Intersil ISL95870AHRUZ, ISL95870AIRUZ, ISL95870BHRZ, ISL95870BIRZ, ISL95870HRUZ Schematic [ru]
...
PWM DC/DC Controller with VID Inputs for Portable
RTN
GND
SREF
EN
C
BOOT
L
O
C
SEN
R
OCSET
Q
HS
Q
LS
3.3V TO 25V
0.5V TO 5V
R
O
CO
CIN
V
IN
V
OUT
C
SOFT
C
VCC
C
PVCC
GPIO
8
7
6
5
13
14
15
16
VO
OCSET
FB
FSEL
VCC
PVCC
LGATE
PGND
11
UGATE
BOOT
2
1
12
9
PGOOD
PHASE
4
3
10
+5V
R
VCC
R
PGOOD
RTN1
R
FB
R
OFS
R
OFS1
R
FB1
RTN1
0
GPU Core-Voltage Regulator
ISL95870, ISL95870A, ISL95870B
The ISL95870, ISL95870A, ISL95870B ICs are Single-Phase
Synchronous-Buck PWM regulators featuring Intersil’s
proprietary R
4
Technology™. The wide 3.3V to 25V input
voltage range is ideal for systems that run on battery or
AC-adapter power sources. The ISL95870A and ISL95870B
are low-cost solutions for applications requiring dynamically
selected slew-rate controlled output voltages. The soft-start
and dynamic setpoint slew-rates are capacitor programmed.
Voltage identification logic-inputs select four (ISL95870A,
ISL95870B) resistor-programmed setpoint reference voltages
that directly set the output voltage of the converter between
0.5V and 1.5V, and up to 5V with a feedback voltage divider.
3
Compared with R
modulator, the R4 modulator has
equivalent light-load efficiency, faster transient performance,
accurately regulated frequency control and all internal
compensation. These updates, together with integrated
MOSFET drivers and schottky bootstrap diode, allow for a
high-performance regulator that is highly compact and needs
few external components. The differential remote sensing for
output voltage and selectable switching frequency are another
