INVT GD300L-2R2G-S2, GD300L-004G-4, GD300L-5R5G-4, GD300L-011G-4, GD300L-7R5G-4 Operation Manual
...Page 1

Goodrive 3 0 0 - L I F T S e r i e s I nver t e r
Page 2

Goodrive300-LIFT series inverter Preface
Preface
Goodrive300-LIFT (GD300L for short) series inverters for lifts are the new generation of lift-dedicated
inverters, which use the GD control platform for development based on CHV180 series inverters.
Applying advanced variable frequency vector control and modular interface design, the product
improves the security reliability, control performance, and ease of commissioning and features the
following:
Compatible with asynchronous and synchronous motors.
Starting torque compensation control with weighing sensors: implements slide prevention by
setting parameters.
Starting torque compensation control without weighing sensors: implements precise control on
gearless synchronous-tractor lifts, which achieves stable startup.
Static identification on initial pole angles of synchronous motors: For permanent magnet
synchronous motors, autotuning can be executed when the motors are static. This simplifies the
commissioning process and is applicable to commission the motors in mechanical connection.
S-curve function: Acceleration (ACC) and deceleration (DEC) S curve algorithms improve the
comfortability during motor ACC, DEC, and stop.
Brake and contactor control function: controls contactors and braking based on lift running logic,
enhancing lift security.
ASR optimization: ASR uses variable proportional and integral gain control, providing dynamic
response in startup and stop states and improving comfortability during constant-speed running.
Forced DEC handling: prevents top-hitting and bottom-clashing during the upward or downward
running of lifts.
Emergency operation function: implements stop at convenient leveling for the equipment of
UPS and storage battery input interfaces.
Energy-saving operation: implemented for using the optional RBU series energy feedback unit.
i
Page 3

Goodrive300-LIFT series inverter Contents
Contents
Preface ............................................................................................................................................ i
Contents ......................................................................................................................................... ii
1 Safety precautions ...................................................................................................................... 1
1.1 What this chapter contains .................................................................................................... 1
1.2 Safety definition .................................................................................................................... 1
1.3 Warning signs ....................................................................................................................... 1
1.4 Safety guide .......................................................................................................................... 2
2 Precautions for quick application .............................................................................................. 5
2.1 What this chapter contains .................................................................................................... 5
2.2 Unpacking inspection ............................................................................................................ 5
2.3 Application confirmation ........................................................................................................ 5
2.4 Environment confirmation ...................................................................................................... 5
2.5 Installation confirmation ......................................................................................................... 6
2.6 Basic commissioning ............................................................................................................. 7
3 Product overview ........................................................................................................................ 8
3.1 What this chapter contains .................................................................................................... 8
3.2 Basic principles ..................................................................................................................... 8
3.3 Product specifications ........................................................................................................... 9
3.4 Name plate ......................................................................................................................... 11
3.5 Type designation key ........................................................................................................... 11
3.6 Rated specifications ............................................................................................................ 12
3.7 Structure diagram ................................................................................................................ 12
4 Installation guide ...................................................................................................................... 14
4.1 What this chapter contains .................................................................................................. 14
4.2 Mechanical installation ........................................................................................................ 14
4.3 Wiring ................................................................................................................................. 20
4.4 Wiring protection ................................................................................................................. 26
5 Keypad operation procedure .................................................................................................... 28
5.1 What this chapter contains .................................................................................................. 28
5.2 Keypad ............................................................................................................................... 28
5.3 Keypad displaying ............................................................................................................... 30
5.4 Keypad operation ................................................................................................................ 31
6 Function parameters ................................................................................................................. 34
6.1 What this chapter contains .................................................................................................. 34
6.2 Function parameters ........................................................................................................... 34
7 Commissioning guidelines ....................................................................................................... 76
7.1 What this chapter contains .................................................................................................. 76
7.2 Wiring between the lift controller and inverter ...................................................................... 77
7.3 Setting basic parameters ..................................................................................................... 77
7.4 Debugging running .............................................................................................................. 79
7.5 Lift running mode ................................................................................................................ 82
8 Fault tracking ................................ ............................................................................................ 95
8.1 What this chapter contains .................................................................................................. 95
8.2 Alarm and fault indications ................................................................................................... 95
ii
Page 4

Goodrive300-LIFT series inverter Contents
8.3 How to reset ........................................................................................................................ 95
8.4 Fault history ........................................................................................................................ 95
8.5 Inverter faults and solutions ................................................................................................. 95
8.6 Common fault analysis ...................................................................................................... 102
9 Maintenance and hardware diagnosis ................................................................................... 108
9.1 What this chapter contains ................................................................................................ 108
9.2 Maintenance intervals ....................................................................................................... 108
9.3 Cooling fan ........................................................................................................................ 110
9.4 Capacitors .......................................................................................................................... 111
9.5 Power cable ...................................................................................................................... 112
10 Communication protocol ...................................................................................................... 113
10.1 What this chapter contains .............................................................................................. 113
10.2 Brief instruction to Modbus protocol ................................................................................. 113
10.3 Application of the inverter ................................................................................................ 114
10.4 RTU command code and communication data illustration ................................................ 119
10.5 Common communication faults ........................................................................................ 134
Appendix A Expansion cards .................................................................................................... 135
A.1 What this chapter contains ................................................................................................ 135
A.2 I/O expansion card ............................................................................................................ 135
A.3 Asynchronous motor PG card ........................................................................................... 137
A.4 Synchronous motor PG card ............................................................................................. 140
A.5 STO instructions ............................................................................................................... 143
Appendix B Technical data ........................................................................................................ 151
B.1 What this chapter contains ................................................................................................ 151
B.2 Ratings ............................................................................................................................. 151
B.3 Grid specifications ............................................................................................................ 152
B.4 Motor connection data ...................................................................................................... 152
B.5 Applicable standards ......................................................................................................... 153
B.6 EMC regulations ............................................................................................................... 153
Appendix C Dimension drawings .............................................................................................. 155
C.1 What this chapter contains ................................................................................................ 155
C.2 Keypad structure .............................................................................................................. 155
C.3 Inverter structure .............................................................................................................. 156
C.4 Dimensions for inverters of AC 3PH 380V(-15%)–440V(+10%) ......................................... 156
Appendix D Peripheral optional parts ....................................................................................... 158
D.1 What this chapter contains ................................................................................................ 158
D.2 Peripheral wiring ............................................................................................................... 158
D.3 Power supply .................................................................................................................... 159
D.4 Cables .............................................................................................................................. 159
D.5 Breaker and electromagnetic contactor ............................................................................. 162
D.6 Reactors ........................................................................................................................... 163
D.7 Filter ................................................................................................................................. 164
D.8 Braking system ................................................................................................................. 166
D.9 Emergency operation systems .......................................................................................... 168
Appendix E Further information................................................................................................ 169
iii
Page 5

Goodrive300-LIFT series inverter Safety precautions
Danger:
Serious physical injury or even death may be caused if related
requirements are not followed.
Warning:
Physical injury or damage to the devices may be caused if related
requirements are not followed.
Note:
Steps to take for ensuring the proper running of the product.
Qualified electricians:
People working on the device must have taken part in professional
electrical and safety training, obtained the certification, and been
familiar with all steps and requirements for installing, performing
commissioning on, operating, and maintaining the device, and are
capable of preventing or dealing with all kinds of emergencies.
Sign
Name
Description
Abbreviation
Danger
Danger
Serious physical injury or even
death may be caused if related
requirements are not followed.
Warning
Warning
Physical injury or damage to the
devices may be caused if
related requirements are not
followed.
Electrostatic discharge
Electrostatic
discharge
Damage to the PCBA board
may be caused if related
requirements are not followed.
Hot sides
Hot sides
The base of the device may
become hot. Do not touch it.
Note
Note
Steps to take for ensuring the
proper running of the device.
Note
1 Safety precautions
1.1 What this chapter contains
Read this manual carefully and follow all safety precautions before moving, installing, operating, and
servicing the product. Otherwise, physical injury or death or damage to the devices may be caused.
For any physical injury or damage to the devices caused by you or your customers due to your
neglect of the safety precautions, our company shall not be held liable.
1.2 Safety definition
1.3 Warning signs
Warning signs are used to warn you about the conditions that may cause severe injury or damage to
the device. They instruct you to exercise caution to prevent danger. The following table describes the
warning signs used in this manual.
-1-
Page 6

Goodrive300-LIFT series inverter Safety precautions
Only qualified electricians are allowed to operate the device.
Do not perform any wiring, inspection, or component replacement operations
when power is applied. Before wiring or inspection, ensure that all input
power supplies are disconnected and wait for at least the waiting time
specified on the inverter, or ensure that the DC bus voltage is lower than 36
V. The following table describes the waiting time.
Inverter model
Minimum waiting time
380V
4kW-30kW
10 minutes
Do not refit the product unauthorizedly; otherwise fire, electric shocks or
other injury may be caused.
The base may become hot when the machine is running. Do not touch it.
Otherwise, you may get burnt.
The electronic parts and components inside the inverter are electrostatic
sensitive parts. Take measurements to prevent electrostatic discharge when
performing operations involving them.
Do not install the inverter on inflammables. Prevent it from coming into
contact with or adhering to inflammables.
Connect the optional brake components (brake resistor, brake unit, or
feedback unit) according to the wiring diagram.
Do not operate the inverter if it is damaged or lack of components.
Do not touch the inverter with wet objects or any of your body parts.
Otherwise, electric shocks may be caused.
1.4 Safety guide
1.4.1 Delivery and installation
Note:
Use proper handling and installation tools to avoid damage to the device or physical injury.
Installers must take mechanical protective measures, such as wearing anti-smashing shoes and
work clothes, to protect personal safety.
Ensure that no physical impact or vibration occurs on the inverter during its transport and
installation.
Do not carry the machine only by its front cover. Otherwise, the machine may fall down.
Install the inverter in a place that will prevent children or other people from touching it.
The inverter cannot meet the low- and medium-voltage protection requirements stipulated in
IEC61800-5-1 if it is installed on a site where the altitude is higher than 2000 m.
Operate the inverter in environments that meet the operation requirements (for details, see
section 4.2.1 "Installation environment").
-2-
Page 7

Goodrive300-LIFT series inverter Safety precautions
Before wiring the terminals of the inverter, disconnect all power supplies
applied to it and wait for at least the waiting time specified on it..
The voltage is high inside the inverter when it is running. Except settings
through the keypad, do not perform any other operations on it.
The inverter cannot be used independently as an "emergency-stop device".
The product cannot be used for motor emergency braking. You need to
configure a mechanical brake device.
When the inverter is used to drive a permanent-magnet synchronous motor
(PMSM), ensure the following in addition to the preceding precautions:
1. All the input power supplies, including the main power supply and
control power supply, are disconnected.
2. The running of the PMSM is stopped, and the voltage on the output
side of the inverter is lower than 36 V.
3. The waiting time after the PMSM is stopped is not shorter than the
waiting time specified on the inverter, and the voltage between (+) and
(-) is lower than 36 V.
4. During the operation, ensure that the PMSM will not rotate again due
to external loads. It is recommended that you configure an effective
external brake device or disconnect the electrical connection between
the PMSM and the inverter.
Prevent screws, cables, and other conductive items from dropping into the inverter.
The leakage current of the inverter may be larger than 3.5 mA during operation. Perform reliable
grounding and ensure that the grounding resistance is lower than 10 Ω. The conductivity of the
PE grounding conductor is the same as that of the phase conductor (with the same sectional
area).
R, S and T are the power input terminals, while U, V and W are the the terminals for output to the
motor. Connect the input power cables and motor cables properly. Otherwise, damage to the
inverter may be caused.
1.4.2 Commissioning and operation
Note:
Do not switch on or off the input power supply of the inverter frequently.
If the inverter has been stored for a long time, check, set the capacity of, and perform a test run
on it before using it. For details about inspection and capacity setting, see chapter 9.
"Maintenance and hardware fault diagnosis".
Close the front cover of the inverter before running it. Otherwise, electric shocks may be caused.
-3-
Page 8

Goodrive300-LIFT series inverter Safety precautions
Only trained and qualified electricians are allowed to maintain, check, and
replace components of the inverter.
Before wiring the terminals of the inverter, disconnect all power supplies
applied to it and wait for at least the waiting time specified on it.
During the maintenance and replacement of components, take measures to
prevent screws, cables, and other conductive items from dropping into the
inverter.
There are heavy metals in the inverter. Deal with it as industrial effluent.
When the life cycle ends, the inverter should enter the recycling system.
Dispose of it separately at an appropriate collection point instead of
placing it in the normal waste stream.
1.4.3 Component maintenance and replacement
Note:
Tighten the screws with proper torque.
During the maintenance and replacement of components, prevent the inverter and its
components from coming into contact with or being attached with inflammables.
Do not perform any insulation or withstand voltage tests on the inverter. Do not use a megameter
to measure the control circuit of the inverter.
During the maintenance and replacement of components, take measurements to prevent
electrostatic discharge for the inverter and its internal components.
1.4.4 What to do after scrapping
-4-
Page 9

Goodrive300-LIFT series inverter Precautions for quick application
1. Whether the packing box is damaged or dampened.
2. Whether the model identifier on the exterior surface of the packing box is consistent with
the purchased model.
3. Whether the interior surface of the packing box is abnormal, for example, in wet condition,
or whether the enclosure of the product is damaged or cracked.
4. Whether the nameplate of the product is consistent with the model identifier on the exterior
surface of the packing box.
5. Whether the accessories (including the user manual, control keypad, and extension cards)
inside the packing box are complete.
1. Mechanical type of the load to be drived by the inverter. Check whether the inverter will be
overloaded in actual operation and whether the power level needs to be raised.
2. Whether the actual running current of the to-be-loaded motor is lower than the rated current
of the inverter.
3. Whether control precision implemented by the inverter meets the requirement of the actual
load.
4. Whether the grid voltage is consistent with the rated voltage of the inverter.
5. Whether you need to configure an extension card to implement the required communication
mode.
1. Whether the ambient temperature in the application is higher than 40°C. If yes, derate the
machine by 3% for every increased 1°C. Do not use the inverter in environments where the
temperature is higher than 50°C.
Note: If the inverter is installed in a cabinet, the ambient temperature is the air temperature
2 Precautions for quick application
2.1 What this chapter contains
This chapter describes the basic principles for the installation and commission of the inverter, which
helps you to quickly complete the installation and commissioning.
2.2 Unpacking inspection
Check the following items after receiving the product.
If any of the problems described in the check items are found, contact the local dealer or our
company.
2.3 Application confirmation
Confirm the following items before using the inverter.
2.4 Environment confirmation
Check the following items before you install and use the inverter.
-5-
Page 10

Goodrive300-LIFT series inverter Precautions for quick application
inside the cabinet.
2. Whether the ambient temperature in application is lower than –10°C. If yes, configure a
heating device.
Note: If the inverter is installed in a cabinet, the ambient temperature is the air temperature
inside the cabinet.
3. Whether the altitude on the site is higher than 1000 m. If yes, derate the machine by 1% for
every increased 100 m.
4. Whether the ambient humidity is higher than 90% or condensation occurs. If yes, take extra
protective measures.
5. Whether there is direct sunlight or biological invasion in the application environment. If yes,
take extra protective measures.
6. Whether there is dust or inflammable and explosive gas in the application environment. If
yes, take extra protective measures.
1. Whether the input power cables and motor cables meet the current-carrying capacity
requirements of the actual load.
2. Whether the peripheral accessories are correctly selected and properly installed, and
whether the installation cables meet the current-carrying capacity requirements of the
accessories, including the input reactor, input filter, output reactor, output filter, DC reactor,
brake unit, and brake resistor.
3. Whether the inverter is installed on non-flammable materials, and whether its heat-emitting
accessories (such as reactor and brake resistor) are kept away from inflammable materials.
4. Whether all the control cables are wired separately from power cables, and whether
electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) specification requirements are taken into full account
during the wiring.
5. Whether all the grounding systems are properly grounded according to the requirements of
the inverter.
6. Whether all the installation spacings of the inverter meet the requirements stated in the
manual.
7. Whether the installation of the inverter meets the requirements stated in the manual.
8. Check that the external connection terminals are tightly fastened and whether the torque
meets the requirements.
9. Whether screws, cables, or other conductive items drop into the inverter. If yes, take them
out.
2.5 Installation confirmation
Check the following items after the installation of the inverter is complete.
-6-
Page 11

Goodrive300-LIFT series inverter Precautions for quick application
1. Select the motor type and set the motor parameters according to the actual motor
parameters, and set the control mode of the inverter.
2. Perform autotuning if required. Remove the motor load, if possible, to perform dynamic
parameter autotuning; and if the load cannot be removed, you can perform static
autotuning.
3. Adjust the ACC/DEC time according to the actual operation conditions of the load.
4. Perform commissioning on the machine in jogging mode and check whether the rotating
direction of the motor meets the requirement. If no, exchange the wires of any two phases
of the motor to change the running direction of the motor.
5. Set all control parameters and then run the machine.
2.6 Basic commissioning
Complete the basic commissioning as follows before using the inverter.
-7-
Page 12

Goodrive300-LIFT series inverter Product overview
3 Product overview
3.1 What this chapter contains
The chapter briefly describes the operation principle, product characteristics, layout, name plate and
type designation information.
3.2 Basic principles
GD300L series inverters special for lifts are wall mountable devices for controlling asynchronous AC
induction motors and permanent magnet synchronous motors.
The diagram below shows the simplified main circuit diagram of the inverter. The rectifier converts
three-phase AC voltage to DC voltage. The capacitor bank of the intermediate circuit stabilizes the
DC voltage. The converter transforms the DC voltage back to AC voltage for the AC motor. The brake
pipe connects the external brake resistor to the intermediate DC circuit to consume the feedback
energy when the voltage in the circuit exceeds its maximum limit.
Figure 3-1 Main circuit for 4–5.5kW inverters
Figure 3-2 Main circuit for 7.5–15kW inverters
-8-
Page 13

