Page 1

®
ISL28286, ISL28486
Data Sheet September 22, 2006
Dual Micropower Single Supply
Rail-to-Rail Input and Output (RRIO)
Precision Op-Amp
The ISL28286 and ISL28486 are Dual and Quad channel
micropower precision operational amplifiers optimized for
single supply operation at 5V down to 2.4V. For equivalent
performance in a single channel op-amp reference EL8186.
The ISL28286 and ISL28486 feature an Input Range
Enhancement Circuit (IREC) which enables both parts to
maintain CMRR performance for input voltages equal to the
positive and negative supply rails. The input signal is
capable of swinging 10% above the positive supply rail and
to ground with only a slight degradation of the CMRR
performance. The output operation is rail to rail.
Both parts draw minimal supply current while meeting
excellent DC-accuracy, AC-performance, noise and output
drive specifications.
The ISL28286 and ISL28486 can be operated from a single
lithium cell or two Ni-Cd batteries. The input range includes
both positive and negative rail.
Ordering Information
PART
PART NUMBER
ISL28286FUZ
(See Note)
ISL28286FUZ-T7
(See Note)
Coming Soon
ISL28486FAZ
(Note)
Coming Soon
ISL28486FAZ-T7
(Note)
NOTE: Intersil Pb-free plus anneal products employ special Pb-free
material sets; molding compounds/die attach materials and 100% matte
tin plate termination finish, which are RoHS compliant and compatible
with both SnPb and Pb-free soldering operations. Intersil Pb-free
products are MSL classified at Pb-free peak reflow temperatures that
meet or exceed the Pb-free requirements of IPC/JEDEC J STD-020.
MARKING
8286Z 50/Tube 10 Ld MSOP
8286Z 7”
28486FAZ 97/Tube 16 Ld QSOP
28486FAZ 7”
TAPE &
REEL PACKAGE
(Pb-free)
10 Ld MSOP
(1500 pcs)
(1000 pcs)
(Pb-free)
(Pb-free)
16 Ld QSOP
(Pb-free)
PKG.
DWG. #
MDPOO43
MDP0043
MDP0040
MDP0040
FN6312.0
Features
• 120µA typ supply current for both channels
• 600µV max offset voltage
• 500pA typ input bias current
• 400kHz gain-bandwidth product
• 115dB PSRR and CMRR
• Single supply operation down to 2.4V
• Input is capable of swinging above V+ and to V- (ground
sensing)
• Rail-to-rail input and output (RRIO)
• Pb-free plus anneal available (RoHS compliant)
Applications
• Battery- or solar-powered systems
• 4mA to 25mA current loops
• Handheld consumer products
• Medical devices
• Thermocouple amplifiers
• Photodiode pre-amps
• pH probe amplifiers
1
