intersil ISL6324A DATA SHEET

®
Hybrid SVI/PVI with I
ISL6324A
2
C
Data Sheet
Monolithic Dual PWM Hybrid Controller
Powering AMD SVI Split-Plane and PVI
Uniplane Processors
The ISL6324A dual PWM controller delivers high efficiency
and tight regulation from two synchronous buck DC/DC
converters. The ISL6324A supports hybrid power control of
AMD processors which operate from either a 6-bit parallel
VID interface (PVI) or a serial VID interface (SVI). The dual
output ISL6324A features a multi-phase controller to support
uniplane VDD core voltage and a single phase controller to
power the Northbridge (VDDNB) in SVI mode. Only the
multi-phase controller is active in PVI mode to support
uniplane VDD only processors.
A precision uniplane core voltage regulation system is provided
by a 2-to-4-phase PWM voltage regulator (VR) controller. The
integration of two power MOSFET drivers, adding flexibility in
layout, reduce the number of external components in the multiphase section. A single phase PWM controller with integrated
driver provides a second precision voltage regulation system
for the North Bridge portion of the processor. This monolithic,
dual controller with integrated driver solution provides a cost
and space saving power management solution.
For applications which benefit from load line programming to
reduce bulk output capacitors, the ISL6324A features output
voltage droop. The multi-phase portion also includes
advanced control loop features for optimal transient response
to load application and removal. One of these features is
highly accurate, fully differential, continuous DCR current
sensing for load line programming and channel current
balance. Dual edge modulation is another unique feature,
allowing for quicker initial response to high di/dt load
transients.
The ISL6324A supports Power Savings Mode by dropping
phases when the PSI_L bit is set. The number of phases
that the ISL6324A will drop to is programmable through an
2
I
C interface. The number of PWM cycles between both
dropping phases when entering Power Savings Mode and
adding phases when exiting Power Savings Mode is also
programmable through the I
The ISL6324A I2C interface also allows independent
programmable output voltage offset for both the Core and
North Bridge regulators. The I
to set the PGOOD and OVP trip levels for both regulators as
well.
2
C interface.
2
C interface can also be used
March 23, 2009
FN6880.0
Features
Processor Core Voltage Regulator Features
• Configuration Flexibility
- 2-Phase Operation with Internal Drivers
- 3- or 4-Phase Operation with External PWM Drivers
• Parallel VID (6-bit) Interface Inputs for PVI Mode
• PSI_L Support via Phase Shedding
• Differential Remote Voltage Sensing
• Optimal Processor Core Voltage Transient Response
- Adaptive Phase Alignment (APA)
- Active Pulse Positioning Modulation
