Page 1

BOSS™ (Broadband Office Storage Server)
a Network Server Appliance (NSA)
User Manual
®
Page 2

Thank you for purchasing IOGEAR®'s BOSS™, one of the most advanced and reasonable network server
replacements on the market. IOGEAR® only manufactures high quality connectivity devices so we are
sure you will be satisfied with your purchase. IOGEAR® is dedicated to customer service and satisfaction,
and wishes you the best with your new BOSS™ network server appliance.
To better serve you, IOGEAR® offers an array of additional USB 2.0, USB, FireWire®, KVM, and other
peripheral products. For more information or to purchase additional IOGEAR products, visit us at
www.IOGEAR.com
We hope you enjoy using your BOSS™ network server appliance, yet another first-rate connectivity
solution from IOGEAR®.
© 2003 IOGEAR® All Rights Reserved. PKG-M0098
IOGEAR® , the IOGEAR® logo are trademarks or registered trademarks of IOGEAR® Inc. Microsoft and Windows are registered trademarks of
Microsoft Corporation. IBM is a registered trademark of International Business Machines, Inc. FireWire, MAC, Macintosh, G3, G4, iMac, Apple are
registered trademarks of Apple Computer, Inc. Classic is a registered trademark, licensed to Apple Computer, Inc. Finder is a trademark of Apple
Computer, Inc. All other brand and product names are trademarks or registered trademarks of their respective holders. IOGEAR® makes no warranty
of any kind with regards to the information presented in this document. All information furnished here is for informational purposes only and is subject
to change without notice. IOGEAR® assumes no responsibility for any inaccuracies or errors that may appear in this document. Reproduction in whole
or part without permission is prohibited.
Page 3

Table of Contents
Package Content and System Requirements
Overview
Features
Benefits and Key Features
1. Pictorial Introduction
1.1 Front View
1.2 Back View
2. Installation
2.1 Hardware Installation
2.2 Check your Computer First
○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○
○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○
○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○
○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○
○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○
○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○
○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○
○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○
○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○
2.3 Connecting to the Web-Based Manager
2.4 Web-Based Manager – Basic
3. Configuration Hierachy
○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○
3.1 Overview of Configuration Menu
3.2 Power Management
4. Network Settings
4.1 DHCP Server
○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○
○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○
○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○
○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○
○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○
○○○○○○○○○○○○○○
○○○○○○○○○○○○○
04
05
06
07
10
10
11
13
13
14
16
18
28
28
29
31
32
Page 4

T able of Contents
4.2 IP Alias
4.3 Multiple NAT
○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○
○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○
4.4 Route Settings
4.5 DDNS
5. FireWall Settings
○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○
○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○
5.1 Virtual Server Settings
5.2 URL Filter Setup
5.3 IP Filter Setup
○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○
5.4 Denial of Service
6. VPN Settings
○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○
6.1 IP Sec Settings
6.2 PPTP Settings
7. User Management
7.1 Users
7.2 Group
8. NAS Management
○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○
○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○
○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○
○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○
○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○
8.1 HD Initialization Wizard
8.2 Advanced
○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○
○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○
○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○
○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○
○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○
○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○
○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○
2
34
35
36
37
39
39
41
42
43
45
45
48
49
50
51
53
53
55
Page 5
Table of Contents
8.3 File Sharing
9. System Management
○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○
○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○
9.1 Administrator Settings
9.2 Event Report Settings
9.3 Firmware Update
9.4 Time Settings
9.5 SNMP
10. System Report
○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○
○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○
○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○
10.1 System Information
10.2 System Log
10.3 URL Log
○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○
○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○
10.4 DHCP Lease Report
Care and Handling
Troubleshootoing
Technical Support
Appendix
○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○
Specification
○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○
○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○
○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○
○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○
Radio and TV Interference
Limited Warranty
○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○
○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○
○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○
○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○
○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○
○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○
○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○
3
57
60
60
62
63
64
65
66
66
68
68
69
70
71
73
74
76
77
78
Page 6

Package Content and System Requirements
This package contains:
• 1 Network Server Appliance
• 1 Power Adapter and Cable
• 1 Ethernet cable (CAT5)
• 1 User Manual
• 1 Quick Start Guide
• 1 Warranty/Registration Card
System Requirements:
Macintosh Users:
• Mac OS X (10.2) or greater
• Internet Explorer 5.2 or newer
PC Users:
• Windows® 98SE, 2000, ME, XP
• Internet Explorer 6.0 or newer
Other:
• Computer with web browser, preferably with
the latest version of Internet Explorer
4
Page 7

Overview
This chapter introduces the specifications, features, and benefits of the BOSS™ network server appliance.
The Integrated server services such as a Network Address Translator (NAT), Virtual Private Network (VPN),
SPI Firewall, and File Server make this one of the most sophisticated server appliances on the market today.
The BOSS™ network server appliance allows a group of trusted computers and networks to connect
quickly and safely. With the BOSS™ network server appliance, Network Administrators as well as home
users can save time in establishing some of the most common services done on servers costing thousands
of dollars.
5
Page 8

Features
Connection Sharing
• Flexible Address Space for NAT service
• IP Alias
• Multiple NAT
Virtual Private Network
• 20 IPSec Tunnels Available
• PPTP Server / Client
Firewall
• SPI (Stateful Packet Inspection)
• Prevent Denial of Service (DoS) Attacks
• Packet/URL Filtering
• Access Control, Virtual Server
System Management
• Web-based Management for Configuring
System
• Firmware Update via HTTP
• Reset To Factory Settings
• Event Alert and Logs
• Statistics of Network Flow
• System Information
Services
• DHCP Client/Server
• Proxy DNS
• RIP
Network
• Programmable Static Route
• Network Protocols Supported: PPPoE, TCP,
UDP, ICMP, ARP, IP
PPP Authentication
• PAP, CHAP, MS CHAPv2
Real Time Clock
File Sharing
• Supports Common Internet File System(CIFS),
Apple(AFP), NFS
User Management
• Local User Account Management
Power Management
• Support Mechanical Off/Soft Off/Sleeping/
Working System States
6
Page 9

Benefits and Key Features
Virtual Private Network (VPN)
With Virtual Private Network, an enterprise can establish a dedicated tunnel among branch offices and/or mobile
employees. All data is encr ypted and decrypted via the pre-defined dedicated tunnel. This prevents hackers
from stealing private information in the public network. With this functionality, any sub-network can be grouped
as though it is in the same network.
SPI Firewall
The BOSS™ network sever appliance provides a powerful firewall capable of preventing hackers from attacking the gateway or internal network, so many famous DoS attacks can be detected and prevented. Whenever
an attack is detected, the system will alert the network manager/home user that an attack has occurred. The
network administrator or home user can then inspect the log information to find the IP address that sent the
packets.
Easy Installation
In order to facilitate use of the Network Server Appliance, the product comes with default settings that allow most
network administrators to install it without any modifications. If the network manager needs to modify any of the
settings, the Network Server Appliance provides an intuitive Web-based user interface to facilitate any changes.
High Performance
For encryption and decryption, the NSA uses a high-speed RISC processor for real-time results. The unit’s
Ethernet ports suppor t 10/100Mbps transfer rates, enablery the system to route network packets quickly.
7
Page 10

Benefits and Key Features
Auto Switching of Cable Type
Two types of cables, straight through and crossed-over, are used to connect Ethernet devices. In the past,
network managers needed to maintain the two types of cables or customize them as needed. The BOSS™ uses
new innovative technology that auto-detects which type of cable is being used and adjusts the ports accordingly.
Ethernet devices thus can be connected together regardless of which type of cables are being used.
Network Attached Storage
Network Attached Storage (NAS) is the concept of simple shared storage on a network. NAS transfers data
using industry standard file sharing protocols such as CIFS, AFP, NFS and FTP. Files can be shared simultaneously by clients regardless of the operating system they are using or the network server they are attached
to. This solution provides convenient common storage resources.
Dynamic Domain Name Service (DNS)
Dynamic DNS allows anyone to reach your host by the name only. Dynamic DNS will map that name to your
current IP address, which changes each time you dial your Internet service provider. With a URL that stays the
same all the time regardless of the IP address your, options become almost as unlimited as a normal content
provider like www.indiatimes.com or www.yahoo.com.
DMZ
DMZ is a host that provides a nonrestrictive zone between a company’s pr ivate network and the outside public
network. It prevents outside users from getting direct access to a server that has company data. It acts as a
8
Page 11