two new functions. For maximum efficiency, the converter
automatically enters diode-emulation mode (DEM) during
light-load conditions such as system standby.
Features
• Input Voltage Range: 3.3V to 25V
• Output Voltage Range: 0.5V to 5V
• Precision Regulation
-Proprietary R
- ±0.5% System Accuracy Over -10°C to +100°C
• Optimal Transient Response
- Intersil’s R
•Output Remote Sense
• Extremely Flexible Output Voltage Programmability
- 2-Bit VID Selects Four Independent Setpoint Voltages for
ISL95870B
- 2-Bit VID Selects Four Dependent or Three Independent
Setpoint Voltages for ISL95870A
- Simple Resistor Programming of Setpoint Voltages
• Selectable 300kHz, 500kHz, 600kHz or 1MHz PWM
Frequency in Continuous Conduction
• Automatic Diode Emulation Mode for Highest Efficiency
• Power-Good Monitor for Soft-Start and Fault Detection
4
™ Frequency Control Loop
4
™ Modulator Technology
December 2, 2013
FN6899.1
Applications
• Mobile PC Graphical Processing Unit VCC Rail
• Mobile PC I/O Controller Hub (ICH) VCC Rail
• Mobile PC Memory Controller Hub (GMCH) VCC Rail
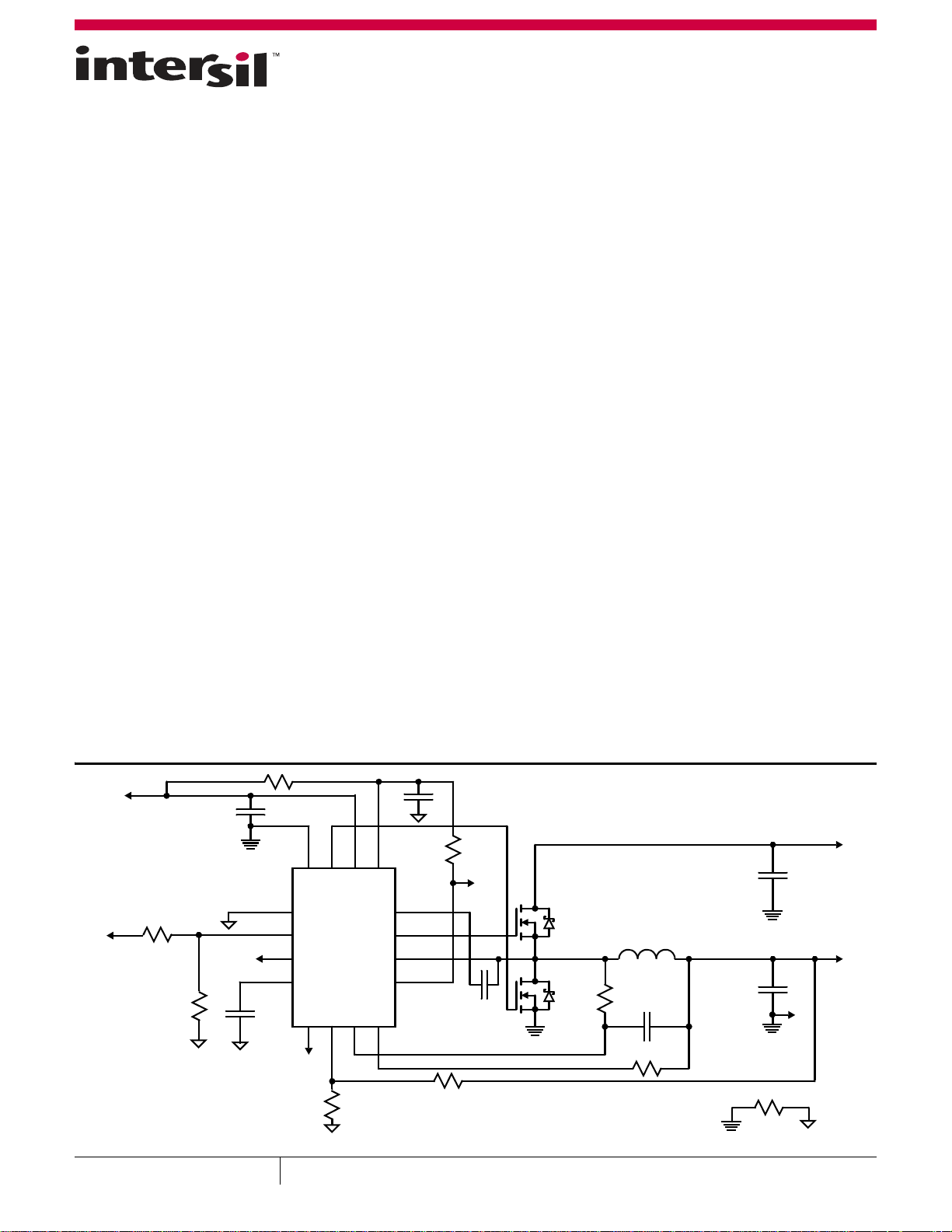
FIGURE 1. ISL95870 APPLICATION SCHEMATIC WITH ONE OUTPUT VOLTAGE SETPOINT AND DCR CURRENT SENSE
1
CAUTION: These devices are sensitive to electrostatic discharge; follow proper IC Handling Procedures.
1-888-INTERSIL or 1-888-468-3774
Intersil (and design) and R3 Technology are trademarks owned by Intersil Corporation or one of its subsidiaries.
| Copyright Intersil Americas LLC 2009, 2013. All Rights Reserved
All other trademarks mentioned are the property of their respective owners.

ISL95870, ISL95870A, ISL95870B
Table of Contents
