Page 1
S
www.BDTIC.com/Intersil
N
IG
S
E
®
D
N
E
M
M
O
EC
R
T
O
N
O
C
E
R
D
N
E
Data Sheet July 13, 2005
M
M
H
E
ED
C
R
O
F
D
P
E
R
5
8
1
5
5
D
W
E
N
C
A
L
T
N
E
M
E
HC55180, HC55181, HC55183,
HC55184
FN4519.7
Extended Reach Ringing SLIC Family
The RSLIC18™ family of ringing subscriber line interface
circuits (RSLIC) supports analog Plain Old Telephone
Service (POTS) in short and medium loop length, wireless
and wireline applications. Ideally suited for remote
subscriber units, this family of products offers flexibility to
designers with high ringing voltage and low power
consumption system requirements.
The RSLIC18 family operates to 100V which translates
directly to the amount of ringing voltage supplied to the end
subscriber. With the high operating voltage, subscriber loop
lengths can be extended to 500Ω (i.e., 5,000 feet) and
beyond.
Other key features across the product family include: low
power consumption, ringing using sinusoidal or trapezoidal
waveforms, robust auto-detection mechanisms for when
subscribers go on or off hook, and minimal external discrete
application components. Integrated test access features are
also offered on selected products to support loopback
testing as well as line measurement tests.
There are five product offerings in the RSLIC18 family:
HC55180, HC55181, HC55183 and HC55184. The
architecture for this family is based on a voltage feed
amplifier design using low fixed loop gains to achieve high
analog performance with low susceptibility to system
induced noise.
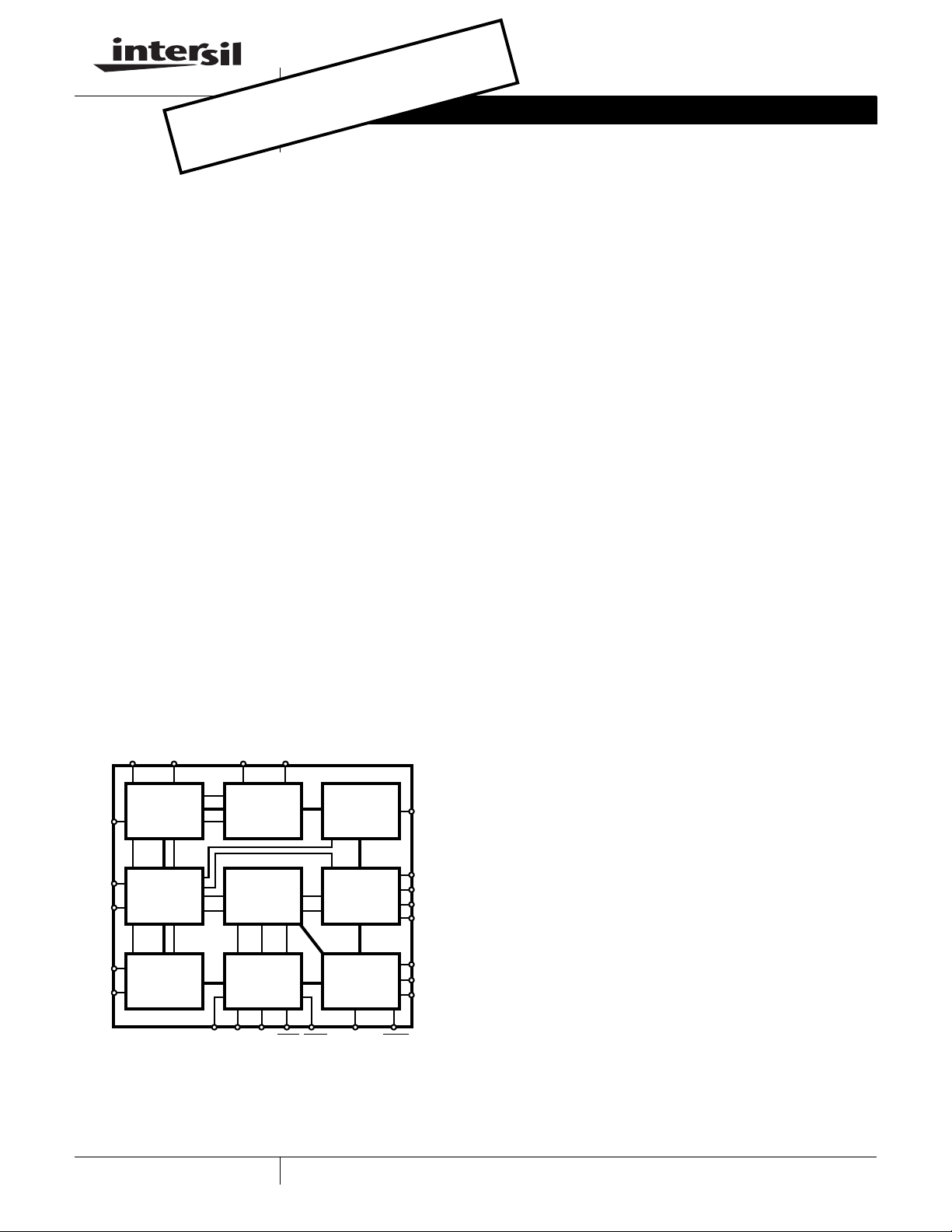
Block Diagram
POL CDC VBHVBL
ALM
RINGING
PORT
4-WIRE
PORT
CONTROL
LOGIC
BSEL SWC
VRS
VRX
VTX
-IN
VFB
F2
F1
F0
ILIM
TIP
RING
SW+
SW-
DC
CONTROL
2-WIRE
PORT
TEST
ACCESS
BATTERY
SWITCH
TRANSMIT
SENSING
DETECTOR
LOGIC
RTD RD DET
E0
Features
• Battery Operation to 100V
• Low Standby Power Consumption of 50mW
• Peak Ringing Amplitude 95V, 5 REN
• Sinusoidal or Trapezoidal Ringing Capability
• Integrated CODEC Ringing Interface
• Integrated MTU DC Characteristics
• Low External Component Count
• Pulse Metering and On Hook Transmission
• Tip Open Ground Start Operation
• Thermal Shutdown with Alarm Indicator
• 28 Lead Surface Mount Packaging
• Dielectric Isolated (DI) High Voltage Design
• HC55180
- Silent Polarity Reversal
- 53dB Longitudinal Balance
- Loopback Test Capability
• HC55181
- Integrated Battery Switch
- Silent Polarity Reversal
- 53dB Longitudinal Balance
- Loopback and Test Access Capability
• HC55183
- Integrated Battery Switch
- 45dB Longitudinal Balance
• HC55184
- Integrated Battery Switch
- Silent Polarity Reversal
- 45dB Longitudinal Balance
• Pb-Free Plus Anneal Available (RoHS Compliant)
Applications
• Wireless Local Loop (WLL)
• Digital Added Main Line (DAML)/Pairgain
• Integrated Services Digital Network (ISDN)
• Small Office Home Office (SOHO) PBX
• Cable/Computer Telephony
Related Literature
• AN9814, User’s Guide for Development Board
• AN9824, Modeling of the AC Loop
1
RSLIC18™ is a trademark of Intersil Corporation. All other trademarks mentioned are the property of their respective owners.
CAUTION: These devices are sensitive to electrostatic discharge; follow proper IC Handling Procedures.
1-888-INTERSIL or 1-888-468-3774
| Intersil (and design) is a registered trademark of Intersil Americas Inc.
Copyright Intersil Americas Inc. 2003, 2005. All Rights Reserved
Page 2

