Page 1

®
www.BDTIC.com/Intersil
ISL6209
Data Sheet March 23, 2007
High Voltage Synchronous Rectified Buck
MOSFET Driver
The ISL6209 is a high frequency, dual MOSFET driver,
optimized to drive two N-Channel power MOSFETs in a
synchronous-rectified buck converter topology in mobile
computing applications. This driver, combined with an Intersil
Multi-Phase Buck PWM controller, such as ISL6216, ISL6244,
and ISL6247, forms a complete single-stage core-voltage
regulator solution for advanced mobile microprocessors.
The ISL6209 features 4A typical sink current for the lower gate
driver. The 4A typical sink current is capable of holding the
lower MOSFET gate during the PHASE node rising edge to
prevent the shoot-through power loss caused by the high dv/dt
of the PHASE node. The operation voltage matches the 30V
breakdown voltage of the MOSFETs commonly used in mobile
computer power supplies.
The ISL6209 also features a three-state PWM input that,
working together with most of Intersil multiphase PWM
controllers, will prevent a negative transient on the output
voltage when the output is being shut down. This feature
eliminates the Schottky diode, that is usually seen in a
microprocessor power system for protecting the
microprocessor, from reversed-output-voltage damage.
The ISL6209 has the capacity to efficiently switch power
MOSFET s at frequencies up to 2MHz. Each driver is capable of
driving a 3000pF load with a 8ns propagation delay and less
than a 10ns transition time. This product implements
bootstrapping on the upper gate with an internal bootstrap
Schottky diode, reducing implementation cost, complexity, and
allowing the use of higher performance, cost effective
N-Channel MOSFETs. Programmable dead-time with gate
threshold monitoring is integrated to prevent both MOSFETs
from conducting simultaneously.
Related Literature
• Technical Brief TB363 “Guidelines for Handling and
Processing Moisture Sensitive Surface Mount Devices
(SMDs)”
• Technical Brief TB389 “PCB Land Pattern Design and
Surface Mount Guidelines for QFN Packages”
• Technical Brief TB447 “Guidelines for Preventing Boot-toPhase Stress on Half-Bridge MOSFET Driver ICs”
FN9132.2
Features
• Drives Two N-Channel MOSFETs
• Shoot-Through Protection
- Active gate threshold monitoring
- Programmable dead-time
• 30V Operation Voltage
•0.4Ω On-Resistance and 4A Sink Current Capability
• Supports High Switching Frequency
- Fast output rise time
- Propagation delay 8ns
• Three-State PWM Input for Power Stage Shutdown
• Internal Bootstrap Schottky Diode
• QFN Package:
- Compliant to JEDEC PUB95 MO-220
QFN - Quad Flat No Leads - Package outline
- Near Chip Scale Package footprint, which improves
PCB efficiency and has a thinner profile
• Pb-Free Plus Anneal Available (RoHS Compliant)
Applications
• Core Voltage Supplies for Intel and AMD® Mobile
Microprocessors
• High Frequency Low Profile DC/DC Converters
• High Current Low Output Voltage DC/DC Converters
• High Input Voltage DC/DC Converter
Ordering Information
PART
NUMBER
ISL6209CB* ISL6209CB -10 to +100 8 Ld SOIC M8.15
ISL6209CBZ*
(Note)
ISL6209CR* 209C -10 to +100 8 Ld 3x3 QFN L8.3x3
*Add “-T” suffix for tape and reel.
NOTE: Intersil Pb-free plus anneal products employ special Pb-free
material sets; molding compounds/die attach materials and 100%
matte tin plate termination finish, which are RoHS compliant and
compatible with both SnPb and Pb-free soldering operations. Intersil
Pb-free products are MSL classified at Pb-free peak reflow
temperatures that meet or exceed the Pb-free requirements of
IPC/JEDEC J STD-020.
PART
MARKING
ISL6209CBZ -10 to +100 8 Ld SOIC
TEMP.
RANGE
(°C) PACKAGE
(Pb-free)
PKG.
DWG. #
M8.15
1
AMD® is a registered trademark of Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. All other trademarks mentioned are the property of their respective owners.
Copyright © Intersil Americas Inc. 2004, 2005, 2007. All Rights Reserved. Intel® is a registered trademark of Intel Corporation.
CAUTION: These devices are sensitive to electrostatic discharge; follow proper IC Handling Procedures.
1-888-INTERSIL or 1-888-468-3774
| Intersil (and design) is a registered trademark of Intersil Americas Inc.