Processor Core Voltage Regulator and North Bridge
Voltage Regulator Shared Features
• Precision Voltage Regulation: ±0.5% System Accuracy
Over-Temperature
• Two Wire, AMD Compliant Serial VID Interface Inputs for
SVI Mode
2
C Interface
•I
- Voltage Margining, OVP and PGOOD Trip Levels
- Enhanced PSI_L State Control
• Fully Differential, Continuous DCR Current Sensing
- Accurate Load Line Programming
- Precision Channel Current Balancing for Core
• Overcurrent Protection
• Multi-tiered Overvoltage Protection
• Variable Gate Drive Bias: 5V to 12V
• Simultaneous Digital Soft-Start of Both Outputs
• Selectable Switching Frequency up to 1MHz
• Pb-Free (RoHS Compliant)
Ordering Information
PART
NUMBER
(Note)
ISL6324ACRZ* ISL6324A CRZ 0 to +70 48 Ld 7x7 QFN L48.7x7
ISL6324AIRZ* ISL6324A IRZ -40 to +85 48 Ld 7x7 QFN L48.7x7
*Add “-T” suffix for tape and reel. Please refer to TB347 for details on
reel specifications.
NOTE: These Intersil Pb-free plastic packaged products employ
special Pb-free material sets, molding compounds/die attach materials,
and 100% matte tin plate plus anneal (e3 termination finish, which is
RoHS compliant and compatible with both SnPb and Pb-free soldering
operations). Intersil Pb-free products are MSL classified at Pb-free peak
reflow temperatures that meet or exceed the Pb-free requirements of
IPC/JEDEC J STD-020.
PART
MARKING
TEMP.
RANGE
(°C)
PACKAGE
(Pb-free)
PKG.
DWG . #
1
CAUTION: These devices are sensitive to electrostatic discharge; follow proper IC Handling Procedures.
1-888-INTERSIL or 1-888-468-3774
| Intersil (and design) is a registered trademark of Intersil Americas Inc.
All other trademarks mentioned are the property of their respective owners.
Copyright Intersil Americas Inc. 2009. All Rights Reserved
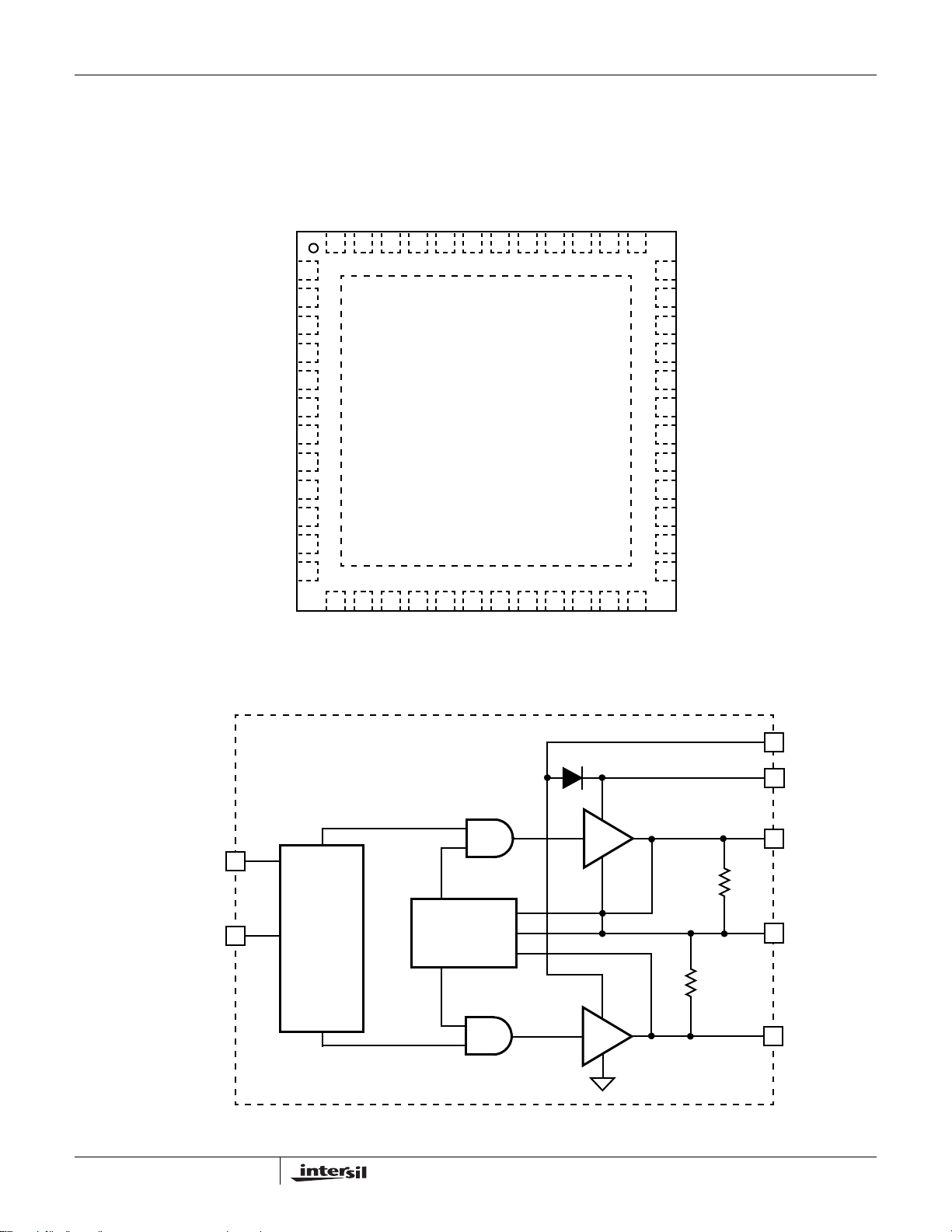
Pinout
ISL6324AISL6324A
ISL6324A HYBRID SVI AND PVI
(48 LD QFN)
TOP VIEW
COMP_NB
ISEN_NB-
ISEN4+
ISEN4-
ISEN3+
ISEN3-
PVCC_NB
LGATE_NB
BOOT_NB
UGATE_NB
PHASE_NB
48 47 46 45 44 43 42 41 40 39 38 37
VDDPWRGD
SDA
VID4
VID5
VCC
FS
RGND
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24
VSEN
FB_NB
ISEN_NB+
VID0/VFIXEN
VID1/SEL
VID2/SVD
VID3/SVC
Integrated Driver Block Diagram
SCL
RSET
RCOMP
FB
49
GND
COMP
36
PWM4
35
PWM3
34
PWROK
33
PHASE1
UGATE1
32
31
BOOT1
30
LGATE1
29
PVCCI_2
LGATE2
28
BOOT2
27
UGATE2
26
PHASE2
25
APA
ISEN1+
ISEN1-
ISEN2+
EN
ISEN2-
PWM
SOFT-START
AND
FAULT LOGIC
2
GATE
CONTROL
LOGIC
SHOOT-
THROUGH
PROTECTION
10kΩ
20kΩ
PVCC
BOOT
UGATE
PHASE
LGATE
March 23, 2009
FN6880.0
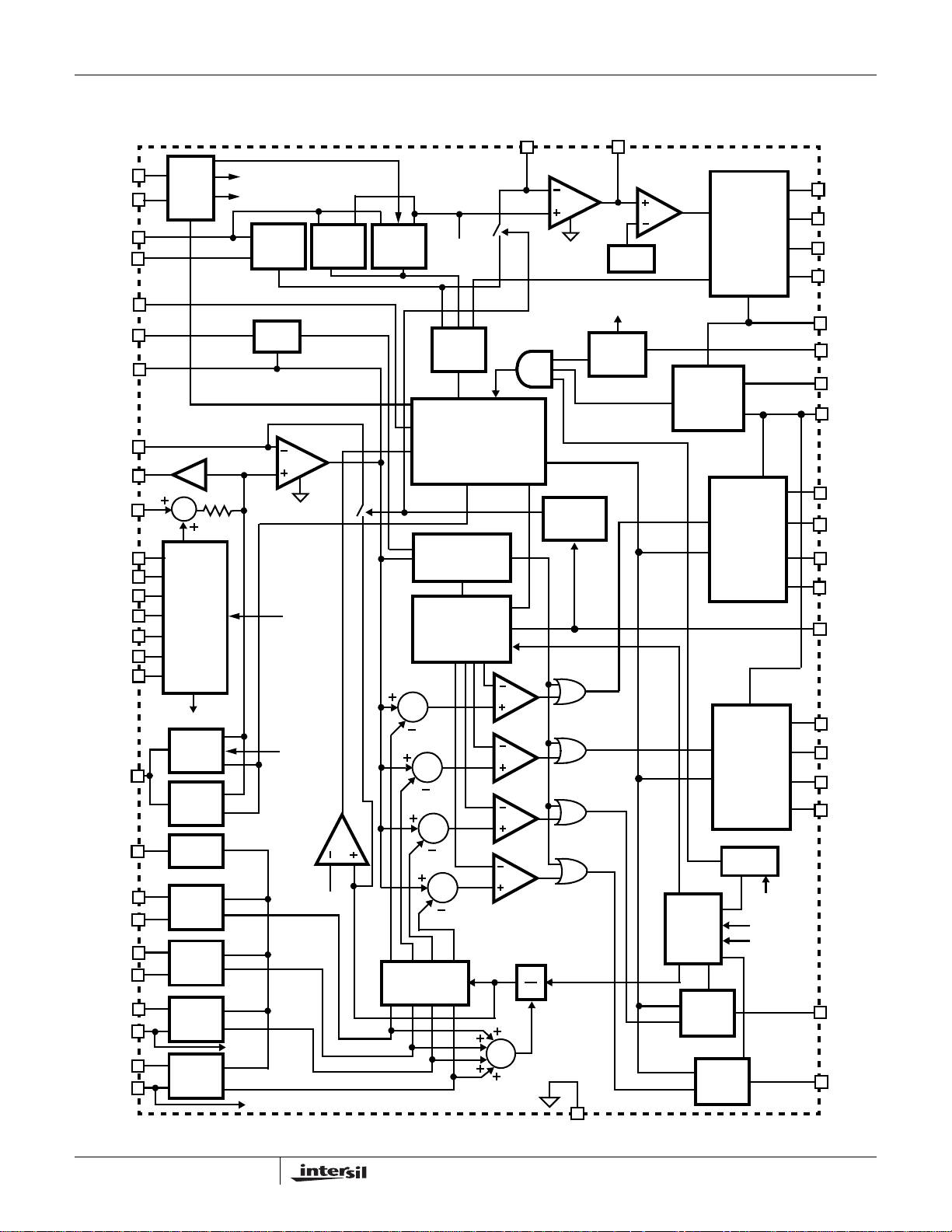
Controller Block Diagram
ISL6324AISL6324A
SCL
SDA
ISEN_NB+
ISEN_NB-
VDDPWRGD
APA
COMP
FB
DVC
RGND
PWROK
VID0/VFIXEN
VID1/SEL
VID2/SVD
VID3/SVC
VID4
VID5
VSEN
RSET
ISEN1+
ISEN1-
ISEN2+
ISEN2-
ISEN3+
ISEN3-
ISEN4+
ISEN4-
I2C
VDDPWRGD_MOD
2X
∑
SVI
SLAVE
BUS
AND
PVI
DAC
NB_REF
OV
LOGIC
UV
LOGIC
RESISTOR
MATCHING
CH1
CURRENT
SENSE
CH2
CURRENT
SENSE
CH3