Goodrive300-LIFT series inverter Product overview
(-)
(+)
Built-in
reactor
Function
Specifications
Power
input
Input voltage (V)
Rated voltage: AC 380V (Available voltage degrees:
220, 380, 400, 415, 440, which can be set by the
function code)
Allowed input working voltage range:
AC 1PH 220V(-15%)–240V(+10%)
AC 3PH 380V(-15%)–440V(+10%)
Input current (A)
Refer to the rated value.
Input frequency (Hz)
50Hz or 60Hz
Allowed range: 47–63Hz
Power
output
Output voltage (V)
0–input voltage
Output current (A)
Refer to 3.6 Rated specifications.
Output power (kW)
Refer to 3.6 Rated specifications.
Output frequency (Hz)
0–400Hz
Technical
control
feature
Control mode
SVPWM, sensorless vector control
Motor type
Asynchronous motor and permanent magnet
synchronous motor
Adjustable-speed ratio
For open-loop vector control: 1:200
For closed-loop vector control: 1:1500
Speed control
accuracy
± 0.5%(open-loop vector); ± 0.05% (closed-loop vector)
Figure 3-3 Main circuit for 18.5–30kW inverters
Note:
• The inverters ≤15kW contain built-in brake units and supports external brake resistors which are
optional.
• The 18.5–30kW inverters contain built-in DC reactors and support external brake units which are
optional.
3.3 Product specifications
-9-
Page 14

Goodrive300-LIFT series inverter Product overview
Function
Specifications
Speed fluctuation
± 0.3%(sensorless vector control)
Torque response
<20ms(sensorless vector control)
Torque control
accuracy
10% (sensorless vector control)
Starting torque
For asynchronous motor sensorless vector control:
0.3Hz/150%
For sensor-included vector control: 0 Hz/200%
Overload capability
150% of rated current: 1 minute
180% of rated current: 10 seconds
200% of rated current: 1 second
Running
control
feature
Frequency setting
method
Digital setting, analog setting, multi-step speed running
setting, and MODBUS communication setting
implement switching between channels.
Voltage
auto-adjustment
Keep constant voltage automatically when the grid
voltage transients.
Fault protection
Provide more than 30 fault protection functions against
faults such as overcurrent, overvoltage, undervoltage,
overheating, phase loss and overload.
Peripheral
interface
Analog input
1 input (AI1): 0–10V/0–20mA
Resolution: ≤20mV
Analog output
1 output (AO1): 0–10V/0–20mA
Resolution: ≤20mV
Digital input
8 common inputs; Max. frequency: 1kHz; internal
impedance: 3.3kΩ;
1 high speed input; Max. frequency: 50kHz
Resolution: ≤2ms
Digital output
1 terminal Y for open collector output
Relay output
3 NO programmable relay outputs;
RO1A NO, RO1C common terminal
RO2A NO, RO2C common terminal
RO3A NO, RO3C common terminal
Contactor capability: 3A/AC250V,1A/DC30V
Power output
Provides 24V/200mA and 10V/50mA power output.
PG expansion card
(optional)
Incremental 5–24V; sine and cosine; absolute value;
UVW
-10-
Page 15

Goodrive300-LIFT series inverter Product overview
Function
IO expansion cards
(optional)
3 common digital inputs
1 analog input AI2
1 NO/NC relay output
1 HDO output
1 Y output
1 RS485 interface (supporting RTU)
1 CAN communication interface
STO expansion card
(optional)
Provides STO security terminal functions.
Bluetooth/Ethernet
expansion card
(optional)
Others
Mountable method
Running environment
temperature
MTBF
Protective degree
Cooling
Brake unit
DC reactor
DC reactors are standard configuration for inverters
≥18.5kW.
EMC filter
Optional filters C2 can be configured, meeting
IEC618000-3 C2 requirements.
Specifications
Commissions devices through Bluetooth or Ethernet
communication.
Wall mounting
-10–50˚C. The inverter must be derated if temperature
is above 40˚C.
100,000 hours
IP20
Forced air cooling
Built in inverters ≤15kW; optional for others
3.4 Name plate
Model: GD300L-5R5G-4
Power(Output): 5.5kW
Input: AC 3PH 380V(-15%)-440V(+10%) 19.5A 47Hz-63Hz
Output: AC 3PH 0V-Uinput 14A 0Hz-400Hz
S/N: Made in China
Shenzhen INVT Electric Co., Ltd.
Figure 3-4 Name plate
Note: The certification mark such as "CE" can be placed only after the product is certified.
3.5 Type designation key
The type designation contains inverter information. You can find the type designation on the type
designation label attached to the inverter or the simple name plate.
-11-
Page 16

Goodrive300-LIFT series inverter Product overview
GD300L – 5R5G – 4 –LIFT
①
② ③
④
Key
Sign
Description
Remarks
Abbreviation
①
Product abbreviation
GD300L is short for Goodrive300-LIFT,
special for lifts.
Rated power
②
Power range + Load
type
5R5: 5.5kW
G: Constant torque load
Voltage degree
③
Voltage degree
S2: AC 2PH 220V (-15%)–240V(+10%)
4: AC 3PH 380V (-15%)–440V(+10%)
No. for market
management
④
Number for market
management
LIFT: inverter special for lifts
Model
Rated output
power(kW)
Rated input
current(A)
Rated output
current(A)
GD300L-1R5G-S2
1.5
14.2
7
GD300L-2R2G-S2
2.2
23
10
GD300L-004G-4
4
13.5
9.5
GD300L-5R5G-4
5.5
19.5
14
GD300L-7R5G-4
7.5
25
18.5
GD300L-011G-4
11
32
25
GD300L-015G-4
15
40
32
GD300L-018G-4
18.5
47
38
GD300L-022G-4
22
56
45
GD300L-030G-4
30
70
60
Operation panel
Control board terminals
PG card expansion
Main circuit terminals
Main circuit cable port
Control cable
port
CHARGE LED
Function card
expansion
Whole-unit
mounting hole
Cover
Cover buckling
position
Vent hole
Figure 3-5 Product type
3.6 Rated specifications
Note: For inverters of 380 V, 4 kW–30 kW, the STO rating is SIL3 PLe CAT.3.
3.7 Structure diagram
Figure 3-6 Components of inverters ≤15 kW
-12-
Page 17

Goodrive300-LIFT series inverter Product overview
Fixed hook for cover
Keypad panel
Control board
Control terminals
PG card expansion
Keypad bracket
Shield plate
Function card expansion
Main circuit terminals
Control cable port
Whole-unit
mounting hole
Fixed hook for cover
Keypad panel
Control board
Control terminals
PG card expansion
Keypad bracket
Shield plate
Function card expansion
Main circuit terminals
Control cable port
Whole-unit
mounting hole
Cover
Cover mounting hole
Vent hole
Figure 3-7 Components of inverters ≥18.5 kW
-13-
Page 18

Goodrive300-LIFT series inverter Installation guide
Only qualified electricians are allowed to carry out what described in this chapter.
Please operate as the instructions in Safety precautions. Ignoring these may
cause physical injury or death or damage to the devices.
Ensure the power supply of the inverter is disconnected during the operation.
Wait for at least the time designated until the CHARGE indicator is off after the
disconnection if the power supply is applied. It is recommended to use the
multimeter to monitor whether the drive DC bus voltage is under 36V.
The installation and design of the inverter should comply with the requirement of
the local laws and regulations in the installation site. If the installation infringes
the requirement, our company will exempt from any responsibility. Additionally, if
users do not comply with the suggestion, some damage beyond the assured
maintenance range may occur.
Environment
Conditions
Installation site
Indoor
Environment
temperature
-10–+50˚C
If the ambient temperature of the inverter is above 40˚C, derate 3% for
every additional 1˚C.
It is not recommended to use the inverter if the ambient temperature is
above 50˚C.
In order to improve the reliability of the device, do not use the inverter
if the ambient temperature changes frequently.
Please provide cooling fan or air conditioner to control the internal
ambient temperature below the required one if the inverter is used in a
closed space such as in the control cabinet.
When the temperature is too low, if the inverter needs to restart to run
after a long stop, it is necessary to provide an external heating device
to increase the internal temperature, otherwise damage to the devices
4 Installation guide
4.1 What this chapter contains
The chapter describes the mechanical installation and electric installation.
4.2 Mechanical installation
4.2.1 Installation environment
The installation environment is the safeguard for a full performance and long-term stable functions of
the inverter. Check the installation environment as follows:
-14-
Page 19

Goodrive300-LIFT series inverter Installation guide
Environment
Conditions
may occur.
Humidity
RH≤90%
No condensation is allowed.
The maximum relative humility should be equal to or less than 60% in
corrosive air.
Storage temperature
-30–+60˚C
Running environment
The inverter installation site should:
keep away from the electromagnetic radiation source;
keep away from contaminative air, such as corrosive gas, oil mist
and flammable gas;
ensure foreign objects, such as metal power, dust, oil, water cannot
enter into the inverter (do not install the inverter on the flammable
materials such as wood);
keep away from radioactive and flammable materials, direct
sunlight, contaminative liquids, salty and vibration environments.
Altitude
<1000m
When the altitude exceeds 1000m but is lower than 3000m, derate 1%
for every additional 100m;
When the altitude exceeds 2000m, configure an isolation transformer
on the input end of the inverter.
When the altitude exceeds 3000m but is lower than 5000m, contact
our company for technical consultation. Do not use the inverter at an
altitude higher than 5000m.
Pollution level
Level 2
Vibration
≤ 5.8m/s2(0.6g)
Installation direction
The inverter needs to be installed on an upright position to ensure
good cooling conditions.
Note:
• GD300L series inverters should be installed in a clean and ventilated environment according to
enclosure classification.
• Cooling air must be clean, free from corrosive materials and electrically conductive dust.
4.2.2 Installation direction
The inverter may be installed on the wall or in a cabinet.
The inverter must be installed in an upright position. Check the installation direction according to the
requirements below. Refer to Appendix C "Dimension drawings" for frame details.
-15-
Page 20

Goodrive300-LIFT series inverter Installation guide
a. Vertical b. Horizontal
c. Transverse
OK NG NG
Cool air
Warm air
Figure 4-1 Inverter installation direction
4.2.3 Installation manner
The inverter is wall mountable.
Figure 4-2 Installation manner
(1) Mark the hole locations, which are shown in the dimension drawings in the appendix.
(2) Fix the screws or bolts to the marked locations.
(3) Put the inverter against the wall.
(4) Tighten the screws in the wall securely.
4.2.4 Single-inverter installation
Note: The minimum space of B and C is 100mm.
Figure 4-3 Single installation
-16-
Page 21

Goodrive300-LIFT series inverter Installation guide
Warm air
Cool air
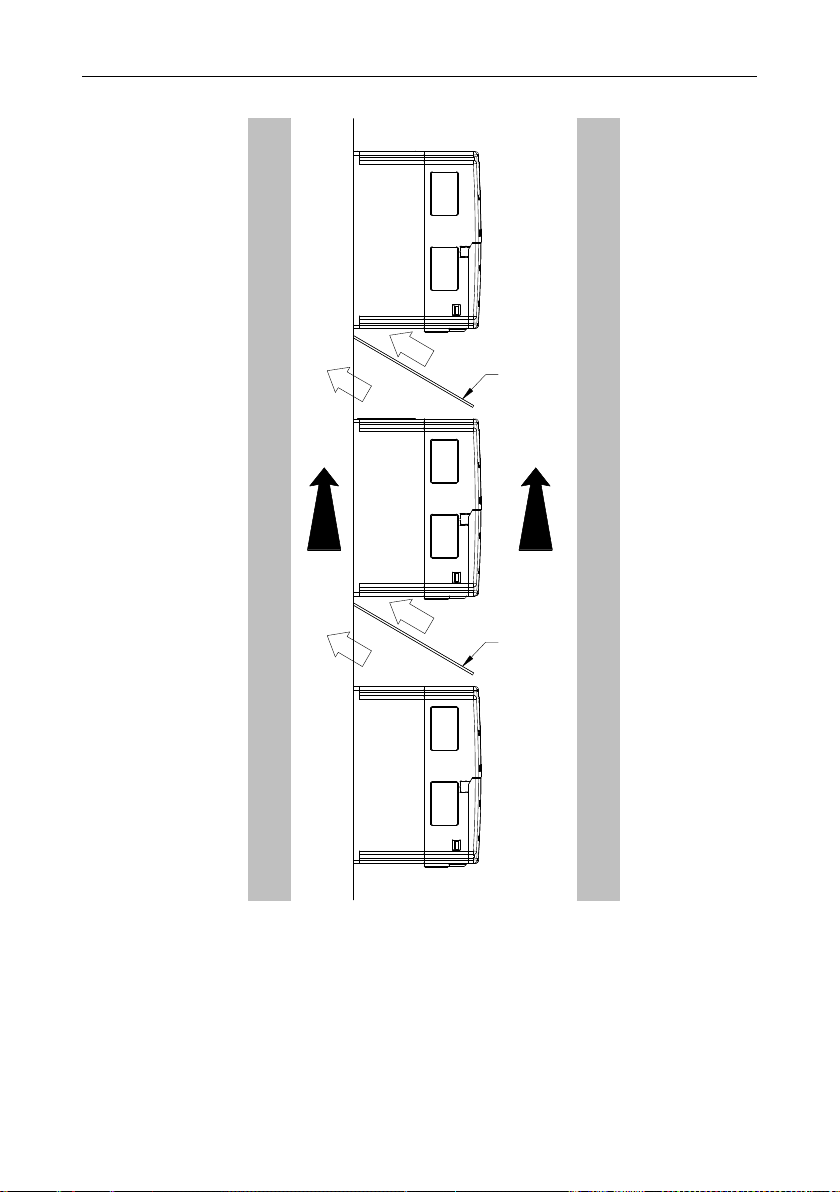
4.2.5 Multiple-inverter installation Parallel installation
Figure 4-4 Parallel installation
Note:
• Before installing inverters in different sizes, align their top positions for the convenience of later
maintenance.
• The minimum space of B, D and C is 100mm.
-17-
Page 22
Goodrive300-LIFT series inverter Installation guide
Cool air
Warm air
Wind screen
Cool air
Warm air
Wind screen
4.2.6 Vertical installation
Note: Windscreens are needed in vertical installation to avoid insufficient cooling due to mutual
Figure 4-5 Vertical installation
impact.
-18-
Page 23

Goodrive300-LIFT series inverter Installation guide
Cool air
Cool air
Cool air
Warm air
Warm air
Warm air
4.2.7 Tilt installation
Figure 4-6 Tilt installation
Note: Ensure the separation of the wind input and output channels in tilt installation for avoiding
mutual impact.
-19-
Page 24

Goodrive300-LIFT series inverter Installation guide
Earth
Breaker or RCCB
Motor
DC reactor
Output
noise filter
Earth
Output AC
reactor
Inverter
Input
interference
filter
Brake resistor
MAgnetic
contactor (MC)
Input AC
reactor
Power supply
4.3 Wiring
4.3.1 Connection to peripheral devices
Figure 4-7 Connection to peripheral devices
-20-
Page 25

Goodrive300-LIFT series inverter Installation guide
R
S
T
W
V
U
PE
M
Inverter of 15kW or lower
(+)
PB
3PH
380V±15%
50/60Hz
Braking resistor
Input
reactor
Input
filter
Fuse
(-)
R
S
T
W
V
U
PE
M
18.5~30kW
P1
(+)
DC reactor
(built-in)
3PH
380V±15%
50/60Hz
(-)
Input
reactor
Input
filter
Fuse
DC-
Braking resistor
DC+
Braking unit
KM1
KM1
4.3.2 Connection diagram of main circuit
Figure 4-8 Connection diagram of main circuit for 380V inverters
Note:
• The fuse, DC reactor, brake unit, brake resistor, input reactor, input filter, output reactor, output
filter are optional parts. Refer to Peripheral optional parts for detailed information.
• The inverters of 18.5–30kW contain built-in DC reactors.
4.3.3 Terminals in main circuit
Figure 4-9 Terminals of main circuit for the inverters of 380V 4–5.5kW
-21-
Page 26

Goodrive300-LIFT series inverter Installation guide
Terminal
Name
Function
R, S, T
Power input of main circuit
3PH AC input terminals, connected to the
grid
(+), (-)
Reserved terminal for connecting
external brake units
Reserved terminal for connecting external
brake units
(+), PB
Reserved terminals for
connecting external brake
resistors
Reserved terminals for connecting
external brake resistors
P1, (+)
Reserved terminals for
connecting external DC reactors
Reserved terminals for connecting
external DC reactors
(-)
DC negative bus output terminal
DC negative bus output terminal
U, V, W
Inverter output
3PH AC output terminals, generally
connected to the motor
Grounding terminal
Grounding terminal
Figure 4-10 Terminals of main circuit for the inverters of 380V 7.5–15 kW
Figure 4-11 Terminals of main circuit for the inverters of 380V 18.5–30kW
Note:
• Do not use an asymmetrically constructed motor cable. If there is a symmetrically constructed
-22-
Page 27

Goodrive300-LIFT series inverter Installation guide
Screw not fastened Screw fastened
grounding conductor in the motor cable in addition to the conductive shield, connect the
grounding conductor to the grounding terminal at the inverter and motor ends.
• Brake resistor, brake unit, and DC reactor are optional parts.
• Route the motor cable, input power cable, and control cables separately.
4.3.4 Wiring of terminals in main circuit
1. Connect the ground wire of the input power cable to the ground terminal (PE) of the inverter, and
connect the 3PH input cable to the terminals R, S, and T, and fasten them up.
2. Connect the ground wire of the motor cable to the ground terminal of the inverter, and connect
the 3PH motor cable to the terminals U, V, and W, and fasten them up.
3. Connect the brake resistor and other accessories that are equipped with cables to the specified
positions.
4. Fasten all the cables outside of the inverter mechanically, if possible.
Figure 4-12 Proper screw fastening
-23-
Page 28