Applications Schematics: ISL95870 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
Applications Schematics: ISL95870A. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
Applications Schematics: ISL95870B. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
Block Diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
ISL95870 Functional Pin Descriptions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
ISL95870A Functional Pin Descriptions. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
ISL95870B Functional Pin Descriptions. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
Absolute Maximum Ratings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
Thermal Information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
Recommended Operating Conditions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
Electrical Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
Theory of Operation. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Power-On Reset . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Start-Up Timing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Start-Up and Voltage-Step Operation for ISL95870 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Start-Up and Voltage-Step Operation for ISL95870A, ISL95870B . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Output Voltage Programming for ISL95870 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
Output Voltage Programming for ISL95870A . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
Output Voltage Programming for ISL95870B . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
High Output Voltage Programming . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
R4 Modulator . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
Stability . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
Transient Response. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
Diode Emulation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
Overcurrent. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
Overvoltage. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
Undervoltage . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
Over-Temperature . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
PGOOD Monitor . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
Integrated MOSFET Gate-Drivers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
Adaptive Shoot-Through Protection. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
General Application Design Guide . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
Selecting the LC Output Filter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
Selecting the Input Capacitor. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
Selecting the Bootstrap Capacitor. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
Driver Power Dissipation. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
MOSFET Selection and Considerations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
Layout Considerations. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
Revision History. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
About Intersil . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
L16.2.6x1.8A
16 LEAD ULTRA THIN QUAD FLAT NO-LEAD PLASTIC PACKAGE . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