Page 2
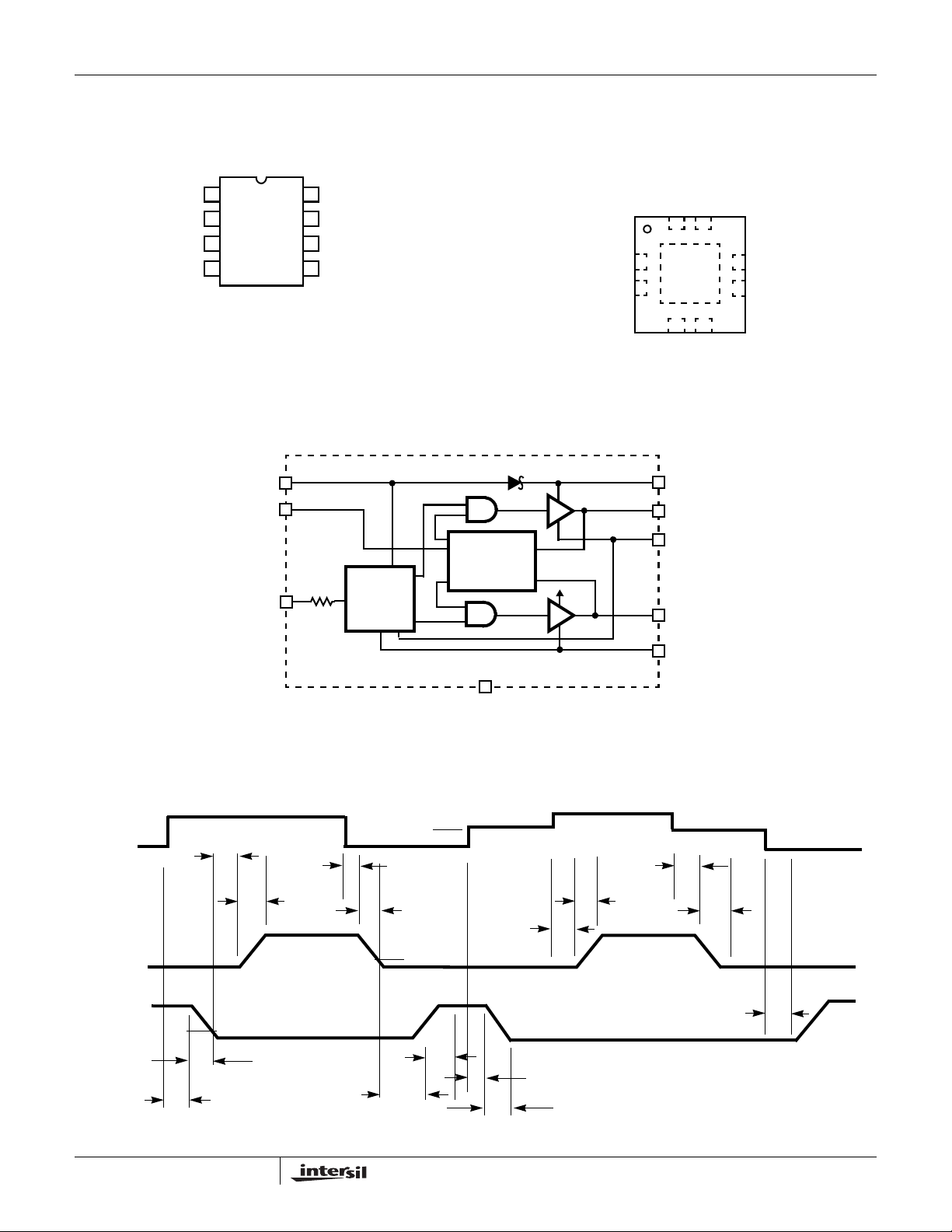
Pinouts
www.BDTIC.com/Intersil
ISL6209
(8 LD SOIC)
TOP VIEW
ISL6209
ISL6209
(8 LD QFN)
TOP VIEW
UGATE
BOOT
PWM
GND
1
2
3
4
ISL6209 Block Diagram
VCC
DELAY
PWM
8
7
6
5
10K
PHASE
DELAY
VCC
LGATE
CONTROL
LOGIC
SHOOT-
THROUGH
PROTECTION
VCC
BOOT
PWM
UGATE
PHASE
7
8
1
2
GND
BOOT
UGATE
PHASE
LGATE
6
6
DELAY
5
VCC
43
LGATE
Timing Diagram
PWM
UGATE
LGATE
t
FL
t
PDLL
t
PDHU
1V
GND
THERMAL PAD (FOR QFN PACKAGE ONLY)
FIGURE 1. BLOCK DIAGRAM
2.5V
t
PDLU
t
RU
t
FU
t
PTS
1V
t
RL
t
t
PDHL
TSSHD
t
FL
t
TSSHD
t
RU
t
FU
t
PTS
2
Page 3
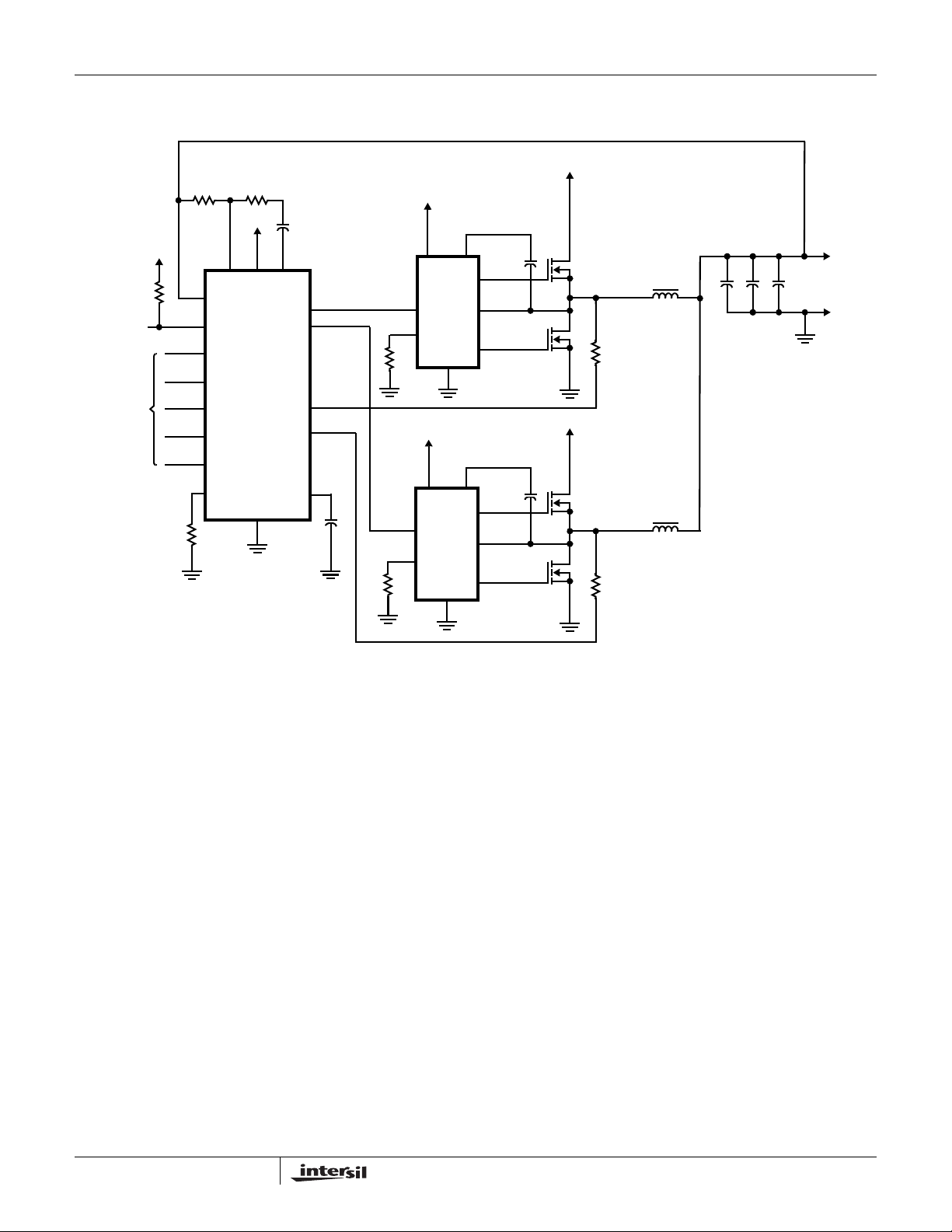
ISL6209
www.BDTIC.com/Intersil
Typical Application - Two Phase Converter Using ISL6209 Gate Drivers
V
BAT
+5V
PGOOD
VID
+5V
FB
VSEN
CONTROL
+5V
COMP
VCC
PWM1
PWM2
MAIN
ISEN1
ISEN2
PWM
DELAY
VCC
DRIVE
ISL6209
+5V
BOOT
UGATE
PHASE
LGATE
V
BAT
+V
CORE
FS
DACOUT
GND
VCC
PWM
DELAY
DRIVE
ISL6209
BOOT
UGATE
PHASE
LGATE
FIGURE 2. TYPICAL APPLICATION
3
Page 4

ISL6209
www.BDTIC.com/Intersil
Absolute Maximum Ratings Thermal Information
Supply Voltage (VCC) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . -0.3V to 7V
Input Voltage (V
BOOT Voltage (V
BOOT To PHASE Voltage (V
PHASE Voltage (Note 1) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .GND - 0.3V to 30V
UGATE Voltage . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . V
LGATE Voltage . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . GND - 0.3V (DC) to VCC + 0.3V
Ambient Temperature Range. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .-40°C to +125°C
, V
DELAY
BOOT-GND
V
PHASE
GND - 2.5V (<20ns Pulse Width, 5μJ) to VCC + 0.3V
) . . . . . . . . . . . . -0.3V to VCC + 0.3V
PWM
). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . -0.3V to 33V
BOOT-PHASE
GND - 8V (<20ns Pulse Width, 10μJ)
- 5V (<20ns Pulse Width, 10μJ) to V
). . . . . . -0.3V to 7V (DC)
-0.3V to 9V (<10ns)
- 0.3V (DC) to V
PHASE
BOOT
BOOT
Thermal Resistance (Typical) θ
SOIC Package (Note 2) . . . . . . . . . . . . 110 N/A
QFN Package (Notes 3, 4). . . . . . . . . . 80 15
Maximum Junction Temperature (Plastic Package) . . . . . . .+150°C
Maximum Storage Temperature Range. . . . . . . . . .-65°C to +150°C
Maximum Lead Temperature (Soldering 10s) . . . . . . . . . . . .+300°C
(SOIC - Lead Tips Only)
Recommended Operating Conditions
Ambient Temperature Range. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .-10°C to +100°C
Maximum Operating Junction Temperature. . . . . . . . . . . . . +125°C
Supply Voltage, V
CAUTION: Stresses above those listed in “Absolute Maximum Ratings” may cause permanent damage to the device. This is a stress only rating and operation of the
device at these or any other conditions above those indicated in the operational sections of this specification is not implied.
NOTES:
1. The Phase Voltage is capable of withstanding -7V when the BOOT pin is at GND.
is measured with the component mounted on a high effective thermal conductivity test board in free air. See Tech Brief TB379 for details.
2. θ
JA
3. θ
is measured in free air with the component mounted on a high effective thermal conductivity test board with “direct attach” features. See
JA
Tech Brief TB379.
4. For θ
, the “case temp” location is the center of the exposed metal pad on the package underside.
JC
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5V ±10%
CC
Electrical Specifications Recommended Operating Conditions, Unless Otherwise Noted.