Goodrive300-LIFT series inverter Installation guide
GD300L inverters
special for lifts
Multi-function input terminal 1
Multi-function input terminal 2
Multi-function input terminal 3
Multi-function input terminal 4
Multi-function input terminal 5
Multi-function input terminal 6
S6
S5
S4
S3
S2
S1
COM
Analog output
0-10V/4-20mA
+24V
Relay 1 output
24V
S7
Multi-function input terminal 7
GND
AI1
+10V
Analog speed
adjustment
0~10V/0-20mA
PW
R03C
Y1
CME
AO1
GND
High-speed input terminal
HDI
Multi-function input terminal 8
S8
R03A
R02C
R02A
R01C
R01A
Relay 2 output
Relay 3 output
CN3
M
U
V
W
PE
R
S
T
P1
(+) (-)
P1
(+)
DC reactor
(built-in for
18.5-30kW)
(-)
-
Braking resistor
+
RB2
RB1
(Inverters of 18.5kW or
higher connect
external braking units)
3PH
50Hz/60Hz
380V(-15%)
~440V(+10%)
CN13
CN14
Multi-function expansion
card interface
External keypad interface
Open collector output Y
S1 S2 S3 S4
+24V COM HDI AO1
R03C
CMEY1PW COM
GND
AI1
S5 S6 S7 S8
R03A
RO1C
+10V
PE
R01A R02A
RO2C
Terminal
Description
S1-S7
Common digital input terminals
1. Internal impedance: 3.3kΩ
2. 12–30V voltage input acceptable
3. Dual-direction input terminals, supporting both NPN and PNP
4. Max input frequency: 1kHz
4.3.5 Connection diagram of control circuit
4.3.6 Terminals in control circuit
Figure 4-13 Connection diagram of control circuit
Figure 4-14 Terminals in control circuit
-24-
Page 29

Goodrive300-LIFT series inverter Installation guide
Terminal
Description
5. All are programmable digital input terminals. Terminal functions can be set by
function codes.
HDI
1. It can serve as the high-frequency pulse input channel, besides the functions of
S1–S8.
2. Max. input frequency: 50kHz
COM
Common terminal of +24V
PW
To provide the input digital power supply from external to internal. Voltage range:
12–24V
+10V
+10V power provided by the local device
AI1
1. Input range: 0–10V/0–20mA for AI1 voltage/current, switched by J3
2. Input impedance: 20kΩ for voltage input; 500Ω for current input
4. Resolution: 5mV as the min. resolution when 10V corresponds to 50Hz.
5. Deviation ±1%, 25˚C
GND
Reference zero potential of +10V
AO1
1. Input range: 0–10V/0–20mA for AO1 voltage/current, switched by J1
2. Deviation ±1%, 25˚C
Y1
1. Switch capacity: 200mA/30V
2. Output frequency range: 0–1kHz
CME
Common terminal of open connector output
RO1A
RO1 relay output, RO1A NO, RO1C common terminal
Contact capacity: 3A/AC250V, 1A/DC30V
RO1C
RO2A
RO2 relay output, RO2A NO, RO2C common terminal
Contact capacity: 3A/AC250V, 1A/DC30V
RO2C
RO3A
RO3 relay output, RO3A NO, RO3C common terminal
Contact capacity: 3A/AC250V, 1A/DC30V
RO3C
4.3.7 Input/Output signal connection
Use the U-shaped contact tag to set the NPN mode or PNP mode and the internal or external power
supply. The default setting is NPN internal mode.
-25-
Page 30

Goodrive300-LIFT series inverter Installation guide
RPB U
POWER
S
T
MOTOR
V
W
(+) (-)
U-shaped short
connector between
+24V and PW
U-shaped short
connector between
COM and CME
S1
S2
COM
PW
+ 24V
COM
+ 24V
Internal power supply (NPN mode)
S1
S2
COM
PW
+ 24V
COM
+24V
+ 24V
External power supply (NPN mode)
S1
S2
COM
PW
+ 24V
COM
+24V
S1
S2
COM
PW
+ 24V
COM
+24V
Internal power supply (PNP mode) External power supply (PNP mode)
Internal power supply (PNP mode)
External power supply (PNP mode)
Figure 4-15 U-shaped contact tag
If the signal is from NPN transistor, please set the U-shaped contact tag between +24V and PW as
below according to the used power supply.
Figure 4-16 NPN modes
If the signal is from PNP transistor, please set the U-shaped contact tag as below according to the
used power supply.
Figure 4-17 PNP modes
4.4 Wiring protection
4.4.1 Protecting the inverter and input power cable in short-circuit situations
Protect the inverter and input power cable against thermal overload in short circuit situations.
Arrange the protection according to the following guidelines.
-26-
Page 31

Goodrive300-LIFT series inverter Installation guide
Input cable
Inverter
Fuse
M3~
If the inverter is connected to multiple motors, a separate thermal overload switch
or a circuit breaker must be used for protecting each cable and motor. These
devices may require a separate fuse to cut off the short-circuit current.
Figure 4-18 Fuse configuration
Note: Select the fuse as the manual indicated. The fuse will protect the input power cable from
damage in short-circuit situations. It will protect the surrounding devices when the internal of the
inverter is short circuited.
4.4.2 Protecting the motor and motor cable in short-circuit situations
The inverter protects the motor and motor cable in a short-circuit situation when the motor cable is
dimensioned according to the rated current of the inverter. No additional protection devices are
needed.
4.4.3 Protecting the motor against thermal overload
According to regulations, the motor must be protected against thermal overload and the current must
be switched off when overload is detected. The inverter includes a motor thermal protection function
that protects the motor and closes the output to switch off the current when necessary.
-27-
Page 32

Goodrive300-LIFT series inverter Keypad operation procedure
No.
Name
Description
1
State LED
RUN/TUNE
LED off means that the inverter is in the
stopping state; LED blinking means the
inverter is in the parameter autotune
state; LED on means the inverter is in the
running state.
FWD/REV
FED/REV LED
LED off means the inverter is in the
forward rotation state; LED on means the
inverter is in the reverse rotation state
LOCAL/REMOT
LED for keypad operation, terminals
operation and remote communication
control
5 Keypad operation procedure
5.1 What this chapter contains
This chapter describes:
Buttons, indicating lights and the screen as well as the methods to inspect, modify and set function
codes by keypad
5.2 Keypad
The keypad is used to control GD300L series inverters special for lifts, read the state data, and adjust
parameters.
Note: The LED keypad is provided as standard configuration. There is another optional LCD keypad
which supports various languages, parameter copy, and 10-line displaying, and is compatible with the
LED keypad in installation dimensions.
Figure 5-1 Keypad
-28-
Page 33

Goodrive300-LIFT series inverter Keypad operation procedure
No.
Name
Description
LED off means that the inverter is in the
keypad operation state; LED blinking
means the inverter is in the terminals
operation state; LED on means the
inverter is in the remote communication
control state.
TRIP
LED for faults
LED on when the inverter is in the fault
state; LED off in normal state; LED
blinking means the inverter is in the alarm
state.
2
Unit LED
Mean the unit displayed currently
Hz
Frequency unit
RPM
Rotating speed unit
A
Current unit
%
Percentage
V
Voltage unit
3
Code
displaying
zone
5-digit LED display displays various monitoring data and alarm code such as
set frequency and output frequency.
0
3
6
9
C
F
L
O
S
v
1
4
7
A
d
H
N
P
t
.
2
5
8
b
E
l
n
r
U
-
Displayed
character
Displayed
character
Displayed
character
Corresponding
character
Corresponding
character
Corresponding
character
4
Digital
potentiom
Reserved
-29-
Page 34

Goodrive300-LIFT series inverter Keypad operation procedure
No.
Name
Description
eter
5
Buttons
PRG
ESC
Programming key
Enter or escape from the first level menu
and remove the parameter quickly.
DATA
ENT
Entry key
Enter the menu step-by-step.
Confirm parameters.
UP key
Increase data or function code
progressively.
DOWN key
Decrease data or function code
progressively.
SHIFT
Right-shift key
Move right to select the displaying
parameter circularly in stopping and
running mode.
Select the parameter modifying digit
during the parameter modification.
Run key
This key is used to operate on the
inverter in key operation mode.
Stop/
Reset key
This key is used to stop in running state
and it is limited by function code P07.05
This key is used to reset all control
modes in the fault alarm state.
QUICK
JOG
Quick key
The function of this key is confirmed by
function code P07.04.
5.3 Keypad displaying
The keypad displaying state of Goodrive300L series inverters is divided into stopping state parameter,
running state parameter, function code parameter editing state and fault alarm state and so on.
5.3.1 Displayed state of stopping parameters
When the inverter is in the stopping state, the keypad will display stopping parameters as shown in
Figure 5-2.
In the stopping state, various kinds of parameters can be displayed. Select the parameters to be
displayed or not by P07.08. See the instructions of P07.08 for the detailed definition of each bit.
In the stopping state, there are 9 stopping parameters can be selected to be displayed or not. They
are: set speed, set frequency, bus voltage, input terminals state, output terminals state, AI1, AI2, and
magnetic pole position. P07.08 determines whether to display the parameters by bit. 》/SHIFT can
shift the parameters form left to right, while QUICK/JOG (P07.04=2) can shift the parameters form
-30-
Page 35

Goodrive300-LIFT series inverter Keypad operation procedure
PRG
ESC
DATA
ENT
SHIFT
RUN
STOP
RST
QUICK
JOG
PRG
ESC
DATA
ENT
SHIFT
RUN
STOP
RST
QUICK
JOG
PRG
ESC
DATA
ENT
SHIFT
RUN
STOP
RST
QUICK
JOG
Parameter displayed in the
stop state
Parameter displayed in the
running state
Faulty state displayed
right to left.
5.3.2 Displayed state of running parameters
After receiving valid running commands, the inverter will enter the running state and the keypad will
display the running parameters. RUN/TUNE LED on the keypad is on, while the FWD/REV is
determined by the current running direction, as shown in Figure 5-2.
In the running state, there are 16 parameters that can be displayed. They are: running speed, set
speed, bus voltage, output voltage, output current, running frequency (Hz on), running rotation speed,
output power, output torque, input terminals state, output terminals state, AI1, AI2, torque
compensation, magnetic pole position, and linear speed. P07.06 determines whether to display the
parameters by bit. 》/SHIFT can shift the parameters form left to right, while QUICK/JOG (P07.04=2)
can shift the parameters from right to left.
5.3.3 Displayed state of fault
If the inverter detects the fault signal, it will enter the fault alarm displaying state. The keypad will
display the fault code by blinking. The TRIP LED on the keypad is on, and the fault reset can be
operated by STOP/RST on the keypad, control terminals or communication commands.
5.3.4 Displayed state of function codes editing
In the state of stopping, running or fault, press PRG/ESC to enter into the editing state (if there is a
password, see P07.00).The editing state is displayed on two classes of menu, and the order is:
function code group/function code number→function code parameter, press DATA/ENT into the
displayed state of function parameter. On this state, you can press DATA/ENT to save the parameters
or press PRG/ESC to exit.
5.4 Keypad operation
Operate the inverter via operation panel. See the detailed structure description of function codes in
the brief diagram of function codes.
Figure 5-2 Displayed state
-31-
Page 36

Goodrive300-LIFT series inverter Keypad operation procedure
The units place is
blinking.
All digits are
blinking.
The units place is
blinking.
The units place is blinking.
The units place is blinking.
Note: When setting the value, you can press and + to modify the value.
PRG
ESC
DATA
ENT
PRG
ESC
PRG
ESC
PRG
ESC
DATA
ENT
DATA
ENT
5.4.1 How to modify the function codes of the inverter
The inverter has three levels menu, which are:
1. Group number of function code (first-level menu)
2. Tab of function code (second-level menu)
3. Set value of function code (third-level menu)
Remarks: Press both PRG/ESC or DATA/ENT to return to the second-level menu from the third-level
menu. The difference is: pressing DATA/ENT will save the set parameters into the control panel, and
then return to the second-level menu with shifting to the next function code automatically; while
pressing PRG/ESC will directly return to the second-level menu without saving the parameters, and
keep staying at the current function code.
Under the third-level menu, if the parameter has no blinking bit, it means the function code cannot be
modified. The possible reasons could be:
1) This function code is not modifiable parameter, such as actual detected parameter, operation
records and so on;
2) This function code is not modifiable in running state, but modifiable in stop state.
Example: Set function code P00.01 from 0 to 1.
Figure 5-3 Sketch map of modifying parameters
5.4.2 How to set the password of the inverter
Goodrive300L series inverters special for lifts provide password protection function to users. Set
P07.00 to gain the password and the password protection becomes valid instantly after quitting from
the function code editing state. Press PRG/ESC again to the function code editing state, "0.0.0.0.0"
will be displayed. Unless using the correct password, you cannot enter it.
Set P07.00 to 0 to cancel password protection function.
The password protection becomes effective 1 minute later after retreating from the function code
editing state. Press PRG/ESC again to the function code editing state, "0.0.0.0.0" will be displayed.
Unless using the correct password, you cannot enter it.
-32-
Page 37

Goodrive300-LIFT series inverter Keypad operation procedure
The units place is
blinking.
All digits are
blinking.
The units place is blinking.
The units place
is blinking.
Note: When setting the value, you can press and + to modify the value.
The units place is
blinking.
The units place
is blinking.
PRG
ESC
PRG
ESC
PRG
ESC
PRG
ESC
DATA
ENT
DATA
ENT
DATA
ENT
The units place is
blinking.
All digits are
blinking.
The units place is blinking.
The units place
is blinking.
Note: When setting the value, you can press and + to modify the value.
The units place is
blinking.
The units place is
blinking.
DATA
ENT
DATA
ENT
DATA
ENT
PRG
ESC
PRG
ESC
PRG
ESC
PRG
ESC
Figure 5-4 Sketch map of password setting
5.4.3 How to watch the inverter state through function codes
Goodrive300L series inverters special for lifts provide group P17 as the state inspection group. You
can enter P17 directly to view the state.
Figure 5-5 Sketch map of state viewing
-33-
Page 38

Goodrive300-LIFT series inverter Function parameters
6 Function parameters
6.1 What this chapter contains
This chapter lists and describes the function parameters.
6.2 Function parameters
The function parameters of GD300L series inverters special for lifts are divided into 30 groups
(P00–P29) by function, of which P18–P19 and P22–P28 are reserved. Each function group contains
certain function codes applying 3-level menus. For example, "P08.08" means the eighth function code
in the P8 group function. P29 group is factory reserved and inaccessible for users.
For the convenience of function codes setting, the function group number corresponds to the first
level menu, the function code corresponds to the second level menu and the function code
corresponds to the third level menu.
1. Below is the instruction of the function lists:
The first line "Function code": codes of function parameter group and parameters;
The second line "Name": full name of function parameters;
The third line "Detailed illustration of parameters": detailed illustration of the function parameters
The fourth line "Default value": the original factory values of the function parameter;
The fifth line "Modify": the modifying character of function codes (the parameters can be modified or
not and the modifying conditions), below is the instruction:
"○": means the set value of the parameter can be modified on stop and running state;
"◎": means the set value of the parameter cannot be modified on the running state;
"●": means the value of the parameter is the real detection value which cannot be modified.
(The inverter has limited the automatic inspection of the modifying character of the parameters to help
users avoid misadjustment.)
2. "Parameter radix" is decimal (DEC), if the parameter is expressed by hex, then the parameter is
separated from each other when editing. The setting range of certain bits are 0–F (Hex).
3. "The default value" means the function parameter will restore to the default value during default
parameters restoring, but the detected parameter or recorded value is not restored.
4. For a better parameter protection, the inverter provides password protection to the parameters.
After setting the password (set P07.00 to any non-zero number), the system will come into the state of
password verification firstly after the user press PRG/ESC to come into the function code editing state.
And then "0.0.0.0.0." will be displayed. Unless the user input right password, they cannot enter into
the system. For the factory setting parameter zone, it needs correct factory password (remind that the
users cannot modify the factory parameters by themselves, otherwise, if the parameter setting is
incorrect, damage to the inverter may occur). If the password protection is unlocked, the user can
modify the password freely and the inverter will work as the last setting one. When P07.00 is set to 0,
-34-
Page 39

Goodrive300-LIFT series inverter Function parameters
Function
code
Name
Detailed instruction of parameters
Default
value
Modify
P00 Group Basic function group
P00.00
Speed control
mode
0: Sensorless vector control (SVC) mode 0
1: SVC mode 1
2: V/F control
3: Closed-loop vector control
2 ◎ P00.01
Run command
channel
0: Keypad ("LOCAL/REMOT" off)
1: Terminal ("LOCAL/REMOT" blinking)
2: Communication ("LOCAL/REMOT" on)
3: CAN ("LOCAL/REMOT" on)
1
◎
P00.02
Lift rated speed
0.100–4.000m/s
1.500m/
s
◎
P00.03
Speed command
selection
0: Keypad
1: AI1
2: AI2
3: Multi-step speed running
4: Remote communication
5: AI1 tracking running
6: CAN communication-based setting
7: CAN communication-based reference
3
◎
P00.04
Max. output
frequency
10.00–600.00Hz
50.00
Hz
◎
P00.05
Keypad set
speed
0–P00.02 (lift rated speed)
1.500m/
s
○
P00.06
Running
direction
0: Default direction
1: Reverse direction
2: Forbid to run in reverse direction
0
◎
P00.07
Carrier
frequency mode
0: Fixed carrier frequency, set by P00.08
1: Auto adjustment
0
◎
the password can be canceled. If P07.00 is not 0 during powering on, then the parameter is protected
by the password. When modify parameters by serial communication, the password function also
follows the above rules.
-35-
Page 40

Goodrive300-LIFT series inverter Function parameters
Function
code
Name
Detailed instruction of parameters
Default
value
Modify
P00.08
Carrier
frequency
setting
Carrier
frequency
Electromagnetic
noise
Noise and leakage
current
Heat
dissipation
High
LowHigh
Low
High
Low
1 kHz
10 kHz
15 kHz
Mapping between models and carrier
frequencies
Model
Default carrier
frequency
380V
1.5–11kW
8 kHz
15–55kW
4 kHz
>75kW
2 kHz
660V
22–55kW
4 kHz
>75kW
2 kHz
Advantage of high carrier frequency: ideal
current waveform, little current harmonic wave
and motor noise.
Disadvantage of high carrier frequency:
increasing switch loss, increasing inverter
temperature, and impact to output capacity. The
inverter needs to derate on high carrier
frequency. Besides, the leakage and electrical
magnetic interference increases. Applying low
carrier frequency is contrary to the above. Too
low carrier frequency will cause unstable
running, torque decreasing and surge.
A reasonable carrier frequency has been set in
factory. In general, you do not need to modify
the parameter. When the frequency used
exceeds the default one, the inverter needs to
derate 20% for each additional 1kHz carrier
frequency. Setting range: 1.2–15.0kHz
Depend
on
model
◎
-36-
Page 41