HC55180, HC55181, HC55183, HC55184
www.BDTIC.com/Intersil
Ordering Information (PLCC Package Only)
LOOP
PART NUMBER 100V 85V
HC55180DIM •• •• -40 to 85 28 Ld PLCC N28.45
HC55181DIM ••• • • -40 to 85 28 Ld PLCC N28.45
HC55183ECMZ (Note) 75V • 45dB 0 to 70 28 Ld PLCC (Pb-free) N28.45
HC55183ECMZ96 (Note) 75V • 45dB 0 to 70 28 Ld PLCC (Pb-free) N28.45
HC55183ECM 75V • 45dB 0 to 70 28 Ld PLCC N28.45
HC55184ECM 75V •• 45dB 0 to 70 28 Ld PLCC N28.45
HC55184ECMZ (Note) 75V • 45dB 0 to 70 28 Ld PLCC (Pb-free) N28.45
HC55184ECMZR4749
(Note)
HC55184ECMZ96R4749
(Note)
HC5518XEVAL1 Evaluation board platform, including CODEC.
NOTE: Intersil Pb-free plus anneal products employ special Pb-free material sets; molding compounds/die attach materials and 100% matte tin plate
termination finish, which are RoHS compliant and compatible with both SnPb and Pb-free soldering operations. Intersil Pb-free products are MSL
classified at Pb-free peak reflow temperatures that meet or exceed the Pb-free requirements of IPC/JEDEC J STD-020.
BATSWPOL
75V • 45dB 0 to 70 28 Ld PLCC (Pb-free) N28.45
75V • 45dB 0 to 70 28 Ld PLCC (Pb-free) N28.45
REV
FULL
BACK
TEST
ONLY LB = 53dB LB = 58dB
TEMP.
RANGE
(°C) PACKAGE
PKG.
DWG. #
Device Operating Modes
OPERATING
MODE F2 F1 F0 E0 = 1 E0 = 0 DESCRIPTION HC55180 HC55181 HC55183 HC55184
Low Power Standby 0 0 0 SHD GKD MTU compliant standby mode with
active loop detector.
Forward Active 0 0 1 SHD GKD Forward battery loop feed.
Unused 0 1 0 n/a n/a This is a reserved internal test mode.
Reverse Active 0 1 1 SHD GKD Reverse battery loop feed.
Ringing 1 0 0 RTD RTD Balanced ringing mode supporting
both sinusoidal, trapezoidal and
ringing waveforms with DC offset.
Forward Loop Back 1 0 1 SHD GKD Internal device test mode.
Tip Open 1 1 0 SHD GKD Tip amplifier disabled and ring
amplifier enabled. Intended for PBX
type applications.
Power Denial 1 1 1 n/a n/a Device shutdown.
••••
••••
•• •
••••
••
••
••••
2
Page 3
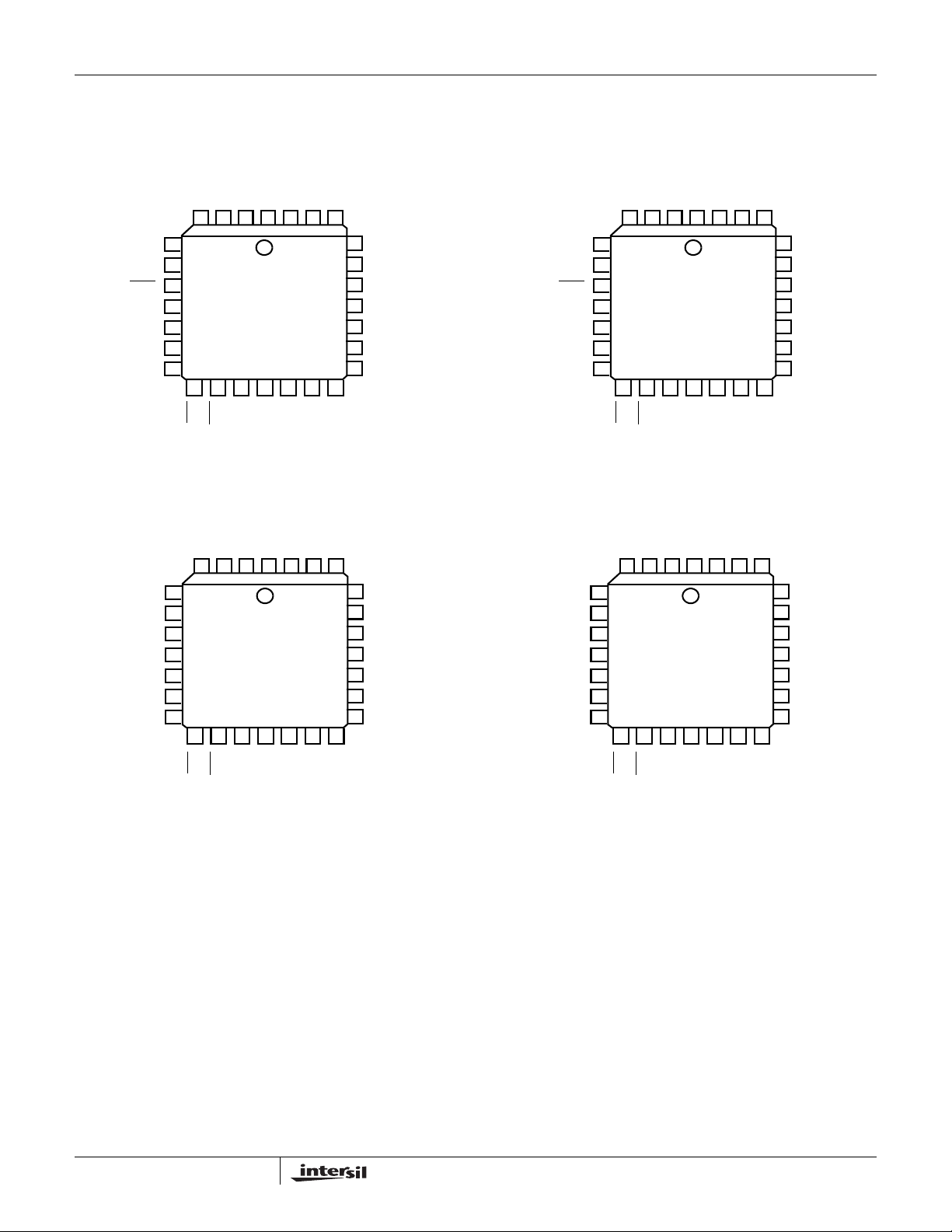
Pinout
www.BDTIC.com/Intersil
SW+
SW-
SWC
F2
F1
F0
E0
HC55180, HC55181, HC55183, HC55184
HC55180
(PLCC)
TOP VIEW
RING
ILIM
RD
TIP
VBL
VBH
13
3
ALM
14
BGND
15
AGND
27
12
16
BSEL
26
28
NC
RTD
25
CDC
24
VCC
23
22
-IN
VFB
21
VTX
20
VRX
19
17
18
VRS
POL
SW+
SW-
SWC
F2
F1
F0
E0
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
DET
VBH
4
13
DET
HC55181
(PLCC)
TOP VIEW
VBL
BGND
3
14
ALM
AGND
RING
ILIM
RD
TIP
27
12
15
16
BSEL
26
28
RTD
25
CDC
24
VCC
23
22
-IN
VFB
21
VTX
20
VRX
19
17
18
NC
VRS
POL
NC
NC
NC
F2
F1
F0
E0
HC55183
(PLCC)
TOP VIEW
RD
RING
NC
ILIM
27
26
RTD
25
CDC
24
VCC
23
22
-IN
VFB
21
VTX
20
VRX
19
17
18
NC
VRS
NC
NC
NC
F2
F1
F0
E0
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
TIP
VBL
VBH
13
3
ALM
14
BGND
15
AGND
12
28
16
BSEL
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
DET
VBH
4
DET
TOP VIEW
VBL
3
13
14
ALM
HC55184
(PLCC)
BGND
TIP
12
15
BSEL
AGND
28
16
RING
27
17
NC
RD
POL
ILIM
26
RTD
25
CDC
24
VCC
23
22
-IN
VFB
21
VTX
20
VRX
19
18
VRS
3
Page 4
HC55180, HC55181, HC55183, HC55184
www.BDTIC.com/Intersil
Absolute Maximum Ratings T
Maximum Supply Voltages
V
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . -0.5V to +7V
CC
- V
V
CC
V
CC
Uncommitted Switch Voltage . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . -110V
Maximum Tip/Ring Negative Voltage Pulse (Note 18). . . . . . . -115V
Maximum Tip/Ring Positive Voltage Pulse (Note 18) . . . . . . . . . .8V
ESD (Human Body Model). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 500V
(180, 181). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 110V
BAT
- V
(183, 184). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 85V
BAT
Operating Conditions
Temperature Range
Industrial (I Suffix) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .-40°C to 85°C
Commercial (C Suffix) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 0°C to 75°C
Positive Power Supply (V
Negative Power Supply (V
Negative Power Supply (V
Uncommitted Switch (loop back or relay driver) . . . . . +5V to -100V
CAUTION: Stresses above those listed in “Absolute Maximum Ratings” may cause permanent damage to the device. This is a stress only rating and operation of the
device at these or any other conditions above those indicated in the operational sections of this specification is not implied .
NOTE:
1. θ
is measured with the component mounted on an evaluation PC board in free air.
JA
). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . +5V ±5%
CC
, VBL) (180, 181) . . . . . -16V to -100V
BH
, VBL) (183, 184) . . . . . . -24V to -75V
BH
Electrical Specifications Unless Otherwise Specified, T
PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNITS
RINGING PARAMETERS (Note 2)
VRS Input Impedance (Note 3) 480 - - kΩ
Differential Ringing Gain VRS to 2-Wire, R
4-Wire to 2-Wire Ringing Off Isolation Active mode, referenced to VRS input. - 60 - dB
2-Wire to 4-Wire Transmit Isolation Ringing mode referenced to the differential ringing
AC TRANSMISSION PARAMETERS (Notes 5, 6)
Receive Input Impedance (Note 3) 160 - - kΩ
Transmit Output Impedance (Note 3) --1Ω
4-Wire Port Overload Level THD = 1% 3.1 3.5 - V
2-Wire Port Overload Level THD = 1% 3.1 3.5 - V
2-Wire Return Loss f = 300Hz - 26 - dB
Longitudinal Current Capability (Per Wire) (Note 3) Test for False Detect 20 - - mA
4-Wire to 2-Wire Insertion Loss -0.20 0.0 +0.30 dB
2-Wire to 4-Wire Insertion Loss -6.22 -6.02 -5.82 dB
4-Wire to 4-Wire Insertion Loss -6.32 -6.02 -5.82 dB
Idle Channel Noise 2-Wire C-Message - 16 19 dBrnC
Idle Channel Noise 4-Wire C-Message - 10 13 dBrnC
= 25°C Thermal Information
A
Thermal Resistance (Typical, Note 1) θ
PLCC Package. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 55
Maximum Junction Temperature Plastic . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 150°C
Maximum Storage Temperature Range . . . . . . . . . -65°C to 150°C
Maximum Lead Temperature (Soldering 10s). . . . . . . . . . . . 300°C
(PLCC - Lead Tips Only)
Die Characteristics
Substrate Potential . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . V
Process . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Bipolar-DI
= 0°C to 70°C for the HC55183, 184 only, all others -40°C to 85°C, VBL = -24V,
= -100V, -85V or -75V, VCC = +5V, AGND = BGND = 0V, loop current limit = 25mA. All AC Parameters are
V
BH
specified at 600Ω 2-wire terminating impedance over the frequency band of 300Hz to 3.4kHz. Protection
resistors = 0Ω. These parameters apply generically to each product offering.
A
= ∞ (Note 4) 78 80 82 V/V
LOAD
amplitude.
f = 1kHz - 32 - dB
f = 2.3kHz - 21 - dB
f = 3.4kHz - 17 - dB
Test for False Detect, Low Power Standby 10 - - mA
Psophometric - -73.5 -71 dBmp
Psophometric - -79.5 -77 dBmp
-60- dB
JA
(°C/W)
BAT
PK
PK
RMS
RMS
4
Page 5