Benefits and Key Features
proxy server as well. Users of the public network outside the company can access only the DMZ host. The DMZ
may typically also have the company’s Web pages so these could be served to the outside world. However, the
DMZ provides access to no other company data. In the event that an outside user penetrated the DMZ host’s
security, the web pages might be corrupted but no other company information would be exposed.
FTP Server
FTP is the most secure, quick, and reliable method of transferring files. The FTP ser ver allows you full control
over who can login to the server appliance and to which to files the user can access or upload data.
Power Management
The power state of the system supports a mechanical off, soft off, sleep and working state. In the mechanical off state, there is no current consumption. As for the sleep and working state, the system functions as
normal. However, whenever the system is idle, it will enter the sleep state to save power.
9
Page 12
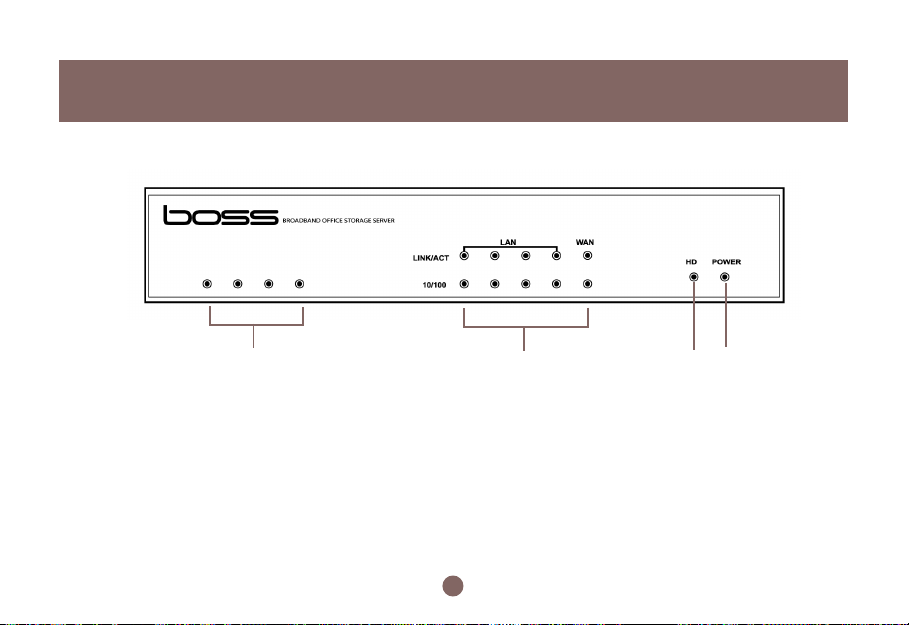
Pictorial Introduction
Front View
1234
1.
System Activity LEDs
2.
LEDs : Link/Activity LEDs for each Ethernet Port, Power LED, Packet Transmit/Receive LEDs
3.
Hard Disk Activity Light
Power Light
4.
10
Page 13
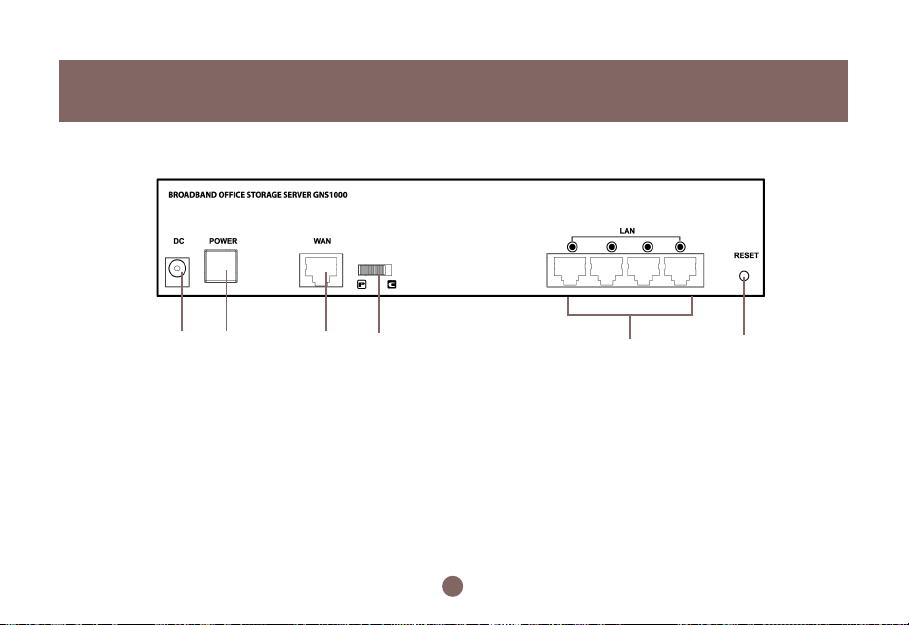
Back View
Pictorial Introduction
56 7 8
Powe r Jack
5.
6.
Power Button
7.
WAN port : 10/100 Mbps
8.
WAN port MDI/MDIX switch
9.
4 LAN ports : 10/100 Mbps
Reset Button
10.
9
11
10
Page 14

Pictorial Introduction
WAN Port
The WAN port is used to connect to an ADSL/Cable modem for linking to the Internet.
WAN MDI/MDIX Switch
The WAN MDI/MDIX switch (MDI= hub or modem side; MDIX= computer or server side) is used to adjust the
cable connection of the W AN port. If the port is connected to a hub, you should mov e the switch to the “hub” side;
if the port is connected to computer, you should move the switch to the computer side. As for the four LAN ports,
there is no need to add additional switches for each cable connection. This is because the LAN ports suppor t
auto MDI/MDIX.
LAN Ports
The LAN ports are used to connect to a PC, server, hub, switch or other network devices on the intranet.
Reset Button
If you forget your password and/or IP settings, you will not be able to access the BOSS™. You can use the
Reset Button to restore the factory settings. To initiate a reset, you must hold the button for at least 5
seconds.
The primary default settings are listed in the Appendix.
12
Page 15
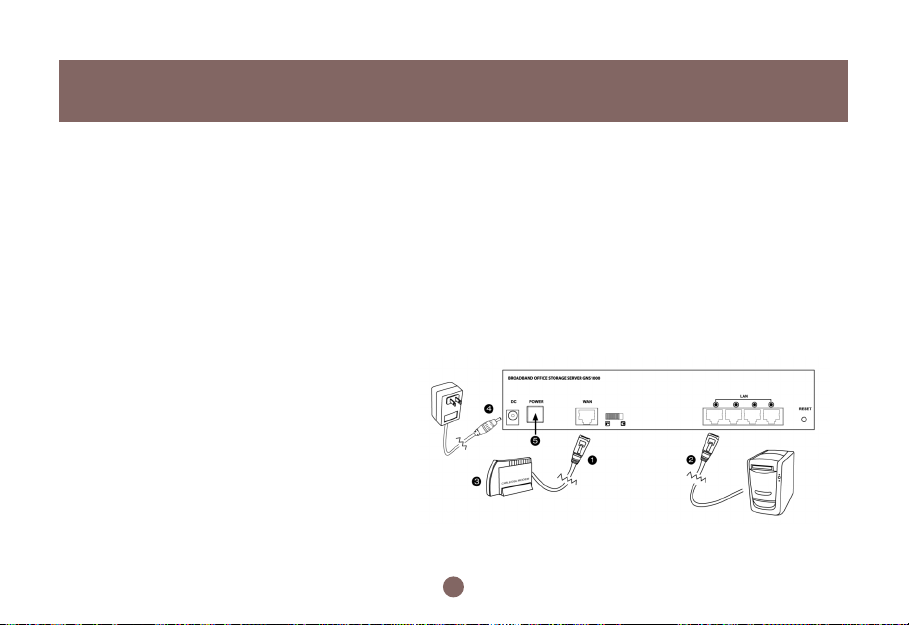
Installation
This chapter will give you brief instructions on how to install the product. In section 2.1, we will configure the
hardware part of the BOSS™ step by step. In section 2.2, we will check whether the IP address of your
computer is assigned by DHCP. Once we complete the installation of the BOSS™ hardware and check your
computer settings, we will use the web-based management to configure the BOSS™ to suit your network
environment. In section 2.3, and 2.4, we will review all the software settings. We will configure it to gain
access to the Internet. If you need additional help or advanced setting details, please refer to the remaining
chapters.
2.1 Hardware Installation
Please follow the steps below to install hardware:
Locate the included Ethernet cable.
1.
Connect one end of it to the DSL or cable
modem or Ethernet reception and the other
end to the WAN port on the BOSS™.
2.
Locate another Ethernet cable.
Connect one end of it to the computer or hub
and the other end to one of the LAN ports on
the BOSS™.
3.
Tur n the DSL or cable modem on or Ethernet
connection on.
If there are more computers or hubs to be
connected, please repeat step 2.
13
Page 16