CAUTION: These devices are sensitive to electrostatic discharge; follow proper IC Handling Procedures.
1-888-INTERSIL or 1-888-468-3774
| Intersil (and design) is a registered trademark of Intersil Americas Inc.
All other trademarks mentioned are the property of their respective owners.
Copyright Intersil Americas Inc. 2006. All Rights Reserved
Page 2
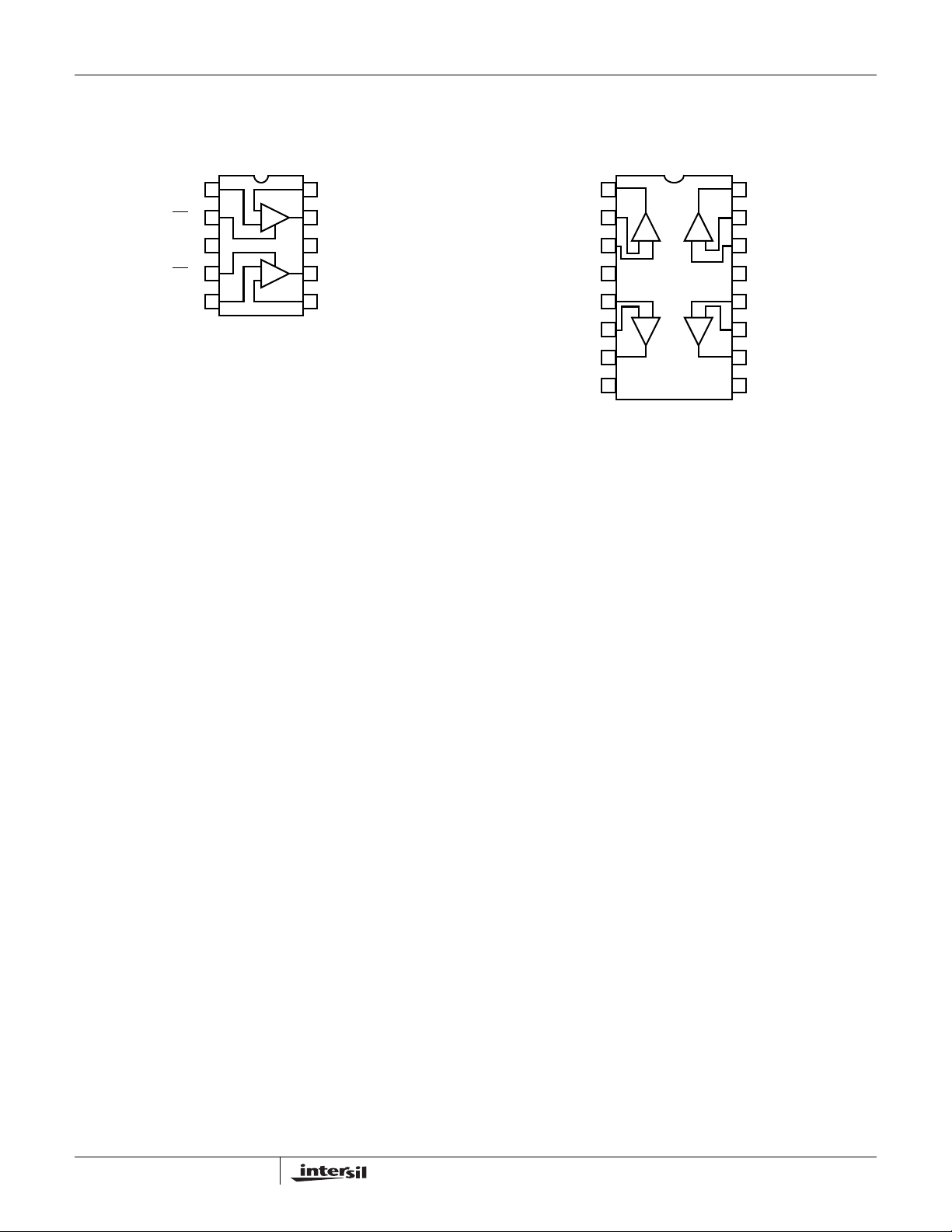
Pinouts
ISL28286
(10 LD MSOP)
TOP VIEW
IN+_A
1
EN
_A
2
V-
3
EN
_B
4
IN+_B IN-_B
5 6
10
IN-_A
-
9
8
7
OUT_A
V+
OUT_B
+
+
-
ISL28286, ISL28486
ISL28486
(16 LD QSOP)
TOP VIEW
OUT_A
1
IN-_A
2
IN+_A
3
V+
4
IN+_B IN+_C
5
IN-_B
-
6
+
-
+
-
+
+
OUT_D
16
IN-_D
15
IN+_D
14
V-
13
12
IN-_C
11
OUT_B
7
NC NC
8 9
10
OUT_C
2
FN6312.0
September 22, 2006
Page 3
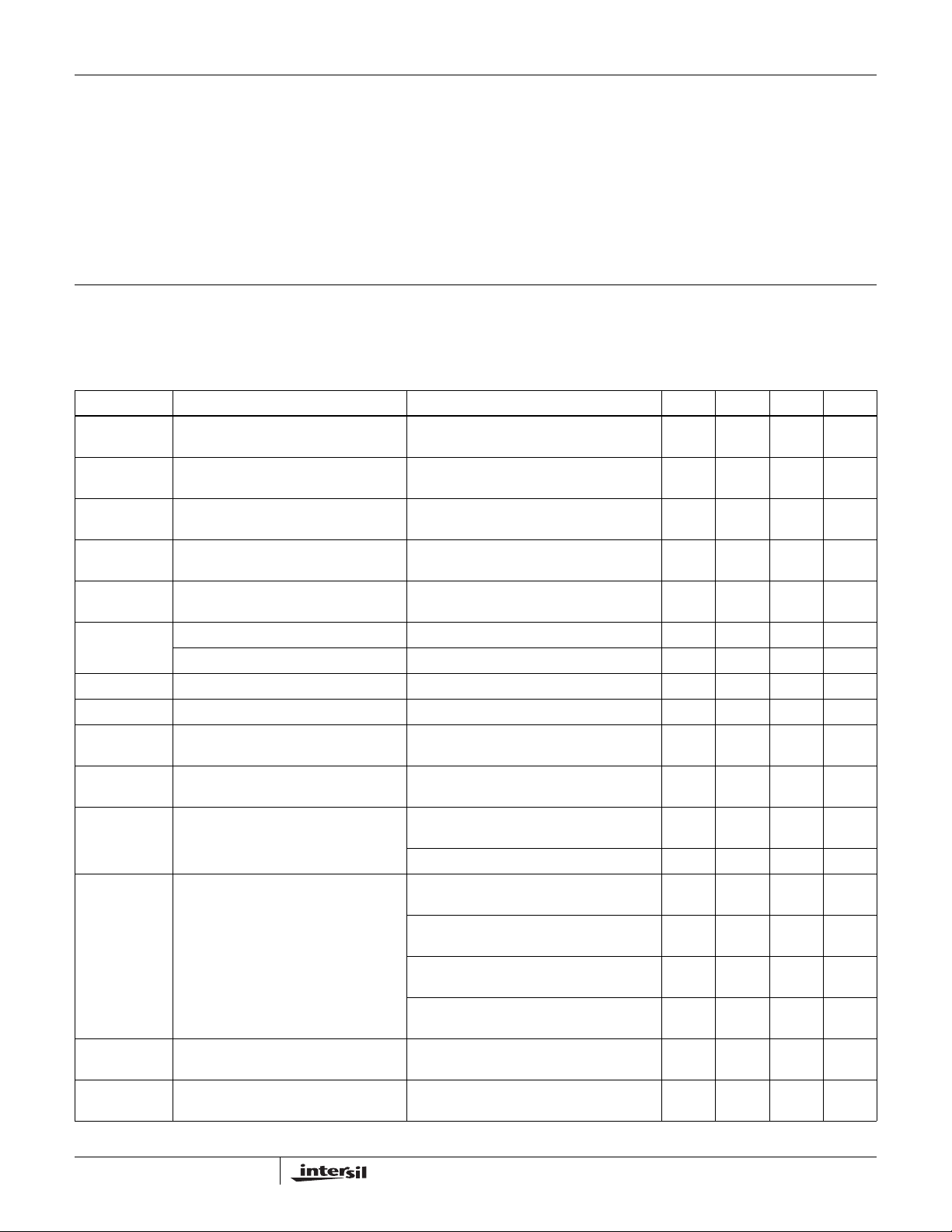
ISL28286, ISL28486
Absolute Maximum Ratings (T
Supply Voltage. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5.5V
Supply Turn On Voltage Slew Rate . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1V/μs
Differential Input Current . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5mA
Differential Input Voltage . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 0.5V
= +25°C)
A
Output Short-Circuit Duration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .Indefinite
Ambient Operating Temperature Range . . . . . . . . .-40°C to +125°C
Storage Temperature Range . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .-65°C to +150°C
Operating Junction Temperature . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . +125°C
Input Voltage . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . V- - 0.5V to V+ + 0.5V
ESD tolerance, Human Body Model . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3kV
ESD tolerance, Machine Model . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .300V
CAUTION: Stresses above those listed in “Absolute Maximum Ratings” may cause permanent damage to the device. This is a stress only rating and operation of the
device at these or any other conditions above those indicated in the operational sections of this specification is not implied.
IMPORTANT NOTE: All parameters having Min/Max specifications are guaranteed. Typical values are for information purposes only. Unless otherwise noted, all tests
are at the specified temperature and are pulsed tests, therefore: TJ = TC = T
Operating Junction
Electrical Specifications V
= 5V, V- = 0V,VCM = 2.5V, TA = +25°C unless otherwise specified.