CURRENT
SENSE
CH4
CURRENT
SENSE
CORE_OVP
DAC_OFS
CURRENT
ISEN3-
ISEN4-
SENSE
APA
DAC_OFS
CORE_OVP
E/A
LOGIC
I_TRIP
UV
OC
I_AVG
NB_OVP
OV
LOGIC
TRIANGLE WAVE
∑
CHANNEL
CURRENT
BALANCE
NB_REF
NB
FAULT
LOGIC
SOFT-START
AND
FAULT LOGIC
LOAD APPL Y
TRANSIENT
ENHANCEMENT
CLOCK AND
GENERATOR
∑
∑
∑
I_AVG
∑
FB_NB
1
N
E/A
DROOP
CONTROL
PWM1
PWM2
GND
COMP_NB
RAMP
EN_12V
ENABLE
LOGIC
PWM3
PWM4
POWER-ON
RESET
CHANNEL
DETECT
PWM3
SIGNAL
LOGIC
PWM4
SIGNAL
LOGIC
MOSFET
DRIVER
MOSFET
DRIVER
MOSFET
DRIVER
PH3/PH4
POR
EN_12V
ISEN3ISEN4-
LGATE_NB
BOOT_NB
UGATE_NB
PHASE_NB
PVCC_NB
EN
VCC
PVCC1_2
BOOT1
UGATE1
PHASE1
LGATE1
FS
BOOT2
UGATE2
PHASE2
LGATE2
PWM3
PWM4
3
FN6880.0
March 23, 2009
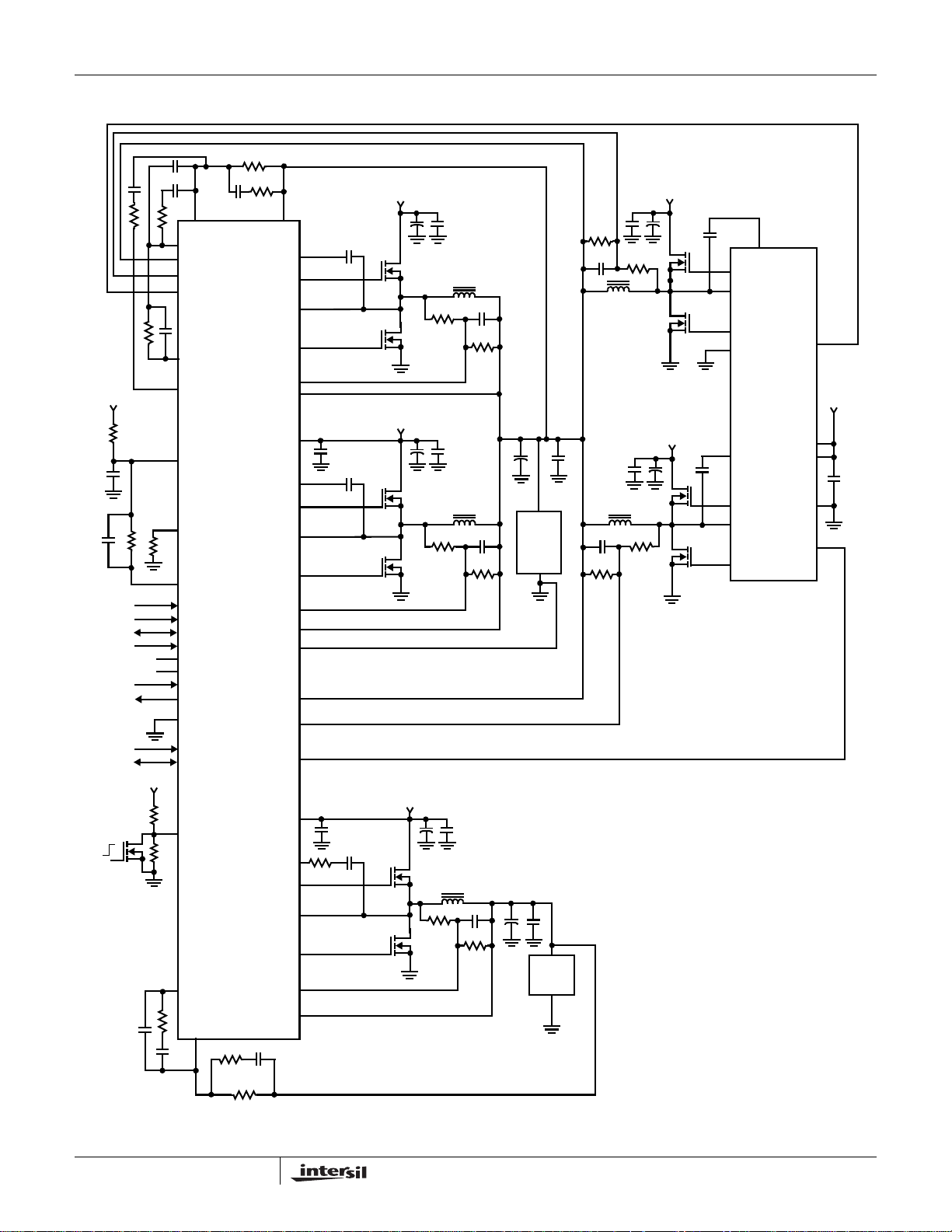
Typical Application - SVI Mode
ISL6324AISL6324A
OFF
ON
+5V
NC
NC
+12V
FB
COMP
ISEN3+
ISEN3PWM3
APA
DVC
VCC
FS
RSET
VFIXEN
SEL
SVD
SVC
VID4
VID5
PWROK
VDDPWRGD
GND
SCL
SDA
ISL6324A
EN
UGATE_NB
VSEN
BOOT1
UGATE1
PHASE1
LGATE1
ISEN1-
ISEN1+
PVCC1_2
BOOT2
UGATE2
PHASE2
LGATE2
ISEN2-
ISEN2+
RGND
ISEN4+
ISEN4-
PWM4
PVCC_NB
BOOT_NB
+12V
+12V
+12V
VDD
CPU
LOAD
+12V
+12V
BOOT1
UGATE1
PHASE1
LGATE1
PGND
ISL6614
BOOT2
UGATE2
PHASE2
LGATE2
PWM1
VCC
PVCC
GND
PWM2
+12V
COMP_NB
FB_NB
PHASE_NB
LGATE_NB
ISEN_NB-
ISEN_NB+
4
NB
LOAD
VDDNB
FN6880.0
March 23, 2009
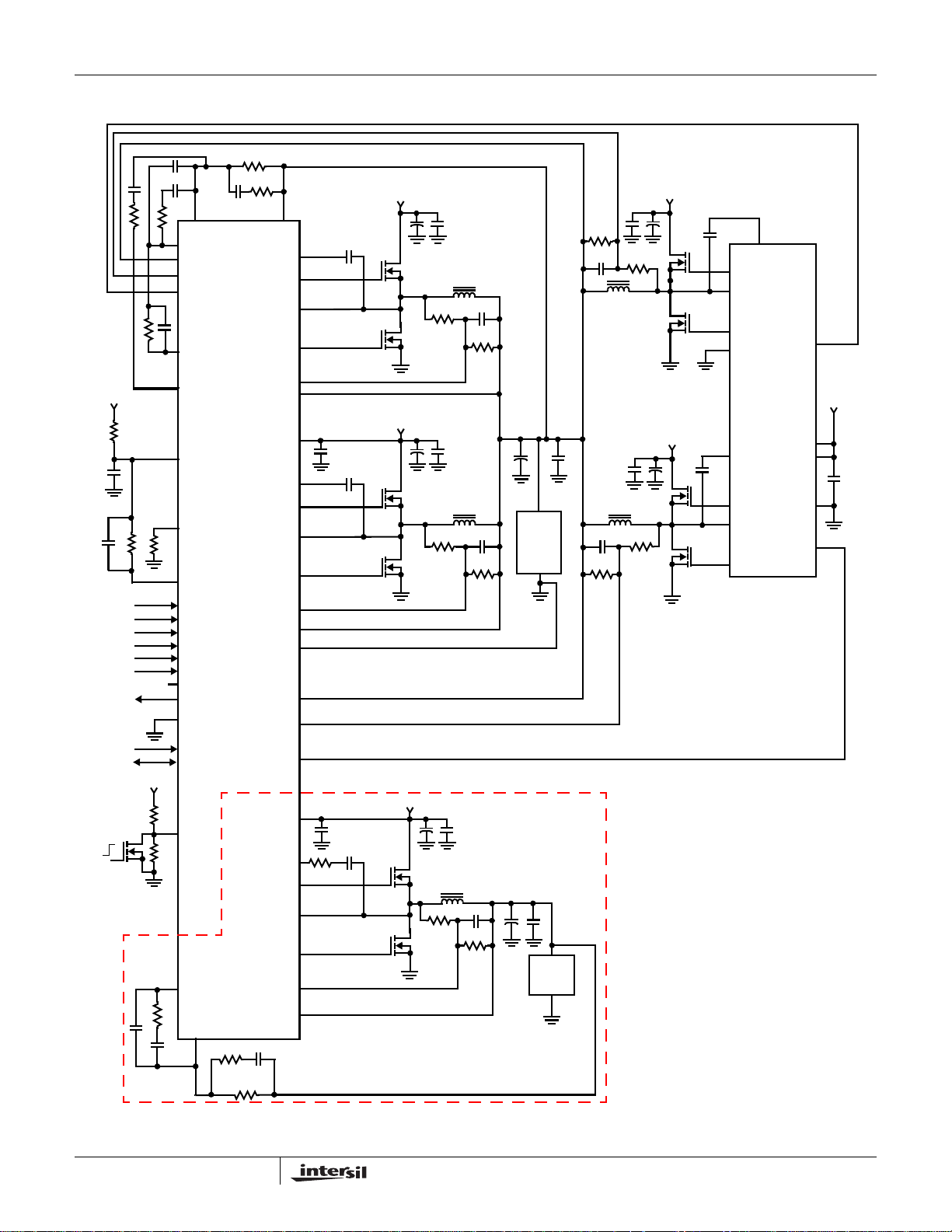
Typical Application - PVI Mode
ISL6324AISL6324A
OFF
ON
+5V
NC
+12V
FB
COMP
ISEN3+
ISEN3PWM3
APA
DVC
VCC
FS
RSET
VID0
VID1/SEL
VID2
VID3
VID4
VID5
PWROK
VDDPWRGD
GND
SCL
SDA
ISL6324A
EN
VSEN
BOOT1
UGATE1
PHASE1
LGATE1
ISEN1-
ISEN1+
PVCC1_2
BOOT2
UGATE2
PHASE2
LGATE2
ISEN2-
ISEN2+
RGND
ISEN4+
ISEN4-
PWM4
PVCC_NB
BOOT_NB
UGATE_NB
+12V
+12V
+12V
VDD
CPU
LOAD
+12V
BOOT1
UGATE1
PHASE1
LGATE1
PGND
ISL6614
+12V
BOOT2
UGATE2
PHASE2
LGATE2
NORTH BRIDGE REGULATOR
DISABLED IN PVI MODE
PWM1
VCC
PVCC
GND
PWM2
+12V
COMP_NB
FB_NB
PHASE_NB
LGATE_NB
ISEN_NB-
ISEN_NB+
5
VDDNB
NB
LOAD
FN6880.0
March 23, 2009
ISL6324AISL6324A
Absolute Maximum Ratings Thermal Information
Supply Voltage (VCC) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . -0.3V to +6.2V
Supply Voltage (PVCC) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .-0.3V to +15V
Absolute Boot Voltage (V
Phase Voltage (V
GND - 8V (<400ns, 20µJ) to 24V (<200ns, V
PHASE
Upper Gate Voltage (V
V
- 3.5V (<100ns Pulse Width, 2µJ) to V
Lower Gate Voltage (V
PHASE
). . . . . . . .GND - 0.3V to GND + 36V
BOOT
). . . . . . . . GND - 0.3V to 15V (PVCC = 12)
BOOT
BOOT
= 12V)
+ 0.3V
+ 0.3V
). . . .V
UGATE
LGATE
PHASE
). . . . . . . GND - 0.3V to PVCC + 0.3V
BOOT-PHASE
- 0.3V to V
GND - 5V (<100ns Pulse Width, 2µJ) to PVCC+ 0.3V
Input, Output, or I/O Voltage . . . . . . . . . GND - 0.3V to VCC + 0.3V
CAUTION: Do not operate at or near the maximum ratings listed for extended periods of time. Exposure to such conditions may adversely impact product reliability and
result in failures not covered by warranty.