Installation
Connect the included power adapter to the power socket on the BOSS™ and then plug the power
4.
adapter into a wall outlet.
5.
Tur n on the BOSS™.
If the link LED of the WAN port is not ON, switch the WAN MDI/MDIX switch to the alternate setting.
The hardware installation is now complete.
2.2 Check Your PC (Windows only)
Do not assign an IP address to your computer.
Please check the following settings on your computer:
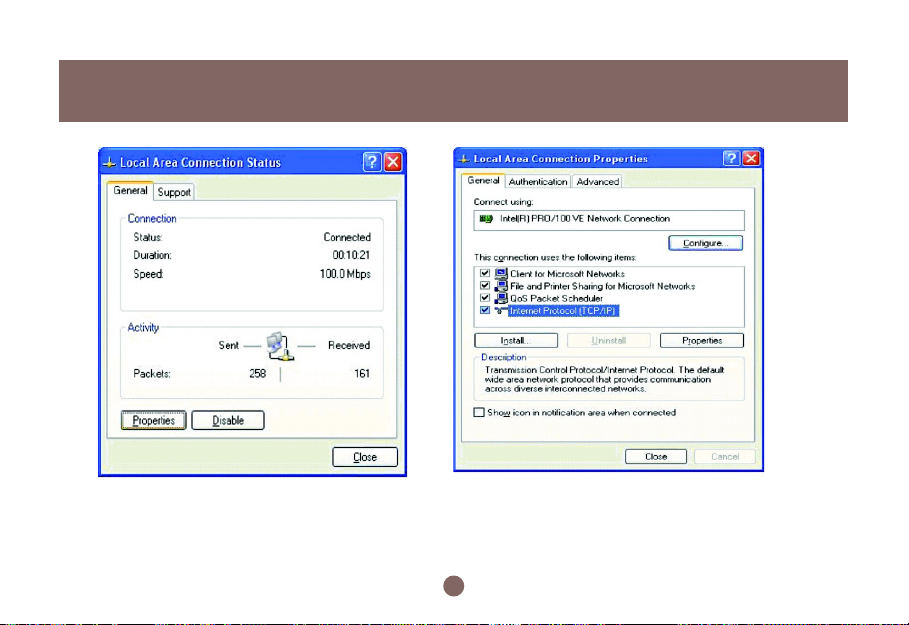
1. Please select sequentially: Start menu -> Settings -> Control panel -> Network connections ->
Local Area Connection. Then a “Local Area Connection Status” window shows up. (Figure 2.2a)
2. Click the Properties button in Local Area Connection Status. Then the “Local Area Connection
Properties” window appears (Figure 2.2b).
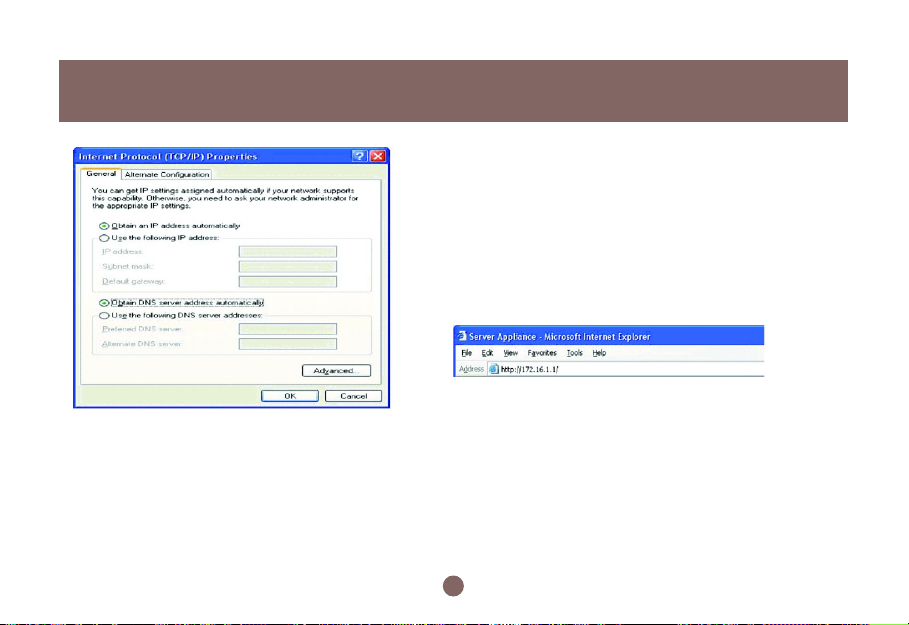
3. Select Internet protocol (TCP/IP) item and then click the Properties button. The “Internet Protocol
(TCP/IP) Properties” window appears (Figure 2.2c).
Select the “Obtain an IP address automatically” radio button, then click the OK button.
14
Page 17
Installation
Figure 2.2a
Figure 2.2b
15
Page 18
Installation
Figure 2.2c
2.3 Connecting to the Web-Based Manager
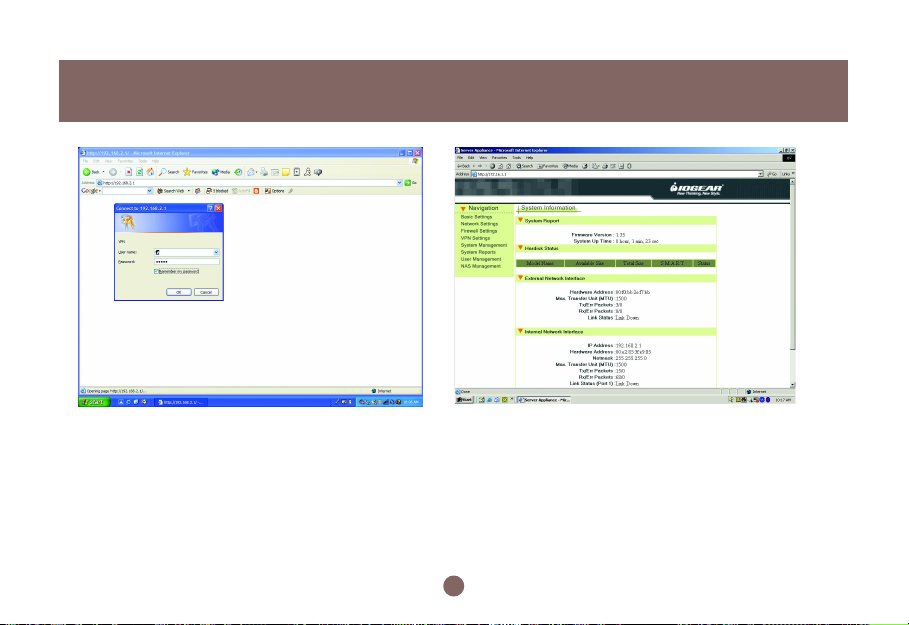
Please follow these steps to connect to the webbased manager:
Open Internet Explorer on the computer that is
1.
DIRECTLY connected to the BOSS™.
Type “http://192.168.2.1” in the address field, then
press the Enter key.
2. An authentication window shows up to prompt you to
type the username and the password.
3. Leave the username blank and type “admin” as a
password. (Figure 2.3a.)
4. Then press OK button. See also page 73.
5. The following window will appear once you have
successfully logged-in. (Figure 2.3b)
6. This is the main menu. From here you can access all
other areas to manage the BOSS™.
16
OSD Operation
Page 19
Installation
Figure 2.3a
Figure 2.3b
17
Page 20
Installation
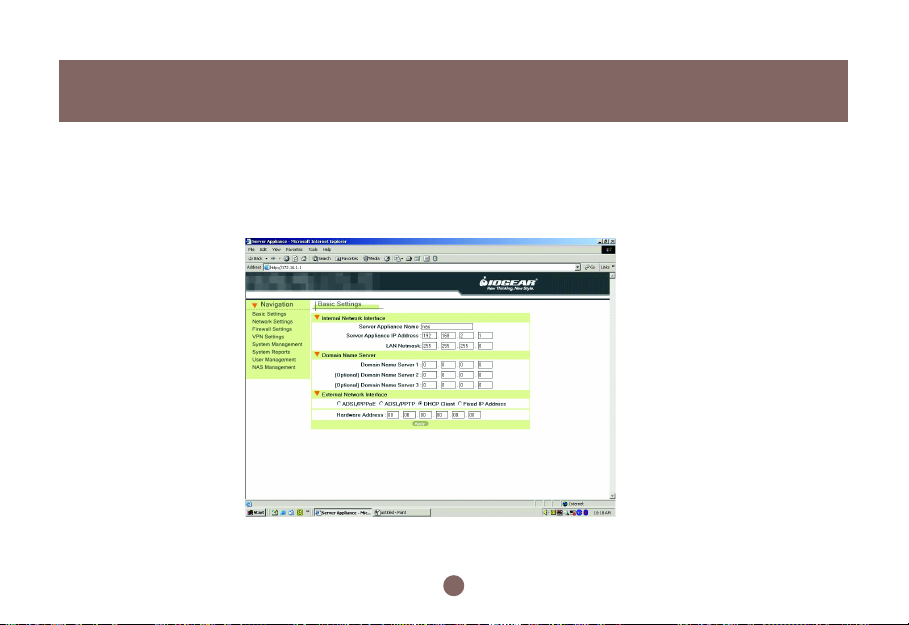
2.4 Web-Based Manager – Basic Settings
Start to configure your network environment by clicking Basic Settings in the left menu. The Basic Settings
page is shown as (Figure 2.4a).
Figure 2.4a
18
Page 21
The Basic Settings page contains, Internal Network
Interface, Domain Name Server, and External Network Interface. We describe these settings in detail
in the following sections. You must click the Apply
button after you finish inputting the settings. You will
see a rebooting window as Figure 2.4b. During the
rebooting phase, do not turn off or unplug the BOSS™.
Installation
Figure 2.4b
19
Page 22
Installation
How the Router Works
The router implements an IP-sharing feature. With only one physical IP address to access the Internet it is
impossible for all computers within the home or office network to use the same IP address to gain access to
the Internet at the same time. However, using the BOSS™, all computers within the home or office network
can access to the Internet even with only one physical IP address. The router transforms one physical IP
address into a range of virtual IP addresses. Each computer within the home or office network will get a
virtual IP address to access to the Internet.
Internal Network Interface
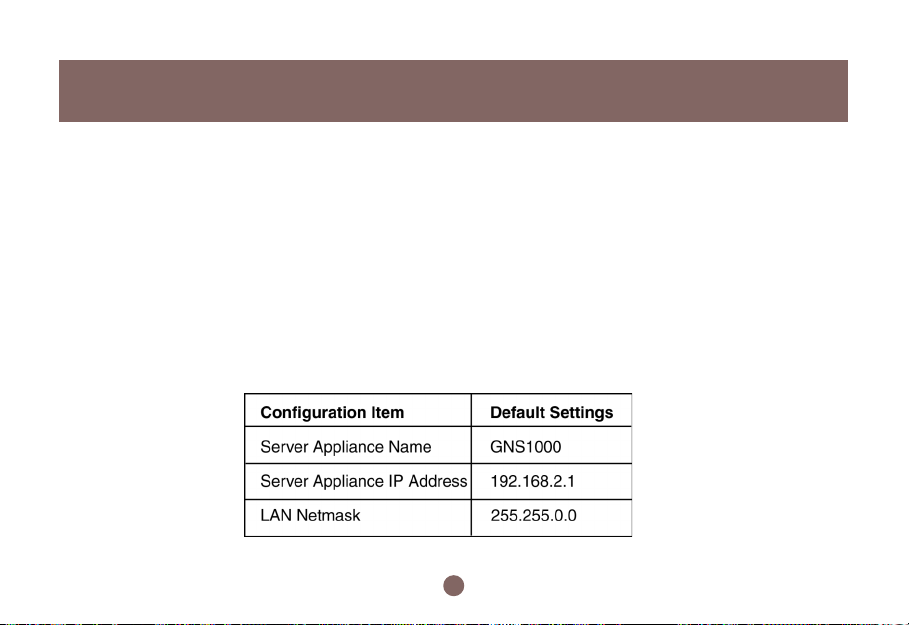
The default settings are:
20
Page 23

