RFT3055LE
Data Sheet August 1999
2.0A, 60V, 0.150 Ohm, N-Channel, Logic
Level, ESD Rated, Power MOSFET
This product is an N-Channel powerMOSFETmanufactured
using the MegaFET process. This process, which uses
feature sizes approaching those of LSI circuits, gives
optimum utilization of silicon, resulting in outstanding
performance. It was designed foruse in applications such as
switching regulators, switching converters, motor drivers,
and relay drivers. These transistors can be operated directly
from integrated circuits.
Formerly developmental type TA49158.
Ordering Information
PART NUMBER PACKAGE BRAND
RFT3055LE SOT-223 3055L
NOTE: RFT3055LE is available only in tape and reel.
File Number
Features
• 2.0A, 60V
•r
• 2kV ESD Protected
• Temperature Compensating PSPICE
• Thermal Impedance SPICE Model
• Peak Current vs Pulse Width Curve
• UIS Rating Curve
• Related Literature
- TB334, “Guidelines for Soldering Surface Mount
= 0.150Ω
DS(ON)
Components to PC Boards”
®
Model
Symbol
D
G
4537.3
Packaging
S
SOT-223
DRAIN
(FLANGE)
SOURCE
DRAIN
GATE
8-143
CAUTION: These devices are sensitive to electrostatic discharge; follow proper ESD Handling Procedures.
PSPICE® is a registered trademark of MicroSim Corporation.
http://www.intersil.com or 407-727-9207
| Copyright © Intersil Corporation 1999
RFT3055LE
Absolute Maximum Ratings T
= 25oC, Unless Otherwise Specified
A
RFT3055LE UNITS
Drain to Source Voltage (Note 1). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .V
Drain to Gate Voltage (RGS = 20kΩ) (Note 1) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .V
Gate to Source Voltage . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . V
DSS
DGR
GS
60 V
60 V
±10 V
Drain Current
Continuous (Figure 2) (Note 2). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .I
Pulsed Drain Current . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . I
Pulsed Avalanche Rating. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . E
Power Dissipation (Note 2) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . P
D
DM
AS
D