PARAMETER SYMBOL TEST CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNITS
VCC SUPPLY CURRENT
Bias Supply Current I
POR Rising -3.44.2V
POR Falling 2.2 2.9 - V
Hysteresis - 500 - mV
BOOTSTRAP DIODE
Forward Voltage V
PWM INPUT
Input Current I
PWM Three-State Rising Threshold V
PWM Three-State Falling Threshold V
Three-State Shutdown Hold-off Time V
SWITCHING TIME
UGATE Rise Time (Note 5) t
LGATE Rise Time (Note 5) t
UGATE Fall Time (Note 5) t
LGATE Fall Time (Note 5) t
UGATE Turn-Off Propagation Delay t
LGATE Turn-Off Propagation Delay t
UGATE Turn-On Propagation Delay t
VCC
PWM
RUGATEVVCC
RLGATE
FUGATEVVCC
FLGATE
PDLUGATEVVCC
PDLLGATEVVCC
PDHUGATEVVCC
PWM pin floating, V
V
F
V
V
V
V
DELAY = VCC
= 5V, forward bias current = 2mA 0.40 0.52 0.60 V
VCC
= 5V - 250 - μA
PWM
= 0V - -250 - μA
PWM
= 5V - - 1.8 V
VCC
= 5V 3.1 - - V
VCC
= 5V, temperature = +25°C - 150 - ns
VCC
= 5V, 3nF Load - 8 - ns
= 5V, 3nF Load - 8 - ns
VCC
= 5V, 3nF Load - 8 - ns
= 5V, 3nF Load - 4 - ns
VCC
= 5V, No Output Load, DELAY = VCC - 13 - ns
= 5V, No Output Load, DELAY = VCC - 13 - ns
= 5V, Outputs Unloaded,
= 5V - 85 - μA
VCC
10 20 30 ns
(°C/W) θJC (°C/W)
JA
4
Page 5

ISL6209
www.BDTIC.com/Intersil
Electrical Specifications Recommended Operating Conditions, Unless Otherwise Noted. (Continued)
PARAMETER SYMBOL TEST CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNITS
LGATE Turn-On Propagation Delay t
OUTPUT
Upper Drive Source Resistance R
Upper Driver Source Current (Note 5) I
Upper Drive Sink Resistance R
Upper Driver Sink Current (Note 5) I
Lower Drive Source Resistance R
Lower Driver Source Current (Note 5) I
Lower Drive Sink Resistance R
Lower Driver Sink Current (Note 5) I
NOTE:
5. Guaranteed by characterization, not 100% tested in production.
PDHLGATEVVCC
UGATE
UGATE
UGATE
UGATE
LGATE
LGATE
LGATE
LGATE
= 5V, Outputs Unloaded,
DELAY = VCC
500mA Source Current - 1.0 2.5 Ω
V
UGATE-PHASE
500mA Sink Current - 1.0 2.5 Ω
V
UGATE-PHASE
500mA Source Current - 1.0 2.5 Ω
V
LGATE
500mA Sink Current - 0.4 1.0 Ω
V
LGATE
= 2.5V - 2.0 - A
= 2.5V - 2.0 - A
= 2.5V - 2.0 - A
= 2.5V - 4.0 - A
10 20 30 ns
Functional Pin Description
UGATE (Pin 1 for SOIC-8, Pin 8 for QFN)
The UGATE pin is the upper gate drive output. Connect to
the gate of high-side power N-Channel MOSFET.
BOOT (Pin 2 for SOIC-8, Pin 1 for QFN)
BOOT is the floating bootstrap supply pin for the upper gate
drive. Connect the bootstrap capacitor between this pin and
the PHASE pin. The bootstrap capacitor provides the charge
to turn on the upper MOSFET. See the Bootstrap Diode and
Capacitor section under DESCRIPTION for guidance in
choosing the appropriate capacitor value.
PWM (Pin 3 for SOIC-8, Pin 2 for QFN)
The PWM signal is the control input for the driver. The PWM
signal can enter three distinct states during operation, see the
three-state PWM Input section under DESCRIPTION for further
details. Connect this pin to the PWM output of the controller. In
addition, place a 500kΩ resistor to ground from this pin. This
allows for proper three-state operation under all start-up
conditions.
GND (Pin 4 for SOIC-8, Pin 3 for QFN)
GND is the ground pin. All signals are referenced to this
node.
LGATE (Pin 5 for SOIC-8, Pin 4 for QFN)
LGA TE is the lower gate drive output. Connect to gate of the
low-side power N-Channel MOSFET.
VCC (Pin 6 for SOIC-8, Pin 5 for QFN)
Connect the VCC pin to a +5V bias supply. Place a high
quality bypass capacitor from this pin to GND.
DELAY (Pin 7 for SOIC-8, Pin 6 for QFN)
The DELAY pin sets the dead-time between gate switching
for the ISL6209. Connect a resistor to GND from this pin to
adjust the dead-time, refer to Figure 4. Tie this pin to VCC to
disable the delay circuitry. See Shoot-Through Protection
section for more detail.
PHASE (Pin 8 for SOIC-8, Pin 7 for QFN)
Connect the PHASE pin to the source of the upper MOSFET
and the drain of the lower MOSFET. This pin provides a
return path for the upper gate driver.
Description
Operation
Designed for speed, the ISL6209 dual MOSFET driver controls
both high-side and low-side N-Channel FETs from one
externally provided PWM signal.
A rising edge on PWM initiates the turn-off of the lower
MOSFET (see Timing Diagram). After a short propagation
delay [t
PDLLGATE
times [t
FLGATE
section. Adaptive shoot-through circuitry monitors the
LGATE voltage and determines the upper gate delay time
[t
PDHUGATE
drops below 1V. This prevents both the lower and upper
MOSFETs from conducting simultaneously, or shootthrough. Once this delay period is completed, the upper gate
drive begins to rise [t
turns on.
A falling transition on PWM indicates the turn-off of the upper
MOSFET and the turn-on of the lower MOSFET. A short
propagation delay [t
upper gate begins to fall [t
], the lower gate begins to fall. Typical fall
] are provided in the Electrical Specifications
], based on how quickly the LGATE voltage
RUGATE
PDLUGATE
], and the upper MOSFET
] is encountered before the
FUGA T E
]. Again, the adaptive
5
Page 6

ISL6209
www.BDTIC.com/Intersil
shoot-through circuitry determines the lower gate delay time
t
PDHLGATE
. The upper MOSFET gate-to-source voltage is
monitored, and the lower gate is allowed to rise, after the
upper MOSFET gate-to-source volt ag e drop s b elow 1V. T he
lower gate then rises [t
RLGA T E
], turning on the lower
MOSFET.