Installation
According to the default settings, we will assign the LAN to network “192.168.2.1” You can add more detailed
configurations later in section 4.1 DHCP Server settings.
For the Network Address Translation (NAT) application, the private network address should be set in the
following address range reserved by the Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA).
All BOSS™ default settings will appear within the window referenced on page 18. The settings should match
those listed in the table below.
Within the Basic Settings window, you may choose another Server Appliance Name, Server Appliance
IP Address, and LAN Netmask. Please enter any new information at this time. We recommend that you change
the name only and keep the rest of the default settings.
21
Page 24

Installation
Class Address Range
A Class 10.0.0.0/10.255.255.255
B Class 172.16.0.0/172.31.255.255
C Class 192.168.0.0/192.168.255.255
Domain Name Server
Your ISP may require a DNS (Domain Name Server) address. Please contact your ISP (cable or DSL provider)
for the needed DNS addresses. Once obtained, please enter the information into the DNS section of the Basic
Settings menu.
22
Page 25

Installation
External Network Interface
External network interface includes ADSL/PPPoE, DHCP Client and Fixed IP Address settings. You must
choose one of three ways to configure the external network interface. They are illustrated as follows:
Example 1: If you are connecting through a fixed IP address from the ISP. (Cable modem users)
Example 2: If you are connecting through a dynamic IP address from the ISP. (Cable modem users)
Example 3: If you usually enter a username and password to access the Internet. (DSL users)
23
Page 26

Installation
Example 1: Fixed IP Address Settings
If you have a fixed IP address obtained from your
ISP to access the Internet, please follow the steps
below:
1. Select the Fixed IP Address radio button.
2. Enter the Public IP Address.
3. Enter the External Gateway.
4. Enter the External Netmask.
5. Click the Apply button.
24
Page 27

Example 2: DHCP Client
Installation
If you have a dynamic IP address provided by your
ISP to access the Internet, please select the DHCP
Client radio button. Once the external IP address is
obtained via the DHCP protocol, there is no need to
give an External IP Address, External Gateway
Address, or Netmask. The DHCP server will
dynamically assign these fields. In general, you
should choose this option if you are connecting the
BOSS™ to a cable modem.
Some cable modem connections need you to
provide a specific hardware address. If this is the
case, you should fill in the hardware address that
you gave your ISP provider into the Hardware
Address field to override the original hardware
address. However, it does not update the or iginal
hardware address stored in EEPROM.
If you would NOT like to override the hardware
address, you should set each field of the Hardware
Address to zero “00” (default setting).
25
Page 28

Installation
Example 3: ADSL Connection
Most ADSL connections do not give you a fixed
IP address. In this case, you must enter the
user name and password provided by your ISP
for authentication. Please follow the steps below.
Please select the ADSL/PPPoE radio button.
1.
In ADSL/PPPoE Setting: Enter the User
2.
Name and Password.
In the Advanced Setting selection in the left menu:
3.
You can enable or disable the Connect-On –
Demand function. Please choose the Disable
radio button to disable this function or choose
the Enable radio button to enable it. If you enable
the Connect-On-Demand field, the BOSS™
will disconnect if the link is idle for the number of
minutes specified in the Idle-Time field.
4.
Click the Apply button to save your settings
or click the connect button to connect
immediately.
26
Page 29

Installation
After completing your configuration, each time the BOSS™ boots, it will try to connect with your ISP and the
ISP will assign the BOSS™ an external IP address. If you would like to connect immediately, you can click
on the Connect symbol. Once successfully connected, the Status field should reflect this. If the Status is still
the same, check to make sure that the username, password, cables, etc. are all correct
ADSL/PPTP Client Setting
If your ISP provides a PPTP server, you could set
up the PPTP client here.
Please follow the steps:
Select the ADSL/PPTP radio button.
1.
2.
Enter the user name. (You get this from your ISP)
Enter the password. (You get this from your ISP)
3.
Enter the IP address of your computer in My IP
4.
Address.
Enter the IP address of the server in Server IP
5.
Address.
In the following chapters, we will cover more
details in configuring your BOSS™.
27
Page 30

Configuration Hierarchies
Configuration Hierarchies and
Power Management
This chapter gives you an overview of all the
configuration options available. The BOSS™ is a
multifunction product. Section 3.1 explains the
corresponding settings for each function. Section 3.2
describes the power management in detail.
3.1 Overview of Configuration Menu
There are eight main categories in configuration
menu, Basic settings, Network settings, Firewall
settings, VPN settings, System management,
System reports, User management and NAS
management. Each item has advanced configura-
tions. See
Figure 3.1.
Figure 3.1
28
Page 31

Power Management
3.2 Power Management
We divided the power management function into three parts. There are Power Down, Wake on LAN, and Hard
Disk Standby.
We describe each part below in detail.
Power Down
You can turn the power down in several ways:
• Power Down by Web
Please select System Management -> Administrator
Settings. In Power Down field, select the
Enable radio button and then click the Apply
button. (Figure 3.2a)
• Power Down by power button
Please click the power button.
• Prompt Power Down
Please press the power button for at least
4 seconds.
Figure 3.2a
29
Page 32

Power Management
Wake On LAN (WOL)
The WOL function allows remote users on the
network to turn on the BOSS™. Please note that the
power adapter is connected to the BOSS™ and
plugged into a power outlet.
Hard Disk Standby
If the hard disk is idle for a while, it can enter Standby
Mode to reduce the consumption of power. In the left
menu, select NAS Management -> HD Initialization
Wizard, in HD Power Management Setting, please
select the time in Turn Off hard disk field (Figure
3.2b). If you select ‘none’, the hard disk will not enter
standby mode even it is always idled. If you select ‘5
Mins’, the hard disk will enter the standby mode once
it is idled more than five minutes. You could also refer
the setting in Section 10.1.
Figure 3.2b
30
Page 33

To Configure Your Network Settings
When you select Network Settings in the left menu
of the web page, five configuration options appear:
DHCP Server, IP Alias, Multiple NAT, Route Settings
and DDNS. Please refer to the corresponding
section for these configurations.
Network Settings
31
Page 34