Derate Above 25oC . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Operating and Storage Temperature . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . TJ, T
STG
Maximum Temperature for Soldering
Leads at 0.063in (1.6mm) from Case for 10s. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . T
Package Body for 10s, See Techbrief 334 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .T
CAUTION: Stresses above those listed in “Absolute Maximum Ratings” may cause permanent damage to the device. This is a stress only rating and operationofthe
device at these or any other conditions above those indicated in the operational sections of this specification is not implied.
L
pkg
2.0
Figure 5
Figures 6, 16, 17
1.1
9.09
-55 to 150
300
260
A
W
mW/oC
o
C
o
C
o
C
NOTE:
1. TJ = 25oC to 125oC.
Electrical Specifications T
= 25oC, Unless Otherwise Specified
A
PARAMETER SYMBOL TEST CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNITS
Drain to Source Breakdown Voltage BV
Gate to Source Threshold Voltage V
Zero Gate Voltage Drain Current I
DSSID
GS(TH)VGS
DSS
= 250µA, VGS = 0V (Figure 11) 60 - - V
= VDS, ID = 250µA (Figure 10) 1 - 2 V
VDS = 60V, VGS = 0V - - 1 µA
VDS = 60V, VGS = 0V, TA = 150oC--50µA
Gate to Source Leakage Current I
Drain to Source On Resistance r
DS(ON)ID
Turn-On Time t
Turn-On Delay Time t
d(ON)
Rise Time t
Turn-Off Delay Time t
d(OFF)
Fall Time t
Turn-Off Time t
Total Gate Charge Q
g(TOT)VGS
Gate Charge at 10V Q
Threshold Gate Charge Q
GSS
ON
OFF
g(5)
g(TH)
VGS = ±10V - - 10 µA
= 2.0A, VGS = 5V (Figure 9) - 0.110 0.150 Ω
VDD = 30V, ID≅ 2.0A,
RL = 15Ω, VGS= 5V,
RGS = 5Ω
(Figure 12)
r
- - 120 ns
-10-ns
-70-ns
-30-ns
f
-25-ns
- - 85 ns
= 0V to 10V VDD = 30V,
VGS = 0V to 5V - 15 18 nC
VGS = 0V to 1V - 1.0 1.2 nC
ID≅ 2.0A,
RL = 15Ω
I
= 1.0mA
g(REF)
-2835nC
(Figure 15)
Input Capacitance C
Output Capacitance C
Reverse Transfer Capacitance C
Thermal Resistance Junction to Ambient R
ISS
OSS
RSS
θJA
VDS = 25V, VGS = 0V,
f = 1MHz
(Figure 12)
- 850 - pF
- 170 - pF
- 100 - pF
Pad Area = 0.171 in2 (see note 2) - - 110
Pad Area = 0.068 in
Pad Area = 0.026 in
2
2
- - 128