This driver is optimized for converters with large step down
ratio, such as those used in a mobile-computer core voltage
regulator. The lower MOSFET is usually sized much larger.
This driver is optimized for converters with large step down
compared to the upper MOSFET because the lower
MOSFET conducts for a much longer time in a switching
period. The lower gate driver is therefore sized much larger
to meet this application requirement. The 0.4Ω on-resistance
and 4A sink current capability enable the lower gate driver to
absorb the current injected to the lower gate through the
drain-to-gate capacitor of the lower MOSFET and prevent a
shoot through caused by the high dv/dt of the phase node.
Three-State PWM Input
A unique feature of the ISL6209 and other Intersil drivers is
the addition of a shutdown window to the PWM input. If the
PWM signal enters and remains within the shutdown window
for a set holdoff time, the output drivers are disabled and
both MOSFET gates are pulled and held low. The shutdown
state is removed when the PWM signal moves outside the
shutdown window. Otherwise, the PWM rising and falling
thresholds outlined in the ELECTRICAL SPECIFICATIONS
determine when the lower and upper gates are enabled.
During start-up, PWM should be in the three-state position
(1/2 V
) until actively driven by the controller IC.
CC
Shoot-Through Protection
The ISL6209 driver delivers shoot-through protection by
incorporating gate threshold monitoring and programmable
dead-time to prevent upper and lower MOSFETs from
conducting simultaneously, thereby shorting the input supply
to ground. Gate threshold monitoring ensures that one gate
is OFF before the other is allowed to turn ON.
During turn-off of the lower MOSFET, the LGATE voltage is
monitored until it reaches a 1V threshold, at which time the
UGATE is released to rise. Internal circuitry monitors the
upper MOSFET gate-to-source voltage during UGATE
turn-off. Once the upper MOSFET gate-to-source voltage
has dropped below a threshold of 1V, the LGA TE is allow ed
to rise.
In addition to gate threshold monitoring, a programmable
delay between MOSFET switching can be accomplished by
placing a resistor from the DELAY pin to ground. This delay
allows for maximum design flexibility over MOSFET
selection. The delay can be programmed from 5ns to 50ns. If
not desired, the DELAY pin must be tied to VCC to disable
the delay circuitry. Gate threshold monitoring is not affected
by the addition or removal of the additional dead-time. Refer
to Figure 3 and Figure 4 for more detail.
FCCM = VCC or GND
GATE A
1V
FCCM = RESISTOR to VCC or GND
GATE A
Adaptive Protection with Delay
t
= 5n - 50ns
delay
1V
FIGURE 3. PROGRAMMABLE DEAD-TIME
4
50
45
40
35
30
25
DEAD-TIME (ns)
20
15
10
5
0
050 200100 150 250 300
R
DELAY
FIGURE 4. ADDITIONAL PROGRAMMED DEAD-TIME
) vs DELAY RESISTOR VALUE
(t
DELAY
GATE B
Adaptive Shoot-Through Protection
GATE B
t
DELAY
(kΩ)
6
Page 7

ISL6209
www.BDTIC.com/Intersil
The equation governing the dead-time seen in Figure 4 is
expressed as:
T
DELAY
160( 10
The equation can be rewritten to solve for R
15–
) R
××[]6ns+=
DELAY
as
DELAY
follows:
R
DELAY
T
DELAY
--------------------------------------------
=
160 10
6ns–()
15–
×
Internal Bootstrap Diode
This driver features an internal bootstrap Schottky diode.
Simply adding an external capacitor across the BOOT and
PHASE pins completes the bootstrap circuit.
The bootstrap capacitor must have a maximum voltage
rating above the maximum battery voltage plus 5V. The
bootstrap capacitor can be chosen from the following
equation:
Q
GATE
------------------------
≥
C
BOOT
ΔV
BOOT
is the amount of gate charge required to fully
GATE
BOOT
term is
where Q
charge the gate of the upper MOSFET. The ΔV
defined as the allowable droop in the rail of the upper drive.
As an example, suppose an upper MOSFET has a gate
charge, Q
, of 25nC at 5V and also assume the droop in
GATE
the drive voltage over a PWM cycle is 200mV. One will find
that a bootstrap capacitance of at least 0.125μF is required.
The next larger standard value capacitance is 0.22μF. A
good quality ceramic capacitor is recommended.