+
Boldface limits apply over the operating temperature range, -40°C to +125°C, temperature data
A
guaranteed by characterization
PARAMETER DESCRIPTION CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNIT
V
OS
ΔV
OS
------------------
ΔTi me
ΔV
OS
--------------- -
ΔT
I
OS
I
B
e
N
Input Offset Voltage -600
-650
±20 600
650
µV
Long Term Input Offset Voltage Stability 1.2 µV/Mo
Input Offset Drift vs Temperature 0.3 µV/°C
Input Offset Current -1.5
-1.5
Input Bias Current -2
-2.5
Input Noise Voltage Peak-to-Peak f = 0.1Hz to 10Hz 4.5 µV
±0.25 2.5
2.5
±0.5 2
2.5
nA
nA
PP
Input Noise Voltage Density fO = 1kHz 48 nV/√Hz
i
N
Input Noise Current Density fO = 1kHz 0.18 pA/√Hz
CMIR Input Voltage Range Guaranteed by CMRR test 05V
CMRR Common-Mode Rejection Ratio V
= 0V to 5V 90
CM
115 dB
80
PSRR Power Supply Rejection Ratio V
A
V
VOL
OUT
Large Signal Voltage Gain VO = 0.5V to 4.5V, RL = 100kΩ 275
Maximum Output Voltage Swing Output low, RL = 100kΩ 3630mV
= 2.4V to 5V 90
+
80
275
V
= 0.5V to 4.5V, RL = 1kΩ 25 V/mV
O
115 dB
500 V/mV
Output low, R
Output high, R
Output high, R
= 1kΩ 130 175
L
= 100kΩ 4.990
L
= 1kΩ 4.800
L
4.97
4.750
SR+ Positive Slew Rate 0.13
0.10
SR- Negative Slew Rate 0.10
0.09
3
mV
225
4.996 V
4.880 V
0.17 0.20
V/µs
0.25
0.13 0.17
V/µs
0.19
FN6312.0
September 22, 2006
Page 4
ISL28286, ISL28486
Electrical Specifications V
= 5V, V- = 0V,VCM = 2.5V, TA = +25°C unless otherwise specified.
+
Boldface limits apply over the operating temperature range, -40°C to +125°C, temperature data
guaranteed by characterization (Continued)
PARAMETER DESCRIPTION CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNIT
GBW Gain Bandwidth Product 400 kHz
I
S,ON
Supply Current, Enabled All channels enabled. 120 156
175
I
S,OFF
+ Short Circuit Sourcing Capability RL = 10Ω 29
I
SC
I
- Short Circuit Sinking Capability RL = 10Ω 24
SC
Supply Current, Disabled All channels disabled. 4 7
9
31 mA
23
26 mA
19
V
V
V
I
ENH
I
ENL
S
INH
INL
Minimum Supply Voltage 2.4 V
Enable Pin High Level 2 V
Enable Pin Low Level 0.8 V
Enable Pin Input Current VEN = 5V 0.7 1.3
1.5
Enable Pin Input Current VEN = 0V -0.1 0 +0.1 µA
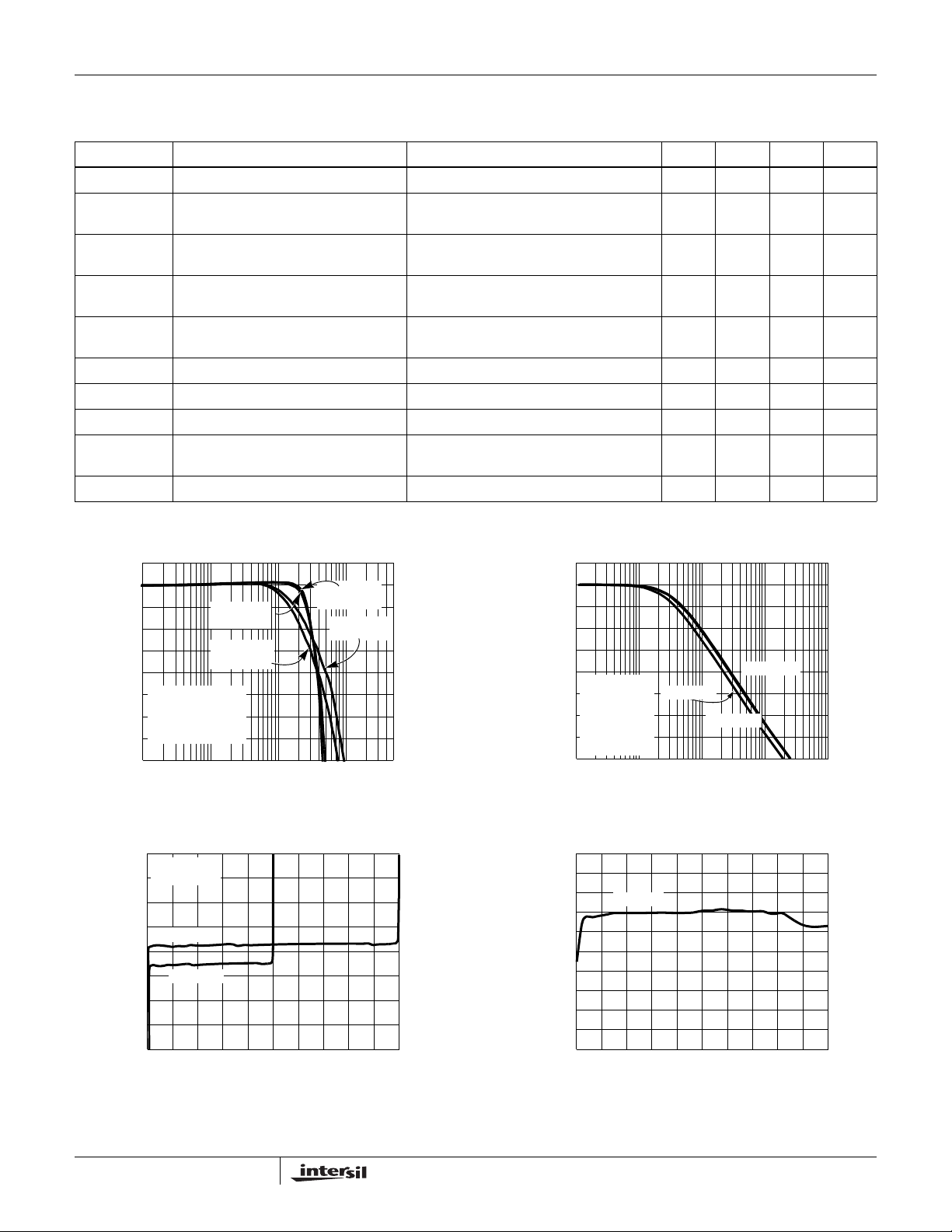
Typical Performance Curves
µA
µA
µA
+1
0
-1
-2
-3
-4
GAIN (dB)
-5
-6
-7
8
Vout = 50mVp-p
= 1
A
V
= 3pF
C
L
R
= 0/RG = INF
F
1k
10k 100k 1M
VS = ±2.5V
RL = 1k
VS = ±2.5V
RL = 10k
FREQUENCY (Hz)
VS = ±1.2V
RL = 1k
VS = ±1.2V
RL = 10k
5M
FIGURE 1. FREQUENCY RESPONSE vs SUPPLY VOLTAGE
200
V
= VDD/2
CM
A
= -1
150
V
100
50
V
= 5V
DD
0
V
-50
-100
-150
INPUT OFFSET VOLTAGE (µV)
-200
05
= 2.5V
DD
1324
OUTPUT VOLTAGE (V)
45
40
35
30
25
20
AV = 100
GAIN (dB)
15
= 10kΩ
R
L
C
= 2.7pF
L
10
R
F/RG
= 221kΩ
R
F
5
R
= 2.23kΩ
G
0
100 10k 100k 1M