- - 147
o
o
o
C/W
C/W
C/W
Source to Drain Diode Specifications
PARAMETER SYMBOL TEST CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNITS
Source to Drain Diode Voltage V
SD
Reverse Recovery Time t
NOTE:
2. 110oC/W measured using FR-4 board with 0.171in2 footprint for 1000 seconds.
8-144
ISD = 2.0A - - 1.5 V
ISD = 2.0A, dISD/dt = 100A/µs - - 100 ns
rr
RFT3055LE
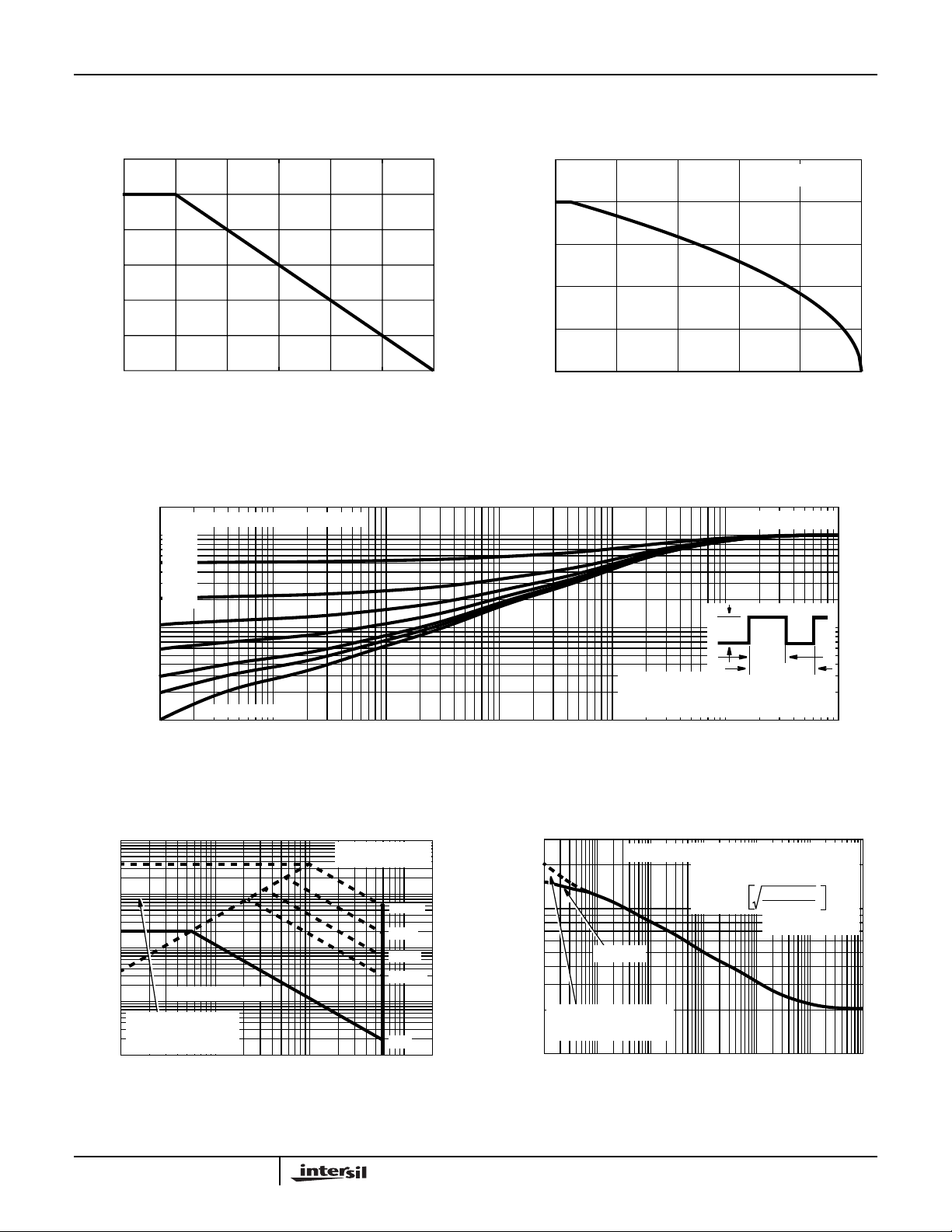
Typical Performance Curves
Unless otherwise specified
1.2
1.0
0.8
0.6
0.4
0.2
POWER DISSIPATION MULTIPLIER
0
0 25 50 75 100 150
125
TA, AMBIENT TEMPERATURE (oC)
FIGURE 1. NORMALIZED POWER DISSIPATION vs AMBIENT
TEMPERATURE
2
DUTY CYCLE - DESCENDING ORDER
0.5
1
0.2
0.1
0.05
0.02
0.01
2.5
R
= 110oC/W
θJA
2.0
1.5
1.0
, DRAIN CURRENT (A)
D
I
0.5
0
25 50 75 100 125 150
TA, AMBIENT TEMPERATURE (oC)
FIGURE 2. MAXIMUM CONTINUOUS DRAIN CURRENT vs
AMBIENT TEMPERATURE
R
= 110oC/W
θJA
0.1
, NORMALIZED
JA
θ
Z
THERMAL IMPEDANCE
-3
SINGLE PULSE
-2
10
0.01
10
FIGURE 3. NORMALIZED MAXIMUM TRANSIENT THERMAL IMPEDANCE
100
10
1
R
= 110oC/W
, DRAIN CURRENT (A)
0.1
D
I
OPERATION IN THIS
AREA MAY BE
LIMITED BY r
0.01
θJA
DS(ON)
0.1 1 10 100
VDS, DRAIN TO SOURCE VOLTAGE (V)
TJ = MAX RATED
TA = 25oC
-1
10
0
10
t, RECTANGULAR PULSE DURATION (s)
30
100µs
10
1ms
10ms
100ms
DC
200
, PEAK CURRENT (A)
DM
I
TRANSCONDUCTANCE
MAY LIMIT CURRENT
IN THIS REGION
1
-3
10
NOTES:
DUTY FACTOR: D = t
PEAK TJ = PDM x Z
1
10
TA = 25oC
VGS = 5V
-2
10
10
P
DM
1/t2
x R
JA
θ
2
10
FOR TEMPERATURES
ABOVE 25oC DERATE PEAK
CURRENT AS FOLLOWS:
I = I
25
-1
0
10
t, PULSE WIDTH (s)
10
t
JA
θ
1
1
t
2
+ T
150 - T
125
R
θJA
A
10
A
= 110oC/W
2
10
3
3
10
FIGURE 4. FORWARD BIAS SAFE OPERATING AREA FIGURE 5. PEAK CURRENT CAPABILITY
8-145

RFT3055LE
Typical Performance Curves
20
If R = 0
tAV = (L)(IAS)/(1.3*RATED BV
10
If R ≠ 0
t
= (L/R)ln[(IAS*R)/(1.3*RATED BV
AV
1
, AVALANCHE CURRENT (A)
AS
I
0.1
0.01 0.1 1 10 100
STARTING TJ = 150oC
tAV, TIME IN AVALANCHE (ms)
DSS
Unless otherwise specified (Continued)
- VDD)
- VDD) +1]
DSS
STARTING TJ = 25oC
NOTE: Refer to Intersil Application Notes AN9321 and AN9322.
