Intersil Corporation HIP0060 Datasheet
July 1997
HIP0060
1.5A, 50V Quad Low Side Power Driver
with Serial Bus Control and Fault Protection
Features
• Quad NDMOS Output Drivers in a High Voltage Power
BiMOS Process
• Over-Stress Protection - Each Output
- Over-Current Limiting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1.5A Min
- Internal Zener Drain-to-Gate Over-Voltage Clamp
Protection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 50V Typ
- Thermal Shutdown Protection
- Open-Load Detection
• Low Quiescent Current . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10mA Max
• Serial Diagnostic Link with SPI Bus
• Diagnostic Interrupt Fault Flag
• 5V CMOS Logic Input Control
• Common Reset for Fault Bits and Output Drivers
• Ambient Operating
Temperature Range. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . -40
o
C to 125oC
Applications
• Automotive and Industrial Systems
• Fuel Injection Drivers
• Solenoids, Relays and Lamp Drivers
• Logic and µP Controlled Drivers
• Robotic Controls
Description
The HIP0060 is a 5V logic controlled Quad Low Side Power
Driver. The outputs are individually protected for over-current
(OC), over-temperature (OT) and over-voltage (OV). If an OC
short circuit in the output load is sensed (I
) in one output
S
power driver, that output current will be independently limited
while the other outputs remain in operation. Over-current is
limited by direct gate feedback. Over-voltage protection is provided by a drain-to-gate zener diode that clamps inductive
switching pulses.
The output drivers are individually controlled through a Gate
Control Latch. Temperature is sensed at each output. If a thermal fault exists, a status flag is set and the output is latched
off. Open-load (OL) and over-temperature (OT) faults sets a
status flag bit as diagnostic output to the SPI bus. For all fault
bits (8), an ORed one-shot interrupt signal is output to the
pin. An
RST reset clears the fault flags and disables all out-
INT
puts while active. The Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI) bus
pins are the Serial Input (SI), Serial Output (SO), Serial Data
Clock (SCK) and the Chip Select (
CS).
The HIP0060 is fabricated in a Power BiMOS IC process, and
is intended for use in automotive and other applications having
a wide range of temperature and electrical stress conditions. It
is particularly suited for driving lamps, relays, and solenoids in
applications where low operating power, high breakdown voltage, and higher output current at high temperatures is required.
Ordering Information
TEMP.
PART NUMBER
HIP0060AB -40 to 125 24 Ld SOIC M24.3
RANGE (oC) PACKAGE
PKG.
NO.
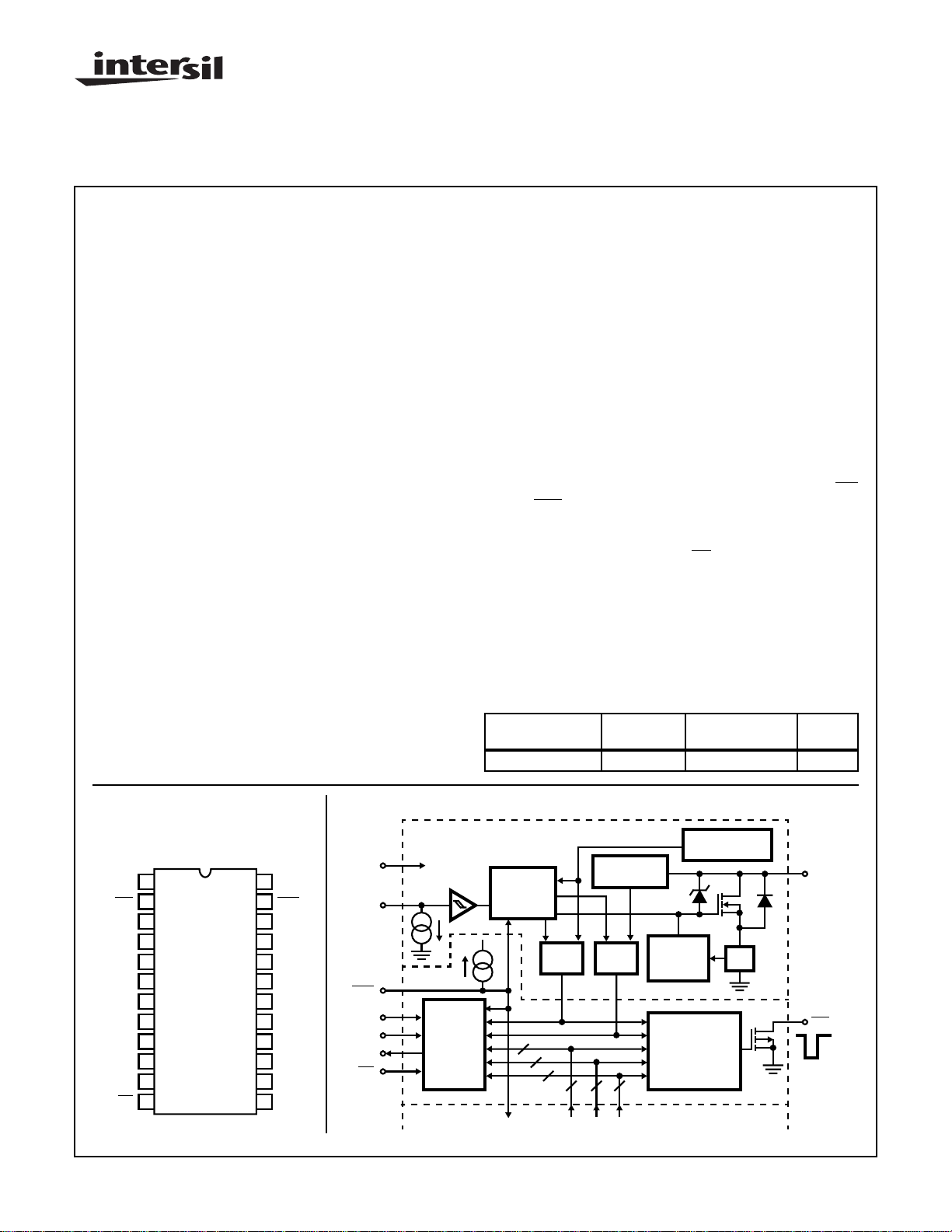
Pinout
HIP0060 (SOIC)
TOP VIEW
1
GND
2
INT
3
INA
OUTA
4
5
GND
6
GND
7
GND
8
GND
9
OUTB
10
INB
11
SI
CS
12
CAUTION: These devices are sensitive to electrostatic discharge; follow proper IC Handling Procedures.