NOTES:
is measured in free air with the component mounted on a high effective thermal conductivity test board with “direct attach” features. See
1. θ
JA
Tech Brief TB379.
2. For θ
, the “case temp” location is the center of the exposed metal pad on the package underside.
JC
3. Limits should be considered typical and are not production tested.
Electrical Specifications Recommended Operating Conditions (0°C to +70°C), Unless Otherwise Specified. Parameters with MIN and/or
MAX limits are 100% tested at +25°C, unless otherwise specified. Temperature limits established by
characterization and are not production tested.
PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNITS
BIAS SUPPLIES
Input Bias Supply Current I
Gate Drive Bias Current - PVCC1_2 Pin I
Gate Drive Bias Current - PVCC_NB Pin I
VCC POR (Power-On Reset) Threshold VCC Rising 4.20 4.35 4.50 V
PVCC POR (Power-On Reset) Threshold PVCC Rising 4.20 4.35 4.50 V
PWM MODULATOR
Oscillator Frequency Accuracy, f
SW
Typical Adjustment Range of Switching
Frequency
Oscillator Ramp Amplitude, V
P-P
Maximum Duty Cycle (Note 3) 99.5 %
CONTROL THRESHOLDS
EN Rising Threshold 0.80 0.88 0.92 V
EN Hysteresis 70 130 190 mV
PWROK Input HIGH Threshold 1.1 V
PWROK Input LOW Threshold 0.95 V
VDDPWRGD Sink Current Open drain, V_VDDPWRGD = 400mV 4 mA
PWM Channel Disable Threshold V
; EN = high 15 22 25 mA
VCC
PVCC1_2
PVCC_NB
; EN = high 1 1.8 3 mA
; EN = high 0.3 0.9 2 mA
VCC Falling 3.70 3.85 4.05 V
PVCC Falling 3.70 3.85 4.05 V
RT = 100kΩ (±0.1%) to Ground, (All Temps)
(Droop Enabled)
= 100kΩ (±0.1%) to VCC, TA = 0°C to +70°C
R
T
(Droop Disabled)
= 100kΩ (±0.1%) to VCC, TA = -40°C to +85°C
R
T
(Droop Disabled)
(Note 3) 0.08 1.0 MHz
(Note 3) 1.50 V
, V
ISEN3-
ISEN4-, VISEN2-
Thermal Resistance θ
(°C/W) θJC (°C/W)
JA
QFN Package (Notes 1, 2). . . . . . . . . . 30 2
Maximum Junction Temperature . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .+150°C
Maximum Storage Temperature Range. . . . . . . . . .-65°C to +150°C
Pb-free Reflow Profile . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .see link below
http://www.intersil.com/pbfree/Pb-FreeReflow.asp
Recommended Operating Conditions
VCC Supply Voltage . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .+5V ±5%
PVCC Supply Voltage . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .+5V to 12V ±5%
Ambient Temperature
ISL6324ACRZ . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 0°C to +70°C
ISL6324AIRZ . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .-40°C to +85°C
225 250 265 kHz
245 275 310 kHz
240 275 310 kHz
4.4 V
6
FN6880.0
March 23, 2009
ISL6324AISL6324A
Electrical Specifications Recommended Operating Conditions (0°C to +70°C), Unless Otherwise Specified. Parameters with MIN and/or
MAX limits are 100% tested at +25°C, unless otherwise specified. Temperature limits established by
characterization and are not production tested. (Continued)
PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNITS
REFERENCE AND DAC
System Accuracy (VDAC > 1.000V) -0.6 0.6 %
System Accuracy (0.600V < VDAC < 1.000V) -1.0 1.0 %
System Accuracy (VDAC < 0.600V) -2.0 2.0 %
DVC Voltage Gain VDAC = 1V 2.0 V
APA Current Tolerance V
ERROR AMPLIFIER
DC Gain R
Gain-Bandwidth Product (Note 3) C
Slew Rate (Note 3) C
Maximum Output Voltage Load = 1mA 3.80 4.20 V
Minimum Output Voltage Load = -1mA 1.3 1.6 V
SOFT-START RAMP
Soft-Start Ramp Rate 2.2 3.0 4.0 mV/µs
PWM OUTPUTS
PWM Output Voltage LOW Threshold I
PWM Output Voltage HIGH Threshold I
CURRENT SENSING - CORE CONTROLLER
Sensed Current Tolerance V
CURRENT SENSING - NB CONTROLLER
Sensed Current Tolerance V
DROOP CURRENT
Tolerance V
OVERCURRENT PROTECTION
Overcurrent Trip Level - Average Channel Normal Operation, R
Overcurrent Limiting- Individual Channel Normal Operation, R
POWER-GOOD
Core Overvoltage Threshold VSEN Rising
Undervoltage Threshold VSEN Falling (Core)
Power Good Hysteresis 50 mV
OVERVOLTAGE PROTECTION
OVP Trip Level Bit 7 of I
OVP Lower Gate Release Threshold 350 400 mV
SWITCHING TIME (Note 3) [See “Timing Diagram” on page 8]
UGATE Rise Time t
LGATE Rise Time t
= 1V 90 100 108 µA
APA
= 10k to ground, (Note 3) 96 dB
L
= 100pF, RL = 10k to ground, (Note 3) 20 MHz
L
= 100pF, Load = ±400µA, (Note 3) 8 V/µs
L
= ±500µA 0.5 V
LOAD
= ±500µA 4.5 V
LOAD
- V
ISENn-
4 Phases, T
ISEN_NB-
R
= 37.6kΩ, 4 Phases, TA = +25°C
SET
- V
ISENn-
4 Phases, T
ISENn+
= +25°C
A
- V
ISEN_NB+
ISENn+
= +25°C
A
= 23.2mV, R
= 23.2mV,
= 23.2mV, R
= 28.2kΩ 87 100 120 µA
SET
SET
SET
= 37.6kΩ,
= 37.6kΩ,
68 88 µA
68 89 µA
68 88 µA
Dynamic VID Change (Note 3) 130 µA
= 28.2kΩ 142 µA
SET
Dynamic VID Change (Note 3) 190 µA
2
Bit 6 of I
Bit 6 of I
ISEN_NB+ Falling (North Bridge)
Bit 6 of I
RUGATE; VPVCC
RLGATE; VPVCC
C data = 0
2
C data = 0
2
C data = 0
2
C data = 0, VDAC ≤ 1.55V 1.73 1.80 1.84 V
= 12V, 3nF Load, 10% to 90% 26 ns
= 12V, 3nF Load, 10% to 90% 18 ns
VDAC +
225mV
VDAC -
325mV
VDAC -
310mV
VDAC +
250mV
VDAC -
300mV
VDAC -
275mV
VDAC +
275mV
VDAC -
270mV
VDAC -
235mV
mV
mV
V
7
FN6880.0
March 23, 2009
ISL6324AISL6324A
Electrical Specifications Recommended Operating Conditions (0°C to +70°C), Unless Otherwise Specified. Parameters with MIN and/or
MAX limits are 100% tested at +25°C, unless otherwise specified. Temperature limits established by
characterization and are not production tested. (Continued)
PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNITS
UGATE Fall Time t
LGATE Fall Time t
UGATE Turn-On Non-overlap t
LGATE Turn-On Non-overlap t
FUGATE; VPVCC
FLGATE; VPVCC
PDHUGATE
PDHLGATE
GATE DRIVE RESISTANCE (Note 3)
Upper Drive Source Resistance V
Upper Drive Sink Resistance V
Lower Drive Source Resistance V
Lower Drive Sink Resistance V
= 12V, 15mA Source Current 2.0 Ω
PVCC
= 12V, 15mA Sink Current 1.65 Ω