Goodrive300-LIFT series inverter Function parameters
Function
code
Name
Detailed instruction of parameters
Default
value
Modify
P00.09
Motor parameter
autotuning
0: No operation
1: Rotating parameter autotuning on empty-load
asynchronous motor
2: Static parameter autotuning on asynchronous
motor
3: Rotating parameter autotuning on empty-load
synchronous motor
4: Static parameter autotuning on synchronous
motor
5: Rotating parameter autotuning on
synchronous motor with load
0
◎
P00.10
Function
restore
parameter
0: No operation
1: Restore the default value
2: Delete the fault records
3: Roll back function parameters, reading
function parameters that are saved when the
LSB of P07.01 is set to 5.
0
◎
P00.11
AVR function
0: Invalid
1: Valid
1
◎
P00.12
Reserved
0-65535
0 ○ P00.13
Reserved
0-65535
0
○
P01 Group Startup and stop control
P01.00
Start mode
0: Start-up directly: start from the starting
frequency P01.01
1: Start-up after DC braking: start the motor from
the starting frequency after DC braking (setting
P01.04 and P01.05)
It is suitable in the cases where reverse rotation
may occur to the low inertia load during starting.
0
◎
P01.01
Starting
frequency of
direct start
Starting frequency of direct start-up means the
original frequency during the inverter starting.
See P01.03 for detailed information.
Setting range: 0.00–50.00Hz
0.00Hz
◎
P01.02
ACC time of start
0.000–0.100s
0.010s
◎
-37-
Page 42

Goodrive300-LIFT series inverter Function parameters
Function
code
Name
Detailed instruction of parameters
Default
value
Modify
P01.03
Retention time of
the starting
frequency
Frequency (f)
f
max
t1
Time (t)
f1 is set through P01.01.
t1 is set through P01.02.
f1
Set a proper starting frequency to increase the
torque of the inverter during starting. During the
retention time of the starting frequency, the
output frequency of the inverter is the starting
frequency. And then, the inverter will run from
the starting frequency to the set frequency. If the
set frequency is lower than the starting
frequency, the inverter will stop running and
keep in the stand-by state. The starting
frequency is not limited in the lower limit
frequency.
Setting range: 0.0–50.0s
0.0s
◎
P01.04
Pre-start braking
current
The inverter will carry out DC braking at the
braking current set before starting and it will
speed up after the DC braking time. If the DC
braking time is set to 0, the DC braking is invalid.
Stronger braking current indicates bigger
braking power. The DC braking current before
starting means the percentage of the rated
current of the inverter.
Setting range of P01.04: 0.0–100.0%
Setting range of P01.05: 0.0–30.0s
0.0%
◎
P01.05
Braking time
before starting
0.0s
◎
-38-
Page 43

Goodrive300-LIFT series inverter Function parameters
Function
code
Name
Detailed instruction of parameters
Default
value
Modify
P01.06
ACC/DEC
selection
Changing mode of the frequency during start-up
and running.
0: Linear type
The output frequency increases or decreases
linearly.
f
max
Output frequency (f)
t1 t2
Time (t)
1: S curve, indicating the output frequency
increases or decreases according to the S
curve.
Generally, S curve is used in scenarios such as
lifts and conveyers which require smooth startup
and stop.
Output frequency (f)
Time (t)
f
max
t1 t2
0
◎
P01.07
Stop mode
0: Decelerate to stop. After the stop command
becomes valid, the inverter decelerates to
decrease the output frequency during the set
time. When the frequency decreases to P01.15,
the inverter stops.
1: Coast to stop: after the stop command
becomes valid, the inverter ceases the output
immediately. And the load coasts to stop at the
mechanical inertia.
0
○
P01.08
Start frequency
in stop braking
Starting frequency of stop braking: The inverter
will carry on stop DC braking when the
frequency is arrived during decelerating to stop.
Demagnetizing time: Before the stop DC
0.00Hz
○
P01.09
Demagnetizing
time
0.00s
○
P01.10
Stop DC braking
current
0.0%
○
-39-
Page 44

Goodrive300-LIFT series inverter Function parameters
Function
code
Name
Detailed instruction of parameters
Default
value
Modify
P01.11
DC braking time
braking, the inverter will close output and begin
to carry on the DC braking after the waiting time.
This function avoids the overcurrent fault caused
by DC braking when the speed is too high.
Stop DC braking current: DC brake added.
Stronger current indicates bigger DC braking
effect.
Braking time of stop braking: Retention time of
DC brake. If the time is 0, the DC brake is
invalid. The inverter will stop at the set
deceleration time.
Running
command
Pre-start
braking
command
Constant speed
ON
OFF
Braking waiting time
during stop
Time t
ACC
DEC DC braking at stop
Setting range of P01.08: 0.00Hz–P00.04 (max.
output frequency)
Setting range of P01.09: 0.00–30.00s
Setting range of P01.10: 0.0–100.0%
Setting range of P01.11: 0.0–50.0s
0.0s
○
P01.12
Stop knee-point
frequency
0.00–10.00Hz
In the process of deceleration to stop, the stop
deleration curve starts after the frequency set in
this parameter is reached.
1.00Hz
○
P01.13
Startup delay
The function determines the brake release after
the running command is given, and the inverter
is in a stand-by state and waits for the delay time
set by P01.13.
Setting range: 0.00–60.00s
0.04s
○
P01.14
Reserved
0–65535
0
○
P01.15
Reserved
0–65535
0
○
-40-
Page 45
Goodrive300-LIFT series inverter Function parameters
Function
code
Name
Detailed instruction of parameters
Default
value
Modify
P02 Group Motor 1
P02.00
Motor type
0: Asynchronous motor
1: Synchronous motor
0
◎
P02.01
Motor rated
power
0.1–3000.0kW
Depend
on
model
◎
P02.02
Motor rated
frequency
0.01Hz–P00.04 (max. frequency)
50.00Hz
◎
P02.03
Motor rated
rotation speed
1–36000rpm
Depend
on
model
◎
P02.04
Motor rated
voltage
0–1200V
Depend
on
model
◎
P02.05
Motor rated
current
0.8–6000.0A
Depend
on
model
◎
P02.06
Stator resistor of
asynchronous
motor
0.001–65.535Ω
Depend
on
model
◎
P02.07
Rotor resistor of
asynchronous
motor
0.001–65.535Ω
Depend
on
model
◎
P02.08
Leakage
inductance of
asynchronous
motor
0.1–6553.5mH
Depend
on
model
◎
P02.09
Mutual
inductance of
asynchronous
motor
0.1–6553.5mH
Depend
on
model
◎
P02.10
Non-load current
of asynchronous
motor
0.1–6553.5A
Depend
on
model
◎
P02.11
Direct axis
inductance of
synchronous
motor
0.01–655.35mH
Depend
on
model
◎
P02.12
Quadrature axis
inductance of
synchronous
motor
0.01–655.35mH
Depend
on
model
◎
P02.13
Back EMF of
synchronous
motor
0–10000
300
◎
-41-
Page 46

Goodrive300-LIFT series inverter Function parameters
Function
code
Name
Detailed instruction of parameters
Default
value
Modify
P02.14
Pulley diameter
100–2000mm
500mm
◎
P02.15
DEC ratio
0.01–10.00
1.00
◎
P02.16
Speed regulation
ratio
0–65535
1000
○
P02.17
Reserved
0–65535
0
○
P03 Group Vector control
P03.00
Speed loop
proportional gain
1
The parameters P03.00–P03.05 only apply to
vector control mode. Below the switching
frequency 1 (P03.02), the speed loop PI
parameters are: P03.00 and P03.01. Above the
switching frequency 2 (P03.05), the speed loop
PI parameters are: P03.03 and P03.04. PI
parameters are gained according to the linear
change of two groups of parameters. It is shown
as below:
PI parameters
Output frequency f
(P03.00,P03.01)
(P03.03,P03.04)
P03.02 P03.05
Setting the proportional coefficient and integral
time of the adjustor can change the dynamic
response performance of vector control speed
loop. Increasing the proportional gain and
decreasing the integral time can speed up the
dynamic response of the speed loop. But too
high proportional gain and too low integral time
may cause system vibration and overshoot. Too
low proportional gain may cause system
vibration and speed static deviation.
PI has a close relationship with the inertia of the
system. Adjust on the base of PI according to
16.0
○
P03.01
Speed loop
integral time 1
0.200s
○
P03.02
Low switching
frequency
5.00Hz
○
-42-
Page 47

Goodrive300-LIFT series inverter Function parameters
Function
code
Name
Detailed instruction of parameters
Default
value
Modify
P03.03
Speed loop
proportional gain
2
different loads to meet various demands.
Setting range of P03.00: 0.0–200.0
Setting range of P03.01: 0.000–10.000s
Setting range of P03.02: 0.00Hz–P03.05
Setting range of P03.03: 0.0–200.0
Setting range of P03.04: 0.000–10.000s
Setting range of P03.05: P03.02–P00.04 (max.
output frequency)
10.0
○
P03.04
Speed loop
integral time 2
0.200s
○
P03.05
High switching
frequency
10.00Hz
○
P03.06
Speed loop
output filter
0–8 (corresponds to 0–28×125 μs)
0
○
P03.07
Compensation
coefficient of
electromotion
slip
Slip compensation coefficient is used to adjust
the slip frequency of the vector control and
improve the speed control accuracy of the
system. Adjusting the parameter properly can
control the speed steady-state error.
Setting range: 50%–200%
100%
○
P03.08
Compensation
coefficient of
braking slip
100%
○
P03.09
Current loop
percentage
coefficient P
Note:
1. These two parameters adjust the PI
adjustment parameter of the current loop which
affects the dynamic response speed and control
accuracy directly. Generally, keep the default
values.
2. Only applicable to the vector control mode 0
without PG (P00.00=0).
Setting range: 0–20000
1000
○
P03.10
Current loop
integral
coefficient I
1000
○
P03.11
Torque upper
limit
0.0–200.0% (motor rated current)
180.0%
○
P03.12
Emergency
operation torque
upper limit
0.0–200.0% (motor rated current)
150.0%
◎
P03.13
Reserved
0–65535
0
○
P03.14
Reserved
0–65535
0
○
P04 Group V/F control
P04.00
Motor torque
boost
Torque boost to the output voltage for the
0.0%
○
-43-
Page 48

Goodrive300-LIFT series inverter Function parameters
Function
code
Name
Detailed instruction of parameters
Default
value
Modify
P04.01
Torque boost
close
features of low frequency torque. P04.00 is for
the max. output voltage Vb.
P04.01 defines the percentage of closing
frequency of manual torque to fb.
Torque boost should be selected according to
the load. The bigger the load is, the bigger the
boost is. Too big torque boost is inappropriate
because the motor will run with over-magnetic,
and the current of the inverter will increase to
raise the temperature of the inverter and
decrease the efficiency.
When the torque boost is set to 0.0%, the
inverter is automatic torque boost.
Torque boost threshold: under the threshold, the
torque boost is valid, but over the threshold, the
torque boost is invalid.
Output voltage (V)
Output frequency (f)
V
b
V
boost
f
stop
f
b
Setting range of P04.00: 0.0% (default),
0.1%–10.0%
Setting range of P04.01: 0.0%–50.0%
20.0%
○
P04.02
Motor V/F slip
compensation
gain
This function code is used to compensate the
change of the rotation speed caused by load
during compensation SVPWM control to
improve the rigidity of the motor. It can be set to
the rated slip frequency of the motor which is
counted as below:
△f=fb-n*p/60
Of which, fb is the rated frequency of the motor,
its function code is P02.02; n is the rated rotating
100.0%
○
-44-
Page 49

Goodrive300-LIFT series inverter Function parameters
Function
code
Name
Detailed instruction of parameters
Default
value
Modify
speed of the motor and its function code is
P02.03; p is the pole pair of the motor. 100.0%
corresponds to the rated slip frequency△f.
Setting range: 0.0–200.0%
P04.03
Motor vibration
control factor at
low frequency
0–100
10
○
P04.04
Motor vibration
control factor at
high frequency
0–100
10
○
P04.05
Motor vibration
control threshold
In SVPWM control mode, current fluctuation
may occur to the motor at some frequency,
especially the motor with big power. The motor
cannot run stably or overcurrent may occur.
These phenomena can be canceled by adjusting
this parameter.
Setting range of P04.03: 0–100
Setting range of P04.04: 0–100
Setting range of P04.05: 0.00Hz–P00.04 (max.
output frequency)
30.00
Hz
○
P04.06
Energy-saving
operation
0: No operation
1: Automatic energy-saving operation (reserved)
0
◎
P04.07
Gain in SM
MTPA control
0~3000
50
○
P04.08
Integral in SM
MTPA control
0~3000
30
○
P05 Group Input terminals
P05.00
HDI input
selection
0: High-speed pulse input. See P05.27–P05.31.
1: Digital input. See P05.12.
0
◎
P05.01
S1 function
selection
0: No function
1: Running up (FWD)
2: Running down (REV)
3: Running in inspection mode (EXM)
4: Emergency running (EMER)
5: Coast to stop (FSTP)
1
◎
P05.02
S2 function
selection
2
◎
-45-
Page 50

Goodrive300-LIFT series inverter Function parameters
Function
code
Name
Detailed instruction of parameters
Default
value
Modify
P05.03
S3 function
selection
6: Fault reset (RET)
7: External fault (EF)
8: Multi-speed running terminal 1 (MS1)
9: Multi-speed running terminal 2 (MS2)
10: Multi-speed running terminal 3 (MS3)
11: Up forced deceleration 1 (UFS1)
12: Up forced deceleration 2 (UFS2)
13: Up forced deceleration 3 (UFS3)
14: Down forced deceleration 1 (DFS1)
15: Down forced deceleration 2 (DFS2)
16: Down forced deceleration 3 (DFS3)
17: Contactor feedback signal (TB)
18: Brake feedback signal (FB)
19: Enable inverter (ENA)
20: Forced decelerate to stop
21: Emergency mode
22: Motor overheat
23: Main power supply input disconnected (for
India)
24: UPS input disconnected by main control (for
India)
25: Base lockout
26–40: Reserved
8
◎
P05.04
S4 function
selection
9 ◎ P05.05
S5 function
selection
3
◎
P05.06
S6 function
selection
4
◎
P05.07
S7 function
selection
0 ◎ P05.08
S8 function
selection
0 ◎ P05.09
S9 function
selection
◎
P05.10
S10 function
selection
◎
P05.11
S11 function
selection
◎
P05.12
HDI function
selection
0
◎
P05.13
Polarity selection
of input terminals
The function code is used to set the polarity of
input terminals.
Set the bit to 0, the input terminal is positive.
Set the bit to 1, the input terminal is negative.
BIT11
BIT10
HDI
S11
BIT9
BIT8
BIT7
BIT6
BIT5
S10
S9
S8
S7
S6
BIT4
BIT3
BIT2
BIT1
BIT0
S5
S4
S3
S2
S1
Setting range: 0x000–0x7FF
0x000
○
P05.14
Digital filter time
Set the sample filter time of S1–S11 and HDI
terminals. If the interference is strong, increase
the parameter to avoid the disoperation.
0.000–1.000s
0.010s
○
-46-
Page 51

Goodrive300-LIFT series inverter Function parameters
Function
code
Name
Detailed instruction of parameters
Default
value
Modify
P05.15
Reserved
Reserved
0
◎
P05.16
Enable power-on
terminal
detection
0: Disable
1: Enable (terminal command power-on
response and terminal command response to
UV fault rectification)
0
◎
P05.17
Lower limit of
AI1
The function code defines the relationship
between the analog input voltage and its
corresponding set value. If the analog input
voltage beyond the set minimum or maximum
input value, the inverter will count at the
minimum or maximum one.
When the analog input is the current input, the
corresponding voltage of 0–20mA is 0–10V.
In different cases, the corresponding rated value
of 100.0% is different. See the application for
detailed information.
The figure below illustrates different
applications:
-100%
100%
Corresponding
setting
AI
-10V
10V
20mA
0
AI3
AI1/AI2
Input filter time: This parameter is used to adjust
the sensitivity of the analog input. Increasing the
value properly can enhance the anti-interference
of the analog, but weaken the sensitivity of the
analog input.
Note: Analog AI1 and AI2 can support 0–10V or
0–20mA input, when AI1 and AI2 selects
0–20mA input, the corresponding voltage of
20mA is 5V. AI3 can support the input of
0.00V
○
P05.18
Corresponding
setting of the
lower limit of AI1
0.0%
○
P05.19
Upper limit of
AI1
10.00V
○
P05.20
Corresponding
setting of
the upper limit of
AI1
100.0%
○
P05.21
AI1 input filter
time
0.030s
○
P05.22
Lower limit of
AI2
0.00V
○
P05.23
Corresponding
setting of the
lower limit of AI2
0.0%
○
P05.24
Upper limit of
AI2
10.00V
○
P05.25
Corresponding
setting of
the upper limit of
AI2
100.0%
○
P05.26
AI2 input filter
time
0.030s
○
-47-
Page 52

Goodrive300-LIFT series inverter Function parameters
Function
code
Name
Detailed instruction of parameters
Default
value
Modify
-10V–+10V.
Setting range of P05.17: 0.00V–P05.19
Setting range of P05.18: -300.0%–300.0%
Setting range of P05.19: P05.17–10.00V
Setting range of P05.20: -300.0%–300.0%
Setting range of P05.21: 0.000s–10.000s
Setting range of P05.22: 0.00V–P05.24
Setting range of P05.23: -300.0%–300.0%
Setting range of P05.24: P05.22–10.00V
Setting range of P05.25: -300.0%–300.0%
Setting range of P05.26: 0.000s–10.000s
P05.27
Lower limit
frequency of HDI
0.000 KHz – P05.29
0.000K
Hz
○
P05.28
Corresponding
setting of HDI
lower limit
frequency
-300.0%–300.0%
0.0%
○
P05.29
Upper limit
frequency of HDI
P05.27 –50.000kHz
50.000K
Hz
○
P05.30
Corresponding
setting of HDI
upper limit
frequency
-300.0%–300.0%
100.0%
○
P05.31
HDI frequency
input filter time
0.000s–10.000s
0.030s
○
P05.32
Analog signal
voltage
threshold for
motor thermal
protection
0.0 V–10.0 V
0.0 V
○
P05.33
Reserved
0–65535
0
○
P06 Group Output terminals
P06.00
HDO output
Function selection of the high-speed pulse
output terminals.
0: Open collector pole high speed pulse output.
The max.pulse frequency is 50.0kHz. See
P06.16–P06.20.
1: Open collector pole output. See P06.03.
0
◎
P06.01
Y1 output
0: No output
1: Lift in operation
2: Up operation
1 ○ P06.02
Y2 output
0
○
-48-
Page 53