HC55180, HC55181, HC55183, HC55184
www.BDTIC.com/Intersil
Electrical Specifications Unless Otherwise Specified, T
= -100V, -85V or -75V, VCC = +5V, AGND = BGND = 0V, loop current limit = 25mA. All AC Parameters are
V
BH
specified at 600Ω 2-wire terminating impedance over the frequency band of 300Hz to 3.4kHz. Protection
resistors = 0Ω. These parameters apply generically to each product offering. (Continued)
PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNITS
DC PARAMETERS (Note 6)
Loop Current Limit Programming Range (Note 5) Max Low Battery = -52V 15 - 45 mA
Loop Current During Low Power Standby Forward polarity only. 18 - 26 mA
LOOP DETECTORS AND SUPERVISORY FUNCTIONS
Switch Hook Programming Range 5-15mA
Switch Hook Programming Accuracy Assumes 1% external programming resistor - ± 2 ± 10 %
Dial Pulse Distortion -1.0- %
Ring Trip Comparator Threshold 2.4 2.7 3.0 V
Ring Trip Programming Current Accuracy - - ± 10 %
Ground Key Threshold -12-mA
Thermal Alarm Output IC junction temperature - 175 - °C
LOGIC INPUTS (F0, F1, F2, E0, SWC, BSEL)
Input Low Voltage --0.8V
Input High Voltage 2.0 - - V
Input Low Current V
Input High Current V
LOGIC OUTPUTS (DET
Output Low Voltage I
Output High Voltage I
POWER SUPPLY REJECTION RATIO
to 2-Wire f = 300Hz - 40 - dB
V
CC
V
to 4-Wire f = 300Hz - 45 - dB
CC
V
to 2-Wire 300Hz ≤ f ≤ 3.4kHz - 30 - dB
BL
V
to 4-Wire 300Hz ≤ f ≤ 3.4kHz - 35 - dB
BL
V
to 2-Wire 300Hz ≤ f ≤ 3.4kHz - 33 - dB
BH
V
to 4-Wire 300Hz ≤ f ≤ 1kHz - 40 - dB
BH
NOTES:
2. These parameters are specified at high battery operation. For the HC55180 the external supply is set to high battery voltage, for the HC55181,
HC55183 and HC55184, BSEL = 1.
3. These parameters are controlled via design or process parameters and are not directly tested. These parameters are characterized upon initial
design release and upon design changes which would affect these characteristics.
4. Differential Ringing Gain is measured with VRS = 0.795 V
for -75V devices.
5. These parameters are specified at low battery operation. For the HC55180, the external supply is set to low battery voltage, for the HC55181,
HC55183 and HC55184, BSEL = 0.
6. Forward Active and Reverse Active performance is guaranteed for the HC55180, HC55181 and HC55184 devices only. The HC55183 is
specified for Forward Active operation only.
, ALM)
= 0°C to 70°C for the HC55183, 184 only, all others -40°C to 85°C, VBL = -24V,
A
= 0.4V -20 - - µA
IL
= 2.4V - - 5 µA
IH
= 5mA - - 0.4 V
OL
= 100µA2.4--V
OH
f = 1kHz - 35 - dB
f = 3.4kHz - 28 - dB
f = 1kHz - 43 - dB
f = 3.4kHz - 33 - dB
1kHz < f ≤ 3.4kHz - 45 - dB
for -100V devices, VRS = 0.663 V
RMS
for -85V devices and VRS = 0.575 V
RMS
RMS
5
Page 6
Electrical Specifications Unless Otherwise Specified, T
www.BDTIC.com/Intersil
loop current limit = 25mA. All AC Parameters are specified at 600Ω 2-wire terminating impedance over the frequency band of 300Hz to 3.4kHz.
Protection resistors = 0Ω.
HC55180 (NOTE 7) HC55181 HC55183, HC55184
PARAMETER
RINGING PARAMETERS (Note 2)
Ringing Voltage
Open Circuit
(Note 8)
6
Ringing Voltage
Load = 1.3K
(Notes 8, 10)
Tip Centering Voltage VB = -85V, RL = ∞ -±2.5-VBH = -85V, RL = ∞ --±2.5VBH = -75V, RL = ∞ --±3V
Ring Centering Voltage V
AC TRANSMISSION PARAMETERS (Notes 5, 6)
2-Wire Longitudinal Balance
(Notes 12, 13)
4-Wire Longitudinal Balance (Note 11) - - - - - - Grade E - 58 - dB
2-Wire to 4-Wire Level Linearity
4-Wire to 2-Wire Level
Linearity
Referenced to -10dBm
THD ≤ 0.5%
= -85V
V
B
THD ≤ 0.5%
= -100V
V
B
THD ≤ 3.0%
V
= -85V
B
THD ≤ 3.0%
= -100V
V
B
VB = -100V, RL = ∞ -±2.0-VBH = -100V, RL = ∞ - - ±2.0 (Note 9) - - - V
= -85V, RL = ∞ -±2.5-VBH = -85V, RL = ∞ --±2.5VBH = -75V, RL = ∞ --±3V
B
= -100V, RL = ∞ -±2.0-VBH = -100V, RL = ∞ - - ±2.0 (Note 9) - - - V
V
B
(Note 11) - - - - - - Grade E 45 53 - dB
Grade C, D - 59 - Grade C, D 53 59 - (Note 11) - - - dB
Grade C, D - 64 - Grade C, D - 64 - (Note 11) - - - dB
+3 to -40dBm, 1kHz - ±0.025- +3 to -40dBm, 1kHz - ±0.025 - +3 to -40dBm, 1kHz - ±0.025-dB
-40 to -50dBm, 1kHz - ±0.050- -40 to -50dBm, 1kHz - ±0.050 - -40 to -50dBm, 1kHz - ±0.050-dB
= 0°C to 70°C for the HC55183, 184 only, all others -40°C to 85°C, VBL = -24V, VCC = +5V, AGND = BGND = 0V,
A
-80-THD ≤ 0.5%
VBH = -85V
-95-THD ≤ 0.5%
VBH = -100V
-80-THD ≤ 3.0%
VBH = -85V
-95-THD ≤ 3.0%
VBH = -100V
80 - - THD ≤ 0.5%
VBH = -75V
95 - - (Note 9) - - - V
80 - - THD ≤ 3.0%
VBH = -75V
95 - - (Note 9) - - - V
70 - - V
70 - - V
UNITSTEST CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX TEST CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX TEST CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX
PEAK
PEAK
PEAK
PEAK
HC55180, HC55181, HC55183, HC55184
-50 to -55dBm, 1kHz - ±0.100- -50 to -55dBm, 1kHz - ±0.100 - -50 to -55dBm, 1kHz - ±0.100-dB
DC PARAMETERS
Loop Current Accuracy
(Notes 5, 6)
Open Circuit Voltage
(|Tip - Ring|, Note 6)
= 25mA - - ± 8.5 IL = 25mA - - ± 8.5 IL = 25mA - - ± 10 %
I
L
V
= -16V - 7.5 - VBL = -16V 6.0 7.5 9.0 VBL = -16V - 7.5 - V
B
= -24V 14 15.5 17 VBL = -24V 14 15.5 17 VBL = -24V 14 15.5 17 V
V
B
> -60V 43 50 - VBH = -60V, BSEL = 1 43 50 - VBH = -60V, BSEL = 1 43 50 - V
V
B
Page 7
Electrical Specifications Unless Otherwise Specified, T
www.BDTIC.com/Intersil
= 0°C to 70°C for the HC55183, 184 only, all others -40°C to 85°C, VBL = -24V, VCC = +5V, AGND = BGND = 0V,
A
loop current limit = 25mA. All AC Parameters are specified at 600Ω 2-wire terminating impedance over the frequency band of 300Hz to 3.4kHz.
Protection resistors = 0Ω. (Continued)
HC55180 (NOTE 7) HC55181 HC55183, HC55184
PARAMETER
Low Power Standby
Open Circuit Voltage
(Tip - Ring, Note 2)
Absolute Open Circuit
7
Voltage (Note 6)
= -48V 43 47 - VBH = -48V 43 - 47 VBH = -48V 43 - 47 V
V
B
> -60V 43 49 - VBH = -60V, BSEL = 1 43 49 - VBH = -60V, BSEL = 1 43 49 - V
V
B
in LPS and FA
V
RG
in RA
V
TG
> -60V
V
B
--53-56V
in LPS and FA
RG
in RA
V
TG
= -60V, BSEL = 1
V
BH
--53-56V
in LPS and FA
RG
in RA
V
TG
= -60V, BSEL = 1
V
BH
--53-56V
TEST ACCESS FUNCTIONS
Switch On Voltage (Note 14) - - - I
= 45mA - 0.30 0.60 (Note 14) - - - V
OL
Loopback Max Battery - - 52 - - 52 (Note 15) - - 52 V
SUPPLY CURRENTS (Supply currents not listed are considered negligible and do not contribute significantly to total power dissipation. All measurements made under open circuit load conditions.)
Low Power Standby
(Note 2)
Forward or Reverse
(Note 5)
Forward
(Note 2)
I
CC
, VB = -100V, -85V - 0.375 0.600 IBH, VBH = -100V, -85V - 0.375 0.600 IBH, VBH = -75V - 0.375 - mA
I
B
I
CC
IB, VB = -24V - 1.0 2.5 I
I
CC
(Note 7) - - - I
2.0 3.7 6.0 I
2.5 4.0 5.0 I
3.5 5.5 8.0 I
CC
CC
BL
CC
BL
2.0 3.7 6.0 I
2.5 4.0 5.0 I
-1.02.5I
3.5 5.5 8.0 I
-1.32.0I
CC
CC
BL
CC
BL
-3.76.0mA
2.0 4.0 6.0 mA
-1.02.5mA
2.0 5.5 8.0 mA
-1.32.5mA
IB, VB = -100V, -85V - 3.2 4.5 IBH, VBH = -100V, -85V - 1.7 2.5 IBH, VBH = -75V - 1.4 3.0 mA
Ringing
(Note 2)
I
CC
-8.5-I
(Note 7) - - - I
CC
BL
-8.5-I
-0.42.0I
CC
BL
-8.5-mA
-0.42.0mA
IB, VB = -100V, -85V - 2.3 5.0 IBH, VBH = -100V, -85V - 1.3 2.5 IBH, VBH = -75V - 1.3 2.5 mA
Forward Loopback
(Note 5)
Tip Open
(Note 5)
Power Denial
(Note 5)
I
CC
, VB = -24V - 19 25.5 I
I
B
I
CC
, VB = -24V - - 1.0 I
I
B
I
CC
, VB = -24V - 0.2 0.5 I
I
B
- 8.5 10.0 I
--5.5I
0.5 3.0 6.0 I
CC
BL
CC
BL
CC
BL
- 8.5 10.0 (Note 15) - - - mA
- 19 25.5 - - - mA
- - 5.5 (Note 16) - - - mA
--1.0 ---mA
0.5 3.0 6.0 I
-0.20.5I
CC
BL
-3.06.0mA
-0.20.5mA
ON HOOK POWER DISSIPATION (Note 17)
Forward or Reverse
(Notes 5, 6)
= -24V - 44 60 VBL = -24V - 44 60 VBL = -24V - 44 60 mW
V
B
UNITSTEST CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX TEST CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX TEST CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX
HC55180, HC55181, HC55183, HC55184
Page 8