Network Settings
4.1 DHCP Server Settings
In DHCP Server settings, we assign the range of
the virtual IP addresses for the four LAN ports of
BOSS™. All devices connected to the LAN ports of
BOSS™ will be dynamically assigned the IP
addresses within the range. You can either enable
the DHCP server or disable it in this screen also.
To Enable the DHCP Server
If you do not have a DHCP server on your
network,
1. Select the Enable radio button. (This is already
enabled by default).
2. Enter a number in Lease time field.
3. Enter the IP address range 1 as “192.168.2.2”
and “192.168.2.250” (default).
4. Enter the IP Address Range 2; otherwise enter
“0” in each field.
5. Enter the IP Address Range 3; otherwise enter
“0” in each field.
6. Enter the IP Address Range 4; otherwise enter
“0” in each field.
32
Page 35

Network Settings
7. Click the Apply button.
When DHCP server is enabled, it will allow DHCP
clients to obtain their network configuration from the
unit. In the figure above, the IP address range of
192.168.2.2 to 192.168.2.250 is dynamically assigned
to individual DHCP clients. The DHCP client may be
assigned an IP address like “192.168.2.XXX”. The IP
address “192.168.2.1” cannot be assigned as it is not
in the range and is also assigned to BOSS™ under
Basic Settings. If you assign another network (e.g.
172.16.2.XXX) to IP address ranges 2, 3, 4, please
refer to section 4.2 for further IP Alias setting. When
no other IP address ranges are assigned, a zero
value should be filled in to indicate that no other IP
addresses are available for assignment.
To Disable the DHCP Server
If you already have a DHCP server on your
network, or you do not have DHCP server on your
network, but you would like to assign a static IP
address to each device connected to the LAN
port of BOSS™.
1. Select Disable radio button
2. Click the Apply button. Or
1. Select Disable radio button.
2. Assign a static IP address to each device
connected to the LAN port.
For example, you have four PCs, PC1, PC2, PC3
and PC4 connected to the LAN port. You must
assign a UNIQUE static IP address i.e.
“192.168.2.34”, “192.168.2.25”, “192.168.2.18”,
“192.168.2.108” to PC1, PC2, PC3 and PC4
respectively. Notice the static IP addresses
assigned are all in the same network with BOSS™.
In Basic Settings, we set “192.168.2.1” as the
private IP address of BOSS™. Therefore, the
network it belongs to is “192.168.X.XXX”.
33
Page 36

Network Settings
4.2 IP Alias
In Basic Settings, we’ve set the private IP address of
BOSS™ as “192.168.2.1”. We will assign the LAN
ports of BOSS™ to the network of “192.168.X.XXX”.
In DHCP server settings, we’ve set the IP addresses
of the LAN as “192.168.2.XXX”. “192.168.X.XXX”
includes “192.168.2.XXX”, and therefore is considered
to be in the same network. There is no problem if the
network interface contains only one IP address range,
but if you want to assign other IP addresses like
“192.168.2.X” to the LAN, then there is an issue.
“192.168.2.X” and “172.16.2.XXX” are not in the same
network. We need IP Aliasing to resolve this issue.
IP Alias allows one network interface to contain more
than one network. It allows the additional network
“172.16.2.XXX” to be recognized by the BOSS™.
Please follow the steps to add another network:
1. Enter “172.16.2.1” in IP Alias 1.
2. Enter “255.255.255.0” in Netmask of IP Alias 1.
3. Click the Apply button.
Note that the IP Alias 1, 172.16.2.1 is assigned to the
BOSS™ and the network is “172.16.2.XXX”.
For additional IP addresses of the internal network
interface to be accepted, enter the other IP address
in IP Alias 2 and IP Alias 3. Enter “0” in each field if
none
34
Page 37

Network Settings
4.3 Multiple NAT
If you get several fixed IP addresses from your
ISP and the ISP restricts the bandwidth for each
fixed IP address, you have to prevent the network
packets from always sending on the same IP
address and the other IP address to sit idle.
Multiple NAT solves this and allows you to
increase the bandwidth. Multiple NAT allows you to
dispatch your network packets evenly to these IP
addresses provided by ISP.
1. Enter the Internal IP Range 1, e.g.
“192.168.2.1/24”. It means the network is
“192.168.2.XXX”
2. Enter the External IP Range 1, the IP address
range you get from your ISP.
3. Enter the Internal IP Range 2, e.g.
“172.16.2.1/24”. It means the network is
“172.16.2.XXX”.
4. Enter the External IP Range 2, the IP address
range you get from your ISP.
35
Page 38

Network Settings
5. Or enter “0” in each field for non-setting
multiple NAT.
6. Click the Apply button.
After you configure the Multiple NAT on the group of
fixed IP addresses, it can increase the bandwidth. The
Internal IP range you entered will be routed to the
corresponding External IP range.
4.4 Route Settings
36
Page 39

Network Settings
The Route Settings page gives you a way to set
the static route. You have to set the static route if
you would like to route your packets to the
specific network and the router of the destination
network does not support RIP (Routing Information Protocol).
If the router supports RIP, it will automatically
exchange routing information with BOSS™ and it
is not necessary to set a static route. Please
refer to the steps and figures to set a static route.
1. Select Enable radio button in Routing Setup.
2. Enter the network in Destination network
column. (e.g. “172.16.6.0/24”)
3. Enter the IP address of the gateway in
Gateway column. (e.g. “192.168.2.249”)
4. Enter the number in the Hop count column.
The number means how many gateways you
have to pass through.
In the figures, the destination network is “172.16.6.X”.
And the packets will be route in or out of the destination network through the gateway “192.168.2.249”.
4.5 DDNS
37
Page 40

Network Settings
Dynamic DNS service allows you to assign a fixed machine name to a dynamic IP address. Dynamic DNS
provides you with the ability to change the IP address of your domain name to point to your dynamically
allocated IP address. This allows you to host your server on a changing IP address.
Please follow the steps below to setup DDNS.
1. Select Enable radio button in DDNS Client Service field.
2. Select the DDNS service provider.
3. Enter the User name. The user name you use to log in to DDNS service.
4. Enter the password. The password you use to log in to DDNS service.
5. Enter the Host name. The host name you register in DDNS service.
6. Click the Apply button.
Every time your computer comes online, you tell the DDNS server what your current address is. Other
users, through DNS, will be sent to the right place.
38
Page 41

When you select the “Firewall Settings” item in the
left menu of the web page, four configuration items
appear, including: Virtual Server settings, URL Filter,
IP Filter setup and Denial of Service. Please refer to
the corresponding section for each of these items.
Firewall Settings
5.1 Virtual Server SettingsSetting up your Firewall
39
Page 42

Firewall Settings
The Virtual Server Service is a way to simulate multiple servers on the intranet. You have several IP
addresses within your LAN; however, inter nal IPs
are not visible to others outside of your network.
When a server is placed on a home or office internal network, that need to be seen by others outside
of the internal network, basic forwarding rules need
to be established, allowing others to see each server
behind the Firewall. To allow this, you will need to
setup a Virtual Server for each server you wish to be
seen on the Internet (by others outside your network). Doing so will allow users from the Internet
access to the specified servers, also allowing you to
give different IP addresses to each server on your
network.
For example, the users accessing port 21 will be
directed to “192.168.2.1”. “1 92.168.2.1” which could
be an FTP server. Users accessing por t 80 will be
directed to “192.168.2.2”, an HTTP server on the
network. For users outside your internal network,
they will feel like many services are running on a
single host. To set up your Firewall, please follow the
steps on Page #12 to setup your Virtual Server s.
1. Select “Virtual Server” from the FireWire Settings menu.
2. Select the “Enab le” radio button in the Virtual Server.
3. Enter an IP Address that will be used for the
selected virtual server. (i.e. 192.168.2.2)
4. Select the virtual servers Protocol. Protocol is application
specific; most servers will use TCP, however, using both
will increase the chances of the correct settings being
chosen. Now select the desired protocol; choose “both”
if you are unsure.
5. Now select which port your Virtual Server will use.
(i.e. port 21)
6. Please repeat the steps above to establish more
virtual servers.
7. Click the Apply button, to activate your new settings.
40
Page 43

Firewall Settings
5.2 URL Filter Setup
The URL Filter function is used to restrict internal users
from accessing specific URL locations or web sites. If
the Site 1 is given as www.yahoo.com, any hosts in the
intranet will not be allowed to connect to www .yahoo .com.
Please follow the steps to enable this feature:
1. Select the Enable radio button in URL Filter.
2. In Site 1, please enter the URL address you wish to
block interal users from accessing.
3. To block additional web addresses , repeat step 2 for
adding new URL’s to the site 2 ~ site 10 fields.
4. Click “Apply” once complete.
If you do not wish to restrict access to the intranet or
Internet, please select the Disable radio button in the
URL Filter.
41
Page 44