FIGURE 6. UNCLAMPED INDUCTIVE SWITCHING CAPABILITY
20
PULSE DURATION = 80µs
DUTY CYCLE = 0.5% MAX
V
= 15V
DD
16
-55oC
12
8
DRAIN CURRENT (A)
D,
I
4
0
0 1.5 3.0 4.5 6.0
VGS, GATE TO SOURCE VOLTAGE (V)
150oC
o
25
C
20
16
12
8
, DRAIN CURRENT (A)
D
I
4
0
VGS = 10V
012345
VDS, DRAIN TO SOURCE VOLTAGE (V)
VGS = 5V
VGS = 4.5V
V
= 4V
GS
PULSE DURATION = 80µs
DUTY CYCLE = 0.5% MAX
TA = 25oC
V
= 3V
GS
FIGURE 7. SATURATION CHARACTERISTICS
2.0
PULSE DURATION = 80µs
DUTY CYCLE = 0.5% MAX
V
1.75
1.5
1.25
1.0
ON RESISTANCE
0.75
NORMALIZED DRAIN TO SOURCE
0.5
= 5V, ID = 2A
GS
-80 -40 0 40 80 120 160
TJ, JUNCTION TEMPERATURE (oC)
FIGURE 8. TRANSFER CHARACTERISTICS FIGURE 9. NORMALIZED DRAIN TOSOURCE ON
1.2
1.1
1.0
0.9
NORMALIZED GATE
THRESHOLD VOLTAGE
0.8
0.7
-80 -40 0 40 80 120 160
TJ, JUNCTION TEMPERATURE (oC)
VGS = VDS, ID = 250µA
FIGURE 10. NORMALIZED GATETHRESHOLD VOLTAGE vs
JUNCTION TEMPERATURE
8-146
RESISTANCE vs JUNCTION TEMPERATURE
1.15
ID = 250µA
1.1
1.05
1.0
BREAKDOWN VOLTAGE
0.95
NORMALIZED DRAIN TO SOURCE
0.9
-80 -40 0 40 80 120 160
TJ, JUNCTION TEMPERATURE (oC)
FIGURE 11. NORMALIZED DRAIN TOSOURCE BREAKDOWN
VOLTAGE vs JUNCTION TEMPERATURE

RFT3055LE
Typical Performance Curves
200
VDD = 30V, ID = 2A, RL = 15Ω
150
100
SWITCHING TIME (ns)
50
0
010
RGS, GATE TO SOURCE RESISTANCE (Ω)
20
Unless otherwise specified (Continued)
t
R
t
F
t
D(OFF)
t
D(ON)
30
40
50
250
200
150
100
, ON-STATE RESISTANCE (mΩ)
DS(ON)
r
50
246810
ID = 2A
I
= 0.5A
D
, GATE TO SOURCE VOLTAGE (V)
V
GS
PULSE DURATION = 80µs
DUTY CYCLE = 0.5% MAX
FIGURE 12. SWITCHING TIME vs GATE RESISTANCE FIGURE 13. SOURCE TO DRAIN ON RESISTANCE vs GATE
VOLTAGE AND DRAIN CURRENT
1200
C
ISS
900
VGS = 0V, f = 1MHz
= CGS + C
C
600
C
300
C, CAPACITANCE (pF)
0
0 5 10 15 20 25 30
OSS
C
RSS
VDS, DRAIN TO SOURCE VOLTAGE (V)
C
C
ISS
RSS
OSS
= C
= CDS + C
GD
GD
GD
10
WAVEFORMS IN
DESCENDING ORDER:
ID = 2A
8
I
= 0.5A
D
6
4
2
, GATE TO SOURCE VOLTAGE (V)
GS
V
0
0 6 12 18 24 30
Q
g
VDD = 15V
, GATE CHARGE (nC)
NOTE: Refer to Intersil Application Notes AN7254 and AN7260.