Goodrive300-LIFT series inverter Function parameters
Function
code
Name
Detailed instruction of parameters
Default
value
Modify
P06.03
HDO output
3: Down operation
4: Fault output
5: Zero speed running
6: Ready for running
7: Braking control
8: Contactor control
9: Frequency arrival
10: Frequency detection threshold (FDT) output
11: FDT reverse output
12: Reserved
13: Light-load direction detection completed
14: Down as the light-load direction detection
result
15: Up as the light-load direction detection result
16: Running 1 (excluding current withdrawal)
17: STO opereation
18: SPI fault output
19: UPS control signal output (for India)
20: Reserved
0
○
P06.04
Relay output
RO1
4
○
P06.05
Relay output
RO2
7
○
P06.06
Relay output
RO3
8
○
P06.07
Relay RO4
output
0
○
P06.08
Polarity of output
terminals
The function code is used to set the pole of the
output terminal.
If the current bit is set to 0, output terminal is
positive. If the current bit is set to 1, output
terminal is negative.
BIT6
BIT5
BIT4
RO4
RO3
RO2
BIT3
BIT2
BIT1
BIT0
RO1
HDO
Y2
Y1
Setting range: 0x0–0x7F
00
○
P06.09
AO1 output
0: Running speed
1: Set speed
2: Running rotation speed
3: Output current
4: Output voltage
5: Output power
6: Output torque
7: AI1 input value
8: AI2 input value
9–14: Reserved
0
○
P06.10
HDO high-speed
pulse output
0
○
P06.11
AO1 output
lower limit
The above function codes define the relative
relationship between the output value and
0.0%
○
P06.12
AO1 output of
lower limit
0.00V
○
-49-
Page 54

Goodrive300-LIFT series inverter Function parameters
Function
code
Name
Detailed instruction of parameters
Default
value
Modify
P06.13
AO1 output
upper limit
analog output. When the output value exceeds
the range of set maximum or minimum output, it
will count according to the low-limit or upper-limit
output.
When the analog output is current output, 1mA
equals to 0.5V.
In different cases, the corresponding analog
output of 100% of the output value is different.
See each application for detailed information.
10V (20mA)
0.0% 100.0%
AO
Setting range of P06.11: -300.0%–P06.13
Setting range of P06.12: -0.00V–10.00V
Setting range of P06.13: -P06.11–300.0%
Setting range of P06.14: -0.00V–10.00V
Setting range of P06.15: -0.000s–10.000s
Setting range of P06.16: -300.0%–P06.18
Setting range of P06.17: -0.00–50.00kHz
Setting range of P06.18: -P06.16–300.0%
Setting range of P06.19: -0.00–50.00kHz
Setting range of P06.20: -0.000s–10.000s
100.0%
○
P06.14
AO1 output of
upper limit
10.00V
○
P06.15
AO1 output filter
time
0.000s
○
P06.16
HDO output
lower limit
0.00%
○
P06.17
HDO output of
lower limit
0.0kHz
○
P06.18
HDO output
upper limit
100.0%
○
P06.19
HDO output of
upper limit
50.00kH
z
○
P06.20
HDO output filter
time
0.000s
○
P06.21
Reserved
0–65535
0 ○ P06.22
Reserved
0–65535
0
○
P07 Group Human-machine interface
P07.00
User's password
0–65535
0
○
P07.01
Parameter copy
Ones place:
0: No operation
1: Upload function parameters to the keypad
from machine
2: Download function parameters (including
motor parameters) from the keypad to machine.
3: Download function parameters (excluding the
motor parameters of P02) from the keypad to
machine.
4: Download function parameters (including only
motor parameters of P02) from the keypad to
0×100
◎
-50-
Page 55

Goodrive300-LIFT series inverter Function parameters
Function
code
Name
Detailed instruction of parameters
Default
value
Modify
machine.
5: Save function parameters (including motor
parameters) of the machine
Note: After completing the 1–5 operations, the
parameter is automatically reset to 0. The
upload and download functions are invalid for
the factory parameters in P29.
Tens place:
Indicates the parameter group to be uploaded or
downloaded. You can set four groups.
Thousands place:
Indicates the response speed of the keypad
0: Low speed
1: Medium speed
2: High speed
P07.02
Reserved
Reserved
0
◎
P07.03
Keypad
0: External keypad
1: Local keypad
2: Both external keypad and local keypad are
valid.
2
○
P07.04
QUICK/JOG
function
selection
0: No function
1: Reserved
2: Shift the display state by the shifting key.
3: Shift between forward rotations and reverse
rotations.
4: Clear UP/DOWN settings.
5: Coast to stop.
6:Reserved
7: Quick commissioning mode (based on
non-factory parameter settings)
7
◎
P07.05
STOP/RST
function
selection
0: Only valid for the keypad control
1: Valid for both keypad and terminals control
2: Valid for both keypad and communication
control
3: Valid for all control modes
0
○
-51-
Page 56

Goodrive300-LIFT series inverter Function parameters
Function
code
Name
Detailed instruction of parameters
Default
value
Modify
P07.06
Selection 1 of
parameters
displayed in
running state
0x0000–0xFFFF
Bit0: Running speed
Bit1: Set speed
Bit2: Bus voltage
Bit3: Output voltage (V on)
Bit4: Output current (A on)
BIT5: Set frequency (Hz on)
BIT6: Running frequency (Hz on)
BIT7: Running rotation speed
BIT8: Output power (% on)
BIT9: Output torque (% on)
BIT10: Input terminal state
BIT11: Output terminal state
BIT12: AI1 (% on)
BIT13: AI2 (% on)
BIT14: Magnetic pole position
Bit15: Linear speed
0x07F
○
P07.07
Selection 2 of
parameters
displayed in
running state
Reserved
0x0000
○
P07.08
Selection of
parameters
displayed in stop
state
0x0000–0xFFFF
BIT0: Set speed
BIT1: Set frequency
BIT2: Bus voltage
BIT3: Input terminal state
BIT4: Output terminal state
BIT5: AI1
BIT6: AI2
BIT7: Magnetic pole position
BIT8–BIT15: Reserved
0x007F
○
P07.09
Speed display
coefficient
0.0–300.0%
100.0%
○
P07.10
Rectifier bridge
module
temperature
0–100.0˚C
0.0
●
P07.11
Converter
module
temperature
0–100.0˚C
0.0
●
P07.12
Software version
1.00–655.35
0.00
●
P07.13
Local
accumulative
running time (h)
0–65535h
0
●
-52-
Page 57

Goodrive300-LIFT series inverter Function parameters
Function
code
Name
Detailed instruction of parameters
Default
value
Modify
P07.14
Local
accumulative
running time
(min)
0–60min
0
●
P07.15
MSB of local
accumulative
running count
0–65535 (P07.15×10000 + P07.16)
0
●
P07.16
LSB of Local
accumulative
running count
0–10000
0
●
P07.17
MSB of inverter
power
consumption
0–65535 kWh (×1000)
0
●
P07.18
LSB of inverter
power
consumption
0.0–999.9 kWh
0.0
●
P07.19
Inverter rated
power
0.4–3000.0kW
0.0
●
P07.20
Inverter rated
voltage
50–1200V
0
●
P07.21
Inverter rated
current
0.1–6000.0A
●
P07.22
Factory bar code
1
0x0000–0xFFFF
●
P07.23
Factory bar code
2
0x0000–0xFFFF
●
P07.24
Factory bar code
3
0x0000–0xFFFF
●
P07.25
Factory bar code
4
0x0000–0xFFFF
●
P07.26
Factory bar code
5
0x0000–0xFFFF
●
P07.27
Factory bar code
6
0x0000–0xFFFF
●
-53-
Page 58

Goodrive300-LIFT series inverter Function parameters
Function
code
Name
Detailed instruction of parameters
Default
value
Modify
P07.28
Type of current
fault
0: No fault
1: Inverter unit U phase protection (OUt1)
2: Inverter unit V phase protection (OUt2)
3: Inverter unit W phase protection (OUt3)
4: ACC overcurrent (OC1)
5: DEC overcurrent (OC2)
6: Constant-speed overcurrent (OC3)
7: ACC overvoltage (OV1)
8: DEC overvoltage (OV2)
9: Constant-speed overvoltage (OV3)
10: Bus undervoltage (UV)
11: Motor overload (OL1)
12: Inverter overload (OL2)
13: Input side phase loss (SPI)
14: Output side phase loss (SPO)
15: Overheat of the rectifier module (OH1)
16:Overheat fault of the converter module (OH2)
17: External fault (EF)
18: 485 communication fault (CE)
19: Current detection fault (ItE)
20: Motor autotune fault (tE)
21: EEPROM operation fault (EEP)
22: PID response offline fault (PIDE)
23: Brake unit fault (bCE)
24: Running time arrival (END)
25: Electrical overload (OL3)
26: Panel communication fault (PCE)
27: Parameter uploading fault (UPE)
28: Parameter downloading fault (DNE)
29: PROFIBUS communication fault (E-DP)
30: Ethernet communication fault (E-NET)
31: CANopen communication fault (E-CAN)
32: Grounding short circuit fault 1 (ETH1)
33: Grounding short circuit fault 2 (ETH2)
34: Speed deviation fault (dEu)
35: Maladjustment (STo)
36: Undervoltage fault (LL)
37: Encoder offline fault (ENC1O)
38: Encoder reverse fault (ENC1D)
39: Encoder Z pulse offline fault (ENC1Z)
40: U disconnection (ENC1U)
●
P07.29
Type of last fault
●
P07.30
Type of last but
one fault
●
P07.31
Type of last but
two fault
●
P07.32
Type of last but
three fault
●
P07.33
Type of last but
four
●
P07.34
Type of last but
five fault
P07.35
Type of last but
six fault
P07.36
Type of last but
seven fault
-54-
Page 59

Goodrive300-LIFT series inverter Function parameters
Function
code
Name
Detailed instruction of parameters
Default
value
Modify
P07.37
Previous 9 fault
type
41–42: Reserved
43: Motor overtemperature fault (OT)
44: Reserved
45: Braking fault (BAE)
46: Contactor fault (CONE)
47: No CD signal (nPoS)
48: No enabling signal (U-EN)
49: STO card fault (SAFE)
50: Channel 1 (STO1_FB_DSP) safety circuit
exception (STL1)
51: Channel 2 (STO1_FB_DSP) safety circuit
exception (STL2)
52: Internal circuit exception (STL3)
53: Safety code FLASH CRC fault (CrCE)
P07.38
Running
frequency at
current fault
0.00Hz
●
P07.39
Ramp reference
frequency at
current fault
0.00Hz
●
P07.40
Output voltage
at current fault
0V
●
P07.41
Output current at
current fault
0.0A
●
P07.42
Bus voltage at
current fault
0.0V
●
P07.43
Max.
temperature at
current fault
0.0˚C
●
P07.44
Input terminals
state at current
fault
0 ●
P07.45
Output terminals
state at current
fault
0 ●
P07.46
Running
frequency at last
fault
0.00Hz
●
-55-
Page 60

Goodrive300-LIFT series inverter Function parameters
Function
code
Name
Detailed instruction of parameters
Default
value
Modify
P07.47
Ramp reference
frequency at last
fault
0.00Hz
●
P07.48
Output voltage
at last fault
0V
●
P07.49
Output current at
last fault
0.0A
●
P07.50
Bus voltage at
last fault
0.0V
●
P07.51
Max.
temperature at
last fault
0.0˚C
●
P07.52
Input terminals
state at last fault
0 ●
P07.53
Output terminals
state at last fault
0
●
P07.54
Running
frequency at last
fault
0.00Hz
●
P07.55
Ramp reference
frequency at last
but one fault
0.00Hz
●
P07.56
Output voltage
at last but one
fault
0V
●
P07.57
Output current at
last but one fault
0.0A
●
P07.58
Bus voltage at
last but one fault
0.0V
●
P07.59
Max.
temperature at
last but one fault
0.0˚C
●
P07.60
Input terminals
state at last but
one fault
0 ●
-56-
Page 61

Goodrive300-LIFT series inverter Function parameters
Function
code
Name
Detailed instruction of parameters
Default
value
Modify
P07.61
Output terminals
state at last but
one fault
0 ●
P07.62
Reserved
0–65535
0
○
P07.63
Reserved
0–65535
0
○
P08 Group Enhanced function
P08.00
Analogic
weighing input
0: None
1: AI1
0
◎
P08.01
Pre-torque offset
0.0–100.0%
45.0%
○
P08.02
Gain at drive
side
0.000–7.000
2.000
○
P08.03
Gain at braking
side
0.000–7.000
2.000
○
P08.04
Brake close
delay
0.00–5.00s
0.10s
◎
P08.05
Brake switch-off
delay
0.00–5.00s
0.10s
◎
P08.06
Brake feedback
detection time
0.0–5.0s
2.0s
◎
P08.07
Brake fault
action
0: Report the fault and stop
1: Stop without fault reporting
0
◎
P08.08
Contactor
feedback
detection time
0.00–5.00s
2.0s
◎
P08.09
Contactor fault
action
0: Report the fault and stop
1: Stop without fault reporting
0
◎
P08.10
Braking
threshold
voltage
320.0–750.0V
700.0V
○
P08.11
Auto fault reset
count
0–10
(OUT and OC do not allow auto fault reset.)
0
○
-57-
Page 62

Goodrive300-LIFT series inverter Function parameters
Function
code
Name
Detailed instruction of parameters
Default
value
Modify
P08.12
Faulty relay
action during
auto fault reset
0x00–0x11
LED ones:
0: Action during undervoltage
1: No action during undervoltage
LED tens:
0: Action during auto fault reset
1: No action during auto fault reset
0x00
○
P08.13
Auto fault reset
interval
0.1–100.0s
0.1s
○
P08.14
Braking
frequency during
stop
0.00–5.00Hz
0.00Hz
○
P08.15
Inverter stop
delay
0.00–5.00s
0.10s
◎
P08.16
Current
withdrawal time
during stop
0.00–5.00s
0.20s
◎
P08.17
Modulation
0: 2PH modulation
1: 3PH modulation
1
◎
P08.18
Overmodulation
validity
0: Invalid
1: Valid
1
◎
P08.19
FDT1 electrical
level detection
value
0.00–P00.04 (max. frequency)
0.20Hz
○
P08.20
FDT1 lag
detection value
0.0–100.0% (FDT1 electrical level)
0.0%
○
P08.21
Frequency
arrival detection
amplitude
0.00–P00.04 (max. frequency)
0.00Hz
○
P08.22
Cooling fan
running mode
0: Normal mode
1: The fan keeps running after power on
0
○
P08.23
Enable light-load
direction search
0: Disabled
1: Enable auto running
2: Enable the function of providing the running
direction
0
◎
P08.24
Light-load
direction
detection time
0.000–5.000s
2.000s
◎
-58-
Page 63

Goodrive300-LIFT series inverter Function parameters
Function
code
Name
Detailed instruction of parameters
Default
value
Modify
P08.25
Enable short
floor control
0: Disable
1: Enable
0
◎
P08.26
Short floor
speed
0.0%–90.0% (P00.02)
40.0%
◎
P08.27
Short floor
running time
0.00–20.00s
2.00
◎
P08.28
Contactor
disconnection
delay
0.00–10.00s
2.00s
◎
P08.29
Enable Keb
sequence
0: Disabled
1: Enabled
0
○
P08.30
Open-loop start
brake open
frequency of
asynchronous
motor
0.00–5.00 Hz
0.00 Hz
○
P09 Group Speed curve setting
P09.00
Multi-step speed
0
0.000–P00.02
0.000m/
s
◎
P09.01
Multi-step speed
1
0.000–P00.02
0.000m/
s
◎
P09.02
Multi-step speed
2
0.000–P00.02
0.000m/
s
◎
P09.03
Multi-step speed
3
0.000–P00.02
0.000m/
s
◎
P09.04
Multi-step speed
4
0.000–P00.02
0.000m/
s
◎
P09.05
Multi-step speed
5
0.000–P00.02
0.000m/
s
◎
P09.06
Multi-step speed
6
0.000–P00.02
0.000m/
s
◎
P09.07
Multi-step speed
7
0.000–P00.02
0.000m/
s
◎
-59-
Page 64

Goodrive300-LIFT series inverter Function parameters
Function
code
Name
Detailed instruction of parameters
Default
value
Modify
P09.08
Multi-step speed
priority
0: CHINESE TYPE
1: ISTANBUL TYPE
2: KONYA TYPE
3: ADANA TYPE
0
◎
P09.09
S-curve ACC
start segment
duration
0.1–360.0s
2.0
◎
P09.10
S-curve ACC
end segment
duration
0.1–360.0s
2.0
◎
P09.11
ACC time
0.1–360.0s
2.0
◎
P09.12
S-curve DEC
start segment
duration
0.1–360.0s
2.0
◎
P09.13
S-curve DEC
end segment
duration
0.1–360.0s
2.0
◎
P09.14
DEC time
0.1–360.0s
2.0
◎
P09.15
S-curve start
segment
duration during
stop
0.1–360.0s
2.0
◎
P09.16
S-curve end
segment
duration during
stop
0.1–360.0s
2.0
◎
P09.17
Running speed
at maintenance
0.001 –P00.02
0.200m/
s
◎
P09.18
ACC/DEC time
at maintenance
0.1–360.0s
4.0s
◎
P09.19
Forced DEC
time
0.1–360.0s
2.0s
◎
P09.20
Emergency
running speed
0.001 –P00.02
m/s
◎
P09.21
Emergency
ACC/DEC time
0.1–360.0s
20.0s
◎
P09.22
Leveling
segment
0–7
0 ◎ P09.23
Leveling speed
0.001 –P00.02
0.010m/
s
◎
0.100
-60-
Page 65