L20.3.2x1.8
20 LEAD ULTRA THIN QUAD FLAT NO-LEAD PLASTIC PACKAGE (UTQFN) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
L20.3x4
20 LEAD QUAD FLAT NO-LEAD PLASTIC PACKAGE . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
2
FN6899.1
December 2, 2013
ISL95870, ISL95870A, ISL95870B
RTN
GND
SREF
EN
C
BOOT
L
O
C
SEN
R
OCSET
Q
HS
Q
LS
3.3V TO 25V
0.5V TO 5V
R
O
CO
CIN
V
IN
V
OUT
C
SOFT
C
VCC
C
PVCC
GPIO
8
7
6
5
13
14
15
16
VO
OCSET
FB
FSEL
VCC
PVCC
LGATE
PGND
11
UGATE
BOOT
2
112
9
PGOOD
PHASE
4
310
+5V
R
VCC
R
PGOOD
RTN1
R
FB
R
OFS
R
OFS1
R
FB1
RTN1
0
RTN
GND
SREF
EN
C
BOOT
L
O
C
SEN
R
OCSET
Q
HS
Q
LS
3.3V TO 25V
0.5V TO 5V
R
O
CO
CIN
V
IN
V
OUT
C
SOFT
C
VCC
C
PVCC
GPIO
8
7
6
5
13
14
15
16
VO
OCSET
FB
FSEL
VCC
PVCC
LGATE
PGND
11
UGATE
BOOT
2
112
9
PGOOD
PHASE
4
310
+5V
R
VCC
R
PGOOD
RTN1
R
FB
R
OFS
R
SEN
R
OFS1
R
FB1
RTN1
0
Applications Schematics: ISL95870
FIGURE 2. ISL95870 APPLICATION SCHEMATIC WITH ONE OUTPUT VOLTAGE SETPOINT AND DCR CURRENT SENSE
FIGURE 3. ISL95870 APPLICATION SCHEMATIC WITH ONE OUTPUT VOLTAGE SETPOINT AND RESISTOR CURRENT SENSE
3
FN6899.1
December 2, 2013
ISL95870, ISL95870A, ISL95870B
VCC
BOOT
UGATE
PHASE
EN
PGOOD
FSEL
VO
PGND
GND
RTN
VID1
VID0
SREF
SET0
SET1
FB
LGATE
PVCC
L
O
C
BOOT
C
SEN
R
OCSET
Q
HS
Q
LS
RTN1
3.3V TO 25V
0.5V TO 5V
R
O
CO
CIN
V
IN
V
OUT
C
SOFT
R
SET1RSET2RSET3
C
VCC
+5V
R
VCC
C
PVCC
GPIO
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
19
18
17
16
15
14
13
12
110
11 20
R
PGOOD
OCSET
R
FB
R
OFS
R
OFS1
R
FB1
RTN1
0
VCC
BOOT
UGATE
PHASE
EN
PGOOD
FSEL
VO
PGND
GND
RTN
VID1
VID0
SREF
SET0
SET1
FB
LGATE
PVCC
L
O
C
BOOT
C
SEN
R
OCSET
Q
HS
Q
LS
RTN1
3.3V TO 25V
0.5V TO 5V
R
O
CO
CIN
V
IN
V