Firewall Settings
5.3 IP Filter Setup
The IP filter function is similar to URL Filter. It provides
further restrictions in access permission. URL Filtering only blocks port number 80 (HTTP) on servers
outside of your own network. In IP filtering, you can
assign a group of IPs to be restricted. You can block
four individual ports or a range of ports at the same
time, so the specific group of intranet hosts cannot
connect to these ports.
To block IPs using the IP filter, please follow the
steps below.
1. Select the “Enable” radio button in the IP Filter.
2. Enter the IP address range in the format “x. x. x. x /
x” (e.g. “172.168.1.0/24”, to restrict this IP group)
3. Select the Protocol of the IP you wish to block. If
you are unsure, select both.
42
Page 45

Firewall Settings
4. Enter the port number of the ports you wish to block
from the selected IP.
There are four fields you can enter port numbers into,
in any order or combination.
5. To block more than 4 ports, enter a range of port
numbers (if any) in the last field.
5.4 Denial of Service
It is highly recommended that the DoS Protection
feature be enabled to prevent attacks on the
network. However, if you allow someone to
manage the router from outside, you should
either disable Detect SYN Flood Attack or
increase the TCP flow. Otherwise, the configuration web pages will not be sent smoothly
43
Page 46

VPN Settings
How to change your VPN settings
VPN (Virtual Private Networking) provides for secure
communication between two separate networks
without using a dedicated leased line. In order to
achieve this functionality, a secure tunnel must be built
between the two sites for secure communication over
the Internet. The BOSS™ supports the two most
popular protocols, IPSec and PPTP.
IPSec provides encryption and authentication
services at the IP layer. Working at this level, IPSec
can protect any traffic carried over IP unlike other
encryption methods that only protect a particular
higher-level protocol.
PPTP (Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol), is a PPPspecific protocol proposed by Microsoft. The BOSS™
implements a PPTP server. The remote user can connect to the PPTP server and access a local host
behind the PPTP server.
When you select the VPN item in left menu of the web
page, IPsec and PPTP configuration options will
appear. Please refer to the corresponding sections for
these configurations.
44
Page 47

VPN Settings
6.1 IPSec Settings
Sometimes there is a need to transfer commercial information from a branch office through the Internet. The information being transferred cannot be sent over the Internet
without encryption. The best solution for most customers
is to establish a secure tunnel between the company and
branch office. IPsec implements this function through the
use of a “pre-share key.” The pre-share key is known
both in main office and branch locations. Please follow the
steps below to build the tunnel:
Please follow the steps below to build a VPN tunnel:
Local Settings:
1. Select the “Enable” radio button in IP Security.
(Figure 6.1a)
2. Enter the Local ID. For identifying this host.
3. Click the Apply button.
4. The IPSec Tunnel List is empty by default. Please
click the “NEW” button to establish a new tunnel.
You will be taken to the IPSec Settings page.
It includes the IPsec tunnel settings and Remote
Host Settings. (Figure 6.1b )
5. In the IPsec tunnel setting: Enter a Connection Name.
(e.g. vpn1). The remote side must also enter the
same connection name to identify the connection.
6. Select the “yes” radio button in Start on boot field.
This will establish the connection upon a system
startup. Select the Disable radio button to a VPN.
7. Enter the Preshare key. The branch has to use the
same Preshare key. See page 44 for more
information on Preshare Keys.
8. Enter a number of hours you wish to have each
VPN session open within the IPsec key
Lifetime field.
45
Page 48

VPN Settings
9. In Remote Host Setting: If the remote computer has
a fixed IP address (e.g. 10.0.0.9). Please select
the Fixed IP radio button.
10. Enter the remote computer’s IP address within the
Remote IP field. (e.g. 10.0.0.9)
11. Enter the remote computer’s Subnet.
(e.g. 172.17.0.0)
12. Enter the Remote Netmask of the remote
computers. (e.g. 255.255.0.0)
13. Now click the Apply button.
14. Please check the IPsec Tunnel List. In the Action
column, click the link up button to connect
immediately, or click the remove button to
remove the tunnel.
Remote Settings:
Please repeat the steps above to create the tunnel.
Note in step 9, the Remote IP field, enter the fixed IP
address of the main company and the corresponding Subnet and Netmask.
Preshare Key:
The Preshare Key field is a secret key that is used to
identify the communicating host during the phase 1
IKE negotiation. It is also used idenfity the users,
much like a password. Simply enter a string of text
(i.e. isakmpkey) into the Preshare key field on both
computers. Each computer will share the same
preshare key. The IPSec Key Lifetime specifies how
long the secret key will be exchanged. If zero value is
given, it will pick up the default setting. For the Remote Host Setting, you can choose the remote type
of communication for a fixed IP gateway or a dynamic IP gateway.
The IPSec Tunnel List displays information for each
tunnel that you build.
46
Page 49

The Name field is the connection name; the Gateway field is the IP address with which the remote
and local computers will communicate; the Destination Subnet field specifies the sub-network address
with which computers will communicate; the Status
field shows you whether the current link is established or not. If the current link is not established,
you can click the Link Up button in the Action field to
request the tunnel to be established. If you need to
re-configure the setting, the Modify button will help
you adjust your settings. When you no longer require the tunnel, click the Remove button and the
corresponding entry will be removed from the table.
VPN Settings
Figure 6.1a,b,c
47
Page 50

VPN Settings
6.2 PPTP Settings
For most companies, the PPTP server creates a secure connection that a remote user can access a local
computer within the company. The remote user has to
run a PPTP client and connect to the PPTP server. The
PPTP server has to validate the remote user as being in
the User List in section 9.1. The server certifies the
PPTP client with a username and password. After passing the certification, the server will assign a private IP
address to the client. The remote user will be treated lik e
a member of the LAN and can access the local hosts
inside the company. To run the PPTP server on the local
side, please follow the steps below:
Local Side:
1. In PPTP Settings page: Select the Enable button in
the PPTP Server field. (Figure 6.2a).
2. Enter the private IP address of the server in the Server
IP Address field.
3. Enter the Client IP Range. The server will assign
the IP to each client within the range.
4. Click the Apply button.
Figure 6.2a
48
Page 51

Manage Your Network Users
The BOSS™ provides a client/server environment for
users to share files over a network. File sharing works
by authorizing the users or groups to access folders by
their username and password. When we create a new
shared folder, we must create a new user/group list
from the current users/groups. When a user/group tries
to access the folder, the system will check the list of
valid users for the folder. If the user/group is included in
the list, the user/group then has permission to access
the folder.
The BOSS™ provides a concise interface to manage all
users and groups for folder access. When you select
User Management from the left menu of the web page,
two configuration items appear including User and Group
settings. Please refer to the corresponding section for
these configurations.
User Management
49
Page 52

User Management
7.1 User
For file sharing to work, we have to allow users and/or
groups. We create the user accounts here. The “admin”
and “guest” accounts are in the system by default.
Please follow these steps to create new users:
1. Click the NEW button in User Management.
(Figure 7.1a)
2. Then the Add/Modify Users page shows up.
3. Enter the Username. (e.g. peter)
4. Enter the Password.
5. Click the Apply button. Then you will be taken back
to the User Management page where the user you
just created will appear on the Users List.
6. Modify or to delete users in the same way. Please
click the corresponding buttons.
7. Please follow the steps above to add more users.
(e.g. Mary, Peter, Sophia, and Tom.)
Figure 7.1a
50
Page 53

7.2 Group
After creating the users, you can categorize the users
into different groups.
In the following example, we will assign Mary to the
teacher group and Tom and Sophia to the student group.
The group management interface is similar to user management. The “everyone” group is there by default. To
create new groups, please follow these steps:
1. Click the NEW button in Groups Management.
2. Then the Add/Modify Groups page shows up. Enter
the group name. (ex. Teacher.)
3. To include more users in this group (e.g. Teacher),
please select the user in the System Users List
(e.g. Mary.)
4. Then clic k the left arrow b utton to add the user to the
Group Members List and vice versa. (e.g. “Mary”
in System Users List will be moved to Group
User Management
members List. Now Mary belongs to the Teacher
group.
5. Click the Apply button. You will be taken back
to the Group page.
6. To create another group, please repeat the steps
above. (e.g. We created a “student” group and
chose “Tom” and “Sophia” to be the members of
the group)
7. The group you created is now in the Groups List.
51
Page 54