Electrical Specifications Unless Otherwise Specified, T
www.BDTIC.com/Intersil
loop current limit = 25mA. All AC Parameters are specified at 600Ω 2-wire terminating impedance over the frequency band of 300Hz to 3.4kHz.
Protection resistors = 0Ω. (Continued)
HC55180 (NOTE 7) HC55181 HC55183, HC55184
PARAMETER
Low Power Standby
(Note 2)
Ringing
(Note 2)
8
OFF HOOK POWER DISSIPATION (Notes 5, 17)
Forward or Reverse V
NOTES:
7. The HC55180 does not provide battery switch operation. Therefore all battery voltage references will be made to V
and V
8. Ringing Voltage is measured with VRS = 0.839 V
9. The HC55183 and HC55184 devices are specified with a single high battery voltage grade.
10. The device represents a low output impedance during ringing. Therefore the voltage across the ringing load is determined by the voltage divider formed by the protection resistance, loop
resistance and ringing load impedance.
11. The HC55180, HC55183 and HC55184 are specified with a single longitudinal balance grade.
12. Longitudinal Balance is tested per IEEE455-1985, with 368Ω per Tip and Ring Terminal.
13. These parameters are tested 100% at room temperature. These parameters are guaranteed not tested across temperature via statistical characterization.
14. The HC55180, HC55183 and HC55184 do not support uncommitted switch operation.
15. The HC55183 and HC55184 do not support the Forward Loopback operating mode.
16. The HC55183 and HC55184 do not support the Tip Open operating mode.
17. The power dissipation numbers are actual device measurements and will be less than worse case calculations based on data sheet supply current limits.
18. Characterized with 2 x 10µs, and 10 x 1000µs first level lightning surge waveforms (GR-1089-CORE).
pins. See the HC55180 Basic Application Circuit.
BH
VB = -85V - 52 - VBH = -85V - 52 75 VBH = -75V - 46 70 mW
= -100V - 59 - VBH = -100V - 59 80 (Note 9) - - - mW
V
B
= -85V - 190 - VBH = -85V - 190 300 VBH = -75V - 170 275 mW
V
B
VB = -100V - 220 - VBH = -100V - 220 325 (Note 9) - - - mW
= -24V - 290 - VBL = -24V - 290 310 VBL = -24V - 280 310 mW
B
for -100V devices, VRS = 0.707 V
RMS
= 0°C to 70°C for the HC55183, 184 only, all others -40°C to 85°C, VBL = -24V, VCC = +5V, AGND = BGND = 0V,
A
. VB is the voltage applied to the common connection of the device VBL
B
for -85V devices and VRS = 0.619 V
RMS
for -75V devices. All measurements are at T = 25°C.
RMS
UNITSTEST CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX TEST CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX TEST CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX
HC55180, HC55181, HC55183, HC55184
Page 9

HC55180, HC55181, HC55183, HC55184
www.BDTIC.com/Intersil
Design Equations
Loop Supervision Thresholds
SWITCH HOOK DETECT
The switch hook detect threshold is set by a single external
resistor, RSH. Equation 1 is used to calculate the value of RSH.
R
600 ISH⁄=
SH
The term I
is the desired DC loop current threshold. The
SH
loop current threshold programming range is from 5mA to
15mA.
GROUND KEY DETECT
The ground key detector senses a DC current imbalance
between the Tip and Ring terminals when the ring terminal is
connected to ground. The ground key detect threshold is not
externally programmable and is internally fixed to 12mA
regardless of the switch hook threshold.
RING TRIP DETECT
The ring trip detect threshold is set by a single external
resistor, R
. IRT should be set between the peak ringing
RT
current and the peak off hook current while still ringing.
1800 IRT⁄=
R
RT
The capacitor C
, in parallel with RRT, will set the ring trip
RT
response time.
(EQ. 1)
(EQ. 2)
4-WIRE TO 2-WIRE GAIN
The 4-wire to 2-wire gain is defined as the receive gain. It is
a function of the terminating impedance, synthesized
impedance and protection resistors. Equation 6 calculates
the receive gain, G
------------------------------------------
G
2
–=
42
ZO + 2RP + Z
.
42
Z
L
L
(EQ. 6)
When the device source impedance and protection resistors
equals the terminating impedance, the receive gain equals
unity.
2-WIRE TO 4-WIRE GAIN
The 2-wire to 4-wire gain (G24) is the gain from tip and ring to
the VTX output. The transmit gain is calculated in Equation 7.
Z
G
24
–=
O
------------------------------------------
ZO + 2RP + Z
(EQ. 7)
L
When the protection resistors are set to zero, the transmit
gain is -6dB.
TRANSHYBRID GAIN
The transhybrid gain is defined as the 4-wire to 4-wire gain
(G
).
44
Z
G
44
ZO2RPZ
++
L
O
---------------------------------------
–=
(EQ. 8)
Loop Current Limit
The loop current limit of the device is programmed by the
external resistor R
. The value of RIL can be calculated
IL
using Equation 3.
1760
------------ -=
R
IL
I
LIM
The term I
is the desired loop current limit. The loop
LIM
(EQ. 3)
current limit programming range is from 15mA to 45mA.
Impedance Matching
The impedance of the device is programmed with the
external component R
the feedback amplifier that provides impedance matching. If
complex impedance matching is required, then a complex
network can be substituted for R
RESISTIVE IMPEDANCE SYNTHESIS
The source impedance of the device, Z
in Equation 4.
R
400 ZO()=
S
The required impedance is defined by the terminating
impedance and protection resistors as shown in Equation 5.
Z
–=
OZL2RP
. RS is the gain setting resistor for
S
.
S
, can be calculated
O
(EQ. 4)
(EQ. 5)
When the protection resistors are set to zero, the transhybrid
gain is -6dB.
COMPLEX IMPEDANCE SYNTHESIS
Substituting the impedance programming resistor, RS, with a
complex programming network provides complex
impedance synthesis.
2-WIRE
NETWORK
C
2
R
1
R
2
FIGURE 1. COMPLEX PROGRAMMING NETWORK
PROGRAMMING
NETWORK
C
P
R
S
R
P
The reference designators in the programming network
match the evaluation board. The component R
different design equation than the R
used for resistive
S
has a
S
impedance synthesis. The design equations for each
component are provided below.
RS400 R12RP()–()×=
R
P
C
PC2
400 R2×=
400⁄=
(EQ. 9)
(EQ. 10)
(EQ. 11)
9
Page 10