VS = ±2.5V
= 99.02
1k
FREQUENCY (Hz)
VS = ±1.25V
VS = ±1.0V
FIGURE 2. FREQUENCY RESPONSE vs SUPPLY VOLTAGE
0
-20
-40
-60
-80
INPUT OFFSET VOLTAGE (µV)
-100
VOS, µV
05
1324
COMMON-MODE INPUT VOLTAGE (V)
FIGURE 3. INPUT OFFSET VOLTAGE vs OUTPUT VOLTAGE FIGURE 4. INPUT OFFSET VOLTAGE vs COMMON-MODE
INPUT VOLTAGE
4
FN6312.0
September 22, 2006
Page 5
ISL28286, ISL28486
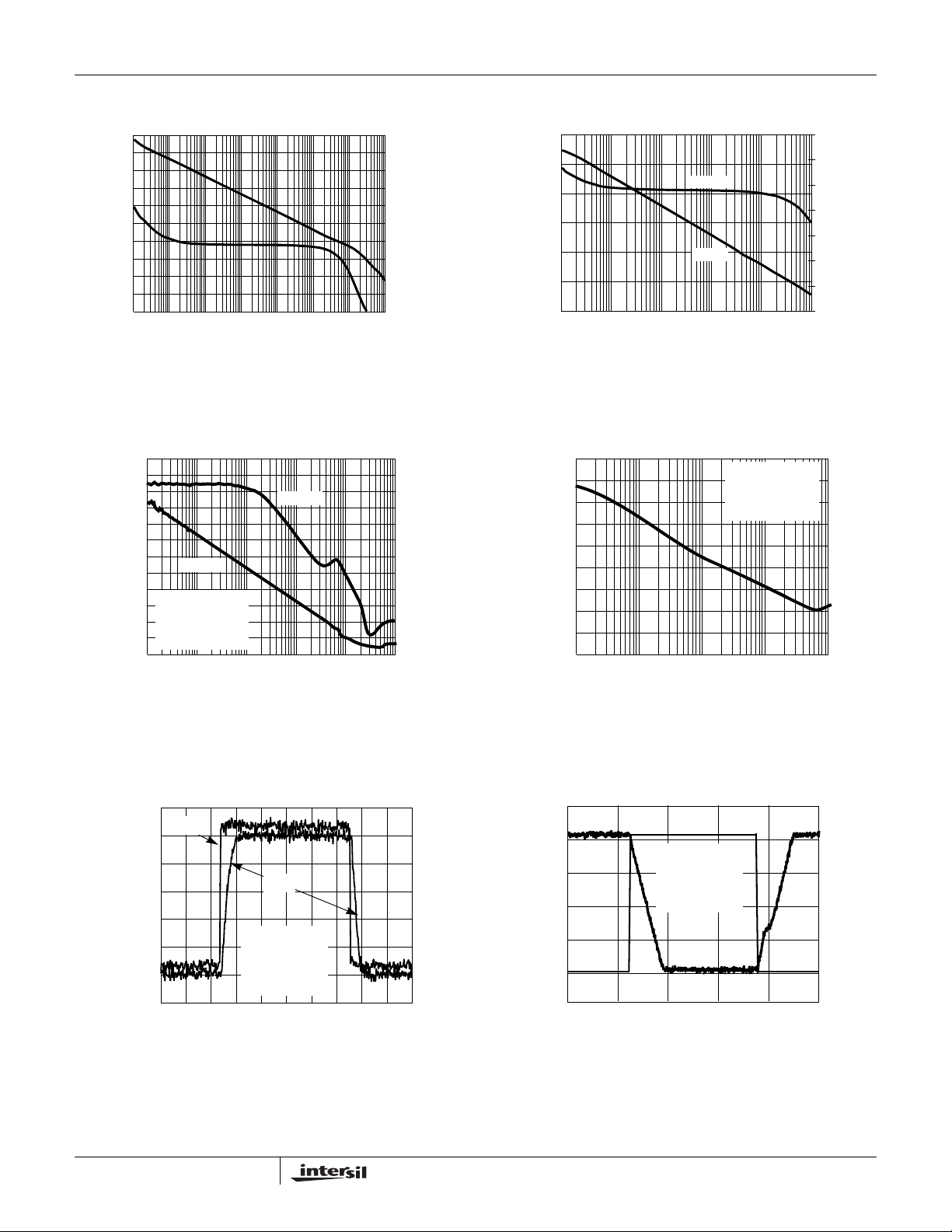
Typical Performance Curves (Continued)
120
80
40
0
GAIN (dB)
-40
-80
1 1k 100k 10M
10
FREQUENCY (Hz)
FIGURE 5. A
120
110
100
90
80
70
60
50
PSRR (dB)
40
VS = 5VDC
30
V
SOURCE
20
R
L
10
AV = +1
0
10 10k 1M
vs FREQUENCY @ 100kΩ LOAD
VOL
PSRR -
= 1Vp-p
= 100k
Ω
100 100k1k
10k 1M100
PSRR +
FREQUENCY (Hz)
FIGURE 7. PSRR vs FREQUENCY FIGURE 8. CMRR vs FREQUENCY
80
40
0
-40
-80
-120
PHASE (°)
100
80
60
40
GAIN (dB)
20
0
-20
10 10k 1M
FIGURE 6. A
100
CMRR(dB)
100
FREQUENCY (Hz)
VOL
90
80
70
60
50
40
30
20
10
10 1k 10k 100k
100
PHASE
GAIN
100k1k
vs FREQUENCY @ 1kΩ LOAD
VS = 5VDC
V
SOURCE
= 100k
R
L
AV = +1
FREQUENCY (Hz)
= 1Vp-p
Ω
200
150
100
50
0
-50
-100
-150
PHASE (°)
2.56
2.54
2.52
2.50
2.48
VOLTS (V)
2.46
2.44
2.42
V
IN
V
OUT
= 5VDC
V
S
V
= 0.1Vp-p
OUT
= 500Ω
R
L
= +1
A
V
0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 20
TIME (µs)
5.0
V
4.0
3.0
2.0
VOLTS (V)
1.0
0
0 100 200 300 400 500
= 5VDC
V
S
V
OUT
= 500Ω
R
L
= -2
A
V
V
TIME (µs)
IN
= 0.1Vp-p
OUT
V
V
OUT
IN
FIGURE 9. SMALL SIGNAL TRANSIENT RESPONSE FIGURE 10. LARGE SIGNAL TRANSIENT RESPONSE
5
FN6312.0
September 22, 2006
Page 6

ISL28286, ISL28486
Typical Performance Curves (Continued)
10.00
1.00
0.10
CURRENT NOISE (pA/√Hz)
0.01
1 10 100 1k 10k
FREQUENCY (Hz)
100k
1k
100
10
VOLTAGE NOISE (nV/√Hz)
1
1 10 100 10k 100k
1k
FREQUENCY (Hz)
FIGURE 11. CURRENT NOISE vs FREQUENCY FIGURE 12. VOLTAGE NOISE vs FREQUENCY
6
5
4
3
VOLTS (V)
2
V
IN
100K
100K
100K
VS +
VS +
100K
100K
100K
-
-
-
DUT
DUT
DUT
+
+
+
1K
1K
1K
VS -
VS -
Function
Function
Function
Generator
Generator
Generator
33140A
33140A
33140A
V+ = 5V
V
OUT
1
VOLTAGE NOISE (1µV/DIV)
4.5µV
P-P
0
0 50 100 150 200
TIME (1s/DIV)
TIME (ms)
FIGURE 13. 0.1Hz TO 10Hz INPUT VOLTAGE NOISE FIGURE 14. INPUT VOLTAGE SWING ABOVE THE V+ SUPPLY
155
135
115
95
75
SUPPL Y CURRENT (µA)
55
35
23.545.5
2.5 54.53
SUPPLY VOLTAGE (V)
EN
Input
1V/DIV0.1V/DIV
0
V
OUT
0
10µs/DIV
AV = -1
V
= 200mVp-p
IN
V+ = 5V
V- = 0V
FIGURE 15. SUPPLY CURRENT vs SUPPLY VOLTAGE FIGURE 16. ENABLE TO OUTPUT DELAY TIME
6
FN6312.0
September 22, 2006
Page 7

ISL28286, ISL28486
Typical Performance Curves (Continued)
150
n = 12
140
MAX
130
120
CURRENT (µA)
110
100
90
-40 -20 0 20 40 60 80 100 120
MEDIAN
MIN
TEMPERATURE (°C)
FIGURE 17. SUPPLY CURRENT vs TEMPERA TURE VS = ±2.5V
ENABLED. R
1.6