FIGURE 14. CAPACITANCE vs DRAIN TO SOURCE VOLTAGE
FIGURE 15. GATE CHARGE WAVEFORMS FOR CONSTANT
GATE CURRENT
8-147

RFT3055LE
Test Circuits and Waveforms
V
DS
BV
DSS
L
VARY tP TO OBTAIN
REQUIRED PEAK I
V
GS
AS
R
G
+
V
DD
-
DUT
0V
P
I
AS
0.01Ω
0
t
FIGURE 16. UNCLAMPED ENERGY TEST CIRCUIT FIGURE 17. UNCLAMPED ENERGY WAVEFORMS
V
I
g(REF)
DS
R
L
V
GS
+
V
DD
-
DUT
V
DD
VGS= 1V
0
V
GS
Q
g(TH)
t
P
I
AS
t
AV
Q
g(TOT)
V
DS
Q
g(5)
VGS= 5V
V
DS
V
DD
VGS= 10V
I
g(REF)
0
FIGURE 18. GATE CHARGE TEST CIRCUIT FIGURE 19. GATE CHARGE WAVEFORM
t
ON
t
d(ON)
90%
10%
t
r
R
L
V
DS
V
GS
V
GS
+
-
V
DS
0
t
d(OFF)
0V
R
GS
DUT
V
GS
10%
0
50%
PULSE WIDTH
90%
FIGURE 20. SWITCHING TIME TEST CIRCUIT FIGURE 21. RESISTIVE SWITCHING WAVEFORMS
t
OFF
50%
t
f
90%
10%
8-148

RFT3055LE
Thermal Resistance vs. Mounting Pad
Area
The maximum rated junction temperature, T
thermal resistance of the heat dissipating path determines
the maximum allowable device power dissipation, P
in an application. Therefore the application’s ambient
temperature, T
must be reviewed to ensure that T
(oC), and thermal impedance R
A
is neverexceeded.
J(MAX)
Equation 1 mathematically represents the relationship and
serves as the basis for establishing the rating of the part.
P
D MAX()
T
--------------------------------------------=
–()
JMAX()TA
R
θJA
In using surface mount devices such as the SOT-223
package, the environment in which it is applied will have a
significant influence on the part’s current and maximum
power dissipation ratings. Precise determination of the
P
is complex and influenced by many factors:
D(MAX)
1. Mounting pad areaonto which the deviceis attached and
whether there is copper on one side or both sides of the
board.
2. The number of copper layersand the thickness of the
board.
3. The use of external heat sinks.
4. The use of thermal vias.
5. Air flow and board orientation.
6. For non steady state applications, the pulse width, the
duty cycle and the transientthermalresponse of thepart,
the board and the environment they are in.
Intersil provides thermal information to assist the designer’s
preliminary application evaluation. Figure 22 defines the
for the device as a function of the top copper
R
θJA
(component side) area. This is for a horizontally positioned
FR-4 board with 1oz copper after 1000 seconds of steady
state power with no air flow.This graph provides the
necessary information for calculation of the steady state
junction temperature or power dissipation. Pulse
applications can be evaluated using the Intersil device Spice
thermal model ormanually utilizing the normalized maximum
transient thermal impedance curve.
J(MAX)
θJA
, and the
D(MAX)
(oC/W)
(EQ. 1)
200
,
150
C/W)
o
(
θJA
R
100
50
FIGURE 22. THERMAL RESISTANCEvs MOUNTING PAD
147oC/W - 0.026in
0.01 0.1 1.0
AREA, TOP COPPER AREA (in2)
AREA
Displayed on the curve are the three R
R
= 75.9 - 19.3 * ln(AREA)
θJA
2
128oC/W - 0.068in
110oC/W - 0.171in
2
values listed in
θJA
2
the Electrical Specifications table. The three points were
chosen to depict the compromise between the copper board
area, the thermal resistance and ultimately the power
dissipation, P
. Thermal resistances corresponding to
D(MAX)
other component side copper areas can be obtained from
Figure 22 or by calculation using Equation 2. The area, in
square inches is the top copper area including the gate and
source pads.