PVCC
= 12V, 15mA Source Current 1.25 Ω
PVCC
= 12V, 15mA Sink Current 0.80 Ω
PVCC
MODE SELECTION
VID1/SEL Input Low EN taken from HI to LO, VDDIO = 1.5V 0.6 V
VID1/SEL Input High EN taken from LO to HI, VDDIO = 1.5V 1.00 V
PVI INTERFACE
VIDx Pull-down VDDIO = 1.5V 30 40 µA
VIDx Input Low VDDIO = 1.5V 0.6 V
VIDx Input High VDDIO = 1.5V 1.00 V
SVI INTERFACE
SVC, SVD Input LOW (VIL) 0.4 V
SVC, SVD Input HIGH (VIH) 0.95 V
Schmitt Trigger Input Hysteresis 0.14 0.35 0.45 V
SVD Low Level Output Voltage 3mA Sink Current 0.285 V
Maximum SVC, SVD Leakage (Note 3) ±5 µA
2
I
C INTERFACE
SCL, SDA Input LOW (VIL) 1.10 V
SCL, SDA Input HIGH (VIH) 1.75 V
Schmitt Trigger Input Hysteresis 0.18 0.35 0.50 V
SDA Low Level Output Voltage 3mA Sink Current 0.2 V
Maximum SCL, SDA Leakage (Note 3) ±5 µA
= 12V, 3nF Load, 90% to 10% 18 ns
= 12V, 3nF Load, 90% to 10% 12 ns
; V
= 12V , 3nF Load, Adaptive 10 ns
PVCC
; V
= 12V, 3nF Load, Adaptive 10 ns
PVCC
Timing Diagram
UGATE
LGATE
t
PDHUGATE
t
8
FLGATE
t
RUGATE
t
t
PDHLGATE
FUGATE
t
RLGATE
FN6880.0
March 23, 2009

ISL6324AISL6324A
Functional Pin Description
VID1/SEL
This pin selects SVI or PVI mode operation based on the state
of the pin prior to enabling the ISL6324A. If the pin is LO prior
to enable, the ISL6324A is in SVI mode and the dual purpose
pins [VID0/VFIXEN, VID2/SVC, VID3/SVD] use their SVI
mode related functions. If the pin held HI prior to enable, the
ISL6324A is in PVI mode and dual purpose pins use their
VIDx related functions to decode the correct DAC code.
VID0/VFIXEN
If VID1 is LO prior to enable [SVI Mode], the pin is functions
as the VFIXEN selection input from the AMD processor for
determining SVI mode versus VFIX mode of operation.
If VID1 is HI prior to enable [PVI Mode], the pin is used as
DAC input VID0. This pin has an internal 30µA pull-down
current applied to it at all times.
VID2/SVD
If VID1 is LO prior to enable [SVI Mode], this pin is the serial
VID data bi-directional signal to and from the master device on
AMD processor. If VID1 is HI prior to enable [PVI Mode], this
pin is used to decode the programmed DAC code for the
processor. In PVI mode, this pin has an internal 30µA pull-down
current applied to it. There is no pull-down current in SVI mode.
VID3/SVC
If VID1 is LO prior to enable [SVI Mode], this pin is the serial
VID clock input from the AMD processor . If VID1 is HI prior to
enable [PVI Mode], the ISL6324A is in PVI mode and this pin
is used to decode the programmed DAC code for the
processor. In PVI mode, this pin has an internal 30µ A
pull-down current applied to it. There is no pull-down current in
SVI mode.
VID4
This pin is active only when the ISL6324A is in PVI mode.
When VID1 is HI prior to enable, the ISL6324A decodes the
programmed DAC voltage required by the AMD processor.
This pin has an internal 30µA pull-down current applied to it at
all times.
VID5
This pin is active only when the ISL6324A is in PVI mode.
When VID1 is HI prior to enable, the ISL6324A decodes the
programmed DAC voltage required by the AMD processor.
This pin has an internal 30µA pull-down current applied to it at
all times.
VCC
VCC is the bias supply for the ICs small-signal circuitry.
Connect this pin to a +5V supply and decouple using a
quality 0.1µF ceramic capacitor.
PVCC1_2
The power supply pin for the multi-phase internal MOSFET
drivers. Connect this pin to any voltage from +5V to +12V
depending on the desired MOSFET gate-drive level.
Decouple this pin with a quality 1.0µF ceramic capacitor.
PVCC_NB
The power supply pin for the internal MOSFET driver for the
Northbridge controller. Connect this pin to any voltage from
+5V to +12V depending on the desired MOSFET gate-drive
level. Decouple this pin with a quality 1.0µF ceramic capacitor .
GND
GND is the bias and reference ground for the IC. The GND
connection for the ISL6324A is through the thermal pad on
the bottom of the package.
EN
This pin is a threshold-sensitive (approximately 0.85V) system
enable input for the controller. Held low, this pin disables both
CORE and NB controller operation. Pulled high, the pin
enables both controllers for operation.
When the EN pin is pulled high, the ISL6324A will be placed
in either SVI or PVI mode. The mode is determined by the
latched value of VID1 on the rising edge of the EN signal.
A third function of this pin is to provide driver bias monitor for
external drivers. A resistor divider with the center tap
connected to this pin from the drive bias supply prevents
enabling the controller before insufficient bias is provided to
external driver. The resistors should be selected such th at
when the POR-trip point of the external driver is reached, the
voltage at this pin meets the above mentioned threshold level .
FS
A resistor, placed from FS to Ground or from FS to VCC,
sets the switching frequency of both controllers. Refer to
Equation 1 for proper resistor calculation.
10.61 1.035 fs()log–[]
10
=
R
T
With the resistor tied from FS to Ground, Droop is enabled.
With the resistor tied from FS to VCC, Droop is disabled.
(EQ. 1)
VSEN and RGND
VSEN and RGND are inputs to the core voltage regulator
(VR) controller precision differential remote-sense amplifier
and should be connected to the sense pins of the remote
processor core(s), VDDFB[H,L].
FB and COMP
These pins are the internal error amplifier inverting input and
output respectively of the core VR controller. FB, VSEN and
COMP are tied together through external R-C networks to
compensate the regulator.
APA
Adaptive Phase Alignment (APA) pin for setting trip level and
adjusting time constant. A 100µA current flows into the APA
pin and by tying a resistor from this pin to COMP the trip
level for the Adaptive Phase Alignment circuitry can be set.
