of a
wired LAN. Through the configurations of encryption, WEP aims to provide security while the
nodes with wireless devices are transferring or receiving data packets over radio waves.
WLAN – Wireless local area network (WLAN) receives and transmits data over the air by
using radio frequency (RF) technology. The vital significance of WLAN is it minimizes the
requirements for wired connections and provides not only data connectivity but also user
mobility. Without the constraint of physical location, wireless LAN allows clients to transmit and
receive data via high-frequency radio waves rather than wires.
54
Page 57

Technical Support
If you are still experiencing problems after reading Product User Manual and the Troubleshooting section, you may either contact our technical support at: 1-949-453-8782
OR, simply click our URL address www.iogear.com to go to our company website and
check the latest version and other information about the product and/or software.
55
Page 58

Radio & TV Interference Statement
WARNING!!! This equipment generates, uses and can radiate radio frequency energy and, if
not installed and used in accordance with the instruction manual, may cause interference to
radio communications. This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for
a Class B computing device pursuant to Subpart J of Part 15 of FCC Rules, which are designed
to provide reasonable protection against such interference when operated in a commercial
environment. Operation of this equipment in a residential area is likely to cause interference, in
which case the user at his own expense will be required to take whatever measures may be
required to correct the interference.
56
Page 59

Limited Warranty
IN NO EVENT SHALL THE DIRECT VENDOR’S LIABILITY FOR DIRECT, INDIRECT,
SPECIAL, INCIDENTAL OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES RESULTING FROM THE USE OF
THE PRODUCT, DISK OR ITS DOCUMENTATION EXCEED THE PRICE PAID FOR THE
PRODUCT.
The direct vendor makes no warranty or representation, expressed, implied, or statutory with
respect to the contents or use of this documentation, and especially disclaims its quality,
performance, merchantability, or fitness for any particular purpose.
The direct vendor also reserves the right to revise or update the device or documentation
without obligation to notify any individual or entity of such revisions, or updates. For further
inquires please contact your direct vendor.
57
Page 60

®
Contact info.
23 Hubble • Irvine, CA 92618 • (P) 949.453.8782 • (F) 949.453.8785 • www.iogear.com
 Loading...
Loading...