θJA
75.9 19.3 Area()ln×–=
(EQ. 2)
R
8-149
RFT3055LE
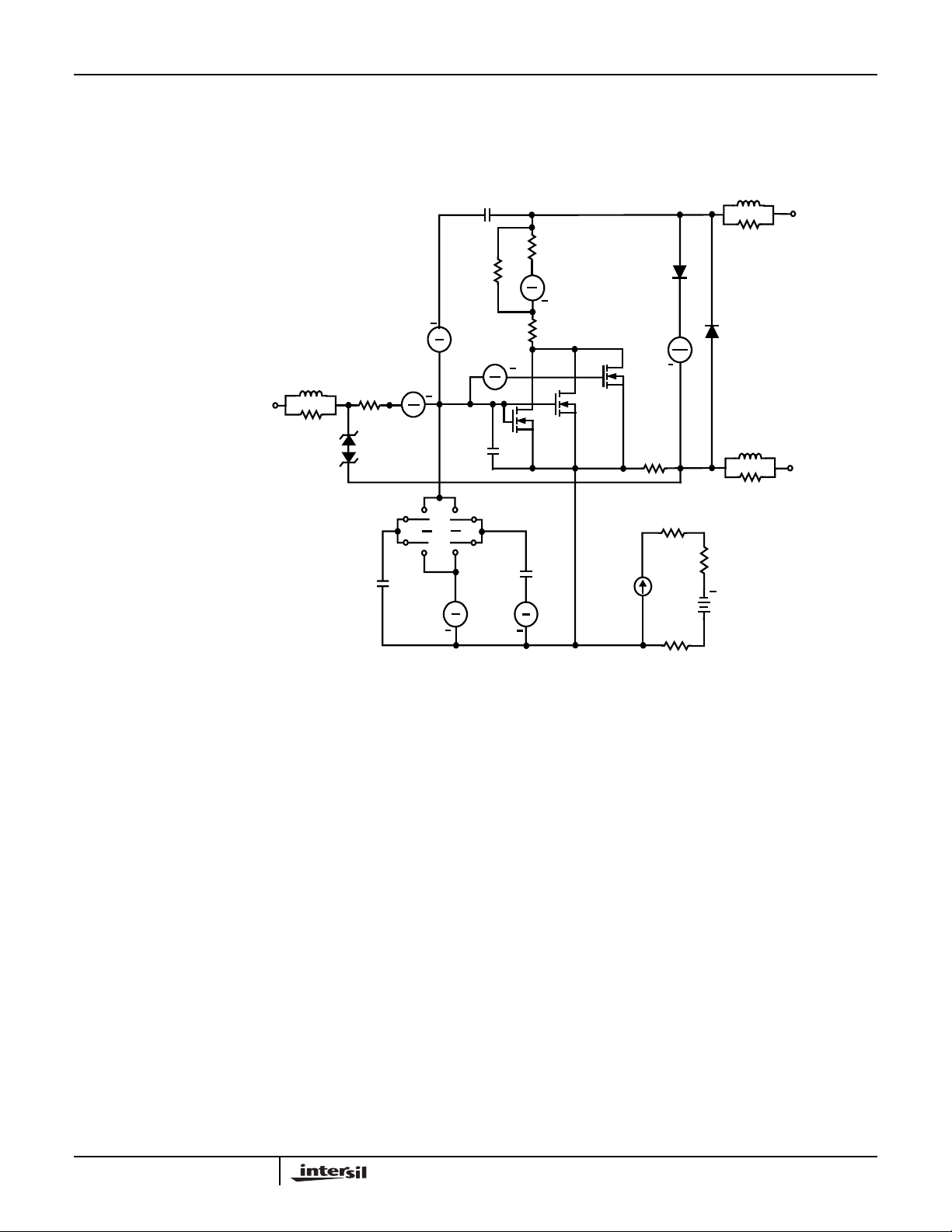
PSPICE Electrical Model
.SUBCKT RFT3055LE 2 1 3 ; REV May 98
CA 12 8 1.68e-9
CB 15 14 1.78e-9
CIN 6 8 7.69e-10
DBODY 7 5 DBODYMOD
DBREAK 5 11 DBREAKMOD
DESD1 91 9 DESD1MOD
DESD2 91 7 DESD2MOD
DPLCAP 10 5 DPLCAPMOD
EBREAK 11 7 17 18 64.28
EDS 14 8 5 8 1
EGS 13 8 6 8 1
ESG 6 10 6 8 1
EVTHRES 6 21 19 8 1
EVTEMP 20 6 18 22 1
IT 8 17 1
LDRAIN 2 5 1e-9
LGATE 1 9 4.6e-9
LSOURCE 3 7 4.6e-9
MMED 16 6 8 8 MMEDMOD
MSTRO 16 6 8 8 MSTROMOD
GATE
1
LGATE
RLGATE
RGATE
9
DESD1
91
DESD2
ESG
EVTEMP
+
20
18
22
MWEAK 16 21 8 8 MWEAKMOD
RBREAK 17 18 RBREAKMOD 1
RDRAIN 50 16 RDRAINMOD 24e-3
RGATE 9 20 9.84
RLDRAIN 2 5 10
RLGATE 1 9 46
RLSOURCE 3 7 46
RSLC1 5 51 RSLCMOD 1e-6
S1A
12
13
S1B
CA
RSLC2 5 50 1e3
RSOURCE 8 7 RSOURCEMOD 49e-3
RVTHRES 22 8 RVTHRESMOD 1
EGS
RVTEMP 18 19 RVTEMPMOD 1
S1A 6 12 13 8 S1AMOD
S1B 13 12 13 8 S1BMOD
S2A 6 15 14 13 S2AMOD
S2B 13 15 14 13 S2BMOD
VBAT 22 19 DC 1
ESLC 51 50 VALUE={(V(5,51)/ABS(V(5,51)))*(PWR(V(5,51)/(1e-6*45),4))}
.MODEL DBODYMOD D (IS = 3.61e-13 RS = 1.78e-2 TRS1 = 1.7e-2 TRS2 = -4.69e-6 CJO = 3.88e-10 TT = 3.6e-8)
.MODEL DBREAKMOD D (RS = 4.73e-1 TRS1 = -2.19e-3 TRS2 = 4.7e-5)
.MODEL DESD1MOD D (BV = 12.5 NBV = 17.5 IBV = 2.5e-4 RS = 22)
.MODEL DESD2MOD D (BV = 12.86 NBV = 22 IBV = 2.5e-4 RS = 0)
.MODEL DPLCAPMOD D (CJO = 4.803e-10 IS = 1e-30 N = 10)
.MODEL MMEDMOD NMOS (VTO = 1.78 KP = 1.5 IS = 1e-30 N = 10 TOX = 1 L = 1u W = 1u RG = 9.84)
.MODEL MSTROMOD NMOS (VTO = 2.08 KP = 10.5 IS = 1e-30 N = 10 TOX = 1 L = 1u W = 1u)