2.0
1.8
1.6
1.4
(µF)
1.2
1.0
0.8
BOOT_CAP
C
0.6
0.4
0.2
20nC
0.0
FIGURE 5. BOOTSTRAP CAPACIT ANCE vs BOOT RIPPLE
Q
GATE
50n
C
VOLTAGE
= 100nC
0.30.0 0.1 0.2 0.4 0.5 0.6 0.90.7 0.8 1.0
ΔV
BOOT_CAP
(V)
Power Dissipation
Package power dissipation is mainly a function of the
switching frequency and total gate charge of the selected
MOSFETs. Calculating the power dissipation in the driver for
a desired application is critical to ensuring safe operation.
Exceeding the maximum allowable power dissipation level
will push the IC beyond the maximum recommended
operating junction temperature of 125°C. The maximum
allowable IC power dissipation for the SO-8 package is
approximately 800mW. When designing the driver into an
application, it is recommended that the following calculation
be performed to ensure safe operation at the desired
frequency for the selected MOSFETs. The power dissipated
by the driver is approximated as:
Pfsw1.5VUQUVLQ
where f
sw
and V
represent the upper and lower gate rail voltage. QU
L
and Q
is the upper and lower gate charge determined by
L
+()I
L
V
+=
VCC
CC
is the switching frequency of the PWM signal. VU
MOSFET selection and any external capacitance added to
the gate pins. The I
VCC VCC
product is the quiescent power
of the driver and is typically negligible.
1000
900
QU =100nC
800
= 200nC
Q
L
700
600
500
400
POWER (mW)
300
200
100
0
0 200 400 600 800 1000 1200 16001400 1800 2000
FIGURE 6. POWER DISSIPATION vs FREQUENCY
QU =50nC
QL = 100nC
FREQUENCY (kHz)
QU = 50nC
= 50nC
Q
L
QU = 20nC
= 50nC
Q
L
Layout Considerations
Reducing Phase Ring
The parasitic inductances of the PCB and power devices
(both upper and lower FETs) could cause increased PHASE
ringing, which may lead to voltages that exceed the absolute
maximum rating of the devices. When PHASE rings below
ground, the negative voltage could add charge to the
bootstrap capacitor through the internal bootstrap diode.
Under worst-case conditions, the added charge could
overstress the BOOT and/or PHASE pins. To prevent this
from happening, the user should perform a careful layout
inspection to reduce trace inductances, and select low lead
inductance MOSFETs and drivers. D
packaged MOSFETs have high parasitic lead inductances,
as opposed to SOIC-8. If higher inductance MOSFETs must
be used, a Schottky diode is recommended across the lower
MOSFET to clamp negative PHASE ring.
2
PAK and DPAK
7
Page 8

ISL6209
www.BDTIC.com/Intersil
A good layout would help reduce the ringing on the phase
and gatenodes significantly:
1. Avoid using vias for decoupling components where
possible, especially in the BOOT-to-PHASE p ath. Little or
no use of vias for VCC and GND is also recommended.
Decoupling loops should be short.
2. All power traces (UGATE, PHASE, LGATE, GND, VCC)
should be short and wide, and avoid using vias. If vias
must be used, two or more vias per layer transition is
recommended.
3. Keep the SOURCE of the upper FET as close as
thermally possible to the DRAIN of the lower FET.
4. Keep the connection in between the SOURCE of lower
FET and power ground wide and short.
5. Input capacitors should be placed as close to the DRAIN
of the upper FET and the SOURCE of the lower FET as
thermally possible.
NOTE: Refer to Intersil Tech Brief TB447 for more information.
Thermal Management
For maximum thermal performance in high current, high
switching frequency applications, connecting the thermal
pad of the QFN part to the power ground with multiple vias,
or placing a low noise copper plane underneath the SOIC
part is recommended. This heat spreading allows the part to
achieve its full thermal potential.
Suppressing MOSFET Gate Leakage
With VCC at ground potential, UGATE and LGATE are high
impedance. In this state, any stray leakage has the potential
to deliver charge to either gate. If UGATE receives sufficient
charge to bias the device on (Note: Internal circuitry prevents
leakage currents from charging above 1.8V), a low
impedance path will be connected between the MOSFET
drain and PHASE. If the input power supply is present and
active, the system could see potentially damaging currents.
Worst-case leakage currents are on the order of pico-amps;
therefore, a 10kΩ resistor, connected from UGATE to
PHASE, is more than sufficient to bleed off any stray leakage
current. This resistor will not affect the normal performance
of the driver or reduce its efficiency.