User Management
52
Page 55

NAS Management
Setting Up Your BOSS™
When you select the NAS Management item from the
left menu of the web page, three configuration items
appear including; HD Initialization Wizard, Advanced
and File Sharing. Please refer to the corresponding
section for the configuration details.
8.1 HD Initialization Wizard
The first time you use the NAS feature, you must initialize the hard disk. The NAS provides an easy way to
initialize the hard disk via the wizard. Follow the wizard
in order to properly setup the drive. Select the HD
Initialization option and refer to the steps below:
1. Select the Enable radio button and click the Apply
button in S.M.A.R.T. field.
2. Within the HD Power Management Setting, you
have the ability to select the duration of time before
the drive is set to an idle status. This will help
preserve power and increase the drives longevity.
Please select an idle time now.
3. In Hard Disk Status, click the Initialize button in the
Action column following the hard drive description.
4. A warning window shows up. Please click the OK
button (Figure 8.1b).
53
Page 56

NAS Management
The Step 1 page should now appear. To set the
5.
information for file sharing, please enter the
workgroup name (make sure this matches the
workgroup on your network), the computer description and share folder name. You can create more
share folders after the initialization process.
6.
Click the Next button to continue HD initialization.
(Click the Cancel button to leave the HD initialization
process.)
7.
The Step 2 page should now appear. In this page we
set which user(s) or group(s) can access the shared
folder. Please refer Chapter 9 to establish the users
and groups.
8.
In the Selection field, select the Users radio button
to share the folder by users or select the Groups
radio button to share by groups.
Click the Next button. At this point, the system starts
9.
to initialize the hard disk. A percentage bar shows
the progress. Note: Users without Java will get an
error message. You can ignore and return to the
main wizard screen to see the current percentage.
It will not update unless you refresh your browser.
When the formatting is finished, it shows “Initializa-
10.
tion – Complete.”
11.
In NAS Management -> File Sharing, the shared
folder you created above should now appear on
the Share Name List.
The HD status should display the hard drive information. It includes the model name, serial number,
size, S.M.A.R.T, status of the HD and the Initialize
button. The S.M.A.R.T. field is disabled by default
and the message in the S.M.A.R.T. column is “Disable.” You can enable the S.M.A.R.T function if your
drive supports this. It will report to the system when
the HD is broken. The message in the S.M.A.R.T
column will change to “Pass” ( Figure 8.1a).
To modify and/or create more share folders, please
refer to section 8.3.
54
Page 57

Figure 8.1a
Figure 8.1b
NAS Management
8.2 Advanced
In NAS Management -> Advanced settings, there are
three protocols for different OS platforms. By default, all
protocols are enabled, but for security reasons users
may want to disable specific protocols.
• For MS-Windows Users
Please follow the steps below:
1. In MS-Windows File Sharing field: please select
the Enable radio button.
2. Enter the Workgroup Name and Computer
Description.
3. Click the Apply button (Figure 8.2a).
55
Page 58

NAS Management
• For Mac Users
Please follow the steps below:
1. In Apple File Sharing field, please select the
Enable radio button.
2. Enter the Name in Apple Zone field.
3. Click the Apply button.
• For Unix-like Platform Users
Please follow the steps below:
1. In Network File System field, please select the
“Enable” radio button.
2. Click the Apply button.
3. Click the New button in NFS Mapping List.
4. A NFS Mapping page will show up.
5. Enter the Remote UID.
6. Enter the Remote IP.
7. Select the Mapping User.
8. Click the Apply button. ( Or click the Cancel
button for none)
56
Page 59

NAS Management
You will go back to the Advanced Setting page. Please
check the NFS Mapping List in NFS Setting section. The
mapping rule you created is in the list.
• FTP Setting
Please select the “Enable” radio button in FTP Server
field and click the Apply button.
To enable the FTP ser ver, you also have to enable
the file sharing and create the user’s account and
password.
8.3 File Sharing
For file sharing, you must create users and groups
first. If already complete, it is time to create the share
folder and assign users/groups. To assign the users/
groups to a folder, please follow the steps below:
The folder created after the HD initialization should
1.
be on the Share Name List.
Click the “NEW” button.
2.
The Files Access Control page should now appear.
Enter the folder name in the Sharing Name field.
3.
(e.g. party) The sharing name is the name of the
folder you would share over the network.
4.
Select one of the radio buttons in the Selection field.
(e.g. select the “Users” radio button) Select the
“Users” radio button if you are allowing access to
the folder based on users. Select the Groups radio
button if you are allowing access to the folder based
on groups.
57
Page 60

NAS Management
5.
In the Method field, select the “Write” method if you
are allowing the user/group to read and write to the
folder. Select the “Read” method if you only want user/
groups to read the folder.
Select the user in “Denying Users List”, then click the
6.
“left arrow.” button to add the user to the “Allowing
Users List” and vice versa.
Click the Apply button. You will be taken back to the
7.
File Sharing page.
8.
Check to see that the folder you created appears on
the Share Names List.
There should now be “Add”, “Remove”, and “Modify”
9.
buttons. They are used to create, delete, or to modify
the shared folders in the Share Names List.
After setting up file sharing, you can access the files
and folders in the NAS through the Network Neighborhood. You can also search for the NAS in the net-
work by the hostname that is set under Basic settings.
Once you select the name in the Network Neighborhood, an authentication window will appear.
58
Page 61

Please enter the user name and password that was
created in section 9.1.
NAS Management
59
Page 62

System Management
Instruction to BOSS™ Management
When you select the System Management item in the
left menu, four configuration items appear including;
Administrator Settings, Event Report Settings,
Firmware Update, Time Settings and SNMP. Please
refer to the corresponding section for these configuration details.
9.1 System Management Administrator Settings
In Administrator Settings, you will find the basic
administrator functions. The settings are easily
modified and managed by the administrator. They are
described on the next page:
60
Page 63

System Management
New Password: The administrator can change the administrator password here. Please enter the new
1.
password you would like to change to. Note that you must fill the new password in both Password change
and Password confirmation fields. If both fields are not the same, the page will not be submitted.
2.
FTP Server: Please select the Enable radio button to establish the FTP server, or select the disable radio
button to turn off the FTP feature.
3.
Confirm New Password: Please enter the new password again.
4.
External Admin.: This feature allows administrators to access the web based configuration menu from the
Internet. The default setting for this feature is disabled for security reasons.
5.
External Admin. Port: Defines a port for the remote administrator to connect to.
Restart device: This function reboots the Network Server Appliance. Select the Enable radio button to
6.
restart BOSS™. The default setting of the function is disabled.
7.
Clear event log: This function is used to clean the system history that is listed in Event Report (section 8.2).
If you choose the No radio button, the event record never clears, even when you reboot the system.
8.
Clear DHCP lease: This function is used to clean the DHCP Lease record listed in section 8.4. Please choose
the Yes radio button to clean the DHCP lease report.
9.
Restore Factory default: To recover the factory settings, please choose the Yes radio button and the factory
defaults will be loaded. Click the Apply button.
61
Page 64

System Management
9.2 Event Report Settings
The Event Report Setting is used to send the admin-
istrator an e-mail alert once an event occurs on the
system. If you select the Disable radio button in Alarm
Mail, the system will not send an alarm to anyone. To
enable the function, please follow the steps:
1. Select Enable radio button in Alarm Mail.
2. Enter the IP Address or Domain Name of the Mail
Server. (e.g. 111.22.33.4 or mail.your.net)
3. Enter the e-mail address (e.g. admin@mail.your.net)
that you want the system to send e-mail to if an event
occurs.
4. Select “Normal” or “Warning” in Alert Level to indicate
when to send the e-mail. If you select “normal,”
events with a normal level will induce the system to
send e-mail to the administrator’s e-mail.
5. Click the Apply button.
62
Page 65

System Management
9.3 Firmware Update
In Firmware Update, the current firmware version is
shown. You can select a new firmware image to update
the unit. If you would like to upgrade your firmware, you
should download the image for the current model and
save the image on your local drive. If the image is already on your drive, please follow these steps:
1. The current fir mware version is shown as 1.06.
2. In Firmware Update, click the Browse button. A
window (see Figure 9.3a) should pop-up. Please
select the image file you have downloaded. After
you confirm your selection, click the open button.
3. The image will be uploaded to the Networ k Ser ver
Appliance It performs some checks on whether
the image is valid. If the image is wrong, it will not
be updated.
Note: Do NOT shutdown the unit or remove the power
source during a firmware update.
Figure 9.3a
63
Page 66

System Management
9.4 Time Settings In Time Settings, you can adjust the system time. The
fields in Time Settings are described below:
1. YY/MM/DD format. Please enter the year in the first
field then select the month and date.
2. HH:MM:SS format. Please enter the hour, minutes
and seconds respectively.
3. Click the Apply button.
Once the system time is set, the system will record the
proper time for system events in the log.
64
Page 67

System Management
9.5 SNMP
The SNMP agent allows users with SNMP client applications to conveniently inspect the network status
of NSA. Please follow the steps below to setup the
SNMP agent.
1. Select the Enable radio button in the SNMP
Agent field.
2. Enter the Community Name. Note that the agent side
and the client side must use the same community name.
3. Enter the contact information in System Contact field.
For example, the phone number or the email account
of the administrator.
4. Enter the location of the unit the System Location field.
Click the Apply button.
65
Page 68