.MODEL MWEAKMOD NMOS (VTO = 1.55 KP = 0.1 IS = 1e-30 N = 10 TOX = 1 L = 1u W = 1u RG = 98.4 RS = 0.1)
.MODEL RBREAKMOD RES (TC1 = 1.06e-3 TC2 = -6.22e-7)
.MODEL RDRAINMOD RES (TC1 = 4.5e-3 TC2 = 6e-5)
.MODEL RSLCMOD RES (TC1 = 0 TC2 = 0)
.MODEL RSOURCEMOD RES (TC1 = 0 TC2 = 0)
.MODEL RVTHRESMOD RES (TC = 0 TC2 = -4e-6)
.MODEL RVTEMPMOD RES (TC1 = -1.9e-3 TC2 = 1.3e-7)
.MODEL S1AMOD VSWITCH (RON = 1e-5 ROFF = 0.1 VON = -4.4 VOFF= -2.4)
.MODEL S1BMOD VSWITCH (RON = 1e-5 ROFF = 0.1 VON = -2.4 VOFF= -4.4)
.MODEL S2AMOD VSWITCH (RON = 1e-5 ROFF = 0.1 VON = -2.0 VOFF= 1.15)
.MODEL S2AMOD VSWITCH (RON = 1e-5 ROFF = 0.1 VON = 1.15 VOFF= -2.0)
.ENDS
DPLCAP
10
RSLC2
6
8
+
EVTHRES
+
6
S2A
14
8
13
S2B
13
+
6
8
19
8
15
EDS
CIN
CB
+
5
5
5
51
MSTRO
14
8
RSLC1
51
+
ESLC
50
RDRAIN
16
21
8
MMED
8
DBREAK
EBREAK
MWEAK
RSOURCE
RBREAK
17
IT
RVTHRES
11
+
17
18
7
18
RVTEMP
19
+
22
LDRAIN
RLDRAIN
DBODY
LSOURCE
RLSOURCE
VBAT
DRAIN
2
SOURCE
3
NOTE: For further discussion of the PSPICE model, consult A New PSPICE Sub-Circuit for the Power MOSFET Featuring Global
Temperature Options; IEEE Power Electronics Specialist Conference Records, 1991, written by William J. Hepp and C. Frank Wheatley.
8-150

SPICE Thermal Model
REV May 98
RFT3055LE
9
JUNCTION
RFT3055LE
Copper Area = 0.077in
CTHERM1 9 8 7.5e-5
CTHERM2 8 7 3.5e-4
CTHERM3 7 6 1.2e-3
CTHERM4 6 5 1.5e-2
CTHERM5 5 4 6.0e-2
CTHERM6 4 3 3.0e-1
CTHERM7 3 2 1.6
CTHERM8 2 1 6
RTHERM1 9 8 8.2e-2
RTHERM2 8 7 2.7e-1
RTHERM3 7 6 1.9
RTHERM4 6 5 3.1
RTHERM5 5 4 12