8
Page 9

Package Outline Drawing
www.BDTIC.com/Intersil
L8.3x3
8 LEAD QUAD FLAT NO-LEAD PLASTIC PACKAGE
Rev 2, 3/07
3.00
6
PIN 1
INDEX AREA
ISL6209
4X
A
B
7
0.65
8
6
PIN #1 INDEX AREA
(4X) 0.15
( 2. 60 TYP )
( 1. 10 )
TOP VIEW
3.00
( 4X 0 . 65 )
( 8X 0 . 28 )
0 . 90 ± 0.1
6
5
BOTTOM VIEW
BOTTOM VIEW
C
4
8X 0.60 ± 0.15
SIDE VIEW
0 . 2 REF
3
4
5
1
2
C
M
0.10 BA
8X 0.28 ± 0.05
SEE DETAIL "X"
BASE PLANE
1 .10 ± 0 . 15
C
0.10
SEATING PLANE
C
0.08
C
TYPICAL RECOMMENDED LAND PATTERN
9
( 8X 0 . 80)
0 . 00 MIN.
0 . 05 MAX.
DETAIL "X"
NOTES:
Dimensions are in millimeters.1.
Dimensions in ( ) for Reference Only.
Dimensioning and tolerancing conform to AMSE Y14.5m-1994.
2.
3.
Unless otherwise specified, tolerance : Decimal ± 0.05
Dimension b applies to the metallized terminal and is measured
4.
between 0.15mm and 0.30mm from the terminal tip.
Tiebar shown (if present) is a non-functional feature.
5.
The configuration of the pin #1 identifier is optional, but must be
6.
located within the zone indicated. The pin #1 indentifier may be
either a mold or mark feature.
Page 10

Small Outline Plastic Packages (SOIC)
www.BDTIC.com/Intersil
ISL6209
N
INDEX
AREA
123
-A-
E
-B-
SEATING PLANE
D
A
-C-
0.25(0.010) BM M
H
L
h x 45°
α
e
B
0.25(0.010) C AM BS
NOTES:
1. Symbols are defined in the “MO Series Symbol List” in Section 2.2 of
Publication Number 95.
2. Dimensioning and tolerancing per ANSI Y14.5M-1982.
3. Dimension “D” does not include mold flash, protrusions or gate burrs.
Mold flash, protrusion and gate burrs shall not exceed 0.15mm (0.006
inch) per side.
4. Dimension “E” does not include interlead flash or protrusions. Interlead flash and protrusions shall not exceed 0.25mm (0.010 inch) per
side.
5. The chamfer on the body is optional. If it is not present, a visual index
feature must be located within the crosshatched area.
6. “L” is the length of terminal for soldering to a substrate.
7. “N” is the number of terminal positions.
8. Terminal numbers are shown for reference only.
9. The lead width “B”, as measured 0.36mm (0.014 inch) or greater
above the seating plane, shall not exceed a maximum value of
0.61mm (0.024 inch).
10. Controlling dimension: MILLIMETER. Converted inch dimensions
are not necessarily exact.
M
A1
C
0.10(0.004)
M8.15 (JEDEC MS-012-AA ISSUE C)
8 LEAD NARROW BODY SMALL OUTLINE PLASTIC PACKAGE
INCHES MILLIMETERS
SYMBOL
A 0.0532 0.0688 1.35 1.75 -
A1 0.0040 0.0098 0.10 0.25 -
B 0.013 0.020 0.33 0.51 9
C 0.0075 0.0098 0.19 0.25 -
D 0.1890 0.1968 4.80 5.00 3
E 0.1497 0.1574 3.80 4.00 4
e 0.050 BSC 1.27 BSC -
H 0.2284 0.2440 5.80 6.20 -
h 0.0099 0.0196 0.25 0.50 5
L 0.016 0.050 0.40 1.27 6
N8 87
α
0° 8° 0° 8° -
NOTESMIN MAX MIN MAX
Rev. 1 6/05
All Intersil U.S. products are manufactured, assembled and tested utilizing ISO9000 quality systems.
Intersil Corporation’s quality certifications can be viewed at www.intersil.com/design/quality
Intersil products are sold by description only. Intersil Corporation reserves the right to make changes in circuit design, software and/or specifications at any time without
notice. Accordingly, the reader is cautioned to verify that data sheets are current before placing orders. Information furnished by Intersil is believed to be accurate and
reliable. However, no responsibility is assumed by Intersil or its subsidiaries for its use; nor for any infringements of patents or other rights of third parties which may result
from its use. No license is granted by implic atio n or other wise u nde r any p a tent or patent rights of Intersil or its subsidi ari es.
For information regarding Intersil Corporation and its products, see www.intersil.com
10
 Loading...
Loading...