System Reports
When you select System Reports in the left menu of
the web page, four configuration items appear including; System Information, System Log, URL Log, and
DHCP Lease Report. Please refer to the corresponding section for these configuration items.
10.1 System InformationGenerating System Reports
The System Information displays some useful infor-
mation about the system. It shows the firmware version,
the system up time and the internal and external network connections. The BOSS™ has one WAN port and
four LAN ports. The WAN port belongs to the external
66
Page 69

System Reports
network interface and the LAN port belongs to the internal network interface. They are described as below:
• Firmware Version: 1.06
• The system up time
• IP Address: the IP Address is shown as your current setting. In Chapter 2, section 2.4, the Basic setting, we
already configure the external interface in one of the three ways, ADSL/PPPoE, DHCP client and Fixed IP
address. In Chapter 4, section 4.1, DHCP Server, we assigned the IP address range to the internal network
interface.
• Hardware Address: Ethernet hardware address
• Netmask: corresponding to the network.
• Max. Transfer Unit: maximum bytes of a packet.
• Tx/Err Packets: e.g. 309/0, means you sent 309 packets and there are “0” packets with errors.
• Rx/Err Packets: e.g. 3573/2, it means you received 3573 packets and there are 2 error packets.
• Link Status: Shows the current transfer speed. e.g. 100Mbps, full duplex.
• The refresh button: Click the refresh button to see if anything has been updated.
If your external connection is not set to a fixed IP address, you can check whether the Network Server
Appliance has obtained an IP address after booting. If there is no external IP address, you should check your
network connection or environment settings.
67
Page 70

System Reports
10.2 System Log
The System Log function reports the system history. It
shows the time that the event occurred, the event
level and a description of the event in the Message
column. If there is an error, the event report will help
determine where and/or what the error is. You can
clear the records under the Administrator Settings.
Please refer to Section 9.1, Clean Event Log.
10.3 URL Log
The URL Log function records the recent connections
for each client. If you would like to view what the user is
browsing, you can click the corresponding Destina-
tion URL in the right most column.
68
Page 71

10.4 DHCP Lease Report
The DHCP Lease Report function reports all leased IP
provided by DHCP server. From this page, you can find
out which host was assigned to which IP address. You
can clear all the records through administrator settings.
Please refer to the Section 9.1, Clean DHCP Lease.
System Reports
69
Page 72

Care & Handling
Your IOGEAR® BOSS™ is a high performance Network Server Appliance. The head that reads the
information on the installed Hard Drive is a fragile piece of technology. Therefore, care must be taken not
to bump the BOSS™ while it is operating. Care must also be taken not to bump the BOSS™ excessively
when the drive is turned off.
To insure maximum reliability of the BOSS™, please follow the guidelines listed below:
• DO NOT block the air circulation around the vents of the BOSS™.
• DO NOT move or bump the BOSS™ while it is operating.
• Keep all cables out of aisles and off desktops where they can be hooked and pulled.
• Keep the BOSS™ firmly secured in the shipping container when shipping the drive.
• Keep the environment around the drive clean and free of excessive dust and chemicals.
• Use a damp cloth to clean the BOSS™. NEVER put cleansers directly on the BOSS™ case.
• Use surge protectors with the BOSS™.
• DO NOT expose the BOSS™ to extreme temperatures.
• DO NOT expose the BOSS™ to direct sun light for extended periods of time.
• DO NOT get the BOSS™ wet.
• DO NOT place the BOSS™ in an area with an excessive amount of dirt.
70
Page 73

TroubleShooting
Basic TroubleShooting
BOSS™
• Make sure you have Critical Updates from the Microsoft® Website at http://windowsupdate.microsoft.com;
then, click on “Product Updates,” select the latest Critical Update package for your Windows® OS, and
then click “Download.”
• Apple users please ensure you have the latest version of your OS. Go to www.apple.com for more information.
• Make sure the drive is turned on before you start-up your computer.
• Make your new BOSS™ the only device hooked into the Network.
• Do not use a hub or repeater in connecting your drive to the computer.
• Use the cable that was shipped with your BOSS™.
• Check all cable connections.
• Use other IOGEAR® cables if you have any extra.
Other Issues
At the very least, make sure your computer has all available updates provided by the manufacture of
both your hardware and software. Updates can be found at http://www.versiontracker.com or
http://www.download.com.
Upgrade your CPU firmware to the latest revision. Please read all text on the download pages to
determine which firmware update is appropriate for your computer.
71
Page 74

TroubleShooting
Notes:
All URLs are subject to change. If the URLs listed in this manual are no longer valid, you can find the
majority of necessary updates at http://www.versiontracker.com or http://www.download.com.
Seagate Trouble Shooting Tip
Set up the jumper on the Seagate drive to the SLAVE position.
Contacting IOGEAR® Service Support
If you are still experiencing problems using your BOSS™ Drive, please follow the directions on pg. 73 on
how to contact IOGEAR®’s Service Support department for your technical support needs.
72
Page 75

Tec hnical Support
To help IOGEAR® customers obtain the highest level of performance from their BOSS™, IOGEAR®’s
Service Support team is available to answer your technical questions. Do not hesitate to call if you are
having trouble getting your drive to work correctly. Service Support can be reached at IOGEAR® from
8am to 5pm Pacific Standard Time, Monday through Friday or at the following address:
23 Hubble Drive
Irvine, CA 92618
You may also reach us online at www.iogear.com/support 24 hours a day.
Please be ready to give a brief description of the problem, and what you were doing when the problem
occurred, before calling Service Support. The Service Support representative will be able to serve you
much quicker if you are prepared to answer the following questions listed below.
1) What version of OS are you using?
2) What type of computer are you using?
3) Can the problem be reproduced? If so, what are the steps necessary to reproduce the problem?
4) When does the problem occur?
5) What have you already tried to get the problem resolved?
6) What is the purchase date and serial number of the drive?
7) Are you on a network? If so, what type of network is it?
8) Were any messages displayed on the screen when the error occurred? If so, what was the exact
wording of the message?
73
Page 76

Appendix
Default Setting Table
Configuration Item Default Settings
Administrator Username <empty>
Administrator Password admin
Internal IP address 192.168.2.1
74
Page 77

Power Button
Appendix
Description of LEDs Status Meaning
Power On Power On
Off Power Off
Heart-Beat Solid/Off System is not working
Flashing System is working
WAN/LAN On Link up
Link/Activity Off Link down
Flash The interface is transmitting/receiving packets
WAN/LAN On The network link is 100 Mbps
10/100 Mbps Off The network link is 10 Mbps
Throughput No LED on Current transfer rate is < 10KB/s
1 LED on Current transfer rate is > 10KB/s
2 LEDs on Current transfer rate is >50KB/s
3 LEDs on Current transfer rate is >100KB/s
4 LEDs on Current transfer rate is >500KB/s
75
Page 78

Specifications
Product Specifications
Function Specification
Power Consumption
Input Voltage
Connector Type
Supported Internal Drives
Storage Temperature
Operating Temperature
Operating Humidity
Dimensions
Case
Power Adapter
12V 3.0A
5 RJ/45 Ports
3.5" ATA 133 or equivalent
32~158°F (0~70°C)
68~122°F (20~50°C)
20~80% RH, (Non Condensing)
10.5 in. (26.67 cm) x 2.5 in.
(6.35 cm) x 6.25 in. (15.9 cm)
Aluminum/Plastic
76
Page 79

Radio & TV Interference Statement
WARNING!!! This equipment generates, uses and can radiate radio frequency energy and, if not installed
and used in accordance with the instruction manual, may cause interference to radio communications. This
equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class B computing device pursuant to
Subpart J of Part 15 of FCC Rules, which are designed to provide reasonable protection against such
interference when operated in a commercial environment. Operation of this equipment in a residential area is
likely to cause interference, in which case the user at his own expense will be required to take whatever
measures may be required to correct the interference.
77
Page 80

Limited Warranty
IN NO EVENT SHALL THE DIRECT VENDOR'S LIABILITY FOR DIRECT, INDIRECT, SPECIAL, INCIDENTAL OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES RESULTING FROM THE USE OF THE PRODUCT, DISK,
OR ITS DOCUMENTATION EXCEED THE PRICE PAID FOR THE PRODUCT.
The direct vendor makes no warranty or representation, expressed, implied, or statutory with respect to
the contents or use of this documentation, and especially disclaims its quality, performance, merchantability, or fitness for any particular purpose.
The direct vendor also reserves the right to revise or update the device or documentation without
obligation to notify any individual or entity of such revisions, or updates. For further inquiries please
contact your direct vendor.
78
Page 81

79
Page 82

®
Contact info.
23 Hubble • Irvine, CA 92618 • (P) 949.453.8782 • (F) 949.453.8785 • www.iogear.com
 Loading...
Loading...