RTHERM6 4 3 38
RTHERM7 3 2 32
RTHERM8 2 1 22
2
RTHERM1
8
RTHERM2
7
RTHERM3
6
RTHERM4
5
CTHERM1
CTHERM2
CTHERM3
CTHERM4
RTHERM5
RTHERM6
RTHERM7
RTHERM8
CTHERM5
4
CTHERM6
3
CTHERM7
2
CTHERM8
1
AMBIENT
8-151

RFT3055LE
All Intersil semiconductor products are manufactured, assembled and tested under ISO9000 quality systems certification.
Intersil semiconductor products are sold by description only. Intersil Corporationreserves the right to make changes in circuit design and/or specifications at any time without notice. Accordingly, the reader is cautioned to verify that data sheets are current before placing orders. Information furnished by Intersil is believed to be accurate and
reliable. However, no responsibility is assumed by Intersil or its subsidiaries for its use; nor for any infringements of patents or other rights of third parties which may result
from its use. No license is granted by implication or otherwise under any patent or patent rights of Intersil or its subsidiaries.
For information regarding Intersil Corporation and its products, see web site http://www.intersil.com
Sales Office Headquarters
NORTH AMERICA
Intersil Corporation
P. O. Box 883, Mail Stop 53-204
Melbourne, FL 32902
TEL: (407) 724-7000
FAX: (407) 724-7240
8-152
EUROPE
Intersil SA
Mercure Center
100, Rue de la Fusee
1130 Brussels, Belgium
TEL: (32) 2.724.2111
FAX: (32) 2.724.22.05
ASIA
Intersil (Taiwan) Ltd.
7F-6, No. 101 Fu Hsing North Road
Taipei, Taiwan
Republic of China
TEL: (886) 2 2716 9310
FAX: (886) 2 2715 3029
 Loading...
Loading...