Goodrive300-LIFT series inverter Function parameters
Function
code
Name
Detailed instruction of parameters
Default
value
Modify
P09.24
DEC time for
creeping to stop
0.1–360.0s
During deceleration to stop, when the speed
reached the value set in P01.12, the curve of
deceleration to stop switches to those set in
P09.15, P09.16, and P09.24.
2.0s
○
P09.25
Speed threshold
for light-load
detection in
open-loop
control
5.00–20.00 Hz
5.00 Hz
○
P10 Group Non-weighing compensation
P10.00
Enable
non-weighing
compensation
0: Disable
1: Enable
0
◎
P10.01
Load
compensation
time
0.000–5.000s
0.400
◎
P10.02
Load
compensation
decrease time
0.000–5.000s
0.100
◎
P10.03
Load
compensation
ASR gain
0–100.0
25.0
○
P10.04
Load
compensation
ASR integral
time
0.01–10.000s
0.160
○
P10.05
Load
compensation
current
coefficient KP
0–1000
1000
○
P10.06
Load
compensation
current
coefficient KI
0–1000
0
○
P10.07
APR gain
0–100.0
0.0
○
P10.08
APR integral
time
0.001–10.000s
0.001
○
-61-
Page 66

Goodrive300-LIFT series inverter Function parameters
Function
code
Name
Detailed instruction of parameters
Default
value
Modify
P10.09
Current loop
filter coefficient
Bit0–2: Current instruction filter count
(compensation completion phase)
Bit3-5: Current instruction filter count
(compensation phase)
Bit6: Speed detection switching( 0:
segmentation; 1 observer)
Bit7-8: Current sampling filter count
Bit14: Enable temperature-based carrier
frequency decrease (0: Enable; 1: Disable)
Bit2–15: Reserved
0
○
P10.10
Reserved
0–65535
0 ○ P10.11
Reserved
0–65535
0
○
P11 Group Protective parameters
P11.00
Phase loss
protection
0x000–0x111
LED ones:
0: Disable input phase loss protection
1: Enable input phase loss protection
LED tens:
0: Disable output phase loss protection
1: Enable output phase loss protection
LED hundreds:
0: Disable hardware input phase loss protection
1: Enable hardware input phase loss protection
0x110
○
P11.01
Frequency-decre
asing at sudden
power loss
0: Disable
1: Enable
0
○
-62-
Page 67

Goodrive300-LIFT series inverter Function parameters
Function
code
Name
Detailed instruction of parameters
Default
value
Modify
P11.02
Frequency
decreasing ratio
at sudden power
loss
Setting range: 0.00Hz/s–P00.04 (max. output
frequency)
After the power loss of the grid, the bus voltage
drops to the sudden frequency-decreasing point,
the inverter begin to decrease the running
frequency at P11.02, to make the inverter
generate power again. The returning power can
maintain the bus voltage to ensure a rated
running of the inverter until the recovery of
power.
Voltage degree
380V
660V
Frequency-decre
asing threshold
460V
800V
Note:
1. Adjust the parameter properly to avoid the
stopping caused by inverter protection during
the switching of the grid.
2. Disable input phase loss protection to enable
this function.
10.00Hz
/s
○
P11.03
Overvoltage stall
protection
0: Disable
1: Enable
0
○
P11.04
Voltage
protection of
overvoltage stall
120–150% (standard bus voltage)
(380V)
136%
○
P11.05
Current limit
action
selection
The actual increasing ratio of motor speed is
lower than the ratio of output frequency because
of the big load during ACC running. It is
necessary to take measures to avoid
overcurrent fault and the inverter trips.
Ones: current limit setting
0: Invalid
1: Always valid
0
◎
P11.06
Automatic
current limit
During the running of the inverter, it will detect
160.0%
◎
-63-
Page 68
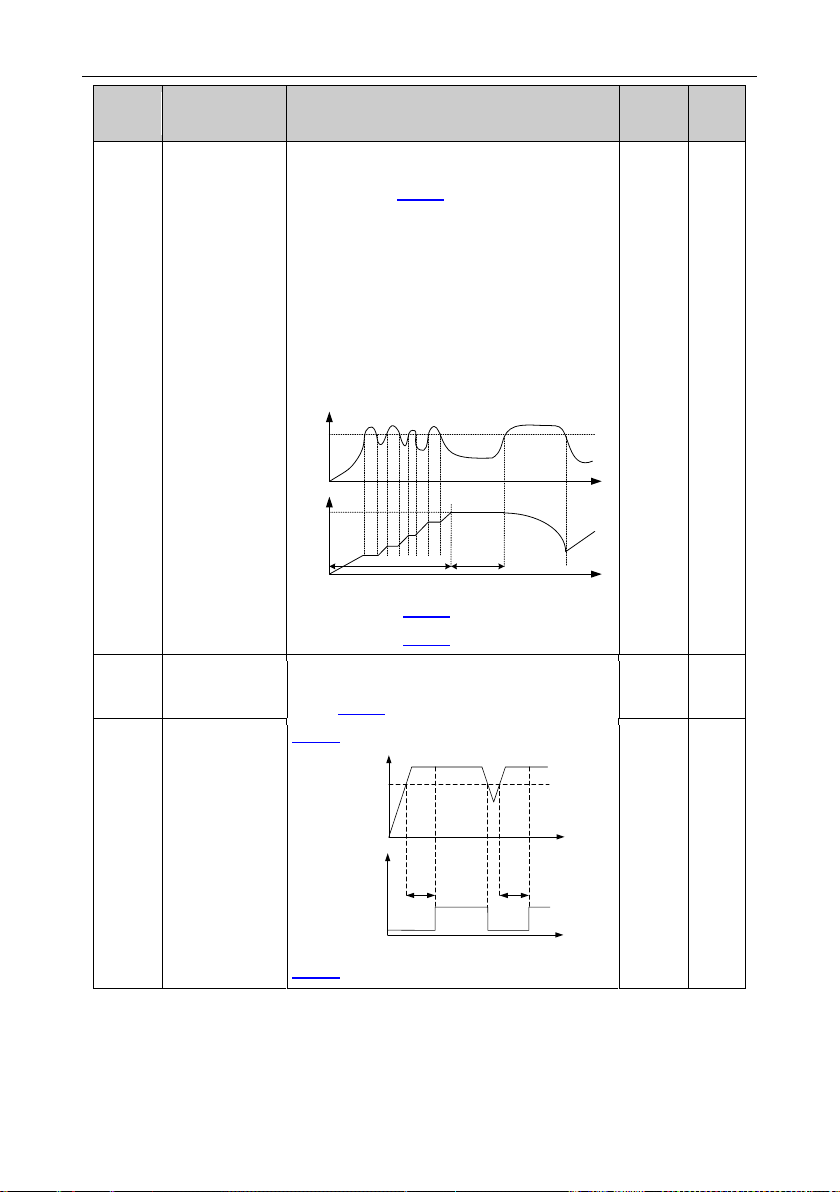
Goodrive300-LIFT series inverter Function parameters
Function
code
Name
Detailed instruction of parameters
Default
value
Modify
P11.07
Frequency-decre
asing ratio
during current
limit
the output current and compare it with the limit
level defined in P11.06. If it exceeds the level,
the inverter will run at stable frequency in ACC
running, or the inverter will derate to run during
the constant running. If it exceeds the level
continuously, the output frequency will keep on
decreasing to the lower limit. If the output
current is detected to be lower than the limit
level, the inverter will accelerate to run.
Output current A
Output frequency
f
Current
limit point
Set
frequency
ACC process
Constant speed
process
Time t
Time t
Setting range of P11.06: 50.0–200.0%
Setting range of P11.07: 0.00–50.00Hz/s
10.00Hz
/s
◎
P11.08
Inverter/motor
overload
alarm
The output current of the inverter or the motor is
above P11.09 and the lasting time is beyond
P11.10, overload alarm will be output.
Y,
RO1, RO2
Output current
Overload alarm
point
Time t
Time t
Alarm time tAlarm time t
P11.08: Enable and define the inverter/motor
0x000
○
P11.09
Overload alarm
detection
Model
G: 150%
○
-64-
Page 69

Goodrive300-LIFT series inverter Function parameters
Function
code
Name
Detailed instruction of parameters
Default
value
Modify
P11.10
Overload alarm
detection
time
overload alarm function.
Setting range: 0x000–0x131
LED ones:
0: Motor overload alarm, relative to the rated
current of the motor
1: Inverter overload alarm, relative to the rated
current of the inverter
LED tens:
0: The inverter continues working after
overload/underload alarm.
1: The inverter continues working after
underload alarm reporting but it stops
running upon an overload fault.
2: The inverter continues working after overload
alarm reporting but it stops running upon an
underload fault.
3: The inverter stops running after
overload/underload alarm reporting.
LED hundreds:
0: Detection all the time
1: Detection in constant running
Setting range of P11.09: 100%–200%
Setting range of P11.10: 0.1–3600.0s
1.0s
○
P11.11
Motor overload
selection
0: No protection
1: Common motor
2: Variable-frequency motor
2
◎
P11.12
Motor overload
protection
coefficient
20.0%–120.0%
100.0
○
P11.13
Speed deviation
detection
0.0–50.0%
10.0%
○
P11.14
Speed deviation
detection time
This parameter is used to set the speed
deviation detection time.
Note: Speed deviation protection is disabled
when P11.14 is set to 0.0.
1.0s
○
-65-
Page 70

Goodrive300-LIFT series inverter Function parameters
Function
code
Name
Detailed instruction of parameters
Default
value
Modify
Speed
Actual detected
value
Set detection
threshold
Time t
t1
t2
t2=P11.14
t1<t2, so the inverter continues running
Running Fault output dEu
Setting range: 0.0–10.0s
P11.15
Emergency
operation
undervoltage
point
0.0–1000.0V
200.0v
◎
P11.16
Operation when
no enabling
signal is found
0: Immediately report the fault and stop
1: Report the fault after stop
0
◎
P11.17
Enabling signal
delay detection
time
0.0–10.0s (running time before an enabling
signal delay is detected)
0.1
○
P12 Group Motor parameters 2 (reserved)
P13 Group Synchronous motor control (reserved)
P14 Group Serial and CAN communication
P14.00
Local
communication
address
Setting range: 1–247
If the slave communication address is set to 0
when the master is writing the frame, the
address is the communication address. All
slaves on the MODBUS fieldbus can receive the
frame, but the salves do not answer.
The local communication address is unique in
the communication network. This is the
fundamental for the point to point
communication between the upper monitor and
the inverter.
Note: The slave address cannot set to 0.
1
○
-66-
Page 71

Goodrive300-LIFT series inverter Function parameters
Function
code
Name
Detailed instruction of parameters
Default
value
Modify
P14.01
Communication
baud ratio
Sets the digital transmission speed between the
upper monitor and the inverter.
0: 1200BPS
1: 2400BPS
2: 4800BPS
3: 9600BPS
4: 19200BPS
5: 38400BPS
6: 57600BPS
7: 115200BPS
Note: The baud rate between the upper PC and
the inverter must be the same. Otherwise, the
communication is not applied. The bigger the
baud rate, the quicker the communication
speed.
4
○
P14.02
Digital bit check
The data format between the upper monitor and
the inverter must be the same. Otherwise, the
communication fails.
0: No check (N,8,1) for RTU
1: Even check (E,8,1) for RTU
2: Odd check (O,8,1) for RTU
3: No check (N,8,2) for RTU
4: Even check (E,8,2) for RTU
5: Odd check(O,8,2) for RTU
1
○
P14.03
Answer delay
0–200ms
The interval time when the drive receives the
data and sent it to the upper monitor. If the
answer delay is shorter than the system
processing time, then the answer delay time is
the system processing time, if the answer delay
is longer than the system processing time, then
after the system deal with the data, waits until
achieving the answer delay time to send the
data to the upper monitor.
5
○
-67-
Page 72

Goodrive300-LIFT series inverter Function parameters
Function
code
Name
Detailed instruction of parameters
Default
value
Modify
P14.04
Communication
timeout fault
duration
0.0 (invalid), 0.1–60.0s
When the function code is set as 0.0, the
parameter is invalid.
When the function code is set as non-zero, if the
interval time between two communications
exceeds this parameter value, the system will
report "485 communication faults" (CE).
Generally, set it as invalid; set the parameter in
the continuous communication to monitor the
communication state.
0.0s
○
P14.05
Transmission
fault processing
0: Alarm and stop freely
1: No alarm and continue to run
2: No alarm and stop according to the stop mode
(only under the communication control)
3: No alarm and stop according to the stop mode
(under all control modes)
0
○
P14.06
Communication
processing
0x00–0x11
LED ones:
0: Write with response: the inverter will respond
to all reading and writing commands of the
upper monitor.
1: Write without response: the inverter only
responds to the reading command other than
the writing command of the drive. The
communication efficiency can be increased by
this method.
LED tens:
0: Communication encrypting invalid
1: Communication encrypting valid
0x00
○
P14.07
CAN
communication
address
0–127 (0 is a broadcast address, indicating that
messages are sent but not replied)
2
○
-68-
Page 73

Goodrive300-LIFT series inverter Function parameters
Function
code
Name
Detailed instruction of parameters
Default
value
Modify
P14.08
CAN
communication
rate
0: 50 k
1: 100 k
2: 125 k
3: 250 k
4: 500 k
0
○
P14.09
CAN
communication
error time
0.0–10.0s
1.0
○
P14.10
Reserved
0–65535
0 ○ P14.11
Reserved
0–65535
0
○
P15 Group Bluetooth communication
P15.00
Expansion card
type
0: No
1: STO
2: IO
3: Bluetooth
1
◎
P15.01
STO function
setting
0: STO alarm locked (the SAFE fault can be
reset)
Alarm locking refers to that after a SAFE fault
occurs and the state is restored, you need to
manually reset.
1: STO alarm not locked
No alarm locking refers to that after a SAFE fault
occurs and the state is restored, the alarm is
automatically deleted.
Note: All of STL1 to STL3 faults are set to alarm
locked, and cannot be reset. After the state is
restored, you need to apply power again for
reset.
0
○
P15.02
Reserved
0–65535
○
P15.03
Reserved
0–65535
○
P15.04
Reserved
0–65535
○
P15.05
Reserved
0–65535
○
P16 Group Ethernet communication
P16.00
Ethernet
communication
speed
0: Self-adapting
1: 100M full duplex
2: 100M semiduplex
3: 10M full duplex
4: 10M semiduplex
3
◎
-69-
Page 74

Goodrive300-LIFT series inverter Function parameters
Function
code
Name
Detailed instruction of parameters
Default
value
Modify
The function code is used to set the Ethernet
communication speed.
P16.01
IP address 1
0–255
Set the IP addresses in Ethernet
communication.
IP address format:
P16.01.P16.02.P16.03.P16.04
IP address example: 192.168.0.1
192 ◎ P16.02
IP address 2
168 ◎ P16.03
IP address 3
28 ◎ P16.04
IP address 4
11
◎
P16.05
Subnet mask 1
0–255
Set the subnet masks in Ethernet
communication.
Subnet mask format:
P16.05.P16.06.P16.07.P16.08
Subnet mask example: 255.255.255.0
255
◎
P16.06
Subnet mask 2
255 ◎ P16.07
Subnet mask 3
255 ◎ P16.08
Subnet mask 4
0 ◎ P16.09
Gateway 1
0–255
Set the gateways in Ethernet communication.
192 ◎ P16.10
Gateway 2
168 ◎ P16.11
Gateway 3
28 ◎ P16.12
Gateway 4
1 ◎ P16.13
Reserved
0–65535
0 ● P16.14
Reserved
0–65535
0
●
P17 Group Monitoring function
P17.00
Set frequency
Display current set frequency of the inverter
Setting range: 0.00Hz–P00.04
0.00Hz
●
P17.01
Output
frequency
Display the current output frequency of the
inverter.
Setting range: 0.00Hz–P00.04
0.00Hz
●
P17.02
Ramp reference
frequency
Display current ramp given frequency of the
inverter.
Setting range: 0.00Hz–P00.04
0.00Hz
●
P17.03
Output voltage
Display current output voltage of the inverter.
Setting range: 0–1200V
0V
●
P17.04
Output current
Display current output current of the inverter.
Setting range: 0.0–5000.0A
0.0A
●
-70-
Page 75

Goodrive300-LIFT series inverter Function parameters
Function
code
Name
Detailed instruction of parameters
Default
value
Modify
P17.05
Motor speed
Display the rotation speed of the motor.
Setting range: 0–65535RPM
0 RPM
●
P17.06
Torque current
Display current torque current of the inverter.
Setting range: -3000.0–3000.0A
0.0A ● P17.07
Exciting current
Display current exciting current of the inverter.
Setting range: -3000.0–3000.0A
0.0A
●
P17.08
Motor power
Display current power of the motor.
Setting range: -300.0–300.0% (relative to the
motor rated power), 0.0% (relative to the motor
rated power)
0.0%
●
P17.09
Output torque
Display the current output torque of the inverter.
Setting range: -250.0–250.0%%
0.0%
●
P17.10
Evaluated motor
frequency
Evaluate the motor rotor frequency on close loop
vector.
Setting range: 0.00–P00.04
0.00Hz
●
P17.11
DC bus voltage
Display current DC bus voltage of the inverter.
Setting range: 0.0–2000.0V
0V
●
P17.12
Digital input
terminals state
Display current Switch input terminals state of
the inverter.
BIT8
BIT7
BIT6
BIT5
HDI
S8
S7
S6
BIT4
BIT3
BIT2
BIT1
BIT0
S5
S4
S3
S2
S1
Setting range: 0000–03FF
0
●
P17.13
Digital output
terminals state
Display current Switch output terminals state of
the inverter.
BIT3
BIT2
BIT1
BIT0
RO2
RO1
HDO
Y
Setting range: 0000–000F
0
●
P17.14
AI1 input voltage
Display analog AI1 input signal.
Setting range: 0.00–10.00V
0.00
●
P17.15
AI2 input voltage
Display analog AI2 input signal.
Setting range: 0.00–10.00V
0.00
●
P17.16
HDI input
frequency
Display HDI input frequency.
Setting range: 0.000–50.000kHz
0.000K
Hz
●
-71-
Page 76