http://www.intersil.com or 407-727-9207
24
V
DD
23
RST
22
IND
21
OUTD
20
GND
19
GND
18
GND
GND
17
OUTC
16
INC
15
SO
14
SCK
13
| Copyright © Intersil Corporation 1999
Block Diagram
CHANNEL A
(1 OF 4)
V
DD
INA
RST
SCK
SI
SO
CS
+5V
8-BIT SPI
(SERIAL
DIAG.
REG)
+
TO
B, C, D
1
GATE
CONTROL
LATCH
2
2
O.T.
BIT
2
FROM B, C, D
OPEN LOAD
DETECTOR
222
O.L.
BIT
OVER TEMP.
DETECTOR
OVER
CURRENT
LIMIT
8 ORed O.T./O.L.
FAULT INPUTS,
ONE-SHOT
MULTI OUTPUT
OUTA
I
S
INT
File Number 4045
HIP0060
Absolute Maximum Ratings Thermal Information
Max Output Voltage, V
Max Output Load Current, I
Logic Input Voltage. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . -0.3V to 7V
Logic Supply Voltage, VDD. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . -0.3V to +7V
Operating Conditions
Ambient Temperature Range . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . -40oC to 125oC
Junction Temperature Range . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . -40oC to 150oC
CAUTION: Stresses above those listed in “Absolute Maximum Ratings” may cause permanent damage to the device. This is a stress only rating and operation
of the device at these or any other conditions above those indicated in the operational sections of this specification is not implied.
NOTES:
1. θJA is measured with the component mounted on an evaluation PC board in free air.
2. The MOSFET Output Drain is internally clamped with a Drain-to-Gate zener diode that turns on the MOSFET; holding the Drain at the
Output Clamp voltage VOC.
3. The output drive is protected by an internal current limit. The ICL over-current limiting threshold parameter specification defines the maximum current. The maximum current with all outputs ON may be further limited by dissipation.
4. Device dissipation is based on thermal resistance capability of the package in a normal operating environment. The junction to ambient
thermal resistance of 60oC/W is defined here as a PC Board mounted device with minimal copper. With approximately 2 square inches
of copper area as a heat sink, it is practical to achieve 35oC/W thermal resistance. Further reduction in the thermal resistance can be
achieved with additional PC Board Copper ground area or an external heat sink structure next to the ground leads at the center of the
package.
(Note 2). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . V
OUT
(Per Output, Note 3) . . . . . . . . I
LOAD
Thermal Resistance (Typical, Notes 1, 4) θJA(oC/W)
OC
CL
SOIC - PC Board Mount, Min. Copper . . . . . . . . . . 60
SOIC - PC Board Mount, 2 sq. in. Copper . . . . . . . . 35
Maximum Storage Temperature Range -55oC to 150oC
Maximum Lead Temperature (Soldering 10s). . . . . . . . . . . . .300oC
(SOIC - Lead Tips Only)
Electrical Specifications V
DD
PARAMETER SYMBOL CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNITS
OUTPUTS DRIVERS (DR0 TO DR7)
Output Channel Resistance r
Over-Current Limiting Threshold I
Output Clamping Voltage V
Output Clamping Energy E
Output OFF Leakage Current I
Open-Load Fault Threshold R
Output Rise Time t
Output Fall Time t
Turn-On Delay t
Turn-Off Delay t
POWER SUPPLY
Power On Reset Threshold V
Logic Supply Current I
V
DD
LOGIC INPUTS (INx, SI, SCK,
RST,CS)
High Level Input Voltage V
Low Level Input Voltage V
Input Hysteresis V
High Output Voltage, SO,
INT V
Low Output Voltage, SO V
Input Pull-Down Current, INx I
Reset Input Pull-Up Current,
RST I
= 4.5V to 5.5V, VSS = 0V, TA = -40oC to 125oC; Unless Otherwise Specified
DSONIOUT
CL
OC
OC
= 0.5A - - 0.8 Ω
1.5 - 3.5 A
40 50 60 V
1ms Single Pulse Width, TA = 25oC,
-85-mJ
(Refer to Figure 3 for SOA Limits).