OUT
C
SOFT
R
SET1RSET2RSET3
C
VCC
+5V
C
PVCC
GPIO
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
19
18
17
16
15
14
13
12
110
11 20
R
PGOOD
OCSET
R
FB
R
OFS
R
SEN
R
OFS1
R
FB1
RTN1
R
VCC
0
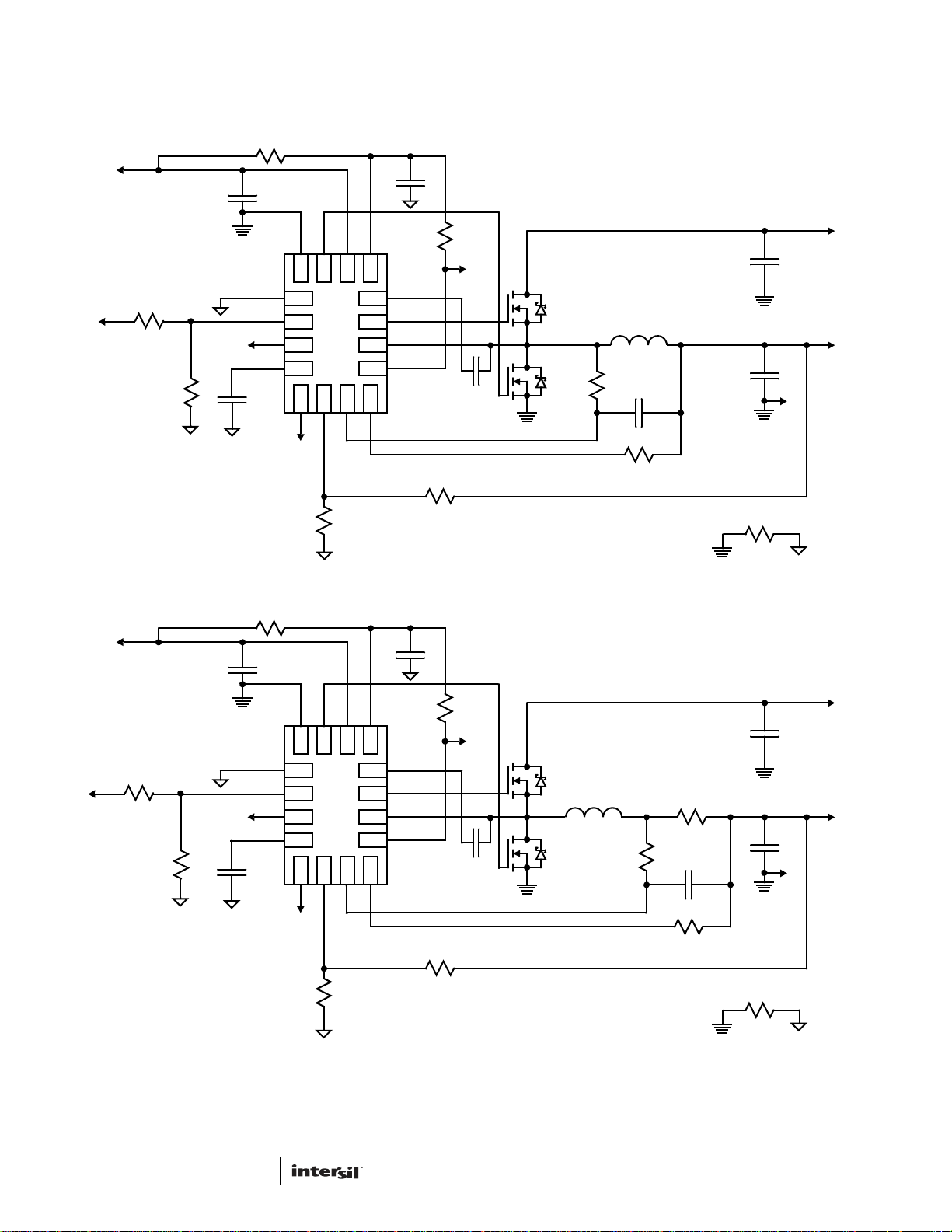
Applications Schematics: ISL95870A
FIGURE 4. ISL95870A APPLICATION SCHEMATIC WITH FOUR OUTPUT VOLTAGE SETPOINTS AND DCR CURRENT SENSE
FIGURE 5. ISL95870A APPLICATION SCHEMATIC WITH FOUR OUTPUT VOLTAGE SETPOINTS AND RESISTOR CURRENT SENSE
4
FN6899.1
December 2, 2013
ISL95870, ISL95870A, ISL95870B
VO
BOOT
UGATE
PHASE
EN
PGOOD
FSEL
RTN
VID1
VID0
SREF
SET0
SET1
PVCC
VCC
L
O
C
BOOT
C
SEN
R
OCSET
Q
HS
Q
LS
3.3V TO 25V
0.5V TO 5V
R
O
CO
CIN
V
IN
V
OUT
C
SOFT
C
VCC
+5V
R
VCC
C
PVCC
GPIO
1
2
3
4
5
6
15
14
13
12
11
189
10 17
R
PGOOD
PGND
LGATE
16
7
8
20
19
R
SET1
R
SET2
R
SET3
R
SET4
R
FB
R
OFS
SET2
FB
OCSET
RTN1
R
OFS1
R
FB1
RTN1
GND
0
VO
BOOT
UGATE
PHASE
EN
PGOOD
FSEL
RTN
VID1
VID0
SREF
SET0
SET1
PVCC
VCC
L
O
C
BOOT
C
SEN
R
OCSET
Q
HS
Q
LS
3.3V TO 25V
0.5V TO 5V
R
O
CO
CIN
V
IN
V
OUT
C
SOFT
C
VCC
+5V
R
VCC
C
PVCC
GPIO
1
2
3
4
5
6
15
14
13
12
11
189
10 17
R
PGOOD
PGND
LGATE
16
7
8
20
19
R
SET1
R
SET2
R
SET3
R
SET4
R
FB
R
OFS
SET2
FB
OCSET
R
SEN
RTN1
R
OFS1
R
FB1
RTN1
GND
0
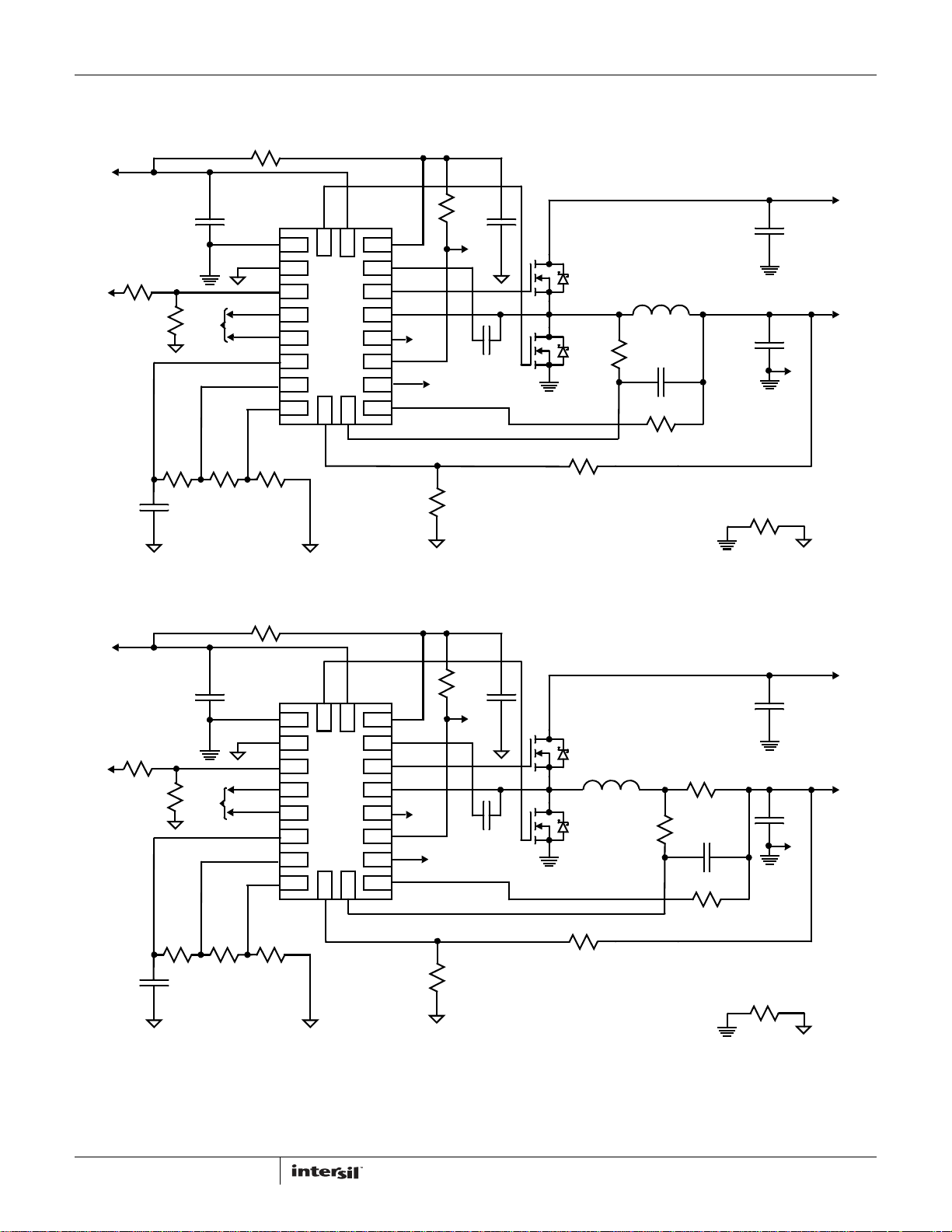
Applications Schematics: ISL95870B
FIGURE 6. ISL95870B APPLICATION SCHEMATIC WITH FOUR OUTPUT VOLTAGE SETPOINTS AND DCR CURRENT SENSE
FIGURE 7. ISL95870B APPLICATION SCHEMATIC WITH FOUR OUTPUT VOLTAGE SETPOINTS AND RESISTOR CURRENT SENSE
5
FN6899.1
December 2, 2013
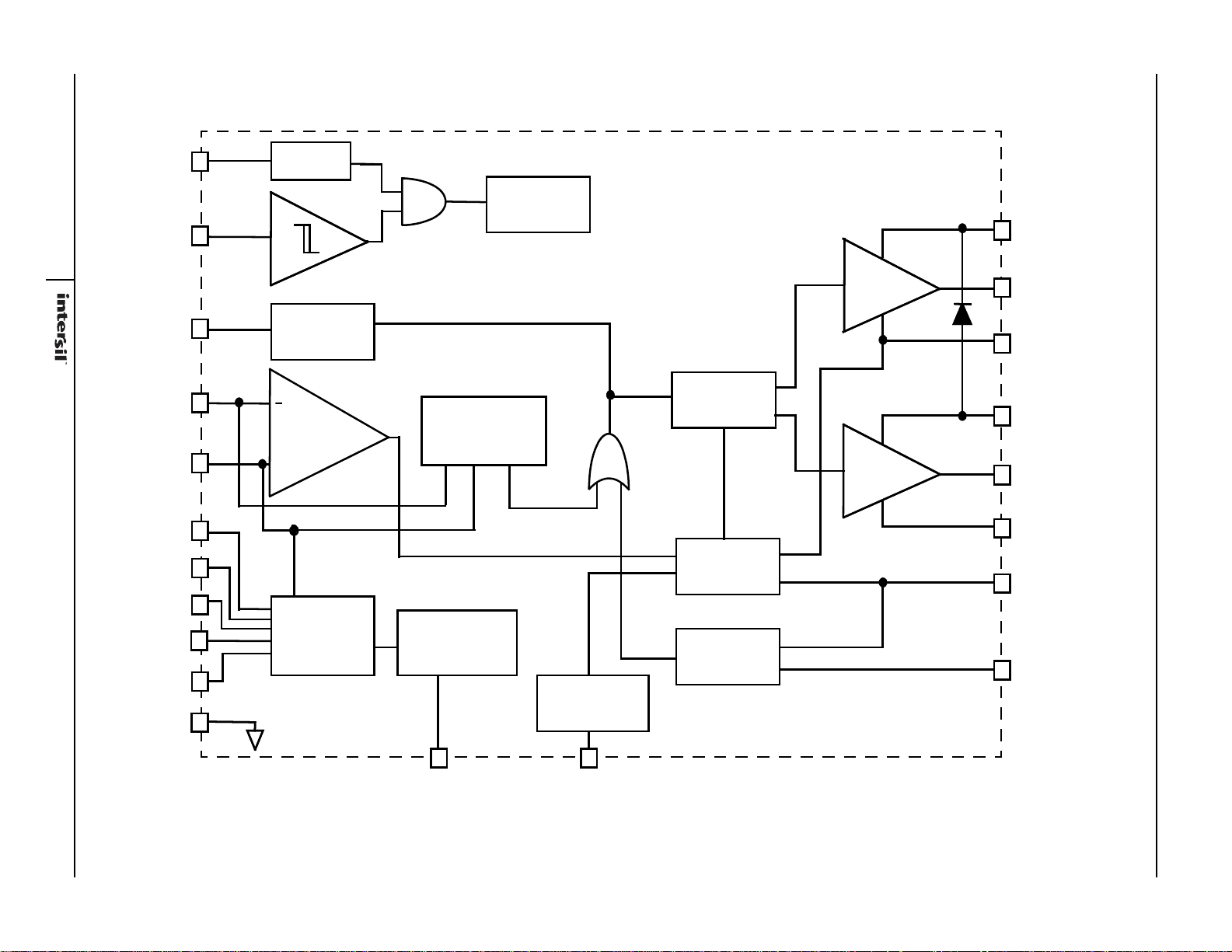
Block Diagram
FIGURE 8. SIMPLIFIED FUNCTIONAL BLOCK DIAGRAM OF ISL95870, ISL95870A, ISL95870B