HC55180, HC55181, HC55183, HC55184
www.BDTIC.com/Intersil
Low Power Standby
Overview
The low power standby mode (LPS, 000) should be used
during idle line conditions. The device is designed to operate
from the high battery during this mode. Most of the internal
circuitry is powered down, resulting in low power dissipation.
If the 2-wire (tip/ring) DC voltage requirements are not
critical during idle line conditions, the device may be
operated from the low battery. Operation from the low
battery will decrease the standby power dissipation.
TABLE 1. DEVICE INTERFACES DURING LPS
INTERFACE ON OFF NOTES
Receive x AC transmission, impedance
Ringing x
Transmit x
2-Wire x Amplifiers disabled.
Loop Detect x Switch hook or ground key.
2-Wire Interface
During LPS, the 2-wire interface is maintained with internal
switches and voltage references. The Tip and Ring
amplifiers are turned off to conserve power. The device will
provide MTU compliance, loop current and loop supervision.
Figure 2 represents the internal circuitry providing the 2-wire
interface during low power standby.
TIP
RING
MTU REF
FIGURE 2. LPS 2-WIRE INTERFACE CIRCUIT DIAGRAM
MTU Compliance
Maintenance Termination Unit or MTU compliance places
DC voltage requirements on the 2-wire terminals during idle
line conditions. The minimum idle voltage is 42.75V. The
high side of the MTU range is 56V. The voltage is expressed
as the difference between Tip and Ring.
The Tip voltage is held near ground through a 600Ω resistor
and switch. The Ring voltage is limited to a maximum of
-49V (by MTU REF) when operating from either the high or
low battery. A switch and 600Ω resistor connect the MTU
reference to the Ring terminal. When the high battery
matching and ringing are
disabled during this mode.
GND
600Ω
TIP AMP
RING AMP
600Ω
voltage exceeds the MTU reference of -49V (typically), the
Ring terminal will be clamped by the internal reference. The
same Ring relationships apply when operating from the low
battery voltage. For high battery voltages (VBH) less than or
equal to the internal MTU reference threshold:
V
RINGVBH
4+=
(EQ. 12)
Loop Current
During LPS, the device will provide current to a load. The
current path is through resistors and switches, and will be
function of the off hook loop resistance (R
LOOP
). This
includes the off hook phone resistance and copper loop
resistance. The current available during LPS is determined
by Equation 13.
I
LOOP
1– 49–()–()600 600 R
++()⁄=
LOOP
(EQ. 13)
Internal current limiting of the standby switches will limit the
maximum current to 20mA.
Another loop current related parameter is longitudinal
current capability. The longitudinal current capability is
reduced to 10mA
per pin. The reduction in longitudinal
RMS
current capability is a result of turning off the Tip and Ring
amplifiers.
On Hook Power Dissipation
The on hook power dissipation of the device during LPS is
determined by the operating voltages and quiescent currents
and is calculated using Equation 14.
P
LPSVBHIBHQ
× VBLI
× VCCI
BLQ
×++=
CCQ
(EQ. 14)
The quiescent current terms are specified in the electrical
tables for each operating mode. Load power dissipation is
not a factor since this is an on hook mode. Some
applications may specify a standby current. The standby
current may be a charging current required for modern
telephone electronics.
Standby Current Power Dissipation
Any standby line current, I
power dissipation term P
power contribution is zero when the standby line current is
zero.
P
SLCISLCVBH
49– 1I
If the battery voltage is less than -49V (the MTU clamp is
off), the standby line current power contribution reduces to
Equation 16.
P
SLCISLCVBH
1I
Most applications do not specify charging current
requirements during standby. When specified, the typical
charging current may be as high as 5mA.
, introduces an additional
SLC
. Equation 15 illustrates the
SLC
x1200++()×=
SLC
x1200++()×=
SLC
(EQ. 15)
(EQ. 16)
10
Page 11

HC55180, HC55181, HC55183, HC55184
www.BDTIC.com/Intersil
Forward Active
Overview
The forward active mode (FA, 001) is the primary AC
transmission mode of the device. On hook transmission, DC
loop feed and voice transmission are supported during forward
active. Loop supervision is provided by either the switch hook
detector (E0 = 1) or the ground key detector (E0 = 0). The
device may be operated from either high or low battery for onhook transmission and low battery for loop feed.
On-Hook Transmission
The primary purpose of on hook transmission will be to
support caller ID and other advanced signalling features.
The transmission over load level while on hook is 3.5V
When operating from the high battery, the DC voltages at Tip
and Ring are MTU compliant. The typical Tip voltage is -4V
and the Ring voltage is a function of the battery voltage for
battery voltages less than -60V as shown in Equation 17.
V
RINGVBH
4+=
Loop supervision is provided by the switch hook detector at
the DET
output. When DET goes low, the low battery should
be selected for DC loop feed and voice transmission.
Feed Architecture
The design implements a voltage feed current sense
architecture. The device controls the voltage across Tip and
Ring based on the sensing of load current. Resistors are
placed in series with Tip and Ring outputs to provide the
current sensing. The diagram below illustrates the concept.
R
B
R
V
OUT
R
L
FIGURE 3. VOLTAGE FEED CURRENT SENSE DIAGRAM
CS
-
+
-
+
K
S
R
A
By monitoring the current at the amplifier output, a negative
feedback mechanism sets the output voltage for a defined
load. The amplifier gains are set by resistor ratios (R
R
) providing all the performance benefits of matched
C
resistors. The internal sense resistor, R
, is much smaller
CS
than the gain resistors and is typically 20Ω for this device.
The feedback mechanism, K
, represents the amplifier
S
configuration providing the negative feedback.
DC Loop Feed
The feedback mechanism for monitoring the DC portion of
the loop current is the loop detector. A low pass filter is used
in the feedback to block voice band signals from interfering
with the loop current limit function. The pole of the low pass
PEAK
(EQ. 17)
V
IN
R
C
, RB,
A
filter is set by the external capacitor C
. The value of the
DC
external capacitor should be 4.7µF.
Most applications will operate the device from low battery
while off hook. The DC feed characteristic of the device will
drive Tip and Ring towards half battery to regulate the DC
loop current. For light loads, Tip will be near -4V and Ring
will be near V
+ 4V. The following diagram shows the DC
VBL
feed characteristic.
V
TR(OC)
, DC (V)
TR
.
V
I
(mA)
LOOP
FIGURE 4. DC FEED CHARACTERISTIC
The point on the y-axis labeled V
m = (∆VTR/∆IL) = 10kΩ
I
LIM
is the open circuit
TR(OC)
Tip to Ring voltage and is defined by the feed battery
voltage.
V
TR OC()VBL
8–=
(EQ. 18)
The curve of Figure 5 determines the actual loop current for
a given set of loop conditions. The loop conditions are
determined by the low battery voltage and the DC loop
impedance. The DC loop impedance is the sum of the
protection resistance, copper resistance (ohms/foot) and the
telephone off hook DC resistance.
FIGURE 5. I
I
SC
I
LIM
(mA)
LOOP
I
LOOP
2R
P
vs R
R
LOOP
LOAD CHARACTERISTIC
LOOP
(Ω)
I
A
I
B
R
KNEE
The slope of the feed characteristic and the battery voltage
define the maximum loop current on the shortest possible
loop as the short circuit current I
I
SCILIM
The term I
LIM
line segment I
V
------------------------------------------------------+=
is the programmed current limit, 1760/RIL. The
A
–
TR OC()2RPILIM
10K
represents the constant current region of the
SC
.
(EQ. 19)
loop current limit function.
I
AILIM
V
--------------------------------------------------------------+=
–
TR OC()RLOOPILIM
10K
(EQ. 20)
The maximum loop impedance for a programmed loop
current is defined as R
V
R
KNEE
TR OC()
------------------------=
I
LIM
KNEE
.
(EQ. 21)
11
Page 12

HC55180, HC55181, HC55183, HC55184
www.BDTIC.com/Intersil
When R
is exceeded, the device will transition from
KNEE
constant current feed to constant voltage, resistive feed. The
line segment I
represents the resistive feed portion of the
B
load characteristic.
V
I
B
TR OC()
------------------------=
R
LOOP
(EQ. 22)
Voice Transmission
The feedback mechanism for monitoring the AC portion of
the loop current consists of two amplifiers, the sense
amplifier (SA) and the transmit amplifier (TA). The AC
feedback signal is used for impedance synthesis. A detailed
model of the AC feed back loop is provided below.
RR
VRX
TIP
RING
20
20
-
+
+
-
R
3R
3R
3R
3R R/2
1:1
0.75R
-
+
R
T
A
+
-
8K
V
SA
VTX
R
S
-IN
C
FB
VFB
The AC feed back loop produces an echo at the V
of the signal injected at V
. The echo must be cancelled to
RX
output
TX
maintain voice quality. Most applications will use a summing
amplifier in the CODEC front end as shown below to cancel
the echo signal.
R
VRX
R
1:1
VTX
T
A
+
-
HC5518x
FIGURE 7. TRANSHYBRID BALANCE INTERFACE
The resistor ratio, R
the transmit gain, G
R
S
-IN
, provides the final adjustment for
F/RB
. The transmit gain is calculated using
TX
R
A
R
F
R
B
-
+
+2.4V
RX OUT
TX IN
CODEC
Equation 25.
R
F
G
=
TX
Most applications set R
G–
24
------- -
R
B
= RB, hence the device 2-wire to
F
4-wire equals the transmit gain. Typically R
is greater than
B
(EQ. 25)
20kΩ to prevent loading of the device transmit output.
FIGURE 6. AC SIGNAL TRANSMISSION MODEL
The gain of the transmit amplifier, set by R
programmed impedance of the device. The capacitor C
, determines the
S
FB
blocks the DC component of the loop current. The ground
symbols in the model represent AC grounds, not actual DC
potentials.
The sense amp output voltage, V
, as a function of Tip and
SA
Ring voltage and load is calculated using Equation 23.
10
V
SA
VTVR–()–
=
------
Z
L
(EQ. 23)
The transmit amplifier provides the programmable gain
required for impedance synthesis. In addition, the output of
this amplifier interfaces to the CODEC transmit input. The
output voltage is calculated using Equation 24.
V
VTX
–=
V
SA
------- -
8K
(EQ. 24)
R
S
Once the impedance matching components have been
selected using the design equations, the above equations
provide additional insight as to the expected AC node
voltages for a specific Tip and Ring load.
Transhybrid Balance
The final step in completing the impedance synthesis design
is calculating the necessary gains for transhybrid balance.
The resistor ratio, R
gain of the device, G
transmit gain requirement and R
, is determined by the transhybrid
F/RA
. RF is previously defined by the
44
is calculated using
A
Equation 26.
R
B
R
----------=
A
G
44
(EQ. 26)
Power Dissipation
The power dissipated by the device during on hook
transmission is strictly a function of the quiescent currents
for each supply voltage during Forward Active operation.
P
FAQVBH
Off hook power dissipation is increased above the quiescent
power dissipation by the DC load. If the loop length is less
than or equal to R
current, I
Equation 28.
P
FA IA()PFA Q()VBLxIA
If the loop length is greater than R
operating in the constant voltage, resistive feed region. The
power dissipated in this region is calculated using Equation 29.
P
FA IB()PFA Q()VBLxIB
I×
VBLI
× VCCI
BHQ
KNEE
, and the power dissipation is calculated using
A
()R
()R
BLQ
, the device is providing constant
()–+=
()–+=
LOOP
KNEE
LOOP
×++=
CCQ
2
xI
A
, the device is
2
xI
B
(EQ. 27)
(EQ. 28)
(EQ. 29)
12
Page 13