V
LK
OLDVOUT
R
F
ON
OFF
DD(POR)
DD
IH
IL
ILHYS
OL
OH
INPD
RPU
= 14.5V - - 180 µA
OUT
= 14.5V, Output Off 4 - 200 kΩ
RL = 30Ω, V
RL = 30Ω, V
RL = 30Ω, V
RL = 30Ω, V
= 14.5V 1 - 12 µs
OUT
= 14.5V 1 - 12 µs
OUT
= 14.5V - - 12 µs
OUT
= 14.5V - - 12 µs
OUT
3.2 - 4.4 V
All Outputs ON or OFF - - 10 mA
0.7xV
DD
--V
- - 0.2xV
0.8 - - V
Current Sink = 1.6mA - - 0.4 V
Current Source = -0.8mA VDD-0.8 - - V
75 - 250 µA
20 - 120 µA
DD
V
2
HIP0060
Electrical Specifications V
PARAMETER SYMBOL CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNITS
DIAGNOSTIC
Pulse Width,
Fault Response Time t
OVER-TEMPERATURE PROTECTION
Over-Temperature Shutdown T
SERIAL PERIPHERAL INTERFACE TIMING (Capacitance Each Pin, C
SCK Period t
SCK Clock High/Low Time t
SCK Rise/Fall Time t
Enable Lead/Lag Time t
Output Data Valid Time t
Data Setup Time t
Disable Time t
INT t
= 4.5V to 5.5V, VSS = 0V, TA = -40oC to 125oC; Unless Otherwise Specified (Continued)
DD
INT
FAULT
SD
CYC
WSCKH,
t
WSCKL
,
rSCK
t
fSCK
,
LEAD
t
LAG
V
SU
DIS
= 200pF)
L
3-25µs
--16µs
160 - -
500 - - ns
200 - - ns
- - 30 ns
250 - - ns
- - 170 ns
- - 30 ns
- - 250 ns
o
C
Description of Diagnostics
OC (Over-Current) Fault Mode
In a short circuit or over-current fault condition when an output is switched on, the output current is limited to the I
maximum as defined in the Electrical Specifications. An OC
fault condition does not shutdown the output. The current is
sensed and feedback is directed to the gate of the MOS Output Driver. The gate voltage is reduced to maintained the
specified level of current limiting. In this mode, the drain voltage will increase and cause increased dissipation.
OT (Over-Temperature) Fault Mode
Under a high dissipation over-temperature fault condition,
the output temperature is detected and compared to a preset
threshold level. When the OT threshold is exceeded, thermal
shutdown for that output occurs. The Gate Control Latch
drive to the output is switched off and a status flag (the OT
Bit) for the fault is set. The output shutdown action is independent of the IN input state. However, the Gate Control
Latch and OL Bit will be reset on the next rising edge of the IN
input and, if the fault still exists, the shutdo wn action will repeat.
Diagnostic action for an OT fault includes feedback of the
fault status to the Serial Diagnostic Register for a SPI bus
data output. Also, as shown in the Block Diagram, the OT
fault status bit information is ORed into a one-shot that
drives an open drain to provide an
put. The
INT output has a specified timing from the one-shot
INT interrupt signal out-
multi and is defined in the Electrical Specifications as t
INT
CL
.
OL (Open-Load) Fault Mode
An open-load fault mode sequence consists of setting a status flag (the OL Bit) when an output open load condition is
detected. If the output impedance is greater than a preset
threshold, as detected when the input is off; the status bit is
set. The OL Bit is reset on the next falling edge of the IN
input signal. The off-on detection sequence will repeat as
long as the output impedance is higher than the detection
threshold, as detected in the off state.
Diagnostic action for an OL fault mode differs from the OT
fault mode by not forcing an output shutdown through the
Gate Controlled Latch. Also, because the OL fault is
detected in the off state, the status flag is reset on the falling
edge of the input instead of the rising edge. The OL output
information to the Serial Diagnostic Register and the
INT pin
is the same as the OT fault mode action.
ORed Fault Bits
It is important to note that the trigger input to the one-shot is
locked-out for the t
occurred in the t
duration and any fault that may have
INT
window will not be displayed at the INT
INT
output. Howev er, all 8 fault bits ma y still be read as data from
the SO output when clock by the SCK input. The
INT fault
output is provided as an interrupt signal to flag the immediate occurrence of a fault and take appropriate action as
defined by the microcontroller to the SPI bus and the users
programming. The
INT fault output may be ORed with other
ICs to provide a system microcontroller interrupt to indicate
the presence of a fault.
3
 Loading...
Loading...