DRIVER
DRIVER
BOOT
UGATE
PHASE
PVCC
LGATE
PGND
OVERCURRENT
OVERVOLTAGE/
SOFT-START
CIRCUITRY
R
4
MODULATOR
DEAD-TIME
GENERATION
PGOOD
CIRCUITRY
REFERENCE
VOLTAGE
CIRCUITRY
POR
VO
OCSET
*SET 0
*SET 1
**SET2
*VID1
*VID0
FB
PGOOD
SREF
VCC
RTN
EN
INTERNAL
COMPENSATION
AMPLIFIER
+
GND
REMOTE SENSE
CIRCUITRY
FSEL
Fs SELECTION
CIRCUITRY
*ISL95870A, ISL95870B ONLY
**ISL95870B ONLY
UNDERVOLTAGE
6
ISL95870, ISL95870A, ISL95870B
December 2, 2013
FN6899.1
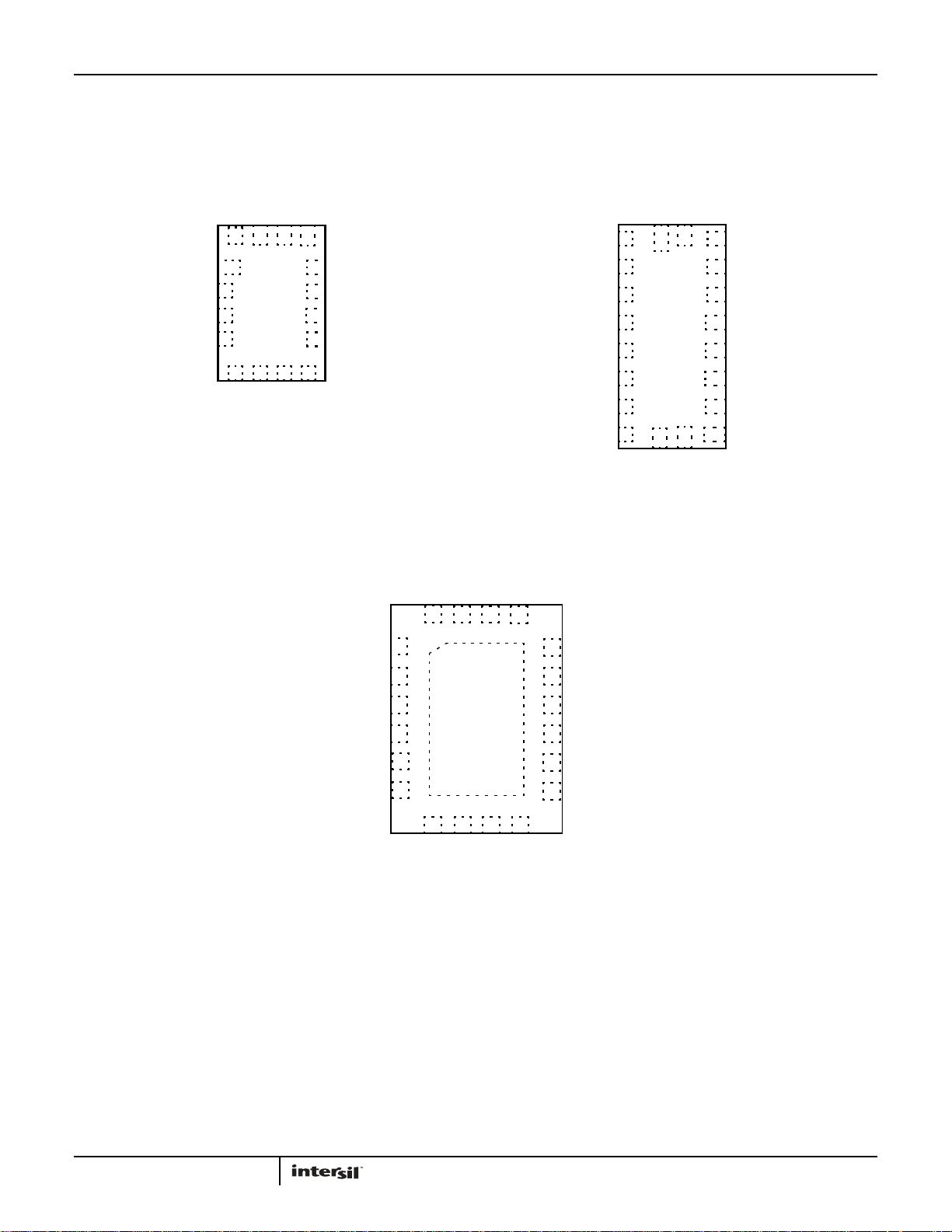
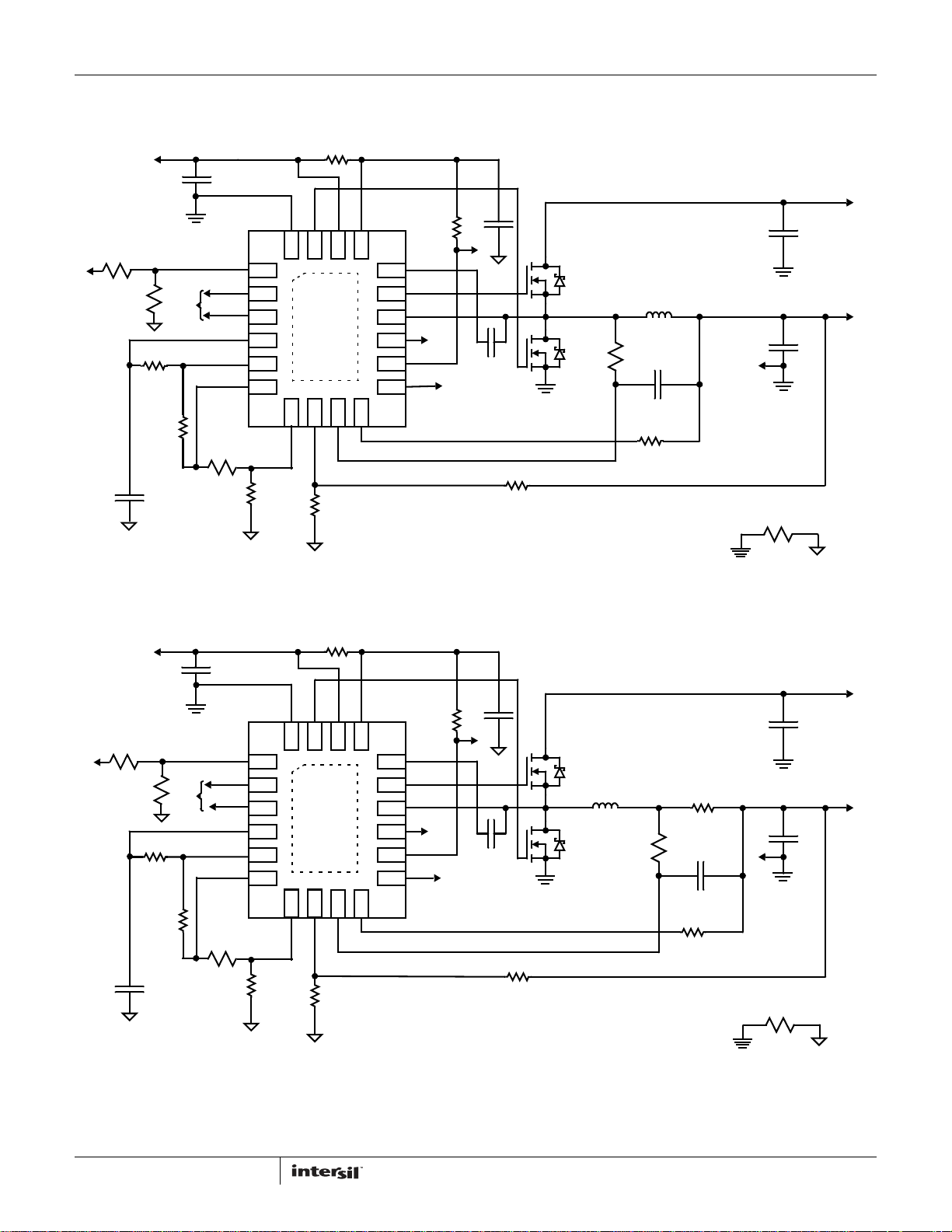
Pin Configurations
12
11
10
9
16
15
14
13
5
6
7
8
1
2
3
4
GND
RTN
EN
SREF
BOOT
UGATE
PHASE
PGOOD
PGND
LGATE
PVCC
VCC
FSEL
FB
OCSET
VO
19
18
17
16
15
14
13
1
20
10
11
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
PGND
GND
RTN
VID1
VID0
SREF
SET0
VCC
BOOT
UGATE
PHASE
EN
PGOOD
FSEL
LGATE
PVCC
FB
OCSET
9
SET1
12
VO
10VO
9OCSET
8FB
7SET2
4
SREF
3VID0
1
2
20
PGND
19
LGATE18PVCC
17
VCC
RTN
VID1
5
6
SET0
SET1
16
15
14
13
BOOT
UGATE
PHASE
EN
12
11
PGOOD
FSEL
GND
ISL95870, ISL95870A, ISL95870B
ISL95870
(16 LD 2.6X1.8 µTQFN)
TOP VIEW
ISL95870A
(20 LD 3.2X1.8 µTQFN)
TOP VIEW
ISL95870B
(20 LD 3X4 QFN)
TOP VIEW
7
FN6899.1
December 2, 2013
ISL95870, ISL95870A, ISL95870B
ISL95870 Functional Pin Descriptions
PIN NUMBER SYMBOL DESCRIPTION
1 GND IC ground for bias supply and signal reference.
2 RTN Negative remote sense input of V
divider should be used at RTN pin, i.e. keep R
3 EN Enable input for the IC. Pulling EN above the rising threshold voltage initializes the soft-start sequence.
4 SREF Soft-start and voltage slew-rate programming capacitor input. Connects internally to the inverting input of the V
setpoint amplifier.