n = 12
1.4
1.2
1
0.8
0.6
0.4
0.2
CURRENT (nA)
0
-0.2
-0.4
-0.6
-40 -20 0 20 40 60 80 100 120
FIGURE 19. I BIAS(+) vs TEMPERATURE V
= INF
L
MAX
MEDIAN
MIN
TEMPERATURE (°C)
= ±2.5V FIGURE 20. I BIAS(+) vs TEMPERATURE VS = ±1.2V
S
4.8
n = 12
4.6
4.4
4.2
MEDIAN
4
CURRENT (µA)
3.8
3.6
3.4
3.2
-40-200 20406080100120
MAX
MIN
TEMPERATURE (°C)
FIGURE 18. SUPPLY CURRENT vs TEMPERA TURE V
DISABLED. R
1.6
n = 12
1.4
1.2
1
0.8
0.6
0.4
CURRENT (nA)
0.2
0
-0.2
-0.4
-40 -20 0 20 40 60 80 100 120
= INF
L
MAX
MEDIAN
MIN
TEMPERATURE (°C)
= ±2.5V
S
1.5
n = 12
1
0.5
0
-0.5
CURRENT (nA)
-1
-1.5
-2
MEDIAN
-40 -20 0 20 40 60 80 100 120
MAX
MIN MIN
TEMPERATURE (°C)
FIGURE 21. I BIAS(-) vs TEMPERATURE V
7
1.5
n = 12
1
0.5
0
-0.5
CURRENT (nA)
-1
-1.5
-40 -20 0 20 40 60 80 100 120
= ±2.5V FIGURE 22. I BIAS(-) vs TEMPERATURE VS = ±1.2V
S
MAX
MEDIAN
TEMPERATURE (°C)
September 22, 2006
FN6312.0
Page 8

ISL28286, ISL28486
Typical Performance Curves (Continued)
2.5
n = 12
2
1.5
1
0.5
0
CURRENT (nA)
-0.5
-1
-1.5
-40 -20 0 20 40 60 80 100 120
MAX
MEDIAN
MIN
TEMPERATURE (°C)
FIGURE 23. INPUT OFFSET CURRENT vs TEMPERATURE
V
= ±2.5V
S
300
200
n = 12
100
0
(µV)
-100
OS
V
-200
-300
-400
-500
-40-200 20406080100120
MAX
MEDIAN
MIN
TEMPERATURE (°C)
FIGURE 25. INPUT OFFSET VOLTAGE vs TEMPERATURE
V
= ±2.5V
S
2.5
n = 12
2
1.5
1
0.5
CURRENT (pA)
0
-0.5
-1
-40 -20 0 20 40 60 80 100 120
MEDIAN
MAX
MIN
TEMPERATURE (°C)
FIGURE 24. INPUT OFFSET CURRENT vs TEMPERATURE
VS = ±1.2V
400
n = 12
300
200
100
(µV)
0
OS
V
-100
-200
-300
-400
-40 -20 0 20 40 60 80 100 120
MAX
MEDIAN
MIN
TEMPERATURE (°C)
FIGURE 26. INPUT OFFSET VOLTAGE vs TEMPERATURE\
VS = ±1.2V
130
n = 12
125
120
115
110
CMRR (dB)
105
100
95
-40 -20 0 20 40 60 80 100 120
MAX
MEDIAN
MIN
TEMPERATURE (°C)
FIGURE 27. CMRR vs TEMPERATURE V
8
140
n = 12
130
120
110
PSRR (dB)
100
90
80
-40 -20 0 20 40 60 80 100 120
= +2.5V TO -2.5V FIGURE 28. PSRR vs TEMPERATURE VS = ±2.5V
CM
MAX
MEDIAN
MIN
TEMPERATURE (°C)
FN6312.0
September 22, 2006
Page 9

ISL28286, ISL28486
Typical Performance Curves (Continued)
4.91
n = 12
4.9
4.89
(V)
4.88
OUT
V
MEDIAN
4.87
4.86
4.85
4.84
-40 -20 0 20 40 60 80 100 120
FIGURE 29. POSITIVE V
V
= ±2.5V
S
4.9985
4.9975
(V)
OUT
V
4.9965
4.998
4.997
4.996
n = 12
MEDIAN
MIN
MAX
MIN
TEMPERATURE (°C)
vs TEMPERATURE RL = 1k
OUT
MAX
200
n = 12
180
160
MEDIAN
(mV)
140
OUT
V
120
100
80
-40 -20 0 20 40 60 80 100 120
FIGURE 30. NEGATIVE V
V
= ±2.5V
S
6
n = 12
5.5
MAX
5
4.5
(mV)
OUT
4
V
3.5
3
MAX
MIN
TEMPERATURE (°C)
vs TEMPERATURE RL = 1k
OUT
MEDIAN
MIN
4.9955
-40 -20 0 20 40 60 80 100 120
FIGURE 31. POSITIVE V
V
= ±2.5V
S
0.032
0.031
0.029
IIL (µA)
0.028
0.027
0.026
FIGURE 33. I
n = 12
0.03
MEDIAN
-40 -20 0 20 40 60 80 100 120