9
FN6880.0
March 23, 2009

ISL6324AISL6324A
ISEN1-, ISEN1+, ISEN2-, ISEN2+, ISEN3-, ISEN3+,
ISEN4-, and ISEN4+
These pins are used for differentially sensing the corresponding
channel output currents. The sensed currents are used for
channel balancing, protection, and core load line regulation.
Connect ISEN1-, ISEN2-, ISEN3-, and ISEN4- to the node
between the RC sense elements surrounding the inductor of
their respective channel. Tie the ISEN+ pins to the VCORE
side of their corresponding channel’s sense capacitor.
UGATE1 and UGATE2
Connect these pins to the corresponding upper MOSFET
gates. These pins are used to control the upper MOSFETs
and are monitored for shoot-through prevention purposes.
Maximum individual channel duty cycle is limited to 93.3%.
BOOT1 and BOOT2
These pins provide the bias voltage for the corresponding
upper MOSFET drives. Connect these pins to appropriately
chosen external bootstrap capacitors. Internal bootstrap
diodes connected to the PVCC1_2 pin provide the
necessary bootstrap charge.
PHASE1 and PHASE2
Connect these pins to the sources of the corresponding
upper MOSFETs. These pins are the return path for the
upper MOSFET drives.
LGATE1 and LGATE2
These pins are used to control the lower MOSFET s. Connect
these pins to the corresponding lower MOSFETs’ gates.
PWM3 and PWM4
Pulse-width modulation outputs. Connect these pins to the
PWM input pins of an Intersil driver IC if 3- or 4-phase
operation is desired. Connect the ISEN- pins of the channels
not desired to +5V to disable them and configure the core
VR controller for 2-phase or 3-phase operation.
PWROK
System wide Power Good signal. If this pin is low, the two
SVI bits are decoded to determine the “metal VID”. When the
pin is high, the SVI is actively running its protocol.
RSET
Connect this pin to the VCC pin through a resistor (R
set the effective value of the internal R
resistors. The values of the R
than 20kΩ and no more than 80kΩ. A 0.1µF capacitor
should be placed in parallel to the R
resistor should be no less
SET
current sense
ISEN
resistor.
SET
SET
) to
VDDPWRGD
During normal operation this pin indicates wh ether both output
voltages are within specified overvoltage and undervolt age
limits. If either output voltage exceeds these limits or a re set
event occurs (such as an overcurrent event), the pin is pulled
low. This pin is always low prior to the end of sof t-start.
DVC
The DVC pin is a buffered version of the reference to the error
amplifier. A series resistor and capaci tor between the DVC pin
and FB pin smooth the voltage transition d uring VID-on-the-fly
operations.
FB_NB and COMP_NB
These pins are the internal error amplifier inverting input and
output respectively of the NB VR controller. FB_NB,
VDIFF_NB, and COMP_NB are tied together through
external R-C networks to compensate the re gu l at o r.
ISEN_NB-, ISEN_NB+
These pins are used for differentially sensing the North
Bridge output current. The sensed current is used for
protection and load line regulation if droop is enabled.
Connect ISEN_NB- to the node between the RC sense
element surrounding the inductor. Tie the ISEN_NB+ pin to
the VNB side of the sense capacitor.
UGATE_NB
Connect this pin to the corresponding upper MOSFET gate.
This pin provides the PWM-controlled gate drive for the
upper MOSFET and is monitored for shoot-through
prevention purposes.
BOOT_NB
This pin provides the bias voltage for the corresponding
upper MOSFET drive. Connect this pin to appropriately
chosen external bootstrap capacitor. The internal bootstrap
diode connected to the PVCC_NB pin provides the
necessary bootstrap charge.
PHASE_NB
Connect this pin to the source of the corresponding upper
MOSFET. This pin is the return path for the upper MOSFET
drive. This pin is used to monitor the voltage drop across the
upper MOSFET for overcurrent protection.
LGATE_NB
Connect this pin to the corresponding MOSFET’s gate. This
pin provides the PWM-controlled gate drive for the lower
MOSFET. This pin is also monitored by the adaptive
shoot-through protection circuitry to determine when the
lower MOSFET has turned off.
SCL
Connect this pin to the clock signal for the I2C bus, which is
a logic level input signal. The clock signal tells the controller
when data is available on th e I
2
C bus.
SDA
Connect this pin to the bidirectional data line of the I2C bus,
which is a logic level input/output signal. All I
over this line, including the address of the device the bus is
trying to communicate with, and what functions the device
should perform.
2
C data is sent
10
FN6880.0
March 23, 2009

ISL6324A
Operation
The ISL6324A utilizes a multi-phase architecture to provide
a low cost, space saving power conversion solution for the
processor core voltage. The controller also implements a
simple single phase architecture to provide the Northbridge
voltage on the same chip.
Multi-phase Power Conversion
Microprocessor load current profiles have changed to the
point that the advantages of multi-phase power conversion
are impossible to ignore. The technical challenges
associated with producing a single-phase converter that is
both cost-effective and thermally viable have forced a
change to the cost-saving approach of multi-phase. The
ISL6324A controller helps simplify implementation by
integrating vital functions and requiring minimal external
components. The “Controller Block Diagram” on page 3
provides a top level view of the multi-phase power
conversion using the ISL6324A controller.
Interleaving
The switching of each channel in a multi-phase converter is
timed to be symmetrically out-of-phase with each of the other
channels. In a 3-phase converter, each channel switches 1/3
cycle after the previous channel and 1/3 cycle before the
following channel. As a result, the three-phase converter has a
combined ripple frequency three times greater than the ripple
frequency of any one phase. In addition, the peak-to-peak
amplitude of the combined inductor currents is reduced in
proportion to the number of phases (Equations 2 and 3).
Increased ripple frequency and lower ripple amplitude mean
that the designer can use less per-channel inductance and
lower total output capacitance for any performance
specification.
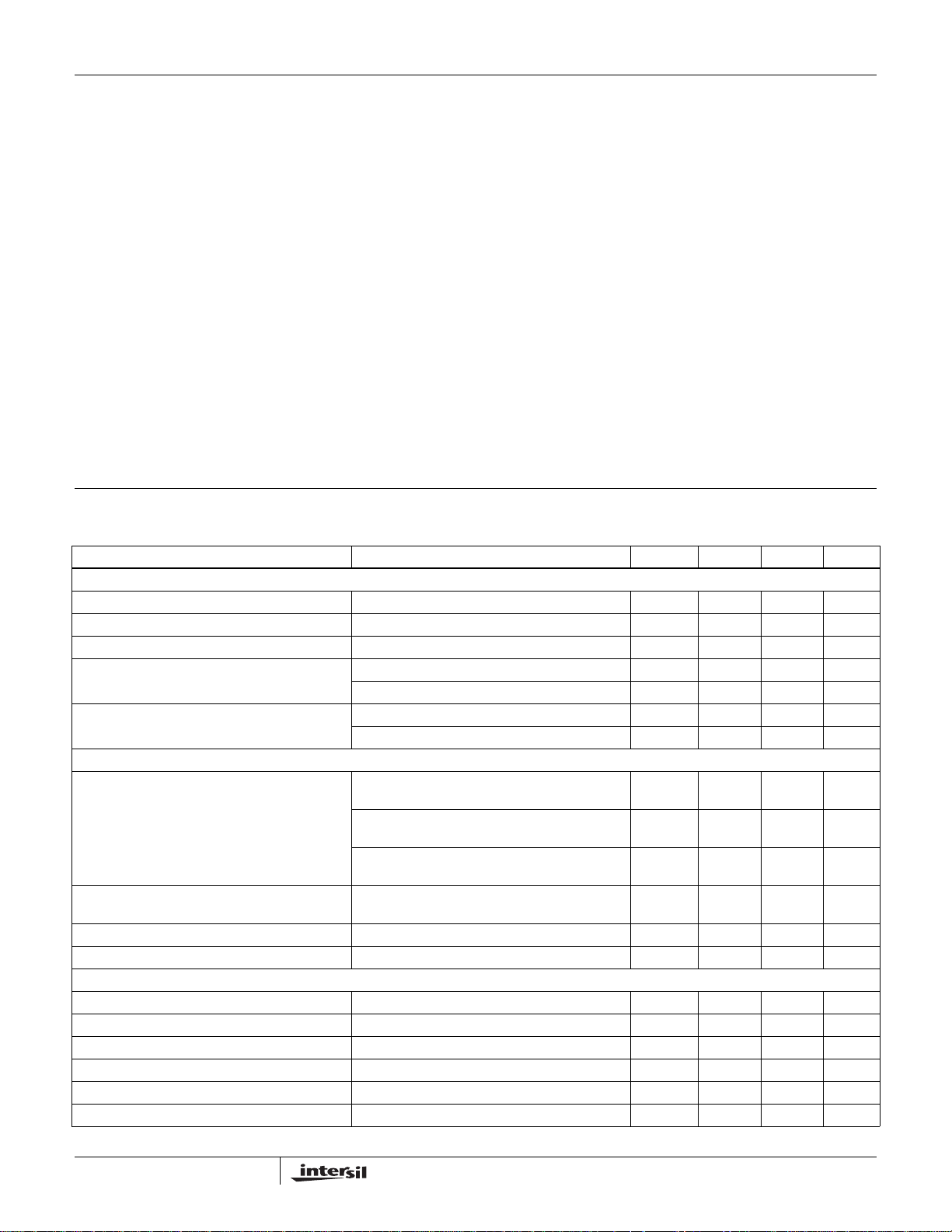
Figure 1 illustrates the multiplicative effect on output ripple
frequency. The three channel currents (IL1, IL2, and IL3)
combine to form the AC ripple current and the DC load
current. The ripple component has three times the ripple
frequency of each individual channel current. Each PWM
pulse is terminated 1/3 of a cycle after the PWM pulse of the
previous phase. The peak-to-peak current for each phase is
about 7A, and the DC components of the inductor currents
combine to feed the load.