Goodrive300-LIFT series inverter Function parameters
Function
code
Name
Detailed instruction of parameters
Default
value
Modify
P17.17
ASR controller
output
Display ASR controller output in vector control
mode, relative to the percentage of the motor
rated torque.
Setting range: -300.0%–300.0% (motor rated
current)
0.0%
●
P17.18
Actual frequency
detected by the
encoder
Actual frequency detected by the encoder. If the
motor rotates forward, the value is positive; if the
motor rotates reverse, the value is negative.
Setting range: -3276.8–3276.7Hz
0.00Hz
●
P17.19
Encoder pulse
count
Position counting of the encoder, 4 times of the
frequency
Setting range: 0–65535
0
●
P17.20
Encoder Z-pulse
count
Setting range: 0–65535
0 ● P17.21
Magnetic pole
position angle
Setting range: 0.00–359.99
0.00
●
P17.22
Initial magnetic
pole position
angle
Relative angle between the encoder position
and motor magnetic pole position.
Setting range: 0.00–359.99
0.00
●
P17.23
Encoder
C-phase AD
value
Sine-cosine encoder C-signal amplitude
0–4095
0 ● P17.24
Encoder
D-phase AD
value
Sine-cosine encoder D-signal amplitude
0–4095
0
●
P17.25
Motor pole pairs
Display the number of motor pole pairs.
0–65535
0
●
P17.26
Function code of
function
parameter
upload/downloa
d fault
Function codes of faults that occur during
function parameter upload or download
0.00–29.00
0
●
P17.27
Reserved
0–65535
●
P17.28
Reserved
0–65535
●
P18 Group Reserved
-72-
Page 77

Goodrive300-LIFT series inverter Function parameters
Function
code
Name
Detailed instruction of parameters
Default
value
Modify
P19 Group Reserved
P20 Group Encoder
P20.00
Encoder type
0: Incremental encoder (AB)
1: ABZUVW encoder
2: Rotary transformer encoder
3: Sin/Cos encoder without CD signals
4: Sin/Cos encoder with CD signals
5: EnDat
0
◎
P20.01
Pulse quantity
Pulse number when the encoder rotates a circle.
Setting range: 0–60000
1024
◎
P20.02
Encoder
direction
Ones: AB direction
0: Forward
1: Reverse
Tens: Reserved
Hundreds place:
CD (UVW) magnetic signal direction
0: Forward
1: Reverse
0x000
◎
P20.03
Offline detection
time
Detection time of encoder offline fault.
Setting range: 0.0–10.0s
1.0s
○
P20.04
Encoder reverse
fault detection
time
Detection time of encoder reverse fault.
Setting range: 0.0–100.0s
0.8s
○
P20.05
Filter times
Setting range: 0x000–0x999
Ones: filter times at low speed, corresponding to
2^(0–9)*125us
Tens: filter times at high speed, corresponding
to 2^(0–9)*125us
Hundreds: segmented speed detection filter,
corresponding to 2^(0–9)*125us
0x133
○
P20.06
Speed ratio of
motor and
encoder
It is necessary to set the parameter when the
encoder does not install on the motor shaft and
the drive ratio is not 1.
Setting range: 0.001–65.535
1.000
○
P20.07
Synchronous
motor control
parameters
Setting range: 0x0000–0xFFFF
Bit0: Enable Z-pulse correction
Bit1: Enable encoder angle correction
Bit2: Enable SVC speed detection
Bit3: Rotary transformer speed detection mode
Bit4: Z-pulse capture mode
Bit5: V/F control without detecting initial encoder
angle
1
○
-73-
Page 78

Goodrive300-LIFT series inverter Function parameters
Function
code
Name
Detailed instruction of parameters
Default
value
Modify
Bit6: Enable CD signal correction
Bit7: Disable sin/cos segmented speed
detection
Bit8: Autotuning without detecting encoder faults
Bit9: Enable Z-pulse detection optimization
Bit10: Disable Z-pulse correction optimization
Bit12: Stop and clear the Z-pulse arrival signal
P20.08
Offline detection
enabling of Z
pulse
Z pulse offline fault is ENC1Z. Z pulse detection
can be enabled to avoid wrong stopping or
control loss which is caused by Z pulse loss
when spindle stopping or incremental encoder is
used in SM control.
0: Disable
1: Enable
0
○
P20.09
Initial angle of
Z-pulse
Relative angle of encoder Z pulse to motor
magnetic position.
Setting range: 0.00–359.99
0
○
P20.10
Pole initial angle
Relative angle of encoder position to motor
magnetic position.
Setting range: 0.00–359.99
0
○
P20.11
Reserved
Reserved
0
◎
P20.12
Speed
optimization
enabling
0: Disable
1: Enable
1
○
P20.13
CD signal gain
0.80–1.20
1.00
◎
P20.14
C signal bias
0–4095
2048
◎
P20.15
D signal bias
0–4095
2048
◎
P20.16
Reserved
0–65535
0 ○ P20.17
Reserved
0–65535
0
○
P21 Group Distance control
P21.00
Enable distance
control
0x00–0x11
Ones place: Enable control over the distance
between high-speed running and creeping
0: Disabled; 1: Enabled
Tens place: Enable control over the distance
between creeping and stop
0: Disabled; 1: Enabled
0
◎
-74-
Page 79

Goodrive300-LIFT series inverter Function parameters
Function
code
Name
Detailed instruction of parameters
Default
value
Modify
P21.01
High-speed
running DEC
distance
0.200-3.000m
1.800
◎
P21.02
Medium- and
low-speed DEC
distance
0.100-3.000m
1.000
◎
P21.03
DEC distance for
creeping to stop
0.010-1.000m
0.080
◎
P21.04
UP DEC
adjustment
distance
-0.300–0.300m
0.000
◎
P21.05
Down DEC
adjustment
distance
-0.300–0.300m
0.000
◎
P21.06
High-speed step
of multi-step
speed running
0–7 3 ◎
P21.07
Medium- and
low-speed step
of multi-step
speed running
0–7 1 ◎
P21.08
Creeping step of
multi-step speed
running
0–7 0 ◎
-75-
Page 80

Goodrive300-LIFT series inverter Commissioning guidelines
Start
Ensure the wiring between
the controller and inverter is
correct.
Set basic parameters.
End
Execute motor parameter
autotuning.
Adjust maintenance running
parameters.
Adjust S-curve parameters
for normal running.
Adjust comfortability.
Adjust the lift leveling
accuracy.
Debug the running mode.
7.1 What this chapter contains
This chapter describes the commissioning guidelines for GD300L inverters special for lifts.
The commissioning process is as follows.
7 Commissioning guidelines
Figure 7-1 Commissioning process
-76-
Page 81

Goodrive300-LIFT series inverter Commissioning guidelines
R
S
T
S1
S2
S3
S4
S5
S6
S7
S8
HDI(S9)
W
V
U
PE
Y1
LR
EO
KM1
Maintenance
Brake feedback
Contactor feedback
Multi-step speed 3
Multi-step speed 2
Multi-step speed 1
Enable
Down
Up
Fault output
RO1
RO2
RO3
Weigh AI1 input
FC(brake
control)
TC(contactor
control)
Car
PG
M
KM2
GD300L inverter
special for lifts
3PH
380V-15%
~440V+15%
50/60Hz
Lift controller
FWD
REV
ENA
MS1
MS2
MS3
TB
FB
EXM
Lift controller
3PH
380V-15%
~440V+10%
50/60Hz
GD300L inverter
special for
lifts
KM2
M
PG
TC(contactor
control)
FC(brake
control)
RO3
RO2
RO1
Fault
output
Enable
Up
Down
Maintenance
Contactor feedback
Brake feedback
KM1
EO
LR
Y1
PE
U
V
W
AI1
FB
TB
EXM
REV
FWD
ENA
T
S
R
Speed command
S1
S2
S3
S7
S8
HDI(S9)
SPD
7.2 Wiring between the lift controller and inverter
7.2.1 Wiring for the multi-step speed running mode
7.2.2 Wiring for the analog speed running mode
7.3 Setting basic parameters
After correct wiring, set application parameters as required. Pay high attention to the parameters
related to peripheral electrical wiring, such as operation mode, control mode, programmable
input/output setting, and feedback selection. Perform commissioning only after these parameters are
correctly set. The table below lists the basic parameters.
Figure 7-2 Typical wiring for the multi-step speed running mode
Figure 7-3 Wiring for the analog speed running mode
-77-
Page 82

Goodrive300-LIFT series inverter Commissioning guidelines
Function code
Name
Recommended
Remarks
P00.00
Speed control mode
0 or 3
0: Open-loop control for
asynchronous motors; 3:
Closed-loop control for
synchronous motors
P00.01
Running command
channel
1
P00.02
Lift rated speed
Based on lift speed
P00.03
Speed command 3
P00.04
Max. output
frequency
50.00Hz
P02.00
Motor type
Based on the
motor.
P02.01
Motor rated power
Tractor parameter
name plate
P02.02
Motor rated
frequency
Tractor parameter
name plate
P02.03
Motor rated rotation
speed
Tractor parameter
name plate
P02.04
Motor rated voltage
Tractor parameter
name plate
P02.05
Motor rated current
Tractor parameter
name plate
P20.00
Encoder type 0
P20.01
Encoder pulse
quantity
Based on the
encoder model
P20.02
Encoder direction 0
P05.01
S1
1
Up
P05.02
S2 2 Down
P05.03
S3
19
Enable
P05.04
S4 8 Multi-step speed 1
P05.05
S5 9 Multi-step speed 2
P05.06
S6
10
Multi-step speed 3
P05.07
S7
17
Contactor feedback
P05.08
S8
18
Brake feedback
P05.12
HDI 3 Maintenance
P06.01
Y output
1
Running feedback output
P06.04
RO1 relay output
4
Fault output
-78-
Page 83

Goodrive300-LIFT series inverter Commissioning guidelines
Function code
Name
Recommended
Remarks
P06.05
RO2 relay output
7
Brake output
P06.06
RO3 relay output
8
Contactor output
Start
P00.01=0
Motor type
(P02.00)
P02.00=1 P02.00=0
Enter the motor name plate.
(P02.01~P02.05)
P00.09=2 P00.09=4
Set the autotuning mode.
(P00.09)
Press “RUN”to start
autotuning.
Display “-END-”
Autotuning
Synchronous
motor
Asynchronous
motor
End
P00.09=3
P00.09=5P00.09=1
7.4 Debugging running
After parameters are correctly set, debug running, including adjusting motor parameter autotuning,
maintenance running, S curve for normal running, comfortability at startup or stop, and lift leveling
accuracy.
7.4.1 Motor parameter autotuning
The control performance of the inverter is based on the established accurate motor model. You have
to carry out the motor autotune before first running. Set the inverter to use the keypad control mode
(P00.01=0), and execute parameter autotuning by using the method described in P00.09. The figure
below describes the autotuning process which takes motor 1 for example.
Figure 7-4 Motor parameter autotuning
-79-
Page 84

Goodrive300-LIFT series inverter Commissioning guidelines
Function code
Name
Setting range
P01.01
Starting frequency of direct
startup
0.00–50.00 [0.00Hz]
P01.03
Starting frequency retention
time
0.0–50.0 [0.0s]
P01.12
Stop knee-point frequency
0.00–10.00 [1.00Hz]
P09.09
S-curve ACC start segment
duration
0.1–360.0 [2.0s]
P09.10
S-curve ACC end segment
duration
0.1–360.0 [2.0s]
P09.11
ACC time
0.1–360.0 [2.0s]
P09.12
S-curve DEC start segment
duration
0.1–360.0 [2.0s]
P09.13
S-curve DEC end segment
duration
0.1–360.0 [2.0s]
P09.14
DEC time
0.1–360.0 [2.0s]
P09.15
S-curve start segment duration
during stop
0.1–360.0 [2.0s]
P09.16
S-curve end segment duration
during stop
0.1–360.0 [2.0s]
P09.24
DEC time for creeping to stop
0.1–360.0 [2.0s]
Note:
• Set the motor parameters according to the motor name plate.
• Note the difference in synchronous and asynchronous motor parameter autotuning modes.
7.4.2 Adjusting maintenance running parameters
Maintenance running can be used to check whether the lift is running properly.
During maintenance, check whether the actual lift running direction is the same as the direction in the
command. If not, exchange any two cables of U, V, and W or set P00.06=1.
Note: For the synchronous motor, changing the motor cables requires autotuning the motor
parameter (pole angle) again. It is recommended to set P00.06 to change the lift running direction.
7.4.3 Adjusting the S curve for normal running
Before normal running, check whether the control logic is correct and wiring is correct. If they are
correct, adjust the S curve. For details, see the descriptions of P09.09–P09.16.
-80-
Page 85

Goodrive300-LIFT series inverter Commissioning guidelines
P09.10
P09.11
P09.09
P01.03
P01.01
P09.13
P09.12
P09.14
P09.15
P09.24
P09.16
Frq
t
Value decreased Value increased
P09.11
P09.09–P09.16 determine the S-curve shape. The S-curve quality directly impacts the comfortability
of the lift at startup or stop. The S-curve parameters are listed in the table above. Figure 7-5 describes
the relationship between these parameters and S-curve.
Figure 7-5 S-curve running
Figure 7-6 S-curve adjusting
Figure 7-6 describes the ACC segment S-curve parameter adjustment, in which the S curve changes
sharply when the time decreases but the S curve changes slightly when the time increases. The
adjustment principle of the DEC segment S-curve parameters and stop segment S-curve parameters
are similar to that for the ACC segment S-curve parameters.
P01.01 indicates the initial frequency during inverter startup. During inverter running, if the set speed
(frequency) is less than the starting frequency of startup, the inverter output frequency is 0. Only
when the set speed (frequency) is greater than or equal to the starting frequency, the inverter starts at
the starting frequency and runs according to the S curve. Setting a proper starting frequency can
reduce startup impact by overcoming the static friction during startup.
P01.03 indicates the starting frequency retention time during inverter startup.
Note: P09.09–P09.16 are key S-curve parameters, impacting passenger comfortability during ACC,
DEC, and stop.
7.4.4 Adjusting comfortability during startup or stop
Startup comfortability can be adjusted by setting the following function codes: P01.01, P01.03, P09.09,
P09.10, P09.11, P03.00, P03.01, and P08.05. If the analog weighing equipment is used, startup
pre-torque compensation must be adjusted. For details, see the descriptions of the function codes.
Stop comfortability can be adjusted by setting the following function codes: P09.15, P09.16, P03.00,
P03.01, and P08.04.
7.4.5 Adjusting lift leveling accuracy
If floors are different in the leveling error, adjust each position of flashboard to keep the same errors
-81-
Page 86

Goodrive300-LIFT series inverter Commissioning guidelines
T3
T4
T5
T6
T7
OFF
OFF
OFF
ON
ON
ON
ON
OFF
ON
ON
ON
ON
Brake feedback
Brake control
Running
MS3
MS2
MS1
Contactor feedback
Contactor control
FWD
t
v
T1
T2
T8
OFF
OFF
OFF
OFF
OFF
ON
on every floor, and adjust creeping speed of elevator (set by multi-step speed) and P09.16 (stop
S-curve end segment duration).
7.5 Lift running mode
There are two running modes for GD300L: multi-step speed and analog quantity speed. The
multi-step speed mode is mainly used.
7.5.1 Multi-step speed mode (brake and contactor are inverter controlled)
In multi-step speed mode, the speed command can be selected by external multi-step terminals. See
Figure 7-2 for the wiring diagram. Brake and contractor are inverter controlled. Detecting the brake,
contactor feedback signal, and maintenance command are controlled by input terminal (EXM). Run
speeds are given by MS1–MS3 and the analog quantity of weighing equipment are applied.
Running sequence description:
1. After receiving the FWD and MS1–MS3 commands from the controller, the inverter sends the
2. After T1, the inverter detects the contactor actuation feedback.
3. With the delay of T2 after receiving the running command, the inverter starts zero-speed
4. The inverter sends the brake control signal with the delay of T3.
5. After T4, the inverter detects the brake is completely open and then starts ACC at the starting
6. After the controller switches off the speed command (MS1–MS3), the inverter decelerates to
Figure 7-7 Lift multi-step speed running sequence chart
contactor actuation command and outputs the running signal.
output.
frequency.
stop according to the S curve. If the frequency reaches P08.14, the inverter outputs the brake
switch-off command with the delay of T5, requiring the controller to remove the running
command.
-82-
Page 87

Goodrive300-LIFT series inverter Commissioning guidelines
Function
code
Name
Recommended value
Remarks
P00.00
Speed control mode
1
SVC 1
P00.01
Running command
1
Terminal control
P00.02
Lift rated speed
1.500m/s
User defined
P00.03
Speed command
3
Multi-step speed
P00.04
Max. output frequency
50.00Hz
User defined
P01.01
Starting frequency of
direct startup
0.00 (closed-loop
control)
0.50 (open-loop
control)
P01.12
Stop knee-point
frequency
1.00
Generally, the speed is
consistent with the leveling
speed. It is usually used to switch
the stop curve. After the speed
decreases to this point, the stop
curves switches to the stop S
curve.
P02.00
Motor type
Determined motor type
According to the parameter
values on the motor name plate
P02.01
Motor rated power
Parameter value on the
motor name plate
P02.02
Motor rated frequency
Parameter value on the
motor name plate
P02.03
Motor rated rotation
speed
Parameter value on the
motor name plate
P02.04
Motor rated voltage
Parameter value on the
motor name plate
P02.05
Motor rated current
Parameter value on the
motor name plate
P03 group
Vector control
Default value
Adjusted based on the running
conditions
P05.01
S1 function selection
1
Upward running (FWD)
7. After T6, the inverter receives the stop command from the controller. With the delay of T7, the
inverter stops output and withdraws the running signal. With the delay of T8, the inverter
disconnects the contactor and the running process ends.
Note: The preceding logic is applicable to contactor and brake signal control by the inverter. For
brake and contactor control signal output, the running signal can be used for contactor control and
then the auxiliary point of the contactor and control system are serially connected for brake control.
The table below lists the typical function codes for multi-step speed running.
-83-
Page 88