(EN) vs TEMPERATURE VS = ±2.5V FIGURE 34. IIH (EN) vs TEMPERATURE VS = ±2.5V
IL
TEMPERATURE (°C)
vs TEMPERATURE RL = 100k
OUT
MAX
MIN
TEMPERATURE (°C)
2.5
-40-200 20406080100120
FIGURE 32. NEGATIVE V
V
= ±2.5V
S
0.95
n = 12
0.9
0.85
0.8
IIH (µA)
0.75
0.65
MEDIAN
0.7
0.6
-40-200 20406080100120
TEMPERATURE (°C)
vs TEMPERATURE RL = 100k
OUT
MAX
MIN
TEMPERATURE (°C)
9
FN6312.0
September 22, 2006
Page 10

ISL28286, ISL28486
Typical Performance Curves (Continued)
0.23
n = 12
0.21
0.19
0.17
0.15
0.13
SLEW RATE (V/µs)
0.11
0.09
-40 -20 0 20 40 60 80 100 120
MAX
MEDIAN
MIN
TEMPERATURE (°C)
FIGURE 35. + SLEW RA TE vs TEMPERATURE VS = ±2.5V
INPUT = ±0.75V A
800
n = 12
700
600
500
MEDIAN
400
AVOL (V/mV)
300
200
MAX
MIN
V
= 2
0.17
n = 12
0.16
0.15
0.14
0.13
CURRENT (pA)
0.12
0.11
0.1
-40-200 20406080100120
MAX
MEDIAN
MIN
TEMPERATURE (°C)
FIGURE 36. - SLEW RATE vs TEMPERATURE V
INPUT = ±0.75V A
750
n = 12
600
MEDIAN
450
AVOL (V/mV)
300
MIN
MAX
V
= 2
= ±2.5V
S
100
-40 -20 0 20 40 60 80 100 120
TEMPERATURE (°C)
FIGURE 37. AVOL CH A vs TEMPERATURE RL = 100K
VO = ±2V V
JEDEC JESD51-7 HIGH EFFECTIVE THERMAL
CONDUCTIVITY TEST BOARD
1.4
1.2
893mW
1
0.8
0.6
0.4
POWER DISSIPATION (W)
0.2
0
0 255075100 150
= ±2.5V
S
Q
S
O
θ
P
J
A
1
=
6
1
1
2
°
C
/
W
AMBIENT TEMPERATURE (°C)
12585
FIGURE 39. PACKAGE POWER DISSIPA TION vs AMBIENT
TEMPERATURE
150
-40-200 20406080100120
TEMPERATURE (°C)
FIGURE 38. AVOL CH B vs TEMPERATURE RL = 100K
VO = ±2V VS = ±2.5V
JEDEC JESD51-3 LOW EFFECTIVE THERMAL
CONDUCTIVITY TEST BOARD
1.2
1
0.8
633mW
0.6
0.4
POWER DISSIPATION (W)
0.2
0
0 25 50 75 100 150
Q
S
O
θ
P
1
J
AMBIENT TEMPERATURE (°C)
6
A
=
1
5
8
°
C
/
W
12585
FIGURE 40. PACKAGE POWER DISSIPA TION vs AMBIENT
TEMPERATURE
10
FN6312.0
September 22, 2006
Page 11

ISL28286, ISL28486
Typical Performance Curves (Continued)
JEDEC JESD51-7 HIGH EFFECTIVE
THERMAL CONDUCTIVITY TEST BOARD
1
0.9
870mW
0.8
0.7
0.6
0.5
0.4
0.3
0.2
POWER DISSIPATION (W)
0.1
0
0 255075100125
AMBIENT TEMPERATURE (°C)
M
S
θ
O
J
P
A
8
=
/
1
1
1
0
5
°
C
/
W
85
FIGURE 41. PACKAGE POWER DISSIPA TION vs AMBIENT
TEMPERATURE
Pin Descriptions
ISL28286
(10 LD MSOP)
1 3 IN+_A Circuit 1 Amplifier A non-inverting input
2EN
3 13 V- Circuit 4 Negative power supply
4EN
5 5 IN+_B Circuit 1 Amplifier B non-inverting input
6 6 IN-_B Circuit 1 Amplifier B inverting input
7 7 OUT_B Circuit 3 Amplifier B output
8 4 V+ Circuit 4 Positive power supply
9 1 OUT_A Circuit 3 Amplifier A output
10 2 IN-_A Circuit 1 Amplifier A inverting input
ISL28486
(16 LD Q SOP) PIN NAME
EQUIVALENT
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
_A Circuit 2 Amplifier A enable pin internal pull-down; Logic “1” selects the disabled state;
Logic “0” selects the enabled state.