T o understand the reduction of ripple current amplitude in the
multi-phase circuit, examine Equation 2, which represents
an individual channel peak-to-peak inductor current.
VINV
–()V
OUT
IN
and V
IN
OUT
are the input and output
OUT
I
------------------------------------------------------=
PP–
LfSV
In Equation 2, V
voltages respectively, L is the single-channel inductor value,
and f
is the switching frequency.
S
(EQ. 2)
The output capacitors conduct the ripple component of the
inductor current. In the case of multi-phase converters, the
capacitor current is the sum of the ripple currents from each
of the individual channels. Compare Equation 2 to the
expression for the peak-to-peak current after the summation
of N symmetrically phase-shifted inductor currents in
Equation 3. Peak-to-peak ripple current decreases by an
amount proportional to the number of channels. Output
voltage ripple is a function of capacitance, capacitor
equivalent series resistance (ESR), and inductor ripple
current. Reducing the inductor ripple current allows the
designer to use fewer or less costly output capacitors.
I
CP P–()
------------------------------------------------------------=
LfSV
OUT
IN
(EQ. 3)
VINNV
–()V
OUT
Another benefit of interleaving is to reduce input ripple
current. Input capacitance is determined in part by the
maximum input ripple current. Multi-phase topologies can
improve overall system cost and size by lowering input ripple
current and allowing the designer to reduce the cost of input
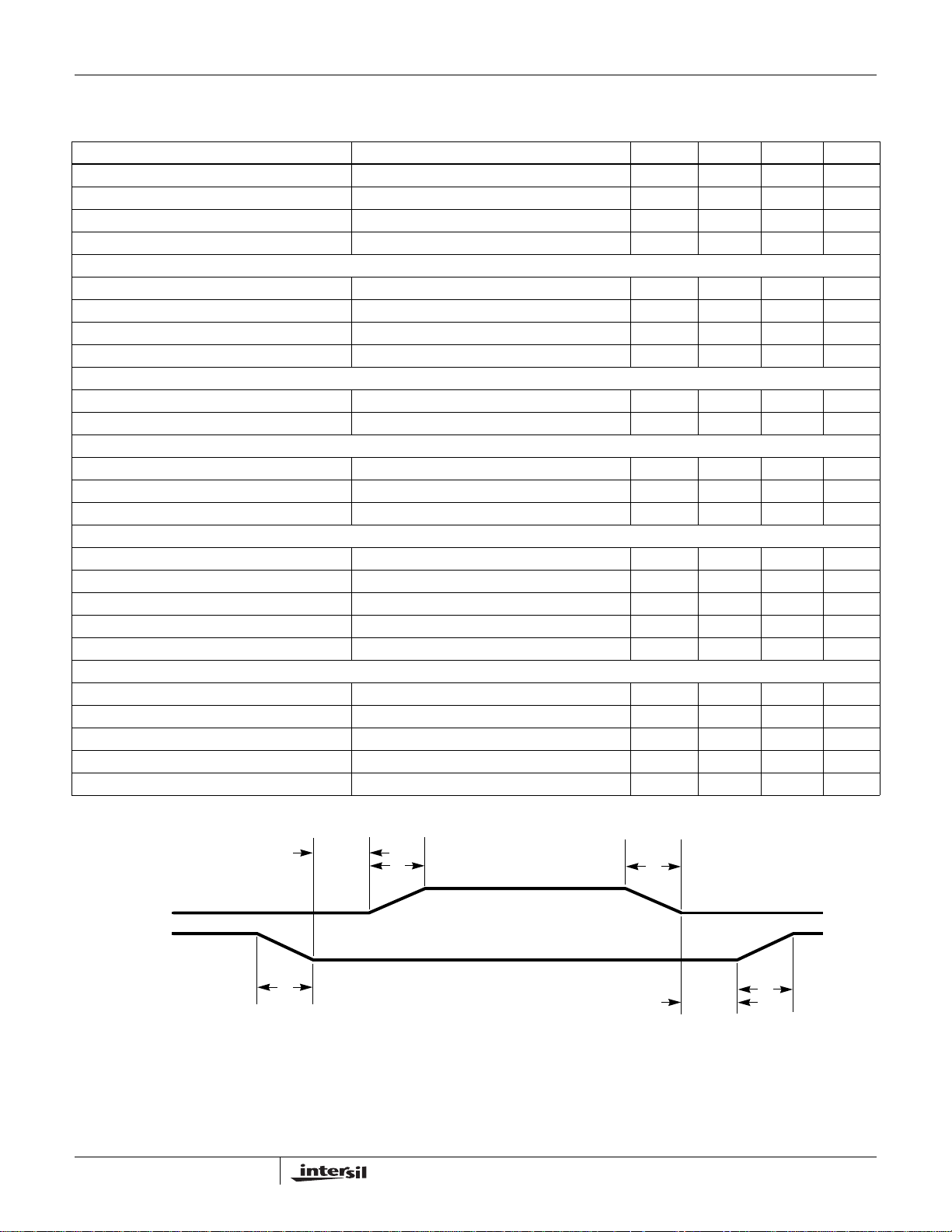
capacitance. The example in Figure 2 illustrates input
currents from a three-phase converter combining to reduce
the total input ripple current.
The converter depicted in Figure 2 delivers 1.5V to a 36A load
from a 12V input. The RMS input capacitor current is 5.9A.
Compare this to a single-phase conve rter also step ping down
12V to 1.5V at 36A. The single-phase converter has
11.9A
input capacitor current. The single-phase converter
RMS
must use an input capacitor bank with twice the RMS current
capacity as the equivalent three-phase converter .
Figures 26, 27 and 28 in the section entitled “Input Capacitor
Selection” on page 35 can be used to determine the input
capacitor RMS current based on load current, duty cycle,
and the number of channels. They are provided as aids in
determining the optimal input capacitor solution.