5 FSEL Input for programming the regulator switching frequency. Pull this pin to VCC for 1MHz switching. Pull this pin to GND
with a 100kΩ resistor for 600kHz switching. Leave this pin floating for 500kHz switching. Pull this pin directly to GND
for 300kHz switching.
6 FB Voltage feedback sense input. Connects internally to the inverting input of the control-loop error amplifier. The converter
is in regulation when the voltage at the FB pin equals the voltage on the SREF pin.
7 OCSET Input for the overcurrent detection circuit. The overcurrent setpoint programming resistor R
pin to the sense node.
8 VO Output voltage sense input for the R
detection circuit.
9 PGOOD Power-good open-drain indicator output. This pin changes to high impedance when the converter is able to supply
regulated voltage.
10 PHASE Return current path for the UGATE high-side MOSFET driver, V
polarity detector input.
11 UGATE High-side MOSFET gate driver output. Connect to the gate terminal of the high-side MOSFET of the converter.
12 BOOT Positive input supply for the UGATE high-side MOSFET gate driver. The BOOT pin is internally connected to the cathode
of the Schottky boot-strap diode. Connect an MLCC between the BOOT pin and the PHASE pin.
13 VCC Input for the IC bias voltage. Connect +5V to the VCC pin and decouple with at least a MLCC to the GND pin.
14 PVCC Input for the LGATE and UGATE MOSFET driver circuits. The PVCC pin is internally connected to the anode of the Schottky
boot-strap diode. Connect +5V to the PVCC pin and decouple with a MLCC to the PGND pin.
15 LGATE Low-side MOSFET gate driver output. Connect to the gate terminal of the low-side MOSFET of the converter.
16 PGND Return current path for the LGATE MOSFET driver. Connect to the source of the low-side MOSFET.
. If resistor divider consisting of RFB and R
OUT
4
modulator. The VO pin also serves as the reference input for the overcurrent
= RFB, and R
FB1
= R
OFS1
IN
OFS
sense input for the R4 modulator, and inductor current
is used at FB pin, the same resistor
OFS
.
connects from this
OCSET
SET
voltage
8
FN6899.1
December 2, 2013
ISL95870, ISL95870A, ISL95870B
ISL95870A Functional Pin Descriptions
PIN NUMBER SYMBOL DESCRIPTION
1 LGATE Low-side MOSFET gate driver output. Connect to the gate terminal of the low-side MOSFET of the converter.
2 PGND Return current path for the LGATE MOSFET driver. Connect to the source of the low-side MOSFET.
3 GND IC ground for bias supply and signal reference.
4 RTN Negative remote sense input of V
divider should be used at RTN pin, i.e. keep R
5 VID1 Logic input for setpoint voltage selector. Use in conjunction with the VID0 pin to select among four setpoint reference
voltages.
6 VID0 Logic input for setpoint voltage selector. Use in conjunction with the VID1 pin to select among four setpoint reference
voltages.
7 SREF Soft-start and voltage slew-rate programming capacitor input and setpoint reference voltage programming resistor input.
Connects internally to the inverting input of the V
8 SET0 Voltage set-point programming resistor input.
9 SET1 Voltage set-point programming resistor input.
10 FB Voltage feedback sense input. Connects internally to the inverting input of the control-loop error transconductance
amplifier. The converter is in regulation when the voltage at the FB pin equals the voltage on the SREF pin.
11 OCSET Input for the overcurrent detection circuit. The overcurrent setpoint programming resistor R
pin to the sense node.
12 VO Output voltage sense input for the R
detection circuit.
13 FSEL Input for programming the regulator switching frequency. Pull this pin to VCC for 1MHz switching. Pull this pin to GND
with a 100kΩ resistor for 600kHz switching. Leave this pin floating for 500kHz switching. Pull this pin directly to GND
for 300kHz switching.
14 PGOOD Power-good open-drain indicator output. This pin changes to high impedance when the converter is able to supply
regulated voltage.
15 EN Enable input for the IC. Pulling EN above the rising threshold voltage initializes the soft-start sequence.
16 PHASE Return current path for the UGATE high-side MOSFET driver, V
polarity detector input.
17 UGATE High-side MOSFET gate driver output. Connect to the gate terminal of the high-side MOSFET of the converter.
18 BOOT Positive input supply for the UGATE high-side MOSFET gate driver. The BOOT pin is internally connected to the cathode
of the Schottky boot-strap diode. Connect an MLCC between the BOOT pin and the PHASE pin.
19 VCC Input for the IC bias voltage. Connect +5V to the VCC pin and decouple with at least a MLCC to the GND pin.
20 PVCC Input for the LGATE and UGATE MOSFET driver circuits. The PVCC pin is internally connected to the anode of the Schottky
boot-strap diode. Connect +5V to the PVCC pin and decouple with a MLCC to the PGND pin.
. If resistor divider consisting of RFB and R
OUT
4
modulator. The VO pin also serves as the reference input for the overcurrent
= RFB, and R
FB1
voltage setpoint amplifier.
SET
OFS1
sense input for the R4 modulator, and inductor current
IN
= R
OFS
is used at FB pin, the same resistor
OFS
.
connects from this
OCSET
9
FN6899.1
December 2, 2013
 Loading...
Loading...