_B Circuit 2 Amplifier B enable pin with internal pull-down; Logic “1” selects the disabled state;
Logic “0” selects the enabled state.
10 OUT_C Circuit 3 Amplifier C output
11 IN-_C Circuit 1 Amplifier C inverting input
12 IN+_C Circuit 1 Amplifier C non-inverting input
14 IN+_D Circuit 1 Amplifier D non-inverting input
15 IN-_D Circuit 1 Amplifier D inverting input
16 OUT_D Circuit 3 Amplifier D output
8, 9 NC - No internal connection
JEDEC JESD51-3 LOW EFFECTIVE
THERMAL CONDUCTIVITY TEST BOARD
0.6
0.5
486mW
0.4
0.3
0.2
0.1
POWER DISSIPATION (W)
0
0 255075100125
AMBIENT TEMPERATURE (°C)
M
S
θ
O
J
P
A
8
=
/
20
1
0
6°
C
/
W
85
FIGURE 42. PACKAGE POWER DISSIPA TION vs AMBIENT
TEMPERATURE
IN-
CIRCUIT 1
V+
V+
IN+
V-
LOGIC
PIN
CIRCUIT 2
V-
CIRCUIT 3
V+
OUT
V-
11
V+
V-
CIRCUIT 4
CAPACITIVELY
COUPLED
ESD CLAMP
September 22, 2006
FN6312.0
Page 12

ISL28286, ISL28486
Applications Information
Introduction
The ISL28286 and ISL28486 are enhanced rail-to-rail input
micropower precision operational amplifiers with an enable
feature. The part is designed to operate from single supply
(2.4V to 5.0V) or dual supply (±1.2V to ±2.5V). The device is
capable of swinging 10% above the positive supply rail and
to ground. The parts maintains CMRR performance for input
voltages equal to the positive supply. The output operation
can swing within about 4mV of the supply rails with a 100kΩ
load (reference Figures 29 through 32).
Rail-to-Rail Input
The input common-mode voltage range of both parts goes
from 10mV above the negative supply to the positive supply
without introducing additional offset errors or degrading
performance associated with a conventional rail-to-rail input
operational amplifier. Many rail-to-rail input stages use two
differential input pairs, a long-tail PNP (or PFET) and an
NPN (or NFET). Severe penalties have to be paid for this
circuit topology. As the input signal moves from one supply
rail to another, the operational amplifier switches from one
input pair to the other causing drastic changes in input offset
voltage and an undesired change in magnitude and polarity
of input offset current.
The ISL28286 and ISL28486 achieves input rail-to-rail
without sacrificing important precision specifications and
degrading distortion performance. The devices’ input offset
voltage exhibits a smooth behavior throughout the entire
common-mode input range. The input bias current versus
the common-mode voltage range gives us an undistorted
behavior from the negative rail and 10% higher than the V+
rail (0.5V higher than V+ when V+ equals 5V).
Input Protection
All input terminals have internal ESD protection diodes to
both positive and negative supply rails, limiting the input
voltage to within one diode beyond the supply rails. Both
parts have additional back-to-back diodes across the input
terminals. If overdriving the inputs is necessary, the external
input current must never exceed 5mA. External series
resistors may be used as an external protection to limit
excessive external voltage and current from damaging the
inputs.
Input Bias Current Compensation
The input bias currents are decimated down to a typical of
500pA while maintaining an excellent bandwidth for a micropower operational amplifier. Inside the ISL28286 and
ISL28478 is an input bias canceling circuit. The input stage
transistors are still biased with an adequate current for
speed but the canceling circuit sinks most of the base
current, leaving a small fraction as input bias current.
Rail-to-Rail Output
A pair of complementary MOSFET devices are used to
achieve the rail-to-rail output swing. The NMOS sinks
current to swing the output in the negative direction. The
PMOS sources current to swing the output in the positive
direction. Both parts with a 100kΩ load will swing to within
4mV of the supply rails.
Enable/Disable Feature
The ISL28286 and ISL28486 offer an EN pin that disables
the device when pulled up to at least 2.0V. In the disabled
state (output in a high imped ance state), the part consumes
typically 4µA. By disabling the part, multiple parts can be
connected together as a MUX. The outputs are tied together
in parallel and a channel can be selected by the EN
EN
pin also has an internal pull down. If left open, the EN pin
pin. The
will pull to the negative rail and the device will be enabled by
default.
Using Only One Channel
The ISL28286 and ISL28486 are Dual and Quad channel
op-amps. If the application only requires one channel when
using the ISL28286 or less than 4 channels when using the
ISL28486, the user must configure the unused channel (s) to
prevent them from oscillating. The unused channel (s) will
oscillate if the input and output pins are floating. This will
result in higher than expected supply currents and possible
noise injection into the channel being used. The proper way
to prevent this oscillation is to short the output to the
negative input and ground the positive input (as shown in
Figure 43).
-
+
FIGURE 43. PREVENTING OSCILLATIONS IN UNUSED
CHANNELS
1/2 ISL28286
1/4 ISL28486
Proper Layout Maximizes Performance
To achieve the maximum performance of the high input
impedance and low offset voltage of the ISL28286 and
ISL28486, care should be taken in the circuit board layout.
The PC board surface must remain clean and free of
moisture to avoid leakage currents between adjacent traces.
Surface coating of the circuit board will reduce surface
moisture and provide a humidity barrier, reducing parasitic
resistance on the board. When input leakage current is a
concern, the use of guard rings around the amplifier inputs
will further reduce leakage currents. Figure 44 shows a
guard ring example for a unity gain amplifier that uses the
low impedance amplifier output at the same voltage as the
high impedance input to eliminate surface leakage. The
guard ring does not need to be a specific width, but it should
form a continuous loop around both inputs. For further
reduction of leakage currents, components can be mounted
12
FN6312.0
September 22, 2006
Page 13

ISL28286, ISL28486
to the PC board using PTFE standoff insulators.