HC55180, HC55181, HC55183, HC55184
www.BDTIC.com/Intersil
Since the current relationships are different for constant
current versus constant voltage, the region of device
operation is critical to valid power dissipation calculations.
Reverse Active
Overview
The reverse active mode (RA, 011) provides the same
functionality as the forward active mode. On hook
transmission, DC loop feed and voice transmission are
supported. Loop supervision is provided by either the switch
hook detector (E0 = 1) or the ground key detector (E0 = 0).
The device may be operated from either high or low battery.
During reverse active the Tip and Ring DC voltage
characteristics exchange roles. That is, Ring is typically 4V
below ground and Tip is typically 4V more positive than
battery. Otherwise, all feed and voice transmission
characteristics are identical to forward active.
Silent Polarity Reversal
Changing from forward active to reverse active or vice versa
is referred to as polarity reversal. Many applications require
slew rate control of the polarity reversal event. Requirements
range from minimizing cross talk to protocol signalling.
The device uses an external low voltage capacitor, C
set the reversal time. Once programmed, the reversal time
will remain nearly constant over various load conditions. In
addition, the reversal timing capacitor is isolated from the AC
loop, therefore loop stability is not impacted.
The internal circuitry used to set the polarity reversal time is
shown below.
I
1
POL
75kΩ
I
2
C
POL
POL
, to
Power Dissipation
The power dissipation equations for forward active operation
also apply to the reverse active mode.
Ringing
Overview
The ringing mode (RNG, 100) provides linear amplification to
support a variety of ringing waveforms. A programmable ring
trip function provides loop supervision and auto disconnect
upon ring trip. The device is designed to operate from the
high battery during this mode.
Architecture
The device provides linear amplification to the signal applied
to the ringing input, V
device is 80V/V. The circuit model for the ringin g p at h is
shown in the following figure.
R
TIP
RING
20
20
R
FIGURE 9. LINEAR RINGING MODEL
The voltage gain from the VRS input to the Tip output is
40V/V. The resistor ratio provides a gain of 8 and the current
mirror provides a gain of 5. The voltage gain from the VRS
input to the Ring output is -40V/V. The equations for the Tip
and Ring outputs during ringing are provided below.
V
BH
V
----------- 40 VRS×()+=
T
2
V
BH
V
----------- 40 VRS×()–=
R
2
. The differential ringing gain of the
RS
R/8
-
+
5:1
V
+
BH
-
+
-
2
800K
-
+
VRS
(EQ. 31)
(EQ. 32)
FIGURE 8. REVERSAL TIMING CONTROL
During forward active, the current from source I1 charges
the external timing capacitor C
and the switch is open.
POL
The internal resistor provides a clamping function for
voltages on the POL node. During reverse active, the switch
closes and I2 (roughly twice I1) pulls current from I1 and the
timing capacitor. The current at the POL node provides the
drive to a differential pair which controls the reversal time of
the Tip and Ring DC voltages.
C
POL
∆time
----------------=
75000
(EQ. 30)
When the input signal at VRS is zero, the Tip and Ring
amplifier outputs are centered at half battery. The device
provides auto centering for easy implementation of
sinusoidal ringing waveforms. Both AC and DC control of the
Tip and Ring outputs is available during ringing. This feature
allows for DC offsets as part of the ringing waveform.
Ringing Input
The ringing input, VRS, is a high impedance input. The high
impedance allows the use of low value capacitors for AC
coupling the ring signal. The V
during the ringing mode, therefore a free running oscillator
may be connected to VRS at all times.
Where ∆time is the required reversal time. Polarized
capacitors may be used for C
. The low voltage at the
POL
POL pin and minimal voltage excursion ±0.75V, are well
suited to polarized capacitors.
When operating from a battery of -100V, each amplifier, Tip
and Ring, will swing a maximum of 95V
maximum signal swing at VRS to achieve full scale ringing is
13
input is enabled only
RS
. Hence, the
P-P
Page 14

HC55180, HC55181, HC55183, HC55184
www.BDTIC.com/Intersil
approximately 2.4V
. The low signal levels are compatible
P-P
with the output voltage range of the CODEC. The digital
nature of the CODEC ideally suits it for the function of
programmable ringing generator. See Applications.
Logic Control
Ringing patterns consist of silent intervals. The ringing to
silent pattern is called the ringing cadence. During the silent
portion of ringing, the device can be programmed to any
other operating mode. The most likely candidates are low
power standby or forward active. Depending on system
requirements, the low or high battery may be selected.
Loop supervision is provided with the ring trip detector. The ring
trip detector senses the change in loop current when the phone
is taken off hook. The loop detector full wave rectifies the
ringing current, which is then filtered with external components
R
and CRT. The resistor RRT sets the trip threshold and the
RT
capacitor C
sets the trip response time. Most applications will
RT
require a trip response time less than 150ms.
Three very distinct actions occur when the devices detects a
ring trip. First, the DET
output is latched low. The latching
mechanism eliminates the need for software filtering of the
detector output. The latch is cleared when the operating
mode is changed externally. Second, the VRS input is
disabled, removing the ring signal from the line. Third, the
device is internally forced to the forward active mode.
Power Dissipation
The power dissipation during ringing is dictated by the load
driving requirements and the ringing waveform. The key to valid
power calculations is the correct definition of average and RMS
currents. The average current defines the high battery supply
current. The RMS current defines the load current.
The cadence provides a time averaging reduction in the
peak power. The total power dissipation consists of ringing
power, P
P
RNGPr
The terms t
interval is t
ratio t
The quiescent power of the device in the ringing mode is
defined in Equation 34.
P
rQ()VBHIBHQ
The total power during the ringing interval is the sum of the
quiescent power and loading power:
P
rPrQ()VBHIAVG
, and the silent interval power, Ps.
r
t
r
--------------
× P
trt
+
s
and tS represent the cadence. The ringing
R
and the silent interval is tS. The typical cadence
R
is 1:2.
R:tS
× VBLI
×
t
s
--------------
×+=
s
trt
+
s
× VCCI
BLQ
------------------------------------------–+=
Z
RENRLOOP
V
2
RMS
+
×++=
CCQ
(EQ. 33)
(EQ. 34)
(EQ. 35)
For sinusoidal waveforms, the average current, I
AVG
, is
defined in Equation 36.
I
AVG
2
-- -
------------------------------------------
=
Z
π
RENRLOOP
V
RMS
2×
+
(EQ. 36)
The silent interval power dissipation will be determined by
the quiescent power of the selected operating mode.
Forward Loop Back
Overview
The forward loop back mode (FLB, 101) provides test
capability for the device. An internal signal path is enabled
allowing for both DC and AC verification. The internal 600Ω
terminating resistor has a tolerance of ±20% . The device is
intended to operate from only the low battery during this
mode.
Architecture
When the forward loop back mode is initiated internal
switches connect a 600Ω load across the outputs of the Tip
and Ring amplifiers.
TIP
TIP AMP
600Ω
RING AMP
RING
FIGURE 10. FORWARD LOOP BACK INTERNAL TERMINATION
DC Verification
When the internal signal path is provided, DC current will
flow from Tip to Ring. The DC current will force DET
indicating the presence of loop current. In addition, the ALM
output will also go low. This does not indicate a thermal
alarm condition. Rather, proper logic operation is verified in
the event of a thermal shutdown. In addition to verifying
device functionality, toggling the logic outputs verifies the
interface to the system controller.
AC Verification
The entire AC loop of the device is active during the forward
loop back mode. Therefore a 4-wire to 4-wire level test
capability is provided. Depending on the transhybrid balance
implementation, test coverage is provided by a one or two
step process.
System architectures which cannot disable the transhybrid
function would require a two step process. The first step
would be to send a test tone to the device while on hook and
not in forward loop back mode. The return signal would be
the test level times the gain R
amplifier. Since the device would not be terminated,
cancellation would not occur. The second step would be to
program the device to FLB and resend the test tone. The
of the transhybrid
F/RA
low,
14
Page 15