IL1 + IL2 + IL3, 7A/DIV
IL3, 7A/DIV
PWM3, 5V/DIV
IL2, 7A/DIV
PWM2, 5V/DIV
IL1, 7A/DIV
PWM1, 5V/DIV
1µs/DIV
FIGURE 1. PWM AND INDUCTOR-CURRENT WA VEFORMS
FOR 3-PHASE CONVERTER
11
FN6880.0
March 23, 2009
ISL6324A
INPUT-CAPACITOR CURRENT, 10A/DIV
CHANNEL 3
INPUT CURRENT
10A/DIV
CHANNEL 2
INPUT CURRENT
10A/DIV
CHANNEL 1
INPUT CURRENT
10A/DIV
1μs/DIV
FIGURE 2. CHANNEL INPUT CURRENTS AND INPUT
CAPACITOR RMS CURRENT FOR 3-PHASE
CONVERTER
Active Pulse Positioning Modulated PWM Operation
The ISL6324A uses a proprietary Active Pulse Positioning
(APP) modulation scheme to control the internal PWM signals
that command each channel’s driver to turn their upper and
lower MOSFETs on and off. The time interval in which a PWM
signal can occur is generated by an internal clock, whose cycle
time is the inverse of the switching frequency set by the resistor
between the FS pin and ground. The advantage of Intersil’s
proprietary Active Pulse Positioning (APP) modulator is that the
PWM signal has the ability to turn on at any point during this
PWM time interval, and turn off immediately after the PWM
signal has transitioned high. This is important because it allows
the controller to quickly respond to output voltage drops
associated with current load spikes, while avoiding the ring
back affects associated with other modulation schemes.
To further improve the transient response, ISL6324A also
implements Intersil’s proprietary Adaptive Phase Alignment
(APA) technique, which turns on all phases together under
transient events with large step current. With both APP and
APA control, ISL6324A can achieve excellent transient
performance and reduce the demand on the output capacitors.
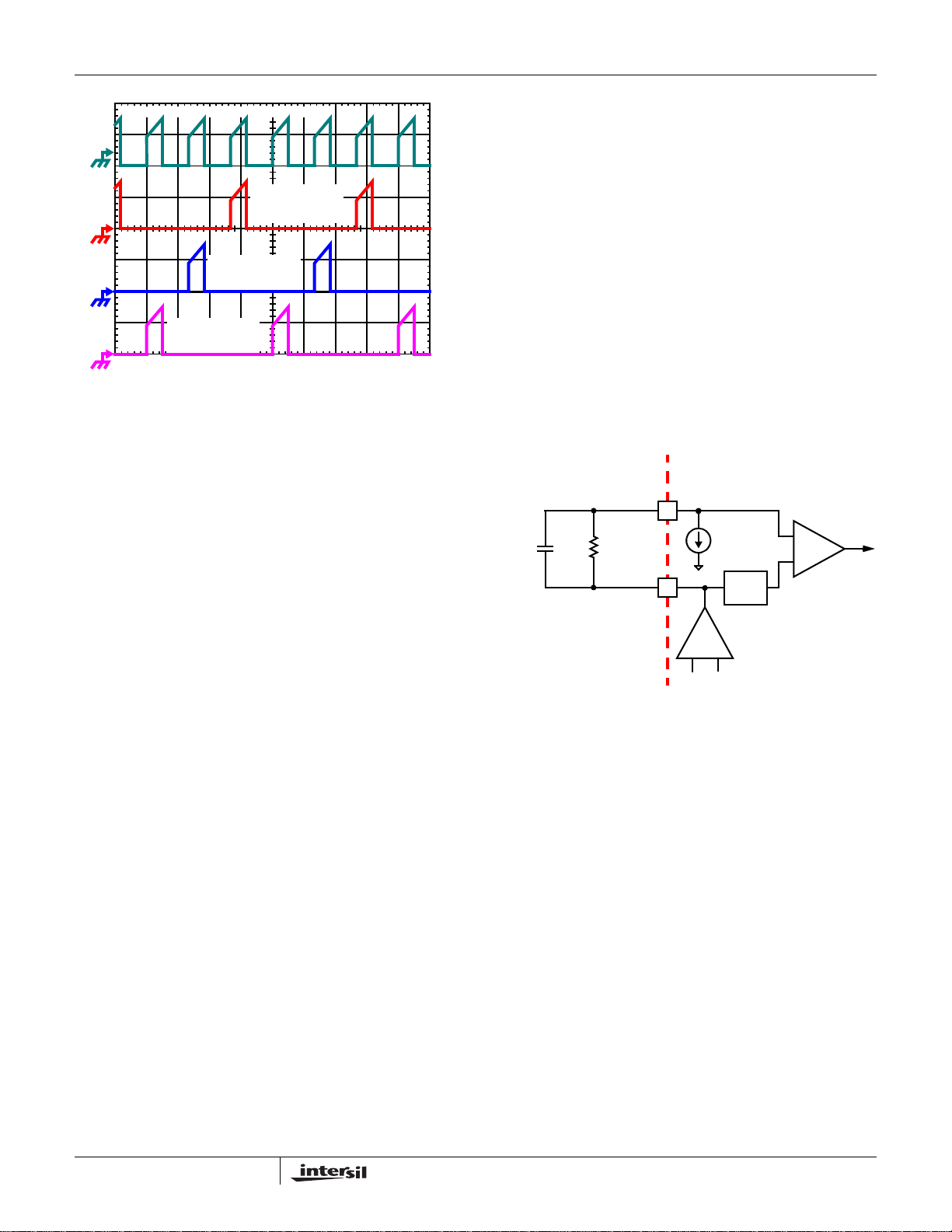
Adaptive Phase Alignment (APA)
To further improve the transient response, the ISL6324A
also implements Intersil’s proprietary Adaptive Phase
Alignment (APA) technique, which turns on all of the
channels together at the same time during large current step
transient events. As Figure 3 shows, the APA circuitry works
by monitoring the voltage on the APA pin and comparing it to
a filtered copy of the voltage on the COMP pin. The voltage
on the APA pin is a copy of the COMP pin voltage that has
been negatively offset. If the APA pin exceeds the filtered
COMP pin voltage an APA event occurs and all of the
channels are forced on.
EXTERNAL CIRCUIT
APA
-
C
R
APA
FIGURE 3. ADAPTIVE PHASE ALIGNMENT DETECTION
APA
V
APA,TRIP
+
COMP
ISL6324A INTERNAL CIRCUIT
100µA
+
APA
-
-
LOW
PASS
FILTER
ERROR
AMPLIFIER
+
CIRCUITRY
TO APA
The PWM output state is driven by the position of the error
amplifier output signal, V
, minus the current correction
COMP
signal relative to the proprietary modulator ramp waveform as
illustrated in Figure 3. At the beginning of each PWM time
interval, this modified V
internal modulator waveform. As long as the modified V
signal is compared to the
COMP
COMP
voltage is lower then the modulator waveform voltage, the
PWM signal is commanded low. The internal MOSFET driver
detects the low state of the PWM signal and turns off the
upper MOSFET and turns on the lower synchronous
MOSFET. When the modified V
voltage crosses the
COMP
modulator ramp, the PWM output transitions high, turning off
the synchronous MOSFET and turning on the upper
MOSFET. The PWM signal will remain high until the modified
V
voltage crosses the modulator ramp again. When this
COMP
occurs the PWM signal will transition low again.
During each PWM time interval the PWM signal can only
transition high once. Once PWM transitions high it can not
transition high again until the beginning of the next PWM
time interval. This prevents the occurrence of double PWM
pulses occurring during a single period.
12
The APA trip level is the amount of DC offset between the
COMP pin and the APA pin. This is the voltage excursion
that the APA and COMP pins must have during a transient
event to activate the Adaptive Phase Alignment circuitry.
This APA trip level is set through a resistor, R
connects from the APA pin to the COMP pin. A 100µA
current flows across R
into the APA pin to set the APA
APA
APA
, that
trip level as described in Equation 4. An APA trip level of
500mV is recommended for most applications. A 0.1µF
capacitor, C
, should also be placed across the R
APA
APA
resistor to help with noise immunity.
V
APA TRIP,
R
APA
100 106–×⋅=
(EQ. 4)
PWM Operation
The timing of each core channel is set by the number of
active channels. Channel detection on the ISEN3- and
ISEN4- pins selects 2-Channel to 4-Channel operation for
the ISL6324A. The switching cycle is defined as the time
between PWM pulse termination signals of each channel.
The cycle time of the pulse signal is the inverse of the
FN6880.0
March 23, 2009
 Loading...
Loading...