Goodrive300-LIFT series inverter Commissioning guidelines
Function
code
Name
Recommended value
Remarks
P05.02
S2 function selection
2
Downward running (REV)
P05.03
S3 function selection
19
Inverter enabling (ENA)
P05.04
S4 function selection
8
Multi-step speed terminal 1
(MS1)
P05.05
S5 function selection
9
Multi-step speed terminal 2
(MS2)
P05.06
S6 function selection
10
Multi-step speed terminal 3
(MS3)
P05.07
S7 function selection
17
Contactor feedback (TB)
P05.08
S8 function selection
18
Brake feedback (FB)
P05.09
S9 function selection
6
Fault reset (RET)
P05.12
HDI terminal
3
Maintenance
P06.01
Y output
1
Running feedback output
P06.04
Relay 1 output
4
Fault output (EO)
P06.05
Relay 2 output
7
Brake control (FC)
P06.06
Relay 3 output
8
Contactor control (TC)
P08.04
Brake close delay
0.1s
P08.05
Brake release delay
0.10s
P08.06
Brake feedback
detection time
2.0
P08.08
Contactor feedback
detection time
2.0
P08.15
Inverter stop delay
0.10s
P09.00
Multi-step speed 0
0 (Zero speed)
Set based on user control
requirements. The speed of step
0 is set to 0 m/s.
P09.01
Multi-step speed 1
Re-leveling speed
P09.02
Multi-step speed 2
Creeping speed
P09.03
Multi-step speed 3
Emergency speed
P09.04
Multi-step speed 4
Reserved
P09.05
Multi-step speed 5
Normally low speed
P09.06
Multi-step speed 6
Normally high speed 1
P09.07
Multi-step speed 7
Normally high speed 2
P09.09
S-curve ACC start
segment duration
2.0s
Adjusted based on the onsite
commissioning
P09.10
S-curve ACC end
segment duration
2.0s
-84-
Page 89

Goodrive300-LIFT series inverter Commissioning guidelines
Function
code
Name
Recommended value
Remarks
P09.11
ACC time
2.0s
P09.12
S-curve DEC start
segment duration
2.0s
P09.13
S-curve DEC end
segment duration
2.0s
P09.14
DEC time
2.0s
P09.15
S-curve start segment
duration during stop
2.0s
P09.16
S-curve end segment
duration during stop
2.0s
P09.17
Maintenance running
speed
0.200m/s
P09.18
Maintenance ACC/
DEC time
4.0s
P09.24
DEC time for creeping
to stop
2.0s
P20.00
Encoder type
Determined encoder
type/pulse quantity
Depend on the encoder used
P20.01
Encoder pulse quantity
P20.02
Encoder direction
0
Modified according to the
commissioning result
FWD
Contactor
control
Contactor
feedback
MS1
MS2
MS3
Running
Brake
control
Brake
feedback
ON
ON
ON
ON
ON
ON
ON
ON
ON
OFF
OFF
OFF
OFF
OFF
OFF
OFF
OFF
t
V
T3
T2
T1
P08.04
P00.01
T4
P08.04
T5
T6
Note: In multi-step speed running mode, multi-step speed 0 must be set to zero speed.
Figure 7-8 Open-loop running sequence
-85-
Page 90

Goodrive300-LIFT series inverter Commissioning guidelines
Function
code
Name
Recommended
value
Remarks
P00.00
Speed control mode
0
SVC 0
P00.01
Running command
1
Terminal
P00.02
Lift rated speed
1.500m/s
User defined
P00.03
Speed command
3
Multi-step speed running
P00.04
Max. output
frequency
50.00Hz
User defined
P01.00
Start mode
1
Start after DC braking
P01.01
Direct start
frequency
0.2Hz
P01.04
Pre-start braking
current
80%
P01.08
Start frequency in
stop braking
0.2Hz
P01.10
Stop DC braking
current
80%
P01.12
Stop knee-point
frequency
5.00
Generally, the speed is consistent with
the leveling speed. It is usually used to
switch the stop curve. After the speed
decreases to this point, the stop curves
switches to the stop S curve.
Running sequence description:
1. After receiving the FWD and MS1–MS3 commands from the controller, the inverter sends the
contactor close command and outputs the running signal.
2. With the delay of T2 after receiving the running command, the inverter starts to accelerate to
the start frequency set in P01.01.
3. After accelerating from the start frequency to the braking frequency (P08.14), the inverter
sends the brake open signal with the delay of T3 (P08.05, brake open delay).
4. After the brake is open, the inverter accelerates to the reference speed.
5. After the controller switches off the speed command (MS1–MS3), the inverter decelerates to
stop according to the S curve. When the frequency reaches P08.14 (stop braking frequency),
the inverter outputs the brake close command with the delay of T4 (P08.04, brake close delay),
requiring the controller to remove the running command.
6. After receiving the stop command sent by the controller, the inverter stops output with the delay
of T5 (P08.15), and the running signals are cancelled. After the delay of T6 (P08.28), the
contactor is opened, and the running process ends.
The table below lists the typical function codes for open-loop running.
-86-
Page 91

Goodrive300-LIFT series inverter Commissioning guidelines
Function
code
Name
Recommended
value
Remarks
P02.00
Motor type
Determined motor
type
According to the parameter values on
the motor name plate
P02.01
Motor rated power
Parameter value on
the motor name
plate
P02.02
Motor rated
frequency
Parameter value on
the motor name
plate
P02.03
Motor rated rotation
speed
Parameter value on
the motor name
plate
P02.04
Motor rated voltage
Parameter value on
the motor name
plate
P02.05
Motor rated current
Parameter value on
the motor name
plate
P03 group
Vector control
Default value
Adjusted based on the running
conditions
P05.01
S1 function
selection
1
Upward running (FWD)
P05.02
S2 function
selection
2
Downward running (REV)
P05.03
S3 function
selection
19
Inverter enabling (ENA)
P05.04
S4 function
selection
8
Multi-step speed terminal 1 (MS1)
P05.05
S5 function
selection
9
Multi-step speed terminal 2 (MS2)
P05.06
S6 function
selection
10
Multi-step speed terminal 3 (MS3)
P05.07
S7 function
selection
17
Contactor feedback (TB)
P05.08
S8 function
selection
18
Brake feedback (FB)
P05.09
S9 function
selection
6
Fault reset (RET)
-87-
Page 92

Goodrive300-LIFT series inverter Commissioning guidelines
Function
code
Name
Recommended
value
Remarks
P05.12
HDI terminal
3
Maintenance
P06.01
Y output
1
Running feedback output
P06.04
Relay 1 output
4
Fault output (EO)
P06.05
Relay 2 output
7
Brake control (FC)
P06.06
Relay 3 output
8
Contactor control (TC)
P08.04
Brake close delay
0.1s
P08.05
Brake release delay
0.10s
P08.06
Brake feedback
detection time
2.0
P08.08
Contactor feedback
detection time
2.0
P08.14
Braking frequency
0.05Hz
P08.15
Inverter stop delay
0.10s
P08.30
Open-loop start
brake open
frequency of
asynchronous motor
0.0 Hz
P09.00
Multi-step speed 0
0 (speed of zero)
Set based on user control requirements.
The speed of step 0 is set to 0 m/s.
P09.01
Multi-step speed 1
Leveling speed
P09.02
Multi-step speed 2
Emergency speed
P09.03
Multi-step speed 3
Common low
speed
P09.04
Multi-step speed 4
Inspection speed
P09.05
Multi-step speed 5
Reserved
P09.06
Multi-step speed 6
Reserved
P09.07
Multi-step speed 7
Common high
speed
P09.09
S-curve ACC start
segment duration
2.0s
Adjusted based on onsite
commissioning
P09.10
S-curve ACC end
segment duration
2.0s
P09.11
ACC time
2.0s
P09.12
S-curve DEC start
segment duration
2.0s
P09.13
S-curve DEC end
2.0s
-88-
Page 93

Goodrive300-LIFT series inverter Commissioning guidelines
Function
code
Name
Recommended
value
Remarks
segment duration
P09.14
DEC time
2.0s
P09.15
S-curve start
segment duration
during stop
2.0s
P09.16
S-curve end
segment duration
during stop
2.0s
P09.17
Maintenance
running speed
0.200m/s
P09.18
Maintenance ACC/
DEC time
4.0s
P09.24
DEC time for
creeping to stop
1.0s
7.5.2 Analog tracking running
This running mode indicates that the speed command is provided by analog input, the inverter
passively runs based on the analog signal as provided, the lift running curve is determined by the
analog change curve generated by the external controller, and the inverter is responsible for driving
the motor to run. The analog tracking running input channel must be provided by AI1 (P00.03=5).
Running sequence
The running sequence in this mode is similar to that in the multi-step speed running mode.
Note:
• During analog tracking running, the inverter internal S curve does not work, the S curve of lift
running is generated by the lift controller. Adjusting P05.17 or P05.22 impacts the sensitivity of
analog input.
• Great analog change ratio will cause inverter running frequency transient, which may result in
inverter overcurrent or overvoltage.
7.5.3 Maintenance running
Figure 7-9 shows the basic wiring for maintenance running.
-89-
Page 94

Goodrive300-LIFT series inverter Commissioning guidelines
R
S
T
ENA
FWD
REV
EXM
FB
TB
W
V
U
PE
Y1
Y2
LR
RD
EO
KM1
Brake feedback
Contactor feedback
Maintain
Down
Up
Enable
Fault output
RO1
RO2
RO3
FC(brake control)
TC(contactor control)
PG
M
KM2
GD300L inverter
special for lifts
3PH
380V±15%
50/60Hz
Lift controller
T3
T4
T5
T6
T7
OFF
OFF
OFF
ON
ON
ON
ON
OFF
ON
ON
ON
Brake feedback
Brake control
Running
Maintenance
Contactor feedback
Contactor control
FWD
t
v
T1
T2
T8
OFF
OFF
OFF
ON
The maintenance running is the same as the normal timing sequence. The maintenance ACC/DEC is
linear. The maintenance speed is set by P09.17.
Figure 7-10 shows the maintenance running timing sequence.
7.5.4 Emergency running
As shown in Figure 7-10, DC UPS connects to the inverter main circuit terminals (+) and (-) through
KM3, D1 and D2 and connects to the control power board through contactor C, the control power
board output connects to the inverter control power input terminals DC+ and DC-, and the main circuit
power connects to the inverter main circuit terminals R, S, and T through KM1.
Figure 7-9 Wiring for maintenance running
Figure 7-10 Maintenance running timing sequence
-90-
Page 95

Goodrive300-LIFT series inverter Commissioning guidelines
3PH
380V±15%
50/60Hz
GD300L
inverter
for lifts
KM2
M
KM1
U
V
W
T
S
R
KM3
DC UPS power
recommended:
300~500V
+
-
+
-
EMER
DC+
DC-
+
Emergency
command
Diode
KM4
Terminal
Description
EMER
Emergency running
FWD
Upward running
REV
Downward running
+, -
Inverter DC bus voltage wiring terminals
DC+, DC-
UPS emergency power wiring terminals
KM1
Control contactor of main power
KM3, KM4
Control contactors of emergency power
T4
T5
T6
T7
T8
OFF
OFF
OFF
ON
ON
ON
ON
OFF
ON
ON
ON
Brake feedback
Brake control
Running
FWD
Contactor feedback
Contactor control
EMER
t
v
T1
T3
T9
OFF
OFF
OFF
ON
OFF
ON
KM3/KM4
OFF
ON
KM1
OFF
T0
T2
Emergency running terminals
Emergency running timing sequence
The meanings of T0–T9 are as follows:
Figure 7-11 Wiring for emergency running
Figure 7-12 Emergency running timing sequence
-91-
Page 96

Goodrive300-LIFT series inverter Commissioning guidelines
Symbol
Description
T0
Delay time from the main power is off to the switch of emergency power
input contactors KM3 and KM4 are on
T1
Delay time from the time when the inverter receives the run signal to the
time when the inverter outputs contactor actuation command
T2
Wait delay time from the time when the inverter outputs contactor
actuation command to the time when the inverter receives the contactor
feedback signal
T3
Relay time from the time when the run command is sent to the time when the
run signal is output
T4
Delay time from the time when the run signal is output to the time when the
brake open signal is sent.
T5
Interval from the brake open command sending time to the feedback time of
brake open.
T6
P08.04 (Brake close delay time)
T7
Wait delay time from the time when the inverter outputs the brake close
command to the time when the inverter receives the stop command from the
external controller
T8
Inverter stop delay time
T9
P08.28 (Contactor switch-off delay)
After the main circuit power is off, contactor B is switched off first. Before the bus voltage decreases to
300V, contactor A and contactor C are switched on.
1. When the main power is off, the controller cuts off main power relay (KM1), after T0, the control
switch of emergency power will be closed, and output emergency command at the same time ,
after T1, the inverter receives the running command (FWD/REW) from the controller.
2. Then after T2, the inverter detects the contactor actuation command signal, and then the
inverter starts to run at zero speed, at the same time outputs running signal (Y1). After T4, the
inverter outputs brake release signal.
3. After T5, the inverter receives brake feedback signal, after affirming the brake is released
completely, the inverter accelerates with emergency acceleration time (P09.21) to reach to
emergency speed (P09.20), and then runs at a constant speed.
4. When the lift runs to the flat floor, the controller will cut off emergency command (EMER), and
the inverter begins to decelerate to stop with emergency deceleration (P09.21), when the
inverter decelerates to P08.14, after T6, the inverter outputs brake close command, and
requires the controller to cut off running command.
5. After T7, the inverter receives stop command, and then after the delay time of T8 and T9, the
-92-
Page 97

Goodrive300-LIFT series inverter Commissioning guidelines
Function
code
Name
Recommended value
Remarks
P02.14
Pulley diameter
100–2000mm
500mm
P02.15
DEC ratio
0.50–50.00
1.00
P21.00
control
0x00–0x11
Ones place: Enable control over the distance
between high-speed running and creeping
0: Disabled; 1: Enabled
Tens place: Enable control over the distance
between creeping and stop
0: Disabled; 1: Enabled
0
P21.01
High-speed running
DEC distance
0.200-3.000m
1.800
P21.02
Medium- and
low-speed DEC
distance
0.100-3.000m
1.000
P21.03
DEC distance for
creeping to stop
0.010-1.000m
0.080
P21.04
UP DEC adjustment
distance
-0.300–0.300m
0.000
P21.05
Down DEC
adjustment distance
-0.300–0.300m
0.000
P21.06
High-speed step of
multi-step speed
running
0–7
3
P21.07
Medium- and
low-speed step of
multi-step speed
running
0–7
1
P21.08
Creeping step of
multi-step speed
running
0–7
0
inverter stops, and outputs contactor releasing command and lift stop signal (Y1). By now, one
operation cycle ends.
7.5.5 Distance control
-93-
Page 98

Goodrive300-LIFT series inverter Commissioning guidelines
Speed switch point
Command
cancelling point
v
t
Speed
switch point
Command
cancelling point
v
t
Distance for
decelerating from
high speed to
creeping speed
Distance for
decelerating from
creeping speed to 0
When distance control P21.00 is set to 0×1, the distance for decelerating from high speed to 0 is
P21.01, and that for decelerating from medium or low speed to 0 is P21.02, as shown in Figure 7-13.
Figure 7-13 Curve of deceleration without creeping
When distance control P21.00 is set to 0×11, the distance for decelerating from high speed to
creeping speed is P21.01, that for decelerating from medium or lower speed to creeping speed is
P21.02, and that for decelerating from creeping speed to 0 is P21.03, as shown in Figure 7-14.
Figure 7-14 Curve of deceleration with creeping
-94-
Page 99

Goodrive300-LIFT series inverter Fault tracking
Only qualified electricians are allowed to maintain the inverter. Read the safety
instructions in chapter Safety precautions before working on the inverter.
Code
Fault
Possible cause
Solution
OUt1
IGBT U phase
protection
The acceleration is too
fast
There is damage to the
internal to IGBT of the
phase
The connection of the
Increase ACC time
Change the power unit
Check the driving wires
Check if there is strong
interference to the external
equipment
OUt2
IGBT V phase
protection
OUt3
IGBT W phase
8 Fault tracking
8.1 What this chapter contains
This chapter tells how to reset faults and view fault history. It also lists all alarm and fault messages
including the possible cause and corrective actions.
8.2 Alarm and fault indications
Fault is indicated by LEDs. See Keypad operation Procedure. When TRIP light is on, an alarm or
fault message on the panel display indicates abnormal inverter state. Using the information given in
this chapter, most alarm and fault cause can be identified and corrected. If not, contact with the INVT
office.
8.3 How to reset
The inverter can be reset by pressing the keypad key STOP/RST, through digital input, or by
switching the power light. When the fault has been removed, the motor can be restarted.
8.4 Fault history
Function codes P07.28–P07.37 store 10 recent faults. Function codes P07.38–P07.45,
P07.46–P07.54, and P07.55–P07.61 show inverter operation data at the time the latest 3 faults
occurred.
8.5 Inverter faults and solutions
Do as the following after the inverter fault:
1. Check to ensure there is nothing wrong with the keypad. If not, please contact with the local
INVT office.
2. If there is nothing wrong, please check P07 and ensure the corresponding recorded fault
parameters to confirm the real state when the current fault occurs by all parameters.
3. See the following table for detailed solution and check the corresponding abnormal state.
4. Eliminate the fault and ask for relative help.
5. Check to eliminate the fault and carry out fault reset to run the inverter.
8.5.1 Inverter faults and solutions
-95-
Page 100

Goodrive300-LIFT series inverter Fault tracking
Code
Fault
Possible cause
Solution
protection
driving wires is not good
The grounding is not
good; Interference causes
maloperation
OV1
ACC overvoltage
The input voltage is
abnormal
There is large energy
feedback
No braking components
Braking energy is not
open
Check the input power
Check if the DEC time of
the load is too short or the
inverter starts during the
rotation of the motor or it
needs to increase the
energy consumption
components
Install the braking
components
Check the setting of relative
function codes
OV2
DEC overvoltage
OV3
Constant
overvoltage
OC1
ACC overcurrent
The acceleration or
deceleration is too fast
The voltage of the grid is
too low
The power of the inverter
is too low
The load transients or is
abnormal
The grounding is short
circuited or the output is
phase loss
There is strong external
interference
The overvoltage stall
protection is not open
Increase the ACC time
Check the input power
Select the inverter with a
larger power
Check if the load is short
circuited (the grounding
short circuited or the wire
short circuited) or the
rotation is not smooth
Check the output
configuration.
Check if there is strong
interference
Check the setting of relative
function codes
OC2
DEC overcurrent
OC3
Constant
overcurrent
UV
Bus undervoltage
fault
The voltage of the power
supply is too low
The overvoltage stall
protection is not open
Check the input power of
the supply line
Check the setting of relative
function codes
OL1
Motor overload
The voltage of the power
supply is too low
Motor rated current is
incorrect
The motor stall or load
Check the power of the
supply line
Reset the rated current of
the motor
Check the load and adjust
-96-
 Loading...
Loading...