HC55180, HC55181, HC55183, HC55184
www.BDTIC.com/Intersil
return signal would be much lower in amplitude than the first
step, indicating the device was active and the internal
termination attenuated the return signal.
System architectures which disable the transhybrid function
would achieve test coverage with a signal step. Once the
transhybrid function is disable, prog ra m th e de vi ce for FL B
and send the test tone. The return signal level is determined
by the 4-wire to 4-wire gain of the device.
Tip Open
Overview
The tip open mode (110) is intended for compatibility for
PBX type interfaces. Used during idle line conditions, the
device does not provide transmission. Loop supervision is
provided by either the switch hook detector (E0 = 1) or the
ground key detector (E0 = 0). The ground key detector will
be used in most applications. The device may be operated
from either high or low battery.
Functionality
During tip open operation, the Tip amplifier is disabled and
the Ring amplifier is enabled. The minimum Tip impedance
is 30kΩ. The only active path through the device will be the
Ring amplifier.
In keeping with the MTU characteristics of the device, Ring
will not exceed -56.5V when operating from the high battery.
Though MTU does not apply to tip open, safety requirements
are satisfied.
On Hook Power Dissipation
The on hook power dissipation of the device during tip open
is determined by the operating voltages and quiescent
currents and is calculated using Equation 37.
P
TOVBHIBHQ
The quiescent current terms are specified in the electrical
tables for each operating mode. Load power dissipation is
not a factor since this is an on hook mode.
× VBLI
× VCCI
BLQ
×++=
CCQ
(EQ. 37)
Thermal Shutdown
In the event the safe die temperature is exceeded, the ALM
output will go low and DET
automatically shut down. When the device cools, ALM
go high and DET
fault persists, ALM
down. Programming power denial will permanently
shutdown the device and stop the self cooling cycling.
will reflect the loop status. If the thermal
will go low again and the part will shut
will go high and the part will
will
Battery Switching
Overview
The integrated battery switch selects between the high
battery and low battery. The battery switch is controlled
with the logic input BSEL. When BSEL is a logic high, the
high battery is selected and when a logic low, the low
battery is selected. All operating modes of the device will
operate from high or low battery except forward loop back.
Functionality
The logic control is independent of the operating mode
decode. Independent logic control provides the most
flexibility and will support all application configurations.
When changing device operating states, battery switching
should occur simultaneously with or prior to changing the
operating mode. In most cases, this will minimize overall
power dissipation and prevent glitches on the DET
The only external component required to support the battery
switch is a diode in series with the V
event that high battery is removed, the diode allows the
device to transition to low battery operation.
supply lead. In the
BH
Low Battery Operation
All off hook operating conditions should use the low battery.
The prime benefit will be reduced power dissipation. The
typical low battery for the device is -24V. However this may
be increased to support longer loop lengths or high loop
current requirements. Standby conditions may also operate
from the low battery if MTU compliance is not required,
further reducing standby power dissipation.
output.
Power Denial
Overview
The power denial mode (111) will shutdown the entire device
except for the logic interface. Loop supervision is not
provided. This mode may be used as a sleep mode or to
shut down in the presence of a persistent thermal alarm.
Switching between high and low battery will have no effect
during power denial.
Functionality
During power denial, both the Tip and Ring amplifiers are
disabled, representing high impedances. The voltages at
both outputs are near ground.
15
High Battery Operation
Other than ringing, the high battery should be used for
standby conditions which must provide MTU compliance.
During standby operation the power consumption is typically
50mW with -100V battery. If ringing requirements do not
require full 100V operation, then a lower battery will result in
lower standby power.
High Voltage Decoupling
The 100V rating of the device will require a capacitor of
higher voltage rating for decoupling. Suggested decoupling
values for all device pins are 0.1µF. Standard surface mount
ceramic capacitors are rated at 100V. For applications
driven at low cost and small size, the decoupling scheme
shown below could be implemented.
Page 16

HC55180, HC55181, HC55183, HC55184
www.BDTIC.com/Intersil
0.22µ 0.22µ
VBH VBL
HC5518X
FIGURE 11. ALTERNATE DECOUPLING SCHEME
As with all decoupling schemes, the capacitors should be as
close to the device pins as physically possible.
Uncommitted Switch
Overview
The uncommitted switch is a three terminal device designed
for flexibility. The independent logic control input, SWC
allows switch operation regardless of device operating
mode. The switch is activated by a logic low. The positive
and negative terminals of the device are labeled SW+ and
SW- respectively.
Relay Driver
The uncommitted switch may be used as a relay driver by
connecting SW+ to the relay coil and SW- to ground. The
switch is designed to have a maximum on voltage of 0.6V
with a load current of 45mA.
+5V
RELAY
,
TIP
RING
TEST
LOAD
SW+
SW-
FIGURE 13. TEST LOAD SWITCHING
SWC
The diode in series with the test load blocks current from
flowing through the uncommitted switch when the polarity of
the Tip and Ring terminals are reversed. In addition to the
reverse active state, the polarity of Tip and Ring are
reversed for half of the ringing cycle. With independent logic
control and the blocking diode, the uncommitted switch may
be continuously connected to the Tip and Ring terminals.
SW+
SW-
FIGURE 12. EXTERNAL RELAY SWITCHING
SWC
Since the device provides the ringing waveform, the relay
functions which may be supported include subscriber
disconnect, test access or line interface bypass. An external
snubber diode is not required when using the uncommitted
switch as a relay driver.
Test Load
The switch may be used to connect test loads across Tip
and Ring. The test loads can provide external test
termination for the device. Proper connection of the
uncommitted switch to Tip and Ring is shown below.
16
Page 17

Basic Application Circuits
www.BDTIC.com/Intersil
HC55180, HC55181, HC55183, HC55184
C
PS1
C
PS3
VCC
VBL
VBH
R
P1
R
P2
C
R
R
RT
RT
SH
TIP
HC55180
RING
RTD
RD
VRX
U
1
VRS
VTX
-IN
VFB
C
RX
C
RS
C
TX
R
S
C
FB
R
IL
ILIM
C
V
CC
DC
CDC
C
POL
POL
E0
F0
F1
F2
DET
ALM
BGNDAGND
FIGURE 14. HC55180 BASIC APPLICATION CIRCUIT
TABLE 2. BASIC APPLICATION CIRCUIT COMPONENT LIST
COMPONENT VALUE TOLERANCE RATING
U1 - Ringing SLIC HC5518x N/A N/A
R
RT
R
SH
R
IL
R
S
, CRS, CTX, CRT, C
C
RX
C
DC
C
PS1
, C
C
PS2
PS3
D
1
, R
R
P1
P2
POL
, C
FB
20kΩ 1% 0.1W
49.9kΩ 1% 0.1W
71.5kΩ 1% 0.1W
210kΩ 1% 0.1W
0.47µF 20% 10V
4.7µF 20% 10V
0.1µF 20% >100V
0.1µF 20% 100V
1N400X type with breakdown > 100V.
Protection resistor values are application dependent and will be determined by protection
requirements. Standard applications will use ≥ 35Ω per side.
Design Parameters: Ring Trip Threshold = 90mA
Impedance = 210kΩ/400 = 525Ω, with 39Ω protection resistors, impedance across Tip and Ring terminals = 603Ω . Where applicable, these
, Switch Hook Threshold = 12mA, Loop Current Limit = 24.6mA, Synthesize Device
PEAK
component values apply to the Basic Application Circuits for the HC55180, HC55181, HC55183 and HC55184. Pins not shown in the Basic
Application Circuit are no connect (NC) pins.
17
Page 18

HC55180, HC55181, HC55183, HC55184
www.BDTIC.com/Intersil
C
PS1
C
PS3
C
R
R
C
R
RT
RT
SH
DC
PS1
C
PS2
VCC VBL
TIP
RING
RTD
RD
IL
ILIM
CDC
U
HC55183
D
1
VBH
VRX
1
VRS
VTX
-IN
VFB
BSEL
E0
F0
F1
F2
DET
ALM
BGNDAGND
C
RX
C
RS
C
TX
R
S
C
FB
C
PS2
C
PS3
VCC VBL
R
P1
R
P2
C
R
R
R
CC
C
C
POL
V
RT
RT
DC
TIP
RING
SW+
SW-
RTD
SH
RD
IL
ILIM
CDC
POL
U
HC55181
D
1
VBH
VRX
1
VRS
VTX
-IN
VFB
SWC
BSEL
E0
F0
F1
F2
DET
ALM
BGNDAGND
C
RX
C
RS
C
TX
R
S
C
FB
C
R
P1
R
P2
V
CC
FIGURE 15. HC55181 BASIC APPLICATION CIRCUIT
C
PS2
C
PS3
R
P1
R
P2
C
RT
R
RT
R
SH
R
IL
C
V
CC
DC
C
POL
C
PS1
TIP
RING
RTD
RD
ILIM
CDC
POL
VCC VBL
U
HC55184
FIGURE 16. HC55182 BASIC APPLICATION CIRCUIT
D
1
VBH
VRX
1
VRS
VTX
-IN
VFB
BSEL
E0
F0
F1
F2
DET
ALM
BGNDAGND
C
RX
C
RS
C
TX
R
S
C
FB
FIGURE 17. HC55184 BASIC APPLICATION CIRCUIT
18
Page 19