HIGH IMPEDANCE INPUT
IN
FIGURE 44. GUARD RING EXAMPLE FOR UNITY GAIN
AMPLIFIER
V+
1/2 ISL28286
Example Application
Thermocouples are the most popular temperature-sensing
device because of their low cost, interchangeability, and
ability to measure a wide range of temperatures. The
ISL28286 (Figure 45) is used to convert the differential
thermocouple voltage into single-ended signal with 10X gain.
The ISL28286's rail-to-rail input characteristic allows the
thermocouple to be biased at ground and the converter to
run from a single 5V supply.
R
4
100kΩ
10kΩR
K TYPE
THERMOCOUPLE
FIGURE 45. THERMOCOUPLE AMPLIFIER
3
10kΩR
2
V+
+
ISL28286
V-
R
1
100kΩ
+
410µV/°C
5V
Current Limiting
The ISL28286 and ISL28486 have no internal currentlimiting circuitry. If the output is shorted, it is possible to
exceed the Absolute Maximum Rating for output current or
power dissipation, potentially resulting in the destruction of
the device.
Power Dissipation
It is possible to exceed the +150°C maximum junction
temperatures under certain load and power-supply
conditions. It is therefore important to calculate the
maximum junction temperature (T
to determine if power supply voltages, load conditions, or
package type need to be modified to remain in the safe
operating area. These parameters are related as follows:
T
JMAXTMAXθJA
xPD
()+=
MAXTOTAL
where:
•P
DMAXTOTAL
is the sum of the maximum power
dissipation of each amplifier in the package (PD
•PD
PD
for each amplifier can be calculated as follows:
MAX
MAX
2*VSI
SMAXVS
( - V
where:
•T
• θ
•PD
•V
•I
•V
= Maximum ambient temperature
MAX
= Thermal resistance of the package
JA
= Maximum power dissipation of 1 amplifier
MAX
= Supply voltage
S
= Maximum supply current of 1 amplifier
MAX
OUTMAX
= Maximum output voltage swing of the
application
) for all applications
JMAX
V
----------------------------
)
OUTMAX
×+×=
MAX
OUTMAX
R
L
(EQ. 1)
)
(EQ. 2)
13
•R
= Load resistance
L
FN6312.0
September 22, 2006
Page 14

Mini SO Package Family (MSOP)
M
C
SEATING
PLANE
0.10 C
N LEADS
0.25 C A B
E1E
B
L1
D
N
1
e
b
A
PIN #1
I.D.
(N/2)
H
0.08 C A B
A
ISL28286, ISL28486
(N/2)+1
M
MDP0043
MINI SO PACKAGE FAMILY
SYMBOL MSOP8 MSOP10 TOLERANCE NOTES
A 1.10 1.10 Max. A1 0.10 0.10 ±0.05 A2 0.86 0.86 ±0.09 -
b 0.33 0.23 +0.07/-0.08 -
c 0.18 0.18 ±0.05 -
D 3.00 3.00 ±0.10 1, 3
E 4.90 4.90 ±0.15 E1 3.00 3.00 ±0.10 2, 3
e 0.65 0.50 Basic -
L 0.55 0.55 ±0.15 L1 0.95 0.95 Basic -
N 8 10 Reference -
Rev. C 6/99
NOTES:
1. Plastic or metal protrusions of 0.15mm maximum per side are not
included.
2. Plastic interlead protrusions of 0.25mm maximum per side are
not included.
3. Dimensions “D” and “E1” are measured at Datum Plane “H”.
4. Dimensioning and tolerancing per ASME Y14.5M-1994.
A2
A1
c
SEE DETAIL "X"
DETAIL X
GAUGE
PLANE
L
3° ±3°
0.25
14
FN6312.0
September 22, 2006
Page 15

ISL28286, ISL28486
Quarter Size Outline Plastic Packages Family (QSOP)
E E1
0.010 C A B
C
SEATING
PLANE
0.004 C
A
N
1
B
L1
c
SEE DETAI L "X"
D
PIN #1
I.D. MARK
e
0.007 C A B
(N/2)+1
A
(N/2)
MDP0040
QUARTER SIZE OUTLINE PLASTIC PACKAGES FAMILY
SYMBOL QSOP16 QSOP24 QSOP28 TOLERANCE NOTES
A 0.068 0.068 0.068 Max. A1 0.006 0.006 0.006 ±0.002 A2 0.056 0.056 0.056 ±0.004 -
b 0.010 0.010 0.010 ±0.002 -
c 0.008 0.008 0.008 ±0.001 D 0.193 0.341 0.390 ±0.004 1, 3
E 0.236 0.236 0.236 ±0.008 -
E1 0.154 0.154 0.154 ±0.004 2, 3
H
b
e 0.025 0.025 0.025 Basic -
L 0.025 0.025 0.025 ±0.009 -
L1 0.041 0.041 0.041 Basic -
N 16 24 28 Reference -
Rev. E 3/01
NOTES:
1. Plastic or metal protrusions of 0.006” maximum per side are not
included.
2. Plastic interlead protrusions of 0.010” maximum per side are not
included.
3. Dimensions “D” and “E1” are measured at Datum Plane “H”.
4. Dimensioning and tolerancing per ASME Y14.5M-1994.
GAUGE
PLANE
L
0.010
4°±4°
A2
A1
DETAIL X
All Intersil U.S. products are manufactured, assembled and tested utilizing ISO9000 quality systems.
Intersil Corporation’s quality certifications can be viewed at www.intersil.com/design/quality
Intersil products are sold by description only. Intersil Corporation reserves the right to make changes in circuit design, software and/or specifications at any time without
notice. Accordingly, the reader is cautioned to verify that data sheets are current before placing orders. Information furnished by Intersil is believed to be accurate and
reliable. However, no responsibility is assumed by Intersil or its subsidiaries for its use; nor for any infringements of patents or other rights of third parties which may result
from its use. No license is granted by implicat ion or oth erwise u nde r any p a tent or p at ent r ights of Intersil or its subsidiaries.
For information regarding Intersil Corporation and its products, see www.intersil.com
15
FN6312.0
September 22, 2006
 Loading...
Loading...