HC55180, HC55181, HC55183, HC55184
www.BDTIC.com/Intersil
Additional Application Diagrams
Reducing Overhead Voltages
The transmission overhead voltage of the device is
internally set to 4V per side. The overhead voltage may be
reduced by injecting a negative DC voltage on the receive
input using a voltage divider (Figure 18). Accordingly, the
2-wire port overload level will decrease the same amount
as the injected offset.
R
2
C
160kΩ
VRX
1:1
HC5518X
FIGURE 18. EXTERNAL OVERHEAD CONTROL
The divider shunt resistance is the parallel combination of
the internal 160kΩ resistor and the external R
R
and R2 should be greater than 500kΩ to minimize the
1
additional power dissipation of the divider. The DC gain
relationship from the divider voltage, V
outputs is shown below.
V
VBL82V
TR–
×()––=
D
RX
V
D
R
1
VBL
, to the Tip and Ring
D
FROM
CODEC
. The sum of
2
(EQ. 38)
applications the synthesized device impedance (i.e., 600Ω)
will not match the 200Ω teletax impedance. The gain set by
R
cancels the impedance matching feedback with respect
T
to the teletax injection point. Therefore the device appears
as a low impedance source for teletax. The resistor R
is
T
calculated using the following equation.
-------------------------------------------------------------- ---- -
R
T
× RS400⁄()++
200 2 R
200
P
×=
R
S
(EQ. 39)
The signal level across a 200Ω load will be twice the injected
teletax signal level. As the teletax level at VTX will equal the
injection level, set R
= RB for cancellation. The value of RB
C
is based on the voice band transhybrid balance
requirements. The connection of the teletax source to the
transhybrid amplifier should be AC coupled to allow proper
biasing of the transhybrid amplifier input
TA
+
-
R
CFB
RT
RS
-INVFB VTX
TELETAX
SOURCE
FIGURE 20. TELETAX SIGNALLING
R
F
B
R
C
-
+
+2.4V
TX IN
CODEC
With a low battery voltage -24V and a divider voltage of
-0.5V, the Tip to Ring voltage is 17V. As a result, the
overhead voltage is reduced from 8V to 7V and the overload
level will decrease from 3.5V
PEAK
to 3.0V
PEAK
.
CODEC Ringing Generation
Maximum ringing amplitudes of the device are achieved with
signal levels approximately 2.4V
. Therefore the low pass
P-P
receive output of the CODEC may serve as the low leve l ring
generator. The ringing input impedance of 480kΩ minimum
should not interfere with CODEC drive capability. A single
external capacitor is required to AC coupled the ringing
signal from the CODEC. The circuit diagram for CODEC
ringing is shown below.
160kΩ
VRX
RX OUT
1:1
HC5518X
FIGURE 19. CODEC RINGING INTERFACE
480K
-
+
VRS
CODEC
Implementing Teletax Signalling
A resistor, RT, is required at the -IN input of the device for
injecting the teletax signal (Figure 19). For most
Ringing With DC Offsets
The balanced ringing waveform consists of zero DC offset
between the Tip and Ring terminals. However, the linear
amplifier architecture provides control of the DC offset during
ringing. The DC gain is the same as the AC gain, 40V/V per
amplifier. Positive DC offsets applied directly to the ringing
input will shift both Tip and Ring away from half battery
towards ground and battery respectively. A voltage divider
on the ringing input may be used to generate the offset
(Figure 21). The reference voltage, V
CODEC 2.4V reference voltage or the 5V supply.
-
+
VRS
480K
HC5518X
FIGURE 21. EXTERNAL OVERHEAD CONTROL
V
REF
An offset during ringing of 30V, would require a DC shift of
15V at Tip and 15V at Ring. The DC offset would be created
by a +0.375V (V
) at the VRS input. The divider resistors
D
should be selected to minimize the value of the AC coupling
capacitor C
and the loading of the ring generator and
RS
voltage reference. The ringing input impedance should also
be accounted for in divider resistor calculations.
, can be either the
REF
R
2
C
RS
V
D
R
1
FROM
RING GEN.
19
Page 20

HC55180, HC55181, HC55183, HC55184
www.BDTIC.com/Intersil
Pin Descriptions
PLCC SYMBOL DESCRIPTION
1 TIP TIP power amplifier output.
2 BGND Battery Ground - To be connected to zero potential. All loop current and longitudinal current flow fr om this ground.
3 VBL Low battery supply connection.
4 VBH High battery supply connection for the most negative battery.
5 SW+ Uncommitted switch positive terminal. This pin is a no connect (NC) on the HC55180, HC55183 and HC55184.
6 SW- Uncommitted switch negative terminal. This pin is a no connect (NC) on the HC55180, HC55183 and HC55184.
7 SWC Switch control input. This TTL compatible input controls the uncommitted switch, with a logic “0” enabling the switch and
8 F2 Mode control input - MSB. F2-F0 for the TTL compatible parallel control inte rface for controlling the various modes of
9 F1 Mode control input.
10 F0 Mode control input.
11 E0 Detector Output Selection Input. This TTL input controls the multiplexing of the SHD (E0 = 1) and GKD (E0 = 0)
12 DET Detector Output - This TTL output provides on-hook/off-hook status of the loop based upon the selected operating mode.
13 ALM Thermal Shutdown Alarm. This pin signals the internal die temperature has exceeded safe operating temperature
14 AGND Analog ground reference. This pin should be externally connected to BGND.
15 BSEL Selects between high and low battery, with a logic “1” selecting the high battery and logic “0” the low battery. This pin is
16 NC This pin is a no connect (NC) for all the devices.
17 POL External capacitor on this pin sets the polarity reversal time. This pin is a no connect on the HC55183.
18 VRS Ringing Signal Input - Analog input for driving 2-wire interface while in Ring Mode.
19 VRX Analog Receive Voltage - 4-wire analog audio input voltage. AC couples to CODEC.
20 VTX Transmit output voltage - Output of impedance matching amplifier, AC couples to CODEC.
21 VFB Feedback voltage for impedance matching. This voltage is scaled to accomplish impedance matching.
22 -IN Impedance matching amplifier summing node.
23 VCC Positive voltage power supply, usually +5V.
24 CDC DC Biasing Filter Capacitor - Connects between this pin and V
25 RTD Ring trip filter network.
26 ILIM Loop Current Limit programming resistor.
27 RD Switch hook detection threshold programming resistor.
28 RING RING power amplifier output.
Internally separate from AGND but it is recommended that it is connected to the same potential as AGND.
logic “1” disabling the switch. This pin is a no connect (NC) on the HC55180, HC55183 and HC55184.
operation of the device.
comparator outputs to the DET
shown on page page 2).
The detected output will either be switch hook, ground key or ring trip (see the Device Operating Modes table shown on
page page 2).
(approximately 175°C) and the device has been powered down automatically.
a no connect (NC) on the HC55180.
output based upon the state at the F2-F0 pins (see the Device Operating Modes table
.
CC
20
Page 21

HC55180, HC55181, HC55183, HC55184
www.BDTIC.com/Intersil
Plastic Leaded Chip Carrier Packages (PLCC)
0.042 (1.07)
0.048 (1.22)
PIN (1) IDENTIFIER
0.020 (0.51) MAX
3 PLCS
C
L
D1
D
0.026 (0.66)
0.032 (0.81)
0.045 (1.14)
MIN
0.050 (1.27) TP
0.042 (1.07)
0.056 (1.42)
EE1
VIEW “A” TYP.
C
L
A1
A
0.013 (0.33)
0.021 (0.53)
0.025 (0.64)
MIN
0.004 (0.10) C
0.025 (0.64)
0.045 (1.14)
D2/E2
D2/E2
VIEW “A”
0.020 (0.51)
MIN
SEATING
-C-
PLANE
NOTES:
1. Controlling dimension: INCH. Converted millimeter dimensions are
not necessarily exact.
2. Dimensions and tolerancing per ANSI Y14.5M-1982.
3. Dimensions D1 and E1 do not include mold protrusions. Allowable
mold protrusion is 0.010 inch (0.25mm) per side. Dimensions D1
and E1 include mold mismatch and are measured at the extreme
material condition at the body parting line.
4. To be measured at seating plane contact point.
-C-
5. Centerline to be determined where center leads exit plastic body.
6. “N” is the number of terminal positions.
N28.45 (JEDEC MS-018AB ISSUE A)
28 LEAD PLASTIC LEADED CHIP CARRIER PACKAGE
R
SYMBOL
A 0.165 0.180 4.20 4.57 -
A1 0.090 0.120 2.29 3.04 -
D 0.485 0.495 12.32 12.57 D1 0.450 0.456 11.43 11.58 3
D2 0.191 0.219 4.86 5.56 4, 5
E 0.485 0.495 12.32 12.57 E1 0.450 0.456 11.43 11.58 3
E2 0.191 0.219 4.86 5.56 4, 5
N28 286
INCHES MILLIMETERS
NOTESMIN MAX MIN MAX
Rev. 2 11/97
All Intersil U.S. products are manufactured, assembled and tested utilizing ISO9000 quality systems.
Intersil Corporation’s quality certifications can be viewed at www.intersil.com/design/quality
Intersil products are sold by description only. Intersil Corporation reserves the right to make changes in circuit design, software and/or specifications at any time without
notice. Accordingly, the reader is ca utioned to verify that data she ets are current before pl acing orders. Information fur nished by Intersil is believed to be accurate and
reliable. However, no responsibility is assumed by Intersil or its subsidiaries for its use; nor for any infringements of patents or other rights of third parties which may result
from its use. No license is granted by implication or othe rwise under any patent or patent rights of Intersil or its subsidiaries.
For information regarding Intersil Corporation and its products, see www.intersil.com
21
 Loading...
Loading...